Page 1
CY14B256K
256 Kbit (32K x 8) nvSRAM with Real Time Clock
Features
STORE/
RECALL
CONTROL
POWER
CONTROL
SOFTWARE
DETECT
STATIC RAM
ARRAY
512 X 512
QuantumTrap
512 X 512
STORE
RECALL
COLUMN IO
COLUMN DEC
ROW DECODER
INPUT BUFFERS
OE
CE
WE
HSB
V
CC
V
CAP
A
13
-
A
0
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
A
10
A
5
A
6
A
7
A
8
A
9
A
12
A
13
A
14
DQ
0
DQ
1
DQ
2
DQ
3
DQ
4
DQ
5
DQ
6
DQ
7
RTC
MUX
A
14
-
A
0
x
1
x
2
INT
V
RTCbat
V
RTCcap
A
11
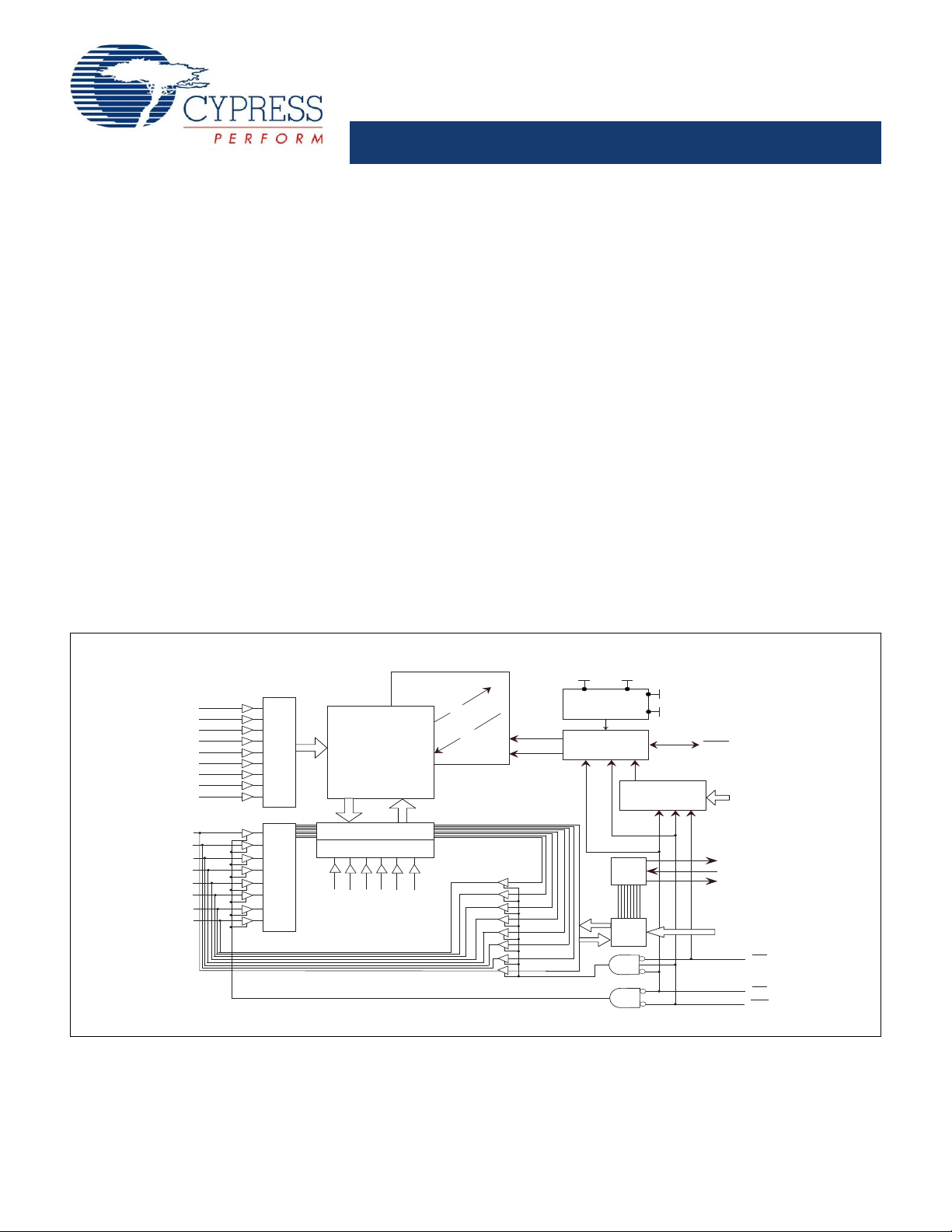
Logic Block Diagram
■ 25 ns, 35 ns, and 45 ns access times
■ Pin compatible with STK17T88
■ Data integrity of Cypress nvSRAM combined with full featured
Real Time Clock
❐ Low power, 350 nA RTC current
❐ Capacitor or battery backup for RTC
■ Watchdog timer
■ Clock alarm with programmable interrupts
■ Hands off automatic STORE on power down with only a small
capacitor
■ STORE to QuantumT rap™ initiated by software, device pin, or
on power down
■ RECALL to SRAM initiated by software or on power up
■ Infinite READ, WRITE, and RECALL cycles
■ High reliability
❐ Endurance to 200K cycles
❐ Data retention: 20 years at 55°C
■ Single 3V operation with tolerance of +20%, -10%
■ Commercial and industrial temperature
■ 48-Pin SSOP (ROHS compliant)
Functional Description
The Cypress CY14B256K combines a 256 Kbit nonvolatile static
RAM with a full-featured real time clock in a monolithic integrated
circuit. The embedded nonvolatile elements incorporate
QuantumTrap technology producing the world’s most reliable
nonvolatile memory. The SRAM is read and written an infinite
number of times, while independent, nonvola tile data resides in
the nonvolatile elements.
The real time clock function provides an accurate clock with leap
year tracking and a programmable high accuracy oscillator. The
alarm function is programmable for one time alarms or periodic
seconds, minutes, hours, or days. There is also a programmable
watchdog timer for process control.
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Revised February 24, 2009
[+] Feedback
Page 2
CY14B256K
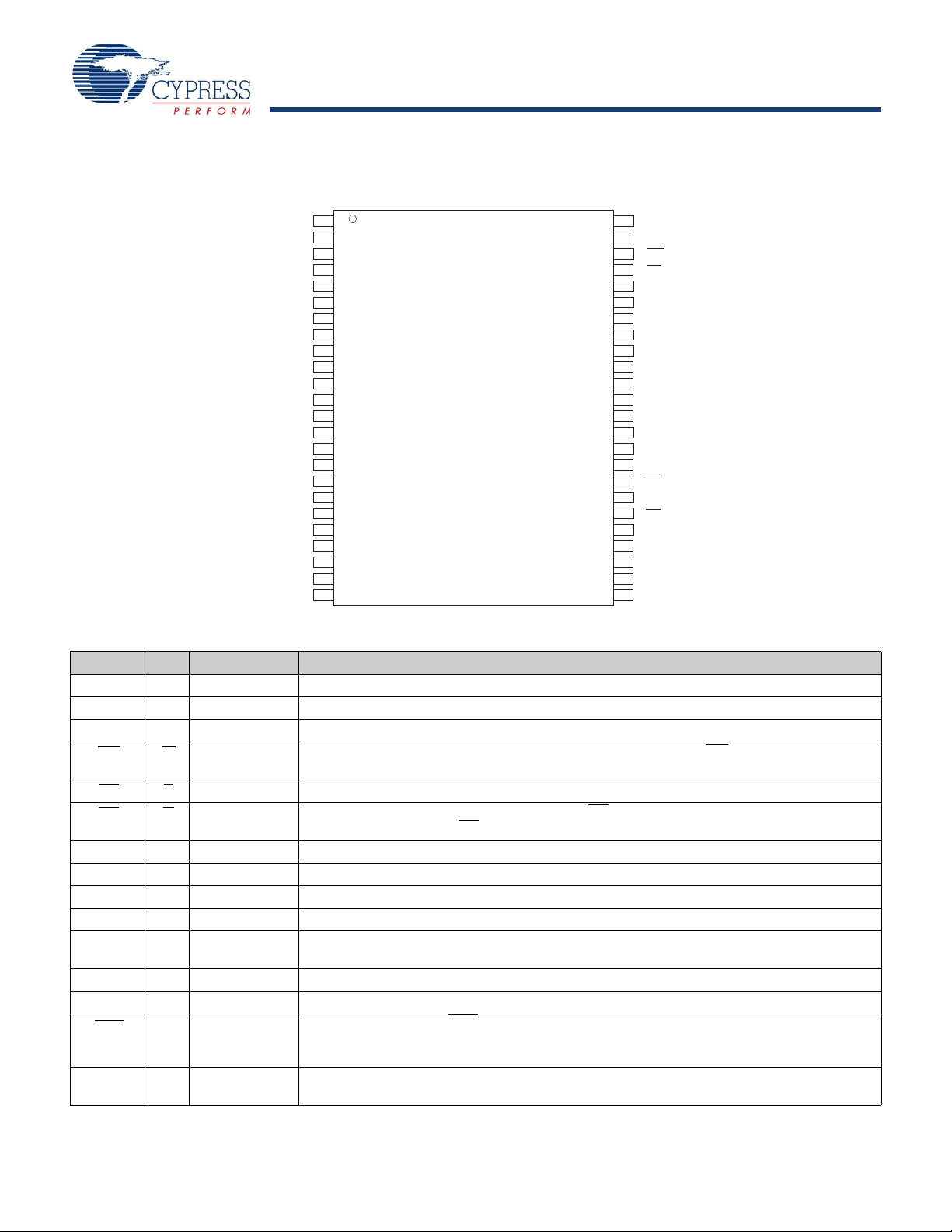
Pin Configurations
V
CAP
A
14
A
12
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
V
CC
HSB
WE
A
13
A
8
A
9
A
11
OE
A
10
DQ
DQ7
6
DQ5
CE
DQ4
DQ3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
INT
NC
NC
NC
V
SS
NC
DQ0
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
DQ1
DQ2
NC
NC
NC
NC
V
SS
NC
V
CC
48-SSOP
Top View
(Not To Scale)
NC
V
RTCbat
X
1
X
2
V
RTCcap
NC
Figure 1. 48-Pin SSOP
Pin Definitions
Pin Name Alt IO Type Description
A
0–A14
DQ0-DQ7 Input or Output Bidirectional Data IO lines. Used as input or output lines depending on operation.
NC No Connect No Connects. This pin is not connected to the die.
WE
CE
OE
X
1
X
2
V
RTCcap
V
RTCbat
INT Output Interrupt Output. It is programmed to respond to the clock alarm, the watchdog timer, and the
V
SS
V
CC
HSB
V
CAP
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 2 of 28
W
E
G
Input Address Inputs. Used to select one of the 32,768 bytes of the nvSRAM.
Input Write Enable Input, Active LOW. When the chip is enabled and WE is LOW, data on the IO
pins is written to the specific address location.
Input Chip Enable Input, Active LOW. When LOW, selects the chip. When HIGH, deselects the chip.
Input Output Enable, Active LOW . The active LOW OE input enables the data output buffers during
read cycles. Deasserting OE
Output Crystal Connection. Drives crystal on start up.
Input Crystal Connection for 32.768 kHz Crystal.
Power Supply Capacitor Supplied Backup RTC Supply Voltage. (Left unconnected if V
Power Supply Battery Supplied Backup RTC Supply Voltage. (Left unconnected if V
power monitor. Programmable to either active HIGH (push or pull) or LOW (open drain).
Ground Ground for the Device. It is connected to ground of the system.
Power Supply Power Supply Inputs to the Device.
Input or Output Hardware Store Busy (HSB). When low, this output indicates a Hardware Store is in progress.
When pulled low external to the chip, it initiates a nonvolatile STORE operation. A weak internal
pull up resistor keeps this pin HIGH if not connected (connection optional).
Power Supply AutoStore Capacitor . Supplies power to nvSRAM during power loss to store data from SRAM
to nonvolatile elements.
high causes the IO pins to tri-state.
RTCbat
is used)
RTCcap
is used)
[+] Feedback
Page 3
CY14B256K
Device Operation
V
CC
V
CC
V
CAP
V
CAP
WE
10k Ohm
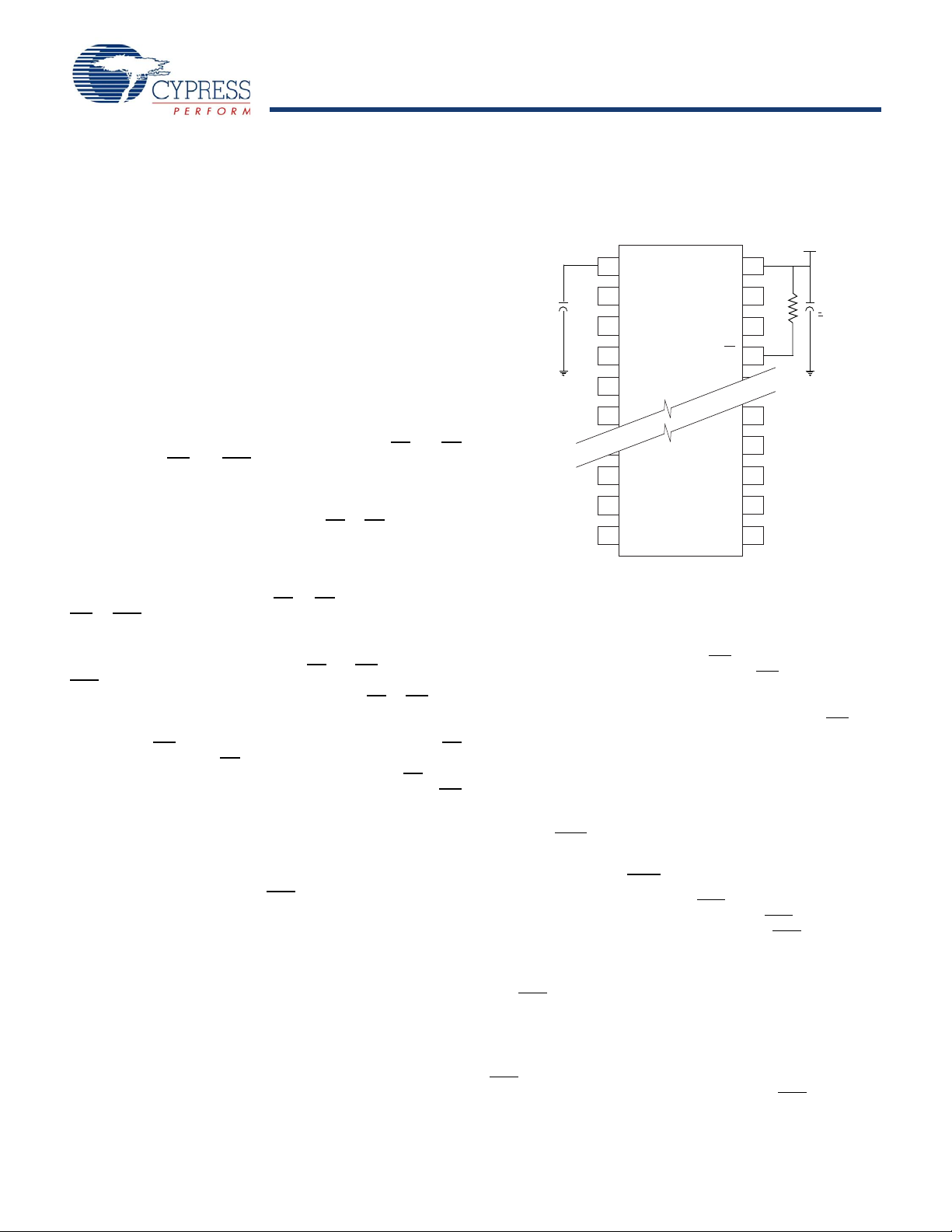
0.1 F
U
The CY14B256K nvSRAM consists of two functional
components paired in the same physical cell. The components
automatically disconnects the V
operation is initiated with power provided by the V
Figure 2. AutoStore Mode
pin from VCC. A STORE
CAP
capacitor.
CAP
are SRAM memory cell and a nonvolatile QuantumTrap cell. The
SRAM memory cell operates as a standard fast static RAM. Data
in the SRAM is transferred to the nonvolatile cell (the STORE
operation), or from the nonvolatile cell to SRAM (the RECALL
operation). Using this unique architecture, all cells are stored and
recalled in parallel. During the STORE and RECALL operations,
SRAM READ and WRITE operations are inhibited. The
CY14B256K supports infinite reads and writes similar to a typical
SRAM. In addition, it provides infinite RECALL operations from
the nonvolatile cells and up to 200K STORE operations.
See the “Truth Table For SRAM Operations” on page22 for a
complete description of read and write modes.
SRAM READ
The CY14B256K performs a READ cycle whenever CE and OE
are LOW while WE and HSB are HIGH. The address specified
on pins A
accessed. When the READ is initiated by an address transition,
the outputs are valid after a delay of t
8 on page 17). If the READ is initiated by CE
are valid at t
Figure 9 on page 17). The data outputs repeatedly respond to
address changes within the t
transitions on any control input pins. This remains valid until
another address change or until CE or OE is brought HIGH, or
WE
or HSB is brought LOW.
SRAM WRITE
A WRITE cycle is performed whenever CE and WE are LOW and
is HIGH. The address inputs are stable before entering the
HSB
WRITE cycle and must remain stable until either CE
HIGH at the end of the cycle. The data on the common IO pins
DQ
0–7
the end of a WE
controlled WRITE. Keep OE HIGH during the entire WRITE cycle
to avoid data bus contention on common IO lines. If OE
LOW, internal circuitry turns off the output buffers t
goes LOW.
AutoStore® Operation
The CY14B256K stores data to nvSRAM using one of the three
storage operations:
1. Hardware store activated by HSB
2. Software store activated by an address sequence
3. AutoStore on device power down
AutoStore operation is a unique feature of QuantumTrap
technology and is enabled by default on the CY14B256K.
During normal operation, the device draws current from V
charge a capacitor connected to the V
charge is used by the chip to perform a single STORE operation.
If the voltage on the V
determines which of the 32,752 data bytes are
0-14
(see the section Figure
AA
or OE, the outputs
ACE
or at t
, whichever is later (see the section
DOE
access time without the need for
AA
or WE goes
is written into the memory if the data is valid t
controlled WRITE or before the end of a CE
HZWE
pin. This stored
pin drops below V
CC
CAP
SWITCH
before
SD
is left
after WE
to
CC
, the part
Figure 2 shows the proper connection of the storage capacitor
(V
) for automatic store operation. Refer to DC Electrical
CAP
Characteristics on page 15 for the size of the V
on the V
chip. A pull up should be placed on WE
pin is driven to 5V by a charge pump internal to the
CAP
to hold it inactive during
power up. This pull up is only effective if the WE
. The voltage
CAP
signal is tri-state
during power up. Many MPUs tri-state their controls on power up.
Verify this when using the pull up. When the nvSRAM comes out
of power-on-recall, the MPU must be active or the WE
held
inactive until the MPU comes out of reset.
To reduce unnecessary nonvolatile stores, AutoStore and
Hardware Store operations are ignored unless at least one
WRITE operation has taken place since the most recent STORE
or RECALL cycle. Software initiated STORE cycles are
performed regardless of whether a WRITE operation has taken
place. The HSB
signal is monitored by the system to detect if an
AutoStore cycle is in progress.
Hardware STORE (HSB) Operation
The CY14B256K provides the HSB pin for controlling and
acknowledging the STORE operations. The HSB
