Page 1
PRELIMINARY
s
C
C
2-Mbit (64K x 32) Flow-Through SRAM
Features
• Can support up to 133-MHz bus operations with zero
wait states.
— Data is transferred on every clock.
• Pin compatible and functionally equivalent to ZBT™
devices
• Internally self-timed output buffer control to eliminate
the need to use
• Registered inputs for flow-through operation
• Byte Write capability
• 64K x 32 common I/O architectu re
• Single 3.3V power supply
• Fast clock-to-output times
— 6.5 ns (for 133-MHz device)
— 8.0 ns (for 100-MHz device)
• Clock Enable (CEN
• Synchronous self-timed writes Offered in Lead-Free
• Asynchronous Output Enable
• Offered in Lead-Free JEDEC-standard 100 TQFP
package
• Burst Capability—linea r or interleaved burst order
OE
) pin to suspend operation
CY7C1333H
with NoBL™ Architecture
• Low standby power
Functional Description
The CY7C1333H is a 3.3V, 64K x 32 Synchronous
Flow-through Burst SRAM designed specifically to support
unlimited true back-to-back Read/Write operations without the
insertion of wait states. The CY7C1333H is equipped with the
advanced No Bus Latency™ (NoBL™) logic required to
enable consecutive Read/Write operations with data being
transferred on every clock cycle. This feature dramatically
improves the throughput of data through the SRAM, especially
in systems that require frequent Write-Read transitions.
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the rising edge of the clock. The clock input is qualified b y
the Clock Enable (CEN
suspends operation and extends the previous clock cycle.
Maximum access delay from the clock rise is 6.5 ns (133-MHz
device).
Write operations are controlled by the two Byte Write Select
(BW
conducted with on-chip synchronous self-timed write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
selection and output three-state control. In order to avoid bus
contention, the output drivers are synchronously three-stated
during the data portion of a write sequence.
