Page 1

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter
User’s Manual
Version 1.0
June 26, 2003
Page 2

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user
is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment and should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between
the radiator & your body.
CE Marking Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
2
Page 3

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION................................................................................. 5
THE WIRELESS ETHERNET ADAPTER FEATURES ............................................................... 5
PACKAGE CONTENTS ........................................................................................................... 6
2.HARDWARE INSTALLATION.................................................. 7
PHYSICAL DETAILS .............................................................................................................. 7
HARDWARE INSTALLATION................................................................................................ 10
CONNECTING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER TO YOUR NETWORK......................................... 11
3. WIRELESS NAVIGATOR INSTALLATION......... 13
INSTALL THE WIRELESS NAV I G A TO R ................................................................................ 13
STARTUP AND LOGIN.......................................................................................................... 17
4. CONFIGURING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER.20
THE INFO TAB .................................................................................................................... 20
THE WIRELESS TAB ........................................................................................................... 21
THE SERVER TAB ............................................................................................................... 23
THE ADMIN TAB................................................................................................................. 23
THE HELP TAB ................................................................................錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
5. FIRMWARE UPGRADE PROCEDURE..................... 25
6. FAQ & TROUBLESHOOTING.............................................. 27
7. GLOSSARY..................................................................................................... 29
8. PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS............................................... 31
3
Page 4

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
About this manual
This user’s manual describes how to install and operate the Wireless Ethernet Adapter
(Adapter). Please read this manual before you install the product.
This manual includes the following topics:
Product description, features and specifications
Hardware installation procedures
Software installation procedures
Trouble shooting procedures
4
Page 5

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the WS300 Wireless Ethernet Adapter. This Ethernet adapter
provides you with an innovative wireless networking solution. The WS300 is easy to set up
and use. With this innovative wireless technology, you can share files and network
resources on the network—without inconvenient wires!
The Wireless Ethernet Adapter Features
LAN Features
DHCP Client – Enable the adapter to act as a DHCP client to receive IP address from
DHCP Server in the wired Ethernet LAN.
Built-in 10BaseT LAN Port – It’s designed to connect the adapter with any
Ethernet-ready devices, such as desktop PC,printer server and network
printer/scanner.
Wireless Features
Standard Compliant – The adapter complies with IEEE802.11b standard, and it is
interoperable with IEEE802.11b-Compliant Equipment
Data Rate Auto Fall-Back - Provides 11, 5.5, 2 and 1Mbps wireless data rate shifting
dynamically to guarantee availability and reliability of wireless connections
Roaming – Provides seamless roaming within 802.11b wireless LAN infrastructure.
Long Distance Reach – Support 80M indoor and 300M outdoors long operating
distance under normal environment condition.
Configuration & Management
Easy to Setup – With windows-based Wireless Navigator Utility, user can easily setup
the IP address of this adapter, and upgrade the firmware.
Easy to manage – User can use any WEB browser from anywhere on the wired or
wireless LAN to configure the adapter easily.
Security
Configuring Protection – Provides password protection to prevent unauthorized users
from changing the configuration
Wireless LAN Security - Provide 64-bit & 128-bit Wired Equivalent Privacy encryption
to protect the wireless data transmissions.
5
Page 6

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Package Contents
One 11Mbps Wireless Ethernet adapter with dipole antenna connected
One CD-ROM (Wireless Navigator utility software & user’s manual included)
One RJ-45 straight LAN Cable
One Power Adapter
One Quick Installation Guide
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
6
Page 7

