Coulter MicroDiff Service manual

COULTER®MicroDiff
C
C
®
Field Service
Technical Manual
PNPN 4237161B4237161B (April(April 1993)1993)
CoulterCoulter CorporationCorporation
Miami,Miami, FLFL 33196-250033196-2500
TM
Coulter Corporation makes no representation that, upon furnishing this service manual, the holder of the manual will have the necessary
technical capabilities and know-how to properly troubleshoot and repair any of the equipment specified in the manual. Coulter
Corporation assumes no liability whatsoever, including consequential and incidental damages, resulting from improper operation of
Coulter instruments after maintenance of Coulter instruments has been performed by persons not employed by Coulter Corporation.
Furthermore, Coulter Corporation assumes no liability whatsovever for any personal injury or property damage resulting from
maintenance and/or repair of Coulter instruments performed by persons not employed by Coulter Corporation.
TRADEMARKS
AccuComp, ACCUVETTE, ACCU-ZYME, AQUA-AD, AUTO-CAL, AUTO-CLONE, "CC"
logo,CARDS,CASH,CHANNELYZER,CHEMOTERGE, COMPLETE CELL ANALYSIS,
COULTER, COULTER CHEMISTRY, COULTER CLENZ, COULTER CLONE, THE
COULTER COUNTDOWN, COULTER COUNTER, COULTER CURRENTS,
COULTERAMA, CYTO-STAT, CYTO-TROL, C-ZYME, DACAL, DACOS, "DACOS" logo,
DART, DIFF3, DIFF3 50, DIFF4, DILU-PACK, E.A.SY. 1, EASY 88, EASY 2, EPICS,
FASTECS, 5C,4C,HEMO-CAL,HEMOTERGE,HEMO-W,IsoFlow,ISOLYSE,ISOPET,
ISOTERGE, ISOTON, KEM-O-MAT, "LFI" logo, LANGLEY FORD, LANGLEY FORD
INSTRUMENTS,LEASE-PAK,LYSES, MDADS, MINI-KEM,NANO-SIZER,OMNISORP,
OptiChem, S-CAL, SOMACOUNT, SOMAFIX, SOMATON, STAIN RIGHT, STILL
COUNTING, THROMBOCOUNTER, THROMBO-FUGE, U.V.-ZYME, ZAP-OGLOBIN,
ZAPONIN and ZETAFUGE are trademarks of Coulter Corporation.
HAZARDS AND OPERATIONAL PRECAUTIONS AND LIMITATIONS
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and IMPORTANTS alert you as follows:
WARNING: Might cause injury.
CAUTION: Might cause damage to the instrument.
IMPORTANT: Might cause misleading results.
"This Service Manual contains confidential information of Coulter Corporation and its receipt or
possession does not convey any rights to reproduce, disclose its contents, or to manufacture, use, or sell
anything it may describe. Reproduction, disclosure, or use without specific written authorization of Coulter