) and a Write Enable (WE) input. All writes are
[A:D]
[1]
) signal, which when deasserted
, CE2, CE3) and an
1
) provide for easy bank
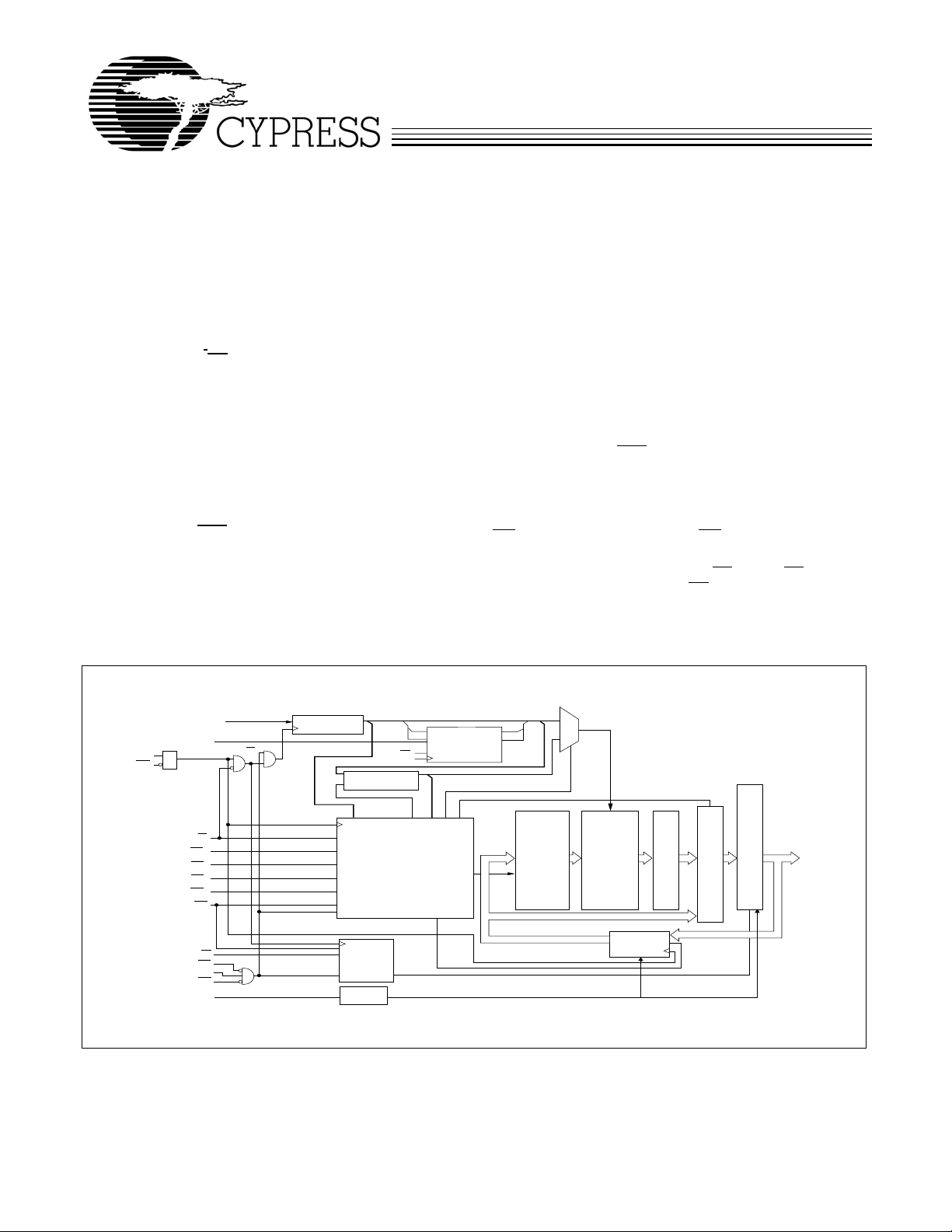
Logic Block Diagram
A0, A1, A
MODE
ADV/LD
BW
BW
BW
BW
C
WE
CE1
CE2
CE3
ZZ
LK
EN
Note:
1. For best-practices recommendations, please refer to the Cypress application note System Design Guidelines on www.cypress.com.
CE
A
B
C
D
OE
ADDRESS
REGISTER
ADV/LD
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER
WRITE REGISTRY
AND DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
READ LOGIC
SLEEP
Control
A1
D1
A0
D0
BURST
C
LOGIC
A1'
Q1
A0'
Q0
O
U
T
P
D
WRITE
DRIVERS
MEMORY
ARRAY
INPUT
REGISTER
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
E
U
A
T
T
A
B
U
S
F
T
F
E
E
E
R
R
S
I
E
N
G
DQ
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose, CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Revised April 11, 2005
[+] Feedback
Page 2
CY7C1333H
Selection Guide
PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H-133 CY7C1333H-100 Unit
Maximum Access Time 6.5 8.0 ns
Maximum Operating Current 225 205 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current 40 40 mA
Shaded area contains advance information. Please contact your local Cypress sales representative for availability of this part.
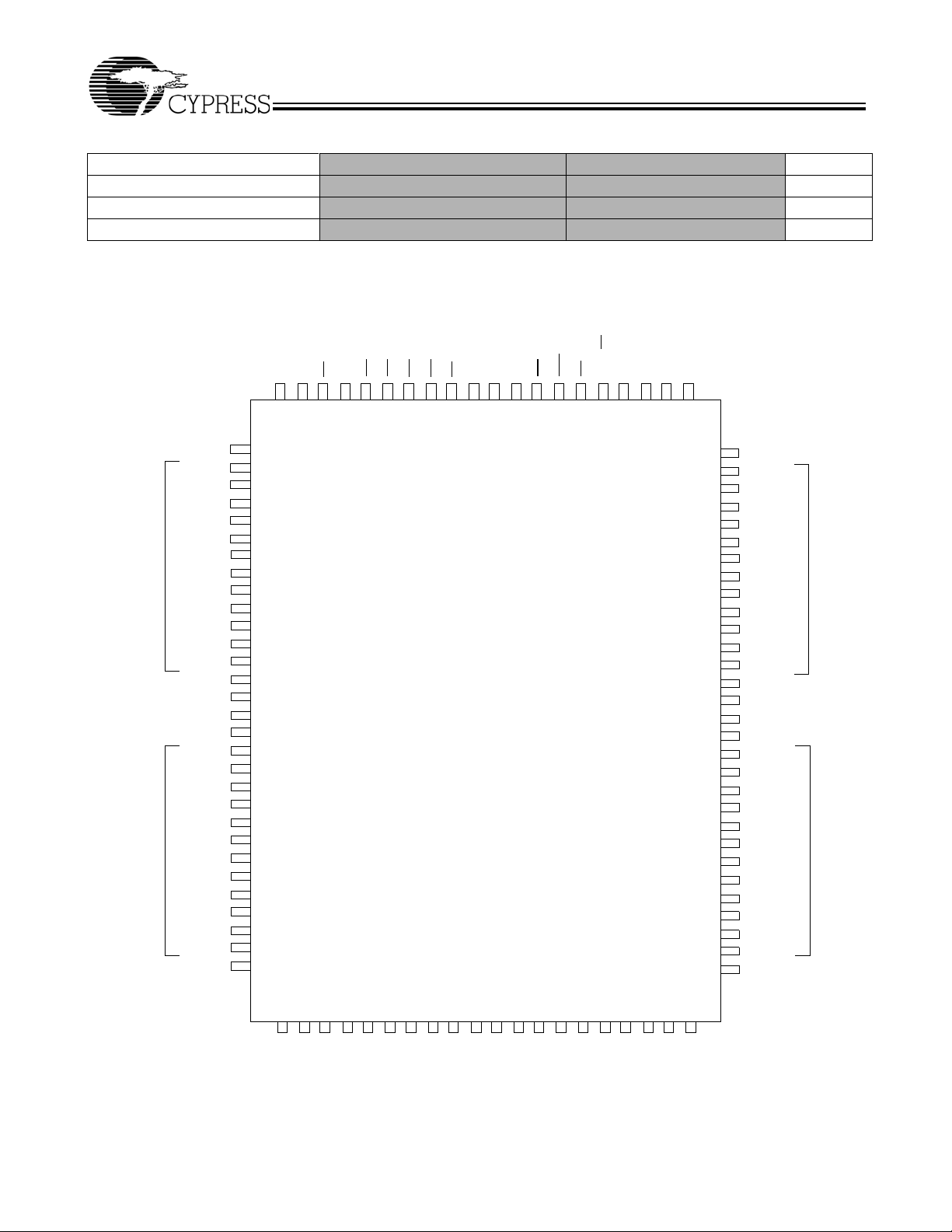
Pin Configurations
100-lead TQFP
BYTE C
BYTE D
V
V
V
V
DQ
DQ
DDQ
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
NC
V
DQ
DQ
DDQ
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
NC
SS
SS
NC
DD
SS
SS
SS
NC
1CE2
A
A
CE
100
9998979695
1
2
C
3
C
4
5
6
C
7
C
8
C
9
C
10
11
12
C
13
C
14
15
16
17
18
D
19
D
20
21
22
D
23
D
24
D
25
D
26
27
28
D
29
D
30
C
BWDBW
BWBBWACE3VDDV
94939291908988878685848382
SS
CLKWECEN
OE
CY7C1333H
ADV/LD
NC(9M)
NC(18M)
A
A
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
NC
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
V
NC
V
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
