Page 1
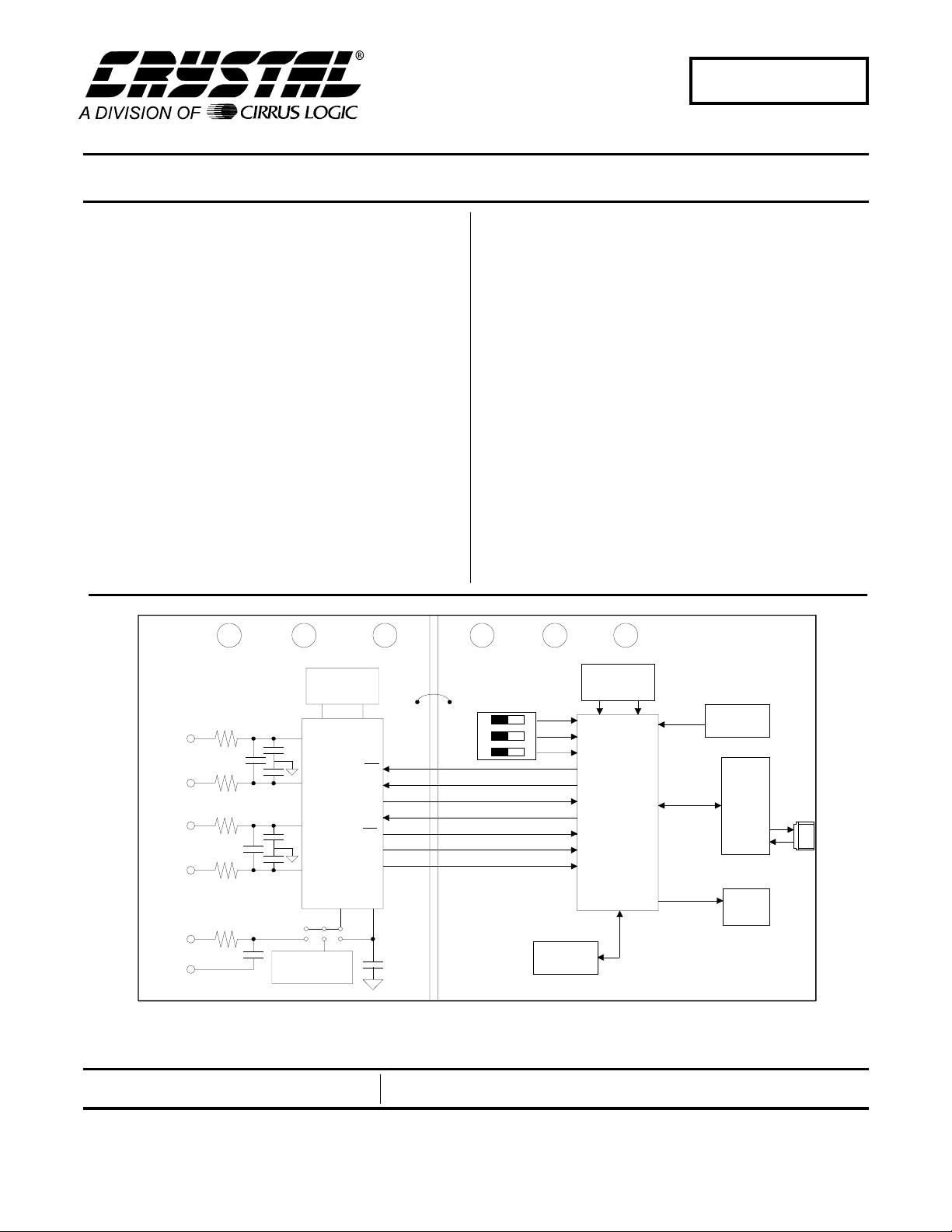
CDB5460
CDB5460 Evaluation Board and Software
Features
lDirect Shunt Sensor and Current
Transformer Interface
lRS-232 Serial Communication with PC
lOn-board 80C51 Microco nt r oller
lOn-board Voltage Reference
lLab Windows/CVI
-Register Setup & Chip Control
-FFT Analysis
-Time Domain Analysis
-Noise Histogram Analysis
lOn-board Data SRAM
lIntegrated RS-232 Test Mode
VIN+
TM
Evaluation Software
AGND
CRYSTAL
4.096 MHz
General Description
The CDB5460 is an inexpensive tool des igned to eval uate the functionality and performance of the CS5460.
The CS5460 Data Sheet is required in conjunction with
the CDB5460 evaluation board.
The evaluation board includes an LT1019 v oltage r eference, an 80C51 microcontroller, an RS 232 transceiver,
and firmware. The 8051 controls the ser ial communication between the evaluation board and the PC via the
firmware, enabling quick and easy acces s to all of the
CS5460’s registers and functions .
The CDB5460 includes software for Data Capture, Time
Domain Analysis, Histogram Analysis, and Frequency
Domain Analysis.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CDB5460 Evaluation Board
DGND
TEST
SWITCHES
VD+
Vu+VA-VA+
CRYSTAL
20.0 MHz
RESET
CIRCUITRY
VIN-
IIN+
IIN-
REF
AGND
CS5460
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
EOUT
VREF
Preliminary Product Information
Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Crystal Semiconductor Products Division
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.crystal.com
CS
SDI
SDO
SCLK
INT
EDIR
OUTIN
32k × 8
SRAM
80C51
Microcontroller
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 1999
(All Rights Reserved)
RS232
TRANSCEIVER
CONNECTOR
LEDs
RS232
MAR ‘99
DS279DB1
1
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART I: HARDWARE ..........................................................................................3
Introduction .............. ................................................................. .................. 3
Evaluation Board Overview ........................................................................ 3
Analog Section .....................................................................................3
Digital Section ...................................................................................... 3
Power Supply Section ..........................................................................9
Using the Evaluation Board ........................................................................ 9
PART II: SOFTWARE ........................................................................................ 10
Installation Procedure ............................................................................... 10
Using the Software ...................................................................................10
Selecting and Testing a COM Port ........................................................... 11
Register Access in the Setup Window ......................... ...... ....... ................11
Conversion Window .................................................................................. 12
Viewing Pulse Rate Output Data .............................................................. 13
Data Collection Window Overview ............................................................ 13
Config Window .......................................................................................... 14
Collecting Data Sets ....................................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ................14
Retrieving Saved Data From a File ........................................................... 15
Analyzing Data .......................................................................................... 15
Histogram Information ..............................................................................15
Frequency Domain Information ................................................................15
Time Domain Information .........................................................................16
PCB LAYOUT ....................................................................................................20
CDB5460
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/
IBM, AT and PS/2 are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Lab Windows and CVI are trademarks of National Instruments.
TM
SPI
is a trademark of Motorola.
TM
Microwire
Preliminary product info rmation describes products which are i n p r od ucti on, b ut for which full characterizat i on da t a i s not yet available. Advance product i nfor-
mation describes products which are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. has made best efforts to ensure that the information
contained in this document is accurate and reli able. However , the i nformati on is sub ject to change with out no tice and i s provi ded “AS IS” withou t warranty of
any kind (express or implied). No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other rig ht s
of third parties. This document i s the propert y of Cirru s Logic, Inc. and implie s no licen se under patent s, copyri ghts, trademarks, or tr ade secrets. No part of
this publication may be copied, reproduced , stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or
otherwise) without the pri or wri tt en consen t of Ci rrus Logic, Inc. Items from any Cirrus Logic websi t e or di sk may be pri nted for use by the user. However, no
part of the printout or electronic files may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical,
photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore, no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture
or sale of any items without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing
in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners which may be registered in some jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
2 DS279DB1
is a trademark of National Semiconductor.
Page 3

