Page 1

CY7C1298H
1-Mbit (64K x 18) Pipelined DCD Sync SRAM
Features
• Registered inputs and outputs for pipelined operation
• Optimal for performance (Double-Cycle deselect)
— Depth expansion without wait state
• 64K × 18-bit common I/O architecture
• 3.3V core power supply (V
• 2.5V/3.3V I/O power supply (V
• Fast clock-to-output times
— 3.5 ns (for 166-MHz device)
• Provide high-performance 3-1-1-1 access rate
• User-selectable burst counter supporting Intel
Pentium
• Separate processor and controller address strobes
• Synchronous self-timed writes
• Asynchronous Output Enable
• Available in JEDEC-standard lead-free 100-Pin TQFP
package
• “ZZ” Sleep Mode option
®
interleaved or linear burst sequences
DD
)
DDQ
)
®
Functional Description
The CY7C1298H SRAM integrates 64K x 18 SRAM cells with
advanced synchronous peripheral circuitry and a two-bit
counter for internal burst operation. All synchronous inputs are
gated by registers controlled by a positive-edge-triggered
Clock Input (CLK). The synchronous inputs include all
addresses, all data inputs, address-pipelining Chip Enable
(CE
), depth-expansion Chip Enables (CE2 and CE3), Burst
1
Control inputs (ADSC
(BW
inputs include the Output Enable (OE
Addresses and chip enables are registered at rising edge of
clock when either Address Strobe Processor (ADSP
Address Strobe Controller (ADSC
burst addresses can be internally generated as controlled by
the Advance pin (ADV
Address, data inputs, and write controls are registered on-chip
to initiate a self-timed Write cycle.This part supports Byte Write
operations (see Pin Descriptions and Truth Table for further
details). Write cycles can be one to two bytes wide as
controlled by the byte write control inputs. GW
causes all bytes to be written. This device incorporates an
additional pipelined enable register which delays turning off
the output buffers an additional cycle when a deselect is
executed.This feature allows depth expansion without penalizing system performance.
The CY7C1298H operates from a +3.3V core power supply
while all outputs operate either with a +2.5V or +3.3V supply.
All inputs and outputs are JEDEC-standard
JESD8-5-compatible.
, and BWE), and Global Write (GW). Asynchronous
[A:B]
).
[1]
, ADSP, and ADV), Write Enables
) and the ZZ pin.
) or
) are active. Subsequent
active LOW
Selection Guide
166 MHz 133 MHz Unit
Maximum Access Time 3.5 4.0 ns
Maximum Operating Current 240 225 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Cur rent 40 40 mA
Note:
