Page 1
CK-SSC Spread Spectrum Clock Generato
r
2
Features
• 3.3V operation
• 48- and 66-MHz frequency support
• Selectable slew rate control
• 350-pS jitter
2
•I
C programmability
• 500-µA power-down current
• Spread Spectrum for best electro magnetic interference
(EMI) reduction
• 8-pin SOIC package
CY25822-
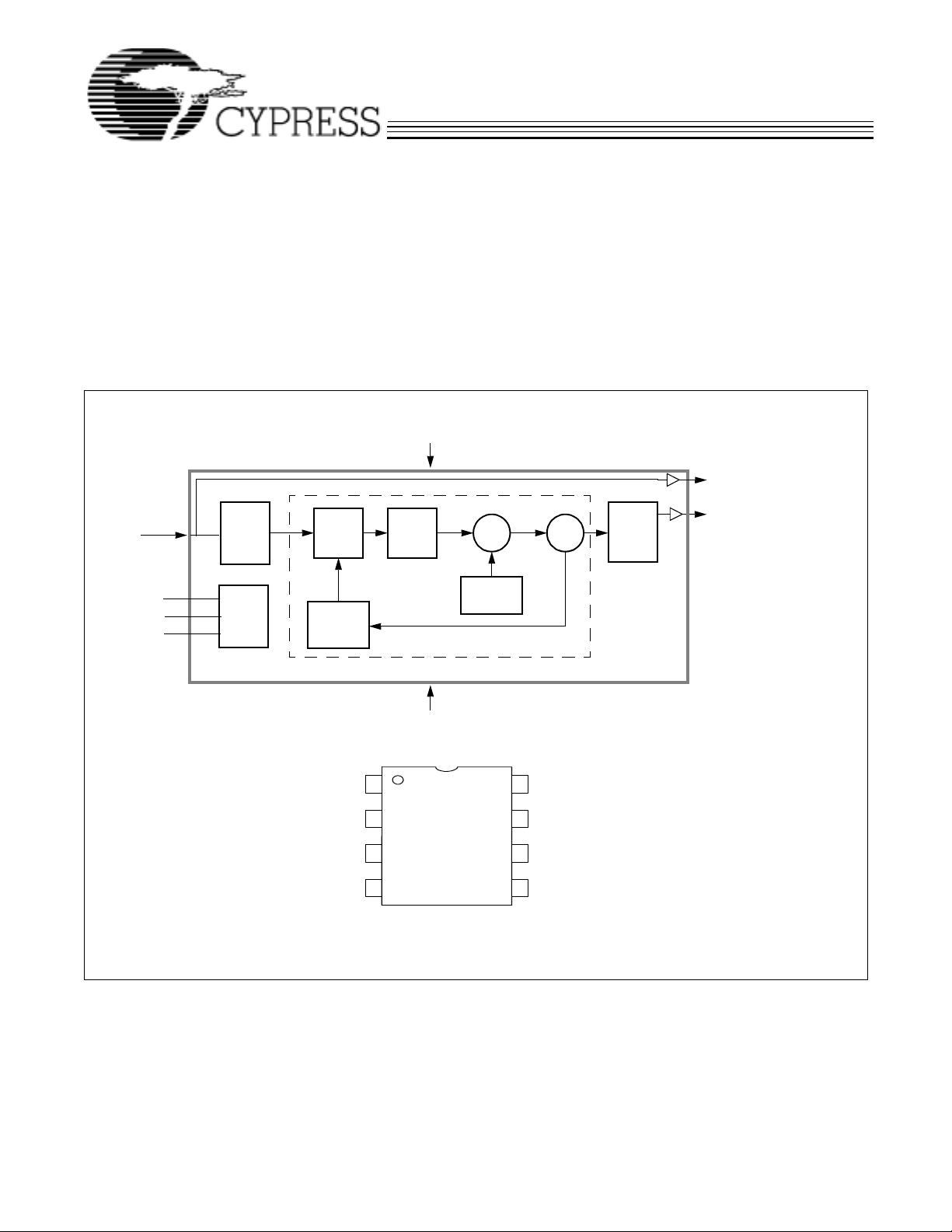
Block Diagram
Clock Input
SDATA
SCLOCK
PWRDWN#
Pin Configuration
Freq. Phase
M
Logic
Control
Detector
Feedback
Divider
CLKIN
N
VDD
GND
Charge
Pump
1
2
CY 25822-2
3
VDD
GND
Σ
Modulating
Waveform
PLL
8
*PW RD WN#
7
SCLOCK
SDATA
6
VCO
DividersDivider
Post
REFOUT
CLKOUT
(SSCG Output)
CLKOUT
4
* 150KΩ P ull-up
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose, CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
