Page 1
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
9-Mbit (256K x 36/512K x 18) Flow-Through SRAM
Features
• Supports 100, 133-MHz bus operations
• Supports 100-MHz bus operations (Automo tiv e )
• 256K × 36/512K × 18 common I/O
• 3.3V –5% and +10% core power supply (V
• 2.5V or 3.3V I/O power supply (V
• Fast clock-to-output times
— 6.5 ns (133-MHz version)
• Provide high-performance 2-1-1-1 access rate
• User-selectable burst counter supporting Intel
Pentium
• Separate processor and controller address strobes
• Synchronous self-timed write
• Asynchronous output enable
• Available in lead-free 100-Pin TQFP package, lead-free
and non lead-free 119-Ball BGA package and 165-Ball
FBGA package
• TQFP Available with 3-Chip Enable and 2-Chip Enable
• IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-Compatible Boundary Scan
•“ZZ” Sleep Mode option
®
interleaved or linear burst sequences
DDQ
)
DD
)
®
Functional Description
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C is a 3 . 3V, 256K x 3 6 / 5 1 2K x 1 8
Synchronous Flow-through SRAMs, respectively designed to
interface with high-speed microprocessors with minimum glue
logic. Maximum access delay from clock rise is 6.5 ns
(133-MHz version). A 2-bit on-chip counter captures the first
address in a burst and increments the address automatically
for the rest of the burst access. All synchronous inputs are
gated by registers controlled by a positive-edge-triggered
Clock Input (CLK). The synchronous inputs include all
addresses, all data inputs, address-pipelining Chip Enable
(CE
), depth-expansion Chip Enables (CE2 and CE
1
Control inputs (ADSC
and BWE
include the Output Enable (OE
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C allows either interleaved or
linear burst sequences, selected by the MODE input pin. A
HIGH selects an interleaved burst sequence, while a LOW
selects a linear burst sequence. Burst accesses can be
initiated with the Processor Address Strobe (ADSP
cache Controller Address Strobe (ADSC
advancement is controlled by the Address Advancement
(ADV) input.
Addresses and chip enables are registered at rising edge of
clock when either Address Strobe Processor (ADSP
Address Strobe Controller (ADSC
burst addresses can be internally generated as controlled by
the Advance pin (ADV).
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C operates from a +3.3V core
power supply while all outputs may operate with either a +2.5
or +3.3V supply. All inputs and outputs are JEDEC-standard
JESD8-5-compatible.
), and Global Write (GW). Asynchronous inputs
, ADSP, and ADV), W rite Enables (BWx,
[1]
) and the ZZ pin.
) inputs. Address
) are active. Subsequent
[2]
), Burst
3
) or the
) or
Selection Guide
133 MHz 100 MHz Unit
Maximum Access Time 6.5 8.5 ns
Maximum Operating Current 250 180 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current Comm/Ind’l 40 40 mA
Automotive
Notes:
1. For best-practices recommendations, please refer to the Cypress application note System Design Guidelines on www.cypress.com.
is for A version of TQFP (3 Chip Enable Option) and 165 FBGA package only. 119 BGA is offered only in 2 Chip Enable.
2. CE
3
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05541 Rev . *F Revised September 14, 2006
60 mA
[+] Feedback
Page 2
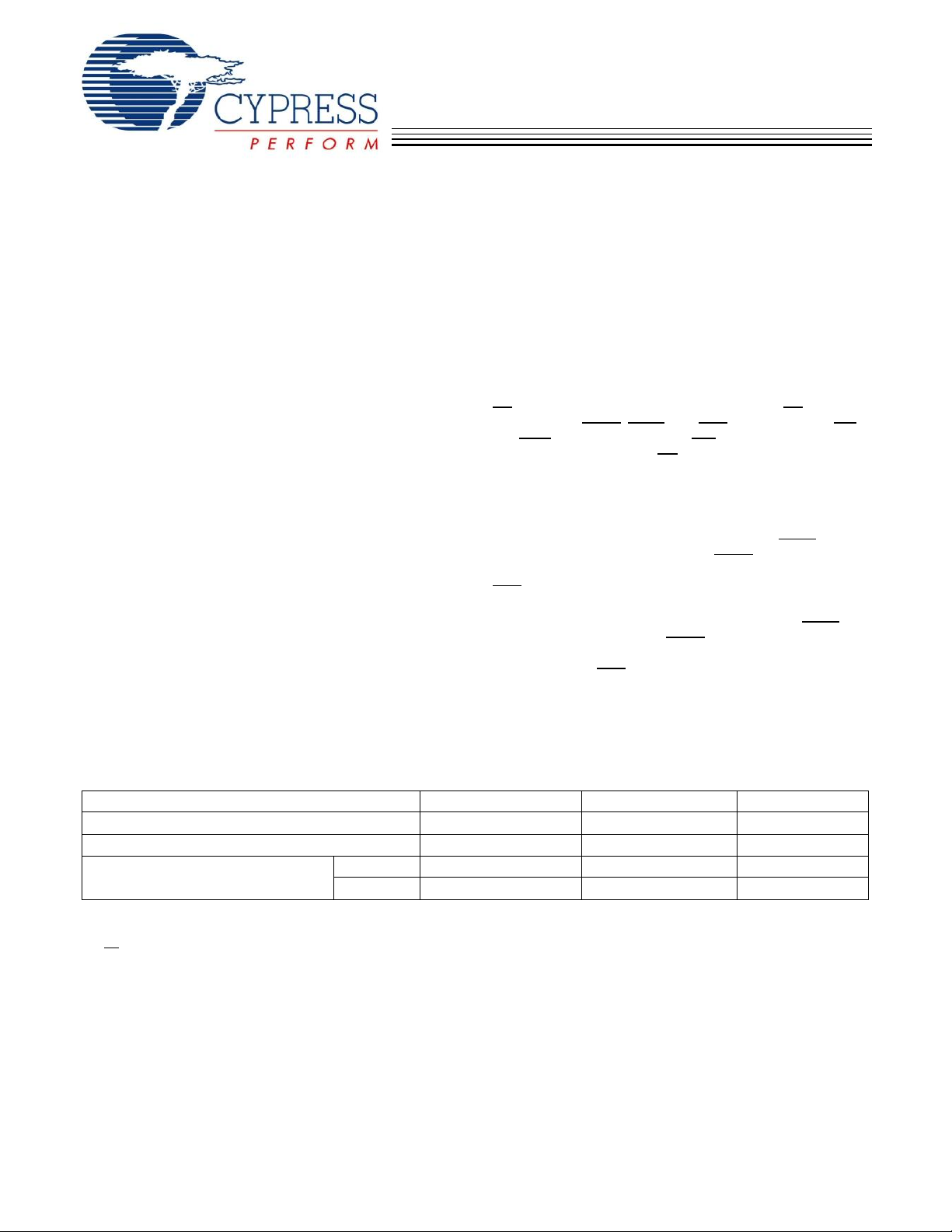
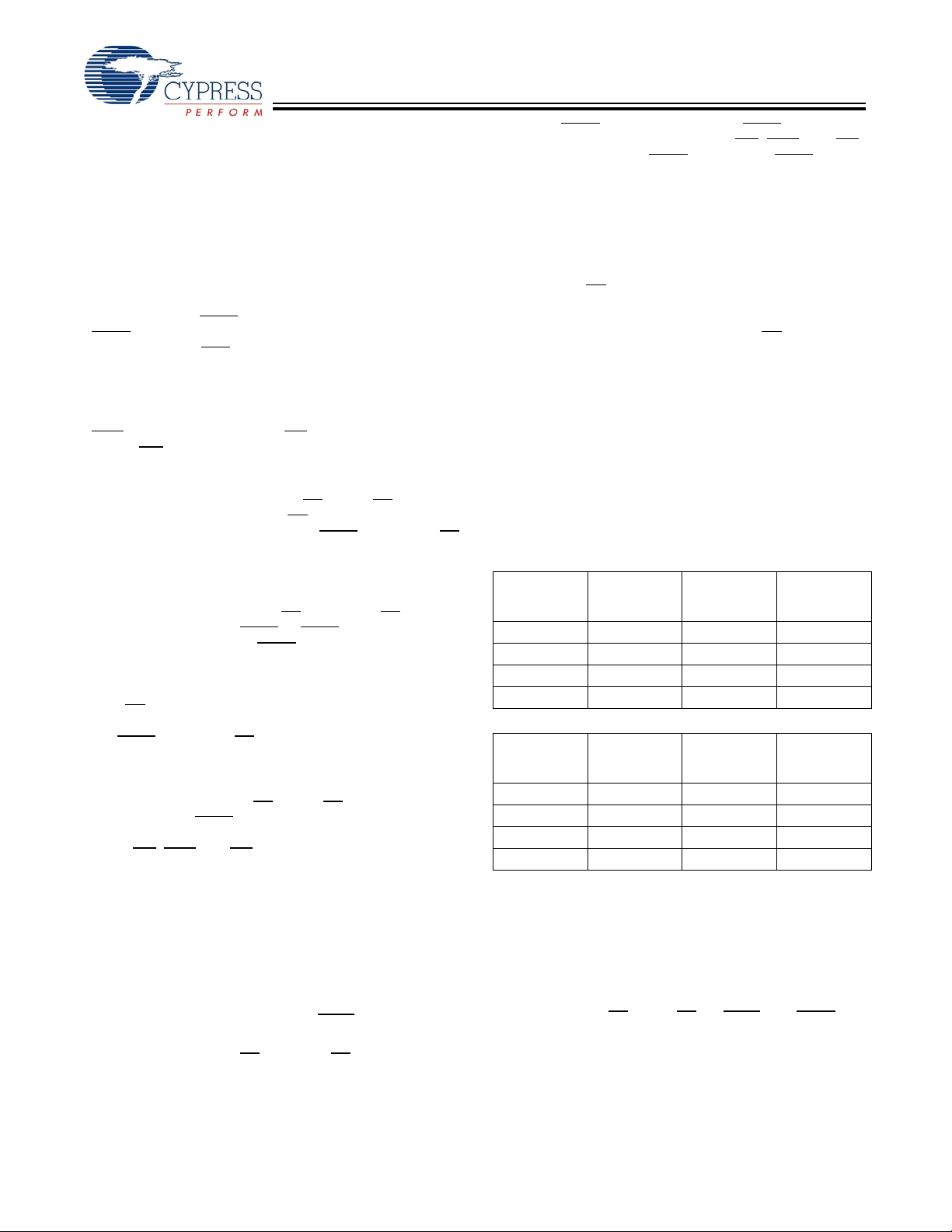
s
A
B
C
D
A
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1361C (256K x 36)
A
A
B
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
0, A1, A
MODE
ADV
CLK
ADSC
ADSP
BW
BW
BW
BW
BWE
GW
CE1
CE2
CE3
ADDRESS
REGISTER
BURST
COUNTER
AND LOGIC
CLR
D
,
DQP
D
D
C
B
A
OE
ZZ
SLEEP
CONTROL
DQ
BYTE
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
C
,
DQP
DQ
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
B
,
DQP
B
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
A
,
DQP
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
ENABLE
REGISTER
C
A
A
[1:0]
Q1
Q0
DQ
D
,
DQP
D
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
C
,
DQP
C
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
B
,
DQP
B
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
A
,
DQP
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
MEMORY
ARRAY
A
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
INPUT
REGISTERS
DQ
DQP
DQP
DQP
DQP
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1363C (512K x 18)
0,A1,A
MODE
ADV
CLK
ADSC
ADSP
B
BW
BW
A
BWE
GW
CE
1
CE
2
CE
3
OE
ZZ
ADDRESS
REGISTER
DQB,DQP
A
,DQP
DQ
ENABLE
REGISTER
SLEEP
CONTROL
B
A
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
A[1:0]
Q1
BURST
COUNTER AND
LOGIC
CLR
Q0
DQB,DQP
B
WRITE DRIVER
DQ
A
,DQP
A
WRITE DRIVER
MEMORY
ARRAY
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
INPUT
REGISTERS
DQs
DQP
DQP
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 2 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 3
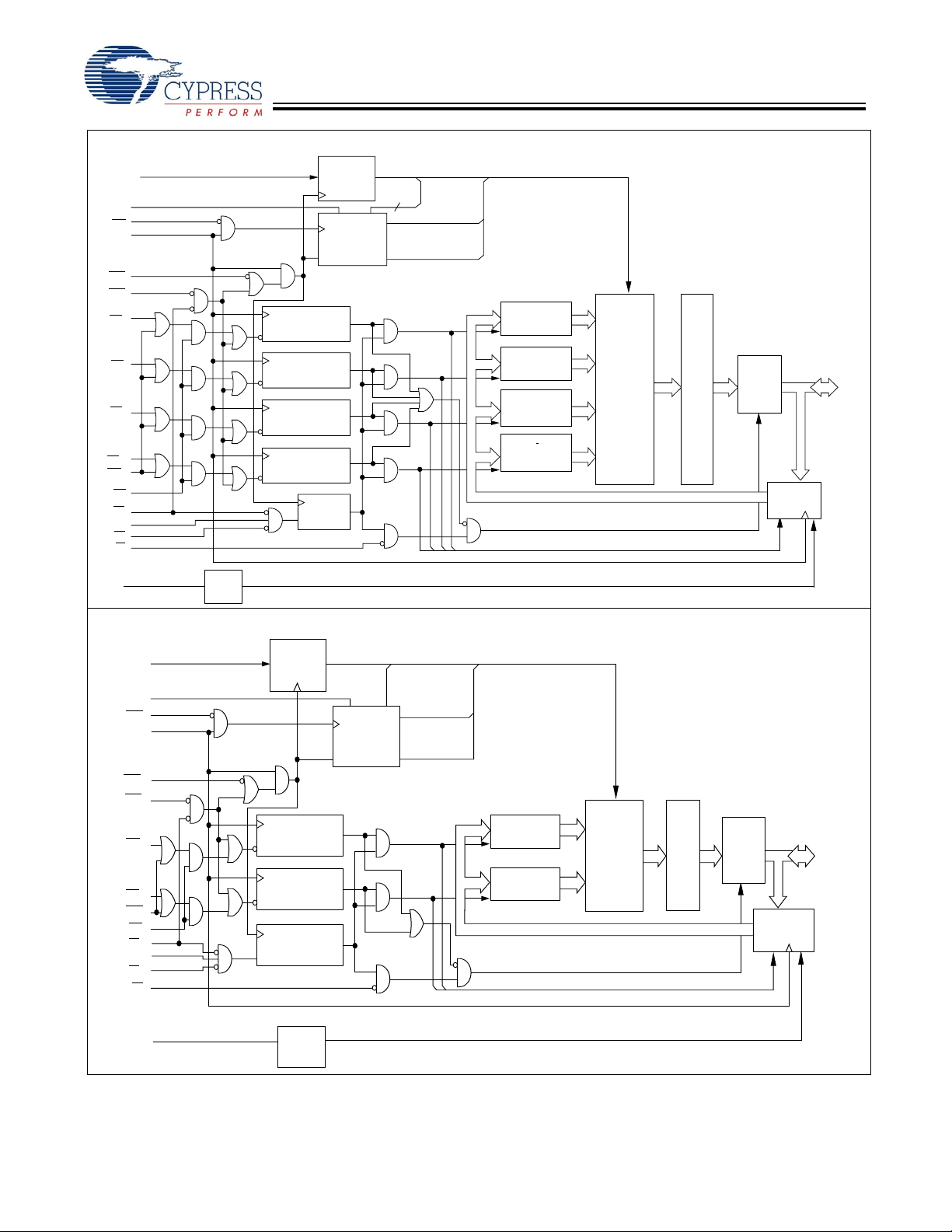
Pin Configurations
100-Pin TQFP Pinout (3 Chip Enables) (A version)
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
1CE2
A
A
BWD
BWC
CE
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
C
1
C
2
C
3
4
5
C
6
C
7
C
8
C
9
10
11
C
12
C
13
14
15
16
SS
17
D
18
D
19
20
21
D
22
D
23
D
24
D
25
26
27
D
28
D
29
D
30
BWB
CY7C1361C
(256K x 36)
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
AAA
1A0
A
A
MODE
BWA
NC
CE3VDDV
SS
NC
V
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
A
DD
NC
V
ADSP
AAAAA
A
A
ADV
81
DQP
80
DQ
79
DQ
78
V
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
50
A
A
1CE2
A
A
NCNCBWBBWA
CE
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
CY7C1363C
(512K x 18)
CE3VDDV
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
ADSP
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
MODE
AAA
1A0
A
A
NC
NC
A
DD
V
NC
AAAAA
SS
V
A
A
ADV
81
A
80
NC
79
NC
78
V
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
NC
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
50
A
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 3 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 4
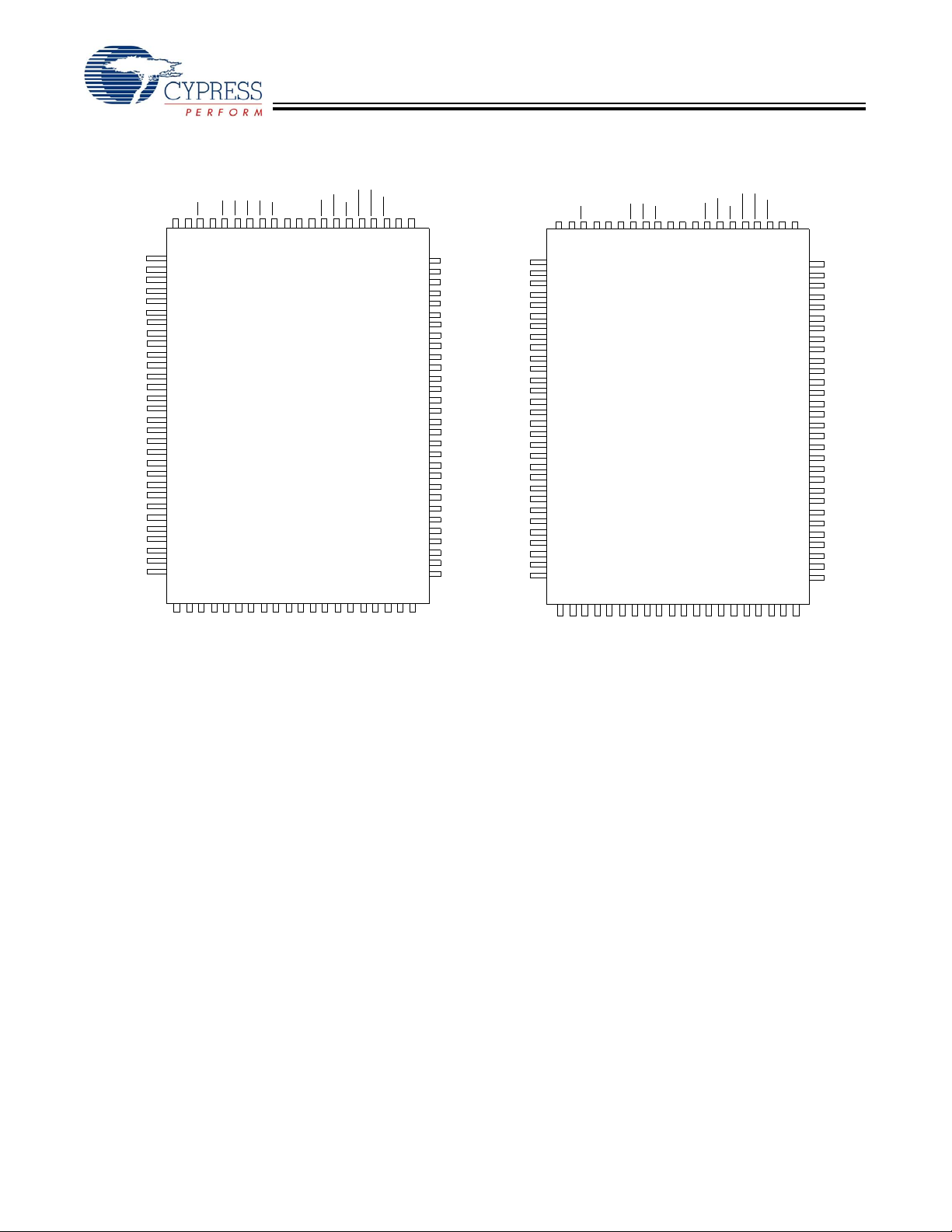
Pin Configurations (continued)
100-Pin TQFP Pinout (2 Chip Enables) (AJ Version)
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
1CE2
A
A
BWD
BWC
CE
BWB
SS
BWA
A
VDDV
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
C
1
C
2
C
3
4
5
C
6
C
7
C
8
C
9
10
11
C
12
C
13
14
15
16
17
D
18
D
19
20
21
D
22
D
23
D
24
D
25
26
27
D
28
D
29
D
30
CY7C1361C
(256K x 36)
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
MODE
AAA
1A0
A
A
NC
NC
SS
DD
V
V
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
AAAAA
NC
NC
ADSP
ADV
A
A
81
DQP
80
DQ
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
50
A
A
1CE2
A
A
NCNCBWBBWA
CE
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
CY7C1363C
(512K x 18)
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
1A0
A
A
MODE
AAA
NC
NC
A
VDDV
SS
V
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
AAAAA
DD
NC
NC
V
ADSP
ADV
A
A
81
A
80
NC
79
NC
78
V
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
NC
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
50
A
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 4 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 5
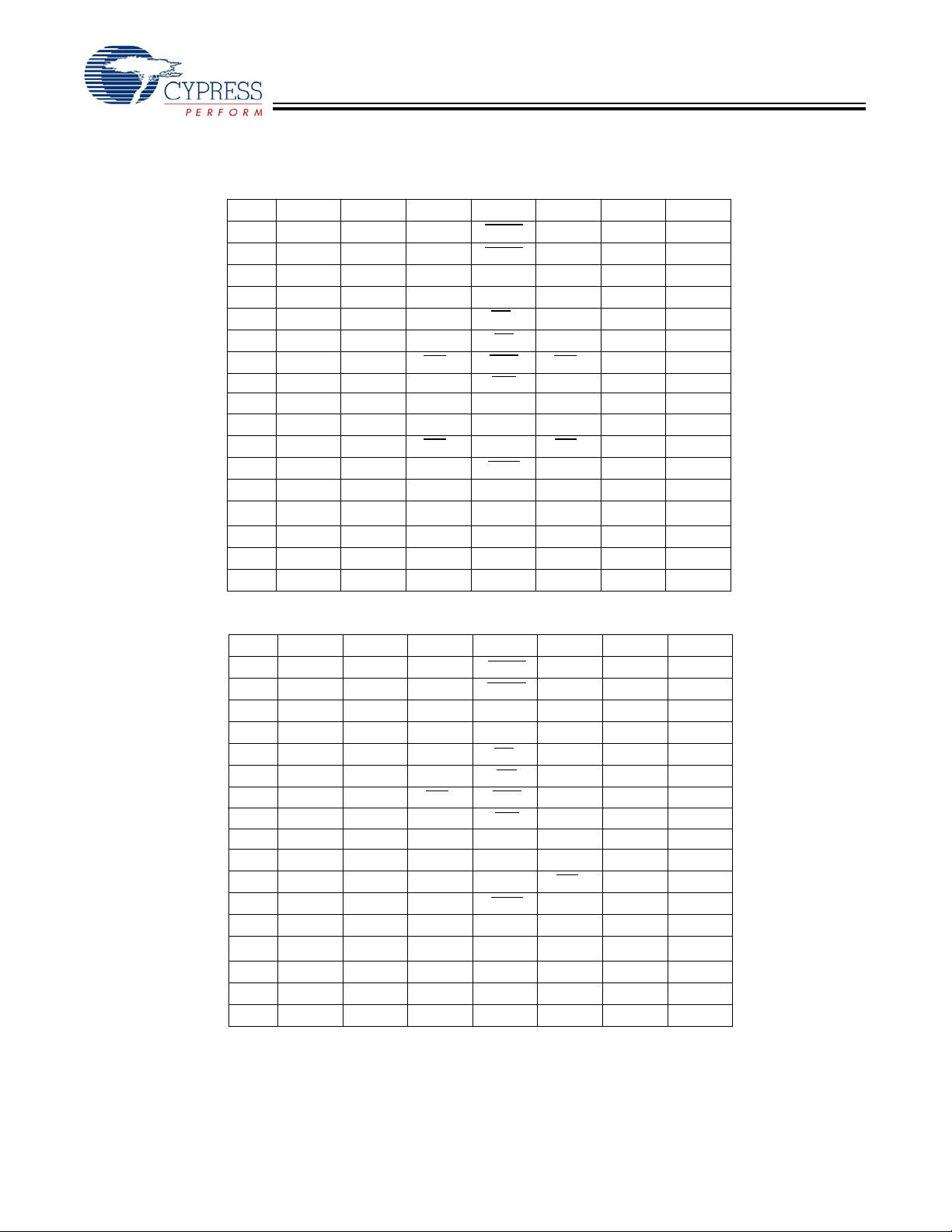
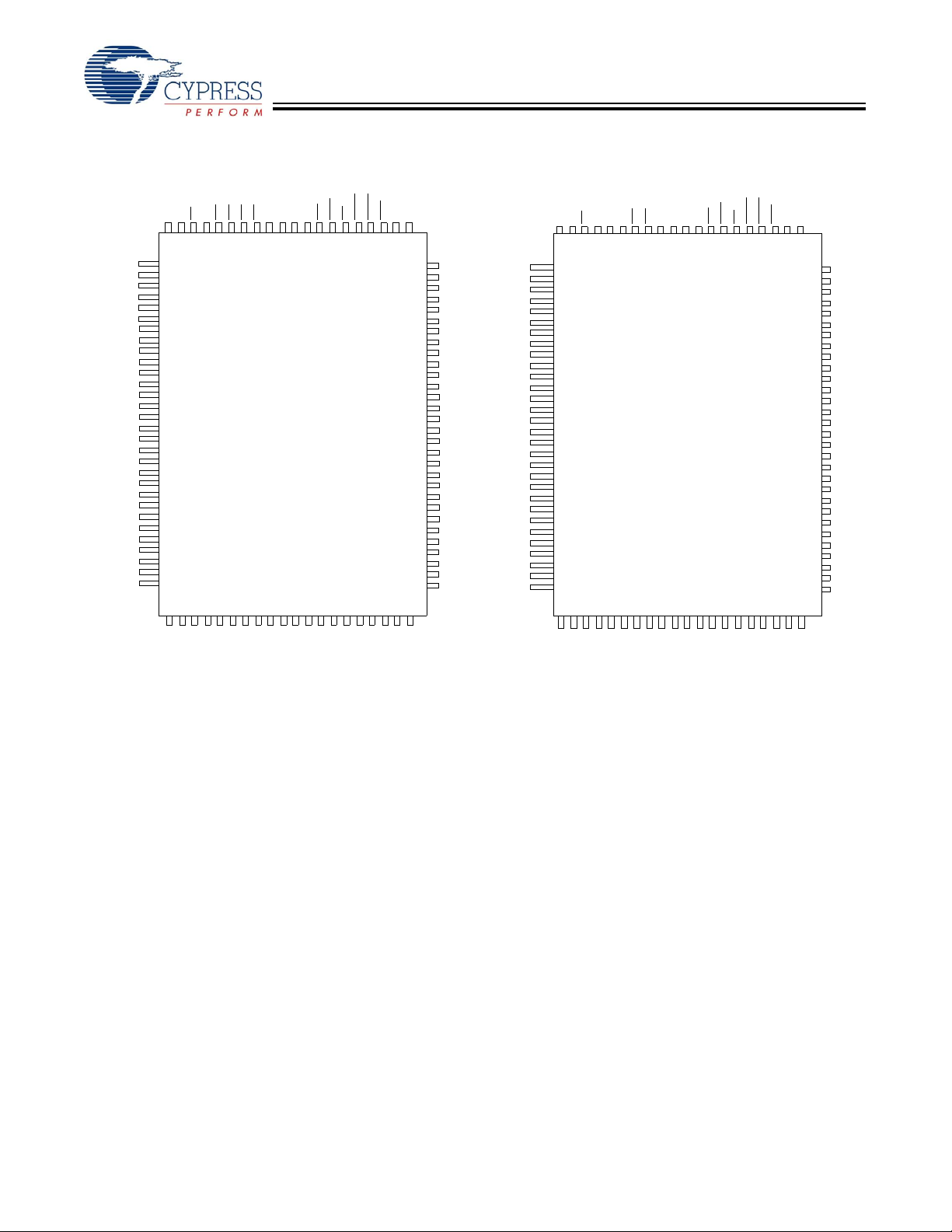
Pin Configurations (continued)
119-Ball BGA Pinout (2 Chip Enables with JTAG)
V
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
DDQ
NC/288M
NC/144M
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
NC
NC
V
DDQ
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
CY7C1361C (256K x 36)
2345671
AA AA
CE
2
A
AA
DQP
C
DQ
C
DQ
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
DD
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
DQ
D
DQP
D
A
V
C
C
C
C
C
V
V
BW
V
SS
SS
SS
SS
NC V
V
BW
V
V
V
SS
SS
SS
SS
D
D
D
D
D
MODE
AAA
ADSP
A
AA
DQP
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
DD
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
A
V
V
V
BW
V
NC
V
BW
V
V
V
NC
A
SS
SS
SS
B
SS
SS
A
SS
SS
SS
ADSC
V
DD
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
C
GW
DD
CLK
D
NC
BWE
A1
A0
V
DD
NC/36MNC/72M
TDOTCKTDITMS
NC
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
V
DDQ
NC/512M
NC/1G
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
DDQ
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
DDQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
DDQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
NC
ZZ
V
DDQ
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
DDQ
NC/288M
NC/144M
B
NC
V
DDQ
NC
DQ
B
V
DDQ
NC
DQ
B
V
DDQ
DQ
B
NC
NC
NC/72M
V
DDQ
CY7C1363C (512K x 18)
2
AA AA
CE
2
NCDQ
DQ
B
NC
DQ
B
NC
V
DD
DQ
B
NC
DQ
B
NC
DQP
B
A
345671
ADSP
A
AA
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
BW
V
SS
NC V
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
MODE
ADSC
V
DD
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
B
GW
DD
CLK
NC
BWE
A1
A0
V
DD
A NC/36M A
V
V
V
V
V
NC
V
BW
V
V
V
NC
TDOTCKTDITMS
A
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
A
AA
DQP
A
NC
DQ
A
NC
DQ
A
V
DD
NC
DQ
A
A
NC
DQ
A
NC
A
AA
NC
V
DDQ
NC/512M
NC/1G
NC
DQ
A
V
DDQ
DQ
A
NC
V
DDQ
DQ
A
NC
V
DDQ
NC
DQ
A
NC
ZZ
V
DDQ
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 5 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 6
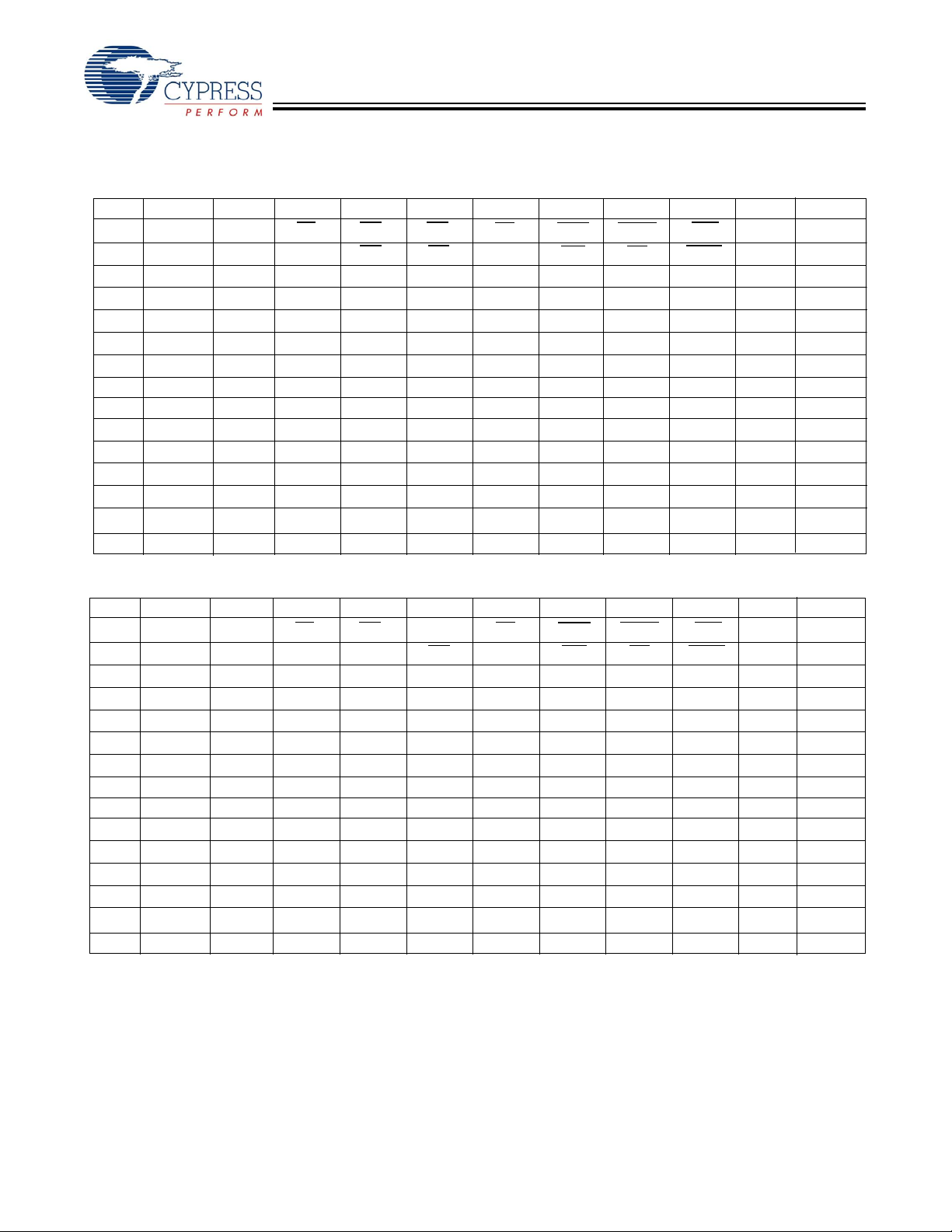
Pin Configurations (continued)
234 5671
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
CE
CE
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
A
A
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
NC/288M
NC/144M
DQP
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
NC
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQP
D
NC
MODE
A
A
NC
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
SS
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
NC
NC/72M
NC/36M
165-Ball FBGA Pinout (3 Chip Enable)
CY7C1361C (256K x 36)
BW
1
BW
2
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
BW
BW
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
B
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
C
D
NC
TDI
TMS
A
CE
3
CLK
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC/18M
A1
A0
BWE
GW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDO
TCK
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
891011
ADSC
OE
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
ADV
ADSP
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
A
A
NC
NC/576M
NC/1G DQP
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
A
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
ZZ
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQP
A
AA
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
CY7C1363C (512K x 18)
2345671
NC/288M
NC/144M
NC
NC
NC V
NC
NC
V
SS
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQP
B
NC
MODE
ACE
A
NC
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
SS
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC/72M
NC/36M
CE
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
A
A
BW
1
2
B
NC BW
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
NC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDI
TMS
A
CE
3
CLK
V
SS
V
SS
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC/18M
A1
BWE
GW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDO
TCKA0
891011
ADSC
OE
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
ADV
ADSP
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
A
A
A
NC/576M
NC/1G DQP
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
A
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZZ
A
A
A
A
NCV
NC
NC
NC
NC
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 6 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 7
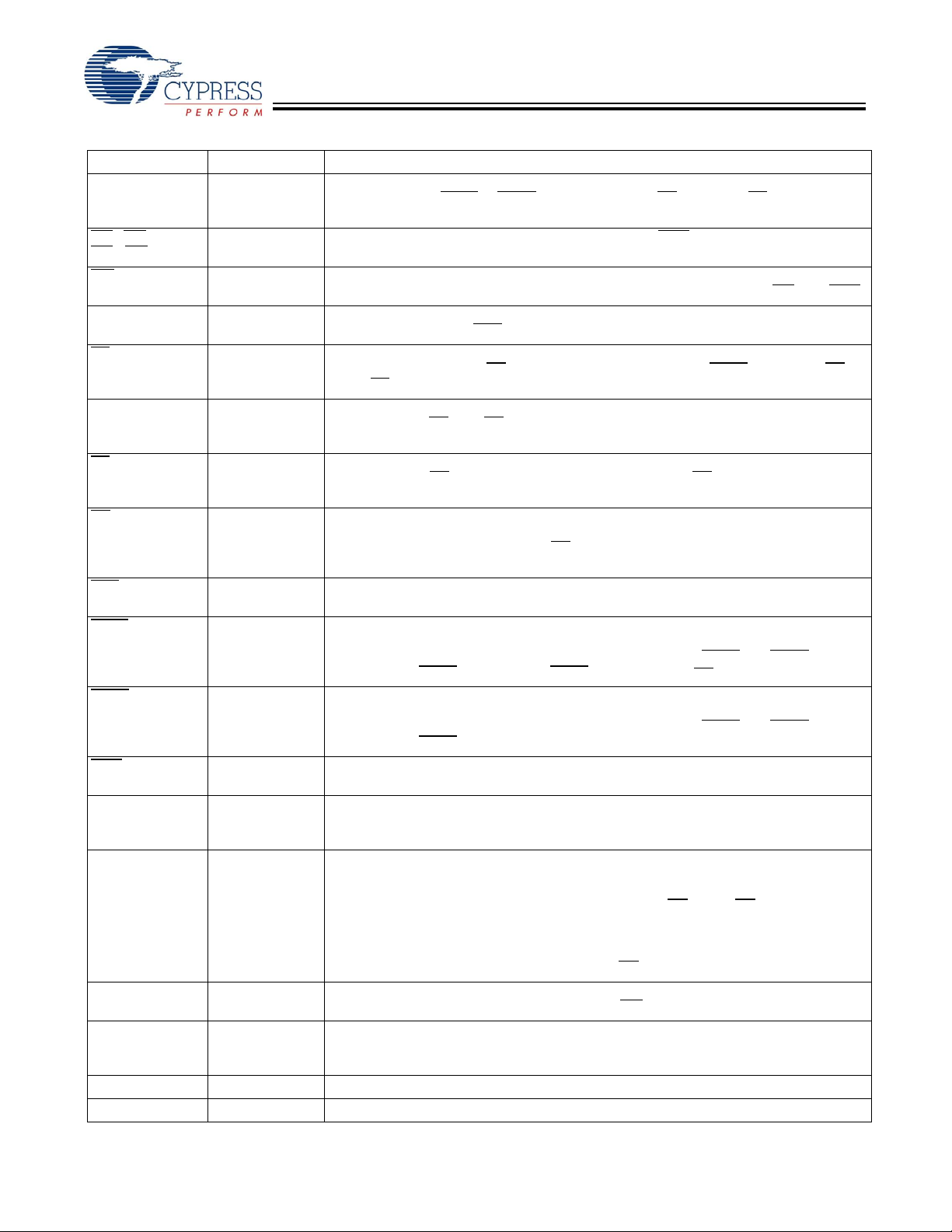
Pin Definitions
Name I/O Description
, A1, A Input-
A
0
,BW
BW
A
BWC,BW
B
D
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
GW Input-
Synchronous
CLK Input-
Clock
CE
CE
CE
1
2
[2]
3
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
OE Input-
Asynchronous
ADV Input-
Synchronous
ADSP Input-
Synchronous
ADSC
Input-
Synchronous
BWE
Input-
Synchronous
ZZ Input-
Asynchronous
DQ
DQP
s
X
I/O-
Synchronous
I/O-
Synchronous
MODE Input-
Static
V
V
DD
DDQ
Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the device.
I/O Power Supply Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
Address Inputs used to select one of the address locations. Sampled at the rising
edge of the CLK if ADSP
active. A
feed the 2-bit counter.
[1:0]
or ADSC is active LOW, and CE1, CE2, and CE
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW. Qualified with BWE to conduct byte writes to the
SRAM. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Global Write Enable Input, active LOW. When asserted LOW on the rising edge of CLK, a
global write is conducted (ALL bytes are written, regardless of the values on BW
Clock Input. Used to capture all synchronous inputs to the device. Also used to increment
the burst counter when ADV is asserted LOW, during a burst operation.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
HIGH. CE
is sampled only when a new external address is loaded.
1
and CE
2
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
a new external address is loaded.
and CE
1
[2]
to select/deselect the device. ADSP is ignored if CE1 is
3
[2]
to select/deselect the device. CE2 is sampled only when
3
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
new external address is loaded.
and CE2 to select/deselect the device.CE3 is sampled only when a
1
Output Enable, asynchronous input, active LOW. Controls the direction of the I/O pins.
When LOW, the I/O pins behave as outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins are
tri-stated, and act as input data pins. OE is masked during the first clock of a read cycle
when emerging from a deselected state.
Advance Input signal, sampled on the rising edge of CLK. When asserted, it automatically increments the address in a burst cycle.
Address Strobe from Processor, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW.
When asserted LOW, addresses presented to the device are captured in the address
registers. A
asserted, only ADSP
are also loaded into the burst counter. When ADSP and ADSC are both
[1:0]
is recognized. ASDP is ignored when
Address Strobe from Controller, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW.
When asserted LOW, addresses presented to the device are captured in the address
registers. A
asserted, only ADSP
are also loaded into the burst counter. When ADSP and ADSC are both
[1:0]
is recognized.
Byte Write Enable Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. This signal
must be asserted LOW to conduct a byte write.
ZZ “sleep” Input, active HIGH. When asserted HIGH places the device in a
non-time-critical “sleep” condition with data integrity preserved. For normal operation,
this pin has to be LOW or left floating. ZZ pin has an internal pull-down.
Bidirectional Data I/O lines . As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data register that is
triggered by the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they deliver the data contained in the
memory location specified by the addresses presented during the previous clock rise of
the read cycle. The direction of the pins is controlled by OE
the pins behave as outputs. When HIGH, DQ
condition.The outputs ar e au to matically tri-stated during the data portion of a write
sequence, during the first clock when emerging from a deselected state, and when the
device is deselected, regardless of the state of OE
Bidirectional Data Parity I/O Lines . Functionally, these signals are identical to DQs.
During write sequences, DQPX is controlled by BWX correspondingly.
Selects Burst Order. When tied to GND selects linear burst sequence. When tied to V
or left floating selects interleaved burst sequence. This is a strap pin and should remain
static during device operation. Mode Pin has an internal pull-up.
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
[2]
are sampled
3
and BWE).
X
is deasserted HIGH.
CE
1
and DQPX are placed in a tri-state
s
.
. When OE is asserted LOW,
DD
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 7 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 8
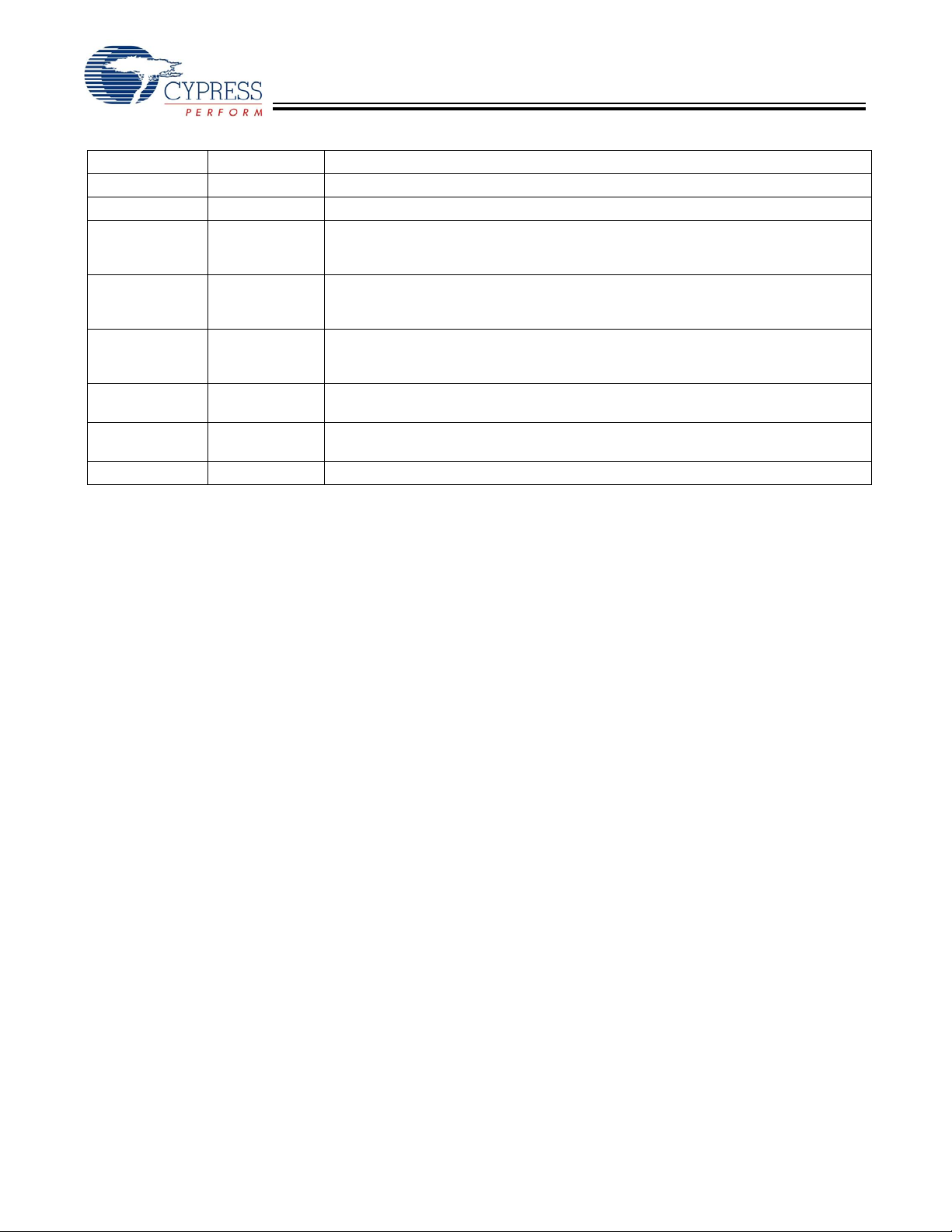
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Pin Definitions (continued)
Name I/O Description
V
SS
V
SSQ
TDO JTA G serial output
TDI JTAG serial input
TMS JTAG serial input
TCK JTAG-
NC – No Connects. Not internally connected to the die. 18M, 36M, 72M, 144M, 288M, 576M
/DNU Ground/DNU This pin can be connected to Ground or should be left floating.
V
SS
Ground Ground for the core of the device.
I/O Ground Ground for the I/O circuitry.
Synchronous
Synchronous
Synchronous
Clock
Serial data-out to the JTAG circuit. Delivers data on the negative edge of TCK. If the
JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin should be left unconnected. This pin is not
available on TQFP packages.
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG
feature is not being utilized, this pin can be left floating or connected to V
up resistor. This pin is not available on TQFP packages.
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG
feature is not being utilized, this pin can be disconnected or connected to V
is not available on TQFP packages.
Clock input to the JTAG circuitry. If the JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin must
be connected to V
and 1G are address expansion pins and are not internally connected to the die.
. This pin is not available on TQFP packages.
SS
through a pull
DD
. This pin
DD
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 8 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 9
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Functional Overview
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the rising edge of the clock. Maximum access d elay from
the clock rise (t
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C supports secondary cache in
systems utilizing either a linear or interleaved burst sequence.
The interleaved burst order supports Pentium and i486™
processors. The linear burst sequence is suited for processors
that utilize a linear burst sequence. The burst order is
user-selectable, and is determined by sampling the MODE
input. Accesses can be initiated with either the Processor
Address Strobe (ADSP
). Address advancement through the burst sequence is
(ADSC
controlled by the ADV
burst counter captures the first address in a burst sequence
and automatically increments the address for the rest of the
burst access.
Byte write operations are qualified with the Byte Write Enable
(BWE
) and Byte Write Select (BWX) inputs. A Global Write
Enable (GW
all four bytes. All writes are simplified with on-chip
synchronous self-timed write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Selects (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
selection and output tri-state control. ADSP
is HIGH.
Single Read Accesses
A single read access is initiated when the following conditions
are satisfied at clock rise: (1) CE
asserted active, and (2) ADSP
the access is initiated by ADSC
deasserted during this first cycle). The address presented to
the address inputs is latched into the address register and the
burst counter/control logic and presented to the memory core.
If the OE input is asserted LOW, the requested data will be
available at the data outputs a maximum to t
rise. ADSP
is ignored if CE1 is HIGH.
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSP
This access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CE
active, and (2) ADSP
presented are loaded into the address register and the burst
inputs (GW
, BWE, and BWX)are ignored during this first clock
cycle. If the write inputs are asserted active (see Write Cycle
Descriptions table for appropriate states that indicate a write)
on the next clock rise, the appropriate data will be latched and
written into the device.Byte writes are allowed. All I/Os are
tri-stated during a byte write.Since this is a common I/O
device, the asynchronous OE input signal must be deasserted
and the I/Os must be tri-stated prior to the presentation of data
to DQs. As a safety precaution, the data lines are tri -stated
once a write cycle is detected, regardless of the state of OE.
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSC
This write access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CE
) is 6.5 ns (133-MHz device).
CDV
) or the Controller Address Strobe
input. A two-bit on-chip wraparound
) overrides all byte write inputs and writes data to
, CE2, CE
1
) provide for easy bank
[2]
) and an
3
is ignored if CE
, CE2, and CE
1
or ADSC is asserted LOW (if
[2]
3
are all
, the write inputs must be
after clock
CDV
, CE2, CE
1
is asserted LOW. The addresses
, CE2, and CE
1
[2]
are all asserted
3
[2]
are all asserted
3
active, (2) ADSC
HIGH, and (4) the write input signals (GW
indicate a write access. ADSC
is asserted LOW, (3) ADSP is deasserted
, BWE, and BWX)
is ignored if ADSP is active
LOW.
The addresses presented are loaded into the address register
and the burst counter/control logic and delivered to the
memory core. The information presented to DQ
written into the specified address location. Byte writes are
allowed. All I/Os are tri-stated when a write is detected, even
a byte write. Since this is a common I/O device, the
asynchronous OE input signal must be deasserted and the
I/Os must be tri-stated prior to the presentation of data to DQ
As a safety precaution, the data lines are tri-stated once a writ e
cycle is detected, regardless of the state of OE.
Burst Sequences
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C provides an on-chip two-bit
wraparound burst counter inside the SRAM. The burst counter
is fed by A
burst order. The burst order is determined by the state of the
, and can follow either a linear or interleaved
[1:0]
MODE input. A LOW on MODE will select a linear burst
sequence. A HIGH on MODE will select an interleaved burst
order. Leaving MODE unconnected will cause the device to
default to a interleaved burst sequence.
Interleaved Burst Address Table
1
(MODE = Floating or V
First
Address
A1: A0
Second
Address
A1: A0
DD
)
Third
Address
A1: A0
00 01 10 11
01 00 11 10
10 11 00 01
11 10 01 00
Linear Burst Address Table (MODE = GND)
First
Address
A1: A0
00 01 10 11
01 10 11 00
10 11 00 01
11 00 01 10
Sleep Mode
The ZZ input pin is an asynchronous input. Asserting ZZ
places the SRAM in a power conservation “sleep” mode. Two
clock cycles are required to enter into or exit from this “sleep”
mode. While in this mode, data integrity is guaranteed.
Accesses pending when entering the “sleep” mode are not
considered valid nor is the completion of the operation
guaranteed. The device must be deselected prior to entering
the “sleep” mode. CE
remain inactive for the duration of t
returns LOW.
Second
Address
A1: A0
, CE2, CE
1
Third
Address
A1: A0
[2]
, ADSP, and ADSC must
3
after the ZZ input
ZZREC
will be
[A:D]
Fourth
Address
A1: A0
Fourth
Address
A1: A0
.
s
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 9 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 10
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
ZZ Mode Electrical Characteristics
Parameter De scription Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
I
DDZZ
t
ZZS
t
ZZREC
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Truth Table
Sleep mode standby current ZZ > VDD – 0.2V Comm/ind’l 50 mA
Automotive 60 mA
Device operation to ZZ ZZ > VDD – 0.2V 2t
ZZ recovery time ZZ < 0.2V 2t
CYC
ZZ active to sleep current This parameter is sampled 2t
CYC
CYC
ZZ Inactive to exit sleep current This parameter is sampled 0 ns
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
ns
ns
ns
Cycle Description
Used CE1CE2CE3ZZ ADSP ADSC ADV WRITE OE CLK DQ
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None H X X L X L X X X L-H Tri-state
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L L X L L X X X X L-H Tri-state
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L X H L L X X X X L-H Tri-state
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L L X L H L X X X L-H Tri-state
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None X X X L H L X X X L-H Tri-state
Sleep Mode, Power-down None X X X H X X X X X X Tri-state
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X L L-H Q
Address
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X H L-H
Write Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X L X L-H
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H L L-H
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H H L-H
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L H L L-H
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L H H L-H
Tri-state
D
Q
Tri-state
Q
Tri-state
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L H H L-H Tri-state
Write Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L L X L-H D
Write Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L L X L-H D
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H H H L-H Tri-state
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H H H L-H Tri-state
Write Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H L X L-H D
Write Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H L X L-H D
Notes:
3. X=”Don't Care.” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW.
4. WRITE
5. The DQ pins are controlled by the current cycle and the OE
6. The SRAM always initiates a read cycle when ADSP
7. OE
= L when any one or more Byte Write enable signals and BWE = L or GW = L. WRITE = H when all Byte write enable signals, BWE, GW = H.
the ADSP
care for the remainder of the write cycle.
inactive or when the device is deselected, and all data bits behave as output when OE
or with the assertion of ADSC. As a result, OE must be driven HIGH prior to the start of the write cycle to allow the outputs to tri-state. OE is a don't
is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock rise. It is masked internally during write cycles. During a read cycle all data bits are tri-state when OE is
signal. OE is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock.
is asserted, regardless of the state of GW, BWE, or BWX. Writes may occur only on subsequent clocks after
is active (LOW).
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 10 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 11

