Page 1
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
3.3V 32K/64K/128K x 8/9
Synchronous Dual-Port Static RAM
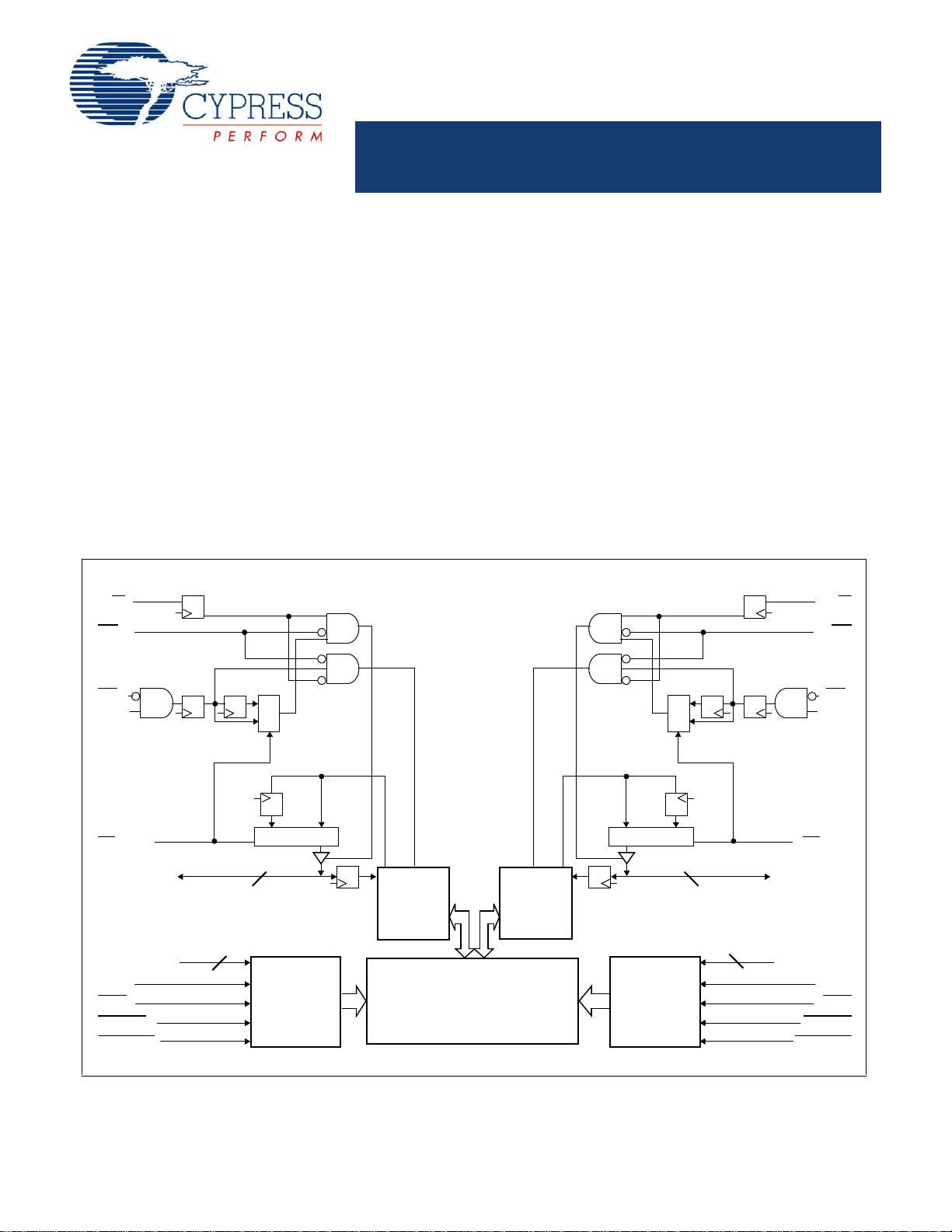
Logic Block Diagram
R/W
L
CE
0L
CE
1L
OE
L
FT/Pipe
L
I/O0L–I/O
7/8L
Control
A
0–A14/15/16L
CLK
L
ADS
L
CNTEN
L
CNTRST
L
R/W
R
1
0
0/1
CE
0R
CE
1R
OE
R
1
0/1
0
FT/Pipe
R
I/O0R–I/O
7/8R
I/O
Control
A
0–A14/15/16R
CLK
R
ADS
R
CNTEN
R
CNTRST
R
1
0
0/1
1
0/1
0
I/O
Counter/
Address
Register
Decode
True Dual-Ported
RAM Array
Counter/
Address
Register
Decode
8/9 8/9
[2]
[2]
[3]
[3]
15/16/17
15/16/17
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Features
■ True Dual-Ported memory cells which enable simultaneous
access of the same memory location
■ 6 Flow-Through and Pipelined devices
■ 32K x 8/9 organizations (CY7C09079V/179V)
■ 64K x 8/9 organizations (CY7C09089V/189V)
■ 128K x 8/9 organizations (CY7C09099V/199V)
■ 3 Modes
■ Flow-Through
■ Pipelined
■ Burst
■ Pipelined output mode on both ports enables fast 100 MHz
operation
■ 0.35-micron CMOS for optimum speed and power
■ High speed clock to data access 6.5[1]/7.5[1]/9/12 ns (max.)
■ 3.3V low operating power
■ Active= 115 mA (typical)
■ Standby= 10 μA (typical)
■ Fully synchronous interface for easier operation
■ Burst counters increment addresses internally
■ Shorten cycle times
■ Minimize bus noise
■ Supported in Flow-Through and Pipelined modes
■ Dual Chip Enables for easy depth expansion
■ Automatic power down
■ Commercial and Industrial temperature ranges
■ Available in 100-pin TQFP
■ Pb-free packages available
Notes
1. See page 6 for Load Conditions.
–I/O7 for x8 devices, I/O0–I/O8 for x9 devices.
2. I/O
0
3. A
0–A14
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Revised December 10, 2008
for 32K, A0–A15 for 64K, and A0–A16 for 128K devices.
