
FOS-5126 Series
20 PORTS 100/1000BASE-X SFP + 4 COMBO PORTS
(10/100/1000BASE-T, 100/1000BASE-X SFP) WITH 2 UPLINK Ports
10 Gbps SFP+ MANAGEMENT SWITCH
Network Management
User’s Manual
Version 0.90
1
2
Revision History
Version
F/W
Date
Description
0.90
1.00.00
20151211
Fisrt release
0.90
1.00.01
20151218
ACL action command revised (Section 2.6.4)

3
Trademarks
CTS is a registered trademark of Connection Technology Systems Inc..
Contents are subject to revision without prior notice.
All other trademarks remain the property of their owners.
Copyright Statement
Copyright Connection Technology Systems Inc..
This publication may not be reproduced as a whole or in part, in any way whatsoever unless prior consent has been obtained from
Connection Technology Systems Inc..
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limitations are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult your local distributors or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
Copyright © 2015 All Rights Reserved.
Company has an on-going policy of upgrading its products and it may be possible that information in this document is not up-todate. Please check with your local distributors for the latest information. No part of this document can be copied or reproduced in
any form without written consent from the company.
Trademarks:
All trade names and trademarks are the properties of their respective companies.

4
Table of Content
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................... 9
1.1 Management Options ................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Management Software ............................................................................................... 10
1.3 Management Preparations ......................................................................................... 11
2. Command Line Interface (CLI) ...................................................................................... 13
2.1 Using the Local Console ............................................................................................. 13
2.2 Remote Console Management - Telnet ...................................................................... 14
2.3 Navigating CLI ............................................................................................................ 14
2.3.1 General Commands ............................................................................................. 15
2.3.2 Quick Keys ........................................................................................................... 15
2.3.3 Command Format ................................................................................................ 16
2.3.4 Login Username & Password .............................................................................. 17
2.4 User Mode .................................................................................................................. 18
2.4.1 Ping Command .................................................................................................... 18
2.4.2 Traceroute Command .......................................................................................... 18
2.5 Privileged Mode .......................................................................................................... 19
2.5.1 Copy-cfg Command ............................................................................................. 19
2.5.2 Firmware Command ............................................................................................ 20
2.5.3 Ping Command .................................................................................................... 21
2.5.4 Reload Command ................................................................................................ 21
2.5.5 Traceroute Command .......................................................................................... 21
2.5.6 Write Command ................................................................................................... 21
2.5.7 Configure Command ............................................................................................ 22
2.5.8 Show Command .................................................................................................. 22
2.6 Configuration Mode .................................................................................................... 23
2.6.1 Entering Interface Numbers ................................................................................. 24
2.6.2 No Command ....................................................................................................... 24
2.6.3 Show Command .................................................................................................. 24
2.6.4 ACL Command ..................................................................................................... 26
2.6.5 Channel-group Command .................................................................................... 29
2.6.6 Dot1x Command .................................................................................................. 31
2.6.7 IP Command ........................................................................................................ 34
2.6.8 IPv6 Command .................................................................................................... 41
2.6.9 LLDP Command .................................................................................................. 42
2.6.10 Loop Detection Command ................................................................................. 45

5
2.6.11 MAC Command ................................................................................................ .. 47
2.6.12 Management Command .................................................................................... 49
2.6.13 Mirror Command ................................................................................................ 49
2.6.14 NTP Command .................................................................................................. 50
2.6.15 QoS Command .................................................................................................. 51
2.6.16 Security Command ............................................................................................ 53
2.6.17 SNMP-Server Command ................................................................................... 54
2.6.18 Spanning-tree Command ................................................................................... 58
2.6.19 Switch Command ................................................................ ............................... 62
2.6.20 Switch-info Command ........................................................................................ 63
2.6.21 Syslog Command ............................................................................................... 64
2.6.22 User Command .................................................................................................. 65
2.6.23 VLAN Command ................................................................................................ 67
2.6.24 Interface Command ........................................................................................... 73
2.6.25 Show interface statistics Command ................................................................... 80
2.6.26 Show sfp Command ........................................................................................... 80
2.6.27 Show running-config & start-up-config Command .............................................. 81
3. SNMP NETWORK MANAGEMENT ................................................................................ 82
4. WEB MANAGEMENT...................................................................................................... 83
4.1 System Information .................................................................................................... 84
4.2 User Authentication ................................ ................................ ................................ .... 86
4.2.1 RADIUS Configuration ......................................................................................... 88
4.3 Network Management ................................................................................................ 88
4.3.1 Network Configuration ......................................................................................... 89
4.3.2 System Service Configuration .............................................................................. 92
4.3.3 RS232/Telnet/Console Configuration ................................................................... 93
4.3.4 Time Server Configuration ................................................................................... 94
4.3.5 Device Community ................................ ................................ ............................... 95
4.3.6 Trap Destination ................................................................................................... 96
4.3.7 Trap Configuration ............................................................................................... 96
4.3.8 Mal-attempt Log Configuration ............................................................................. 97
4.4 Switch Management ................................................................................................... 98
4.4.1 Switch Configuration .......................................................................................... 100
4.4.2 Port Configuration .............................................................................................. 101
4.4.3 Link Aggregation ................................................................................................ 101
4.4.3.1 Distribution Rule .......................................................................................... 102
4.4.3.2 Port Trunking ............................................................................................... 103

6
4.4.3.3 LACP Port Configuration ............................................................................. 105
4.4.4 Rapid Spanning Tree ......................................................................................... 107
4.4.4.1 RSTP Switch Settings ................................................................................. 108
4.4.4.2 RSTP Aggregated Port Settings ................................................................ .. 109
4.4.4.3 RSTP Physical Port Settings ....................................................................... 110
4.4.5 802.1X Configuration ......................................................................................... 114
4.4.5.1 802.1X System Settings .............................................................................. 115
4.4.5.2 802.1X Port Admin State ............................................................................. 115
4.4.5.3 802.1X Port Reauthenticate ........................................................................ 116
4.4.6 MAC Address Management ............................................................................... 117
4.4.6.1 MAC Table Learning ................................................................................... 117
4.4.6.2 Static MAC Table Configuration .................................................................. 117
4.4.7 VLAN Configuration ........................................................................................... 118
4.4.7.1 Port-Based VLAN ........................................................................................ 119
4.4.7.2 802.1Q VLAN Concept ................................................................................ 120
4.4.7.3 Introduction to Q-in-Q .................................................................................. 123
4.4.7.4 802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................................. 124
4.4.7.4.1 VLAN Interface ............................................................................................... 124
4.4.7.4.2 Trunk VLAN table ............................................................................................ 125
4.4.7.4.3 Management VLAN ........................................................................................ 126
4.4.7.4.4 QinQ VLAN configuration................................................................................ 127
4.4.8 QoS Configuration ............................................................................................. 128
4.4.8.1 QoS Priority ................................................................................................. 129
4.4.8.2 QoS Rate Limit ............................................................................................ 131
4.4.9 IGMP/MLD Snooping ......................................................................................... 132
4.4.9.1 IGMP/MLD Configure .................................................................................. 134
4.4.9.2 IGMP/MLD VLAN ID Configuration ............................................................. 135
4.4.9.3 IPMC Segment ............................................................................................ 135
4.4.9.4 IPMC Profile ................................................................................................ 136
4.4.9.5 IGMP/MLD Filtering ..................................................................................... 137
4.4.10 Static Multicast Configuration ........................................................................... 138
4.4.11 Port Mirroring ................................................................................................... 139
4.4.12 Security Configuration ...................................................................................... 140
4.4.12.1 DHCP Option 82/DHCPv6 Option 37 Settings .......................................... 141
4.4.12.2 DHCP Option 82 Configuration ................................................................. 144
4.4.12.3 IP Source Guard Settings .......................................................................... 145
4.4.12.4 Port Isolation ............................................................................................. 146

7
4.4.12.5 Filter Configuration .................................................................................... 146
4.4.12.6 Static IP/IPv6 Table Configuration ............................................................. 148
4.4.12.7 Configure DHCP Snooping........................................................................ 149
4.4.12.8 Storm Control ............................................................................................ 150
4.4.13 Access Control List (ACL) Configuratiom ......................................................... 150
4.4.14 LLDP Configuration ......................................................................................... 152
4.4.15 Loop Detection Configuration ......................................................................... 154
4.5 Switch Monitor .......................................................................................................... 156
4.5.1 CPU & Memory Statistics ................................................................................... 157
4.5.2 Switch Port State ................................................................................................ 158
4.5.3 Port Traffic Statistics .......................................................................................... 159
4.5.4 Port Packet Error Statistics ................................................................................ 160
4.5.5 Port Packet Analysis Statistics ........................................................................... 161
4.5.6 LACP Monitor ..................................................................................................... 162
4.5.6.1 LACP Port Status ........................................................................................ 163
4.5.6.2 LACP Statistics ............................................................................................ 164
4.5.7 RSTP Monitor .................................................................................................... 165
4.5.7.1 RSTP Bridge Overview ............................................................................... 165
4.5.7.2 RSTP Port Status ........................................................................................ 166
4.5.7.3 RSTP Statistics ........................................................................................... 167
4.5.8 802.1X Monitor................................................................................................... 167
4.5.8.1 802.1X Port Status ...................................................................................... 168
4.5.8.2 802.1X Statistics .......................................................................................... 169
4.5.9 IGMP/MLD Monitor ............................................................................................ 170
4.5.9.1 IGMP Snooping Status ................................................................................ 170
4.5.9.2 IGMP Group Table ...................................................................................... 171
4.5.9.3 MLD Snooping Status ................................................................................. 171
4.5.9.4 MLD Group Table ........................................................................................ 172
4.5.10 SFP Information ............................................................................................... 173
4.5.10.1 SFP Port Info ............................................................................................. 173
4.5.10.2 SFP Port State .......................................................................................... 174
4.5.11 DCHP Snooping ............................................................................................... 175
4.5.12 MAC Address Table ......................................................................................... 176
4.5.13 LLDP Status ..................................................................................................... 176
4.5.14 Loop Detection Status ...................................................................................... 177
4.5.15 IEEE 802.1q Tag VLAN Table .......................................................................... 178
4.6 System Utility ............................................................................................................ 178

8
4.6.1 Ping .................................................................................................................... 179
4.6.2 Event Log ........................................................................................................... 180
4.6.3 HTTP Upgrade ................................................................................................... 180
4.6.4 TFP/TFTP Upgrade............................................................................................ 181
4.6.5 Load Factory Settings ........................................................................................ 182
4.6.6 Load Factory Settings Except Network Configuration ........................................ 183
4.7 Save Configuration ................................................................................................... 183
4.8 Reset System ................................ ................................ ........................................... 184
4.9 Logout ...................................................................................................................... 184
APPENDIX A: Free RADIUS readme ............................................................................... 185
APPENDIX B: Set Up DHCP Auto-Provisioning ............................................................. 186
APPENDIX C: VLAN Application Note ............................................................................ 195

9
1. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for using the 20 100/1000Mbps SFP ports plus 4 10/100/1000Mbps combo ports and 2
SFP+ 10Gbps ports Managed Switch that is specifically designed for FTTx applications. The
Managed Switch provides a built-in management module that enables users to configure and
monitor the operational status both locally and remotely. This User’s Manual will explain how to
use command-line interface and Web Management to configure your Managed Switch. The
readers of this manual should have knowledge about their network typologies and about basic
networking concepts so as to make the best of this user’s manual and maximize the Managed
Switch’s performance for your personalized networking environment.
1.1 Management Options
Switch management options available are listed below:
Local Console Management
Telnet Management
SNMP Management
WEB Management
SSH Management
Local Console Management
Local Console Management is done through the RS-232 RJ-45 Console port located on the front
panel of the Managed Switch. Direct RS-232 cable connection between the PC and the Managed
switch is required for this type of management.
Telnet Management
Telnet runs over TCP/IP and allows you to establish a management session through the network.
Once the Managed switch is on the network with proper IP configurations, you can use Telnet to
login and monitor its status remotely.
SSH Management
SSH Management supports encrypted data transfer to prevent the data from being “stolen” for
remote management. You can use PuTTY, a free and open source terminal emulator application
which can act as a client for the SSH, to gain access to the Managed Switch.
SNMP Management
SNMP is also done over the network. Apart from standard MIB (Management Information Bases),
an additional private MIB is also provided for SNMP-based network management system to
compile and control.
Web Management
Web Management is done over the network and can be accessed via a standard web browser,
such as Microsoft Internet Explorer. Once the Managed switch is available on the network, you
can login and monitor the status of it through a web browser remotely or locally. Local Consoletype Web management, especially for the first time use of the Managed Switch to set up the
needed IP, can be done through one of the 10/100/1000Base-TX 8-pin RJ-45 ports located at the
front panel of the Managed Switch. Direct RJ-45 LAN cable connection between a PC and the
Managed Switch is required for Web Management.

10
1.2 Management Software
The following is a list of management software options provided by this Managed Switch:
Managed Switch CLI interface
SNMP-based Management Software
Web Browser Application
Console Program
The Managed Switch has a built-in Command Line Interface called the CLI which you can use to:
Configure the system
Monitor the status
Reset the system
You can use CLI as the only management system. However, other network management options,
SNMP-based management system, are also available.
You can access the text-mode Console Program locally by connecting a VT-100 terminal - or a
workstation running VT100 emulation software - to the Managed Switch RS-232 RJ-45 Console
port directly. Or, you can use Telnet to login and access the CLI through network connection
remotely.
SNMP Management System
Standard SNMP-based network management system is used to manage the Managed Switch
through the network remotely. When you use a SNMP-based network management system, the
Managed Switch becomes one of the managed devices (network elements) in that system. The
Managed Switch management module contains an SNMP agent that will respond to the requests
from the SNMP-based network management system. These requests, which you can control, can
vary from getting system information to setting the device attribute values.
The Managed Switch’s private MIB is provided for you to be installed in your SNMP-based
network management system.
Web Browser Application
You can manage the Managed Switch through a web browser, such as Internet Explorer or
Google Chrome, etc.. (The default IP address of the Managed Switch port can be reached at
“http://192.168.0.1”.) For your convenience, you can use either this Web-based Management
Browser Application program or other network management options, for example SNMP-based
management system as your management system.

11
1.3 Management Preparations
After you have decided how to manage your Managed Switch, you are required to connect cables
properly, determine the Managed switch IP address and, in some cases, install MIB shipped with
your Managed Switch.
Connecting the Managed Switch
It is very important that the proper cables with the correct pin arrangement are used when
connecting the Managed switch to other switches, hubs, workstations, etc..
10 Gigabit / 1000Base-X / 100Base-FX SFP Port
The small form-factor pluggable (SFP) is a compact optical transceiver used in optical data
communication applications. It interfaces a network device mother board (for a switch, router
or similar device) to a fiber optic or unshielded twisted pair networking cable. It is a popular
industry format supported by several fiber optic component vendors.
SFP transceivers are available with a variety of different transmitter and receiver types,
allowing users to select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the required
optical reach over the available optical fiber type.
SFP slot for 3.3V mini GBIC module supports hot swappable SFP fiber transceiver. Before
connecting the other switches, workstation or Media Converter, make sure both side of the
SFP transfer are with the same media type, for example, 1000Base-SX to 1000Base-SX,
1000Bas-LX to 1000Base-LX, and check the fiber-optic cable type matches the SFP transfer
model. To connect to 1000Base-SX transceiver, use the multi-mode fiber cable with male
duplex LC connector type for one side. To connect to 1000Base-LX transfer, use the singlemode fiber cable with male duplex LC connector type for one side.
10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 Auto-MDI/MDIX Port
4 x 10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 Auto-MDI/MDIX ports are located at the front of the Managed
Switch. These RJ-45 ports allow user to connect their traditional copper-based Ethernet/Fast
Ethernet devices to the network. All these ports support auto-negotiation and MDI/MDIX
auto-crossover, i.e. either crossover or straight through CAT-5 UTP or STP cable may be
used.
RS-232 RJ-45 Port
The RS-232 RJ-45 port is located at the front of the Managed Switch. This RJ-45 port is used
for local, out-of-band management. Since this RJ-45 port of the Managed switch is DTE, a
null modem is also required to be connected to the Managed Switch and the PC. By
connecting this RJ-45 port, it allows you to configure & check the status of Managed Switch
even when the network is down.

12
IP Addresses
IP addresses have the format n.n.n.n, (The default factory setting is 192.168.0.1).
IP addresses are made up of two parts:
The first part (for example 192.168.n.n) refers to network address that identifies the network
where the device resides. Network addresses are assigned by three allocation organizations.
Depending on your location, each allocation organization assigns a globally unique network
number to each network which intends to connect to the Internet.
The second part (for example n.n.0.1) identifies the device within the network.
Assigning unique device numbers is your responsibility. If you are unsure of the IP addresses
allocated to you, consult with the allocation organization where your IP addresses were
obtained.
Remember that an address can be assigned to only one device on a network. If you connect to
the outside network, you must change all the arbitrary IP addresses to comply with those you have
been allocated by the allocation organization. If you do not do this, your outside communications
will not be performed.
A subnet mask is a filtering system for IP addresses. It allows you to further subdivide your
network. You must use the proper subnet mask for the proper operation of a network with subnets
defined.
MIB for Network Management Systems
Private MIB (Management Information Bases) is provided for managing the Managed Switch
through the SNMP-based network management system. You must install the private MIB into
your SNMP-based network management system first.
The MIB file is shipped together with the Managed Switch. The file name extension is “.mib” that
allows SNMP-based compiler can read and compile.