CDB5460
PART I: HARDWARE
Introduction
The CDB5460 evaluation board provides a quick
means of evaluating the CS5460 Analog-to-Digital
Converters (ADCs) and Computational Unit. The
CDB5460 evaluation board’s analog section operates from either a single +5 V or dual ±2.5 V power
supply. The evaluation board interfaces the
CS5460 to an IBMTM compatible PC via an RS232 interface. To accomplish this, the board comes
equipped with an 80C51 microcontroller and a 9pin RS-232 cable which physically interfaces the
evaluation board to the PC. Additionally, analysis
software provides easy access to the internal registers of the CS5460, and provides a means to display
the performance in the time domain or frequency
domain.
Evaluation Board Overview
The 3 dB corner of the filter is approximately 50K
Hz differential and common mode.
The evaluation board provides three voltage reference options, on-chip, on-board and external, as
shown in Figure 2. Table 1 illustrates the options
available. With HDR4’s jumpers in position REFOUT, the on-chip reference provides 2.5 volts.
With HDR4’s jumpers in position LT1019, the
LT1019 provides 2.5 volts (the LT1019 was chosen
for its low drift, typically 5ppm/°C). By setting
HDR4’s jumpers to position REF+, the user can
supply an external voltage reference to J2’s REF+
and VA- inputs. Application Note 4 on the web
(http://www.cirrus.com/products//pubs.html) details various voltage references.
Reference Description HDR4
LT1019
Selects on board
LT1019 Reference
(5ppm/
°C)
O O LT1019
O O REF+
O O REFOUT
The board is partitioned into two main sections: analog and digital. The analog section consists of the
CS5460 and a precision voltage reference. The digital section consists of the 80C51 microcontroller,
32 Kilobytes of SRAM, the hardware test switches,
the reset circuitry, and the RS-232 interface. The
board also has a user friendly power supply connection.
Analog Section
The CS5460 is designed to accurately measure and
calculate: Energy, Instantaneous Power, I
V
while operating from a 4.096 MHz crystal.
RMS
As shown in Figure 1 there are four BNC connectors (J9, J10, J11, J12) provided for converter input
connections. A Shunt Sensor or Current Trans-
former can be connected to the conver ter’s curr ent
inputs via J10 (IIN+) and J9 (IIN-). A voltage divider can be connected to the converter’s voltage
input via J12 (VIN+) and (J11) (VIN-). Note, a
simple RC network filters the sensor’s output to reduce any interference picked up by the input leads.
RMS
, and
REF+
REFOUT
Selects external
reference
Selects the reference
supplied by CS5460
Table 1. Reference Selection
O O LT1019
O O REF+
O O REFOUT
O O LT1019
O O REF+
O O REFOUT
The CS5460 serial interfaces are SPITM and MicrowireTM compatible. The interface control lines
(CS, SDI, SDO, and SCLK) are connected to the
80C51 microcontroller via port one. To interface an
external microcontroller, these control lines are
also connected to HDR6 (Header 6). However to
accomplish this, the evaluation board must be modified in one of three ways: 1) cut the interface control traces going to the microcontroller, 2) remove
resistors R4, R7, R8, and R13, or 3) remove the microcontroller.
Digital Section
Figures 3 and 4 illustrate the schematic of the digital section. It contains the microcontroller, test
DS279DB1 3
Page 4