[+] Feedback
Page 2
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
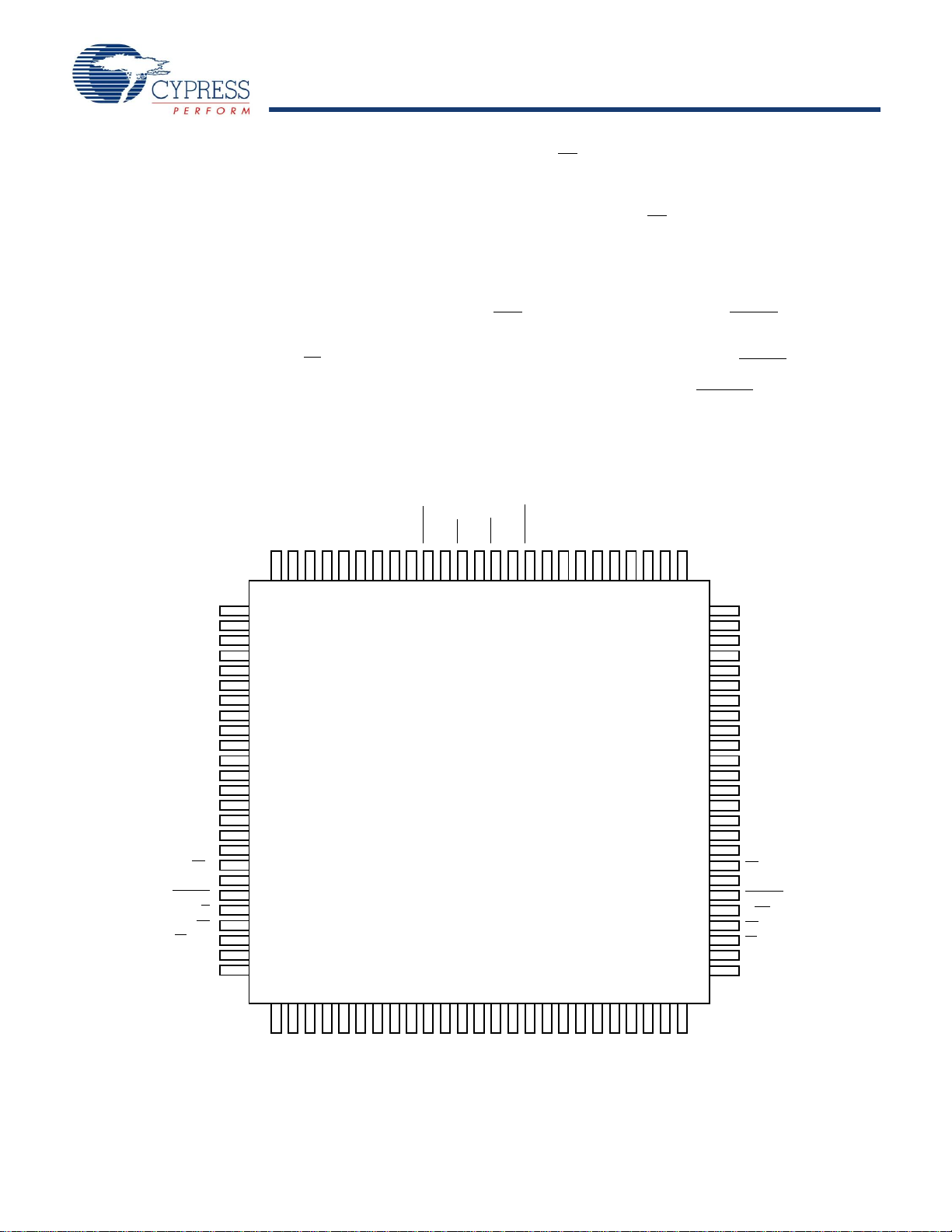
Functional Description
1
3
2
92 91 90 848587 868889 83 82 81 7678 77798093949596979899100
59
60
61
67
66
64
65
63
62
68
69
70
75
73
74
72
71
NC
NC
A7R
A8R
A9R
A10R
A15R
A12R
A14R
GND
NC
NC
CE
0R
A13R
A11R
NC
NC
CE1R
CNTRST
R
R/WR
OER
FT
/PIPER
GND
NC
A16R
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
NC
NC
A7L
A8L
A9L
A10L
A15L
A12L
A14L
VCC
NC
NC
CE0L
A13L
A11L
NC
NC
CE1L
CNTRSTL
R/W
L
OEL
FT
/PIPEL
NC
NC
A16L
17
16
15
9
10
12
11
13
14
8
7
6
4
5
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
NCNCA6L
A5L
A4L
A3L
CLKL
A1L
CNTENL
GND
ADSR
A0R
A1R
A0L
A2L
CLKR
CNTENR
A2R
A3R
A4R
A5R
A6RNCNC
ADSL
34 35 36 424139 403837 43 44 45 5048 494746
NC
NC
NC
I/O7R
I/O6R
I/O5R
I/01R
I/O3R
I/O2R
GND
VCC
GND
I/O2L
VCC
I/O4R
I/O0L
I/O1L
I/O3L
I/O4L
I/O5L
I/O6L
I/O7L
NC
GND
I/O0R
3332313029282726
[5]
[5]
[6]
[6]
[7]
[7]
The CY7C09079V/89V/99V and CY7C09179V/89V/99V are
high speed synchronous CMOS 32K, 64K, and 128K x 8/9
dual-port static RAMs. Two ports are provided, permitting
independent, simultaneous access for reads and writes to any
location in memory.
[4]
Registers on control, address, and data
lines enable minimal setup and hold times. In pipelined output
mode, data is registered for decreased cycle time. Clock to data
valid t
used to bypass the pipelined output register to eliminate access
CD2
= 6.5 ns
latency. In flow-through mode, data is available t
the address is clocked into the device. Pipelined output or
[1]
(pipelined). Flow-through mode can also be
= 18 ns after
CD1
flow-through mode is selected via the FT/Pipe pin.
Each port contains a burst counter on the input address register.
The internal write pulse width is independent of the
LOW-to-HIGH transition of the clock signal. The internal write
pulse is self-timed to enable the shortest possible cycle times.
Pin Configurations
Figure 1. 100-Pin TQFP (Top View) - CY7C09099V (128K x 8), CY7C09089V (64K x 8),CY7C09079V (32K x 8)
A HIGH on CE
the internal circuitry to reduce the static power consumption. The
or LOW on CE1 for one clock cycle powers down
0
use of multiple Chip Enables enables easier banking of multiple
chips for depth expansion configurations. In the pipelined mode,
one cycle is required with CE0 LOW and CE1 HIGH to reactivate
the outputs.
