
VoIP V2 Paging Server
The IP Endpoint Company
Operations Guide
SIP Compliant
Part #011092
Document Part #930367H
for Firmware Version 6.2.0
CyberData Corporation
3 Justin Court
Monterey, CA 93940
(831) 373-2601

Operations Guide 930367H
Technical Support
The fastest way to get technical support for your VoIP product is to
submit a VoIP Technical Support form at the following website:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/contactsupportvoip.html
We have several technical support staff monitoring this form and they will
contact you within 12 hours after receiving a submission.
Phone: (831) 373-2601, Ext. 333
Email: support@cyberdata.net
Fax: (831) 373-4193
Company and product information is at www.cyberdata.net.
The IP Endpoint Company
SIP Compliant 011092
COPYRIGHT NOTICE:
© 2011, CyberData Corporation, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
This manual and related materials are the copyrighted property of CyberData Corporation. No part
of this manual or related materials may be reproduced or transmitted, in any form or by any means
(except for internal use by licensed customers), without prior express written permission of
CyberData Corporation. This manual, and the products, software, firmware, and/or hardware
described in this manual are the property of CyberData Corporation, provided under the terms of an
agreement between CyberData Corporation and recipient of this manual, and their use is subject to
that agreement and its terms.
DISCLAIMER: Except as expressly and specifically stated in a written agreement executed by
CyberData Corporation, CyberData Corporation makes no representation or warranty, express or
implied, including any warranty or merchantability or fitness for any purpose, with respect to this
manual or the products, software, firmware, and/or hardware described herein, and CyberData
Corporation assumes no liability for damages or claims resulting from any use of this manual or
such products, software, firmware, and/or hardware. CyberData Corporation reserves the right to
make changes, without notice, to this manual and to any such product, software, firmware, and/or
hardware.
OPEN SOURCE STATEMENT: Certain software components included in CyberData products are
subject to the GNU General Public License (GPL) and Lesser GNU General Public License (LGPL)
“open source” or “free software” licenses. Some of this Open Source Software may be owned by
third parties. Open Source Software is not subject to the terms and conditions of the CyberData
COPYRIGHT NOTICE or software licenses. Your right to copy, modify, and distribute any Open
Source Software is determined by the terms of the GPL, LGPL, or third party, according to who
licenses that software.
Software or firmware developed by Cyberdata that is unrelated to Open Source Software is
copyrighted by CyberData, subject to the terms of CyberData licenses, and may not be copied,
modified, reverse-engineered, or otherwise altered without explicit written permission from
CyberData Corporation.
TRADEMARK NOTICE: CyberData Corporation and the CyberData Corporation logos are
trademarks of CyberData Corporation. Other product names, trademarks, and service marks may be
the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Revision Information
Revision 930367H, which corresponds to firmware version 6.2.0, was released on September 6, 2011,
and has the following changes:
• Adds Section 1.1, “How to Identify This Product”.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide
Important Safety Instructions
GENERAL ALERT
GENERAL ALERT
1. Read these instructions.
2. Keep these instructions.
3. Heed all warnings.
4. Follow all instructions.
5. Do not use this apparatus near water.
6. Clean only with dry cloth.
7. Do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the manufacturer’s
instructions.
8. Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves, or other apparatus
(including amplifiers) that produce heat.
9. Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or grounding-type plug. A polarized plug has
two blades with one wider than the other. A grounding type plug has two blades and a third
grounding prong. The wide blade or the third prong are provided for your safety. If the
provided plug does not fit into your outlet, consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete
outlet.
10. Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched particularly at plugs, convenience
receptacles, and the point where they exit from the apparatus.
11. Only use attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
12. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is required when the apparatus has
been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug is damaged, liquid has been
spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the apparatus has been exposed to rain or
moisture, does not operate normally, or has been dropped.
13. Prior to installation, consult local building and electrical code requirements.
Warning
Electrical H azard: This product should be installed by a lice nsed electrician
according to al l local electrical and building codes.
Warning
Electrical H azard: To prevent injury, this apparatus mus t be securely attached to
the floor/wall in accordance with the installation instructions.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Pictorial Alert Icons
GENERAL ALERT
Hazard Levels
Danger: Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury. This is limited to the most extreme situations.
Warning: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
General Alert
This pictoral alert indicates a potentially hazardous situation. This ale rt will be
followed by a haza rd level heading and more specific information about the
hazard.
Ground
This pictora l alert indicates the Earth grounding connection point.
Caution: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury. It may also alert users against unsafe practices.
Notice: Indicates a statement of company policy (that is, a safety policy or protection of property).
The safety guidelines for the equipment in this manual do not purport to address all the safety
issues of the equipment. It is the responsibility of the user to establish appropriate safety, ergonomic,
and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Potential
safety hazards are identified in this manual through the use of words Danger, Warning, and
Caution, the specific hazard type, and pictorial alert icons.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Abbreviations and Terms
Abbreviation or Term Definition
A-law A standard companding algorithm, used in European digital
communications systems to optimize, i.e., modify, the dynamic range of an
analog signal for digitizing.
AVP Audio Video Profile
Cat 5 TIA/EIA-568-B Category 5
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
LAN Local Area Network
LED Light Emitting Diode
Mbps Megabits per second.
NTP Network Time Protocol
PBX Private Branch Exchange
PoE Power over Ethernet (as per IEEE 802.3af standard)
RTFM Reset Test Function Management
SIP Session Initiated Protocol
u-law A companding algorithm, primarily used in the digital telecommunication
UC Unified Communications
VoIP Voice over Internet Protocol
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Contents
Chapter 1 Product Overview 1
1.1 How to Identify This Product ..............................................................................................................1
1.2 Product features .....................................................................................................................................2
1.3 Supported ................................................................................................................................................2
1.4 Product Specifications ...........................................................................................................................3
Chapter 2 Setting Up the V2 Paging Server 4
2.1 Parts List ..................................................................................................................................................4
2.2 Typical Installation .................................................................................................................................5
2.3 Connecting the V2 Paging Server ........................................................................................................6
2.4 Configuring the V2 Paging Server ....................................................................................................10
2.5 Upgrading the Firmware ...................................................................................................................44
i
2.3.1 Connect to the Power Source ...................................................................................................6
2.3.2 Connect to the Network ............................................................................................................6
2.3.3 Confirm that the V2 Paging Server is Up and Running .......................................................7
Confirm Power on, Network Connectivity, and Connection Speed ....................................7
Verify Network Activity .............................................................................................................7
2.3.4 Announcing the IP Address ......................................................................................................8
2.3.5 Restore the Factory Default Settings ........................................................................................9
2.4.1 Gather the Required Configuration Information ................................................................10
Static or DHCP Addressing? ....................................................................................................10
Username and Password for Configuration GUI .................................................................10
SIP Settings .................................................................................................................................10
2.4.2 V2 Paging Server Web Page Navigation ................................................................................11
2.4.3 Log in to the Configuration GUI ............................................................................................12
2.4.4 Configure the Device Parameters ...........................................................................................15
2.4.5 Configure the Network Parameters ......................................................................................17
2.4.6 Configure the SiP Parameters .................................................................................................19
Point-to-Point Configuration ....................................................................................................22
2.4.7 Configure the Night Ringer Parameters ................................................................................23
2.4.8 Configure the Paging Groups (PGROUPS) Parameters ......................................................25
2.4.9 Operating the Paging Server ...................................................................................................28
2.4.10 Configure the Audio Parameters ..........................................................................................29
User-created Audio Files ...........................................................................................................32
2.4.11 Configure the Event Parameters ...........................................................................................34
Example Packets for Events ......................................................................................................36
2.4.12 Configure the Autoprovisioning Parameters ......................................................................39
Autoprovisioning .......................................................................................................................41
Upgrade the Firmware ..............................................................................................................45
Appendix A Setting Up a TFTP Server 46
A.1 Set up a TFTP Server ..........................................................................................................................46
A.1.1 In a LINUX Environment ........................................................................................................46
A.1.2 In a Windows Environment ...................................................................................................46
Appendix B Troubleshooting/Technical Support 47
B.1 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) ..................................................................................................47
B.1.1 Documentation ..........................................................................................................................47
B.2 Contact Information ............................................................................................................................48
B.3 Warranty ...............................................................................................................................................49
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