1. For best-practices recommendations, please refer to the Cypress application note System Design Guidelines on www.cypress.com.
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Revised July 5, 2006
[+] Feedback
Page 2
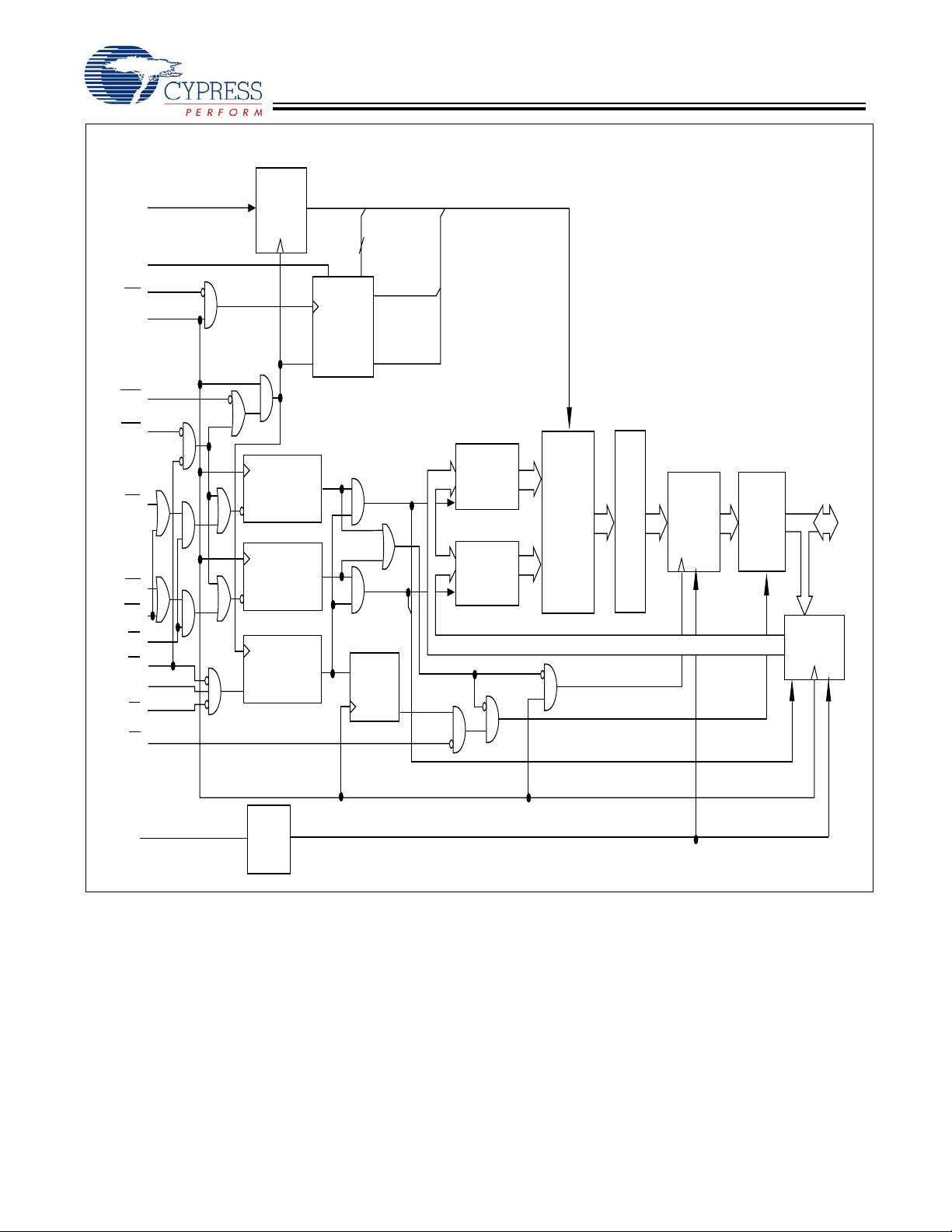
Functional Block Diagram
A
B
A
CY7C1298H
0, A1, A
MODE
ADV
CLK
ADSC
ADSP
BW
B
BW
A
BWE
GW
CE
1
CE
2
CE
3
ADDRESS
REGISTER
2
A
Q1
BURST
COUNTER AND
LOGIC
CLR
Q0
DQ
B,
DQP
B
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
A ,
DQP
A
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
ENABLE
REGISTER
PIPELINED
ENABLE
[1:0]
DQ
B ,
DQP
B
BYTE
WRITE DRIVER
MEMORY
DQ
A,
DQP
A
ARRAY
BYTE
WRITE DRIVER
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
E
INPUT
REGISTERS
DQ
s,
DQP
DQP
OE
ZZ
SLEEP
CONTROL
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 2 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 3
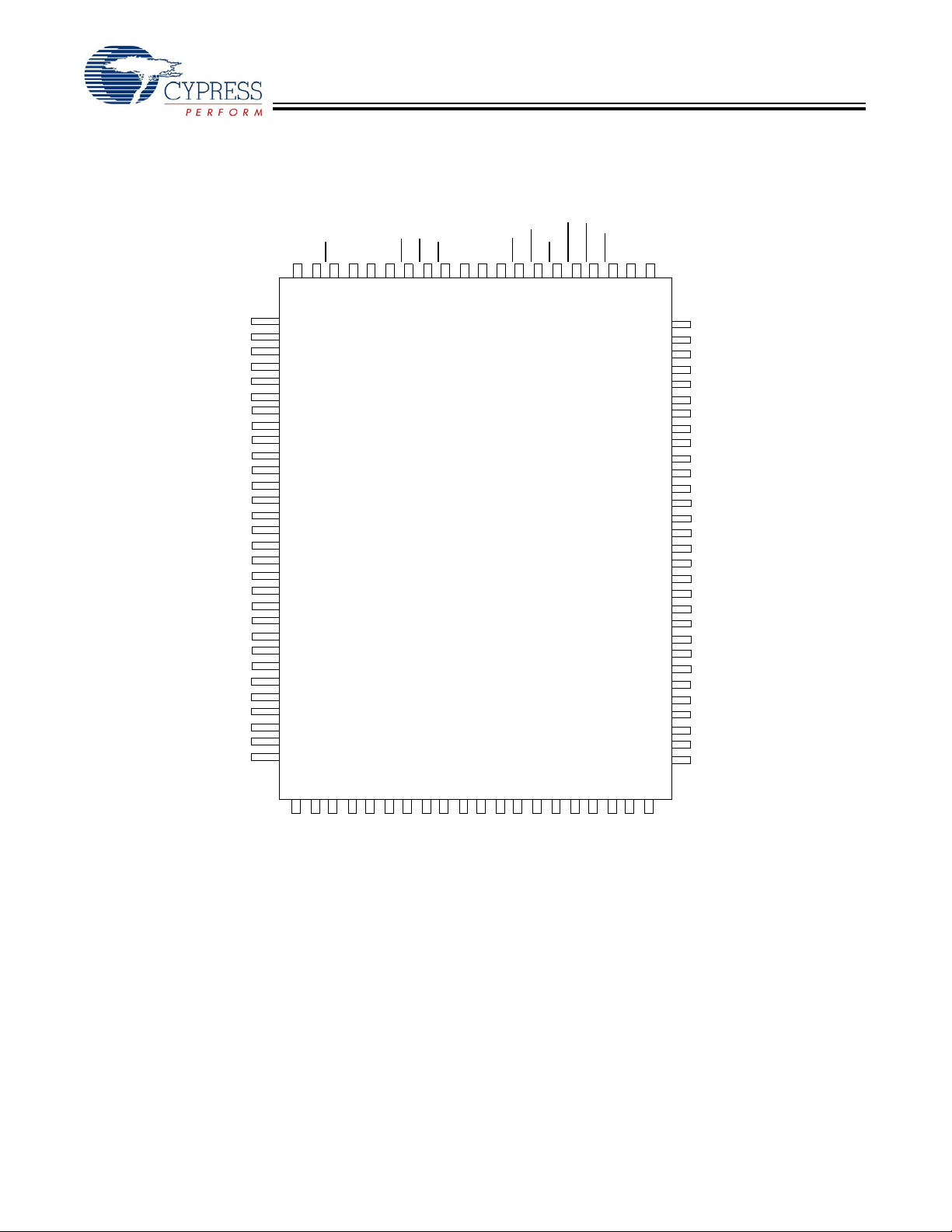
Pin Configurations
CY7C1298H
100-Pin TQFP
Top View
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
NC
V
NC
V
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
DD
SS
1CE2
A
100
A
99
NCNCBWBBW
CE
97969594939291
98
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B
B
8
9
10
11
B
B
12
13
14
15
16
17
B
B
18
19
20
21
B
B
B
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
A
CE3VDDV
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
90
898887
CY7C1298H
ADSP
ADV
8584838281
86
A
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
A
A
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
DQP
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
NC
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
A
MODE
A
1A0
A
A
A
SS
V
NC/36M
NC/72M
V
DD
A
NC/9M
NC/18M
A
A
A
50
A
NC/4M
NC/2M
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 3 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 4
CY7C1298H
Pin Descriptions
Pin Type Description
, A Input-
A0, A
BW
GW
1
[A:B]
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
BWE
Input-
Synchronous
CLK Input-
Clock
CE
CE
CE
OE
1
2
3
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Asynchronous
ADV
Input-
Synchronous
ADSP
Input-
Synchronous
ADSC
Input-
Synchronous
ZZ Input-
Asynchronous
DQs
DQP
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
[A:B]
I/O-
Synchronous
Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the device.
Ground Ground for the core of the device.
I/O Power
Supply
I/O Ground Ground for the I/O circuitry.
MODE Input-
Static
