CYPRESS CY7C1339F User Manual
查询CY7C1339F-100AC供应商查询CY7C1339F-100AC供应商
CY7C1339F
4-Mbit (128K x 32) Pipelined Sync SRAM
Features
• Registered inputs and outputs for pipelined operation
• 128K × 32 common I/O architecture
• 3.3V core power supply
• 2.5V / 3.3V I/O operation
• Fast clock-to-output times
— 2.6 ns (for 250-MHz device)
— 2.6 ns (for 225-MHz device)
— 2.8 ns (for 200-MHz device)
— 3.5 ns (for 166-MHz device)
— 4.0 ns (for 133-MHz device)
— 4.5 ns (for 100-MHz device)
• Provide high-performance 3-1-1-1 access rate
• User-selectable burst counter supporting Intel
Pentium
interleaved or linear burst sequences
• Separate processor and controller address strobes
• Synchronous self-timed writes
• Asynchronous output enable
• Offered in JEDEC-standard 100-pin TQFP and 119-ball
BGA packages
• “ZZ” Sleep Mode Option
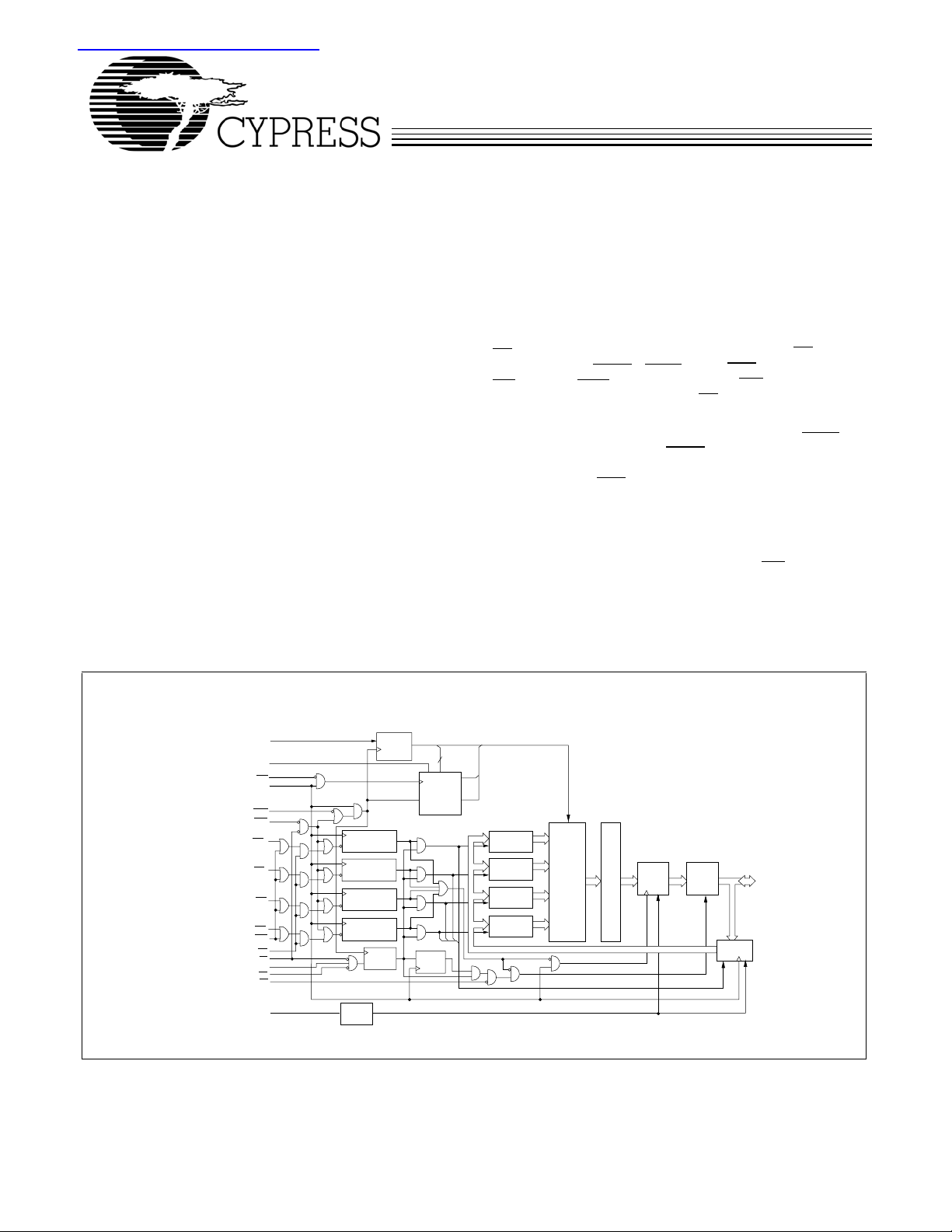
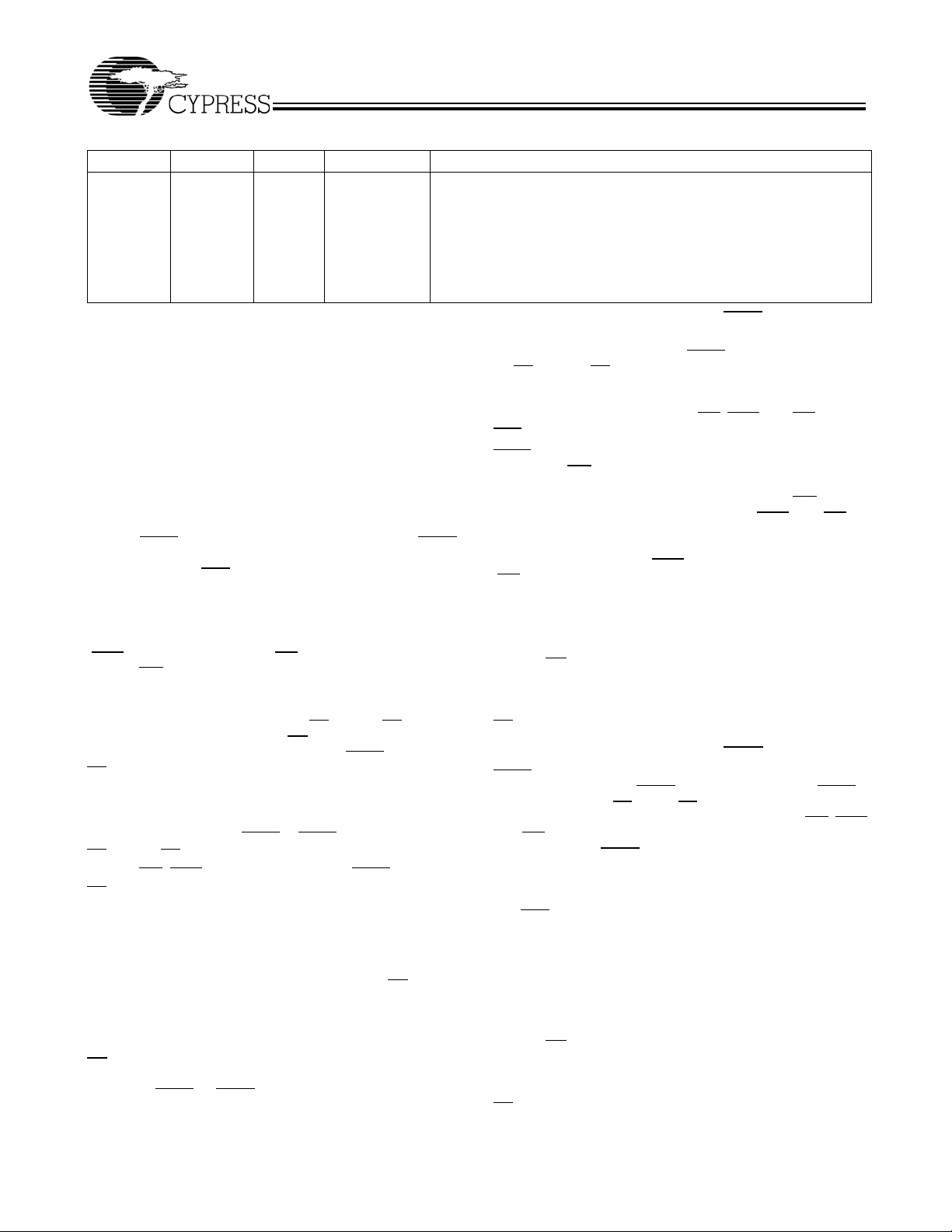
Logic Block Diagram
Functional Description
[1]
The CY7C1339F SRAM integrates 131,072 x 32 SRAM cells
with advanced synchronous peripheral circuitry and a two-bit
counter for internal burst operation. All synchronous inputs are
