CTS HES-3112-CL-DR SERIES User Manual

1
HES-3112-CL-DR SERIES
10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 and 100/1000BASE-X SFP Combo to
100/1000BASE-X ETHERNET MANAGED MEDIA CONVERTER
Network Management
User’s Manual
Version 1.0

2
Trademarks
CTS is a registered trademark of Connection Technology Systems Inc..
Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
All other trademarks remain the properties of their owners.
Copyright Statement
Copyright 2013 Connection Technology Systems Inc..
This publication may not be reproduced as a whole or in part, in any way whatsoever unless prior consent has been obtained
from Connection Technology Systems Inc..
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limitations are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult your local distributors or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Copyright © 2013 All Rights Reserved.
Company has an on-going policy of upgrading its products and it may be possible that information in this document is not
up-to-date. Please check with your local distributors for the latest information. No part of this document can be copied or
reproduced in any form without written consent from the company.
Trademarks:
All trade names and trademarks are the properties of their respective companies.

3
Table of Content
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Interfaces...................................................................................................................... 6
1.2 Management Preparations ........................................................................................... 7
1.2.1 Connecting the Managed Media Converter ........................................................... 7
1.2.2 Assigning IP Addresses ......................................................................................... 7
1.3 LED Definitions ............................................................................................................. 8
1.4 Button Definitions ......................................................................................................... 8
2. Command Line Interface (CLI) ........................................................................................ 9
2.1 Remote Console Management-Telnet .......................................................................... 9
2.2 Navigating CLI ................................................................................................ ............ 10
2.2.1 General Commands ............................................................................................. 10
2.2.2 Quick Keys ........................................................................................................... 11
2.2.3 Command Format ................................................................................................ 11
2.2.4 Login Username & Password .............................................................................. 13
2.3 User Mode .................................................................................................................. 13
2.4 Privileged Mode .......................................................................................................... 14
2.4.1 Copy-cfg Command ............................................................................................. 14
2.4.2 Firmware Command ............................................................................................ 15
2.4.3 Reload Command ................................................................................................ 15
2.4.4 Write Command ................................................................................................... 16
2.4.5 Configure Command ............................................................................................ 16
2.5 Configuration Mode .................................................................................................... 16
2.5.1 Entering Interface Numbers ................................................................................. 17
2.5.2 No Command ....................................................................................................... 17
2.5.3 Show Command .................................................................................................. 17
2.5.4 Interface Command ............................................................................................. 17
2.5.5 IP Command ........................................................................................................ 19
2.5.6 MAC Command ................................ ................................ ................................ ... 20
2.5.7 Management Command ...................................................................................... 21
2.5.8 NTP Command .................................................................................................... 21
2.5.9 QoS Command .................................................................................................... 22
2.5.10 Security Command ............................................................................................ 27

4
2.5.11 SNMP-Server Command ................................................................................... 28
2.5.12 Switch Command ............................................................................................... 31
2.5.13 Switch-info Command ........................................................................................ 31
2.5.14 User Command .................................................................................................. 32
2.5.15 VLAN Command ................................................................................................ 34
2.5.16 Show interface statistics Command ................................................................... 36
2.5.17 Show sfp Command ........................................................................................... 37
2.5.18 Show log Command........................................................................................... 37
2.5.19 Show default-config, running-config and start-up-config Command .................. 37
3. WEB MANAGEMENT ..................................................................................................... 38
3.1 System Information .................................................................................................... 40
3.2 User Authentication .................................................................................................... 42
3.3 Network Management ................................................................................................ 44
3.3.1 Network Configuration ......................................................................................... 45
3.3.2 System Service Configuration .............................................................................. 47
3.3.3 Time Server Configuration ................................................................................... 47
3.3.4 Device Community ............................................................................................... 48
3.3.5 Trap Destination ................................................................................................... 49
3.3.6 Trap Configuration ............................................................................................... 50
3.4 Converter Management .............................................................................................. 51
3.4.1 Converter Configuration ....................................................................................... 52
3.4.2 Storm Control ....................................................................................................... 52
3.4.3 Port Configuration ................................................................................................ 53
3.4.4 Rate Limit Configuration ...................................................................................... 54
3.4.5 QoS Priority Configuration ................................................................................... 55
3.4.6 VLAN Configuration ............................................................................................. 59
3.4.6.1 Port Based VLAN .......................................................................................... 60
3.4.6.1.1 Configure VLAN ...................................................................................... 61
3.4.6.2 IEEE 802.1q Tag VLAN ................................................................................. 62
3.4.6.2.1 Configure VLAN ...................................................................................... 62
3.4.6.2.2 Configure Default Port VLAN ID ............................................................. 63
3.4.6.3 Q-in-Q VLAN Configuration ........................................................................... 64
3.4.7 Filter Configuration .............................................................................................. 65
3.5 Converter Monitor ....................................................................................................... 66