V
DQ
DQ
NC
DDQ
SS
SS
DDQ
SS
DD
DDQ
SS
SS
DDQ
B
B
B
B
BYTE B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
BYTE A
A
A
A
A
A
31323334353637383940414243
A
A
A
A
A1
A0
MODE
NC/144M
NC/288M
SS
DD
V
V
44454647484950
A
A
A
NC(72M)
NC(36M)
A
A
A
NC/4M
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 2 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 3
PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Pin Definitions (100-pin TQFP Package)
Name I/O Description
A0, A1, A Input-
Synchronous
BW
WE
[A:D]
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
ADV/LD
Input-
Synchronous
CLK Input-Clock Clock Input. Used to capture all synchronous inputs to the device. CLK is qualified with CEN. CLK
CE
CE
CE
OE
1
2
3
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Asynchronous
CEN
Input-
Synchronous
ZZ Input-
Asynchronous
DQ
s
I/O-
Synchronous
Mode Input
Strap Pin
V
V
V
DD
DDQ
SS
Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the device.
I/O Power
Supply
Ground Ground for the device.
NC – No Connects. Not Internally connected to the die.
Address Inputs used to select one of the 64K address locations. Sampled at the rising edge
of the CLK. A
are fed to the two-bit burst counter.
[1:0]
Byte Write Input s , acti ve LO W. Qualified with WE to conduct Writes to the SRAM. Sampled on
the rising edge of CLK.
Write Enable Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK if CEN is active LOW. This
signal must be asserted LOW to initiate a Write sequence.
Advance/Load Input . Used to advance the on-chip address counter or load a new address. When
HIGH (and CEN
address can be loaded into the device for an access. After being deselected, ADV/LD
is asserted LOW) the internal burst counter is advanced. When LOW, a new
should be
driven LOW in order to load a new address.
is only recognized if CEN
is active LOW.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
, and CE3 to select/deselect the device.