Corporation is strictly forbidden."
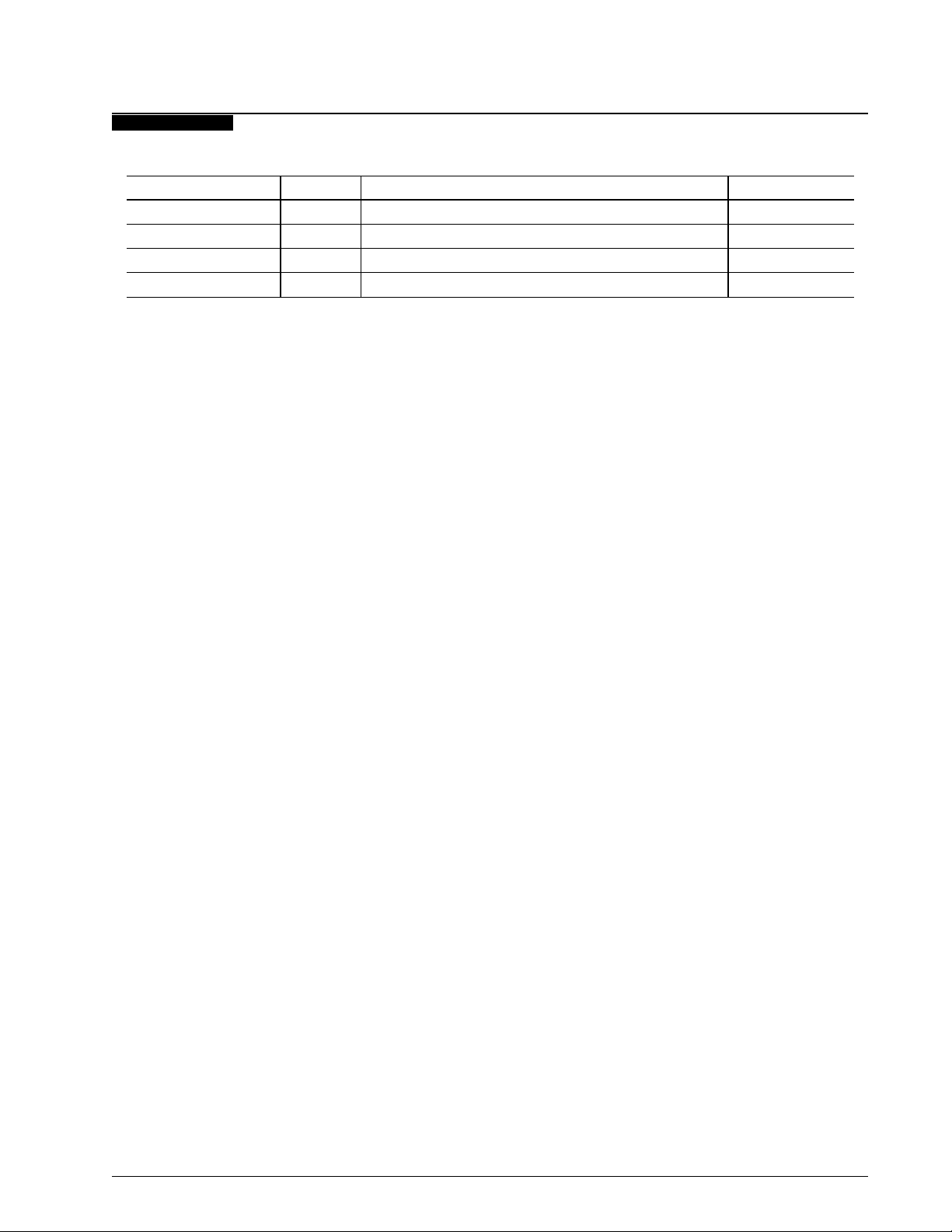
REVISION STATUS
Issue Date Amended Pages Software Level
Draft 5/92
Initial 5/92
A 7/92
B 4/93 2-3, 2-4, 2-9, 2-10, 2-12, 2-15, 3-5, 3-6, Chapter 8 1D
PN 4237161B (April 1993) i

REVISION STATUS
ii PN 4237161A (July 1992)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS, 1-1
1.1 GENERAL SAFETY, 1-1
WARNING, 1-1
CAUTION, 1-1
IMPORTANT, 1-1
Note, 1-1
1.2 ELECTRONIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, 1-1
1.3 BIOLOGICAL SAFETY, 1-2
2 INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION, 2-1
2.1 SPECIFICATIONS, 2-1
Dimensions/Weight, 2-1
Power, 2-1
Input, 2-1
Consumption, 2-1
Ambient Operating Temperature, 2-1
Humidity, 2-1
Recommended Reagents, 2-1
Controls and Calibrators, 2-1
Fluid Volumes, 2-2
Interfering Substances, 2-2
2.2 INTRODUCTION TO THE COULTER MicroDiff, 2-2
Function, 2-2
Mode of Operation, 2-2
2.3 DIFFERENTIAL MEASUREMENT, 2-2
2.4 OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW, 2-2
2.5 DILUTER, 2-3
General, 2-3
Count Valve 1 (VL1), 2-5
Dilution Valve 2 (VL2), 2-5
Stepper Motor Driver Card, 2-5
2.6 VENT VALVE VACUUM SENSE CARD, 2-8
2.7 ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY, 2-8
General, 2-8
Motherboard, 2-9
Linear Power Supply, 2-10
PN 4237161B (April 1993) iii

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Power Supply Components, 2-10
Switching Power Supply, 2-13
Data Acquisition Card, 2-14
Multi Stepper Motor Control Card (MSMC), 2-15
Input Output Resource Adapter Card (IORA), 2-17
Keyboard, 2-18
Display, 2-19
3 MICRODIFF INSTALLATION PROCEDURE, 3-1
3.1 PREINSTALLATION CHECKS, 3-1
Space and accessibility, 3-1
Power Requirements, 3-1
Ambient Temperature and Humidity, 3-1
3.2 INITIAL SETUP, 3-2
Uncrating Instrument, Accessories and
Supplies, 3-2
Reagent Connections, 3-2
Printer Connection, 3-3
Power ON, 3-3
3.3 INSTRUMENT CONFIGURATION, 3-3
3.4 PRELIMINARY OPERATION CHECKS, 3-4
3.5 SETTING AIM FACTORS, 3-5
3.6 CALIBRATION, 3-5
3.7 RUNNING CONTROLS, 3-6
4 SERVICE/REPAIR PROCEDURES, 4-1
4.1 TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED, 4-1
4.2 DRIVER CARD REPLACEMENT, 4-1
Removal, 4-1
Installation, 4-1
4.3 PVAC CARD REPLACEMENT, 4-1
Installation, 4-2
4.4 MOTHERBOARD REPLACEMENT, 4-2
Removal, 4-2
Installation, 4-3
4.5 SYRINGE REPLACEMENT, 4-3
Removal, 4-3
