Page 1

Culligan®
Iron-Cleer® Plus
Automatic
Water Filter
Owners Guide
Page 2
Thank You
And Welcome To Your New World Of Better Living With
Culligan Water.
This system and its installation must comply with state and local regulations.
The System is ONLY to be supplied with cold water.
The Culligan® Iron Cleer® water filter has been tested and certified by WQA
against WQA S-200 for the effective reduction of iron up to 1,400 gallons for
10” units and 2,000 gallons for 12” units.
Do not use with water that is microbiologically unsafe or of unknown quality without adequate
disinfection before or after the system.
For installations in Massachusetts, the Massachusetts Plumbing Code 248 CMR shall
be adhered to. Consult your licensed plumber for installation of the system. This
system and its installation must comply with state and local regulations. The use of
saddle valves is not permitted.
If this is your first experience having filtered, conditioned water in your home, you’ll be amazed at the
marvelous difference it makes. We promise that you’ll never want to be without it again.
Congratulations, too, on selecting one of the “first family” of water filters in the prestigious Culligan
Iron-Cleer. With Culligan’s many years of knowledge and experience in water treatment, you can be
confident that the model you selected has been designed and engineered to provide years of service
with a minimum of care and attention.
Products manufactured and marketed by Culligan International Company (Culligan) and its affiliates
are protected by patents issued or pending in the United States and other countries. Culligan reserves
the right to change the specifications referred to in this literature at any time, without prior notice.
Culligan, Culligan Iron-Cleer, Cullar, Filtr-Cleer, Cullneu, Accusoft, Culligan Man and www.culligan.
com are trademarks of Culligan International Company or its affiliates.
Attention Culligan Customer:
The installation, service and maintenance of this equipment should be rendered by a qualified and
trained service technician. Your local independently operated Culligan dealer employs trained service
and maintenance personnel who are experienced in the installation, function and repair of Culligan
equipment. This publication is written specifically for these individuals and is intended for their use.
We encourage Culligan users to learn about Culligan products, but we believe that product
knowledge is best obtained by consulting with your Culligan dealer. Untrained individuals who use
this manual assume the risk of any resulting property damage or personal injury.
ii
Page 3

Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Operating Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Familiarization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Programming. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Statistic Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
When and How to Bypass your Water Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Things to Check Before You Call for Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Preventative Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Troubleshooting Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Performance Data Sheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Records and Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table of
Contents
iii
Page 4

This page intentionally left blank.
iv
Page 5
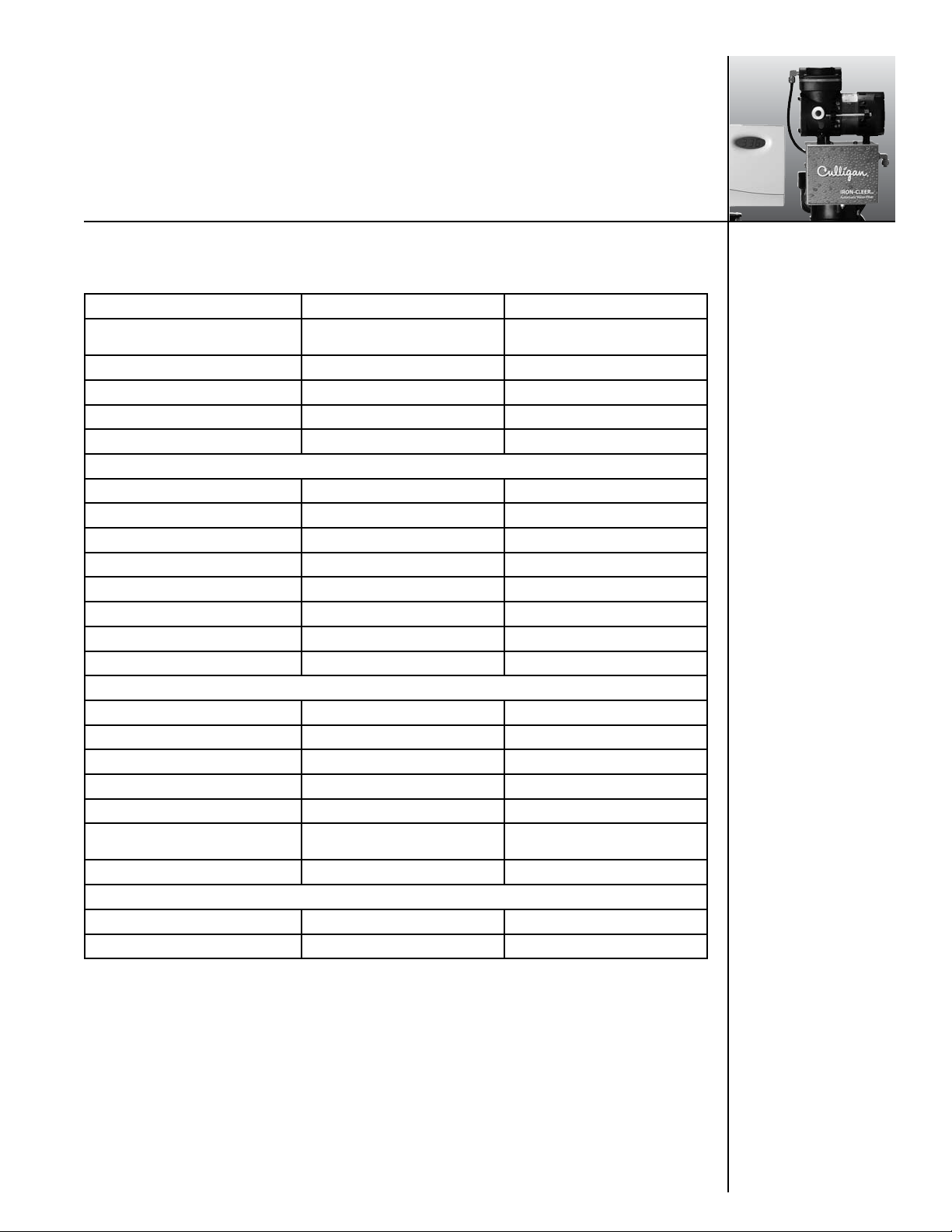
10” Iron Cleer 12” Iron Cleer
Control Valve
1” 5-cycle reinforced
thermoplastic
1” 5-cycle reinforced
thermoplastic
Timer Electro-mechanical Electro-mechanical
Overall Conditioner Height 67” 65”
Media Tank Dimensions (D x H) 2 ea. 10” x 54” tanks 2 ea. 12” x 52” tanks
Filter Media Type 1.0 cu. ft. birm 1.5 cu. ft. birm
Underbedding
G-50 35 lbs. 35 lbs.
Cullsan U 25 lbs. 25 lbs.
Capacity
Freeboard
1
2
1400 gallons 2000 gallons
21” 18”
Max. Clear Water (Soluble) Iron 10 ppm 10 ppm
Max. Hydrogen Sulfide 5.0 ppm 5.0 ppm
Minimum Alkalinity 100 ppm 100 ppm
pH 7.0 - 8.5 7.0 - 8.5
Service Flow @ Pressure Drop (Clean Bed)
Normal 5 gpm @ 9 psi 7 gpm @ 10 psi
Maximum
3
6 gpm @ 11 psi 9 gpm @ 14 psi
Operating Pressure 20-60 psi 20-60 psi
Operating Temperature 33-120° F (1-48° C) 33-120° F (1-48° C)
Electrical Requirements 120 Volts/60 Hz 120 Volts/60 Hz
Power Consumption, Continuous/
Maximum
3 watts/203 watts 3 watts/203 watts
Drain Flow, Maximum 10 gpm (5.5 gpm min. req.) 10 gpm (8.0 gpm min. req.)
Regeneration Time
Backwash 5 - 20 minutes 5 - 20 minutes
Fast Rinse 5 - 20 minutes 5 - 20 minutes
SpecificationsCulligan® Iron Cleer® Plus Filters
1 Capacity based on 4 gpm and 10 mg/L of dissolved iron.
2 Measured from top of media bed to top of inlet fitting.
3 Max flow rates & pressure drop characteristics have not been validated by the Water Quality
Association.
The max specified flow rate at which the system will deliver treated water as validated by the Water
Quality Association is defined as service flow.
1
Page 6