2
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
and CE3 to select/deselect the device.
1
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
and CE2 to select/deselect the device.
1
Output Enable, asynchronous input, active LOW. Combined with the synchronous logic block
inside the device to control the direction of the I/O pins. When LOW, the I/O pins are allowed to
behave as outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins are three-stated, and act as input data pins.
OE
is masked during the data portion of a Write sequence, during the first clock when emerging
from a deselected state, when the device has been deselected.
Clock Enable Input, active LOW. When asserted LOW the Clock signal is recognized by the
SRAM. When deasserted HIGH the Clock signal is masked. Since deasserting CEN
deselect the device, CEN
can be used to extend the previous cycle when required.
does not
ZZ “Sleep” Input. This active HIGH input places the device in a non-time critical “sleep” condition
with data integrity preserved. During normal operation, this pin can be connected to V
floating.
SS
or left
Bidirectional Data I/O Lines. As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data register that is triggered
by the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they deliver the data contained in the memory location
specified by address during the clock rise of the Read cycle. The direction of the pins is controlled
by OE
and the internal control logic. When OE is asserted LOW, the pins can behave as outputs.
When HIGH, DQ
during the data portion of a Write sequence, during the first clock when emerging from a deselected
state, and when the device is deselected, regardless of the state of OE
are placed in a three-state condition. The outputs are automatically three-stated
s
.
Mode Input. Selects the burst order of the device.
When tied to Gnd selects linear burst sequence. When tied to V
burst sequence.
or left floating selects interleaved
DD
Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
4M, 9M,18M,36M, 72M, 144M, 256M, 576M and 1G are address expansion pins and are not
internally connected to the die.
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 3 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 4
PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Functional Overview
The CY7C1333H is a synchronous flow-through burst SRAM
designed specifically to eliminate wait states during
Write-Read transitions. All synchronous inputs pass through
input registers controlled by the rising edge of the clock. The
clock signal is qualified with the Clock Enable input signal
(CEN
). If CEN is HIGH, the clock signal is not recognized and
all internal states are maintained. All synchronous operations
are qualified with CEN. Maximum access delay from the clock
rise (t
Accesses can be initiated by asserting all three Chip Enables
(CE
Enable (CEN
the address presented to the device will be latched. The
access can either be a Read or Write operation, depending on
the status of the Write Enable (WE
conduct Byte Write operations.
Write operations are qualified by the Write Enable (WE
writes are simplified with on-chip synchronous self-timed write
circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
All operations (Reads, Writes, and Deselects) are pipelined.
ADV/LD should be driven LOW once the device has been
deselected in order to load a new address for the next
operation.
Single Read Accesses
A read access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CEN
and CE
signal WE
LOW. The address presented to the address inputs is latched
into the address register and presented to the memory arra y
and control logic. The control logic determines that a read
access is in progress and allows the requested data to
propagate to the output buffers. The data is available within 6.5
ns (133-MHz device) provided OE
clock of the read access, the output buffers are controlled by
OE and the internal control logic. OE must be driven LOW in
order for the device to drive out the requested data. On the
subsequent clock, another operation (Read/Write/Deselect)
can be initiated. When the SRAM is deselected at clock rise
by one of the chip enable signals, its output will be three-stated
immediately.
Burst Read Accesses
The CY7C1333H has an on-chip burst counter that allows the
user the ability to supply a single address and conduct up to
four Reads without reasserting the address inputs. ADV/LD
must be driven LOW in order to load a new addre ss into the
SRAM, as described in the Single Read Access section above.
The sequence of the burst counter is determined by the MODE
input signal. A LOW input on MODE selects a linear burst
mode, a HIGH selects an interleaved burst sequence. Both
burst counters use A
wrap around when incremented sufficiently. A HIGH input on
ADV/LD
the state of chip enable inputs or WE
) is 6.5 ns (133-MHz device).
CDV
, CE2, CE3) active at the rising edge of the clock. If Clock
1
) is active LOW and ADV/LD is asserted LOW,
). BW
can be used to
[A:D]
). All
, CE2, CE3) and an
1
) simplify depth expansion.
is asserted LOW, (2) CE1, CE2,
are ALL asserted active, (3) the Write Enable input
3
is deasserted HIGH, and 4) ADV/LD is asserted
is active LOW. After the first
and A1 in the burst sequence, and will
0
will increment the internal burst counter regardless of
. WE is latched at the
beginning of a burst cycle. Therefore, the type of access (Read
or Write) is maintained throughout the burst sequence.