Installation, 4-4
iv PN 4237161A (July 1992)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
4.6 VACUUM PUMP REPLACEMENT, 4-4
Removal, 4-4
Installation, 4-4
4.7 LYSE PUMP REPLACEMENT, 4-5
Removal, 4-5
Installation, 4-5
4.8 LYSE PUMP VERIFICATION/ADJUSTMENT, 4-5
4.9 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY REPLACEMENT, 4-6
Removal, 4-6
Installation, 4-6
4.10 DISKETTE DRIVE REPLACEMENT, 4-7
Removal, 4-7
Installation, 4-7
4.11 DAC CARD REPLACEMENT, 4-7
Removal, 4-7
Installation, 4-8
4.12 MSMC CARD REPLACEMENT, 4-8
Removal, 4-8
Installation, 4-8
4.13 IORA CARD REPLACEMENT, 4-8
Removal, 4-8
Installation, 4-9
4.14 DISPLAY REPLACEMENT, 4-9
Removal, 4-9
Installation, 4-9
4.15 KEYPAD REPLACEMENT, 4-10
Removal, 4-10
Installation, 4-10
4.16 RED/WHITE BATH/APERTURE COMPONENT
REPLACEMENT, 4-11
Hgb Detector/LED, 4-11
Removal, 4-11
Installation, 4-12
Aperture Electrode Housing
Replacement, 4-12
Removal, 4-12
Installation, 4-13
Bath, 4-13
Removal, 4-13
Installation, 4-14
PN 4237161B (April 1993) v

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 5 INTENTIONALLY OMITTED
6 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS, 6-1
CHAPTER 7 INTENTIONALLY OMITTED
8 ILLUSTRATED PARTS LIST, 8-1
8.1 PARTS LIST IN PART NUMBER ORDER, 8-1
8.2 ILLUSTRATED PARTS LISTS, 8-6
APPENDIX A ERROR CODES, A-1
A.1 MicroDiff ERROR CODES, A-1
ILLUSTRATIONS
2.1 Diluter Components, 2-4
2.2 Stepper Motor Driver Card, 2-6
2.3 Motherboard, 2-9
2.4 Linear Power Supply, 2-11
2.5 Regulator Card, 2-12
2.6 Data Acquisition Card, 2-14
2.7 Multi Stepper Motor Control Card, 2-16
2.8 Input/Output Resource Adapter Card, 2-18
8.1 Diluter, 8-6
8.2 Syringe Drive, 8-8
8.3 Linear Power Supply, 8-10
8.4 Bath, Rear View, 8-11
8.5 Bath, Front View, 8-12
8.6 Keypad and Display, 8-13
8.7 Diluent and Count Valve Display, 8-14
8.8 Carriage Assembly, 8-16
TABLES
2.1 Stepper Motor Driver Card Connections, 2-7
2.2 Stepper Motor Driver Card Test Points, 2-8
2.3 Terminal Block Connections, 2-12
2.4 MSMC Jumpers, 2-17
2.5 IORA Jumpers, 2-7
vi PN 4237161A (July 1992)

1.1 GENERAL SAFETY
WARNING
CAUTION
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS 1
Throughout this manual you will encounter the headings WARNING,
CAUTION, IMPORTANT, and Note. These are provided to inform you
of potentially hazardous situations and important or helpful information.