B.3.1 Warranty & RMA Returns within the United States ...........................................................49
B.3.2 Warranty & RMA Returns Outside of the United States ....................................................49
B.3.3 Spare in the Air Policy .............................................................................................................49
B.3.4 Return and Restocking Policy .................................................................................................50
B.3.5 Warranty and RMA Returns Page ..........................................................................................50
Appendix C How to Use the Multicast Extensions 51
C.1 Sending IP Multicast Datagrams ......................................................................................................51
C.2 Receiving IP Multicast Datagrams ...................................................................................................53
C.3 Establishing a Default Multicast Interface .......................................................................................54
C.4 Mtest ......................................................................................................................................................55
Index 56
ii
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

1 Product Overview
VoIP PAGING SERVER,V2
RoHS COMPLIANT
011092B / 021036D
Model number
WWW.CYBERDATA.NET
092000001
The VoIP V2 Paging Server is a POE-enabled, single SIP-endpoint enabling user defined paging
zones through a multicasting connection to CyberData VoIP speakers.
SIP compliant IP-PBX's that do not support grouping of SIP endpoints or paging can now support
up to 100 different paging zones.
1.1 How to Identify This Product
To identify the VoIP V2 Paging Server, look for a model number label similar to the one shown in
Figure 1-1. The model number on the label should be 011092.
Figure 1-1. Model Number Label
1
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

1.2 Product features
● SIP compliancy
● 10/100BaseT Ethernet Connection
● Multi-zone paging for up to 100 Zones
● TFTP and web-based firmware upgrades
● PoE enabled
● Connector for optional external power supply
● Unbalanced line-level input and output for mono audio
1.3 Supported
● HTTP Web-based configuration
Provides an intuitive GUI for easy system configuration and verification of speaker operations.
● DHCP Client
● TFTP Client
● RTP Version 2 Multicast and Unicast
● Audio Codec
• G.711 U-law
•DTMF detection
Product Overview
Product features
2
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