5
3.5.1 Converter Port State ............................................................................................ 66
3.5.2 Port Counters Rates ............................................................................................ 67
3.5.2.1 Port Traffic Statistics (Rates) ......................................................................... 68
3.5.2.2 Port Packet Error Statistics (Rates) ............................................................... 68
3.5.2.3 Port Packet Analysis Statistics (Rates) ......................................................... 69
3.5.3 Port Counters Events ........................................................................................... 70
3.5.3.1 Port Traffic Statistics (Events) ....................................................................... 70
3.5.3.2 Port Packet Error Statistics (Events) ............................................................. 71
3.5.3.3 Port Packet Analysis Statistics (Events) ........................................................ 72
3.5.4 SFP Information ................................................................................................... 73
3.5.4.1 SFP Port Info ................................................................................................. 73
3.5.4.2 SFP Port State .............................................................................................. 74
3.5.5 MAC Address Table ............................................................................................. 74
3.6 System Utility .............................................................................................................. 75
3.6.1 Event Log ............................................................................................................. 76
3.6.2 Update ................................................................................................................. 76
3.6.3 Load Factory Settings .......................................................................................... 77
3.6.4 Load Factory Settings Except Network Configuration .......................................... 78
3.7 Save Configuration ..................................................................................................... 78
3.8 Reset System ............................................................................................................. 79
3.9 Logout ........................................................................................................................ 79
APPENDIX A: DHCP Auto-Provisioning Setup ................................................................ 80
6
1. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for using the 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 or 1000BASE-X SFP to 100/1000BASE-X
ETHERNET MANAGED MEDIA CONVERTER. The Managed Media Converter is fully
compliant with IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3z and 802.3ab standards. By employing store and
forward switching mechanism, the Media Converter provides low latency and faster data
transmission. The built-in management module allows users to configure this Media
Converter and monitor the operation status locally or remotely through network. This
converter supports advanced functions such as QoS, Q-in-Q VLAN Tunneling and Rate
Limiting. Users can configure the required settings of the Media Converter and monitor its
real-time operational status via Command Line Interface (CLI). For detailed descriptions on
how to use CLI, please refer to Section 2.
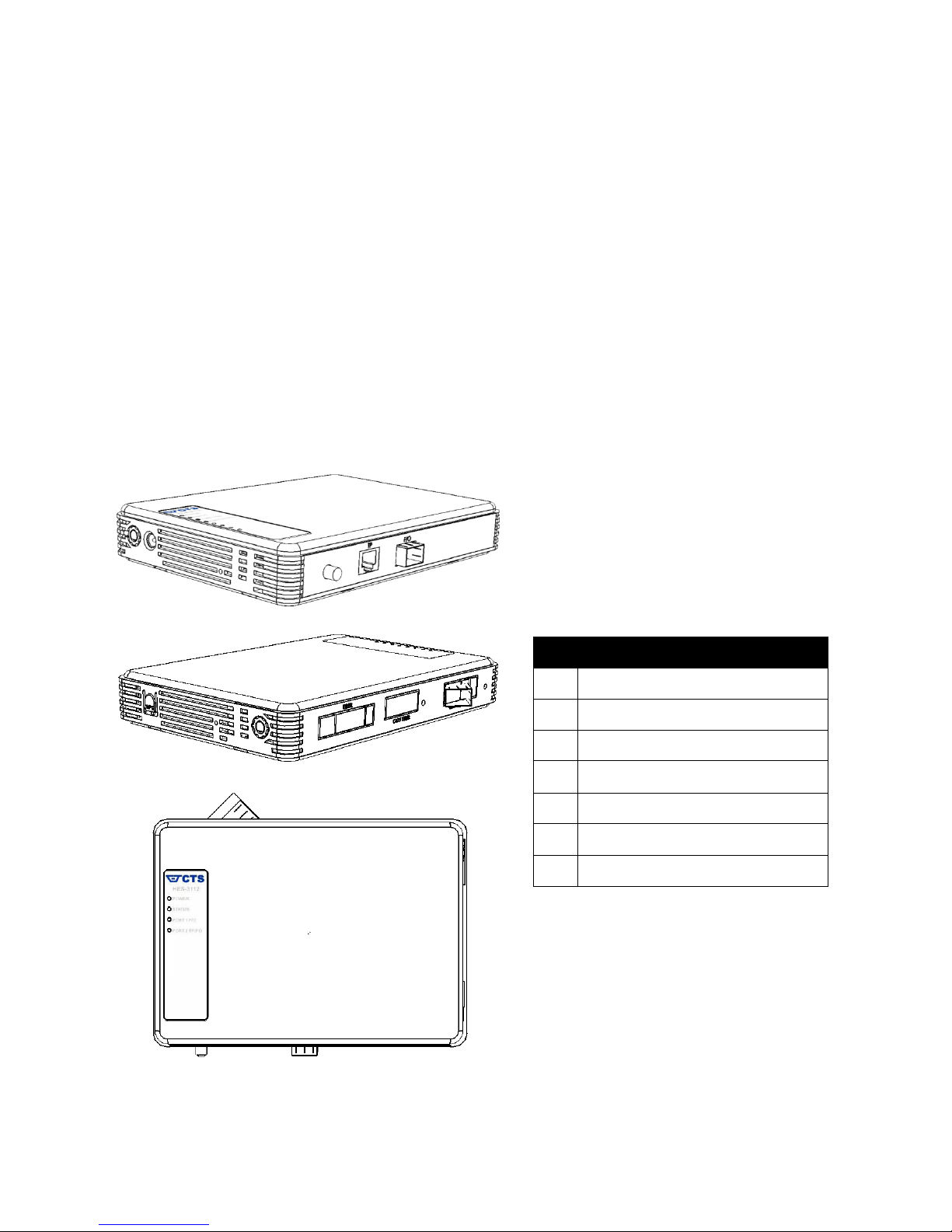
1.1 Interfaces
No.
Interface
Smart Lighting Control
LAN TP RJ-45
LAN Fiber SFP Slot
DC Power Jack
Reset Button
WAN Fiber Port
LED Indicators