A WARNING indicates a situation or procedure that, if ignored, can
cause serious personal injury. A WARNING will appear in bolded text
for easy identification.
A CAUTION indicates a situation or procedure that, if ignored, can
cause damage to equipment. A CAUTION also appears in bolded text.
IMPORTANT
An IMPORTANT indicates a situation or procedure that, if ignored can
result in erroneous test results. An IMPORTANT also appears in bolded
text.
Note
A Note contains information that is important to remember or helpful in
performing a procedure.
1.2 ELECTRONIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
Remove rings and other metal jewelry before performing maintenance
or service on the electronic components of instrument.
PN 4237161A (July 1992) 1-1

WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
1.3 BIOLOGICAL SAFETY
CAUTION
To prevent damage to delicate electronic components, always be sure
power is OFF before removing or replacing printed circuit boards and
components.
WARNING
To prevent possible injury or biological contamination, service
personnel must wear gloves and eye protection when servicing the
instrument with the doors open.
Use care when working with pathogenic materials. Means must be
available to decontaminate the instrument, provide ventilation, and to
dispose of waste liquid. Refer to the following publications for further
guidance on decontamination.
Biohazards Safety Guide, 1974, National Institute of Health.
Classifications of Etiological Agents on the Basis of Hazards, 3d ed.,
June 1974, Center for Disease Control, U.S. Public Health Service.
In areas of high risk, operator must be trained in person. Telephone
instruction is prohibited.
1-2 PN 4237161A (July 1992)

2.1 SPECIFICATIONS
Dimensions/Weight
Power
INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION 2
Height 49.5 cm (19.5 in.)
Width 43.2 cm (17 in.)
Depth 40.6 cm (16 in.)
Weight 34 Kg (75 lb)
Input
• 100 Vac (±10%) 50/60 Hz
• 120 Vac (±10%) 50/60 Hz
• 220 Vac (±10%) 50/60 Hz
• 240 Vac (±10%) 50/60 Hz
Consumption
Less than 200 watts
Ambient Operating Temperature
16°C to 32°C (60°F to 90°F)
Humidity
0 to 95% without condensation
Recommended Reagents
COULTER MICRO-PAK (diluent and lytic reagent) P/N 8547007
COULTER CLENZ
Controls and Calibrators
4C®PLUS Cell Control Tri Pac P/N 7547003
®
S-CAL
Calibrator Kit P/N 7547005
®
Cleaning Agent P/N 8546931
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-1

INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
Fluid Volumes
• Whole Blood Aspirated: 12 µL
• ISOTON
• LYSE S
®
III diluent consumption per cycle: 18.64 mL
®
III Diff reagent consumption per cycle: 415 µL
Interfering Substances
Refer to Product Reference Manual for known interfering substances
2.2 INTRODUCTION TO THE COULTER MicroDiff
Function
The MicroDiff is an automated hematology analyzer for in vitro
diagnostic use in clinical laboratories. The MicroDiff reports a 16
parameter Complete Blood Count, including a six parameter WBC
differential, from whole blood.
Mode of Operation
The MicroDiff has one operating mode. The sample is introduced to the
instrument by removing the cap from the sample tube, presenting the
sample to the aspirator probe, and starting the cycle.
2.3 DIFFERENTIAL MEASUREMENT
The MicroDiff performs WBC differentials from whole-blood samples. It
provides lymphocyte, monocyte and granulocyte percentages and
absolute numbers using Coulter histogram differential technology.
The white blood cells are counted and sized for the WBC histogram in a
single 100-µm WBC aperture.
2.4 OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
The cycle is started by pressing the 〈ASP〉button on the keypad:
1. The aspirate syringe is driven down to aspirates 12 µL of sample and
a small amount of air.
2. The diluent syringe fills with diluent for the WBC dilution.
3. The bath drains.
2-2 PN 4237161B (April 1993)

OPERATIONAL OVERVIEW
4. The aspirator probe moves to the bath and dispenses the sample into
the bath. The diluent syringe dispenses diluent through the probe
into the bath making a 215:1 dilution.
5. Mixing bubbles from the air pump (PM1) enter the bath to mix the
solution.
6. The aspirate syringe is driven down again to aspirate 100 µl of the
dilution from the bath into the probe, where it is held for the
RBC/Plt dilution.
7. The lyse pump (PM5) dispenses 415 µL of lyse to the bath for a final |
WBC dilution of 251:1 and the sample is mixed again.
