Curtis Instruments MultiMode 1243 Generation 2 User Manual

MANUAL
© 2002 CURTIS INSTRUMENTS, INC.
DESIGN OF CURTIS PMC 1200 SERIES
CONTROLLERS PROTECTED BY U.S.
PATENT NO. 4626750.
CURTIS INSTRUMENTS, INC.
200 Kisco Avenue
Mount Kisco, NY 10509 USA
Tel: 914-666-2971
Fax: 914-666-2188
www.curtisinst.com
1243GEN2 Manual, p/n 37044
Rev. A: October 2002
1 2 4 3
M OD EL
MultiMode™
MOTOR CONTROLLER
Generation 2

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
ii
CONTENTS
1. OVERVIEW ............................................................................. 1
2. INSTALLATION AND WIRING ........................................... 4
Mounting the Controller .................................................... 4
Connections: Low Current ................................................ 6
Connections: High Current ............................................... 6
Wiring: Controller ............................................................. 7
Wiring: Throttle ................................................................ 9
5kΩ–0, 2-wire potentiometer throttle (“Type 1”) ...... 10
Single-ended 0–5V, current source, 3-wire pot,
and electronic throttles (“Type 2”) ..................... 11
0–5kΩ, 2-wire potentiometer throttle (“Type 3”) ...... 13
Wigwag 0–5V and 3-wire pot throttles ...................... 14
Wiring: Fault Outputs ..................................................... 14
Wiring: Spyglass Display.................................................. 15
Wiring: Emergency Reverse ............................................. 16
Wiring: Emergency Reverse Check .................................. 16
Wiring: Auxiliary Driver .................................................. 16
Contactor, Switches, and Other Hardware........................ 17
3. PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS..................................... 19
Battery Parameter ............................................................. 21
Battery Voltage ........................................................... 21
Acceleration Parameters .................................................... 21
Drive Current Limit, M1–M4 ................................... 21
Acceleration Rate, M1–M4 ........................................ 21
Quick Start ................................................................ 21
Current Ratio ............................................................. 22
Braking Parameters ........................................................... 23
Braking Current Limit, M1–M4 ................................ 23
Deceleration Rate, M1–M4 ....................................... 23
Throttle Deceleration Rate ......................................... 23
Restraint, M1–M4 ..................................................... 23
Braking Rate, M1–M4 ............................................... 24
Taper Rate .................................................................. 25
Variable Braking ......................................................... 25
Interlock Braking Parameters ............................................ 26
Interlock Braking Rate ............................................... 26
Max. Forward Regen .................................................. 26
Max. Reverse Regen ................................................... 26
CONTENTS
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
iii
Min. Forward Regen .................................................. 27
Min. Reverse Regen ................................................... 27
Max. Load Volts ......................................................... 27
Min. Load Volts ......................................................... 27
Electromagnetic Brake Parameters .................................... 28
Aux Type .................................................................... 28
EM Brake PWM ........................................................ 28
Aux Delay .................................................................. 28
Interlock Brake Delay ................................................ 28
Speed Parameters .............................................................. 31
Max. Forward Speed, M1–M4 ................................... 31
Max. Reverse Speed, M1–M4 .................................... 31
Creep Speed ............................................................... 31
Load Compensation ................................................... 31
Throttle Parameters .......................................................... 32
Throttle Type ............................................................. 32
Throttle Deadband .................................................... 32
Throttle Max ............................................................. 34
Throttle Map ............................................................. 36
Pot Low Fault ............................................................. 38
Field Parameters................................................................ 38
Min. Field Current Limit ........................................... 38
Max. Field Current Limit ........................................... 38
Field Map Start .......................................................... 38
Field Map................................................................... 39
Field Check ................................................................ 40
Main Contactor Parameters .............................................. 40
Main Contactor Interlock .......................................... 40
Main Contactor Open Delay ..................................... 40
Main Contactor Diagnostics ...................................... 40
Sequencing Fault Parameters............................................. 41
Anti-Tiedown............................................................. 41
High Pedal Disable (HPD) ........................................ 41
Static Return to Off (SRO) ........................................ 42
Sequencing Delay ....................................................... 42
Emergency Reverse Parameters ......................................... 43
Emergency Reverse Current Limit ............................. 43
Emergency Reverse Check .......................................... 43
Emergency Reverse Direction Interlock...................... 43
Motor Protection Parameters ............................................ 44
Warm Speed ............................................................... 44
Motor Warm Resistance ............................................. 44
Motor Hot Resistance ................................................ 44
Motor Resistance Compensation ................................ 44
CONTENTS
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
iv
Hourmeter Parameters ...................................................... 45
Adjust Hours High .................................................... 45
Adjust Hours Middle ................................................. 45
Adjust Hours Low ...................................................... 45
Set Total Hours .......................................................... 45
Set Traction Hours ..................................................... 46
Total Service Hours .................................................... 46
Traction Service Hours ............................................... 46
Total Disable Hours ................................................... 46
Traction Disable Hours .............................................. 46
Traction Fault Speed .................................................. 47
Service Total ............................................................... 47
Service Traction .......................................................... 47
Hourmeter Type ......................................................... 48
Pump Meter ............................................................... 48
Battery Discharge Indicator (BDI) Parameters.................. 49
Full Voltage ................................................................ 49
Empty Voltage............................................................ 49
Reset Voltage .............................................................. 49
Battery Adjust ............................................................ 50
BDI Disable ............................................................... 50
BDI Limit Speed ........................................................ 50
Fault Code Parameters ...................................................... 51
Fault Code ................................................................. 51
BDI Lockout .............................................................. 51
Controller Cloning ........................................................... 52
4. INSTALLATION CHECKOUT ............................................ 53
5. VEHICLE PERFORMANCE ADJUSTMENT ..................... 55
Major Tuning ................................................................... 55
Tuning the active throttle range ................................. 55
Tuning the controller to the motor ............................ 58
Setting the unloaded vehicle top speed ....................... 60
Equalizing loaded and unloaded vehicle speed ........... 61
Fine Tuning ...................................................................... 62
Response to reduced throttle ...................................... 62
Response to increased throttle .................................... 63
Smoothness of direction transitions ............................ 63
Ramp climbing .......................................................... 64
CONTENTS
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1
234567890
1

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
v
6. PROGRAMMER MENUS .................................................... 65
1243GEN2 Program Menu ................................................ 65
1243
GEN2 Monitor Menu................................................. 69
1243
GEN2 System Faults Menu......................................... 70
7. DIAGNOSTICS AND TROUBLESHOOTING .................. 71
Programmer Diagnostics ................................................... 71
Spyglass Diagnostics ......................................................... 71
Status LED Diagnostics .................................................... 74
Fault Output LED Diagnostics......................................... 75
8. CONTROLLER MAINTENANCE ...................................... 76
Cleaning ........................................................................... 76
Diagnostic History ........................................................... 76
APPENDIX A Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ............... A-1
APPENDIX B 1311 Programmer Operation .............................. B-1
APPENDIX C Programmable Parameters Index ......................... C-1
APPENDIX D Specifications....................................................... D-1
CONTENTS
1234567890
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1
23456789
0
1234567890

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
vi
FIGURES
FIG. 1: Curtis 1243GEN2 electronic motor controller........................... 1
FIG. 2: Mounting dimensions, Curtis 1243GEN2 controller ................. 4
FIG. 3: Basic wiring configuration, Curtis 1243GEN2 controller .......... 7
FIG. 4: Wiring for 5kΩ–0 throttle (“Type 1”) ................................... 10
FIG. 5: Wiring for 20kΩ potentiometer used as
a wigwag-style throttle (“Type 1”).......................................... 10
FIG. 6: Wiring for 0–5V throttles (“Type 2”) .................................... 11
FIG. 7: Wiring for current source throttle (“Type 2”) ........................ 12
FIG. 8: Wiring for 3-wire potentiometer throttle (“Type 2”) ............. 12
FIG. 9: Wiring for Curtis ET-XXX electronic throttle (“Type 2”) ...... 13
FIG. 10: Wiring for 0–5kΩ throttle (“Type 3”) ................................... 14
FIG. 11: Wiring for fault outputs ........................................................ 15
FIG. 12: Wiring for Curtis Spyglass display ......................................... 15
FIG. 13: Ramp restraint maps for controller with the minimum
field set at 3 amps, maximum field at 18 amps, and
braking current limit at 300 amps ......................................... 24
FIG. 14: Electromagnetic brake parameters, in the context
of the four delay parameters ................................................... 29
FIG. 15: Effect of adjusting the throttle deadband parameter .............. 33
FIG. 16: Effect of adjusting the throttle max parameter ................. 34, 35
FIG. 17: Throttle maps for controller
with maximum speed set at 100%
and creep speed set at 0 ......................................................... 36
FIG. 18: Throttle maps for controller
with maximum speed set at 100%
and creep speed set at 10% .................................................... 37
FIGURES

