Craftsman 351228050, 351228030 Owner’s Manual

Operator's Manual
10" and 12"
LEFT-TILTING ARBOR SAW
Model No.
351.228050
351.228030
CAUTION:
Read and follow all Safety
Rules and Operating
Instructions before First
Use of this Product. Keep
this Manual with Tool.
Sears, Roebuck and Co., Hoffman Estates, IL 60179 U.S.A.
www.sears.com/craftsman
23013.00 Draft (01/04/05)

Warranty ......................................... 2
Safety Rules .................................... 2-5
Unpacking ....................................... 5
Assembly ...................................... 5-8
Installation ...................................... 8-9
Operation ..................................... 9-13
Maintenance .................................... 13
Troubleshooting .................................. 14
Parts Illustration and List ........................ 16-26
EspaSol ...................................... 28-43
FULL ONE YEAR WARRANTY
If this product fails due to a defect in material or workmanship
within one year from the date of purchase, Sears will at its
option repair or replace it free of charge. Contact your nearest
Sears Service Center (1-800-4-MY-HOME) to arrange for
product repair, or return this product to place of purchase for
replacement.
If this product is used for commercial or rental purposes, this
warranty will apply for 90 days from the date of purchase.
This warranty applies only while this product is used in the
United States.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may also
have other rights which vary from state to state.
Sears, Roebuck and Co., Dept. 817WA, Hoffman Estates,
IL 60179
WARNING: For your own safety, read all of the instructions
and precautions before operating tool.
CAUTION: Always follow proper operating procedures as
defined in this manual -- even if you are familiar with use of
this or similar tools. Remember that being careless for even a
fraction of a second can result in severe personal injury.
BE PREPARED FOR JOB
• Wear proper apparel. Do not wear loose clothing, gloves,
neckties, rings, bracelets or other jewelry which may get
caught in moving parts of machine.
• Wear protective hair covering to contain long hair.
• Wear safety shoes with non-slip soles.
• Wear safety glasses complying with United States ANSI
Z87.1. Everyday glasses have only impact resistant lens-
es. They are NOT safety glasses.
• Wear face mask or dust mask if operation is dusty.
• Be alert and think clearly. Never operate power tools when
tired, intoxicated or when taking medications that cause
drowsiness.
PREPARE WORK AREA FOR JOB
• Keep work area clean. Cluttered work areas invite acci-
dents.
• Do not use power tools in dangerous environments. Do not
use power tools in damp or wet locations. Do not expose
power tools to rain.
• Work area should be properly lighted.
• Keep visitors at a safe distance from work area.
• Keep children out of workplace. Make workshop childproof.
Use padlocks, master switches or remove switch keys to
prevent any unintentional use of power tools.
• Keep power cords from coming in contact with sharp
objects, oil, grease and hot surfaces.
TOOL SHOULD BE MAINTAINED
• Always unplug tool prior to inspection.
• Consult manual for specific maintaining and adjusting pro-
cedures.
• Keep tool lubricated and clean for safest operation.
• Remove adjusting tools. Form habit of checking to see that
adjusting tools are removed before switching machine on.
• Keep all parts in working order. Check to determine that
the guard or other parts will operate properly and perform
their intended function.
• Check for damaged parts. Check for alignment of moving
parts, binding, breakage, mounting and any other condi-
tion that may affect a tool's operation.
• A guard or other part that is damaged should be properly
repaired or replaced. Do not perform makeshift repairs.
(Use parts list provided to order replacement parts.)
• Maintain proper adjustment of rip fence and blade guard.
• Never adjust saw while running. Disconnect power to avoid
accidental start-up.
• Have damaged or worn power cords replaced immediately.
• Keep blade sharp for efficient and safest operation.
KNOW HOW TO USE TOOL
• Use right tool for job. Do not force tool or attachment to do
a job for which it was not designed.
• Disconnect tool when changing blade.
• Avoid accidental start-up. Make sure that the tool is in the
"off" position before plugging in, turning on safety discon-
nect or activating breakers.
• Do not force tool. It will work most efficiently at the rate for
which it was designed.
• Keep hands away from blade and moving parts and cutting
surfaces.
• Never leave tool running unattended. Turn the power off
and do not leave tool until it comes to a complete stop.
• Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance.
• Never stand on tool. Serious injury could occur if tool is
tipped or if blade is unintentionally contacted.
• Know your tool. Learn the tool's operation, application and
specific limitations.
• Handle workpiece correctly. Press firmly against table.
Protect hands from possible injury.
• Turn machine off if it jams. Blade jams when it digs too
deeply into workpiece. (Motor force keeps it stuck in the
work.)
• Feed work into the blade only as recommended in
"Operation."
WARNING: For your own safety, do not operate your saw until it
is completely assembled and installed according to instructions.
© Sears, Roebuckand Co.
2
STABILITY OF SAW
If there is any tendency for the saw to tip ever or move during
certain cutting operations, such as cutting extremely heavy
panels or long heaw boards, the saw should be bolted down.
If you attach any kind of extensions over 24" wide to either
end of the saw, make sure you either bolt the saw to the floor,
as appropriate, or support the outer end of the extension from
the bench or floor, as appropriate.
LOCATION
The saw should be positioned so neither the operator nor a
casual observer is forced to stand in line with the saw blade.
KICKBACKS
A kickback occurs during a rip-type operation when a part or
all of workpiece is thrown back violently toward operator.
Keep your face and body to one side of the saw blade, out of
line with a possible kickback.
Kickbacks and possible injury from them can usually be avoid-
ed by:
• Maintaining rip fence parallel to saw blade.
• Keeping saw blade sharp. Replace or sharpen antikick-
back pawls when points become dull.
• Keeping saw blade guard, spreader, and antikickback
pawls in place and operating properly. The spreader must
be in alignment with the saw blade and the pawls must
stop a kickback once it has started. Check their action
before ripping.
• Not ripping work that is twisted or warped or does not
have a straight edge to guide along the rip fence.
• Not releasing work until you have pushed it all the way
past the saw blade.
• Using a push stick for ripping widths less than 6 inches.
• Not confining the cutoff piece when ripping or crosscutting.
PROTECTION: EYES, HANDS, FACE, BODY, EARS
• If any part of your saw is missing, malfunctioning, or has
been damaged or broken (such as the motor switch, elec-
tronic controls, other operating control, a safety device or
power cord), cease operating immediately until the partic-
ular part is properly repaired or replaced.
• Wear safety goggles that comply with United States ANSI
Z87.1 and a face shield or dust mask if operation is dusty.
Wear ear plugs or muffs during extended periods of oper-
ation.
• Small loose pieces of wood or other objects that contact
the rear of the revolving blade can be thrown back at the
operator at excessive speed. This can usually be avoided
by keeping the guard and spreader in place for all thru-
sawing operations (sawing entirely thru work) and by
removing all loose pieces from the table with a long stick
of wood immediately after they are cut off.
• Use extra caution when the guard assembly is removed for
resawing, dadoing, or rabbeting--replace guard as soon
as that operation is completed.
• Never turn the saw ON before clearing the table of all
tools, wood scraps, etc., except the workpiece and related
feed or support devices for the operation planned.
• Never place your face or body in line with the cutting tool.
• Never place your fingers or hands in path of saw blade or
other cutting tool.
• For rip or rip-type cuts, the following end of a workpiece to
which a push stick or push board is applied must be
square (perpendicular to the fence) in order that feed
pressure applied to the workpiece by the push stick or
block does not cause the workpiece to come away from
the fence, and possibly cause a kickback.
• During rip and rip-type cuts, workpiece must be held down
on table and against fence with a push stick, push block,
or featherboards, as applicable (see Figures la and lb).
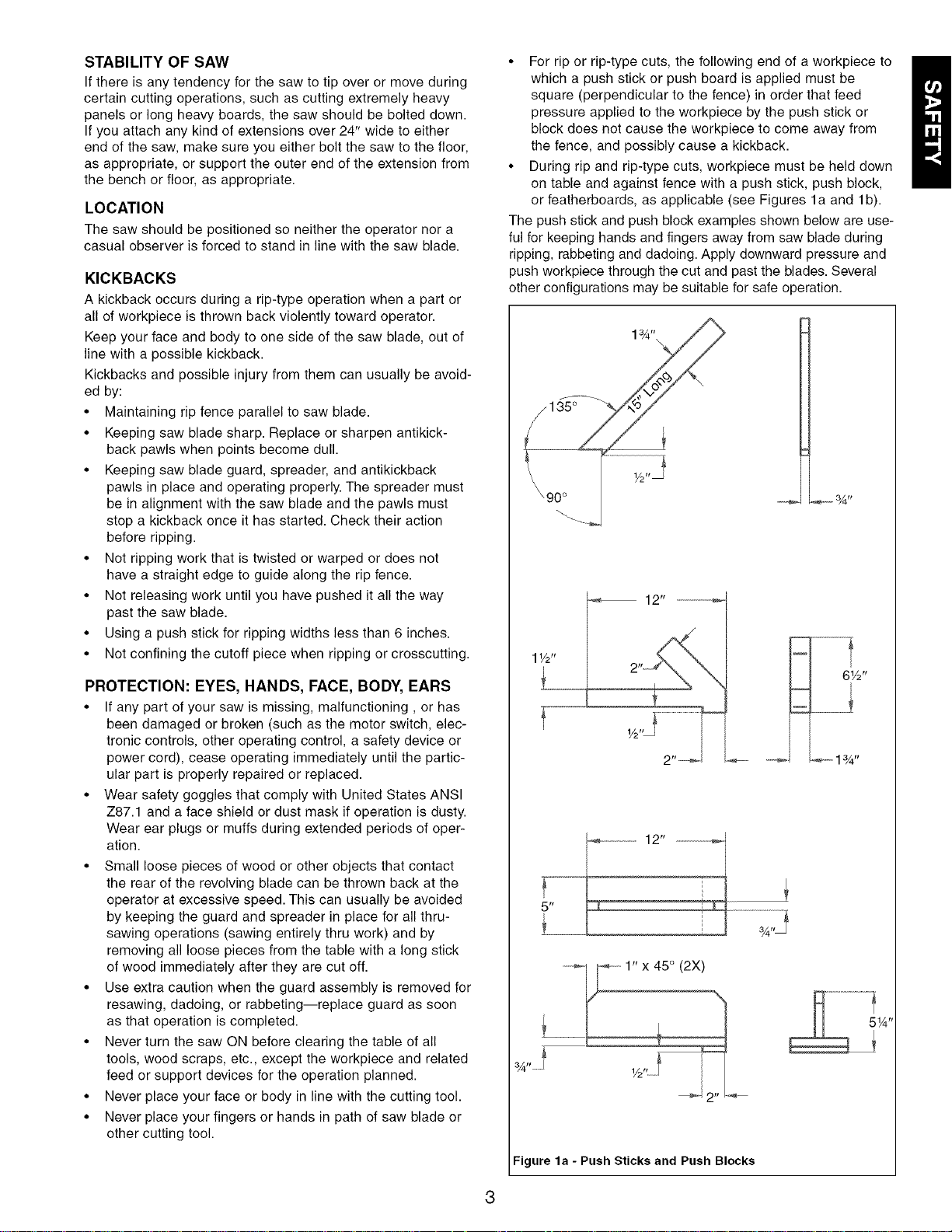
The push stick and push block examples shown below are use-
ful for keeping hands and fingers away from saw blade during
ripping, rabbeting and dadoing. Apply downward pressure and
push workpiece through the cut and past the blades. Several
other configurations may be suitable for safe operation.