Counter enable inputs are provided to stall the operation of the
address input and use the internal address generated by the
internal counter for fast interleaved memory applications. A
port’s burst counter is loaded with the port’s Address Strobe
(ADS
). When the port’s Count Enable (CNTEN) is asserted, the
address counter increments on each LOW-to-HIGH transition of
that port’s clock signal. This reads/writes one word from/into
each successive address location until CNTEN
is deasserted.
The counter can address the entire memory array and loops
back to the start. Counter Reset (CNTRST
) is used to reset the
burst counter.
All parts are available in 100-pin Thin Quad Plastic Flatpack
(TQFP) packages.
Notes
4. When writing simultaneously to the same location, the final value cannot be guaranteed.
5. This pin is NC for CY7C09079V.
6. This pin is NC for CY7C09079V and CY7C09089V.
7. For CY7C09079V and CY7C09089V, pin #23 connected to V
compatible with an IDT 5V x16 flow-through device.
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 2 of 21
CC
is pin compatible with an IDT 5V x8 pipelined device; connecting pin #23 and #53 to GND is pin
[+] Feedback
Page 3
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
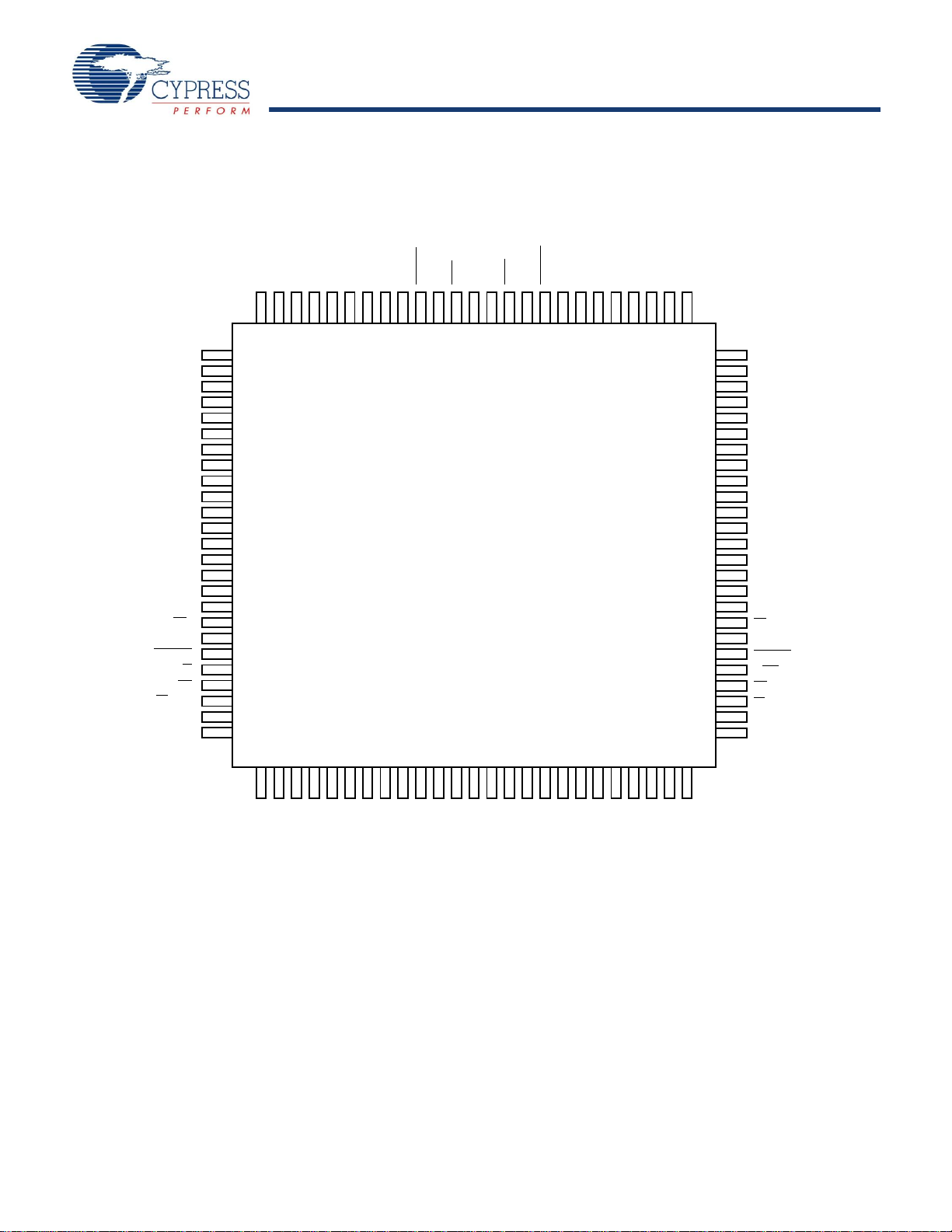
Pin Configurations (continued
1
3
2
92 91 90 848587 868889 83 82 81 7678 77798093949596979899100
59
60
61
67
66
64
65
63
62
68
69
70
75
73
74
72
71
NC
NC
A7R
A8R
A9R
A10R
A15R
A12R
A14R
GND
NC
NC
CE0R
A13R
A11R
NC
NC
CE1R
CNTRSTR
R/WR
OER
FT/PIPER
GND
NC
A16R
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
NC
NC
A7L
A8L
A9L
A10L
A15L
A12L
A14L
VCC
NC
NC
CE0L
A13L
A11L
NC
NC
CE1L
CNTRSTL
R/WL
OEL
FT/PIPEL
NC
NC
A16L
17
16
15
9
10
12
11
13
14
8
7
6
4
5
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
NCNCA6L
A5L
A4L
A3L
CLKL
A1L
CNTENL
GND
GND
CNTENR
A0R
A0L
A2L
ADSR
CLKR
A1R
A2R
A3R
A4R
A5R
A6R
NC
ADSL
34 35 36 424139 403837 43 44 45 5048 494746
NC
NC
I/O8R
I/O7R
I/O6R
I/O5R
I/01R
I/O3R
I/O2R
GND
VCC
GND
I/O2L
VCC
I/O4R
I/O0L
I/O1L
I/O3L
I/O4L
I/O5L
I/O6L
I/O7L
I/O8L
GND
I/O0R
3332313029282726
[8]
[8]
[9][9]
Figure 2. 100-Pin TQFP (Top View0 - CY7C09199V (128K x 9), CY7C09189V (64K x 9),CY7C09179V (32K x 9)
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 3 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 4
