Page 1

D E S I G N E D T O L E A D
BSI Series
Gas-Fired Natural Draft Steam Boilers
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
These instructions must be affixed on or adjacent to the boiler
Models:
WARNING: Improper installation,
• BSI069
• BSI103
• BSI138
• BSI172
• BSI207
• BSI241
• BSI276
• BSI310
• BSI345
• BSI379
adjustment, alteration, service or
maintenance can cause property
damage, injury, or loss of life. For
assistance or additional information, consult a qualified installer,
service agency or the gas
supplier. Read these instructions
carefully before installing.
Manufacturer of Hydronic Heating Products
P.O. Box 14818 3633 I. Street
Philadelphia, PA 19134
Tel: (215) 535-8900 • Fax: (215) 535-9736 • www.crownboiler.com
1
Page 2

Table of Contents
I. Product Description .................................................. 1
II. Specifications ............................................................. 2
III. Before Installing ......................................................... 3
IV. Locating the Boiler ...................................................... 3
V. Air for Combustion & Ventilation .............................. 4
VI. Venting ....................................................................... 8
VII. Gas Piping ................................................................ 11
VIII. System Piping .......................................................... 12
IX. Indirect Water Heater Piping............................................15
X. Wiring ........................................................................ 16
XI. Start-Up & Checkout ............................................... 23
XII. Service & Maintenance .......................................... 31
XIII. Troubleshooting ..................................................... 34
XIV. Parts ......................................................................... 41
Appendix A: Knockdown Boiler Assembly..........................47
I Product Description
The BSI series boilers are low pressure cast iron gas fired steam boilers designed for use in closed steam heating systems.
These boilers are Category I draft diverter equipped appliances, which must be vented by natural draft using a lined masonry
or listed metal chimney system. An adequate supply of air for combustion, ventilation and dilution of flue gases must be
available in the boiler room. These boilers are not designed for use in process or other “open” steam systems
2
1
Page 3
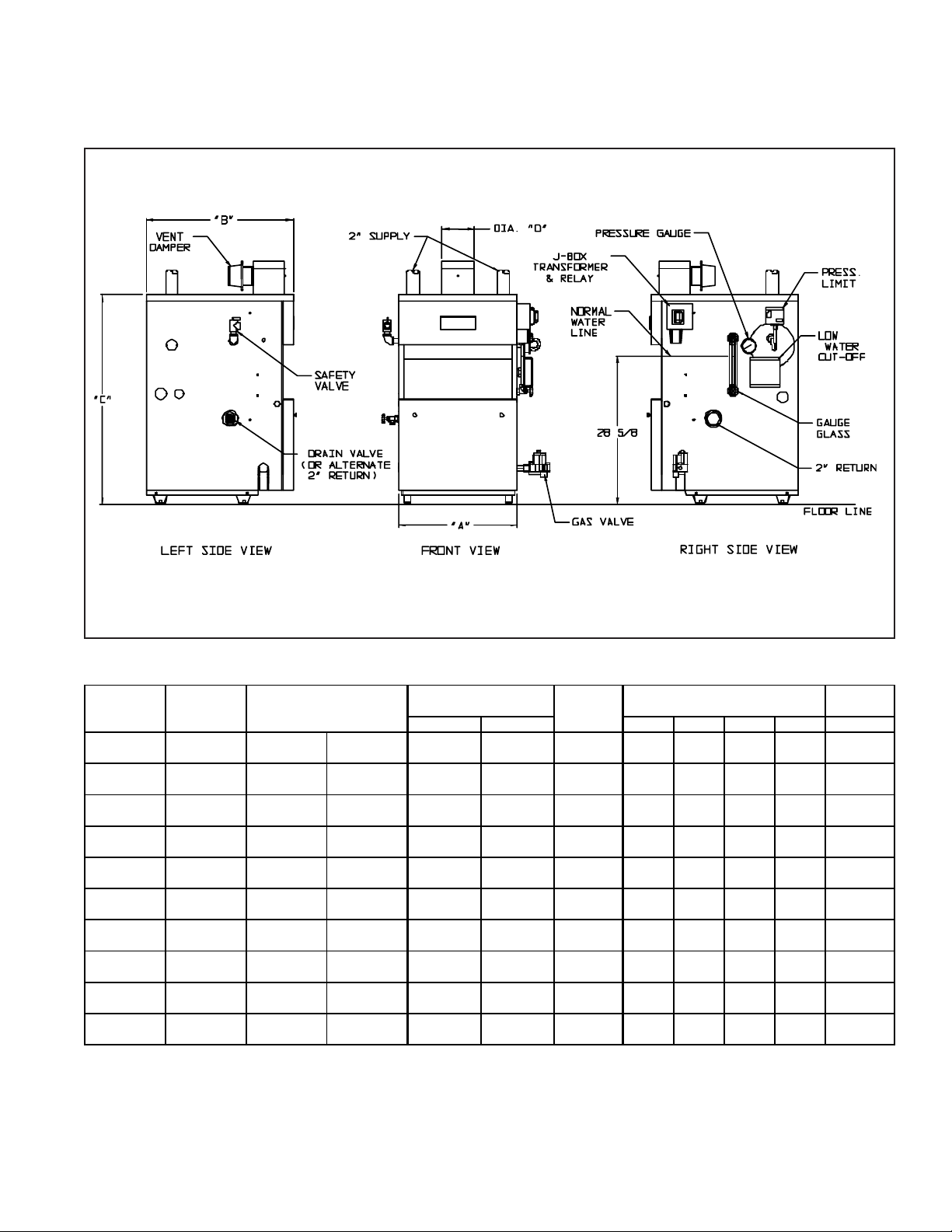
II Specifications
N
FIGURE 1: BSI BOILERS - GENERAL CONFIGURATION
TABLE 1: BSI SPECIFICATIONS
BASIC
BOILER
MODEL
BSI069S 80.0
BSI069E 81.9
BSI103S 80.0
BSI103E 82.0
BSI138S 80.3
BSI138E 82.0
BSI172S 80.6
BSI172E 82.1
BSI207S 80.9
BSI207E 82.1
BSI241S 80.0
BSI241E 82.2
BSI276S 80.3
BSI276E 82.2
BSI310S
BSI310E
BSI345S
BSI345E
BSI379S
BSI379E
*Combustion efficiency
** Volume to normal water line
NOTE: BSI345 and BSI379 not available for use with LP gas.
Suffix E = Intermittent Ignition, Suffix S = Standing Pilot. Add Suffix N for Natural Gas or Suffix L for Propane Gas to basic BSI model
number (example: BSI207SN, BSI207SL)
UMBER
OF
SECTIONS
3 428 40 7/16
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
INPUT
(MBH) (MBH) (Sq. ft) (MBH) (%) "A" "B" "C" "D" (Gal)
69
103
138
172
207
241
276
310
345
379
HEATING
CAPACITY
57
85
113
142
171
199
227
255
284
312
I=B=R NET RATING,
STEAM AFUE
179
267
354
446
533
621
708
800
892
979
43
64
85
107
128
149
170
192
214
235
82.5*
82.5*
82.5*
DIMENSIONS (in.)
12 3/4
16
19 1/4 28 40 7/16 6
22 1/2 28 40 7/16
25 3/4 30 40 7/16 7
29
32 1/4 30 40 7/16 8
35 1/2
38 3/4 30 45 7/16 9
42
28 40 7/16
30 40 7/16 7
30 45 7/16 8
30 45 7/16 9
5
6
WATER
VOL. **
5.1
6.5
7.9
9.3
10.7
12.1
13.5
14.9
16.3
17.7
3
2
Page 4
III Before Installing
1) Safe, reliable operation of this boiler depends upon installation by a professional heating contractor in strict accordance
with this manual and the requirements of the authority having jurisdiction.
• In the absence of an authority having jurisdiction, installation must be in accordance with this manual and the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest edition.
• Where required by the authority having jurisdiction, this installation must conform to the Standard for Controls and
Safety Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers (ANSI/ASME CSD-1)-latest edition.
Warning
This Product Must be Installed By A Licensed Plumber Or Gas Fitter
when Installed Within The Commonwealth Of Massachusetts
2) Make sure that a properly sized chimney is available which is in good condition. Consult the authority having jurisdiction,
Part VI of this manual, and the National Fuel Gas Code for additional information on venting requirements.
3) Make sure that the boiler is correctly sized. Use an industry accepted sizing method such as the I=B=R Installation
Guide for Residential Hydronic Heating Systems (Pub. #200) and I=B=R Heat Loss Calculation Guide (Pub. #H21 or
#H22) published by the Hydronics Institute in Berkeley Heights NJ.
4) Make sure that the boiler received is configured for the correct gas (natural or LP).
used with natural gas.
5) Boilers installed at altitudes above 2000 ft. require different burners and main burner orifice than those at sea level. Make
sure that the boiler is configured for use at the correct altitude.
6) If this boiler was received as a knockdown boiler, follow the instructions in Appendix A to assemble the boiler.
The BSI345 and BSI379 may only be
IV Locating the Boiler
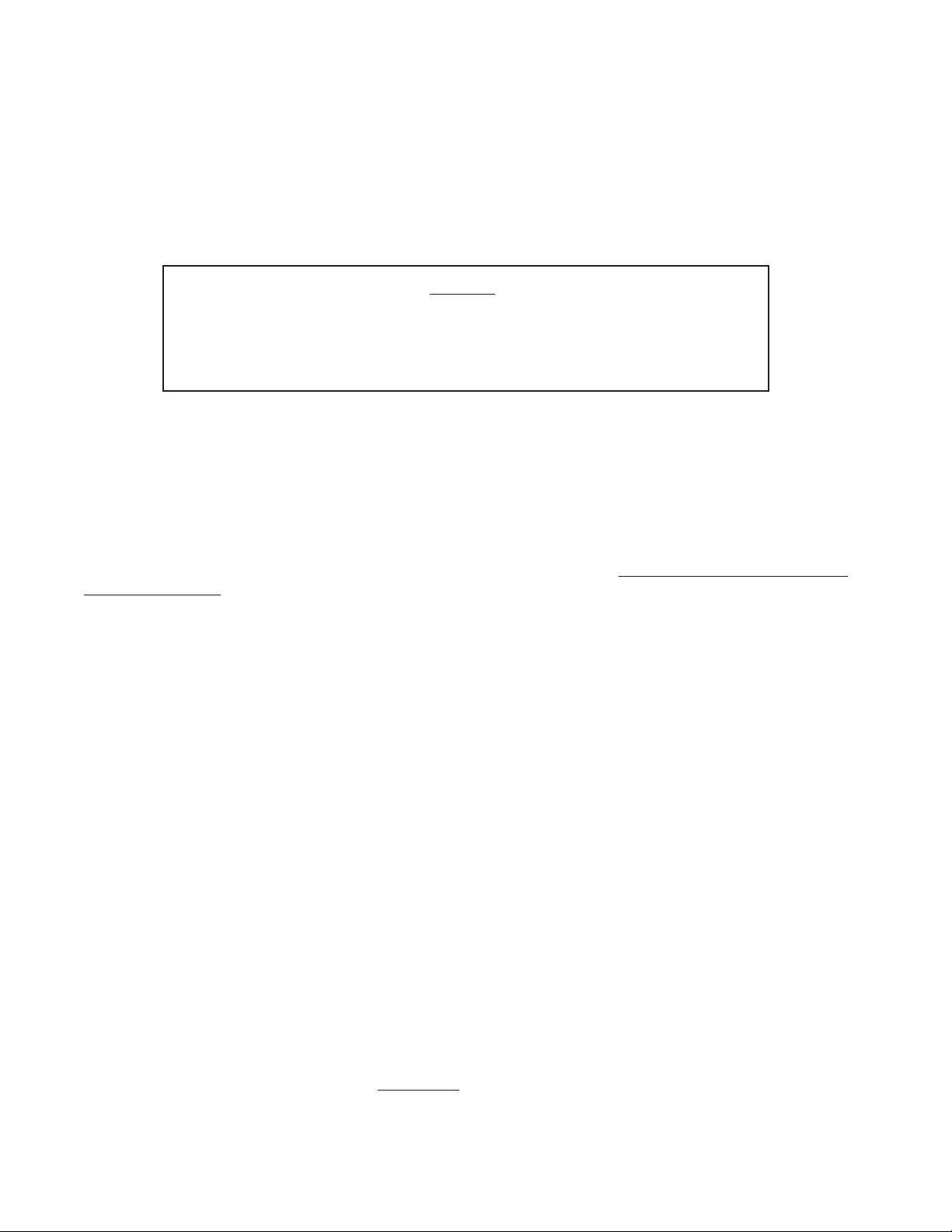
1) Clearances:
• Observe the minimum clearances shown below. These clearances apply to all combustible construction, as well as
noncombustible walls, ceilings and doors. Also see Figure 2.
Front – 18”
Right Side – 18”
Left Side – 6”
Rear – 6”
Top – 17”
• A 24” service clearance from the jacket is recommended on the left, right, and front of the boiler. These clearances
may be reduced to those shown in Figure 2, however servicing the boiler will become increasingly difficult as these
service clearances are reduced.
• If the right side 24” service clearance is reduced, adequate clearance must be maintained to easily read and access the
controls. Alternatively, access may be provided using a door
2) This boiler may be installed directly over a non-carpeted combustible floor.
3) The boiler must be installed on a hard level surface.
4
3
Page 5
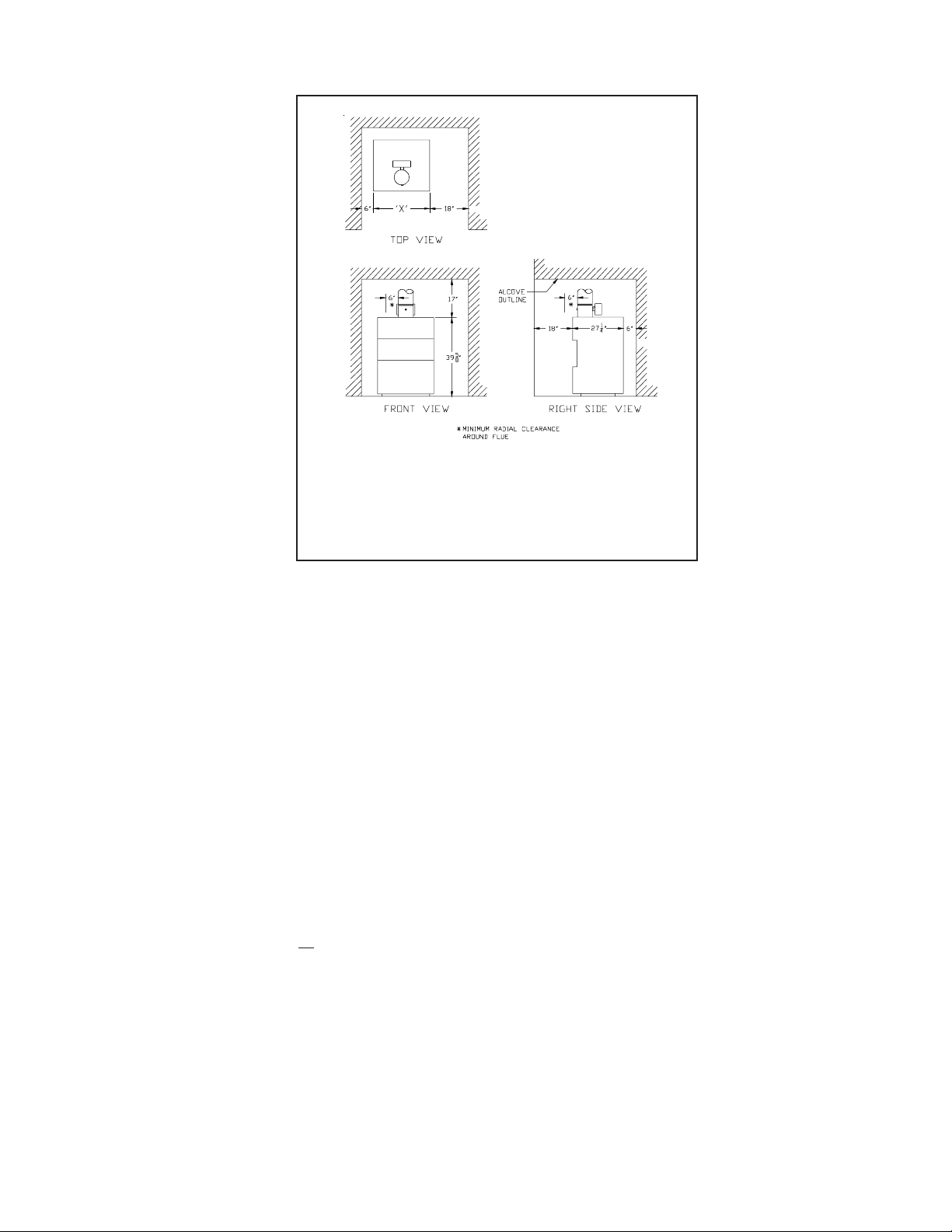
FIGURE 2: BSI BOILERS - CLEARANCES TO ALL
TYPES OF COMBUSTIBLE CONSTRUCTION AND
NONCOMBUSTIBLE CEILINGS, WALLS, AND
DOORS.
4) Do not install this boiler in a location where gasoline or other flammable vapors or liquids will be stored or used. Do not
install this boiler in an area where large amounts of airborne dust will be present, such as a workshop.
5) The boiler should be located as close to the chimney as possible.
6) Do not install this boiler directly on a surface that may get wet. Raise the boiler on a pad.
V Air for Combustion and Ventilation
Sufficient fresh air must be supplied for combustion, ventilation and flue gas dilution. Provisions for combustion, ventilation
and flue gas dilution air for gas utilization equipment vented by natural draft must be made in accordance with local building
codes or, in absence of such codes, in accordance with sections 5.3.3 and 5.3.4 (“Air for Combustion and Ventilation”) of the
National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1.
To ensure an adequate supply of combustion, ventilation and flue gas dilution air supply, start by determining whether the
boiler is to be installed in a building of unusually tight construction. A good definition of a building of unusually tight
construction is one which has all of the following features:
• Walls and ceilings exposed to outside atmosphere have a continuous water vapor retarder with a rating of 1 perm or
less with openings gasketed and sealed
• Weather stripping has been added on openable windows and doors
• Caulking and sealants are applied to areas such as joints around window and door frames, between sole plates and
floors, between wall-ceiling joints, between wall panels, at penetrations for plumbing, electrical, and gas lines, and at
other openings.
5
4
Page 6