1.4 Product Specifications
Table 1-1. Product Specifications
Specification
Regulatory Compliance FCC Class A, UL 60950, CE
Power Requirement PoE or 48V DC
Connection Speed 10/100 Mbps
Protocol SIP compliant
Audio standard Unbalanced line-level input and output for mono audio
Line In:
Input Signal Amplitudes
Input Impedance
Line Out:
Output Signal Amplitudes
Output Level
Total Harmonic Distortion
Output Impedance
Part Number 011092
2.0 VPP maximum
10k Ohm
2.0 VPP maximum
+2dBm nominal
0.5% maximum
10k Ohm
Product Overview
Product Specifications
3
Dimensions 6.11” L x 4.05” W x 1.15” H
Weight 1.2 pounds
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2 Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
The topics in this chapter provide information on setting up, configuring, and using the SiP VoIP
and PoE Speaker.
2.1 Parts List
The packaging for the V2 Paging Server includes the parts in Tab le 2-2.
Table 2-2. Parts List
Quantity Part Name Illustration
1 V2 Paging Server
1 Installation Quick Reference Guide
4
1 Mounting Template (located on the last
page of the Installation Quick
Reference)
1 Mounting Kit (part #070057A)
which includes:
(2) #4-6 x 7/8" Mounting Anchors
(2) #4 x 1-1/4" Round Phillips Wood
Screws
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.2 Typical Installation
CyberData
VoIP Speakers
PoE VoIP V2 Paging Server
134526
Generic PoE Switch
SIP Server
VoIP Phone
Figure 2-2 illustrates how the V2 Paging Server is normally installed as part of a paging system.
Figure 2-2. Typical Installation
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Typical Installation
5
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.3 Connecting the V2 Paging Server
48V DC
Chassis ground
Before you connect the V2 Paging Server, be sure that you have received all of the parts described in
Section 2.1, "Parts List".
2.3.1 Connect to the Power Source
To use PoE, plug a Cat 5 Ethernet cable from the V2 Paging Server Ethernet port to your network.
As an alternative to PoE, you can plug one end of a +48V DC power supply into the Paging Server,
and plug the other end into a receptacle. If required, connect the earth grounding wire to the chassis
ground on the back of the unit.
Figure 2-3. Connecting to the Power Source
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Connecting the V2 Paging Server
6
2.3.2 Connect to the Network
Plug one end of a standard Ethernet cable into the Paging Server Ethernet port. Plug the other end
into your network.
Figure 2-4. Connecting to the Ne twork
48V DC
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Status
(GREEN/BLUE LED)
Paging
(GREEN LED)
Link
(GREEN/
AMBER LED)
Activity
(GREEN LED)
Connecting the V2 Paging Server
2.3.3 Confirm that the V2 Paging Server is Up and Running
The LEDs on the front of the V2 Paging Server verify the unit’s operations.
Figure 2-5. Paging Server LEDs
2.3.3.1 Confirm Power on, Network Connectivity, and Connection Speed
7
When you plug in the Ethernet cable or power supply:
•The round, GREEN/BLUE Status LED on the front of the V2 Paging Server comes on indicating
that the power is on. Once the device has been initialized, this LED blinks at one second
intervals.
• The square, GREEN/AMBER Link LED above the Ethernet port indicates that the network
connection has been established. The Link LED changes color to confirm the auto-negotiated
connection speed:
• The Link LED is GREEN at 10 Mbps.
• The Link LED is AMBER at 100 Mbps.
•The GREEN Paging LED comes on after the device is booted and initialized. This LED blinks
when a page is in progress. You can disable Beep on Initialization on the Device Configuration
page.
2.3.3.2 Verify Network Activity
The square, GREEN Activity LED blinks when there is network traffic.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.3.4 Announcing the IP Address
RTFM Switch
To announce the IP address for the V2 Paging Server, briefly press and then quickly release the
RTFM switch. See
Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6. RTFM Switch
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Connecting the V2 Paging Server
8
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.3.5 Restore the Factory Default Settings
RTFM Switch
The V2 Paging Server is delivered with factory set default values for the parameters in Ta b le 2-3. Use
the RTFM switch (see Figure 2-7) on the back of the unit to restore these parameters to the factory
default settings.
Figure 2-7. RTFM Switch
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Connecting the V2 Paging Server
9
Note When you perform this procedure, the factory default settings are restored. The default
parameters for access are shown in
Ta bl e 2-3.
Table 2-3. Factory Default Settings
Parameter Factory Default Setting
IP Addressing DHCP
IP Address
Web Access Username admin
Web Access Password admin
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
a
a
a
10.10.10.10
255.0.0.0
10.0.0.1
a. Default if there is not a DHCP server present.
To restore these parameters to the factory default settings:
1. Press and hold the RTFM switch until the status and paging lights come on.
2. Continue to press the switch until after the indicator lights go off, and then release it.
3. The V2 Paging Server settings are restored to the factory defaults.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4 Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Use this section to configure the VoIP paging server.
2.4.1 Gather the Required Configuration Information
Have the following information available before you configure the V2 Paging Server.
2.4.1.1 Static or DHCP Addressing?
Know whether your system uses static or dynamic (DHCP) IP addressing. If it uses static
addressing, you also need to know the values to assign to the following V2 Paging Server
parameters:
• IP Address
•Subnet Mask
•Default Gateway
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
10
2.4.1.2 Username and Password for Configuration GUI
Determine the Username and Password that will replace the defaults after you initially log in to the
configuration GUI.
• The Username is case-sensitive, and must be from four to 25 alphanumeric characters long.
• The Password is case-sensitive, and must be from four to 20 alphanumeric characters long.
2.4.1.3 SIP Settings
To configure the SIP parameters, determine whether you want to register with the server. If you do,
determine the number of minutes the registration lease remains valid, and whether you want to
automatically unregister when you reboot. To configure the SIP parameters, you also need to
determine the values for these parameters:
• SIP Server IP Address
• Remote and Local SIP Port Numbers
• SIP User ID, and Authenticate ID and Password for this User ID
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.2 V2 Paging Server Web Page Navigation
Ta bl e 2-4 shows the navigation buttons that you will see on every V2 Paging Server web page.
Table 2-4. V2 Paging Amplifier Web Page Navigation
Web Page Item Description
Link to the Home page.
Link to the Device Configuration page.
Link to the Networking page.
Link to go to the SIP Configuration page.
Link to go to the Nightringer page.
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
11
Link to go to the Paging Groups Configuration page.
Link to the Audio Configuration page.
Link to the Event Configuration page.
Link to the Autoprovisioning Configuration page.
Link to the Update Firmware page.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.3 Log in to the Configuration GUI
1. Open your browser to the V2 Paging Server IP address.
Note If the network does not have access to a DHCP server, the device will default to an IP
address of 10.10.10.10.
Note Make sure that the PC is on the same IP network as the V2 Paging Server.
Note You may also download CyberData’s VoIP Discovery Utility program which allows you to
easily find and configure the default web address of the CyberData VoIP products.
CyberData’s VoIP Discovery Utility program is available at the following website address:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/voip/discovery_utility.html
The unit ships in DHCP mode. To get to the Home page, use the discovery utility to scan for
the device on the network and open your browser from there.
Note To work with the V2 Paging Server configuration after the initial configuration, log in using
the IP address you assign to the device.
provides instructions for entering the IP address.
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Section 2.4.5, "Configure the Network Parameters"
12
Change the
Default Username
and Password
2. When prompted, use the following default Username and Password to open the configuration
Home page:
Username: admin
Password: admin
To change the default Web access Username and Password:
1. Enter the new Username from four to 25 alphanumeric characters in the Change Username
field. The Username is case-sensitive.
2. Enter the new Password from four to 20 alphanumeric characters in the Change Password field.
The Password is case-sensitive.
3. Enter the new password again in the Re-enter New Password field.
Click Save Settings.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide
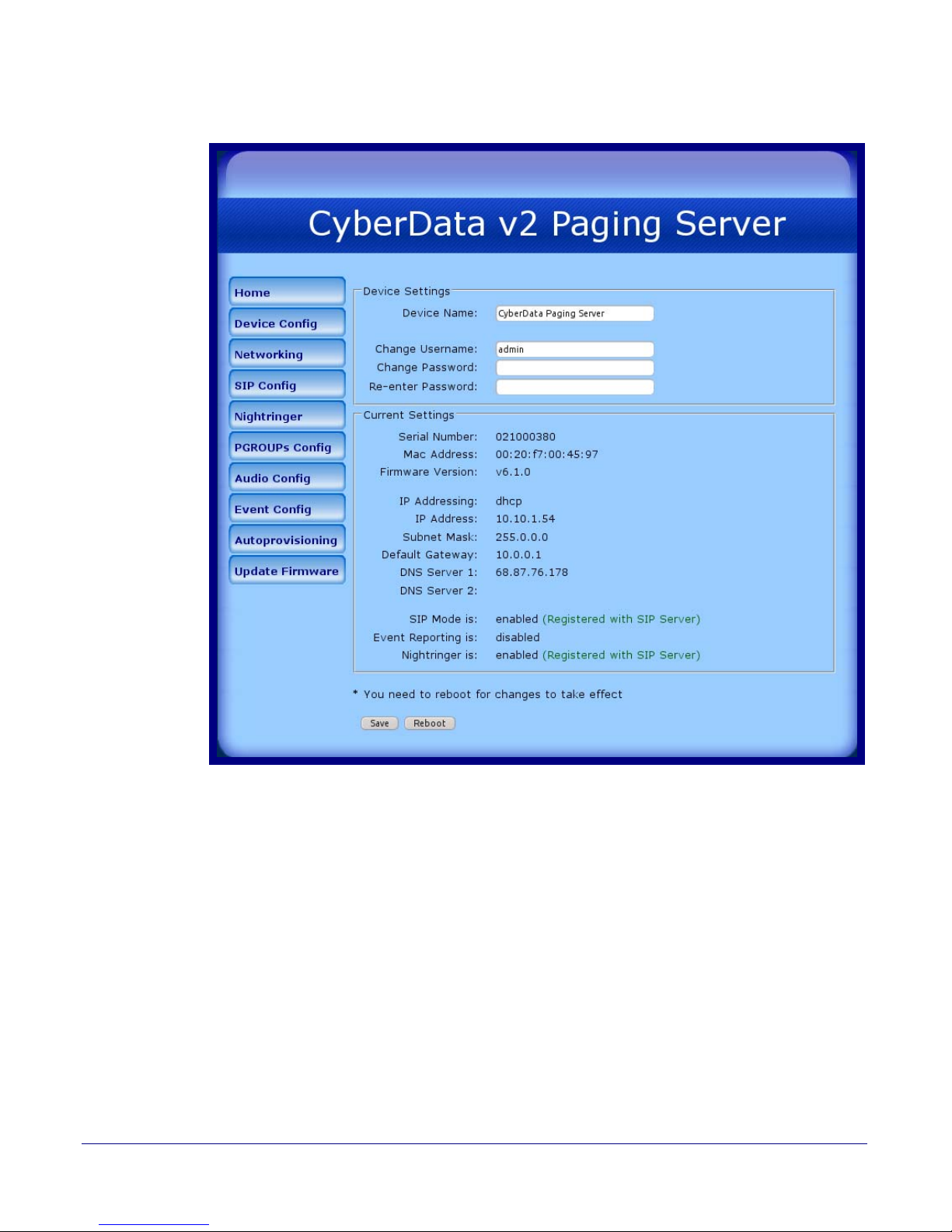
Figure 2-8. Home Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
13
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
4. On the Home Page, review the setup details and navigation buttons described in Tabl e 2-5.
Table 2-5. Home Page Overview
Web Page Item Description
Device Settings
Device Name Shows the device name (25 character limit).
Change Username Type in this field to change the username (25 character limit).
Change Password Type in this field to change the password (19 character limit).
Re-enter Password Type the password again in this field to confirm the new password
(19 character limit).
Current Settings
Serial Number Shows the device serial number.
Mac Address Shows the device Mac address.
Firmware Version Shows the current firmware version.
IP Addressing Shows the current IP addressing setting (DHCP or Static).
IP Address Shows the current IP address.
14
Subnet Mask Shows the current subnet mask address.
Default Gateway Shows the current default gateway address.
DNS Server 1 Shows the current DNS Server 1 address.
DNS Server 2 Shows the current DNS Server 2 address.
SIP Mode is Shows the current status of the SIP Mode.
Event Reporting is Shows the current status of the Event Reporting.
Nightring is Shows the current status of the Nightringer.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
At this point you can:
• Review the V2 Paging Server’s Current Settings. Use the RTFM switch to restore the factory
default settings. See
2.3.5 "Restore the Factory Default Settings".
• Configure the network parameters. Click Network Setup and refer to Section 2.4.5, "Configure
the Network Parameters" for instructions.
• Configure the SIP parameters. Click SIP Setup and see Section 2.4.6, "Configure the SiP
Parameters".
• Configure the PGROUPS parameters. Click PGROUPS Setup and see Section 2.4.8, "Configure
the Paging Groups (PGROUPS) Parameters" for instructions.
Note Click the Upgrade Firmware button any time you need to upload new versions of the
firmware. Refer to
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide
Section 2.5, "Upgrading the Firmware" for instructions.