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Partial Truth Table for Read/Write
Function (CY7C1361C) GW BWE BW
[3, 8]
D
BW
C
BW
B
BW
A
Read H H X X X X
Read HLHHHH
Write Byte (A, DQP
Write Byte (B, DQP
Write Bytes (B, A, DQP
Write Byte (C, DQP
Write Bytes (C, A, DQP
Write Bytes (C, B, DQP
Write Bytes (C, B, A, DQP
Write Byte (D, DQP
Write Bytes (D, A, DQP
Write Bytes (D, B, DQP
Write Bytes (D, B, A, DQP
Write Bytes (D, B, DQP
Write Bytes (D, B, A, DQP
Write Bytes (D, C, A, DQP
)HLHHHL
A
)HLHHLH
B
, DQPB)HLHHLL
A
) HLHLHH
C
, DQPA) HLHLHL
C
, DQPB)HLHLLH
C
, DQPB, DQPA)HLHLLL
C
)HLLHHH
D
, DQPA)HLLHHL
D
, DQPA)HLLHLH
D
, DQPB, DQPA)H L L H L L
D
, DQPB)HLLLHH
D
, DQPC, DQPA)H L L L H L
D
, DQPB, DQPA)HLLLLH
D
Write All Bytes HLLLLL
Write All Bytes L X X X X X
Truth Table for Read/Write
[3, 8]
Function (CY7C1363C)
GW
BWE BW
B
BW
Read H H X X
Read H L H H
Write Byte A – (DQ
Write Byte B – (DQ
and DQPA)HLHL
A
and DQPB)HLLH
B
Write All Bytes H L L L
Write All Bytes L X X X
Note:
8. Table only lists a partial listing of the byte write combinations. An y Combination of BW
is valid Appropriate write will be done based on which byte write is active.
X
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 11 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 12