For Buildings of Other than Unusually Tight Construction
1) Determine whether the boiler is to be installed in a confined space - A confined space is defined by the National Fuel
Gas Code as having a volume less than 50 cubic feet per 1000 BTU/hr input of all appliances installed in that space. To
determine whether the boiler room is a confined space:
a. Total the input of all appliances in the boiler room in thousands of BTU/hr. Round the result to the next highest 1000
BTU/hr.
b. Find the volume of the room in cubic feet. The volume of the room in cubic feet is:
Length (ft) x width (ft) x ceiling height (ft)
In calculating the volume of the boiler room, consider the volume of adjoining spaces only if no doors are installed
between them. If doors are installed between the boiler room and an adjoining space, do not consider the volume of the
adjoining space, even if the door is normally left open.
c. Divide the volume of the boiler room by the input in thousands of BTU/hr. If the result is less than 50, the boiler room is a
confined space.
Example:
A BSI172EN and a water heater are to be installed in a room measuring 6 ft - 3 in x 7 ft with an 8 ft ceiling. The water heater
has an input of 30000 BTU/hr:
Total input in thousands of BTU/hr = (172000 BTU/hr + 30000 BTU/hr)/1000 = 202
Volume of room = 6.25 ft x 7 ft x 8 ft = 350 ft
350/202 = 1.73. Since 1.73 is less than 50, the boiler room is a confined space.
3
2) Unconfined Space - Natural infiltration into the boiler room will normally provide adequate air for combustion and
ventilation without additional louvers or openings into boiler room.
3) Confined Space - Provide two openings into the boiler room, one near the floor and one near the ceiling. The top edge of
the upper opening must be within 12” of the ceiling and the bottom edge of the lower opening must be within 12” of the
floor (Figure 3).
• Each opening must have a free area of 1 square inch per 1000 BTU/hr input of all gas burning appliances in the boiler
room. The minimum opening dimension is 3 inches. Minimum opening free area is 100 square inches per opening.
• If the total volume of both the boiler room and the room to which the openings connect is less than 50 cubic feet per 1000
BTU/hr of total appliance input, install a pair of identical openings into a third room. Connect additional rooms with
openings until the total volume of all rooms is at least 50 cubic feet per 1000 BTU/hr of input.
• The “free area” of an opening takes into account the blocking effect of mesh, grills, and louvers. Where screens are used,
they must be no finer than ¼” (4 x 4) mesh.
• If providing openings into adjacent rooms is undesirable, combustion and ventilation air can be brought into the boiler
room from outdoors. See the instructions under “For Buildings of Unusually Tight Construction”.
For Buildings of Unusually Tight Construction
1) Openings must be installed between the boiler room and the outdoors or a ventilated space, such as an attic or crawl
space, which communicates directly with the outdoors.
2) Two openings are required. The top edge of the upper opening must be within 12 inches of the ceiling. The bottom edge
of the lower opening must be within 12 inches of the floor.
3) Size openings and ducts as follows:
• Vertical ducts or openings directly outdoors (Figure 4, Figure 5, and Figure 6) - Each opening must have a free cross
sectional area of 1 square inch per 4000 BTU/hr of the total input of all gas-fired appliances in the boiler room but not less
than 100 square inches. Minimum opening size is 3 inches.
• Openings to outdoors via horizontal ducts (Figure 7) - Each opening must have a free cross sectional area of 1 square
inch per 2000 BTU/hr of the total input of all gas fired appliances in the boiler room but not less than 100 square inches.
Minimum opening size is 3 inches.
• The “free area” of an opening takes into account the blocking effect of mesh, grills, and louvers. Where screens are used,
they must be no finer than ¼” (4 x 4) mesh.
6
576
Page 7
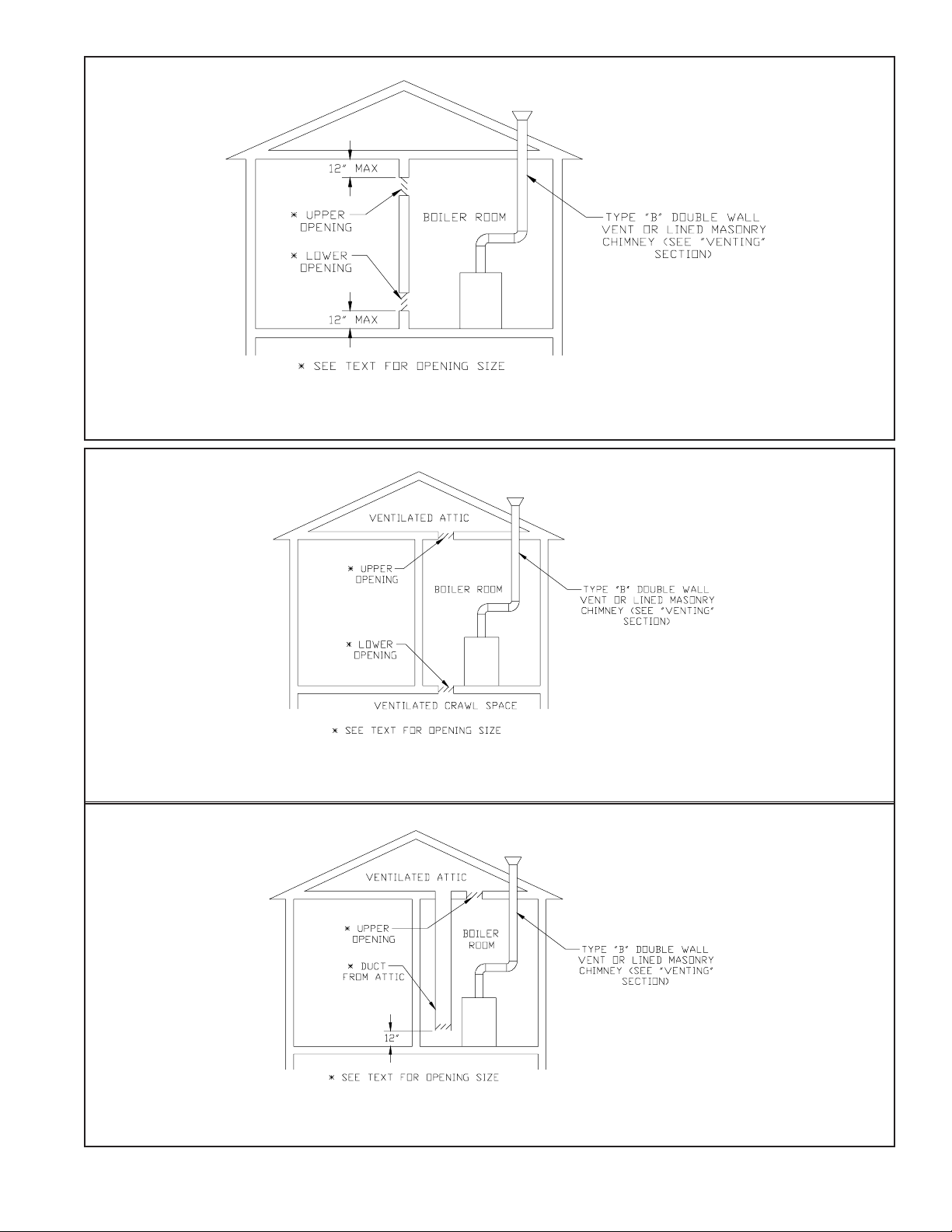
FIGURE 3: BOILER INSTALLED IN CONFINED SPACE,
ALL AIR FROM INSIDE
FIGURE 4: ALL AIR FROM OUTDOORS,
VENTILATED CRAWL SPACE AND ATTIC
FIGURE 5: ALL AIR FROM OUTDOORS,
VIA VENTILATED ATTIC
Page 8
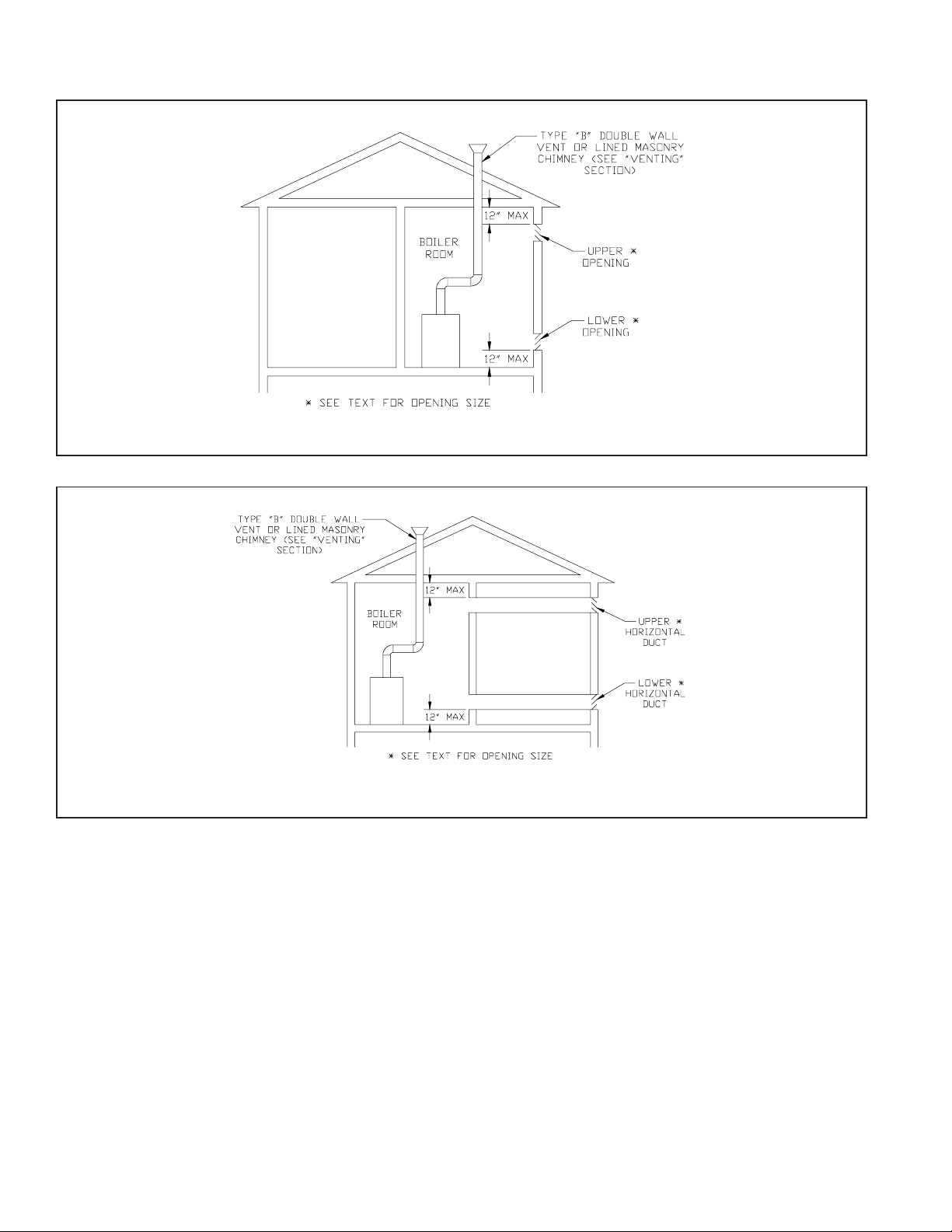
FIGURE 6: ALL AIR FROM OUTDOORS, USING
OPENINGS INTO BOILER ROOM
FIGURE 7: ALL AIR FROM OUTDOORS, USING
HORIZONTAL DUCTS INTO BOILER ROOM
8
7
Page 9

VI Venting
Vent installation must be in accordance with local building codes, or the local authority having jurisdiction, or the National
Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI Z 223.1.
A typical vent installation is illustrated by Figure 8. The components of vent installation are the vent damper (if used), vent
connector and chimney.
1) Acceptable Chimneys - The following chimneys may be used to vent BSI series boilers:
• Listed Type B or L gas vent - Install in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, the terms of its listing, and
applicable codes.
• Masonry Chimney - The masonry chimney must be constructed in accordance with the Standard for Chimneys,
Fireplaces, Vents, and Solid Fuel Burning Appliances (NFPA 211) and lined with a clay liner or other listed lining
system. Do not vent a BSI series boiler into an unlined chimney.
2) Acceptable Vent Connectors - The following may be used for vent connectors:
• Listed type B or L Gas Vent
• Single Wall Galvanized Pipe - Use 0.018” (26 gauge or heavier). The size and location of the chimney may not permit
the use of a single wall connector in some cases. See the National Fuel Gas Code. Do not use single wall pipe for
vent connectors in attics.
• Other Vent Connectors Permitted by the National Fuel Gas Code.
3) Chimney and Vent Connector Sizing - Size the chimney and vent connector in accordance with the National Fuel Gas
Code.
4) Exterior Chimneys - An exterior chimney has one or more sides exposed to the outdoors below the roof line. There are two
conditions under which an exterior chimney may be used:
• In some very restrictive cases, BSI series boilers may be vented into an exterior ceramic lined masonry chimney. See
the National Fuel Gas Code for information on when exterior chimneys may be used.
• An exterior masonry chimney may be used if it is lined with B vent or a listed chimney lining system.
5) This boiler may be vented using a listed power venter. The power venter must be sized and installed in accordance with
the power venter manufacturer’s instructions, the terms of the power venter listing, and applicable codes. The boiler must
be electrically interlocked with the power venter to prevent boiler operation if the power venter fails to operate. Before
deciding to use a power venter, make certain that the flue gas exiting the power venter will not damage adjacent
construction or other structures. Also make certain that the power venter terminal will not be subjected to winds which
could effect power venter operation.
6) Do not connect the vent of this appliance into any portion of a mechanical vent system operating under positive
pressure.
7) Do not connect the boiler into a chimney flue serving an open fireplace or other solid fuel appliance.
8) Prior to boiler installation, inspect chimney for obstructions or other defects and correct as required. Clean chimney as
necessary.
9) Vent pipe should slope upward from draft diverter not less than one inch in four feet. No portion of vent pipe should run
downward or have sags. Vent pipe must be securely supported.
10) The vertical section of vent pipe coming off the boiler should be as tall as possible, while still maintaining the proper
clearance from the horizontal vent connector to combustibles and the proper pitch called for in (9) above.
11) Vent pipe should be installed above the bottom of the chimney to prevent blockage.
12) Vent pipe must be inserted flush with inside face of the chimney liner and the space between vent pipe and chimney
sealed tight.
13) Do not install the vent damper in any portion of the vent system which is used by appliances other than the boiler being
installed.
9
8
Page 10