4 DS279DB1
HDR2X2
TP34
TP35
TP39
TP40
AGND
AGND
AGND
AGND
HDR1
12
34
HDR2X2
HDR2
21
43
HDR2X2
HDR8
21
43
HDR2X2
HDR9
12
34
AGND
AGND
AGND
AGND
C32
.01UF
COG
C33
.01UF
COG
C34
.01UF
COG
C35
.01UF
COG
VIN+
VIN-
IIN+
IIN-
AGND
J12
BNC_RA
J11
BNC_RA
J10
BNC_RA
J9
BNC_RA
R17 301
R18 301
0.1%
0.1%
301R25
0.1%
301R26
0.1%
C2
4700PF
COG
C3
4700PF
COG
D+
C30
10UF
DGND
XOUT
C15
.1UF
CPUCLK
VREFOUT
VREFIN
4.0960MHZ
C38
10PF
COG
DGND
XOUT
SCLK
SDO
/CS
VIN+
VIN-
Y2
U3
1
TP135
TP145
TP147
TP153
TP155
TP157
TP134
TP136TP137
TP138TP139
TP140TP141
TP142TP143
TP144
TP146
TP148TP149
TP150TP151
TP152
TP154
TP156
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
XOUT
CPUCLK
VD+
DGND
SCLK
SDO
/CS
NC
VIN+
VINVREFOUT
/EDIR
/EOUT
/INT
/RESET
PFMON
IIN+
IIN-
AGNDVREFIN
CS5460_EP
XIN
C39
10PF
COG
HDR2X2
HDR10
21
43
DGND
CPUCLK
/CS
SDI
SDO
SCLK
/INT
/EDIR
/EOUT
/RESET
DGND
Figure 1. Analog Schematic Part 1
XIN
SDI
VA+
24
TP111
23
TP113
22
TP115
21
TP117
20
TP119
19
TP121
18
NC
17
16
TP127
15
TP129
14
1312
TP133
HDR11X2
HDR6
TP110
XIN
TP112
SDI
TP114
/EDIR
TP116
/EOUT
TP118
/INT
TP120
/RESET
TP122TP123
TP124TP125
PFMON
TP126
IIN+
TP128
IIN-
TP130TP131
TP132
C14
.1UF
21
XTAL1
43
65
87
109
1211
1413
1615
1817
2019
2221
DCLK
DGND
PFMON
VA+
C29
10UF
A-
JP2
VA+
AGND
R19
10K
R28
15K
CDB5460
Page 5
DS279DB1 5
VA+
2
C20
.1UF
A- A-
J2
REF+
A-
1
2
TERM_BLOCK
D+
10K
URESET /RESET
U4
LT1019CN8_2P5
OUTIN
TRIM
HTR
TEMP
GND
4
A-
R21 301
0.1%
A-
DGND
UCS
R12
USDI
USCLK
UDCLK
DGND
6
5
7
3
R31
U9
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/G1
/G2
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
VCC
GND
TC74VHC541FW
R30
10K
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
R24
10K
49.9
A-
C1
.1UF
A- A-
20
18
/CS
17
SDI
16
SCLK
15
DCLK
14
13
12
11
10
DGND
VREFOUT
.1UF
DGND
C44
C16
.1UF
HDR3X2
HDR4
21
43
VREFIN
65
C40
.1UF
D+
1
1/G
2
SDO
/INT
/EDIR
/EOUT
XTAL1
1A1
4
1A2
6
1A3
8
1A4
19
2/G
11
2A1
13
2A2
15
2A3
17
2A4
SN74HCT244N
DGND
Figure 2. Analog Schematic Part 2
U8
VCC
1Y1
1Y2
1Y3
1Y4
2Y1
2Y2
2Y3
2Y4
GND
20
18
16
14
12
10
USDO
UINT
UEDIR
UEOUT
JP1
9
7
5
3
UXTAL1
DGND
VDDD
C41
.1UF
CDB5460
DGND
Page 6