T
O
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
IEEE 1149.1 Serial Boundary Scan (JTAG)
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C incorporates a serial boundary
scan test access port (TAP) in the BGA package only. The
TQFP package does not offer this functionality. This part
operates in accordance with IEEE Standard 1149.1-1900, but
doesn’t have the set of functions required for full 1149.1
compliance. These functions from the IEEE specification are
excluded because their inclusion places an added delay in the
critical speed path of the SRAM. Note the TAP controller
functions in a manner that does not conflict with the operation
of other devices using 1149.1 fully compliant TAPs. The TAP
operates using JEDEC-standard 3.3V or 2.5V I/O logic levels.
The CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C contains a TAP controller,
instruction register, boundary scan register, bypass register,
and ID register.
Disabling the JTAG Feature
It is possible to operate the SRAM without using the JTAG
feature. To disable the TAP controller, TCK must be tied LOW
(V
) to prevent clocking of the device. TDI and TMS are inter-
SS
nally pulled up and may be unconnected. They may alternately
be connected to V
left unconnected. Upon power-up, the device will come up in
through a pull-up resistor. TDO should be
DD
a reset state which will not interfere with the operation of the
device.
TAP Controller State Diagram
TEST-LOGIC
1
RESET
0
0
RUN-TEST/
IDLE
1
SELECT
DR-SCAN
1 1
CAPTURE-DR
SHIFT-DR
EXIT1-DR
PAUSE-DR
0 0
EXIT2-DR
UPDATE-DR
1 0
1
0
0
0 0
1
1 1
0 0
0
1
1
IR-SCAN
CAPTURE-IR
SHIFT-IR
EXIT1-IR
PAUSE-IR
EXIT2-IR
UPDATE-IR
1
SELECT
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
Test MODE SELECT (TMS)
The TMS input is used to give commands to the TAP controller
and is sampled on the rising edge of TCK. It is allowable to
leave this ball unconnected if the TAP is not used. The ball is
pulled up internally, resulting in a logic HIGH level.
Test Data-In (TDI)
The TDI ball is used to serially input information into the
registers and can be connected to the input of any of the
registers. The register between TDI and TDO is chosen by the
instruction that is loaded into the TAP instruction register. TDI
is internally pulled up and can be unconnected if the TAP is
unused in an application. TDI is connected to the most significant bit (MSB) of any register. (See Tap Controller Block
Diagram.)
Test Data-Out (TDO)
The TDO output ball is used to serially clock data-out from the
registers. The output is active depending upon the current
state of the TAP state machine. The output changes on the
falling edge of TCK. TDO is connected to the least significant
bit (LSB) of any register. (See Tap Controller State Diagram.)
TAP Controller Block Diagram
0
Bypass Register
012
TDI TD
TCK
MS TAP CONTROLLER
Selection
Circuitry
Performing a TAP Reset
A RESET is performed by forcing TMS HIGH (V
rising edges of TCK. This RESET does not affect the operation
of the SRAM and may be performed while the SRAM is
operating.
At power-up, the TAP is reset internally to ensure that TDO
comes up in a High-Z state.
Instruction Register
012293031 ...
Identification Register
012..x ...
Boundary Scan Register
S
election
Circuitr
y
DD
) for five
The 0/1 next to each state represents the value of TMS at the
rising edge of TCK.
TAP Registers
Registers are connected between the TDI and TDO balls and
allow data to be scanned into and out of the SRAM test
Test Access Port (TAP)
Test Clock (TCK)
The test clock is used only with the TAP controller. All inputs
are captured on the rising edge of TCK. All outputs are driven
from the falling edge of TCK.
circuitry. Only one register can be selected at a time through
the instruction register. Data is serially loaded into the TDI ball
on the rising edge of TCK. Data is output on the TDO bal l on
the falling edge of TCK.
Instruction Register
Three-bit instructions can be serially loaded into the instruction
register. This register is loaded when it is placed between the
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 12 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 13