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
vii
TABLES
FIG. 19: Throttle maps for controller
with maximum speed set at 90%
and creep speed set at 10% .................................................... 37
FIG. 20: Field current relative to armature current,
with field map parameter set at 50% and 20% ...................... 39
FIG. 21: Curtis 840 Spyglass, 3-LED and 6-LED models .................... 73
FIG. B-1 Curtis 1311 handheld programmer ..................................... B-1
TABLES
TABLE 1: Throttle wiper input (Pin 6) threshold values .......................... 9
TABLE 2: Mode selection ....................................................................... 18
TABLE 3: Configuration options: auxiliary driver .................................. 30
TABLE 4: Programmable throttle types .................................................. 32
TABLE 5: Standard battery voltages ....................................................... 49
TABLE 6: Fault categories ...................................................................... 50
TABLE 7: Troubleshooting chart ............................................................ 72
TABLE 8: Status LED fault codes .......................................................... 74
TABLE 9: Fault category codes ............................................................... 75
TABLE D-1: Specifications .................................................................... E-1

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
1
1 — OVERVIEW
OVERVIEW
Curtis 1243 Generation 2 MultiMode™ controllers are separately excited
motor speed controllers designed for use in a variety of small industrial vehicles
and in material handling equipment. These programmable controllers are
simple to install, efficient, and cost effective, while offering more features than
the original 1243.
1
Fig. 1 Curtis 1243GEN2
MultiMode™ electronic
motor controller.
The 1243GEN2 MultiMode™ controller provides smooth precise control
of motor speed and torque. A full-bridge field control stage is combined with a
half-bridge armature power stage to provide solid state motor reversing and full
regenerative braking without additional relays or contactors.
The controller’s rugged IP53 housing and packaging are built to with-
stand shock and vibration. State-of-the-art surface mount logic board fabrication makes the 1243
GEN2 controller even more reliable than the original 1243.
The 1243GEN2 is fully programmable through the Curtis 13XX handheld
programmer. In addition to configuration flexibility, the programmer provides
diagnostic and test capability.

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
2
1 — OVERVIEW
Like all Curtis motor controllers, the 1243GEN2 offers superior operator control
of the vehicle’s motor drive speed. Features include:
✓ Interlock braking with load sensor to meet required braking distance
without unnecessary harsh braking at light loads
✓ Maintenance monitor responds to preset vehicle operating hours and
drive hours as programmed by the OEM
✓ Two hourmeters—total KSI-on hours and traction hours—and the
associated maintenance timers are built into the controller
✓ BDI calculations performed within controller
✓ Estimates motor temperature based on field resistance and cuts back
maximum speed if the motor is overheated
✓ Diagnostic checks for field open and field shorted faults
✓ Supports PWM electromagnetic brake with maximum continuous
current of 2 amps
✓ Supports Type 4 throttle
✓ Active precharge of controller capacitor bank extends life of main
contactor
✓ Compatibility with Curtis 1307/1311 handheld programmers for quick
and easy testing, diagnostics, and parameter adjustment
✓ MultiMode™ allows four user-selectable vehicle operating modes
✓ Continuous armature current control, reducing arcing and brush wear
✓ Complete diagnostics through the handheld programmer, the built-in
Status LED, and the optional 840 Spyglass display
✓ Two fault outputs provide diagnostics to remotely mounted displays
✓ Regenerative braking allows shorter stopping distances, increases battery
charge, and reduces motor heating
✓ Automatic braking when throttle is reduced provides a compression
braking feel and enhances safety
✓ Brake/Drive Interlock meets ISO stopping distance requirements
✓ Ramp restraint feature provides automatic electronic braking
that restricts vehicle movement while in neutral
✓ Meets EEC fault detect requirements
✓ Linear cutback of motor drive current during overtemperature or
undervoltage