6 DS279DB1
20.000 MHZ
Y1
VDDD
URESET
1N4148
R9
R29
BYPASS CAP
D4
750K
DGND
200
C18
.1UF
JP4
NRST
SN74HC00N
SW_B3W_1100
DGND
RESET
S2
C19
.1UF
1
2
U2
VCC
GND
VDDD
DGND
DGND
TP33
TP32
TP31
TP30
TP11
TP10
TP9
TP8
UXTAL1
UM1
8751-8
19
XTAL1
18
XTAL2
31
EA
9
RST
1
1.0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1.7
8-BIT MICRO
PORT1
#
8751
PSEN
ALE
PROG
P0.0
PORT0
AD
P0.7
P2.0
PORT2
A
P2.7
P3.0/RXD
P3.1/TXD
P3.2/\INT0
P3.3/\INT1
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
P3.6/\WR
P3.7/\RD
TP14
29
30
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
TP15
TP38
TP23
TP24
TP29
TP28
TP27
TP26
TP25
TP69
TP1
TP2
TP3
TP4
TP5
TP6
TP7
FROM RS-232
TP43
TO RS-232
TP42
TP16
TP17
TP18
TP19
TP20
TP21
DGND
R1
R2
R3
DGND
TP22
200
200
200
200
200
DGND
R11
5.11K
C23
33PF
COG
C24
33PF
COG
DGND
14
3
7
USCLK
UDCLK
S1
OPEN
SW_DIP_3
USDI
USDO
UCS
3
2
1
R13
R16
R4
R7
R8
R10
5.11K
DGND
D2
1
2
3
8
7
6
54
LED_555_5003
C7
47UF
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P2.4
P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
ALE
200
200
200
VDDD
DGND
C17
.1UF
HDR2X2
HDR7
21
43
P3.2
UINT
UEDIR
UEOUT
P3.6
P3.7
CDB5460
Figure 3. Digital Schematic Part 1
Page 7
DS279DB1 7
U6
VCC
/W
A13
A8
A9
A11
/G
A10
/E
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
SN74HC00N
9
10
1
C2+
2
GND
3
C2-
4
VSS
5
RX1
6
TX1
7
RX2
8
TX2
9
RX3
TX3
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
1514
U2
TP12
TP13
P3.6
P2.5
P2.0
P2.1
P2.3
P3.7
P2.2
P0.7
P0.6
P0.5
P0.4
P0.3
8
C27
10UF
10UF
FROM-PC
TO-PC
P2.6
C28
DGND
DGND
VDDDP2.6
C43
.1UF
U2
SN74HC00N
12
13
U2
SN74HC00N
4
5
DGND
DGND
11
6
5
9
4
8
3
7
2
6
1
DE9F_RA
CSUSBP2.7
J8
CDB5460
ALE
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
DGND
1
/OC
11
C
3
1D
4
2D
7
3D
8
4D
13
5D
14
6D 6Q
17
7D
18
8D
SN74HC373N
U5
VCC
GND
1Q
2Q
3Q
4Q
5Q
7Q
8Q
2
5
6
9
12
15
16
19
20
10
C26
10UF
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
DGND
P2.4
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
10UF
DGND
C42
.1UF
C25
R1410K
1
A14
2
A12
3
A7
4
A6
5
A5
6
A4
7
A3
8
A2
9
A1
10
A0
11
DQ0
12
DQ1
13
DQ2
VSS
MCM6206DP20
VDDD
VDDD
20
19
18
17
16
TP71
15
TP72
14
13
12
11 10
U1
C1+
VCC
C1-
VDD
DO1
DI1
DO2
DI2
DO3
DI3
MC145407P
Figure 4. Digital Schematic Part 2
Page 8

8 DS279DB1
VA-
CON_BANANA
J3
DGND AGND
CON_BANANA
J14
Z1
P6KE6V8P
DGND
Vu+
CON_BANANA
J4
Z2
P6KE6V8P
DGND
CON_BANANA
J6
AGND
47UF
C5
C6
47UF
HDR3X2
HDR3
21
A-
.1UF
C10
AGNDAGNDAGND
C12
.1UF
AGND
43
65
DGND
DGNDDGND
VD+
CON_BANANA
J13
VA+
CON_BANANA
J5
Z4
P6KE6V8P
C11
47UF
C21
.1UF
DGND
VA+
AGND
Z3
P6KE6V8P
AGND
C8
47UF
AGND
C13
.1UF
Figure 5. Power Supply Schematic
R15
FERRITE_BEAD
10
HDR4X2
HDR5
21
43
L2
65
87
VDDD
D+
CDB5460
Page 9

CDB5460
Power Supplies Power Post Connections Jumpers
Analog Digital VA+ VA- AGND DGND VD+ Vu+ HDR5 HDR3
+5V +5V +5 NC GND GND +5 NC
+5V +3V +5 NC GND GND +3 +5
±2.5V
switches, a Motorola MC145407 interface chip,
and 32K bytes of SRAM. The test switches aid in
debugging communication problems between the
CDB5460 and the PC. The microcontroller derives
its clock from an 20.0 MHz crystal. From this, the
controller is configured to communicate via RS232 at 9600 baud, no parity, 8-bit data, and 1 stop
bit.
Power Supply Section
+3V +2.5 -2.5 NC GND +3 +5
Table 2. Power Su pply Connections
Using the Evaluation Board
The CS5460 is a highly integrated device, containing dual ADCs with a computational unit. The
CS5460 and CDB5460 data sheets should be read
thoroughly and understood before using the
CDB5460 evaluation board. The CS5460 contains
a programmable gain amplifier (PGA), two ∆Σ
modulators, two high rate filters, an on-chip reference, and power calculation engine to compute Energy, V
Figure 5 illustrates the power supply connections to
the evaluation board. The VA+ post supplies the
positive analog section of the evaluation board, the
LT1019 and the ADC. The VA- post supplies the
negative analog voltage circuitry. Note, this terminal is grounded when powering the CDB5460 from
a single +5 Volt analog supply. The VD+ post supplies the digital section of the ADC and level
shifter. The Vu+ post supplies the digital section of
the evaluation board, the 80C51, the reset circuitry,
and the RS-232 interface circuitry. Note, the
board’s digital section supplied via Vu+ post, must
be +5Volts only. Table 2 shows the varies power
connections with the required jumper setting on
HDR3 and HDR5.
PGA sets the input levels of the current channel at
either 30 mV
2.5 V). The on-chip reference can provide the necessary 2.5 V reference. This output (VREFOUT),
along with a 10 µF capacitor, is used to supply the
VREFIN pin with 2.5 V. The ∆Σ modulators and
high rate digital filter allows the user to measure instantaneous voltage, current, and power at a output
word rate of 4000 Hz when a 4.096 MHz clock
source is used. Table 3 describes the varies headers,
jumpers and DIP switches on the CDB5460 evaluation board. DIP switch S1 is used to control the
80C51. Table 4 illustrates the varies setting of the
DIP Switch S1. Note, S1-3 is a no connect and not
used. The S1-1 switch should be set to the OPEN
position for normal operation. When testing the
RS-232 link in the PC software, close S1-1. The
RMS
, I
RMS
RMS
O O VDDD
Vu+
O O VDDD
VD+
O O V+
VD+
O O V+
VA+
O O VDDD
Vu+
O O VDDD
VD+
O O V+
VD+
O O V+
VA+
O O VDDD
Vu+
O O VDDD
VD+
O O V+
VD+
O O V+
VA+
VA-
A-
AGND
VA-
A-
AGND
VA-
A-
AGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
O O DGND
, and Instantaneous Power. The
or 150 mV
(for VREFIN =
RMS
DS279DB1 9
Page 10