7
1.2 Management Preparations
The Managed Media Converter can be accessed through both Telnet connection and a web
browser, such as Internet Explorer or Netscape, and etc.. Before you can access the
Managed Media Converter to configure it, you need to connect cables properly.
1.2.1 Connecting the Managed Media Converter
It is extremely important that proper cables are used with correct pin arrangements when
connecting Managed Media Converter to other devices such as switches, hubs, workstations,
etc..
100/1000 Base-X Fiber Port
The 100/1000Base-X fiber port is located at the rear panel of the Managed Media
Converter. This port is primarily used for uplink connection and can operate at
1000M/Full or Half Duplex mode. WDM Simplex SC type of connector or SFP slot is
available. Use proper single-mode optical fiber cable to connect this port with the other
Ethernet Fiber port.
10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 and 100/1000Base-X SFP Combo Port
The 10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 and 1000Base-X SFP combo port is located on the
front panel of the Managed Media Converter. This combo port allows connection via
copper or fiber interface.
1.2.2 Assigning IP Addresses
IP addresses have the format n.n.n.n, for example 168.168.8.100.
IP addresses are made up of two parts:
The first part (168.168.XXX.XXX in the example) indicates network address identifying
the network where the device resides. Network addresses are assigned by three
allocation organizations. Depending on your location, each allocation organization
assigns a globally unique network number to each network that wishes to connect to
the Internet.
The second part (XXX.XXX.8.100 in the example) identifies the device within the
network. Assigning unique device numbers is your responsibility. If you are unsure of
the IP addresses allocated to you, consult the allocation organization from which your
IP addresses were obtained.
Remember that an address can be assigned to only one device on a network. If you connect
to the outside, you must change all the arbitrary IP addresses to comply with those you have
been allocated by the allocation organization. If you do not do this, your outside
communications will not be connected.
8
A subnet mask is a filtering system for IP addresses. It allows you to further subdivide your
network. You must use the proper subnet mask for a proper operation of a network with
subnets defined.
1.3 LED Definitions
LED
Definition
Color
Operation
POWER
Power Status
Off
The device is powered off.
Green
The device is powered on.
STATUS
System Status
Orange
The system is booting up.
Green
The system is working normally.
Orange
Blinking
When the system is set back to default
factory setting, the Status LED indicator
will blink in orange for 3 times.
When the system is restarted, the Status
LED indicator will blink in orange once.
WAN F/O
WAN Port
Status
OFF
The link is down.
Green
The link is up and works at 100Mbps.
Orange
The link is up and works at 1000Mbps.
Blinking
The traffic is present.
LAN TP /
F/O
LAN Port Status
Off
The link is down.
Green
The link is up and works at 10/100Mbps.
Orange
The link is up and works at 1000Mbps.
Blinking
The traffic is present.
1.4 Button Definitions
Button
Operation
Smart Lighting
Control Button
System Status LED and Port Link LEDs will be turned off by
pressing the button. Only Power LED indicator stays on.
Reset Button
Insert a pin or paper clip to press the Reset button for 5
seconds to restart the device, and 10 seconds to reset the
device to factory defaults.

9
2. Command Line Interface (CLI)
This chapter guides you to use Command Line Interface (CLI) via Telnet connection,
specifically in:
Configuring the system
Resetting the system
Upgrading newly released firmware
2.1 Remote Console Management-Telnet
You can use Command Line Interface to manage the Managed Media Converter via Telnet
session. For first-time users, you must first assign a unique IP address to the Managed Media
Converter before you can manage it remotely. Use the RJ-45 port on the front panel as the
temporary management console port to login to the device with the default username and
password and then assign the IP address using IP command in Global Configuration mode.
Follow steps described below to access the Managed Media Converter through Telnet
session:
Step 1. Use the RJ-45 port on the front panel as a temporary management console port
to login to the Managed Media Converter.
Step 2. Run Telnet client and connect to 192.168.0.1. For first-time users, make sure
the IP address of your PC or workstation is assigned to an IP address between
192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.254 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Step 3. When asked for a username, enter “admin”. When asked for a password, leave
the password field blank and press Enter (by default, no password is required.)
Step 4. If you enter CLI successfully, the prompt display Converter> (the model name of
your device together with a greater than sign) will appear on the screen.
Step 5. Once you enter CLI successfully, you can set up the Media Converter‟s IP
address, subnet mask and the default gateway using “IP” command in Global
Configuration mode. The telnet session will be terminated immediately once the
IP address of the Media Converter has been changed.
Step 6. Use new IP address to login to the Managed Media Converter via Telnet
session again.
Limitation: Only one active Telnet session can access the Managed Media Converter at
a time.