gated by registers controlled by a positive-edge-triggered
Clock Input (CLK). The synchronous inputs include all
addresses, all data inputs, address-pipelining Chip Enable
(
), depth-expansion Chip Enables (CE2 and
CE
1
Control inputs (
(
BW
inputs include the Output Enable (
[A:D]
, and
BWE
,
ADSC
), and Global Write (GW). Asynchronous
ADSP
,
and
OE
), Write Enables
ADV
) and the ZZ pin.
CE
), Burst
3
Addresses and chip enables are registered at rising edge of
clock when either Address Strobe Processor (
Address Strobe Controller (
) are active. Subsequent
ADSC
ADSP
) or
burst addresses can be internally generated as controlled by
the Advance pin (
ADV
).
Address, data inputs, and write controls are registered on-chip
to initiate a self-timed Write cycle.This part supports Byte Write
operations (see Pin Descriptions and Truth Table for further
details). Write cycles can be one to four bytes wide as
controlled by the byte write control inputs.
causes all bytes to be written.
LOW
when active
GW
The CY7C1339F operates from a +3.3V core power supply
while all outputs may operate with either a +2.5 or +3.3V
supply. All inputs and outputs are JEDEC-standard
JESD8-5-compatible.
A0,A1, A
MODE
ADV
CLK
ADSC
ADSP
BW
D
BW
C
BW
B
BW
A
BWE
GW
CE
1
CE
2
CE
3
OE
ZZ
1
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
WRITEREGISTER
SLEEP
CONTRO L
DQ
BYTE
DQ
BYTE
DQ
BYTE
DQ
BYTE
REGISTER
D
C
B
A
ENABLE
ADDRESS
REGISTER
2
BURST
COUNTE R
CLR
LOGIC
PIPELINED
ENABLE
AND
A
[1:0]
Q1
Q0
D
DQ
BYTE
WRITEDRIVER
C
DQ
BYTE
WRITEDRIVER
B
DQ
BYTE
WRITEDRIVER
DQ
A
BYTE
WRITEDRIVER
MEMORY
ARRAY
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
E
INPUT
REGISTERS
DQs
Note:
1. For best–practices recommendations, please refer to the Cypress application note System Design Guidelines on www.cypress.com.
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose, CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Revised April 09, 2004
CY7C1339F
Selection Guide
250 MHz 225 MHz 200 MHz 166 MHz 133 MHz 100 MHz Unit
Maximum Access Time
Maximum Operating Current 325 290 265 240 225 205 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current
Shaded areas contain advanced information. Please contact your local Cypress sales representative for availability of these parts.
