CTS ESW-3128SFP Service Manual

ESW-3128 Series
24 PORTS 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ-45 WITH 4 COMBO PORTS
(10/100/1000BASE-T, 100/1000BASE-X SFP) UPLINK
MANAGEMENT SWITCH
Network Management
User’s Manual
Version 0.90
1

2
Revision History
Version
F/W
Date
Description
0.90
1.00.00
20150618
Fisrt release

3
Trademarks
CTS is a registered trademark of Connection Technology Systems Inc..
Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
All other trademarks remain the property of their owners.
Copyright Statement
Copyright Connection Technology Systems Inc..
This publication may not be reproduced as a whole or in part, in any way whatsoever unless prior consent has been obtained from
Connection Technology Systems Inc..
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limitations are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult your local distributors or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
Copyright © 2015 All Rights Reserved.
Company has an on-going policy of upgrading its products and it may be possible that information in this document is not up-todate. Please check with your local distributors for the latest information. No part of this document can be copied or reproduced in
any form without written consent from the company.
Trademarks:
All trade names and trademarks are the properties of their respective companies.

4
Table of Content
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................... 9
1.1 Management Options ................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Management Software ............................................................................................... 10
1.3 Management Preparations ......................................................................................... 11
2. Command Line Interface (CLI) ...................................................................................... 13
2.1 Using the Local Console ............................................................................................. 13
2.2 Remote Console Management - Telnet ...................................................................... 14
2.3 Navigating CLI ............................................................................................................ 14
2.3.1 General Commands ............................................................................................. 15
2.3.2 Quick Keys ........................................................................................................... 15
2.3.3 Command Format ................................................................................................ 16
2.3.4 Login Username & Password .............................................................................. 17
2.4 User Mode .................................................................................................................. 18
2.4.1 Ping Command .................................................................................................... 18
2.4.2 Traceroute Command .......................................................................................... 18
2.5 Privileged Mode .......................................................................................................... 19
2.5.1 Copy-cfg Command ............................................................................................. 19
2.5.2 Firmware Command ............................................................................................ 20
2.5.3 Ping Command .................................................................................................... 21
2.5.4 Reload Command ................................................................................................ 21
2.5.5 Traceroute Command .......................................................................................... 21
2.5.6 Write Command ................................................................................................... 21
2.5.7 Configure Command ............................................................................................ 22
2.5.8 Show Command .................................................................................................. 22
2.6 Configuration Mode .................................................................................................... 23
2.6.1 Entering Interface Numbers ................................................................................. 24
2.6.2 No Command ....................................................................................................... 24
2.6.3 Show Command .................................................................................................. 24
2.6.4 ACL Command ..................................................................................................... 26
2.6.5 Channel-group Command .................................................................................... 29
2.6.6 Dot1x Command .................................................................................................. 31
2.6.7 IP Command ........................................................................................................ 34
2.6.8 IPv6 Command .................................................................................................... 41
2.6.9 LLDP Command .................................................................................................. 42
2.6.10 Loop Detection Command ................................................................................. 45

5
2.6.11 MAC Command .................................................................................................. 46
2.6.12 Management Command .................................................................................... 47
2.6.13 Mirror Command ................................................................................................ 48
2.6.14 NTP Command .................................................................................................. 49
2.6.15 QoS Command .................................................................................................. 50
2.6.16 Security Command ............................................................................................ 51
2.6.17 SNMP-Server Command ................................................................................... 53
2.6.18 Spanning-tree Command ................................................................................... 56
2.6.19 Switch Command ................................................................ ............................... 61
2.6.20 Switch-info Command ........................................................................................ 62
2.6.21 Syslog Command ............................................................................................... 63
2.6.22 User Command .................................................................................................. 64
2.6.23 VLAN Command ................................................................................................ 66
2.6.24 Interface Command ........................................................................................... 72
2.6.25 Show interface statistics Command ................................................................... 78
2.6.26 Show sfp Command ........................................................................................... 79
2.6.27 Show running-config & start-up-config Command .............................................. 79
3. SNMP NETWORK MANAGEMENT ................................................................................ 80
4. WEB MANAGEMENT...................................................................................................... 81
4.1 System Information .................................................................................................... 83
4.2 User Authentication .................................................................................................... 84
4.2.1 RADIUS Configuration ......................................................................................... 86
4.3 Network Management ................................................................................................ 86
4.3.1 Network Configuration ......................................................................................... 87
4.3.2 System Service Configuration .............................................................................. 90
4.3.3 RS232/Telnet/Console Configuration ................................................................... 91
4.3.4 Time Server Configuration ................................ ................................................... 92
4.3.5 Device Community ................................ ................................ ............................... 93
4.3.6 Trap Destination ................................................................................................ ... 94
4.3.7 Trap Configuration ............................................................................................... 95
4.3.8 Mal-attempt Log Configuration ............................................................................. 95
4.4 Switch Management ................................................................................................... 96
4.4.1 Switch Configuration ............................................................................................ 98
4.4.2 Port Configuration ................................................................................................ 98
4.4.3 Link Aggregation .................................................................................................. 99
4.4.3.1 Distribution Rule .......................................................................................... 100
4.4.3.2 Port Trunking ............................................................................................... 101

6
4.4.3.3 LACP Port Configuration ............................................................................. 103
4.4.4 Rapid Spanning Tree ......................................................................................... 105
4.4.4.1 RSTP Switch Settings ................................................................................. 106
4.4.4.2 RSTP Aggregated Port Settings ................................................................ .. 107
4.4.4.3 RSTP Physical Port Settings ....................................................................... 108
4.4.5 802.1X Configuration ......................................................................................... 112
4.4.5.1 802.1X System Settings .............................................................................. 113
4.4.5.2 802.1X Port Admin State ............................................................................. 113
4.4.5.3 802.1X Port Reauthenticate ........................................................................ 114
4.4.6 MAC Address Management ............................................................................... 115
4.4.6.1 MAC Table Learning ................................................................................... 115
4.4.6.2 Static MAC Table Configuration .................................................................. 116
4.4.7 VLAN Configuration ........................................................................................... 117
4.4.7.1 Port-Based VLAN ........................................................................................ 117
4.4.7.2 802.1Q VLAN Concept ................................................................................ 118
4.4.7.3 Introduction to Q-in-Q .................................................................................. 121
4.4.7.4 802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................................. 122
4.4.7.4.1 VLAN Interface ............................................................................................... 122
4.4.7.4.2 Trunk VLAN table ............................................................................................ 123
4.4.7.4.3 Management VLAN ........................................................................................ 124
4.4.7.4.4 QinQ VLAN configuration................................................................................ 125
4.4.8 QoS Configuration ............................................................................................. 126
4.4.8.1 QoS Priority ................................................................................................. 127
4.4.8.2 QoS Rate Limit ............................................................................................ 130
4.4.9 IGMP/MLD Snooping ......................................................................................... 130
4.4.9.1 IGMP/MLD Configure .................................................................................. 132
4.4.9.2 IGMP/MLD VLAN ID Configuration ............................................................. 134
4.4.9.3 IPMC Segment ............................................................................................ 134
4.4.9.4 IPMC Profile ................................................................................................ 135
4.4.9.5 IGMP/MLD Filtering ..................................................................................... 136
4.4.10 Static Multicast Configuration ........................................................................... 137
4.4.11 Port Mirroring ................................................................................................... 138
4.4.12 Security Configuration ...................................................................................... 139
4.4.12.1 DHCP Option 82/DHCPv6 Option 37 Settings .......................................... 140
4.4.12.2 DHCP Option 82 Configuration ................................................................. 143
4.4.12.3 IP Source Guard Settings .......................................................................... 145
4.4.12.4 Filter Configuration .................................................................................... 145