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
2.Hardware Installation
Physical Details
Rear Panel
INIT Button
LAN Cable
Selection Switch
LAN Connection
Power Input
INIT Button “INIT” mean “Initiation”. While pressing the button, the adapter will
reboot and reset current settings to factory default settings. The left
indicator “DIAG” on adapter will be off and then begin blinking.
Then this initiation action will be completed when the indicator
“ DIAG” is always green instead of blinking.
LAN Cable
Selection Switch
Crossover: the RJ-45 port Tx and Rx lines are
X
reversed. Use this setting when you use the supplied
straight cable connected to PC. It is also the factory
default setting.
II
Straight: the RJ-45 port Tx and Rx lines are normal.
Use this setting when you have the supplied straight
cable connected to Hub/switch
Power Input Only use the power adapter supplied with the Ethernet adapter
LAN Connection Use standard Ethernet cable (RJ-45 connector) to connect your
PC, hub/switch or broadband router/modem to this port.
7
Page 8
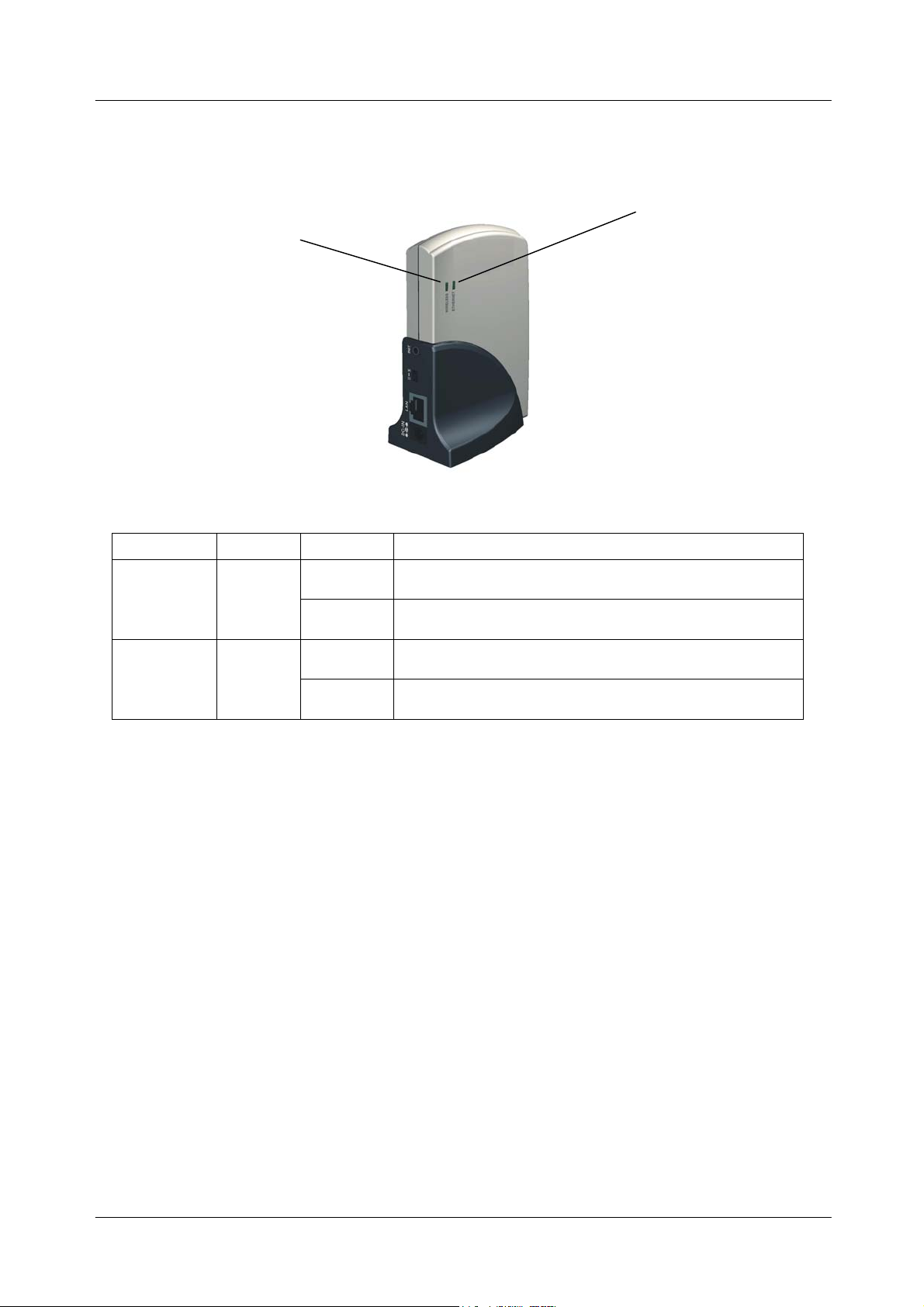
11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
LED Indications
Wireless
Ethernet
LED Color Status Description
Ethernet
Wireless
Green
Green
ON The Access Point power on
OFF The Access Point power off
OFF No data forwarding between wireless and LAN ports.
Blinking Sending or Receiving data via wireless
8
Page 9