14) Vent damper installation is mandatory on all sizes from the BSI069 to BSI276. The BSI310 through BSI379 may be ordered
with or without vent damper. If supplied, install vent damper (see Figure 9) as follows:
a) Open vent damper carton and remove installation instructions. Read the instructions thoroughly before proceeding.
Verify that vent damper is same size as draft diverter outlet. See Figure 1. Unpack vent damper carefully. Do not force
closed damper blade. Forcing vent damper closed may result in damaged gear train and void warranty.
b) Vent damper is factory shipped having approximately ¾” diameter hole in the vent damper blade, which must be left
open for boilers equipped with standing pilot, and should be plugged on boilers with an intermittent pilot system,
using the plug supplied with the damper.
Mount the vent damper on the flue collar without modification to either and secure with sheet metal screws. Make
sure screws do not interfere with damper blade operation. Vent damper blade position indicator must be visible to
users.
c) The damper wire harness is shipped wired into the boiler junction box. Plug the loose end of this harness into the
damper and secure the flexible conduit to the damper using a connector nut provided.
d) Install vent connector pipe and vent fittings from vent damper outlet to chimney or gas vent. Secure with sheet metal
screws and support as required.
Removing an Existing Boiler from a Common Chimney
In some cases, when an existing boiler is removed from a common chimney, the common venting system may be too large for
the remaining appliances. At the time of removal of an existing boiler the following steps shall be followed with each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system placed in operation, while the other appliances remaining connected to
the common venting system are not in operation.
a) Seal any unused opening in the common venting system.
b) Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and horizontal pitch and determine there is no blockage or
restriction, leakage, corrosion and other deficiencies which could cause an unsafe condition.
c) Insofar as practical, close all building doors and windows and all doors between the space in which all the appliances
remaining connected to the common venting system are located and other spaces of the building. Turn on clothes
dryers and any appliance not connected to the common venting system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range
hoods and bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close
fireplace dampers.
d) Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so the appliance
will operate continuously.
e) Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after five (5) minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame of a
match or candle, or smoke from a cigarette, cigar, or pipe.
f) After it has been determined that each appliance remaining connected to the common venting system properly vents
when tested as outlined above, return doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and any other gas-burning
appliances to their previous condition of use.
g) Any improper operation of the common venting system should be corrected so the installation conforms with the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1. When resizing any portion of the common venting system, the common
venting system should be resized to approach the minimum size as determined using the appropriate tables in the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1.
10
9
Page 11
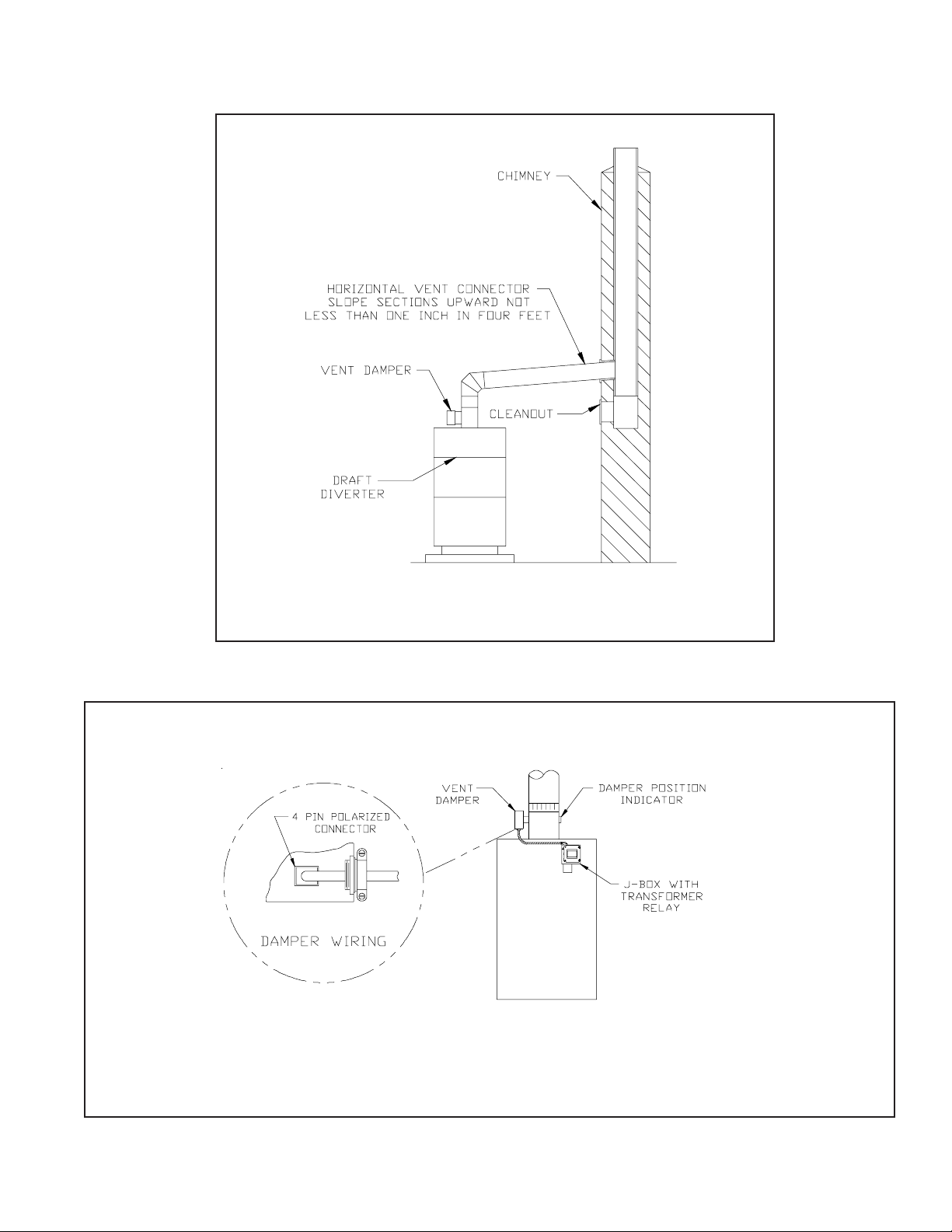
FIGURE 8: BSI BOILER TYPICAL VENT SYSTEM
INSTALLATION AND COMPONENTS
RIGHT SIDE VIEW
FIGURE 9: VENT DAMPER INSTALLATION DETAILS
11
10
Page 12
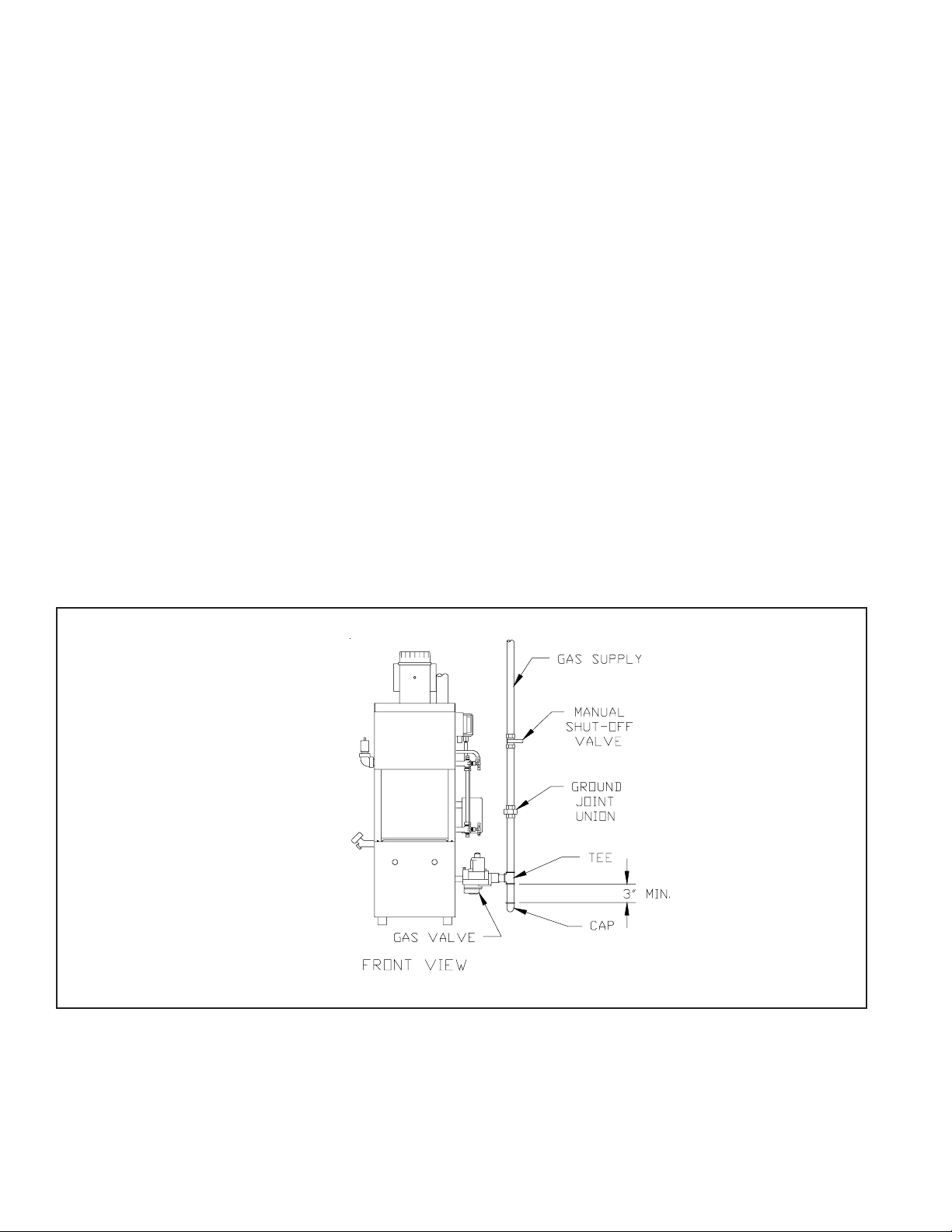
VII Gas Piping
Gas piping to the boiler must be sized to deliver adequate gas for the boiler to fire at the nameplate input at a line pressure
between the minimum and maximum values shown on the rating plate. For more information on gas line sizing, consult the
utility or Chapter 2 of the National Fuel Gas Code.
Figure 10 shows typical gas piping connection to the BSI boiler. A sediment trap must be installed upstream of all gas
controls. Install a manual shut-off valve outside the jacket and ground joint union as shown.
The boiler and its gas connection must be leak tested before placing the boiler in operation. When doing this, the boiler
and its individual shut-off must be disconnected from the rest of the system during any pressure testing of that system at
pressures in excess of 1/2 psi. When pressure testing the gas system at pressures of 1/2 psi or less, isolate the boiler from the
gas supply system by closing its individual manual shut-off valve.
FIGURE 10: GAS CONNECTION TO BOILER
*
* State of Massachusetts Requires Manual
Shut-off Valve to be “T” Handle Type
12
11
Page 13

VIII System Piping
CAUTION
• INSTALL BOILER SO THAT THE GAS IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS ARE PROTECTED
FROM WATER (DRIPPING, SPRAYING, RAIN, ETC.) DURING APPLIANCE OPERATION AND SERVICE
(CIRCULATOR REPLACEMENT, ETC.).
• OPERATION OF THIS BOILER IN A SYSTEM HAVING SIGNIFICANT AMOUNTS OF DISSOLVED OXYGEN
CAN CAUSE SEVERE HEAT EXCHANGER CORROSION DAMAGE.
General Piping Notes
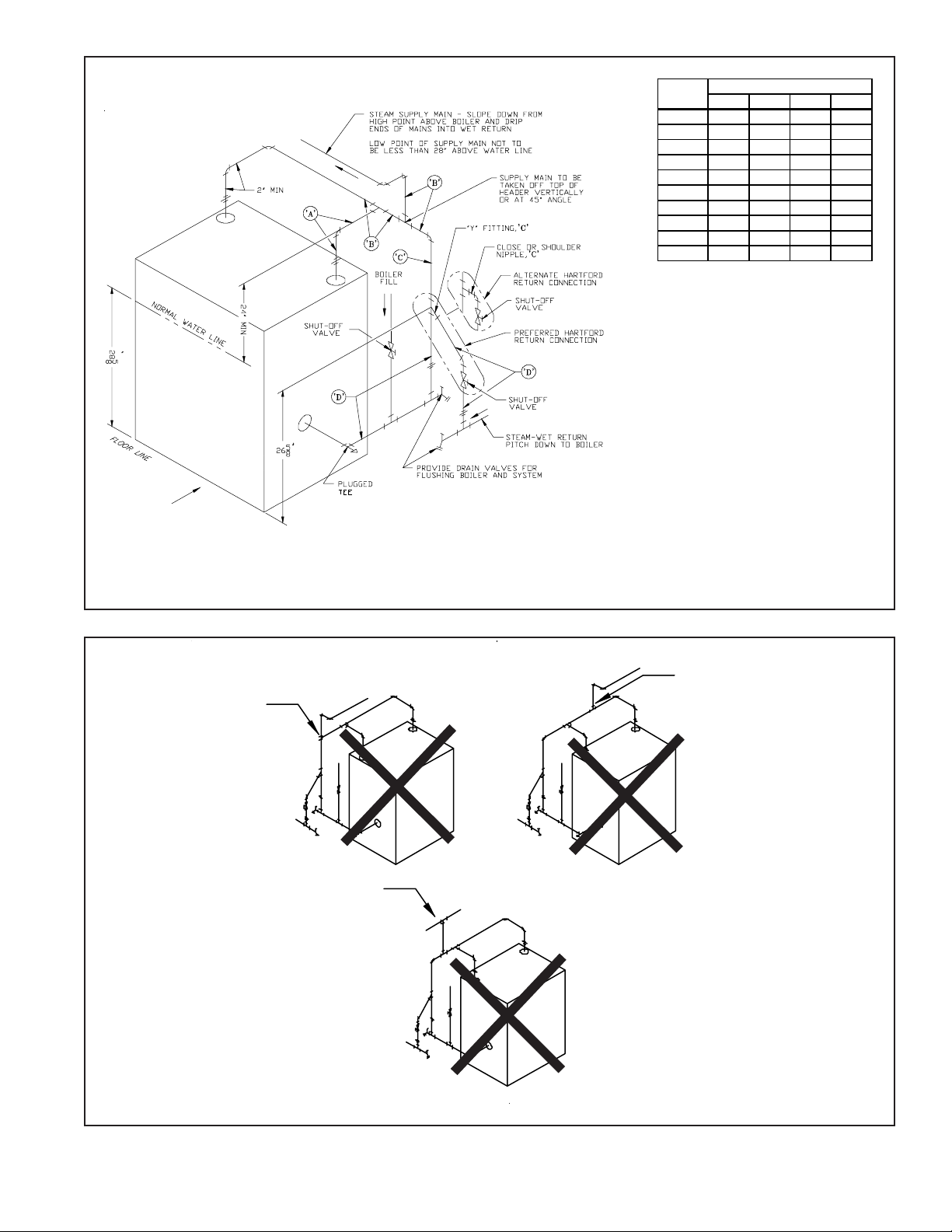
Figure 11 shows recommended near boiler piping for most common types of gravity return steam systems. Additional
information on steam system design may be found in Installation Guide for Residential Hydronic Heating Systems (Pub.
#200) published by the Hydronics Institute in Berkeley Heights NJ.
One of the primary purposes of this near boiler piping is to separate tiny water droplets from the steam exiting the boiler so
that “dry” steam is sent to the system. If the near boiler piping is not correct, wet steam will enter the system and the
following problems may occur:
• Short cycling on low water
• Boiler or system Flooding
• Hammering
• Failure to heat one or more radiators
Avoid the three common piping mistakes shown in Figure 12. This applies even if the existing boiler has one of the piping
mistakes shown in Figure 12 and appears to be working. If two or more steam mains must be connected to the boiler, connect a
separate take-off for each main into the header between the riser(s) and equalizer. Also note the following points:
1) A size reduction must be made to connect the header to the equalizer. This reduction must be made in the equalizer line. Do
not make this size reduction in the horizontal header.
2) One pipe steam systems require air vents on each radiator, as well as at the end of each main. For the system to work
properly, these vents must be properly installed, sized, and be in good condition. Inspect and replace any defective vents. If
there are no vents at the ends of the mains, install them.
3) Do not attempt to manifold multiple BSIs with gravity returns.
4) For installations with condensate or boiler feed pumps, follow the pump manufacturer’s piping instructions. Such systems
generally do not require Hartford loops.
5) Do not use a check valve in place of, or in addition to, a Hartford loop on a gravity return system.
6) Pipe the fill connection from a clean source of cold water. When the water supply is from a well, make sure that a strainer is
installed in the well system.
7) Piping with a Chiller - If the boiler is used in conjunction with a chiller, pipe the boiler in parallel with chiller. Use isolation
valves to prevent chilled water from entering the boiler.
13
12
Page 14