7
4.4.12.5 Static IP/IPv6 Table Configuration ............................................................. 147
4.4.12.6 Configure DHCP Snooping........................................................................ 148
4.4.12.7 Storm Control ............................................................................................ 149
4.4.13 Access Control List (ACL) Configuratiom ......................................................... 149
4.4.14 LLDP Configuration ......................................................................................... 151
4.4.15 Loop Detection Configuration ......................................................................... 153
4.5 Switch Monitor .......................................................................................................... 154
4.5.1 Switch Port State ................................................................................................ 155
4.5.2 Port Traffic Statistics .......................................................................................... 156
4.5.3 Port Packet Error Statistics ................................................................................ 157
4.5.4 Port Packet Analysis Statistics ........................................................................... 157
4.5.5 LACP Monitor ..................................................................................................... 158
4.5.5.1 LACP Port Status ........................................................................................ 159
4.5.5.2 LACP Statistics ............................................................................................ 160
4.5.6 RSTP Monitor .................................................................................................... 161
4.5.6.1 RSTP Bridge Overview ............................................................................... 161
4.5.6.2 RSTP Port Status ........................................................................................ 162
4.5.6.3 RSTP Statistics ........................................................................................... 162
4.5.7 802.1X Monitor................................................................................................... 163
4.5.7.1 802.1X Port Status ...................................................................................... 164
4.5.7.2 802.1X Statistics .......................................................................................... 165
4.5.8 IGMP/MLD Monitor ............................................................................................ 165
4.5.8.1 IGMP Snooping Status ................................................................................ 165
4.5.8.2 IGMP Group Table ...................................................................................... 166
4.5.8.3 MLD Snooping Status ................................................................................. 167
4.5.8.4 MLD Group Table ........................................................................................ 167
4.5.9 SFP Information ................................................................................................. 168
4.5.9.1 SFP Port Info ............................................................................................... 168
4.5.9.2 SFP Port State ............................................................................................ 169
4.5.10 DCHP Snooping ............................................................................................... 169
4.5.11 MAC Address Table .......................................................................................... 170
4.5.12 LLDP Status ..................................................................................................... 171
4.5.13 Loop Detection Status ...................................................................................... 171
4.5.14 IEEE 802.1q Tag VLAN Table .......................................................................... 172
4.6 System Utility ............................................................................................................ 172
4.6.1 Ping .................................................................................................................... 173
4.6.2 Event Log ........................................................................................................... 174

8
4.6.3 HTTP Upgrade ................................................................................................... 174
4.6.4 FTP/TFTP Upgrade ........................................................................................... 175
4.6.5 Load Factory Settings ........................................................................................ 177
4.6.6 Load Factory Settings Except Network Configuration ........................................ 177
4.7 Save Configuration ................................................................................................... 177
4.8 Reset System ................................ ................................ ........................................... 178
4.9 Logout ...................................................................................................................... 178
APPENDIX A: Free RADIUS readme ............................................................................... 179
APPENDIX B: Set Up DHCP Auto-Provisioning ............................................................. 180
APPENDIX C: VLAN Application Note ............................................................................ 189

9
1. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for using the 24 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports plus 4 10/100/1000Mbps combo ports
Managed Switch that is specifically designed for FTTx applications. The Managed Switch provides
a built-in management module that enables users to configure and monitor the operational status
both locally and remotely. This User’s Manual will explain how to use command-line interface and
Web Management to configure your Managed Switch. The readers of this manual should have
knowledge about their network typologies and about basic networking concepts so as to make the
best of this user’s manual and maximize the Managed Switch’s performance for your personalized
networking environment.
1.1 Management Options
Switch management options available are listed below:
Local Console Management
Telnet Management
SNMP Management
WEB Management
SSH Management
Local Console Management
Local Console Management is done through the RS-232 RJ-45 Console port located on the front
panel of the Managed Switch. Direct RS-232 cable connection between the PC and the Managed
switch is required for this type of management.
Telnet Management
Telnet runs over TCP/IP and allows you to establish a management session through the network.
Once the Managed switch is on the network with proper IP configurations, you can use Telnet to
login and monitor its status remotely.
SSH Management
SSH Management supports encrypted data transfer to prevent the data from being “stolen” for
remote management. You can use PuTTY, a free and open source terminal emulator application
which can act as a client for the SSH, to gain access to the Managed Switch.
SNMP Management
SNMP is also done over the network. Apart from standard MIB (Management Information Bases),
an additional private MIB is also provided for SNMP-based network management system to
compile and control.
Web Management
Web Management is done over the network and can be accessed via a standard web browser,
such as Microsoft Internet Explorer. Once the Managed switch is available on the network, you
can login and monitor the status of it through a web browser remotely or locally. Local Consoletype Web management, especially for the first time use of the Managed Switch to set up the
needed IP, can be done through one of the 10/100/1000Base-TX 8-pin RJ-45 ports located at the
front panel of the Managed Switch. Direct RJ-45 LAN cable connection between a PC and the
Managed Switch is required for Web Management.

10
1.2 Management Software
The following is a list of management software options provided by this Managed Switch:
Managed Switch CLI interface
SNMP-based Management Software
Web Browser Application
Console Program
The Managed Switch has a built-in Command Line Interface called the CLI which you can use to:
Configure the system
Monitor the status
Reset the system
You can use CLI as the only management system. However, other network management options,
SNMP-based management system, are also available.
You can access the text-mode Console Program locally by connecting a VT-100 terminal - or a
workstation running VT100 emulation software - to the Managed Switch RS-232 RJ-45 Console
port directly. Or, you can use Telnet to login and access the CLI through network connection
remotely.
SNMP Management System
Standard SNMP-based network management system is used to manage the Managed Switch
through the network remotely. When you use a SNMP-based network management system, the
Managed Switch becomes one of the managed devices (network elements) in that system. The
Managed Switch management module contains an SNMP agent that will respond to the requests
from the SNMP-based network management system. These requests, which you can control, can
vary from getting system information to setting the device attribute values.
The Managed Switch’s private MIB is provided for you to be installed in your SNMP-based
network management system.
Web Browser Application
You can manage the Managed Switch through a web browser, such as Internet Explorer or
Google Chrome, etc.. (The default IP address of the Managed Switch port can be reached at
“http://192.168.0.1”.) For your convenience, you can use either this Web-based Management
Browser Application program or other network management options, for example SNMP-based
management system as your management system.

11
1.3 Management Preparations
After you have decided how to manage your Managed Switch, you are required to connect cables
properly, determine the Managed switch IP address and, in some cases, install MIB shipped with
your Managed Switch.
Connecting the Managed Switch
It is very important that the proper cables with the correct pin arrangement are used when
connecting the Managed switch to other switches, hubs, workstations, etc..
1000Base-X / 100Base-FX SFP Port
The small form-factor pluggable (SFP) is a compact optical transceiver used in optical data
communication applications. It interfaces a network device mother board (for a switch, router
or similar device) to a fiber optic or unshielded twisted pair networking cable. It is a popular
industry format supported by several fiber optic component vendors.
SFP transceivers are available with a variety of different transmitter and receiver types,
allowing users to select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the required
optical reach over the available optical fiber type.
SFP slot for 3.3V mini GBIC module supports hot swappable SFP fiber transceiver. Before
connecting the other switches, workstation or Media Converter, make sure both side of the
SFP transfer are with the same media type, for example, 1000Base-SX to 1000Base-SX,
1000Bas-LX to 1000Base-LX, and check the fiber-optic cable type matches the SFP transfer
model. To connect to 1000Base-SX transceiver, use the multi-mode fiber cable with male
duplex LC connector type for one side. To connect to 1000Base-LX transfer, use the singlemode fiber cable with male duplex LC connector type for one side.
10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 Auto-MDI/MDIX Port
10/100/1000Base-T RJ-45 Auto-MDI/MDIX ports are located at the front of the Managed
Switch. These RJ-45 ports allow user to connect their traditional copper-based Ethernet/Fast
Ethernet devices to the network. All these ports support auto-negotiation and MDI/MDIX
auto-crossover, i.e. either crossover or straight through CAT-5 UTP or STP cable may be
used.
RS-232 RJ-45 Port
The RS-232 RJ-45 port is located at the front of the Managed Switch. This RJ-45 port is used
for local, out-of-band management. Since this RJ-45 port of the Managed switch is DTE, a
null modem is also required to be connected to the Managed Switch and the PC. By
connecting this RJ-45 port, it allows you to configure & check the status of Managed Switch
even when the network is down.

12
IP Addresses
IP addresses have the format n.n.n.n, (The default factory setting is 192.168.0.1).
IP addresses are made up of two parts:
The first part (for example 192.168.n.n) refers to network address that identifies the network
where the device resides. Network addresses are assigned by three allocation organizations.
Depending on your location, each allocation organization assigns a globally unique network
number to each network which intends to connect to the Internet.
The second part (for example n.n.0.1) identifies the device within the network.
Assigning unique device numbers is your responsibility. If you are unsure of the IP addresses
allocated to you, consult with the allocation organization where your IP addresses were
obtained.
Remember that an address can be assigned to only one device on a network. If you connect to
the outside network, you must change all the arbitrary IP addresses to comply with those you have
been allocated by the allocation organization. If you do not do this, your outside communications
will not be performed.
A subnet mask is a filtering system for IP addresses. It allows you to further subdivide your
network. You must use the proper subnet mask for the proper operation of a network with subnets
defined.
MIB for Network Management Systems
Private MIB (Management Information Bases) is provided for managing the Managed Switch
through the SNMP-based network management system. You must install the private MIB into
your SNMP-based network management system first.
The MIB file is shipped together with the Managed Switch. The file name extension is “.mib” that
allows SNMP-based compiler can read and compile.

