CTC Store IPDSLAM-A8-A16 User Manual

USER MANUAL
IP DSLAM for ADSL
IPDSLAM-A8/A16

TABLE OF CONTENTS
List of Figures.................................................................................... vi
List of Tables..................................................................................... vii
About This Manual.............................................................................. 1
What’s the difference between ATM based DSLAM and IP based
DSLAM?............................................................................................... 3
1. Introduction................................................................................... 5
1.1 General.........................................................................................................5
1.2 ADSL IP DSLAM Overview .........................................................................6
1.3 ADSL IP DSLAM Application......................................................................9
1.4 ADSL IP DSLAM Features ........................................................................10
1.5 ADSL IP DSLAM Specifications...............................................................11
2. Getting Started............................................................................ 12
2.1 General.......................................................................................................12
2.2 Unpacking your ADSL IP DSLAM.............................................................13
2.3 Hardware Installation................................................................................14
Safety Instruction............................................................................................................14
ADSL IP DSLAM Rear Panel Connection......................................................................15
ADSL IP DSLAM Front Panel Connection......................................................................16
2.4 Ways of Management Connection...........................................................17
Embedded Web Interface(EmWeb)................................................................................17
Command Line Interface (CLI).......................................................................................17
Telnet Client....................................................................................................................18
3. System Administration with EmWeb ........................................ 19
3.1 Log In with Embedded Web Interface......................................................19
3.2 Embedded Web Interface Menu...............................................................20
3.3 Default (Factory) Configuration Settings {Default Setting}...................23
3.4 Displaying the System Information of your ADSL IP DSLAM {System
Information}..........................................................................................................24
3.5 Save your Configuration to Flash {Save to Flash}.................................25

3.6 Displaying Current Event {Current Event}..............................................26
3.7 Configuring ADSL IP DSLAM ...................................................................28
Configuring Port Filtering {Set Port Filter} ......................................................................28
Configuring IP and Location {System IP / Location}.......................................................29
Configuring Date and Time {System Date and Time}.....................................................30
Changing your Password {Changing Password}............................................................30
3.8 DSL Line Configuration............................................................................31
Creating a Line Profile {Create Line Profile}...................................................................31
Creating a Alarm Profile {Create Alarm Profile} ...........................................................32
Displaying and Modifying a Line Profile {Current Line Profile}.......................................33
Displaying and Modifying a Alarm Profile {Current Alarm Profile} ..................................34
3.9 Port Configuration ....................................................................................35
DSL Port Configuration{DSL Port Configuration}............................................................35
PVC Configuration{PVC Configuration}..........................................................................36
List of Subscriber {List of Subscriber}.............................................................................38
Routing Table {Routing Table} ........................................................................................39
3.10 Management Configuration......................................................................40
Configuring SNMP Access Parameters and Trap IPs {SNMP}.......................................40
Configuring Management IP {Management IP}..............................................................41
3.11 Performance Monitor................................................................................42
ADSL Physical Layer PM {Physical Layer Info}..............................................................42
ADSL Channel Layer PM {Channel Layer Info}..............................................................43
ADSL Physical Layer PM within Current 15 Minutes and a Day Duration {Current
Phy-Layer PM}................................................................................................................44
ADSL Channel Layer PM within Current 15 Minutes and a Day Duration {Current
Channel-Layer PM} ........................................................................................................46
ADSL Physical Layer PM within Previous 15 Minutes Duration {15 MIN Phy-Layer PM}
........................................................................................................................................47
ADSL Physical Layer PM within Previous 1 Day Duration {1 DAY Phy-Layer PM}........48
ADSL Channel Layer PM within Previous 15 Minutes Duration {15 MIN Channel-Layer
PM}.................................................................................................................................49
ADSL Channel Layer PM within Previous 1 Day Duration {1 DAY Channel-Layer PM}.50
3.12 Miscellanea................................................................................................51
IGMP Snooping Configuration {IGMP_Snooping Config}...............................................51
IGMP Snooping Status {IGMP_Snooping Status} ..........................................................51
SNTP Status {SNTP Status} ...........................................................................................53
4. System Administration with CLI ................................................ 55
4.1 Command Structure..................................................................................55
Calling Commands.........................................................................................................60
4.2 General Configuration ..............................................................................61
4.3 Event Viewing and Deleting .....................................................................62
Displaying the Current Event..........................................................................................62
iii