request a hardware STORE cycle. When the HSB
low, the CY14B256K conditionally initiates a STORE operation
after t
the SRAM takes place since the last STORE or RECALL cycle.
. An actual STORE cycle only begins if a WRITE to
DELAY
The HSB pin also acts as an open drain driver that is internally
driven low to indicate a busy condition, while the STORE
(initiated by any means) is in progress. This pin is externally
pulled up if it is used to drive other inputs.
SRAM READ and WRITE operations, that are in progress when
HSB is driven low by any means, are given time to complete
before the STORE operation is initiated. After HSB
the CY14B256K continues SRAM operations for t
pin is used to
pin is driven
goes LOW,
. During
DELAY
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 3 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 4
CY14B256K
t
, multiple SRAM READ operations take place. If a WRITE
DELAY
is in progress when HSB
to complete. However, any SRAM WRITE cycles requested after
HSB
goes LOW are inhibited until HSB returns HIGH.
is pulled LOW, it allows a time, t
DELAY
During any STORE operation, regardless of how it is initiated,
the CY14B256K continues to drive the HSB
pin LOW, releasing
it only when the STORE is complete. After completing the
STORE operation, the CY14B256K remains disabled until the
HSB
pin returns HIGH.
If HSB
is not used, it is left unconnected.
Hardware RECALL (Power Up)
During power up or after any low power condition
(V
CC<VSWITCH
V
again exceeds the sense voltage of V
CC
cycle is automatically initiated and takes t
), an internal RECALL request is latched. When
, a RECALL
SWITCH
HRECALL
to complete.
Software STORE
Data is transferred from the SRAM to the nonvolatile memory by
a software address sequence. The CY14B256K software
STORE cycle is initiated by executing sequential CE
READ cycles from six specific address locations in exact order.
During the STORE cycle, an erase of the previous nonvolatile
data is first performed, followed by a program of the nonvolatile
elements. After a STORE cycle is initiated, further READs and
WRITEs are inhibited untill the cycle is completed.
Because a sequence of READs from specific addresses is used
for STORE initiation, it is important that no other READ or WRITE
accesses intervene in the sequence. If it intervenes, the
sequence is aborted and no STORE or RECALL takes place.
To initiate the software STORE cycle, the following READ
sequence is performed:
1. Read address 0x0E38, Valid READ
2. Read address 0x31C7, Valid READ
3. Read address 0x03E0, Valid READ
4. Read address 0x3C1F, Valid READ
5. Read address 0x303F , Valid READ
6. Read address 0x0FC0, Initiate STORE cycle
The software sequence is clocked with CE
controlled READs. After the sixth address in the sequence is
OE
controlled READs or
entered, the STORE cycle commences and the chip is disabled.
controlled
It is important to use READ cycles and not WRITE cycles in the
,
sequence, although it is not necessary that OE
valid sequence. After the t
is activated again for READ and WRITE operations.
cycle time is fulfilled, the SRAM
STORE
be LOW for a
Software RECALL
Data is transferred from the nonvolatile memory to the SRAM by
a software address sequence. A software RECALL cycle is
initiated with a sequence of READ operations in a manner similar
to the software STORE initiation. To initiate the RECALL cycle,
the following sequence of CE
controlled READ operations is
performed:
1. Read address 0x0E38, Valid READ
2. Read address 0x31C7, Valid READ
3. Read address 0x03E0, Valid READ
4. Read address 0x3C1F, Valid READ
5. Read address 0x303F, Valid READ
6. Read address 0x0C63, Initiate RECALL cycle
Internally, RECALL is a two step procedure. First, the SRAM data
is cleared and then the nonvolatile information is transferred into
the SRAM cells. After the t
ready for READ and WRITE operations. The RECALL operation
cycle time, the SRAM is again
RECALL
in no way alters the data in the nonvolatile elements.
Data Protection
The CY14B256K protects data from corruption during low
voltage conditions by inhibiting all externally initiated STORE
and WRITE operations. The low voltage condition is detected
when V
is less than V
CC
SWITCH
.
If the CY14B256K is in a WRITE mode (both CE and WE are low)
at power up after a RECALL, or after a STORE, the WRITE is
inhibited until a negative transition on CE or WE is detected. This
protects against inadvertent writes during power up or brown out
conditions.
Noise Considerations
The CY14B256K is a high speed memory and must have a high
frequency bypass capacitor of approximately 0.1 µF connected
between V
as possible. As with all high speed CMOS ICs, careful routing of
power, ground, and signals reduce circuit noise.
and VSS using leads and traces that are as short
CC
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 4 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 5
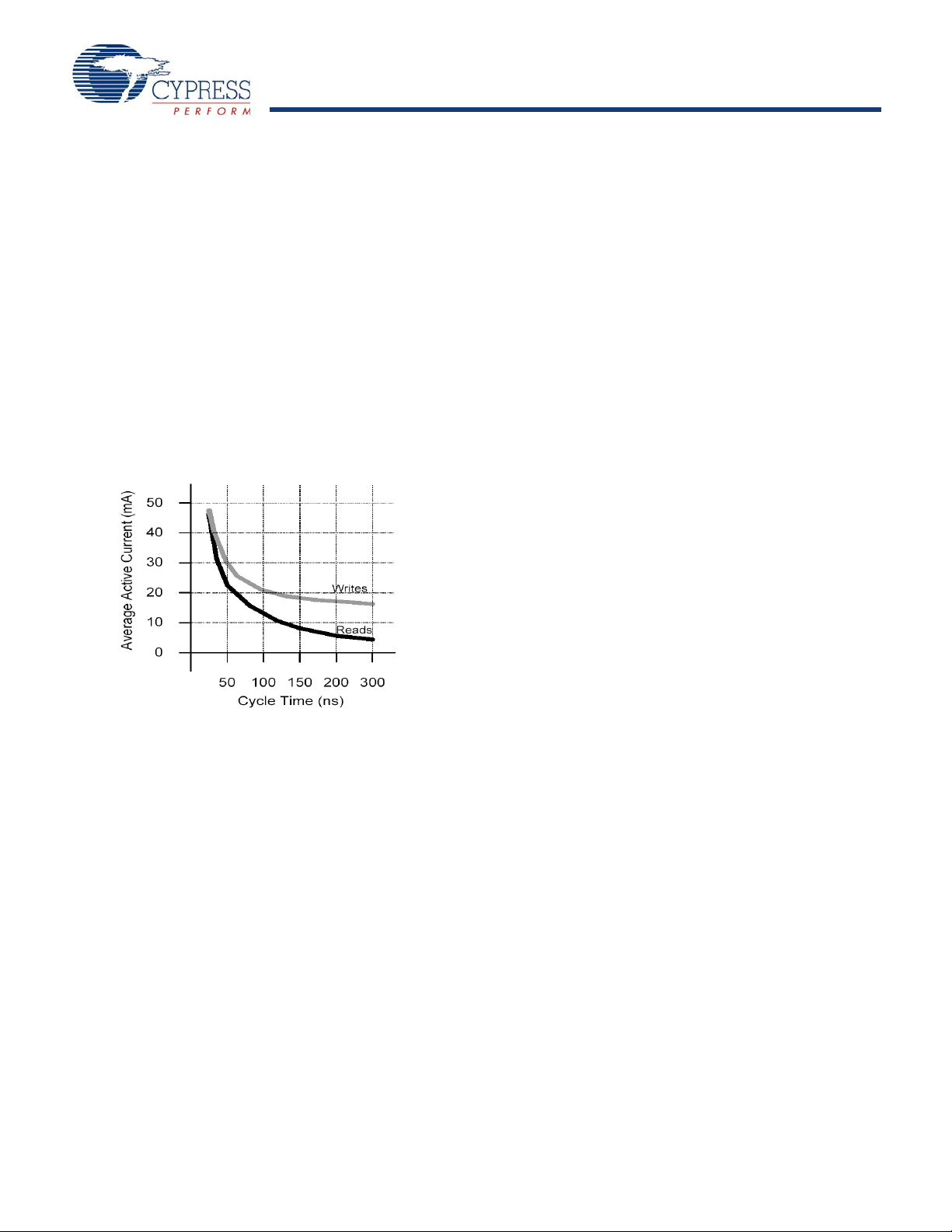
CY14B256K
Low Average Active Power
CMOS technology provides the CY14B256K the benefit of
drawing significantly less current when it is cycled at times longer
than 50 ns. Figure 3 shows the relationship between ICC and
READ and/or WRITE cycle time. Worst case current
consumption is shown for commercial temperature range, V
3.6V, and chip enable at maximum frequency. Only standby
current is drawn when the chip is disabled. The overall average
current drawn by the CY14B256K depends on the following
items:
1. 1The duty cycle of chip enable
2. The overall cycle rate for accesses
3. The ratio of READs to WRITEs
4. The operating temperature
5. The V
CC
level
6. IO loading
Figure 3. Current versus Cycle Time
CC
Best Practices
nvSRAM products have been used effectively for over 15 years.
While ease-of-use is one of the product’s main system values,
experience gained working with hundreds of applications has
resulted in the following suggestions as best practices:
=
■ The nonvolatile cells in an nvSRAM are programmed on the
test floor during final test and quality assurance. Incoming
inspection routines at customer or contract manufacturer’s
sites sometimes reprograms these values. Final NV patterns
are typically repeating patterns of AA, 55, 00, FF, A5, or 5A.
The end product’s firmware should not assume that an NV array
is in a set programmed state. Routines that check memory
content values to determine first time system configuration and
cold or warm boot status must always program a unique NV
pattern (for example, complex 4-byte pattern of 46 E6 49 53
hex or more random bytes) as part of the final system manufacturing test to ensure these system routines work consistently.
■ The OSCEN bit in the Calibration register at 0x7FF8 should be
set to 1 to preserve battery life when the system is in storage
(see Stopping and Starting the Oscillator on page 7).
■ The Vcap value specified in this data sheet includes a minimum
and a maximum value size. The best practice is to meet this
requirement and not exceed the maximum Vcap value because
the higher inrush currents may reduce the reliability of the
internal pass transistor. Customers who want to use a larger
Vcap value to make sure there is extra store charge should
discuss their Vcap size selection with Cypress.
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 5 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 6
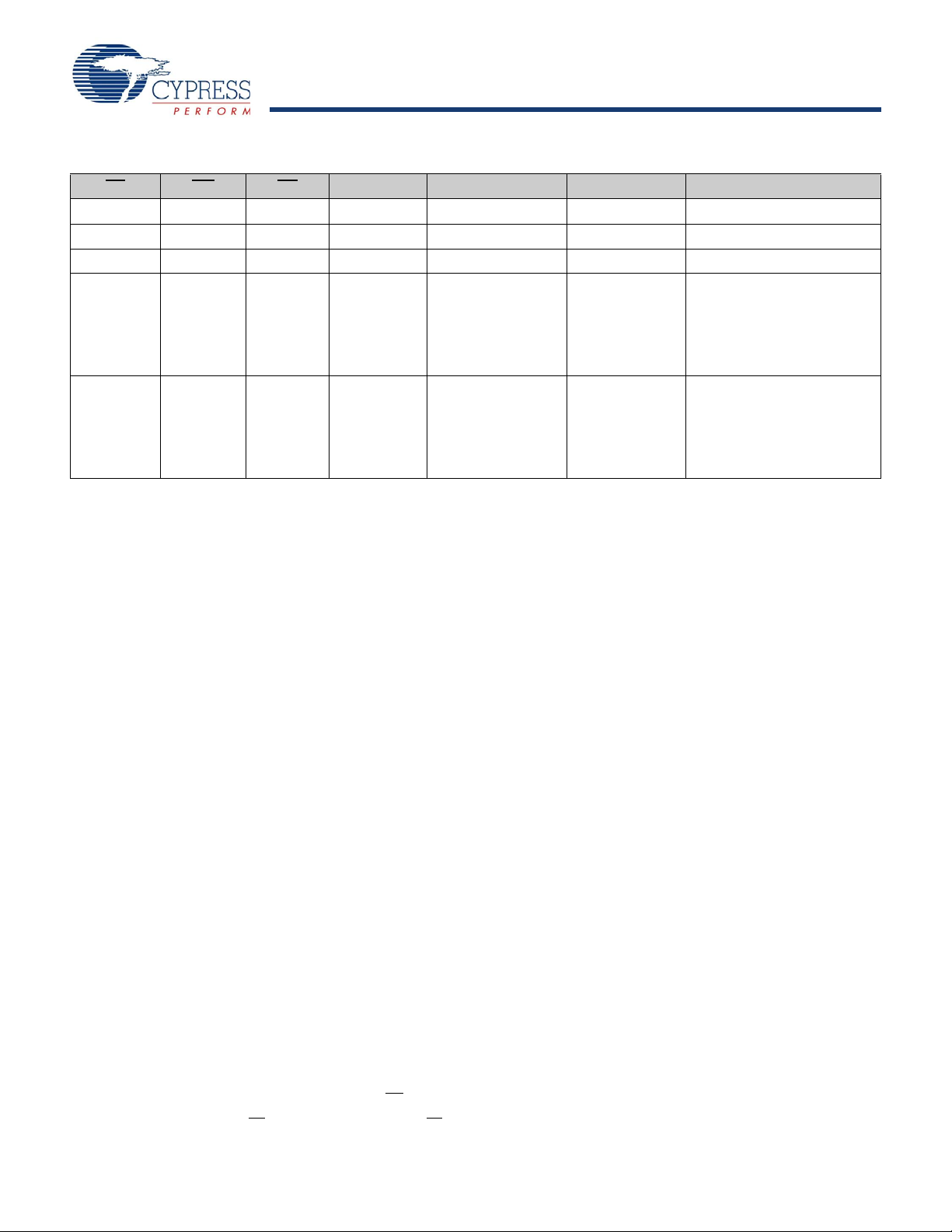
CY14B256K
Table 1. Mode Selection
Notes
1. The six consecutive address locations are in the order listed. WE
is HIGH during all six cycles to enable a nonvolatile cycle.
2. While there are 15 address lines on the CY14B256K, only the lower 14 lines are used to control software modes.
3. IO state depends on the state of OE
. The IO table shown is based on OE Low.
CE WE OE
A13–A0 Mode IO Power
H X X X Not Selected Output High Z Standby
L H L X Read SRAM Output Data Active
L L X X Write SRAM Input Data Active
L H L 0x0E38
0x31C7
0x03E0
0x3C1F
0x303F
0x0FC0
L H L 0x0E38
0x31C7
0x03E0
0x3C1F
0x303F
0x0C63
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Nonvolatile STORE
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Read SRAM
Nonvolatile RECALL
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output High Z
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output Data
Output High Z
Active I
Active
CC2
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3]
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 6 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 7

