Page 1

Comparison between CY14B256L
Note
1. STK14C88-3 applications usually specify the use of 68 µF or 100 µF capacitors, which fall within the range of the CY14B256L device.
and STK14C88-3 nvSRAM
AN20639
Author: Shivendra Singh
Associated Project: No
Associated Part Family: CY14B256L and STK14C88-3
Associated Application Notes: None
Application Note Abstract
This application note compares the CY14B256L (0.25 μm) and the STK14C88-3 (0.8 μm) devices and presents the results.
Introduction
CY14B256L and STK14C88-3 are both 256K (32K x 8), 3V
nvSRAMs in two different technologies, 0.25 μm and 0.8 μm
respectively. These parts are functionally similar and can be
used in the same applications. However there are differences
in parameters, which should be considered when replacing
one part with the other.
The specifications in the data sheets of CY14B256L (0.25
μm) and STK14C88-3 (0.8 μm) are compared. Table 1 lists
the differences between these two devices. This comparison
Most applications use autostore and autorecall features of
nvSRAM. To simplify the comparison, all electrical parameters which may affect the application performance directly or
indirectly are considered. Designers must consider these differences, and if necessary do appropriate changes in their
design.
Only those specifications that differ between CY14B256L
(0.25 μm) and STK14C88-3 (0.8 μm) nvSRAM are listed in
Table 1. These specifications may cause functional issues
when replacing one part with the other.
is not intended to be comprehensive, because there are subtle differences that are not relevant in most applications.
Table 1. Comparison Table
Specification CY14B256L (35 nsec) STK14C88-3 (35 nsec)
Endurance 200,000 cycles 1,000,000 cycles
Retention 20 year 100 year
DC Electrical Characteristics
Vcc 2.7V min 3.6V max 3.0V min 3.6V max
Icc1 55 mA max 52 mA max
Icc3 10 mA max 9 mA max
Icc4 3 mA max 2 mA max
V
IH
[1]
Vcap
C
in
AC Switching Characteristics
t
OHA
t
LZCE
t
LZWE
2.0V min Vcc + 0.3V max 2.2V min Vcc + 0.5V max
17 µF min 120 µF max 68 µF min 220 µF max
7 pF max 5 pF max
3 ns min 5 ns min
3 ns min 5 ns min
3 ns min 5 ns min
November 11, 2008 Document No. 001-20639 Rev. *C 1
[+] Feedback
Page 2
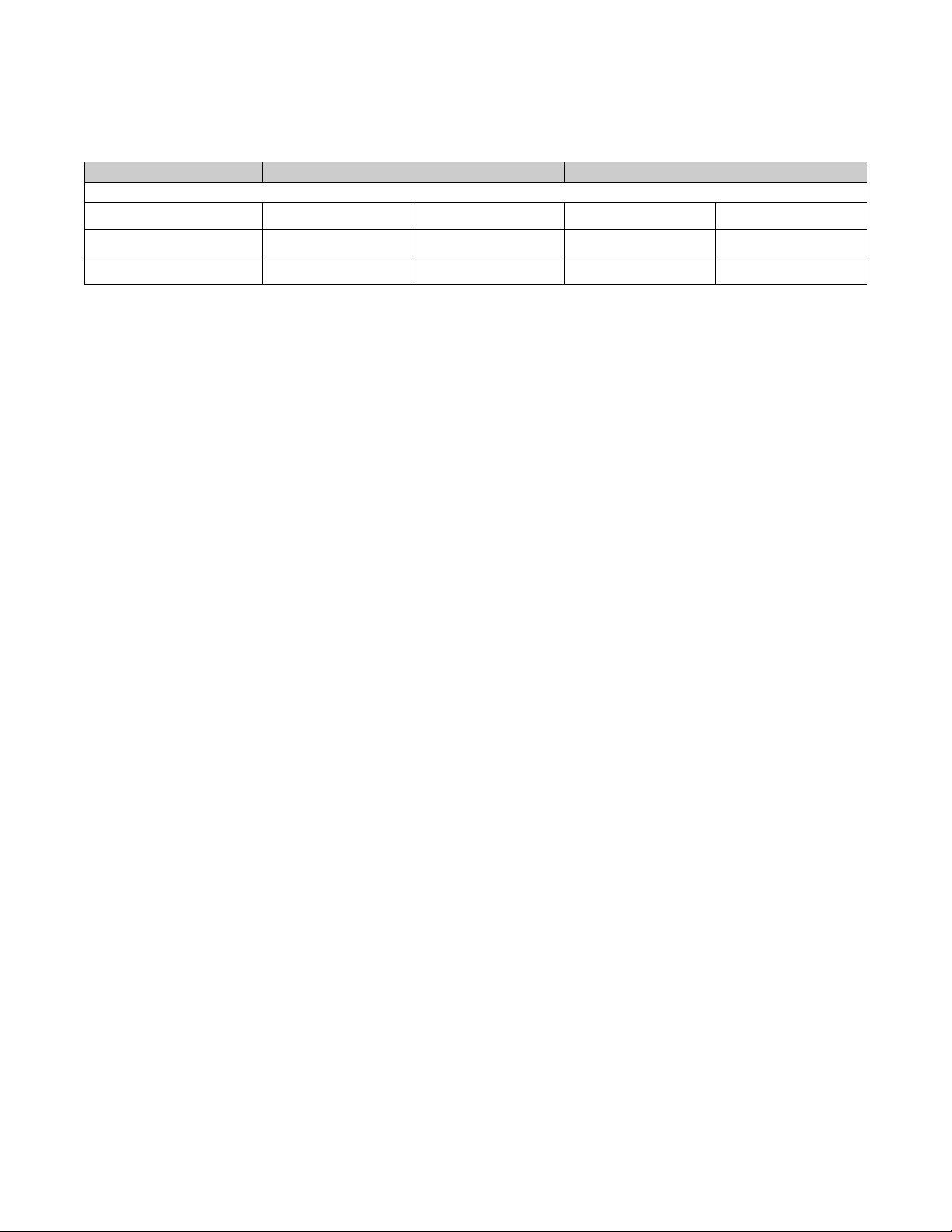
Table 1. Comparison Table (continued)
Notes
2. The power up recall specification is the most dra matic differ ence between the two devices. To accommodat e the much slower specification of the CY14B256L
device, system timing modifications may be required.
3. Store timing differences are not an issue because it occurs as a background operation when the system is powering down.
4. Even though there are small differences here they are unlikely to cause system level problems.
Specification CY14B256L (35 nsec) STK14C88-3 (35 nsec)
Auto Store/Power Up Recall
[3]
[4]
[2]
20 ms max 550 µs max
12.5 ms max 10 ms max
No minimum 2.65V max 2.7V min 2.95V max
t
HRECALL
t
STORE
V
SWITCH
Summary
In most applications you can directly substitute the CY14B256L for the STK14C88-3 nvSRAM.
AN20639