Single Write Accesses
Write access are initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) CEN
and CE
is asserted LOW. The address presented to the address bus
are ALL asserted active, and (3) the write signal WE
3
is asserted LOW, (2) CE1, CE2,
is loaded into the Address Register. The write signals are
latched into the Control Logic block. The data lines are
automatically three-stated regardless of the state of the OE
input signal. This allows the external logic to present the data
on DQs.
On the next clock rise the data presented to DQs (or a subset
for Byte Write operations, see Truth Ta ble for details) inputs is
latched into the device and the write is complete. Additional
accesses (Read/Write/Deselect) can be initiated on this cycle.
The data written during the Write operation is controlled by
BW
capability that is described in the Truth Table. Asserting the
signals. The CY7C1333H provides Byte Write
[A:D]
Write Enable input (WE) with the selected Byte Write Select
input will selectively write to only the desired bytes. Bytes not
selected during a Byte Write operation will remain unaltered.
A synchronous self-timed Write mechanism has been
provided to simplify the Write operations. Byte Write capability
has been included in order to greatly simplify
Read/Modify/Write sequences, which can be reduced to
simple Byte Write operations.
Because the CY7C1333H is a common I/O device, data
should not be driven into the device while the outputs are
active. The Output Enable (OE
) can be deasserted HIGH
before presenting data to the DQ inputs. Doing so will
three-state the output drivers. As a safety precaution, DQs are
automatically three-stated during the data portion of a Write
cycle, regardless of the state of OE
.
Burst Write Accesses
The CY7C1333H has an on-chip burst counter that allows the
user the ability to supply a single address and conduct up to
four Write operations without reasserting the address inputs.
ADV/LD
must be driven LOW in order to load the initial
address, as described in the Single Write Access section
above. When ADV/LD
rise, the Chip Enables (CE
ignored and the burst counter is incremented. The correct
BW
in order to write the correct bytes of data.
inputs must be driven in each cycle of the burst write,
[A:D]
is driven HIGH on the subsequent clock
, CE2, and CE3) and WE inputs are
1
Sleep Mode
The ZZ input pin is an asynchronous input. Asserting ZZ
places the SRAM in a power conservation “sleep” mode. Two
clock cycles are required to enter into or exit from this “sleep”
mode. While in this mode, data integrity is guaranteed.
Accesses pending when entering the “sleep” mode are not
considered valid nor is the completion of the operation
guaranteed. The device must be deselected prior to entering
the “sleep” mode. CE
for the duration of t
, CE2, and CE3, must remain inactive
1
after the ZZ input returns LOW.
ZZREC
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 4 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 5

PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Linear Burst Address Table (MODE = GND)
First
Address
A1, A0
Second
Address
A1, A0
Third
Address
A1, A0
Fourth
Address
A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 10 11 00
10 11 00 01
11 00 01 10
Interleaved Burst Sequence
First
Address
A1, A0 A1, A0 A1, A0 A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 00 11 10
10 11 00 01
11 10 01 00
Second
Address
Third
Address
Fourth
Address
ZZ Mode Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Description T e st Condition s Min. Max. Unit
I
DDZZ
t
ZZS
t
ZZREC
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Truth Table
Operation
Deselect Cycle None H X X L L X X X L L->H Three-State
Deselect Cycle None X X H L L X X X L L->H Three-State
Deselect Cycle None X L X L L X X X L L->H Three-State
Continue Deselect
Cycle
READ Cycle
(Begin Burst)
READ Cycle
(Continue Burst)
NOP/DUMMY READ
(Begin Burst)
DUMMY READ
(Continue Burst)
WRITE Cycle
(Begin Burst)
WRITE Cycle
(Continue Burst)
NOP/WRITE ABORT
(Begin Burst)
WRITE ABORT
(Continue Burst)
IGNORE CLOCK
EDGE (Stall)
Sleep MODE None X X X H X X X X X X Three-State
Notes:
2. X = “Don't Care.” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW. BWx
Selects are asserted, see Truth Table for details.
3. Write is defined by BW
4. When a Write cycle is detected, all I/Os are three-stated, even during Byte Writes.
5. The DQ pins are controlled by the current cycle and the OE
= H, inserts wait states.