CY14B256K
Real Time Clock Operation
nvTIME Operation
The CY14B256K consists of internal registers that contain clock,
alarm, watchdog, interrupt, and control functions. RTC registers
use the last 16 address locations of the SRAM. Internal doubl e
buffering of the clock and the clock and timer information
registers prevent accessing transitional internal clock data
during a read or write operation. Double buffering also
circumvents disrupting normal timing counts or clock accuracy of
the internal clock while accessing clock data. Clock and Alarm
registers store data in BCD format.
The RTC register addresses for CY14B256K range from 0x7FF0
to 0x7FFF. Refer to RTC Register Map[5, 6] on page 11 and
Register Map Detail on page 12 for detailed description.
Clock Operations
The Clock registers maintain time up to 9,999 years in one
second increments. The user sets the time to any calendar time
and the clock automatically keeps track of days of the week,
month, leap years, and century transitions. There are eight
registers dedicated to the clock functions that are used to set
time with a write cycle and to read time during a read cycle.
These registers contain the time of day in BCD format. Bits
defined as ‘0’ are currently not used and are reserved for future
use by Cypress.
Reading the Clock
The double buffered RTC register structure reduces the chance
of reading incorrect data from the clock. The user should stop
internal updates to the CY14B256K time keeping registers
before reading clock data, to prevent reading of data in transition.
Stopping the internal register updates does not affect clock
accuracy.
The updating process is stopped by writing a ‘1’ to the read bit
‘R’ (in the flags register at 0x7FF0), and does not restart until a
‘0’ is written to the read bit. The RTC registers are then read while
the internal clock continues to run. After a ‘0’ is written to the read
bit (‘R’), all CY14B256K registers are simultaneously updated
within 20 ms.
Setting the Clock
Setting the write bit ‘W’ (in the flags register at 0x7FF0) to a ‘1’
stops updates to the time keeping registers and enables the time
to be set. The correct day, date, and time is then written into the
registers in 24 hour BCD format. The time written is referred to
as the “Base Time”. This value is stored in nonvolatile registers
and used in the calculation of the current time. Resetting the
write bit to ‘0’ transfers the register values to the actual clock
counters, after which the clock resumes normal operation.
Backup Power
The RTC in the CY14B256K is intended for permanently
powered operation. The V
depending on whether a capacitor or battery is chosen for the
application. When the primary power, V
V
the device switches to the backup power supply.
SWITCH
The clock oscillator uses very little current, which maximizes the
backup time available from the backup source. Regardless of the
RTCcap
or V
pin is connected
RTCbat
, fails and drops below
CC
clock operation with the primary source removed, the data stored
in the nvSRAM is secure, having been stored in the no nvolatile
elements when power was lost.
During backup operation, the CY14B256K consumes a
maximum of 300 nanoamps at 2 volts. The user should choose
capacitor or battery values according to the application. Backup
time values based on maximum current specifications are shown
in the following table. Nominal backup times are approximately
three times longer.
T able 2. RTC Backup Time
Capacitor Value Backup Time
0.1F 72 hours
0.47F 14 days
1.0F 30 days
Using a capacitor has the advantage of recharging the backup
source each time the system is powered up. If a battery is used,
a 3V lithium is recommended and the CY14B256K sources
current only from the battery when the primary power is removed.
The battery is not, however, recharged at any time by the
CY14B256K. The battery capacity must be chosen for total anticipated cumulative down time required over the life of the system.
Stopping and Starting the Oscillator
The OSCEN bit in the calibration register at 0x7FF8 controls the
enable and disable of the oscillator. This active LOW bit is
nonvolatile and is shipped to customers in the “enabled” (set to
0) state. To preserve the battery life when the system is in
storage, OSCEN bit must be set to ‘1’. This turns off the oscillator
circuit, extending the battery life. If the OSCEN bit goes from
disabled to enabled, it takes approximately 5 seconds (10
seconds maximum) for the oscillator to start.
While system power is off, if the voltage on the backup supply
(V
the oscillator may fail.The CY14B256K has the ability to dete ct
oscillator failure when system power is restored. This is recorded
in the OSCF (Oscillator Failed bit) of the Flags register at
address 0x7FF0. When the device is powered on (V
above V
If the OSCEN bit is enabled and the oscillator is not active within
the first 5 ms, the OSCF bit is set to “1”. The system must check
for this condition and then write ‘0’ to clear the flag. Note that in
addition to setting the OSCF flag bit, the time registers are reset
to the “Base Time” (see “Setting the Clock” on page 7), which is
the value last written to the time keeping registers. The Control
or Calibration registers and the OSCEN bit are not affected by
the “oscillator failed” condition.
The value of OSCF must be reset to ‘0’ when the time registers
are written for the first time. This initializes the state of this bit
which may have become set when the system was first powered
on.
To reset OSCF, set the write bit “W” (in the flags register at
0x7FF0) to “1” to enable writes to the Flag register. Write a “0” to
the OSCF bit and then reset the write bit to “0” to disable writes.
RTCcap
or V
SWITCH
) falls below their respective minimum level,
RTCbat
), the OSCEN bit is checked for “enabled” status.
CC
goes
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 7 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 8