5
REFOUT
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Revised March 18, 2003
[+] Feedback
Page 2
-2
Pin Description
Pin No. Pin Name Pin Type Pin Description
1 CLKIN Input 48-MHz or 66-MHz Clock Input.
2 VDD Power Power Supply for PLL and Outputs.
3 GND Ground Ground for Outputs.
4 CLKOUT Output 48-MHz or 66-MHz Spread Spectrum Clock Output.
5REFOUTOutput Non-spread Spectrum Reference Clock Output.
2
6 SDATA I/O I
7 SCLOCK Input I
8 PWRDWN# Output LVTTL Input for PowerDown# Active Low.
C-compatible SDATA.
2
C-compatible SCLOCK.
CY25822
Serial Data Interface
T o enha nce the flexibi lity and functi on of the clock sy nthesizer ,
a two-signal serial interface is provided. Through the Serial
Data Interface, various device functions such as individual
clock output buffers, etc., can be individually enabled or
disabled.
The registers associated with the Serial Data Interface
initializes to thei r defa ult s etting upon pow er-up, a nd th erefore
use of this interfac e is option al. Clo ck de vice regis ter cha nges
are normally made upon system initialization, if any are
required. The interface can also be used during system
operation for power management functions.
Ta ble 1. Command Code Definition
Bit Description
7 0 = Block read or block write operation
1 = Byte read or byte write operation
(6:0) Byte offset for byte read or byte write operation. For block read or block write operations, these bits should be ’0000000’
Table 2. Block Read and Block Write Protocol
Block Write Protocol Block Read Protocol
Bit Description Bit Description
1Start 1Start
2:8 Slave address – 7 bits 2:8 Slave address – 7 bits
9 Write = 0 9 Write = 0
10 Acknowledge from slave 10 Acknowledge from slave
11:18 Command Code – 8 bits
'00000000' stands for block operation
19 Acknowledge from slave 19 Acknowledge from slave
20:27 Byte Count – 8 bits 20 Repeat start
28 Acknowledge from slave 21:27 Slave address – 7 bits
29:36 Data byte 1 – 8 bits 28 Read = 1
37 Acknowledge from slave 29 Acknowledge from slave
38:45 Data byte 2 – 8 bits 30:37 Byte count from slave – 8 bits
46 Acknowledge from slave 38 Acknowledg e
.... ...................... 39:46 Data byte from slave – 8 bits
.... Data Byte (N–1) –8 bits 47 Acknowledge
.... Acknowledge from slave 48:55 Data byte from slave – 8 bits
Data Protocol
The clock driver serial protocol accepts byte write, byte read,
block write, and blo ck read op eration from the c ontrol ler. For
block write/read operation, the bytes must be accessed in
sequential order from lowest to highest byte (most significant
bit first) with the ability to stop after any complete byte has
been transferred. For byte write and byte rea d o pera tio ns , th e
system controller can access individual indexed bytes. The
offset of the indexe d byte is encoded in the command co de, as
described in Table 1.
The block write and block read protocol is outlined in Table 2
while Table 3 outlines the corresponding byte write and byte
read protocol.The s lave receive r addre ss i s 110101 00 (D 4h).