10
2.2 Navigating CLI
After you successfully access to the Managed Media Converter, you will be asked for a login
username. Enter your authorized username and password, and then you will be directed to
the User Mode. In CLI management, the User Mode only provides users with basic functions
to operate the Managed Switch. If you would like to configure advanced features of the
Managed Switch, such as, VLAN, QoS, and Rate limit control, you must enter the
Configuration Mode. The following table provides an overview of modes available in this
Managed Media Converter.
Command Mode
Access Method
Prompt Displayed
Exit Method
User Mode
Login username &
password
Converter>
logout
Privileged Mode
From user mode, enter
the enable command
Converter#
disable, exit, logout
Configuration
Mode
From the enable mode,
enter the config or
configure command
Converter(config)#
exit
NOTE: By default, the model name will be used for the prompt display. You can change
the prompt display to the one that is ideal for your network environment using the “hostname” command. However, for convenience, the prompt display “Converter” will be used
throughout this user’s manual.
2.2.1 General Commands
This section introduces you some general commands that you can use in all modes, including
“help”, “exit”, “history” and “logout”.
Entering the command…
To do this…
Available Modes
help
Obtain a list of available
commands in the current mode.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
exit
Return to the previous mode or
login screen.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
history
List all commands that have been
used.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
logout
Logout from the CLI or terminate
Telnet session.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
11
2.2.2 Quick Keys
In CLI, there are several quick keys that you can use to perform several functions. The
following table summarizes the most frequently used quick keys in CLI.
Keys
Purpose
tab
Enter an unfinished command and press “Tab” key to complete the
command.
?
Press “?” key in each mode to get available commands.
Unfinished
command
followed by ?
Enter an unfinished command or keyword and press “?” key to complete
the command and get command syntax help.
Examples:
Converter#h?
help Show available commands
history Show history commands
Converter#he?
<cr>
Converter#help
Up arrow
Use Up arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the most recent key-in commands.
Down arrow
Use Down arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the commands that are entered first.
2.2.3 Command Format
While in CLI, you will see several symbols very often. As mentioned above, you might already
know what “>”, “#” and (config)# represent. However, to perform what you intend the device to
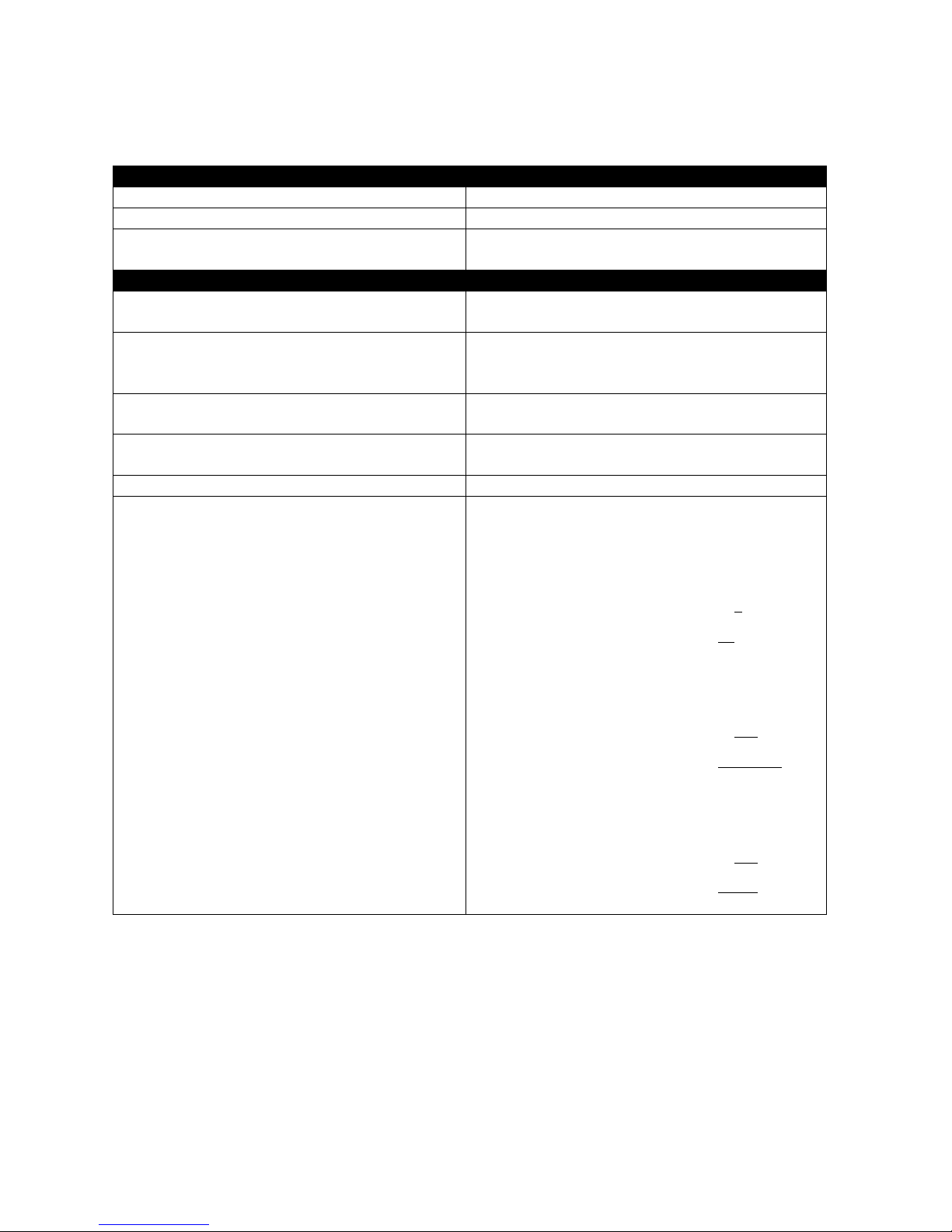
do, you have to enter a string of complete command correctly. For example, if you want to
assign IP address for the Managed Media Converter, you need to enter the following
command with the required parameter and IP, subnet mask and default gateway:
IP command syntax: Converter(config)#ip address [A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X] [A.B.C.D]
Converter(config)#ip address 192.168.1.198 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.254
This means that
you are in Global
Configuration mode
This allows you to
assign IP address.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway address.
Hostname
12
The following table lists common symbols and syntax that you will see very frequently in this
User‟s Manual for your reference:
Symbols
Brief Description
>
Currently, the device is in User Mode.
#
Currently, the device is in Privileged Mode.
(config)#
Currently, the device is in Global
Configuration Mode.
Syntax
Brief Description
[ ]
Brackets mean that this field is required
information.
[A.B.C.D ]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter an IP address or gateway
address.
[255.X.X.X]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter the subnet mask.
[port-based | 802.1p | dscp | vid]
There are four options that you can choose.
Specify one of them.
[1-8191]
Specify a value between 1 and 8191.
[0-7] 802.1p_list
[0-63] dscp_list
Specify one or more values or a range of
values.
For example: specifying one value
Converter(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1 0
Converter(config)#qos dscp-map 10 3
For example: specifying three values
(separated by commas)
Converter(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1,3 0
Converter(config)#qos dscp-map 10,13,15 3
For example: specifying a range of values
(separating by a hyphen)
Converter(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1-3 0
Converter(config)#qos dscp-map 10-15 3
13
2.2.4 Login Username & Password
Default Login
After you enter Telnet session, a login prompt will appear to request a valid and authorized
username and password combination. For first-time users, enter the default login username
“admin” and “press Enter key” in password field (no password is required for default setting).
When system prompt shows “Converter>”, it means that the user has successfully entered
the User Mode.
For security reasons, it is strongly recommended that you add a new login username and
password using User command in Configuration Mode. When you create your own login
username and password, you can delete the default username (admin) to prevent
unauthorized accesses.
Forgot Your Login Username & Password?
If you forgot your login username and password, you can use the “reset button” to set all
configurations back to factory defaults. Once you have performed system reset to defaults,
you can login with default username and password. Please note that if you use this method to
gain access to the Managed Media Converter, all configurations saved in Flash will be lost. It
is strongly recommended that a copy of configurations is backed up in your local hard-drive or
file server from time to time so that previously-configured settings can be restored to the
Managed Media Converter for use after you gain access again to the device.
2.3 User Mode
In User mode, only a limited set of commands are provided. Please note that in Use Mode,
you have no authority to configure advanced settings. You need to enter Privileged mode and
Configuration mode to set up advanced functions. For a list of commands available in User
Mode, enter the question mark (?) or “help” command after the system prompt displays
“Converter>”.
Command
Description
exit
Quit the User mode or close the terminal connection.
help
Display a list of available commands in User mode.
history
Display the command history.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
enable
Enter the Privileged mode.