13
2. Command Line Interface (CLI)
This chapter introduces you how to use Command Line Interface CLI, specifically in:
Local Console
Telnet
Configuring the system
Resetting the system
The interface and options in Local Console and Telnet are the same. The major difference is the
type of connection and the port that is used to manage the Managed Switch.
2.1 Using the Local Console
Local Console is always done through the RS-232 RJ-45 port and requires a direct connection
between the switch and a PC. This type of management is useful especially when the network is
down and the switch cannot be reached by any other means.
You also need the Local Console Management to setup the Switch network configuration for the
first time. You can setup the IP address and change the default configuration to the desired
settings to enable Telnet or SNMP services.
Follow these steps to begin a management session using Local Console Management:
Step 1. Attach the serial cable to the RS-232 RJ-45 port located at the front of the Switch.
Step 2. Attach the other end to the serial port of a PC or workstation.
Step 3. Run a terminal emulation program using the following settings:
Emulation VT-100/ANSI compatible
BPS 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow Control None
Enable Terminal keys
Step 4. Press Enter to access the CLI (Command Line Interface) mode.
14
2.2 Remote Console Management - Telnet
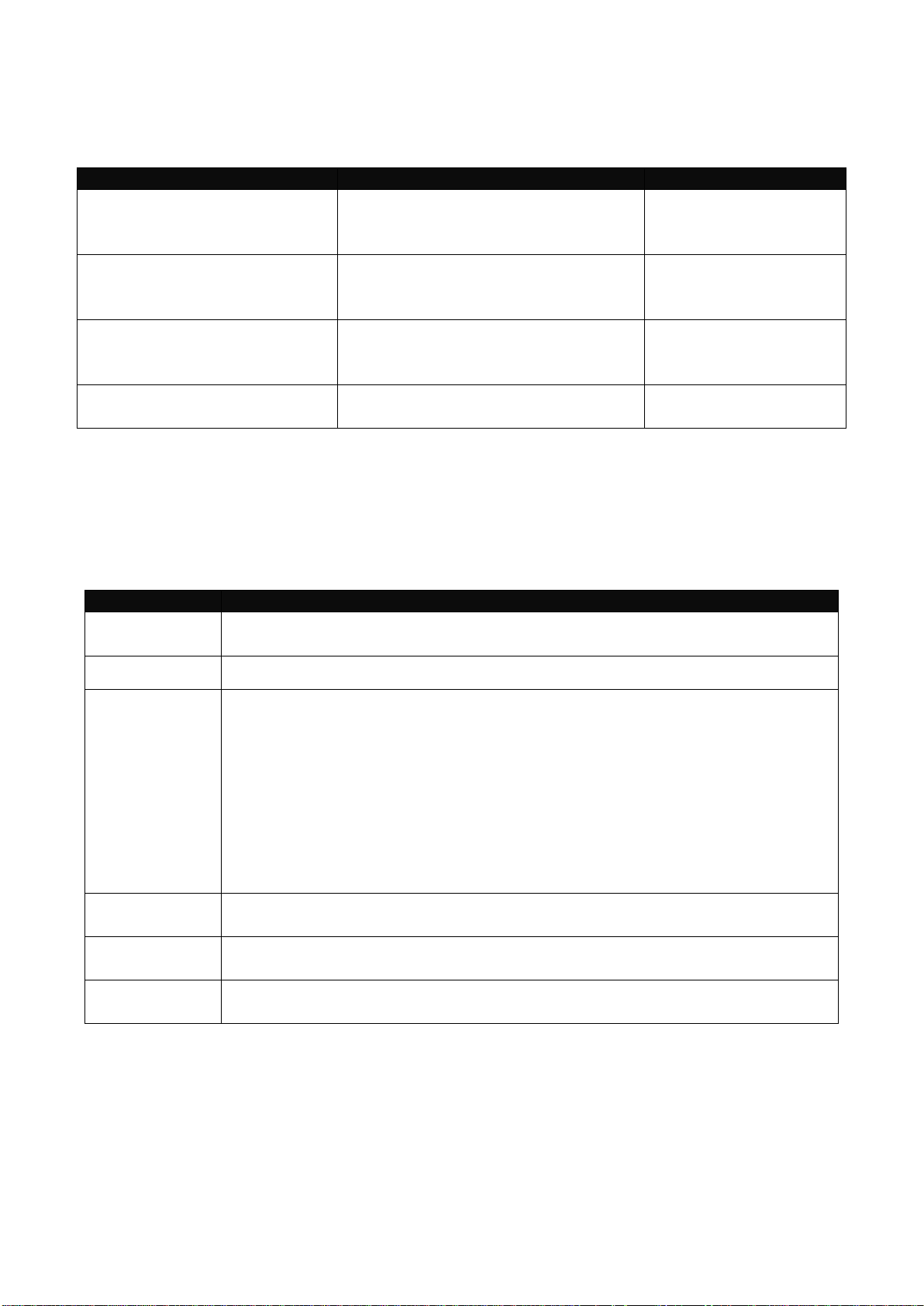
Command Mode
Access Method
Prompt Displayed
Exit Method
User mode
Login username &
password
Switch>
logout, exit
Privileged mode
From user mode, enter
the enable command
Switch#
disable, exit, logout
Configuration
mode
From the enable mode,
enter the config or
configure command
Switch(config)#
exit, Ctrl + Z
NOTE: By default, the model name will be used for the prompt display. You can change
the prompt display to the one that is ideal for your network environment using the
hostname command. However, for convenience, the prompt display “Switch” will be used
throughout this user’s manual.
You can manage the Managed Switch via Telnet session. However, you must first assign a
unique IP address to the Switch before doing so. Use the Local Console to login the Managed
Switch and assign the IP address for the first time.
Follow these steps to manage the Managed Switch through Telnet session:
Step 1. Use Local Console to assign an IP address to the Managed Switch
IP address
Subnet Mask
Default gateway IP address, if required
Step 2. Run Telnet
Step 3. Log into the Switch CLI
Limitations: When using Telnet, keep the following in mind:
Only two active Telnet sessions can access the Managed Switch at the same time.
2.3 Navigating CLI
When you successfully access the Managed Switch, you will be asked for a login username. Enter
your authorized username and password, and then you will be directed to User mode. In CLI
management, the User mode only provides users with basic functions to operate the Managed
Switch. If you would like to configure advanced features of the Managed Switch, such as, VLAN,
QoS, Rate limit control, you must enter the Configuration mode. The following table provides an
overview of modes available in this Managed Switch.
15
2.3.1 General Commands
Entering the command…
To do this…
Available Modes
help
Obtain a list of available
commands in the current mode.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
exit
Return to the previous mode or
login screen.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
history
List all commands that have been
used.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
Configuration Mode
logout
Logout from the CLI or terminate
Console or Telnet session.
User Mode
Privileged Mode
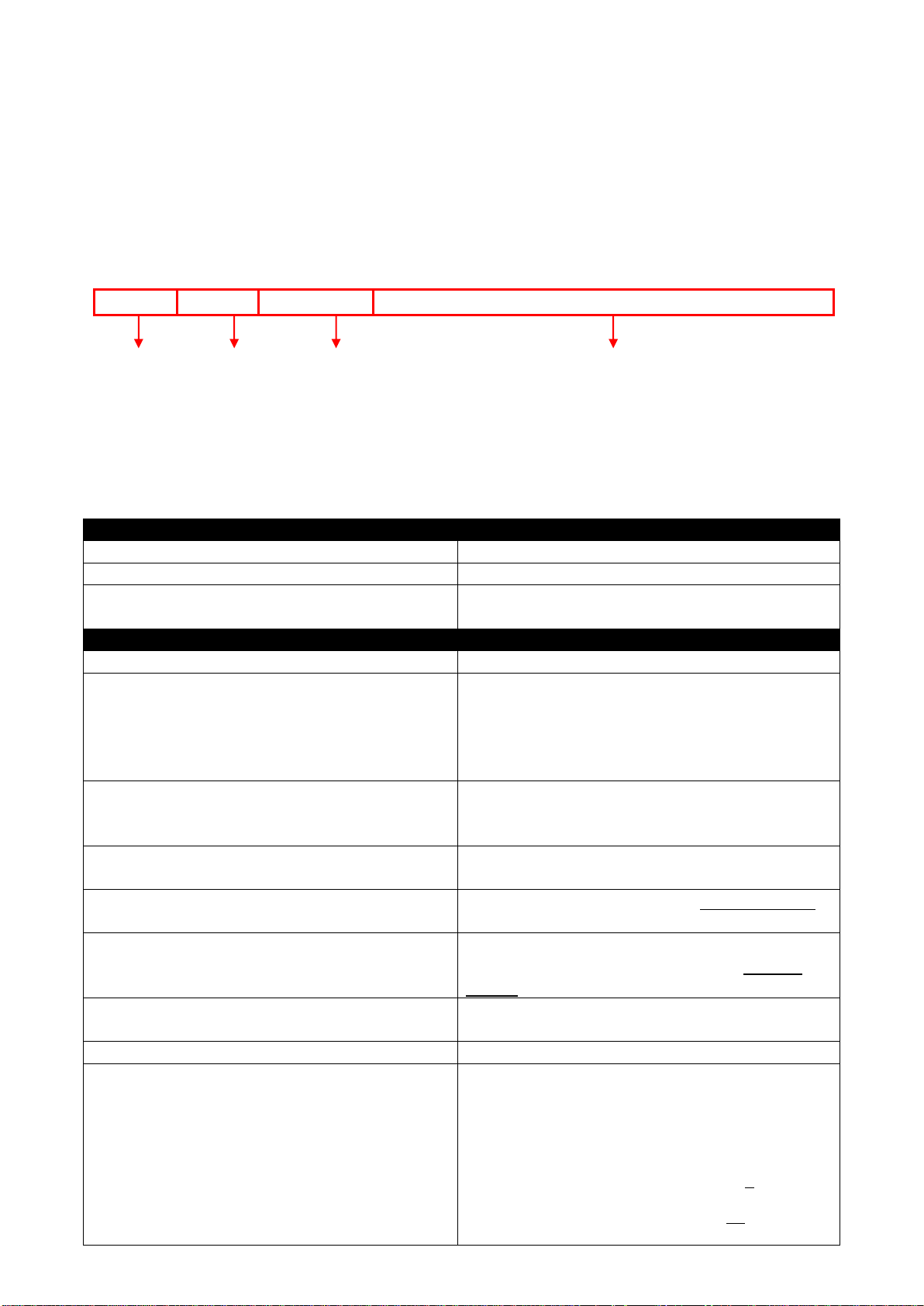
Keys
Purpose
tab
Enter an unfinished command and press “Tab” key to complete the
command.
?
Press “?” key in each mode to get available commands.
Unfinished
command
followed by ?
Enter an unfinished command or keyword and press “?” key to complete
the command and get command syntax help.
Example: List all available commands starting with the characters that
you enter.
Switch#h?
help Show available commands
history Show history commands
A space
followed by ?
Enter a command and then press Spacebar followed by a “?” key to view
the next parameter.
Up arrow
Use Up arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the most recent key-in commands.
Down arrow
Use Down arrow key to scroll through the previous entered commands,
beginning with the commands that are entered first.
This section introduces you some general commands that you can use in User, Enable, and
Configuration mode, including “help”, “exit”, “history” and “logout”.
2.3.2 Quick Keys
In CLI, there are several quick keys that you can use to perform several functions. The following
table summarizes the most frequently used quick keys in CLI.
16
2.3.3 Command Format
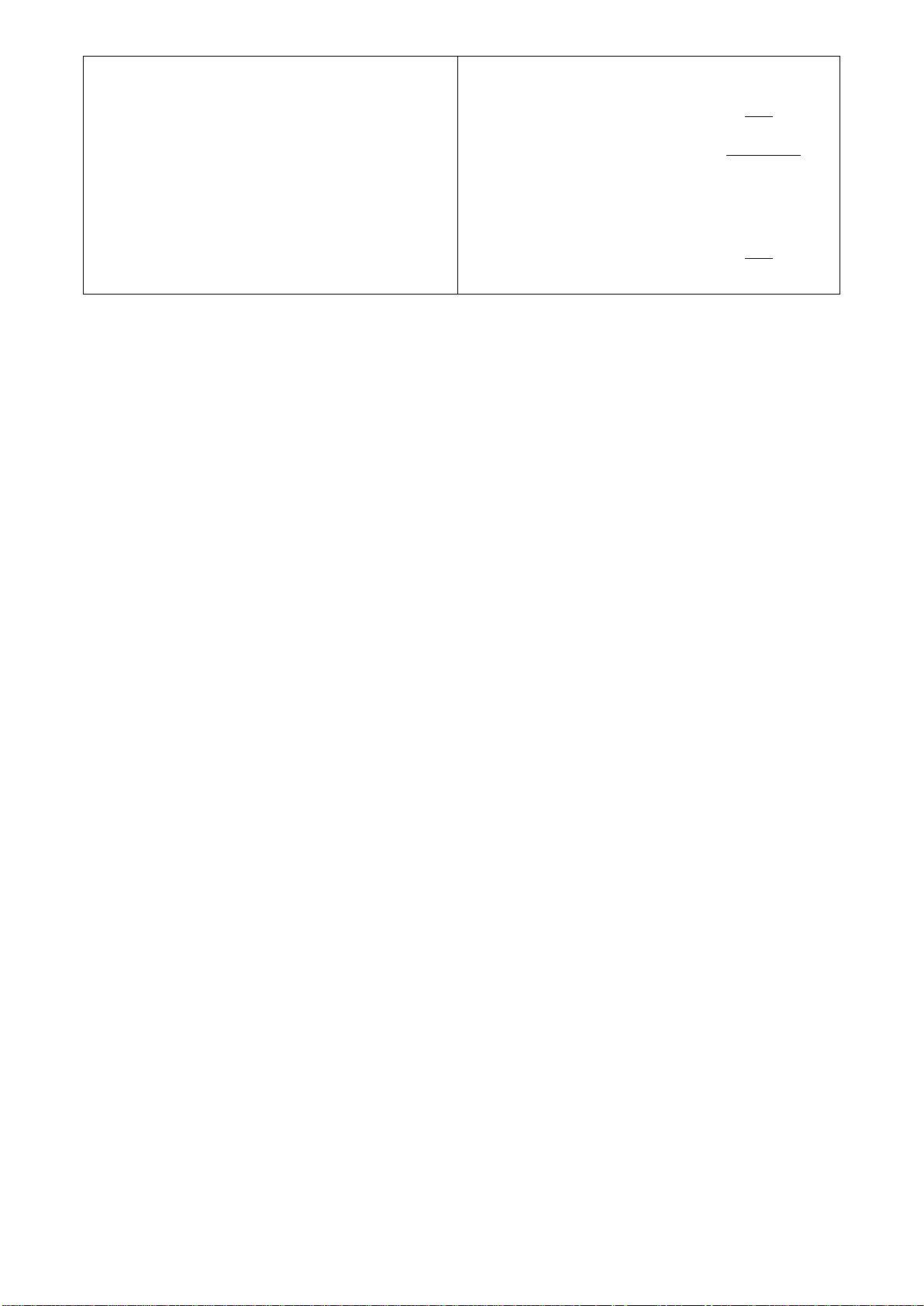
Symbols
Brief Description
>
Currently, the device is in User mode.
#
Currently, the device is in Privileged mode.
(config)#
Currently, the device is in Global
Configuration mode.
Syntax
Brief Description
[ ]
Reference parameter.
[-s size] [-r repeat] [-t timeout]
These three parameters are used in ping
command and are optional, which means
that you can ignore these three parameters
if they are unnecessary when executing
ping command.
[A.B.C.D ]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter an IP address or gateway
address.
[255.X.X.X]
Brackets represent that this is a required
field. Enter the subnet mask.
[port]
Enter one port number. See section 1.6.21
for edtailed explanations.
[port_list]
Enter a range of port numbers or server
discontinuous port numbers. See section
1.6.21 for edtailed explanations.
[forced_false | auto]
There are three options that you can
choose. Specify one of them.
[1-8191]
Specify a value between 1 and 8191.
[0-7] 802.1p_list
[0-63] dscp_list
Specify one value, more than one value or a
range of values.
Example 1: specifying one value
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10 3
Example 2: specifying three values
This means that
you are in Global
Configuration
mode
This allows you to
assign IP address.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway address.
Hostname
While in CLI, you will see several symbols very often. As mentioned above, you might already
know what “>”, “#” and (config)# represent. However, to perform what you intend the device to do,
you have to enter a string of complete command correctly. For example, if you want to assign IP
address for the Managed Switch, you need to enter the following command with the required
parameter and IP, subnet mask and default gateway:
IP command syntax: Switch(config)#ip address [A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X] [A.B.C.D]
Switch(config)#ip address 192.168.1.198 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.254
The following table lists common symbols and syntax that you will see very frequently in this
User’s Manual for your reference:
17
(separated by commas)
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1,3 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10,13,15 3
Example 3: specifying a range of values
(separated by a hyphen)
Switch(config)#qos 802.1p-map 1-3 0
Switch(config)#qos dscp-map 10-15 3
2.3.4 Login Username & Password
Default Login
When you enter Console session, a login prompt for username and password will appear to
request a valid and authorized username and password combination. For first-time users, enter
the default login username “admin” and “press Enter key” in password field (no password is
required for default setting). When system prompt shows “Switch>”, it means that the user has