6. CEN
7. Device will power-up deselected and the I/Os in a three-state condition, regardless of OE
is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock rise. It is masked internally during Write cycles. During a read cycle DQs = Three-state when OE is inacti ve
8. OE
or when the device is deselected, and DQ
Sleep mode standby current ZZ > VDD − 0.2V 40 mA
Device operation to ZZ ZZ > VDD − 0.2V 2t
ZZ recovery time ZZ < 0.2V 2t
CYC
ZZ Active to sleep current This parameter is sampled 2t
CYC
CYC
ZZ inactive to exit sleep current This parameter is sampled 0 ns
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
ADDRESS
Used CE1CE2 CE3ZZ ADV/LD WE BWXOE CEN CLK DQ
None X X X L H X X X L L->H Three-State
External L H L L L H X L L L->H Data Out (Q)
Next X X X L H X X L L L->H Data Out (Q)
External L H L L L H X H L L->H Three-State
Next X X X L H X X H L L->H Three-State
External L H L L L L L X L L->H Data In (D)
Next X X X L H X L X L L->H Data In (D)
None L H L L L L H X L L->H Three-State
Next X X X L H X H X L L->H Three-State
Current X X X L X X X X H L->H -
= 0 signifies at least one Byte Write Select is active, BWx = Valid signifies that the desired Byte Write
, and WE. See Truth Table for Read/Write.
[A:D]
signal. OE is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock.
.
= data when OE is active.
s
ns
ns
ns
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 5 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 6

PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Truth Table for Read/Write
Function
[2, 3]
WE
BW
A
BW
B
BW
C
BW
D
Read HXXXX
Write No Bytes Written LHHHH
Write Byte A – (DQ
Write Byte B – (DQ
Write Byte C – (DQ
Write Byte D – (DQ
) LLHHH
A
)LHLHH
B
)LHHLH
C
) LHHHL
D
Write All Bytes L L L L L
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 6 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 7

PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Maximum Ratings
(Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guidelines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature .................................–65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied.............................................–55°C to +125°C
Supply Voltage on VDD Relative to GND ......–0.5V to +4.6V
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in Tri-State...........................................–0.5V to V
DC Input Voltage....................................–0.5V to V
DDQ
DD
+ 0.5V
+ 0.5V
Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Current into Outputs (LOW).........................................20 mA
Static Discharge Voltage.......................................... > 2001V
(per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch-up Current...................................... ... ........... > 200 mA
Operating Range
Range
Com’l 0°C to +70°C 3.3V – 5%/+10% 3.3V – 5% to
Ind’l -40°C to +85°C
[9,10]
Ambient
Temperature (TA)V
DD
V
DDQ
V
DD
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
V
V
V
V
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
DD
DDQ
OH
OL
IH
IL
X
OZ
DD
SB1
SB2
SB3
SB4
Power Supply Voltage 3.135 3.6 V
I/O Supply Voltage for 3.3V I/O 3.135 V
Output HIGH Voltage for 3.3V I/O, I
Output LOW Voltage for 3.3V I/O, I
= –4.0 mA 2.4 V
OH
= 8.0 mA 0.4 V
OL
DD
Input HIGH Voltage for 3.3V I/O 2.0 VDD + 0.3V V
Input LOW Voltage
Input Load Current (except
ZZ and MODE)
Input Current of MODE Input = V
Input Current of ZZ Input = V
[9]
for 3.3V I/O –0.3 0.8 V
GND ≤ VI ≤ V
SS
Input = V
Input = V
DD
SS
DD
DDQ
–5 5 µA
–30 µA
5 µA
–5 µA
30 µA
Output Leakage Current GND ≤ VI ≤ VDD, Output Disabled –5 5 µA
V
Operating Supply
DD
Current
Automatic CE Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
Automatic CE Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CE Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CE Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
V
= Max., I
DD
f = f
= 1/t
MAX
V
= M a x , Device Deselected,
DD
V
≥ VIH or VIN ≤ VIL, f = f
IN
inputs switching
V
= M a x , Device Deselected,
DD
≥ VDD – 0.3V or VIN ≤ 0.3V,
V
IN
f = 0, inputs static
V
= M a x , Device Deselected,
DD
V
≥ V
IN
DDQ
f = f
V
V
f = 0, inputs static
, inputs switching
MAX
= M a x , Device Deselected,
DD
≥ V
IN
DD
= 0 mA,
OUT
CYC
– 0.3V or VIN ≤ 0.3V,
– 0.3V or VIN ≤ 0.3V ,
MAX
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 225 mA
10-ns cycle, 100 MHz 205 mA
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 90 mA
,
10-ns cycle, 100 MHz 80 mA
All speeds 40 mA
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 75 mA
10-ns cycle, 100 MHz 65 mA
All speeds 45 mA
V
Thermal Resistance
[11]
100 TQFP
Parameters Description Test Conditions
Θ
JA
Θ
JC
Notes:
9. Overshoot: V
10.Power-up: Assumes a linear ramp from 0V to V
11.Test ed initially and after any design or process changes that may affect these parameters.