CY14B256K
Calibrating the Clock
The RTC is driven by a quartz controlled oscillator with a nominal
frequency of 32.768 kHz. Clock accuracy depends on the quality
of the crystal and calibration. The crystal oscillators typically
have an error of +
employs a calibration circuit that improves the accuracy to +1/–2
ppm at 25°C. This implies an error of +2.5 seconds to -5 seconds
per month.
The
calibration circuit adds or subtracts counts from the oscillator
divider circuit to achieve this accuracy. The number of pulses that
are suppressed (subtracted, negative calibration) or split (added,
positive calibration) depends upon the value loaded into the five
calibration bits found in Calibration register at 0x7FF8. The
calibration bits occupy the five lower order bits in the Calibration
register. These bits are set to represent any value between ‘0’
and 31 in binary form. Bit D5 is a sign bit, where a ‘1’ indicates
positive calibration and a ‘0’ indicates negative calibration.
Adding counts speeds the clock up and subtracting counts slows
the clock down. If a binary ‘1’ is loaded into the register, it corresponds to an adjustment of 4.068 or –2.034 ppm offset in oscillator error, depending on the sign.
Calibration occurs within a 64 minute cycle. The first 62 minutes
in the cycle may, once per minute, have one second shortened
by 128 or lengthened by 256 oscillator cycles. If a binary ‘1’ is
loaded into the register, only the first two minutes of the 64
minute cycle is modified. If a binary 6 is loade d, the first 12 ar e
affected, and so on. Therefore, each calibration step has the
effect of adding 512 or subtracting 256 oscillator cycles for every
125,829,120 actual oscillator cycles, that is, 4.068 or –2.034 ppm
of adjustment per calibration step in the Calibration register.
To determine the required calibration, the CAL bit in the Flags
register (0x7FF0) must be set to ‘1’. This causes the INT pin to
toggle at a nominal frequency of 512 Hz. Any deviation
measured from the 512 Hz indicates the degree and direction of
the required correction. For example, a reading of 512.01024 Hz
indicates a +20 ppm error. Hence, a decimal value of –10
(001010b) must be loaded into the Calibration register to offset
this error.
Note Setting or changing the Calibration register does not affect
the test output frequency.
To set or clear CAL, set the write bit “W” (in the flags register at
0x7FF0) to “1” to enable writes to the Flag register. W rite a value
to CAL, and then reset the write bit to “0” to disable writes.
20ppm to +35ppm. However, CY14B256K
Alarm
The alarm function compares user programmed values of alarm
time and date (stored in the registers 0x7FF1-5) with the corresponding time of day and date values. When a match occurs, the
alarm internal flag (AF) is set and an interrupt is generated on
INT pin if Alarm Interrupt Enable (AIE) bit is set.
There are four alarm match fields - date, hours, minutes, and
seconds. Each of these fields has a match bit that is used to
determine if the field is used in the alarm match logic. Setting the
match bit to ‘0’ indicates that the corresponding fie ld is used in
the match process. Depending on the match bits, the alarm
occurs as specifically as once a month or as frequently as once
every minute. Selecting none of the match bits (all 1s) indicates
that no match is required and therefore, alarm is disabled.
Selecting all match bits (all 0s) causes an exact time and date
match.
There are two ways to detect an a lar m ev ent: by re adi ng t he AF
flag or monitoring the INT pin. The AF flag in the flags register at
0x7FF0 indicates that a date or time match has occurred. The
AF bit is set to “1” when a match occurs. Reading the flags or
control register clears the alarm flag bit (and all others). A
hardware interrupt pin may also be used to detect an alarm
event.
Note CY14B256K requires the alarm match bit for seconds
(0x7FF2 - D7) to be set to ‘0’ for proper operation of Alarm Flag
and Interrupt.
Alarm registers are not nonvolatile and, therefore, need to be
reinitialized by software on power up. To set, clear or enable an
alarm, set the ‘W’ bit (in Flags Register - 0x7FF0) to ‘1’ to enable
writes to Alarm Registers. After writing the alarm value, clear the
‘W’ bit back to “0” for the changes to take effect.
Watchdog Timer
The Watchdog Timer is a free running down counter that uses
the 32 Hz clock (31.25 ms) derived from the crystal oscillator.
The oscillator must be running for the watchdog to function. It
begins counting down from the value loaded in the Watchdog
Timer register.
The timer consists of a loadable register and a free running
counter. On power up, the watchdog time out value in register
0x7FF7 is loaded into the Counter Load register. Counting
begins on power up and restarts from the loadable value any time
the Watchdog Strobe (WDS) bit is set to ‘1’. The counter is
compared to the terminal value of ‘0’. If the counter reaches this
value, it causes an internal flag and an optional interrupt output.
You can prevent the time out interrupt by setting WDS bit to ‘1’
prior to the counter reaching ‘0’. This causes the counter to
reload with the watchdog time out value and to be restarted. As
long as the user sets the WDS bit prior to the counter reaching
the terminal value, the interrupt and WDF flag never occur.
New time out values are written by setting the watchdog write bit
to ‘0’. When the WDW is ‘0’, new writes to the watchdog time out
value bits D5-D0 are enabled to modify the time out value. When
WDW is ‘1’, writes to bits D5-D0 are ignored. The WDW function
enables a user to set the WDS bit without concern that the
watchdog timer value is modified. A logical diagram of the
watchdog timer is shown in Figure 4. Note that setting the
watchdog time out value to ‘0’ disables the watchdog function.
The output of the watchdog timer is the flag bit WDF that is set if
the watchdog is allowed to time out. The flag is set upon a
watchdog time out and cleared when the user reads the Flags or
Control registers. If the watchdog time out occurs, the user also
enables an optional interrupt source to drive the INT pin.
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 8 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 9