Deleting the Event of ADSL IP DSLAM ..........................................................................62
Reset Port.......................................................................................................................62
Restart the ADSL IP DSLAM..........................................................................................63
Resetting all Configurations to Default Setting...............................................................63
System Upgrade.............................................................................................................63
Logging Out your ADSL IP DSLAM................................................................................64
4.4 Configuring Your ADSL IP DSLAM ..........................................................64
System Configuration.....................................................................................................64
Port-Filtering Configuration.............................................................................................66
IP Configuration..............................................................................................................67
Time Configuration.........................................................................................................68
SNTP configuration ........................................................................................................69
Changing the Password .................................................................................................70
4.5 Configuring DSL........................................................................................71
Creating Line Profile and Alarm Profile...........................................................................71
Modifying DSL Profile and Alarm Profile.........................................................................74
Deleting a DSL Profile and Alarm Profile........................................................................75
Displying a DSL Profile and Alarm Profile.......................................................................76
4.6 Port Configuration ....................................................................................79
Enabling and Disabling a port.........................................................................................79
Attaching DSL Profile......................................................................................................79
Displaying the Current Status and Information of ADSL Line .........................................80
PVC Configuration..........................................................................................................81
Subscriber Configuration................................................................................................85
Routing Table configuration............................................................................................87
4.7 Management Configuration......................................................................89
Configuring SNMP Access Parameters..........................................................................89
Configuring Trap IP.........................................................................................................90
Configuring Management IP...........................................................................................91
Displaying Management IP.............................................................................................91
Deleting Management IP................................................................................................92
4.8 IGMP configuration...................................................................................93
Displaying IGMP Status..................................................................................................93
Displaying IGMP Group..................................................................................................94
Configuring IGMP...........................................................................................................94
4.9 Performance Monitor................................................................................95
Displaying the Physical Layer Information...................................................................95
Displaying the Channel Layer Information......................................................................96
Displaying Physical Performance St atistics within Current 15 Minutes and 1 Day Duration
........................................................................................................................................96
Displaying Channel Performance St atistics within Current 15 Minutes and 1 Day Duration
........................................................................................................................................98
Displaying Physical Performance St atistics during Previous 15 Minutes or 1 Day Duration
......................................................................................................................................100
Displaying Channel Performance St atistics during Previous 15 Minutes or 1 Day Duration
......................................................................................................................................101
iv

4.10 Ethernet Rate Mode Configuration........................................................102
Show Ethernet Rate Mode ...........................................................................................102
Modifying Ethernet Rate Mode.....................................................................................102
4.11 DHCP Server Configuration ...................................................................103
Show DHCP Sever Configuration.................................................................................103
Modifying DHCP Server ...............................................................................................103
4.12 Configuring User Account......................................................................104
Creating User Account..................................................................................................104
Modifying User Account................................................................................................106
Displaying the Information of User Account..................................................................106
4.13 Deleting User Account............................................................................107
5. Configuration Backup and Restore ........................................ 108
5.1 Configuration Restore ............................................................................109
5.2 ADSL IP DSLAM upgrade procedure..................................................... 111
5.3 IP DSLAM rescue procedure while system crashed............................112
6. Troubleshooting.........................................................................116
Problems with Starting up ADSL IP DSLAM.................................................................117
Problems with Configuration.........................................................................................117
Problems with SNMP.................................................................................................... 118
Problems with Telnet ....................................................................................................118
Problems with Password.............................................................................................. 118
Appendix-A: Pin Assignment.............................................................. I
Appendix-B The SNTP timezone abbrivation..................................IV
Appendix-C The Default Setting of ADSL IP DSLAM.....................VII
Glossary............................................................................................VIII
v

List of Figures
Figure 0-1 PPPoE application in Traditional ATM-based ADSL Network.......................3
Figure 0-2 PPPoE application in ADSL IP DSLAM with Ethernet-All-The-Way Network4
Figure 1-1 ADSL IP DSLAM Front View ........................................................................6
Figure 1-2 ADSL IP DSLAM Rear View.........................................................................7
Figure 1-3 ADSL IP DSLAM LED Identification .............................................................7
Figure 2-1 ADSL IP DSLAM Rear Panel Connection ..................................................15
Figure 2-2 ADSL IP DSLAM Front Panel Connections................................................16
vi