(AC) < V
IH
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Case)
+1.5V (Pulse width less than t
DD
DD
T est conditions follow standard test methods and
procedures for measuring thermal impedance,
per EIA/JESD51
/2), undershoot: VIL(AC)> –2V (Pulse width less than t
CYC
(min.) within 200 ms. During this time VIH < VDD and V
DDQ
< VDD.
CYC
/2).
Package Unit
30.32 °C/W
6.85 °C/W
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 7 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 8

PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
Capacitance
[11]
Parameter Description Test Conditions 100 TQFP Package Unit
C
IN
C
CLOCK
C
I/O
Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
V
= 3.3V
Clock Input Capacitance 5 pF
I/O Capacitance 5 pF
V
DD
DDQ
=3.3V
5pF
AC Test Loads and Waveforms
3.3V I/O Test Load
OUTPUT
Z
= 50Ω
0
R
L
3.3V
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
5pF
VL= 1.5V
INCLUDING
(a)
Switching Characteristics
Over the Operating Range
JIG AND
SCOPE
Parameter Description
t
POWER
VDD(Typical) to the First Access
[14]
Clock
t
CYC
t
CH
t
CL
Clock Cycle Time 7.5 10 ns
Clock HIGH 2.5 4.0 ns
Clock LOW 2.5 4.0 ns
Output Times
t
CDV
t
DOH
t
CLZ
t
CHZ
t
OEV
t
OELZ
t
OEHZ
Data Output Valid after CLK Rise 6.5 8.0 ns
Data Output Hold after CLK Rise 2.0 2.0 ns
Clock to Low-Z
Clock to High-Z
[15, 16, 17]
15, 16, 17]
OE LOW to Output Valid 3.5 3.5 ns
OE LOW to Output Low-Z
OE HIGH to Output High-Z
[15, 16, 17]
[15, 16, 17]
Set-up Times
t
AS
t
ALS
t
WES
t
CENS
t
DS
t
CES
Notes:
12.Timing reference level is 1.5V when V
13.Test conditions shown in (a) of AC Test Loads, unless otherwise noted.
14.This part has a voltage regulator internally; t
can be initiated.
, t
15.t
CHZ
CLZ,tOELZ
16.At any given voltage and temperature, t
data bus. These specifications do not imply a bus contention conditi on, but re flect pa r ameters gua ranteed over worst case user co ndit ion s. Devi ce is designed
to achieve Three-state prior to Low-Z under the same system conditions
17.This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
Address Set-up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
ADV/LD Set-up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
WE, BW
Set-up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
[A:D]
CEN Set-up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
Data Input Set-up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
Chip Enable Set-Up before CLK Rise 1.5 2.0 ns
=3.3V
DDQ
is the time that the power needs to be supplied above V
POWER
, and t
are specified with AC test conditions shown in p art (b) of AC Test Loads. Transition is measured ± 200 mV from stead y-st ate voltage.
OEHZ
is less than t
OEHZ
OELZ
and t
R = 317Ω
(b)
[12, 13]
is less than t
CHZ
ALL INPUT PULSES
10%
90%
R = 351Ω
V
DDQ
GND
≤ 1 ns
(c)
133 MHz 100 MHz
1 1 ms
0 0 ns
3.5 3.5 ns
0 0 ns
3.5 3.5 ns
minimum initially before a Read or Write operat ion
DD
to eliminate bus contention between SRAMs when sharing the same
CLZ
90%
10%
≤ 1 ns
UnitMin. Max. Min. Max.