NC No Connects. Not internally connected to the die. 2M, 4M, 9M, 18M, 72M, 144M, 288M, 576M and
Address Inputs used to select one of the 64K address locations. Sampled at the rising edge
of the CLK if ADSP
or ADSC is active LOW, and CE1, CE2, and CE3 are sampled active. A
fed to the two-bit counter.
[1:0]
are
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW. Qualified with BWE to conduct byte writes to the SRAM.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Global Write Enable Input, active LOW. When asserted LOW on the rising edge of CLK, a global
write is conducted (ALL bytes are written, regardless of the values on BW
and BWE).
[A:B]
Byte Write Enable Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. This signal must be
asserted LOW to conduct a byte write.
Clock Input. Used to capture all synchronous inputs to the device. Also used to increment the burst
counter when ADV
is asserted LOW, during a burst operation.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
and CE3 to select/deselect the device. ADSP is ignored if CE1 is HIGH. CE1 is sampled only
2
when a new external address is loaded.
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
and CE3 to select/deselect the device. CE
1
is sampled only when a new external address is
2
loaded.
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction with
CE
and CE2 to select/deselect the device. CE3 is sampled only when a new external address is
1
loaded.
Output Enable, asynchronous input, active LOW. Controls the direction of the I/O pins. When
LOW, the I/O pins behave as outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins are tri-stated, and act as
input data pins. OE
is masked during the first clock of a read cycle when emerging from a deselected
state.
Advance Input signal, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW. When asserted, it
automatically increments the address in a burst cycle.
Address Strobe from Processor, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW. When
asserted LOW, addresses presented to the device are captured in the address registers. A
also loaded into the burst counter. When ADSP
nized. ASDP
is ignored when CE1 is deasserted HIGH.
and ADSC are both asserted, only ADSP is recog-
[1:0]
are
Address Strobe from Controller, sampled on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW. When
asserted LOW, addresses presented to the device are captured in the address registers. A
also loaded into the burst counter. When ADSP
and ADSC are both asserted, only ADSP is recog-
[1:0]
are
nized.