Pin Configurations
2.6 2.6 2.8 3.5 4.0 4.5 ns
40 40 40 40 40 40 mA
BYTE C
BYTE D
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
NC
DQ
DQ
DDQ
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
SSQ
DDQ
DQ
DQ
NC
V
NC
V
DQ
DQ
DDQ
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
SSQ
DDQ
DQ
DQ
NC
DD
SS
AACE1CE2BWDBWCBWBBWACE3VDDVSSCLKGWBWEOEADSC
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
1
C
C
2
3
4
5
C
C
C
C
6
7
8
9
10
11
C
C
D
D
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
100-pin TQFP
CY7C1339F
20
21
D
D
D
D
22
23
24
25
26
27
D
D
28
29
30
ADSP
ADVAA
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
81
NC
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
V
NC
V
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
NC
DDQ
SSQ
SSQ
DDQ
SS
DD
DDQ
SSQ
SSQ
DDQ
B
B
B
BYTE B
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
BYTE A
A
A
A
A
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
1
A
AAA
0
A
A
NC
NC
SS
V
V
DD
NC
NC
AAA
AAA
50
A
MODE
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Page 2 of 17
Pin Configurations (continued)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
NC
DDQ
CY7C1339F
119-ball BGA
CY7C1339F (128K × 32)
2345671
AA AA
CE
2
A
AA
C
C
C
C
D
D
D
D
NCDQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
C
C
C
C
DD
D
D
D
D
A
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
BW
V
SS
NC V
V
SS
BW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
MODE
AA A
ADSP
ADSC
V
DD
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
c
GW
DD
CLK
D
NC
BWE
A1
A0
V
DD
A
V
V
V
BW
V
NC
V
BW
V
V
V
NC
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
NC
AA
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
B
DQ
V
DD
DQ
DQ
A
DQ
DQ
NC
A
NCNC
NCNCNCNC
NC
V
DDQ
NC
NC
DQ
B
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
B
DDQ
B
B
DDQ
A
A
DDQ
A
A
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
NC
ZZ
V
DDQ
Pin Definitions
Name BGA TQFP I/O Description
A
, A1, A P4,N4,
0
A2,C2,R2,
A3,B3,C3,
T3,T4,A5,
B5,C5,T5,
A6,C6,R6
37,36,
32,33,34,
35,44,45,
46,47,48,
49,50,81,
82,99,
Input-
Synchronous
100
BW
A,BWB
BWC,BW
GW
BWE
L5,G5,G3,L393,94,95,
D
H4
M4 87 Input-
96
88 Input-
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous
Synchronous
CLK K4 89 Input-
Clock
CE
CE
1
2
E4 98 Input-
Synchronous
B2 97 Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs used to select one of the 128K address locations.
Sampled at the rising edge of the CLK if
and CE
counter.
, and CE3 are sampled active. A1, A0 are fed to the two-bit
1, CE2
.
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW. Qualified with BWE
byte writes to the SRAM. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK
Global Write Enable Input, active LOW. When asserted LOW on the
rising edge of CLK, a global write is conducted (ALL bytes are written,
regardless of the values on BW
[A:D]
Byte Write Enable Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of
CLK. This signal must be asserted LOW to conduct a byte write.
Clock Input. Used to capture all synchronous inputs to the device. Also
used to increment the burst counter when ADV
a burst operation.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Used in conjunction with CE
ADSP
is ignored if CE1 is HIGH.
and CE3 to select/deselect the device.
2
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Used in conjunction with CE
and CE3 to select/deselect the device.
1
and BWE).
ADSP
or
is active LOW,
ADSC
is asserted LOW, during
to conduct
.
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Page 3 of 17
Pin Definitions (continued)
Name BGA TQFP I/O Description
CE
3
OE
ADV
ADSP
ADSC
- 92 InputSynchronous
F4 86 Input-
Asynchronous
G4 83 Input-
Synchronous
A4 84 Input-
Synchronous
B4
85 Input-
Synchronous
ZZ T7 64 Input-
Asynchronous
DQs
K6,L6,M6,
N6,K7,L7,
N7,P7,E6,
F6,G6,H6,
D7,E7,G7,
H7,D1,E1,
G1,H1,E2,
F2,G2,H2,
K1,L1,N1,
P1,K2,L2,
52,53,56,
57,58,59,
62,63,68,
69,72,73,
74,75,78,
79,2,3,6,
7,8,9,12,
13,18,19,
22,23,24,
25,28,29
I/O-
Synchronous
M2,N2
V
DD
J2,J4,R4 15,41,65,91Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the device.