11:18 Command Code – 8 bits
'00000000' stands for block operation
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 2 of 9
[+] Feedback
Page 3
-2
Table 2. Block Read and Block Write Protocol (continued)
.... Data Byte N –8 bits 56 Acknowledge
.... Acknowledge from slave .... Data bytes from slave/Acknowledge
.... Stop .... Data byte N from slave – 8 bits
.... Not Acknowledge
.... Stop
Table 3. Byte Read and Byte Write Protocol
Byte Write Protocol Byte Read Protocol
Bit Description Bit Description
1Start 1Start
2:8 Slave address – 7 bits 2:8 Slave address – 7 bits
9 Write = 0 9 Write = 0
10 Acknowledge from slave 10 Acknowledge from slave
11:18 Command Code – 8 bits
'1xxxxxxx' stands for byte operation, bits[6:0] of
the command code represents the offset of the
byte to be accessed
19 Acknowledge from slave 19 Acknowledge from slave
20:27 Data byte from master – 8 bits 20 Repeat start
28 Acknowledge from slave 21:27 Slave address – 7 bits
29 Stop 28 Read = 1
11:18 Command Code – 8 bits
'1xxxxxxx' st ands fo r byte op eration, bits [6:0]
of the command code represents the offset of
the byte to be accessed
29 Acknowledge from slave
30:37 Data byte from slave – 8 bits
38 Not Acknowledge
39 S top
CY25822
Byte 0: Control Register
Bit @Pup Pin# Name Pin Description
714SS0 –
604SS1 –
504SS2 –
404SS3 –
3 1 Not Applicable Reserved, must be written as 1
214, 5CLKOUT,
REFOUT
1 1 4 CLKOUT Spread Spectrum enable
0 0 Not Applicable No Pins
Ta ble 4. Spread Spectrum Select
SS3 SS2 SS1 SS0 Spread Mode Spread Amount%
0 0 0 0 Down 0.8
0 0 0 1 Down 1.0
0 0 1 0 Down 1.25
0 0 1 1 Down 1.5
0 1 0 0 Down 1.75
Power-down three-state enable
0 = three-state outputs, 1 = drive outputs low
(Applies only in Power Down State)
0 = spread off, 1 = spread on
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 3 of 9
[+] Feedback
Page 4

-2
Ta ble 4. Spread Spectrum Select (continued)
SS3 SS2 SS1 SS0 Spread Mode Spread Amount%
0 1 0 1 Down 2.0
0 1 1 0 Down 2.5
0 1 1 1 Down 3.0
1000 Center ±0.3
1001 Center ±0.4
1010 Center ±0.5
1011 Center ±0.6
1100 Center ±0.8
1101 Center ±1.0
1110 Center ±1.25
1111 Center ±1.5
Byte 1: Control Register
Bit @Pup Pin# Name Pin Description
7 1 5 REFEN REFOUT enable
0 = disabled, 1 = enabled
6 1 5 REFSLEW REFOUT edge rate control
0 = slow, 1 = nominal
5 0 Not Applicable Reserved.
4 0 Not Applicable Reserved
3 1 4 CLKSLEW CLKOUT edge rate control
0 = slow, 1 = nominal
2 1 4 CLKEN CLKOUT enable
0 =disabled, 1 = enabled
1 0 Not Applicable Reserved
0 0 Not Applicable Reserved
CY25822
Bytes 2 through 5: Reserved Registers PWRDWN# (Power-down) Clarification
Byte 6: Vendor/Revision ID Register
Bit @Pup Pin# Name Pin Descr iption
7 0 – – Revision ID Bit 3
6 0 – – Revision ID Bit 2
5 0 – – Revision ID Bit 1
4 0 – – Revision ID Bit 0
3 1 – – Vendor ID Bit 3
2 0 – – Vendor ID Bit 2
1 0 – – Vendor ID Bit 1
0 0 – – Vendor ID Bit 0
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 4 of 9
The PWRDWN# (Power-down) pin is used to shut off ALL
clocks prior to shutting off power to the device. PWRDWN# is
an asynchronous active LOW input. This signal is synchronized internally to t he device powering dow n the clock sy nthesizer . PWRDWN# is an asynchronous function for powerin g up
the system. When PWRDWN# is low, all clocks are driven to
a LOW value and held there and the VCO and PLLs are also
powered down. All clocks are shut down in a synchronous
manner so has not to cause glitches while transitioning to the
low ‘stopped’ state. When PWRDWN# is deasserted the
clocks should remain stopped until the VCO is stable and
within specification (t
tri-stated or driven low depending on the state of the tri-state
enable I
driven state are driven low.