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Notes
8. This pin is NC for CY7C09179V.
9. This pin is NC for CY7C09179V and CY7C09189V
Selection Guide
Description
(MHz)
f
MAX2
(Pipelined)
Max. Access Time
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V-6
100 83 67 50
6.5 7.5 9 12
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
[1]
CY7C09179V/89V/99V-7
(ns) (Clock to Data,
Pipelined)
Typical Operating
Current I
CC
(mA)
Typical Standby
Current for I
(mA) (Both Ports
SB1
175 155 135 115
25 25 20 20
TTL Level)
Typical Standby
Current for I
(μA) (Both Ports
SB3
10 μA 10 μA10 μA 10 μA
CMOS Level)
Pin Definitions
Left Port Right Port Description
A0L–A
16L
ADS
L
CE0L,CE
CLK
CNTEN
CNTRST
I/O0L–I/O
OE
R/W
FT/PIPE
1L
L
L
L
8L
L
L
L
GND Ground Input.
NC No Connect.
V
CC
A0R–A
16R
ADS
R
CE0R,CE
CLK
R
CNTEN
CNTRST
I/O0R–I/O
OE
R
R/W
R
FT/PIPE
Address Inputs (A0–A14 for 32K; A0–A15 for 64K; and A0–A16 for 128K devices).
Address Strobe Input. Used as an address qualifier. This signal should be asserted LOW to
access the part using an externally supplied address. Asserting this signal LOW also loads
the burst counter with the address present on the address pins.
Chip Enable Input. To select either the left or right port, both CE0 AND CE1 must be asserted
1R
to their active states (CE
≤ VIL and CE1 ≥ VIH).
0
Clock Signal. This input can be free running or strobed. Maximum clock input rate is f
Counter Enable Input. Asserting this signal LOW increments the burst address counter of its
R
respective port on each rising edge of CLK. CNTEN
asserted LOW.
Counter Reset Input. Asserting this signal LOW resets the burst address counter of its
R
respective port to zero. CNTRST
Data Bus Input/Output (I/O0–I/O7 for x8 devices; I/O0–I/O8 for x9 devices).
8R
is not disabled by asserting ADS or CNTEN.
Output Enable Input. This signal must be asserted LOW to enable the I/O data pins during
read operations.
Read/Write Enable Input. This signal is asserted LOW to write to the dual port memory array.
For read operations, assert this pin HIGH.
Flow-Through/Pipelined Select Input. For flow-through mode operation, assert this pin LOW.
R
For pipelined mode operation, assert this pin HIGH.
Power Input.
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
[1]
-9
is disabled if ADS or CNTRST are
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
-12
.
MAX
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 4 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 5
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Maximum Ratings
Notes
10. The Voltage on any input or I/O pin cannot exceed the power pin during power-up.
11. Industrial parts are available in CY7C09099V and CY7C09199V only.
12. CE
L
and CER are internal signals. To select either the left or right port, both CE0 AND CE1 must be asserted to their active states (CE0 ≤ VIL and CE1 ≥ VIH).
Exceeding maximum ratings may impair the useful life of the
device. These user guidelines are not tested.