13
2. Command Line Interface (CLI)
This chapter introduces you how to use Command Line Interface CLI, specifically in:
Local Console
Telnet
Configuring the system
Resetting the system
The interface and options in Local Console and Telnet are the same. The major difference is the
type of connection and the port that is used to manage the Managed Switch.
2.1 Using the Local Console
Local Console is always done through the RS-232 RJ-45 port and requires a direct connection
between the switch and a PC. This type of management is useful especially when the network is
down and the switch cannot be reached by any other means.
You also need the Local Console Management to setup the Switch network configuration for the
first time. You can setup the IP address and change the default configuration to the desired
settings to enable Telnet or SNMP services.
Follow these steps to begin a management session using Local Console Management:
Step 1. Attach the serial cable to the RS-232 RJ-45 port located at the front of the Switch.
Step 2. Attach the other end to the serial port of a PC or workstation.
Step 3. Run a terminal emulation program using the following settings:
Emulation VT-100/ANSI compatible
BPS 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow Control None
Enable Terminal keys
Step 4. Press Enter to access the CLI (Command Line Interface) mode.
14
2.2 Remote Console Management - Telnet
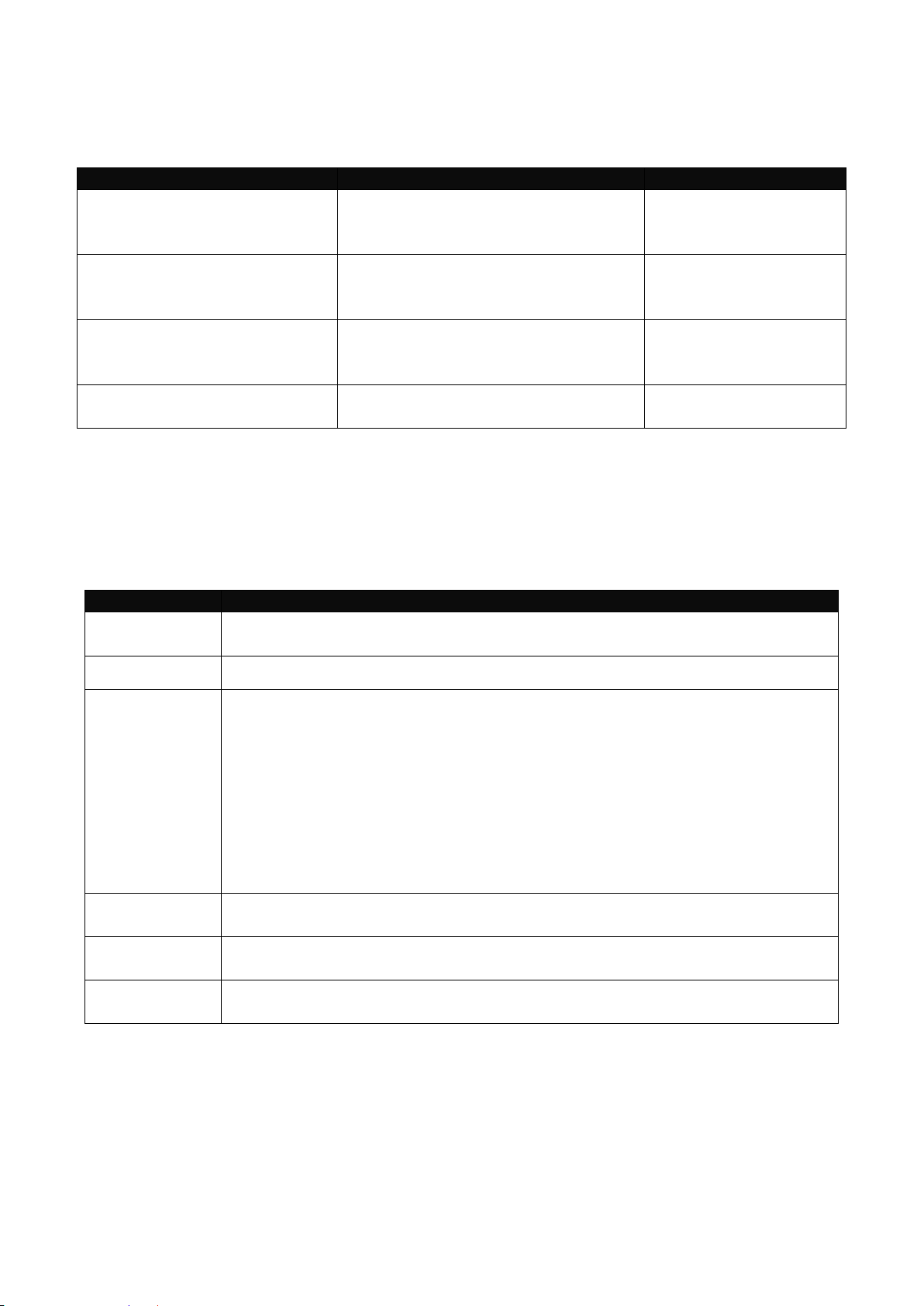
Command Mode
Access Method
Prompt Displayed
Exit Method
User mode
Login username &
password
Switch>
logout, exit
Privileged mode
From user mode, enter
the enable command
Switch#
disable, exit, logout
Configuration
mode
From the enable mode,
enter the config or
configure command
Switch(config)#
exit, Ctrl + Z
NOTE: By default, the model name will be used for the prompt display. You can change
the prompt display to the one that is ideal for your network environment using the
hostname command. However, for convenience, the prompt display “Switch” will be used
throughout this user’s manual.
You can manage the Managed Switch via Telnet session. However, you must first assign a
unique IP address to the Switch before doing so. Use the Local Console to login the Managed
Switch and assign the IP address for the first time.
Follow these steps to manage the Managed Switch through Telnet session:
Step 1. Use Local Console to assign an IP address to the Managed Switch
IP address
Subnet Mask
Default gateway IP address, if required
Step 2. Run Telnet
Step 3. Log into the Switch CLI
Limitations: When using Telnet, keep the following in mind:
Only two active Telnet sessions can access the Managed Switch at the same time.
2.3 Navigating CLI
When you successfully access the Managed Switch, you will be asked for a login username. Enter
your authorized username and password, and then you will be directed to User mode. In CLI
management, the User mode only provides users with basic functions to operate the Managed
Switch. If you would like to configure advanced features of the Managed Switch, such as, VLAN,
QoS, Rate limit control, you must enter the Configuration mode. The following table provides an
overview of modes available in this Managed Switch.
15
2.3.1 General Commands
Entering the command…
To do this…
Available Modes
help
Obtain a list of available
commands in the current mode.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
exit
Return to the previous mode or
login screen.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
history
List all commands that have been
used.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
logout
Logout from the CLI or terminate
Console or Telnet session.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Keys
Purpose
tab
Enter an unfinished command and press “Tab” key to complete the
command.
?
Press “?” key in each mode to get available commands.
Unfinished
command
followed by ?
Enter an unfinished command or keyword and press “?” key to complete
the command and get command syntax help.
Example: List all available commands starting with the characters that
you enter.
Switch#h?
help Show available commands
history Show history commands
A space
followed by ?
Enter a command and then press Spacebar followed by a “?” key to view
the next parameter.
Up arrow
Use Up arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the most recent key-in commands.
Down arrow
Use Down arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the commands that are entered first.
This section introduces you some general commands that you can use in User, Enable, and
Configuration mode, including “help”, “exit”, “history” and “logout”.
2.3.2 Quick Keys
In CLI, there are several quick keys that you can use to perform several functions. The following
table summarizes the most frequently used quick keys in CLI.
16
2.3.3 Command Format
Symbols
Brief Description
>
Currently, the device is in User mode.
#
Currently, the device is in Privileged mode.
(config)#
Currently, the device is in Global
Configuration mode.
Syntax
Brief Description
[ ]
Reference parameter.
[-s size] [-r repeat] [-t timeout]
These three parameters are used in ping
command and are optional, which means
that you can ignore these three parameters
if they are unnecessary when executing
ping command.
[A.B.C.D ]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter an IP address or gateway
address.
[255.X.X.X]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter the subnet mask.
[port]
Enter one port number. See section 1.6.21
for edtailed explanations.
[port_list]
Enter a range of port numbers or server
discontinuous port numbers. See section
1.6.21 for edtailed explanations.
[forced_false | auto]
There are three options that you can
choose. Specify one of them.
[1-8191]
Specify a value between 1 and 8191.
[0-7] 802.1p_list
[0-63] dscp_list
Specify one value, more than one value or a
range of values.
Example 1: specifying one value
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10 3
Example 2: specifying three values
This means that
you are in Global
Configuration
mode
This allows you to
assign IP address.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway address.
Hostname
While in CLI, you will see several symbols very often. As mentioned above, you might already
know what “>”, “#” and (config)# represent. However, to perform what you intend the device to do,
you have to enter a string of complete command correctly. For example, if you want to assign IP
address for the Managed Switch, you need to enter the following command with the required
parameter and IP, subnet mask and default gateway:
IP command syntax: Switch(config)#ip address [A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X] [A.B.C.D]
Switch(config)#ip address 192.168.1.198 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.254
The following table lists common symbols and syntax that you will see very frequently in this
User’s Manual for your reference:
17
(separated by commas)
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1,3 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10,13,15 3
Example 3: specifying a range of values
(separated by a hyphen)
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1-3 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10-15 3
2.3.4 Login Username & Password
Default Login
When you enter Console session, a login prompt for username and password will appear to
request a valid and authorized username and password combination. For first-time users, enter
the default login username “admin” and “press Enter key” in password field (no password is
required for default setting). When system prompt shows “Switch>”, it means that the user has
successfully entered the User mode.
For security reasons, it is strongly recommended that you add a new login username and
password using User command in Configuration mode. When you create your own login
username and password, you can delete the default username (admin) to prevent unauthorized
accesses.
Enable Mode Password
Enable mode is password-protected. When you try to enter Enable mode, a password prompt will
appear to request the user to provide the legitimate passwords. Enable mode password is the
same as the one entered after login password prompt. By default, no password is required.
Therefore, press Enter key in password prompt.
Forgot Your Login Username & Password
If you forgot your login username and password, you can use the “reset button” on the front panel
to set all configurations back to factory defaults. Once you have performed system reset to
defaults, you can login with default username and password. Please note that if you use this
method to gain access to the Managed Switch, all configurations saved in Flash will be lost. It is
strongly recommended that a copy of configurations is backed up in your local hard-drive or file
server from time to time so that previously-configured settings can be reloaded to the Managed
Switch for use when you gain access again to the device.
18
2.4 User Mode
Command
Description
exit
Quit the User mode or close the terminal connection.
help
Display a list of available commands in User mode.
history
Display the command history.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
ping
Test whether a specified network device or host is reachable or not.
traceroute
Trace the route to HOST
enable
Enter the Privileged mode.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> ping
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [s size (1-
65500)bytes] [-t
timeout (1-99)secs]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-s size (1-
65500)bytes]
Enter the packet size that would be sent. The
allowable packet size is from 1 to 65500 bytes.
(optional)
[-t timeout (1-99)
secs]
Enter the timeout value when the specified IP
address is not reachable. (optional)
Example
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8 –s 128 –t 10
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –s 128 –t 10
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> traceroute
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [h (1-100)hops]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-h (1-100)hops]
Specify max hops between the local host and the
remote host
Example
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8 –h 30
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –h 30
In User mode, only a limited set of commands are provided. Please note that in User mode, you
have no authority to configure advanced settings. You need to enter Enable mode and
Configuration mode to set up advanced functions of the Switch. For a list of commands available
in User mode, enter the question mark (?) or “help” command after the system prompt displays
Switch>.
2.4.1 Ping Command
Ping is used to test the connectivity of end devices and also can be used to self test the network
interface card. Enter the ping command in User mode. In this command, you can add an optional
packet size value and an optional value for the number of times that packets are sent and received.
2.4.2 Traceroute Command
Traceroute is used to trach the path between the local host and the remote host. Enter the
traceroute command in User mode. In this command, you can add an optional max hops value
for the number of hops that packets are sent and received.
19
2.5 Privileged Mode
Command
Description
copy-cfg
Restore or backup configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
disable
Exit Enable mode and return to User Mode.
exit
Exit Enable mode and return to User Mode.
firmware
Allow users to update firmware via FTP or TFTP.
help
Display a list of available commands in Enable mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
ping
Test whether a specified network device or host is reachable or not.
reload
Restart the Managed Switch.
traceroute
Trace the route to HOST
write
Save your configurations to Flash.
configure
Enter Global Configuration mode.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# copy-cfg
from ftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file name]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address of your FTP
server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# copy-cfg
from tftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address of your TFTP
server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
Example
Switch# copy-cfg from ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf misadmin1 abcxyz
Switch# copy-cfg from tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# copy-cfg to
ftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file name] [running
| default | startup ]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
[running | default
Specify backup config to be running, default or
The only place where you can enter the Privileged (Enable) mode is in User mode. When you
successfully enter Enable mode (this mode is password protected), the prompt will be changed to
Switch# (the model name of your device together with a pound sign). Enter the question mark (?)
or help command to view a list of commands available for use.
2.5.1 Copy-cfg Command
Use “copy-cfg” command to backup a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server and restore the
Managed Switch back to the defaults or to the defaults but keep IP configurations.
1. Restore a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
2. Backup configuration file to FTP or TFTP server.
20
[user_name]
[password]
| startup ]
startup
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# copy-cfg to
tftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [running
| default | startup ]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
[running | default
| startup ]
Specify backup config to be running, default or
startup
Example
Switch# copy-cfg to ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf running misadmin1 abcxyz
Switch# copy-cfg to tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf startup
Command / Example
Switch# copy-cfg from default
Switch# reload
Command / Example
Switch# copy-cfg from default keep-ip
Switch# reload
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# firmware
upgrade ftp
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [Image1| Image-2]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to
upgrade.
[Image-1| Image2]
Choose image-1 or image-2 for the firmware to
be upgraded to.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# firmware
upgrade tftp
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [Image1| Image-2]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to
upgrade.
[Image-1| Image2]
Choose image-1 or image-2 for the firmware to
be upgraded to.
Example
Switch# firmware upgrade ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin Image-1 edgeswitch10
abcxyz
Switch# firmware upgrade tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin Image-2
3. Restore the Managed Switch back to default settings.
4. Restore the Managed Switch back to default settings but keep IP configurations.
2.5.2 Firmware Command
To upgrade firmware via TFTP or FTP server.

21
2.5.3 Ping Command
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> ping
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [s size (1-
65500)bytes] [-t
timeout (1-99)secs]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-s size (1-
65500)bytes]
Enter the packet size that would be sent. The
allowable packet size is from 1 to 65500 bytes.
(optional)
[-t timeout (1-99)
secs]
Enter the timeout value when the specified IP
address is not reachable. (optional)
Example
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8 –s 128 –t 10
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –s 128 –t 10
Command / Example
Switch# reload
Command / Example
Switch# reload Image-2
OK!
Switch# reload
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> traceroute
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [h (1-100)hops]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-h (1-100)hops]
Specify max hops between the local host and the
remote host
Example
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8 –h 30
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –h 30
Command / Example
Switch# write
Save Config Succeeded!
2.5.4 Reload Command
1. To restart the Managed Switch.
2. To specify the image for the next restart before restarting.
2.5.5 Traceroute Command
2.5.6 Write Command
To save running configurations to startup configurations, enter the write command. All unsaved
configurations will be lost when you restart the Managed Switch.

22
Command / Example
Switch#config
Switch(config)#
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#
2.5.7 Configure Command
The only place where you can enter Global Configuration mode is in Privileged mode. You can
type in “configure” or “config” for short to enter Global Configuration mode. The display prompt will
change from “Switch#” to “Switch(config)#” once you successfully enter Global Configuration
mode.
2.5.8 Show Command
The “show” command is very important for network administrators to get information about the
device, receive outputs to verify a command’s configurations or troubleshoot a network
configuration error. It can be used in Privileged or Configuration mode. The following describes
different uses of “show” command.
1. Display system information
Enter “show switch-info” command in Privileged or Configuration mode, and then the following
information will appear.
Company Name: Display a company name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info company-
name [company-name]” command to edit this field.
System Object ID: Display the predefined System OID.
System Contact: Display contact information for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
contact [sys-contact]” command to edit this field.
System Name: Display a descriptive system name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
name [sys-name]” command to edit this field.
System Location: Display a brief location description for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info
sys-location [sys-location]” command to edit this field.
Model Name: Display the product’s model name.
Host Name: Display the product’s host name.
Firmware Version1: Display the firmware version 1 (image-1) used in this device.
Firmware Version2: Display the firmware version 2 (image-2) used in this device.
M/B Version: Display the main board version.
Fiber Type: Display information about the slide-in or fixed fiber type.
Fiber Wavelength: Display the slide-in or fixed fiber’s TX and RX wavelength information.

23
Serial Number: Display the serial number of this Managed Switch.
Command
Description
acl
Set up access control entries and lists.
channel-group
Configure static link aggregation groups or enable LACP function.
dot1x
IEEE 802.1X global configuration commands
exit
Exit the configuration mode.
help
Display a list of available commands in Configuration mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
ip
Set up the IPv4 address and enable DHCP mode & IGMP snooping.
Ipv6
To enable ipv6 function and set up IP address
lldp
LLDP global configuration mode
loop-detection
Configure loop-detection to prevent loop between switch ports by locking them.
mac
Set up MAC learning function of each port
management
Set up console/telnet/web/SSH access control and timeout value.
mirror
Set up target port for mirroring.
ntp
Set up required configurations for Network Time Protocol.
qos
Set up the priority of packets within the Managed Switch.
Date Code: Display the Managed Switch Firmware date code.
Up Time: Display the up time since last restarting.
Local Time: Display local time.
Current Run In: Display the current running firmware image.
Reboot Run To: Display the firmware image which will run after next restarting.
Case Fan : Display the status of case fans.
Power (A-B): Display the status of powers.
Battery State: Display the status of battery (For BAT version only).
2. Display or verify currently-configured settings
Refer to the following sub-sections. “Interface command”, “IP command”, “MAC command”, “QoS
command”, “Security command”, “SNMP-Server command”, “User command”, “VLAN command”
sections, etc.
3. Display interface information or statistics
Refer to “Show interface statistics command” and “Show sfp information command” sections.
4. Show default, running and startup configurations
Refer to “show default-setting copmmand”, “show running-config command” and “show start-upconfig command” sections.
2.6 Configuration Mode
When you enter “configure” or “config” and press “Enter” in Privileged mode, you will be directed to
Global Configuration mode where you can set up advanced switching functions, such as QoS,
VLAN and storm control security globally. All commands entered will apply to running-configuration
and the device’s operation. From this level, you can also enter different sub-configuration modes
to set up specific configurations for VLAN, QoS, security or interfaces.
24
security
Configure broadcast, unknown multicast, unknown unicast storm control settings.
snmp-server
Create a new SNMP community and trap destination and specify the trap types.
spanning-tree
Set up RSTP status of each port and aggregated ports.
switch
Set up acceptable frame size and address learning, etc.
switch-info
Set up acceptable frame size and address learning, etc.
syslog
Set up required configurations for Syslog server.
user
Create a new user account.
vlan
Set up VLAN mode and VLAN configuration.
no
Disable a command or set it back to its default setting.
interface
Select a single interface or a range of interfaces.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.
Commands
Description
Switch(config)# interface 1
Switch(config-if-1)#
Enter a single interface. Only interface 1 will
apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1,3,5
Switch(config-if-1,3,5)#
Enter three discontinuous interfaces,
separated by commas. Interface 1, 3, 5 will
apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Switch(config-if-1-3)#
Enter three continuous interfaces. Use a
hyphen to signify a range of interface
numbers. In this example, interface 1, 2, and
3 will apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1,3-5
Switch(config-if-1,3-5)#
Enter a single interface number together with
a range of interface numbers. Use both
comma and hypen to signify the combination
of different interface numbers. In this
example, interface 1, 3, 4, 5 will apply
commands entered.
2.6.1 Entering Interface Numbers
In the Global Configuration mode, you can configure a command that only applies to interfaces
specified. For example, you can set up each interface’s VLAN assignment, speeds, or duplex
modes. To configure, you must first enter the interface number. There are four ways to enter your
interface numbers to signify the combination of different interfaces that apply a command or
commands.
2.6.2 No Command
Almost every command that you enter in Configuration mode can be negated using “no” command
followed by the original or similar command. The purpose of “no” command is to disable a function,
remove a command, or set the setting back to the default value. In each sub-section below, the
use of no command to fulfill different purposes will be introduced.
2.6.3 Show Command
The “show” command is very important for network administrators to get information about the
device, receive outputs to verify a command’s configurations or troubleshoot a network
configuration error. It can be used in Privileged or Configuration mode. The following describes
different uses of “show” command.
1. Display system information
Enter “show switch-info” command in Privileged or Configuration mode, and then the following
information will appear.