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Used in conjunction with CE
and CE2 to select/deselect the device.
1
connected for BGA. Where referenced, CE
throughout this document for BGA.
Output Enable, asynchronous input, active LOW. Controls the
direction of the I/O pins. When LOW, the I/O pins behave as outputs.
When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins are three-stated, and act as input data
pins. OE
is masked during the first clock of a read cycle when emerging
from a deselected state.
Advance Input signal, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active
LOW. When asserted, it automatically increments the address in a burst
cycle.
Address Strobe from Processor, sampled on the rising edge of
CLK, active LOW. When asserted LOW, addresses presented to the
device are captured in the address registers. A1, A0 are also loaded into
the burst counter. When ADSP
is recognized. ASDP
is ignored when CE1 is deasserted HIGH.
and ADSC are both asserted, only ADSP
Address Strobe from Controller, sampled on the rising edge of
CLK, active LOW. When asserted LOW, addresses presented to the
device are captured in the address registers. A1, A0 are also loaded into
the burst counter. When ADSP
and ADSC are both asserted, only ADSP
is recognized.
ZZ “sleep” Input, active HIGH. When asserted HIGH places the device
in a non-time-critical “sleep” condition with data integrity preserved. For
normal operation, this pin has to be LOW or left floating. ZZ pin has an
internal pull-down.
Bidirectional Data I/O lines. As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data
register that is triggered by the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they
deliver the data contained in the memory location specified by the
addresses presented during the previous
The direction of the pins is controlled by OE
the pins behave as outputs. When HIGH, DQs are placed in a three-state
condition.
CY7C1339F
Not
is assumed active
3
clock rise of the read cycle.
. When OE is asserted LOW,
V
SS
D3,E3,F3,
K3,M3,N3,
17,40,67,
90
Ground Ground for the core of the device.
P3,D5,E5,
F5,H5,K5,
M5,N5,P5
V
DDQ
A1,F1,J1,
M1,U1,A7,
F7,J7,M7,
4,11,20,
27,54,61,
70,77
I/O Power
Supply
Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
U7
V
SSQ
- 5,10,21,
26,55,60,
I/O Ground Ground for the I/O circuitry.
71,76
MODE R3 31 Input-
Static
Selects Burst Order. When tied to GND selects linear burst sequence.
When tied to V
is a strap pin and should remain static during device operation. Mode
or left floating selects interleaved burst sequence. This
DD
Pin has an internal pull-up.
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Page 4 of 17
Pin Definitions (continued)
Name BGA TQFP I/O Description
NC B1,C1,R1,
T1,D2,P2,
T2,U2,J3,
U3,D4,L4,
U4,J5,U5,
B6,D6,P6,
T6,U6,B7,
C7,R5,R7
1,14,16,
30,38,39,
42,43,51,
66,80
No Connects. Not internally connected to the die
CY7C1339F
Functional Overview
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the rising edge of the clock. All data outputs pass through
output registers controlled by the rising edge of the clock.
Maximum access delay from the clock rise (t
(166-MHz device).
The CY7C1339F supports secondary cache in systems
utilizing either a linear or interleaved burst sequence. The
interleaved burst order supports Pentium and i486
processors. The linear burst sequence is suited for processors
that utilize a linear burst sequence. The burst order is user
selectable, and is determined by sampling the MODE input.
Accesses can be initiated with either the Processor Address
Strobe (ADSP) or the Controller Address Strobe (ADSC).
Address advancement through the burst sequence is
controlled by the ADV
input. A two-bit on-chip wraparound
burst counter captures the first address in a burst sequence
and automatically increments the address for the rest of the
burst access.