successfully entered the User mode.
For security reasons, it is strongly recommended that you add a new login username and
password using User command in Configuration mode. When you create your own login
username and password, you can delete the default username (admin) to prevent unauthorized
accesses.
Enable Mode Password
Enable mode is password-protected. When you try to enter Enable mode, a password prompt will
appear to request the user to provide the legitimate passwords. Enable mode password is the
same as the one entered after login password prompt. By default, no password is required.
Therefore, press Enter key in password prompt.
Forgot Your Login Username & Password
If you forgot your login username and password, you can use the “reset button” on the front panel
to set all configurations back to factory defaults. Once you have performed system reset to
defaults, you can login with default username and password. Please note that if you use this
method to gain access to the Managed Switch, all configurations saved in Flash will be lost. It is
strongly recommended that a copy of configurations is backed up in your local hard-drive or file
server from time to time so that previously-configured settings can be reloaded to the Managed
Switch for use when you gain access again to the device.
18
2.4 User Mode
Command
Description
exit
Quit the User mode or close the terminal connection.
help
Display a list of available commands in User mode.
history
Display the command history.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
ping
Test whether a specified network device or host is reachable or not.
traceroute
Trace the route to HOST
enable
Enter the Privileged mode.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> ping
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [s size (1-
65500)bytes] [-t
timeout (1-99)secs]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-s size (1-
65500)bytes]
Enter the packet size that would be sent. The
allowable packet size is from 1 to 65500 bytes.
(optional)
[-t timeout (1-99)
secs]
Enter the timeout value when the specified IP
address is not reachable. (optional)
Example
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8 –s 128 –t 10
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –s 128 –t 10
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> traceroute
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [h (1-100)hops]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-h (1-100)hops]
Specify max hops between the local host and the
remote host
Example
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8 –h 30
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –h 30
In User mode, only a limited set of commands are provided. Please note that in User mode, you
have no authority to configure advanced settings. You need to enter Enable mode and
Configuration mode to set up advanced functions of the Switch. For a list of commands available
in User mode, enter the question mark (?) or “help” command after the system prompt displays
Switch>.
2.4.1 Ping Command
Ping is used to test the connectivity of end devices and also can be used to self test the network
interface card. Enter the ping command in User mode. In this command, you can add an optional
packet size value and an optional value for the number of times that packets are sent and received.
2.4.2 Traceroute Command
Traceroute is used to trace the path between the local host and the remote host. Enter the
traceroute command in User mode. In this command, you can add an optional max hops value
for the number of hops that packets are sent and received.
19
2.5 Privileged Mode
Command
Description
copy-cfg
Restore or backup configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
disable
Exit Enable mode and return to User Mode.
exit
Exit Enable mode and return to User Mode.
firmware
Allow users to update firmware via FTP or TFTP.
help
Display a list of available commands in Enable mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
logout
Logout from the Managed Switch.
ping
Test whether a specified network device or host is reachable or not.
reload
Restart the Managed Switch.
traceroute
Trace the route to HOST
write
Save your configurations to Flash.
configure
Enter Global Configuration mode.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# copy-cfg
from ftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file name]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address of your FTP
server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# copy-cfg
from tftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address of your TFTP
server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you
want to restore.
Example
Switch# copy-cfg from ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf misadmin1 abcxyz
Switch# copy-cfg from tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# copy-cfg to
ftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file name] [running
| default | startup ]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
[running | default
Specify backup config to be running, default or
The only place where you can enter the Privileged (Enable) mode is in User mode. When you
successfully enter Enable mode (this mode is password protected), the prompt will be changed to
Switch# (the model name of your device together with a pound sign). Enter the question mark (?)
or help command to view a list of commands available for use.
2.5.1 Copy-cfg Command
Use “copy-cfg” command to backup a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server and restore the
Managed Switch back to the defaults or to the defaults but keep IP configurations.
1. Restore a configuration file via FTP or TFTP server.
2. Backup configuration file to FTP or TFTP server.
20
[user_name]
[password]
| startup ]
startup
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# copy-cfg to
tftp [A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [running
| default | startup ]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file name]
Enter the configuration file name that you want to
backup.
[running | default
| startup ]
Specify backup config to be running, default or
startup
Example
Switch# copy-cfg to ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf running misadmin1 abcxyz
Switch# copy-cfg to tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.conf startup
Command / Example
Switch# copy-cfg from default
Switch# reload
Command / Example
Switch# copy-cfg from default keep-ip
Switch# reload
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch# firmware
upgrade ftp
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [Image1| Image-2]
[user_name]
[password]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your FTP server.
[file name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to
upgrade.
[Image-1| Image2]
Choose image-1 or image-2 for the firmware to
be upgraded to.
[user_name]
Enter the username for FTP server login.
[password]
Enter the password for FTP server login.
Switch# firmware
upgrade tftp
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[file_name] [Image1| Image-2]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
[file_name]
Enter the firmware file name that you want to
upgrade.
[Image-1| Image2]
Choose image-1 or image-2 for the firmware to
be upgraded to.
Example
Switch# firmware upgrade ftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin Image-1 edgeswitch10
abcxyz
Switch# firmware upgrade tftp 192.168.1.198 HS_0600_file.bin Image-2
3. Restore the Managed Switch back to default settings.
4. Restore the Managed Switch back to default settings but keep IP configurations.
2.5.2 Firmware Command
To upgrade firmware via TFTP or FTP server.