CY14B256K
Figure 4. Watchdog Timer Block Diagram
1 Hz
Oscillator
Clock
Divider
Counter
Zero
Compare
WDF
WDS
Load
Register
WDW
D
Q
Q
Watchdog
Register
write to
Watchdog
Register
32 Hz
32,768 KHz
Power Monitor
The CY14B256K provides a power management scheme with
power fail interrupt capability. It also controls the internal switch
to backup power for the clock and protect s the memory f rom low
V
access. The power monitor is based on an internal band gap
CC
reference circuit that compares the V
threshold.
voltage to V
CC
As described in the “AutoStore® Operation” on page 3, when
V
operation is initiated from SRAM to the nonvolatile elements,
is reached as VCC decays from power loss, a data store
SWITCH
securing the last SRAM data state. Power is also switched from
V
to the backup supply (battery or capacitor) to operate the
CC
RTC oscillator.
When operating from the backup source, read and write opera-
tions to nvSRAM are inhibited and the clock functions are not
available to the user. The clock continues to operate in the
background. The updated clock data is available to the user
t
HRECALL
“AutoStore or Power Up RECALL” on page 19).
delay after VCC is restored to the device (see
Interrupts
The CY14B256K has a Flags register, Interrupt register and
Interrupt logic that can signal interrupt to the microcontroller.
There are three potential sources for interrupt: watchdog ti mer,
power monitor, and alarm timer. Each of these can be individually
enabled to drive the INT pin by appropriate setting in the Interrupt
register (0x7FF6). In addition, each has an associated flag bit in
the Flags register (0x7FF0) that the host processor uses to
determine the cause of the interrupt. The INT pin driver has two
bits that specify its behavior when an interrupt occurs.
An Interrupt is raised only if both a flag is raised b y one of the
three sources and the respective interrupt enable bit in Interrupts
SWITCH
register is enabled (set to ‘1’). After an interrupt source is active,
two programmable bits, H/L and P/L, determine the behavior of
the output pin driver on INT pin. These two bits are located in the
Interrupt register and can be used to drive level or pulse mode
output from the INT pin. In pulse mode, the pulse width is
internally fixed at approximately 200 ms. This mode is intended
to reset a host microcontroller. In the level mode, the pin goes to
its active polarity until the Flags register is read by the user. This
mode is used as an interrupt to a host microcontroller. The
control bits are summarized in the following section.
Interrupt Register
Watchdog Interrupt Enable - WIE. When set to ‘1’, the
watchdog timer drives the INT pin and an internal flag when a
watchdog time out occurs. When WIE is set to ‘0’, the watchdog
timer only affects the WDF flag in Flags register.
Alarm Interrupt Enable - AIE. When set to ‘1’, the alarm match
drives the INT pin and an internal flag. When AIE is set to ‘0’, the
alarm match only affects the AF flagin Flags register.
Power Fail Interrupt Enable - PFE. When set to ‘1’, the power
fail monitor drives the pin and an internal flag. When PFE is set
to ‘0’, the power fail monitor only affects the PF flag in Flags
register.
High/Low - H/L. When set to a ‘1’, the INT pin is active HIGH
and the driver mode is push pull. The INT pin drives high only
when V
is active LOW and the drive mode is open drain. Active LOW
is greater than V
CC
. When set to a ‘0’, the INT pin
SWITCH
(open drain) is operational even in battery backup mode.
Pulse/Level - P/L. When set to a ‘1’ and an interrupt occurs, the
INT pin is driven for approximately 200 ms. When P/L is set to a
‘0’, the INT pin is driven high or low (determined by H/L) until the
Flags or Control register is read.
When an enabled interrupt source activates the INT pin, an
external host reads the Flags registers to determine the cause.
Remember that all flags are cleared when the register is read. If
the INT pin is programmed for Level mode, then the condition
clears and the INT pin returns to its inactive state. If the pin is
programmed for Pulse mode, then reading the flag also clears
the flag and the pin. The pulse does not complete its specified
duration if the Flags register is read. If the INT pin is used as a
host reset, then the Flags or Control register is not read during a
reset.
Flags Register
The Flag register has three flag bits: WDF , AF , and PF, which can
be used to generate an interrupt. These flags are set by the
watchdog timeout, alarm match, or power fail monitor respectively. The processor can either poll this register or enable inter-
rupts to be informed when a flag is set. These flags are automatically reset once the register is read. The flags register is
automatically loaded with the value 00h on power up (except for
the OSCF bit. See “Stopping and Starting the Oscillator” on
page 7.)
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 9 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 10