CDB5460
Name Function Description Default Setting Default Jumpers
HDR1
HDR2
HDR3
HDR4
HDR5
Used to switch VIN+ on the CS5460 between J12
and AGND.
Used to switch VIN- on the CS5460 between J11
and AGND.
Used to switch VA-, A-, and AGND to DGND.Refer
to Table 2
Used to switch the VREFIN from external J2
header, to the on board LT1019 reference, or to the
on-chip reference VREFOUT. Refer to Table 1
Used to switch VU+, VD+, and VA+ to VDDD and/or
V+. Refer to Table 2
VIN+ Set to BNC J12
VIN- Set to BNC J11
Negative Analog
Power Supply Set to
0 V
VREFIN Set to on-
chip reference
VREFOUT
Digital Power Supply
Set to +5V
O O VIN+
O O AGND
O O VINO O AGND
VA-
O O DGND
A-
O O DGND
O O DGND
AGND
O O LT1019
O O REF+
O O REFOUT
O O VDDD
Vu+
O O VDDD
VD+
O O V+
VD+
O O V+
VA+
HDR6 Used to connect an external micro-controller. Connected to 80C51 NC
HDR7
HDR8
Used in conjunction with the self test modes to test
the UART/RS-232 communication link between the
microcontroller and a PC.
Used to switch IIN+ on the CS5460 between J10
and AGND.
RS-232 Set to Normal
Mode
IIN+ Set to BNC J10
O O
O O
O O IIN+
O O AGND
HDR7
HDR9
HDR10
JP2
Used to switch IIN- on the CS5460 between J9 and
AGND.
Used to switch XIN on the CS5460 to HDR6 when
an extrenal micro-controller is used.
Used to connect PFMON pin on the CS5460 to
monitor Power Supply VA+
JP4 Used to connect the RESET Button to the CS5460
DIP switch to control 80C51
S1
S1-1 is used to select RS-232 test mode
S1-2 is used to select crystal to 80C51
Table 3. Header, Jumper, DIP Switch Descriptions
IIN- Set to BNC J11
XIN Set for on-board
4.096 MHz XTAL
PFMON Set Monitor
VA+
RESET Set not con-
nected to CS5460
S1-1 Set Normal
S1-2 Set 20 MHz
O O IINO O AGND
O O DGND
O O XIN
O O JP2
O O JP4
1 23
OPEN
10 DS279DB1
Page 11

CDB5460
1 23
OPEN
1 23
OPEN
1 23
OPEN
1 23
OPEN
80C51 Mode S1
80C51 is in Normal Operating Mode
S1-1 OPEN
S1-2 CLOSED 20 MHz Crystal
80C51 is in Normal Operation Mode
S1-1 OPEN
S1-2 OPEN 11.059 MHz Crystal
80C51 is in Test Mode
S1-1 CLOSED
S1-2 CLOSED 20 MHz Crystal
80C51 is in Test Mode
S1-1 CLOSED
S1-2 OPEN 11.059 MHz Crystal
Table 4. DIP Switch S1 Setting
S1-2 switch selects the crystal source for the
80C51. There are two crystal options available,
11.059 MHz and 20 MHz. If S1-2 is OPEN the
11.059 MHz crystal is selected, and when S1-2 is
CLOSED the 20 MHz crystal is selected.
PART II: SOFTWARE
Installation Procedure
1) Turn on the PC, running Windows 95TM or
later.
2) Insert the Installation Diskett e #1 into the PC.
3) Select the Run option from the Start menu.
4) At the prompt, type: A:\SETUP.EXE
<enter>.
5) The program will begin installation.
6) If it has not already been installed on the PC,
the user will be prompted to enter the directory in which to install the CVI Run-Time
EngineTM. The Run-Time EngineTM manages
executables created with Lab Windows/CVITM. If the default directory is
acceptable, select OK and the Run-Time
EngineTM will be installed there.
7) After the Run-Time EngineTM is installed, the
user is prompted to enter the directory in
which to install the CDB5460 software.
Select OK to accept the default directory.
8) Once the program is installed, it can be run by
double clicking on the Eval5460 icon, or
through the Start menu.
The evaluation board comes with software and an
RS-232 cable to link the evaluation board to the
PC. The evaluation software was developed with
Lab Windows/CVITM, a software development
package from National Instruments. The software
was designed to run under Windows 95TM or later,
Note: The software is written to run with 640 x 480 resolution; however, it will work with 1024 x 768 resolution.
If the user interface seems to be a little small, the user
might consider setting the display settings to 640 x 480.
(640x480 was chosen to accommodate a variety of
computers).
Using the Software
and requires about 3MB of hard drive space (2MB
for the CVI Run-Time EngineTM, and 1MB for the
evaluation software). After installing the software,
read the readme.txt file for any last minute updates
or changes. More sophisticated analysis software
can be developed by purchasing the development
package from National Instruments (512-794-
0100).
Before launching the software, the user should set
up the CDB5460 evaluation board by using the correct jumper and DIP switch settings as described in
Part I, and connect it to an open COM port on the
PC using the RS-232 serial cable. Once the board is
powered on, the user can start the software package.
When the software is launched, the Start-Up window appears first (Figure 6). This window contains
information concerning the software’s title, revi-
DS279DB1 11
Page 12