25
Company Name: Display a company name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info company-
name [company-name]” command to edit this field.
System Object ID: Display the predefined System OID.
System Contact: Display contact information for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
contact [sys-contact]” command to edit this field.
System Name: Display a descriptive system name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
name [sys-name]” command to edit this field.
System Location: Display a brief location description for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info
sys-location [sys-location]” command to edit this field.
Model Name: Display the product’s model name.
Host Name: Display the product’s host name.
Firmware Version1: Display the firmware version 1 (image-1) used in this device.
Firmware Version2: Display the firmware version 2 (image-2) used in this device.
M/B Version: Display the main board version.
Fiber Type: Display information about the slide-in or fixed fiber type.
Fiber Wavelength: Display the slide-in or fixed fiber’s TX and RX wavelength information.
Serial Number: Display the serial number of this Managed Switch.
Date Code: Display the Managed Switch Firmware date code.
Up Time: Display the up time since last restarting.
Local Time: Display local time.
Current Run In: Display the current running firmware image.
Reboot Run To: Display the firmware image which will run after next restarting.
Case Fan (1-6): Display the status of case fans.
Power (A-B): Display the status of powers.
Battery State: Display the status of battery (For BAT version only).
2. Display or verify currently-configured settings
Refer to the following sub-sections. “Interface command”, “IP command”, “MAC command”, “QoS
command”, “Security command”, “SNMP-Server command”, “User command”, “VLAN command”
sections, etc.
3. Display interface information or statistics
Refer to “Show interface statistics command” and “Show sfp information command” sections.
26
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# acl [1-192]
[1-192]
The total number of ACL rule can be
created is 192. Use this command to
enter ACL configuration mode for each
ACL rule. When you enter each ACL
rule, you can further configure detailed
settings for this rule.
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
action [deny | copy(mirror) |
redirect]
[deny | copy(mirror)
| redirect]
Deny, copy(mirror) or redirect the
action for this rule.
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
action-port [port]
[port]
Specify action port (1~26)
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
apply
Application effective
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv4 any
Specify destination IPv4 address as
“ANY”
4. Show default, running and startup configurations
Refer to “show default-setting copmmand”, “show running-config command” and “show start-upconfig command” sections.
2.6.4 ACL Command
27
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv4 address
[A.B.C.D] [0-255.X.X.X]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify destination IPv4 address
[0-255.X.X.X]
Specify destination IPv4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv6 any
Specify destination IPv6 address as
“ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv6 address
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify destination IPv6 address
[10~128]
Specify destination IPv6 prefix-length
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-l4-port any
Specify destination Layer4 port as
“ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-l4-port [165535] [0xWXYZ]
[1-65535]
Specify destination Layer4 port
[0xWXYZ]
Specify destination Layer4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-mac any
Specify destination MAC as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Specify destination MAC
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
Specify destination MAC mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
ethertype [any | 0xWXYZ]
[any | 0xWXYZ]
Specify Ethertype or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
ingress-port [any | port-list]
[any | port-list]
Specify ingress port(s) or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
protocol [any | 0xWX]
[any | 0xWX]
Specify IPv4 protocol and IPv6 next
header or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
rate-limit [16-1048560]
[16-1048560]
Specify rate limitation from 16 to
1048560 kbps
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv4 any
Specify source IPv4 address as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv4 address
[A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify source IPv4 address
[255.X.X.X]
Specify source IPv4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv6 any
Specify source IPv6 address as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv6 address
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify source IPv6 address
[10~128]
Specify source IPv6 prefix-length
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-l4-port any
Specify source Layer4 port as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-l4-port [1-65535]
[0xWXYZ]
[1-65535]
Specify source Layer4 port
[0xWXYZ]
Specify source Layer4 mask
28
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-mac any
Specify source MAC as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Specify source MAC
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
Specify source MAC mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
tos [any | 0xWX]
[any | 0xWX]
Specify IPv4 TOS and IPv6 traffic class
or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
vid [any | 1-4094]
[any | 1-4094]
Specify 802.1q VLAN ID or “ANY”
No command
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no action
Undo action command
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no action-port
Undo action port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-ipv4
Undo destination-ipv4 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-ipv6
Undo destination-ipv6 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-l4-port
Undo destination-l4-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-mac
Undo destination-mac specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no ingress-port
Undo ingress-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no ethertype
Undo ethertype specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no protocol
Undo protocol specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no rate-limit
Undo rate-limit specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-ipv4
Undo source-ipv4 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-ipv6
Undo source-ipv6 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-l4-port
Undo source-l4-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-mac
Undo source-mac specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no tos
Undo TOS specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no vid
Undo vid specification
Show command
Description
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
show
Display ACL rule configuration
29
2.6.5 Channel-group Command
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Specify a name for this link
aggregation group.
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group trunking [group_name]
[port_list]
[group_name]
Use “interface” command to
configure a group of ports’ link
aggregation link membership.
Assign the selected ports to the
specified link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-ip
Load-balancing depending on
destination IP address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-ip
Load-balancing depending on
source IP address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-L4-port
Load-balancing depending on
destination L4 port.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-L4-port
Load-balancing depending on
source L4 port.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-mac
Load-balancing depending on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-mac
Load-balancing depending on
source MAC address.
No command
Switch(config)# no channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Delete a link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group trunking
[port_list]
Remove the selected ports from
a link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule destination-ip
Disable load-balancing based on
destination IP address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule source-ip
Disable load-balancing based on
source IP address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule destination-L4-port
Disable load-balancing based on
destination L4 port.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule source-L4-port
Disable load-balancing based on
source L4 port.
Switch(config)# no channel-group type
destination-mac
Disable load-balancing based on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group type
source-mac
Disable load-balancing based on
destination MAC address.
1. Configure a static link aggregation group (LAG).
30
Show command
Switch(config)# show channel-group
trunking
Show or verify link aggregation
settings.
Switch(config)# show channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Show or verify a specific link
aggregation group’s settings
including aggregated port
numbers and load-balancing
status.
Channel-group command example
Switch(config)# channel-group trunking corenetwork
Create a link aggregation group
called “corenetwork”.
Switch(config)# channel-group type destination-mac
Load-balancing depending on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# channel-group type source-mac
Load-balancing depending on
source MAC address.
Channel-group & Interface
command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp
Enable LACP on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp key [0-255]
[0-255]
Specify a key to the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp role [active]
[active]
Specify the selected interfaces to
active LACP role.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp
Disable LACP on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp key
Reset the key value of the selected
interfaces to the factory default.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp role
Reset the LACP type of the selected
interfaces to the factory default
(passive mode).
Show command
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp
Show or verify each interface’s LACP
settings including current mode, key
value and LACP type.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
LACP settings.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp status
Show or verify each interface’s current
LACP status.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp status [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
current LACP status.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp statistics
Show or verify each interface’s current
LACP traffic statistics.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp statistics [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
current LACP statistics.
2. Use “Interface” command to configure link aggregation groups dynamically (LACP).

31
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp statistics clear
Clear all LACP statistics.
Channel-group & interface command example
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Enter port 1 to port 3’s interface mode.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# channel-group lacp
Enable LACP on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# channel-group lacp key 10
Set a key value “10” to the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# channel-group lacp role
active
Set the selected interfaces to active
LACP type.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# dot1x
Enable dot1x function. When
enabled, the Managed Switch acts
as a proxy between the 802.1Xenabled client and the
authentication server. In other
words, the Managed Switch
requests identifying information from
the client, verifies that information
with the authentication server, and
relays the response to the client.
Switch(config)# dot1x reauthperiod [0-3600]
[0-3600]
Specify a period of authentication
time that a client authenticates with
the authentication server. The
allowable value is between 0 and
3600 seconds.
Switch(config)# dot1x
reauthentication
Enable re-authentication function.
Switch(config)# dot1x secret
[shared_secret]
[shared_secret]
Specify a shared secret of up to 30
characters. This is the identification
word or number assigned to each
RADIUS authentication server with
which the client shares a secret.
Switch(config)# dot1x server
[A.B.C.D | A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify the RADIUS Authentication
server IP/IPv6 address.
Switch(config)# dot1x timeout [1255]
[1-255]
Specify the time value in seconds.
The Managed Switch will wait for a
period of time for the response from
the authentication server to an
authentication request before it
times out. The allowable value is
between 1 and 255 seconds.
2.6.6 Dot1x Command

32
No command
Switch(config)# no dot1x
Disable IEEE 802.1x function.
Switch(config)# no dot1x reauthperiod
Reset the re-authentication period
value back to the default setting (60
seconds).
Switch(config)# no dot1x
reauthentication
Disable re-authentication function.
Switch(config)# no dot1x secret
Remove the original shared secret.
Switch(config)# no dot1x server
Remove the specified server IP
address.
Switch(config)# no dot1x timeout
Reset the timeout value back to the
default setting (10 seconds).
Show command
Switch(config)# show dot1x
Show or verify 802.1x settings.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
interface
Show or verify each interface’s
802.1x settings including port status
and authentication status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected
interfaces’ 802.1x settings including
port status and authentication status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
statistics
Show or verify 802.1x statistics.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
statistics [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected
interfaces’ statistics.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
status
Show or verify 802.1x status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
status [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected
interfaces’ 802.1x status.
Dot1x command example
Switch(config)# dot1x
Enable IEEE 802.1x function.
Switch(config)# dot1x reauth-period 3600
Set the reauthentication period to
3600 seconds.
Switch(config)# dot1x reauthentication
Enable re-authentication function.
Switch(config)# dot1x secret agagabcxyz
Set the shared secret to
“agagabcxyz”
Switch(config)# dot1x server 192.168.1.10
Set the 802.1x server IP address to
192.168.1.10.
Switch(config)# dot1x timeout 120
Set the timeout value to 120
seconds.

33
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ IEEE 802.1x settings.
Dot1x & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
dot1x port-control [auto |
unauthorized]
Specify the selected ports to “auto” or
“unauthorized”.
“auto”: This requires 802.1X-aware
clients to be authorized by the
authentication server. Accesses from
clients that are not dot1x aware will be
denied.
“unauthorized”: This forces the
Managed Switch to deny access to all
clients, neither 802.1X-aware nor
802.1X-unaware.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
dot1x reauthenticate
Re-authenticate the selected
interfaces.
No command
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
dot1x port-control
Reset the selected interfaces’ 802.1x
state to the factory default (authorized
state).
“authorized”: This forces the
Managed Switch to grant access to all
clients, both 802.1X-aware and
802.1x-unaware. No authentication
exchange is required. By default, all
ports are set to “authorized”.
Show command
Switch(config)# show dot1x
Show or verify 802.1x settings.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
interface
Show or verify each interface’s 802.1x
settings including port status and
authentication status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
802.1x settings including port status
and authentication status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
statistics
Show or verify 802.1x statistics.
Switch(config)# show dot1x
statistics [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
statistics.
Switch(config)# show dot1x status
Show or verify 802.1x status.
Switch(config)# show dot1x status
[port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
802.1x status.

34
Dot1x & interface command example
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-1-3)# dot1x port-control auto
Set the selected ports to “auto” state.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# dot1x reauthenticate
Re-authenticate the selected
interfaces immediately.
IP command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ip
address [A.B.C.D]
[255.X.X.X] [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the desired IP address for your Managed
Switch.
[255.X.X.X]
Enter subnet mask of your IP address.
[A.B.C.D]
Enter the default gateway address.
Switch(config)# ip
address dhcp
Enable DHCP mode.
No command
Switch(config)#no ip address
Remove the Managed Switch’s IP address.
Switch(config)# no ip address dhcp
Disable DHCP mode.
Show command
Switch(config)#show ip address
Show the current IP configurations or verify the
configured IP settings.
IP command example
Switch(config)# ip address
192.168.1.198 255.255.255.0
192.168.1.254
Set up the Managed Switch’s IP to
192.168.1.198, subnet mask to 255.255.255.0,
and default gateway to 192.168.1.254.
Switch(config)# ip address dhcp
Get an IP address automatically.
IP DHCP Snooping Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping
Enable DHCP snooping function.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server [port_list]
[port_list]
Configure DHCP server ports.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server-ip
Globally enable DHCP server trust IP.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server-ip [1-4]
[1-4]
Enable DHCP server trust IP address (1 to
4).
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server-ip [1-4] ipaddress [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[1-4]
Enable DHCP server trust IP address (1 to
4).
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify DHCP server trust IP address.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping initiated [0-9999]
[0-9999]
Specify the time value (0~9999 Seconds)
that packets might be received.
2.6.7 IP Command
1. Set up an IP address of the Managed Switch or configure the Managed Switch to get an
IP address automatically from DHCP server.
2. Enable DHCP relay function.

35
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping leased [180-259200]
[180-259200]
Specify packets’ expired time (180~259200
Seconds).
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping option
Enable DHCP Option 82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping remote
Enable DHCP Option 82 Remote ID
suboption
Switch(config)# ip dhcp
snooping remote id [id_name]
[id_name]
You can configure the remote ID to be a
string of up to 63 chaaracters. The default
remote ID is the switch MAC address.
No command
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping
Disable DHCP Snooping function.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server
Remove DHCP server ports.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping dhcp-server-ip
Reset the DHCP server trust IP to the
default setting.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping initiated
Reset the initiated value back to the default
setting.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping leased
Reset the leased value back to the default
setting.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping option
Disable DHCP Option 82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping remote
Disable DHCP Option 82 Remote ID
suboption
Switch(config)# no ip dhcp
snooping remote id
Clear Remote ID description.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ip address
Show the current IP configurations or verify
the configured IP settings.
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp
snooping
Show each interface’s DHCP Snooping
settings.
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp
snooping interface
Show each port’s DHCP Snooping Option
82 and trust port settings.
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp
snooping interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the specified ports’ DHCP Snooping
Option 82 and trust port settings.
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp
snooping status
Show DHCP Snooping status.
IP DHCP Snooping example
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping
Enable DHCP snooping function.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping dhcp-server
[port_list]
Configure DHCP server ports.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping initiated 10
Specify the time value that packets might
be received to 10 seconds.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping leased 240
Specify packets’ expired time to 240
seconds.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping option
Enable DHCP Option 82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping remote id 123
The remote ID is configured “123”
DHCP & Interface Command
Parameter
Description
3. Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ DHCP Snooping settings.

36
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port numbers
separated by commas or a range of ports
with a hyphen. For example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping circuit
Enable DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
suboption.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping circuit id
[id_name]
[id_name]
Specify the VLAN and port identifier using
a VLAN ID in the range of 1 to 4094.
Besides, you can configure the circuit ID to
be a string of up to 63 characters. The
default circuit ID is the port identifier, the
format of which is vlan-mod-port.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping option
Enable the selected interfaces’ DHCP
Option 82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping trust
Configure the selected interfaces to DHCP
Option 82 trust ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping server-trust
Configure the selected interfaces to DHCP
server trust ports.
No command
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port numbers
separated by commas or a range of ports
with a hyphen. For example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping option
Set the selected interfaces to non-DHCP
Option 82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping trust
Set the selected interfaces’ to non-DHCP
Option 82 trust ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping server-trust
Set the selected interfaces’ to non-DHCP
server trust ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping circuit
Disable DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
suboption.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping circuit id
Clear DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
description.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp snooping
Show each port’s DHCP Snooping Option
82 and trust port settings.
Switch(config)# show ip dhcp snooping
interface [port_list]
Show the specified ports’ DHCP Snooping
trust port settings.
DHCP & Interface Example
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Enter several discontinuous port numbers
separated by commas or a range of ports
with a hyphen. For example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip dhcp snooping
option
Set the selected interfaces to DHCP Option
82 Relay Agent.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip dhcp snooping trust
Set the selected interfaces to DHCP Option
82 trust ports.
4. Enable or disable IGMP/MLD snooping globally.
IGMP, Internet Group Management Protocol, is a communication protocol used to manage the
membership of Internet Protocol multicast groups. IGMP is used by IP hosts and adjacent
multicast routers to establish multicast group memberships. It can be used for online streaming
video and gaming, and allows more efficient use of resources when supporting these uses.

37
IGMP Snooping is the process of listening to IGMP traffic. IGMP snooping, as implied by the name,
Command / Example
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping
Enable IGMPv1,v2/MLDv1 Snooping
function.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping flooding
Set forwarding mode for unregistered (notjoined) IP multicast traffic. The traffic will
flood when enabled. However, the traffic
will forward to router-ports only when
disabled.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping immediate-leave
Enable immediate leave function.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping max-response-time [1255] (1/10secs)
[1-255]
(1/10secs)
This determines the maximum amount of
time allowed before sending an IGMP
response report. (Default value 100, One
Unit=0.1 second)
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping mcast-router [port_list]
[port_list]
Specify multicast router ports.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping query-interval [1-6000]
secs
[1-6000]
Specify Query time interval. This is used to
set the time interval between transmitting
IGMP/MLD queries.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping version-3
Enable IGMPv3/MLDv2 Snooping function.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping vlan [1-4094]
[1-4094]
Specify a VLAN ID. This enables
IGMP/MLD Snooping on a specified VLAN.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
snooping vlan [1-4094] query
[1-4094]
Enable a querier on the specified VLAN.
No command
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping
Disable IGMP/MLD Snooping function.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping flooding
Disable flooding function. Traffic will
forward to router-ports only when disabled.
is a feature that allows the switch to "listen in" on the IGMP conversation between hosts and
routers by processing the layer 3 packets IGMP packets sent in a multicast network.
When IGMP snooping is enabled in a switch it analyses all the IGMP packets between hosts
connected to the switch and multicast routers in the network. When a switch hears an IGMP report
from a host for a given multicast group, the switch adds the host's port number to the multicast list
for that group. And, when the switch hears an IGMP Leave, it removes the host's port from the
table entry.
IGMP snooping can very effectively reduce multicast traffic from streaming and other bandwidth
intensive IP applications. A switch using IGMP snooping will only forward multicast traffic to the
hosts interested in that traffic. This reduction of multicast traffic reduces the packet processing at
the switch (at the cost of needing additional memory to handle the multicast tables) and also
reduces the workload at the end hosts since their network cards (or operating system) will not
have to receive and filter all the multicast traffic generated in the network.
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is a component of the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) suite.
MLD is used by IPv6 routers for discovering multicast listeners on a directly attached link, much
like IGMP is used in IPv4.