_135 °
[
\90 °
12.............................i
11/2"
[
[
[
6½"
- l
½
2
12"5 t_ ........
i.
Figure la - Push Sticks and Push Blocks
........1¾"
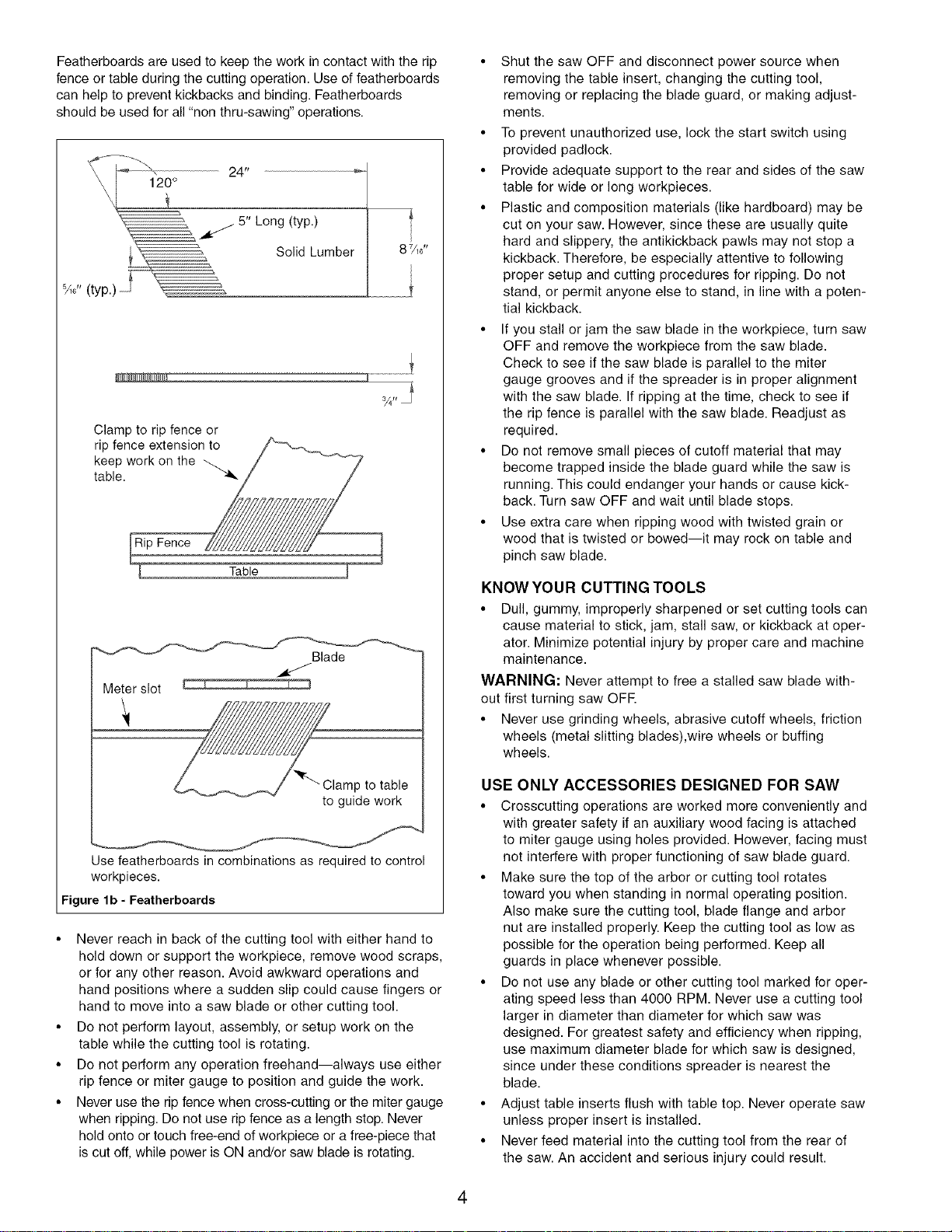
Featherboards are used to keep the work in contact with the rip
fence or table during the cutting operation. Use of featherboards
can help to prevent kickbacks and binding. Featherboards
should be used for all "non thru-sawing" operations.
24"
5" Long (typ.)
Solid Lumber
_A_"(typ.)
Clamp to rip fence or
rip fence extension to //'_',._\_..., ......
_e_lP.work on the __/
t
87A_"
1
• Shut the saw OFF and disconnect power source when
removing the table insert, changing the cutting tool,
removing or replacing the blade guard, or making adjust-
ments.
• To prevent unauthorized use, lock the start switch using
provided padlock.
• Provide adequate support to the rear and sides of the saw
table for wide or long workpieces.
• Plastic and composition materials (like hardboard) may be
cut on your saw. However, since these are usually quite
hard and slippery, the antikickback pawls may not stop a
kickback. Therefore, be especially attentive to following
proper setup and cutting procedures for ripping. Do not
stand, or permit anyone else to stand, in line with a poten-
tial kickback.
• If you stall or jam the saw blade in the workpiece, turn saw
OFF and remove the workpiece from the saw blade.
Check to see if the saw blade is parallel to the miter
gauge grooves and if the spreader is in proper alignment
with the saw blade. If ripping at the time, check to see if
the rip fence is parallel with the saw blade. Readjust as
required.
• Do not remove small pieces of cutoff material that may
become trapped inside the blade guard while the saw is
running. This could endanger your hands or cause kick-
back. Turn saw OFF and wait until blade stops.
• Use extra care when ripping wood with twisted grain or
wood that is twisted or bowed--it may rock on table and
pinch saw blade.
Blade
Meter slot
amp to table
to guide work
Use featherboards in combinations as required to control
workpieces.
Figure lb - Featherboards
• Never reach in back of the cutting tool with either hand to
hold down or support the workpiece, remove wood scraps,
or for any other reason. Avoid awkward operations and
hand positions where a sudden slip could cause fingers or
hand to move into a saw blade or other cutting tool.
• Do not perform layout, assembly, or setup work on the
table while the cutting tool is rotating.
• Do not perform any operation freehand--always use either
rip fence or miter gauge to position and guide the work.
• Never use the rip fence when cross-cutting or the miter gauge
when ripping. Do not use rip fence as a length stop. Never
hold onto or touch free-end of workpiece or a free-piece that
is cut off, while power is ON and/or saw blade is rotating.
KNOW YOUR CUTTING TOOLS
• Dull, gummy, improperly sharpened or set cutting tools can
cause material to stick, jam, stall saw, or kickback at oper-
ator. Minimize potential injury by proper care and machine
maintenance.
WARNING: Never attempt to free a stalled saw blade with-
out first turning saw OFE
• Never use grinding wheels, abrasive cutoff wheels, friction
wheels (metal slitting blades),wire wheels or buffing
wheels.
USE ONLY ACCESSORIES DESIGNED FOR SAW
• Crosscutting operations are worked more conveniently and
with greater safety if an auxiliary wood facing is attached
to miter gauge using holes provided. However, facing must
not interfere with proper functioning of saw blade guard.
• Make sure the top of the arbor or cutting tool rotates
toward you when standing in normal operating position.
Also make sure the cutting tool, blade flange and arbor
nut are installed properly. Keep the cutting tool as low as
possible for the operation being performed. Keep all
guards in place whenever possible.
• Do not use any blade or other cutting tool marked for oper-
ating speed less than 4000 RPM. Never use a cutting tool
larger in diameter than diameter for which saw was
designed. For greatest safety and efficiency when ripping,
use maximum diameter blade for which saw is designed,
since under these conditions spreader is nearest the
blade.
• Adjust table inserts flush with table top. Never operate saw
unless proper insert is installed.
• Never feed material into the cutting tool from the rear of
the saw. An accident and serious injury could result.