Byte Write operations are qualified with the Byte Write Enable
(BWE
) and Byte Write Select (BW
Enable (GW
) overrides all Byte Write inputs and writes data to
) inputs. A Global Write
[A:D]
all four bytes. All writes are simplified with on-chip
synchronous self-timed Write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Selects (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
, CE2, CE3) and an
1
) provide for easy bank
selection and output three-state control. ADSP
CE
is HIGH.
1
Single Read Accesses
This access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) ADSP
or ADSC is asserted LOW, (2)
CE1, CE2, CE3 are all asserted active, and (3) the Write
signals (GW
CE
is HIGH. The address presented to the address inputs (A)
1
is stored into the address advancement logic and the Address
, BWE) are all deserted HIGH. ADSP is ignored if
Register while being presented to the memory array. The
corresponding data is allowed to propagate to the input of the
Output Registers. At the rising edge of the next clock the data
is allowed to propagate through the output register and onto
the data bus within 3.5 ns (166-MHz device) if OE
LOW. The only exception occurs when the SRAM is emerging
from a deselected state to a selected state, its outputs are
always three-stated during the first cycle of the access. After
the first cycle of the access, the outputs are controlled by the
OE
signal. Consecutive single Read cycles are supported.
Once the SRAM is deselected at clock rise by the chip select
and either ADSP or ADSC signals, its output will three-state
immediately.
) is 3.5 ns
CO
is ignored if
is active
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSP
This access is initiated when both of the following conditions
are satisfied at clock rise: (1) ADSP
(2) CE
presented to A is loaded into the address register and the
, CE2, CE3 are all asserted active. The address
1
is asserted LOW, and
address advancement logic while being delivered to the
memory array. The Write signals (GW
ADV
inputs are ignored during this first cycle.
ADSP
-triggered Write accesses require two clock cycles to
complete. If GW
is asserted LOW on the second clock rise, the
, BWE, and BW
[A:D]
) and
data presented to the DQs inputs is written into the corresponding address location in the memory array. If GW is HIGH,
then the Write operation is controlled by BWE
signals. The CY7C1339F provides Byte Write capability that is
and BW
[A:D]
described in the Write Cycle Descriptions table. Asserting the
Byte Write Enable input (BWE
(BW
Bytes not selected during a Byte Write operation will remain
) input, will selectively write to only the desired bytes.
[A:D]
) with the selected Byte Write
unaltered. A synchronous self-timed Write mechanism has
been provided to simplify the Write operations.
Because the CY7C1339F is a common I/O device, the Output
Enable (OE) must be deserted HIGH before presenting data
to the DQs inputs. Doing so will three-state the output drivers.
As a safety precaution, DQs are automatically three-stated
whenever a Write cycle is detected, regardless of the state of
OE
.
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSC
ADSC Write accesses are initiated when the following conditions are satisfied: (1) ADSC
deserted HIGH, (3) CE
(4) the appropriate combination of the Write inputs (GW
and BW
desired byte(s). ADSC
) are asserted active to conduct a Write to the
[A:D]
is asserted LOW, (2) ADSP is
, CE2, CE3 are all asserted active, and
1
, BWE,
-triggered Write accesses require a
single clock cycle to complete. The address presented to A is
loaded into the address register and the address
advancement logic while being delivered to the memory array.
The ADV
input is ignored during this cycle. If a global Write is
conducted, the data presented to the DQs is written into the
corresponding address location in the memory core. If a Byte
Write is conducted, only the selected bytes are written. Bytes
not selected during a Byte Write operation will remain
unaltered. A synchronous self-timed Write mechanism has
been provided to simplify the Write operations.
Because the CY7C1339F is a common I/O device, the Output
Enable (OE
) must be deserted HIGH before presenting data
to the DQs inputs. Doing so will three-state the output drivers.