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
3
✓ Linear cutback of regenerative braking current during overvoltage
✓ High pedal disable (HPD) and static return to off (SRO) interlocks
prevent vehicle runaway at startup
✓ Internal and external watchdog circuits ensure proper software operation
✓ Fully protected inputs and short-circuit protected output drivers.
Curtis Model 840 Spyglass Display [optional]
✓ 3-wire serial interface
✓ Sequences between hourmeter, BDI, and error displays
✓ Single alphanumeric, non-backlit, 8 character, 5 mm LCD display for
hourmeter, BDI, and fault messages
✓ Display updated by dedicated unidirectional serial port
✓ Available in 52 mm round case, DIN case, and as a bare board, each
with an 8-pin Molex connector; cases feature front seal to IP65 and rear
seal to IP40; shock and vibration protection to SAE J1378
✓ Operating temperature range -10°C to 70°C; models with lower
temperature ratings available for freezer applications
Familiarity with your Curtis controller will help you install and operate it
properly. We encourage you to read this manual carefully. If you have questions,
please contact the Curtis office nearest you.
1 — OVERVIEW
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
4
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
MOUNTING THE CONTROLLER
The controller can be oriented in any position, but the location should be
carefully chosen to keep the controller as clean and dry as possible. If a
clean, dry mounting location cannot be found, a cover must be used to
shield the controller from water and contaminants. When selecting the
mounting position, be sure to also take into consideration (1) that access is
needed at the front of the controller to plug the programmer into its connector,
and (2) that the built-in Status LED is visible only through the view port in the
label on top of the controller.
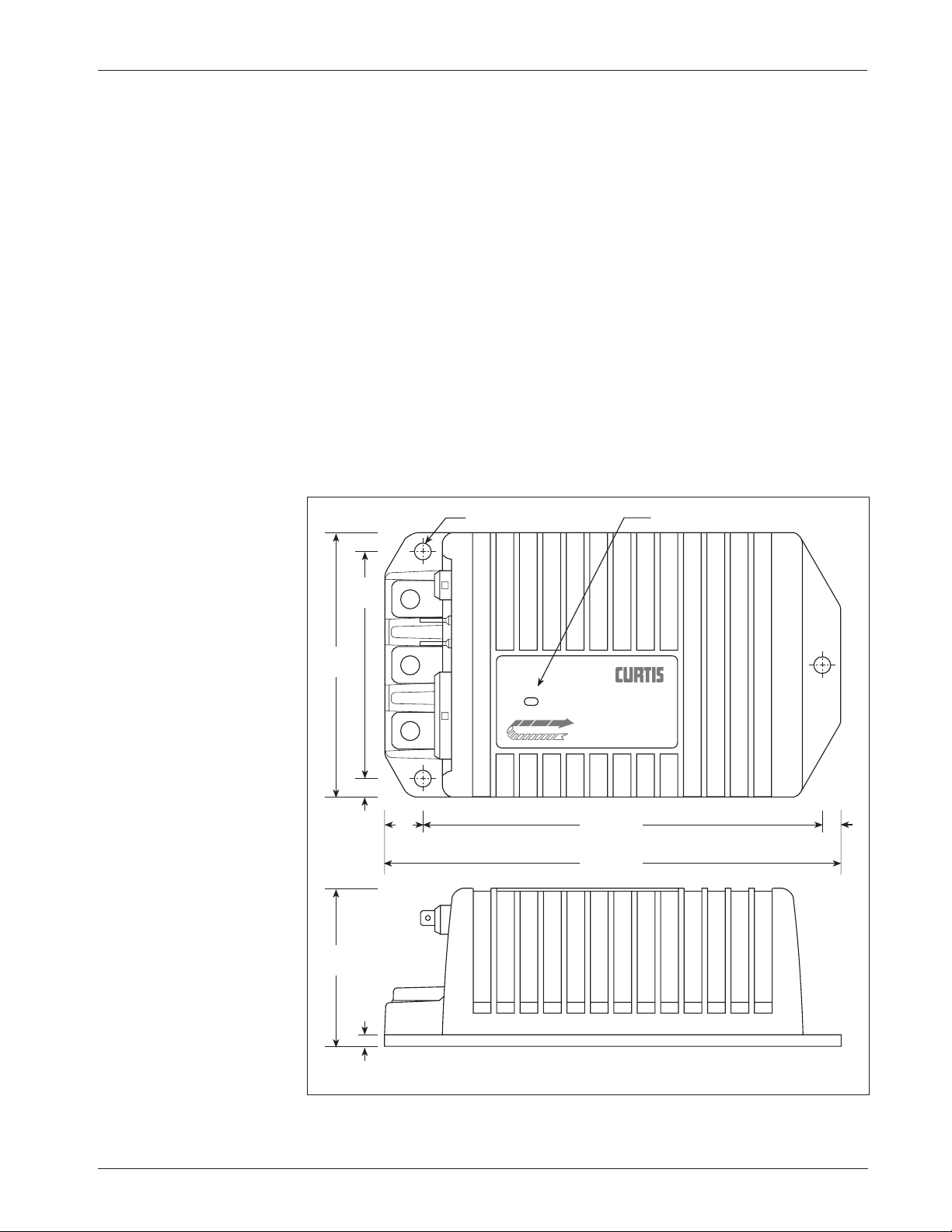
The outline and mounting hole dimensions for the 1243GEN2 controller
are shown in Figure 2. To ensure full rated power, the controller should be
fastened to a clean, flat metal surface with three 6 mm (1/4") diameter screws,
using the holes provided.
2
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Controller
Fig. 2 Mounting
dimensions, Curtis
1243
GEN2 controller.
Dimensions in millimeters (and inches)
C
L
SEPE
X
198 (7.78)
6.4 (0.25) dia., 3 plcs
68
(2.68)
114
(4.50)
173 (6.81)
17
(0.66)
7.9
(0.31)
99
(3.88)
4.8
(0.19)
7.9
(0.31)
STAT US
Status LED
TRACTION CONTROLLER
TM
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
5
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Controller
The mounting surface must be at least a 300×300×3 mm (12"×12"×1/8")
aluminum plate, or its equivalent, and subjected to a minimum 3 mph airflow
to meet the specified time/current ratings. Although not usually necessary, a
thermal joint compound can be used to improve heat conduction from the
controller heatsink to the mounting surface.
You will need to take steps during the design and development of your
end product to ensure that its EMC performance complies with applicable
regulations; suggestions are presented in Appendix A.
The 1243GEN2 controller contains ESD-sensitive components. Use
appropriate precautions in connecting, disconnecting, and handling the controller. See installation suggestions in Appendix A for protecting the controller
from ESD damage.
Working on electric vehicles is potentially dangerous. You should
protect yourself against runaways, high current arcs, and outgassing from
lead acid batteries:
RUNAWAYS — Some conditions could cause the vehicle to run out of
control. Disconnect the motor or jack up the vehicle and get the drive
wheels off the ground before attempting any work on the motor control
circuitry.
HIGH CURRENT ARCS — Electric vehicle batteries can supply very high
power, and arcs can occur if they are short circuited. Always open the
battery circuit before working on the motor control circuitry. Wear safety
glasses, and use properly insulated tools to prevent shorts.
LEAD ACID BATTERIES — Charging or discharging generates hydrogen gas,
which can build up in and around the batteries. Follow the battery
manufacturer’s safety recommendations.
Wear safety glasses.
☞
C A U T I O N
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
6
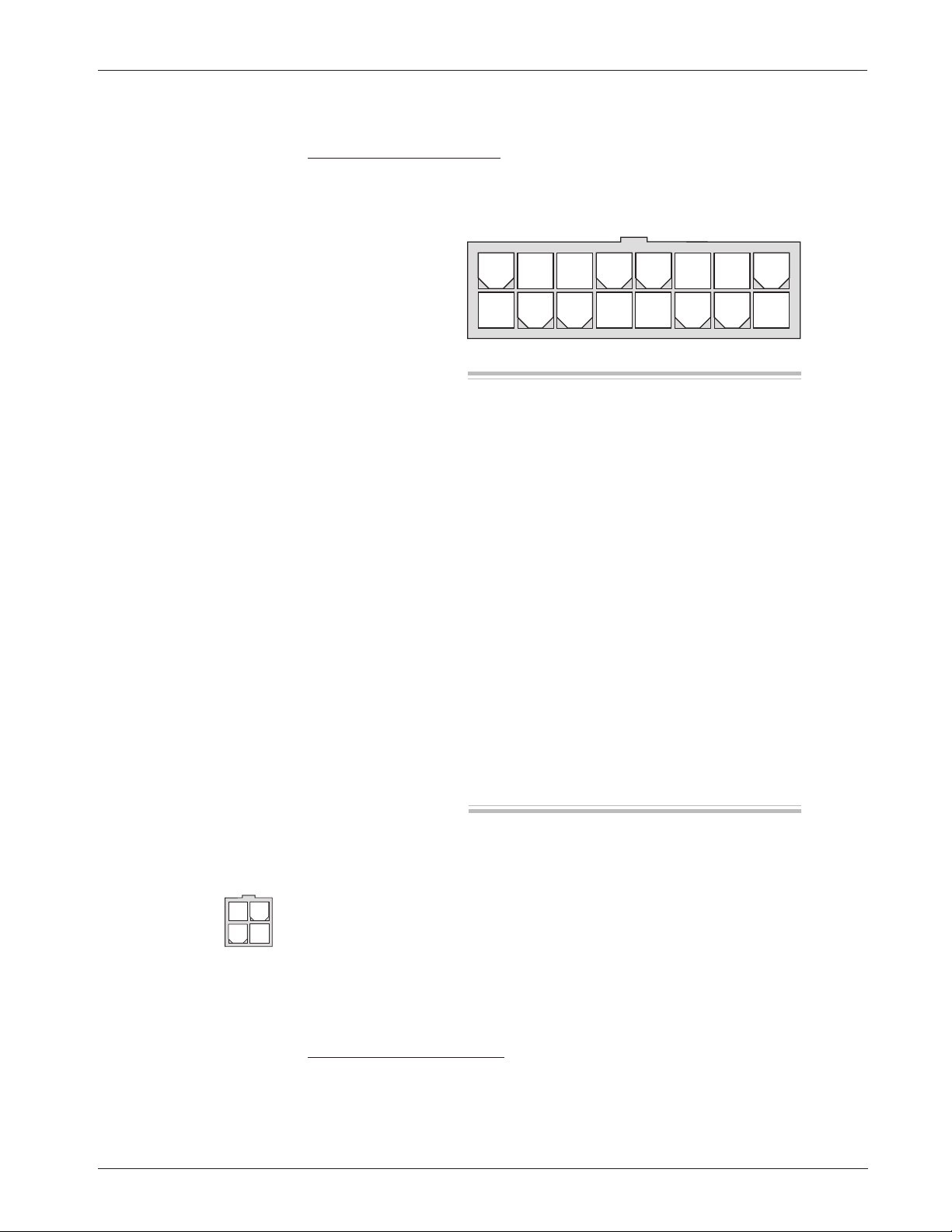
CONNECTIONS
Low Current Connections
A 16-pin Molex low current connector in the controller provides the low current
logic control connections:
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Controller
The mating connector is a 16-pin Molex Mini-Fit Jr. connector p/n 39-01-2165
using type 5556 terminals.
A 4-pin low power connector is provided for the handheld programmer. A
complete 1311 programmer kit, including the appropriate connecting cable,
can be ordered from Curtis.
The 4-pin connector can also be used for the Spyglass display. The display
is unplugged when the programmer is used.
High Current Connections
Three tin-plated solid copper bus bars are provided for high current connections
to the battery (B+ and B-) and the motor armature (M-). Cables are fastened to
the bus bars by M8 bolts. The 1243GEN2 case provides the capture nuts required
Pin 1 load sensor input [optional]
Pin 2 Fault 1 output / pump input
Pin 3 Fault 2 output
Pin 4 main contactor driver output
Pin 5 throttle: 3-wire pot high
Pin 6 throttle: 0–5V; pot wiper
Pin 7 throttle: pot low
Pin 8 auxiliary driver output (typically
used for an electromagnetic brake)
Pin 9 Mode Select 2 input
Pin 10 emerg. reverse check output [optional]
Pin 11 reverse input
Pin 12 forward input
Pin 13 emergency reverse input
Pin 14 Mode Select 1 input
Pin 15 interlock input
Pin 16 keyswitch input (KSI)
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
Pin 1 receive data (+5V)
Pin 2 ground (B-)
Pin 3 transmit data (+5V)
Pin 4 +15V supply (100mA)
34
12
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
7
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Controller
for the M8 bolts. The maximum bolt insertion depth below the surface of the
bus bar is 1.3 cm (1/2"). Bolt shafts exceeding this length may damage the controller.
The torque applied to the bolts should not exceed 16.3 N·m (12 ft-lbs).
Two 1/4" quick connect terminals (S1 and S2) are provided for the
connections to the motor field winding.
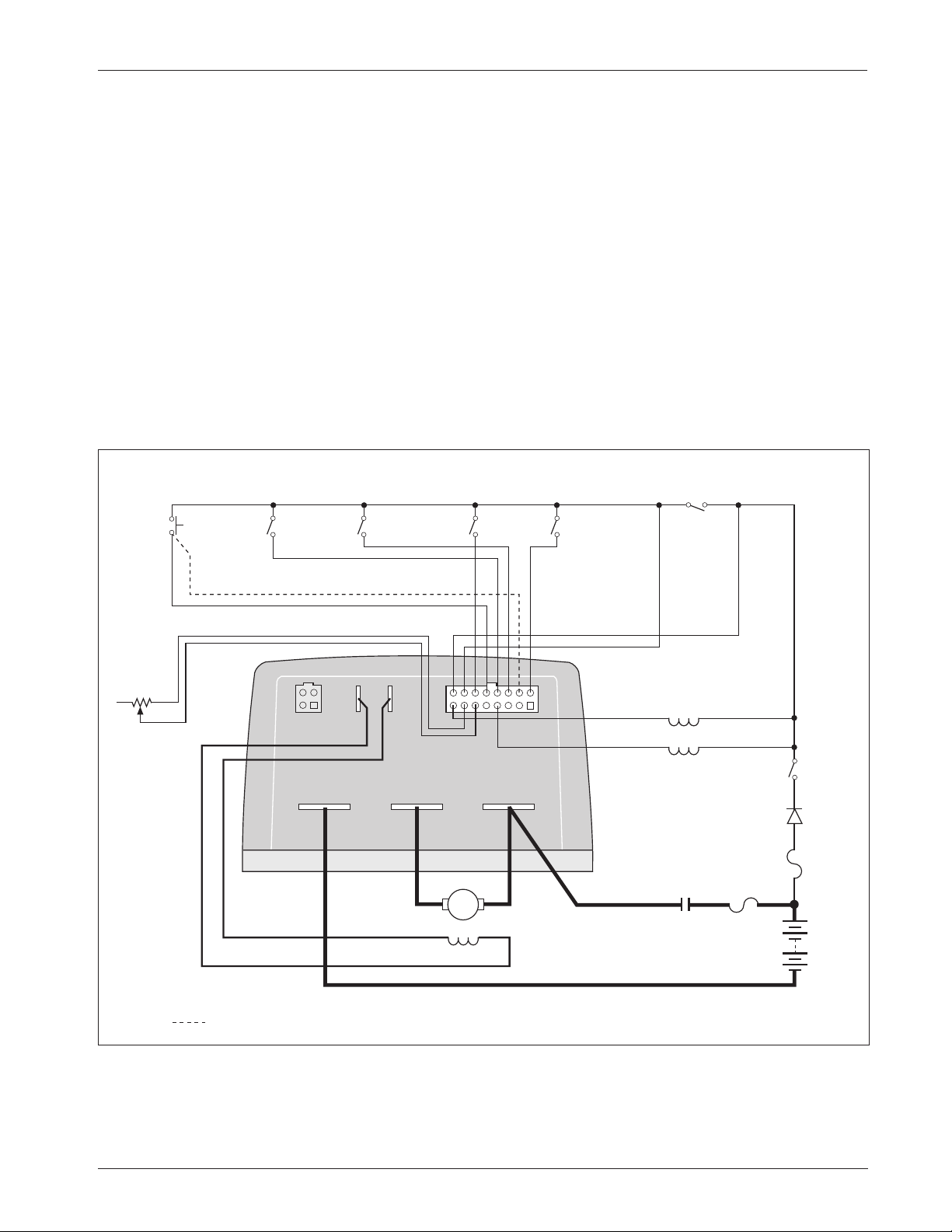
WIRING: Standard Configuration
Figure 3 shows the typical wiring configuration for most applications. For
walkie applications the interlock switch is typically activated by the tiller, and
an emergency reverse switch on the tiller handle provides the emergency reverse
signal.
For rider applications the interlock switch is typically a seat switch or a
foot switch, and there is no emergency reverse.
Fig. 3 Standard wiring configuration, Curtis 1243GEN2 controller.
S1 S2
B- M- B+
INTERLOCK
5 kΩ POT
THROTTLE
(TYPICAL)
EMERGENCY
REVERSE
emergency reverse wiring check (optional)
FORWARD
MAIN
CONTACTOR
COIL
POLARITY
PROTECTION
DIODE
REVERSE
MODE
SELECT
1
MODE
SELECT
2
ELECTRO-
MAGNETIC
BRAKE
KEY
SWITCH
POWER
FUSE
A
MAIN
CONTACTOR
B+
B-
A2 A1
S2 S1
CONTROL
FUSE
1
9
8
16