4
THINK SAFETY
Safety is a combination of operator common sense and alert-
ness at all times when the saw is being used.
Never use another person as a substitute for a table exten-
sion, or as additional support for a workpiece that is longer or
wider than basic saw table, or to assist in feeding, supporting
or pulling the workpiece.
Do not pull the workpiece through the saw blade--position
your body at the infeed side of the guard; start and complete
the cut from that same side. This will require added table sup-
port for long or wide workpieces that extend beyond the
length or width of the saw table.
CAUTION: Follow safety instructions that appear on the front
of your saw.
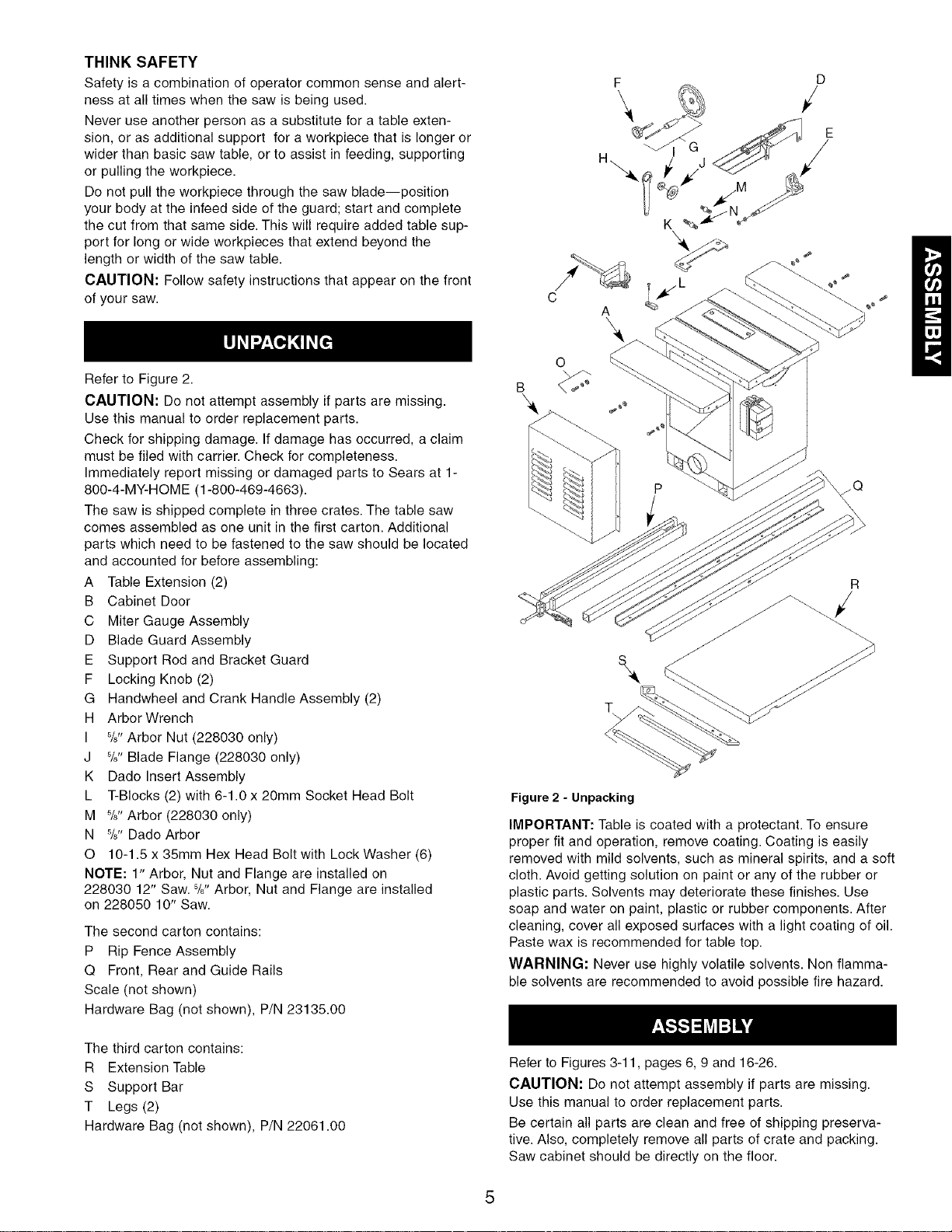
Refer to Figure 2.
CAUTION: Do not attempt assembly if parts are missing.
Use this manual to order replacement parts.
Check for shipping damage. If damage has occurred, a claim
must be filed with carrier. Check for completeness.
Immediately report missing or damaged parts to Sears at 1-
800-4-MY-HOME (1-800-469-4663).
The saw is shipped complete in three crates. The table saw
comes assembled as one unit in the first carton. Additional
parts which need to be fastened to the saw should be located
and accounted for before assembling:
A Table Extension (2)
B Cabinet Door
C Miter Gauge Assembly
D Blade Guard Assembly
E Support Rod and Bracket Guard
F Locking Knob (2)
G Handwheel and Crank Handle Assembly (2)
H Arbor Wrench
I %" Arbor Nut (228030 only)
J %" Blade Flange (228030 only)
K Dado Insert Assembly
L T-Blocks (2) with 6-1.0 x 20mm Socket Head Bolt
M %" Arbor (228030 only)
N %" Dado Arbor
O 10-1.5 x 35mm Hex Head Bolt with Lock Washer (6)
NOTE: 1" Arbor, Nut and Flange are installed on
228030 12" Saw. %" Arbor, Nut and Flange are installed
on 228050 10" Saw.
The second carton contains:
P Rip Fence Assembly
Q Front, Rear and Guide Rails
Scale (not shown)
Hardware Bag (not shown), P/N 23135.00
D
,/
C
O
B
R
Figure 2 - Unpacking
IMPORTANT: Table is coated with a protectant. To ensure
proper fit and operation, remove coating. Coating is easily
removed with mild solvents, such as mineral spirits, and a soft
cloth. Avoid getting solution on paint or any of the rubber or
plastic parts. Solvents may deteriorate these finishes. Use
soap and water on paint, plastic or rubber components. After
cleaning, cover all exposed surfaces with a light coating of oil.
Paste wax is recommended for table top.
WARNING: Never use highly volatile solvents. Non flamma-
ble solvents are recommended to avoid possible fire hazard.
The third carton contains:
R Extension Table
S Support Bar
T Legs (2)
Hardware Bag (net shown), P/N 22061.00
Refer to Figures 3-11, pages 6, 9 and 16-26.
CAUTION: Do not attempt assembly if parts are missing.
Use this manual to order replacement parts.
Be certain all parts are clean and free of shipping preserva-
tive. Also, completely remove all parts of crate and packing.
Saw cabinet should be directly on the floor.
SAW INSTALLATION
Positioning the saw on a level surface (shimming may be
required) will improve stability and accuracy and prevent
warpage and failure of cast components and welds. Level the
saw using shims or machine mounts. The stationary saw's
base is fitted with four mounting holes. The holes are located
within an orange recess. Use these holes to secure stationary
saw to the floor. This saw should be permanently fastened to
the floor. This will decrease vibration and increase stability.
GUARD SUPPORT ROD INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 8, page 20.
• Install guard support rod (No. 36). Insert rod through hole
in rear trunnion (No. 31) and secure with lock washer and
nut (Nos. 29 and 30). Upper rear spreader support is slot-
ted for adjustment of the blade guard assembly. Alignment
and final tightening of support rod (No. 36) will occur when
blade guard is installed.
ARBOR EXTENSION INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 7, page 18.
• Wipe clean taper and threads of arbor extension (No. 41).
It is recommended when installing that a dry lubricant be
used on taper end of arbor extension.
• Install arbor extension (No. 41) into arbor (No. 39).
Standard arbor extension for 12" saw (228030) is 1" O.D.
x 3" long. By hand, thread arbor extension by inserting
8mm hex wrench (not shown) into 8ram socket at outboard
end of extension and tighten. Arbor itself is held in place
with spanner wrench (No. 10). Place spanner wrench on
inside blade flange with two prongs on spanner wrench
inserted into two holes in flange. Seat arbor extension
firmly. However, it is not necessary to excessively tighten.
NOTE: To remove an arbor extension, follow the preceding
steps in reverse order.
BLADE INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 7, page 18.
NOTE: Blade is not supplied with saw.
• Remove arbor nut and blade flange (Nos. 43 and 42) from
the arbor.
• Check that arbor diameter matches mounting hole of
blade. 12" saw, 228030, is supplied with a 1" standard
arbor extension. 10" saw, 228050, is supplied with a %"
standard arbor extension. If necessary, remove incorrect
arbor extension using spanner wrench (No. 10) and hex
wrench supplied.
• Mount required arbor extension to arbor; be sure that
arbor and arbor extension are clean and free of dirt, chips,
etc. Tighten arbor extension securely in arbor.
• Mount blade onto the arbor extension. Be sure blade is
mounted so that it spins in proper direction. Replace arbor
flange and nut. Tighten nut securely.
IMPORTANT: Blade rotates towards front of saw. When
installing blade, make sure teeth are pointing towards front of
the saw.
NOTE: Do not over tighten arbor nut. Use the arbor wrench to
just "snug" it.
ASSEMBLE HANDWHEELS
Refer to Figures 8 and 9, pages 20 and 22.
• Both handwheels are identical. Attach crank handles (Fig.
9, No. 13) securely to handwheels (Fig. 9, No. 27).
• Handwheels are attached to tilt adjustment shaft (Fig. 8,
No. 4) and height adjustment shaft (Fig. 8, No. 24).