Introduction
Operation
Step 1.
Aeration Operation Service Cycle
In the service cycle, raw water enters the inlet port of the aeration tank and is directed through the
inlet diffuser. The oxidation process begins when the water passes through the inlet diffuser and
cascades through a head of air. This air/ water contact oxidizes the iron, manganese, hydrogen
sulfide in the water. The water is directed toward the bottom of the tank and travels through the pickup tube. It then passes through the outlet of the aeration tank to the inlet of the filter tank.
Filter Tank Operation Service Cycle
Raw water enters the filter tank through the inlet port of the filter control valve. Upon system demand
for filtered water, water is directed to the top of the tank and flows downward through the multimedia
filter bed toward the lower distributor. Oxidized iron particles are trapped by the filter bed as the
water passes through. Filtered water enters the lower distributor and travels up the distributor tube to
the outlet port on the filter valve.
Step 2.
Aeration Operation Air Recharge Cycle
When energized, the air pump sends air through the solenoid valve into one end of the shuttle valve.
Once air pressure in the shuttle valve is greater than the water supply pressure at the other end of the
shuttle valve, the piston shifts to the open position. In the open position, the bleed-off port discharges
excess water and old air to the drain port through a flow restrictor. Simultaneously, the air inlet port
opens to provide a direct connection between the air pump and the top of the aeration tank. The air
pump runs for a preset period of time recharging the head of air in the aeration tank.
Air Recharge Shut Off
The timer turns power off to the air pump and the solenoid valve at the end of the recharge cycle.
The solenoid valve then closes the port between the air pump and the shuttle valve. The port between
the shuttle valve and the atmosphere opens and releases air pressure. This allows water pressure to
shift the piston to the closed position. With the piston in the closed position, the air recharge inlet
port is closed and direct communication between the bleed off tube and the drain port is also closed.
Timer Operation
A timer controls the air recharge cycle and how frequently it occurs. The timer simultaneously
energizes the air pump and the solenoid valve. After a preset amount of time, the timer shuts off the
air pump and de-energizes the solenoid valve.
Solenoid Valve Operation
The solenoid valve is a three-way valve having ports that connect to the air pump, shuttle valve and
the atmosphere. In the service cycle, the solenoid valve is de-energized and closes the port to the
air pump, providing a positive shut-off to the pump. This prevents water from backing up into the air
pump and damaging the pump. In the air recharge cycle, the solenoid valve closes the port to the
atmosphere and opens the port from the air pump.
2
Page 7