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
TDI and TDO balls as shown in the Tap Controller Block
Diagram. Upon power-up, the instruction register is loaded
with the IDCODE instruction. It is also loaded with the IDCODE
instruction if the controller is placed in a reset state as
described in the previous section.
When the TAP controller is in the Capture-IR state, the two
least significant bits are loaded with a binary “01” pattern to
allow for fault isolation of the board-level serial test data path.
Bypass Register
To save time when serially shifting data through registers, it is
sometimes advantageous to skip certain chips. The bypass
register is a single-bit register that can be pla ced betwee n the
TDI and TDO balls. This allows data to be shifted through the
SRAM with minimal delay. The bypass register is set LOW
(V
) when the BYPASS instruction is executed.
SS
Boundary Scan Register
The boundary scan register is connected to all the input and
bidirectional balls on the SRAM.
The boundary scan register is loaded with the contents of the
RAM I/O ring when the TAP controller is in the Capture-DR
state and is then placed between the TDI and TDO balls when
the controller is moved to the Shift-DR state. The EXTEST,
SAMPLE/PRELOAD and SAMPLE Z instructions can be used
to capture the contents of the I/O ring.
The Boundary Scan Order tables show the order in which the
bits are connected. Each bit corresponds to one of the bumps
on the SRAM package. The MSB of the register is connected
to TDI and the LSB is connected to TDO.
Identification (ID) Register
The ID register is loaded with a vendor-specific, 32-bit code
during the Capture-DR state when the IDCODE command is
loaded in the instruction register. The IDCODE is hardwired
into the SRAM and can be shifted out when the TAP controller
is in the Shift-DR state. The ID register has a vendor code and
other information described in the Identification Register
Definitions table.
TAP Instruction Set
Overview
Eight different instructions are possible with the three-bit
instruction register. All combinations are listed in the
Instruction Codes table. Three of these instructions are listed
as RESERVED and should not be used. The other five instructions are described in detail below.
The TAP controller used in this SRAM is not fully compliant to
the 1149.1 convention because some of the mandatory 1 149.1
instructions are not fully implemented.
The TAP controller cannot be used to load address data or
control signals into the SRAM and cannot preload the I/O
buffers. The SRAM does not implement the 1149.1 commands
EXTEST or INTEST or the PRELOAD portion of
SAMPLE/PRELOAD; rather, it performs a capture of the I/O
ring when these instructions are executed.
Instructions are loaded into the TAP controller during the
Shift-IR state when the instruction register is placed between
TDI and TDO. During this state, instructions are shifted
through the instruction register through the TDI and TDO balls.
To execute the instruction once it is shifted in, the TAP
controller needs to be moved into the Update-IR state.
EXTEST
EXTEST is a mandatory 1149.1 instruction which is to be
executed whenever the instruction register is loaded with all
0s. EXTEST is not implemented in this SRAM TAP controller,
and therefore this device is not compliant to 1149.1. The TAP
controller does recognize an all-0 instruction.
When an EXTEST instruction is loaded into the instruction
register, the SRAM responds as if a SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction has been loaded. There is one difference between
the two instructions. Unlike the SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction, EXTEST places the SRAM outputs in a High-Z
state.
IDCODE
The IDCODE instruction causes a vendor-specific, 32-bit code
to be loaded into the instruction register. It also places the
instruction register between the TDI and TDO balls and allows
the IDCODE to be shifted out of the device when the TAP
controller enters the Shift-DR state.
The IDCODE instruction is loaded into the instruction reg ister
upon power-up or whenever the TAP controller is given a test
logic reset state.
SAMPLE Z
The SAMPLE Z instruction causes the boundary scan register
to be connected between the TDI and TDO balls when the TAP
controller is in a Shift-DR state. It also places all SRAM outputs
into a High-Z state.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
SAMPLE/PRELOAD is a 1149.1-mandatory instruction. When
the SAMPLE/PRELOAD instructions are loaded into the instruction register and the TAP controller is in the Capture-DR
state, a snapshot of data on the inputs and output pins is captured in the boundary scan register.
The user must be aware that the TAP controller clock can only
operate at a frequency up to 20 MHz, while the SRAM clock
operates more than an order of magnitude faster. Because
there is a large difference in the clock frequencies, it is possible that during the Capture-DR state, an input or output will
undergo a transition. The TAP may then try to capture a signal
while in transition (metastable state). This will not harm the
device, but there is no guarantee as to the value th at will be
captured. Repeatable results may not be possible.
To guarante e th at the boun dary scan register will capture the
correct value of a signal, the SRAM signal must be stabilized
long enough to meet the TAP controller's capture set-up plus
hold times (t
captured correctly if there is no way in a design to stop (o r
slow) the clock during a SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction. If this
is an issue, it is still possible to capture all other signals and
simply ignore the value of the CK and CK# captured in the
boundary scan register.
Once the data is captured, it is possible to shift out the data by
putting the TAP into the Shift-DR state. This places the boundary scan register between the TDI and TDO pins.
and tCH). The SRAM clock input might not be
CS
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 13 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 14