As a safety precaution, DQs are automatically three-stated
whenever a Write cycle is detected, regardless of the state of
OE
.
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Page 5 of 17
CY7C1339F
Burst Sequences
The CY7C1339F provides a two-bit wraparound counter, fed
by A1, A0, that implements either an interleaved or linear burst
sequence. The interleaved burst sequence is designed specifically to support Intel Pentium applications. The linear burst
sequence is designed to support processors that follow a
linear burst sequence. The burst sequence is user selectable
through the MODE input.
Asserting ADV
LOW at clock rise will automatically increment
the burst counter to the next address in the burst sequence.
Both Read and Write burst operations are supported.
Sleep Mode
The ZZ input pin is an asynchronous input. Asserting ZZ
places the SRAM in a power conservation “sleep” mode. Two
clock cycles are required to enter into or exit from this “sleep”
mode. While in this mode, data integrity is guaranteed.
Accesses pending when entering the “sleep” mode are not
considered valid nor is the completion of the operation
guaranteed. The device must be deselected prior to entering
t
he “sleep” mode. CE
remain inactive for the duration of t
returns LOW.
, CE2, CE3, ADSP, and ADSC must
1
after the ZZ input
ZZREC
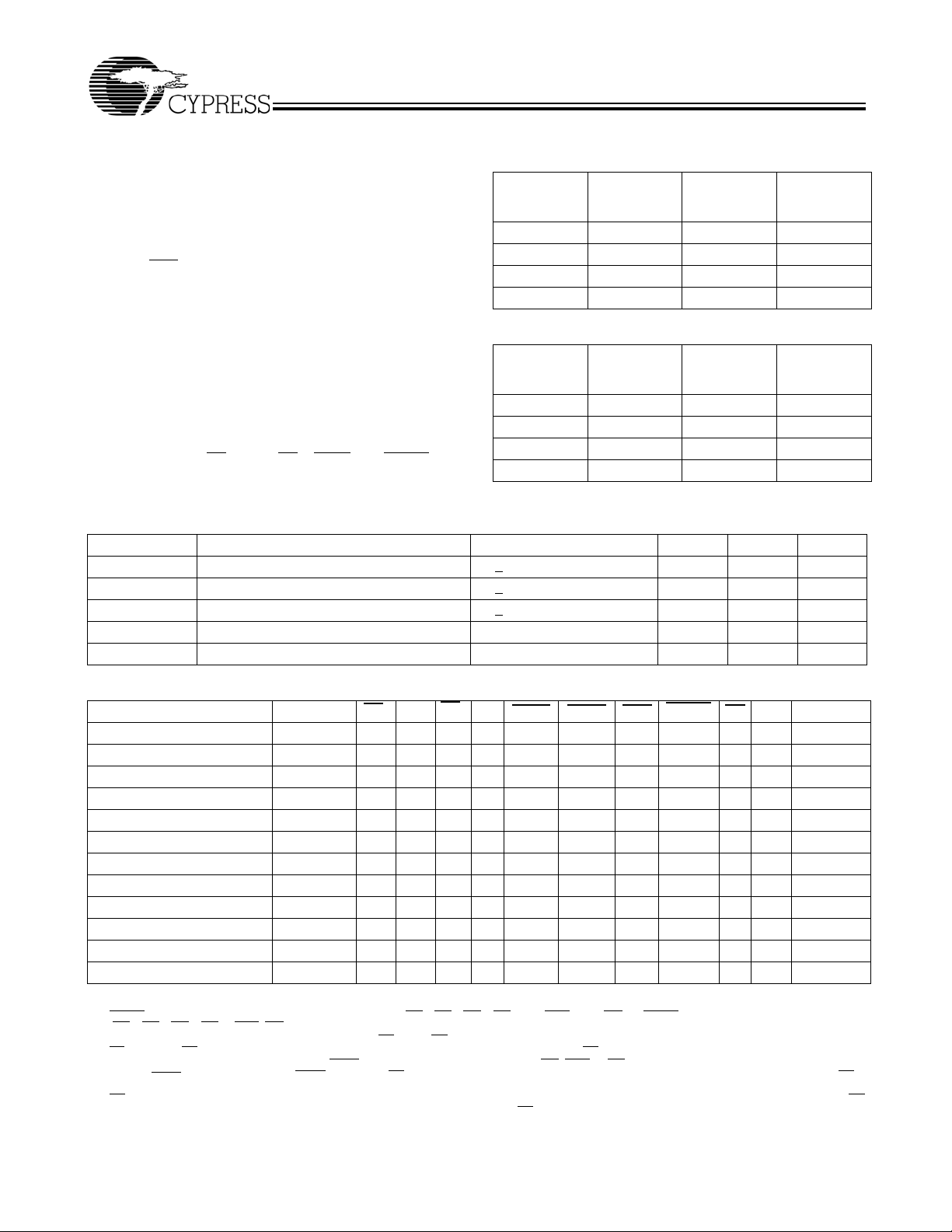
Interleaved Burst Address Table
(MODE = Floating or V
First
Address
A1, A0
Second
Address
A1, A0
DD
)
Third
Address
A1, A0
Fourth
Address
A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 00 11 10
10 11 00 01
11 10 01 00
Linear Burst Address Table (MODE = GND)
First
Address
A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 10 11 00
10 11 00 01
11 00 01 10
Second
Address
A1, A0
Third
Address
A1, A0
Fourth
Address
A1, A0
ZZ Mode Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
I
DDZZ
t
ZZS
t
ZZREC
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Truth Table
Operation Add. Used
Deselect Cycle, Power-down None H X X L X L X X X L-H three-state
Deselect Cycle, Power-down None L L X L L X X X X L-H three-state
Deselect Cycle, Power-down None L X H L L X X X X L-H three-state