Shuttle Valve Operation
In the service position, water pressure holds the shuttle valve piston in the closed position, trapping
the airhead in the aeration tank and closes the air recharge inlet port and drain port. During air
recharge cycle, air pressure is greater than the water pressure and forces the shuttle valve piston
in the open piston. The shuttle valve has an internal pressure relief valve that will relieve pressure
(greater than 100 psi) that may build up in the aeration tank. This precautionary function protects
components from failure due to excessive pressure.
Step 3.
Filter Tank Operation - Backwash Cycle
Reversing the flow of water through the filter bed and backwashing dirty water to the drain cleans
the filter bed. Raw water enters the filter control valve through the inlet port and is directed down the
distributor tube and out the lower distributor at the bottom of the tank, flowing upward through the
multimedia filter bed toward the top of the tank into the control valve. Water is then directed through
a specific flow restrictor and out the drain port to be discharged to drain.
Step 4.
Filter Tank Operation - Rinse Cycle
The rinse cycle packs the clean filter bed. Raw water enters the control valve through the inlet port
and is directed downward through the filter bed into the bottom distributor, up the distributor tube
into the control valve. Water is then directed through a specific flow restrictor and out the drain port
to be discharged to drain.
Introduction
(cont.)
Operation Of Aeration Pump
The Iron-Cleer® system introduces air into the aeration tank and bleeds off the old head of air
automatically. The exchange of the air into the aeration tank is controlled independently of the
recharge frequency of the filter media tank, allowing the air to be exchanged on a more frequent
basis. During an air exchange cycle, the air compressor pumps fresh air into the aeration tank and
the air eliminator solenoid exhausts the old air.
Advantages Over Other Systems
1. No chemicals or salt.
2. No air injectors, venturis, or micronizers.
3. No floats to regulate air volume in aeration tank which “foul” from iron.
4. Two-tank system consisting of a pressurized aeration tank and multi-media depth filter.
5. 110V aeration pump to recharge aeration tank.
6. Can be used on shared wells, municipal water supplies or with buried pressure tanks without
additional equipment.
7. Better filtration results.
3
Page 8
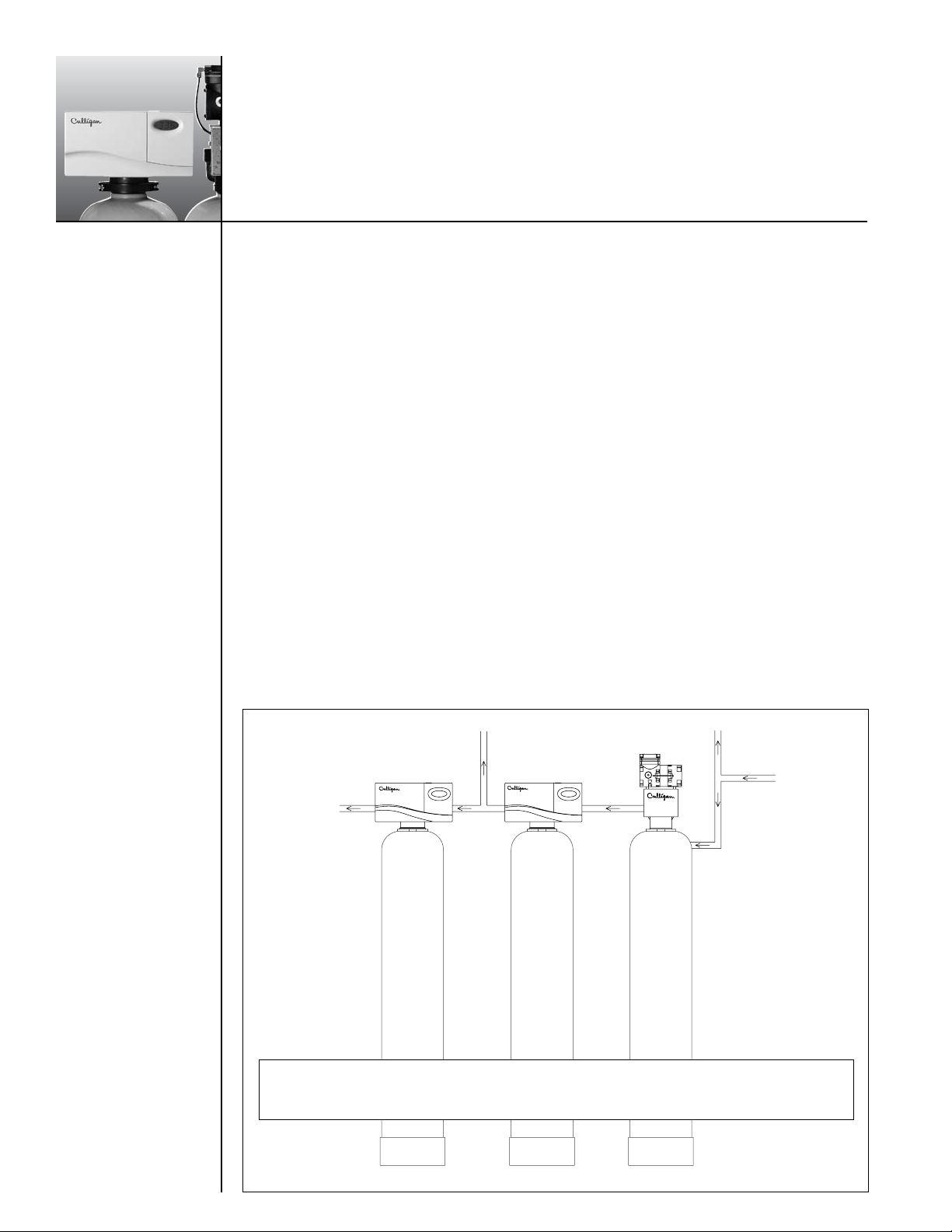
Softened &
Filtered Water
Filtered Non-Softened Water
Water
Softener
Iron-Cleer
Filter Tank
Unfiltered Water To Outside Hosebibs
Iron-Cleer
Aeration
Tank
Raw Water In
Iron-Cleer
Operating
Conditions
The concentration limits listed below reflect the maximum individual limit that each contaminant was
tested for separately without any interference of other contaminants in the influent water.
In reality, however, we know that these contaminants may be present in combination which may limit
the filter’s ability to remove these contaminants in higher concentrations. In some cases, individual
sellers of this equipment have had success removing higher concentrations of contaminants - iron, for
example - above the limitations we have listed. If you are considering the installation of this system
for the reduction/removal of iron, manganese and/or hydrogen sulfide beyond the printed operating
conditions below, we recommend that you consult the manufacturer for proper application. Installation
of this system under these circumstances may void part(s) and/or all of the system warranty.
pH — The pH level of the influent water must be 6.5 - 8.5. A pH level of 7.0 - 8.5 is optimal for iron
reduction and a pH level of 6.5 - 7.5 is optimal for hydrogen sulfide reduction.
Iron — This system is rated for a maximum of 10 ppm of ferrous (clear water) and/or ferric (red
water) iron. Consult the factory if iron bacteria is present.
Hydrogen Sulfide — Often referred to as rotten egg odor, hydrogen sulfide will be reduced
significantly on water supplies containing less than 5 ppm. Consult the manufacturer if hydrogen
sulfide concentrations is greater than 5 ppm.
Organic Matter (Tannins) — The presence of organic matter such as tannins will prevent the
oxidation process of converting the dissolved element, such as iron or manganese, to a non-soluble
precipitate or solid substance, allowing it to be filtered out. The Iron-Cleer® is not designed to remove
organic bound iron.
4
Note: Waste connections or drain outlets shall be designed and constructed to provide for
connection to the sanitary waste system through an air gap of 2 pipe diameters or 25.4 mm
(1 in.) whichever is larger.
Figure 1
Page 9