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
9
Page 10
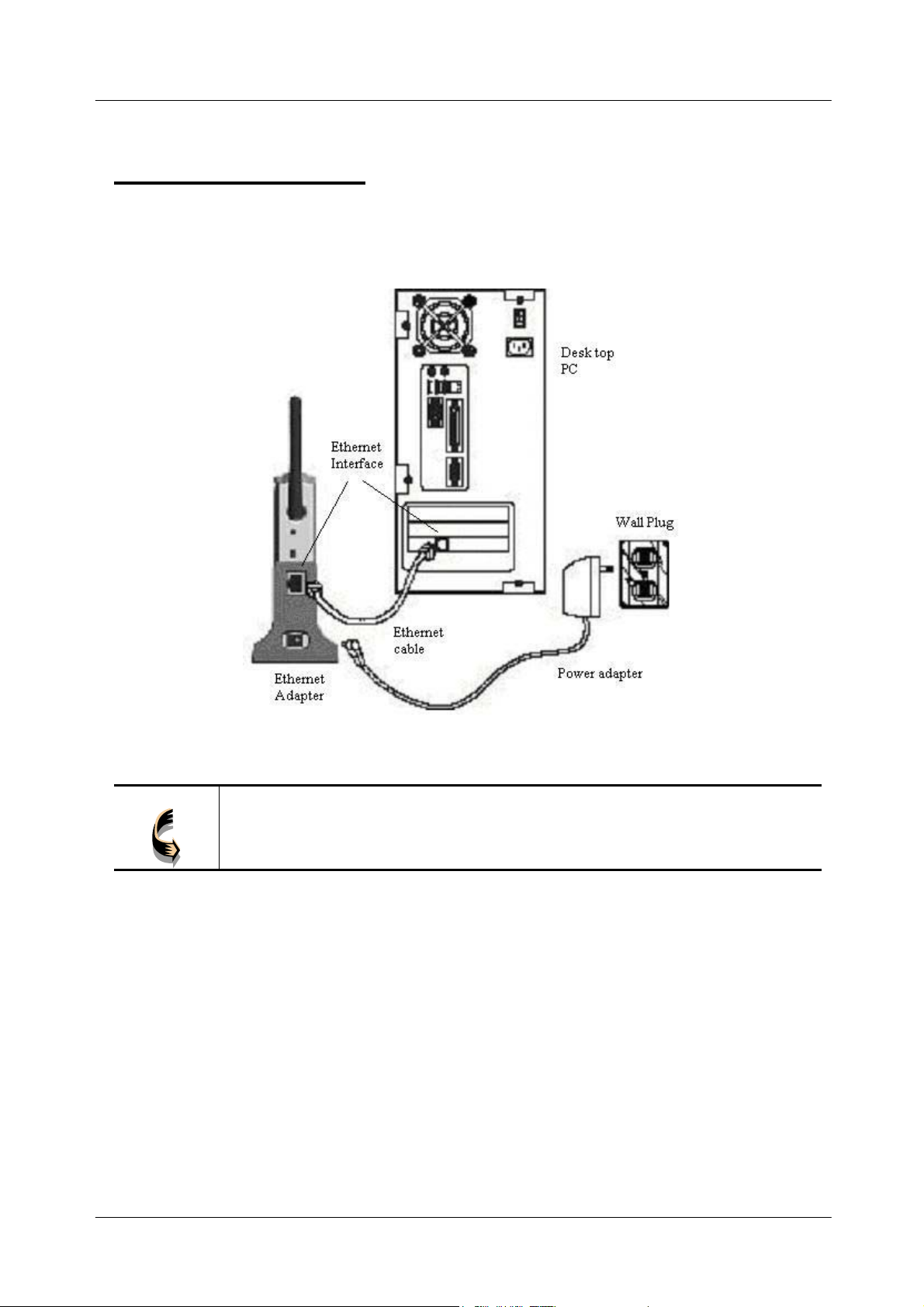
11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Hardware Installation
Following illustration is an example showing how to install adapter with your PC.
Be sure to use the supplied power adapter.
Note!
You may also connect the adapter to other Ethernet-ready device, such as printer
server.
10
Page 11
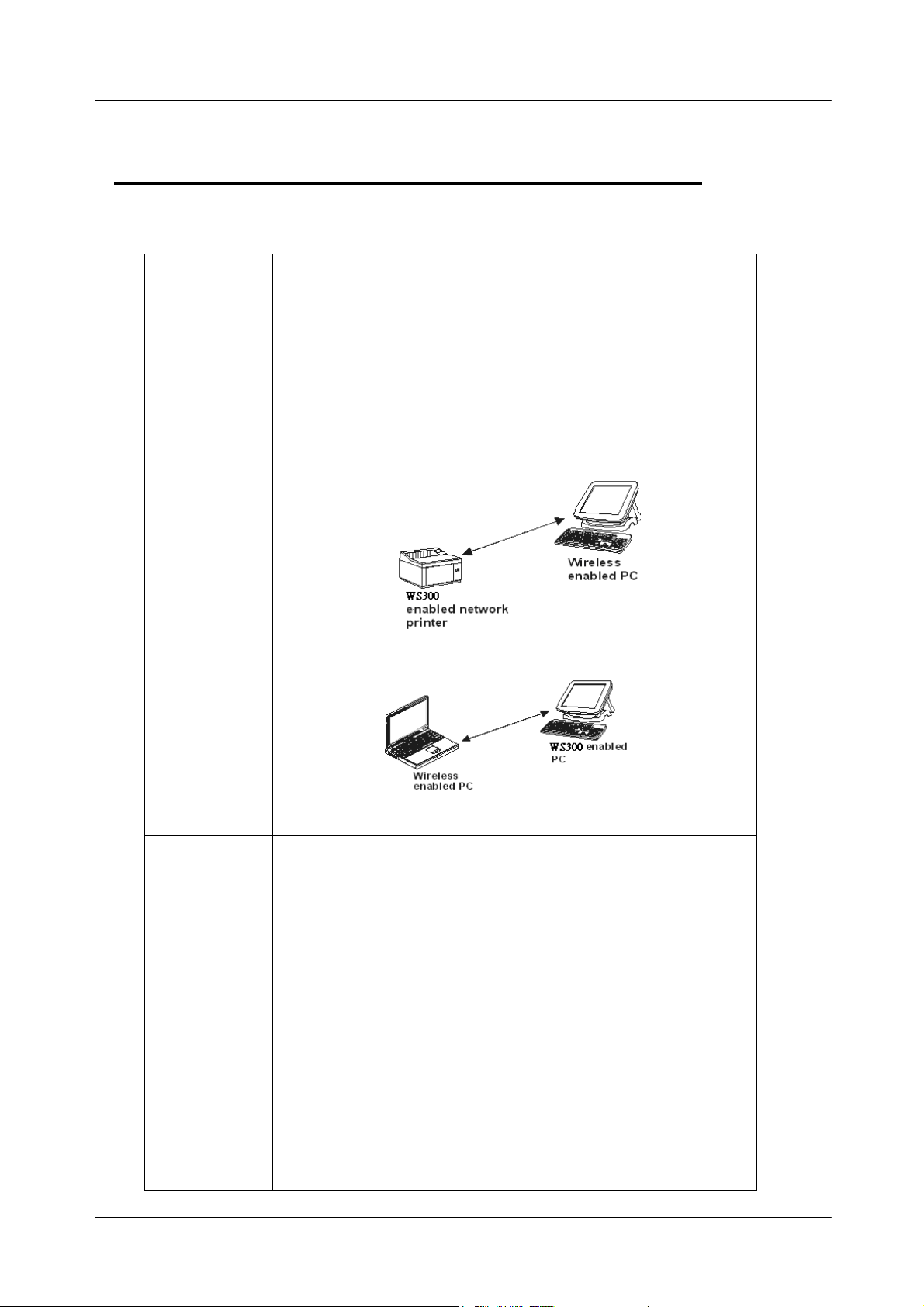
11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
g
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter to Your Network
There are two network scenarios as below:
Ad-hoc
Networking
Also known as a peer-to-peer network, an ad-hoc network is
one that allows all workstations and computers in the network
to act as servers to all other users on the network.
Users on the network can share files, print to a shared printer,
and access the Internet with a shared modem. However, with
ad-hoc networking, users can only communicate with other
wireless LAN computers that are in the same wireless LAN
workgroup, and are within range.
<PC to Network Printer>
Infrastructure
Networking
<PC to PC >
Infrastructure networking differs from ad-hoc networking in