List of Tables
Table 1-1 ADSL IP DSLAM LED Description.................................................................8
Table 3-1 Sysinfo field definition ..................................................................................24
Table 3-2 Event log description....................................................................................26
Table 3-3 Create Line Profile Field Definitions.............................................................31
Table 3-4 Create Alarm Profile Field Definitions ..........................................................32
Table 3-5 PVC Configuration Field Definitions.............................................................36
Table 3-6 Physical Layer Info Field Definitions ............................................................42
Table 3-7 Channel Layer Information Field Definitions ................................................43
Table 3-8 Current Phy-Layer PM Information Field Definitions....................................44
Table 3-9 Current Channel-Layer PM Information Field Definitions.............................46
Table 3-10 15 MIN Phy-Layer PM Information Field Definition....................................47
Table 3-11 1-DAY Phy-Layer PM Information Field Definition......................................48
Table 3-12 15 MIN Phy-Layer PM Information Field Definition....................................49
Table 3-13 1 DAY Phy-Layer PM Information Field Definition......................................50
Table 3-14 IGMP Snooping Table Definition ................................................................52
Table 4-1 CLI Command - Action List ..........................................................................56
Table 4-2 CLI Command – Identifier List........................................................................56
Table 4-3 Relation between <action> and <identifier>.................................................57
Table 4-4 CLI Command – Parameter List...................................................................57
Table 4-5 “show event” Field Definition........................................................................62
Table 4-6 Sysinfo field definition ..................................................................................65
Table 4-7 “show portfilter” Filed Definition....................................................................66
Table 4-8 Sysip Field Definition....................................................................................67
Table 4-9 Time Field Definition.....................................................................................68
Table 4-10 “show lineprof” Field Definition...................................................................76
Table 4-11 “show alarmprof” Field Definition................................................................77
Table 4-12 “show port” Field Definition ........................................................................80
Table 4-13 “show adslline” Field Definition ..................................................................81
Table 4-14 Ways of PVC configuration either with VLAN tag or without VLAN tag......82
Table 4-15 “show connection” Field Definition .............................................................84
Table 4-16 “show vid” Field Definition..........................................................................85
Table 4-17 “show subscriber” Field Definition..............................................................85
Table 4-18 “show snmp” Field Definition......................................................................89
Table 4-19 “show trapdest” Field Definition..................................................................90
Table 4-20 “show manip” Field Definition.....................................................................92
Table 4-21 “show adslphysical” Field Definition...........................................................95
Table 4-22 “show adslchannel” Field Definition” ..........................................................96
Table 4-23 “show adslphperf” Field Definition..............................................................97
Table 4-24 “show adslchperf” Field Definition..............................................................99
Table 4-25 “show adslphintl” Field Definition .............................................................100
Table 4-26 “show adslchintl” Field Definition..............................................................101
Table 4-27 “show dhcpd” Field Definition...................................................................103
Table 7-1 Troubleshooting the Start-up your ADSL IP DSLAM.................................. 117
Table 7-2 Troubleshooting the ADSL IP DSLAM configured setting.......................... 117
Table 7-3 Troubleshooting the SNMP server.............................................................118
Table 7-4 Troubleshooting Telnet............................................................................... 118
Table 7-5 Troubleshooting the password...................................................................118
T able A-1 ADSL IP DSLAM CID port pin assignment...................................................I
T able A-2 Null modem cable pin assignment (for PC to CID port connection).............I
T able A-3 ADSL IP DSLAM uplink port pin assignment...............................................I

Introduction
T able A-4 Uplink and downlink port (Xn) pin assignment............................................II
T able A-5 8 ports ADSL LINE Connector pin assignment ...........................................II
T able A-6 8 ports POTS splitter PHONE Connector pin assignment ..........................II
viii

ADSL IP DSLAM
About This Manual
Audience
This book is intended for anyone who installs, manages, and configures the
ADSL IP DSLAM, one product of ADSL IP DSLAM Series, via CID/RS-232 or
Telnet/Ethernet CLI command interface. The ADSL IP DSLAM is a standalone
IP-based DSLAM which can concentrate and manage 8/16 ADSL ports.
You must have a basic understanding of ADSL related technologies, be
knowledgeable about data communications, and familiar with VT-100 terminal
emulation tools.
Purpose
This book describes how to install, manage, and configure the ADSL IP
DSLAM system via CLI command Line interface through CID/RS-232 interface
or Telnet/Ethernet interface.
Organization
This book provides task-based instructions for installing and using the CLI
interface to configure and administrate the ADSL IP DSLAM System. The
manual is organized as follows:
Chapter Title & Description
1
Introduction
Provides an overview of ADSL IP DSLAM System, including
features, fucntions, applications of the ADSL IP DSLAM.
2
Getting Started
Presents platform and system requirements as well as
procedures and instructions for installing the ADSL IP DSLAM.
3
System Administration with EmWeb
Provides all the instructions and procedures necessary for you to
administer your ADSL IP DSLAM with EmWeb interface.
4
System Administration with CLI
Provides all the instructions and procedures necessary for you to
Administer your ADSL IP DSLAM with CLI interface.
5
Configuration Back Up, Restore,Update and Rescue
Provides the procedures to back up configuration settings from
ADSL IP DSLAM and restore to ADSL IP DSLAM. Moreover, the
upade and rescue porcedures are also introduced.
1