Power Loss
The AccuSoft® circuit board is equipped with a Hi-Cap Capacitor and EEPROM memory chip. The
capacitor is capable of maintaining the time, for at least two days, in the event of a power outage.
The EEPROM ensures that the individual programming parameters of your filter are not lost.
If the power outage lasts long enough to drain the Hi-Cap Capacitor, the control will flash “12:00
PM” when power is returned to the control. The unit will continue to keep time from the moment
power is restored, and will initiate a full regeneration at the preset regeneration time. The time of day
will need to be reset in order to return the regeneration to its preset time.
If you live in an area where power outages occur with a regular frequency, a battery backup option
is available for ensuring that the time of day is properly maintained. Contact your Culligan Dealer for
more information.
Regeneration
To initiate a regeneration at the preset time, press the “REGEN” button. The “REG” light will light. To
initiate an immediate regeneration, press and hold the “REGEN” button for at least three seconds. The
“REG” will light and blink. An immediate regeneration will also occur if a power outage has lasted
for more than three hours and the Immediate Regeneration option is chosen. Ask your Culligan Dealer
about this feature.
A regeneration at the Time of Regeneration will occur if so signaled by the Soft-Minder meter. The
“REG” enunciator on the display will also be lit.
Familiarization
Service
Culligan’s Iron-Cleer® water filter is equipped with a self diagnostic program to insure optimal
operation of your water filter. Should service become necessary, a phone icon will appear in the
display. If this condition occurs, call your local Culligan Dealer for assistance. The phone icon and
error code will be the only items displayed when service is required on the control.
5
Page 10

Familiarization
Setting Time Of Day
1. Press Program until 'tod' is displayed.
2. Use arrow keys to adjust minutes.
3. Press Regen once then adjust hours.
4. Continue to press Program to exit menu & save.
Program
Regen
Information
Press Regen once to begin regeneration tonight.
Or hold for immediate regeneration.
(cont.)
Modes of Operation
Manual Regeneration
Pressing and holding the regen button for 3 seconds will initiate an immediate regeneration. The
beeper is to give one beep at the start of manual regeneration (when the motor starts to turn). In
delay mode, pressing and releasing the regen button will light the regen icon for regeneration to
occur at the set delay time. Pressing and releasing the regen button again will turn off the regen
icon.
Power Loss
The AccuSoft® circuit board is equipped with a Hi-Cap Capacitor and EEPROM memory chip. The
capacitor is capable of maintaining the time, for at least one day, in the event of a power outage.
The EEPROM ensures that the individual programming parameters of your softener are not lost.
If the power outage lasts long
enough to drain the Hi-Cap
Capacitor, the control will flash
“12:00 PM” when power is
returned to the control. The
unit will continue to keep time
from the moment power is
restored, and will initiate a
full regeneration at the preset
regeneration time. The time of
day will need to be reset in
order to return the regeneration
to its preset time.
If you live in an area where
power outages occur with a
regular frequency, a battery
backup option is available for
ensuring that the time of day is
properly maintained. Contact
your Culligan Dealer for more
information.
Program
Key
Toggle
Down
Display
Regeneration
Key
Information
Key
Toggle
Up
6
Display Back-lit LCD display.
Program Key Depress to enter and move through the programming steps.
Regeneration
Key
Press and hold the key for three (3) seconds to initiate an immediate regeneration.
When pressed during programming the time of day, this key will allow the user to
toggle between the hours and minutes setting of timing program segments.
Information
Key
Each time depressed, the Information key will display statistical information
such a flow rate, time of day. Use with the Toggle Down key to display other
statistical information.
Toggle
Down Key
In the programming mode this key will move the user through the programming
function in a descending mode. If depressed for greater than three seconds, the rate
at which the display scrolls through data will increase.
Toggle Up
Key
In the programming mode this key will move the user through the programming
function in an ascending mode. If depressed for greater than three seconds, the rate
at which the display scrolls through the data will increase.
This key will also allow the user to manually step through the cycles of regeneration.
Page 11