14
2.4 Privileged Mode
The only place where you can enter the Privileged (Enable) Mode is in User Mode. When you
successfully enter Enable mode, the prompt will be changed to Converter# (the model name
of your device together with a pound sign). Enter the question mark (?) or help command to
view a list of commands available for use.
Command
Description
copy-cfg
Restore or backup configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
disable
Exit Enable Mode and return to User Mode.
exit
Exit Enable Mode and return to User Mode.
firmware
Upgrade Firmware via FTP or TFTP server.
help
Display a list of available commands in Enable Mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
reload
Restart the Managed Switch.
write
Save your configurations to Flash.
configure
Enter Global Configuration mode.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.
2.4.1 Copy-cfg Command
Use “copy-cfg” command to backup a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server or restore the
Managed Media Converter back to the defaults.
1. Restore a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
Command
Parameter
Description
Converter# copy-cfg
from ftp [A.B.C.D]
[file name]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Converter# copy-cfg
from tftp [A.B.C.D]
[file_name]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
Example
Converter# copy-cfg from ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf misadmin1 abcxyz
Converter# copy-cfg from tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf
2. Restore the Managed Media Converter back to default settings.
Command / Example
Converter# copy-cfg from default
NOTE: There are two ways to set the Managed Media Converter back to the factory default
settings. Users can use the “copy-cfg from default” command in CLI or simply press the
“Reset Button” located on the front panel to restore the device back to the initial state.

15
3. Restore the Managed Media Converter back to default settings but keep IP
configurations.
Command / Example
Converter# copy-cfg from default keep-ip
4. Backup a configuration file to FTP/TFTP server.
Command
Parameter
Description
Converter# copycfg to ftp [A.B.C.D]
[file_name]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Converter# copycfg to tftp [A.B.C.D]
[file_name]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
Example
Converter# copy-cfg to ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf misadmin1 abcxyz
Converter# copy-cfg to tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf
2.4.2 Firmware Command
To upgrade Firmware via FTP or TFTP server.
Command
Parameter
Description
Converter#
firmware upgrade
ftp [A.B.C.D]
[file_name]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to upgrade.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Converter#
firmware upgrade
tftp [A.B.C.D]
[file_name]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to upgrade.
Example
Converter# firmware upgrade ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin converter10 abcxyz
Converter# firmware upgrade tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin
2.4.3 Reload Command
To restart the Managed Media Converter, enter the reload command.
Command / Example
Converter# reload

16
2.4.4 Write Command
To save running configurations to startup configurations, enter the write command. All
unsaved configurations will be lost when you restart the Managed Media Converter.
Command / Example
Converter# write
2.4.5 Configure Command
You can enter Global Configuration Mode only from Privileged Mode. You can type in
“configure” or “config” to enter Global Configuration Mode. The display prompt will change
from “Converter#” to “Converter(config)#” once you successfully enter Global Configuration
Mode.
Command / Example
Converter# config
Converter(config)#
Converter# configure
Converter(config)#
2.5 Configuration Mode
When you enter “configure” or “config” and press “Enter” in Privileged Mode, you will be
directed to Global Configuration Mode where you can set up advanced functions, such as
QoS, VLAN, and storm control security globally. Any command entered will be applied to
running-configuration and the device‟s operation. From this level, you can also enter different
sub-configuration modes to set up specific configurations for VLAN, QoS, security or
interfaces.
Command
Description
exit
Exit the Configuration Mode.
help
Display a list of available commands in Configuration Mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
ip
Set up the IP address and enable DHCP mode & IGMP snooping.
mac
Set up each port‟s MAC learning function.
management
Set up the system service type.
ntp
Set up required configurations for Network Time Protocol.
qos
Set up the priority of packets within the Managed Converter.
security
Set up storm control settings.
snmp-server
Create a new SNMP community and trap destination and specify the trap types.
switch
Enable or disable SFP and counter polling function.
switch-info
Specify company name, host name, system location, etc..
user
Create a new user account.
vlan
Set up VLAN mode and VLAN configuration.
no
Disable a command or set it back to its default setting.
interface
Set up the selected interfaces‟ advanced features.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.

17
2.5.1 Entering Interface Numbers
In the Global Configuration Mode, you can configure a command that is only applied to
interfaces specified. For example, you can set up each interface‟s VLAN assignment, speed,
or duplex mode. To configure, you must first enter the interface number. There are four ways
to enter your interface numbers to signify the combination of different interfaces that apply to
a command or commands.
Commands
Description
Converter(config)# interface 1
Converter(config-if-1)#
Enter LAN interface. Only LAN port will apply the
commands entered.
Converter(config)# interface 2
Converter(config-if-2)#
Enter WAN interface. Only LAN port will apply the
commands entered.
Converter(config)# interface 1,2
Converter(config-if-1,2)#
Enter LAN and WAN interfaces at the same time.
Both LAN and WAN ports will apply the commands
entered.
The “interface” command can be used together with “QoS” and “VLAN” commands. For
detailed usages, please refer to QoS and VLAN sections below.
2.5.2 No Command
Most commands that you enter in Configuration mode can be negated using “no” command
followed by the same or original command. The purpose of “no” command is to disable a
function, remove a command, or set the setting back to the default value. In each sub-section
below, the use of no command to fulfill different purposes will be introduced.
2.5.3 Show Command
The command “show” is very important for network administrators to get information about
the device, receive outputs to verify a command‟s configurations or troubleshoot a network
configuration error. “Show” command can be used in Privileged or Configuration mode.
2.5.4 Interface Command
Use this command to set up various port configurations LAN port and WAN port.
Interface Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter LAN interface by issuing “1”, and WAN
interface by “2”. Enter both of LAN and
WAN at the same time by issuing “1,2”.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
auto-negotiation
Set the selected interface to autonegotiation. When auto-negotiation is
enabled, speed configuration will be
ignored.