• Place key (Fig. 8, No. 6) in keyway. Assemble handwheel
to shaft engaging set screw (Fig. 9, No. 28) with key in
shaft. Position handwheel onto shaft as far as possible
without interfering with movement. Tighten set screw.
• Install locking knobs (Fig. 9, No. 23). Insert threaded por-
tion of knobs into end of shafts. Gently hand tighten until it
stops. This is locked position. To unlock, back out knob
three complete turns. For now, leave handwheels unlocked.
NOTE: Do not over tighten locking knobs.
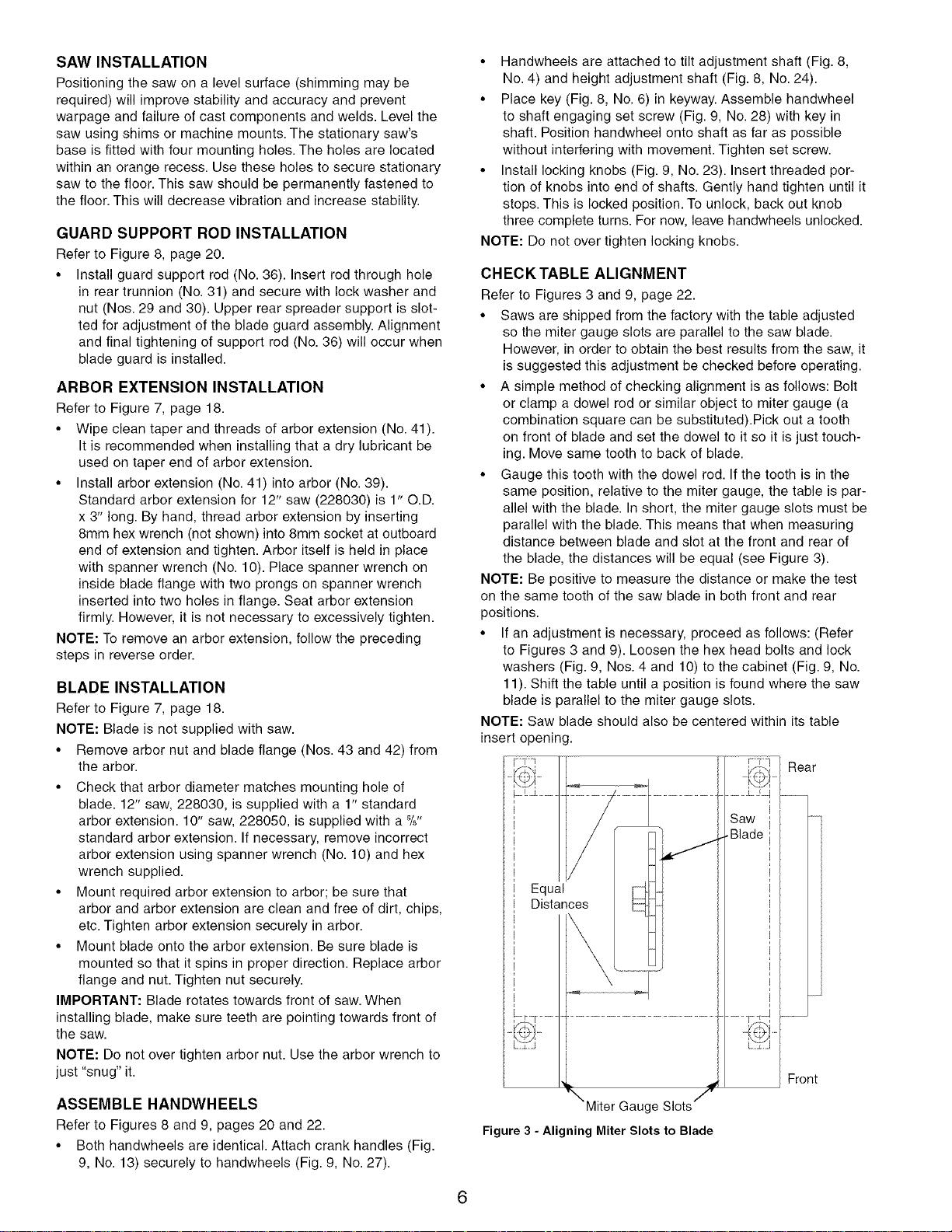
CHECK TABLE ALIGNMENT
Refer to Figures 3 and 9, page 22.
• Saws are shipped from the factory with the table adjusted
so the miter gauge slots are parallel to the saw blade.
However, in order to obtain the best results from the saw, it
is suggested this adjustment be checked before operating.
• A simple method of checking alignment is as follows: Bolt
or clamp a dowel rod or similar object to miter gauge (a
combination square can be substituted).Pick out a tooth
on front of blade and set the dowel to it so it is just touch-
ing. Move same tooth to back of blade.
• Gauge this tooth with the dowel rod. If the tooth is in the
same position, relative to the miter gauge, the table is par-
allel with the blade. In short, the miter gauge slots must be
parallel with the blade. This means that when measuring
distance between blade and slot at the front and rear of
the blade, the distances will be equal (see Figure 3).
NOTE: Be positive to measure the distance or make the test
on the same tooth of the saw blade in both front and rear
positions.
• If an adjustment is necessary, proceed as follows: (Refer
to Figures 3 and 9). Loosen the hex head bolts and lock
washers (Fig. 9, Nos. 4 and 10) to the cabinet (Fig. 9, No.
11). Shift the table until a position is found where the saw
blade is parallel to the miter gauge slots.
NOTE: Saw blade should also be centered within its table
insert opening.
Rear
Front
Miter Gauge Slots
Figure 3 - Aligning Miter Slots to Blade
6

• Tighten four hex head bolts and lock washers (Figure 9,
Nos. 4 and 10) very securely. This procedure will set the
table in parallel position and prevent the table from shifting.
MOUNTTABLE EXTENSIONS
Refer to Figure 9, page 22.
• Be certain both edges of table (No. 1) and table extension
(No. 2) are clean and free from any preservative, debris or
burrs.
• Attach each table extension with three hex head bolts, lock
and flat washers (Nos. 3, 4 and 29). Fasten the hex head
bolts and lock washers to matching tapped holes in table.
Hand tighten.
• Using a straightedge, set top of extension flush with the
table top. Extension should also be centered front to rear.
First, slightly tighten the center bolt. If either end is not
flush, tap extension up or down with rubber mallet. Bring
extension in line with table. Securely tighten one bolt at a
time, keeping extension flush with table top.
MOUNT RIP FENCE RAILS AND EXTENSION TABLE
Refer to Figures 9 and 10, pages 22 and 24.
• Attach rip fence front rail (Fig. 10, No. 6) to front of table
(Fig. 9, No. 1). Rails will extend out approximately 36" from
right side of saw.
NOTE: Front rail is 2 x 2", rear rail is 1_/2x 1W'.
• Place front rail, oriented as shown in Figure 10, against
the table and locate the holes in the table. Fasten rail to
table with pan head screws (Fig. 10, No. 7) and with
washers and nuts (Fig. 10, Nos. 27, 28 and 29) on the
inside of the table. Finger tighten loosely. Tighten securely
after all fasteners have been attached.
• Place rear rail (Fig. 10, No. 31), oriented as shown in
Figure 10, against the table and locate the holes in the
table. Place hex head bolt (Fig. 10, No. 32) through hole in
rail, through spacer (Fig. 10, No. 30), and then through
hole in table. Secure with washers and hex nut (Fig. 10,
Nos. 27, 28 and 29) inside table. Finger tighten loosely.
Tighten securely after all fasteners have been attached.
• Attach one 8mm hex nut and foot to each leg (Fig 10, Nos.
38, 39 and 42).
• Attach each leg to the support bar using two 8ram hex
head bolts and lock washers (Fig. 10, Nos. 4, 5 and 41).
Set this assembly aside.
• Position extension table (Fig. 10, No. 40) between the table
saw rails, with the holes in the table and rails aligned.
NOTE: The notch in the table should be positioned at the
right side of the front rail. Use clamps to secure table or
have another person support table.
• Secure extension table to the front rail using two 8ram flat
head screws, flat washers and hex nuts (Fig. 10, Nos. 36, 37
and 38). Secure the left side of the extension table to the
rear rail using a 10x35mm hex head bolt, flat washer and
hex nut (Fig. 10, Nos. 32, 27 and 29). Secure the right side
of the extension table to the rear rail using a 10x70mm hex
head bolt, flat washer and hex nut (Fig. 10, Nos. 35, 27 and
29).
• Place the guide rail (Fig. 10, No. 2) on top of the front rail
at this time. Do not attach scale to guide rail at this time.
• Place a hex nut and flat washer (Fig. 10, Nos. 27 and 29)
onto the 10x70mm hex head bolt. Position the leg-support
bar assembled previously underneath table and with the
10x70mm hex head bolt through the vertical bend of the
support bar. Align holes in the support bar, front rail and
guide rail. Secure with 8ram hex head bolt and lock wash-
er (Fig. 10, Nos. 4 and 5).
• Completely secure guide rail to front rail using five hex
head bolts (Fig. 10, Nos. 2, 4, 5 and 6).
• Place a hex nut and flat washer (Fig. 10, Nos. 27 and 29)
onto the 10 x 70ram hex head bolt. Tighten hex nuts
securely on both sides of the vertical bend of the support
bar.
• Adjust feet level to floor and secure in position with hex nuts.
SCALE INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 10, page 24.
• Position left side of rip fence against right side of blade.
Mark the guide rail (No. 2) at the zero position indicated by
red line on lens (No. 20).
• Remove the rip fence and apply a strip of masking tape
along the guide rail _/4"deep from front edge of rail.