The CLKIN input must be on and within specified operating
parameters before PWRDWN# is a sserted and it must rem ain
in this state while PWRDWN# is asserted.
2
C register bit. C Y25822 clo cks that ar e stopped in the
). A stopped clock is either
STABLE
[+] Feedback
Page 5

-2
PWRDWN#
CLKOUT
REFOUT
CY25822
Figure 1. Power-down Assertion
PD#
CLKOUT
REFOUT
<3.0ms
Figure 2. Power-down Deassertion
CLKOUT and REFOUT Enable Clarification
The CLKOUT enable an d REFOUT enable I2C register bits are
used to shot-of f the CLKOUT and REFOUT cl ocks individual ly .
The VCO and crys tal oscillator must remain on. A shu tdown
clock is driven low. ALL clocks need to be stopped in a
predictable manner. All clocks need to be shutdown without
any glitches or other abnormal behavior while transitioning to
a stopped state. Similarly when CLKOUT or REFOUT is
enabled the clock must start in a predictable manner without
any glitches or abnormal behavior.
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 5 of 9
[+] Feedback
Page 6

CY25822
-2
Table 5. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Description Condition Min. Max. Unit
V
DD
V
DD_A
V
IN
T
S
T
A
T
J
ESD
HBM
UL–94 Flammability Rating @1/8 in. V–0
MSL Moisture Sensitivity Level 1
Core Supply Voltage –0.5 4.6 V
Analog Supply Voltage –0.5 4.6 V
Input Voltage Relative to V
SS
–0.5 V
+ 0.5 VDC
DD
Temperature, Storage Non Functional –65 +150 °C
Temperature, Operating Ambient Functional 0 70 °C
Temperature, Junction Functional – 150 °C
ESD Protection (Human Body Model) MIL-STD-883, Method 3015 2000 – Volts
Ta ble 6. DC Parameters (T
= 0°C to +70°C, VDD = 3.3V ± 5%)
A
Parameter Description Condition Min. Max Unit Notes
V
V
V
I
I
V
IL1
IL2
DD
IH
IL
OH
Supply Voltage – 3.135 3.465 V V
Input High Voltage – 2.0 V
Input Low Voltage – V
Input Leakage Current SCLOCK
– 0.3 0.8 V
SS
–25 +25 µA
+ 0.3 V
DD
or SDATA
Input Leakage Current PWRDWN# –75 –15 µA
Output Hi gh Voltage I
= –4 mA 2.4 – V Single edge is required to
OH
= 3.3 ± 5%
DD
be monotonic when transitioning through this region .
V
OL
Output Low Voltage I
= 4 mA – 0.4 V Single edge is required to
OL
be monotonic when transitioning through this region .
C
IN
C
OUT
L
IN
T
A
I
DD1
I
DD2
I
PD
Ta ble 7. AC Parameters (T
Input Pin Capacitance – – 5 pF
Output Pin Capacitanc e – – 6 pF
Pin Inductance – – 7 nH
Ambient Temperature – 0 70 °C No air flow
Supply Current @ 66 MHz – 50 mA
Supply Current @ 48 MHz – 40 mA
Power Down Supply Current – – 500 µA
= 0°C to +70°C, VDD = 3.3V ± 5%)
A
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Max. Unit Notes
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
RISEH1
t
FALLH1
t
RISEL1
CLK High Time, 48MHz Measured @2.4V 9.45 10.95 ns Specification applies to
48MHz output mode.