8. The WBC solution is drawn through the WBC aperture for 12 s to
count and size the WBCs.
9. After WBC analysis, and just before the WBC sample drains from
the bath, the Hgb reading is taken.
2.5 DILUTER
General
10. The bath is drained and rinsed and Hgb Blank is taken. |
11. The diluent syringe fills with diluent for the RBC/Plt dilution.
12. The 100 µL of the 215:1 solution, stored in the aspirate probe, is
dispensed into the bath with diluent to obtain a final RBC/Plt
dilution of 6250:1.
13. Mixing bubbles from PM1 enter the bath to mix the solution.
14. The RBC/Plt dilution is drawn through the RBC/Plt aperture for 12 s
to count and size the RBCs and Plts.
15. The bath is drained and rinsed.
16. The aperture is zapped, and the system is prepared for the next test |
sequence.
The diluter section of the MicroDiff processes the sample for analysis.
The locations of the components are illustrated in Figure 2.1.
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-3
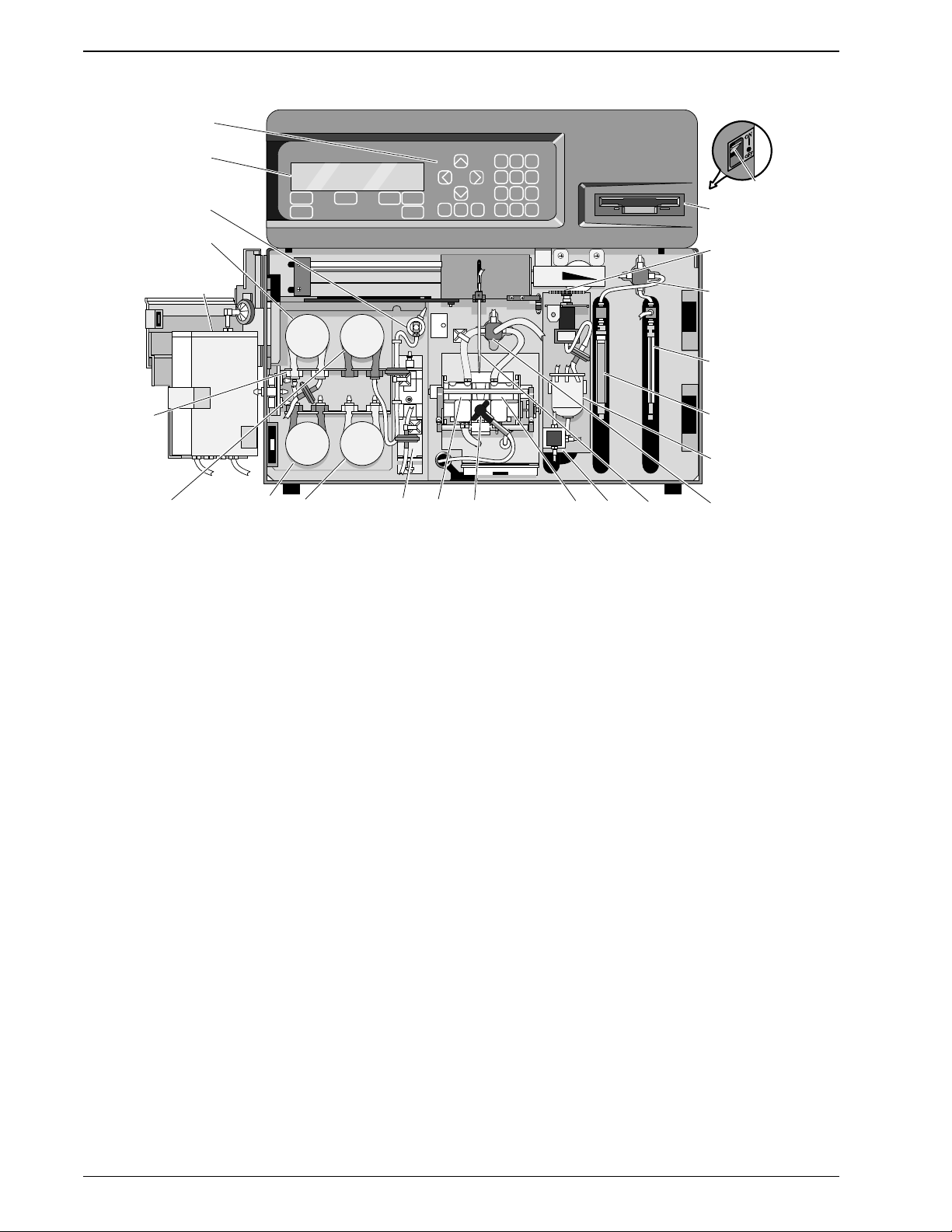
INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
2
1
18
20
3
10
ON/OFF
SWITCH
19
9
222117
1. LCD DISPLAY
2. KEYPAD
3. DISK DRIVE
4. ASPIRATOR PROBE
5. ASPIRATION SYRINGE
6. DILUENT SYRINGE
7. VL2 DILUENT VALVE
8. LYSE PUMP PM5
9. LYSE DECTECTOR
10. VACUUM REGULATOR
11. VACUUM ISOLATOR
12. VL1 COUNT VALVE
13. BATH-WBC APERTURE
14. BATH-RBC APERTURE
15. HGB LED
16. LV3 DRAIN SOLENOID
17. AIR PUMP PM1
18. LV4 AIR MIX SOLENOID
19. DILUENT RESERVOIR
20. DILUENT PUMP PM2
21. RINSE PUMP PM3
22. WASTE PUMP PM4
7
5
6
11
124161315148
7161-01
Figure 2.1 Diluter Components|
The MicroDiff uses two syringes driven by stepper motors to aspirate
sample and deliver diluent. The syringe volumes are:
• Aspirate syringe 100 µL