Piping Installation
1) Remove parts bag from boiler crate.
2) Install safety valve (spindle must be in vertical position) into tapping on boiler left side (see Figure 1) using the 3/4” NPT
nipples and elbow supplied.
3) Pipe the discharge of the safety relief valve to a location where water or steam will not create a hazard or cause property
damage if the valve opens. The end of the discharge pipe must terminate in an unthreaded pipe. If the safety valve
discharge is not piped to a drain it must terminate at least 6 inches above the floor. The termination of the safety valve
discharge piping must be in an area where it is not likely to become plugged by debris or subjected to freezing.
DANGER
• PIPE SAFETY VALVE DISCHARGE TO A SAFE LOCATION.
• DO NOT INSTALL A VALVE IN THE SAFETY VALVE DISCHARGE LINE.
• DO NOT MOVE SAFETY VALVE FROM FACTORY LOCATION.
• DO NOT PLUG SAFETY VALVE DISCHARGE.
• DO NOT INSTALL A SAFETY VALVE WITH A SETTING GREATER THAN 15 PSI.
4) Install drain valve into tapping on boiler left side using the 2 x 3/4 bushing provided (see Figure 1).
5) Connect system supply and return to boiler. See Figure 11. The BSI069 - BSI172 require only one supply riser. Two supply
risers are required on the BSI207 and larger sizes.
6) Piping with a Chiller - If the boiler is used in conjunction with a chiller, pipe the boiler in parallel with chiller. Use isolation
valves to prevent chilled water from entering the boiler.
14
131514
Page 15
BOI L ER
FRONT
MODEL
BSI069 * 2 1 1/2 1 1/4
BSI103 * 2 1 1/2 1 1/4
BSI138 * 2 1 1/2 1 1/4
BSI172 * 2 1 1/2 1 1/4
BSI207 2 3 1 1/2 1 1/4
BSI241 2 3 2 1 1/2
BSI276 2 3 2 1 1/2
BSI310 2 3 2 1 1/2
BSI345 2 3 2 1 1/2
BSI379 2 3 2 1 1/2
* SECOND 2" SUPPLY RI SER OPTIONAL
MINIMUM PI PE DI A. (IN NPT )BOILER
"A" "B" "C" "D"
FIGURE 11: STEAM BOILER PIPING FOR GRAVITY RETURN
WRONG - HEADER
BULLHEADED
INTO TAKE-OFF
AND EQUALIZER
WRONG - TAKE-OFF
BULLHEADED INTO
TWO MAINS
WRONG - TAKE-OFF
BETWEEN RISERS
FIGURE 12: COMMON NEAR-BOILER PIPING MISTAKES
Page 16
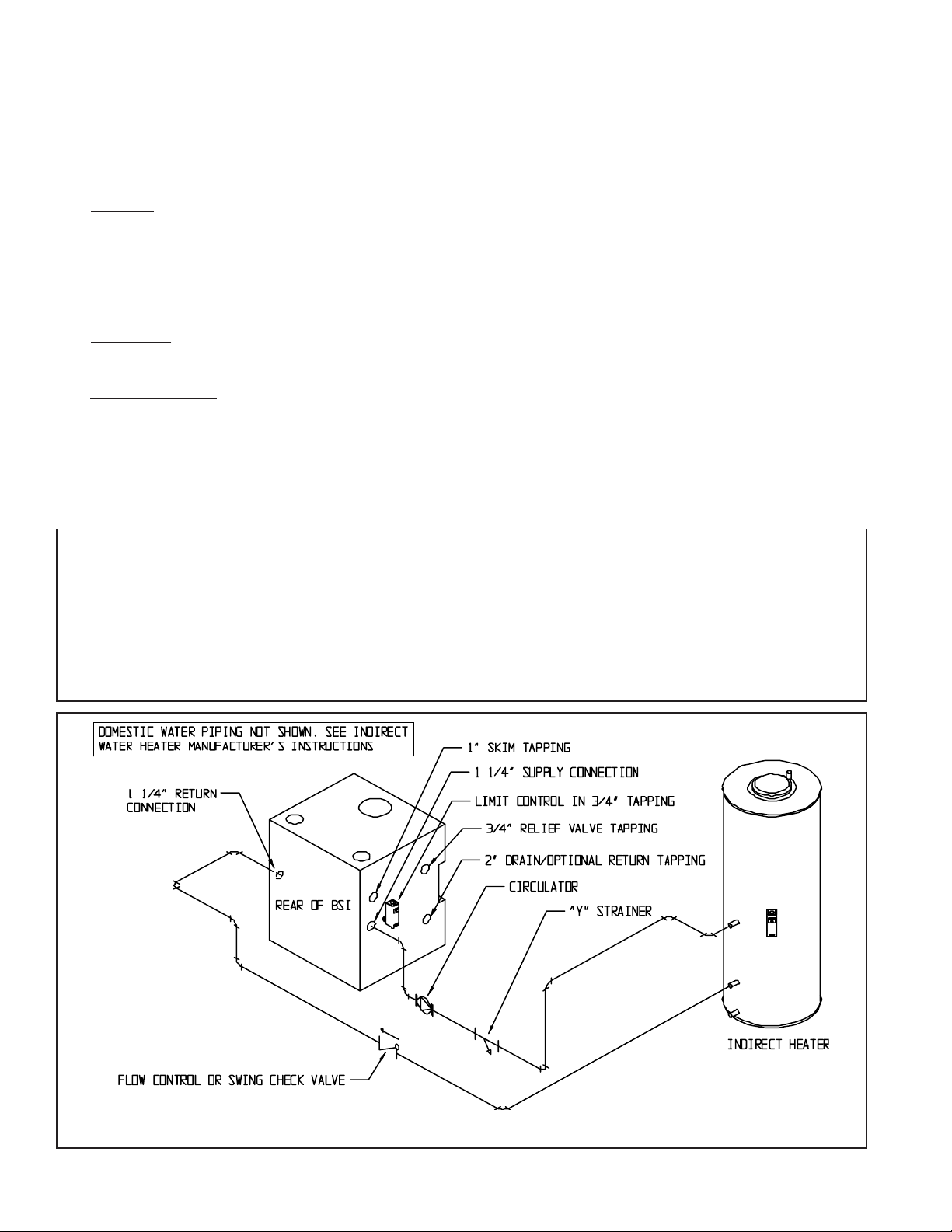
IX Indirect Water Heater Piping
All BSI series boilers are equipped with tappings to permit the connection of a Crown Mega-Stor, or other indirect water
heater. In this type of system, hot boiler water is drawn from below the water line and passed through the heat exchanger in
the indirect water heater. This section describes boiler-side piping only. Refer to the indirect water heater instruction manual
for domestic water piping. The components in this system and their functions are as follows:
1)
Circulator - Mount the circulator as shown in Figure 13. The circulator should be located as low and as close to the boiler
as practical. Do not install valves, or other devices having a significant pressure drop, between the boiler and the circulator
inlet. All piping between the boiler and the circulator inlet should be 1”, regardless of the size of the piping required in the
rest of the system. See Figure 15 in Part X for wiring information.
2) “Y” Strainer - Install a “Y” strainer to prevent sediment from accumulating inside the indirect water heater.
3) Check Valve - Prevents gravity circulation through the indirect water heater when the boiler is responding to a call for
heat.
4) Boiler Limit Control - Use a SPST break-on-rise temperature limit control such as the Honeywell L4006A. Do not set the
limit above 180F as doing so may cause the boiler to steam when there is no call for heat. See Figure 15 for wiring
information.
5) Valves and Unions - Install shut-off valves, drain valves, and unions in locations that will facilitate maintenance of the
system. Do not install any valves between the boiler and circulator inlet.
IMPORTANT
• Some indirect water heaters may not be suitable for use with a steam boiler. Consult the water heater
manufacturer’s guidelines before installing it in this type of system.
• Boiler water temperatures and flow rates in this type of system may be considerably lower than those upon which the
water heater manufacturer’s ratings are based. This may result in substantially longer water heater recovery times.
FIGURE 13: INDIRECT WATER HEATER BOILER-SIDE PIPING
16
15
Page 17
X Wiring
WARNING
All wiring and grounding must be done in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence of such
requirements, with the National Electrical Code (ANSI/NFPA 70)
1) 120 Volt Wiring - The boiler should be provided with its own 15A branch circuit with fused disconnect. All 120 volt
connections are made inside the junction box on the left side of the boiler. Remove the transformer to gain access to this
box (also see Figures 16 through 19):
• Hot (“black”) - Wire nut to black transformer lead
• Neutral (“white”) - Wire nut to white transformer lead
• Ground (“green” or bare) - Ground screw inside junction box.
2) Thermostat Wiring - Follow thermostat manufacturer instructions. To insure proper thermostat operation, avoid installation
in areas of poor air circulation, hot spots (near any heat source or in direct sunlight), cold spots (outside walls, walls
adjacent to unheated areas, locations subject to drafts). Provide Class II circuit between thermostat and boiler. Connect
thermostat wire leads to the blue transformer lead and brown relay lead inside the junction box. Set the heat anticipator to
0.2A.
Feeder Wiring for Boilers Equipped with Hydrolevel CG400A Low Water Cut-offs
CAUTION
Do not attempt to connect a McDonnell & Miller model #101A feeder, or other feeder without a delay, to a BSI boiler
equipped with a Hydrolevel CG400 low water cutoff. Doing so could destroy the boiler transformer and/or flood the system.
1) Using Hydrolevel VXT-24 TWO-WIRE feeder - Do not alter factory boiler wiring. Connect VXT-24 to CG400A as follows:
• Connect the BLACK lead on the feeder to terminal A on the LWCO
• Connect the WHITE lead on the feeder to terminal 2 on the LWCO
2) Using Hydrolevel VXT-24 THREE-WIRE feeder - Do not alter factory boiler wiring. Connect VXT-24 to CG400A as follows:
• Connect the BLACK lead on the feeder to terminal 1 on the LWCO
• Connect the WHITE lead on the feeder to terminal 2 on the LWCO
• Connect the RED lead on the feeder to terminal A on the LWCO
3) Using McDonnell & Miller WF2-U-24 feeder - Do not alter factory boiler wiring. Connect WF2-U-24 to CG400A as follows:
• Connect terminal W on the feeder to terminal A on the LWCO
• Connect terminal N on the feeder to terminal 2 on the LWCO
• Connect terminal H on the feeder to terminal 1 on the LWCO
17
16
Page 18

Feeder Wiring for Boilers Equipped with McDonnell & Miller #67 Low Water Cut-offs
Figures 14a and 14b show feeder wiring for McDonnell & Miller #101A, McDonnell & Miller WF2-U-24 and Hydrolevel VXT24 feeders on boilers equipped with #67 low water cutoffs. The following points apply to all feeder wiring to #67 low water
cut-offs:
• Use a separate transformer to power the feeder. Do not use the transformer on the boiler.
• It is not necessary to touch any of the 24 volt factory boiler wiring when connecting a feeder to a #67 equipped
boiler.
• Do NOT install a jumper between terminals 2 and 3 on the #67 low water cutoff.
Indirect Water Heater Wiring
Figure 15 shows field wiring for an indirect water heater. A Honeywell R845A or equivalent DPST relay and transformer is
required. The high limit described in Part IX must also be supplied by the installer. A call for heat from the indirect water
heater thermostat will energize the relay making both sets of contacts. One set of these contacts then energizes the circulator.
The other set of contacts will make the “T” and “T” contacts on the burner primary control, firing the burner. If the boiler
water temperature exceeds the high limit setting of 180F, the high limit will open the “T” - “T” circuit and the burner will shut
down.
If there is a call for space heat, the heating thermostat will make the “T”-”T” circuit and the boiler will fire without regard to
the status of the indirect water heater. The low water cut-off and pressure limit control will interrupt 120 volt power to the
burner in the event of a low water or excessive pressure condition.
CAUTION
DO NOT INSTALL
JUMPER BETWEEN 2 & 3
ON #67 L.W.C.O.
FIGURE 14a: WIRING MCDONNELL & MILLER 101A OR TWO-WIRE HYDROLEVEL VXT-24 FEEDER TO BOILER
EQUIPPED WITH #67 L.W.C.O.
18
17
Page 19

CAUTION
DO
JUMPER BETWEEN 2 & 3
ON #67 L.W.C.O.
NOT INSTALL
FIGURE 14b: WIRING MCDONNELL & MILLER WF2-U-24 FEEDER OR THREE-WIRE HYDROLEVEL
VXT-24 FEEDER TO BOILER EQUIPPED WITH #67 L.W.C.O.
FIGURE 15: WIRING INDIRECT WATER HEATER TO BOILER
19
18
Page 20

BSI Control System – Sequence of Operation
(Refer to Figures 16 through 19 for ladder and connection diagrams)
Sequence of Operation, Standing Pilot
1) When the boiler is energized, 24 volts is immediately applied to terminals “1” (blue) and “4” (yellow) on the vent
damper. Assuming that there is no call for heat, and that the damper switch is in the “automatic” position, the damper will
close. On boilers equipped with Hydrolevel CG400A probe type low water cut-offs, voltage is also always applied to
terminals “1” (blue) and “2” (yellow) on the low water cut-off to power the water level sensing circuit. On boilers equipped
with #67 float type low water cut-offs, power is always applied to terminal “2” on the #67 LWCO.
2) Assuming that water is above the cut-off level, power will appear at terminal “3” on the CG400 LWCO or terminal “1” on the
#67 LWCO.
3) Assuming that steam pressure is below the pressure limit setting, power will appear on one side of relay contact 1R1
(Gray lead). Relay 1R is the R8225 mounted under the junction box.
4) A call for heat from the thermostat energizes relay coil 1R causing contacts 1R1 to make. Current then flows through
contacts 1R1 to pin terminal “2” (orange) at the vent damper and the damper opens.
5) Once the vent damper is fully open, an end switch inside the damper will make, energizing pin “3” (red) at the damper.
6) Current passes from terminal “3” on the vent damper though the flame rollout and blocked vent (“spill”) switches.
Under normal conditions, both of these switches are made and voltage will therefore immediately appear across the combination gas control (“gas valve”) terminals “TH” and “TR”.
7) When the boiler is first placed into operation, the pilot must be lit. The pilot heats a thermocouple which generates a small
amount of electricity sufficient to hold open the safety shut-off valve in the combination gas control.
the thermocouple and the safety shut-off valve is self contained and completely independent of all other wiring on the boiler.
This safety shut-off valve is upstream of the 24 volt valves in the gas control which open in response to a call for heat. If the
pilot is not lit, the safety shut-off valve will remain closed and gas will not reach the 24 volt valves.
8) Assuming that the pilot is established and proven by the thermocouple, the application of 24 volts across the combination gas valve terminals energizes the redundant 24 volt solenoid valves in the combination gas control, resulting in gas
flow through the control and burner operation.
The circuit connecting
Sequence of Operation, Intermittent Ignition
1) When the boiler is energized, 24 volts is immediately applied to terminals “1” (blue) and “4” (yellow) on the vent
damper. Assuming that there is no call for heat, and that the damper switch is in the “automatic” position, the damper will
close. On boilers equipped with Hydrolevel CG400A probe type low water cut-offs, voltage is also always applied to
terminals “1” (blue) and “2” (yellow) on the low water cut-off to power the water level sensing circuit. On boilers equipped
with #67 float type low water cut-offs, power is always applied to terminal “2” on the #67 LWCO.
2) Assuming that water is above the cut-off level, power will appear at terminal “3” on the CG400 LWCO or terminal “1” on the
#67 LWCO.
3) Assuming that steam pressure is below the pressure limit setting, power will appear on one side of relay contact 1R1
(Gray lead). Relay 1R is the R8225 mounted under the junction box.
4) A call for heat from the thermostat energizes relay coil 1R causing contacts 1R1 to make. Current then flows through
contacts 1R1 to pin terminal “2” (orange) at the vent damper and the damper opens.
5) Once the vent damper is fully open, an end switch inside the damper will make, energizing pin “3” (red) at the damper.
6) Current passes from terminal “3” on the vent damper though the flame rollout and blocked vent (“spill”) switches.
Under normal conditions, both of these switches are made and voltage will therefore immediately appear across terminals
“24V” and “24V (GND)” on the ignition module.
7) Upon application of voltage across the “24V” and “24V (GND)” terminals, the ignition module will start an ignition spark
at the pilot and apply 24 volts across the pilot valve (terminals “PV” and “MV/PV”).
8) Once the pilot is established, the pilot flame will act as a diode, converting the AC current at the electrode to a half
wave DC current at the pilot’s ground strap. This DC current flows through the boiler to the “GND (BURNER)” connection
on the ignition module. For the ignition module to recognize that a pilot flame is present, the DC current flowing into this
terminal must be in excess of approximately 1.0 uA.
9) Once the ignition module detects the presence of a pilot flame, voltage is applied across the main valve (terminals “MV”
and “MV/PV”), opening the valve and establishing main flame.
10) The way in which the ignition module handles failure to establish pilot or the loss of an already established pilot
depends upon the exact ignition module supplied with the boiler. For more information on module operation, consult the
ignition module instructions supplied with the boiler or the local Crown representative.
20
192120
Page 21