123456
T
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
PRELOAD allows an initial data pattern to be placed at the
latched parallel outputs of the boundary scan register cells
prior to the selection of another boundary scan test operation.
The shifting of data for the SAMPLE and PRELOAD phases
can occur concurrently when required—that is, while data
captured is shifted out, the preloaded data can be shifted in.
TAP Timing
Test Clock
(TCK)
est Mode Select
(TMS)
Test Data-In
(TDI)
Test Data-Out
(TDO)
t
TMSS
t
TDIS
t
t
TMSH
t
TDIH
TH
BYPASS
When the BYPASS instruction is loaded in the instruction
register and the TAP is placed in a Shift-DR state, the bypass
register is placed between the TDI and TDO balls. The
advantage of the BYPASS instruction is that it shortens the
boundary scan path when multiple devices are connected
together on a board.
Reserved
These instructions are not implemented but are reserved for
future use. Do not use these instructions.
t
TL
t
CYC
t
TDOX
t
TDOV
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
TAP AC Switching Characteristics
Over the Operating Range
[9, 10]
Parameter Parameter Min. Max. Unit
Clock
t
TCYC
t
TF
t
TH
t
TL
TCK Clock Cycle Time 50 ns
TCK Clock Frequency 20 MHz
TCK Clock HIGH Time 20 ns
TCK Clock LOW Time 20 ns
Output Times
t
TDOV
t
TDOX
Set-up Times
t
TMSS
t
TDIS
t
CS
TCK Clock LOW to TDO Valid 10 ns
TCK Clock LOW to TDO Invalid 0 ns
TMS Set-Up to TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
TDI Set-Up to TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
Capture Set-Up to TCK Rise 5 ns
Hold Times
t
TMSH
t
TDIH
t
CH
Notes:
9. t
and tCH refer to the setup and hold time requirements of latching data from the boundary scan register.
CS
10.Test conditions are specified using the load in TAP AC test conditions. t
TMS Hold after TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
TDI Hold after Clock Rise 5 ns
Capture Hold after Clock Rise 5 ns
= 1 ns.
R/tF
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 14 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 15