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
8
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Controller
Standard Power Wiring
Motor armature wiring is straightforward, with the armature’s A1 connection
going to the controller’s B+ bus bar and the armature’s A2 connection going to
the controller’s M- bus bar.
The motor’s field connections (S1 and S2) are less obvious. The direction
of vehicle travel with the forward direction selected will depend on how the
motor’s S1 and S2 connections are made to the controller’s two field terminals
(S1 and S2) and how the motor shaft is connected to the drive wheels through
the vehicle’s drive train.
CAUTION:
The polarity of the S1 and S2 connections
will affect the operation of the emergency reverse feature. The forward and
reverse switches and the S1 and S2 connections must be configured so that the
vehicle drives away from the operator when the emergency reverse button is
pressed.
Standard Control Wiring
Wiring for the input switches and contactors is shown in Figure 3; the pins are
identified on page 6. In the standard wiring configuration, the auxiliary driver
at Pin 8 is used to drive an electromagnetic brake.
The main contactor coil must be wired directly to the controller as shown
in Figure 3. The controller checks for welded or missing contactor faults and
uses the main contactor coil driver output to disconnect the battery from the
controller and motor when specific faults are present. If the main contactor coil
is not wired to Pin 4, the controller will not be able to open the main contactor
in serious fault conditions and the system will therefore not meet EEC safety
requirements.
☞
C A U T I O N