• Using the zero mark as the starting point and the masking
tape as a guide, apply the adhesive scale (No. 1) to guide
rail. Press scale firmly into place using heaw finger pres-
sure.
RIP FENCE ASSEMBLY INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 10, page 24.
• Position rip fence assembly at end of saw. Be certain lock-
ing lever (No. 14) is in UP unlocked position.
• Place rip fence assembly onto rails, positioning plastic pad
(No. 24) on rear rail (No. 31), and then placing rip fence
onto guide rail (No. 2).
• Rip fence should now ride freely on rip fence rails. Once
rip fence is completely installed, it should be thoroughly
adjusted. (See Operation, page 11, Rip fence adjustment.)
BLADE GUARD INSTALLATION
Refer to Figures 5 and 8, pages 16 and 20 (Model 228050).
Refer to Figures 6 and 8, pages 17 and 20 (Model 228030).
• Lower blade as far as possible and set tilt angle at 90°.
• Check that front support bracket (Fig. 8, No. 28) is in posi-
tion. Loosen hex head bolt and flat washer (Fig. 8, Nos. 27
and 26). Do not remove. Position the blade guard so it
points toward front of saw. Attach front of spreader (Fig. 5
or 6, No. 6) to front support bracket (Fig. 8, No. 28) with
hex bolt, and washer (Fig. 8, Nos. 27 and 26). Hand tight-
en, allow for adjustment.
• Attach rear of spreader to upper rear spreader support
(Fig. 8, No. 40). Fasten with hex head bolt and flat washer
(Fig. 8, Nos. 26 and 27). Hand tighten; allow for adjust-
ment. Blade guard assembly is now attached, but it is not
useable until completely adjusted. The clear blade guard
(Fig. 5 or 6, No. 2) should point forward.
IMPORTANT: Be certain acrylic blade guard and antikickback
pawls are spring loaded, forcing them down to table surface.
Both blade guard and antikickback pawls should automatically
return to table surface after being lifted.
NOTE: The teeth of the antikickback pawls (Figures 5 or 6,
No. 9) should be angled toward the rear of saw.
This safety device is to help prevent workpiece from being
thrown back at operator.

ADJUSTING BLADE GUARD
Refer to Figures 8 and 9, pages 20 and 22.
NOTE: Spreader must be parallel to saw blade and in middle
of cut (kerf) made by saw blade. In short, spreader must
always be in exact plane as saw blade. If not, it will interfere
with existing workpiece in addition to causing poor and unsafe
guard operation.
• Raise blade to full height. Adjust tilt angle of blade to 90 °.
Use a hand square to be certain blade is perpendicular to
table. Lock tilt angle at 90° with tilt handwheel locking
knob (Fig. 9, No. 23). If tilt angle will not go to 90 °, an
adjustment to the 90 ° stop is necessary. (See Operation,
page 10, 90 ° Stop Adjustment.)
• When adjusting spreader, use a straightedge lengthwise
along blade to be certain spreader is trailing in middle of
kerf (cut). In addition use a 90° hand square to make sure
spreader is perpendicular to the table, as is the blade.
• Align front of spreader with blade. If necessary, adjust front
support bracket. In order to adjust support bracket, it may
be necessary to lower saw blade. To adjust, loosen socket
head bolts (Fig. 8, No. 23). When completed, secure sock-
et head bolts tightly.
• To adjust the height of the front of the spreader, loosen
front support bracket hex head bolt and flat washer and
position spreader up or down. Lock spreader into position
by tightening hex head bolt and flat washer. Height of
spreader should be adjusted to allow blade guard to con-
tact table.
• Align rear of spreader. Rear of spreader can be adjusted
by upper rear spreader support. To adjust, loosen hex
head bolt and flat washer (Fig. 8, Nos. 37 and 26). Slot will
allow upper rear spreader support adjustment left or right.
Tighten hex head bolt and flat washer. After spreader is
lined up in middle of kerf, tighten guard support rod (Fig.
8, No. 36) with hex nut and lock washer (Fig. 8, Nos. 29
and 30). Tighten securely.
NOTE: It may be necessary to lower or remove blade to tight-
en hex nut and lock washer.
• Adjust angle of spreader to table. Loosen hex head bolt
and lock washer (Fig. 8, Ref. Nos. 37 and 38). Rotate
lower rear support spreader (Fig. 8, No. 39) until spreader
is perpendicular to table. Tighten hex head bolt and lock
washer.
NOTE: It may be necessary to also loosen hex head bolt and
flat washer on front of support bracket. Adjust height so top
edge is parallel. Lock into position. Tighten both front and rear
bolts and washers (Figure 8, Nos. 27 and 26).
• Blade guard is now assembled and adjusted. Spreader
should be parallel with saw blade and in middle of kerf. If
this is not true, repeat all adjustment steps. Before operat-
ing saw, recheck all blade guard fasteners to be certain all
are securely tightened.
IMPORTANT: Before operating saw, be certain blade guard
and antikickback pawls automatically return to table surface.
TABLE INSERTS INSTALLATION
Refer to Figure 9, page 22.
• Be certain standard insert (No. 5) and Dado Insert (No. 6)
are clean. Lower blade below table. Place standard insert
into position with cut-out on blade side.
• Surface of insert should be flush with table surface. Using
a straightedge, check insert to see if it is flush with table.
To adjust insert, remove insert from table and turn it
upside down on work bench.
• Each corner of table insert is fitted with an adjusting
setscrew (No. 7). Adjust each corner of insert up or down
to bring insert flush with table top. Be certain all four
setscrews are firmly seated on table casting.
• Repeat procedure for dado insert (No. 6). Replace stan-
dard table insert (No. 5).
CAUTION: Only use dado insert (Fig. 9, No. 6) with dado
blade set. Only use standard insert (Fig. 9, No. 5) with stan-
dard blade. Never attempt to interchange; only use table
insert with the blade it was intended to be used with.
INSTALL MITER GAUGE
Refer to Figures 9 and 11, pages 22 and 26.
• The miter gauge comes preassembled. Unpack the miter
gauge and clean thoroughly. Be certain miter gauge
T-slots in table are also thoroughly cleaned.
• The miter gauge is guided through the T-slot with a roller
guide at the front of guide bar. To insert miter gauge, first
insert roller guide into T-slot at front of table (Fig. 9, No. 1).
WIRE TABLE SAW
WARNING: Be certain switch is in OFF position. Disconnect
the source of all power. Keep circuit breaker open or in OFF
position.
The Craftsman 10" and 12" saws are designed to be used
with 230V-single-phase-power.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
WARNING: Make sure unit is off and disconnected from
power source before inspecting any wiring.
The motor is installed and the wiring connected as illustrated
in the wiring schematic (see Figure 4).
• When wiring the saw to the source, install a fused safety
disconnect switch between the saw and the circuit break-
er. Be certain the safety disconnect switch is capable of
being locked in the OFF position. The safety disconnect
switch is a safety precaution which allows the operator to
lock the saw OFF so it is unable to receive power. This
feature is intended to prevent accidental start-up when
maintaining or servicing saw. In addition, it is intended to
prevent unauthorized and possible hazardous use by oth-
ers. A key lock switch is provided on the tool for the same
reasons.
• The safety disconnect switch is fused. Protect the saw with
a 20 amp time-delay fuse or 20 amp manual reset circuit
breaker. Do not use fuses or breakers with a greater
amperage rating.
• Wire the saw to a breaker box or fuse box with adequate
capacity wire to accommodate the stationary saw's volt-
age and amp load.
IMPORTANT: Be certain saw is wired to a circuit protected by
a 20 amp breaker or fuse.
8
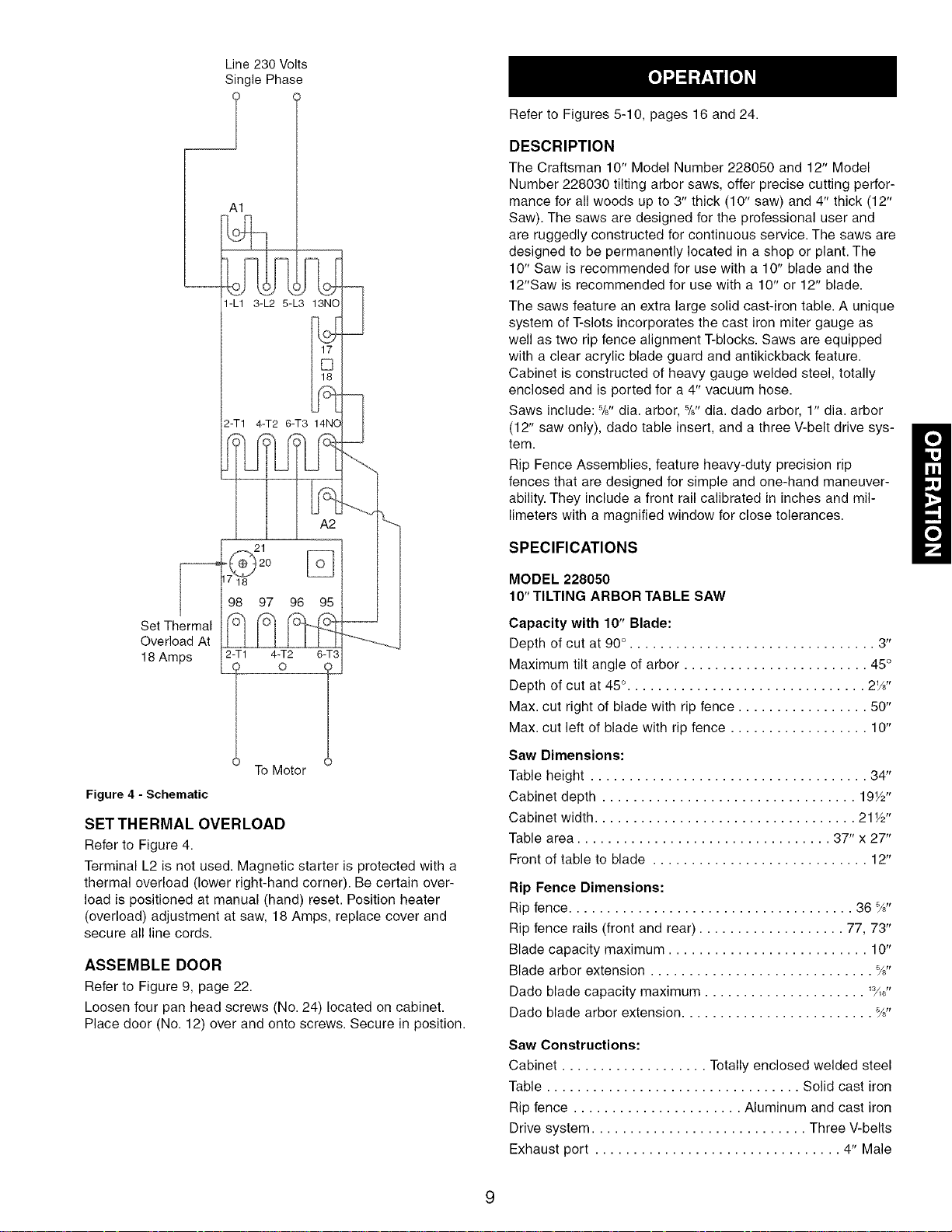
Line 230 Volts
Single Phase
A1
1-1_1 g-k2 5-1_3 lgNO_
2-T] 4-T2 6-Tg 14NO_
J
Refer to Figures 5-10, pages 16 and 24.