November 11, 2008 Document No. 001-20639 Rev. *C 2
[+] Feedback
Page 3

Document History Page
Document Title: Comparison between CY14B256L and STK14C88-3 nvSRAM
Document Number: 001-20639
Revision ECN No.
Change
** 1410463 ZSK 08/23/07 New application note
*A 1639723 ZSK 10/16/07 Changed title
*B 1758963 ZSK 11/19/07 Minor change
*C 2610582 NXR 11/20/08 Changed title. Updated content to reflect change in part number
Orig. of
Submission
Date Description of Change
AN20639
All trademarks or registered trad emarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners
Cypress Semiconductor
198 Champion Court
San Jose, CA 95134-1709
Phone: 408-943-2600
Fax: 408-943-4730
http://www.cypress.com
© Cypress Semiconductor Corpo ration, 2007-2008. The information contained he rein is subject to change without noti ce. Cypress Semiconductor
Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any
license under patent or other rights. Cypres s products a re not warr anted nor intended t o be use d for medic al, life s upport, li fe saving , critical contr ol or
safety applications, unless pursuant to an ex press written agre ement with Cypres s. Furthermore, Cy press does not au thorize its products for use as critical
components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of
Cypress products in life-support sy stems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all ris k of such use and in doing so i ndemnifies Cypress
against all charges.
This Source Code (software and/or firmware ) is owned by Cypr ess Semicon ductor Co rporati on (Cypres s) and is protec ted by and subject to worldwide
patent protection (United States and foreign), United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Cypress hereby grants to licensee a personal,
non-exclusive, non-transferable license to copy, use, modify, create derivative works of, and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for
the sole purpose of creating custom software and or firmware in support of licensee product to be used only in conjunction with a Cypress integrat ed circuit
as specified in the applicable agreement. Any reproduction, modification, translation, compilation, or representation of this Source Code except as specified
above is prohibited without the ex press written permission of Cypress.
Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING , BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to
make changes without further notice to the materials described herein. Cypress does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit described herein. Cypress does not authorize its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or
failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress' product in a life-support systems application implies
that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress aga inst all charges.
Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement.
November 11, 2008 Document No. 001-20639 Rev. *C 3
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...