ZZ “sleep” Input, active HIGH. When asserted HIGH places the device in a non-time-critical
“sleep” condition with data integrity preserved. For normal operation, this pin has to be LOW or left
floating. The ZZ pin has an internal pull-down.
Bidirectional Data I/O lines. As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data register that is triggered by
the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they deliver the data contained in the memory location specified
by the addresses presented during the previous clock rise of the read cycle. The direction of the
pins is controlled by OE
and DQP
are placed in a tri-state condition.
[A:B]
. When OE is asserted LOW, the pins behave as outputs. When HIGH, DQs
Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
Selects Burst Order. When tied to GND selects linear burst sequence. When tied to V
floating selects interleaved burst sequence. This is a strap pin and should remain static during
DD
or left
device operation. Mode Pin has an internal pull-up.
1G are address expansion pins and are not internally connected to the die.
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 4 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 5
CY7C1298H
Functional Overview
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled
by the rising edge of the clock. All data outputs pass through
output registers controlled by the rising edge of the clock.
The CY7C1298H supports secondary cache in systems
utilizing either a linear or interleaved burst sequence. The
interleaved burst order supports Pentium and i486‰
processors. The linear burst sequence is suited for processors
that utilize a linear burst sequence. The burst order is user
selectable, and is determined by sampling the MODE input.
Accesses can be initiated with either the Processor Address
Strobe (ADSP
Address advancement through the burst sequence is
controlled by the ADV input. A two-bit on-chip wraparound
burst counter captures the first address in a burst sequence
and automatically increments the address for the rest of the
burst access.
Byte write operations are qualified with the Byte Write Enable
(BWE
) and Byte Write Select (BW
Enable (GW) overrides all byte write inputs and writes data to
all four bytes. All writes are simplified with on-chip
synchronous self-timed write circuitry.
Synchronous Chip Selects CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
selection and output tri-state control. ADSP
is HIGH.
Single Read Accesses
This access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise: (1) ADSP
chip selects are all asserted active, and (3) the write signals
(GW
, BWE) are all deasserted HIGH. ADSP is ignored if CE
is HIGH. The address presented to the address inputs is
stored into the address advancement logic and the Address
Register while being presented to the memory core. The corresponding data is allowed to propagate to the input of the
Output Registers. At the rising edge of the next clock the data
is allowed to propagate through the output register and onto
the data bus within t
occurs when the SRAM is emerging from a deselected state
to a selected state, its outputs are always tri-stated during the
first cycle of the access. After the first cycle of the access, the
outputs are controlled by the OE
read cycles are supported.
The CY7C1298H is a double-cycle deselect part. Once the
SRAM is deselected at clock rise by the chip select and either
ADSP
or ADSC signals, its output will tri-state immediately
after the next clock rise.
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSP
This access is initiated when both of the following conditions
are satisfied at clock rise: (1) ADSP
(2) chip select is asserted active. The address presented is
loaded into the address register and the address
advancement logic while being delivered to the memory core.
The write signals (GW
ignored during this first cycle.
ADSP
triggered write accesses require two clock cycles to
complete. If GW
data presented to the DQx inputs is written into the corresponding address location in the memory core. If GW
then the write operation is controlled by BWE
) or the Controller Address Strobe (ADSC).
) inputs. A Global Write
[A:B]
, CE2, CE3 and an
1
) provide for easy bank
is ignored if CE
or ADSC is asserted LOW, (2)
if OE is active LOW. The only exception
co
signal. Consecutive single
is asserted LOW, and
, BWE, and BW
) and ADV inputs are
[A:B]
is asserted LOW on the second clock rise, the
is HIGH,
and BW
[A:B]
signals. The CY7C1298H provides byte write capability that
is described in the Write Cycle Description table. Asserting the
Byte Write Enable input (BWE) with the selected Byte Write
input will selectively write to only the desired bytes. Bytes not
selected during a byte write operation will remain unaltered. A
synchronous self-timed write mechanism has been provided
to simplify the write operations.
Because the CY7C1298H is a common I/O device, the Output
Enable (OE
to the DQ
a safety precaution, DQ are automatically tri-stated whenever
) must be deasserted HIGH before presenting data
inputs. Doing so will tri-state the output drivers. As
a write cycle is detected, regardless of the state of OE.
Single Write Accesses Initiated by ADSC
ADSC write accesses are initiated when the following conditions are satisfied: (1) ADSC
is asserted LOW, (2) ADSP is
deasserted HIGH, (3) chip select is asserted active, and (4)
the appropriate combination of the write inputs (GW
and BW
desired byte(s). ADSC
) are asserted active to conduct a write to the
[A:B]
triggered write accesses require a
single clock cycle to complete. The address presented is
loaded into the address register and the address
advancement logic while bei ng d elive re d to the m emory co re.