6
Troubleshooting
Provides some potential problems and possible remedies and
helps you diagnose and solve the problems.
7
Appendix A
Presents the pin assignment for ADSL IP DSLAM
8
Appendix B
Presents the SNTP time zone abbrivation.
9
Appendix C
Present the deafult settings of ADSL IP DSLAM
9
Glossary
Defines the key terms and acronyms mentioned in this maunal.
Document Conventions
ADSL IP DSLAM
Screen displays use these conventions:
# Login with Administrator privilege
% Login with operator privilege
> Login with guest privilege
Commands descriptions use these conventions:
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional
< > Essential values
< x | y | z > Alternative keywords are grouped in < > and separated by
vertical bars
Others
Note
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions.
2

ADSL IP DSLAM
What’s the difference between ATM based
DSLAM and IP based DSLAM?
Fig 0-1 & Fig 0-2 display the differences between traditional ATM-based
DSLAM and ADSL IP DSLAM in PPPoE application sample.
Figure 0-1 PPPoE application in Traditional ATM-based ADSL Network
As Fig 0-1 displays, in traditional ATM-based ADSL network, the user
application information is encapsulated by ADSL CPE into ATM cells in
pre-defined VC(Virtual Channel, PVC), and then upstream the ATM cells to
DSLAM via ADSL link. (In this example, the user information (PPPoE
encapsulated) is encapsulated by ATU-R using RFC-1483 Bridge-mode
encapsulation format.)
All the ATM cells belong to the specified VC is concentrated by the DSLAM,
and switched in the ATM network clouds, to the defined destination (ISPs,
Offices, ..), at there the ATM cells and PPPoE frames is resolved by the
Broadband Access Server, and the user application information is serviced.
3

ADSL IP DSLAM
Figure 0-2 PPPoE application in ADSL IP DSLAM with Ethernet-All-The-Way
Network
In addition to traditional ATM-based ADSL network. As Fig 0-2 displays, the
user application information is still encapsulated by ADSL CPE into ATM cells
in pre-defined VC (Virtual Channel, PVC), and then upstream the ATM cells to
DSLAM via ADSL link.
In the ADSL IP DSLAM, all the ATM cells belong to the specified VC are
decapsulated back to the original PPPoE encapsulated Ethernet packet (if
VLAN-mode of the specified ADSL port is disabled), or mapped to the
pre-defined Ethernet-VLAN packets (if VLAN-mode of the specified ADSL port
is enabled). ADSL IP DSLAM concentrates all Ethernet-with/without VLAN-tag
packets from 16 ports’ ADSL and uplinks to ISP’s Ethernet-All-The-Way
network. The PPPoE frames will be resolved at Broadband Access Server
(BAS), and the user application information was serviced.
The ADSL IP DSLAM supports ADSL CPE Bridge-mode (RFC-1483 Bridge
mode and router mode). For performance concern, ADSL IP DSLAM will not
act as BRAS to process user application information directly.
ADSL IP DSLAM provides Ethernet-with/without VLAN tag to ATM-PVC
mapping feature for the ISP to isolate user’s data with security and to provide
lots of service enhancement capabilities. ADSL IP DSLAM supports 2 ATM
PVC links for each ADSL CPE.
4

1. Introduction
1.1 General
This chapter will help you understand the function and application of your
ADSL IP DSLAM. It covers
ADSL IP DSLAM
ADSL IP DSLAM Overview
This section describes the overview of your ADSL IP DSLAM. The ADSL IP
DSLAM is cost effective solution for you to complete immediate
implementation of multiple of services in private and public networks.
ADSL IP DSLAM Application
ADSL IP DSLAM can be applied in MTU/MDU/MHU and Ethernet-all-the-way
application.
ADSL IP DSLAM Features
This section describes the features of ADSL IP DSLAM and its specification.
5