“BURNER”
V8295A
(BSI310-379 ONLY)
“BURNER”
L
N
FIGURE 16: WIRING DIAGRAM, STANDING PILOT AND HYDROLEVEL CG-400A LOW WATER CUTOFF
VENT DAMPER (NOTE 2)
NOTE 3
LESS VENT
V8295A
(BSI310-379 ONLY)
DAMPER
L
N
2. VENT DAMPER REQUIRED ON BSI069 - BSI276, OPTIONAL ON BSI310 - BSI379
3. ON BOILERS LESS VENT DAMPER, DAMPER HARNESS NOT USED. RED AND
BLUE LEADS SHOWN ARE JUMPERED TOGETHER USING RED JUMPER WIRE
FIGURE 17: WIRING DIAGRAM, STANDING PILOT AND McDONNELL & MILLER MODEL 67 LOW WATER CUTOFF
Page 22

Safety Control Operation - Standing Pilot and Intermittent Ignition
Hydrolevel CG400A Low Water Cut-off - Interrupts burner operation if the water in the boiler drops below a safe level. As the
water drops past the cut-off point, the amber lamp on the CG400 will glow. The CG400 will interrupt power to the burners 15
seconds after the water level drops past the cut-off point. This feature prevents short cycling of the burners due to a bouncing
water line. The burners will then remain off until 30 seconds after the water level has been raised above the cut-off point.
The CG400 is also equipped with a feature which will shut down the burners after they have been firing for 10 minutes, regardless
of the water level status. The CG400 then keeps the burners off for 90 seconds, allowing the water level and any foam which is
present to settle. During this 90 second interval, the green LED on the CG400 will glow. If the water level is still above the cut-off
line at the end of this 90 second interval, the CG400 will restart the burners.
The vent damper will close when the low water cut-off interrupts burner operation.
McDonnell & Miller #67 Low Water Cut-off - Interrupts burner operation if the water in the boiler drops below a safe level.
Burner operation is restored when the water level in the boiler is raised above the cut-off point.
The vent damper will close when the low water cut-off interrupts burner operation.
Pressure Limit Control - Interrupts burner operation when the pressure in the boiler exceeds the “Cut-in” setting plus the
differential setting. The “Cut-in” setting is shown on the outside of the control and is adjusted using the screw on the top of the
control. The differential is adjusted using the white thumb wheel on the inside of the control. Burner operation is restored when
the pressure in the boiler drops to the “Cut-in” pressure.
The vent damper will close when the pressure limit control interrupts burner operation.
VENT DAMPER (NOTE2)
NOTE 3
“BURNER”
TH
TR
“BURNER”
LESS VENT
DAMPER
HONEYWELL
VR8204/VR8304
SERIES GAS VALVES
(BSI069 - 345)
ROBERTSHAW
+
7000DERHC
GAS VALVE
(BSI379)
2. VENT DAMPER REQUIRED ON BSI069 - BSI276, OPTIONAL ON BSI310 - BSI379
3. ON BOILERS LESS VENT DAMPER, DAMPER HARNESS NOT USED. RED AND BLUE
LEADS ARE JUMPED TOGETHER USING RED JUMPER WIRE.
FIGURE 18: WIRING DIAGRAM, INTERMITTENT IGNITION AND HYDROLEVEL CG-400A LOW WATER CUTOFF
22
21
Page 23

Blocked Vent (“Spill”) Switch - Automatically interrupts burner operation in the event that flue gas spills from the draft diverter
opening. This switch is equipped with a reset button which must be pressed to restore normal burner operation. An open blocked
vent switch is indicative of a problem with the vent system. If the blocked vent switch opens, the cause of the venting problem
must be found and corrected by a qualified gas service technician before the blocked vent switch is reset.
Flame Roll-out Switch - Automatically interrupts burner operation when flames or excessive heat are present in vestibule. The flame
roll-out switch is a single use device which must be replaced by an identical switch in order to restore normal operation. An open
flame roll-out switch is usually indicative of a plugged heat exchanger. The cause of the flame roll-out must be found and
corrected by a qualified gas service technician, and the switch replaced with an identical one, before the boiler is returned to
operation.
VENT DAMPER (NOTE 2)
NOTE 3
LESS VENT
DAMPER
HONEYWELL
VR8204/VR8304
SERIES GAS VALVES
(BSI069 - 345)
ROBERTSHAW
+
TH
TR
7000DERHC
GAS VALVE
(BSI379)
2. VENT DAMPER REQUIRED ON BSI069 - BSI276, OPTIONAL ON BSI310 -BSI379
3. ON BOILERS LESS VENT DAMPER, DAMPER HARNESS IS NOT USED. RED AND
BLUE LEADS SHOWN ARE JUMPED TOGETHER USING RED JUMPER WIRE.
FIGURE 19: WIRING DIAGRAM, INTERMITTENT IGNITION AND McDONNELL & MILLER MODEL
#67 LOW WATER CUTOFF
23
22
Page 24

NOTE
SAFE LIGHTING AND OTHER PERFORMANCE CRITERIA WERE MET WITH THE GAS MANIFOLD AND
CONTROL ASSEMBLY PROVIDED ON THE BOILER WHEN THE BOILER UNDERWENT THE TESTS
SPECIFIED IN Z21.13.
XI Start-up and Checkout
Use the following procedure for initial start-up of the boiler:
1) Make sure that the boiler is filled with water to the normal water line (28 3/4 inches above the floor or pad on which the
boiler is installed)
2) Check all new gas piping for leaks and purge piping sections that are filled with air. See Part 4 of the National Fuel Gas
Code for additional information on testing and purging gas lines.
WARNING
•
NEVER USE A FLAME TO CHECK FOR GAS LEAKS.
• MAKE SURE THAT THE AREA AROUND THE BOILER IS CLEAR AND FREE FROM COMBUSTIBLE
MATERIALS, GASOLINE, AND OTHER FLAMMABLE VAPORS AND LIQUIDS.
• DAMPER MUST BE IN OPEN POSITION WHEN APPLIANCE MAIN BURNER IS OPERATING.
3) Verify that vent system is complete and free of obstructions before attempting to fire boiler.
4) Inspect all wiring for loose or uninsulated connections.
5) Make sure the main burners are seated properly in the rear of burner tray and on orifices.
6) Adjust steam pressure limit control for a cut-in pressure of 0.5 psi and a differential pressure of 1 psi.
7) Adjust thermostat to the highest setting.
8) Start the boiler using the appropriate lighting instructions for the gas valve on the boiler on pages 25-28.
9) Upon initial start-up, the gas train will be filled with air. Even if the gas line has been completely purged of air, it may take
several tries for ignition before a flame is established. Once a flame has been established for the first time, subsequent
calls for burner operation should result in a flame on the first try.
10) Observe pilot burner flame:
• See Figure 20 for standing pilot. Pilot burner should produce single steady medium blue flame covering around 3/8”
to ½” of thermocouple tip.
• See Figure 21 for intermittent ignition. Pilot burner produces three flames. The center one should be a steady medium
blue flame covering around 3/8” to ½” of spark electrode/flame rod.
12) Make sure vent damper is in open position when main burners are firing.
13) Inspect the main burner flames visible through the observation port in burner access panel. The flame should be stable
and mostly blue (see Figure 22). No yellow tipping should be present; however, intermittent flecks of yellow and orange in
the flame are normal.
14) Check entire gas train for leaks using soap and water or other approved leak detection method while boiler is firing. Fix
any leaks found immediately.
15) Run gas valve safety shutdown test:
• For standing pilot boiler models, disconnect the thermocouple from gas valve. Both pilot burner and main burners
should stop firing.
• For intermittent ignition boiler models, with main burners firing, disconnect ignition cable from ignition module. Both
pilot burner and main burners should stop firing.
24
23
Page 25

16) Check the manifold pressure and adjust if necessary. To do this, use the following procedure:
WARNING
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THE FOLLOWING PROCEDURE EXACTLY COULD RESULT IN OVER-FIRING OF
THE BOILER AND A CARBON MONOXIDE HAZARD.
a) Connect a manometer to the inlet pressure tap on the gas valve (see Figures 23 and 24).
b) Check the inlet pressure with all gas appliances on and off. The inlet pressure at the boiler must be within the
following limits regardless of what combination of appliances is firing:
Inlet Press (inches w.c.) Natural Gas LP Gas
Min. 5.0 11.0
Max. 14.0 13.0
If the inlet pressure falls outside of these limits, find and correct the cause of the problem before proceeding further.
c) Connect a manometer to the manifold (outlet) pressure tap on the gas valve (see Figures 23 and 24).
d) Read the manifold pressure. It should be set at:
Natural Gas LP Gas
Manifold Press. (inches w.c.) 3.5 10.0
e) If a manifold pressure adjustment is needed, make the adjustment by turning the pressure regulator (see Figures 23
and 24) screw clockwise to raise the pressure and counter clockwise to reduce the pressure. If a manifold pressure
adjustment is made, recheck the line pressure to be certain that it is still within acceptable limits. Replace the cover
screw on the regulator.
FIGURE 20: STANDING PILOT
BURNER FLAME
FIGURE 21: INTERMITTENT IGNITION
PILOT BURNER FLAME
25
24
Page 26

LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOILERS EQUIPPED WITH HONEYWELL
VR8200 AND VR8300 SERIES GAS VALVES (STANDING PILOT)
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or explosion
may result causing property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
A. This appliance has a pilot which must be
lighted by hand. When lighting the pilot, follow
these instructions exactly.
B. BEFORE LIGHTING smell all around the
appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next
to the floor because some gas is heavier than
air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any appliance.
Do not touch any electric switch; do not
use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from
a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP! Read the safety information above on
this label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. Remove front access panel.
5. Rotate the gas control knob clockwise to OFF.
RESET BUTTON
GAS OUTLET
GAS INLET
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call
the fire department.
C. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas
control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will
not push in or turn by hand, don’t try to repair it,
call a qualified service technician. Force or
attempted repair may result in a fire or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the appliance and to
replace any part of the control system and any
gas control which has been under water.
8. Turn Knob on gas control counterclockwise
to “PILOT”.
9. Push down and hold the red reset button while
you light pilot burner with a match.
After about one minute, release reset button.
Pilot should remain lit. If it goes out, turn gas
control knob clockwise to OFF. To relight,
repeat steps 5-9.
If button does not pop up when released, stop
and immediately call your service technician
or gas supplier.
If the pilot will not stay lit after several tries,
turn the gas control knob to “OFF” and call
your service technician or gas supplier.
GAS CONTROL KNOB
GAS VALVE - TOP VIEW
(SHOWN IN “ON” POS ITION)
6. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, including near the floor. If you then
smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety inform ation above on this label. If you don’t smell gas,
go to the next step.
7. Find pilot - follow metal pilot
tube from gas control to
pilot burner.
PILOT
BURNER
THERMOCOUPLE
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
26
25
10. After pilot remains lit when red reset button is
released, turn gas control knob counterclockwise
to ON.
11. Replace front access panel.
12. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
13. Set thermostat to desired setting.
3. Push in gas control knob slightly and turn
clockwise to “OFF”. Do not Force.
146-80-254 Rev. 0
(Standing Pilot)
Page 27

LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOILERS EQUIPPED WITH ROBERTSHAW
7000ERHC SERIES GAS VALVES (STANDING PILOT)
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE LIGHTING
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or explosion
may result causing property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
A. This appliance has a pilot which must be
lighted by hand. When lighting the pilot, follow
these instructions exactly.
B. BEFORE LIGHTING smell all around the
appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next
to the floor because some gas is heavier than
air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any appliance.
Do not touch any electric switch; do not
use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from
a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP! Read the safety information above on
this label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. Remove front access panel.
5. Rotate the gas control knob clockwise to OFF.
POSITION
INDICATOR
PILOT
ON OFF
GAS CONTROL KNOB
SHOWN IN "OFF" POSITION
6. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, including near the floor. If you then
smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety inform ation above on this label. If you don’t smell gas,
go to the next step.
7. Find pilot - follow metal pilot
tube from gas control to
pilot burner.
PILOT
BURNER
GAS
INLET
THERMOCOUPLE
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call
the fire department.
C. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas
control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will
not push in or turn by hand, don’t try to repair it,
call a qualified service technician. Force or
attempted repair may result in a fire or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the appliance and to
replace any part of the control system and any
gas control which has been under water.
8. Turn Knob on gas control counterclockwise
to “PILOT”.
9. Push down and hold the Knob while
you light pilot burner with a match.
After about one minute, release reset button.
Pilot should remain lit. If it goes out, turn gas
control knob clockwise to OFF. To relight,
repeat steps 5-9.
If button does not pop up when released, stop
and immediately call your service technician
or gas supplier.
If the pilot will not stay lit after several tries,
turn the gas control knob to “OFF” and call
your service technician or gas supplier.
10. After pilot remains lit when red reset button is
released, turn gas control knob counterclockwise
to ON.
11. Replace front access panel.
12. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
13. Set thermostat to desired setting.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
27
26
3. Push in gas control knob slightly and turn
clockwise to “OFF”. Do not Force.
Page 28

LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOILERS EQUIPPED WITH HONEYWELL
VR8204 AND VR8304 SERIES GAS VALVES (INTERMITTENT PILOT)
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE LIGHTING
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or explosion
may result causing property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
A. This appliance is equipped with an ignition
device which automatically lights the pilot.
Do try to light the pilot by hand.
not
B. BEFORE LIGHTING smell all around the
appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next
to the floor because some gas is heavier than
air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any appliance.
Do not touch any electric switch; do not
use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from
a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP! Read the safety information above on
this label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition
device which automatically lights the pilot.
Do try to light the pilot by hand.not
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call
the fire department.
C. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas
control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will
not push in or turn by hand, don’t try to repair it,
call a qualified service technician. Force or
attempted repair may result in a fire or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the appliance and to
replace any part of the control system and any
gas control which has been under water.
5. Remove front access panel.
6. Rotate the gas control knob clockwise to OFF.
7. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, including near the floor. If you then
smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety inform ation above on this label. If you don’t smell gas
go to the next step.
GAS CONTROL KNOB
(SHOWN IN “ON” P OSITION)
GAS OUTLET
GAS VALVE - TOP VIEW
GAS INLET
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
8. Rotate the gas control knob counter clockwise
to “ON”.
9. Replace front access panel.
10. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
11. Set thermostat to desired setting.
12. If the appliance will not operate, follow the
instructions “To Turn Off Gas To Appliance” and
call your service technician or gas supplier.
3. Push in gas control knob slightly and turn
clockwise to “OFF”. Do not Force.
28
27
146-80-255 Rev. 0
(Electronic Ignition)
Page 29

LIGHTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOILERS EQUIPPED WITH ROBERTSHAW
7000DERHC SERIES GAS VALVES (INTERMITTENT PILOT)
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE LIGHTING
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or explosion
may result causing property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
A. This appliance is equipped with an ignition
device which automatically lights the pilot.
not
Do try to light the pilot by hand.
B. BEFORE LIGHTING smell all around the
appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next
to the floor because some gas is heavier than
air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any appliance.
Do not touch any electric switch; do not
use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from
a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP! Read the safety information above on
this label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition
device which automatically lights the pilot.
Do try to light the pilot by hand.not
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call
the fire department.
C. Use only your hand to push in or turn the gas
control knob. Never use tools. If the knob will
not push in or turn by hand, don’t try to repair it,
call a qualified service technician. Force or
attempted repair may result in a fire or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the appliance and to
replace any part of the control system and any
gas control which has been under water.
5. Remove front access panel.
6. Rotate the gas control knob clockwise to OFF.
7. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, including near the floor. If you then
smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety inform ation above on this label. If you don’t smell gas
go to the next step.
POSI TI ON
INDICATOR
ON OFF
GAS CONTROL KNOB
SHOWN IN "OFF" POSITION
GAS
INLET
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if
service is to be performed.
8. Rotate the gas control knob counter clockwise
to “ON”.
9. Replace front access panel.
10. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
11. Set thermostat to desired setting.
12. If the appliance will not operate, follow the
instructions “To Turn Off Gas To Appliance” and
call your service technician or gas supplier.
3. Push in gas control knob slightly and turn
clockwise to “OFF”. Do not Force.
29
28
Page 30

FIGURE 22a: MAIN BURNER FLAME - 1” BURNERS
17) Test thermostat operation while the boiler is running. Turn the thermostat to the lowest setting. For standing pilot boiler
models, pilot burner should remain lit but the main burners should stop firing. For intermittent ignition boiler models both pilot
burner and main burners should stop firing. Raise the thermostat back to the highest setting. The main burners (for standing
pilot boiler models) or pilot burner and main burners (for intermittent ignition boiler models) should relight.
18) Verify low water cutoff operation while the boiler is running. Slowly open drain valve and drain boiler until the water level
drops below low water cutoff line. Water still should be visible in the gauge glass when the low water cutoff shuts down the
main burners. For standing pilot boiler models, pilot burner should remain lit when the main burners stop firing. For
intermittent ignition boiler models both pilot burner and main burners should stop firing. Make sure pressure limit, thermostat
or other controls have not shut off the boiler. Upon test completion refill the boiler to the normal water level.
19) Check pressure limit control operation. When steam pressure is registered on pressure gauge, lower pressure limit setting
below gauge reading. For standing pilot boiler models, pilot burner should remain lit when the main burners stop firing. For
intermittent ignition boiler models, both pilot burner and main burners should stop firing. Raise pressure limit setting above
gauge reading. The main burners( for standing pilot boiler models) or pilot burner and main burners ( for intermittent ignition
boiler models) should relight.
20) After the boiler has operated for approximately 30 minutes, check the boiler and heating system piping for leaks. Repair any
leaks found at once.
21) Inspect the vent system for flue gas leaks. Repair any leaks found before leaving the boiler in operation.
22) Replacement of a steam boiler tends to break loose accumulated scale from the system. During the first week of operation,
blow down the #67 low water cut-off at least three times following the blow down instructions on the yellow sticker adjacent
to the low water cut-off.
FIGURE 22b: MAIN BURNER FLAME - 40mm
(“HIGH ALTITUDE”) BURNERS
23) After new boiler has been installed and put into continuous operation for several days, clean the boiler of oil, grease,
sludge, and other contaminants that may have been present in existing piping. This will prevent unsteady water line and
water carry over into supply main. The boiler boil-out should be done as follows:
a) Turn off gas supply to boiler per the appropriate Lighting and Operating instructions on page 25 - 28.
b) Drain water from boiler until about one inch of water is visible in gauge glass.
c) Run a hose or temporary piping from the boiler drain valve to a location where hot water can be safely discharged.
Drain approximately five gallons of water from the boiler and mix-in an appropriate amount of an approved boil-out
compound. Remove safety valve and refill the boiler with prepared solution through funnel inserted into elbow under
the safety valve. Run a hose or temporary piping from safety valve tapping to a location where hot water can be
safely discharged. DO NOT INSTALL ANY VALVES IN THIS LINE.
d) Light off the boiler per the appropriate instructions on page 25 - 28. Run boiler for several hours, boiling the water,
without generating steam pressure. Open the water feed valve sufficiently to allow a slight overflow of water through
the safety valve tapping drain line. Continue boiling until water coming out is clear.
30
29
Page 31

FIGURE 23a: GAS VALVE DETAIL - HONEYWELL VR8200 OR VR8300 (STANDING PILOT)
FIGURE 23b: GAS VALVE DETAIL - ROBERTSHAW 7000ERHC AND HONEYWELL V8295 (STANDING PILOT)
FIGURE 24a: GAS VALVE DETAIL - HONEYWELL VR8204 AND VR8304 (INTERMITTENT IGNITION)
FIGURE 24b: GAS VALVE DETAIL - ROBERTSHAW 7000DERHC (INTERMITTENT IGNITION)
31
30
Page 32

e) Turn off gas supply to boiler per the appropriate Lighting and Operating instructions on pages 25 - 28. Drain hot
water from boiler through boiler drain valve to a location where hot water can be safely discharged. Refill the boiler
to normal water line level. If water in the gauge glass does not look clear, repeat above boil-out procedure again until
water is clears.
f) Reinstall safety valve and related piping.
g) Conduct pH and Alkalinity test of water in the system. The pH reading should be in 7 to 11 range.
NOTE
When substantial amount of make-up water is used due to lost condensate, or when make-up water is hard or corrosive,
water treatment is required. Contact qualified water treatment company for recommended water treatment compounds
and procedures.
XII Service and Maintenance
On a continuous basis:
1) Keep the area around the boiler free and clear from combustible materials, gasoline, and other flammable vapors and
liquids.
2) Keep the area around the boiler and boiler room ventilation openings clear of objects which might obstruct the flow of
combustion and ventilation air.
On at least a weekly basis:
For boilers equipped with a #67 low water cut-off, blow down the low water cut-off following the instructions on the yellow
sticker adjacent to the low water cut-off. During this blow down, the low water cutoff should shut down the burners. If it does
not the low water cut-off should be replaced immediately.
On an annual basis:
1) Turn off electrical power and gas supply to the boiler
2) Inspect the flue passages for signs of blockage. If there is any carbon in the combustion chamber or the flue passages,
clean the heat exchanger before proceeding further. See the cleaning procedure below.
3) Remove any debris found in the combustion chamber, being careful not to disturb combustion chamber insulation.
4) Remove all burners, noting the location of the pilot main burner. If burners show signs of deterioration, they should be
replaced (some discoloration around the burner ports is normal). Clean the burners by first brushing the ports with a soft
bristle brush and then vacuuming out any debris through the venturi opening.
5) Inspect the pilot assembly:
• Standing Pilots - Check the thermocouple for deterioration (some discoloration of the thermocouple is normal). If any
deterioration is present, replace the thermocouple. Inspect the pilot assembly for deposits and deterioration. Clean or
replace the pilot assembly as necessary.
• Intermittent Pilots - Clean any deposits found on the electrode and grounding strap. The ideal gap between the
electrode and the ground strap is 1/8”. Inspect the porcelain for cracks or other deterioration. Replace pilot assembly
if deterioration is found.
6) Inspect the combustion chamber insulation for deterioration.
7) (Intermittent Pilot Boilers) - Inspect the ignition cable insulation for cracks or other deterioration. If deterioration is found,
CAUTION
LABEL ALL WIRES PRIOR TO DISCONNECTION WHEN SERVICING CONTROLS. WIRING ERRORS CAN CAUSE
IMPROPER AND DANGEROUS OPERATION. VERIFY PROPER OPERATION AFTER SERVICING
32
31
Page 33

replace cable.
8) Reinstall burners, being careful to put the pilot main burner in its original location.
9) Inspect all boiler wiring for loose connections or deterioration.
10) Inspect the vent system:
• Make sure that the vent system is free of obstructions.
• Make sure that all vent system supports are intact.
• Inspect joints for signs of condensate or flue gas leakage.
• Inspect venting components for corrosion or other deterioration. Replace any defective vent components.
11) Inspect the boiler and system for leaks.
12) Inspect the low water cut-off:
• For Hydrolevel CG400A low water cut-offs - Remove and inspect the probe for scale and sediment buildup. Clean any
sediment or scale from the probe with a scouring pad or steel wool. Consult the Hydrolevel CG400 manual for any
additional maintenance information. Test the low water cut-off before placing the boiler back into service.
• For McDonnell & Miller #67 low water cut-offs - Remove and inspect switch and float mechanism. Inspect float bowl
for mud accumulation. Clean as required. Replace the switch and float mechanism every five years or 100,000 cycles.
Consult the McDonnell and Miller #67 manual for any additional maintenance information. Test the low water cut-off
before placing the boiler back into service.
13) Allow the boiler to cool to room temperature. Remove the drain valve and 2 x 3/4 bushing on the left side of the boiler. Use
a flashlight to inspect the bottom row of pushnipples for accumulated scale or mud. If a significant amount is present, use the
following procedure to clean the inside of the heat exchanger:
a) Temporarily install a 1 1/4 inch or larger full port ball valve in place of the boiler drain. Temporarily pipe the outlet
of this valve to a location where hot water and steam can be safely discharged.
b) Make sure that this valve is closed and that the water level is at the normal water line.
c) If a king valve is present in the steam main takeoff, close it. Alternatively, temporarily replace enough of the
vents on the mains and/or radiators with plugs so that 2-5 psi can be developed when the boiler is fired.
d) Fire the boiler and allow it to steam until 2-5 psi is registered on the gauge.
e) Turn off the burners and immediately fully open the 1-1/4 valve.
f) Allow the boiler to blow down until either the water runs clear or the water level reaches the bottom of the gauge
glass.
g) Allow all parts of the boiler to cool to room temperature. Drain the boiler completely and remove the 1-1/4 valve.
h) If significant mud or scale is still present in the bottom of the boiler, repeat steps (b) through (g) until all mud or
scale is removed.
i) Once all mud or scale is removed, replace the 1-1/4 valve and temporary blow-down piping with the standard drain
valve. After all parts of the boiler are at room temperature, refill the boiler to the normal water line.
14) Place the boiler back in operation using the procedure outlined in “Start-up”. Check the pilot line and any other gas piping
NOTE
A large accumulation of mud or scale in the bottom of the heat exchanger is usually a sign of excessive feedwater make-up.
Such accumulations can cause severe heat exchanger damage. If mud or scale accumulations are found:
• Make sure that all vents are in working order. Vents should not permit any passage of steam or water.
• Check all steam and return piping for leaks. Be aware that buried return piping can leak and go undetected
during normal operation.
33
32
Page 34

disturbed during the inspection process for leaks.
Heat Exchanger Cleaning Procedure
1) Turn off electrical power and gas supply to the boiler
2) Disconnect the damper and vent connector from the boiler.
3) Remove the upper front and top jacket panels. If possible, remove the rear and left side jacket panels
4) Remove the burners.
5) Remove the blocked vent (“spill”) switch
6) Remove the ¼-20 nuts and washers holding the flue collector onto the heat exchanger.
7) Carefully remove the flue collector gasket strips and set them aside.
8) Remove the flue collector from the heat exchanger.
9) Clean the flue passageways using a stiff bristle brush. Be certain that all foreign material is removed from the gaps
between the pins
10) Clean the bottom surfaces of the heat exchanger
11) Put a light in the combustion chamber and look through the flue passages from the top to verify that they have been
thoroughly cleaned.
12) Replace the flue collector gasket strips. If desired, RTV silicone sealant with a 500F intermittent duty temperature may be
substituted for this rope gasket. The flue collector must be thoroughly sealed to the heat exchanger.
13) Replace the ¼-20 nuts and washers that hold down the flue collector
14) Reattach all the jacket components.
15) Reinstall burners, being careful to put the pilot main burner in its original location.
WARNING
SOOT DEPOSITS IN THE FLUE PASSAGES ARE A SIGN THAT THE BOILER MAY BE OPERATING AT HIGH
CARBON MONOXIDE (CO) LEVELS. AFTER CLEANING THE BOILER OF SOOT DEPOSITS, CHECK THE CO
LEVEL IN THE FLUE GAS TO INSURE THAT THE BOILER IS OPERATING PROPERLY.
If it is necessary to check CO, use a combustion analyzer, or other instrument which is designed to measure CO in flue gas.
A CO “sniffer” designed for testing CO levels in ambient air cannot be used to check boiler combustion. Take a flue gas
sample by inserting a sample probe through the draft diverter opening and into the flue collector so that the sample is taken
in the area directly over the heat exchanger. Do not take a sample until the boiler has been firing for at least five minutes.
A normal CO reading for a BSI series boiler is less than 50ppm (0.005%). A reading of more than 100ppm (0.01%) is indicative of a combustion problem.
Some causes of excessive CO include:
• Incorrectly sized main burner orifice for the altitude at which boiler is installed
• Crooked or out-of-round orifice holes (never attempt to drill orifice for this boiler in the field)
• Partially plugged flue passages
• Improper manifold pressure
• Foreign material in burner venturis or burner ports
• Leak in seal between flue collector and heat exchanger
• Inadequate supply of combustion air
16) Replace the blocked vent switch.
17) Reconnect the damper and vent system.
34
33
Page 35

XIII Troubleshooting
The following pages contain troubleshooting charts for use in diagnosing control problems. To use these charts, go to the
box marked “Start” at the top of the chart on page 35 or 37 and follow the appropriate path though the chart until a box with a
list of possible causes is reached. If the problem is known to be within the ignition system, go directly to the appropriate
troubleshooting guide for the boiler (standing pilot on page 39 or intermittent ignition on page 40). In using these charts, the
following should be kept in mind:
1) These charts are only meant to be used by a professional heating technician as an aid in diagnosing control problems.
2) Where applicable, follow all precautions outlined in the appropriate lighting instructions on pages 25 - 28.
3) In general, these charts assume that there are no loose or miswired electrical connections. Before using these charts,
inspect all electrical connections on the boiler to make sure that they are tight. Also, check the wiring on the boiler
against the appropriate wiring diagram in Figures 16 - 19.
4) The possible causes at the end of each branch in these charts are not listed in order of likelihood. All controls on the BSI
are tested at least once in the manufacturing process and a defective control or component is generally the least likely
cause. Before replacing a component, try to rule out all other possible causes.
5) These troubleshooting charts assume that the vent damper is closed at the beginning of the troubleshooting process.
With the 120 volts applied to the boiler and no call for heat, the damper should go to the closed position. If it does not,
do the following:
• Confirm that 120 volts is applied to the boiler and that there is no call for heat.
• Make sure that the switch on the damper is in the “automatic” position.
• Unplug the harness from the damper and check for 24 volts across pin #1 (blue) and pin #4 (yellow).
• If voltage is present, the damper is defective or there is an obstruction in the path of the damper blade.
• If no voltage is present, there is either a loose connection in the damper harness or the transformer is defective.
6) If the charts indicate that the transformer is defective, it is possible that this transformer has been destroyed by a short
circuit in the boiler wiring. Before replacing the transformer, carefully inspect all low voltage wiring on the boiler for
places where it is touching the frame of the boiler or wiring on the other side of the transformer.
7) If the charts indicate that the R8225 relay is defective, there is a good chance that a second transformer is present in the
thermostat circuit, resulting in the application of 48 volts across the relay coil. In older buildings, this transformer may be
hidden in a location far from the boiler. If this second transformer exists, it must be found and removed before the R8225 is
replaced.
8) When checking voltage across damper harness pins, be careful not to insert the meter probes into the pins. Doing so may
damage the pin, resulting in a loose connection when the harness is reconnected.
35
34
Page 36

Troubleshooting Chart for BSI Boilers Equipped with
Hydrolevel CG400A Low Water Cut-offs and Vent Dampers
Caution: Read page 34 before attempting to use this chart
START
The rmos tat
calls for heat
120 v olts ac ros s
black and w hite
transformer
Y
*Pow er o f f
*Blow n fuse or
tripped
breaker
*Mis w ired or
loose 120 volt
connection
leads?
Vent
damper
open?
Is there an audible
click as R8225 relay
pulls in w hen the
thermostat calls for
heat?
N
24 volts acros s
blue and y ellow
w ires inside
N
N
N
Is 24 vo l t s
present across
brow n and
yellow leads on
R8225 relay?
junction box?
Y
24 volts pr es ent
betw een each
press ur e limit
connection and
yellow transformer
connection?
Y
Y
24 volts betw een
P2 and 2 on
CG400 LWCO?
Y
Y
N
N
* Jumper miss ing
betw een 1 and P1 on
CG400
* Poor co nnec tion
betw een transformer
and terminals 1 & 2 on
CG400
N
* Boiler off on pressure limit
* Defective pressure limit
Y
Is y ellow
LED lit on
LWCO?
N
* Boiler off on low w ater
* Loos e probe connec tion
* Poor ground path f rom
heat exchanger to CG400
case
Y
* De fec tiv e
transf ormer
See Note #6 on
page 34
* Bad connection in
thermostat w iring
* Defective thermos tat
* Thermostat misw ired or
misapplied
Disconnect
thermostat and
temporar ily jump
boiler thermostat
connec tions
together
Y
Does rela y
pull in now ?
* Def ectiv e
R82 25
See Note #7
on page 34
N
36
35
* Loos e
connection
betw een
transf ormer
and R8225
coil
24 volts present
across blue lead on
R8225 and y ellow
transf ormer leads?
N
Y
* Def ec tiv e R8225
Page 37