The Culligan® AccuSoft® Plus circuit board controls all
of the filter functions. These settings are programmed
at the time of installation. The following is a list of all
the microprocessor functions, in the event that any of
the settings need to be adjusted.
%
Display Icons
The display is to be backlit and have the icons as shown below.
Custom LCD Display
Six standard 12-segment alpha-numeric characters, a decimal separating the first and second
character, a colon separating the second and third character positions, AM, PM, REGEN,
EFFICIENCY MODE, TODAY’S, AVG DAILY, WATER USAGE, SOFTWATER, REMAINING, %, MINS,
BACKWASH, BRINE RINSE, FAST RINSE, REFILL, GALLONS, LITERS, FLOW RATE, GPM, LPM Icons
A further description of each programming setting and the corresponding display is outlined below.
For a display that has an icon that is displayed solid for the 2 second time period prior to bringing
up the settings, the settings menu can be reached prior to the two second time out by pressing the “+”
or “-” key.
• Beeper Setting - This setting is used to turn the beeper on or
off for each key press actuation. The display will show “bEEP
X” where X is either “Y” or “N”. The “Y” or “N” will be toggled
with the “Up” and “Down” keys. Setting the Beep option to “N”
will only disable the beeper for key press actuation. The beeper
will still be active for error and alarm codes.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the next programming step.
Programming
• Time of Day - This setting is used to program the current time
of day. When in this step the display will first show “tod” for two
seconds.
After “tod” is displayed, “12:00 PM” will display (or the current
set time if already programmed) and the minutes will flash. The
minutes are adjusted with the “Up” or “Down” key until the
correct value is displayed.
Press the “Regen” key to flash the hours. Adjust with the “Up” or
“Down” key until the correct time is displayed.
Pressing the “Program” key will move to the next programming
step. Pressing “Regen” will move back to the minutes adjust.
Minutes Flashing
Hours Flashing
7
Page 12

Programming
(cont.)
• Time of Regeneration - This setting is used to program the
time at which a regeneration is to occur in the delay mode, or in
immediate mode with time clock backup on. The display will first
show “tor” for two seconds.
After “tor” is shown the display will then show the default of 2:00
AM (or the current programmed time of regeneration if already
set). The time can be adjusted in 30 minute increments by
pressing the “Up” or “Down” keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the
next programming step.
• Cycle 1 Time (Backwash) – This setting is used to program
the backwash cycle. The time of the cycle is kept in minutes.
The display will show the “Backwash” and “Mins” icons and the
cycle time in the right most digits. Adjust the value with the “Up”
or “Down“ keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the
next programming step.
• Cycle 2 Time (Pause) – This setting is used to set the time in
minutes for cycle 2. This cycle is usually brine draw / slow rinse
for softeners and a settling time for filters. The display will show
the “BRINE RINSE” and “MINS” icons and the cycle time in the
right most digits. Adjust the value with the “Up” or “Down“ keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the
next programming step.
Time Flashing
• Cycle 3 Time (Fast Rinse) – This setting is used to set the time
in minutes for cycle 3. This cycle is usually fast rinse for softeners
and filters. For softener applications it may include the refill
operation. The display will show the “FAST RINSE”, “/”,“REFILL”
and “MINS” icons for 4-cycle valves or “FAST RINSE” and
“MINS” icons for 5-cycle valves and filters with the cycle time in
the right most digits. Adjust the value with the “Up” or “Down“ keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the next programming step.
• Regeneration Interval - This setting is used to set the days
between regeneration in time clock mode. It is also active in
meter mode if the time clock backup DIP switch # 10 is set to on.
The display will show “REGEN” icon and “dAYS” as well as the
numbers to change. Adjust the value with the “Up” or “Down”
keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the next programming step.
8
Page 13

• Filter Media Life (Change Media) - This setting is used
in Filter Mode ONLY with flow meter attached. It enables or
disables an alarm code (“CHANGE MEDIA”) that indicates the
end of life for the filter media. The display will show “LIFE” in
the left most characters and toggle between “Y” and “N” in
the right most character with the “+” and “-“ keys. If “NO” is
selected, the alarm is disabled and the ‘Total Capacity’ setting will be treated as it is in Flow
Meter Mode (softener). If “YES” is selected, the alarm is enabled and will sound when the
‘Total Flow/Life of Unit’ statistic = ‘Total Capacity’ setpoint, indicating that it is time to change
the filter media.
Pressing “Program” key will save and advance to the next step.
• Total Capacity Set Point (Max Capacity) - This setting
is used to program a value that corresponds to the maximum
capacity that can be expected from a unit before it is completely
exhausted (no reserve). This setting will only appear if a flow
meter is connected to the circuit board. The display will show
the “REGEN” icon and “MAXCAP” for two seconds and then
display the “REGEN” and “GALLONS” or “LITERS” icons
(depending on DIPswitch #7 setting) and the setting numbers to
adjust. Adjust the value with the “Up” or “Down” keys.
When the capacity used equals this total capacity setting with
the “Life” feature off, the control will regenerate either immediately or at the time of regen based
on the “hidden programming menu” setting.
With the “Life” feature on, the control will use this setting to trigger the “Change Media” alarm.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the next programming step.
9999 99
Programming
(cont.)
• Batch Set Point - This setting is used to set the trip point for
regeneration when in flow meter operation. It will only appear
if a flow meter is connected. The programmed setting displays
the actual set point to trigger regeneration. The display will
show the “REGEN” icon and “bAtCH” for two seconds and
then display the “REGEN” and “GALLONS” or “LITERS” icons
(depending on dip#7 setting) and the setting numbers to adjust.
Adjust the value with the “Up” or “Down” keys.
Pressing the “Program” key will save the setting and move to the
next programming step.
OOO8 7O
9
Page 14