T
F
T
F
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
3.3V TAP AC Test Conditions
Input pulse levels................................................ VSS to 3.3V
Input rise and fall times................................................ ...1 ns
Input timing reference levels...........................................1.5V
Output reference levels...................................................1.5V
Test load termination supply voltage...............................1.5V
3.3V TAP AC Output Load Equivalent
1.5V
50Ω
DO
Z = 50Ω
O
20p
2.5V TAP AC Test Conditions
Input pulse levels.................................................VSS to 2.5V
Input rise and fall time .....................................................1 ns
Input timing reference levels.........................................1.25V
Output reference levels ................................................1.25V
Te st load termination supply voltage ............................1.25V
2.5V TAP AC Output Load Equivalent
1.25V
50Ω
DO
Z = 50Ω
O
20p
TAP DC Electrical Characteristics And Operating Conditions
(0°C < TA < +70°C; VDD = 3.3V ±0.165V unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Description Description Conditions Min. Max. Unit
V
OH1
V
OH2
V
OL1
V
OL2
V
IH
V
IL
I
X
Identification Register Definitions
Output HIGH Voltage IOH = –4.0 mA V
I
= –1.0 mA V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage IOH = –100 µA V
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 8.0 mA V
I
= 8.0 mA V
OL
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 100 µA V
Input HIGH Voltage V
Input LOW Voltage V
Input Load Current GND < VIN < V
CY7C1361C
Instruction Field
(256K x36)
Revision Number (31:29) 000 000 Describes the version number.
Device Depth (28:24)
[12]
01011 0101 1 Reserved for Internal Use
Device Width (23:18) 119-BGA 101001 101001 Defines memory type and architecture
Device Width (23:18) 165-FBGA 000001 000001 Defines memory type and architecture
Cypress Device ID (17:12) 100110 010110 Defines width and density
Cypress JEDEC ID Code (11:1) 00000110100 00000110100 Allows unique identification of SRAM vendor.
ID Register Presence Indicator (0) 1 1 Indicates the presence of an ID register.
[11]
= 3.3V 2.4 V
DDQ
= 2.5V 2.0 V
DDQ
= 3.3V 2.9 V
DDQ
V
= 2.5V 2.1 V
DDQ
= 3.3V 0.4 V
DDQ
= 2.5V 0.4 V
DDQ
= 3.3V 0.2 V
DDQ
V
= 2.5V 0.2 V
DDQ
= 3.3V 2.0 VDD + 0.3 V
DDQ
V
= 2.5V 1.7 VDD + 0.3 V
DDQ
= 3.3V –0.5 0.7 V
DDQ
V
= 2.5V –0.3 0.7 V
DDQ
DDQ
CY7C1363C
(512K x18) Description
–5 5 µA
Notes:
11.All voltages referenced to V
12.Bit #24 is “1” in the Register Definitions for both 2.5V and 3.3V versions of this device.
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 15 of 31
(GND).
SS
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Scan Register Sizes
Register Name Bit Size (x 36) Bit Size (x 18)
Instruction 3 3
Bypass 1 1
ID 32 32
Boundary Scan Order (119-ball BGA package) 71 71
Boundary Scan Order (165-ball FBGA package) 71 71
Identification Codes
Instruction Code Description
EXTEST 000 Captures I/O ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
IDCODE 001 Loads the ID register with the vendor ID code and places the register between TDI and TDO.
SAMPLE Z 010 Captures I/O ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
RESERVED 01 1 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD 100 Captures I/O ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
RESERVED 101 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
RESERVED 1 1 0 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
BYPASS 111 Places the bypass register between TDI and TDO. This operation does not affect SRAM
Forces all SRAM outputs to High-Z state.
This operation does not affect SRAM operations.
Forces all SRAM output drivers to a High-Z state.
Does not affect SRAM operation.
operations.
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 16 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 17

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
119-Ball BGA Boundary Scan Order
CY7C1361C (256K x 36) CY7C1363C (512K x 18)
Bit # ball ID
1
K4
2H4 GW
3M4BWE
4F4 OE
5B4ADSC
6A4ADSP
Name Bit # ball ID
CLK 37 P4 A0 1
38 N4 A1 2 H4 GW 38 N4 A1
39 R6 A 3 M4 BWE 39 R6 A
40 T5 A 4 F4 OE 40 T5 A
41 T3 A 5 B4 ADSC 41 T3 A
42 R2 A 6 A4 ADSP 42 R2 A
7 G4 ADV 43 R3 MODE 7 G4 ADV
8C3 A 44 P2 DQP
9B3 A 45 P1 DQ
Signal
10 D6 DQP
11 H7 DQ
12 G6 DQ
13 E6 DQ
14 D7 DQ
15 E7 DQ
16 F6 DQ
17 G7 DQ
18 H6 DQ
46 L2 DQ
B
47 K1 DQ
B
48 N2 DQ
B
49 N1 DQ
B
50 M2 DQ
B
51 L1 DQ
B
52 K2 DQ
B
53 Internal Internal 17 G7 DQ
B
54 H1 DQ
B
19 T7 ZZ 55 G2 DQ
20 K7 DQ
21 L6 DQ
22 N6 DQ
23 P7 DQ
24 N7 DQ
25 M6 DQ
26 L7 DQ
27 K6 DQ
28 P6 DQP
56 E2 DQ
A
57 D1 DQ
A
58 H2 DQ
A
59 G1 DQ
A
60 F2 DQ
A
61 E1 DQ
A
62 D2 DQP
A
63 C2 A 27 Internal Internal 63 C2 A
A
64 A2 A 28 Internal Internal 64 A2 A
A
29 T4 A 65 E4 CE
30 A3 A 66 B2 CE
31 C5 A 67 L3 BWD 31 C5 A 67 Internal Internal
32 B5 A 68 G3 BW
33 A5 A 69 G5 BW
34 C6 A 70 L5 BW
35 A6 A 71 Internal Internal 35 A6 A 71 Internal Internal
36 B6 A 36 B6 A
Signal
Name Bit # ball ID
K4
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
1
2
C
B
A
8 C3 A 44 Internal Internal
9 B3 A 45 Internal Internal
10 T2 A 46 Internal Internal
11 Internal Internal 47 Internal Internal
12 Internal Internal 48 P2 DQP
13 Internal Internal 49 N1 DQ
14 D6 DQP
15 E7 DQ
16 F6 DQ
18 H6 DQ
19 T7 ZZ 55 G2 DQ
20 K7 DQ
21 L6 DQ
22 N6 DQ
23 P7 DQ
24 Internal Internal 60 Internal Internal
25 Internal Internal 61 Internal Internal
26 Internal Internal 62 Internal Internal
29 T6 A 65 E4 CE
30 A3 A 66 B2 CE
32 B5 A 68 Internal Internal
33 A5 A 69 G3 BW
34 C6 A 70 L5 BW
Signal
Name Bit # ball ID
Signal
Name
CLK 37 P4 A0
43 R3 MODE
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
50 M2 DQ
51 L1 DQ
52 K2 DQ
53 Internal Internal
54 H1 DQ
56 E2 DQ
57 D1 DQ
58 Internal Internal
59 Internal Internal
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
1
2
B
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 17 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 18