ADSL IP DSLAM
1.2 ADSL IP DSLAM Overview
Using the latest ADSL technology, ADSL IP DSLAM offers service providers a
very cost-effective solution for immediate implementation of multiple services
in private and public networks.
ADSL IP DSLAM can concentrate and manage up to 16 ADSL lines. User can
use local RS-232 CID and/or remote TELNET/SNMP to manage the ADSL IP
DSLAM directly
Since the ATM backbone coverage is not so general in the real broadband
network environment. Instead of traditional DSLAM system provides ATM
uplink interface, the ADSL IP DSLAM concentrates 8/16 ports of the ATM over
ADSL traffic which is encapsulated by ADSL CPEs, and maps each user’s
data encapsulated in ATM-PVC to Ethernet-with/without VLAN-tag packet
(depends on the VLAN was enabled or not for the specified ATM ports), and
then uplink to Telco or ISP directly, User can enable VLAN-PVC mapping
capability for each ADSL port independently. The ADSL IP DSLAM acts as
bridge for the ADSL ports without enabling the VLAN-PVC mapping feature.
ADSL IP DSLAM provides both Ethernet-VLAN and non-VLAN to ATM-PVC
mapping feature and bridge mode for the ISP to isolate user’s data with
security and to provide lots of service enhancement capabilities. ADSL IP
DSLAM supports 2 ATM PVC links for each ADSL CPE.
Figure 1-1 ADSL IP DSLAM Front View
As Fig 1-1 displays, in the front view of ADSL IP DSLAM, there are several
LEDs to indicate current system and link status and one 10/100 Mega Ethernet
interface for uplink.
The ADSL IP DSLAM can be managed via SNMP, but each ADSL IP DSLAM
will cost one IP address, and the performance of the ADSL IP DSLAM will be
little affected due to CPU usage for the SNMP agent processing.
As Fig 1-2 displays, in the rear-panel, there is one power adaptor, both -42V ~
-56V DC or 90V ~ 240V AC power module can be selected. There are two DSL
module slots, each module provides 8-port with built-in POTS-splitter ADSL
module, totally 16 ADSL CPE users can be supported in one ADSL IP DSLAM.
CID
Fast Ethernet uplink
for uplink
6

ADSL IP DSLAM
8-port ADSL module
with built-in splitter
Fan
AC power
module
Figure 1-2 ADSL IP DSLAM Rear View
Fig 1-3 displays the LED identification of ADSL IP DSLAM, and Table-1
describes its color definition and status description.
Figure 1-3 ADSL IP DSLAM LED Identification
7
ADSL IP DSLAM
Table 1-1 ADSL IP DSLAM LED Description
<LED ID> Color Description
Power Green Lit when power on
Maint Green Lit when maintance commands were issued
Alarm Green Lit when MJ/MN events happen
Faullt Green Lit when system error is detected
Link Green Lit when Uplink Ethernet interface was connected
Act Green Blink when information is transmitted through uplink
Ethernet interface
ID-0 & ID-1 &
ID-2
ADSL1 –
ADSL16
Note: Do not power off your ADSL IP DSLAM when LEDs “MAINT”,
“ALARM” and “FAULT” are blinking simultaneously.
Green ID0, ID1,ID2 : off off off ------when power on
Green/
Blinking
Orange/
No light/
Red
Lit Solid Green when ADSL link is in active state;
Lit Blinking Orange when the specified ADSL link is
in connection training state;
LED off when ADSL link is not in service
Lit Solid Red when loss of signal occurs
8
ADSL IP DSLAM
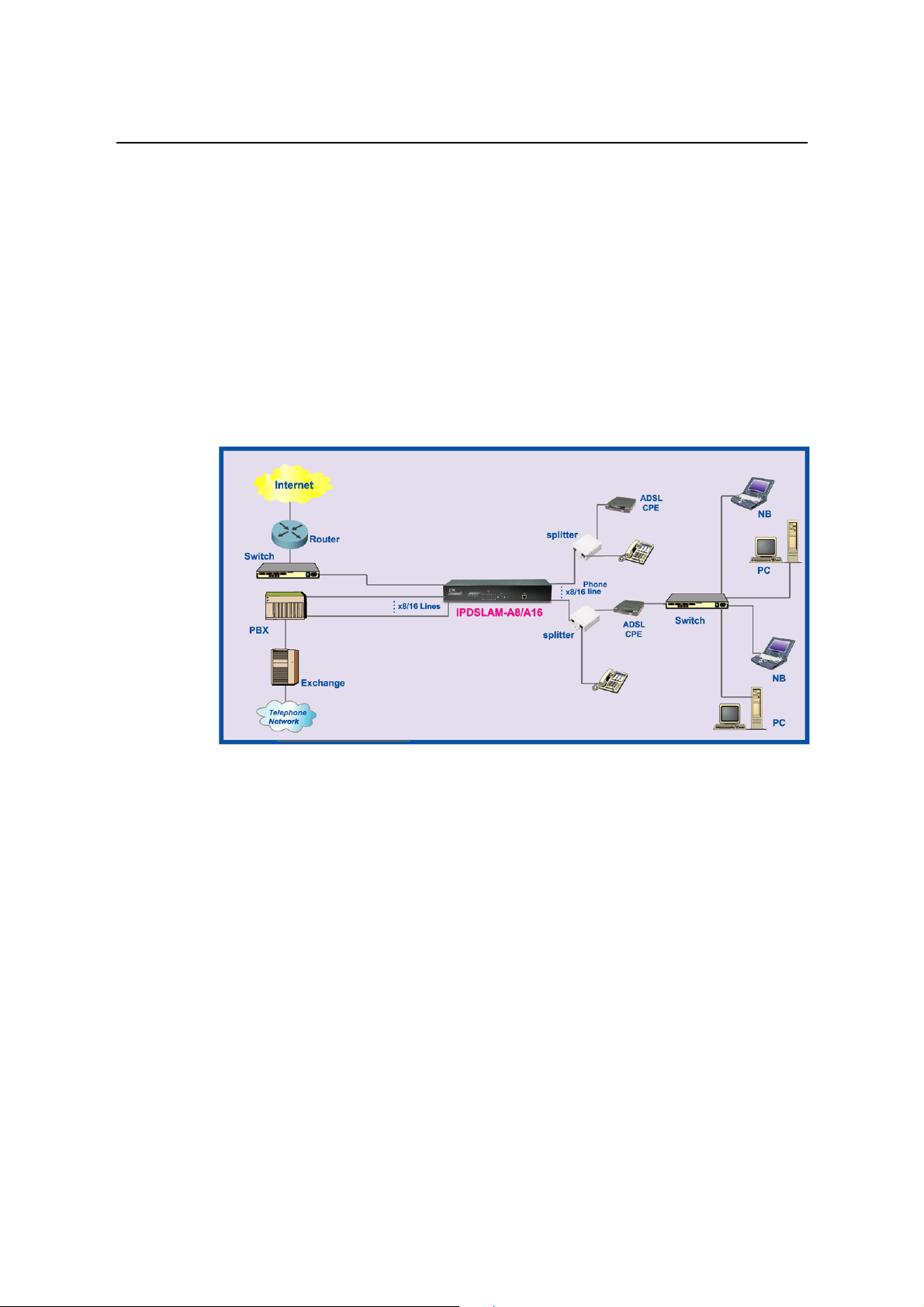
1.3 ADSL IP DSLAM Application
As the following figure shown, ADSL IP DSLAM consists of two network
modules. Each network module provides eight ADSL ports with built-in POTS
splitters so that it provides broadband data service over existing copper wires
without affecting the conventional voice service. ADSL IP DSLAM, therefore, is
a perfect solution for both central office co-location and MTU/MHU markets.
9