Statistic
Functions
The statistical functions are reached by pressing the “Information” key. Repetitive presses of the
“Information” key will cycle through the standard statistics mode until cycled back to time of day
display. Once either of the Information menus is entered the information shown for each display is
outlined below:
• Flow Rate - This display will only show if the flow meter is
attached to the control. The display shall show the current flow
rate of the water passing through the control. The display will
show the “Flow Rate” and “GPM” icons and the current flow
rate passing through the flow meter for as long as the “-” key or
“Information” key is not pressed.
• Capacity Remaining (%)(standard statistics) - This
display will only show if the flow meter is attached to the control.
The display shows the percent capacity remaining before
regeneration will be triggered. The display will show the “Water
Usage”, “Remaining” and “%” icons.
• Today’s Water Usage - This display will only show if the
flow meter is attached to the control. The display will show the
accumulated flow of water for the current day. The value is to
start totalizing at 12:00 AM and reset to 0 at 11:59:59 PM. The
display will show the “Today’s”, “Water Usage” and “Gallons”
icons and the total days flow.
%
• Average Daily Water Usage - This display will only show if
the flow meter is attached to the control. The display will show
a running 7-day average of daily water usage. The display will
show the “Avg Daily”, “Water Usage” and “Gallons” icons and
the averaged flow value.
10
Page 15

Normally, all water except outside lines passes through the water conditioner. There are times when
About 1-1/4”
the water conditioner should be bypassed, using the Cul-Flo-Valv® Bypass, or a 3-way bypass valve.
You should bypass:
1. If lines to outside faucets do not bypass the water conditioner, and you do not want to waste
conditioned water on lawn sprinkling or other outside uses.
2. If you are going away on vacation and want to save salt by not having the unit recharge while
you’re away.
Bypass Valve
In the back of Culligan water conditioners is a push-button Cul-Flo-Valv® Bypass. To bypass unit,
simply turn the blue knob clockwise. To return to soft water service, reverse the procedure - turn the
blue knob counter-clockwise.
When and
How to
Bypass
Your Water
Conditioner
Bypassed
To BYPASS, turn the blue knob clockwise (see directional arrow on end of knob)
until the knob stops as shown. DO NOT OVERTIGHTEN!
A screwdriver shank may be
used in the slot (arrow) as a
lever for extra turning force if
needed.
Soft Water
To return to SERVICE, turn the blue knob counter-clockwise (see directional arrow on end of knob)
until the knob stops as shown. DO NOT OVERTIGHTEN!
11
Page 16

Aeration Tank – Bypass Valve Operation
Normal Operation
Bypass Operation
“Treated” Water
Exits
Supply Water
Enters
Supply Water
Exits
Supply Water
Enters
Shut-Off Mode
No Water
Exits
Supply Water is Shut
Off From The House
and The Valve
Diagnostic Mode
Supply Water
Exits
Supply Water
Enters
How to
Bypass Your
Water Filter
(cont.)
Aeration Tank Bypass ValveWhen and
12
Page 17

If you unexpectedly experience problem water, make these simple checks before calling your Culligan
dealer. One of the following conditions may be the reason for your interruption of service.
Important
If any of the following conditions is found, the water filter should be manually recharged according to
instructions on page 5 after you have corrected the problem.
Power Supply
Check your power supply cord. Is it plugged fully into the electric outlet? Be certain that the outlet
is not controlled by a wall switch which has been turned off. Reset conditioner to proper time of day
and then plug in.
Blown Fuse
Check the house fuse or circuit breaker panel. Replace a blown-out fuse or reset an open circuit
breaker.
Power Failure
Any interruption in your power supply or time changes - such as daylight savings - will disrupt your
filter’s recharge schedule by causing the timer to run off-schedule. Reset timer to proper time of day.
Bypass Valves
Check to see if they are in the proper position. Cul-Flo-Valv® Bypass, if used, should be in the
“Service” position. If hand valves are used, see that inlet and outlet valve are opened and that the
bypass valve is closed.
Things to
Check Before
You Call for
Service
No Water
If you aren’t getting any water flow at all, make sure your water supply is working. Open a tap
ahead of the filter (outside tap) to see if you have any water pressure. If you have water pressure,
check the bypass valve. If it is in the Service position, put it into the bypass and call your Culligan
dealer for service.
Increased Usage
Guests, family additions, new water-using appliances, etc., all will result in more water usage and will
require more capacity from your filter. You can reprogram your recharging schedule by following the
directions on pages 7 – 9. Call your Culligan dealer for advice and save a service call.
13
Page 18

Recommended
Preventative
Maintenance
The Culligan Iron Cleer water filter has been designed to provide a good, consistent service life.
Because of the nature of problem water, we recommend that the local Culligan dealer provide regular
maintenance/service contracts for the proper operation of your systems. The water filter service
begins with a multi point inspection of your water filter system in an effort to uncover any and all
problems that may exist. Listed below is a recommended list of maintenance items to be inspected at
a minimum of once a year (or more frequently depending on the raw water quality).
14
Test Water
Hardness
Hydrogen Sulfide
Chlorine
Other
Comments:
Bypass Valve
Bypass in Service or Bypass?
Condition of bypass valve
Operation OK?
Control Valve
Condition of Seal Pack
Condition of Solenoid Valve
Condition of Motor:
Condition of Flow Control
Condition of Switches:
Condition of Check Valve
Condition of Shuttle Valve
Condition of Compressor
Control settings Before After
Check /reset Circuit Board
Check time of regeneration
Time delay relay setting “On Time” in seconds
Time delay relay setting “Off Time” in minutes
Backwash minutes
Fast Rinse minutes
Cycle control Test Cycle OK?
Media Tank
Freeboard inches:
Media Condition
Feed Product
Iron
TDS
Output PSI
Backwash
Fast rinse
Page 19