18
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
combo-mode [fiber-priority |
copper-priority | fiber-only |
copper-only|]
[fiber-priority |
copper-priority
| fiber-only |
copper-only]
This is only applicable to the LAN port. Set
up the combo mode for the LAN port.
[fiber-priority]: Both fiber and copper LAN ports
are available, but when both interfaces are
detected, fiber will be the transmission medium.
[copper-priority]: Both fiber and copper LAN
ports are available, but when both interfaces are
detected, copper will be the transmission
medium.
[fiber-only]: Only fiber LAN port is available.
[copper-only]: Only copper LAN port is
available.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
description [description]
[description]
Specify a descriptive name for the selected
interface.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
duplex_full
Set the selected interface to full duplex
mode.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
flowcontrol
Enable the selected interface‟s flow control
function.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
shutdown
Administratively disable the selected port‟s
status.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
speed [1000 |100 | 10]
[1000 |100
| 10]
Set up the selected interface‟s speed.
Speed configuration only works when “no
auto-negotiation” command is issued.
No Command
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no auto-negotiation
Set auto-negotiation setting to the default
setting.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no duplex
Set the selected port‟s duplex mode to the
default setting.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no speed
Set the selected port‟s speed to the default
setting.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no flowcontrol
Set the selected port‟s flow control function
to the default setting.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no description
Remove the entered description name for
the selected port.
Converter(config-if-PORT)#
no shutdown
Administratively enable the selected port‟s
status.
Show Command
Switch(config)# show interface
Show each port‟s current configuration.
Switch(config)# show interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Show the selected ports‟ current
configuration.
Switch(config)# show interface status
Show each interface‟s port status including
media type, forwarding state, speed, duplex
mode, flow control and link up/down status.
Switch(config)# show interface
status [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the selected ports‟ status including
media type, forwarding state, speed, duplex
mode, flow control and link up/down status.

19
Interface Command Example
Converter(config)# interface 1
Configure LAN interface.
Converter(config)# interface 1,2
Configure both LAN and WAN interfaces.
Converter(config-if-1)# auto-negotiation
Set LAN interface to auto-negotiation.
Converter(config-if-1)#
combo-mode fiber-priority
Set LAN interface‟s combo mode to fiberpriority mode.
Converter(config-if-1)# duplex full
Set LAN interface to full duplex mode.
Converter(config-if-2)# speed 100
Set WAN interface‟s speed to 100Mbps.
Converter(config-if-1)# shutdown
Disable the LAN interface status.
2.5.5 IP Command
Configure IP address and related settings regarding DHCP and IP Source Binding function.
1. Set up or remove the IP address of the Managed Converter.
IP Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)#
ip address
[A.B.C.D]
[255.X.X.X]
[A.B.C.D]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the desired IP address for the Managed
Converter.
[255.X.X.X]
Enter subnet mask of your IP address.
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the default gateway address.
No Command
Converter(config)# no ip address
Remove the Converter‟s IP address.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show ip
address
Show the current IP configurations or verify the
configured IP settings.
IP Command Example
Converter(config)# ip address
192.168.1.198 255.255.255.0
192.168.1.254
Set up the Converter‟s IP to 192.168.1.198, subnet
mask to 255.255.255.0, and default gateway to
192.168.1.254.
2. Configure DHCP function.
IP Command
Description
Converter(config)# ip address dhcp
Enable DHCP mode.
Converter(config)# ip dhcp snooping
Enable DHCP Snooping function
Converter(config)# ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server [port_list]
[port_list]
Specify DHCP server trust ports.
No Command
Converter(config)# no ip address dhcp
Disable DHCP mode.
Converter(config)# no ip dhcp snooping
Disable DHCP Snooping function
Converter(config)# no dhcp snooping dhcpserver
Set DHCP server trust port configuration
back to the default.

20
3. Configure IP source binding function.
IP Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# ip source
Enable IP source binding function.
Converter(config)#
ip source binding [1-12]
[1-12]
Enable the specified entry.
Converter(config)#
ip source binding [1-12] ipaddress [A.B.C.D]
[port_list]
Set up the IP address for the specified
entry.
No Command
Converter(config)# no ip source
Disable IP source binding function.
Converter(config)#
no ip source binding [1-12]
[1-12]
Disable the specified entry.
Converter(config)#
no ip source binding [1-12] ipaddress
Set the IP address of the specified entry
back to the default.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show ip source
Show IP source binding setting.
2.5.6 MAC Command
Set up MAC address table aging time. Entries in the MAC address table containing source
MAC addresses and their associated ports will be deleted if they are not accessed within the
specified aging time.
MAC Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# mac addresstable aging-time [7-600000]
[7-600000]
Specify MAC address table aging time
from 7 to 600000 seconds.
No Command
Converter(config)# no mac address-table
aging-time
Set MAC address table aging time to the
default value (300 seconds).
Show Command
Converter(config)# show mac
aging-time
Show current MAC address table aging
time.
Converter(config)# show mac
address-table
Show MAC addresses learned by the
Managed Converter
Converter(config)# show mac
address-table interface [1-2]
[1-2]
Show MAC addresses learned from the
LAN port (1) or WAN port (2).
Converter(config)# show mac
address-table top
Show MAC addresses learned by the
Managed Converter from the first entry.
MAC Command Example
Converter(config)# mac address-table agingtime 600
Set MAC address table aging time to 600
seconds.