CY14B256K
Figure 5. Interrupt Block Diagram
WDF - Watchdog Timer Flag
WIE - Watchdog Interrupt
PF - Power Fail Flag
PFE - Power Fail Enable
AF - Alarm Flag
AIE - Alarm Interrupt Enable
P/L - Pulse Level
H/L - High/Low
Enable
Watchdog
Timer
Power
Monitor
Clock
Alarm
VINT
WDF
WIE
PF
PFE
AF
AIE
P/L
Pin
Driver
H/L
INT
V
CC
V
SS
C
1
C
2
RF
Y
1
X
1
X
2
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
DQ
0
Recommended Values:
Y1 = 32.768KHz
RF = 10M Ohm
C1 = 0 (install cap footprint, but leave unloaded)
C2 = 56 pF +
10% (do not vary from this value)
Note
4. Schottky diodes, (V
F
< 0.4V with IF at 100mA) are recommended at pins A0 - A3 and DQ0 in applications where undershoot exceeds -0.5V. Please see application note
AN49947 for further details.
Figure 6. RTC Recommended Component Configuration
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 10 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 11

CY14B256K
T able 3. RTC Register Map
Note
5. ( ) designates values shipped from the factory.
6. The unused bits of RTC registers are reserved for future use and should be set to ‘0’ .
7. Is a binary value, not a BCD value.
Register
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
[5, 6]
BCD Format Data
[5]
Function/Range
0x7FFF 10s Years Years Years: 00–99
0x7FFE 0 0 0 10s Months Months Months: 01–12
0x7FFD 0 0 10s Day of Month Day Of Month Day of Month: 01–31
0x7FFC 0 0 0 0 0 Day of Week Day of Week: 01–07
0x7FFB 0 0 10s Hours Hours Hours: 00–23
0x7FFA 0 10s Minutes Minutes Minutes: 00–59
0x7FF9 0 10s Seconds Seconds Seconds: 00–59
0x7FF8 OSCEN
(0)
0x7FF7 WDS (0) WDW (0) WDT (000000) Watchdog
0x7FF6 WIE (0) AIE (0) PFE (0) 0 H/L (1) P/L (0) 0 0 Interrupts
0 Cal Sign
(0)
Calibration (00000) Calibration Values
[7]
[7]
0x7FF5 M (1) 0 10s Alarm Date Alarm Day Alarm, Day of Month: 01–31
0x7FF4 M (1) 0 10s Alarm Hours Alarm Hours Alarm, Hours: 00–23
0x7FF3 M (1) 10 Alarm Minutes Alarm Minutes Alarm, Minutes: 00–59
0x7FF2 M (1) 10 Alarm Seconds Alarm, Seconds Alarm, Seconds: 00–59
0x7FF1 10s Centuries Centuries Centuries: 00–99
0x7FF0 WDF AF PF OSCF 0 CAL (0) W (0) R (0) Flags
[7]
[7]
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 11 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 12
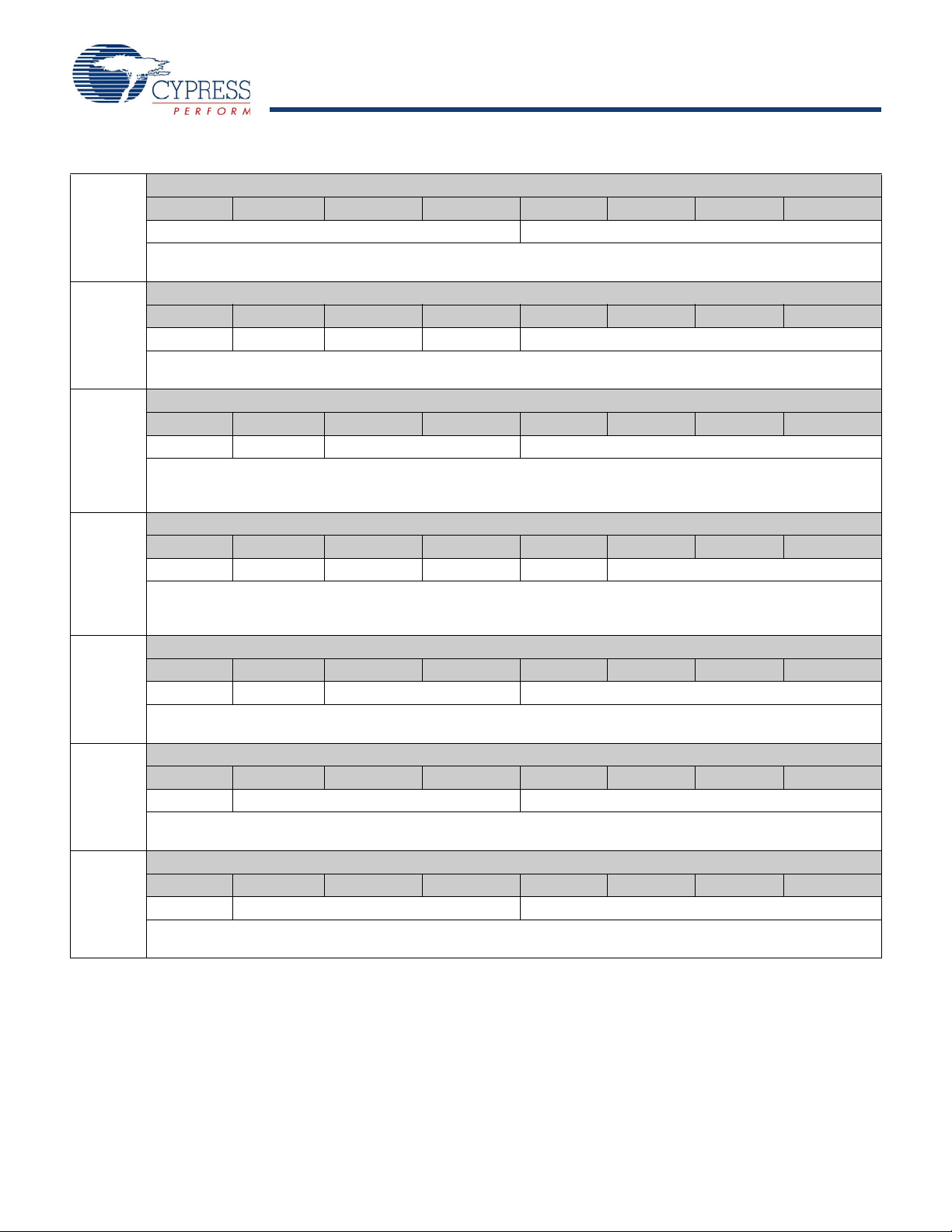
CY14B256K
Table 4. Register Map Detail
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0x7FFF
Contains the lower two BCD digits of the year. Lower nibble (four bits) contains the value for years; upper nibble (four
bits) contains the value for 10s of years. Each nibble operates from 0 to 9. The range for the register is 0–99.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0x7FFE
0x7FFD
0x7FFC
0x7FFB
0x7FFA
0x7FF9
0 0 0 10s Month Months
Contains the BCD digits of the month. Lower nibble (four bits) contains the lower digit and operates from 0 to 9; upper
nibble (one bit) contains the upper digit and operates from 0 to 1. The range for the register is 1–12.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 0 10s Day of Month Day of Month
Contains the BCD digits for the date of the month. Lower nibble (four bits) contains the lower digit and operates from 0
to 9; upper nibble (two bits) contains the 10s digit and operates from 0 to 3. The range for the register is 1–31. Leap
years are automatically adjusted for.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 0 0 0 0 Day of Week
Lower nibble (three bits) contains a value that correlates to day of the week. Day of the week is a ring counter that counts
from 1 to 7 then returns to 1. The user must assign meaning to the day value, because the day is not integrated with the
date.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 0 10s Hours Hours
Contains the BCD value of hours in 24 hour format. Lower nibble (fou r bits) contains the lower digit and operates from
0 to 9; upper nibble (two bits) contains the upper digit and operates from 0 to 2. The range for the register is 0–23.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 10s Minutes Minutes
Contains the BCD value of minutes. Lower nibble (four bits) contains the lower digit and operates from 0 to 9; upper
nibble (three bits) contains the upper minutes digit and operates from 0 to 5. The range for the register is 0–59.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 10s Seconds Seconds
Contains the BCD value of seconds. Lower nibble (four bits) contains the lower digit and operates from 0 to 9; upper
nibble (three bits) contains the upper digit and operates from 0 to 5. The range for the register is 0–59.
Time Keeping - Years
10s Years Years
Time Keeping - Months
Time Keeping - Date
Time Keeping - Day
Time Keeping - Hours
Time Keeping - Minutes
Time Keeping - Seconds
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 12 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 13

CY14B256K
Table 4. Register Map Detail (continued)
Calibration/Control
0X7FF8
OSCEN Oscillator Enable. When set to 1, the oscillator is stopped. When set to 0, the oscillator runs. Disabling the oscillator
Calibration
Sign
Calibration These five bits control the calibration of the clock.
0x7FF7
WDS Watchdog Strobe. Setting this bit to 1 reloads and restarts the watchdog timer. Setting the bit to 0 has no effect. The bit
WDW Watchdog Write Enable. Setting this bit to 1 disables any WRITE to the watchdog timeout value (D5–D0). This allows
WDT Watchdog timeout selection. The watchdog timer interval is selected by the 6-bit value in this register. It represents a
0x7FF6
WIE Watchdog Interrupt Enable. When set to 1 and a watchdog timeout occurs, the watchdog timer drives the INT pin and
AIE Alarm Interrupt Enable. When set to 1, the alarm match drives the INT pin and the AF flag. When set to 0, the alarm
PFIE Power Fail Enable. When set to 1, the alarm match drives the INT pin and the PF flag. When set to 0, the power fail
0 Reserved for future use
H/L High/Low. When set to 1, the INT pin is driven active HIGH. When set to 0, the INT pin is open drain, active LOW.
P/L Pulse/Level. When set to 1, the INT pin is driven active (determined by H/L) by an interrupt source for approximately
0x7FF5
M Match. When this bit is set to 0, the date value is used in the alarm match. Setting this bit to 1 causes the matc h circ uit
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
OSCEN 0 Calibration
Sign
saves battery or capacitor power during storage.
Determines if the calibration adjustment is applied as an addition (1) to or as a subtraction (0) from the time-base.
WatchDog Timer
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WDS WDW WDT
is cleared automatically after the watchdog timer is reset. The WDS bit is write only. Reading it always returns a 0.
the user to set the watchdog strobe bit without disturbing the timeout value. Setting this bit to 0 allows bits D5–D0 to be
written to the watchdog register when the next write cycle is complete. This function is explained in detail in the “Watchdog
Timer” on page 8.
multiplier of the 32 Hz count (31.25 ms). The range of timeout value is 31.25 ms (a setting of 1) to 2 seconds (setting of
3 Fh). Setting the watchdog timer register to 0 disables the timer. These bits can be written only if the WDW bit was set
to 0 on a previous cycle.
Interrupt Status/Control
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WIE AIE PFIE 0 H/L P/L 0 0
the WDF flag. When set to 0, the watchdog timeout affects only the WDF flag.
match only affects the AF flag.
monitor affects only the PF flag.
200 ms. When set to 0, the INT pin is driven to an active level (as set by H/L) until the flags register is read.
Alarm - Day
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
M 0 10s Alarm Date Alarm Date
Contains the alarm value for the date of the month and the mask bit to select or deselect the date value.
to ignore the date value.
Calibration
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 13 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 14

CY14B256K
Table 4. Register Map Detail (continued)
Alarm - Hours
0x7FF4
M Match. When this bit is set to 0, the hours value is used in the alarm match. Setting this bit to 1 causes the match circuit
0x7FF3
M Match. When this bit is set to 0, the minutes value is used in the alarm match. Setting this bit to 1 causes the match
0x7FF2
M Match. When this bit is set to 0, the seconds value is used in the alarm match. Setting this bit to 1 causes the match
0x7FF1
0x7FF0
WDF Watchdog Timer Flag. This read only bit is set to 1 when the watchdog timer is allowed to reach 0 without being reset
AF Alarm Flag. This read only bit is set to 1 w hen the tim e and date match the values stored in the alarm registers with the
PF Power Fail Flag. This read only bit is set to 1 when power falls below the power fail threshold V
OSCF Oscillator Fail Flag. Set to 1 on power up if the oscillator is enabled and not running in the first 5 ms of operation. This
CAL Calibration Mode. When set to 1, a 512 Hz square wave is output on the INT pin. When set to 0, the INT pin resumes
W Write Enable: Setting the W bit to 1 freezes updatesof the RTC registers. The user can then write to RTC registers, Alarm
R Read Enable: Setting R bit to 1, stops clock updates to user RTC registers so that clock updates are not seen during
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
M 10s Alarm Hours Alarm Hours
Contains the alarm value for the hours and the mask bit to select or deselect the hours value.
to ignore the hours value.
Alarm - Minutes
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
M 10s Alarm Minutes Alarm Minutes
Contains the alarm value for the minutes and the mask bit to select or deselect the minutes value.
circuit to ignore the minutes value.
Alarm - Seconds
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
M 10s Alarm Seconds Alarm Seconds
Contains the alarm value for the seconds and the mask bit to select or deselect the seconds’ value.
circuit to ignore the seconds value.
Time Keeping - Centuries
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
10s Centuries Centuries
Contains the BCD value of centuries. Lower nibble contains the lower digit and operates from 0 to 9; upper nibble contains
the upper digit and operates from 0 to 9. The range for the register is 0-99 centuries.
Flags
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WDF AF PF OSCF 0 CAL W R
by the user. It is cleared to 0 when the Flags register is read or on power-up.
match bits = 0. It is cleared when the Flags register is read or on power-up.
. It is cleared to
0 when the Flags register is read or on power-up.
indicates that RTC backup power failed and clock value is no longer valid. The user must reset this bit to 0 to clear this
condition (Flag). The chip does not clear this flag. This bit survives power cycles.
normal operation. This bit defaults to 0 (disabled) on power up.
registers, Calibration register, Interrupt register and Flags register. Setting the W bit to 0 causes the contents of the RTC
registers to be transferred to the time keeping counters if the time has been changed (a new base time is loaded). This
bit defaults to 0 on power up.
the reading process. Set R bit to 0 to resume clock updates to the holding register. Setting this bit does not require W
bit to be set to 1. This bit defaults to 0 on power up.
SWITCH
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 14 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 15