Complaint Problem Cause Solution
Iron bleedthrough or
staining.
A. Inadequate
backwash of filter
B. Fails to
regenerate
1. Plugged drain line flow
control
2. Insufficient water supply from
well.
3. Plugged aeration tank inlet
diffuser or pick-up tube.
4. Media bed fouled. 4. Call your Culligan dealer for
1. Interrupted electrical service. 1. Assure continuous electrical
2. Faulty circuit board. 2. Replace circuit board.
3. Faulty drive motor. 3. Replace drive motor.
4. Circuit board set incorrectly. 4. Reset circuit board.
1. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
2. Check for minimum specified
flow and pressure requirements
of filter system.
3. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
service.
supply (check plug, breaker,
fuses, etc.).
Troubleshooting
Guide
C. Water
contaminant
levels are greater
than limits
established by
Culligan.
D. Inadequate
aeration
E. Exceeding
recommended
filter system flow
rate.
F. Regeneration
during service
flow demand.
G. Raw water
bleeding through
filter.
1. It is not uncommon for local
water conditions to change.
1. Loss of air through inlet check
valve.
2. Loss of air through air leak. 2. Call your Culligan dealer for
3. Faulty aeration pump.
a. Electrical failure a. Assure permanent electrical
b. Pneumatic failure b. Call your Culligan dealer for
c. Damp environment c. Call your Culligan dealer for
4. Air loss through high
demand.
1. Service flow rate demand is
higher than filter system design
flow rate.
1. Time of day set incorrectly. 1. Call your Culligan dealer for
1. Internal control valve leak. 1. Call your Culligan dealer for
1. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
1. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
service.
service (check plug, breaker,
fuses, terminal block on control
valve, etc.).
service.
service.
4. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
1. Call your Culligan dealer for
service.
service.
service.
15
Page 20

Troubleshooting
Guide (cont.)
Complaint Problem Cause Solution
Water leaking
from relief
valve.
Water is
effervescent
Loss of pressure A. See complaint #1, problem A & B
Air spurting at
outside or nonfiltered water
fixtures.
Air spurting
from filtered
water fixtures.
Loss of media
through drain
line.
Excessive
noise during
regeneration.
A. Dirt lodged under
seat of valve.
B. Faulty or defective
relief valve
A. This can be
expected when water
is aerated under
pressure.
A. Inlet check valve
not sealing.
A. Reduced pressure
in distribution system.
A. New filter
backwashed during
first 24 hours after
installation.
B. Air passing
through filter during
backwash.
A. Howling or
whistling noise
during regeneration
cycle.
1. Pressure has exceeded
rating on relief valve and
caused valve to open
1. Water supply has been
naturally aerated under well
system pressure. As water is
released to the atmosphere,
air molecules separate from
the water molecules.
1. Improper installation
location.
2. Foreign material preventing
check valve.
3. Worn or faulty check valve. 3. Call your Culligan dealer
1. Service flow demand is
greater than water supply
available from well pump
system.
2. Water flow is restricted by
supply piping and/or water
treatment equipment.
1. New filter media is
shipped in a dry condition
and must soak for 24 hours to
become fully saturated before
a backwash cycle.
1. Excess air accumulated in
aeration tank from aeration
pump.
2. Excess air accumulated in
filter system from water supply
or well pump.
1. Inadequate drain line size. 1. Call your Culligan dealer
2. Drain line is vibrating
against other pipes, conduits,
pipe hangers, heat ducts,
floor joists,etc.
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
1. This natural phenomenon
will typically dissipate to the
atmosphere in a matter of
seconds. If preferred, water
can be drawn and stored
in an open container prior
to use (i.e. fill a pitcher and
store in the refrigerator for
cool, fresh drinking water).
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
2. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
for service.
1. Repair or replace well
pump system.
2. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
1. Clean drain line flow
control, control valve body,
seals, spacers and piston
assemblies
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
2a. Repair well pump
system.
2b. If the cause was due
to temporary loss of water
main pressure; the problem
will most likely correct itself
with the return of continuous
pressure.
for service.
2. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
16
Page 21

Complaint Problem Cause Solution
Water is
running
to drain
continuously.
Blue green
staining.
Compressor
doesn’t run.
Compressor run
with excessive
noise.
Compressor
runs
continuously.
A. Control valve is
stuck in regeneration
cycle.
A. Corrosive water
condition in copper
distribution piping
system.
1. Electrical service
to control(s) has been
interrupted.
2. Faulty circuit board. 2. Replace circuit board..
3. Faulty drive motor. 3. Call your Culligan dealer
4. Foreign material lodged in
piston.
1. Low pH condition of the
raw water supply.
2. In rare occasions, highly
aerated water in combination
with a specific water supply
can create a slightly corrosive
condition.
1. Compressor unplugged. 1. Plug it in.
2. Relay settings incorrect. 2. Call your Culligan dealer
3. Bad relay. 3. Call your Culligan dealer
1. Dead head pressure is 65
psi.
2. Dead head pressure is 65
psi.
1. Incorrect relay settings 1. Call your Culligan dealer
2. Bad relay. 2. Call your Culligan dealer
1. Assure continuous
electrical service is
available. (check plug,
breaker, fuse, etc.)
for service.
4. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
2. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
for service.
for service.
1. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
2. Call your Culligan dealer
for service.
for service.
for service.
Troubleshooting
Guide (cont.)
17
Page 22