Storage Temperature................................. –65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with Power Applied.. –55
Supply Voltage to Ground Potential................–0.5V to +4.6V
DC Voltage Applied to
Outputs in High Z State ...........................–0.5V to V
DC Input Voltage ..................................... –0.5V to V
Output Current into Outputs (LOW)............................. 20 mA
[10]
°C to +125°C
+0.5V
CC
+0.5V
CC
Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description
Static Discharge Voltage............................................ >2001V
Latch-Up Current..................................................... >200 mA
Operating Range
Ambient
Temperature V
–40°C to +85°C 3.3V ± 300 mV
-9 -12
-6
Range
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 3.3V ± 300 mV
Industrial
[11]
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
[1]
-7
[1]
CC
V
V
V
V
I
OZ
I
CC
I
SB1
I
SB2
I
SB3
I
SB4
OH
OL
IH
IL
Output HIGH Voltage (V
–4.0 mA)
Output LOW Voltage (V
+4.0 mA)
= Min. IOH =
CC
= Min. IOH =
CC
Typ
Min
Max
2.4 2.4 2.4 2.4 V
0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 V
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Input HIGH Voltage 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 V
Input LOW Voltage 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 V
Output Leakage Current –10 10 –10 10 –10 10 –10 10 μA
Operating Current
(V
= Max. I
CC
Outputs Disabled
Standby Current (Both
Ports TTL Level)
≥ VIH, f = f
& CE
R
Standby Current (One
Port TTL Level)
≥ VIH, f = f
CE
R
OUT
= 0 mA)
[12]
MAX
[12]
CEL |
MAX
Standby Current (Both
Ports CMOS Level)
CEL & CER ≥ VCC – 0.2V,
Commercial. 175 320 155 275 135 225 115 205 mA
Industrial
[11]
275 390 185 295 mA
Commercial. 25 95 25 85 20 65 20 50 mA
CEL
Industrial
[11]
85 120 35 75 mA
Commercial. 115 175 105 165 95 150 85 140 mA
Industrial
Commercial. 10 250 10 250 10 250 10 250 μA
[12]
Industrial
[11]
[11]
165 210 105 160 mA
10 250 10 250 μA
f = 0
Standby Current (One
Port CMOS Level)
[12]
CEL | CER ≥ VIH, f = f
Commercial 105 135 95 125 85 115 75 100 mA
MAX
Industrial
[11]
125 170 95 125 mA
Unit
Capacitance
Parameter Description Test Conditions Max Unit
C
IN
C
OUT
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 5 of 21
Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
V
= 3.3V
Output Capacitance 10 pF
CC
10 pF
[+] Feedback
Page 6
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
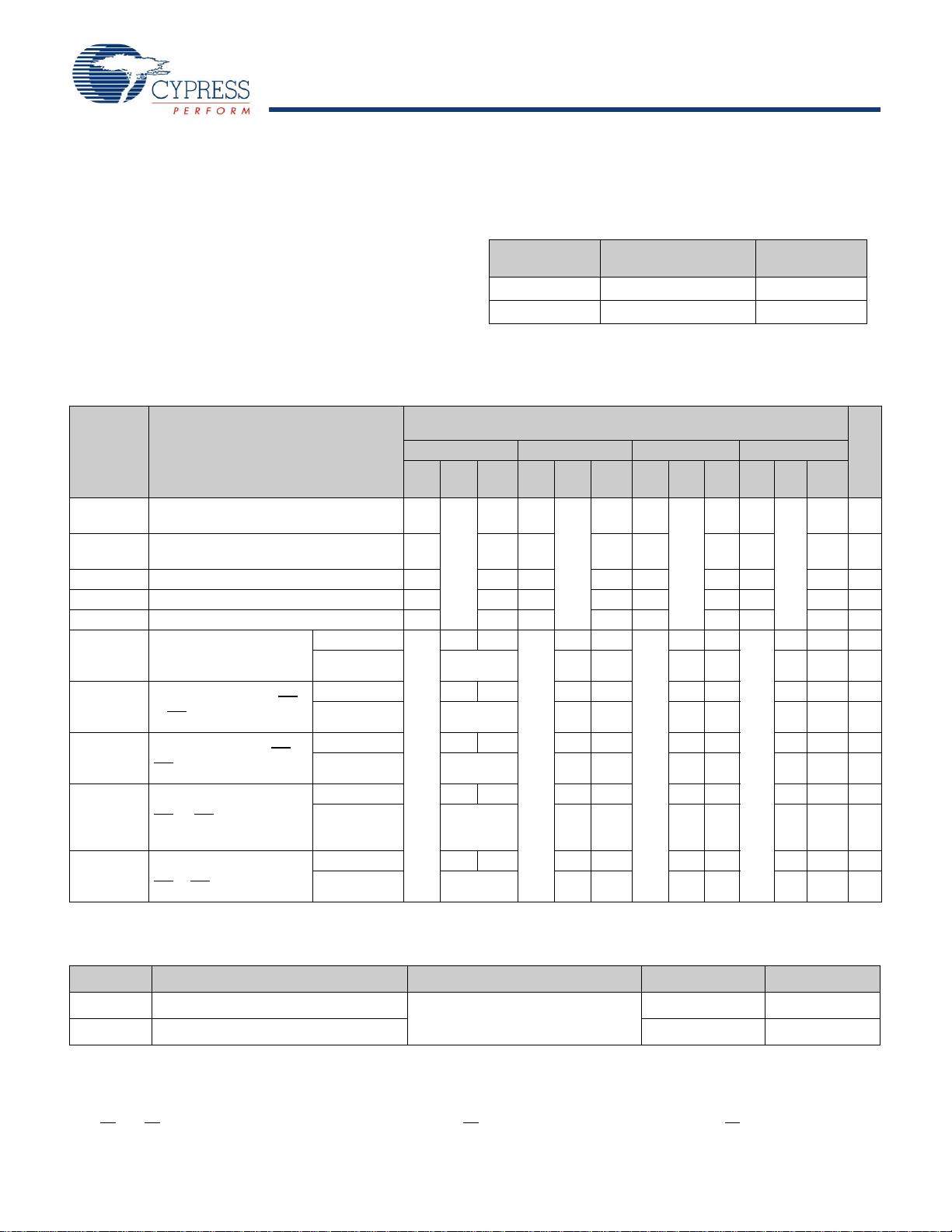
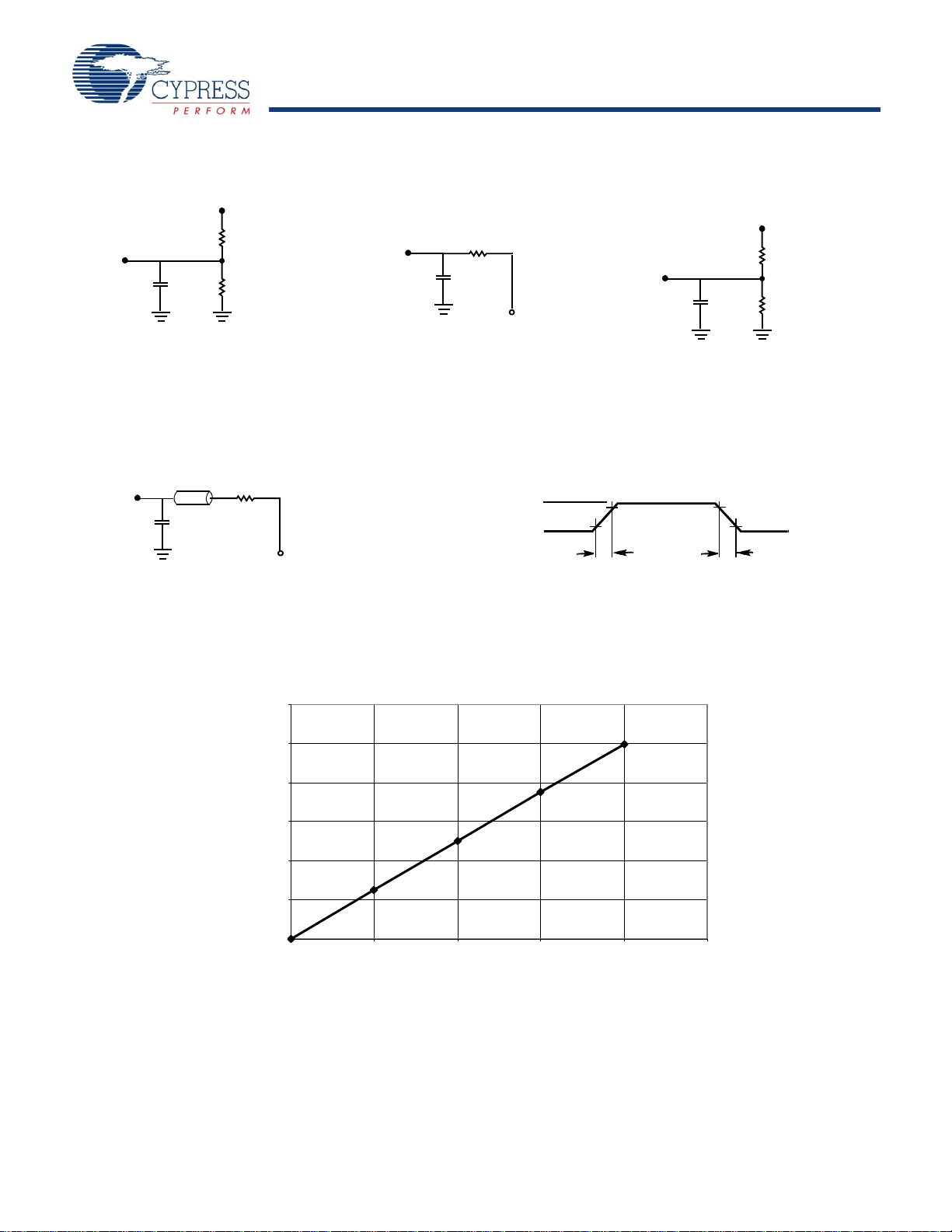
Figure 3. AC Test Loads
(a) Normal Load (Load 1)
R1 = 590Ω
3.3V
OUTPUT
R2 = 435Ω
C= 30
pF
V
TH
=1.4V
OUTPUT
C= 30 pF
(b) Thévenin Equivalent (Load 1)
(c) Three-State Delay(Load 2)
R1 = 590Ω
R2 = 435Ω
3.3V
OUTPUT
C= 5pF
R
TH
= 250Ω
(Used for t
CKLZ
, t
OLZ
, & t
OHZ
including scope and jig)
VTH=1.4V
OUTPUT
C
(a) Load 1 (-6 and -7 only)
R = 50
Ω
Z0 = 50
Ω
3.0V
GND
90%
90%
10%
3ns
3
ns
10%
ALL INPUTPULSES
≤
≤
0.00
0.1 0
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
1 0 15 20 25 30 35
Capacitance (pF)