38
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping immediate-leave
Disable immediate leave function.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping max-response-time
Reset maximum response time back to the
factory default.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping mcast-router [port_list]
[port_list]
Remove the selected ports from the router
port list.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping query-interval
Reset Query interval value back to the
factory default.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping vlan [1-4094]
[1-4094]
Disable IGMP/MLD Snooping on the
specified VLAN.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping vlan [1-4094] query
[1-4094]
Disable a querier on the specified VLAN.
Show command
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
snooping
Show current IGMP/MLD snooping status
including immediate leave function.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
snooping groups
Show IGMP/MLD group table.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
snooping status
Show IGMP/MLD Snooping status.
IGMP Filtering command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ip igmp filter
Enable IGMP Filtering function.
Switch(config)# ip igmp profile
[profile_name]
[profile_name]
Specify a name for this profile.
Switch(config-profile-ID)#
segment [1-400]
[1-400]
Specify an existing segment ID.
Switch(config)# ip igmp
segment [1-400]
[1-400]
Specify a segment ID.
Switch(config-segment-ID)#
name [segment_name]
[segment_name]
Specify a name for this segment.
Switch(config-segment-ID)#
range [E.F.G.H] [E.F.G.H]
[E.F.G.H]
[E.F.G.H]
Specify a multicast IP range.
No command
Switch(config)# no ip igmp filter
Disable IGMP Filtering function.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
segment [1-400]
[1-400]
Delete the specified segment. Only
the segment that does not belong to
any profiles can be deleted.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp
profile [profile_name]
[profile_name]
Delete the specified profile.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
filter
Show IGMP Filtering setting.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
filter interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the specified ports’ IGMP
Filtering status.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
profile
Show IP multicast profile information.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
profile [profile_name]
[profile_name]
Show the specified profile’s setting.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
segment
Show IP multicast segment
information.
Switch(config)#show ip igmp
[1-400]
Show the specified segment’s setting.
Configure IGMP Filtering policies.

39
segment [1-400]
Switch(config-segment-ID)#
show
Show the selected segment’s setting.
Switch(config-profile-ID)# show
Show the selected profile’s setting.
IGMP Filtering command example
Switch(config)# ip igmp filter
Enable IGMP Filtering function.
Switch(config)# ip igmp segment 50
Create a segment “50”.
Switch(config-segment-50)# name Silver
Specify a name “Silver” for this
segment 50.
Switch(config-segment-50)# range 224.10.0.2
229.10.0.1
Specify a multicast IP range
224.10.0.2 to 229.10.0.1.
Switch(config)# ip igmp profile Silverprofile
Specify a name “Silverprofile” for this
profile.
Switch(config-profile-Silverprofile)# segment 50
Silverprofile includes segment 50.
IGMP & Interface Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
igmp filter
Enable IGMP Filter on the selected
ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
igmp filter profile [profile_name]…
[profile_name]
…
Assign the selected ports to a profile.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
igmp max-groups [1-512]
[1-512]
Specify the maximum number of
multicast streams.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
igmp static-multicast-ip [E.F.G.H |
E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L] vlan [1-4094]
[E.F.G.H |
E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L
]
Create a static multicast IP to VLAN
entry.
Specify static multicast IP address.
[1-4094]
Specify a VLAN ID
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
sourceguard [dhcp | fixed-ip]
[dhcp | fixed-ip]
Specify authorized access
information for the selected ports.
dhcp: DHCP server assigns IP
address.
fixed IP: Only Static IP (Create
Static IP table first).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# ip
sourceguard static-ip [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] vlan [1-4094]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:
H]
Add a static IP address to static IP
address table.
Specify an IP address.
[1-4094]
Specify a VLAN ID.
No command
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ IGMP Filtering function.

40
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp filter
Disable IGMP Filter on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp filter profile
[profile_name]
[profile_name]
Remove the selected ports from the
specified profile.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp max-groups
Set the maximum number of
multicast streams back to the factory
default (512 channels).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp static-multicast-ip
[E.F.G.H | E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L] vlan [14094]
[E.F.G.H |
E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L
]
Remove this static multicast IP to
VLAN entry.
Specify static multicast IP address.
[1-4094]
Specify a VLAN ID.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip sourceguard
Set the accepted IP source to the
factory default (unlimited).
unlimited: Non-Limited (Allows both
static IP and DHCP-assigned IP).
This is the default setting.
Switch(config-if- PORT-PORT)#
no ip sourceguard static-ip
[A.B.C.D | A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] vlan
[1-4094]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:
H]
Specify an IP address that you want
to remove from IP source binding
table.
[1-4094]
Specify a VLAN ID.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
filter
Show IGMP Filtering setting.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
filter interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the specified ports’ IGMP
Filtering status.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
profile
Show IP multicast profile information.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
profile [profile_name]
[profile_name]
Show the specified profile’s setting.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
segment
Show IP multicast segment
information.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
segment [1-400]
[1-400]
Show the specified segment’s
setting.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp
static-multicast-ip
Show static multicast IP table.
Switch(config-segment-ID)# show
Show the selected segment’s setting.
Switch(config-profile-ID)# show
Show the selected profile’s setting.
Switch(config)# show ip
sourceguard interface
Show each interface’s IP
sourceguard type.
Switch(config)# show ip
sourceguard static-ip
Show the IP source binding table for
sourceguard function.
IGMP & Interface example
Switch(config)# interface1-3
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip igmp filter
Enable IGMP Filter on port 1 to port
3.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip igmp filter profile
Silverprofile
Assign the selected ports to the
specified profile “Silverprofile”.

41
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip igmp max-groups 400
Set the maximum number of
multicast streams to 400.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# ip igmp static-multicast-ip
vlan 50
Create a static multicast IP to VLAN
entry.
2.6.8 IPv6 Command
Brief Introduction to IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long and number about 3.4×1038. IPv6 addresses are written in eight
groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons, such as
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
IPv6 unicast addresses other than those that start with binary 000 are logically divided into two
parts: a 64-bit network prefix and a 64-bit interface identifier.
Stateless Autoconfiguration
IPv6 lets any host generate its own IP address and check if it's unique in the scope where it will be
used. IPv6 addresses consist of two parts. The leftmost 64 bits are the subnet prefix to which the
host is connected, and the rightmost 64 bits are the identifier of the host's interface on the subnet.
This means that the identifier need only be unique on the subnet to which the host is connected,
which makes it much easier for the host to check for uniqueness on its own.
Link local address
The first step a host takes on startup or initialization is to form a link-local address from its MAC
address and the link-local prefix FE80::/10. This is done by putting the prefix into the leftmost bits
and the MAC address (in EUI-64 format) into the rightmost bits, and if there are any bits left in
between, those are set to zero.
Global address
This is done in the same fashion as the link-local address, but instead of the link-local prefix FE80::
it will use the prefix supplied by the router and put it together with its identifier (which by default is
the MAC address in EUI-64 format).
Some IPv6 addresses are reserved for special purposes, such as loopback, 6to4 tunneling, and
Teredo tunneling, as outlined in RFC 5156. Also, some address ranges are considered special,
such as link-local addresses for use on the local link only, Unique Local addresses (ULA), as
described in RFC 4193, and solicited-node multicast addresses used in the Neighbor Discovery
Protocol.
DHCPv6
IPv6 hosts may automatically generate IP addresses internally using stateless address
autoconfiguration, or they may be assigned configuration data with DHCPv6.
Set up the IPv6 address of the Managed Switch or configure the Managed Switch to get an

42
IP address automatically from DHCPv6 server.
IPv6 command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ipv6
address autoconfig
Configuration of IPv6 addresses using
stateless autoconfiguration.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address dhcp auto
Configure DHCPv6 function in auto
mode.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address dhcp force
Configure DHCPv6 function in force
mode.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address dhcp rapidcommit
Allows the two-way message exchange
instead of 4-way for address
assignment.
“ipv6 address dhcp” commands are functional only when autoconfiguration is enabled.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address global
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H/10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H/10~128]
Specify switch IPv6 global address and
prefix-length.
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify switch IPv6 default gateway.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address link-local
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H/10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H/10~128]
Specify switch IPv6 link-local address
and prefix-length.
Switch(config)# ipv6
enable
Enable IPv6 processing.
No command
Switch(config)# no ipv6
address autoconfig
Disable IPv6 stateless autoconfig.
Switch(config)# no ipv6
address dhcp
Disable DHCPv6 function.
Switch(config)# no ipv6
address dhcp rapidcommit
Disable rapid-commit feature.
Switch(config)# ipv6
address global
Clear IPv6 global address entry
Switch(config)# ipv6
address link-local
Clear IPv6 link-local address entry
Switch(config)# no ipv6
enable
Disable IPv6 processing.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ipv6 address
Display IPv6 information of the
Managed Switch.
IPv6 command example
Switch(config)# ipv6 address autoconfig
Enable Ipv6 autoconfiguration.
Switch(config)# ipv6 address dhcp auto
Enable DHCPv6 auto mode.
2.6.9 LLDP Command
LLDP stands for Link Layer Discovery Protocol and runs over data link layer. It is used for network
devices to send information about themselves to other directly connected devices on the network.
By using LLDP, two devices running different network layer protocols can learn information about
each other. A set of attributes are used to discover neighbor devices. These attributes contains
type, length, and value descriptions and are referred to TLVs. Details such as port description,
system name, system description, system capabilities, and management address can be sent and
received on this Managed Switch. Use Spacebar to select “ON” if you want to receive and send
the TLV.

43
LLDP command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# lldp
hold-time [1-3600]
[1-3600]
Specify the amount of time in seconds. A receiving
device will keep the information sent by your
device for a period of time you specify here before
discarding it. The allowable hold-time value is
between 1 and 3600 seconds.
Switch(config)# lldp
initiated-delay [0-300]
[0-300]
Specify a period of time the Managed Switch will
wait before the initial LLDP packet is sent. The
allowable initiated-delay value is between 0 and
300 seconds.

44
Switch(config)# lldp
interval [1-180]
[1-180]
Specify the time interval for updated LLDP packets
to be sent. The allowable interval value is between
1 and 180 seconds.
Switch(config)# lldp
packets [1-16]
[1-16]
Specify the amount of packets that are sent in
each discovery. The allowable packet value is
between 1 and 16 seconds.
Switch(config)# lldp tlvselect capability
Enable Capability attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlvselect managementaddress
Enable Management Address attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-
select port-description
Enable Port Description attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlvselect systemdescription
Enable System Description attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-
select system-name
Enable System Name attribute to be sent.
No command
Switch(config)# no lldp hold-time
Reset the hold-time value back to the default
setting.
Switch(config)# no lldp initiated-delay
Reset the initiated-delay value back to the default
setting.
Switch(config)# no lldp interval
Reset the interval value back to the default setting.
Switch(config)# no lldp packets
Reset the packets-to-be-sent value back to the
default setting.
Switch(config)# no lldp tlv-select
capability
Disable Capability attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# no lldp tlv-select
management-address
Disable Management Address attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# no lldp tlv-select portdescription
Disable Port Description attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# no lldp tlv-select
system-description
Disable System Description attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# no lldp tlv-select
system-name
Disable System Name attribute to be sent.
Show command
Switch(config)# show lldp
Show or verify LLDP settings.
Switch(config)# show lldp interface
Show or verify each interface’s LLDP port state.
Switch(config)# show lldp interface
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’ LLDP port
state.
Switch(config)# show lldp status
Show current LLDP status.
LLDP command example
Description
Switch(config)# lldp hold-time 60
Set the hold-time value to 60 seconds.
Switch(config)# lldp initiated-delay 60
Set the initiated-delay value to 60 seconds
Switch(config)# lldp interval 10
Set the updated LLDP packets to be sent in very
10 seconds.
Switch(config)# lldp packets 2
Set the number of packets to be sent in each
discovery to 2.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-select
capability
Enable Capability attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-select
management-address
Enable Management Address attribute to be sent.

45
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-select portdescription
Enable Port Description attribute to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-select systemdescription
Enable System Description to be sent.
Switch(config)# lldp tlv-select systemname
Enable System Name to be sent.
LLDP & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# lldp
Enable LLDP on the selected
interfaces.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no lldp
Disable LLDP on the selected
interfaces.
Show command
Switch(config)# show lldp
Show or verify LLDP configurations.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# loop-detection
Enable Loop Detection function.
Switch(config)# loop-detection allvlan
Check All VLAN box to enable loop
detection on all trunk-VLAN-vid
configured in VLAN Command
(Section 2.6.23)
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ LLDP settings.
2.6.10 Loop Detection Command
In a real network, it is possible the people misconnect the network cable to incur loop condition. In
a worst case, the network is out of service thereafter. This section gives a guide to configure the
Loop Detection function of the system to prevent the system from loop.
After a proper setting of Loop Detection function, the system detects loop condition by periodically
sending loop detection packet. Once the system receives the loop detection packet from itself, it is
claimed that it detects loop condition. Then, the system takes the following 3 actions
1. It blocks the relevant port to prevent broadcast storms. In other words, the system stops
forwarding all the traffic via the looped port. However, the system will process the loop
detection packet received on the looped port.
2. It slowly blinks the LED of looped port in orange.
3. It periodically sends loop detection packet to detect the existence of loop condition.
When the system does not receives any loop detection packet from itself for a period of configured
Looped port unlock-interval. The system claims the loop condition disappears. Then, the system
takes the following 3 actions
1. It un-blocks the relevant port. In other words, the system normally forwards all the traffic via the
relevant port.
2. It stops slowly blinking the LED of looped port in orange.
3. It periodically sends loop detection packet to detect the existence of loop condition.
Note: Under loop condition, the LED of looped port continues to slowly blink orange even the
connected network cable is unplugged out of looped port.

46
NOTE: When All VLAN check-box is
checked, it invalidates the configured
“Specific VLAN”.
Switch(config)# loop-detection
interval [1-180]
[0-180]
This is the time interval (in seconds)
that the device will periodically send
loop detection packets to detect the
presence of looped network. The
valid range is from 1 to 180 seconds.
The default setting is 1 seconds.
Switch(config)# loop-detection
unlock-interval [1-1440]
[1-1440]
This is the time interval for the
system to detect the existence of
loop condition. System un-blocks the
looped port if it does not receive any
loop-detection packet during the
configured unlock-interval. The
unlock-interval can be set from 1 to
1440 minutes. The default setting is
1440 minutes.
Note:
1. Be aware that Looped port unlockinterval converted into seconds
should be greater than or equal to
Detection Interval seconds multiplied
by 10. The ‘10’ is a magic number
which is for the system to claims the
loop detection disappears when the
system does not receive the loopdetection packet from itself at least
10 times. In general, it can be
summarized by a formula below:
60* “Looped port unlock-interval”
≧
10* “Detection Interval“
2. When a port is detected as a
looped port, the system keeps the
looped port in blocking status until
loop situation is gone. In other words,
the system stops forwarding all the
traffic via the looped port. However,
the system will process the loopdetection packet received on the
looped port.
Switch(config)# loop-detection
vlan-id [1-4094]
[1-4094]
Set up loop detection on specified
VLAN. The maximum number of
VLAN ID is up to 4 sets.
NOTE: The configured “Specific
VLAN” takes effect when All VLAN
check-box is unchecked.
No command
Switch(config)# no loop-detection
Disable Loop Detection function.
Switch(config)# no loop-detection
all-vlan
Disable loop detection on all trunkVLAN-vid.

47
Switch(config)# no loop-detection
interval
Reset Loop Detection time interval to
default setting.
Switch(config)# no loop-detection
unlock-interval
Reset Loop Detection unlock time
interval to default setting.
Switch(config)# no loop-detection
vlan-id
Disable loop detection on a specified
VLAN.
Show command
Switch(config)# show loopdetection
Show Loop Detection settings.
Switch(config)# show loopdetection status
Show Loop Detection status of all
ports.
Switch(config)# show loopdetection status [port_list]
[port_list]
Show Loop Detection status of the
ports.
Loop Detection command example
Switch(config)# loop-detection interval 60
Set the Loop Detection time interval
to 60 seconds.
Switch(config)# loop-detection unlock-interval 120
Set the Loop Detection unlock time
interval to 120 minutes.
Switch(config)# loop-detection vlan-id 100
Set the Loop Detection VLAN ID to
100.
Dot1x & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
loop-detection
Enable Loop Detection function on the
specific ports.
No command
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
loop-detection
Disable Loop Detection function on
the specific ports.
MAC Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# mac addresstable aging-time [0-172800s]
[0172800s]
Enter the aging time for MAC addresses in
seconds. 0= never aging out.
No command
Switch(config)# no mac
address-table aging-time
Set MAC address table aging time to the
default value (300 seconds).
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ Loop Detection settings.
2.6.11 MAC Command
Set up MAC address table aging time. Entries in the MAC address table containing source MAC
addresses and their associated ports will be deleted if they are not accessed within aging time.

48
Show command
Switch(config)# show mac
address-table
Show MAC addresses learned by the
Managed Switch
Switch(config)# show mac
address-table clear
Clear MAC address table.
Switch(config)# show mac
address-table interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Show MAC addresses learned by the
specified interfaces.
Switch(config)# show mac
learning
Show MAC learning setting of each
interface.
Switch(config)# show mac
static-mac
Show static MAC address table.
Switch(config)#show mac
aging-time
Show current MAC address table aging
time or verify configured aging time.
MAC command example
Switch(config)#mac address-table aging-time
200
Set MAC address aging time to 200
seconds.
MAC & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# mac address-table
static-mac [xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
vlan [1-4094]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Create a MAC address to VLAN entry.
Specify a MAC address.
[1-4094]
Specify the VLAN where the packets
with the Destination MAC address can
be forwarded.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# mac learning
Enable MAC learning function.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no mac addresstable static-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx] vlan [14094]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Remove the specified MAC address
from the address table.
[1-4094]
Specify the VLAN to which the
specified MAC belongs.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no mac learning
Disable MAC learning function.
Show command
Switch(config)# show mac address-table
Show MAC addresses learned by the
Managed Switch
Switch(config)# show mac address-table clear
Clear MAC address table.
Switch(config)# show mac address-table interface
[port_list]
Show MAC addresses learned by the
specified interfaces.
Switch(config)# show mac address-table mac
[mac-addr]
Show the specific MAC address
information.
Switch(config)# show mac learning
Show MAC learning setting of each
interface.
Switch(config)# show mac static-mac
Show static MAC address table.
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ MAC Table settings.