2.4.4 Configure the Device Parameters
1. Click the Device Configuration button to open the Device Configuration page. See Figure 2-9.
Figure 2-9. Device Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
15
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
2. On the Device Configuration page, you may enter values for the parameters indicated in
Ta bl e 2-6.
Table 2-6. Device Configuration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Miscellaneous Settings
Beep on Initialization When selected, you will hear a beep when the speaker initializes.
16
Enable Line In to Line Out
When selected, audio is sent from the line -in to the line-out output.
Loopback
Enable Line-In to Multicast When selected, the line-in audio will be multicast to the address and
port specified on the web page.
Note: Ideally, the specified address and port will match that of a low
priority MGROUP (such as background music) on the speakers or
paging amplifiers.
Note: When line-in to multicast is selected, do not set that multicast
address and port to the same multicast address and port that is used
by one of your PGROUPS. Otherwise, when you call the PGROUP,
the Paging Server will be unable to send the new audio stream
because the port will already be in use by the line-in to multicast
stream.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Test Audio button to do an audio test. When the Test
Audio button is pressed, you will hear a voice message for testing the
device audio quality and volume.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
3. After changing the parameters, click the Save button.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.5 Configure the Network Parameters
Configuring the network parameters enables your network to recognize the V2 Paging Server and
communicate with it. Click Network Setup on the Home page to open the Network Configuration
page.
Figure 2-10. Network Setup Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
17
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
On the Network Setup page, enter values for the parameters indicated in Tab le 2-7.
Table 2-7. Network Config uration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Stored Network Settings Shows the settings stored in non-volatile memory.
IP Addressing Select either DHCP IP Addressing or Static IP Addressing by
marking the appropriate radio button. If you select Static, configure
the remaining parameters indicated in
go to Step 3.
IP Address Enter the Static IP address.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask address.
Default Gateway Enter the Default Gateway address.
DNS Server 1 Enter the DNS Server 1 address.
DNS Server 2 Enter the DNS Server 2 address.
Current Network Settings Shows the current network settings.
IP Address Shows the current Static IP address.
Table 2-7. If you select DHCP,
18
Subnet Mask Shows the current Subnet Mask address.
Default Gateway Shows the current Default Gateway address.
DNS Server 1 Shows the current DNS Server 1 address.
DNS Server 2 Shows the current DNS Server 2 address.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
On this page:
1. Specify whether you use Static or DHCP IP Addressing by marking the appropriate radio
button. Then, if you select Static, go to
Step 2.
2. For Static IP Addressing, also enter values for the following parameters:
• The V2 Paging Server’s IP Address: The V2 Paging Server is delivered with a factory default
IP address. Change the default address to the correct IP address for your system.
•The Subnet Mask.
•The Default Gateway.
3. Click Save when you are finished.
4. Click Reboot for the new settings to take effect.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.6 Configure the SiP Parameters
The SIP parameters enable the V2 Paging Server to contact and register with the SIP server. On the
Home page, click SIP Config to open the SIP Configuration page.
Figure 2-11. SIP Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
19
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
5. On the SIP Setup page, enter values for the parameters indicated in Tab l e 2-8.
Table 2-8. SIP Configuration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
SIP Settings
SIP Server Type the SIP server represented as either a numeric IP address
in dotted decimal notation or the fully qualified host name (255
character limit [FQDN]).
Remote SIP Port Type the Remote SIP Port number (default 5060)
(8 character limit).
Local SIP Port Type the Local SIP Port number (default 5060)
(8 character limit).
Outbound Proxy Type the Outbound Proxy as either a numeric IP address in
dotted decimal notation or the fully qualified host name
(255 character limit [FQDN]).
Outbound Proxy Port Type the Outbound Proxy Port number (8 character limit).
SIP User ID Type the SIP User ID (up to 64 alphanumeric characters).
Authenticate ID Type the Authenticate ID
(up to 64 alphanumeric characters).
20
Authenticate Password Type the Authenticate Password (up to 64 alphanumeric
characters).
Register with a SIP Server Enable or disable SIP Registration.
For information about Point-to-Point Configuration, see 2.4.6.1,
"Point-to-Point Configuration".
Re-registration Interval (in seconds) Type the SIP Registration lease time in seconds (default is 60
minutes) (8 character limit). Re-registration Interval (in seconds)
Unregister on Reboot When selected, on boot, the device will first register with a SIP
server with a expiration delay of 0 seconds. This has the effect
of unregistering any current devices on this extension.
Buffer SIP Calls When this is enabled, SIP calls to the device will be stored in
memory and will play when either the call is terminated or the
buffer is full. The receive buffer is 2MB in size and this is equal
to about four minutes of ulaw encoded audio.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
1. Enter the IP address of the SIP Server.
2. Enter the port numbers used for SIP signaling:
a. Remote SIP Port
b. Local SIP Port
3. Enter the SIP registration parameters:
a. SIP User ID
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
b. Authenticate ID
c. Authenticate Password
4. For SIP Registration, designate whether you want the VoIP Paging Server to register with your
SIP server.
5. At Unregister on Reboot:
a. Select Yes to automatically unregister the V2 Paging Server when you reboot it.
b. Select No to keep the V2 Paging Server registered when you reboot it.
6. In the Register Expiration field, enter the number of seconds the V2 Paging Server registration
lease remains valid with the SIP Server. The V2 Paging Server automatically re-registers with
the SIP server before the lease expiration timeout.
7. Click Save.
8. Click Reboot for the new settings to take effect.
21
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.6.1 Point-to-Point Configuration
Device is set to NOT register with a SIP server
When the board is set to not register with a SIP server, it's possible to set the device to dial out to a
single endpoint. To do this, do the following:
1. On the SIP Configuration page (Figure 2-12), make sure that the Register with a SIP Server
parameter is not selected.
2. Type the IP address of the remote device that you want to contact into the Dial out Extension
field
Note The delayed DTMF functionality is available in the Point-to-Point Mode.
Note Establishing point-to-point SiP calls may not work with all phones.
Figure 2-12. SIP Configuration Page Set to Point-to-Point Mode
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
22
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.7 Configure the Night Ringer Parameters
1. Click on the Nightringer button to open the Nightringer Configuration page. See Figure 2-13.
Figure 2-13. Nightringer Configuration Setup
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
23
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
2. On the Nightringer Configuration page, enter values for the parameters indicated
in Tabl e 2-9.
Table 2-9. Nightringer Co nfiguration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Enable Nightringer When the nightringer is enabled, the unit will attempt to
register a second extension with the SIP server. Any calls
made to this extension will play a ringtone.
Nightringer Settings
SIP Server Type the SIP server represented as either a numeric IP
address in dotted decimal notation.
Remote SIP Port Type the Remote SIP Port number (default 5060)
(8 character limit).
Local SIP Port Type the Local SIP Port number (default 5061)
(8 character limit).
Note: This value cannot be the same as the Local SIP Port
found on the SIP Configuration Page.
User ID Type the User ID (up to 64 alphanumeric characters).
Authenticate ID Type the Authenticate ID (up to 64 alphanumeric
characters).
Authenticate Password Type the Authenticate Password (up to 64 alphanumeric
characters).
24
Re-registration Interval (in seconds) Type the SIP Registration lease time in seconds (default is
60 minutes) (8 character limit). Re-registration Interval (in
seconds)
Relay Rings to Multicast When selected, a user-defined audio file is sent to the
specified multicast address and port when the night ringer is
activated.
Multicast Address Type the Multicast address.
Multicast Port Type the Multicast port number.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
3. After changing the parameters, click on the Save button.
4. Click Reboot for the new settings to take effect.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
2.4.8 Configure the Paging Groups (PGROUPS) Parameters
Note A PGROUP is a way of assigning multicast addresses and port numbers when configuring
multicast paging speakers.
To assign a multicast address, you must first configure the CyberData VoIP speakers that
you want to put into a paging zone by entering a particular multicast address and port
number combination in the web configuration for these speakers.
1. Click on the PGROUPS Setup button to open the PGROUPS Setup page. See Figure 2-14.
Figure 2-14. PGROUPS Setup
25
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Figure 2-15. PGROUPS Setup (continued)
26
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Figure 2-16. PGROUPS Setup (continued)
27
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
2. On the PGROUPS Setup page, enter values for the parameters indicated in Ta bl e 2-10.
Table 2-10. PGROUPS Setup Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Bypass DTMF When selected, bypassing the DTMF will result in all calls
being relayed to PGROUP 0.
# Shows the paging group number.
Address Enter the IP address of the PGROUP.
Por t Enter the port number of the PGROUP.
Name Enter a name for the PGROUP.
TTL The TTL field allows you to adjust the TTL. TTL is "time to
live" and it describes how many networks (routers) a packet
will go through before it is discarded. For more information,
see
Appendix C, ”How to Use the Multicast Extensions.
Lineout The Lineout field determines whether or not the V2 Paging
Server will play audio out of the line-out port in addition to
forwarding it to the Pgroup.
3. After changing the parameters, click Save Settings.
28
2.4.9 Operating the Paging Server
• When you call to make a page, the V2 Paging Server generates a tone over the phone.
• When you hear this tone, enter the two-digit code for the zone that you want to page.
• The V2 Paging Server establishes a connection to a zone.
• The V2 Paging Server generates another tone to the phone.
• When you hear this tone, you can begin speaking.
Note For page-all, you simply configure all speakers with a particular multicast address and port
number combination, which represents one of the 100 zones that the paging server will
support initially. Each speaker can still be part of 100 other paging zones in addition to the
one page-all zone.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.10 Configure the Audio Parameters
Click the Audio Config button to open the Audio Configuration page. See Figure 2-17. The Audio
Configuration page is used to add custom audio to the board. User uploaded audio will take
precedence over the audio files shipped with the Intercom.
Figure 2-17. Audio Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
29
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Figure 2-18. Audio Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
30
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
On the Audio Configuration page, enter values for the parameters indicated in Ta bl e 2-11.
Note Each entry on the Audio Configuration page replaces one of the stock audio files on the
board. When the input box displays the word default, the V2 Paging Server is using the
stock audio file. If that file is replaced with a user file, it will display the uploaded filename.
Table 2-11. Audio Configuration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Audio Files
0-9 The name of the audio configuration option is the same as the spoken
audio that plays on the board (24 character limit).
'0' corresponds to the spoken word “zero.”
'1' corresponds to the spoken word “one.”
'2' corresponds to the spoken word “two.”
'3' corresponds to the spoken word “three.”
'4' corresponds to the spoken word “four.”
'5' corresponds to the spoken word “five.”
'6' corresponds to the spoken word “six.”
'7' corresponds to the spoken word “seven.”
'8' corresponds to the spoken word “eight.”
'9' corresponds to the spoken word “nine.”
31
Dot Corresponds to the spoken word “dot.” (24 character limit).
Audiotest Corresponds to the message “This is the CyberData IP speaker test
message...” (24 character limit).
Pagetone Corresponds to a simple tone that is unused by default (24 character limit).
Invalid PGROUP Corresponds to the message “Invalid PGROUP” (24 character limit).
Your IP Address is Corresponds to the message “Your IP address is...” (24 character limit).
Rebooting Corresponds to the spoken word “Rebooting” (24 character limit).
Restoring default Corresponds to the message “Restoring default” (24 character limit).
Night Ring Specifies the ringtone for nightring. By default this parameter uses the
same audio file that is selected for the Ring Tone parameter.
The Browse button will allow you to navigate to and select an audio file.
The Play button will play that audio file.
The Delete button will delete any user uploaded audio and restore the
stock audio file.
The Save button will download a new user audio file to the board once
you've selected the file by using the Browse button. The Save button will
delete any pre-existing user-uploaded audio files.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.10.1 User-created Audio Files
User created audio files should be saved in the following format:
RIFF (little-endian) data, WAVE audio, Microsoft PCM, 16 bit, mono 8000 Hz
You can use the free utility Audacity to convert audio files into this format. See Figure 2-19 through
Figure 2-21.
Figure 2-19. Audacity 1
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
32
Figure 2-20. Audacity 2
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