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
9
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
WIRING: Throttle
Wiring for various throttles is described below. They are categorized as Type 1,
2, 3, and 4 throttles in the program menu of the handheld programmer. Note:
In the text, throttles are identified by their nominal range and not by their actual
active range.
Appropriate throttles for use with the 1243GEN2 controller include twowire 5kΩ–0 throttles (“Type 1”); 0–5V throttles, current source throttles,
three-wire potentiometer throttles, and electronic throttles wired for singleended operation (all “Type 2”); two-wire 0–5kΩ throttles (“Type 3”), and
0–5V and three-wire potentiometer throttles wired for wigwag operation
(“Type 4”). The operating specifications for these throttle types are summarized
in Table 1. Refer to Section 3: Programmable Parameters, for information on
the effects of the Throttle Deadband and Throttle Max parameters on the
minimum and maximum throttle thresholds.
If the throttle you are planning to use is not covered, contact the Curtis
office nearest you.
Table 1 THROTTLE WIPER INPUT THRESHOLD VALUES
MAXIMUM THROTTLE HPD THROTTLE MINIMUM
THROTTLE THROTTLE DEADBAND (25% throttle MAX THROTTLE
TYPE PARAMETER FAULT (0% speed request) active range) (100% modulation) FAULT
1 (5kΩ–0) Wiper Voltage 5.00 V 3.80 V 2.70 V 0.20 V 0.06 V
Wiper Resistance 7.50 kΩ 5.50 kΩ 3.85 kΩ 0 kΩ —
2 (0–5V) Wiper Voltage 0.06 V 0.20 V 1.50 V 5.00 V 5.80 V
Wiper Resistance — — — — —
3 (0–5kΩ) Wiper Voltage 0.06 V 0.20 V 1.30 V 3.80 V 5.00 V
Wiper Resistance — 0 kΩ 1.65 kΩ 5.50 kΩ 7.50 kΩ
4 (0–5V) Wiper Voltage 0.50 V 2.50 V (fwd) * 3.10 V (fwd) 4.40 V (fwd) 4.50 V
2.50 V (rev) * 1.90 V (rev) 0.60 V (rev)
Wiper Resistance — — — — —
Notes: The Throttle Deadband and Throttle Max thresholds are valid for nominal 5kΩ
potentiometers or 5V sources with the default Throttle Deadband and Throttle
Max parameter settings of 0% and 100% respectively. These threshold values
will change with variations in the Throttle Deadband and Throttle Max parameter settings
.
The HPD thresholds are 25% of the active throttle range and therefore
dependent on the programmed Throttle Deadband and Throttle Max settings
(which define the active range).
The wiper voltage is measured with respect to B-.
The wiper resistance is measured from pot low to pot wiper. The potentiometer
must be disconnected from the controller when making this measurement.
* With a 0% Throttle Deadband setting, there is no neutral point on
a Type 4 throttle. A Throttle Deadband setting of at least 8% is
recommended for Type 4 throttles.
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
10
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
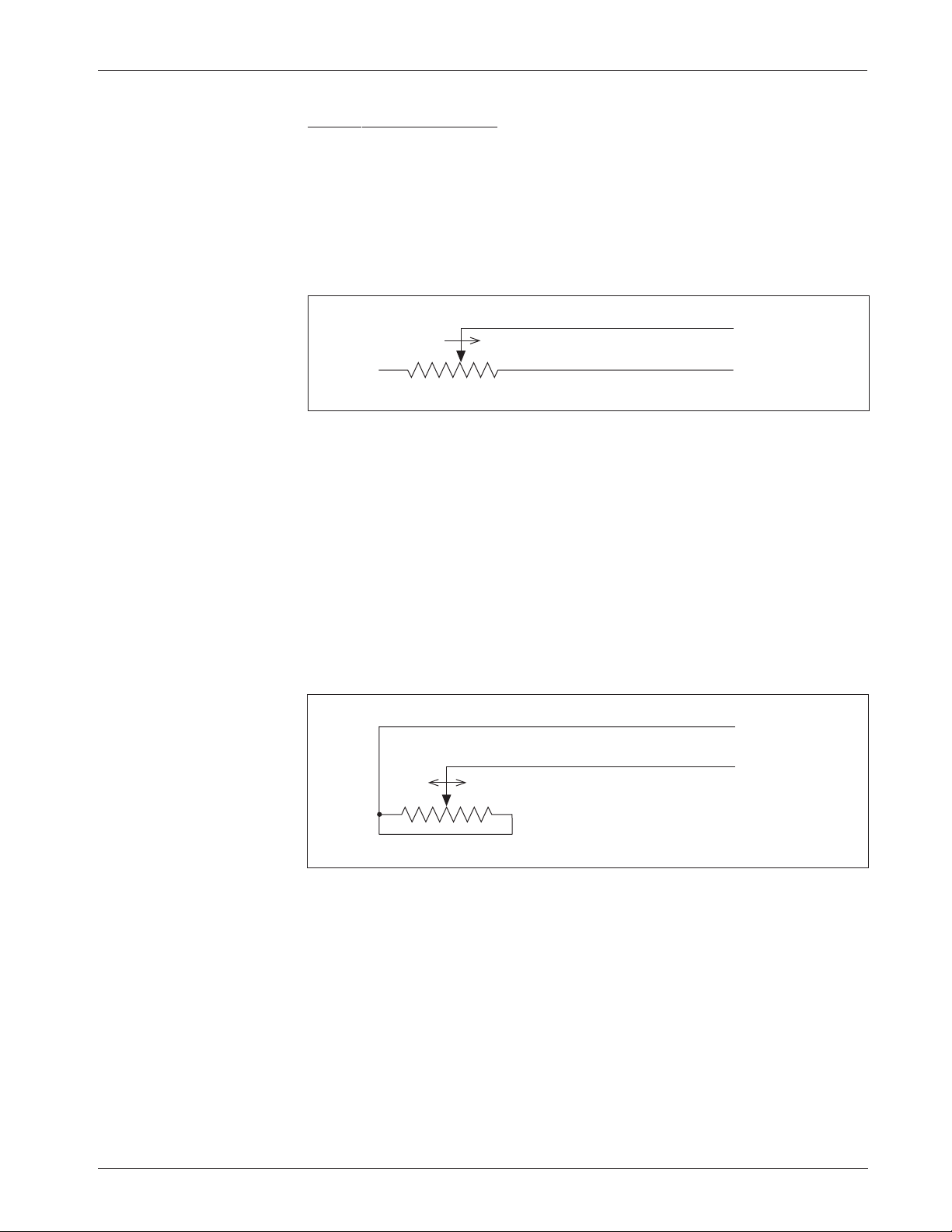
5kΩ–0 Throttle (“Type 1”)
The 5kΩ–0 throttle (called a “Type 1” throttle in the programming menu of the
13XX programmer) is a 2-wire resistive throttle that connects between the Pot
Wiper and Pot Low pins (Pins 6 and 7), as shown in Figure 4. It doesn’t matter
which wire goes on which pin. For Type 1 throttles, zero speed corresponds to
5 kΩ measured between the two pins and full speed corresponds to 0 Ω. (Note:
This wiring is also shown in the standard wiring diagram, Figure 3.)
Fig. 4 Wiring for 5k
Ω
–0
throttle (“Type 1”).
In addition to accommodating the basic 5kΩ–0 throttle, the Type 1
throttle is the easiest with which to implement a wigwag-style throttle.
Using a 20kΩ potentiometer wired as shown in Figure 5, the pot wiper can
be set such that the controller has 5 kΩ between Pins 6 and 7 when the
throttle is in the neutral position. The throttle mechanism can then be
designed such that rotating it either forward or back decreases the resistance
between Pins 6 and 7, which increases the controller output. The throttle
mechanism must provide signals to the controller’s forward and reverse
inputs independent of the throttle pot resistance. The controller will not
sense direction from the pot resistance.
Fig. 5 Wiring for 20k
Ω
potentiometer used as a
wigwag-style throttle
(“Type 1”).
20 kΩ
FASTERFASTER
Pot Wiper input (Pin 6)
Pot Low input (Pin 7)
Broken wire protection is provided by the controller sensing the current
flow from the wiper input through the potentiometer and into the Pot Low pin.
If the Pot Low input current falls below 0.65 mA or its voltage below 0.06 V, a
throttle fault is generated and the controller is disabled. Note: The Pot Low pin
(Pin 7) must not be tied to ground (B-).
5kΩ–0
Pot Low input (Pin 7)
Pot Wiper input (Pin 6)
FASTER
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
11
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
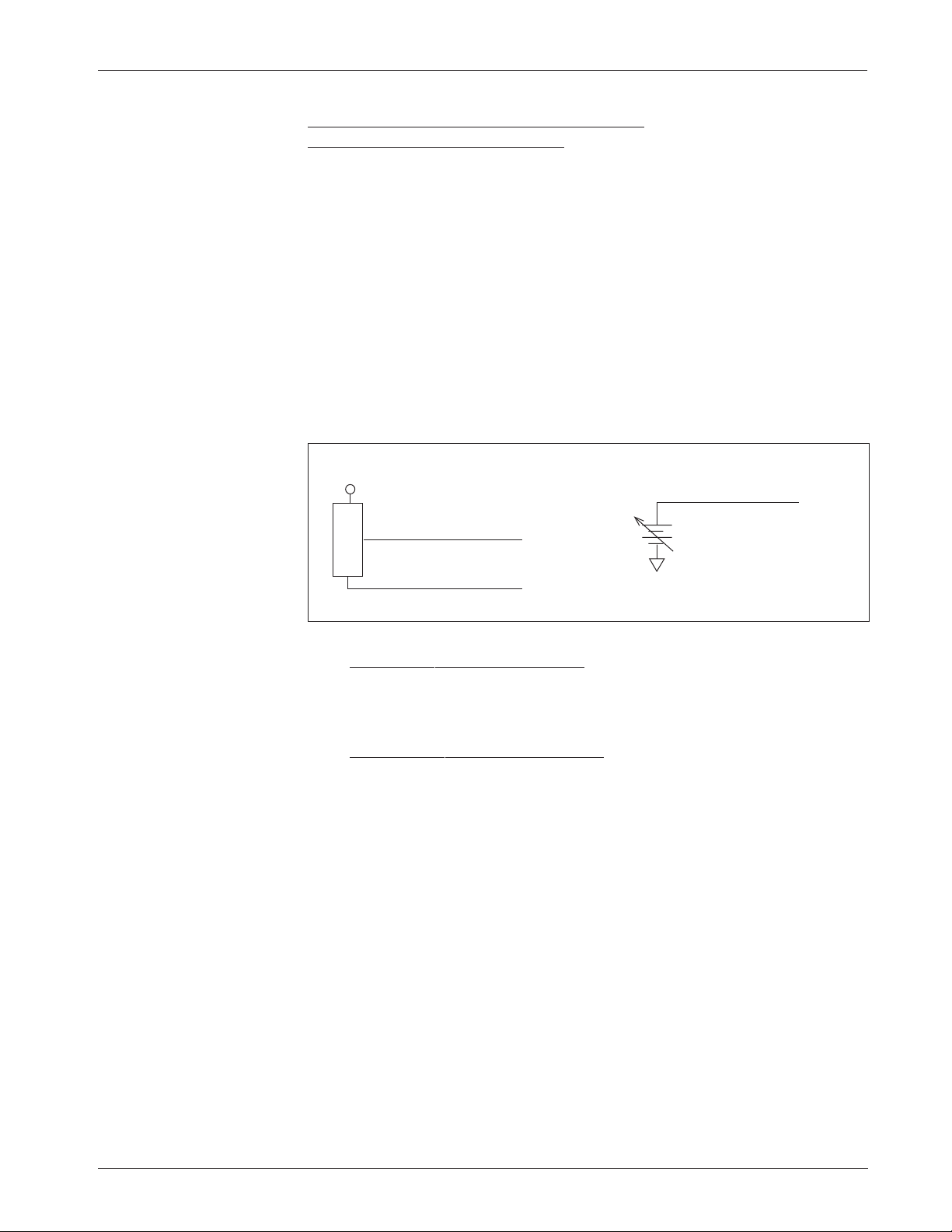
0–5V, Current Source, 3-Wire Potentiometer,
and Electronic Throttles (“Type 2”)
With these throttles (“Type 2” in the programming menu) the controller looks
for a voltage signal at the wiper input (Pin 6). Zero speed will correspond to 0 V
and full speed to 5 V (measurements made relative to B-). A voltage source,
current source, 3-wire potentiometer, or electronic throttle can be used with this
throttle type. The wiring for each is slightly different and each has varying levels
of throttle fault detection associated with it.
0–5V Throttle
Two ways of wiring the 0–5V throttle are shown in Figure 6. The active range
for this throttle is from 0.2 V (at 0% Throttle Deadband) to 5.0 V (at 100%
Throttle Max), measured relative to B-.
Fig. 6 Wiring for
0–5V throttles (“Type 2”).
Sensor-referenced 0–5V throttles must provide a Pot Low current greater
than 0.65 mA to prevent shutdown due to pot faults. It is recommended that
the maximum Pot Low current be limited to 55 mA to prevent damage to the
Pot Low circuitry.
Ground-referenced 0–5V throttles require setting the Pot Low Fault
parameter (see Section 3, page 38) to Off; otherwise the controller will register
a throttle fault and will shut down. For ground-referenced 0–5V throttles, the
controller will detect open breaks in the wiper input but cannot provide full
throttle fault protection. Also, the controller recognizes the voltage between the
wiper input and B- as the applied throttle voltage and not the voltage from the
voltage source relative to the Pot Low input.
For either throttle input, if the 0–5V throttle input (Pin 6) exceeds 5.5 V
relative to B-, the controller will register a fault and shut down.
+
-
B-
+
SENSOR GROUND
SENSOR OUTPUT (0–5V)
S E N S O R
Pot Low input (Pin 7)
0–5V input (Pin 6)
0–5V input (Pin 6)
Pot Low Fault setting = OFF
☞
Sensor-referenced 0–5V source Ground-referenced 0–5V source
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
12
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
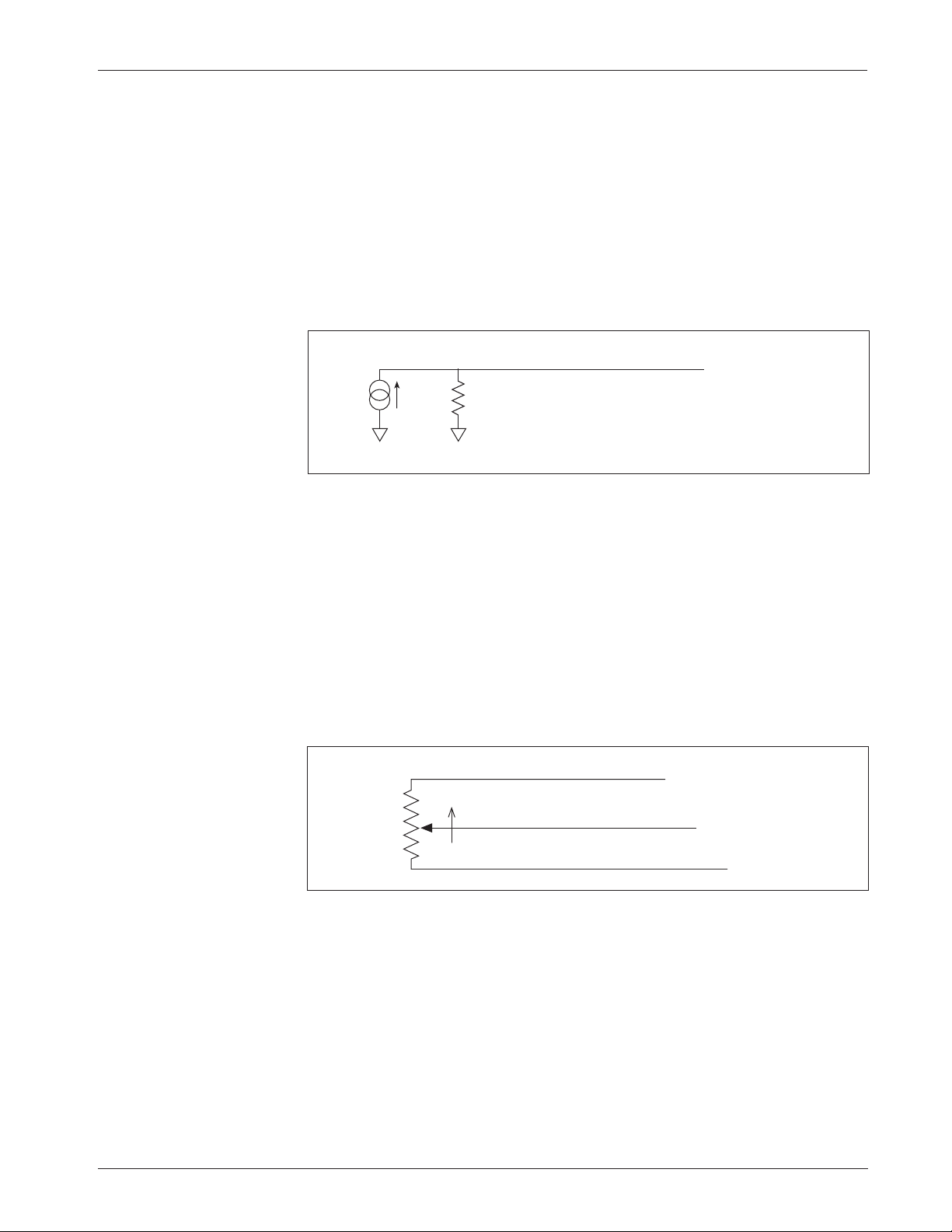
Current Sources As Throttles
A current source can also be used as a throttle input, wired as shown in Figure 7.
A resistor, R
throttle
, must be used to convert the current source value to a voltage.
The resistor should be sized to provide a 0–5V signal variation over the full
current range.
The Pot Low Fault parameter (see Section 3, page 38) must be set to Off;
otherwise the controller will register a throttle fault and will shut down. It is the
responsibility of the vehicle manufacturer to provide appropriate throttle fault
detection in applications using a current source as a throttle.
Fig. 8 Wiring for 3-wire
potentiometer throttle
(“Type 2”).
1kΩ–10kΩ
Pot Wiper input (Pin 6)
Pot Low input (Pin 7)
Pot High output (Pin 5)
FASTER
Fig. 7 Wiring for current
source throttle (“Type 2”).
3-Wire Potentiometer (1kΩ–10kΩ) Throttle
A 3-wire pot with a total resistance value anywhere between 1 kΩ and 10 kΩ can
be used, wired as shown in Figure 8. The pot is used in its voltage divider mode,
with the voltage source and return being provided by the 1243GEN2 controller.
Pot High (Pin 5) provides a current limited 5V source to the pot, and Pot Low
(Pin 7) provides the return path. If a 3-wire pot is used and the Pot Low Fault
parameter (see Section 3, page 38) is set to On, the controller will provide full
throttle fault protection in accordance with EEC requirements. Note: the Pot
Low pin (Pin 7) must not be tied to ground (B-).
R
throttle
I
source
B-B-
0–5V input (Pin 6)
Pot Low Fault setting = OFF
☞
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
13
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
Curtis ET-XXX Electronic Throttle
The Curtis ET-XXX provides a 0–5V throttle and forward/reverse inputs for the
1243GEN2 controller. Wiring for the ET-XXX is shown in Figure 9. When an
electronic throttle is used, the Pot Low Fault parameter (see Section 3, page 38)
must be set to Off; otherwise the controller will register a throttle fault and will
shut down.
There is no fault detection built into the ET-XXX, and the controller will
detect only open wiper faults. It is the responsibility of the vehicle manufacturer
to provide any additional throttle fault detection necessary.
The ET-XXX can be integrated into a control head to provide wigwagstyle throttle control. Alternatively, a complete control head assembly is available from Curtis. This control head assembly—the CH series—combines the
ET-XXX throttle with a variety of standard control head switch functions for
use in walkie and lift truck applications.
0–5kΩ Throttle (“Type 3”)
The 0–5kΩ throttle (“Type 3” in the programming menu) is a 2-wire resistive
throttle that connects between the Pot Wiper and Pot Low pins (Pins 6 and 7)
as shown in Figure 10. Zero speed corresponds to 0 Ω measured between the two
pins and full speed corresponds to 5 kΩ. This throttle type is not appropriate
for use in wigwag-style applications.
Broken wire protection is provided by the controller sensing the current
flow from the wiper input through the potentiometer and into the Pot Low pin.
If the Pot Low input current falls below 0.65 mA or its voltage below 0.06 V,
Fig. 9 Wiring for Curtis
ET-XXX electronic throttle
(“Type 2”).
GREEN
ORANGE
BLACK
BLACK/WHITE
WHITE
WHT/BRN
B+
KEYSWITCH
connector
WHT/GRN
Reverse input (Pin 11)
KSI (Pin 16)
0–5V input (Pin 6)
Forward input (Pin 12)
Pot Low Fault setting = OFF
☞
B-
B-