49
Switch(config)#show mac aging-time
Show current MAC address table
aging time or verify currently
configured aging time.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# management
console timeout [5-300]
[5-300]
To disconnect the Managed Switch when
console management is inactive for a
certain period of time.
The allowable value is from 5 to 300
seconds.
Switch(config)# management
ssh
To management the Managed Switch via
SSH.
Switch(config)# management
telnet
To management the Managed Switch via
Telnet.
Switch(config)# management
telnet port [1-65535]
[1-65535]
When telnet is enabled, you can set up the
port number that allows telnet access.
The default port number is set to 23.
However, you can also identify a port
number between 1 and 65535.
Switch(config)# management
web
To manage the Managed Switch via Web
management.
No command
Switch(config)# no management console
timeout
Reset console timeout to default (300
seconds).
Switch(config)# no management ssh
Disable SSH management.
Switch(config)# no management telnet
Disable Telnet management.
Switch(config)# no management telnet port
Set Telnet port back to the default setting.
The default port number is 23.
Switch(config)# no management web
Disable Web management.
Show command
Switch(config)# show management
Show or verify current management
settings including management platform
that can be used and Telnet port number.
Management command example
Switch(config)# management console timeout
300
The console management will timeout
(logout automatically) when it is inactive
for 300 seconds.
Switch(config)# management telnet
Enable Telnet management.
Switch(config)# management telnet port 23
Set Telnet port to port 23.
Switch(config)# management web
Enable Web management.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# mirror
destination [port]
[port]
Specify the preferred destination port
(1~26) for mirroring.
Switch(config)# mirror source
[port_list]
[port_list]
Specify a source port number or several
source port numbers for port mirroring.
2.6.12 Management Command
2.6.13 Mirror Command

50
No command
Switch(config)# no mirror destination
Disable port mirroring function or remove
mirroring destination port.
Switch(config)# no mirror source
Remove mirroring source ports.
Show command
Switch(config)# show mirror
Show or verify current port mirroring
destination and source ports.
Mirror command example
Switch(config)# mirror destination 26
The selected source ports’ data will mirror
to port 26.
Switch(config)# mirror source 1-10
Port 1 to 10’s data will mirror to the
destination (target) port.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# ntp
Enable the Managed Switch to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Switch(config)# ntp
daylight-saving
Enable the daylight saving function.
Switch(config)# ntp
daylight-saving recurring
Enable daylight saving with recurring
mode.
Switch(config)# ntp
daylight-saving date
Enable daylight saving with date mode.
Switch(config)# ntp offset
[Mm,w,d,hh:mmMm,w,d,hh:mm]
[Mm,w,d,hh:mmMm,w,d,hh:mm]
Offset setting for daylight saving function
of recurring mode.
Mm=1-12, w=1-5, d=0-6(0=Sun, 6=Sat)
Hh=0-23, mm=0-59, Days=1-365
Switch(config)# ntp offset
[Days,hh:mm-Days,hh:mm]
[Days,hh:mmDays,hh:mm]
Offset setting for daylight saving function
of date mode.
Mm=1-12, w=1-5, d=0-6(0=Sun, 6=Sat)
Hh=0-23, mm=0-59, Days=1-365
Switch(config)# ntp server1
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify the primary time server IP/IPv6
address.
Switch(config)# ntp server2
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify the secondary time server IP/IPv6
address.
Switch(config)# ntp syninterval [1-8]
[1-8]
Specify the interval time to synchronize
from NTP time server.
1=1hour, 2=2hours, 3=3hours,
4=4hours
5=ghours, 6=8hours, 7=12hours,
8=24hours
Switch(config)# ntp timezone [0-135]
[0-135]
Specify the time zone to which the
Managed Switch belongs.
Use space and a question mark to view
the complete code list of 147 time zones.
For example, “Switch(config)# ntp time-
2.6.14 NTP Command

51
zone ?”
No command
Switch(config)# no ntp
Disable the Managed Switch to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Switch(config)# no ntp daylight-saving
Disable the daylight saving function.
Switch(config)# no ntp offset
Set the offset value back to the default
setting.
Switch(config)# no ntp server1
Delete the primary time server IP address.
Switch(config)# no ntp server2
Delete the primary time server IP address.
Switch(config)# no ntp syn-interval
Set the synchronization interval back to
the default setting.
Switch(config)# no ntp time-zone
Set the time-zone setting back to the
default.
Show command
Switch(config)# show ntp
Show or verify current time server
settings.
NTP command example
Switch(config)# ntp
Enable the Managed Switch to
synchronize the clock with a time server.
Switch(config)# ntp daylight-saving date
Enable the daylight saving function at
ddate mode
Switch(config)# ntp offset [100,12:00101,12:00]
Daylight saving time date start from the
100th day of the year to the 101th day of
the year.
Switch(config)# ntp server1 192.180.0.12
Set the primary time server IP address to
192.180.0.12.
Switch(config)# ntp server2 192.180.0.13
Set the secondary time server IP address
to 192.180.0.13.
Switch(config)# ntp syn-interval 4
Set the synchronization interval to 4 hours.
Switch(config)# ntp time-zone 3
Set the time zone to GMT-8:00 Vancouver.
QoS command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# qos [802.1p | dscp]
[802.1p | dscp]
Specify QoS mode
Switch(config)# qos dscp-map [063] [0-7]
[0-63]
Specify a DSCP value.
[0-7]
Specify a queue value.
Switch(config)# qos managementpriority [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify management default
802.1p bit
Switch(config)# qos queuing-mode
[weight]
[weight]
Specify QoS queuing mode as
weight mode
Switch(config)# qos queueweighted
Specify the queue weighted
Switch(config)# qos remarking dscp
Globally enable DSCP bit
remarking
Switch(config)# qos remarking dscp
[by-dscp]
[by-dscp]
Specify DSCP bit remarking
mode
Switch(config)# qos remarking
dscp-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Specify DSCP and priority
mapping ID
2.6.15 QoS Command
1. Set up Qos

52
Switch(config)# qos remarking
802.1p
Globally enable 802.1p bit
remarking
Switch(config)# qos remarking
802.1p-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Specify 802.1p and priority
mapping ID
Switch(config)# qos 802.1p-map [07] [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify a 802.1p value.
[0-7]
Specify a queue value.
No command
Switch(config)# no qos dscp-map
[0-63]
[0-63]
Undo specify a DSCP value
Switch(config)# no qos
management-priority
Undo specify management
default 802.1p bit
Switch(config)# no queuing-mode
Specify QoS queuing mode as
strict mode
Switch(config)# no qos queueweighted
Undo specify the queue
weighted
Switch(config)# no qos remarking
dscp
Undo specify DSCP bit
remarking mode
Switch(config)# no qos remarking
dscp-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Undo specify DSCP and priority
mapping ID
Switch(config)# no qos remarking
802.1p
Disable 802.1p bit remarking
Switch(config)# no qos remarking
802.1p-map [1-8]
[1-8]
Undo specify a 802.1p value
Switch(config)# no qos 802.1p-map
Undo 802.1p mapping
Show command
Switch(config)# show qos
Show QoS configuration
Switch(config)# show qos interface
Show QoS interface overall
information
Switch(config)# show qos interface
[port-list]
[port-list]
Show QoS interface per port(s)
Switch(config)# show qos remarking
Show QoS remarking
information
QoS & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
qos rate-limit ingress [0,50010000000] kbps
[0,50010000000]
kbps
Specify ingress rate limit value. “0”
represents disable.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
qos rate-limit egress [0,5001000000] kbps
[0,5001000000]
kbps
Specify egress rate limit value. “0”
represents disable.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
qos user-priority [0-7]
[0-7]
Specify the default priority bit to the
selected interfaces.
2. Use “interface” command to configure a group of ports’ QoS settings.

53
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no qos rate-limit
ingress
Delete QoS ingress rate limit
setting.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no qos rate-limit
egress
Delete QoS egress rate limit setting.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no qos userpriority
Set the user priority value setting
back to the factory default.
Security command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# security portisolation
Enable port isolation function. If port
isolation is set to enable, the ports can‟t
communicate to each other.
Switch(config)# security portisolation up-link-port
[port_list]
[port_list]
Specify the ports as uplinks that are
allowed to communicate with.
Switch(config)# security
storm-protection broadcast
[1-1024k]
[1-1024k]
Specify the maximum broadcast packets
per second (pps). Any broadcast packets
exceeding the specified threshold will then
be dropped.
The packet rates that can be specified are
listed below:
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1k, 2k,
4k, 8k, 16k, 32k, 64k, 128k, 256k, 512k,
1024k
NOTE: To view a list of allowable values
that can be specified you can press
“spacebar” and then followed by “?”. For
example, “Switch(config)# security stormprotection broadcast ?”
Switch(config)# security
storm-protection multicast [11024k]
[1-1024k]
Specify the maximum unknown multicast
packets per second (pps). Any unknown
multicast packets exceeding the specified
threshold will then be dropped.
The packet rates that can be specified are
listed below:
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1k, 2k,
4k, 8k, 16k, 32k, 64k, 128k, 256k, 512k,
1024k
NOTE: To view a list of allowable values
2.6.16 Security Command
When a device on the network is malfunctioning or application programs are not well designed or
properly configured, broadcast storms may occur, network performance may be degraded or, in
the worst situation, a complete halt may happen. The Managed Switch allows users to set a
threshold rate for broadcast traffic on a per switch basis so as to protect network from
broadcast/unknown multicast/ unknown unicast storms. Any broadcast/unknown
multicast/unknown unicast packets exceeding the specified value will then be dropped.
Enable or disable broadcast/unknown multicast/unknown unicast storm control.

54
that can be specified you can press
“spacebar” and then followed by “?”. For
example, “Switch(config)# security stormprotection multicast ?”
Switch(config)# security
storm-protection unicast [11024k]
[1-1024k]
Specify the maximum unkown unicast
packets per second (pps). Any unkown
unicast packets exceeding the specified
threshold will then be dropped.
The packet rates that can be specified are
listed below:
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1k, 2k,
4k, 8k, 16k, 32k, 64k, 128k, 256k, 512k,
1024k
NOTE: To view a list of allowable values
that can be specified you can press
“spacebar” and then followed by “?”. For
example, “Switch(config)# security stormprotection unicast ?”
No command
Switch(config)# no portisolation
Disable port isolation function.
Switch(config)# no portisolation up-link-port
[port_list]
[port_list]
Reset the ports as downlinks.
Switch(config)# no security
storm-protection broadcast
Disable broadcast storm control.
Switch(config)# no security
storm-protection multicast
Disable unkown multicast storm control.
Switch(config)# no security
storm-protection unicast
Disable unkown unicast storm control.
Show command
Switch(config)# show
security storm-protection
Show current storm control settings.
Security command example
Switch(config)# security storm-protection
broadcast 1024k
Set the maximum broadcast packets per
second (pps) to 1024k. Any broadcast
packets exceeding this specified threshold
will then be dropped.
Switch(config)# security storm-protection
multicast 1024k
Set the maximum unknown multicast
packets per second (pps) to 1024k. Any
unknown multicast packets exceeding this
specified threshold will then be dropped.
Switch(config)# security storm-protection
unicast 1024k
Set the maximum unkown unicast packets
per second (pps) to 1024k. Any unknown
unicast packets exceeding the specified
threshold will then be dropped.
2.6.17 SNMP-Server Command
1. Create a SNMP community and set up detailed configurations for this community.

55
Snmp-server command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# snmpserver
Enable SNMP server function globally.
Switch(config)# snmpserver community
[community]
[community]
Specify a SNMP community name of up to
20 alphanumeric characters.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# active
Enable this SNMP community account.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# description
[Description]
[Description]
Enter the description for this SNMP
community of up to 35 alphanumerical
characters.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# level [admin | rw |
ro]
[admin | rw |
ro]
Specify the access privilege for this SNMP
account.
admin: Full access right, including
maintaining user account, system
information, loading factory settings, etc..
rw: Read & Write access privilege. Partial
access right, unable to modify user
account, system information and load
factory settings.
ro: Read Only access privilege.
No command
Switch(config)# no snmpserver
Disable SNMP function.
Switch(config)# no snmpserver community
[community]
[community]
Delete the specified community.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# no active
Disable this SNMP community account. In
this example “mycomm” community is
disabled.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# no description
Remove the SNMP community
descriptions for “mycomm”.
Switch(config-communityNAME)# no level
Remove the configured access privilege.
This will set this community’s level to
“access denied”.
Show command
Switch(config)# show snmp-server
Show or verify whether SNMP is enabled
or disabled.
Switch(config)# show snmp-server
community
Show or verify each SNMP server
account’s information.
Switch(config)# show snmp-server
community [community]
Show the specified SNMP server account’s
settings.
Switch(config-community-NAME)# show
Show the selected community’s settings.
Exit command
Switch(config-community-NAME)# exit
Return to Global Configuration mode.
Snmp-server example
Switch(config)# snmp-server community
mycomm
Create a new community “mycomm” and
edit the details of this community account.

56
Switch(config-community-mycomm)# active
Activate the SNMP community “mycomm”.
Switch(config-community-mycomm)#
description rddeptcomm
Add a description for “mycomm”
community.
Switch(config-community-mycomm)# level
admin
Set “mycomm” community level to admin
(full access privilege).
Trap-destination command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# snmp-server
trap-destination [1-10]
[1-10]
Create a trap destination account.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# active
Enable this SNMP trap destination
account.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# community
[community]
[community]
Enter the community name of network
management system.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# destination
[A.B.C.D | A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Enter the trap destination IP/IPv6 address
for this trap destination account.
No command
Switch(config)# no snmpserver trap-dest [1-10]
[1-10]
Delete the specified trap destination
account.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# no active
Disable this SNMP trap destination
account.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# no community
Delete the configured community name.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# no description
Delete the configured trap destination
description.
Show command
Switch(config)# show snmpserver trap-destination
Show SNMP trap destination account
information.
Switch(config)# show snmpserver trap-destination [1-10]
[1-10]
Show the specified SNMP trap destination
account information.
Switch(config-trapACCOUNT)# show
Show and verify the selected trap
destination account’s information.
Exit command
Switch(config-trap-ACCOUNT)# exit
Return to Global Configuration mode.
Trap-destination example
Switch(config)# snmp-server trapdestination 1
Create a trap destination account.
Switch(config-trap-1)# active
Activate this trap destination account.
Switch(config-trap-1)# community mycomm
Refer this trap destination account to the
community “mycomm”.
Switch(config-trap-1)# description
redepttrapdest
Add a description for this trap destination
account.
Switch(config-trap-1)# destination
192.168.1.254
Set trap destination IP address to
192.168.1.254.
2. Set up a SNMP trap destination.

57
Trap-type command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# snmpserver trap-type [all | authfail | battery-mode | casefan | cold-start | port-link |
power-down | warm-start]
[all | auth-fail
| batterymode | casefan | coldstart | portlink | powerdown | warmstart]
Specify a trap type that will be sent when a
certain situation occurs.
all: A trap will be sent when authentication
fails, broadcast packets exceed the
threshold value, the device cold /warm
starts, port link is up or down and power is
down.
auth-fail: A trap will be sent when any
unauthorized user attempts to login.
battery-mode: A trap will be sent when the
battery mode is changed.
case-fan: A trap will be sent when the fan is
not working or fails.
cold-start: A trap will be sent when the
device boots up.
port-link: A trap will be sent when the link
is up or down.
power-down: A trap will be sent when the
device’s power is down.
warm-start: A trap will be sent when the
device restarts.
No command
Switch(config)# no snmpserver trap-type [all | authfail | battery-mode | casefan | cold-start | port-link |
power-down | warm-start]
[all | auth-fail
| batterymode | casefan | coldstart | portlink | powerdown | warmstart]
Specify a trap type that will not be sent
when a certain situation occurs.
Show command
Switch(config)# show snmp-server
community
Show community configuration.
Switch(config)# show snmp-server trapdestination
Show trap destination configuration.
Switch(config)# show snmp-server traptype
Show the current enable/disable status of
each type of trap.
Trap-type example
Switch(config)# snmp-server trap-type all
All types of SNMP traps will be sent.
3. Set up SNMP trap types that will be sent.

58
Spanning-tree command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# spanningtree aggregated-port
Enable Spanning Tree Protocl function
on aggregated ports.
Switch(config)# spanningtree aggregated-port cost [0200000000]
[0-200000000]
Specify aggregated ports’ path cost.
Switch(config)# spanningtree aggregated-port priority
[0-15]
[0-15]
Specify aggregated ports’ priority.
0=0, 1=16, 2=32, 3=48, 4=64, 5=80
6=96, 7=112, 8=128, 9=144, 10=160
11=176, 12=192, 13=208, 14=224,
15=240
Switch(config)# spanningtree aggregated-port edge
Enable aggregated ports to shift to
forwarding state when the link is up.
If you know a port is directly connected
to an end device (that doesn't support
RSTP) then set it as an edge port to
ensure maximum performance. This will
tell the switch to immediately start
forwarding traffic on the port and not
bother trying to establish a RSTP
connection. Otherwise, turn it off.
Switch(config)# spanningtree aggregated-port p2p
[forced_true | forced_false |
auto]
[forced_true |
forced_false |
auto]
Set the aggregated ports to non-point to
point ports (forced_false) or allow the
Managed Switch to detect point to point
status automatically (auto). By default,
aggregated ports are set to point to point
ports (forced_true).
Switch(config)# spanning-
[4-30]
Specify the Forward Delay value in
2.6.18 Spanning-tree Command
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), defined in the IEEE Standard 802.1D, creates a spanning tree
within a mesh network of connected layer-2 bridges (typically Ethernet switches) and disables the
links which are not part of that tree, leaving a single active path between any two network nodes.
Multiple active paths between network nodes cause a bridge loop. Bridge loops create several
problems. First, the MAC address table used by the switch or bridge can fail, since the same MAC
addresses (and hence the same network hosts) are seen on multiple ports. Second, a broadcast
storm occurs. This is caused by broadcast packets being forwarded in an endless loop between
switches. A broadcast storm can consume all available CPU resources and bandwidth.
Spanning tree allows a network design to include spare (redundant) links to provide automatic
backup paths if an active link fails, without the danger of bridge loops, or the need for manually
enabling/disabling these backup links.
To provide faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change, an evolution of the
Spanning Tree Protocol: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), introduced by IEEE with
document 802.1w. RSTP is a refinement of STP; therefore, it shares most of its basic operation
characteristics. This essentially creates a cascading effect away from the root bridge where each
designated bridge proposes to its neighbors to determine if it can make a rapid transition. This is
one of the major elements which allow RSTP to achieve faster convergence times than STP.