CY14B256K
Maximum Ratings
Notes
8. The HSB
pin has IOUT = –10 μA for VOH of 2.4V, this parameter is characterized but not tested.
9. The INT pin is open drain and does not source or sink current when Interrupt register bit D3 is low.
Exceeding maximum ratings may impair the useful life of th e
device. These user guidelines are not tested.
Storage Temperature .................................–65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied ............................................ –55°C to +125°C
Supply Voltage on V
Voltage Applied to Outputs
in High Z State.......................................–0.5V to V
Input Voltage.............................................–0.5V to Vcc+0.5V
Transient Voltage (<20 ns) on
Any Pin to Ground Potential..................–2.0V to V
Relative to GND..........–0.5V to 4.1V
CC
CC
CC
+ 0.5V
+ 2.0V
Package Power Dissipation
Capability (T
= 25°C)...................................................1.0W
A
Surface Mount Pb Soldering
Temperature (3 Seconds).......................................... +260°C
DC Output Current (1 output at a time, 1s duration) ... 15 mA
Static Discharge Voltage.......................................... > 2001V
(MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch Up Current................................................... > 200 mA
Operating Range
Range Ambient Temperature V
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 2.7V to 3.6V
Industrial –40°C to +85°C 2.7V to 3.6V
CC
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over the Operating Range (VCC = 2.7V to 3.6V)
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
I
CC1
Average VCC Current tRC = 25 ns
t
= 35 ns
RC
= 45 ns
t
RC
Dependent on output loading and cycle rate.
Values obtained without output loads.
I
= 0 mA.
OUT
I
CC2
I
CC3
I
CC4
Average V
during STORE
Average VCC Current
at t
AVAV
25°C Typical
Average V
Current during
Current
CC
= 200 ns, 3V,
CAP
All Inputs Do Not Care, VCC = Max
Average current for duration t
WE
> (VCC – 0.2V). All other inputs cycling.
Dependent on output loading and cycle rate.
Values obtained without output loads.
All Inputs Do Not Care, VCC = Max
Average current for duration t
AutoStore Cycle
[8, 9]
STORE
STORE
Commercial 65
55
50
Industrial 70
60
55
10 mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
3mA
3mA
I
SB
VCC Standby Current WE > (VCC – 0.2V). All others V
Standby current level after nonvolatile cycle is complete.
Inputs are static. f = 0 MHz.
I
I
V
V
V
V
V
IX
OZ
IH
IL
OH
OL
CAP
Input Leakage
Current
Off State Output
Leakage Current
Input HIGH Voltage 2.0 VCC + 0.5 V
Input LOW Voltage VSS – 0.5 0.8 V
Output HIGH Voltage I
Output LOW Voltage I
Storage Capacitor Between V
VCC = Max, VSS < V
VCC = Max, VSS < V
= –2 mA 2.4 V
OUT
= 4 mA 0.4 V
OUT
CAP
< V
IN
CC
< VCC, CE or OE > V
IN
pin and VSS, 5V Rated 17 120 μF
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 15 of 28
< 0.2V or > (VCC – 0.2V).
IN
IH
3mA
-1 +1 μA
-1 +1 μA
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY14B256K
Data Retention and Endurance
3.0V
Output
5 pF
R1 577Ω
R2
789Ω
3.0V
Output
30 pF
R1 577Ω
R2
789Ω
For Tri-state Specs
Input Pulse Levels..................................................0 V to 3 V
Input Rise and Fall Times (10% - 90%)........................ <
5 ns
Input and Output Timing Reference Levels................... 1.5 V
Parameter Description Min Unit
DATA
NV
C
R
Data Retention 20 Years
Nonvolatile STORE Operations 200 K
Capacitance
These parameters are guaranteed but not tested.
Parameter Description Test Conditions Max Unit
C
C
IN
OUT
Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
V
= 0 to 3.0 V
Output Capacitance 7 pF
CC
7pF
Thermal Resistance
These parameters are guaranteed but not tested.
Parameter Description Test Conditions 48-SSOP Unit
Θ
Θ
Thermal Resistance
JA
(Junction to Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
JC
(Junction to Case)
Test conditions follow standard test methods and
procedures for measuring thermal impedance, in
accordance with EIA / JESD51.
Figure 7. AC Test Loads
32.9 °C/W
25.56 °C/W
AC Tes t Conditions
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 16 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 17

CY14B256K
AC Switching Characteristics
W
5&
W
$$
W
2+$
$''5(66
'4'$7$287
'$7$9$/,'
$''5(66
W
5&
&(
W
$&(
W
/=&(
W
3'
W
+=&(
2(
W
'2(
W
/=2(
W
+=2(
'$7$9$/,'
$&7,9(
67$1'%<
W
38
'4'$7$287
,&&
Notes
10.WE
is HIGH during SRAM Read Cycles.
11.Device is continuously selected with CE and OE both Low.
12.Measured ±200 mV from steady state output voltage.
13.These parameters are guaranteed by design and are not tested.
14.HSB
must remain HIGH during READ and WRITE cycles.
Parameter
Cypress
Parameter
Parameter
SRAM Read Cycle
t
ACE
t
RC
t
AA
t
DOE
t
OHA
t
LZCE
t
HZCE
t
LZOE
t
HZOE
t
PU
t
PD
[10]
[11]
[11]
[12]
[12]
[12]
[12]
[13]
[13]
t
ELQV
t
AVAV, tELEH
t
AVQV
t
GLQV
t
AXQX
t
ELQX
t
EHQZ
t
GLQX
t
GHQZ
t
ELICCH
t
EHICCL
Alt.
Chip Enable Access Time 25 35 45 ns
Read Cycle Time 25 35 45 ns
Address Access Time 25 35 45 ns
Output Enable to Data Valid 12 15 20 ns
Output Hold After Address Change 3 3 3 ns
Chip Enable to Output Active 3 3 3 ns
Chip Disable to Output Inactive 10 13 15 ns
Output Enable to Output Active 0 0 0 ns
Output Disable to Output Inactive 10 13 15 ns
Chip Enable to Power Active 0 0 0 ns
Chip Disable to Power Standby 25 35 45 ns
Description
Figure 8. SRAM Read Cycle 1: Address Controlled
25 ns 35 ns 45 ns
Min Max Min Max Min Max
[10, 11, 14]
Unit
Figure 9. SRAM Read Cycle 2: CE and OE Controlled
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 17 of 28
[10, 14]
[+] Feedback
Page 18

CY14B256K
AC Switching Characteristics (continued)
t
WC
t
SCE
t
HA
t
AW
t
SA
t
PWE
t
SD
t
HD
t
HZWE
t
LZWE
ADDRESS
CE
WE
DATA IN
DATA OUT
DATA VALID
HIGH IMPEDANCE
PREVIOUS DATA
t
WC
ADDRESS
t
SA
t
SCE
t
HA
t
AW
t
PWE
t
SD
t
HD
CE
WE
DATA IN
DATA OUT
HIGH IMPEDANCE
DATA VALID
Notes
15.If WE
is Low when CE goes Low, the outputs remain in the High Impedance State.
16.CE
or WE are greater than VIH during address transitions.
Parameter
Cypress
Parameter
SRAM Write Cycle
t
WC
t
PWE
t
SCE
t
SD
t
HD
t
AW
t
SA
t
HA
t
HZWE
t
LZWE
[12, 15]
[12]
t
AVAV
t
WLWH, tWLEH
t
ELWH, tELEH
t
DVWH, tDVEH
t
WHDX, tEHDX
t
AVWH, tAVEH
t
AVWL, tAVEL
t
WHAX, tEHAX
t
WLQZ
t
WHQX
Alt.
Parameter
Write Cycle Time 25 35 45 ns
Write Pulse Width 20 25 30 ns
Chip Enable To End of Write 20 25 30 ns
Data Setup to End of Write 10 12 15 ns
Data Hold After End of Write 0 0 0 ns
Address Setup to End of Write 20 25 30 ns
Address Setup to Start of Write 0 0 0 ns
Address Hold After End of Writ e 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable to Output Disable 10 13 15 ns
Output Active After End of Write 3 3 3 ns
Description
Figure 10. SRAM Write Cycle 1: WE Controlled
25 ns 35 ns 45 ns
Min Max Min Max Min Max
[14, 16]
Unit
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 18 of 28
Figure 11. SRAM Write Cycle 2: CE Controlled
[+] Feedback
Page 19

CY14B256K
AutoStore or Power Up RECALL
V
CC
V
SWITCH
t
STORE
t
STORE
t
HRECALL
t
HRECALL
AutoStore
POWER-UP RECALL
Read & Write Inhibited
STORE occurs only
if a SRAM write
has happened
No STORE occurs
without atleast one
SRAM write
t
VCCRISE
Notes
17.t
HRECALL
starts from the time V
CC
rises above V
SWITCH
.
18.If an SRAM Write does not taken place since the last nonvolatile cycle, no STORE takes place.
19.Industrial Grade Devices require 15 ms Max.
Parameter Description
t
HRECALL
t
STORE
V
SWITCH
t
VCCRISE
[17]
[18, 19]
Power Up RECALL Duration 40 ms
STORE Cycle Duration Commercial 12.5 ms
Low Voltage Trigger Level 2.65 V
VCC Rise Time 150 μs
CY14B256K
Min Max
Industrial 15 ms
Figure 12. AutoStore/Power Up RECALL
Unit
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 19 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 20