DESCRIPTION
The Craftsman 10" Model Number 228050 and 12" Model
Number 228030 tilting arbor saws, offer precise cutting perfor-
mance for all woods up to 3" thick (10" saw) and 4" thick (12"
Saw). The saws are designed for the professional user and
are ruggedly constructed for continuous service. The saws are
designed to be permanently located in a shop or plant. The
10" Saw is recommended for use with a 10" blade and the
12"Saw is recommended for use with a 10" or 12" blade.
The saws feature an extra large solid cast-iron table. A unique
system of T-slots incorporates the cast iron miter gauge as
well as two rip fence alignment T-blocks. Saws are equipped
with a clear acrylic blade guard and antikickback feature.
Cabinet is constructed of heavy gauge welded steel, totally
enclosed and is ported for a 4" vacuum hose.
Saws include: 5/8"dia. arbor, %" dia. dado arbor, 1" dia. arbor
(12" saw only), dado table insert, and a three V-belt drive sys-
tem.
Rip Fence Assemblies, feature heavy-duty precision rip
fences that are designed for simple and one-hand maneuver-
ability. They include a front rail calibrated in inches and mil-
limeters with a magnified window for close tolerances.
Set Thermal
Overload At
18Amps 4-T2
I-°
To Motor
Figure 4 - Schematic
SETTHERMAL OVERLOAD
Refer to Figure 4.
Terminal L2 is not used. Magnetic starter is protected with a
thermal overload (lower right-hand corner). Be certain over-
load is positioned at manual (hand) reset. Position heater
(overload) adjustment at saw, 18 Amps, replace cover and
secure all line cords.
ASSEMBLE DOOR
Refer to Figure g, page 22.
Loosen four pan head screws (No. 24) located on cabinet.
Place door (No. 12) over and onto screws. Secure in position.
SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL 228050
10" TILTING ARBOR TABLE SAW
Capacity with 10" Blade:
Depth of cut at 90° . ............................... 3"
Maximum tilt angle of arbor ........................ 45°
Depth of cut at 45°. .............................. 2W'
Max. cut right of blade with rip fence ................. 50"
Max. cut left of blade with rip fence .................. 10"
Saw Dimensions:
Table height .................................... 34"
Cabinet depth ................................. 19W'
Cabinet width .................................. 21W'
Table area ................................. 37" x 27"
Front of table to blade ............................ 12"
Rip Fence Dimensions:
Rip fence ..................................... 36 %"
Rip fence rails (front and rear) ................... 77, 73"
Blade capacity maximum .......................... 10"
Blade arbor extension ............................. %"
Dade blade capacity maximum ..................... 'Y,_"
Dade blade arbor extension ......................... %"
Saw Constructions:
Cabinet ................... Totally enclosed welded steel
Table ................................. Solid cast iron
Rip fence ...................... Aluminum and cast iron
Drive system ............................ Three V-belts
Exhaust port ................................ 4" Male

Mitergauge.............. CastironwithT-slotrollerguide
Bladeguard.............. Acrylicwithantikickbackpawls
Switch............. Lockingmagneticstarterwithoverload
ArborR.P.M........................ 4,000RPMapprox.
Motor:.................. 3HP,3450RPM,capacitorstart,
capacitorrun,230V,16A,single-phase,ballbearing,
SearsPartNo.23058.00
Grossweightwithmotor....................... 490Ibs
MODEL228030
12"TILTINGARBORTABLESAW
Capacitywith12"Blade:
Depthofcutat90°................................ 4"
Maximumtiltangleofarbor........................ 45°
Depthofcutat45° .............................. 23A''
Max. cut right of blade with rip fence ................. 50"
Max. cut left of blade with rip fence .................. 9W'
Saw Dimensions:
Table height .................................... 34"
Cabinet depth ................................... 23"
Cabinet width ................................... 26"
Table area .................................. 48 x 30"
Front of table to blade ........................... 123A''
Rip Fence Dimensions:
Rip fence ...................................... 40"
Rip fence rails (front and rear) ................... 77, 67"
Blade capacity maximum .......................... 12"
Blade arbor extension ....................... %" and 1"
Dado blade capacity maximum ..................... '%_"
Dado blade arbor extension ......................... %"
Saw Constructions:
Cabinet ................... Totally enclosed welded steel
Saw Constructions (Continued)
Table ................................. Solid cast iron
Rip fence ...................... Aluminum and cast iron
Drive system ............................... 3 V-belts
Exhaust port ................................ 4" Male
Miter gauge ............ Cast iron with a T-slot roller guide
Blade guard .............. Acrylic with antikickback pawls
Switch ............. Locking magnetic starter with overload
Arbor RPM ........................ 4,000 RPM approx.
Motor ............................... 3HP, 3450 RPM,
capacitor start, capacitor run,
230V, 16A, single-phase, ball bearing,
Sears Part No. 23058.00
Gross weight with motor ....................... 656 Ibs
WARNING: Disconnect power before attempting any of the
following procedures. Be certain switch is in OFF position and
safety disconnect (or breaker) is in OFF or open position. Saw
blade must not be moving. Saw blade will rotate freely after
motor is turned off. Allow blade to come to a complete stop
before attempting any of the following procedures.
WARNING: The operation of any power tool can result in
foreign objects being thrown into the eyes, which can result in
severe eye damage. Always wear safety goggles complying
with United States ANSI Z87.1 before commencing power tool
operation.
BLADE HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Figures 7 and 9, pages 18 and 22.
• Blade height is controlled by handwheel (Fig. 9, No. 27) on
the front of the saw.
• To adjust height, loosen locking hand knob (Fig. 9, No. 23).
Rotate knob counterclockwise approximately three turns.
Turn handwheel to desired blade height.
CAUTION: For safety, blade should be raised only '/8"above
the surface of the material to be cut. However, if hollow
ground blades are used, raise blade to its maximum height to
allow for greater blade clearance.
• Lock blade height into position. Lock handwheel (Fig. 9,
No. 27) by tightening locking knob (Fig. 9, No. 23) clock-
wise. Tighten only until snug.
IMPORTANT: Do not over tighten. Only a small amount of
pressure is necessary to lock handwheel securely.
• The blade height mechanism has upper and lower limit
stops (Fig. 7, Nos. 17 and 37). These limit stops are set at
the factory and need no further adjustment.
BLADE TILT ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Figures 8 and 9, pages 20 and 22.
• The saw blade can be set at any angle between 90 ° and
45°. Blade tilt is controlled by the handwheel (Fig. 9, No.
27) on the left side of the saw. The indicator (Fig. 8, No. 15)
on front of saw shows the tilt angle of the blade.
• To adjust tilt, loosen locking hand knob (Fig. 9, No. 23).
Rotate knob counterclockwise at least three turns. Turn
handwheel to desired blade angle. Lock blade angle into
position.
• Lock handwheel (Fig. 9, No. 27) by tightening locking hand
knob (Fig. 9, No. 23) clockwise. Tighten only until snug.
• The saw is equipped with positive stops at 90° and 45°.
These positive stops allow operator to position saw blade
at 90 ° and 45° quickly and accurately.
90 ° STOP ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Figure 8, page 20.
• Raise saw blade above table as far as possible. Set blade
at 90 ° to table by turning the tilting handwheel. Place a
square on table and check to see if blade is perpendicular
to the table. When checking put square flush against saw
blade. Do not put square on teeth of saw blade.
• If 90 ° adjustment is necessary, loosen Iocknut (No. 19) on
adjusting bolt (No. 21) and turn adjusting bolt.
• Using the square, rotate the tilting handwheel until blade is
90° to table. When exactly at 90 °, turn adjusting bolt (No.
21) against the lug on the front trunnion. Do not turn too
far; recheck 90 °. Tighten Iocknut securely.