59
tree delay-time [4-30]
seconds. The allowable value is between
4 and 30 seconds.
Switch(config)# spanningtree hello-time [1-10]
[1-10]
Specify the Hello Time value in seconds.
The allowable value is between 4 and 30
seconds.
Switch(config)# spanningtree max-age [6-200]
[6-200]
Specify the Maximum Age value in
seconds. The allowable value is between
6 and 200.
Switch(config)# spanningtree priority [0-15]
[0-15]
Specify a priority value on a per switch
basis. The allowable value is between 0
and 15.
0=0, 1=4096, 2=8192, 3=12288,
4=16384
5=20480, 6=24576, 7=28672, 8=32768
9=36864, 10=40960,
11=45056,12=49152
13=53248, 14=57344, 15=61440
Switch(config)# spanningtree version [compatible |
normal]
[compatible |
normal]
Set up RSTP version.
“compatible” means that the Managed
Switch is compatible with STP.
“normal” means that the Managed
Switch uses RSTP.
No command
Switch(config)# no spanningtree aggregated-port
Disable STP on aggregated ports.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree aggregated-port cost
Reset aggregated ports’ cost to the
factory default.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree aggregated-port priority
Reset aggregated ports’ priority to the
factory default.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree aggregated-port edge
Disable aggregated ports’ edge ports
status.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree aggregated-port p2p
Reset aggregated ports to point to point
ports (forced_true).
Switch(config)# no spanningtree delay-time
Reset the Forward Delay time back to
the factory default.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree hello-time
Reset the Hello Time back to the factory
default.
Switch(config)# no spanningtree max-age
Reset the Maximum Age back to the
factory default.
Show command
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree
Show or verify STP settings on the per
switch basis.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree aggregatedport
Show or verify STP settings on
aggregated ports.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree interface
Show each interface’s STP information
including port state, path cost, priority,
edge port state, and p2p port state.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Show the selected interfaces’ STP
information including port state, path
cost, priority, edge port state, and p2p

60
port state.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree statistics
Show each interface and each link
aggregation group’s statistics information
including the total RSTP packets
received, RSTP packets transmitted,
STP packets received, STP packets
transmitted, TCN (Topology Change
Notification) packets received, TCN
packets transmited, illegal packets
received, and unknown packets
received.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree statistics
[port_list | llag]
[port_list | llag]
Show the selected interfaces or link
aggregation groups’ statistics information
including the total RSTP packets
received, RSTP packets transmitted,
STP packets received, STP packets
transmitted, TCN (Topology Change
Notification) packets received, TCN
packets transmited, illegal packets
received, and unknown packets
received.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree status
Show current RSTP port status.
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree status [port_list
| llag]
[port_list | llag]
Show the selected interfaces or link
aggregation groups’ statistics information
Switch(config)# show
spanning-tree overview
Show the current STP state.
Spanning-tree command example
Description
Switch(config)# spanning-tree aggregatedport
Enable Spanning Tree on aggregated
ports.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree aggregatedport cost 100
Set the aggregated ports’ cost to 100.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree aggregatedport priority 0
Set the aggregated ports’ priority to 0
Switch(config)# spanning-tree aggregatedport edge
Set the aggregated ports to edge ports.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree aggregatedport p2p forced_true
Set the aggregated ports to P2P ports.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree delay-time 20
Set the Forward Delay time value to 10
seconds.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree hello-time 2
Set the Hello Time value to 2 seconds.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree max-age 15
Set the Maximum Age value to 15
seconds.
Spanning tree & Interface
command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ Spanning Tree settings.

61
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
spanning-tree
Enable spanning-tree protocol on
the selected interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
spanning-tree cost [1-200000000]
[1200000000]
Specify cost value on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
spanning-tree priority [0-15]
[0-15]
Specify priority value on the
selected interfaces.
0=0, 1=4096, 2=8192, 3=12288,
4=16384
5=20480, 6=24576, 7=28672,
8=32768
9=36864, 10=40960,
11=45056,12=49152
13=53248, 14=57344, 15=61440
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
spanning-tree edge
Set the selected interfaces to edge
ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
spanning-tree p2p [forced_fasle |
auto]
[forced_fasle
| auto]
Set the aggregated ports to nonpoint to point ports (forced_false) or
allow the Managed Switch to detect
point to point status automatically
(auto). By default, aggregated ports
are set to point to point ports
(forced_true).
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
spanning-tree
Disable spanning-tree protocol on
the selected interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
spanning-tree cost
Set the cost value back to the
factory default.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
spanning-tree priority
Set the priority value back to the
factory default.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
spanning-tree edge
Set the selected interfaces to nonedge ports.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
spanning-tree p2p
Set the selected interface to point to
point ports.
Show command
Switch(config)# show spanningtree
Show or verify STP settings on the
per switch basis.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree aggregated-port
Show or verify STP settings on
aggregated ports.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree interface
Show each interface’s STP
information including port state, path
cost, priority, edge port state, and
p2p port state.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the selected interfaces’ STP
information including port state, path
cost, priority, edge port state, and
p2p port state.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree statistics
Show each interface and each link
aggregation group’s statistics
information including the total RSTP
packets received, RSTP packets
transmitted, STP packets received,
STP packets transmitted, TCN

62
(Topology Change Notification)
packets received, TCN packets
transmited, illegal packets received,
and unknown packets received.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree statistics [port_list | llag]
[port_list |
llag]
Show the selected interfaces or link
aggregation groups’ statistics
information including the total RSTP
packets received, RSTP packets
transmitted, STP packets received,
STP packets transmitted, TCN
(Topology Change Notification)
packets received, TCN packets
transmited, illegal packets received,
and unknown packets received.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree status
Show current RSTP port status.
Switch(config)# show spanningtree status [port_list | llag]
[port_list |
llag]
Show the selected interfaces or link
aggregation groups’ statistics
information
Switch(config)# show spanningtree overview
Show the current STP state.
Spanning-tree & interface command example
Description
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-1-3)# spanning-tree cost 100
Set the selected interfaces’ cost to
100.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# spanning-tree priority 0
Set the selected interfaces’ priority
to 0
Switch(config-if-1-3)# spanning-tree edge
Set the selected ports to edge ports.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# spanning-tree p2p
forced_false
Set the selected ports to non-P2P
ports.
Switch command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 000F [permit]
[permit]
Permit packets from the address
ranging from 0180C2000000 to
0180C200000F.
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 202F [permit]
[permit]
Permit packets from the address
ranging from 0180C2000020 to
0180C200002F.
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 10
[permit]
[permit]
Permit packets from the address
0180C2000010.
Switch(config)# switch mtu [15189600]
[1518-9600] bytes
Specify the maximum
transmission unit in bytes. The
allowable MTU value is between
1518 and 9600 bytes.
Switch(config)# switch statistics
polling port [1-26]
Specify the number of ports for
data acquisition at a time.
2.6.19 Switch Command

63
Switch(config)# switch statistics
polling interval
Specify the time interval in 1/10
seconds for data acquisition.
No command
Switch(config)# no switch bpdu 00-0F
Undo permit packets from the
address ranging from
0180C2000000 to
0180C200000F.
Switch(config)# no switch bpdu 20-2F
Undo permit packets from the
address ranging from
0180C2000020 to
0180C200002F.
Switch(config)# no switch bpdu 10
Undo permit packets from the
address 0180C2000010.
Switch(config)# no switch mtu
Reset MTU size to default 1518
bytes.
Show command
Switch(config)# show switch bpdu
Show current BPDU information.
Switch(config)# show switch mtu
Show current maximum
transmission unit setting.
Switch command example
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 00-0F permit
Permit packets from the address
ranging from 0180C2000000 to
0180C200000F.
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 20-2F permit
Permit packets from the address
ranging from 0180C2000020 to
0180C200002F.
Switch(config)# switch bpdu 10 permit
Permit packets from the address
0180C2000010.
Switch(config)# switch mtu 9600
Set the maximum transmission
unit to 9600 bytes.
Switch-info Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# switch-info
company-name
[company_name]
[company_name]
Enter a company name, up to 55
alphanumeric characters, for this Managed
Switch.
Switch(config)# switch-info
dhcp-vendor-id
[dhcp_vendor_id]
[dhcp_vendor_id]
Enter a DHCP vendor ID, up to 55
alphanumeric characters, for this Managed
Switch.
Switch(config)# switch-info
host-name [host_name]
[host_name]
Enter a new hostname, up to 30
alphanumeric characters, for this Managed
Switch. By default, the hostname prompt
shows the model name of this Managed
Switch. You can change the factoryassigned hostname prompt to the one that
2.6.20 Switch-info Command
1. Set up the Managed Switch’s basic information, including company name, hostname,
system name, etc..

64
is easy for you to identify during network
configuration and maintenance.
Switch(config)# switch-info
system-contact
[sys_contact]
[sys_contact]
Enter contact information for this Managed
switch, up to 55 alphanumeric characters.
Switch(config)# switch-info
system-location
[sys_location]
[sys_location]
Enter a brief description, up to 55
alphanumeric characters, of the Managed
Switch location. Like the name, the
location is for reference only, for example,
“13th Floor”.
Switch(config)# switch-info
system-name [sys_name]
[sys_name]
Enter a unique name, up to 55
alphanumeric characters, for this Managed
Switch. Use a descriptive name to identify
the Managed Switch in relation to your
network, for example, “Backbone 1”. This
name is mainly used for reference only.
No command
Switch(config)# no switch-info company-name
Delete the entered company name
information.
Switch(config)# no switch-info dhcp-vendor-id
Delete the entered DHCP vendor ID
information.
Switch(config)# no switch-info system-contact
Delete the entered system contact
information.
Switch(config)# no switch-info system-location
Delete the entered system location
information.
Switch(config)# no switch-info system-name
Delete the entered system name
information.
Switch(config)# no switch-info host-name
Set the hostname to the factory default.
Show command
Switch(config)# show switch-info
Show or verify switch information including
company name, system contact, system
location, system name, model name,
firmware version and fiber type.
Switch-info example
Switch(config)# switch-info company-name
telecomxyz
Set the company name to “telecomxyz”.
Switch(config)# switch-info system-contact
info@company.com
Set the system contact field to
“info@compnay.com”.
Switch(config)# switch-info system-location
13thfloor
Set the system location field to “13thfloor”.
Switch(config)# switch-info system-name
backbone1
Set the system name field to “backbone1”.
Switch(config)# switch-info host-name
edgeswitch10
Change the Managed Switch’s hostname
to “edgeswitch10”.
Syslog command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# syslog
Enable system log function.
Switch(config)# syslog
server1 [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Specify the primary system log server
IP/IPv6address.
2.6.21 Syslog Command

65
Switch(config)# syslog
server2 [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Specify the secondary system log server
IP/IPv6 address.
Switch(config)# syslog
server3 [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Specify the third system log server IP/IPv6
address.
No command
Switch(config)# no syslog
Disable System log function.
Switch(config)# no syslog server1
Delete the primary system log server IP
address.
Switch(config)# no syslog server2
Delete the secondary system log server IP
address.
Switch(config)# no syslog server3
Delete the third system log server IP
address.
Show command
Switch(config)# show syslog
Show current system log settings.
Switch(config)# show log
Show event logs currently stored in the
Managed Switch. These event logs will be
saved to the system log server that you
specify.
Syslog command example
Switch(config)# syslog
Enable System log function.
Switch(config)# syslog server1
192.180.2.1
Set the primary system log server IP address
to 192.168.2.1.
Switch(config)# syslog server2
192.168.2.2
Set the secondary system log server IP
address to 192.168.2.2.
Switch(config)# syslog server3
192.168.2.3
Set the third system log server IP address to
192.168.2.3.
User command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# user name
[user_name]
[user_name]
Enter the new account’s username. The
authorized user login name is up to 20
alphanumeric characters. Only 3 login
accounts can be registered in this device.
Switch(config-userNAME)# active
Activate this user account.
Switch(config-userNAME)# description
[description]
[description]
Enter the brief description for this user
account.
Switch(config-userNAME)# level [admin | rw |
ro]
[admin | rw |
ro]
Specify this user’s access level.
admin (administrator): Full access right,
including maintaining user account & system
2.6.22 User Command
1. Create a new login account.

66
information, loading factory settings, etc..
rw (read & write): Partial access right,
unable to modify user account & system
information and load factory settings.
ro (read only): Read-Only access privilege
Switch(config-userNAME)# password
[password]
[password]
Enter the password, up to 20 alphanumeric
characters, for this user account.
No command
Switch(config)#no user
name [username]
[username]
Delete the specified account.
Switch(config-userNAME)# no active
Deactivate the selected user account.
Switch(config-userNAME)# no description
Remove the configured description.
Switch(config-userNAME)# no password
Remove the configured password value.
Switch(config-userNAME)# no level
Reset access level privilege back to the
factory default (access denied).
Show command
Switch(config)# show user
name
List all user accounts.
Switch(config)# show user
name [user_name]
[user_name]
Show the specific account’s information.
Switch(config-userNAME)# show
Show or verify the newly-created user
account’s information.
User command example
Switch(config)#user name miseric
Create a new login account “miseric”.
Switch(config-user-miseric)# description
misengineer
Add a description to this new account
“miseric”.
Switch(config-user-miseric)# password
mis2256i
Set up a password for this new account
“miseric”
Switch(config-user-miseric)# level rw
Set this user account’s privilege level to
“read and write”.
User command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# user radius
Enable RADIUS authentication.
Switch(config)# user radius
radius-port [1025-65535]
[102565535]
Specify RADIUS server port number.
Switch(config)# user radius
retry-time [0-2]
[0-2]
Specify the retry value. This is the number of
times that the Managed Switch will try to
reconnect if the RADIUS server is not
reachable.
Switch(config)# user radius
secret [secret]
[secret]
Specify a secret up to 31 alphanumeric
characters for RADIUS server. This secret
key is used to validate communications
between RADIUS servers.
2. Configure RADIUS server settings.

67
Switch(config)# user radius
server1 [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Specify the primary RADIUS server IP/IPv6
address.
Switch(config)# user radius
server2 [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F
:G:H]
Specify the secondary RADIUS server
IP/IPv6 address.
No command
Switch(config)# no user radius
Disable RADIUS authentication.
Switch(config)# no user radius radius-port
Set the radius port setting back to the factory
default.
Switch(config)# no user radius retry-time
Set the retry time setting back to the factory
default.
Switch(config)# no user radius secret
Remove the configured secret value.
Switch(config)# no user radius server1
Delete the specified IP address.
Switch(config)# no user radius server2
Delete the specified IP address.
Show command
Switch(config)#show user radius
Show current RADIUS settings.
User command example
Switch(config)# user radius
Enable RADIUS authentication.
Switch(config)# user radius radius-port
1812
Set RADIUS server port number to 1812.
Switch(config)# user radius retry-time 2
Set the retry value to 2. The Managed Switch
will try to reconnect twice if the RADIUS
server is not reachable.
Switch(config)# user radius secret
abcxyzabc
Set up a secret for validating
communications between RADIUS clients.
Switch(config)# user radius server1
192.180.3.1
Set the primary RADIUS server address to
192.180.3.1.
Switch(config)# user radius server2
192.180.3.2
Set the secondary RADIUS server address
to 192.180.3.2.
2.6.23 VLAN Command
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical
scheme rather than the physical layout. VLAN can be used to combine any collections of LAN
segments into a group that appears as a single LAN. VLAN also logically segments the network
into different broadcast domains. All broadcast, multicast, and unknown packets entering the
Switch on a particular VLAN will only be forwarded to the stations or ports that are members of
that VLAN.
VLAN can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth and improve security by limiting traffic
to specific domains. A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logics instead of physical
locations. End nodes that frequently communicate with each other are assigned to the same VLAN,
no matter where they are physically located on the network. Another benefit of VLAN is that you
can change the network topology without physically moving stations or changing cable
connections. Stations can be ‘moved’ to another VLAN and thus communicate with its members
and share its resources, simply by changing the port VLAN settings from one VLAN to another.

68
This allows VLAN to accommodate network moves, changes and additions with the greatest
Preamble
SFD
DA
SA
Type/LEN
PAYLOAD
FCS
Original frame
Preamble
SFD
DA
SA
TAG
TCI/P/C/VID
Type/LEN
PAYLOAD
FCS
802.1q
frame
PRE Preamble
62 bits
Used to synchronize traffic
SFD Start Frame Delimiter
2 bits
Marks the beginning of the header
DA Destination Address
6 bytes
The MAC address of the destination
SA Source Address
6 bytes
The MAC address of the source
TCI Tag Control Info
2 bytes set to 8100 for 802.1p and Q tags
P Priority
3 bits
Indicates 802.1p priority level 0-7
C Canonical Indicator
1 bit
Indicates if the MAC addresses are in
Canonical format - Ethernet set to "0"
VID VLAN Identifier
12 bits
Indicates the VLAN (0-4095)
T/L Type/Length Field
2 bytes
Ethernet II "type" or 802.3 "length"
Payload < or = 1500 bytes User data
FCS Frame Check Sequence
4 bytes
Cyclical Redundancy Check
flexibility.
802.1Q VLAN Concept
Port-Based VLAN is simple to implement and use, but it cannot be deployed cross switches VLAN.
The 802.1Q protocol was developed in order to provide the solution to this problem. By tagging
VLAN membership information to Ethernet frames, the IEEE 802.1Q can help network
administrators break large switched networks into smaller segments so that broadcast and
multicast traffic will not occupy too much available bandwidth as well as provide a higher level
security between segments of internal networks.
Introduction to 802.1Q frame format:
Important VLAN Concepts for 802.1Q VLAN Configuration:
There are two key concepts to understand.
- Access-VLAN specifies the VLAN ID to the switch port that will assign the VLAN ID to
untagged traffic from that port. A port can only be assigned to one Access-VLAN at a time.
When the port is configured as Access Mode, the port is called an Access Port, the link
to/from this port is called an Access Link. The VLAN ID assigned is called PVID.
- Trunk-VLAN specifies the set of VLAN IDs that a given port is allowed to receive and send
tagged packets. A port can be assigned to multiple Trunk-VLANs at a time. When the port is
configured as Trunk Mode, the port is called a Trunk Port, the link to/from this port is called a
Trunk Link. The VLAN ID assigned is called VID.
A port can be configured as below 802.1q VLAN modes :

69
- Access Mode :
Configuration
Result
Trunk-VLAN = 10, 11, 12
Access-VLAN = 20
Mode = Access
PortX is an Access Port
PortX’s VID is ignored
PortX’s PVID is 20
PortX sends Untagged packets (PortX takes away VLAN tag if the
PVID is 20)
PortX receives Untagged packets only
Trunk-VLAN = 10,11,12
Access-VLAN = 20
Mode = Trunk
PortX is a Trunk Port
PortX’s VID is 10,11 and 12
PortX’s PVID is ignored
PortX sends and receives Tagged packets VID 10,11 and 12
Trunk-VLAN = 10,11,12
Access-VLAN = 20
Mode = Trunk-native
PortX is a Trunk-native Port
PortX’s VID is 10,11 and 12
PortX’s PVID is 20
PortX sends and receives Tagged packets VID 10,11 and 12
PortX receives Untagged packets and add PVID 20
VLAN & Interface command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan access-vlan [14094]
[1-4094]
Specify the selected ports’ Access-
VLAN ID (PVID).
Access Links (the link to/from access ports) are the most common type of links on any VLAN
switch. All network hosts (such as PCs) connect to the switch's Access Links in order to
gain access to the local network. We configure only one Access-VLAN per port, that is, the
VLAN ID the network hosts will be allowed to access.
It is important to note at this point that any network host connected to an Access Port is
totally unaware of the VLAN assigned to the port. The network host simply assumes it is part
of a single broadcast domain, just as it happens with any normal switch. During data transfers,
any VLAN information or data from other VLANs is removed so the recipient has no
information about them.
- Trunk Mode :
Trunk Links (the link to/from trunk ports) is configured to carry packets for multiple VLANs.
These types of ports are usually found in connections between switches. These links require
the ability to carry packets from multiple VLANs because VLANs span over multiple switches.
- Trunk Native Mode :
A Trunk-native port can carry untagged packets simultaneously with the 802.1Q tagged
packets. When you assign a default Access-VLAN to the trunk-native port, all untagged traffic
travels on the default Access-VLAN for the trunk-native port, and all untagged traffic is
assumed to belong to this Access-VLAN. This Access-VLAN is referred to as the native VLAN
ID for a Trunk-native Port. The native VLAN ID is the VLAN ID that carries untagged traffic on
trunk-native ports.
Example : PortX configuration
1. Use “Interface” command to configure a group of ports’ 802.1q VLAN settings.