that it includes an access point. Unlike the ad-hoc structure
where users on the LAN contend the shared bandwidth, on
an infrastructure network, the access point can manage the
bandwidth to maximize bandwidth utilization.
Additionally, the access point enables users on a wireless
LAN to access an existing wired network, allowing wireless
users to take advantage of the wired networks resources,
such as Internet, email, file transfer, and printer sharing.
Infrastructure networking has the following advantages over
ad-hoc networking:
Extended range: each wireless LAN computer within the
range of the access point can communicate with other
wireless LAN computers within range of the access point.
Roamin
: the access point enables a wireless LAN computer
11
Page 12
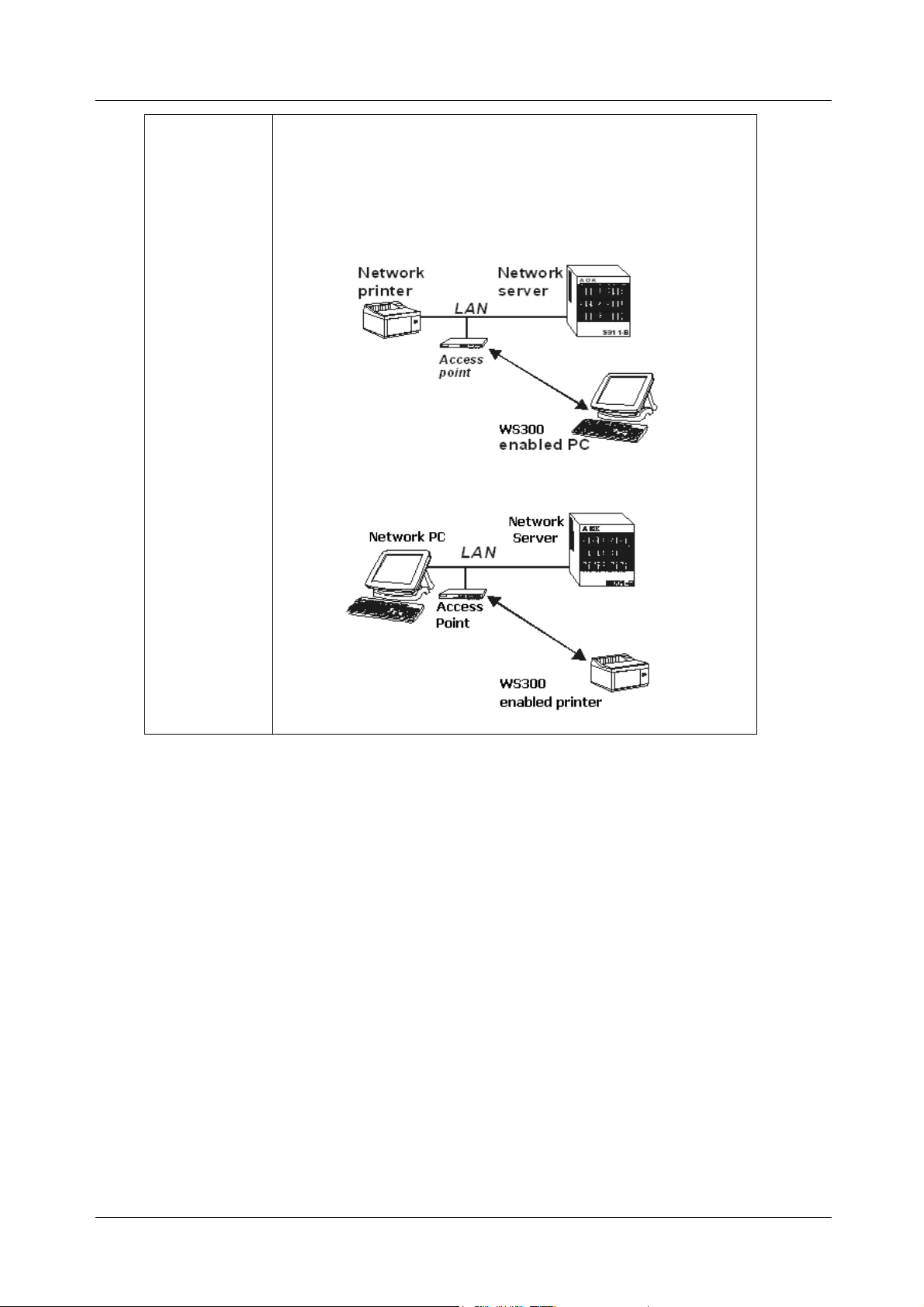
11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
to move through a building and still be connected to the LAN.
Wired to wireless LAN connectivity: the access point
bridges the gap between wireless LANs and their wired
counterparts.
<PC to LAN>
<Printer to LAN>
In the next charter, you will be guided to how to connect the adapter to wireless LAN
12
Page 13