• Diluent syringe 5000 µL
The instrument uses four stepper motor driven peristaltic pumps to
generate mixing bubbles, drain the bath, deliver rinse to the bath, and
draw diluent from diluent pack into the diluent reservoir.
Two stepper motor driven switching valves, Count Valve 1 and Dilution
Valve 2, control the flow and direction of the fluidics and pneumatics.
2-4 PN 4237161B (April 1993)

Count Valve 1 (VL1)
The count valve is a three-position valve that routes count vacuum to the
WBC and RBC apertures.
Dilution Valve 2 (VL2)
The dilution valve is a four-position valve that:
• Routes diluent to the bath through the aspirate probe.
• Provides a path to the diluent supply to fill diluent syringe.
• Routes the sweep flow diluent from the diluent reservoir through
the sweep flow can to the RBC aperture.
Stepper Motor Driver Cards
Two Stepper Motor Driver cards, in the Diluter, provide the drive voltage
to the stepper motors, the opto switches, the lyse pump, solenoids, and
the cycle counter.
DILUTER
Stepper Motor Driver Card 1 drives the following components:
• Diluent Pump • Air Pump
• Rinse Pump • Waste Pump
• Lyse Pump • Air Mix Solenoid
• Diluent Reservoir Sensor • Lyse Level Sensor
• Cycle Counter
Stepper Motor Driver Card 2 drives the following components:
• Dilution Valve • Dilution Valve Home Opto Switch
• Traverse Motor • Traverse Home Opto Switch
• Count Valve Motor • Count Valve Opto Switch
• Aspirate Syringe Motor • Aspirate Syringe Opto Switch
• Diluent Syringe Motor • Diluent Syringe Opto Switch
• Vacuum Pump ON • Power ON
The location of the electrical connections and test points on the Stepper
Motor Driver Cards is shown in Figure 2.2. Tables 2.1 and 2.2 list the
connectors and test points.