Performance
Data Sheet
Culligan® 10” and 12” Iron-Cleer® Water Filters
Important Notice — Read this data sheet and compare the capabilities of the unit to your actual
water treatment needs. Culligan recommends that you have your water supply tested to determine
these needs before purchasing a water treatment unit.
Culligan knows the more informed you are about your water treatment system, the more confident
you will be about its performance. It’s because of this more than sixty five years of commitment to our
customers that Culligan is providing this Performance Data Sheet to its customers.
Manufacturer Culligan International Company
9399 West Higgins Road, Suite 1100, Rosemont, IL 60018
(847)430-2800
www.culligan.com
Substance Reduction
Model Substance
USEPA SDWA*
MCL (MG/L)
10” Iron-Cleer Iron 0.3 mg/L 99% 9.82 mg/L < 0.1
12” Iron-Cleer Iron 0.3 mg/L 99% 9.82 mg/L < 0.1
* United States Environmental Protection Agency Safe Drinking Water Act
Testing Conditions
Capacity: 1,400 gallons (10” Iron-Cleer)
2,000 gallons (12” Iron-Cleer)
Temperature: 63°F - 73°F
Flow Rate: 5 gpm (10” Iron-Cleer)
7 gpm (12” Iron-Cleer)
pH: 8.0
Percent
Reduction
Average Influent
Concentration Level
Average Effluent
Concentration Level
Pressure: 60 psi
Acidity: Non-Corrosive
Rated Pressure Drop @ 5 gpm: 9 psi (10” Iron-Cleer)
Rated Pressure Drop @ 7 gpm: 10 psi (12” Iron-Cleer)
18
Operating Conditions
Water Pressure Limits: 20 - 60 psi
Temperature Limits: 33 - 120°F
Electrical Characteristics: 120V/60 Hz 3 Watts continuous
Systems tested and certified by WQA against WQA S-200 for the effective reduction of
iron.
This system has been tested according to NSF/ANSI 42 for the reduction of iron. The concentration of iron in
water entering the system was reduced to a concentration less than or equal to the permissible limit for water
leaving the system as specified in NSF/ANSI 42.
Testing was performed under laboratory conditions, actual results may vary.
Performance Indicator: If water flow decreases or a noticeable odor returns, the filter should be reconditioned. If
conditions do not improve, contact your local Culligan Man. He can determine if your filter requires servicing.
Regeneration Frequency: Regeneration frequency will vary depending upon water conditions.
Refer to your Installation and Operation Instructions, Parts List and Printed Warrantees for more specific product
information. To avoid contamination from improper handling and installation, your system should only be installed
and serviced by your Culligan Man. Performance may vary based on local water conditions. The substances
reduced by this product are not necessarily in your water.
Buyer Signature Date
Page 23

Important Data on Your Water Filter
It is advisable to have the salesperson or installer fill in the information below for your future
reference. If this has not been done, please ask for it, as it is necessary if you contact your dealer.
Identification
Model Name Catalog No.
Control Model No. Control Serial No.
Date of Installation Tank Serial No.
Settings
Time of Recharge: ______ a.m. ______ p.m.
Regeneration Interval __________ days (Time clock models)
Records and
Data
Number of people in household
Water Analysis
Total Hardness _______ (gpg) Total Iron _______ (ppm)
Hydrogen Sulfide____________ (ppm)
Other
19
Page 24

Culligan
Limited
Warranty
Culligan® Iron-Cleer® Automatic Water Filters
You have just purchased one of the finest water conditioners made. As an expression of our
confidence in Culligan International Company products, your water conditioner is warranted to
the original end-user, when installed in accordance with Culligan specifications, against defects in
material and workmanship from the date of original installation, as follows:
For a period of ONE YEAR The entire conditioner
For a period of FIVE YEARS The AccuSoft® circuit board
For a period of TEN YEARS The control valve body, excluding internal parts
The conditioner tank
If a part described above is found defective within the specified period, you should notify your independently operated Culligan dealer and arrange a time during normal business hours for the dealer
to inspect the water conditioner on your premises. Any part found defective within the terms of this
warranty will be repaired or replaced by the dealer. You pay only freight from our factory and local
dealer charges.
We are not responsible for damage caused by accident, fire, flood, freezing, Act of God, misuse,
misapplication, neglect, oxidizing agents (such as chlorine, ozone, chloramines and other related
components), alteration, installation or operation contrary to our printed instructions, or by the use of
accessories or components which do not meet Culligan specifications, is not covered by this warranty.
Refer to the specifications section in the Installation and Operating manual for application parameters.
Our product performance specifications are furnished with each water conditioning unit. To the
extent permitted by law, culligan disclaims all implied warranties, including without
limitation warranties of merchantability and fitness for particular purpose; to the
extent required by law, any such implied warranties are limited in duration to the
one-year period specified above for the entire conditioner. As a manufacturer, we do
not know the characteristics of your water supply or the purpose for which you are purchasing a
water conditioner. The quality of water supplies may vary seasonally or over a period of time, and
your water usage rate may vary as well. Water characteristics can also differ considerably if your
water conditioner is moved to a new location. For these reasons, we assume no liability for the
determination of the proper equipment necessary to meet your requirements, and we do not authorize
others to assume such obligations for us. Further, we assume no liability and extend no warranties,
express or implied, for the use of this product with a non-potable water source. Our obligations
under this warranty are limited to the repair or replacement of the failed parts of
the water conditioner, and we assume no liability whatsoever for direct, indirect,
incidental, consequential, special, general, or other damages.
20
Some states do not allow the exclusion of implied warranties or limitations on how long an implied
warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to you. Similarly, some states do not allow the
exclusion of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not apply
to you. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary
from state to state. Consult your telephone directory for your local independently operated Culligan
dealer, or write Culligan International Company for warranty and service information.
Culligan International Company
9399 West Higgins Road, Suite 1100
Rosemont, IL 60018
(847)430-2800
www.culligan.com
Page 25

You Get Your Water Expert, The Culligan Man
We’re here to provide you with fast, dependable service, making sure any problems you have are
taken care of. The Culligan Man has been around for over seventy years, delivering dependable
service all along. That’s why people say “Hey, Culligan Man!”® Because we’re the water experts.
And that’s who you want taking care of your water.
®
The Culligan Promise
At Culligan, we understand that a water quality improvement system is an investment in your
family’s well-being. That’s why our 1,350 independently operated dealers worldwide don’t just sell
products; they sell water quality you can count on. We stand behind our products with written limited
warranties and our unequaled Culligan service. No matter where you live, you can depend on
Culligan expertise to work for you — today and tomorrow.
With Culligan
You Get
More Than
A Quality
Product
© 2007 Culligan International Company 01019923A
21
 Loading...
Loading...