21
2.5.7 Management Command
Management Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# management
[ssh | telnet | web]
[ssh | telnet |
web]
Enable SSH, telnet or Web GUI
management interface.
No Command
Converter(config)# no
management [ssh | telnet | web]
[ssh | telnet |
web]
Disable SSH, telnet or Web GUI
management interface.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show management
Show the current status of management
interfaces.
Management Command Example
Converter(config)# management ssh
Enable SSH management interface.
NOTE: Enabling SSH via telnet will terminate the telnet session immediately; likewise,
enabling telnet via SSH will terminate the SSH session immediately.
2.5.8 NTP Command
Set up required configurations for Network Time Protocol.
NTP Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# ntp
Enable the Managed Converter to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Converter(config)# ntp server1
[A.B.C.D]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify the primary time server IP
address.
Converter(config)# ntp server2
[A.B.C.D]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify the secondary time server IP
address.
Converter(config)# ntp syninterval [1-8]
[1-8]
Specify the interval time to synchronize
with the NTP time server.
1: 1 hour ; 2: 2 hours; 3: 3 hours; 4: 4 hours
5: 6 hours; 6: 8 hours; 7: 12 hours; 8: 24 hours
Converter(config)# ntp time-zone
[0-136]
[0-136]
Specify the time zone to that the Managed
Converter belongs. Use any key to view
the complete code list of 136 time zones.
For example, “Converter(config)# ntp timezone ?”
No Command
Converter(config)# no ntp
Disable the Managed Converter to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Converter(config)# no ntp server1
Delete the primary time server IP address.
Converter(config)# no ntp server2
Delete the secondary time server IP
address.
Converter(config)# no ntp syn-interval
Set the synchronization interval back to
the default setting.
Converter(config)# no ntp time-zone
Set the time-zone setting back to the
default setting.

22
Show Command
Converter(config)# show ntp
Show or verify current time server settings.
NTP Command Example
Converter(config)# ntp
Enable the Managed Converter to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Converter(config)# ntp server1 192.180.0.12
Set the primary time server IP address to
192.180.0.12.
Converter(config)# ntp server2 192.180.0.13
Set the secondary time server IP address
to 192.180.0.13.
Converter(config)# ntp syn-interval 5
Set the synchronization interval to 6 hours.
Converter(config)# ntp time-zone 3
Set the time zone to GMT-8:00 Vancouver.
2.5.9 QoS Command
1. Specify the desired QoS mode.
QoS Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos
[802.1p | dscp]
[802.1p | dscp]
Specify one QoS mode.
802.1p: Use “qos 802.1p-map” command
to further assign the priority bit to the
queue.
dscp: Use “qos dscp-map” command to
assign the DSCP value to the queue.
No Command
Converter(config)# no qos
Disable QoS function.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show qos
Show or verify QoS configurations.
QoS Command Example
Converter(config)# qos dscp
Enable QoS function and use DSCP
mode.
2. Set up the DSCP and queue mapping.
DSCP-Map Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos dscpmap [0-63] dscp_list [0-3]
[0-63]
dscp_list
Specify the corresponding DSCP value
assigned to a priority queue.
[0-3]
Specify a queue to which the specified
DSCP value is assigned.
No command
Converter(config)# no qos dscp-map [0-63]
dscp_list
Set the queue of the specific DCSP value
back to the default.
DSCP-Map Example
Converter(config)# qos dscp-map 50 3
Mapping DSCP value 50 to priority queue
3.

23
3. Set up management traffic priority.
Management-Priority Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos
management-priority [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify management traffic default
802.1p priority bit.
No command
Converter(config)# no qos management-priority
Set management traffic priority back to
the default.
Management-Priority Example
Converter(config)# qos management-priority 4
Set management traffic priority to 4.
NOTE: To check the setting of management traffic priority, please refer to 2.5.15 VLAN
Command.
4. Set up QoS queuing mode.
Queuing-Mode Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos queuingmode [weight]
[weight]
By default, “strict” queuing mode is used.
If you want to use “weight” queuing mode,
you need to disable “strict” queuing mode.
Strict mode: Traffic assigned to queue 3
will be transmitted first, and the traffic
assigned to queue 2 will not be
transmitted until queue 3‟s traffic is all
transmitted, and so forth.
Weight mode: All queues have fair
opportunity of dispatching. Each queue
has the specific amount of bandwidth
according to its assigned weight.
No Command
Converter(config)# no qos queuing-mode
Set the queuing mode to Strict mode.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show qos
Show or verify QoS configurations.
Queuing-Mode Example
Converter(config)# qos queuing-mode weight
Change the queuing mode from strict to
Weight.

24
5. Set up queue weight.
Queuing-Weighted Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos queuingweighted [1:2:4:8]
[ _:_:_:_ ]
(1-32)
By default, queuing weight is “1:2:4:8”.
Specify the value from 1 to 32.
No Command
Converter(config)# no qos queuing-weighted
Set the queuing weight back to the
default.
Queuing-Weighted Example
Converter(config)# qos queuing-weighted
1:7:14:21
Specify the queue weight as 1:7:14:21.
6. Set up 802.1p, VID and DSCP remarking
Remarking Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos remarking
[dscp | vid | 802.1p]
[dscp | vid |
802.1p]
Enable the specific remarking mode,
DSCP, VID, or 802.1p Remarking.
No Command
Converter(config)# no qos remarking [dscp |
vid | 802.1p]
Disable DSCP, VID or 802.1p remarking.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show qos remarking
Show current DSCP, VID and 802.1p
remarking configuration.
Remarking Example
Converter(config)# qos remarking 802.1p
Enable 802.1p remarking.
Converter(config)# no qos remarking dscp
Disable DSCP remarking.
7. Set up DSCP, VID and 802.1p priority mapping
DSCP Remarking Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# qos remarking
dscp-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Configure the mapping of DSCP
remarking mode.
[1-8]: Select the mapping entry
Converter(config-dscp-map-ID)#
active
Enable the mapping entry.
Converter(config-dscp-map-ID)#
rx-dscp [0-63]
[0-63]
Specify the DSCP value to be remarked.
Converter(config-dscp-map-ID)#
new-dscp [0-63]
[0-63]
Specify the DSCP remarking value.
Converter(config-dscp-map-ID)#
exit
Exit the entry.
No command
Converter(config)# no qos
remarking dscp-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Set the specific entry back to the default
setting.
Converter(config-dscp-map-ID)#
no [ active | rx-dscp | new-dscp]
[ active |
rx-dscp |
new-dscp]
Disable the mapping entry, or set DSCP
value or DSCP remarking value back to
the default setting.