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
3. Wireless Navigator Installation
Install the Wireless Navigator
The Wireless Navigator Utility is provided to allow user easily to configure the adapter
through any Windows-based PC. This section describes procedures for installing the
Wireless Navigator Utility to PC.
Note!
Please make sure that your PC already has TCP/IP protocol installed. If not, please
contact your administrator for details if you have problems of setting up this TCP/IP
protocol in your PC.
Note!
Step 1: Insert the installation CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. Run SETUP.EXE program
on the CD-ROM. The following window will be shown automatically.
Even your adapter is not connected with PC, but other Ethernet device, such as
printer server. You still can install the Wireless Navigator in any PC located in the
same IP subnet with the adapter. This utility can search the adapter via both wired
and wireless Ethernet so that you still manage the adapter remotely.
13
Page 14

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Step 2: After InstallShield Wizard preparation finished, the following window will be shown.
Click the Next button to continue.
Step 3: Key in your User Name and Company Name, and click Next button to continue.
Step 4: The screen will show you the default destination chosen by the utility. If you want to
install the Wireless Navigator in another location, click the Browse button and select
an alternate destination. Click the Next button, when you are ready to continue. The
14
Page 15

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
setup program will then begin to install the programs into the destination folder.
Step 5: The screen will show you the Program Folder that the utility will use. You may type
a new folder name to create a new program folder, or select one from the existing
folder list, and click Next button to continue.
Step 6: The Wireless Navigator has been installed now. Please click the Finish button to
complete installation.
15
Page 16

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Note!
To remove Wireless Navigator Utility, click the Start button, and select Programs,
Wireless Navigator, and Uninstall, and then follow the instruction on screen.
16
Page 17

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Startup and Login
Follow the procedures below to startup Wireless Navigator and connect to the adapter.
Before you start the following procedures, please be sure that all the cables are well
connected between PC and adapter, and your wireless LAN network is working. The utility
will automatically search the adapter connected with the PC
1. Refer to previous section " Install the Wireless Navigator to your PC" in order to
startup the configuration.
2. Click Start and select Programs, Wireless Navigator and then Wireless Navigator. Or,
just double-click the Wireless Navigator icon on your desktop screen.
3. The Wireless Navigator starts up, and searches the adapter.
17
Page 18

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
4. The utility will show the adapter found and other wireless devices found in the same
network, where your PC is located.
Note!
If the adapter is not shown in the list, please make sure all the cables are well
connected.
5. Double-click on the adapter, then you will access into its built-in web server, and it will
show as below. Then directly click OK button. (Default user name is “root” and
password is “admin”).
Note!
If you cannot access into adapter’s built-in web server, please make sure if
your PC now is in the same subnet with adapter. Please use right-click of
mouse to click on the adapter listed in Wireless Navigator. “Set IP address”
option will pop out, and then change IP address of AP to the same subnet as
your PC.
18
Page 19

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
6. Now you have entered the built-in web server of this adapter, and you can start
configuration procedures described in the next character.
19
Page 20

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
4. Configuring the Ethernet Adapter
The Info Tab
(Connected with wireless LAN)
SSID: displays current SSID this
adapter uses.
If the adapter found no AP or any
other ad-hoc device, then SSID will
show “non-spec” . Please make
sure that your wireless LAN is
working properly under the effective
reach range of the adapter
Channel: displays the channel that
the adapter uses now.
BSSID: displays MAC address of the
AP that the adapter is connecting
with.
Transmission Rate: the transfer
data rate that the adapter is using in
wireless LAN
Link Quality (%): displays the
wireless LAN connection integrity
when connected to an AP.
MAC address: displays the unique
serial number burned into the
adapter that identifies itself from
other Ethernet devices.
IP address: displays the adapter’s
current IP address assigned by AP
or router.
Firmware Version: displays the
adapter’s current firmware version
Wireless Version: displays the
wireless module firmware version
20
Page 21