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
165-Ball FBGA Boundary Scan Order
CY7C1361C (256K x 36) CY7C1363C (512K x 18)
Bit # ball ID
Name Bit # ball ID
1 B6 CLK 37 R6 A0 1 B6 CLK 37 R6 A0
Signal
2B7 GW
3A7BWE
4B8 OE
5A8ADSC
6B9ADSP
7A9ADV
38 P6 A1 2 B7 GW 38 P6 A1
39 R4 A 3 A7 BWE 39 R4 A
40 P4 A 4 B8 OE 40 P4 A
41 R3 A 5 A8 ADSC 41 R3 A
42 P3 A 6 B9 ADSP 42 P3 A
43 R1 MODE 7 A9 ADV 43 R1 MODE
8B10 A 44 N1 DQP
9A10 A 45 L2 DQ
10 C11 DQP
11 E10 DQ
12 F10 DQ
13 G10 DQ
14 D10 DQ
15 D11 DQ
16 E11 DQ
17 F11 DQ
18 G11 DQ
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
46 K2 DQ
B
47 J2 DQ
48 M2 DQ
49 M1 DQ
50 L1 DQ
51 K1 DQ
52 J1 DQ
53 Internal Internal 17 F11 DQ
54 G2 DQ
19 H11 ZZ 55 F2 DQ
20 J10 DQ
21 K10 DQ
22 L10 DQ
23 M10 DQ
24 J11 DQ
25 K11 DQ
26 L11 DQ
27 M11 DQ
28 N11 DQP
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
56 E2 DQ
57 D2 DQ
58 G1 DQ
59 F1 DQ
60 E1 DQ
61 D1 DQ
62 C1 DQP
63 B2 A 27 Internal Internal 63 B2 A
64 A2 A 28 Internal Internal 64 A2 A
A
29 R11 A 65 A3 CE
30 R10 A 66 B3 CE
31 P10 A 67 B4 BW
32 R9 A 68 A4 BW
33 P9 A 69 A5 BW
34 R8 A 70 B5 BW
35 P8 A 71 A6 CE
36 P11 A 36 P11 A
Signal
Name Bit # ball ID
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
1
2
D
C
B
A
3
8 B10 A 44 Internal Internal
9 A10 A 45 Internal Internal
10 A11 A 46 Internal Internal
1 1 Internal Internal 47 Internal Internal
12 Internal Internal 48 N1 DQP
13 Internal Internal 49 M1 DQ
14 C11 DQP
15 D11 DQ
16 E11 DQ
18 G11 DQ
19 H11 ZZ 55 F2 DQ
20 J10 DQ
21 K10 DQ
22 L10 DQ
23 M10 DQ
24 Internal Internal 60 Internal Internal
25 Internal Internal 61 Internal Internal
26 Internal Internal 62 Internal Internal
29 R11 A 65 A3 CE
30 R10 A 66 B3 CE
31 P10 A 67 Internal Internal
32 R9 A 68 Internal Internal
33 P9 A 69 A4 BW
34 R8 A 70 B5 BW
35 P8 A 71 A6 CE
Signal
Name Bit # ball ID
50 L1 DQ
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
51 K1 DQ
52 J1 DQ
53 Internal Internal
54 G2 DQ
56 E2 DQ
57 D2 DQ
58 Internal Internal
59 Internal Internal
Signal
Name
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
1
2
B
A
3
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 18 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 19

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Maximum Ratings
(Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guidelines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature ................................–65°C to + 150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied............................................–55°C to + 125°C
Supply Voltage on V
Supply Voltage on V
Relative to GND.......–0.5V to + 4.6V
DD
Relative to GND.....–0.5V to + V
DDQ
DD
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in tri-state................................... ... ... ...–0.5V to V
DC Input Voltage....................................–0.5V to V
DDQ
DD
+ 0.5V
+ 0.5V
Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Current into Outputs (LOW).........................................20 mA
Static Discharge Voltage........................................... >2001V
(per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch-up Current..................................................... >200 mA
Operating Range
Range
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 3.3V – 5%/+10% 2.5V – 5%
Industrial –40°C to +85°C
Automotive –40°C to +125°C
[13, 14]
Ambient
Temperature V
DD
V
to V
DDQ
DD
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
V
V
DD
DDQ
Power Supply Voltage 3.135 3.6 V
I/O Supply Voltage for 3.3V I/O 3.135 V
DD
for 2.5V I/O 2.375 2.625 V
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
Output HIGH Voltage for 3.3V I/O, I
for 2.5V I/O, I
= −4.0 mA 2.4 V
OH
= −1.0 mA 2.0 V
OH
Output LOW Voltage for 3.3V I/O, IOL= 8.0 mA 0.4 V
Input HIGH Voltage
for 2.5V I/O, I
[13]
for 3.3V I/O 2.0 VDD + 0.3V V
= 1.0 mA 0.4 V
OL
for 2.5V I/O 1.7 VDD + 0.3V V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage
[13]
for 3.3V I/O –0.3 0.8 V
for 2.5V I/O –0.3 0.7 V
I
X
I
OZ
I
DD
I
SB1
I
SB2
I
SB3
I
SB4
Input Leakage Current
GND ≤ VI ≤ V
except ZZ and MODE
Input Current of MODE Input = V
Input = V
Input Current of ZZ Input = V
Input = V
SS
DD
SS
DD
Output Leakage Current GND < VI < V
VDD Operating Supply
Current
Automatic CE
Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
Automatic CE
Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CE
Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CE
Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
V
= Max., I
DD
f = f
MAX
= 1/t
Max. VDD, Device Deselected,
V
> VIH or VIN < VIL, f = f
IN
inputs switching
Max. V
V
IN
f = 0, inputs static
, Device Deselected,
DD
> VDD – 0.3V or VIN < 0.3V,
Max. VDD, Device Deselected,
V
IN
f = f
> V
MAX
– 0.3V or VIN < 0.3V,
DDQ
, inputs switching
Max. VDD, Device Deselected,
> VIH or VIN < V
V
IN
f = 0, inputs static
DDQ
–5 5 µA
–30 µA
–5 µA
Output Disabled –5 5 µA
DDQ,
OUT
CYC
= 0 mA,
7.5-ns cycle,133 MHz 250 mA
10-ns cycle,100 MHz 180
All speeds (Comm/Ind’l) 110 mA
MAX,
10-ns cycle,100 MHz
(Automotive)
All speeds 40 mA
All speeds (Comm/Ind’l) 100 mA
10-ns cycle,100 MHz
(Automotive)
All speeds (Comm/Ind’l) 40 mA
IL
10-ns cycle,100 MHz
(Automotive)
5 µA
30 µA
150 mA
120 mA
60 mA
V
Notes:
13.Overshoot: V
14.T
Power-up
(AC) < VDD +1.5V (Pulse width less than t
IH
: Assumes a linear ramp from 0V to VDD(min.) within 200ms. During this time VIH < VDD and V
/2), undershoot: VIL(AC) > –2V (Pulse width less than t
CYC
DDQ
< VDD.
CYC
/2).
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 19 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 20

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Capacitance
[15]
Parameter De scription Test Conditions
C
Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
IN
C
C
CLK
I/O
Clock Input Capacitance 5 5 5 pF
Input/Output Capacitance 5 7 7 pF
Thermal Resistance
[15]
V
V
DD
DDQ
= 3.3V
= 2.5V
Parameter Description Test Conditions
Θ
Θ
JA
JC
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Case)
Test conditions follow standard
test methods and procedures
for measuring thermal
impedance, per EIA/JESD51
AC Test Loads and Waveforms
3.3V I/O Test Load
OUTPUT
Z
= 50Ω
0
R
L
VT= 1.5V
(a) (b)
3.3V
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
5pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
2.5V I/O Test Load
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
Z
0
= 1.25V
V
T
R
L
(a) (b)
Note:
15.Tested initially and after any design or process change that may affect these parameters.
2.5V
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
5pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
R = 317Ω
R = 351Ω
R = 1667Ω
R = 1538Ω
100 TQFP
Max.
119 BGA
Max.
165 FBGA
Max. Unit
555pF
100 TQFP
Package
119 BGA
Package
165 FBGA
Package Unit
29.41 34.1 16.8 °C/W
6.31 14.0 3.0 °C/W
V
DDQ
GND
≤ 1 ns
ALL INPUT PULSES
10%
90%
90%
10%
≤ 1 ns
(c)
V
DDQ
GND
≤ 1 ns
ALL INPUT PULSES
10%
90%
90%
10%
≤ 1 ns
(c)
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 20 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 21

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description
t
POWER
Clock
t
CYC
t
CH
t
CL
Output Times
t
CDV
t
DOH
t
CLZ
t
CHZ
t
OEV
t
OELZ
t
OEHZ
Set-up Times
t
AS
t
ADS
t
ADVS
t
WES
t
DS
t
CES
Hold Times
t
AH
t
ADH
t
WEH
t
ADVH
t
DH
t
CEH
VDD(Typical) to the first Access
Clock Cycle Time 7.5 10 ns
Clock HIGH 3.0 4.0 n s
Clock LOW 3.0 4.0 ns
Data Output Valid After CLK Rise 6.5 8.5 ns
Data Output Hold After CLK Rise 2.0 2.0 ns
Clock to Low-Z
Clock to High-Z
[17, 18, 19]
[17, 18, 19]
OE LOW to Output Valid 3.5 3.5 ns
OE LOW to Output Low-Z
OE HIGH to Output High-Z
Address Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
ADSP, ADSC Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
ADV Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
GW, BWE, BW
Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
[A:D]
Data Input Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Chip Enable Set-up 1.5 1.5 ns
Address Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
ADSP, ADSC Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
GW, BWE, BW
Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
[A:D]
ADV Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Data Input Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Chip Enable Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
[16]
[17, 18, 19]
[17, 18, 19]
[20, 21]
–133 –100
UnitMin. Max. Min. Max.
11ms
00ns
3.5 3.5 ns
00ns
3.5 3.5 ns
Notes:
16.This part has a voltage regulator internally; t
can be initiated.
, t
17.t
CHZ
18.At any given voltage and temperature, t
data bus. These specifications do not imply a bus contention co nditi on, b ut ref lect pa r ameters gu aran te ed over worst case user condit ions. Device is desig ned
to achieve High-Z prior to Low-Z under the same system conditions.
19.This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
20.Timing reference level is 1.5V when V
21.Test conditions shown in (a) of AC Test Loads unless otherwise noted.
CLZ,tOELZ
, and t
are specified with AC test conditions shown in par t (b) of AC Test Loads. Transition is measured ± 200 mV from steady- state vo ltage.
OEHZ
OEHZ
DDQ
is the time that the power needs to be supplied above VDD(minimum) initially, before a rea d or write operation
POWER
is less than t
= 3.3V and is 1.25V when V
OELZ
and t
is less than t
CHZ
= 2.5V.
DDQ
to eliminate bus contention between SRAMs when sharing the same
CLZ
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 21 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 22