70
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan trunk-vlan [14094]
[1-4094]
Specify the selected ports’ Trunk-
VLAN ID (VID).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode access
Set the selected ports to access mode
(untagged).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk
Set the selected ports to trunk mode
(tagged).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk native
Set the selected ports to trunk-native
mode. (Tagged and untagged)
Note : When you assign a default
Access-VLAN to the trunk-native
port, all untagged traffic travels on
the default Access-VLAN for the
trunk-native port, and all untagged
traffic is assumed to belong to this
Access-VLAN.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan port-based [name]
[name]
Set the selected ports to a specified
port-based VLAN.
Note :
Need to create a port-based VLAN
group under VLAN global
configuration mode before joining
it.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan dot1q-vlan access-vlan
Set the selected ports’ PVID to the
default setting.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan dot1q-vlan mode
Remove VLAN dot1q mode.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk
native
Disable native VLAN for untagged
traffic.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan dot1q-vlan trunk-vlan [14094]
[1-4094]
Remove the selected ports’ from the
specified trunk VLAN.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan port-based [name]
[name]
Delete the selected ports from the
specified port-based VLAN.
VLAN & interface command example
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Enter port 1 to port 3’s interface mode.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# vlan dot1q-vlan accessvlan 10
Set port 1 to port 3’s Access-VLAN ID
(PVID) to 10.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
access
Set the selected ports to access mode
(untagged).
Switch(config-if-1-3)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
trunk native
Enable native VLAN for untagged
traffic.
Switch(config-if-1-3)# vlan port-based
mktpbvlan
Set the selected ports to the specified
port-based VLAN “mktpbvlan”.
2. Modify a 802.1q VLAN and a management VLAN rule or create a port-based VLAN group.
Port-based VLAN can effectively segment one network into several broadcast domains.
Broadcast, multicast and unknown packets will be limited to within the VLAN. Port-Based VLAN is

71
uncomplicated and fairly rigid in implementation and is useful for network administrators who wish
VLAN dot1q command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q-vlan
[1-4094]
[1-4094]
Enter a VID number to modify an
existing 802.1q VLAN.
Note :
802.1q VLAN ID need to be
created under interface global
command. In here you can only
modify it instead of creating a
new VLAN ID.
Switch(config-vlan-ID)# name
[vlan_name]
[vlan_name]
Specify a descriptive name for this
VLAN ID, max 15 characters.
Switch(config)# vlan isolation
Enable port isolation function. If
port isolation is set to enable, the
ports can‟t communicate to each
other.
Switch(config)# vlan isolation uplink-port [port_list]
[port_list]
Specify the ports as uplinks that
are allowed to communicate with.
Switch(config)# vlan
management-vlan [1-4094]
management-port [port_list] mode
[trunk | access]
[1-4094]
Enter the management VLAN ID.
[port_list]
Specify the management port
number.
[trunk |
access]
Specify whether the management
port is in trunk or access mode.
“trunk” mode: Set the selected
ports to tagged.
“access” mode: Set the selected
ports to untagged.
Switch(config)# vlan port-based
[name]
[name]
Specify a name for this port-based
VLAN.
No command
Switch(config-vlan-ID)# no name
Remove the descriptive name for
the specified VLAN ID.
Switch(config)# no vlan isolation
Disable port isolation function.
Switch(config)# no vlan isolation
up-link-port [port_list]
[port_list]
Reset the ports as downlinks.
Switch(config)# no vlan portbased [name]
[name]
Delete the specified port-based
VLAN.
Show command
Switch(config)# show vlan dot1qvlan tag-vlan
Show IEEE 802.1q tag VLAN table
Switch(config)# show vlan dot1qvlan trunk-vlan
Show configure trunk VLAN table
Switch(config-vlan-ID)# show
Show the membership status of
this VLAN ID
Switch(config)# show vlan
Show all ports’ VLAN assignment
to quickly and easily set up VLAN so as to isolate the effect of broadcast packets on their network.

72
interface
and VLAN mode.
Switch(config)# show vlan
interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Show the selected ports’ VLAN
assignment and VLAN mode.
Switch(config)# show vlan portbased
Show port-based VLAN table.
Exit command
Switch(config-vlan-ID)# exit
Return to Global configuration
mode.
Port-based VLAN example
Switch(config)# vlan port-based MKT_Office
Create a port-based VLAN
“MKT_Office”.
Switch(config)# vlan management-vlan 1
management-port 1-3 mode access
Set VLAN 1 to management VLAN
(untagged) and port 1~3 to
management ports.
Switch(config)# interface 1-22
Enter port 1 to port 22’s interface
mode.
Switch(config-if-1-22)# vlan dot1q-vlan trunkvlan 10, 20
Set port 1 to port 22’s Trunk-VLAN ID
(VID) to 10 and 20.
Switch(config-if-1-22)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
trunk
Set the selected ports to Trunk Mode
(tagged).
Switch(config-if-1-22)#exit
Exit current ports interface mode
Switch(config)# interface 23-44
Enter port 23 to port 44’s interface
mode.
Switch(config-if-23-44)# vlan dot1q-vlan
access-vlan 50
Set port 23 to port 44’s Access-VLAN
ID (PVID) to 50.
Switch(config-if-23-44)# vlan dot1q-vlan trunkvlan 30,40
Set port 23 to port 44’s Trunk-VLAN
ID (VID) to 30 and 40.
Switch(config-if-23-44)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
trunk native
Set the selected ports to Trunk-native
Mode (tagged and untagged).
Switch(config-if-1-4)#exit
Exit current ports interface mode
Switch(config)# interface 45-46
Enter port 45 to port 46’s interface
mode.
Switch(config-if-45-46)# vlan dot1q-vlan
access-vlan 60
Set port 45 to port 46’s Access-VLAN
ID (PVID) to 60.
802.1q VLAN Configuration Example
1. Create 802.1q VLAN IDs

73
Switch(config-if-45-46)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
access
Set the selected ports to Access Mode
(untagged).
Switch(config-if-45-46)#exit
Exit current ports interface mode
Switch(config)# interface 47-48
Enter port 47 to port 48’s interface
mode.
Switch(config-if-47-48)# vlan dot1q-vlan
access-vlan 70
Set port 47 to port 48’s Access-VLAN
ID (PVID) to 70.
Switch(config-if-47-48)# vlan dot1q-vlan mode
access
Set the selected ports to Access Mode
(untagged).
Switch(config-if-47-48)#exit
Exit current ports interface mode
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q-vlan 10, 20
Enter VLAN 10,20
Switch(config-vlan-10,20)# name Sales
Enater name for VLAN 10 and 20
Switch(config-vlan-10,20)# exit
Exit VLAN 10 and 20
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q-vlan 30,40,50
Enter VLAN 30,40 and 50
Switch(config-vlan-30,40,50)# name RD
Enater name for VLAN 30,40 and 50
Switch(config-vlan-30,40,50)# exit
Exit VLAN 30,40 and 50
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q-vlan 60
Enter VLAN 60
Switch(config-vlan-60)# name SQA
Enater name for VLAN 60
Switch(config-vlan-60)# exit
Exit VLAN 60
Switch(config)# vlan dot1q-vlan 70
Enter VLAN 70
Switch(config-vlan-70)# name PME
Enater name for VLAN 70
Switch(config-vlan-70)# exit
Exit VLAN 70
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several port numbers separated by
commas or a range of port numbers.
For example: 1,3 or 2-4
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
auto-negotiation
Set the selected interfaces’ to autonegotiation. When auto-negotiation is
enabled, speed configuration will be
ignored.
No command
2. Modify 802.1q VLAN IDs’ names.
2.6.24 Interface Command
Use “interface” command to set up configurations of several discontinuous ports or a range of
ports.
1. Entering interface numbers.
Note : You need to enter interface numbers first before issuing below 2-15 commands.
2. Enable port auto-negotiation.

74
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no auto-negotiation
Set auto-negotiation setting to the default
setting.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp
Set the selected interfaces’ to be
aggregated via LACP.
Note : At lease 2 ports, not more than 8
ports can be aggregated.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp key [0-255]
[0-255]
Configure LACP key, 0-255.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp role
Specify LACP role as passive.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp role active
Specify LACP role as active.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group trunking
[group_name]
[group_name]
Specify ports to the trunking group.
Note1 : At lease 2 ports, not more than
8 ports can be aggregated.
Note2 : Ports can not be in LACP and
port-trunking mode at the same time.
Note3 : A port-trunking group need to
created before assigning ports to it
(see 2.6.5 “channel-group”)
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no channel-group lacp
Diable LACP
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group trunking
Disable port-trunking
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
description [description]
[description]
Type in the description for the port(s),
max 35 characters.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no description
Clear port description.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
duplex [full]
[full]
Configure port duplex to full.
No command
3. Set up link aggregation or port-trunking.
4. Set up port description.
5. Set up port duplex mode.

75
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no duplex
Configure port duplex to half.
Note1 : Only 1-20 copper ports can be
configured as half duplex.
Note2 : Auto-negotiation needs to be
disabled before configuring duplex
mode.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
flowcontrol
Enable flow control on port(s).
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no flowcontrol
Disable flow control on port(s).
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping option
Enable DHCP option 82 on port(s).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping circuit
Enable DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
suboption.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping circuit id
[id_name]
[id_name]
Specify the VLAN and port identifier using
a VLAN ID in the range of 1 to 4094.
Besides, you can configure the circuit ID
to be a string of up to 63 characters. The
default circuit ID is the port identifier, the
format of which is vlan-mod-port.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping trust
Configure port(s) as DHCP option 82 trust
port(s)
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip dhcp snooping server-trust
Configure port(s) as DHCP server trust
port(s)
Note : A port / ports can not be
configured as option 82 trust and
server trust at the same time.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping option
Disable DHCP option 82 on port(s).
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping trust
Unconfigure port(s) as DHCP option 82
trust port(s)
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping server-trust
Unconfigure port(s) as DHCP server trust
port(s)
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping circuit
Disable DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
suboption.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip dhcp snooping circuit id
Clear DHCP Option 82 Circuit ID
description.
6. Enable flow control operation.
7. Set up port DHCP and IGMP parameters.
Setup DHCP snooping/relay sub-commands

76
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip igmp filter
Enable IGMP filter
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip igmp filter profile
[profile_name]
[profile_name]
Specify an IGMP filter profile
Note : Need to create an IGMP filter
profile first at Switch Management->IGMP Snooping-->IPMC profile.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip igmp max-groups [1-512]
[1-512]
Specify the max IGMP group number.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip igmp static-multicast-ip
[E.F.G.H | E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L] vlan
[1-4094]
[E.F.G.H |
E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L]
Specify static multicast address.
[1-4094]
Specify VLAN ID.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp filter
Disable IGMP filter
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp filter profile
[profile_name]
[profile_name]
Un-specify an IGMP filter profile
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp max-groups
Un-specify the max IGMP groups number.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip igmp static-multicast-ip
[E.F.G.H | E:F:G:H:I:J:K:L] vlan
[1-4094]
Un-specify static multicast address and
VLAN ID.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip sourceguard [dhcp|fixed-ip]
[dhcp|fixed-ip]
Configure IP sourceguard setting as
either DHCP or fixed-IP.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
ip sourceguard static-ip [A.B.C.D
| A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] vlan [1-4094]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify static IP address.
[1-4094]
Specify VLAN ID.
Note : Static IP can only be configured
when IP sourceguard is set to fixed-ip
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no ip sourceguard
Reset IP sourceguard setting to default
(unlimited).
Command
Parameter
Description
Setup IGMP snooping/MLD sub-commands
Setup IP source guard
8. Enable loop-detection per port.

77
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
loop-detection
Enable loop detection on port(s).
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
loop-detection
Disable loop detection on port(s).
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)#
mac address-table static-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx] vlan [14094]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:]
Specify a static MAC address
[1-4094]
Specify VLAN ID
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)#
mac learning
Enable MAC address learning
No command
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)#
no mac address-table staticmac [xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx] vlan [14094]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:]
Delete static MAC address entry
[1-4094]
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)#
no mac learning
Disable MAC address learning
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
media-type [sfp]
[sfp]
Configure the media type of the port(s) as
SFP.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
media-type
Configure the media type of the port(s) as
copper.
Note : Only port 21-24 can be
configured as copper.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
qos rate-limit ingress [0,50010000000]
[0,50010000000]
Configure ingress rate limit, from
500Kbps to 10000Mbps. “0” represents
disable.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
qos rate-limit egress [0,50010000000]
[0,50010000000]
Configure egress rate limit, from 500Kbps
to 10000Mbps. “0” represents disable.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no qos rate-limit ingress
Undo ingress rate limit.
9. Configure MAC table learning and static MAC table.
10. Configure media type.
11. Configure QoS rate limit.

78
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no qos rate-limit egress
Undo egress rate limit.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
shutdown
Disable interface.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no shutdown
Enable interface.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree
Enable spanning-tree
protocol
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree cost
[0-200000000]
[0-200000000]
Specify port path cost
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree priority
[0-15]
[0-15]
Specify bridge priority
0=0, 1=4096, 2=8192,
3=12288, 4=16384
5=20480, 6=24576,
7=28672, 8=32768
9=36864, 10=40960,
11=45056,12=49152
13=53248, 14=57344,
15=61440
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree edge
Specify the port as edge
port so to enable it to
move directly to forwarding
state upon link-up.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree p2p
[forced_true|forced_false|auto]
[forced_true|forced_false|auto]
Specify the port as point to
point port and its mode.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no spanning-tree
Disable spanning-tree
protocol.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no spanning-tree
cost
Undo specify port path
cost.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# spanning-tree priority
Undo specify bridge
priority.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no spanning-tree
edge
Undo specify the port as
edge port.
Switch(config-if-PORTPORT)# no spanning-tree p2p
Undo specify the port as
point to point port.
12. Shutdown interface.
13. Configure RSTP parameters per port.
14. Set up port speed.

79
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
speed [1000|100|10]
[1000|100|10]
Set port speed as 1000Mbps, 100Mbps or
10Mbps.
Note1 : Speed can only be configured
when auto-negotiation is disabled.
Note2: Fiber ports can not be
configured as 10Mbps.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no speed
Undo port speed setting.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan access-vlan [14094]
[1-4094]
Configure port PVID.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan trunk-vlan [14094]
[1-4094]
Configure port VID.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode access
Configure port as dot-1q access port.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk
Configure port as dot-1q trunk port.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk
native
Configure port as dot-1q trunk native port.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan port-based [name]
[name]
Join port to specific port-based VLAN
group.
Note : Need to create a port-based
VLAN group first at Switch
Management-->VLAN Configuration->Port Based VLAN-->Configure VLAN.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan access-vlan
Undo configure port PVID.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan trunk-vlan
Undo configure port VID.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
vlan dot1q-vlan mode
Undo VLAN mode configuration.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan dot1q-vlan mode trunk
native
Undo VLAN trunk native mode
configuration.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
no vlan port-based [name]
[name]
Undo join port to specific port-based
VLAN group.
15. Set up VLAN parameters per port.

80
2.6.25 Show interface statistics Command
Command
Parameters
Description
Switch(config)# show interface
Show overall interface
configurations.
Switch(config)# show interface
[port_list]
[port_list]
Show interface configurations of
selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics analysis
Display packets analysis (events)
for each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics analysis [port_list]
[port_list]
Display packets analysis for the
selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics analysis rate
Display packets analysis (rates) for
each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics analysis rate [port_list]
[port_list]
Display packets analysis (rates) for
the selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics clear
Clear all statistics.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics clear [port_list]
[port_list]
Clear statistics of selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics error
Display error packets statistics
(events) for each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics error [port_list]
[port_list]
Display error packets statistics
(events) for the selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics error rate
Display error packets statistics
(rates) for each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics error rate [port_list]
[port_list]
Display error packets statistics
(rates) for the selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics traffic
Display traffic statistics (events) for
each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics traffic [port_list]
[port_list]
Display traffic statistics (events) for
the selected ports.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics traffic rate
Display traffic statistics (rates) for
each port.
Switch(config)# show interface
statistics traffic rate [port_list]
[port_list]
Display traffic statistics (rates) for
the selected ports.
Command
Description
Switch(config)# show sfp information
Display SFP information including
temperature, voltage, TX Bias, TX
power, and RX power.
Switch(config)# show sfp state
Show the slide-in SFP modules’ current
temperature, safety Bias power, TX
The command “show interface statistics” that can display port traffic statistics, port packet error
statistics and port analysis history can be used either in Privileged mode # and Global
Configuration mode (config)#. “show interface statistics” is useful for network administrators to
diagnose and analyze port traffic real-time conditions.
2.6.26 Show sfp Command
When you slide-in SFP transceiver, detailed information about this module can be viewed by
issuing this command.