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
The Wireless Tab
Wireless Mode: lets you select the
network scenarios, either Ad-Hoc or
Infrastructure. Default setting is
“Infrastructure”
SSID: lets you set the Service Set
Identifications:
Default SSID is “Any”. When set to
any, the adapter is allowed access to
any nearby AP.
Channel: enables you to select a
transmission channel.
Transmission Rate: displays a list
of transfer rates.
AP density: enables you to set the
relative number of access points
near the WS300. Use this setting to
reduce channel overlap and
interference:
• Low: 1-2 nearby APs
• Medium: 3-4 nearby APs
• High: 5 or more nearby APs
When connected in an infrastructure
or ad-hoc mode, a list of nearby APs
or peers is displayed at the bottom of
the Info screen. When you re-load
the web page, the list will be
updated.
WEP enabled: Allows you to enable
or disable Wired Equivalency Privacy
(WEP) for encryption, with either 64or 128-bit encryption.
WEP key length: Enables you to
choose either a 64- or 128-bit
encryption scheme. Be sure that
the adapter’s WEP key must be the
same as the AP’s, otherwise adapter
still can not communicate with
wireless LAN.
Note: Some APs do not support 128-bit
encryption
21
Page 22

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
The Wireless Tab (Continued)
WEP key 1 ~ 4: Enables you to
create an encryption scheme for
Wireless LAN transmissions.
Manually enter a set of values for
each key.
For 64-bit WEP encryption, a key of
10 hexadecimal characters in length
must be filled in.
For 128-bit WEP encryption, a key of
26 hexadecimal characters in length
must be filled in.. Be sure that the
key in the AP shall be the same as in
adapter, otherwise the
communication will not work.
Note: 128-bit encryption requires
more system resources than 64-bit
encryption. Use 64-bit encryption for
better performance.
Note!
WEP key to use: sets which WEP
key (1 ~ 4) to use when sending
data. To connect to a Wi-Fi
compliant wireless device, key #1
must be selected.
Note: The receiver must use the same
key.
You may need to reboot the adapter, and then re-load the page to see
any new settings.
22
Page 23

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
The Server Tab
IP Address Mode: Select “Static” or
“DHCP” mode. For “Static” mode,
the IP address settings are given by
user. For “DHCP” mode, IP settings
will be overridden by a DHCP server
on your network. The default setting
is “Static”
IP Address: The static IP address
you may assign to the adapter. The
default value is “192.168.1.200
Subnet Mask: The subnet mask you
want to assign for the adapter. The
default value is “255.255.255.0
Gateway: The gateway you want to
assign for the adapter. The default
value is “192.168.1.1
Device Name: optional device name
setting
Allow upgrade : Check the box, and
then it is allowed to upgrade
firmware.
Cloning Bridge
”.
”.
”.
Note!
You may need to reboot the adapter, and then re-load the page to see
any new settings.
The Stations Tab
The bridge table: display the stations
IP address and Mac address
23
Page 24

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
The Admin Tab
Note!
User Name: Default user name is
none.
Password: Default password is none.
For security concerns, please change
it after finish the configuration.
Reboot Bridge: When any setting
was changed, the adapter MUST be
reboot so that the change can be
confirmed.
Reset to defaults: This option will
ERASE all the current settings, and
restore to the factory default settings.
You may need to reboot the adapter, and then re-load the page to see
any new settings.
24
Page 25

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
5. Firmware Upgrade Procedure
1. Click Start and select Programs, Wireless Navigator and then Wireless Navigator.
Or, just double-click the Wireless Navigator icon on your desktop screen.
2. The Wireless Navigator starts up.
3. The utility starts searching for the adapter and APs. Choose the adapter that you would
like to upgrade the firmware, and use the right-click of the mouse to enter the “Upgrade
FW” option
25
Page 26

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
4. The download will begin. Key in the new firmware file name and location or click
browsing to find the file in your computer.
5. After entering the file information, click OK to continue.
6. The downloading begins.
7. After download finished, the adapter will reset automatically, and the left indicator
“DIAG” on AP will be off and then begin flashing. When the indicator “ DIAG” is always
off again, the firmware upgrade is completed and successfully.
26
Page 27

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
6. FAQ & Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems usually encountered during the installation and
operation of the Wireless Access Point. Please refer to the following descriptions to solve
the problems. If you can’t find an answer here, please contact your dealer for further
advices.
Q1: My PC can’t locate the Wireless Ethernet adapter. How to check the
problem?
A: Please follow the procedures below:
Check if the Ethernet cable is well connected.
Check if the IP addresses of your PC and Wireless Ethernet adapter both are on
the same IP network. If not, you may use Wireless Navigator to set up adapter’s
IP address, or change your PC’s IP address.
Q2: My adapter cannot communicate with Wireless Access Point. How to
check the problem?
A: Please follow the procedures below:
Check if you can use Wireless Navigator utility to access to the adapter first. If not,
please go through the procedure of Q1.
Check if the adapter is set to Infrastructure correctly.
Check if the SSID of your adapter is the same as AP’s. If not, please set it the
same as the SSID of AP’s.
Check if the WEP is enabled either in your adapter or access point. If yes, please
make sure that your adapter and the Wireless Access Point both have the same
setting for WEP, such as the key tables must match.
At last, please check if radio interference is causing a problem; see if connection
is possible when close to the Wireless Access Point. Remember that the
connection range can be as short as 100 feet in poor environment.
Q3: The Wireless connection speed is very slow. How to improve the
problem?
A: The wireless system will connect at the highest possible speed, depending on the
distance and the environment condition. To obtain the highest possible connection speed,
you have to try to adjust the Ethernet adapter’s location and its antenna’s direction. If you
find the interference is the problem, changing to another channel may show the
improvement.
27
Page 28