ADSL IP DSLAM
1.4 ADSL IP DSLAM Features
VLAN support
The ADSL IP DSLAM supports mapping of Ethernet-VLAN to ATM-PVC
feature for security concern.
Compact design for limited space
The ADSL IP DSLAM occupies 1.5 U of standard Telco rack space. Its
compactness is perfect for collocation and basement installation. With the
built-in POTS splitters, service providers even no need to allocate extra space
for POTS splitter shelves.
Standalone System Design
For the area of less than 16 subscribers, network designer can use ADSL IP
DSLAM to provide service directly.
10

ADSL IP DSLAM
1.5 ADSL IP DSLAM Specifications
11

2. Getting Started
2.1 General
This chapter provides the installation instruction for the hardware installation
and system configuration of your ADSL IP DSLAM so that you can start up
quickly. It includes the following sections:
ADSL IP DSLAM
2
Unpacking your ADSL IP DSLAM
This section describes how to unpacking your ADSL IP DSLAM, and part
number explanation.
Hardware Installation
This section describes the power connection, loop connection and CID
connection.
Ways of management connection
This section describes how to engage in management connection by EmWeb,
CLI and Telnet.
12

ADSL IP DSLAM
2.2 Unpacking your ADSL IP DSLAM
This section describes how to unpack your ADSL IP DSLAM. For a box of
ADSL IP DSLAM, there may contain the following materials:
1. ADSL IP DSLAM
2. Mounting bracket package
3. RJ-45 Ethernet cable
4. Power cord (AC power module only)
5. RS 232 cable to facilitate the connection between CID and PC
6. CD including user manaul and Quick Start Guide
7. A copy of Quick Start Guide
8. Accessory package
¾ Any other accessories requested at time of ordering.
Check the contents of the package and inspect the unit for any signs of
damage. Report any defects to vendor’s customer service representative.
Retain all packing materials for future shipment.
13