Δ
(ns) for all -7 access times
Note
13. Test Conditions: C = 10 pF.
Figure 4. AC Test Loads (Applicable to -6 and -7 only)
Figure 5. Load Derating Curve
[13]
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 6 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 7
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
f
MAX1
f
MAX2
t
CYC1
t
CYC2
t
CH1
t
CL1
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
R
t
F
t
SA
t
HA
t
SC
t
HC
t
SW
t
HW
t
SD
t
HD
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
t
SRST
t
HRST
t
OE
[14, 15]
t
OLZ
[14, 15]
t
OHZ
t
CD1
t
CD2
t
DC
[14, 15]
t
CKHZ
[14, 15]
t
CKLZ
Port to Port Delays
t
CWDD
t
CCS
Notes
14. Test conditions used are Load 2.
15. This parameter is guaranteed by design, but it is not production tested.
f
Flow-Through 53 45 40 33 MHz
Max
f
Pipelined 100 83 67 50 MHz
Max
Clock Cycle Time - Flow-Through 19 22 25 30 ns
Clock Cycle Time - Pipelined 10 12 15 20 ns
Clock HIGH Time - Flow-Through 6.5 7.5 12 12 ns
Clock LOW Time - Flow-Through 6.5 7.5 12 12 ns
Clock HIGH Time - Pipelined 4 5 6 8 ns
Clock LOW Time - Pipelined 4 5 6 8 ns
Clock Rise Time 3 3 3 3 ns
Clock Fall Time 3 3 3 3 ns
Address Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
Address Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
Chip Enable Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
Chip Enable Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
R/W Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
R/W Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
Input Data Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
Input Data Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
ADS Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
ADS Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
CNTEN Set-Up Time 3.5 4.5 5 5 ns
CNTEN Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
CNTRST Set-Up Time 3.5 4 4 4 ns
CNTRST Hold Time 0 0 1 1 ns
Output Enable to Data Valid 8 9 10 12 ns
OE to Low Z 2 2 2 2 ns
OE to High Z 1 7 1 7 1 7 1 7 ns
Clock to Data Valid - Flow-Through 15 18 20 25 ns
Clock to Data Valid - Pipelined 6.5 7.5 9 12 ns
Data Output Hold After Clock HIGH 2 2 2 2 ns
Clock HIGH to Output High Z 2 9 2 9 2 9 2 9 ns
Clock HIGH to Output Low Z 2 2 2 2 ns
Write Port Clock HIGH to Read Data Delay 30 35 40 40 ns
Clock to Clock Set-Up Time 9 10 15 15 ns
-6
CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
[1]
-7
[1]
-9 -12
Unit
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 7 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 8

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
Notes
16. OE
is asynchronously controlled; all other inputs are synchronous to the rising clock edge.
17. ADS
= VIL, CNTEN and CNTRST = VIH.
18. The output is disabled (high-impedance state) by CE
0=VIH
or CE1 = VIL following the next rising edge of the clock.
19. Addresses do not have to be accessed sequentially since ADS
= VIL constantly loads the address on the rising edge of the CLK. Numbers are for reference
only.
t
CH1
t
CL1
t
CYC1
t
SC
t
HC
t
DC
t
OHZ
t
OE
t
SC
t
HC
t
SW
t
HW
t
SA
t
HA
t
CD1
t
CKHZ
t
DC
t
OLZ
t
CKLZ
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+3
Q
n
Q
n+1
Q
n+2
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
R/W
ADDRESS
DATA
OUT
OE
Figure 6. Read Cycle for Flow-Through Output (FT
/PIPE = VIL)
[16, 17, 18, 19]
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 8 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 9

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
CYC2
t
SC
t
HC
t
SW
t
HW
t
SA
t
HA
A
n
A
n+1
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
R/W
ADDRESS
DATA
OUT
OE
A
n+2
A
n+3
t
SC
t
HC
t
OHZ
t
OE
t
OLZ
t
DC
t
CD2
t
CKLZ
Q
n
Q
n+1
Q
n+2
1 Latency
D
3
D
1
D
0
D
2
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
A
5
D
4
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
A
5
t
SA
t
HA
t
SC
t
HC
t
SA
t
HA
t
SC
t
HC
t
SC
t
HC
t
SC
t
HC
t
CKHZ
t
DC
t
DC
t
CD2
t
CKLZ
t
CD2
t
CD2
t
CKHZ
t
CKLZ
t
CD2
t
CKHZ
t
CKLZ
t
CD2
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
CYC2
CLK
L
ADDRESS
(B1)
CE
0(B1)
DATA
OUT(B2)
DATA
OUT(B1)
ADDRESS
(B2)
CE
0(B2)
Figure 7. Read Cycle for Pipelined Operation (FT
/PIPE = VIH)
[16, 17, 18, 19]
-
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 9 of 21
Figure 8. Bank Select Pipelined Read
[20, 21]
[+] Feedback
Page 10

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
t
SA
t
HA
t
SW
t
HW
t
SD
t
HD
MATCH
VALID
t
CCS
t
SWtHW
t
DC
t
CWDD
t
CD1
MATCH
t
SAtHA
MATCH
NO
MATCH
NO
VALID VALID
t
DC
t
CD1
CLK
L
R/W
L
ADDRESS
L
DATA
INL
ADDRESS
R
DATA
OUTR
CLK
R
R/W
R
Switching Waveforms (continued)
Figure 9. Left Port Write to Flow-Through Right Port Read
[22, 23, 24, 25]
Notes
20. In this depth expansion example, B1 represents Bank #1 and B2 is Bank #2; Each Bank consists of one Cypress dual-port device from this datasheet. ADDRESS
= ADDRESS
and ADS = VIL; CE
21. OE
22. The same waveforms apply for a right port write to flow-through left port read.
and ADS = VIL; CE1, CNTEN, and CNTRST = VIH.