The ADV input is ignored during this cycle. If a global write is
conducted, the data presented to the DQ
corresponding address location in the memory core. If a byte
1
write is conducted, only the selected bytes are written. Bytes
is written into the
X
not selected during a byte write operation will remain
unaltered. A synchronous self-timed write mechanism has
been provided to simplify the write operations.
Because the CY7C1298H is a common I/O device, the Output
Enable (OE) must be deasserted HIGH before presenting data
to the DQ
1
a safety precaution, DQ
whenever a write cycle is detected, regardless of the state of
inputs. Doing so will tri-state the output drivers. As
X
are automatically tri-stated
X
OE.
Burst Sequences
The CY7C1298H provides a two-bit wraparound counter, fed
by A
sequence. The interleaved burst sequence is designed specif-
, that implements either an interleaved or linear burst
[1:0]
ically to support Intel Pentium applications. The linear burst
sequence is designed to support processors that follow a
linear burst sequence. The burst sequence is user se lectable
through the MODE input. Both read and write burst operations
are supported
Asserting ADV
LOW at clock rise will automatically increment
the burst counter to the next address in the burst sequence.
Both read and write burst operations are supported.
Sleep Mode
The ZZ input pin is an asynchronous input. Asserting ZZ
places the SRAM in a power conservation “sleep” mode. Two
clock cycles are required to enter into or exit from this “sleep”
mode. While in this mode, data integrity is guaranteed.
Accesses pending when entering the “sleep” mode are not
considered valid nor is the completion of the operation
guaranteed. The device must be deselected prior to entering
the “sleep” mode. CE
inactive for the duration of t
LOW.
s, ADSP, and ADSC must remain
after the ZZ input returns
ZZREC
, BWE,
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 5 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 6

CY7C1298H
Interleaved ‘Burst Address Table
(MODE = Floating or V
First
Address
A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 00 11 10
10 11 00 01
11 10 01 00
Truth Table
Operation
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None H X X L X L X X X L-H Tri-S tate
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L L X L L X X X X L-H Tri-S tate
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L X H L L X X X X L-H Tri-S tate
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L L X L H L X X X L-H Tri-S tate
Deselected Cycle, Power-down None L X H L H L X X X L-H Tri-S tate
ZZ Mode, Power-Down None X X X H X X X X X X Tri-State
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L L X X X H L-H Tri-State
Write Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X L X L-H D
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Begin Burst External L H L L H L X H H L-H Tri-State
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L H H L-H Tri-State
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L H H L-H Tri-State
Write Cycle, Continue Burst Next X X X L H H L L X L-H D
Write Cycle, Continue Burst Next H X X L X H L L X L-H D
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H H H L-H Tri-State
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H H L L-H Q
Read Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H H H L-H Tri-State
Write Cycle, Suspend Burst Current X X X L H H H L X L-H D
Write Cycle, Suspend Burst Current H X X L X H H L X L-H D
Second
Address
A1, A0
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
)
DD
Third
Address
A1, A0
Fourth
Address
A1, A0
Address
Used CE1CE2CE3ZZ ADSP ADSC ADV WRITE OE CLK DQ
Linear Burst Address Table (MODE = GND)
First
Address
A1, A0
00 01 10 11
01 10 11 00
10 11 00 01
11 00 01 10
Second
Address
A1, A0
Third
Address
A1, A0
Fourth
Address
A1, A0
Notes:
2. X = “Don't Care.” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW.
3. WRITE = L when any one or more Byte Write enable signals (BW
BWE
, GW = H.
4. The DQ pins are controlled by the current cycle and the OE
5. The SRAM always initiates a read cycle when ADSP
after the ADSP
don't care for the remainder of the write cycle.
is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock rise. It is masked internally during write cycles. During a read cycle all data bits are tri-state when OE is
6. OE
inactive or when the device is deselected, and all data bits behave as output when OE
or with the assertion of ADSC. As a result, OE must be driven HIGH prior to the start of the write cycle to allow the outputs to tri-state. OE is a
is asserted, regardless of the state of GW, BWE, or BW
,BWB) and BWE = L or GW = L. WRITE = H when all Byte write enable signals (BWA, BWB),
A
signal. OE is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock.
is active (LOW).