Timing Diagrams
G
Read Cycle Timing
[22]
t
CYC
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
CLK
ADSP
ADSC
ADDRESS
W, BWE,BW
X
CE
ADV
t
ADS
t
AS
t
CES
A1
t
CH
t
ADH
t
AH
t
CEH
t
t
WES
CL
t
t
ADH
ADS
A2
t
WEH
Deselect Cycle
t
t
ADVH
ADVS
ADV suspends burst
OE
Data Out (Q)
High-Z
t
OEV
t
CLZ
t
CDV
Single READ
t
OEHZ
Q(A1)
t
OELZ
t
DOH
Q(A2)
t
CDV
Q(A2 + 1)
Q(A2 + 2)
BURST
Q(A2 + 3)
Q(A2)
Q(A2 + 1)
Burst wraps around
to its initial state
t
CHZ
Q(A2 + 2)
READ
Note:
22.On this diagram, when CE
is LOW: CE1 is LOW, CE2 is HIGH and CE3 is LOW. When CE is HIGH: CE1 is HIGH or CE2 is LOW or CE3 is HIGH.
DON’T CARE
UNDEFINED
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 22 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 23

Timing Diagrams (continued)
D
Write Cycle Timing
[22, 23]
t
CYC
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
CLK
ADSP
ADSC
ADDRESS
BWE,
BW
X
GW
CE
ADV
t
t
CL
CH
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
AH
AS
A1
Byte write signals are ignored for first cycle when
ADSP initiates burst
t
t
CEH
CES
A2 A3
t
WES
t
WEH
ADSC extends burst
ADV suspends burst
t
ADS
t
ADH
t
WES
t
ADVS
t
WEH
t
ADVH
OE
t
DS
Data in (D)
ata Out (Q)
Note:
23.
Full width write can be initiated by either GW
High-Z
BURST READ BURST WRITE
t
OEHZ
D(A1)
Single WRITE
t
DH
D(A2)
D(A2 + 1)
D(A2 + 1)
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
LOW; or by GW HIGH, BWE LOW and BWX LOW.
D(A2 + 2)
D(A2 + 3)
D(A3 + 1)
D(A3)
Extended BURST WRITE
D(A3 + 2)
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 23 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 24

Timing Diagrams (continued)
t
D
Read/Write Cycle Timing
[22, 24, 25]
CYC
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
CLK
t
ADS
t
t
CH
ADH
t
CL
ADSP
ADSC
t
t
AH
AS
ADDRESS
BWE, BW
A1 A5 A6
X
A2
t
t
CEH
CES
A3 A4
t
t
WEH
WES
CE
ADV
OE
t
t
DH
Data In (D)
ata Out (Q)
DS
High-Z
Q(A1)
Q(A2)
t
OEHZ
Back-to-Back READs
D(A3)
Single WRITE
t
OELZ
t
CDV
Q(A4) Q(A4+1)
BURST READ
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
Notes:
24.The data bus (Q) remains in high-Z following a WRITE cycle, unless a new read access is initiated by ADSP
25.
is HIGH.
GW
Q(A4+2)
or ADSC.
D(A5) D(A6)
Q(A4+3)
Back-to-Back
WRITEs
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 24 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 25

Timing Diagrams (continued)
A
ZZ Mode Timing
[26, 27]
CLK
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
t
ZZ
t
ZZREC
ZZ
I
SUPPLY
LL INPUTS
(except ZZ)
Outputs (Q)
t
ZZI
I
DDZZ
High-Z
t
RZZI
DESELECT or READ Only
DON’T CARE
Notes:
26.Device must be deselected when entering ZZ mode. See Cycle Descriptions table for all possible signal conditions to deselect the device.
27.DQs are in high-Z when exiting ZZ sleep mode.
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 25 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 26

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Ordering Information
Not all of the speed, package and temperature ranges are available. Please contact your local sales representative or
Speed
(MHz) Ordering Code
133 CY7C1361C-133AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133AXC
CY7C1361C-133AJXC 51-85050 1 00-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133AJXC
CY7C1361C-133BGC 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-133BGC
CY7C1361C-133BGXC 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133BGXC
CY7C1361C-133BZC 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-133BZC
CY7C1361C-133BZXC 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133BZXC
CY7C1361C-133AXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133AXI
CY7C1361C-133AJXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133AJXI
CY7C1361C-133BGI 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-133BGI
CY7C1361C-133BGXI 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133BGXI
CY7C1361C-133BZI 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-133BZI
CY7C1361C-133BZXI 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-133BZXI
visit www.cypress.com for actual products offered.
Package
Diagram Part and Package Type
(3 Chip Enable)
(2 Chip Enable)
(3 Chip Enable)
(2 Chip Enable)
Operating
Range
Commercial
lndustrial
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 26 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 27

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Ordering Information (continued)
Not all of the speed, package and temperature ranges are available. Please contact your local sales representative or
Speed
(MHz) Ordering Code
100 CY7C1361C-100AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100AXC
CY7C1361C-100AJXC 51-85050 1 00-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100AJXC
CY7C1361C-100BGC 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-100BGC
CY7C1361C-100BGXC 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100BGXC
CY7C1361C-100BZC 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-100BZC
CY7C1361C-100BZXC 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100BZXC
CY7C1361C-100AXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100AXI
CY7C1361C-100AJXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100AJXI
CY7C1361C-100BGI 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-100BGI
CY7C1361C-100BGXI 51-85115 119-ball Ball Grid Array (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100BGXI
CY7C1361C -100BZI 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1363C-100BZI
CY7C1361C-100BZXI 51-85180 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free
CY7C1363C-100BZXI
100 CY7C1361C-100AXE 51-85050 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free Automotive
visit www.cypress.com for actual products offered.
Package
Diagram Part and Package Type
(3 Chip Enable)
(2 Chip Enable)
(3 Chip Enable)
(2 Chip Enable)
Operating
Range
Commercial
lndustrial
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 27 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 28

Package Diagrams
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.25
GAUGE PLANE
0°-7°
0.60±0.15
1.00 REF.
20.00±0.10
22.00±0.20
100-Pin TQFP (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) (51-85050)
16.00±0.20
14.00±0.10
100
1
30
31 50
0° MIN.
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.20 MIN.
A
DETAIL
81
80
0.30±0.08
0.65
TYP.
51
STAND-OFF
0.05 MIN.
0.15 MAX.
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
1.40±0.05
12°±1°
(8X)
SEATING PLANE
NOTE:
1. JEDEC STD REF MS-026
2. BODY LENGTH DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH
MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH SHALL NOT EXCEED 0.0098 in (0.25 mm) PER SIDE
BODY LENGTH DIMENSIONS ARE MAX PLASTIC BODY SIZE INCLUDING MOLD MISMATCH
3. DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS
51-85050-*B
SEE DETAIL
0.20 MAX.
1.60 MAX.
0.10
A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 28 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 29

Package Diagrams (continued)
A1 CORNER
2165437
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
119- Ba ll BGA (14 x 22 x 2.4 mm) (51-85115)
Ø1.00(3X) REF.
1.27
19.50
20.32
22.00±0.20
10.16
CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Ø0.05 M C
Ø0.25MCAB
Ø0.75±0.15(119X)
2143657
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
0.70 REF.
12.00
30° TYP.
0.90±0.05
0.25 C
SEATING PLANE
C
0.56
2.40 MAX.
0.15 C
0±0.10
A
B
0.15(4X)
3.81
7.62
14.00±0.20
51-85115-*B
1.27
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 29 of 31
[+] Feedback
Page 30

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Package Diagrams (continued)
165 FBGA 13 x 15 x 1.40 MM BB165D/BW165D
165-Ball FBGA (13 x 15 x 1.4 mm) (51-85 180)
TOP VIEW
TOP VIEW
PIN 1 CORNER
15.00±0.10
A
0.25 C
15.00±0.10
A
0.53±0.05
0.25 C
0.36
B
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
B
0.53±0.05
C
0.36
PIN 1 CORNER
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
SEATING PLANE
C
13.00±0.10
13.00±0.10
SEATING PLANE
1110986754321
1110986754321
14.00
15.00±0.10
15.00±0.10
A
A
0.15(4X)
1.40 MAX.
0.15 C
0.15 C
1.40 MAX.
0.35±0.06
0.35±0.06
11
1.00
1.00
14.00
7.00
7.00
B
B
0.15(4X)
NOTES :
SOLDER PAD TYPE : NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED (NSMD)
PACKAGE WEIGHT : 0.475g
JEDEC REFERENCE : MO-216 / DESIGN 4.6C
PACKAGE CODE : BB0AC
i486 is a trademark, and Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel C orporation. PowerPC is a trademark of IBM
Corporation. All product and company names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of their respective holders.
11
5.00
BOTTOM VIEW
5.00
10.00
13.00±0.10
BOTTOM VIEW
Ø0.05 M C
Ø0.05 M C
Ø0.25MCAB
-0.06
Ø0.25 M C A B
Ø0.50 (165X)
+0.14
Ø0.50 (165X)
10.00
13.00±0.10
PIN1CORNER
-0.06
2345678910
+0.14
1.00
1.00
PIN 1 CORNER
1
2345678910
1
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
J
J
K
K
L
L
M
M
N
N
P
P
R
R
NOTES :
SOLDER PAD TYPE : NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED (NSMD)
PACKAGE WEIGHT : 0.475g
JEDEC REFERENCE : MO-216 / DESIGN 4.6C
PACKAGE CODE : BB0AC
51-85180-*A
51-85180-*A
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 30 of 31
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006. The information contained herein i s su bj ect to ch ange without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corpo ration assu mes no resp onsib ility for th e us e
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be
used for medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with Cypress. Furthermore, Cypres s does not auth orize its
products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
[+] Feedback
Page 31

CY7C1361C
CY7C1363C
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C1361C/CY7C1363C 9-Mbit (256K x 36/512K x 18) Flow-Through SRAM
Document Number: 38-05541
REV. ECN NO. Issue Date
** 241690 See ECN RKF New data sheet
*A 278969 See ECN RKF Changed Boundary Scan order to match the B rev of these devices.
*B 332059 See ECN PCI Removed 117-MHz Spee d Bin
*C 377095 See ECN PCI Changed I
*D 408298 See ECN RXU Changed address of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation on Page# 1
*E 433033 See ECN NXR Included Automotive range.
*F 501793 See ECN VKN Added the Maximum Rating for Supply Voltage on V
Orig. of
Change Description of Change
Address expansion pins/balls in the pinouts for all packages are modified
as per JEDEC standard
Added Address Expansion pins in the Pin Definitions Table
Changed Device Width (23:18) for 119-BGA from 000001 to 101001
Added separate row for 165 -FBGA Device Width (23:18)
Changed I
Changed I
Modified V
Corrected I
≥ VIH or VIN ≤ VIL) in the Electrical Characteristics table
(V
IN
Changed Θ
and 6.13 °C/W
from 35 mA to 50 mA
DDZZ
and I
SB1
OL, VOH
Test Condi tion from (VIN ≥ V
SB4
and ΘJc for TQFP Package from 25 and 9 °C/W to 29.41
JA
from 40 mA to 110 and 100 mA, respectively
SB3
test conditions
DD
respectively
Changed Θ
14.0 °C/W
and ΘJc for BGA Package from 25 and 6°C/W to 34.1 and
JA
respectively
Changed Θ
and 3.0 °C/W respectively
JA
and Θ
for FBGA Package from 27 and 6 °C/W to 16.8
Jc
Added lead-free information for 100-pin TQFP, 119 BGA and 165 FBGA
packages
Updated Ordering Information Table
from 30 to 40 mA
Modified test condition in note# 14 from V
SB2
IH
< V
from “3901 North First Street” to “198 Champion Court”
Changed tri state to tri-state.
Modified “Input Load” to “Input Leakage Current except ZZ and MODE”
in the Electrical Characteristics Table.
Replaced Package Name column with Package Diagram in the Ordering
Information table.
Updated the ordering information.
Changed t
AC Switching Characteristics table.
, t
from 25 ns to 20 ns and t
TH
TL
TDOV
Updated the Ordering Information table.
– 0.3V or VIN ≤ 0.3V) to
DD to VIH
from 5 ns to 10 ns in T AP
< V
Relative to GND
DDQ
DD
Document #: 38-05541 Rev. *F Page 31 of 31
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...