ADSL IP DSLAM
2.3 Hardware Installation
• The ADSL IP DSLAM can be installed in a standard 19-inch rack, by using
the mounting brackets provided.
• Mount the shelf on the rack using the large screws provided.
• Follows the following procedures to connect and wire the system.
Safety Instruction
The following is the safety instructions for ADSL IP DSLAM before installation:
1. Read and follows all warning notices and instructions of this user manual.
2. The maximum recommended operating temperature for the ADSL IP
DSLAM is 50ºC. Care must be taken to allow sufficient air circulation or space
between units when the ADSL IP DSLAM is installed inside a closed rack
assembly and racks should safely support the combined weight of all ADSL IP
DSLAM.
3. The connections and equipment that supply power to the ADSL IP DSLAM
should be capable of operating safely with the maximum power requirements
of the ADSL IP DSLAM. In the event of a power overload, the supply circuits
and supply wiring should not become hazardous.
4. The AC adapter must plug in to the right supply voltage. Make sure that the
supplied AC voltage is correct and stable. If the input AC voltage is over 10%
lower than the standard may cause the ADSL IP DSLAM to malfunction.
5. Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord of the AC adapter, and do
not locate the product where anyone can walk on the power cord.
6. Generally, when installed after the final configuration, the product must
comply with the applicable safety standards and regulatory requirements of the
country in which it is installed. If necessary, consult for technical support.
7. A rare condition can create a voltage potential between the earth grounds of
two or more buildings. If products installed in separate building are
interconnected, the voltage potential can cause a hazardous condition.
Consult a qualified electrical consultant to determine whether or not this
phenomenon exists and, if necessary, implement corrective action before
interconnecting the products. If the equipment is to be used with
telecommunications circuit, take the following precautions:
14

ADSL IP DSLAM
• Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
• Never install telephone jacks in wet location unless the jack is specially
designed for wet location.
• Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone
line has been disconnected at the network interface.
• Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines (other than a
cordless telephone) during an electrical storm. There is a remote risk of electric
shock from lightning.
• Do not use a telephone or other equipment connected to telephone lines to
report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
ADSL IP DSLAM Rear Panel Connection
The following figure shows the rear panel connection of ADSL IP DSLAM:
Figure 2-1 ADSL IP DSLAM Rear Panel Connection
Step 1: Ground the ADSL IP DSLAM by connecting a grounded wire
Step 2: Connect the ADSL line connector, a 50-pin centronic connector, of
ADSL IP DSLAM to CPE by using telco cable. Each line connector supports 8
ports of ADSL for Data path from MDF(Main Distribution Frame).
Step 3: Connect the phone connector, a 50-pin centronic connector, of ADSL
IP DSLAM to Exchange/PBX by using telco cable. phone connector is an
optional module supporting Voice path to Exchange/PBX; it must be along with
Line Connector.
Step 4: Connect the power adapter and plug it into an outlet.
15

ADSL IP DSLAM
ADSL IP DSLAM Front Panel Connection
Connect the uplink port of ADSL IP DSLAM to internet by using the RJ-45
cable, and Connect the CID port to the console terminal by using the RS-232
cable(Null modem cable) in order to Administer your ADSL IP DSLAM
through CLI.
UplinkConsole
Console Terminal
For Manufacture
Maintenance Only
Figure 2-2 ADSL IP DSLAM Front Panel Connections
Note: Please refer to Appendix A: pin assignment of telco cable, RJ-45 and
RS-232 cable.
16

ADSL IP DSLAM
2.4 Ways of Management Connection
This section will tell you how to connect and manage your ADSL IP DSLAM
through EmWeb, CLI and EMS.
Embedded Web Interface(EmWeb)
The embedded Web Interface (EmWeb), comprised of HTML files, is more
user- friendly than CLI for your configuring ADSL IP DSLAM. The HTML files
embedded in ADSL IP DSLAM are dynamically linked to the system’s
functional command sets. You can access the EmWeb from any Web Browser.
Following the following procedure to connect the embedded Web management
interface:
1. Establish a connection to the internet
2. Open the Web browser
3. Enter the IP address of the ADSL IP DSLAM (Default IP:
192.168.100.111)
4. Log in as usual. (User account: Admin; Password: Admin)
To access any menu item on EmWeb, simply click on the item you want. The
corresponding work screen will then appear on the right side frame. By
pressing the Apply button will allow you to achieve your configuration,
whereas pressing Cancel button will clear all your changes without applying
them. In some menus, there will be Modify item will allow you to modify the
existing configuration.
Command Line Interface (CLI)
The Command Line Interface is the most primary character based
configuration interface. Some of configurations not provided in EmWeb can be
configured through CLI. You can access CLI from the terminal emulation
software.
The procedure of connecting to the CLI is as follows:
1. Start up the terminal emulation software on the management station.
If necessary, reconfigure the terminal-emulation software to match the
17