CDB5460
sion number, copyright date, etc. At the top of the
screen is a menu bar which displays user options.
The menu bar item Menu is initially disabled to
prevent conflicts with other serial communications
devices, such as the mouse or a modem. After se lecting a COM port, the Menu item will become
available.
Selecting and Testing a COM Port
Upon start-up, the user is prompted to select the serial communications port which will interface to
the CDB5460 board. To select the COM port, pull
down the Setup menu option, and select either
COM1 or COM2 (the DISK option is used for previously saved files, and is discussed later). Testing
the COM port to verify communication between
the PC and the eva luation board is not necessary,
but can help to troubleshoot some problems. The
procedure for testing the communication link follows.
1) Pull down the Setup menu option again, and
select TEST RS-232.
2) When prompted, set DIP switch 1 (the leftmost DIP switch) to the closed position, reset
the board, and press OK to perform the test.
3) If the test passes, set DIP switch 1 to the open
position, and reset the board to return to normal operating mode.
4) If the test fails, check the serial port connections, power connections, jumpers, and DIP
switch settings on the board, and run the test
again from step 1.
Once the serial link is established between the PC
and the evaluation board, the user is ready to access
the internal registers of the CS5460, collect data,
and perform analysis on the collected data.
Register Access in the Setup Window
The Evaluation software provides access to the
CS5460’s internal registers in the Setup Window
(Figure 7). The user can enter the Setup Window by
pulling down Menu and selecting Setup Window,
or by pressing F2 on the keyboard.
In the Setup Window, all of the CS5460’s registers
are displayed in hexadecimal value, and also decoded to provide easier access. Refer to the
CS5460 data sheet for information on register functionality and meanings.
Refresh Screen Button : The Refresh Screen button will update the contents of the screen by reading all the register values from the part. This usually takes a couple of seconds, but it is a good idea to press the Refresh Screen button when entering the Setup Window, or after modifying any registers to reflect the current status of the part.
CS5460 Crystal Frequency: The CS5460 accepts a wide range of crystal input frequencies, and c an therefore run at many different sample rates. The crystal frequency being used on the CS5460 should be entered in this box to provide accurate frequency calculations in the FFT window. This will also help the software decide which functions can be performed reliably with the evaluation system.
Configuration Register: In the Configuration Register box, the contents of the Configuration Register can be modified by typing a hexadecimal value in the HEX: box, or by changing any of the values below the HEX: box to the desired settings. Note: When changing the value of the reset bit to ‘1’ (RS, bit 7 in the Configuration Register), the part will be reset, and all registers will return to their default values. Press the Refresh Screen button after performing a reset to update the screen with the new register values.
Note: Although the CDB5460 software allows the
user to modify any of the bits in the Configuration
Register, changing certain bits may cause the software and board to behave erratically. For the e valuation system to function properly, the Interrupt
Output function should be set to the default Active
Low, and the Eout / Edir Function should be set to
the default Normal. This applies only to the
12 DS279DB1
Page 13

CDB5460
CDB5460 evaluation system, and not to the
CS5460 chip itself.
Mask Register / Status Register: The Mask and Status Registers are displayed in hexadecimal and decoded in this box to show what each of the bits means. The Mask Register can be modified by typing a value in the HEX: box, or by checking the appropriate check boxes for the bits that are to be masked. The Status Register cannot be directly modified. It can only be reset by pressing the Clear Status Register Button. The HEX: box for this register, and the LEDs are display only. A LED that is on means that the corresponding bit in the Status Register is set (except the Invalid Command bit, which is inverted).
Note: The value present in the Mask register may
be changed by the software during certain operations to provide correct functionality of the
CDB5460 board.
Cycle Count / Pulse Rate / Time Base Registers:
These three boxes display the values of the Cycle
Count, Pulse Rate, and Time Base Registers in both
hexadecimal and decimal format. All three registers can be modified by typing a value in the corresponding Value: or HEX: box.
Offset / Gain Registers: In the Offset and Gain Register boxes, the offset and gain registers for both channels are displayed in hexadecimal and decimal. These registers can all be modified directly by typing the desired value in the hexadecimal display boxes.
Performing Calib rations: Offset and gain calibrations can be performed on both the voltage and current channels of the CS5460. Offset calibration should be performed before gain calibration to ensure accurate results.
Offset Calibrations:
1) Ground the channel(s) you want to calibrate
directly at the channel header(s). HDR1 and
HDR2 for the voltage channel, and HDR8
and HDR9 for the current channel. The channel(s) could also be grounded directly at the
BNC connectors.
2) Press the corresponding Calibrate button (Cal
V, Cal I, or Cal Both) in the Offset Register
box.
3) The calibration value(s) will automatically
update when the calibration is completed.
Gain Calibrations:
1) Attach a full-scale calibration signal to the
BNC connector(s), and make sure the corresponding channel headers (HDR1, HDR2,
HDR8, and HDR9) are set to the input position.
2) Press the corresponding Calibrate button (Cal
V, Cal I, or Cal Both) in the Gain Register
box.
3) The calibration value(s) will automatically
update when the calibration is completed.
Conversion Window
The Conversion Window (Figure 8) allows the user
to see the results of single and continuous conversions on all six data registers, perform data averaging, utilize the power-saving modes of the CS5460,
and reset the CS5460’s serial port. The Conversion
Window can be accessed by pulling down the
Menu option, and selecting Conversion Window,
or by pressing F3.
Single Conversion Button: On pressing this button, single conversions will be performed repeatedly until the user presses the Stop button. After each conversion is complete, the Result data column will update with the values present in each data register. The Mean and Standard Deviation columns will update every N cycles, where N is the number in the Samples to Average box. Note: It can take many collection cycles after pressing the Stop button before the data actually sops being collected.
DS279DB1 13
Page 14