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
14
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Throttle
Fig. 10 Wiring for
0–5k
Ω
throttle
(“Type 3”).
a throttle fault is generated and the controller is disabled. Note: The Pot Low
pin (Pin 7) must not be tied to ground (B-).
Wigwag-Style 0–5V Voltage Source and 3-Wire Pot Throttle (“Type 4”)
These throttles (“Type 4” in the programming menu) operate in true wigwag
style. No signals to the controller’s forward and reverse inputs are required; the
action is determined by the wiper input value. The interface to the controller for
Type 4 devices is similar to that for Type 2 devices. The neutral point will be with
the wiper at 2.5 V, measured between Pin 6 and B-.
The controller will provide increasing forward speed as its wiper input
value (Pin 6) is increased, with maximum forward speed reached at 4.5 V. The
controller will provide increasing reverse speed as the wiper input value is
decreased, with maximum reverse speed reached at 0.5 V. The minimum and
maximum wiper voltage must not exceed the 0.5V and 4.5V fault limits.
When a 3-wire pot is used and the Pot Low Fault parameter (see Section 3,
page 36) is set to On, the controller provides full fault protection for Type 4
traction throttles. Any potentiometer value between 1 kΩ and 10 kΩ is supported. When a voltage throttle is used, it is the responsibility of the OEM to
provide appropriate throttle fault detection.
Note: If your Type 4 throttle has an internal neutral switch, this internal
neutral switch should be wired to the forward switch input (Pin 12). The
controller will behave as though no throttle is requested when the neutral
switch is high, and will use the throttle value when the neutral switch is low.
WIRING: Fault Outputs
The 1243GEN2 has two fault signal outputs (Pins 2 and 3), which can be used
to provide diagnostic information to a display panel. These current-sinking
outputs can drive LEDs or other loads requiring less than 10 mA. Since these
outputs are intended to drive LEDs, each contains a dropping resistor; as a
result, these outputs will not pull down to B-. Wiring is shown in Figure 11.
The Fault 1 and Fault 2 outputs can be programmed to display fault
information in either of two formats: Fault Code format or Fault Category
format (see Section 3, page 51).
Alternatively, Pin 2 can be used to provide a pump input signal (see pump
meter parameter, Section 3, page 48); Pin 3 can be used to interface an external
auxiliary enable circuit (see BDI lockout parameter, Section 3, page 51).
0–5kΩ
Pot Low input (Pin 7)
Pot Wiper input (Pin 6)
FASTER
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
15
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Spyglass Display
Fig. 11 Wiring for fault
outputs, when used to drive
LEDs. Alternatively, Pin 2
can be used for a pump
meter input, and Pin 3 can
be used to interface an
external enable circuit.
B-
+
-
Fault 1 output (Pin 2)
Fault 2 output (Pin 3)
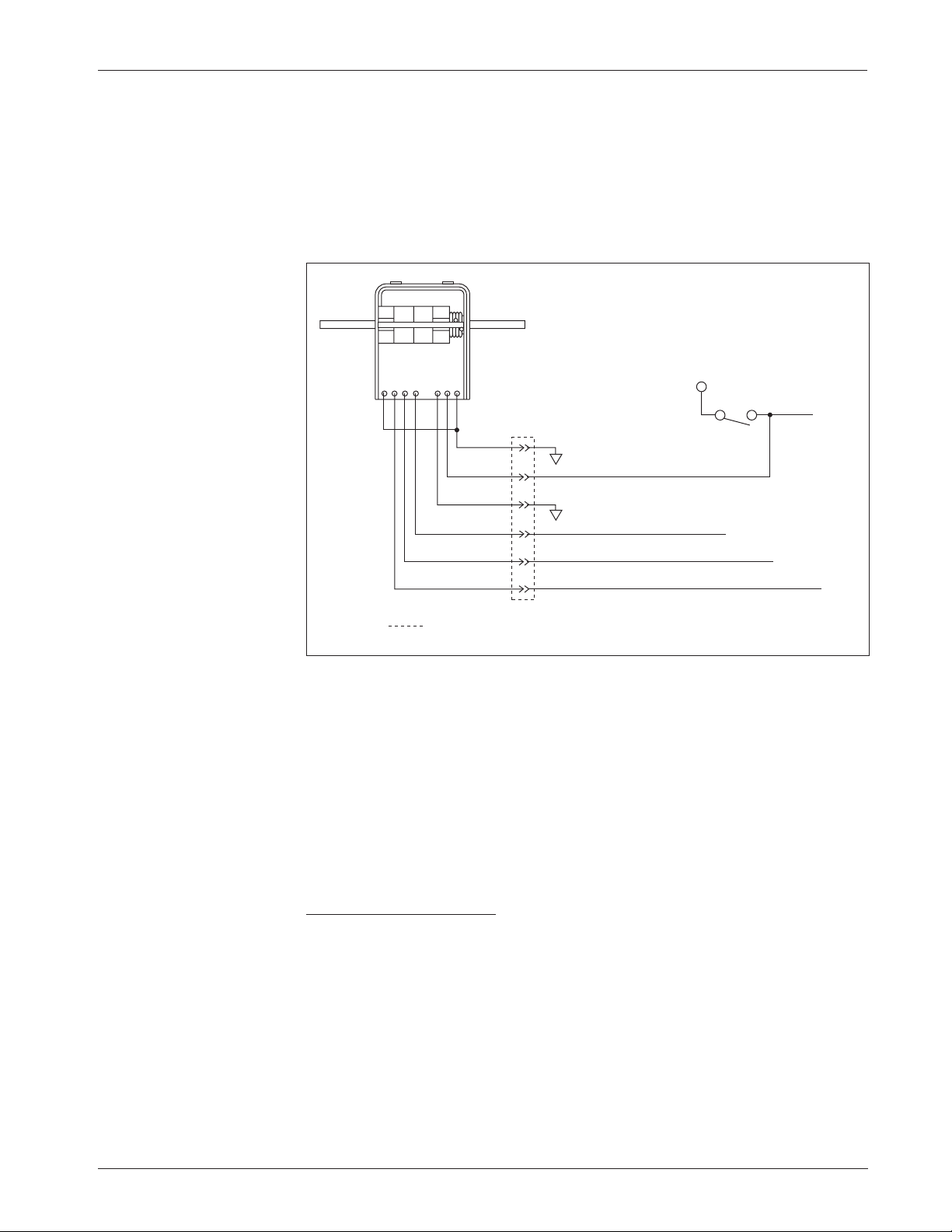
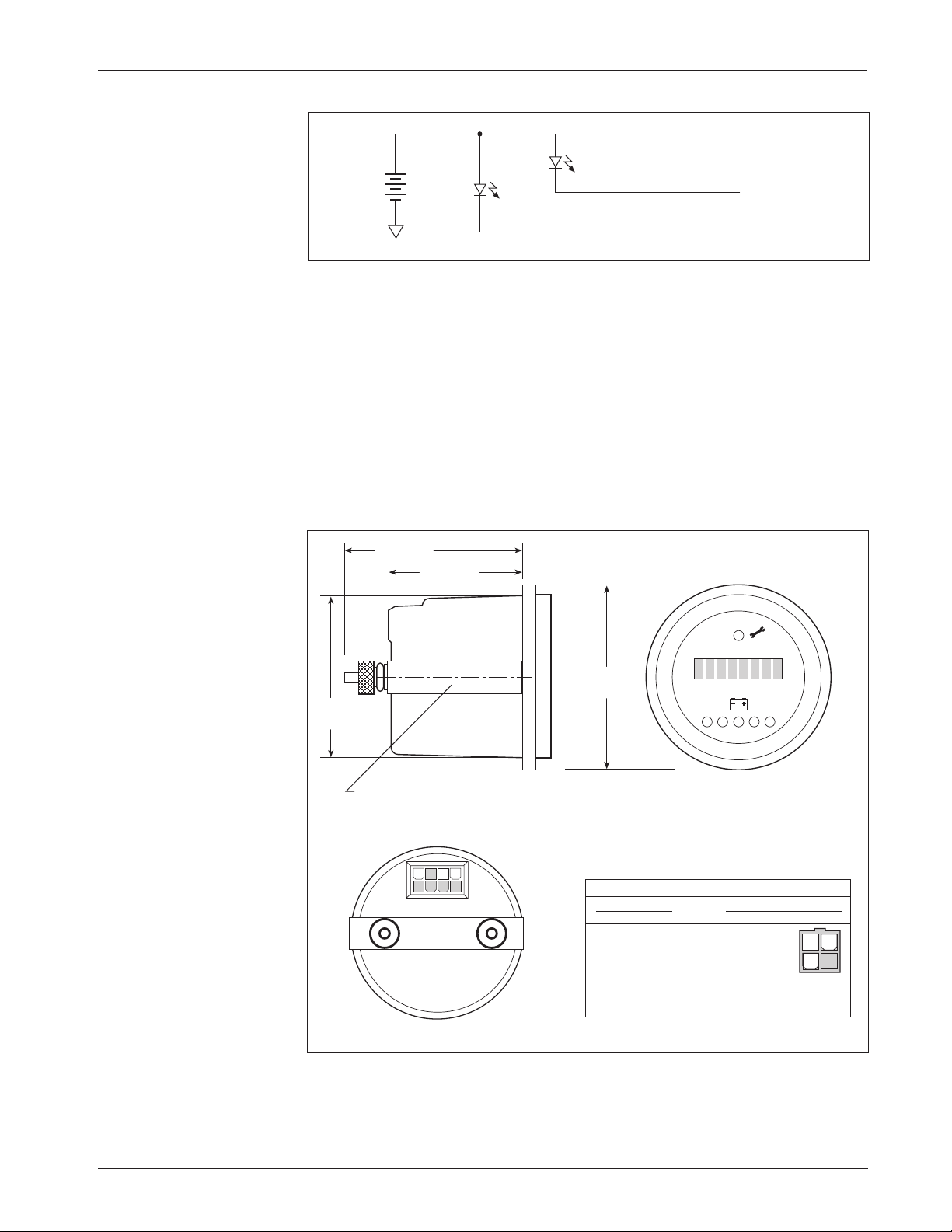
WIRING: Spyglass Display
The Curtis 840 Spyglass features an 8-character LCD display that sequences
between hourmeter, BDI %, and fault messages. Depending on the model,
either three or six indicator LEDs are also located on the face of the gauge. See
Section 7 (Diagnostics and Troubleshooting) for more information on the
Spyglass displays.
The mating 8-pin connector is Molex 39-01-2085, with 39-00-0039
(18–24 AWG) pins.
Fig. 12 Wiring guide and
mounting dimensions for
Curtis Spyglass (6-LED
model shown; dimensions
and wiring are identical for
the 3-LED model).
SPYGLASS 1243·GEN·2 CONTROLLER
PIN # FUNCTION PIN #
1–4 N.C. –
5 +12V, +15V 4
6 receive data 3
7 N.C. –
8 ground (B+) 2
58
(2.25)
44 (1.75)
8
58 (2.25)
52
(2.0)
“U” clamp for
up to 6 (0.25)
panel thickness
5
4 1
WIRING GUIDE
34
12
0 1
Dimensions in millimeters (and inches)