When you export an audio file with Audacity, save the output as:
WAV (Microsoft) signed 16 bit PCM
• WAV (Microsoft) signed 16 bit PCM.
Figure 2-21. WAV (Micr osoft) signed 16 bit PCM
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
33
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.11 Configure the Event Parameters
Click the Event Config button to open the Event Configuration page (Figure 2-22). The Event
Configuration page specifies a remote server that can be used to receive HTTP POST events when
actions take place on the board.
Figure 2-22. Event Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
34
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Ta bl e 2-12 shows the web page items on the Event Configuration page.
Table 2-12. Event Configuration
Web Page Item Description
Enable Event Generation When selected, Event Generation is enabled.
Remote Event Server
Remote Event Server IP Type the Remote Event Server IP address.
(64 character limit)
Remote Event Server Port Type the Remote Event Server port number.
(8 character limit)
Remote Event Server URL Type the Remote Event Server URL.
(127 character limit)
Events
Enable Call Active Events When selected, Call Active Events are enabled.
Enable Call Terminated Events When selected, Call Terminated Events are enabled.
Enable Night Ring Events When selected, there is a notification when the unit
receives a night ring.
Enable Power On Events When selected, Power On Events are enabled.
35
Enable 60 Second Heartbeat Events When selected, 60 Second Heartbeat Events are
enabled.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Test Event button to test an event.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.11.1 Example Packets for Events
The server and port are used to point to the listening server and the 'Remote Event Server URL' is
the destination URL (typically the script running on the remote server that's used to parse and
process the POST events).
Note The XML is URL-encoded before transmission so the following examples are not completely
accurate.
Here are example packets for every event:
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 197
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>POWERON</event>
</cyberdata>
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
36
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 199
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>HEARTBEAT</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 196
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>BUTTON</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 201
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>CALL_ACTIVE</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 205
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>CALL_TERMINATED</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 197
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>RINGING</event>
</cyberdata>
37
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 234
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>MULTICAST_START</event>
<index>8</index>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 233
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>MULTICAST_STOP</event>
<index>8</index>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 234
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>RELAY_ACTIVATED</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 234
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>RELAY_DEACTIVATED</event>
</cyberdata>
POST xmlparse_engine HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.3.79
User-Agent: CyberData/1.0.0
Content-Length: 234
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<cyberdata NAME='CyberData VoIP Device' MAC='0020f70015b6'>
<event>NIGHTRINGING</event>
</cyberdata>
38
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.12 Configure the Autoprovisioning Parameters
1. Click the Autoprovisioning button to open the Autoprovisioning Configuration page.
See Figure 2-23.
Figure 2-23. Autoprovisioning Configuration Page
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
39
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
2. On the Autoprovisioning Configuration page, you may enter values for the parameters
indicated in
Ta bl e 2-13.
Table 2-13. Autoprovisioning Configuration Parameters
Web Page Item Description
Autoprovisioning
Enable Autoprovisioning See 2.4.12.1, "Autoprovisioning".
Get Autoprovisioning from DHCP See 2.4.12.1, "Autoprovisioning".
Autoprovisioning Server (IP Address) See 2.4.12.1, "Autoprovisioning" (15 character limit).
40
Autoprovisioning Autoupdate
(in minutes)
Type the desired time (in minutes) that you want the
Autoprovisioning feature to update (6 character limit).
Autoprovisioning file name Displays the Autoprovisioning file name.
Click the Save button to save your configuration settings.
Note: You need to reboot for changes to take effect.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
3. After changing the parameters, click the Save button.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.4.12.1 Autoprovisioning
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
41
Enable
Autoprovisioning
Option
Networking
Get
Autoprovisioning
from DHCP
With autoprovisioning enabled, the board will get its configuration from a remote TFTP server on
startup or periodically on a scheduled delay. Autoprovisioned values will override values stored in
on-board memory and will be visible on the web page. The board gets its autoprovisioning
information from an XML-formatted file hosted from a TFTP server. CyberData will provide a
template for this XML file and the user can modify it for their own use.
To use autoprovisioning, create a copy of the autoprovisioning template with the desired settings
and name this file with the mac address of the device to configure (for example:
0020f7350058.config). Put this file into your TFTP server directory and manually set the TFTP server
address on the board.
It is not necessary to set every option found in the autoprovisioning template. As long as the XML is
valid, the file can contain any subset. Options not autoprovisioned will default to the values stored
in the on board memory. For example if you only wanted to modify the device name, the following
would be a valid autoprovisioning file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<specific>
<MiscSettings>
<DeviceName>auto V2 Paging Server</DeviceName>
</MiscSettings>
</specific>
The board will only apply networking settings or firmware upgrades after a reboot.
When this option is checked, the device will automatically fetch its autoprovisioning server address
from the DHCP server. The device will use the address specified in OPTION 150 (TFTP-servername) or OPTION 66. If both options are set, the device will use OPTION 150.
Refer to the documentation of your DHCP server for setting up OPTION 150.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
To set up a Linux DHCPD server to serve autoprovisioning information (in this case using both
option 66 and 150), here's an example dhcpd.conf:
# dhcpd.conf
#
# Configuration file for ISC dhcpd (see 'man dhcpd.conf')
#
ddns-update-style ad-hoc;
option option-150 code 150 = ip-address;
subnet 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 {
max-lease-time 120;
default-lease-time 120;
option routers 10.0.0.1;
option subnet-mask 255.0.0.0;
option domain-name "voiplab";
option domain-name-servers 10.0.0.1;
option time-offset -8; # Pacific Standard Time
42
Autoprovisioning
Server (IP Address)
Autoprovisioning
Autoupdate
Autoprovisioned
Firmware Upgrades
option tftp-server-name "10.0.0.254";
option option-150 10.0.0.254;
range 10.10.0.1 10.10.2.1;}
Instead of using DHCP to provide the autoprovisioning tftp server address, you can specify an
address manually.
If Autoprovisioning is enabled and the Autoprovisioning Autoupdate value is something other
than 0 minutes, a service is started on startup that will wait the configured number of minutes and
then try to re-download its autoprovisioning file. It will compare its previously autoprovisioned file
with this new file and if there are differences, it will reboot the board.
An Autoprovisioned firmware upgrade only happens after a reboot, will take roughly three
minutes, and the web page will be unresponsive during this time.
The 'FirmwareVersion' value in the xml file must match the version stored in the 'FirmwareFile'.
<FirmwareVersion>v5.0.5b01</FirmwareVersion>
<FirmwareFile>505b01-uImage-ceilingspeak</FirmwareFile>
If these values are mismatched, the board can get stuck in a loop where it goes through the
following sequence of actions:
1. The board downloads and writes a new firmware file.
2. After the next reboot, the board recognizes that the firmware version does not match.
3. The board downloads and writes the firmware file again.
CyberData has timed a firmware upgrade at 140 seconds. Therefore, if you suspect the board is
stuck in a loop, either remove or comment out the FirmwareVersion line in the XML file and let the
board boot as it normally does.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Configuring the V2 Paging Server
Note For information about TFTP servers, see Appendix A: "Setting Up a TFTP Server".
43
Autoprovisioned
Audio Files
Audio files are stored in non-volatile memory and an autoprovisioned audio file will only have to be
downloaded once for each device. Loading many audio files to the device from the web page could
cause it to appear unresponsive. If this happens, wait until the transfer is complete and then refresh
the page.
The device uses the file name to determine when to download a new audio file. This means that if
you used autoprovisioning to upload a file and then changed the contents of this file at the TFTP
server, the device will not recognize that the file has changed (because the file name is the same).
Since audio files are stored in non-volatile memory, if autoprovisioning is disabled after they have
been loaded to the board, the audio file settings will not change. You can force a change to the audio
files on the board by one of the following two ways:
•Click Delete for each file that you want to restore to the factory default audio file on the Audio
Configuration page.
• Change the autoprovisioning file with the word “default” set as the file name.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.5 Upgrading the Firmware
1. Click the Update Firmware button to open the Upgrade Firmware page. See Figure 2-24.
Figure 2-24. Upgrade Firmware P a ge
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Upgrading the Firmware
44
Ta bl e 2-14 shows the web page items on the Upgrade Firmware page.
Table 2-14. Upgrade Firmware Parameters
Web Page Item Description
File Upload
Firmware Version Shows the current firmware version.
Please specify a file Click the Browse button to navigate to the application
firmware file that you want to upload.
Click on the Submit button to automatically upload the
selected firmware and reboot the system.
Click on the Reboot button to reboot the system.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