21
2.5.3 Ping Command
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> ping
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [s size (1-
65500)bytes] [-t
timeout (1-99)secs]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-s size (1-
65500)bytes]
Enter the packet size that would be sent. The
allowable packet size is from 1 to 65500 bytes.
(optional)
[-t timeout (1-99)
secs]
Enter the timeout value when the specified IP
address is not reachable. (optional)
Example
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8
Switch> ping 8.8.8.8 –s 128 –t 10
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –s 128 –t 10
Command / Example
Switch# reload
Command / Example
Switch# reload Image-2
OK!
Switch# reload
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch> traceroute
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H] [h (1-100)hops]
[A.B.C.D |
A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Enter the IP/IPv6 address that you would like to
ping.
[-h (1-100)hops]
Specify max hops between the local host and the
remote host
Example
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8
Switch> traceroute 8.8.8.8 –h 30
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888
Switch> ping 2001:4860:4860::8888 –h 30
Command / Example
Switch# write
Save Config Succeeded!
2.5.4 Reload Command
1. To restart the Managed Switch.
2. To specify the image for the next restart before restarting.
2.5.5 Traceroute Command
2.5.6 Write Command
To save running configurations to startup configurations, enter the write command. All unsaved
configurations will be lost when you restart the Managed Switch.

22
Command / Example
Switch#config
Switch(config)#
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#
2.5.7 Configure Command
The only place where you can enter Global Configuration mode is in Privileged mode. You can
type in “configure” or “config” for short to enter Global Configuration mode. The display prompt will
change from “Switch#” to “Switch(config)#” once you successfully enter Global Configuration
mode.
2.5.8 Show Command
The “show” command is very important for network administrators to get information about the
device, receive outputs to verify a command’s configurations or troubleshoot a network
configuration error. It can be used in Privileged or Configuration mode. The following describes
different uses of “show” command.
1. Display system information
Enter “show switch-info” command in Privileged or Configuration mode, and then the following
information will appear.
Company Name: Display a company name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info company-
name [company-name]” command to edit this field.
System Object ID: Display the predefined System OID.
System Contact: Display contact information for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
contact [sys-contact]” command to edit this field.
System Name: Display a descriptive system name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
name [sys-name]” command to edit this field.
System Location: Display a brief location description for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info
sys-location [sys-location]” command to edit this field.
Model Name: Display the product’s model name.
Host Name: Display the product’s host name.
Firmware Version1: Display the firmware version 1 (image-1) used in this device.
Firmware Version2: Display the firmware version 2 (image-2) used in this device.
M/B Version: Display the main board version.
Fiber Type: Display information about the slide-in or fixed fiber type.
Fiber Wavelength: Display the slide-in or fixed fiber’s TX and RX wavelength information.

