Crown CE-4000 Brochure
C E S E R I E S
CE 4000
LOAD
Duty
Cycle
Current Draw(Amps) Thermal Dissipation Thermal Dissipation Thermal DissipationCurrent Draw(Amps) Current Draw(Amps)
AC Mains
Power
Draw
(Watts)
AC Mains
Power
Draw
(Watts)
AC Mains
Power
Draw
(Watts)
100-120 230-240 btu/hr kcal/hr
151601
1.3
2.5
296
182
723
1.9
3.8
452
213
845
2.6
5.2
607
182723
1.9
3.8
452
244
968
3.3
6.5
796
306
1213
4.6
9.1
1075
231845
2.6
5.2
608
306
1213
4.6
9.1
1075
398
1580
6.6
13.1
1542
244968
3.3
6.5
763
367
1457
5.9
11.8
1387
491
1947
8.6
17.1
2010
2751090
3.9
7.8
919
429
1702
7.2
14.4
1698
583
2314
10.6
21.1
2478
100-120 230-240 btu/hr kcal/hr 100-120 230-240 btu/hr kcal/hr
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
8 DUAL / 16 BRIDGEΩ Ω 4Ω ΩDUAL / 8 BRIDGE
2Ω ΩDUAL / 8 BRIDGE
CE 4000
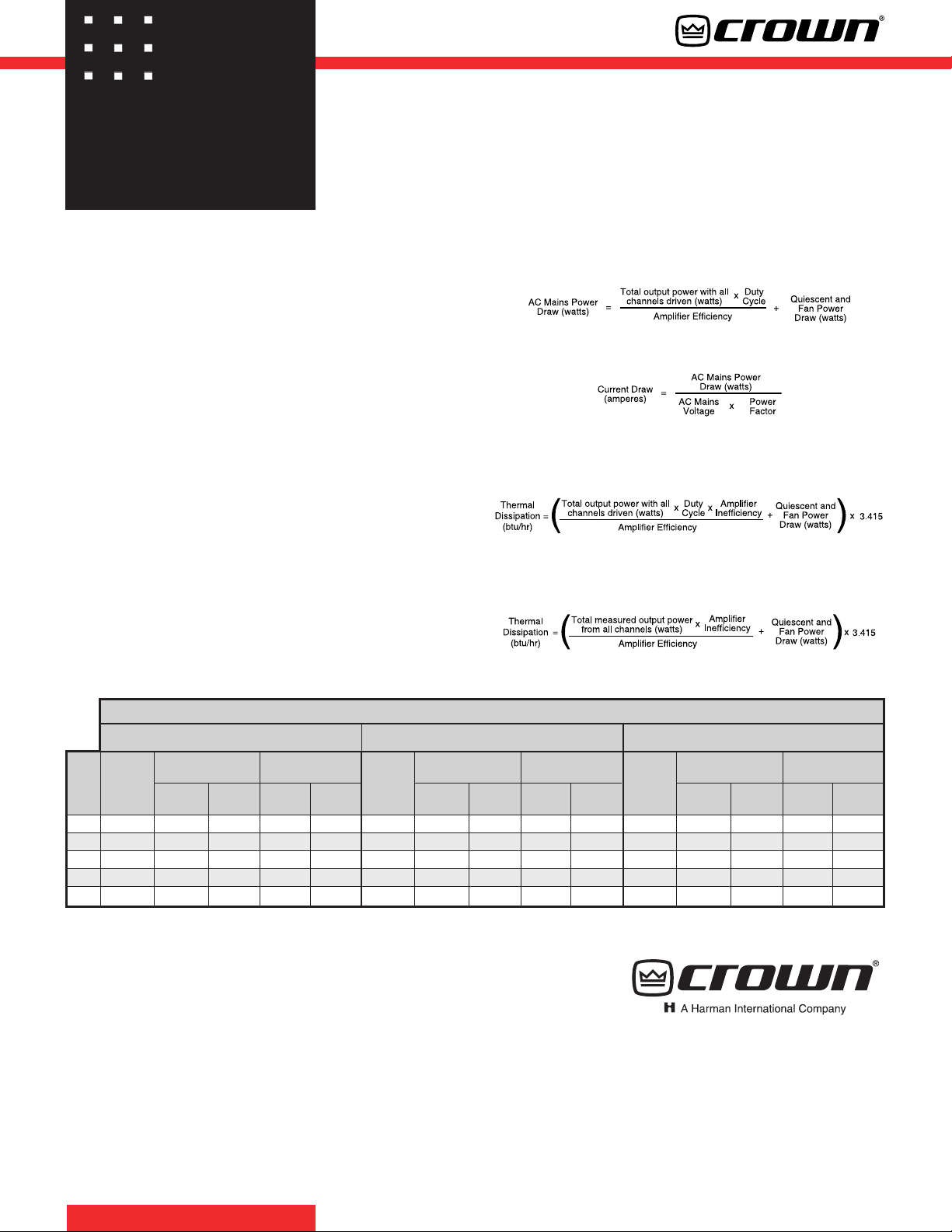
AC Power Draw and Thermal Dissipation
This document provides detailed information about the amount of power
and current drawn from the AC mains by the CE 4000 amplier and
the amount of heat produced under various conditions. The calculations
presented here are intended to provide a realistic and reliable depiction of
the amplier. The following assumptions or approximations were made:
• The amplier’s available channels are loaded and full power is being
delivered.
• The amplier efciency at standard 1-kHz power is estimated to be
77%.
• Quiescent power draw is approximately 140 watts.
• When running at full speed, typical power draw for the internal fan
is 12 watts or less.
• The estimated duty cycles take into account the typical crest factor for
each type of source material.
• Duty cycle of pink noise is 50%.
• Duty cycle of highly compressed rock ‘n’ roll midrange is 40%.
• Duty cycle of rock ‘n’ roll is 30%.
• Duty cycle of background music is 20%.
• Duty cycle of continuous speech is 10%.
• Duty cycle of infrequent, short duration paging is 1%.
Here are the equations used to calculate the data presented in Figure 1:
The following equation converts power draw in watts to current draw in
amperes:
The value used for Power Factor is 0.98. The Power Factor variable is
needed to compensate for the difference in phase between the AC mains
voltage and current. The following equation is used to calculate thermal
dissipation:
The value used for inefciency is 0.23 (1.00–0.77). The factor 3.415
converts watts to btu/hr. Thermal dissipation in btu is divided by the
constant 3.968 to get kcal. If you plan to measure output power under
real-world conditions, the following equation may also be helpful:
Figure 1 Power Draw, Current Draw and Thermal Dissipation at Various Duty Cycles
For more details refer to the applicable Reference Manual or
Contact Crown Audio Technical Support. The provided data
should not be construed as specications.
Crown is a registered trademark of Crown International, Inc.
Printed in U.S.A.
© 2000 Crown International, Inc.
08/00 131511-1
Crown International, Inc.
P.O. Box 1000
Elkhart, IN 46515-1000
TEL: 219-294-8200
FAX: 219-294-8FAX
www.crownaudio.com
 Loading...
Loading...