2.5.0.1 Upgrade the Firmware
To upload the firmware from your computer:
1. Retrieve the latest V2 Paging Server firmware from the VoIP V2 Paging Server Downloads page
at:
http://www.cyberdata.net/products/voip/digitalanalog/pagingserverv2/downloads.html
2. Unzip the V2 Paging Server version file. This file may contain the following:
•Firmware file
• Release notes
3. Log in to the V2 Paging Server home page as instructed in Section 2.4.3, "Log in to the
Configuration GUI".
4. Click the Update Firmware button to open the Upgrade Firmware page. See Figure 2-24.
5. Click Browse, and then navigate to the location of the V2 Paging Server firmware file.
6. Click Submit.
Note This starts the upload process. Once the V2 Paging Server has uploaded the file, the
Uploading Firmware countdown page appears, indicating that the firmware is being
written to flash. The V2 Paging Server will automatically reboot when the upload is
complete. When the countdown finishes, the Upgrade Firmware page will refresh. The
uploaded firmware filename should be displayed in the system configuration (indicating
successful upload and reboot).
Setting Up the V2 Paging Server
Upgrading the Firmware
45
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Appendix A: Setting Up a TFTP Server
A.1 Set up a TFTP Server
Autoprovisioning requires a TFTP server for hosting the configuration file.
A.1.1 In a LINUX Environment
To set up a TFTP server on LINUX:
1. Create a directory dedicated to the TFTP server, and move the files to be uploaded to that
directory.
2. Run the following command where /tftpboot/ is the path to the directory you created in
Step 1: the directory that contains the files to be uploaded. For example:
in.tftpd -l -s /tftpboot/your_directory_name
46
A.1.2 In a Windows Environment
You can find several options online for setting up a Windows TFTP server. This example explains
how to use the Solarwinds freeware TFTP server, which you can download at:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/voip/solarwinds.html
To set up a TFTP server on Windows:
1. Install and start the software.
2. Select File/Configure/Security tab/Tra n sm i t O nly.
Make a note of the default directory name, and then move the firmware files to be uploaded to that
directory.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Appendix B: Troubleshooting/Technical
Support
B.1 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Go to the following URL to see CyberData’s list of frequently asked questions:
http://www.cyberdata.net/products/voip/digitalanalog/pagingserverv2/faqs.html
B.1.1 Documentation
The documentation for this product is released in an English language version only. You can
download PDF copies of CyberData product documentation at:
http://www.cyberdata.net/products/voip/digitalanalog/pagingserverv2/docs.html
47
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

B.2 Contact Information
Contact CyberData Corporation
3 Justin Court
Monterey, CA 93940 USA
www.CyberData.net
Phone: 800-CYBERDATA (800-292-3732)
Fax: 831-373-4193
Sales Sales 831-373-2601 Extension 334
48
Contact Information
Technical
Support
Returned
Materials
Authorization
RMA Status Form If you need to inquire about the repair status of your product(s), please use the CyberData RMA
The fastest way to get technical support for your VoIP product is to submit a VoIP Technical Support
form at the following website:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/contactsupportvoip.html
We have several technical support staff monitoring this form and they will contact you within 12
hours after receiving a form submission.
Phone: (831) 373-2601, Ext. 333
Email: support@cyberdata.net
To return the product, contact the Returned Materials Authorization (RMA) department:
Phone: 831-373-2601, Extension 136
Email: RMA@CyberData.net
When returning a product to CyberData, an approved CyberData RMA number must be printed on
the outside of the original shipping package. No product will be accepted for return without an
approved RMA number. Send the product, in its original package, to the following address:
CyberData Corporation
3 Justin Court
Monterey, CA 93940
Attention: RMA "your RMA number"
Status form at the following web address:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/rmastatus.html
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

B.3 Warranty
CyberData warrants its product against defects in material or workmanship for a period of two
years from the date of purchase. Should the product fail within the warranty period, CyberData will
repair or replace the product free of charge. This warranty includes all parts and labor.
Should the product fail out-of-warranty, a flat rate repair charge of one half of the purchase price of
the product will be assessed. Repairs that are in warranty but are damaged by improper
modifications or abuse, will be charged at the out-of-warranty rate. Products shipped to CyberData,
both in and out-of-warranty, are shipped at the expense of the customer. Shipping charges for
repaired products shipped back to the customer by CyberData, will be paid by CyberData.
CyberData shall not under any circumstances be liable to any person for any special, incidental,
indirect or consequential damages, including without limitation, damages resulting from use or
malfunction of the products, loss of profits or revenues or costs of replacement goods, even if
CyberData is informed in advance of the possibility of such damages.
B.3.1 Warranty & RMA Returns within the United States
49
Warranty
If service is required, you must contact CyberData Technical Support prior to returning any
products to CyberData. Our Technical Support staff will determine if your product should be
returned to us for further inspection. If Technical Support determines that your product needs to be
returned to CyberData, an RMA number will be issued to you at this point.
Your issued RMA number must be printed on the outside of the shipping box. No product will be
accepted for return without an approved RMA number. The product in its original package should
be sent to the following address:
CyberData Corporation
3 Justin Court.
Monterey, CA 93940
Attn: RMA "xxxxxx"
B.3.2 Warranty & RMA Returns Outside of the United States
If you purchased your equipment through an authorized international distributor or reseller, please
contact them directly for product repairs.
B.3.3 Spare in the Air Policy
CyberData now offers a Spare in the Air no wait policy for warranty returns within the United States
and Canada. More information about the Spare in the Air policy is available at the following web
address:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/warranty/spareintheair.html
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