• Check tilt indicator pointer. If necessary, adjust pointer so it
points to 0° mark on scale. To adjust pointer, remove
handwheel and loosen screw (No. 13). Be sure to tighten
screw securely after adjustment is completed.
10

45 ° STOP ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Figure 8, page 20.
• Tilt the saw blade to 45°. Using a combination square,
check to see if blade is 45 ° to the table.
• If 45 ° adjustment is necessary, adjust 45 ° stop in the same
manner as the 90° stop. The only exception is that adjust-
ment bolt and Iocknut (Nos. 21 and 19) are on the other
end of the rack. Adjust the indicator if necessary.
MITER GAUGE ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Figure 11, page 26.
• Miter gauge supplied with saw is equipped with individually
adjustable index stops at 90° and 45°, right and left.
Adjustment to index stops can be made by loosening lock-
ing nut (No. 12) and tightening or loosening three adjust-
ing screws (No. 5). Be sure to tighten locking nut (No. 12)
after adjustment is made.
• Face of miter gauge has two holes for purpose of attach-
ing auxiliary facing.
• Miter gauge is accurately constructed for precision work.
Miter gauge is guided through T-slot with a roller guide
(No. 10) mounted at front of guide bar (No. 3). Roller guide
adds to miter gauge's stability and prevents the guide bar
from leaving T-slot.
• To operate miter gauge, simply loosen lock handle (No. 1)
and move miter gauge (No. 4) to desired angle. The miter
gauge will stop at 90 ° and 45 °, both right and left. To posi-
tion miter gauge past these points, simply push down
gauge stop (No. 7). Position miter gauge at desired angle
and tighten lock handle.
• Be positive the edge of workpiece next to face of miter
gauge is straight and tight against miter gauge so that the
workpiece does not rock or rotate. Always use both hands
when operating the miter gauge.
• The miter gauge is used for cross-cutting, compound miter
cutting, miter cutting, rabbeting, bevel cutting and dadoing.
RIP FENCE ADJUSTMENT
The saw's rip fence is precision manufactured, incorporating
fine adjustments for accurate cuts. The saw is built to allow
the operator to accurately adjust the rip fence without prob-
lems in a matter of seconds. The saw uses a unique system
of T-blocks. These T-blocks, when correctly placed, give the
operator an immediate index to properly adjust and set the rip
fence into position.
ALIGN RIP FENCE PARALLEL WITH BLADE AND
MITER GAUGE SLOTS
Refer to Figure 9, page 22.
• The rip fence is aligned using both T-blocks in either miter
gauge slot. Secure both T-blocks to one slot (front and
rear on table) with socket head bolts (No. 30). Position the
T-blocks on the table so the T is in the slot and the entire
block is on the table and not hanging over an edge. These
blocks are now the index (stops) used to align the rip fence.
• Unlock rip fence and position it against T-blocks. While
against blocks, place the locking lever in down position
locking fence in place. The rip fence is aligned when it is
flush against both T-blocks. Adjust rip fence if necessary.
ADJUST RIP FENCE
Refer to Figure 10, page 24.
NOTE: When adjusting the fence (No. 8), always adjust
T-blocks to the face of the fence which the workpiece con-
tacts. T-blocks should always be between blade and fence.
• Unlock rip fence adjust using set screws (No. 11) so that
fence will be flush with both T-blocks. Lock rip fence against
T-blocks with lever (No. 14).
• Rip fence should now be aligned with both T-blocks. If rip
fence is not aligned, unlock fence and repeat adjustment.
Remove T-blocks.
• Occasionally, after aligning rip fence with T-blocks, check
to see if rip fence is aligned with blade. If rip fence is in
alignment with T-blocks and is not in alignment with blade,
table is not parallel with blade. To adjust table see
Assembly, page 6, "Check table alignment."
• Calibrating the scale can now be completed. The rip fence
scale is located on the guide rail (No. 2). The scale is used
to measure the distance between the right side of the
blade and rip fence. The scale is viewed through the mag-
nified window on the guide casting.
• Raise blade as far as possible. Gently move the rip fence
against the right side of the blade. In this position the indi-
cator should read zero. If not, lock the fence in place with
lever (No. 14). Loosen screws (No. 23) and position lens
bracket (No. 21) so that indicator reads zero and retighten
screws.
• The height of the rip fence can be adjusted by the plastic
screws (No. 19).
• Check to be certain rip fence is aligned with blade and
indicator reads zero. If not, repeat adjustment steps.
RIP FENCE OPERATION
Refer to Figure 10, page 24.
• Unlock the fence by lifting the locking lever (No. 14). Using
the scale for placement, position the rip fence. Lock the rip
fence into position by placing the locking lever in the down
position.
• The rip fence is used for the following operations: ripping,
bevel ripping, ploughing, resawing, rabbeting and dadoing.
WARNING: For your own safety, always observe the follow-
ing safety precautions.
• Never make any cut freehand (without using miter gauge
or rip fence). Blade can bind in the cut and cause a kick-
back.
• Always lock miter gauge or rip fence securely when in use.
• Remove rip fence from the table when miter gauge is in
use.
• Remove miter gauge from table when rip fence is in use.
• Make sure blade guard is installed for all "thru sawing"
operations. Replace guard immediately after completion of
resawing, rabbeting and dadoing.
Frequently check action of antikickback pawls by passing
the workpiece alongside the spreader while saw is off. Pull
the workpiece toward you. If the pawls do not dig into the
workpiece and hold it, the pawls must be sharpened. (See
Maintenance section, page 13.)
• Have blade extend approximately _/8"above top of work-
piece. Additional blade exposure increases hazard poten-
tial.
11

• Do not stand directly in front of blade in case of a kick-
back. Stand to either side of the blade.
• Keep your hands clear of the blade and out of the path of
the blade.
• If the blade stalls or stops while cutting, turn switch OFF
and safety disconnect OFF before attempting to free the
blade.
• Do not reach over or behind the blade to pull the work-
piece through the cut, to support long or heavy work-
pieces, to remove small cut-off pieces of material or for
any other reason.
• Do not pick up small pieces of cut-off material from the
table. Remove them by pushing them off table with a long
stick. Otherwise they could be thrown back at you by the
rear of the blade.
• Do not remove small pieces of cut-off material that may
become trapped inside blade guard while saw is on. This
could endanger your hands or cause a kickback. Turn saw
off. After blade has stopped turning, lift guard and remove
the piece.
• Always lower blade below the table level when machine is
not in use.
TYPES OF CUTS/OPERATIONS
CROSSCUTTING
Performed with miter gauge set at "0". Crosscutting is known
as cutting work across the grain at 90°, or square with both
the edge and the fiat side of the wood.
MITER CUTTING
Performed with miter gauge, is known as cutting wood at an
angle other than 90 ° with the edge of the wood.
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING
Performed with miter gauge, is same as crosscutting except
that the wood is also cut at an angle other than 90° with the
flat side of the wood (blade is at an angle).
COMPOUND MITER CUTTING
Performed with miter gauge, is a combination of miter cutting
and bevel crosscutting. Cut is made at angle other than 90 ° to
both the edge and flat side of wood.
RIPPING
Performed with rip fence, is known as cutting a piece of wood
with the grain or lengthwise. Position the fence to the desired
width of rip and lock in place. When ripping long boards or
large panels always use a work support.
BEVEL RIPPING
Performed with rip fence, the same as ripping. However, blade
is set at an angle other than 90 °.
RESAWlNG
Performed with rip fence, is known as ripping a piece of wood
through its thickness. Do not attempt to resaw bowed or
warped material.
NOTE: It may be necessary to remove blade guard and use
work supports as well as push blocks when performing this
operation.
WARNING: Install blade guard immediately upon completion
of resawing operation.
PLOUGHING
Performed with rip fence, is grooving with grain long way of
workpiece. Use proper hold downs and feed devices.
RABBETING
Performed with either miter gauge or rip fence. Rabbeting is
known as cutting out a section of the corner of a piece of
material, across an end or along an edge. To make a rabbet
requires cuts which do not go all the way through the materi-
al. Therefore, blade guard must be removed. Install blade
guard immediately upon completion of rabbeting operation.
Rabbet cuts can also be made using dado head.
DADOING
Performed with either miter gauge or rip fence. Dadoing is
done with a set of blades (dado set) rather than standard 10
or 12" saw blades. The dado set is used to groove wood simi-
lar to ploughing and rabbeting. However, the dado set allows
operator to remove more material in one pass. The operator,
with a dado set, can vary width of cut up to '_".
Instructions for operating dado set are contained in owner's
manual furnished with dado set. Dadoing requires cuts which
do not go all the way through material. Therefore, blade guard
must be removed. Dado sets have different characteristics
than saw blades. As a result, saw must be fitted with special
parts that are furnished with saw.
The Craftsman stationary saw dado set maximum capacity is
% I.D. x 8" O.D. x _" width.
When using a dado set, the following parts must be substitut-
ed (see Figure 7 and 9): %" dade arbor extension (Fig. 7, Ne.
36) and dado table insert (Fig. 9, No. 6). (See Assembly.)
IMPORTANT: Always use correct insert. When using the dado
set, use caution. Use featherboards and push sticks as applic-
able.
WARNING: Always immediately replace the standard blade
arbor, standard blade, blade guard and blade insert when you
are finished dadoing.
NOTE: 12" Saw only. To replace blade, the standard 1" arbor
extension (not shown) should be used.
CUTTING OVERSIZED WORKPIECES
When cutting long workpieces or large panels, always support
workpiece that is not on table. Use adjustable roller stand or
make simple support by clamping a piece of plywood to saw
horse. Add facings to miter gauge or rip fence as needed.