CDB5460
Continuous Conversions Button: This button functions similarly to the Single Conversion button, except that continuous conversions are performed instead. The data on the screen is updated in the same fashion, and the Stop button terminates this action. There are some speed limitations when performing this function, and if any of these limitations are exceeded, the user will be prompted to change some settings before proceeding.
Re-Initialize Serial Port Button: When this button is pressed, the software will send the synchronization sequence discussed in the CS5460 data sheet to the part. This sequence brings the
CS5460’s serial port back to a known state. It does
not reset any of the registers in the part.
Standby / Slee p Mode Butto ns: When these buttons are pressed, the part will enter either Standby or Sleep power saving modes. To return to normal mode, use the Power Up button.
Power Up Button: This button is used to send the Power Up/Halt command to the CS5460. The part will return to normal operating mode and halt any conversions that are being done at this time.
Average boxes. After each integration period, the
Pulse Count and Frequency columns will be updated. The Average Freq. and Standard Deviation columns will only be updated after all of the
integrations have been collected. The software
stops collecting data when the user presses the Stop
button, or when the data collection is finished. Due
to some speed limitations of the on-board microcontroller, some higher pulse rates cannot be accurately collected. If the pulse rate is too high, a
warning message will appear.
Data Collection Window Overview
The Data Collection Window (Figures 10, 11, and
12) allows the user to collect sample sets of data
from the CS5460 and analyze them using time domain, FFT, and histogram plots. The Data Collection Window is accessible through the Menu
option, or by pressing F5.
Time Domain / FFT / Histogram Selector: This menu selects the type of data processing to perform on the collected data and display in the plot area. Refer to the section on Analyz ing Data for more information.
Viewing Pulse Rate Output Data
The CS5460 features a pulse-rate energy output.
The CDB5460 has the capability to demonstrate
the functionality of this output in the Pulse Rate
Output Window (Figure 9). The Pulse Rate Output
Window can be accessed by pressing the F4 key, or
by pulling down the Menu option, and selecting
Pulse Rate Window.
Integration Period Box: This box allows the user to select the length of time which pul ses will be collected over.
Periods To Average Box: This box allows the user to average a number of integration periods together.
Start Button: When the Start button is pressed, the CDB5460 will capture pulse rate data according to the values in the Integration Period and Periods to
14 DS279DB1
Collect Button: This button will collect data from the part, to be analyzed in the plot area. See the section on Collecting Data Sets for more information.
Config Button: This button will bring up the configuration window, in which the user can modify the data collection specifications. See the discussion of the Config Window in this document.
Output Button: This button will bring up a window in which the user can output the data to a data file for later use, print out a plot, or print out the entire screen.
Note: When saving data, only the data channel being displayed on the plot will be saved to a file.
Zoom Button: This button allows the user to zoom in on the plot by selecting two point s in t he plot area. Press the Restore button to return to the normal
Page 15

CDB5460
data plot, or press the Zoom button again to zoom
in even further.
Channel Select Buttons: Depending on the number of channels of information that has bee n collected, between 1 and 3 channel select buttons will appear below the graph, allowing the user to choose the appropriate channel for display. In the Time Domain mode, an additional button labeled "Overlay" will be present, to allow the user to display all of the channels on the same plot.
Config Window
The Config Window allows the user to set up the
data collection and analysis parameters.
Number of Samples: This box allows the user to select the number of samples to collect, between 16 and 8192. Due to memory size on the CDB5460, the maximum is 4096 samples when collecting two channels, and 2048 samples when collecting three channels.
Average: When doing FFT processing, this box will determine the number of FFTs to average. FFTs will be collected and averaged when the Collect button is pressed.
FFT Window: This box allows the user to select the type of windowing algorithm for FFT processing. Windowing algorithms include the Blackman, Blackman-Harris, Hanning, 5-term Hodie, and 7term Hodie. The 5-term Hodie and 7-term Hodie are windowing algorithms developed at Crystal Semiconductor.
Histogram Bin Width: This box allows for a variable "bin width" when plotting histograms of the collected data. Each vertical bar in the histogram plot will contain the number of output codes contained in this box. Increasing this number may allow the user to view histograms with larger input ranges.
Pages to Collect: This box determines the number of data "pages" that the microcontroll er will collect before sending data to the PC. Each page consists
of the number of samples collected, and only the
last page will be returned to the PC for processing.
This function is useful at higher sampling frequencies to minimize board-le vel no ise a t the beginning
of the conversion set.
Data to Collect: These six check boxes allow the user to select the data channels that will be collected and returned to the PC for processing. Up to three channels can be selec ted at once. There are some restrictions on the speed and number of samples to collect when selecting more than one channel. A warning message will appear on pressing the Collect button in the Data Collection Window if any speed limits appear to be exceeded, but the data collection will still take place.
Accept Button: When this button is pressed, the current settings will be saved, and the user will return to the Data Collection Window.
Collecting Data Sets
To collect a sample data set:
1) In the Data Collection Windo w , press the Config button to bring up the Configuration Window and view the current settings.
2) Select the appropriate settings from the available options (see the section on the Configuration Window) and press the Accept button.
3) The Data Collection Window should still be
visible. Press the Collect button to begin collecting data. A progress indicator bar will
appear at the bottom of the screen during the
data collection process.
4) Data is first collected from the CS5460 and
stored in SRAM, and then transferred from
the SRAM to the PC through the RS-232
serial cable. Depending on the value of the
Cycle Count Register and the number of samples being collected, this process may take a
long time. The process can be terminated by
pressing the Stop button, but if this is done,
the user should also press Reset on the
CDB5460 board.
DS279DB1 15
Page 16