B.3.4 Return and Restocking Policy
For our authorized distributors and resellers, please refer to your CyberData Service Agreement for
information on our return guidelines and procedures.
For End Users, please contact the company that you purchased your equipment from for their
return policy.
B.3.5 Warranty and RMA Returns Page
The most recent warranty and RMA information is available at the CyberData Warranty and RMA
Returns Page at the following web address:
http://www.cyberdata.net/support/warranty/index.html
50
Warranty
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Appendix C: How to Use the Multicast
Extensions
C.1 Sending IP Multicast Datagrams
Note The following information is also available at the following site:
http://www.kohala.com/start/mcast.api.txt
IP multicasting is currently supported only on AF_INET sockets of type SOCK_DGRAM and
SOCK_RAW, and only on subnetworks for which the interface driver has been modified to support
multicasting.
To send a multicast datagram, specify an IP multicast address in the range 224.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255 as the destination address in a sendto() call.
By default, IP multicast datagrams are sent with a time-to-live (TTL) of 1, which prevents them from
being forwarded beyond a single subnetwork. A new socket option allows the TTL for subsequent
multicast datagrams to be set to any value from 0 to 255, in order to control the scope of the
multicasts:
51
u_char ttl;
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_MULTICAST_TTL, &ttl, sizeof(ttl))
Multicast datagrams with a TTL of 0 will not be transmitted on any subnet, but may be delivered
locally if the sending host belongs to the destination group and if multicast loopback has not been
disabled on the sending socket (see below). Multicast datagrams with TTL greater than one may be
delivered to more than one subnet if there are one or more multicast routers attached to the first-hop
subnet. To provide meaningful scope control, the multicast routers support the notion of TTL
"thresholds", which prevent datagrams with less than a certain TTL from traversing certain subnets.
The thresholds enforce the following convention:
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 0 are restricted to the same host
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 1 are restricted to the same subnet
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 32 are restricted to the same site
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 64 are restricted to the same region
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 128 are restricted to the same continent
multicast datagrams with initial TTL 255 are unrestricted in scope.
"Sites" and "regions" are not strictly defined, and sites may be further subdivided into smaller
administrative units, as a local matter. An application may choose an initial TTL other than the ones
listed above. For example, an application might perform an "expanding-ring search" for a network
resource by sending a multicast query, first with a TTL of 0, and then with larger and larger TTLs,
until a reply is received, perhaps using the TTL sequence 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32.
The multicast router accompanying this release refuses to forward any multicast datagram with a
destination address between 224.0.0.0 and 224.0.0.255, inclusive, regardless of its TTL. This range of
addresses is reserved for the use of routing protocols and other low-level topology discovery or
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Sending IP Multicast Datagrams
maintenance protocols, such as gateway discovery and group membership reporting. The current
specification for IP multicasting requires this behavior only for addresses 224.0.0.0 and 224.0.0.1; the
next revision of the specification is expected to contain this more general restriction.
Each multicast transmission is sent from a single network interface, even if the host has more than
one multicast-capable interface. (If the host is also serving as a multicast router, a multicast may be
FORWARDED to interfaces other than originating interface, provided that the TTL is greater than 1.)
The system manager establishes the default interface to be used for multicasting as part of the
installation procedure, described below. A socket option is available to override the default for
subsequent transmissions from a given socket:
struct in_addr addr;
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_MULTICAST_IF, &addr, sizeof(addr)) where "addr" is the local IP
address of the desired outgoing interface. An address of INADDR_ANY may be used to revert to
the default interface. The local IP address of an interface can be obtained via the SIOCGIFCONF
ioctl. To determine if an interface supports multicasting, fetch the interface flags via the
SIOCGIFFLAGS ioctl and see if the IFF_MULTICAST flag is set. (Normal applications should not
need to use this option; it is intended primarily for multicast routers and other system services
specifically concerned with internet topology.)
If a multicast datagram is sent to a group to which the sending host itself belongs (on the outgoing
interface), a copy of the datagram is, by default, looped back by the IP layer for local delivery.
Another socket option gives the sender explicit control over whether or not subsequent datagrams
are looped back:
52
u_char loop;
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_MULTICAST_LOOP, &loop, sizeof(loop))
where "loop" is 0 to disable loopback, and 1 to enable loopback. This option provides a performance
benefit for applications that may have no more than one instance on a single host (such as a router or
a mail demon), by eliminating the overhead of receiving their own transmissions. It should
generally not be used by applications for which there may be more than one instance on a single
host (such as a conferencing program) or for which the sender does not belong to the destination
group (such as a time querying program).
A multicast datagram sent with an initial TTL greater than 1 may be delivered to the sending host
on a different interface from that on which it was sent, if the host belongs to the destination group on
that other interface. The loopback control option has no effect on such delivery.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

C.2 Receiving IP Multicast Datagrams
Before a host can receive IP multicast datagrams, it must become a member of one or more IP
multicast groups. A process can ask the host to join a multicast group by using the following socket
option:
struct ip_mreq mreq;
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, &mreq, sizeof(mreq))
where "mreq" is the following structure:
struct ip_mreq {
struct in_addr imr_multiaddr;/* multicast group to join */
struct in_addr imr_interface;/* interface to join on */
}
Every membership is associated with a single interface, and it is possible to join the same group on
more than one interface. "imr_interface" should be INADDR_ANY to choose the default multicast
interface, or one of the host's local addresses to choose a particular (multicast-capable) interface. Up
to IP_MAX_MEMBERSHIPS (currently 20) memberships may be added on a single socket.
53
Receiving IP Multicast Datagrams
To drop a membership, use:
struct ip_mreq mreq;
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_DROP_MEMBERSHIP, &mreq, sizeof(mreq))
where "mreq" contains the same values as used to add the membership. The memberships
associated with a socket are also dropped when the socket is closed or the process holding the socket
is killed. However, more than one socket may claim a membership in a particular group, and the
host will remain a member of that group until the last claim is dropped.
The memberships associated with a socket do not necessarily determine which datagrams are
received on that socket. Incoming multicast packets are accepted by the kernel IP layer if any socket
has claimed a membership in the destination group of the datagram; however, delivery of a
multicast datagram to a particular socket is based on the destination port (or protocol type, for raw
sockets), just as with unicast datagrams. To receive multicast datagrams sent to a particular port, it is
necessary to bind to that local port, leaving the local address unspecified (i.e., INADDR_ANY).
More than one process may bind to the same SOCK_DGRAM UDP port if the bind() is preceded by:
int one = 1;
setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &one, sizeof(one))
In this case, every incoming multicast or broadcast UDP datagram destined to the shared port is
delivered to all sockets bound to the port. For backwards compatibility reasons, THIS DOES NOT
APPLY TO INCOMING UNICAST DATAGRAMS -- unicast datagrams are never delivered to more
than one socket, regardless of how many sockets are bound to the datagram's destination port.
SOCK_RAW sockets do not require the SO_REUSEADDR option to share a single IP protocol type.
The definitions required for the new, multicast-related socket options are found in <netinet/in.h>.
All IP addresses are passed in network byte-order.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Establishing a Default Multicast Interface
A final multicast-related extension is independent of IP: two new ioctls, SIOCADDMULTI and
SIOCDELMULTI, are available to add or delete link-level (e.g., Ethernet) multicast addresses
accepted by a particular interface. The address to be added or deleted is passed as a sockaddr
structure of family AF_UNSPEC, within the standard ifreq structure. These ioctls are for the use of
protocols other than IP, and require superuser privileges. A link-level multicast address added via
SIOCADDMULTI is not automatically deleted when the socket used to add it goes away; it must be
explicitly deleted. It is inadvisable to delete a link-level address that may be in use by IP. (These
ioctls already exist in SunOS and Ultrix; they are new to BSD Unix.)
Drivers that have been modified to support multicasting also support the IFF_PROMISC and
IFF_ALLMULTI interface flags, to the degree possible.
The kernel modification required to support Van Jacobson's traceroute program is also included in
this release.
Examples of usage of the above facilities can be found in the programs accompanying this
distribution, such as "ping", "mtest" and "rwhod".
C.3 Establishing a Default Multicast Interface
54
Selection of the default multicast interface is controlled via the kernel (unicast) routing table. If there
is no multicast route in the table, all multicasts will, by default, be sent on the interface associated
with the default gateway. If that interface does not support multicast, attempts to send will receive
an ENETUNREACH error.
A route may be added for a particular multicast address or for all multicast addresses, to direct them
to a different default interface. For example, to specify that multicast datagrams addressed to
224.0.1.3 should, by default, be sent on the interface with local address 36.2.0.8, use the following:
/etc/route add 224.0.1.3 36.2.0.8 0
To set the default for all multicast addresses, other than those with individual routes, to be the
interface with local address 36.11.0.1, use:
/etc/route add 224.0.0.0 36.11.0.1 0
If you point a multicast route at an interface that does not support multicasting, an attempt to
multicast via that route will receive an ENETUNREACH error.
If needed, these commands normally would be added to the /etc/rc.ip or /etc/rc.local file, to take
effect every time the system is booted.
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