23
Serial Number: Display the serial number of this Managed Switch.
Command
Description
acl
Set up access control entries and lists.
channel-group
Configure static link aggregation groups or enable LACP function.
dot1x
IEEE 802.1X global configuration commands
exit
Exit the configuration mode.
help
Display a list of available commands in Configuration mode.
history
Show commands that have been used.
ip
Set up the IPv4 address and enable DHCP mode & IGMP snooping.
Ipv6
To enable ipv6 function and set up IP address
lldp
LLDP global configuration mode
loop-detection
Configure loop-detection to prevent loop between switch ports by locking them.
mac
Set up MAC learning function of each port
management
Set up console/telnet/web/SSH access control and timeout value.
mirror
Set up target port for mirroring.
ntp
Set up required configurations for Network Time Protocol.
qos
Set up the priority of packets within the Managed Switch.
Date Code: Display the Managed Switch Firmware date code.
Up Time: Display the up time since last restarting.
Local Time: Display local time.
Current Run In: Display the current running firmware image.
Reboot Run To: Display the firmware image which will run after next restarting.
Case Fan (1-6): Display the status of case fans.
Power (A-B): Display the status of powers.
Battery State: Display the status of battery (For BAT version only).
2. Display or verify currently-configured settings
Refer to the following sub-sections. “Interface command”, “IP command”, “MAC command”, “QoS
command”, “Security command”, “SNMP-Server command”, “User command”, “VLAN command”
sections, etc.
3. Display interface information or statistics
Refer to “Show interface statistics command” and “Show sfp information command” sections.
4. Show default, running and startup configurations
Refer to “show default-setting copmmand”, “show running-config command” and “show start-upconfig command” sections.
2.6 Configuration Mode
When you enter “configure” or “config” and press “Enter” in Privileged mode, you will be directed to
Global Configuration mode where you can set up advanced switching functions, such as QoS,
VLAN and storm control security globally. All commands entered will apply to running-configuration
and the device’s operation. From this level, you can also enter different sub-configuration modes
to set up specific configurations for VLAN, QoS, security or interfaces.
24
security
Configure broadcast, multicast, unknown unicast storm control settings.
snmp-server
Create a new SNMP community and trap destination and specify the trap types.
spanning-tree
Set up RSTP status of each port and aggregated ports.
switch
Set up acceptable frame size and address learning, etc.
switch-info
Set up acceptable frame size and address learning, etc.
syslog
Set up required configurations for Syslog server.
user
Create a new user account.
vlan
Set up VLAN mode and VLAN configuration.
no
Disable a command or set it back to its default setting.
interface
Select a single interface or a range of interfaces.
show
Show a list of commands or show the current setting of each listed command.
Commands
Description
Switch(config)# interface 1
Switch(config-if-1)#
Enter a single interface. Only interface 1 will
apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1,3,5
Switch(config-if-1,3,5)#
Enter three discontinuous interfaces,
separated by commas. Interface 1, 3, 5 will
apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1-3
Switch(config-if-1-3)#
Enter three continuous interfaces. Use a
hyphen to signify a range of interface
numbers. In this example, interface 1, 2, and
3 will apply commands entered.
Switch(config)# interface 1,3-5
Switch(config-if-1,3-5)#
Enter a single interface number together with
a range of interface numbers. Use both
comma and hypen to signify the combination
of different interface numbers. In this
example, interface 1, 3, 4, 5 will apply
commands entered.
2.6.1 Entering Interface Numbers
In the Global Configuration mode, you can configure a command that only applies to interfaces
specified. For example, you can set up each interface’s VLAN assignment, speeds, or duplex
modes. To configure, you must first enter the interface number. There are four ways to enter your
interface numbers to signify the combination of different interfaces that apply a command or
commands.
2.6.2 No Command
Almost every command that you enter in Configuration mode can be negated using “no” command
followed by the original or similar command. The purpose of “no” command is to disable a function,
remove a command, or set the setting back to the default value. In each sub-section below, the
use of no command to fulfill different purposes will be introduced.
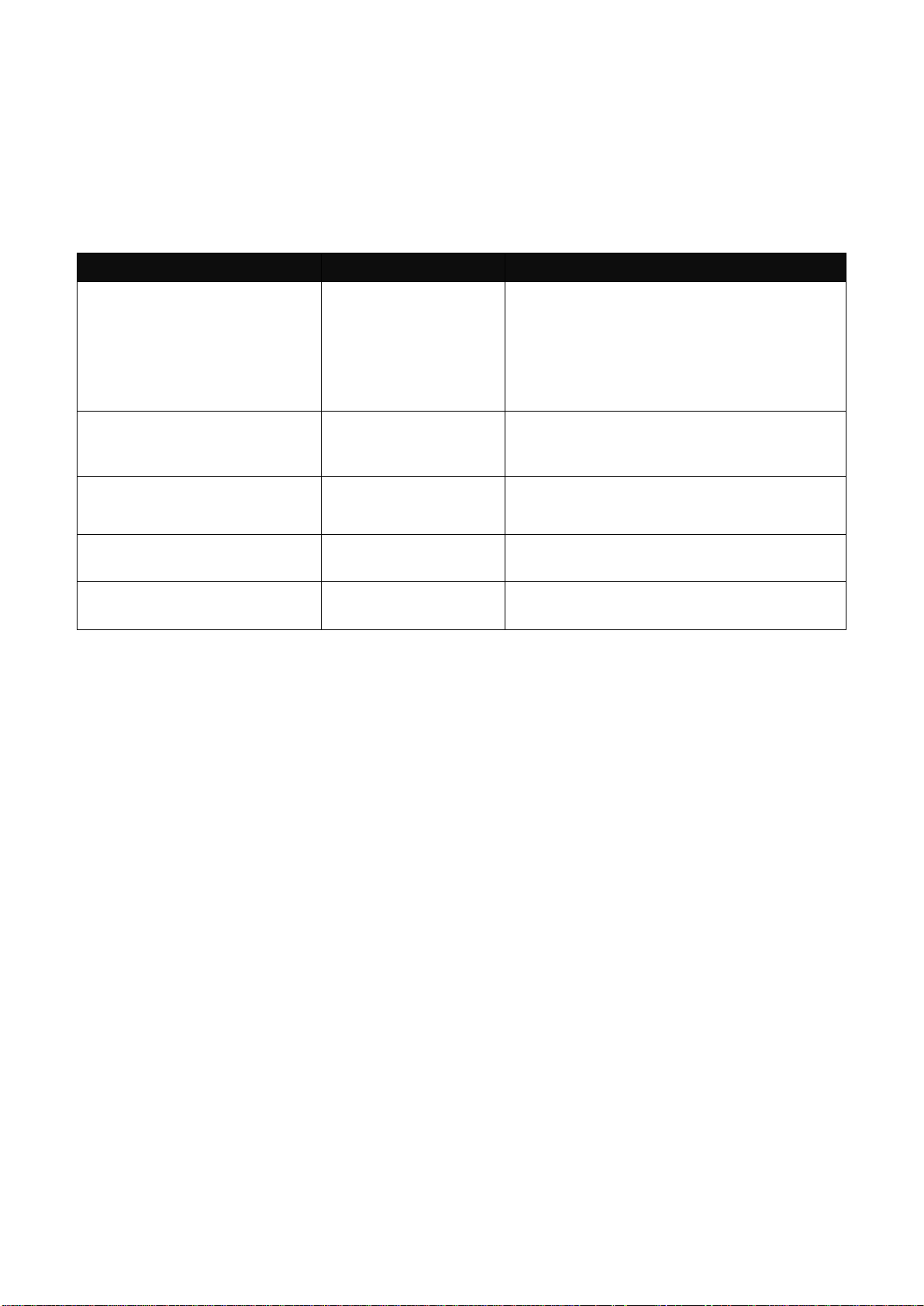
2.6.3 Show Command
The “show” command is very important for network administrators to get information about the
device, receive outputs to verify a command’s configurations or troubleshoot a network
configuration error. It can be used in Privileged or Configuration mode. The following describes
different uses of “show” command.
1. Display system information
Enter “show switch-info” command in Privileged or Configuration mode, and then the following
information will appear.