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
16
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Emerg. Reverse and Aux Driver
☞
C A U T I O N
WIRING: Emergency Reverse
To implement the emergency reverse feature, Pin 13 (the emergency reverse
input) must be connected to battery voltage as shown in the standard wiring
diagram, Figure 3.
The controller provides maximum braking torque as soon as the emergency reverse switch is closed. The vehicle will then be automatically driven in
the reverse direction at the programmed emergency reverse current limit until
the emergency reverse switch is released.
CAUTION:
The polarity of the S1 and S2 connections will affect the
operation of the emergency reverse feature. The forward and reverse switches
and the S1 and S2 connections must be configured so that the vehicle drives
away from the operator when the emergency reverse button is pressed.
WIRING: Emergency Reverse Check
An optional wire connected directly to the emergency reverse switch provides for
broken wire detection when that feature is programmed On (see Section 3,
page 43). The emergency reverse check output wire periodically pulses the
emergency reverse circuit to check for continuity in the wiring. If there is no
continuity, the controller output is inhibited until the wiring fault is corrected.
The emergency reverse check wire is connected to Pin 10 as shown by the
dotted line in the standard wiring diagram, Figure 3. If the option is selected
and the check wire is not connected, the vehicle will not operate. If the option
is not selected and the check wire is connected, no harm will occur—but
continuity will not be checked.
WIRING: Auxiliary Driver
The 1243GEN2 provides an auxiliary driver at Pin 8. This low side driver is
designed to energize an electromagnetic brake coil, as shown in the standard
wiring diagram (Figure 3). The output is rated at 2 amps and is overcurrent
protected. A coil suppression diode is provided internally to protect the driver
from inductive spikes generated at turn-off. The recommended wiring is shown
in the standard wiring diagram, Figure 3. The contactor coil or driver load
should not be connected directly to B+, which would cause the controller to be
always biased On via a path through the coil suppression diode to the KSI input.
Although it is typically used to drive an EM brake, the auxiliary driver can
be used to drive a pump contactor or hydraulic steering assist in applications
not requiring an EM brake.
Note: Because the auxiliary driver is typically used for an EM brake, the
programmable parameters related to this driver are described in the electromagnetic brake parameter group; see page 28.