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 8 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 9

PRELIMINARY
123456789
10
C
CY7C1333H
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range (continued)
Parameter Description
Hold Times
t
AH
t
ALH
t
WEH
t
CENH
t
DH
t
CEH
Address Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
ADV/LD Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
WE, BW
Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
[A:D]
CEN Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Data Input Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Chip Enable Hold after CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Switching Waveforms
t
CENS
t
CES
[18, 19, 20]
t
CENH
t
CEH
t
CYC
t
t
CL
CH
Read/Write Waveforms
CLK
CEN
CE
ADV/LD
[12, 13]
133 MHz 100 MHz
Min. Max. Min. Max.
Unit
WE
BW[A:D]
ADDRESS
DQ
A1 A2
t
t
AH
AS
D(A1) D(A2) Q(A4)Q(A3)
t
t
DH
DS
A3
t
t
D(A2+1)
OE
OMMAND
WRITE
D(A1)
WRITE
D(A2)
BURST
WRITE
D(A2+1)
READ
Q(A3)
CDV
CLZ
A4
READ
Q(A4)
t
DOH
t
OEHZ
BURST
READ
Q(A4+1)
A5 A6 A7
t
t
OEV
CHZ
t
OELZ
Q(A4+1)
WRITE
D(A5)
t
DOH
READ
Q(A6)
D(A5)
WRITE
D(A7)
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
Notes:
For this waveform ZZ is tied LOW.
18.
19.When CE
20.Order of the Burst sequence is determined by the status of the MODE (0 = Linear, 1 = Interleaved). Burst operations are optional.
is LOW, CE1 is LOW, CE2 is HIGH and CE3 is LOW. When CE is HIGH, CE1 is HIGH or CE2 is LOW or CE3 is HIGH.
D(A7)Q(A6)
DESELECT
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 9 of 12
[+] Feedback
Page 10

Switching Waveforms (continued)
45678910
123
C
A
NOP, STALL and DESELECT Cycles
CLK
CEN
CE
ADV/LD
WE
BW
[A:B]
[18, 19, 21]
PRELIMINARY
CY7C1333H
ADDRESS
DQ
OMMAND
ZZ Mode Timing
CLK
ZZ
I
SUPPLY
LL INPUTS
(except ZZ)
Outputs (Q)
A1 A2
D(A1)
[22, 23]
READ
Q(A2)
A3 A4
Q(A2)D(A1) Q(A3)
STALL NOP READ
READ
Q(A3)
WRITE
D(A4)
STALLWRITE
D(A4)
A5
Q(A5)
t
CHZ
Q(A5)
t
DOH
DESELECT CONTINUE
DESELECT
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
t
ZZ
t
ZZI
I
DDZZ
DESELECT or READ Only
High-Z
t
RZZI
t
ZZREC
DON’T CARE
Ordering Information
Speed
(MHz) Ordering Code
133 CY7C1333H-133AXC A101 Lead-Free 100-lead Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1333H-133AXI A101 Lead-Free 100-lead Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Industrial
100
CY7C1333H-100AXC A101 Lead-Free 100-lead Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Commercial
CY7C1333H-100AXI A101 Lead-Free 100-lead Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Industrial
Shaded area contains advance information. Please contact your local Cypress sales representative for availability of this part.
21.The IGNORE CLOCK EDGE or STALL cycle (Clock 3) illustrated CEN
22.Device must be deselected when entering ZZ mode. See Truth Table for all possible signal conditions to deselect the device.
23.I/Os are in three-state when exiting ZZ sleep mode.
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 10 of 12
Package
Name Package Type
being used to create a pause. A write is not performed during this cycle.
Operating
Range
Commercial
[+] Feedback
Page 11

Package Diagram
PRELIMINARY
100-lead Thin Plastic Quad Flatpa c k (1 4 x 20 x 1. 4 mm ) A 10 1
CY7C1333H
51-85050-*A
NoBL and No Bus Latency are trademarks of Cypress Semiconductor. ZBT is a trademark of Integrated Device Technology. All
product and company names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of their respective holders.
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 11 of 12
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2004. The information contained herein is su bj ect to ch an ge wi t hou t notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the u se
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be
used for medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with Cypress. Furthermore, Cy press does not authorize its
products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
[+] Feedback
Page 12

PRELIMINARY
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C1333H 2-Mbit (64K x 32) Flow-Through SRAM with NoBL™ Architecture
Document Number: 001-00209
REV. ECN NO. Issue Date
** 347377 See ECN PCI New Datasheet
Orig. of
Change Description of Change
CY7C1333H
Document #: 001-00209 Rev. ** Page 12 of 12
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...