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Q4: Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless
network?
A: This will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a network.
Consult the application’s user guide to determine if it supports operation over a network.
Q5: Can I play computer games with other members of the wireless network?
A: Yes, as long as the game supports multiple players over a LAN (local area network).
Refer to the game’s user guide for more information.
Q6: What is the IEEE 802.11b standard?
A: The IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating a
standard for the industry. The objective is to enable wireless LAN hardware from different
manufacturers to communicate.
Q7: What’s Ad-hoc?
A: An Ad-hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected
as an independent wireless LAN. Ad-hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a departmental scale
for a branch or SOHO operation.
Q8: What is Infrastructure?
A: An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration.
Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central database, or
wireless application for mobile workers.
Q9: What is Roaming?
A: Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while
moving freely throughout an area greater than that covered by a single Wireless Network
Access Point. Before using the roaming function, the workstation must make sure that it is
the same SSID with the Wireless Access Point of dedicated coverage area.
Q10: What is Spread Spectrum?
A: Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the
military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed
to trade off bandwidth efficiency for reliability, integrity, and security. In the other words,
more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of narrowband transmission, but the trade off
produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the
receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a receiver
28
Page 29

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
is not turned to the right frequency, a spread-spectrum signal looks like background noise.
There are two main alternatives, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency
Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).
Q11: What is WEP?
A: WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit or 128-bit
as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
7. Glossary
This section explains the glossary of terms used in this manual that are required to
configure the network
.
Wireless Channel
If there is more than one Wireless LAN network with different ESS-ID on the same floor,
and they are communicating with each other, the baud rate may be slowed, due to the
same radio frequency being used. If this happens, you can still communicate regardless of
other LAN networks by using to use different frequencies (wireless channels).
Note: If they are communications using the wireless LAN, be sure to set all the Units the
same wireless channel.
DHCP Server
When configuring the network TCP/IP, be sure to set the IP address in each personal
computer and other devices. When there is a DHCP server on the network, it can assign IP
addresses automatically to the personal computers and the Access Point on the network.
For the Windows NT server and dial-up router, or other DHCP server function, refer to the
Windows 2000, Windows NT, or dial-up router manual, or consult the manufacturer.
ESS-ID
This ID is used to prevent cross-communication during communication between the Access
Point and personal computers within the wireless LAN. The Wireless LAN personal
computers that have the same ESS-ID as the Access Point can communicate with the
Access Point. The ESS-ID is case sensitive. You can enter a maximum of 32 alphanumeric
characters, and the underline "_".
LAN (Local Area Network)
Read as one word. A LAN is a network in a comparatively small area, such as campus or
29
Page 30

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
within a single building. The LAN baud rate varies from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
MAC Address (Media Access Control Address)
The MAC address is a physical address specific to each network card. The MAC address is
configured from a total of six bytes as follows: A vendor code comprising the lead three
bytes and a 3-byte user code. The vendor code is managed and assigned by IEEE. The
user code is managed using a unique (unduplicated) number from the network card
manufacturer. That is, the MAC address is assigned as a physical address unique
throughout the world. In an Ethernet LAN, the MAC address is used as a base to create a
frame for sending and receiving.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP is a protocol equivalent to the network and transport levels of the OSI reference
model, and it is defined using RFC. Consequently, different terminals can communicate with
each other using TCP/IP.
• Normally, TCP/IP includes the application protocols TELNET and FTP.
• TCP/IP is the standard Internet protocol.
WEP (Encryption)
By setting an encryption key in the Access Point, you can prevent wireless packets from
being decrypted externally.
Firmware
Firmware is the name given to the software (programs) built into hardware such as the
router, modem, and terminal adapter. This software is built into the hardware, so it can be
said to be in-between hardware and software.
Protocol
Protocols are the procedures and regulations for sending and receiving data between the
network terminals. For example, if two computers are communicating, you can send the
correct information according to the regulations by formatting all required information. The
protocol such as which terminal sends first, what type of message, what type of message
the receiving terminal should send in reply, the data format, and responses to
communications errors are same of examples.
Roaming Function
Using the roaming function and moving from one room to another room, you can switch the
Access Point automatically. With the roaming function, you can easily move from the office
30
Page 31

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
to the conference room while maintaining access to the network.
8. Product Specifications
This chapter describes the specifications of the product and the LAN port connector.
Wireless LAN Interface
Standards
IEEE 802.11/11b Compliant
Antenna
Built-in chip Antenna
Frequency Range
2.4〜2.4835GHz ( Industrial Scientific Medical Band )
DSSS - Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Data Transmission Rate
11Mbps / 5.5Mbps / 2Mbps / 1Mbps Auto Fall-Back
Access Mode
Infrastructure mode
Ad-hoc mode
Data Security
Provides both 64-bit & 128-bit WEP Encryption
Output Power
15 ~16.5 dBm
Receiving Sensitivity
-82dBm Min.
31
Page 32