CY14B256K
Software Controlled STORE/RECALL Cycles
t
RC
t
RC
t
SA
t
SCE
t
HA
t
STORE
/ t
RECALL
DATA VALID
DATA VALID
6#SSERDDA1#SSERDDA
HIGH IMPEDANCE
ADDRESS
CE
OE
DQ (DATA)
t
RC
t
RC
6#SSERDDA1#SSERDDA
ADDRESS
t
SA
t
SCE
t
HA
t
STORE
/ t
RECALL
DATA VALID
DATA VALID
HIGH IMPEDANCE
CE
OE
DQ (DATA)
Notes
20.The software sequence is clocked with CE
controlled or OE controlled READs.
21.The six consecutive addresses are read in the order listed in the Mode Selection on page 6. WE
is HIGH during all six consecutive cycles.
Parameter
t
RC
t
SA
t
CW
t
HA
t
RECALL
Alt.
Parameter
t
AVAV
t
AVEL
t
ELEH
t
EHAX
Description
STORE/RECALL Initiation Cycle Time 25 35 45 ns
Address Setup Time 0 0 0 ns
Clock Pulse Width 20 25 30 ns
Address Hold Time 1 1 1 ns
RECALL Duration 170 170 170 μs
[20, 21]
25 ns 35 ns 45 ns
Min Max Min Max Min Max
Unit
Figure 13. CE
Controlled Software STORE/RECALL Cycle
Figure 14. OE Controlled Software STORE/RECALL Cycle
[21]
[21]
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 20 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 21

CY14B256K
Hardware STORE Cycle
W
+/+;
W
6725(
W
+/%/
W
'(/$<
'$7$9$/,'
'$7$9$/,'
+,*+,03('$1&(
+,*+,03('$1&(
+6%,1
'4'$7$287
+6%287
W
3+6%
Notes
22.Read and Write cycles in progress before HSB
are given this amount of time to complete.
23.This is the amount of time it takes to take action on a soft sequence command. Vcc power must remain HIGH to effectively register command.
24.Commands such as STORE and RECALL lock out IO until operation is complete which further increases this time. See specific command.
Parameter
[22]
t
DELAY
t
PHSB
Alt.
Parameter
t
HLHX
Time Allowed to Complete SRAM Cycle 1 70 μs
Hardware STORE Pulse Width 15 ns
Soft Sequence Commands
Parameter Description
[23, 24]
t
SS
Soft Sequence Processing Time 70 μs
Description
Figure 15. Hardware STORE Cycle
Min Max
Figure 16. Soft Sequence Processing
CY14B256K
Min Max
CY14B256K
[23, 24]
Unit
Unit
W
66
W
&:
6RIW6HTXHQFH
&RPPDQG
W
&:
$GGUHVV
&(
9
&&
6RIW6HTXHQFH
&RPPDQG
$GGUHVV $GGUHVV $GGUHVV $GGUHVV
W
6$
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 21 of 28
W
66
[+] Feedback
Page 22

CY14B256K
RTC Characteristics
Notes
25.From either V
RTCcap
or V
RTCbat.
26.Typical = 3.0V during normal operation.
27.Typical = 2.4V during normal operation.
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
[25]
I
BAK
RTC Backup Current Commercial 300 nA
Industrial 350 nA
RTCbat
RTCcap
[26]
RTC Battery Pin Voltage 1.8 3.3 V
[27]
RTC Capacitor Pin Voltage 1.2 2.7 V
V
V
tOCS RTC Oscillator Time to StartAt Min Temperature from Power up or Enable 10 sec
At 25°C Temperature from Power up or Enable 5 sec
Truth Table For SRAM Operations
HSB should remain HIGH for SRAM Operations.
CE WE OE Inputs and Outputs Mode Power
H X X High Z Deselect/Power down Standby
L H L Data Out (DQ
L H H High Z Output Disabled Active
L L X Data in (DQ
–DQ7); Read Active
0
–DQ7); Write Active
0
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 22 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 23

CY14B256K
Part Numbering Nomenclature
CY 14 B 256 K - SP 25 X C T
Option:
T-Tape and Reel
Blank - Std.
Speed:
25 - 25 ns
45 - 45 ns
Data Bus:
K - x8 + RTC
Density:
256 - 256 Kb
Voltage:
B - 3.0V
Cypress
nvSRAM
14 - AutoStore + Software Store + Hardware Store
Package:
SP - 48-SSOP
35 - 35 ns
Temperature:
C - Commercial (0 to 70°C)
I - Industrial (–40 to 85°C)
Pb-Free
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 23 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 24

CY14B256K
Ordering Information
All the below mentioned parts are Pb-free. Contact your local Cypress sales representative for availability of these parts.
Speed
(ns)
25 CY14B256K-SP25XC 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Commercial
CY14B256K-SP25XCT
CY14B256K-SP25XI 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Industrial
CY14B256K-SP25XIT
35 CY14B256K-SP35XC 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Commercial
CY14B256K-SP35XCT
CY14B256K-SP35XI 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Industrial
CY14B256K-SP35XIT
45 CY14B256K-SP45XC 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Commercial
CY14B256K-SP45XCT
CY14B256K-SP45XI 51-85061 48-pin SSOP Industrial
CY14B256K-SP45XIT
Ordering Code
Package
Diagram
Package Type
Operating
Range
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 24 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 25

CY14B256K
Package Diagrams
51-85061-*C
Figure 17. 48-Pin Shrunk Small Outline Package (51-85061)
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 25 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 26

CY14B256K
Document History Page
Document Title: CY14B256K 256 Kbit (32K x 8) nvSRAM with Real Time Clock
Document Number: 001-06431
Rev. ECN Orig. of Change
** 425138 TUP See ECN New data sheet
*A 437321 TUP See ECN Show data sheet on external Web
*B 471966 TUP See ECN Changed V
*C 503277 PCI See ECN Changed from “Advance” to “Preliminary”
*D 597004 TUP See ECN Removed V
*E 69 6097 VKN See ECN Added footnote 7 related to HSB
*F 1349963 UHA/SFV See ECN Changed from Preliminary to Final
*G 2483006 GVCH/PYRS 05/05/08 Changed tolerance from +15%, -10% to +20%, -10%
Submission
Date
Description of Change
from 2.2V to 2.0V
Changed t
Changed Endurance from one million cycles to 500K cycles
IH(min)
from 60 μs to 100 μs
RECALL
Changed Data Retention from 100 years to 20 years
Added Soft Sequence Processing Time Waveform
Updated Part Numbering Nomenclature and Ordering Information
Added RTC Characteristics Table
Added RTC Recommended Component Configuration
Changed the term “Unlimited” to “Infinite”
Changed endurance from 500K cycles to 200K cycles
Device operation: Tolerance limit changed from +20% to +15% in
the
Features Section and Operating Range Table
Removed Icc1 values from the DC table for 25 ns and 35 ns
industrial grade
Changed V
Added temperature specifications to data retention - 20 years at
SWITCH(min)
from 2.55V to 2.45V
55°C
Updated Part Nomenclature Table and Ordering Information Table
CALL table
Changed t
Added t
Cycle table
DELAY(max)
Removed t
Changed t
Changed V
SWITCH(min)
specification from 20 ns to 1 ns
GLAX
specification
HLBL
specification from 70 μs(min) to 70 μs(max)
SS
CAP(max)
specification from AutoStore/Power Up RE-
specification of 70 μs in the Hardware STORE
from 57 μF to 120 μF
Added footnote 8 related to INT pin
Changed t
Removed ABE bit from Interrupt register
GLAX
to t
GHAX
Added Note 5 regarding the W bit in the Flag register
Updated Ordering Information Table
Changed Operating voltage range from 2.7V-3.45V to 2.7V-3.6V
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 26 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 27

CY14B256K
Document Title: CY14B256K 256 Kbit (32K x 8) nvSRAM with Real Time Clock
Document Number: 001-06431
Rev. ECN Orig. of Change
Submission
Date
*H 2663934 GVCH/PYRS 02/24/09 Updated Features section
Updated pin definition of WE
Updated “Reading the clock”, “Backup Power”, “Stopping and
starting the Oscillator” and “Alarm” descriptions under RTC
operation
Modified “Figure 4. RTC Recommended Component Configuration”
Added footnote 4
Added footnote 6
Added default values to RTC Register Map” table
Updated flag register description in Register Map Detail” table
Added Industrial specs for 25ns and 35ns speed
Changed V
Added “Data Retention and Endurance” table on page 15
from vcc+0.3 to Vcc+0.5
IH
Added thermal resistance values
Added alternate parameters in the AC switching characteristics
table
Renamed t
Changed t
Changed t
Renamed t
Renamed t
Renamed t
Updated Figure 16
to t
OH
OHA
HRECALL
RECALL
AS
GHAX
HLHX
from 20 to 40ms
spec from 100μs to 170μs (Including tss of 70us)
to t
SA
to t
to t
Added truth table for SRAM operations
Description of Change
pin
HA
PHSB
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Page 27 of 28
[+] Feedback
Page 28

CY14B256K
Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information
Worldwide Sales and Design Support
Cypress maintains a worldwide network of offices, solution centers, manufacturer’s representatives, and distributors. T o find the office
closest to you, visit us at cypress.com/sales.
Products
PSoC psoc.cypress.com
Clocks & Buffers clocks.cypress.com
Wireless wireless.cypress.com
Memories memory.cypress.com
Image Sensors image.cypress.com
PSoC Solutions
General p soc.cypress.com/solutions
Low Power/Low Voltage psoc.cypress.com/low-power
Precision Analog psoc.cypress.com/precision-analog
LCD Drive psoc.cypress.com/lcd-drive
CAN 2.0b psoc.cypress.com/can
USB psoc.cypress.com/usb
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006-2009. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used
for medical, life support, life sa vin g, critical control or safety applications, un l ess p ur sua nt to an express written agreement with C ypr ess. Fur th ermo r e, Cyp r ess d oe s no t a uth or iz e its products for use
as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress products in life-support
systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign),
United States co pyright la ws and inte rnatio na l tre aty prov isi ons. Cyp ress he reby g rant s to lice nsee a p erson al, no n-ex clusi ve, non-tra nsferable license to copy, use, modify, create derivative works of,
and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for the sole purpo se of creating custom sof tware and or firm ware in support of licen see product to be use d only in conjunction with a Cypress
integrated circuit as specified in th e applicable agreement. Any reproductio n, modification, translation, co mpilation, o r representati on of this Sour ce Code except as specified above is prohibited without
the express written permission of Cypress.
Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to make changes without further notice to the materials described herein. Cypress does not
assume any liability arising out of the ap plicati on or u se o f any pr oduct o r circui t descri bed h erein. Cypr ess does not aut horize it s product s for use a s critical compo nent s in life-support systems whe re
a malfunction or failure may reasonab ly be expected to resu lt in significant injury t o the user. The inclusion of Cypress’ prod uct in a life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer
assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement.
Document Number: 001-06431 Rev. *H Revised February 24, 2009 Page 28 of 28
All products and company names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of their respective holders.
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...