. Writes may occur only on subsequent clocks
[A: B]
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 6 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 7

CY7C1298H
Truth Table for Read/Write
Function GW BWE BW
[2,3]
A
BW
B
Read H H X X
Read H L H H
Write byte A – (DQA and DQPA)H L L H
Write byte B – (DQ
and DQPB)H L H L
B
Write all bytes H L L L
Write all bytes L X X X
ZZ Mode Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
I
DDZZ
t
ZZS
t
ZZREC
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Sleep mode standby current ZZ > VDD − 0.2V 40 mA
Device operation to ZZ ZZ > VDD − 0.2V 2t
ZZ recovery time ZZ < 0.2V 2t
CYC
ZZ Active to Sleep current This parameter is sampled 2t
CYC
CYC
ns
ns
ns
ZZ inactive to exit Sleep current This parameter is sampled 0 ns
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 7 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 8

CY7C1298H
Maximum Ratings
(Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guidelines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature...................................–65°C to + 150°
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied............................................–55°C to + 125°C
Supply Voltage on V
Supply Voltage on V
Relative to GND.......–0.5V to + 4.6V
DD
Relative to GND.....–0.5V to + V
DDQ
DD
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in tri-state.............................. .. ... ......... –0.5V to V
DDQ
+ 0.5V
Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
DC Input Voltage.................... ... ... ......... –0.5V to V
Current into Outputs (LOW)........................... ..............20 mA
Static Discharge Voltage...........................................> 2001V
(per MIL-STD-883,Method 3015)
Latch -up Current....................................................> 200 mA
Operating Range
Range
Com’l 0°C to +70°C 3.3V −5%/+10% 2.5V −5%
Ind’l –40°C to +85°C
[7,8]
Ambient
Temperature (TA)V
DD
DD
to V
+ 0.5V
V
DDQ
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
V
V
DD
DDQ
Power Supply Voltage 3.135 3.6 V
I/O Supply Voltage for 3.3V I/O 3.135 V
DD
for 2.5V I/O 2.375 2.625 V
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
V
IL
Output HIGH Voltage for 3.3V I/O, I
for 2.5V I/O, I
Output LOW Voltage for 3.3V I/O, I
for 2.5V I/O, I
Input HIGH Voltage
[7]
for 3.3V I/O 2.0 V
for 2.5V I/O 1.7 V
Input LOW Voltage
[7]
for 3.3V I/O –0.3 0.8 V
= –4.0 mA 2.4 V
OH
= –1.0 mA 2.0 V
OH
= 8.0 mA 0.4 V
OL
= 1.0 mA 0.4 V
OL
+ 0.3V V
DD
+ 0.3V V
DD
for 2.5V I/O –0.3 0.7 V
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
X
OZ
DD
SB1
SB2
SB3
SB4
Input Leakage Current
GND ≤ VI ≤ V
except ZZ and MODE
Input Current of MODE Input = V
Input = V
Input Current of ZZ Input = V
Input = V
SS
DD
SS
DD
Output Leakage Current GND ≤ VI ≤ V
VDD Operating Supply
Current
Automatic CS
Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
Automatic CS
Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CS
Power-down
Current—CMOS Inputs
Automatic CS
Power-down
Current—TTL Inputs
V
= Max., I
DD
f = f
V
V
f = f
V
V
V
V
or V
V
f = f
V
V
= 1/t
MAX
= Max., Device Deselected,
DD
≥ VIH or VIN ≤ VIL,
IN
= 1/t
MAX
= Max., Device Deselected,
DD
≤ 0.3V or
IN
> V
IN
DD
> V
IN
MAX
DD
≥ VIH or VIN ≤ VIL, f = 0
IN
– 0.3V, f = 0
DDQ
= Max., Device Deselected,
≤ 0.3V or
IN
– 0.3V,
DDQ
= 1/t
= Max., Device Deselected,
DDQ
–5 5 µA
–30 µA
–5 µA
Output Disabled –5 5 µA
DDQ,
OUT
CYC
= 0 mA,
6-ns cycle, 166 MHz 240 mA
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 225 mA
6-ns cycle, 166 MHz 100 mA
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 90 mA
CYC
All speeds 40 mA
6-ns cycle, 166 MHz 85 mA
7.5-ns cycle, 133 MHz 75 mA
CYC
All speeds 45 mA
5 µA
30 µA
DD
V
Notes:
7. Overshoot: V
8. Power-up: Assumes a linear ramp from 0V to V
(AC) < VDD +1.5V (Pulse width less than t
IH
(min.) within 200 ms. During this time VIH < VDD and V
DD
/2), undershoot: VIL(AC)> –2V (Pulse width less than t
CYC
DDQ
< VDD.
CYC
/2).
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 8 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 9

CY7C1298H
Capacitance
[9]
Parameter Description T e st Con dit ion s
C
Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
IN
C
CLK
C
I/O
Thermal Characteristics
Clock Input Capacitance 5 pF
Input/Output Capacitance 5 pF
[9]
V
V
DD
DDQ
= 3.3V
= 2.5V
Parameter Description Test Conditions
Θ
Θ
JA
JC
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to case)
Test conditions follow standard test
methods and procedures for measuring
thermal impedance, per EIA/JESD51
AC Test Loads and Waveforms
3.3V I/O Test Load
OUTPUT
Z
0
3.3V
= 50Ω
R
VT= 1.5V
(a) (b)
= 50Ω
L
OUTPUT
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
5pF
R = 317Ω
V
GND
R = 351Ω
DDQ
≤ 1 ns
ALL INPUT PULSES
10%
90%
100 TQFP
Max. Unit
5pF
100 TQFP
Package Unit
30.32 °C/W
6.85 °C/W
90%
10%
≤ 1 ns
(c)
2.5V I/O Test Load
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
Z
0
= 1.25V
V
T
R
L
2.5V
OUTPUT
= 50Ω
5pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
R = 1667Ω
R =1538Ω
(a) (b)
Note:
9. Tested initially and after any design or proc ess change that may affect these parameters.
V
DDQ
GND
≤ 1 ns
ALL INPUT PULSES
10%
90%
(c)
90%
10%
1 ns
≤
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 9 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 10

CY7C1298H
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description
t
POWER
Clock
t
CYC
t
CH
t
CL
Output Times
t
CO
t
DOH
t
CLZ
t
CHZ
t
OEV
t
OELZ
t
OEHZ
Set-up Times
t
AS
t
ADS
t
ADVS
t
WES
t
DS
t
CES
Hold Times
t
AH
t
ADH
t
ADVH
t
WEH
t
DH
t
CEH
VDD(Typical) to the first Access
Clock Cycle Time 6.0 7.5 ns
Clock HIGH 2.5 3.0 ns
Clock LOW 2.5 3.0 ns
Data Output V a lid Af ter CLK Rise 3.5 4.0 ns
Data Output Hold After CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Clock to Low-Z
Clock to High-Z
[11, 12, 13]
[11, 12, 13]
OE LOW to Output Valid 3.5 4.0 ns
OE LOW to Output Low-Z
OE HIGH to Output High-Z
Address Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
ADSC, ADSP Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
ADV Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
GW, BWE, BW
Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
[A:B]
Data Input Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Chip Enable Set-up Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Address Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
ADSP, ADSC Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
ADV Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
GW, BWE, BW
Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
[A:B]
Data Input Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Chip Enable Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
[10]
[11, 12, 13]
[11, 12, 13]
[14, 15]
166 MHz 133 MHz
UnitMin. Max. Min. Max.
11ms
00ns
3.5 4.0 ns
00ns
3.5 4.0 ns
Notes:
10.This part has a voltage regulator internally; tpower is the time that the power need s to be supplied above V
can be initiated.
, t
11. t
CHZ
12.At any given voltage and temperature, t
data bus. These specifications do not imply a bus contention condition, but reflect p ar ameters gu aran teed over worst case user condi tions. De vi ce is desig ned
to achieve High-Z prior to Low-Z under the same system conditions.
13.This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
14.Timing reference level is 1.5V when V
15.Test conditions shown in (a) of AC Test Loads unless otherwise noted.
CLZ,tOELZ
, and t
are specified with AC test conditions shown in part (b) of AC Test Loads. Tran sition is measured ± 20 0 mV from steady- stat e voltage.
OEHZ
is less than t
OEHZ
= 3.3V and is 1.25V when V
DDQ
OELZ
and t
is less than t
CHZ
DDQ
= 2.5V.
to eliminate bus contention between SRAMs when sharing the same
CLZ
minimum initially before a read or write operation
DD
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 10 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 11

Switching Waveforms
G
Read Timing
[16]
t
CY7C1298H
CYC
CLK
ADSP
ADSC
ADDRESS
W, BWE,BW
CE
ADV
OE
Data Out (Q)
[A:B]
t
t
CL
CH
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
AH
AS
A1
t
WES
t
t
CEH
CES
A2 A3
t
WEH
t
t
ADVH
ADVS
Burst continued with
new base address
Deselect
cycle
ADV suspends burst
t
OEHZ
t
OELZ
High-Z
t
CLZ
t
CO
t
Q(A1)
Single READ BURST READ
t
OEV
t
CO
DOH
Q(A2) Q(A2 + 1) Q(A2 + 2)
Q(A2) Q(A2 + 1) Q(A3)Q(A2 + 3)
Burst wraps around
to its initial state
t
CHZ
Note:
16.On this diagram, when CE
DON’T CARE
is LOW, CE1 is LOW, CE2 is HIGH and CE3 is LOW. When CE is HIGH, CE1 is HIGH or CE2 is LOW or CE3 is HIGH.
UNDEFINED
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 11 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 12

Switching Waveforms (continued)
D
Write Timing
[16, 17]
t
CYC
CY7C1298H
CLK
ADSP
ADSC
ADDRESS
BWE,
BW
[A:B]
GW
CE
t
t
CL
CH
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
ADH
ADS
t
t
AH
AS
A1
A2 A3
Byte write signals are ignored for first cycle when
ADSP initiates burst
t
t
CEH
CES
t
WES
t
WEH
ADSC extends burst
t
ADS
t
ADH
t
WES
t
ADVS
t
WEH
t
ADVH
ADV
ADV suspends burst
OE
t
t
DH
DS
Data in (D)
High-Z
t
OEHZ
D(A1)
D(A2) D(A2 + 1) D(A2 + 1) D(A3) D(A3 + 1) D(A3 + 2)D(A2 + 3)
D(A2 + 2)
ata Out (Q)
BURST READ BURST WRITE
Single WRITE
Extended BURST WRITE
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
Note:
17.Full width write can be initiated by either GW
LOW; or by GW HIGH, BWE LOW and BW
[A:B]
LOW.