Deselect Cycle, Power-down None L L X L H L X X X L-H three-state
Deselect Cycle, Power-down None L X H L H L X X X L-H three-state
Snooze Mode, Power-down None X X X H X X X X X X three-state
READ Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X L L-H Q
READ Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X H L-H three-state
WRITE Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X L X L-H D
READ Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H L L-H Q
READ Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H H L-H three-state
READ Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L H L L-H Q
Notes:
2. X = “Don't Care.” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW.
3. WRITE
4. The DQ pins are controlled by the current cycle and the
5. CE
6. The SRAM always initiates a read cycle when ADSP
7.
= L when any one or more Byte Write enable signals (BWA, BWB, BWC, BWD) and BWE = L or GW= L. WRITE = H when all Byte write enable signals
(BW
, BWB, BWC, BWD), BWE, GW = H.
A
, CE2, and CE3 are available only in the TQFP package. BGA package has only 2 chip selects CE1 and CE2.
1
after the
ADSP
a don't care for the remainder of the write cycle
is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock rise. It is masked internally during write cycles. During a read cycle all data bits are three-state when OE
OE
is
inactive or when the device is deselected, and all data bits behave as output when
Snooze mode standby current ZZ > VDD – 0.2V 40 mA
Device operation to ZZ ZZ > VDD – 0.2V 2t
ZZ recovery time ZZ < 0.2V 2t
CYC
ZZ active to snooze current This parameter is sampled 2t
CYC
CYC
ZZ Inactive to exit snooze current This parameter is sampled 0 ns
[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
or with the assertion of
CE
CE
1
signal. OE is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock.
OE
is asserted, regardless of the state of GW, BWE, or BW
. As a result, OE must be driven HIGH prior to the start of the write cycle to allow the outputs to three-state. OE is
ADSC
CE
2
ZZ
3
ADSP
OE
ADSC ADV
is active (LOW)
.
WRITE
. Writes may occur only on subsequent clocks
[A: D]
CLK DQ
OE
ns
ns
ns
Document #: 38-05217 Rev. *C Page 6 of 17
 Loading...
Loading...