23. CE
0
= VIL for the right port, which is being read from. OE = VIH for the left port, which is being written to.
24. OE
25. It t
≤ maximum specified, then data from right port READ is not valid until the maximum specified for t
CCS
until t
CCS
+ t
(B2)
CD1
.
. t
, CE
1(B1)
1(B2)
does not apply in this case.
CWDD
, R/W, CNTEN, and CNTRST = VIH.
CWDD
. If t
>maximum specified, then data is not valid
CCS
(B1)
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 10 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 11

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
CYC2
t
CL2
t
CH2
t
HC
t
SC
t
HW
t
SW
t
HA
t
SA
t
HW
t
SW
t
CD2
t
CKHZ
tSDt
HD
t
CKLZ
t
CD2
NO OPERATION WRITEREAD READ
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
R/W
ADDRESS
DATA
IN
DATA
OUT
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+2
D
n+2
A
n+3
A
n+4
Q
n
Q
n+3
Figure 10. Pipelined Read-to-Write-to-Read (OE
= VIL)
[19, 26, 27, 28]
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 11 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 12

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
CYC2
t
CL2
t
CH2
t
HC
t
SC
t
HW
t
SW
t
HA
t
SA
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+3
A
n+4
A
n+5
t
HW
t
SW
tSDt
HD
D
n+2
t
CD2
t
OHZ
READ READWRITE
D
n+3
t
CKLZ
t
CD2
Q
n
Q
n+4
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
R/W
ADDRESS
DATA
IN
DATA
OUT
OE
Figure 11. Pipelined Read-to-Write-to-Read (OE
Controlled)
[19, 26, 27, 28]
Notes
26. Output state (HIGH, LOW, or high-impedance) is determined by the previous cycle control signals.
27. CE
and ADS = VIL; CE1, CNTEN, and CNTRST = VIH.
0
28. During “No Operation”, data in memory at the selected address may be corrupted and should be re-written to ensure data integrity.
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 12 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 13

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
CH1
t
CL1
t
CYC1
t
SC
t
HC
t
SW
t
HW
t
SA
t
HA
t
SW
t
HW
t
SD
t
HD
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+2
A
n+3
A
n+4
D
n+2
Q
n
Q
n+1
Q
n+3
t
CD1
t
CD1
t
DC
t
CKHZ
t
CD1
t
CD1
t
CKLZ
t
DC
READ
NO
OPERATION
WRITE READ
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
ADDRESS
R/W
DATA
IN
DATA
OUT
Q
n
t
CH1
t
CL1
t
CYC1
t
SC
t
HC
t
SW
t
HW
t
SA
t
HA
t
CD1
t
DC
t
OHZ
READ
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+3
A
n+4
A
n+5
D
n+2
D
n+3
t
SW
t
HW
t
SD
t
HD
t
CD1
t
CD1
t
CKLZ
t
DC
Q
n+4
t
OE
WRITE READ
CLK
CE
0
CE
1
ADDRESS
R/W
DATA
IN
DATA
OUT
OE
Figure 12. Flow-Through Read-to-Write-to-Read (OE
[17, 19, 26, 27, 28]
= VIL)
Figure 13. Flow-Through Read-to-Write-to-Read (OE Controlled)
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 13 of 21
[17, 20, 26, 27, 28]
[+] Feedback
Page 14

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
COUNTER HOLD
READ WITH COUNTER
t
SA
t
HA
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
CYC2
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
Q
x-1
Q
x
Q
n
Q
n+1
Q
n+2
Q
n+3
t
DC
t
CD2
READ WITH COUNTER
READ
EXTERNAL
ADDRESS
CLK
ADDRESS
ADS
DATA
OUT
CNTEN
A
n
t
CH1
t
CL1
t
CYC1
t
SA
t
HA
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
A
n
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
CLK
ADDRESS
ADS
CNTEN
Q
x
Q
n
Q
n+1
t
DC
COUNTER HOLD
READ WITH COUNTER
READ
EXTERNAL
ADDRESS
READ
WITH
COUNTER
Q
n+3
Q
n+2
DATA
OUT
t
CD1
Figure 14. Pipelined Read with Address Counter Advance
[29]
and OE = VIL; CE1, R/W and CNTRST = VIH.
0
Note
29. CE
Figure 15. Flow-Through Read with Address Counter Advance
[29]
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 14 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 15

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
CYC2
A
n
A
n+1
A
n+2
A
n+3
A
n+4
D
n+1
D
n+1
D
n+2
D
n+3
D
n+4
A
n
D
n
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
t
SD
t
HD
WRITE EXTERNAL
WRITE WITH COUNTER
ADDRESS
WRITE WITH
COUNTER
WRITE COUNTER
HOLD
CLK
ADDRESS
INTERNAL
CNTEN
ADS
DATA
IN
ADDRESS
t
SA
t
HA
Switching Waveforms (continued)
Figure 16. Write with Address Counter Advance (Flow-Through or Pipelined Outputs)
[30, 31]
Notes
and R/W = VIL; CE1 and CNTRST = VIH.
30. CE
0
31. The “Internal Address” is equal to the “External Address” when ADS
= VIL and equals the counter output when ADS = VIH.
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 15 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
CH2
t
CL2
t
CYC2
CLK
ADDRESS
INTERNAL
CNTEN
ADS
DATA
IN
ADDRESS
CNTRST
R/W
DATA
OUT
Q
0
Q
1
Q
n
D
0
A
X
01A
n
A
n+1
t
SAD
t
HAD
t
SCN
t
HCN
t
SRST
t
HRST
tSDt
HD
t
SWtHW
A
n
A
n+1
t
SAtHA
COUNTER
RESET
WRITE
ADDRESS 0
READ
ADDRESS 0
READ
ADDRESS 1
READ
ADDRESS n
Figure 17. Counter Reset (Pipelined Outputs)
[19, 26, 32, 33]
Notes
32. CE
= VIL; CE1 = VIH.