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 12 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 13

Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
Read/Write Timing
[16, 18, 19]
CYC
CY7C1298H
CLK
ADSP
ADSC
ADDRESS
BWE, BW
[A:B]
CE
ADV
OE
Data In (D)
Data Out (Q)
A1
t
ADS
t
AS
t
CES
High-Z
High-Z
A2
t
CH
t
ADH
t
AH
t
CEH
t
CLZ
t
CL
A3
t
WES
t
OEHZ
t
DS
D(A3)
t
CO
Q(A2)Q(A1)
A4 A5 A6
t
WEH
t
DH
t
OELZ
Q(A4) Q(A4+1) Q(A4+2)
Q(A4+3)
D(A5) D(A6)
Single WRITE
BURST READBack-to-Back READs
Back-to-Back
WRITEs
DON’T CARE
Notes:
18.The data bus (Q) remains in High-Z following a WRITE cycle, unless a new read access initiated by ADSP
is HIGH.
19.GW
UNDEFINED
or ADSP.
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 13 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 14

Switching Waveforms (continued)
A
CLK
[20, 21]
t
ZZ
ZZ Mode Timing
CY7C1298H
t
ZZREC
I
SUPPLY
LL INPUTS
(except ZZ)
Outputs (Q)
ZZ
t
ZZI
I
DDZZ
High-Z
t
RZZI
DESELECT or READ Only
DON’T CARE
Notes:
20.Device must be deselected when entering ZZ mode. See truth table for all possible signal conditions to deselect the device.
21.I/Os are in High-Z when exiting ZZ sleep mode.
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 14 of 16
[+] Feedback
Page 15

CY7C1298H
Ordering Information
Not all of the speed, package and temperature ranges are available. Please contact your local sales representative or
Speed
(MHz) Ordering Code
100 CY7C1298H-100AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free Commercial
CY7C1298H-100AXI Industrial
133 CY7C1298H-133AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Lead-Free Commercial
CY7C1298H-133AXI Industrial
Package Diagram
visit www.cypress.com for actual products offered.
Package
Diagram Package Type
100-Pin TQFP (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) (51-85050)
16.00±0.20
14.00±0.10
100
1
81
80
0.30±0.08
Operating
Range
1.40±0.05
20.00±0.10
22.00±0.20
GAUGE PLANE
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.25
0°-7°
0.60±0.15
1.00 REF.
30
31 50
0° MIN.
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.20 MIN.
A
DETAIL
0.65
TYP.
51
STAND-OFF
0.05 MIN.
0.15 MAX.
SEATING PLANE
NOTE:
1. JEDEC STD REF MS-026
2. BODY LENGTH DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH
MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH SHALL NOT EXCEED 0.0098 in (0.25 mm) PER SIDE
BODY LENGTH DIMENSIONS ARE MAX PLASTIC BODY SIZE INCLUDING MOLD MISMATCH
3. DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS
12°±1°
(8X)
51-85050-*B
0.20 MAX.
1.60 MAX.
0.10
SEE DETAIL
A
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks, and i486 is a trademark, of Intel Corporat ion. PowerPC is a registe red trademark
of IBM. All product and company names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of their respective holders.
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 15 of 16
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006. The information contained herein is subject to change withou t n oti ce. C ypr ess S emi con duct or Corpo ration assu mes no resp onsib ility for the u se
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be
used for medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with Cypress. Furthermore, Cypress does not authorize its
products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY7C1298H
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C1298H 1-Mbit (64K x 18) Pipelined DCD Sync SRAM
Document Number: 38-05665
REV. ECN NO. Issue Date
** 343896 See ECN PCI New Data Sheet
*A 430678 See ECN NXR Changed address of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation on Page# 1 from
*B 481916 See ECN VKN Converted from Preliminary to Final.
Orig. of
Change Description of Change
“3901 North First Street” to “198 Champion Court”
Added 2.5VI/O option
Changed Three-State to Tri-State
Included Maximum Ratings for V
Modified “Input Load” to “Input Leakage Current except ZZ and MODE” in the
relative to GND
DDQ
Electrical Characteristics Table
Modified test condition from V
Replaced Package Name column with Package Diagram in the Ordering
IH
< V
DD to VIH
< V
Information table
Updated the Ordering Information table.
DD
Document #: 38-05665 Rev. *B Page 16 of 16
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...