11Mbps Wireless Ethernet Adapter User's Manual
Roaming
IEEE 802.11 Compliant
Channels
11 Channels (US, Canada)
13 Channels (Europe)
14 Channels (Japen)
Coverage Area
Indoors: up to 50M (165 ft.) @11Mbps
up to 80M (265 ft.) @5.5 Mbps or lower
Outdoors: up to 150M (500 ft.) @11 Mbps
up to 300M (1000 ft.) @5.5 Mbps or lower
(Depending on environment)
Operating Environment
Operating Temperature: 0oC to 50oC degree
Storage Temperature: –25
Humidity 10% to 90% non-condensing
o
C to 70oC degree
32
Page 33

802.11b Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Product Specification
WS310-A
Revision 1.0
Revision History
Date Version Author Remark
04/30/2003 0.8 Nathan Yen
06/26/2003 1.0 Lena Hsiao
Formal release
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 1/7
Page 34

Introduction
The WS310-A is a compact wireless Ethernet client bridge,
tailor-made for home and SOHO users in order to utilize the
advantage of wire-free connectivity. This device simply and
efficiently transmits the traffic between 10M Ethernet and 11M
WLAN. It can easily bring the Ethernet-ready network devices,
such as network printer/scanner/copier, desktop and notebook, into
wireless LAN network without any inconvenient cable wiring
efforts.
Major Features
Adopt Agere HermesII WLAN chipsets, which are well-proven
solution in the market today.
Uses 2.4GHz ISM band, which fully complies with IEEE
802.11b
Low interference & high susceptibility guarantee reliable
performance.
Dynamically shifts between 11, 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps network
speed, based on signal strength, for maximum availability and
reliability of connection.
Equipped with one standard 10Base-T interface for connecting
with Ethernet-ready networked resources, such as PC and
printer/scanner.
Ensures great security by providing the 64-bit and 128-bit WEP
(Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption defined in the IEEE
802.11b standard.
No driver is needed, neutral to any PC’s OS.
For bridging one client, it supports transparent bridging.
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 2/7
Page 35

For multiple-client bridging, will support only with TCP/IP
protocol.
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 3/7
Page 36

Benefits
Make Ethernet-ready peripheral wireless, such as network
printer/scanner/copier in office, and web camera, and X-Box at
home.
An alternative to enable non-Windows PC and server wireless,
such as Linux PC/server and Mac.
Convenient wireless network extension solution to bridge
multiple Ethernet-ready peripherals or PCs from the corner of
office.
Specifications
PHYSICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Housing
Stand type with no screw design
(Depending on customization)
Ethernet Interface
Antenna
LED Display
Crossover
Selection
Initiate button
Power adapter
Dimensions (mm)
WLAN Standards
Media Access
Protocol
Frequency
10Base-T (RJ-45) interface
Internal chip Antenna
Two LEDs indicating the status of Ethernet and Wireless
To connect to PC or Ethernet-ready devices
Restore all settings to factory default settings
Input: 5V DC, 1A
70.44 x 23 (44.48 with flat stand) x 108.54
(Depending on customization)
RADIO SPECIFICATIONS
IEEE802.11/11b Industry Standards
IEEE802.11
Industrial Scientific Medical Band,
World: 2.400GHz〜2.484GHz
Japan: 2.400GHz~2.484GHz plus 2.471GHz~2.487GHz
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 4/7
Page 37

Operating
Channels
Data Rate Shifting
Modulation
Technique
Bit Error Rate
Transmit Power
Max Receiver
Sensitivity
Coverage Area
Security
Configuration
Utility (Wireless
Navigator)
11 Channels (USA, Canada)
13 Channels (Europe)
14 Channels (Japan)
11Mbps / 5.5Mbps / 2Mbps / 1Mbps
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS), BPSK / QPSK /
CCK
1E-5 @ -82dBm
15 dBm ± 2dBm
82 dBm @ 11Mbps
-
-85 dBm @ 5.5Mbps
-88 dBm @ 2Mbps
- 91 dBm @ 1Mbps
Indoor: 50M @11Mbps , 80M @5.5Mbps or lower
Outdoor: 150M @ 11Mbps , 300M @ 5.5Mbps or lower
64-bit & 128-bit WEP Encryption
FIRMWARE/SOFTWARE SPECIFICATIONS
Support Windows 95/98/Me/NT 4.0/2000 and Windows XP
Management
Built-in Web-based management
1. Indicate current WLAN connection status
2. Configure Infrastructure/Adhoc, SSID, Channel, security
settings, Site Survey and etc.
3. MAC cloning to enable on-line TV gaming, such as X-box
and PS2
Firmware Upgrade
TFTP, or by Configuration Utility
TFTP, ARP, IP, UDP, ICMP, TCP, DHCP client, HTTP for
Protocols
firmware upgrade and web-based management,
ENVIRONMENTAL
o
C to 50oC degree
o
C to 70oC degree
Temperature
Relative humidity
Operating Temperature: 0
Storage Temperature: –25
10% to 90% non-condensing
OTHERS
Warranty
1 year
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 5/7
Page 38

Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 6/7
Page 39

Application Diagram
Cybertan, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Page 7/7
 Loading...
Loading...