25
Company Name: Display a company name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info company-
name [company-name]” command to edit this field.
System Object ID: Display the predefined System OID.
System Contact: Display contact information for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
contact [sys-contact]” command to edit this field.
System Name: Display a descriptive system name for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info sys-
name [sys-name]” command to edit this field.
System Location: Display a brief location description for this Managed Switch. Use “switch-info
sys-location [sys-location]” command to edit this field.
Model Name: Display the product’s model name.
Host Name: Display the product’s host name.
Firmware Version1: Display the firmware version 1 (image-1) used in this device.
Firmware Version2: Display the firmware version 2 (image-2) used in this device.
M/B Version: Display the main board version.
Fiber Type: Display information about the slide-in or fixed fiber type.
Fiber Wavelength: Display the slide-in or fixed fiber’s TX and RX wavelength information.
Serial Number: Display the serial number of this Managed Switch.
Date Code: Display the Managed Switch Firmware date code.
Up Time: Display the up time since last restarting.
Local Time: Display local time.
Current Run In: Display the current running firmware image.
Reboot Run To: Display the firmware image which will run after next restarting.
Case Fan (1-6): Display the status of case fans.
Power (A-B): Display the status of powers.
Battery State: Display the status of battery (For BAT version only).
2. Display or verify currently-configured settings
Refer to the following sub-sections. “Interface command”, “IP command”, “MAC command”, “QoS
command”, “Security command”, “SNMP-Server command”, “User command”, “VLAN command”
sections, etc.
3. Display interface information or statistics
Refer to “Show interface statistics command” and “Show sfp information command” sections.
26
Command
Parameter
Description
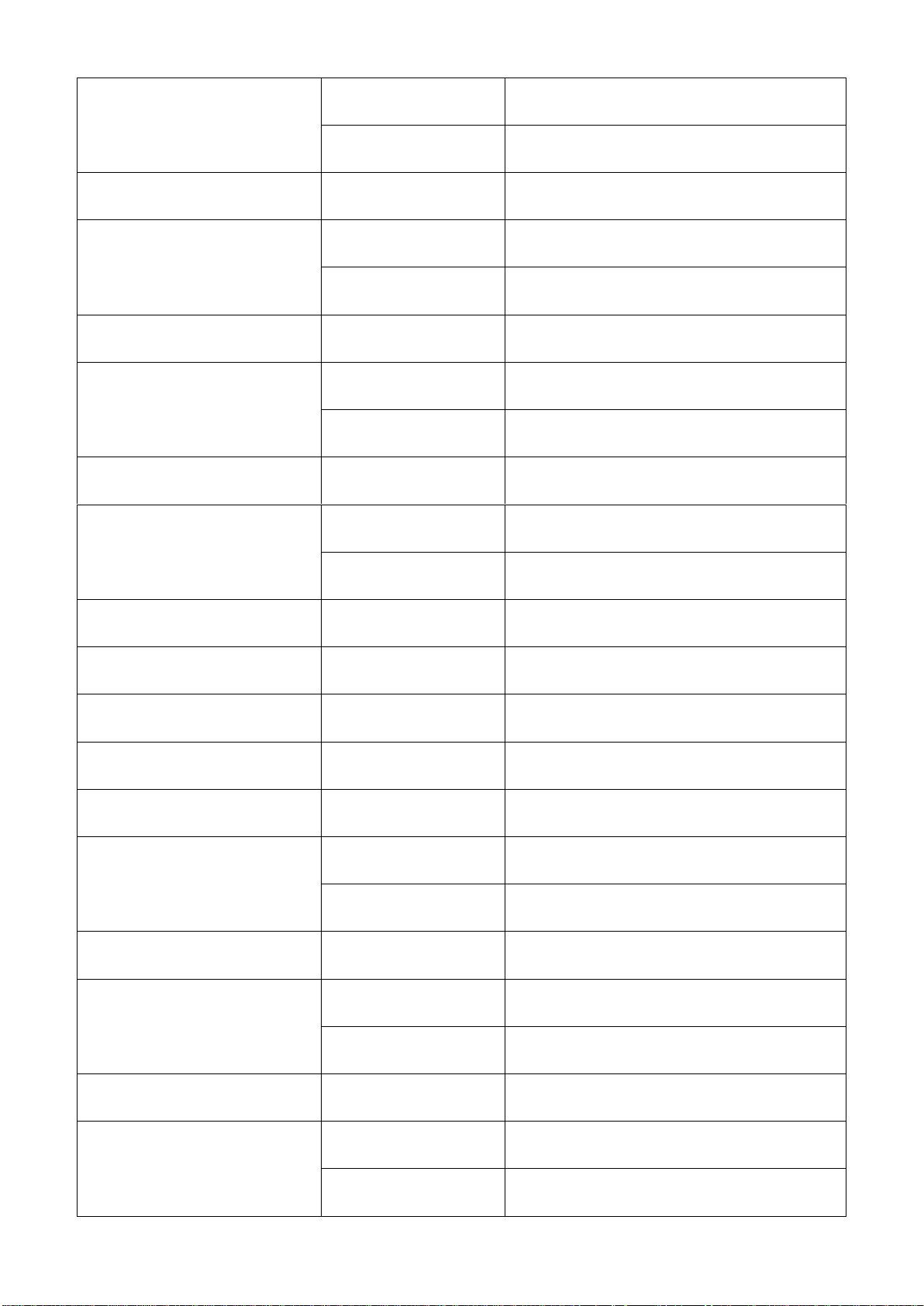
Switch(config)# acl [1-192]
[1-192]
The total number of ACL rule can be
created is 192. Use this command to
enter ACL configuration mode for each
ACL rule. When you enter each ACL
rule, you can further configure detailed
settings for this rule.
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
action [permit | copy |
redirect]
[permit | copy |
redirect]
Permit, copy or redirect the action for
this rule.
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
action-port [port]
[port]
Specify action port (1~28)
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
apply
Application effective
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv4 any
Specify destination IPv4 address as
“ANY”
4. Show default, running and startup configurations
Refer to “show default-setting copmmand”, “show running-config command” and “show start-upconfig command” sections.
2.6.4 ACL Command
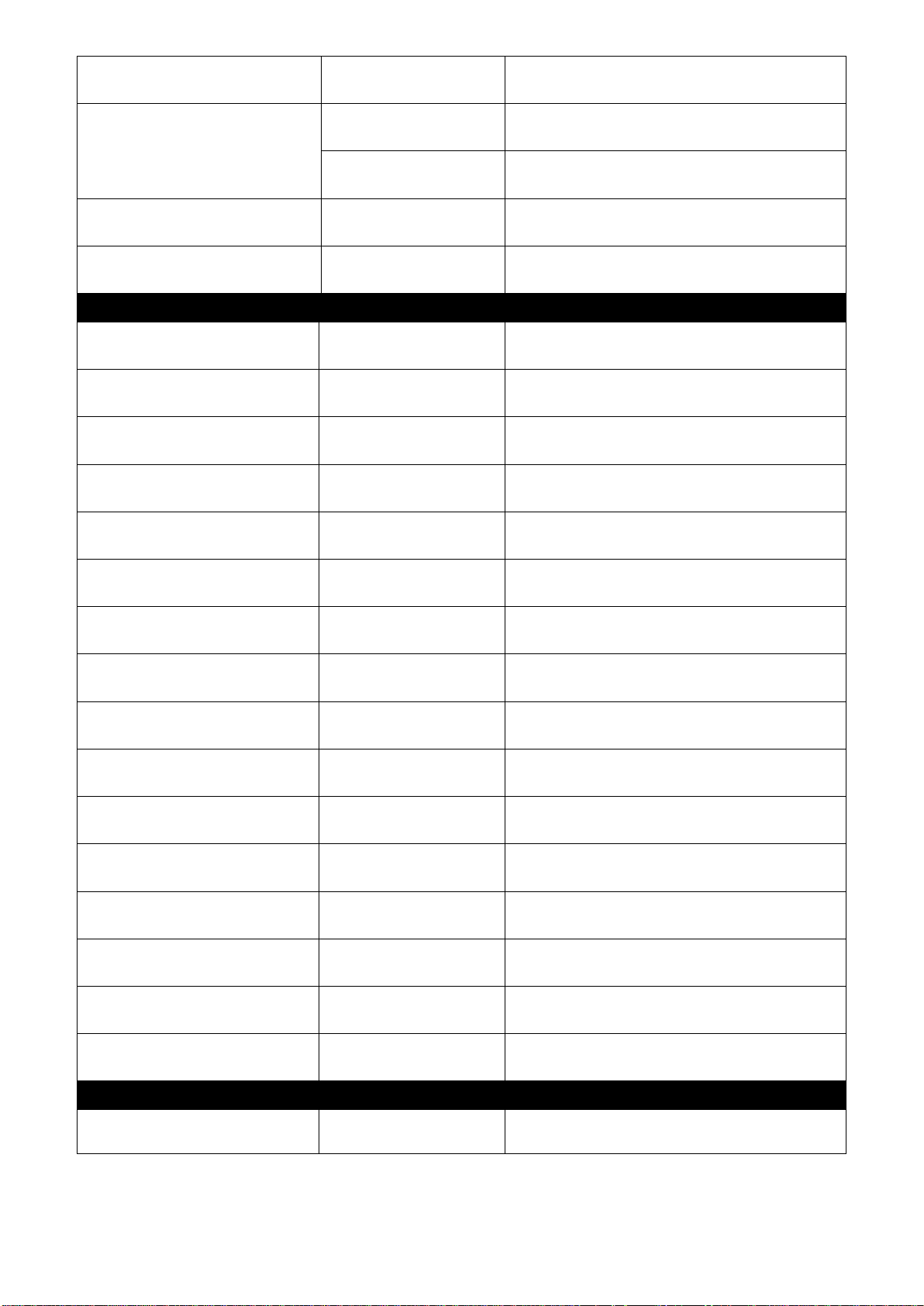
27
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv4 address
[A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify destination IPv4 address
[255.X.X.X]
Specify destination IPv4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv6 any
Specify destination IPv6 address as
“ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-ipv6 address
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify destination IPv6 address
[10~128]
Specify destination IPv6 prefix-length
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-l4-port any
Specify destination Layer4 port as
“ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-l4-port [165535] [0xWXYZ]
[1-65535]
Specify destination Layer4 port
[0xWXYZ]
Specify destination Layer4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-mac any
Specify destination MAC as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
destination-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Specify destination MAC
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
Specify destination MAC mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
ethertype [any | 0xWXYZ]
[any | 0xWXYZ]
Specify Ethertype or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
ingress-port [any | port-list]
[any | port-list]
Specify ingress port(s) or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
protocol [any | 0xWX]
[any | 0xWX]
Specify IPv4 protocol and IPv6 next
header or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
rate-limit [16-1048560]
[16-1048560]
Specify rate limitation from 16 to
1048560 kbps
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv4 any
Specify source IPv4 address as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv4 address
[A.B.C.D] [255.X.X.X]
[A.B.C.D]
Specify source IPv4 address
[255.X.X.X]
Specify source IPv4 mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv6 any
Specify source IPv6 address as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-ipv6 address
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
[10~128]
[A:B:C:D:E:F:G:H]
Specify source IPv6 address
[10~128]
Specify source IPv6 prefix-length
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-l4-port any
Specify source Layer4 port as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-l4-port [1-65535]
[0xWXYZ]
[1-65535]
Specify source Layer4 port
[0xWXYZ]
Specify source Layer4 mask
28
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-mac any
Specify source MAC as “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
source-mac
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
[xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
Specify source MAC
[ff:ff:ff:00:00:00]
Specify source MAC mask
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
tos [any | 0xWX]
[any | 0xWX]
Specify IPv4 TOS and IPv6 traffic class
or “ANY”
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
vid [any | 1-4094]
[any | 1-4094]