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
17
CONTACTOR, SWITCHES, and OTHER HARDWARE
Main Contactor
A main contactor should be used with any 1243GEN2 controller; otherwise the
controller’s fault detects will not be able to fully protect the controller and motor
drive system from damage in a fault condition. The main contactor allows the
controller and motor to be disconnected from the battery. This provides a
significant safety feature in that the battery power can be removed from the drive
system if a controller or wiring fault results in full battery power being applied
to the motor. If the Contactor Diagnostics parameter (see Section 3, page 40)
is On, the controller will conduct a missing contactor check and a welded
contactor check each time the main contactor is requested to close and will not
proceed with the request if a fault is found.
A single-pole, single-throw (SPST) contactor with silver-alloy contacts,
such as an Albright SW80 or SW180—available from Curtis—is recommended for use as the main contactor. The contactor coils should be specified
with a continuous rating at the nominal battery pack voltage.
The main contactor coil driver output (Pin 4) is rated at 2 amps, is overcurrent protected, and is checked for open coil faults. A built-in coil suppression diode is connected between the main contactor coil driver output and the
keyswitch input. This protects the main contactor coil driver from failure due
to inductive voltage kickback spikes when the contactor is turned off.
Keyswitch and Interlock Switch
The vehicle should have a master on/off switch to turn the system off when not
in use. The keyswitch input provides logic power for the controller.
The interlock switch—which is typically implemented as a tiller switch,
deadman footswitch, or seatswitch—provides a safety interlock for the system.
The keyswitch and interlock switch provide current to drive the main
contactor coil and all other output driver loads as well as the controller’s internal
logic circuitry and must be rated to carry these currents.
Forward, Reverse, Mode Select, and Emergency Reverse Switches
These input switches can be any type of single-pole, single-throw (SPST) switch
capable of switching the battery voltage at 10 mA. Typically the emergency
reverse switch is a momentary switch, active only while it is being pressed.
Reverse Polarity Protection Diode
For reverse polarity protection, a diode should be added in series between the
battery and KSI. This diode will prohibit main contactor operation and current
flow if the battery pack is accidentally wired with the B+ and B- terminals
exchanged. It should be sized appropriately for the maximum contactor coil and
fault diode currents required from the control circuit. The reverse polarity
protection diode should be wired as shown in the standard wiring diagram,
Figure 3 (page 7).
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Main Contactor & Switches, etc.

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
18
Circuitry Protection Devices
To protect the control circuitry from accidental shorts, a low current fuse
(appropriate for the maximum current draw) should be connected in series
between the battery and KSI. Additionally, a high current fuse should be wired
in series with the main contactor to protect the motor, controller, and batteries
from accidental shorts in the power system. The appropriate fuse for each
application should be selected with the help of a reputable fuse manufacturer or
dealer. The standard wiring diagram, Figure 3, shows the recommended location
for each fuse.
Mode Select Switch Operation
The two mode select switches (Mode Select 1 and Mode Select 2) together define
the four operating modes. The switch combinations are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 MODE SELECTION
MODE MODE
OPERATING MODE SELECT SELECT
SWITCH 1 SWITCH 2
MultiMode™ 1 OPEN OPEN
MultiMode™ 2 CLOSED OPEN
MultiMode™ 3 OPEN CLOSED
MultiMode™ 4 CLOSED CLOSED
Load Sensor [optional]
The 1243GEN2 provides a load sensor input at Pin 1. The controller can be
programmed to vary the strength of regen braking depending on the load sensor
input. The load sensor, if one is used, should be sized to handle your application’s
maximum expected load without exceeding 5 V.
2 — INSTALLATION & WIRING:
Switches, etc.

Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
19
3 — PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
The 1243GEN2 controller has a number of parameters that can be programmed
using a Curtis handheld programmer. These programmable parameters allow
the vehicle’s performance characteristics to be customized to fit the needs of
individual vehicles or vehicle applications.
The OEM can specify the default value for each parameter and can also
designate whether a parameter will have User or OEM access rights. Accordingly, programmers are available in User and OEM versions. The User programmer can adjust only those parameters with User access rights, whereas the
OEM programmer can adjust all the parameters. For information about 1311
programmer operation, see Appendix B.
The MultiMode™ feature of the 1243GEN2 controller allows operation in
four distinct modes. These modes can be programmed to provide four different
sets of operating characteristics, which can be useful for operating in different
conditions, such as slow precise indoor maneuvering in Mode 1; faster, long
distance, outdoor travel in Mode 4; and application-specific special conditions
in Modes 2 and 3. Eight parameters can be configured independently in each
of the four modes:
— acceleration rate (M1–M4)
— braking current limit (M1–M4)
— braking rate (M1–M4)
— deceleration rate (M1–M4)
— drive current limit (M1–M4)
— maximum forward speed (M1–M4)
— maximum reverse speed (M1–M4)
— restraint (M1–M4).
To better describe their interrelationships, the individual parameters are
grouped into categories as follows:
Battery Parameters
Acceleration Parameters
Braking Parameters
Interlock Braking Parameters
Electromagnetic Brake Parameters
Speed Parameters
Throttle Parameters
Field Parameters
Contactor Parameters
Sequencing Fault Parameters
Emergency Reverse Parameters
Motor Protection Parameters
Hourmeter Parameters
BDI Parameters
Fault Code Parameters
3
Curtis 1243GEN2 Manual
20
3 — PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
Battery Parameter ...................... p.21
Battery Voltage
Acceleration Parameters ............ p. 21
Drive Current Limit, M1–M4
Acceleration Rate, M1–M4
Quick Start
Current Ratio
Braking Parameters ................... p.23
Braking Current Limit, M1–M4
Deceleration Rate, M1–M4
Throttle Deceleration Rate
Restraint, M1–M4
Braking Rate, M1–M4
Taper Rate
Variable Braking
Interlock Braking
Parameters ................................... p.26
Interlock Braking Rate
Max. Forward Regen
Max. Reverse Regen
Min. Forward Regen
Min. Reverse Regen
Max. Load Volts
Min. Load Volts
Electromagnetic Brake
Parameters ................................... p.28
Auxiliary Driver Type
Electromagnetic Brake PWM
Auxiliary Driver Delay
Interlock Brake Delay
Speed Parameters ....................... p.31
Max. Forward Speed, M1–M4
Max. Reverse Speed, M1–M4
Creep Speed
Load Compensation
Throttle Parameters ................... p.32
Throttle Type
Throttle Deadband
Throttle Max
Throttle Map
Pot Low Fault
Field Parameters ......................... p.38
Min. Field Current Limit
Max. Field Current Limit
Field Map Start
Field Map
Field Check
Main Contactor Parameters ..... p.40
Main Contactor Interlock
Main Contactor Open Delay
Main Contactor Diagnostics
Sequencing Fault Parameters ... p.41
Anti-Tiedown
High Pedal Disable (HPD)
Static Return to Off (SRO)
Sequencing Delay
Emergency Reverse
Parameters ................................... p.43
Emerg. Reverse Current Limit
Emerg. Reverse Check
Emerg. Reverse Direction Interlock
Motor Protection Parameters ... p. 44
Warm Speed
Motor Warm Resistance
Motor Hot Resistance
Motor Resistance Compensation
Hourmeter
Parameters
.................... p.45
Adjust Hours High
Adjust Hours Middle
Adjust Hours Low
Set Total Hours
Set Traction Hours
Total Service Hours
Traction Service Hours
Total Disable Hours
Traction Disable Hours
Traction Fault Speed
Service Total
Service Traction
Hourmeter Type
Pump Meter
BDI Parameters ........... p. 49
Full Voltage
Empty Voltage
Reset Voltage
Battery Adjust
BDI Disable
BDI Limit Speed
Fault Code
Parameters .................... p. 51
Fault Code
BDI Lockout
Individual parameters are described in the following text in
the order they are listed on this page. They are listed by the
abbreviated names that are displayed in the programmer’s
Program Menu. Not all of these parameters are displayed
on all controllers; the list for any given controller depends
on its specifications.
The programmer displays the parameters in a different
order. For a list of the individual parameters in the order in
which they appear in the Program Menu, see Section 6:
Programmer Menus.
☞
 Loading...
Loading...