C.4 Mtest
55
Mtest
The mtest directory contains a small program for testing the multicast membership sockopts and
ioctls. It accepts the following commands, interactively:
j g.g.g.g i.i.i.i - join IP multicast group
l g.g.g.g i.i.i.i - leave IP multicast group
a ifname e.e.e.e.e.e - add ether multicast address
d ifname e.e.e.e.e.e - del ether multicast address
m ifname 1/0 - set/clear ether allmulti flag
p ifname 1/0 - set/clear ether promisc flag
q - quit
where g.g.g.g is an IP multicast address, e.g., 224.0.2.1
i.i.i.i is the IP address of a local interface or 0.0.0.0
ifname is an interface name, e.g., qe0
e.e.e.e.e.e is an Ethernet address in hex, e.g., 1.0.5e.0.2.1
1/0 is a 1 or a 0, to turn the flag on or off
The "p" command to change the promiscuous flag does not work under SunOS, because it uses a
different ioctl for that purpose.
Mtest is useful for establishing targets for multicast ping testing. The results of mtest filter
manipulation can be seen by using the "netstat -nia" command (see next section).
CyberData Corporation 930367H Operations Guide

Index
56
Symbols
+48V DC power supply 6
Numerics
100 Mbps indicator light 7
A
activity light 7
address, configuration login 12
addressing
DHCP 10, 18
static 10, 18
admin username and password 12
Audio Codec 2
audio configuration 29
night ring tone parameter 31
audio configuration page 29
authenticate ID and password for SIP server
registration 21
autoprovisioning 41
autoprovisioned audio files 43
autoprovisioned firmware upgrades 42
autoprovisioning autoupdate 42
autoprovisioning enabled option 41
autoprovisioning from DHCP 41
autoprovisioning server (IP address) 42
networking 41
autoprovisioning configuration 39, 40
B
baseT ethernet connection 2
blue status light 7
C
cat 5 ethernet cable 6
changing
the web access password 15
changing default username and password for
configuration GUI 12
configurable parameters 14, 16, 18
configuration information 10
configuration page
configurable parameters 14, 16, 18
connecting the V2 paging server 6
connection speed 7
specification 3
verifying 7
contact information 48
contact information for CyberData 48
Current Network Settings 18
current network settings 18
current settings, reviewing 14
CyberData contact information 48
D
default
gateway 9
IP address 9
subnet mask 9
username and password 9
default gateway 9, 18
default gateway for static addressing 18
default login address 12
default password for configuration GUI 12
default settings, restoring 9
default username and password for configuration
GUI 12
device configuration 15
device configuration parameters 40
the device configuration page 39
device configuration page 15
device configuration parameters 16
device configuration password
changing for web configuration access 15
DHCP addressing 10, 18
DHCP Client 2
DHCP IP addressing 18
dimensions 3
discovery utility program 12
DNS server 18
door sensor 31
DTMF detection 2
Operations Guide 930367H CyberData Corporation

57
E
enable night ring events 35
ethernet port 6
event configuration
enable night ring events 35
expiration time for SIP server lease 20, 21, 24
F
features 2
firmware
where to get the latest firmware 45
firmware upgrade parameters 44
firmware, upgrade 14, 44
G
green link light 7
GUI username and password 12
local SIP port 20
log in address 12
logging in to configuration GUI 12
M
MGROUP 25
multicast TTL 28, 51
multi-zone paging 2
N
navigation (web page) 11
navigation table 11
network activity, verifying 7
network configuration page 17
network parameters, configuring 17
network setup button 14, 17
network, connecting to 6
nightringer settings 24
H
hazard levels 5
http web-based configuration 2
I
identifying your product 1
input specifications 3
IP address 9, 18
SIP server 20
IP addressing 18
default
IP addressing setting 9
L
lease, SIP server expiration time 20, 21, 24
line input specifications 3
line output specifications 3
line-in to multicast setting
multicast, line-in to multicast setting
line-in, line-in to multicast setting 16
link light 7
Linux, setting up a TFTP server on 46
O
orange link light 7
output specifications 3
P
paging server
configuration 10
part number 3
parts list 4
password
configuration GUI 10, 12
for SIP server login 20
restoring the default 9
SIP server authentication 21
pgroups 25
pgroups configuration 14
point-to-point configuration 22
port
ethernet 6
local SIP 20
remote SIP 20
power
connecting to 6
requirement 3
product overview 1
Operations Guide 930367H CyberData Corporation

58
R
reboot 44
unregistering from SIP server during 21
registration and expiration, SIP server
lease expiration 21
regulatory compliance 3
remote SIP port 20
required configuration for web access username and
password 10, 12
resetting the IP address to the default 47
restoring factory default settings 9
return and restocking policy 50
RMA returned materials authorization 48
RMA status 48
RTP Audio Version 2 2
S
safety instructions 4
sales 48
server
SIP 14
TFTP 46
server address, SIP 20
service 48
SIP
local SIP port 20
user ID 20
SIP configuration
SIP Server 20
SIP configuration page 19
SIP configuration parameters 20
outbound proxy 20
registration and expiration, SIP server lease 20, 24
unregister on reboot 20
user ID, SIP 20
SIP registration 20
SIP remote SIP port 20
SIP server 20
password for login 20
unregister from 20
user ID for login 20
SIP server configuration 14
SIP server parameters, configuring 10
SIP settings 20
SIP setup button 14, 19
Spare in the Air Policy 49
speaker operations, verifying 15
specifications 3
static addressing 10, 18
static IP addressing 18
status light 7
Stored Network Settings 18
subnet mask 9, 18
subnet mask static addressing 18
supported protocols 2
T
tech support 48
technical support, contact information 48
TFTP server 2, 46
U
unregister from SIP server 21
upgrade firmware 14, 44
upgrade firmware button 14
user ID
for SIP server login 20
user ID for SIP server registration 20
username
changing for web configuration access 15
restoring the default 9
username for configuration GUI 10, 12
V
verifying
connection speed 7
network activity 7
network connectivity 7
speaker operations 15
W
warranty 49
warranty & RMA returns outside of the United States 49
warranty & RMA returns within the United States 49
warranty and RMA returns page 50
warranty policy at CyberData 49
web access password 9
web access username 9
web configuration log in address 12
web page
navigation 11
web page navigation 11
weight 3
Windows, setting up a TFTP server on 46
Operations Guide 930367H CyberData Corporation

Y
yellow activity light 7
59
Operations Guide 930367H CyberData Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...