Specify 802.1q VLAN ID or “ANY”
No command
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no action
Undo action command
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no action-port
Undo action port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-ipv4
Undo destination-ipv4 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-ipv6
Undo destination-ipv6 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-l4-port
Undo destination-l4-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no destination-mac
Undo destination-mac specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no ingress-port
Undo ingress-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no ethertype
Undo ethertype specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no protocol
Undo protocol specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no rate-limit
Undo rate-limit specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-ipv4
Undo source-ipv4 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-ipv6
Undo source-ipv6 specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-l4-port
Undo source-l4-port specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no source-mac
Undo source-mac specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no tos
Undo TOS specification
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
no vid
Undo vid specification
Show command
Description
Switch(config-acl-RULE)#
show
Display ACL rule configuration
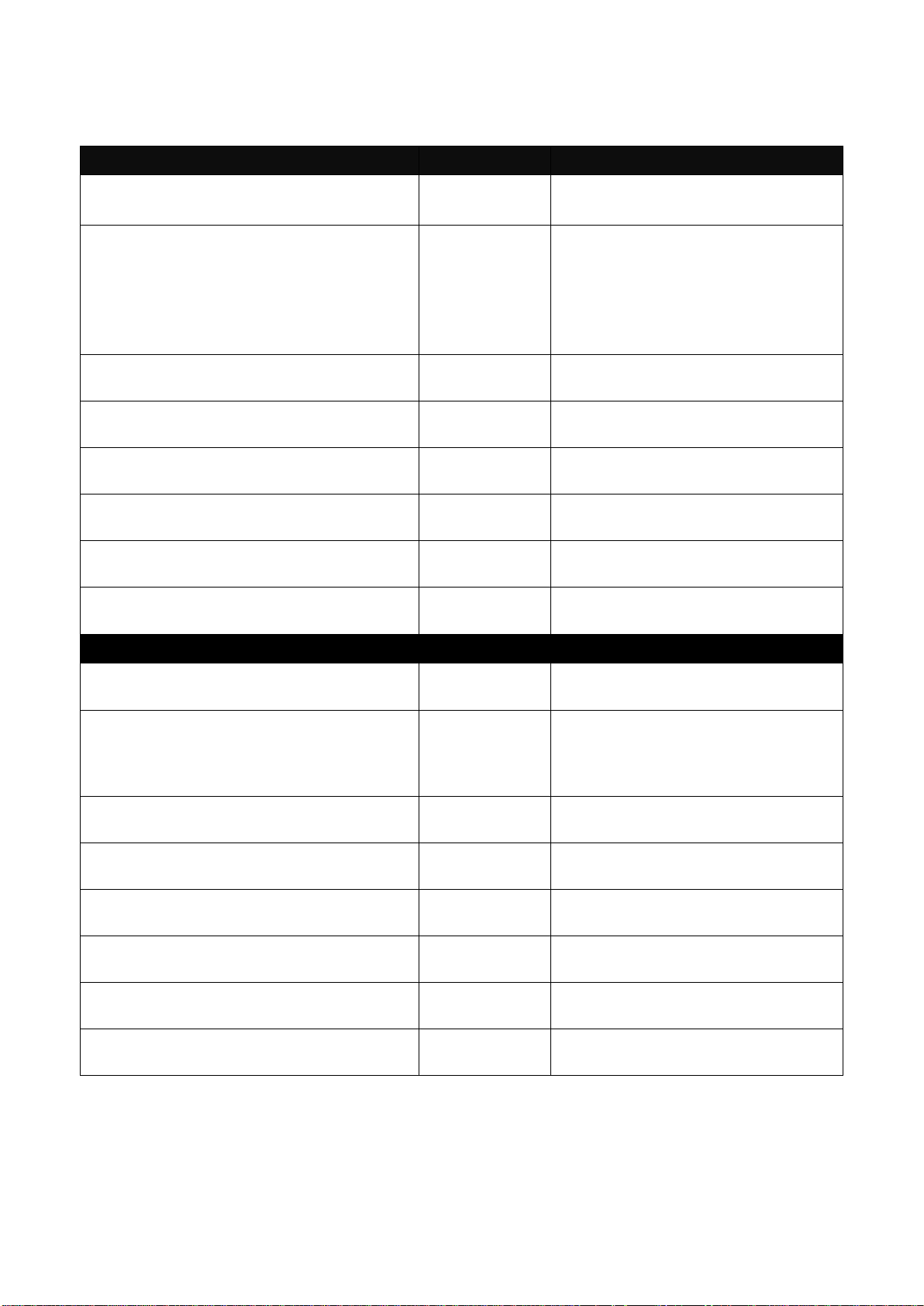
29
2.6.5 Channel-group Command
Command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Specify a name for this link
aggregation group.
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group trunking [group_name]
[port_list]
[group_name]
Use “interface” command to
configure a group of ports’ link
aggregation link membership.
Assign the selected ports to the
specified link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-ip
Load-balancing depending on
destination IP address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-ip
Load-balancing depending on
source IP address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-L4-port
Load-balancing depending on
destination L4 port.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-L4-port
Load-balancing depending on
source L4 port.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule destination-mac
Load-balancing depending on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# channel-group
distribution-rule source-mac
Load-balancing depending on
source MAC address.
No command
Switch(config)# no channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Delete a link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group trunking
[port_list]
Remove the selected ports from
a link aggregation group.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule destination-ip
Disable load-balancing based on
destination IP address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule source-ip
Disable load-balancing based on
source IP address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule destination-L4-port
Disable load-balancing based on
destination L4 port.
Switch(config)# no channel-group
distribution-rule source-L4-port
Disable load-balancing based on
source L4 port.
Switch(config)# no channel-group type
destination-mac
Disable load-balancing based on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# no channel-group type
source-mac
Disable load-balancing based on
destination MAC address.
1. Configure a static link aggregation group (LAG).
30
Show command
Switch(config)# show channel-group
trunking
Show or verify link aggregation
settings.
Switch(config)# show channel-group
trunking [group_name]
[group_name]
Show or verify a specific link
aggregation group’s settings
including aggregated port
numbers and load-balancing
status.
Channel-group command example
Switch(config)# channel-group trunking corenetwork
Create a link aggregation group
called “corenetwork”.
Switch(config)# channel-group type destination-mac
Load-balancing depending on
destination MAC address.
Switch(config)# channel-group type source-mac
Load-balancing depending on
source MAC address.
Channel-group & Interface
command
Parameter
Description
Switch(config)# interface [port_list]
[port_list]
Enter several discontinuous port
numbers separated by commas or a
range of ports with a hyphen. For
example:1,3 or 2-4
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp
Enable LACP on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp key [0-255]
[0-255]
Specify a key to the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)#
channel-group lacp role [active]
[active]
Specify the selected interfaces to
active LACP role.
No command
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp
Disable LACP on the selected
interfaces.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp key
Reset the key value of the selected
interfaces to the factory default.
Switch(config-if-PORT-PORT)# no
channel-group lacp role
Reset the LACP type of the selected
interfaces to the factory default
(passive mode).
Show command
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp
Show or verify each interface’s LACP
settings including current mode, key
value and LACP type.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
LACP settings.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp status
Show or verify each interface’s current
LACP status.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp status [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
current LACP status.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp statistics
Show or verify each interface’s current
LACP traffic statistics.
Switch(config)# show channelgroup lacp statistics [port_list]
[port_list]
Show or verify the selected interfaces’
current LACP statistics.
2. Use “Interface” command to configure link aggregation groups dynamically (LACP).
 Loading...
Loading...