CLK, Low Time, 48MHz Measured @0.4V 8.50 10.10 ns Specification applies to
48MHz output mode.
CLK High Time, 66MHz Measured @2.4V 6.85 7.90 ns Specification applies to
66.7MHz output mode.
CLK Low Time, 66MHz Measured @0.4V 5.95 6.95 ns Specification applies to
66.7MHz output mode.
Rising Edge Rate Measured from 0.4V to 2.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Falling Edge Rate Measured from 2.4V to 0.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Rising Edge Rate Measured from 0.4V to 2.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
2.0 5.0 V/ns High Buffer S t re ngth
Refer to I
2.0 5.0 V/ns High Buffer S t re ngth
Refer to I
1.33 4.0 V/ns Low Buffer Strength
Refer to I
2
2
2
C Control
C Control
C Control
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 6 of 9
[+] Feedback
Page 7

CY25822
-2
Ta ble 7. AC Parameters (TA = 0°C to +70°C, VDD = 3.3V ± 5%) (continued)
Parameter Description Conditions Min. Max. Unit Notes
t
FALLL1
t
RISEH2
t
FALLH2
t
RISEL2
t
FALLL2
T
CYC1
T
CYC2
LTJ 10µS Period Jitter
t
START
Table 8. Signal Loading Table
Clock Name Max Load (pF)
CLKOUT, REFOUT 15
Falling Edge Rate Measured from 2.4V to 0.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Rise Time Measured from 0.4V to 2.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Fall Time Measured from 2.4V to 0.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Rise Time Measured from 0.4V to 2.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
Fall Time Measured from 2.4V to 0.4V
REFOUT and CLOCKOUT
1.33 4.0 V/ns Low Buffer Strength
Refer to I
0.4 1.0 ns High Buffer Strength
Refer to I
0.4 1.0 ns High Buffer Strength
Refer to I
0.5 1.5 ns Lo w Buffer Strength
Refer to I
0.5 1.5 ns Lo w Buffer Strength
Refer to I
Cycle to Cycle Jitter REFOUT – 500 ps SSCG is ON
Cycle to Cycle Jitter CLOCKOUT – 250 ps SSCG is ON
(100KHz, Frequency Modulation Amplitude)
Applies to REFOUT at all
times and CLOCKOU T when
SSCG is Off
–2.0ns –
Start up time From VDD = 2.0 V – 3.0 ms All outputs disabled
2
C Control
2
C Control
2
C Control
2
C Control
2
C Control
Ordering Information
Part Number Package Type Product Flow
CY25822SC–2 8-pin SOIC Commercial, 0°C to 70°C
CY25822SC–2T 8-pin SOIC – Tape and Reel Commercial, 0°C to 70°C
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 7 of 9
[+] Feedback
Page 8

2
Package Diagram
CY25822-
8-lead (150-Mil) SOIC – S8
51-85066-*B
Purchase of I2C components from Cypress, o r one of its s ublicensed Associated Com panies, c onveys a lic ense under the Philips
2
C Patent Rights to u se these component s in an I2C system, provided th at the system con forms to the I2C St andard Specifica tion
I
as defined by Philips.All product and company names mentioned in this document are trademarks of their respective holders.
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 8 of 9
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2003. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use
of any circuitry other than cir cuitry embodi ed in a Cypress S emiconductor product . Nor does it convey or imply any license un der patent or other ri ghts. Cypre ss Semiconductor does not autho rize
its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
Semiconductor products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress Semiconductor against all charges.
[+] Feedback
Page 9

-2
Document History Page
Document Title: CY25822-2 CK-SSC Spread Spectrum Clock Generator
Document Number: 38-07531
REV. ECN NO.
** 124462 03/19/03 RGL New Data Sheet
Issue
Date
Orig. of
Change Description of Change
CY25822
Document #: 38-07531 Rev. ** Page 9 of 9
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...