81
power, RX power and voltage.
Command
Description
Switch(config)# show running-config
Show configurations currently used in
the Manged Switch. Please note that
you must save running configurations
into your switch flash before rebooting
or restarting the device.
Switch(config)# show start-up-config
Display system configurations that are
stored in flash.
2.6.27 Show running-config & start-up-config Command

82
3. SNMP NETWORK MANAGEMENT
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application-layer protocol that facilitates
the exchange of management information between network devices. It is part of the TCP/IP
protocol suite. SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and
solve network problems, and plan for network growth.
SNMP consists of following key components.
Managed device is a network node that contains SNMP agent. Managed devices collect and
store management information and make this information available to NMS using SNMP.
Managed device can be switches/Hub, etc..
MIB (Management Information Base) defines the complete manageable entries of the managed
device. These MIB entries can be either read-only or read-write. For example, the System Version
is read-only variables. The Port State Enable or Disable is a read-write variable and a network
administrator can not only read but also set its value remotely.
SNMP Agent is a management module resides in the managed device that responds to the
SNMP Manager request.
SNMP Manager/NMS executes applications that monitor and control managed devices. NMS
provide the bulk of the processing and memory resources required for the complete network
management. SNMP Manager is often composed by desktop computer/work station and software
program such like HP OpenView.
Totally 4 types of operations are used between SNMP Agent & Manager to change the MIB
information. These 4 operations all use the UDP/IP protocol to exchange packets.
GET: This command is used by an SNMP Manager to monitor managed devices. The SNMP
Manager examines different variables that are maintained by managed devices.
GET Next: This command provides traversal operation and is used by the SNMP Manager to
sequentially gather information in variable tables, such as a routing table.
SET: This command is used by an SNMP Manager to control managed devices. The NMS
changes the values of variables stored within managed devices.
Trap: Trap is used by the managed device to report asynchronously a specified event to the
SNMP Manager. When certain types of events occur, a managed device will send a trap to alert
the SNMP Manager.
The system built-in management module also supports SNMP management. Users must install
the MIB file before using the SNMP based network management system. The MIB file is on a disc
or diskette that accompanies the system. The file name extension is .mib, which SNMP based
compiler can read.
Please refer to the appropriate documentation for the instructions of installing the system private
MIB.

83
4. WEB MANAGEMENT
You can manage the Managed Switch via a Web browser. However, you must first assign a
unique IP address to the Managed Switch before doing so. Use the RS-232 RJ-45 console port or
use a RJ45 LAN cable and any of the 10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 ports of the Managed Switch (as
the temporary RJ-45 Management console port) to login to the Managed Switch and set up the IP
address for the first time. (The default IP of the Managed Switch can be reached at
“http://192.168.0.1”. You can change the Managed Switch’s IP to the needed one later in its
Network Management menu.)
Follow these steps to manage the Managed Switch through a Web browser:
Use the RS-232 RJ-45 console port or one of the 10/100/1000Base-TX RJ-45 ports (as the
temporary RJ-45 Management console port) to set up the assigned IP parameters of the Managed
Switch, including IP address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway of the Managed Switch (if
required)
Run a Web browser and specify the Managed Switch’s IP address to reach it. (The Managed
Switch’s default IP can be reached at “http://192.168.0.1” before any change.)
Login to the Managed Switch to reach the Main Menu.
Once you gain the access, a Login window appears like this:
Enter the default username (admin) and password (by default, no password is required) to login to
the main screen page.
After a successful login, the Main Menu screen shows up. The rest of the menu functions in the
Web Management are similar to those described at the Console Management and are also
described below.

84
1. System Information: Name the Managed Switch, specify the location and check the current
version of information.
2. User Authentication: View the registered user list. Add a new user or remove an existing
user.
3. Network Management: Set up or view the IP address and related information of the Managed
Switch required for network management applications.
4. Switch Management: Set up switch/port configuration, VLAN configuration and other
functions.
5. Switch Monitor: View the operation status and traffic statistics of the ports.
6. System Utility: Ping, Firmware Upgrade, Load Factory Settings, etc..
7. Save Configuration: Save all changes to the system.
8. Reset System: Reset the Managed Switch.
9. Logout: Log out the management interface.
4.1 System Information
Select System Information from the Main Menu and then the following screen shows up.

85
Company Name: Display a company name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info company-
name [company-name]” command to edit this field.
System Object ID: Display the predefined System OID.
System Contact: Display contact information for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
contact [sys-contact]” command to edit this field.
System Name: Display a descriptive system name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
name [sys-name]” command to edit this field.
System Location: Display a brief location description for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info
sys-location [sys-location]” command to edit this field.
DHCP/DHCPv6 Vendor ID: Enter the Vendor ID used for DHCP/DHCPv6 relay agent function.
Model Name: Display the product’s model name.
Host Name: Display the product’s host name.
Image1 Firmware Version: Display the firmware version 1 (image-1) used in this device.
Image2 Firmware Version2: Display the firmware version 2 (image-2) used in this device.
M/B Version: Display the main board version.

86
Serial Number: Display the serial number of this Managed Switch.
Date Code: Display the Managed Switch Firmware date code.
Up Time: Display the up time since last restarting.
Local Time: Display local time.
Case Fan (1-6): Display the status of case fans.
Power (A-B): Display the status of powers.
4.2 User Authentication
To prevent any unauthorized operations, only registered users are allowed to operate the
Managed Switch. Users who want to operate the Managed Switch need to register into the user
list first.
To view or change current registered users, select User Authentication from the Main Menu and
then the following screen page shows up.
Up to 10 Users can be registered.
Click New to add a new user and then the following screen page appears.
Click Edit to view and edit a registered user setting.
Click Delete to remove a current registered user setting.
Click RADIUS Configuration for authentication setting via RADIUS.

87
NOTE: To prevent incautious operations, users cannot delete their own account, modify
their own user name and change their own account state.
Current/Total/Max Users: View-only field.
Current: This shows the number of current registered users.
Total: This shows the total number of users who have already registered.
Max: This shows the maximum number available for registration. The maximum number is
10.
Account State: Enable or disable this user account.
User Name: Specify the authorized user login name, up to 20 alphanumeric characters.
Password: Enter the desired user password, up to 20 alphanumeric characters.
Retype Password: Enter the password again for double-checking.
Description: Enter a unique description up to 35 alphanumeric characters for the user. This is
mainly for reference only.
Console Level: Select the desired privilege for the console operation from the pull-down menu.
Four operation privileges are available in the Managed Switch:
Administrator: Full access right, including maintaining user account, system information,
loading factory settings, etc..
Read & Write: Partial access right, unable to modify user account, system information and
items under System Utility menu.
Read Only: Read-Only access priviledge.

88
NOTE: For advanced RADIUS Server setup, please refer to APPENDIX A or the “free
RADIUS readme.txt” file on the disc provided with this product.
4.2.1 RADIUS Configuration
Click RADIUS Configuration in User Authentication and then the following screen page
appears.
When RADIUS Authentication is enabled, User login will be according to those settings on the
RADIUS server(s).
Secret Key: The word to encrypt data of being sent to RADIUS server.
RADIUS Port: The RADIUS service port on RADIUS server.
Retry Time: Times of trying to reconnect if the RADISU server is not reachable.
RADIUS Server Address: IP address of the first RADIUS server.
2nd RADIUS Server Address: IP address of the second RADIUS server.
4.3 Network Management
In order to enable network management of the Managed Switch, proper network configuration is
required. To do this, click the folder Network Management from the Main Menu and then the
following screen page appears.

89
1. Network Configuration: Set up the required IP configuration of the Managed Switch.
2. System Service Configuration: Enable or disable the specified network services.
3. RS232/Telnet/Console Configuration: View the RS-232 serial port setting, specific Telnet
and Console services.
4. Time Server Configuration: Set up the time server’s configuration.
5. Device Community: View the registered SNMP community name list. Add a new community
name or remove an existing community name.
6. Trap Destination: View the registered SNMP trap destination list. Add a new trap destination
or remove an existing trap destination.
7. Trap Configuration: View the Managed Switch trap configuration. Enable or disable a
specific trap.
8. Mal-attempt Log Configuration: Set up the Mal-attempt Log server’s configuration.
4.3.1 Network Configuration
Click the option Network Configuration from the Network Management menu and then the
following screen page appears.

90
Enable IPv4: Check to enable IPv4 on the Managed Switch
MAC Address: This view-only field shows the unique and permanent MAC address
assigned to the Managed switch. You cannot change the Managed Switch’s MAC address.
Configuration Type: There are two configuration types that users can select from the pull-
down menu, "DHCP" and "Manual". When "DHCP" is selected and a DHCP server is also
available on the network, the Managed Switch will automatically get the IP address from the
DHCP server. If "Manual" is selected, users need to specify the IP address, Subnet Mask
and Gateway.
IP Address: Enter the unique IP address of this Managed Switch. You can use the default
IP address or specify a new one when the situation of address duplication occurs or the
address does not match up with your network. (The default factory setting is 192.168.0.1.)
Subnet Mask: Specify the subnet mask. The default subnet mask values for the three
Internet address classes are as follows:
Class A: 255.0.0.0
Class B: 255.255.0.0
Class C: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: Specify the IP address of a gateway or a router, which is responsible for the
delivery of the IP packets sent by the Managed Switch. This address is required when the
Managed Switch and the network management station are on different networks or subnets.
The default value of this parameter is 0.0.0.0, which means no gateway exists and the
network management station and Managed Switch are on the same network.

91
Current State: This View-only field shows currently assigned IP address (by DHCP or
manual), Subnet Mask and Gateway of the Managed Switch.
Enable IPv6: Check to enable IPv6 on the Managed Switch
Auto-configuration: Enable Auto-configuration for the Managed Switch to get IPv6
address automatically or disable it for manual configuration.
IPv6 Link-local Address/Prefix length: The Managed Switch will form a link-local
address from its MAC address and the link-local prefix FE80::/10. This is done by putting
the prefix into the leftmost bits and the MAC address (in EUI-64 format) into the rightmost
bits, and if there are any bits left in between, those are set to zero.
IPv6 Global Address/Prefix length: This is done in the same fashion as the link-local
address, but instead of the link-local prefix FE80:: it will use the prefix supplied by the router
and put it together with its identifier (which by default is the MAC address in EUI-64 format).
IPv6 Gateway: Specify the IP address of a gateway or a router, which is responsible for the
delivery of the IP packets sent by the Managed Switch. This address is required when the
Managed Switch and the network management station are on different networks or subnets.
DHCPv6: Enable or disable DHCPv6 function
Disable: Disable DHCPv6.
Enable auto mode: Configure DHCPv6 function in auto mode.
Enable force mode:. Configure DHCPv6 function in force mode.
Rapid Commit: Check to enable Rapid Commit which allows the server and client to use a
two-message exchange to configure clients, rather than the default four-message exchange,
DHCPv6 unique identifier (DUID): View only field shows The DHCP Unique Identifier
(DUID).
Current State: This View-only field shows currently assigned IPv6 address (by auto-
configuration or manual) and Gateway of the Managed Switch.

92
NOTE: This Managed Switch also supports auto-provisioning function that enables DHCP
clients to automatically download the latest Firmware and configuration image from the
server. For information about how to set up a DHCP server, please refer to APPENDIX B.
Source Binding state: Enable or disable IP source binding.
State: Disable or enable
IP/IPv6 Address: Specify the IP address for source binding.
4.3.2 System Service Configuration
Click the option System Service Configuration from the Network Management menu and then
the following screen page appears.

93
Telnet Service: To enable or disable the Telnet Management service.
SNMP Service: To enable or Disable the SNMP Management service.
Web Service: To enable or Disable the Web Management service.
4.3.3 RS232/Telnet/Console Configuration
Click the option RS232/Telnet/Console Configuration from the Network Management menu
and then the following screen page appears.
Baud Rate: 9600 bps, RS-232 setting, view-only field.
Stop Bits: 1, RS-232 setting, view-only field.
Parity Check: None, RS-232 setting, view-only field.
Word Length: 8, RS-232 setting, view-only field.

94
Flow Control: None, RS-232 setting, view-only field.
NOTE: SNTP is used to get the time from those NTP servers. It is recommended that the
Telnet Port: Specify the desired TCP port number for the Telnet console. The default TCP port
number of the Telnet is 23.
System Time Out: Specify the desired time that the Managed Switch will wait before
disconnecting an inactive console/telnet.
4.3.4 Time Server Configuration
Click the option Time Server Configuration from the Network Management menu and then the
following screen page appears.
Time Synchronization: To enable or disable time synchronization.
Time Server IP/IPv6 Address: NTP time server address.
2nd Time Server IP/IPv6 Address: When the default time server is down, the Managed Switch
will automatically connect to the 2nd time server.
Synchronization Interval: The time interval to synchronize from NTP time server.
Time Zone: Select the appropriate time zone from the pull-down menu.
Daylight Saving Time: To enable or disable the daylight saving time function. It is a way of
getting more daytime hour(s) by setting the time to be hour(s) ahead in the morning.
Daylight Saving Time Date Start: Click the pull-down menu to select the start date of daylight
saving time.
Daylight Saving Time Date End: Click the pull-down menu to select the end date of daylight
saving time.

95
time server is in the same LAN with the Managed Switch or at least not too far away. In
this way, the time will be more accurate.
4.3.5 Device Community
Click the option Device Community from the Network Management menu and then the following
screen page appears.
Up to 10 Device Communities can be set up.
Click New to add a new community and then the following screen page appears.
Click Edit to view the current community settings.
Click Delete to remove a registered community.
Current/Total/Max Agents: View-only field.
Current: This shows the number of currently registered communities.
Total: This shows the number of total registered community users.

96
Max Agents: This shows the number of maximum number available for registration. The
NOTE: When the community browses the Managed Switch without proper access right,
the Managed Switch will not respond. For example, if a community only has Read & Write
privilege, then it cannot browse the Managed Switch’s user table.
default maximum number is 10.
Account State: Enable or disable this Community Account.
Community: Specify the authorized SNMP community name, up to 20 alphanumeric characters.
Description: Enter a unique description for this community name, up to 35 alphanumeric
characters. This is mainly for reference only.
SNMP Level: Click the pull-down menu to select the desired privilege for the SNMP operation
4.3.6 Trap Destination
Click the option Trap Destination from the Network Management menu and then the following
screen page appears.
State: Enable or disable the function of sending trap to the specified destination.
Destination: Enter the specific IP address of the network management system that will receive
the trap.
Community: Enter the community name of the network management system.
4.3.7 Trap Configuration
Click the option Trap Configuration from the Network Management menu and then the following
screen page appears.

97
Cold Start Trap: Enable or disable the Managed Switch to send a trap when the Managed Switch
is turned on.
Warm Start Trap: Enable or disable the Managed Switch to send a trap when the Managed
Switch restarts.
Authentication Failure Trap: Enable or disable the Managed Switch to send authentication
failure trap after any unauthorized users attempt to login.
Port Link Up/Down Trap: Enable or disable the Managed Switch to send port link up/link down
trap.
Fan Trap: Enable or disable the Managed Switch to send a trap when the fan is not working or
fails.
System Power Down Trap (1st Destination Only): Send a trap notice while the Managed Switch
is power down.
4.3.8 Mal-attempt Log Configuration
Click the option Trap Configuration from the Network Management menu and then the following
screen page appears.

98
When DHCP snooping filters unauthorized DHCP packets on the network, the Mal-attempt log will
allow the Managed Switch to send event notification message to Log server.
Log Server: Enable or disable Mal-attempt log function.
SNTP Status: View-only field that shows the SNTP server status.
Log Server IP/IPv6: Specify the default Log server IP/IPv6 address.
Log Server IP/IPv62: Specify the second Log server IP/IPv6 address. When the default Log
Server is down, the Managed Switch will automatically contact the second or third Log server.
Log Server IPv63: Specify the third Log server IP/IPv6 address. When the default Log Server is
down, the Managed Switch will automatically contact the second or third Log server.
4.4 Switch Management
In order to manage the Managed switch and set up required switching functions, click the folder
icon Switch Management from the Main Menu and then several options and folders will be
displayed for your selection.

99
1. Switch Configuration: Set up frame size, address learning, etc.
2. Port Configuration: Enable or disable port speed, flow control, etc.
3. Link Aggregation: Set up port trunk and LACP port configuration.
4. Rapid Spanning Tree: Set up RSTP switch settings, aggregated port settings, physical port
settings, etc.
5. 802.1X Configuration: Set up the 802.1X system, port Admin state, port reauthenticate.
6. MAC Address Management: Set up MAC address, enable or disable MAC security, etc.
7. VLAN Configuration: Set up VLAN mode and VLAN configuration.
8. QoS Configuration: Set up the priority queuing, rate limit and storm control.
9. IGMP/MLD Snooping: Configuring IGMP/MLD Snooping parameters.
10. Static Multicast Configuration: To create, edit or delete Static Multicast table.
11. Port Mirroring: Set up target port mirrors source port to enable traffic monitoring.
12. Security Configuration: Set up DHCP option 82 agent relay, port setting, filtering and static IP
table configuration.
13. Access Control List Management: Set up access control entries and lists.
14. LLDP Configuration: Enable or disable LLDP on ports and set up LLDP-related attributes.

100
15. Loop Detection Configuration: Enable or disable Loop Detection function and set up Loop
Detection configuration.
4.4.1 Switch Configuration
Click the option Switch Configuration from the Switch Management menu and then the
following screen page appears.
Maximum Frame Size: Specify the maximum frame size between 1518 and 9600 bytes. The
default maximum frame size is 9600bytes.
MAC Address Aging Time: Specify MAC Address aging time between 0 and 77925 seconds. “0”
means that MAC addresses will never age out.
Statistics Polling Port: Specify the number of ports for data acquisition at a time.
Statistics Polling Interval: Specify the time interval in 1/10 seconds for data acquisition.
The statistics data is listed on Section 4.5.3, 4.5.4 and 4.5.5.
Layer 2 Control Protocol
0180C200000X: Select either “Not Filter” or “Filter”. When “Filter” is selected, packets from
the address ranging from 0180C2000000 to 0180C200000F will be dropped. Multicast MAC
addresses from 0180C2000000 to 0180C200000F are reserved for use by 802.1/802.3
protocols. The purpose for each multicast address is described briefly below:
0180C200002X: Select either “Not Filter” or “Filter”. When “Filter” is selected, packets from
the address ranging from 0180C2000020 to 0180C200002F will be dropped. Multicast
 Loading...
Loading...