CDB5460
5) Once the data has been collected, it can be analyzed, printed, or saved to disk.
Retrieving Saved Data From a File
The CDB5460 software allows the user to save data
to a file, and retrieve it later when needed. To load
a previously saved file:
1) Pull down the Setup option and select Disk. A
file menu will appear.
2) Find the data file in the list and select it. Press
the Select button to return.
3) Go to the Data Collection Window, and press
the Collect button.
4) The data from the file should appear on the
screen. To select a different file, repeat the
procedure.
Analyzing Data
The evaluation software provides three types of
analysis tests - Time Domain, Frequency Domain,
and Histogram. The Time Domain analysis processes acquired conversions to produce a plot of
Conversion Sample Number versus Magnitude.
The Frequency Domain analysis processes acquired conversions to produce a magnitude versus
frequency plot using the Fast-Fourier transform
(results up to Fs/2 are calculated and plotted). Also,
statistical noise calculations are calculated and displayed. The Histogram analysis test processes acquired conversions to produce a histogram plot.
Statistical noise calculations are also calculated and
displayed.
MAGNITUDE: Displays the y-axis value of the cursor on the Histogram.
MAXIMUM: Indicator for the maximum value of the collected data set.
MEAN: Indicator for the mean of the data sample se t. MINIMUM: Indicator for the minimum value of
the collected data set. STD. DEV.: Indicator for the Standard Deviation
of the collected data set. VARIANCE: Indicates the Variance for the cur-
rent data set.
Frequency Domain Information
The following describe the indicators associated
with FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) Analysis. FFT
data can be plotted in the Data Collection Window
by setting the Time Domain / FFT / Histogram selector to FFT (Figure 11).
FREQUENCY: Displays the x-axis value of the cursor on the FFT display.
MAGNITUDE: Displays the y-axis value of the cursor on the FFT display.
S/D: Indicator for the Signal-to-Distortion Ratio, 4 harmonics are used in the calculations (decibels).
S/N+D: Indicator for the Signal-to-Noise + Distortion Ratio (decibels).
SNR: Indicator for the Signal-to-Noise Ratio, first 4 harmonics are not included (decibels).
S/PN: Indicator for the Signal-to-Peak Noise Ratio (decibels).
Histogram Information
The following is a description of the indicators associated with Histogram Analysis. Histograms can be
plotted in the Data Collection Window by setting the
Time Domain / FFT / Histogram selector to Histogram (Figure 12).
BIN: Displays the x-axis value of the cursor on the Histogram.
16 DS279DB1
# of AVG: Displays the number of FFT’s averaged in the current display.
Time Domain Information
The following controls and indicators are associated with Time Domain Analysis. Time domain data
can be plotted in the Data Collection Window by setting the Time Domain / FFT / Histogram selector to
Time Domain (Figure 10).
Page 17

CDB5460
COUNT: Displays current x-position of the cursor on the time domain display.
MAGNITUDE: Displays current y-position of the cursor on the time domain display.
MAXIMUM: Indicator for the maximum value of the collected data set.
MINIMUM: Indicator for the minimum value of the collected data set.
Figure 6. Start-Up Window
DS279DB1 17
Page 18

CDB5460
Figure 7. Setup Window
Figure 8. Conversion Window
18 DS279DB1
Page 19

CDB5460
Figure 9. Pulse Rate Output Window
Figure 10. Time Domain Analysis
DS279DB1 19
Page 20

CDB5460
Figure 11. FFT Analysis
Figure 12. Histogram Analysis
20 DS279DB1
Page 21

PCB LAYOUT
The CS5460 should be placed entirely over an analog ground plane with both the VA- and DGND
pins of the device connected to the analog plane.
Place the analog-di gital plane split immediat ely adjacent to the digital portion of the chip. Figures 14
and 15 show the layout of the CDB5460.
Note: See Applications Note 18 for more detailed layout
guidelines. Before layout, please call for our Free Schematic Review Service.
CDB5460
DS279DB1 21
Page 22

22 DS279DB1
Figure 13. Silkscreen
CDB5460
Page 23

DS279DB1 23
Figure 14. Circuit Side
CDB5460
Page 24

24 DS279DB1
Figure 15. Solder Side
CDB5460
Page 25

• Notes •
Page 26

 Loading...
Loading...