0
33. No dead cycle exists during counter reset. A READ or WRITE cycle may be coincidental with the counter reset.
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 16 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 17

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Table 1. Read/Write and Enable Operation
Notes
34. “X” = “Don’t Care”, “H” = V
IH
, “L” = VIL.
35. ADS
, CNTEN, CNTRST = “Don’t Care.”
36. OE
is an asynchronous input signal.
37. When CE
changes state in the pipelined mode, deselection and read happen in the following clock cycle.
38. CE
0
and OE = VIL; CE1 and R/W = VIH.
39. Data shown for flow-through mode; pipelined mode output will be delayed by one cycle.
40. Counter operation is independent of CE
0
and CE1.
[34, 35, 36]
Inputs Outputs
OE CLK CE
0
CE
1
R/W I/O0–I/O
9
X H X X High-Z Deselected
Operation
[37]
X X L X High-Z Deselected
X L H L D
L L H H D
IN
OUT
Write
Read
H X L H X High-Z Outputs Disabled
Table 2. Address Counter Control Operation
Address
Previous
Address
CLK ADS CNTEN CNTRST I/O Mode Operation
X X X X L D
A
n
X A
X A
X L X H D
n
n
H H H D
H L H D
[34, 38, 39, 40]
out(0)
out(n)
out(n)
out(n+1)
Reset Counter Reset to Address 0
Load Address Load into Counter
Hold External Address Blocked—Counter
Disabled
Increment Counter Enabled—Internal Address
Generation
[37]
[37]
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 17 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 18

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Ordering Information
32K x8 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
[1]
6.5
7.5
9 CY7C09079V-9AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09079V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
64K x8 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
6.5
7.5
9 CY7C09089V-9AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09089V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
128K x8 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
[1]
6.5
[1]
7.5
9 CY7C09099V-9AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09099V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09079V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[1]
CY7C09079V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09079V-7AI A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
[1]
CY7C09089V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09089V-6AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[1]
CY7C09089V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09089V-12AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09089V-12AXI A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09099V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09099V-6AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09099V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09099V-7AI A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09099V-7AXI A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09099V-9AI A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09099V-12AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
32K x9 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
[1]
6.5
7.5
9 CY7C09179V-9C A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09179V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 18 of 21
CY7C09179V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09179V-6AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[1]
CY7C09179V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09179V-12AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[+] Feedback
Page 19

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
64K x9 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
[1]
6.5
7.5
9 CY7C09189V-9AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09189V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09189V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09189V-6AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[1]
CY7C09189V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09189V-12AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
128K x9 3.3V Synchronous Dual-Port SRAM
Speed (ns) Ordering Code Package Name Package Type Operating Range
[1]
6.5
7.5
9 CY7C09199V-9AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
12 CY7C09199V-12AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09199V-6AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09199V-6AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
[1]
CY7C09199V-7AC A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09199V-7AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09199V-9AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
CY7C09199V-9AI A100 100-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09199V-9AXI A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Industrial
CY7C09199V-12AXC A100 100-Pin Pb-Free Thin Quad Flat Pack Commercial
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 19 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 20

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Package Diagram
51-85048-*B
Figure 18. 100-Pin Thin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) A100 (51-85048)
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Page 20 of 21
[+] Feedback
Page 21

CY7C09079V/89V/99V
CY7C09179V/89V/99V
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C09079V/89V/99V, CY7C09179V/89V/99V 3.3V 32K/64K/128K x 8/9Synchronous Dual Port Static
RAM
Document Number: 38-06043
Rev. ECN No.
Orig. of
Change
Orig. of
Change
Description of Change
** 110191 SZV 09/29/01 Change from Spec number: 38-00667 to 38-06043
*A 122293 RBI 12/27/02 Power up requirements added to Operating Conditions Information
*B 365034 PCN See ECN Added Pb-Free Logo
Added Pb-Free Part Ordering Information:
CY7C09089V-6AXC, CY7C09089V-12AXC, CY7C09099V-6AXC,
CY7C09099V-7AI, CY7C09099V-7AXI, CY7C09099V-12AXC,
CY7C09179V-6AXC, CY7C09179V-12AXC, CY7C09189V-6AXC,
CY7C09189V-12AXC, CY7C09199V-6AXC, CY7C09199V-7AXC,
CY7C09199V-9AXC, CY7C09199V-9AXI, CY7C09199V-12AXC
*C 2623658 VKN/PYRS 12/17/08 Added CY7C09089V-12AXI part in the Ordering information table
Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information
Worldwide Sales and Design Support
Cypress maintains a worldwide network of offices, solution centers, manufacturer’s representatives, and distributors. To find the office
closest to you, visit us at cypress.com/sales.
Products
PSoC psoc.cypress.com
Clocks & Buffers clocks.cypress.com
Wireless wireless.cypress.com
Memories memory.cypress.com
Image Sensors image.cypress.com
PSoC Solutions
General psoc.cypress.com/solutions
Low Power/Low Voltage psoc.cypress.com/low-power
Precision Analog psoc.cypress.com/precision-analog
LCD Drive psoc.cypress.com/lcd-drive
CAN 2.0b psoc.cypress.com/can
USB psoc.cypress.com/usb
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2005-2008. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of
any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used for
medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with Cypress. Furthermore, Cypress does not authorize its products for use as
critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress products in life-support systems
application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign),
United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Cypress hereby grants to licensee a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to copy, use, modify, create derivative works of,
and compile the Cypress Sou rce Code and derivative works for the sole purpose of cr eating custom software and or firmware in support of licensee product to be used only in conjunction with a Cypress
integrated circuit as specified in the applicable agreement. Any reproduction, modification, translation, compilation, or representation of this Source Code except as specified above is prohibited without
the express written permission of Cypress.
Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to make changes without further notice to the materials described herein. Cypress does not
assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described herein. Cypress does not authorize its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where
a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress’ product in a life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer
assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement.
Document #: 38-06043 Rev. *C Revised December 10, 2008 Page 21 of 21
All products and company names mentioned in this document may be the trademarks of their respective holders.
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...