Main
burners
light?
N
Do burners
Y
shut down when
pressure
exceeds limit
setting?
Y
Do burners shut
down when water
level drops below
cut-off point?
Y
END
24 volts across
red damper lead
and yellow
transformer
lead?
Y
24 volts across
standing pilot gas
valve terminals or
terminals 5&6 on
S8600 module?
24 volts across 1&4
(blue&yellow) and 2&4
(orange&yellow ) on
damper end of
harness?
N
N
Y
* Defective damper
* Defective or loose
damper harness
* Obstruction in
path of damper
blade
* Refer to standing pilot
or intermittent ignition
troubleshooting chart
(page 39 or 40).
24 volts
across spill
switch?
N
Y
24 volts
across rollout
switch?
* Defective
pressure limit
control
* Blockage in
siphon tube
N
*Grounded probe or probe
lead
* Defective L.W.C.O.
DO NOT OPERATE BOILER
UNTIL THIS PROBLEM IS
CORRECTED
YN
*Chimney blockage
*Chimney system not
contructed in accordance
with Parts 7 and 10 of
National Fuel Gas Code .
*Down draft
*Inadequate combustion air
supply in boiler room
Y
* Defective or
loose damper
harness
N
* Defective or loose
damper harness
* Defective damper
motor
*Obstruction in path
of damper blade
37
36
N
*Loose electrical
connection in spill
switch or rollout
switch wiring or gas
valve common
*Rollout switch open.
Replace with exact
replacement (see parts
list). Check for blocked
heat exchanger.
Page 38

Troubleshooting Chart for BSI Boilers Equipped with
McDonnell & Miller #67 Low Water Cut-offs and Vent Dampers
Caution: Read page 34 before attempting to use this chart
START
The rmos tat
calls f or heat
120 volts across
black and w hite
transf ormer
Y
*Po w e r of f
*Blow n fuse or
tripped
breaker
*Mis w ir e d o r
loose 120 volt
connection
leads?
Vent
damper
open?
Is there an audible
click as R8225 relay
pulls in w hen the
thermostat calls for
heat?
N
24 volts across
blue and yellow
w ires inside
N
N
N
Is 24 volts
present acros s
brow n and
yellow leads on
R8225 relay ?
junction box?
Y
24 volts present
betw een each
pressure limit
connection and
yellow transf ormer
connection?
Y
Y
betw een terminal # 1
Y
N
24 volts
on 67 LWCO and
yellow tranf ormer
connection?
Y
N
* Boiler of f on pres sure limit
* Defective pressure limit
Y
N
* Boiler off on low water
* Def ec tiv e
transf ormer
See Note #6 on
page 34
* Bad connection in
thermostat w iring
* Def ec tiv e thermostat
* Thermostat misw ired or
misapplied
Disconnect
thermostat and
tempor arily jump
boiler thermostat
connections
together
Y
Does r elay
pull in now ?
* Def ec tiv e
R8225
See Note #7
on page 34
N
38
37
* Loos e
connection
betw een
transf ormer
and R8225
coil
24 volts present
across blue lead on
R8225 and yellow
transf ormer leads?
N
Y
* Def ect iv e R8225
Page 39

Main
burners
light?
N
Do burners
Y
shut down when
pressure
exceeds limit
setting?
Y
Do burners shut
down when water
level drops below
cut-off point?
Y
END
24 volts across
red damper lead
and yellow
transformer
lead?
Y
24 volts across
standing pilot gas
valve terminals or
terminals 5&6 on
S8600 module?
24 volts across 1&4
(blue&yellow) and 2&4
(orange&yellow ) on
damper end of
harness?
N
N
Y
* Defective damper
* Defective or loose
damper harness
* Obstruction in
path of damper
blade
* Refer to standing pilot
or intermittent ignition
troubleshooting chart
(page 39 or 40).
24 volts
across spill
switch?
N
Y
24 volts
across rollout
switch?
* Defective
pressure limit
control
* Blockage in
siphon tube
N
*LWCO float bowl filled with
mud
* Defective LWCO
DO NOT OPERATE BOILER
UNTIL THIS PROBLEM IS
CORRECTED
YN
*Chimney blockage
*Chimney system not
contructed in accordance
with Parts 7 and 10 of
National Fuel Gas Code .
*Down draft
*Inadequate combustion air
supply in boiler room
Y
* Defective or
loose damper
harness
N
* Defective or loose
damper harness
* Defective damper
motor
*Obstruction in path
of damper blade
39
38
N
*Loose electrical
connection in spill
switch or rollout
switch wiring or gas
valve common
*Rollout switch open.
Replace with exact
replacement (see parts
list). Check for blocked
heat exchanger.
Page 40

Standing Pilot Ignition System Troubleshooting Chart
START
(24 VOLTS PRESENT ACROSS TH AND TR
ON GAS VALVE, BUT MAIN BURNERS DO
NOT LIGHT)
Y
Ensure knob
Pilot lit?
N
Turn control on
gas valve t o
PILOT. Depress
red button and
light pilot. Hold
button for at
least one
minute.
Does pilot
light?
N
on gas valve is
set to ON
Y
Turn control
on gas valve
to ON .
stay lit when
red button is
Y
Does pilot
released?
Main
burners
light?
N
Caution: Read page 34 before
Y
*Defective gas
val ve
Disc onnec t
thermocouple from
gas valve. Connect a
N
volt meter to the
thermoc ouple. Light
the pilot and hold
down the red butt on
while reading the
voltage across the
thermocouple.
attempting to use this chart
Does pilot
stay lit?
N
Y
END
*Loose
thermocouple
connec tion at
gas valve.
*Defect ive
thermocouple.
*Condensation
quenching pilot.
*Low line
press ure.
Line pressure
within the range
indicated on
boiler's rating
plate?
Y
*Pilot tubing
blocked, k ink ed
or leaking
*Pilot orifice
blocked
*Gas li ne not
purged of air
*Pilot improperly
adjus ted.
N
Consult gas
supplier.
*Defective thermocouple
*Pilot improperly
adjusted
*Pilot tube blocked, kink ed, or
leaking
*Pilot orifice partially plugged
Is voltage at
least 18mV?
40
394140
Y
N
*Loose or defective
thermocouple
connection at gas valve
*Defective gas valve
Page 41

Intermittent Ignition System Troubleshooting Chart
START
(24 volts is present across 5 and 6 on S8600
module, but main burners do not light)
Spark
across
ignitor/sensor
gap?
Can you
hear
sparking?
Y
Y
Pilot
lights?
N
24 volts
across
terminals 2&3
at S8600?
Y
Y
N
*Defective
S8600 module
spark st op
when pilot
Does
lights?
NN
Caution: Read page 34 before
attempting to use this chart
Y
terminals 1&2
Main
burner
lights?
N
24VAC
across
on S8600?
Y
Y
END
N
*Defecti ve
S8600
module
N
*Faulty
S8600
module
*Break in
spark cable
insulation
*Break in pilot
porcelain
*Incorrect pilot
spark gap
*Loose
connection in
spark cable
24 volts
across PV &
MV/PV at gas
val ve ?
Y
*Defective EI
wiring
harness .
* Low line pres sure
*Plugged, kink ed or leaking
pilot tubing
*Plugged pilot orifice
*Gas line not purged of air
N
*Loose connect ion in
ignition c able or
ground wire
*Pil ot el ect rode
porcelain cracked
*Pilot flame not
covering gap
between elect rode
and grounding
strap
*Low gas pressure
at gas valve inlet
24 volts
between MV &
MV/PV on gas
val ve ?
N
*Defective EI
harnes s
*Defective
gas valve
Y
*Loose
ground
connection
*Defective pilot assembly
*Defective gas valve
*Defective S8600
module
Page 42

XIV PARTS
0345379
)
The following parts may be obtained from any Crown distributor. To find the closest Crown distributor, consult the area Crown
representative or the factory at:
Crown Boiler Co.
Customer Service
P.O. Box 14818
Philadelphia PA. 19134
www.crownboiler.com
For boilers installed at elevations above 2000 ft, consult the local Crown representative or the factory for the correct main burner
orifice.
KEY # DESCRIPTION
1 BSI HEAT EXCHANGER ASSY. 1 ea. 850013 8 50014 850015 850016 850017 850018 8500 19 850 020 850021 850022
* BSI/CWI LEFT END SECTION 7500 01 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* BSI RIGHT END SECTION 850002 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* BSI/CWI INTERMEDIATE SECTI ON 750003 1 ea. 2 ea. 3 ea. 4 ea. 5 ea. 6 ea. 7 ea. 8 ea. 9 ea . 1 0 ea.
* UPPER PUSHNIPPLE 275075 2 ea. 3 ea. 4 ea. 5 ea. 6 ea. 7 ea. 8 ea. 9 ea. 10 ea. 11 e a.
* LOWER PUSHNIPPLE 275070 2 ea. 3 ea. 4 ea. 5 ea. 6 ea. 7 ea. 8 ea. 9 ea. 10 ea. 11 ea.
2 BASE TRAY 1 ea. 700643 700644 700645 700646 700 647 700648 700649 700650 700651 700652
3 BASE WRAPPER 1 ea. 700663 700664 700665 700666 700 667 700668 700669 700670 700671
4 BURNER TRAY (1" BURNERS) 1 ea. 7006 83 700684 700685 700686 700687 700688 700689 700690 700691
4 BURNER TRAY (40mm BURNERS) 1 ea. 7516 83 751684 751685 751686 751687 751688 751689 751690
BASE FRONT PANEL ASSY. ( I NCLUDES
5
INSULATION
6 BURNER ACCESS PANEL 1 ea. 700623 700624 700625 700626 700627 700628 700629 700630 700631
7 BASE END INSULATION 720601 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea . 2 ea.
8 BASE REAR INSULATI ON 1 ea. 720603 720604 720605 720606 720 607 720608 720609 720610 720611 720612
9 BASE LEG ASSY. 700110 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 6 ea. 6 ea.
10 1/4-20 X 1/2" SELF TAPPING SCREW 900100 20 ea. 20 ea. 20 ea. 20 ea. 21 ea. 21 ea. 21 ea. 21 ea. 25 ea. 25 ea.
11 1/2" x 2" SEALING STRI P 90 0146 3.7 ft 4.2 f t 4.8 f t 5. 3 ft 5. 9 ft 6.4 ft
12 ROLLOUT SWITCH G4AM0600240C 960122 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
13 ROLLOUT SWITCH BRACKET 900121 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
14 #8 x 3/4" SELF TAPPING SCREW 90-048 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
15 #10 x 1/2" SHEET METAL SCREW 90-212 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea.
16 5/16 USS FL AT WASHER 900102 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
17 5/16- 18 LOCK NUT 900103 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
18 5/16- 18 x 1-1/ 4 SELF TAPPING SCREW 9001 01 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
20 DRAFT DI VERTER ASSEMBLY 1 ea. 850123 85012 4 8501 25 8501 26 850127 850128 850129 850130 850131 85 0132
21 1/2" x 1" SEALING STRI P 90 0145 3 ft 3. 3 ft 3.5 ft 3.8 ft 4.1 f t 4.4 f t
22 1/4- 20 x 1-1/4" CARRI AGE BOLT 90-201 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
23 1/4" USS FLAT WASHER 90 -215 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea . 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
24 1/4-20 WING NUT 900125 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
BLOCKED VENT SWI TCH ASSY.
(INCLUDES MOUNTING BRACKET)
QTY. OR
CROWN P.N.
1 ea. 700603 700604 700605 700606 700 607 700608 700609 700610 700611 700612
960123
69 103 138 172 207 241 276
1 ea. 1 ea.25
QUANTITY PER BOILER OR CROWN P.N.
7.0 f t 7. 5 ft 8.0 ft 8.5 ft
4.6 f t 4. 9 ft 5.2 ft 5.5 ft
31
700672
700692
1 ea.1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.1 ea.
700632
* NOT PICTURED
42
41
Page 43

43
42
Page 44

(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
)
KEY # DESCRIPTION
1" BURNER W ITH PILOT BRACKET
41
(Q350 PILO T)
1" BURNER WITH PILOT BRACKET
(Q327 NAT , Q348 PILOTS)
1" BURNER WITH PILOT BRACKET
41
(Q327 LP PILO T)
42 1" BURNER LES S PILO T BRAC KET 150501 2 ea. 4 ea . 6 ea. 8 ea. 11 ea. 1 3 ea. 15 ea. 17 ea. 20 ea. 22 ea.
43 MANI FOLD (1" BURNERS) 1 ea. 700153 700154 700155 700156 700157 700158 700159 700160 700161 700162
44 NAT GAS ORIFICE (#42 DRILL SIZE) 950298 3 ea.
44 NAT GAS ORIFICE (#44 DRILL SIZE) 950300 5 ea. 7 ea. 9 ea.
44 NAT GAS ORIFICE (#47 DRILL SIZE) 950303 12 ea. 14 ea. 16 ea. 18 ea. 21 ea.
44 NAT GAS ORIFICE (#48 DRILL SIZE) 950304 23 ea.
LP GAS
44
44
44
45 GAS VALVE (STND. PILOT, NA T GAS) 3507010
45 GAS VALVE (STND. PILOT, NA T GAS) 3507350
45 GAS VALVE (E.I., NAT GAS) 3507020
45 GAS VALVE (STND. PILOT, NA T GAS) 3507110
45 GAS VALVE (STND. PILOT, NA T GAS) 3507355
45 GAS VALVE (E.I., NAT GAS) 3507120
45 GAS VALVE (STND. PILOT, NA T GAS)** 3507300
45 GAS VAL VE (STND. PILOT, NAT G AS)**
45 GAS VALVE (E.I., NAT GAS)
45 GAS VAL VE
45 GAS VAL VE
45
45
46 PILOT ASSY. (STND. PILOT, NAT GAS) 3504050
46 PILOT ASSY. (STND. PILOT, NAT GAS) 3504005
46a PILOT ASSY. (E.I., NAT GA S) 35-4700
46 PILOT ASSY.
46a PILOT ASS Y.
47 THERMOCOUPLE 1 ea. 35-1040 35-1040 35-1040 35-1040 35-1040 35 -1040 3501141 3501142 3501142 3501142
47a IGNIT ION CABLE 1 ea. 35 01124 3501124 3501 124 3501130 3501130 3501130
48 PILOT TUBING*** 1 ea. 90-042 90-042 90-042 90-043 90-043 90-043
49 35-1600
50 35-1650
51
51
51a
51
51a
60
60
61 40m m BURNER LESS PILOT BRACKET 15 0541 1 ea. 2 ea. 3 e a. 4 ea. 5 ea . 6 ea. 7 ea. 8 ea.
62 MANI FOLD (40mm BURNERS) 1 ea. 701253 701254 701255 701256 701257 701258 701259 701260
63
ORIFICE
LP GAS
ORIFICE
LP GAS
ORIFICE
(EXCEPT 40mm BURNERS) (VR8200C6008)
(40mm BURNERS ONLY)
(EXCEPT 40mm BURNERS) (VR8300C4134)
(40mm BURNERS ONLY)
(ROBERTSHAW 7000ERHC-S7C)
(ROBERTSHAW 7000DE RHC)
GAS VALVE
GAS VALVE
1/8 SHORT FERRULE (INCLUDED WITH
GAS VALVE)
1/8 LONG FERRULE (INCLUDED WITH
PILOT ASSEMB LY)
CAR12 PILOT ORIFICE (Q350 PILOT,
NAT GAS) - INCLUDED WITH PILOT
A26 PILO T ORIFICE (Q327 PILOT, NAT
GAS) - INCLUDED WITH PILOT ASSY.
KF24 PILOT ORI FICE (Q 348 PILOT, NA T
GAS) - INCLUDED WITH PILOT ASSY.
K14 PILO T ORIFICE (Q327 PILOT,
GAS
) - INCLUDED W ITH PILOT ASSY.
K16 PILO T ORIFICE (Q348 PILOT
GAS
- INCLUDED W ITH PIL OT ASSY.
40mm BURNER WITH PILOT BRACKET
(Q350 PILO TS)
40mm BURNER WITH PILOT BRACKET
(Q327, Q348 PIL OTS)
MAIN BURNER ORIFICE-CONSULT
CROWN REPRESEN TATIV E FOR
CORRECT SIZE
#54 DRILL SIZE
#55 DRILL SIZE
#1.25mm DRILL SIZE
STND. PILOT,
E.I. PILOT,
STND. PILOT,
E.I.,
LP GAS
LP GAS
STND. PILOT,
LP GAS
E.I.,
LP GAS
LP GAS
LP GAS
LP
LP
QTY. OR
CROWN P.N.
150502
150500
150503
950329 3 ea.
950330 5 ea. 7 ea. 9 ea.
950336 12 ea. 14 ea. 16 ea. 18 e a.
VR8200C6032
(VR820 4C6000 )
VR8300C4183
(VR8304P4298)
(V8295A1024)
3507305
3507310
3507210
(VR820 0C6040 )
3507220
(VR820 4C6018 )
3507230
(VR830 0C4548 )
3507240
(VR8304P4280)
(Q350A1644)
(Q327A1949)
(Q348A1275)
35-4020
(Q327A1915)
35-4600
(Q348A1259)
(392449)
(392449-4)
150540 1 ea.
150542
69 103 138 172 207 241 276
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
2 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
QUANTITY PER BOILER OR CROWN P.N.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.41
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
4 ea. 5 ea. 6 ea. 7 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
310 345 379
1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
3501136 3501136 3501136 3501136
900041 900041 900041
1 ea.
1 ea.
8 ea. 9 ea.3 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea.
** These Valves Piped in Series to Provide Redundant Shut-off
***1/4 Pilot Tubing Used with Robertshaw Valves
44
43
Page 45