switch console port settings.
2. Enter Admin when prompted for a user name and password. The ADSL IP
Telnet Client
ADSL IP DSLAM supports only one Telnet client that you can use to connect
with. Telnet provides a simple terminal emulation that allows you to see and
interact with the CLI of ADSL IP DSLAM. As with any remote connection, the
network interface IP address for the ADSL IP DSLAM must be established.
ADSL IP DSLAM
Bits per second 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
DSLAM prompt appears when you have logged in to the management
interface successfully.
Note: as to the default setting of ADSL IP DSLAM, please refer to the
Appendix-C.
18

ADSL IP DSLAM
3. System Administration with EmWeb
This chapter provides all the instruction and procedure necessary for you to
administer your ADSL IP DSLAM with EmWeb interface.
3.1 Log In with Embedded Web Interface
3
This section describes how to log into Embedded Web Interface.
Open a web browser with the default IP address: http://192.168.100.111
The log in screen appears as follows:
1. Enter your user name. If it is an initial installation, enter Admin for user
name.
2. Enter your password. If it is an initial installation, enter Admin for
password.
Note: For safety concern, it is recommended to change the password. For
changing the password, go to the Changing Password in the System
menu. See page 30.
19

ADSL IP DSLAM
3.2 Embedded Web Interface Menu
This section describes the overview of the embedded Web interface menu,
EmWeb. After your successfully logging into the EmWeb, the screen will
appears as follows:
Default Setting
Display the information of default (factory) setting of your ADSL IP DSLAM.
See page 23.
System Information
Display the system time, system up time, system up period of your ADSL IP
DSLAM. It also provides you with the information of software version,
hardware version. See page 24.
Save to Flash
Allow you to save your configuration in Flash. See page 25.
Current Event
Allow you to view the alarm and event status of your ADSL IP DSLAM. See
page 26.
System
Set Port Filter: Allow you configure the port filtering function. See page
28.
System IP / Location: Allow you to configure the IP address and location
of your ADSL IP DSLAM. See page 29.
System Date and Time: Allow you to configure the SNTP status, Time
zone, date and time of your ADSL IP DSLAM. See page 30.
20

ADSL IP DSLAM
Changing Password: Allow you to change your password. See page 30.
DSL Profile Configuration
Create Line Profile: Allow you to create ADSL line profile. See page 31.
Create Alarm Profile: Allow you to create ADSL alarm profile. See page
31.
Current Line Profile: Allow you to view, modify, or delete existing ADSL
line profiles. See page 33.
Current Alarm Profile: Allow you to view, modify, or delete existing ADSL
alarm profiles. See page 34.
Port Configuration
DSL Port configuration: Allow you to display, modify and delete the
status of the port. It provides the configuration of a port’s status. See page
35.
PVC Configuration: Allow you to configure PVC and VID on a port and
set the priority. It also provides the modification and delete function. See
page 36.
List of Subscriber: Allow you to view the existing information of
subscribers and modify them. See page 38.
Routing Table: allow you to configure the routing table. See page 39.
Management
SNMP: Allow you to configure SNMP access parameters and trap IPs. See
page 41.
Management IP: Allow you to configure the management IPs so that only
with those configured management IPs can access to your ADSL IP
DSLAM remotely. See page 41.
DSL Port Performance
Physical Layer Info: Allow you to view the performance information on
physical layer by specifying the definite unit. See page 42.
Channel Layer Info: Allow you to view the performance information on
channel layer by specifying the definite unit. See page 43.
Current Phy-Layer PM: Allow you to view the physical layer performance
collected within current 15 minutes and a day duration. See page 44.
Current Channel-Layer PM: Allow you to view the channel layer
21

ADSL IP DSLAM
performance collected within current 15 minutes and a day duration. See
page 46.
15 MIN Phy-Layer PM: Allow you to view the physical layer performance
during previous 15 minutes interval. See page 47.
1 DAY Phy-Layer PM: Allow you to view the physical layer performance
during previous 1 day interval. See page 48.
15 MIN Channel-Layer PM: Allow you to view the channel layer
performance during previous 15 minutes interval. See page 49.
1 DAY Channel-Layer PM: Allow you to view the channel layer
performance during previous 1 day interval. See page 50.
Miscellanea
IGMP Snooping Config: Allow you to configure the IGMP Snooping. See
page 51.
IGMP Snooping Status: allow you to view IGMP snooping status. See
page 51.
22
 Loading...
Loading...