IMPORTANT: Do not allow facings to interfere with operation
of blade guard.
DUST COLLECTING
• Saw is fitted with a 4" male exhaust port. When a dust col-
lector is used, cover louvers on door. This will create a
better vacuum within cabinet and result in more efficient
sawdust removal. It is recommended to tape louvers
closed or seal with a sheet of plastic.
IMPORTANT: If dust collector is NOT used when saw is run-
ning, be sure louvers are open (for good air circulation to
keep motor from overheating).
• Before starting saw, see that all adjustments are properly
made and guards in place. With power disconnected, turn
pulley by hand to make sure everything is correct before
connecting power and starting saw.
12

STARTING SAW
WARNING: Never operate saw without blade guards in
place. Be sure blade is not in contact with workpiece when
motor is started. Start motor and allow saw to come to full
speed.
WARNING: Make sure the electrical characteristics of motor
nameplate and power source are the same.
• Saw is fitted with a safety ON/OFF switch on front of
cabinet.
• To turn saw on, stand to either side of the blade--never in
line with it. Push green START. Always allow saw blade to
come up to full speed before cutting.
• Do not turn motor switch ON and OFF rapidly. This action
overheats the motor and may cause saw blade to loosen.
• Never leave saw while the power is on.
• To turn saw off, push red STOP. Never leave saw until cut-
ting tool has come to a complete stop.
WARNING: For your own safety, lower blade or cutting tool
below table surface. If blade is tilted, return it to vertical posi-
tion. Turn off safety disconnect or circuit breaker when saw is
not in use.
BLADE SELECTION
Blade selection is based on type of material being cut and
how it will be cut. There are three general types of saw
blades: rip saw blades cut with grain of wood, cut-off saw
blades cut across grain, and combination saw blades cut with
grain, across grain and any angle to grain.
Blades vary in many aspects. When selecting a blade, the fol-
lowing blade characteristics should match up with operation
to be performed and type of material to be cut: type of steel;
quality of steel; tooth style; tooth set; carbide tipped; grind;
number of teeth and size.
IMPORTANT: Your saw is only as accurate and efficient as
blade or cutting tool used.
First, be certain to use the appropriate type of cutting tool for
the operation to be performed. Second, it is strongly recom-
mended that high-quality blades and cutting tools be used. Be
certain blades and cutting tools are kept sharp and in good
working order. Check blades periodically and replace or
sharpen if necessary.
WARNING: Do not attempt under any circumstances, to
service, repair, dismantle, or disassemble any mechanical
or electrical components without physically disconnecting all
power sources.
CLEANING
• Clean off any preservative on bright (machined) parts
with appropriate solvent (mineral spirits). Avoid getting
cleaning fluid on any rubber parts as they tend to deterio-
rate rubber.
• Use soap and soft water on rubber and plastic parts.
• After cleaning, lubricate unpainted surfaces with a light
application of medium consistency machine oil. This lubri-
cation should be repeated at least once every six months.
NOTE: Instead of oil, a good quality paste wax can be
applied to rip fence and table surface. Paste wax will enhance
movement of workpieces. In addition to providing lubrication,
paste wax will help prevent rusting.
• Keep your machine and your workshop clean. Do not
allow sawdust to accumulate on saw or inside cabinet.
Frequently vacuum or blow out any sawdust that may
accumulate within cabinet.
• Be certain motor and internal mechanisms are clean and
are frequently vacuumed or blown free of any dirt.
• For motor maintenance, follow instructions provided with
motor.
LUBRICATION
All bearings on the arbor are shielded ball bearings. These
bearings are permanently lubricated at the factory.
• As needed, clean the grease off the rack and worm gears
of height and tilt mechanism. Lubricate rack and gears
with a medium viscosity machine oil.
• Be sure to lubricate trunnion ways and all bushings.
• Occasionally oil all other bearing points, including blade
guard assembly, miter gauge and rip fence.
• For motor lubrication, follow instructions provided with the
motor.
SERVICE
• Replace belts and worn parts as needed. If power cords
are worn, cut, or damaged in any way, have them
replaced immediately.
• Make sure teeth of antikickback pawls are always sharp.
• Sharpen dull teeth using a few light strokes of a smooth
cut flat file.
• Service motor according to the instructions provided. The
motor should be serviced only by a qualified electrician.
13
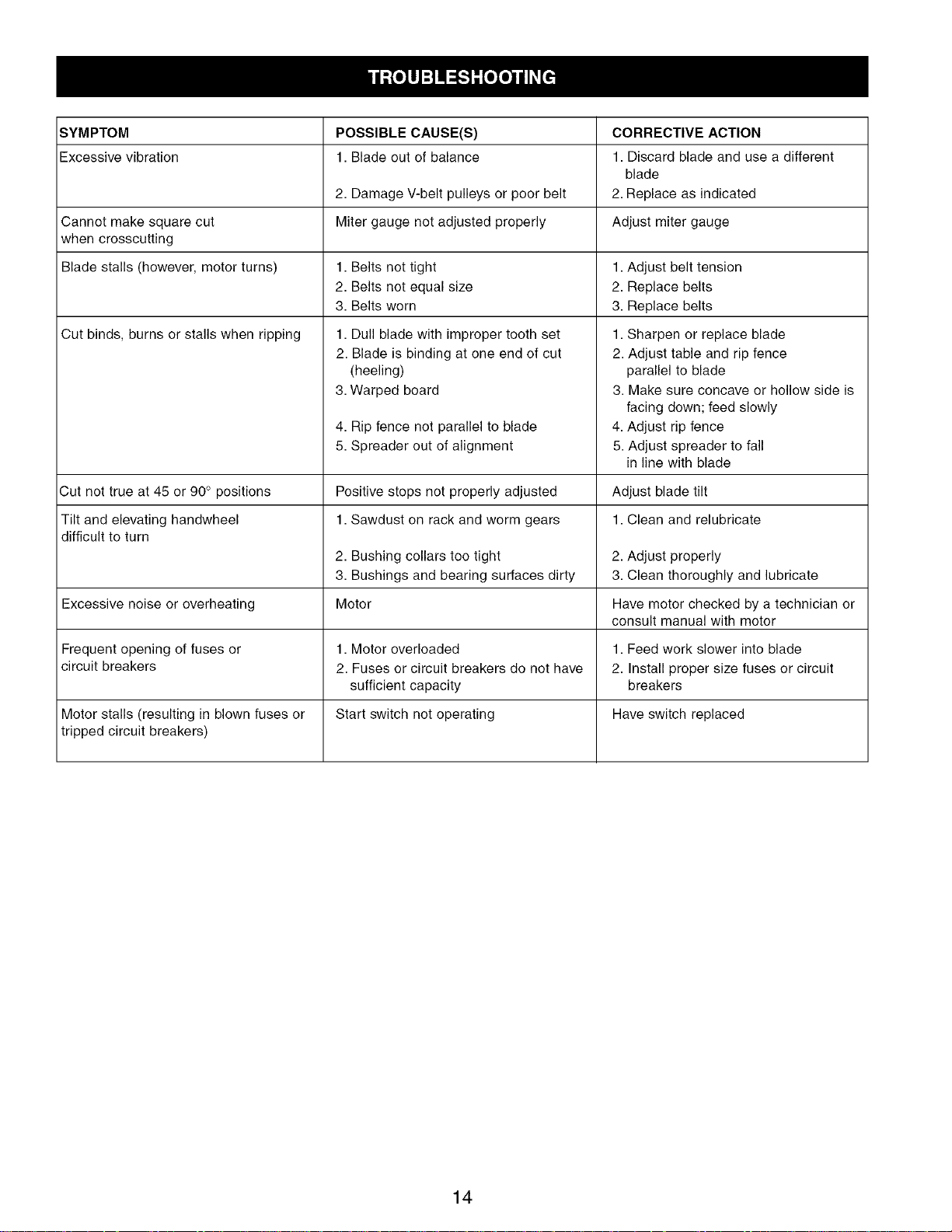
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE CAUSE(S) CORRECTIVE ACTION
Excessive vibration 1. Blade out of balance 1. Discard blade and use a different
blade
2. Damage V-belt pulleys or poor belt 2. Replace as indicated
Cannot make square cut Miter gauge not adjusted properly Adjust miter gauge
when crosscutting
Blade stalls (however, motor turns) 1. Belts not tight 1. Adjust belt tension
2. Belts not equal size 2. Replace belts
3. Belts worn 3. Replace belts
Cut binds, burns or stalls when ripping 1. Dull blade with improper tooth set
2. Blade is binding at one end of cut
(heeling)
3. Warped board
4. Rip fence not parallel to blade
5. Spreader out of alignment
Cut not true at 45 or 90° positions Positive stops not properly adjusted Adjust blade tilt
Tilt and elevating handwheel 1. Sawdust on rack and worm gears 1. Clean and relubricate
difficult to turn
2. Bushing collars too tight 2. Adjust properly
3. Bushings and bearing surfaces dirty 3. Clean thoroughly and lubricate
Excessive noise or overheating Motor Have motor checked by a technician or
Frequent opening of fuses or 1. Motor overloaded 1. Feed work slower into blade
circuit breakers 2. Fuses or circuit breakers do not have 2. Install proper size fuses or circuit
sufficient capacity breakers
Motor stalls (resulting in blown fuses or Start switch not operating Have switch replaced
tripped circuit breakers)
1. Sharpen or replace blade
2. Adjust table and rip fence
parallel to blade
3. Make sure concave or hollow side is
facing down; feed slowly
4. Adjust rip fence
5. Adjust spreader to fall
in line with blade
consult manual with motor
14
 Loading...
Loading...