45
44
Page 46

KEY #
75 LEFT SIDE JACKET PANEL 1 ea. 850301 850301 850301 850301 8503012 8503012 850301 2 8503015 8503015 8503015
76 RIGHT SIDE JACKET PANEL 1 ea. 850300 850300 850300 850 300 8503002 8503002 8503002 850 3005 8503005 8503005
77 REAR JACKET PANEL 1 ea. 850303 850304 850305 850306 85030 7 850308 850309 850310 850311 850312
78 TOP JACKET PANEL 1 ea. 850323 850324 850325 850326 850327 850328 850329 850330 850331 850332
79 LOWER FRONT PANEL 1 ea. 850363 850364 850365 850366 850367 850368 850369 850370 850371 850372
80 UPPER FRONT PANEL 1 ea. 850353 850354 850355 850356 850357 850358 850359 850360 850361 850362
81 DIVERTER PANEL 1 ea. 850373 850374 850375 850376 850377 850378 850379 850380 850381 850382
82 VESTIBULE PANEL 1 ea. 850383 850384 8503 85 850386 850387 850388 850389 850390 850391 850392
83 HORIZONTAL JACKET CLIP 800340 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea.
84 VERTICAL JACKET CLIP 800341 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea.
85 #10 X 1/2" SHEET METAL SCREW 90-212 2 8 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 ea. 28 e a. 28 ea.
86 DOOR KNOB 90-210 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea.
87 8-32 X 1/4" H.W .H. SCREW 90-211 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea. 2 ea.
IGNITION MODULE (E.I. BOILERS) 35-5000
*
(NATURAL GAS ONLY) (S8600F1000 )
IGNITION MODULE (E.I. BOILERS) 35-5050
*
(NATURAL OR LP GAS) (S8600M1013)
* MODULE BRACKET (E.I. BOILERS) 905000 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
88 VENT DAMPER 1 ea. 96-030 96-031 96-032 96-032 96-033 96-033 96-035 96-035 96-036 96-036
89 GLASS SET 950077 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
90 FLOAT TYPE L.W.C.O. (#67 CR-2) 400676 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
90a PROBE TYPE L.W.C.O. (CG400) 400821 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
91 PRESSURE GUAGE 95-070 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
92 3/4" SAFETY VALVE (15 psi) 95-079 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
93 90 DEGREE PIG-TAIL 95-060B 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
94 PRESSURE LIMIT (PA404A1009) 35-502 0 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
95 3/4" BOILER DRAIN 95-041 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
96 JUNCTION BOX 960155 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* TRANSFORMER MOUNTING PLATE 960156 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
98 24V TRANSFORMER (AT140D1012) 3502300 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
99 8-32 X 1/2" SELF TAPPING SCREW 90-223 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea. 4 ea.
100 SPST RELAY (R8225B1049) 3505540 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* DAMPER W IRE HARNESS 9601300 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* BLOCKED VENT SWITCH HARNESS 9601270 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* J-BOX - R.O. SWITCH HARNES S 9601280 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 e a. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* #67 L.W.C.O. - J-BOX HARNESS 9601367 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* CG400 L.W .C.O - J -BOX HARNESS 9601405 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 e a. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* PRESSURE LI MIT - J-BOX HARNESS 9601210 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
* INTERMITTENT IGNITION HARNESS 9601100 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
RED JUMPER HARNESS (LESS-DAMPER
BOILERS ONLY
DESCRIPTION
)
QTY. OR
CROWN P.N.
69 103 138 172 207 241 276
1 ea.
1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea.1 ea.1 ea.1 ea.1 ea.1 ea.1 ea.
QUANTITY PER BOILER OR CROWN P.N.
1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea. 1 ea.
310 345 379
1 ea. 1 ea.
1 ea. 1 ea.* 9601355
1 ea.
* NOT PICTURED
46
45
Page 47

47
46
Page 48

Appendix A: Knockdown Boiler Assembly Instructions
A. Before Installing
1) Thoroughly inspect the cast iron heat exchanger for any shipping damage, i.e. cracks in the castings, broken lugs or
punctures due to mishandling.
2) Do not use the heat exchanger if there is any damage to it.
3) Inspect the joints between the sections for openings. Reseal any openings with high temperature silicone sealant..
4) Keep the base in the shipping carton until it is time to perform the assembly. This keeps foreign material from
contaminating the burners or creating other hazards. Do not use the base assembly if there are any signs of visible
damage.
5) Review all of the installation requirements in this installation manual.
B. Base Assembly Preparation
1) The combination base-burner-manifold is shipped assembled from the factory. (The combination gas valve is
shipped assembled and can be found in the "Base Box".)
2) Smear a thin layer of silicone in several places across the top of the base to adhere the fiber gasket strip.
3) Install the fiber gasket strip, which was shipped in the "Base Box" (Figure A1).
4) Place the base assembly in the location where the boiler is to be installed. Refer to Section III and IV in the installation manual for additional information on placement.
C. Heat Exchanger and Flue Collector Installation
1) Position the heat exchanger above the base with the return connection located toward the front of the boiler and the
lugs, located on each end of the boiler, centered over the studs, which are on each end of the base (Figure A1).
Lower the heat exchanger over the studs, taking care not to disturb the studs which may push out if the heat
exchanger comes in contact with them. Also, take care not to disturb the ceramic fiber gasket.
2) Once the heat exchanger has been placed on the base, inspect the gasket for proper seal. Repair or replace gasket if
necessary.
3) Secure the heat exchanger with 5/16" lock nuts with nylon inserts and washers from the hardware bag.
4) Loosen nuts on tie rods until they are finger tight.
5) Fiber gasket strips are used to seal the flue collector to the heat exchanger (this is the same material used between
the heat exchanger and base). Install this gasketing on the top of the heat exchanger (Figure A1). A few dabs of
silicone may be used to keep this gasketing from shifting when the flue collector is installed.
6) Install the flue collector as shown in Figure A1. Secure with the 1/4-20 carriage bolt, nuts, and washers provided.
7) Carefully inspect the joint between the flue collector and the heat exchanger to verify that the gasket is properly
positioned.
8) Install the blocked vent switch using the #8 sheet metal screw provided as shown in Figure A1.
D. Jacket Installation
NOTE
Before installing the jacket, make sure to plug any tappings which are not going to be used. Also make sure that no tappings
are plugged which will be needed. See Figure A3 of this appendix, as well as Parts XIII and IX of the installation manual.
1) Attach the diverter Panel to the vestibule panel using two #10 sheet metal screws. Install these screws in the
outside holes.
2) Slip this diverter/vestibule panel assembly behind the draft diverter opening in the draft diverter assembly (Figure
A2). Attach to the diverter assembly using #10 sheet metal screws.
3) Attach the right side panel to the base and vestibule panel using four #10 sheet metal screws.
4) Orient the rear jacket panel so that the two notches are up. Slip the rear panel under the flange on the rear of the
side panel installed in the previous step and secure with three #10 sheet metal screws.
48
474948
Page 49

FIGURE A1: BASE, HEAT EXCHANGER, FLUE COLLECTOR ASSEMBLY
Page 50

5) Install the left side panel in the same manner as the right side.
6) Attach the front corners of the diverter panel to the side jacket panels using #10 sheet metal screws.
7) Install the horizontal (angle) jacket clips in the front edge of the side jacket panels. Slide this clip through the
rectangular slot that is about halfway up the front edge of the side jacket panels and secure with the 8-32 self
tapping screws provided.
8) Slip the Vertical Jacket Clip through the rectangular slot that is near the bottom of the front edge of the side jacket
panels. Secure with the 8-32 sheet metal screws provided.
9) Install the top jacket panel. Use #10 sheet metal screws to attach it to the rear jacket panel and the top-front corners
of the side panels.
10) Install the upper-front jacket panel. Insert the flange on the top of this panel under the top panel. Run two #10 sheet
metal screws into the horizontal jacket clips through the holes in the bottom of this panel.
11) Attach the door knobs to the Lower-Front Panel using 8-32 x 1/2 machine screws.
12) The labels have been applied at the factory. Verify the location of the labels according to the list below:
a) Clearance Label - Located on the top jacket panel.
b) Lighting Instructions - Located on the lower left corner of the right side panel next to the gas manifold
c) Lowest Permissible Water Level Plate - Located next to the bottom water gauge tapping.
d) Blow Down Card - Located just above the "Lowest Permissible" Water Level Plate
e) Wiring Diagram - Located on the inside of the removable door
f) "CROWN" Nameplate - Located on the top center of the outside of the removable door
g) Rating Plate - Located on the upper left of the right side panel
D. Gas Valve Installation
1) The gas valve assembly has been pre-piped with one half of a piping union and is to be connected to the other half of
the union located on the gas manifold.
2) Connect the pilot tubing from the pilot burner to the gas valve pilot tapping.
3) Connect the thermocouple lead to the gas valve (standing pilot boilers only).
E. Control and Trim Installation
(Refer to Figure A3 for Tapping Locations)
1) Install the pressure limit control into tapping “H” with the siphon. A ¾” x ¼” bushing has been factory installed. Do
not twist or otherwise bend the control upon installation.
2) Install the pressure gauge into tapping “B”. A ¾” x ¼” bushing has been factory installed. Tighten with wrench
applied to the square shank on the back of the gauge. Do not apply pressure on the gauge case since this may ruin the
calibration of the gauge.
3) Steam boiler with McDonnell Miller #67 float Low Water Cutoff
a) Install the low water cutoff per the instructions packed with the control.
b) Screw brass nipples with one side of the brass union into tappings “C”.
c) Attach the gauge glass / low water cutoff assembly to the other side of the brass union.
d) If not already present on the jacket, attach the blow-down card to the left side jacket panel, just above the “Lowest
Permissible Water Level” plate.
e) Provide blow down discharge piping.
4) Steam Boiler with Probe Low Water Cutoff
a) Install low water cutoff probe into tapping “B”. Handle probe with care.
b) Attach low water cutoff control to probe per the instructions packed with the control.
c) Install the gauge glass fittings and ½” extensions into tappings “C”. The lower fitting has a small drain cock.
d) Install gauge glass and protective rods in fittings.
5) Install safety valve (spindle must be in vertical position) into tapping “H” on the boiler left side (See Figure 1 in the
installation manual) using the ¾” NPT nipples and elbow supplied. Pipe the discharge of the safety relief valve to a
location where water or steam will not create a hazard or cause property damage if the valve opens. The end of the
discharge pipe must terminate in an unthreaded pipe. The safety valve discharge piping must be in an area where it is
not likely to become plugged by debris or subjected to freezing.
6) Install drain valve into tapping “J” on the boiler left side using 2 x ¾ bushing provided. (See Figure 1 in the installation
manual).
7) See Section VIII System Piping in the installation manual for instructions on completing the piping of this boiler
including the safety valve and drain valve provided by the factory.
50
495150
Page 51

FIGURE A2: JACKET INSTALLATION
Page 52

F. Electrical Wiring Connections
(Also refer to wiring diagrams in Part X of the installation manual)
1) A pre-wired junction box assembly specific to the control package ordered with the boiler has been provided by the factory.
2) Orient the junction box so the black relay, which is mounted to the outside of the junction box, is facing down.
3) Mount the junction box assembly to the right side jacket using the holes provided (See Figure 1 in the installation manual).
To do this, temporarily remove the transformer and attach the box with two #10 sheet metal screws through the holes on the
back side of the box.
4) Pressure Limit Switch - Route the grey wire pair through the bushing on the pressure limit control and connect one of the
leads numbered “0” to one of the two terminals on the switch and the other lead numbered “0” to the other terminal on the
switch.
5) Blocked Vent Switch - Locate the two wires marked “8” (one of these wires is black, the other is black with a white trace).
Connect these wires to the terminals on the blocked vent switch (it does not matter which of these wires is connected to
which terminal on the blocked vent switch). Install the strain relief provided in the hole in the jacket through which these
wires pass.
6) Flame Roll-Out Switch:
a) Route the black wire marked “10” through the bushing located on the left jacket panel and connect it to one side of the
flame roll-out switch.
b) Route the red wire marked “7” through the bushing located on the left jacket panel and connect it to the other side of the
flame roll-out switch.
7)
McDonnell Miller Series 67 Low Water Cutoff:
a) Route the black wire numbered “1” and the black wire with the white trace numbered “2” through the fitting on the end
of the low water cutoff.
b) Connect lead numbers “1” and “2” to the low water cutoff terminals marked “1” and “2” respectively.
8) Hydrolevel CG-400 Probe Low Water Cutoff:
a) Mount the end of the BX cable containing the 3-wire Molex plug and the single red wire to the control box with the BX
cable fitting nut supplied.
b) Insert the Molex plug into the receptacle mounted on the CG400 terminal board.
c) Attach the red wire to the terminal marked “BURNER”.
9) Standing Pilot Gas Valve (Honeywell VR8200, VR8300 or Robertshaw Model 7000ERHC-S7C) - Connect wire “6” (black with
a white trace) to the “TH” terminal on the gas valve. Connect wire “5” (red with a yellow trace) to the TR terminal on the gas
valve.
Note: Boilers equipped with the Robertshaw 7000ERHC are also equipped with a Honeywell Model V8295 gas valve to
provide redundancy. This valve should be factory pre-wired to the 7000ERHC with one black lead connected to the “TH”
terminal and the other black lead connected to the “TR” terminal on the 7000ERHC gas valve.
10) Honeywell Intermittent Ignition System:
a) Mount the S8600 series ignition control to the left side of the jacket just above the gas manifold using the standoff
bracket supplied and #10 sheet metal screws.
b) Locate the intermittent ignition harness plugged into the gas valve assembly. This harness has red, blue, and yellow
wires and has molex plugs on both ends. Plug the loose end of the harness into the S8600 module.
c) Plug the green burner ground wire numbered “4” to terminal 4 on the S8600. Check that the ground wire has been routed
under the burners and that the other end is attached to the pilot assembly under the lower mounting screw.
d) Plug the red wire with the yellow trace, numbered “5”, to terminal 5 on the S8600 module.
e) Plug the black wire with the white trace, numbered “6”, to terminal 6 on the S8600 module.
f) Plug the orange Pilot Ignition Cable, numbered “9”, to terminal 9 on the S8600 module. Verify that this cable has been
routed under the burners and that the other end is plugged onto the pilot assembly electrode.
G. Complete Installation
Follow the instructions that start on page 1 of this manual to complete boiler installation.
52
51
Page 53

FIGURE A3: TAPPING LOCATIONS (SEE TEXT FOR TAPPING USES)
53
52
Page 54

CROWN
Boiler Co
Manufacturer of Hydronic Heating Products
P.O. Box 14818 3633 I. Street
Philadelphia, PA 19134
Tel: (215) 535-8900 • Fax: (215) 535-9736 • www.crownboiler.com
54
 Loading...
Loading...