25
VID Remarking command
Converter(config)# qos remarking
vid-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Configure the mapping of VID remarking
mode.
[1-8]: Select the mapping entry
Converter(config-vid-map-ID)#
active
Enable the mapping entry.
Converter(config-vid-map-ID)#
vlan-id [1-4094]
[1-4094]
Specify the VLAN to be remarked.
Converter(config-vid-map-ID)#
priority [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify the 802.1p remarking value.
Converter(config-vid-map-ID)#
exit
Exit the entry.
No Command
Converter(config)# no qos
remarking vid-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Set the specific entry back to the default
setting.
Converter(config-vid-map-ID)# no
[ active | vlan-id | priority]
[ active |
vlan-id |
priority]
Disable the mapping entry, or set VLAN
ID or 802.1p remarking value back to the
default setting.
802.1p Remarking Command
Converter(config)# qos remarking
802.1p-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Configure the mapping of 802.1p
remarking mode.
[1-8]: Select the mapping entry
Converter(config-802.1p-map-ID)#
active
Enable the mapping entry.
Converter(config-802.1p-map-ID)#
rx-802.1p [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify the 802.1p value to be remarked.
Converter(config-802.1p-map-ID)#
new-802.1p [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify the 802.1p remarking value.
Converter(config-802.1p-map-ID)#
exit
Exit the entry.
DSCP Remarking No command
Converter(config)# no qos
remarking 802.1p-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Set the specific entry back to the default
setting.
Converter(config-802.1p-map-ID)#
no [ active | 802.1p | priority]
[ active |
802.1p |
priority]
Disable the mapping entry, or set 802.1p
value or 802.1p remarking value back to
the default setting.
Show Command
Converter(config-dscp/vid/802.1p-map-ID)#
show
Display the mapping configuration of the
specific entry under DSCP, VID or 802.1p
mode.
Priority Mapping Example (VID for Example)
Converter(config)# qos remarking vid-map 1
Configure vid-map entry 1.
Converter(config-vid-map-1)# active
Enable vid-map entry 1.
Converter(config-vid-map-1)# vlan-id 100
Assign VID 100 to vid-map entry 1.
Converter(config-vid-map-1)# priority 2
Set 802.1p remarking value as 2.
Converter(config-vid-map-1)# exit
Exit vid-map entry 1.

26
8. Assign a tag priority to the specific queue.
802.1p-map Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)#qos 802.1pmap [0-7] 802.1p_list [0-3]
[0-7]
802.1p_list
Assign one or several 802.1p priority bits
for mapping.
Set up the corresponding priority value
Priority
Level
Low
Normal
Medium
High
802.1p
Value
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
7
[0-3]
Assign a queue value for mapping.
No Command
Converter(config)#no qos 802.1pmap [0-7] 802.1p_list
[0-7]
802.1p_list
Assign an 802.1p priority bit or several
802.1p priority bits that you want to delete
or remove.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show qos
Show or verify QoS configurations.
802.1p-map Example
Converter(config)# qos 802.1p-map 6-7 3
Map priority bit 6 and 7 to queue 4.
Converter(config)# no qos 802.1p-map 6-7
Delete or remove 802.1p priority bit 6 and
7‟s mapping.
9. Use interface command to set up port user priority and ingress/egress rate limit.
QoS & Interface Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter LAN interface by issuing “1”, and
WAN by “2”. Enter both of LAN and WAN
at the same time by issuing “1,2”.
Converter(config-if-POR)# qos
rate-limit ingress 0
Disable selected interface‟s ingress rate
limit function.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# qos
rate-limit ingress [32-1000000]
[32-1000000]
kbps
Specify the ingress rate between 32 and
1000000.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# qos
rate-limit egress 0
Disable selected interface‟s egress rate
limit function.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# qos
rate-limit egress [32-1000000]
[32-1000000]
kbps
Specify the egress rate between 32 and
1000000.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# qos
user-priority [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify the user priority for the selected
interface.
No Command
Converter(config-if-PORT)# no qos userpriority
Set port user priority setting to the default.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# no qos rate-limit
ingress
Set QoS ingress rate limit setting to the
default.
Converter(config-if-PORT)# no qos rate-limit
egress
Set QoS ingress rate limit setting to the
default.

27
Show Command
Converter(config)# show qos
interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces‟
ingress and egress rate configurations.
Converter(config)# show qos interface
Show or verify each interface‟s ingress
and egress rate configurations.
Converter(config)# show qos
Show or verify QoS configurations.
QoS & Interface Example
Converter(config)# interface 1
Enter LAN interface.
Converter(config-if-1)# qos rate-limit ingress
1550
Configure the selected interfaces‟ ingress
rate-limit to 1550.
Converter(config-if-1)# qos rate-limit egress 3
1550
Set the selected interfaces‟ queue 3 to
egress rate 1550.
2.5.10 Security Command
When a device on the network is malfunctioning or application programs are not well
designed or properly configured, broadcast storms may occur, which may degrade network
performance or in the worst situation cause a complete halt. The Managed Converter allows
users to set a threshold rate for broadcast traffic so as to protect network from broadcast
storms. Any broadcast packet exceeding the specified value will then be dropped.
Security Command
Parameter
Description
Converter(config)# security
storm-protection
Enable storm protection function.
Converter(config)# security
storm-protection rates [321000000] kbps
[32-1000000]
kbps
Specify the maximum broadcast packet
rate.
No Command
Converter(config)# no security storm-protection
Disable storm protection globally.
Converter(config)# no security storm-protection
rates
Set broadcast packet rate back to the
default.
Show Command
Converter(config)# show security stormprotection
Show storm control settings.
 Loading...
Loading...