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-5
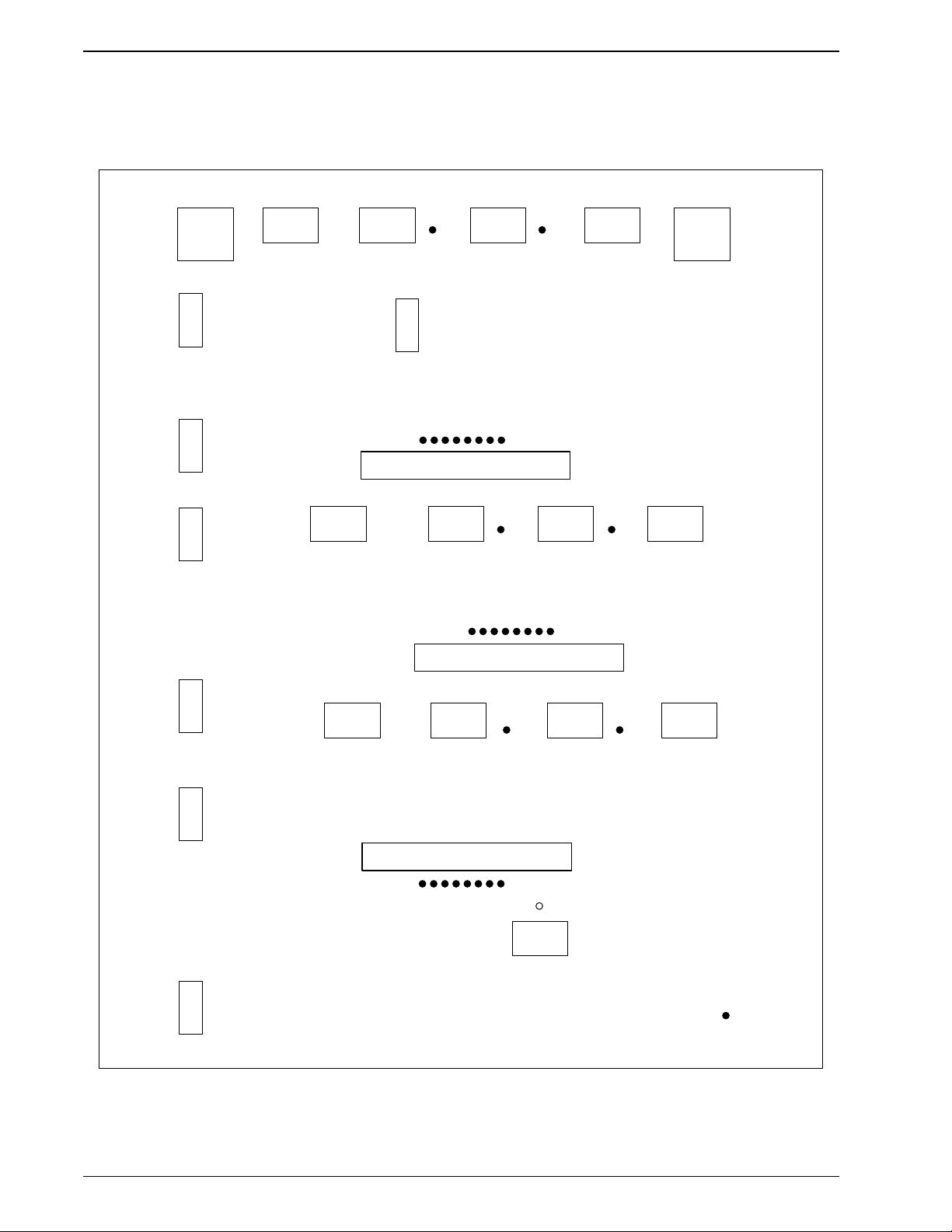
INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
MOTOR DRIVER CARD
J18
J
3
0
J
2
9
J
2
8
J19 J20 J21 J22
TP4 TP5
J
3
1
T
T
T
T
T
T
P
P
P
9
8
7
T
T
P
P
P
P
P
1
1
1
1
6
3
2
1
0
J17
J12 J13 J14 J15
TP14 TP15
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
P
P
P
1
1
1
9
8
7
T
P
P
P
P
P
1
2
2
2
2
6
3
2
1
0
J10
J23
J
2
7
J5 J6 J7 J8
TP24 TP25
J
2
6
J3
T
T
T
T
T
P
2
8
T
P
P
P
P
P
2
2
2
3
3
9
7
6
3
1
J
2
TP3
T
T
P
P
3
3
2
0
J1
TP34
5
7161-02
Figure 2.2 Stepper Motor Driver Card
2-6 PN 4237161B (April 1993)
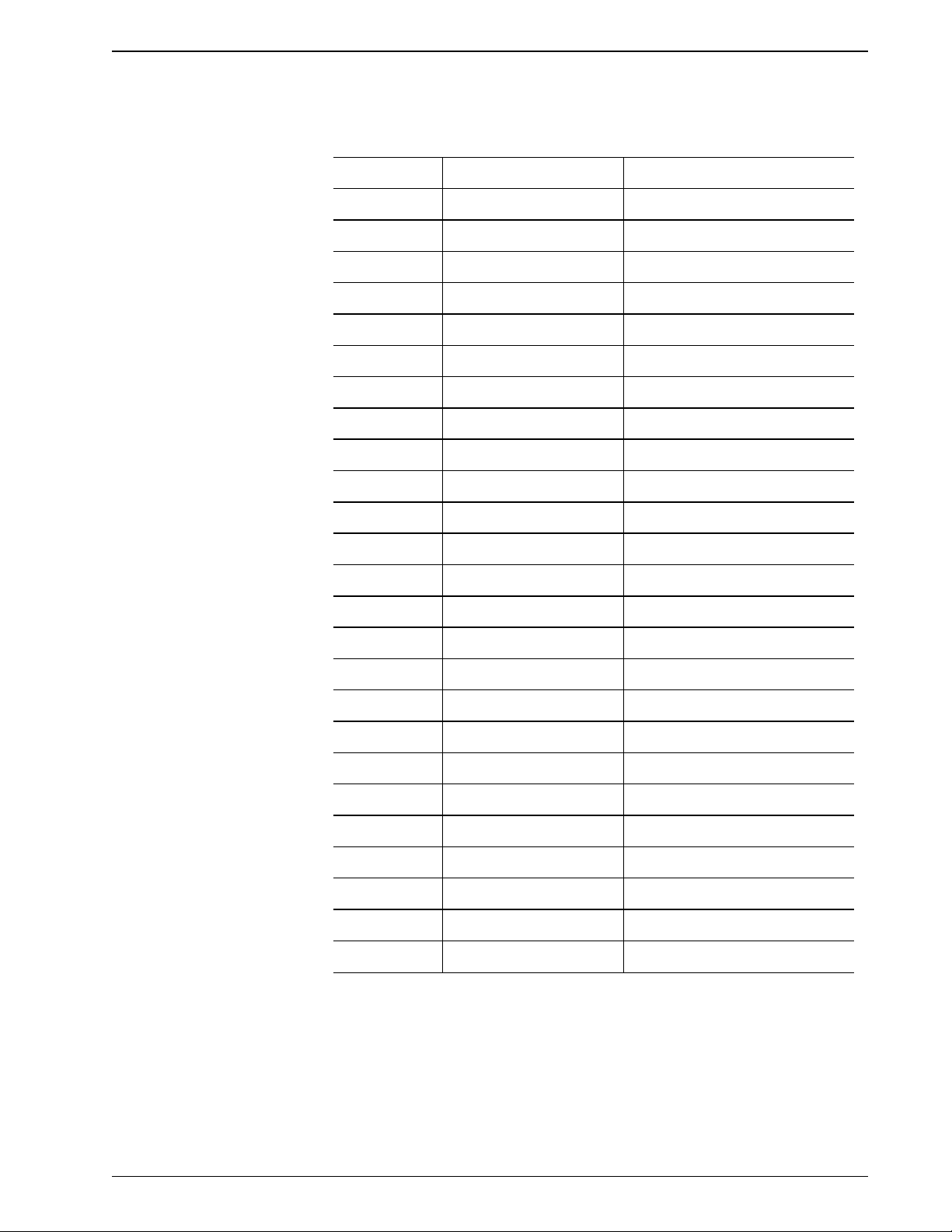
Table 2.1 Stepper Motor Driver Card Connections
Connector Driver 1 Driver 2
J1 +24 Volts +24 Volts
J3 MSMC 1 J1 MSMC 2 J1
J5 Not Used Count Valve Motor
J6 Not Used Count Valve Opto
J7 Not Used Traverse Opto
J8 Not Used Traverse Motor
J10 MSMC 1 J2 MSMC 2 J2
J12 Air Mix Motor Diluent Valve Motor
J13 Not Used Diluent Valve Opto
J14 Diluent Level Sense Not Used
DILUTER
J15 Diluent Fill Motor Not Used
J17 MSMC 1 J3 MSMC 2 J3
J18 Resistor Bank Resistor Bank
J19 Rinse Motor Aspirate Syringe Motor
J20 Not Used Aspirate Syringe Opto
J21 Lyse Level Sense Diluent Syringe Opto
J22 Waste Motor Diluent Syringe Motor
J23 Resistor Bank Resistor Bank
J25 Not Used Not Used
J26 Not Used Iso Chamber VentValve
J27 Air Mix Solenoid Vacuum Sense Vent Valve
J28 Cycle Counter Vacuum Pump ON Signal
J29 Lyse Pump Drain Solenoid
J30 Not Used Power ON to Relay Card
J31 Not Used +12 Volts
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-7
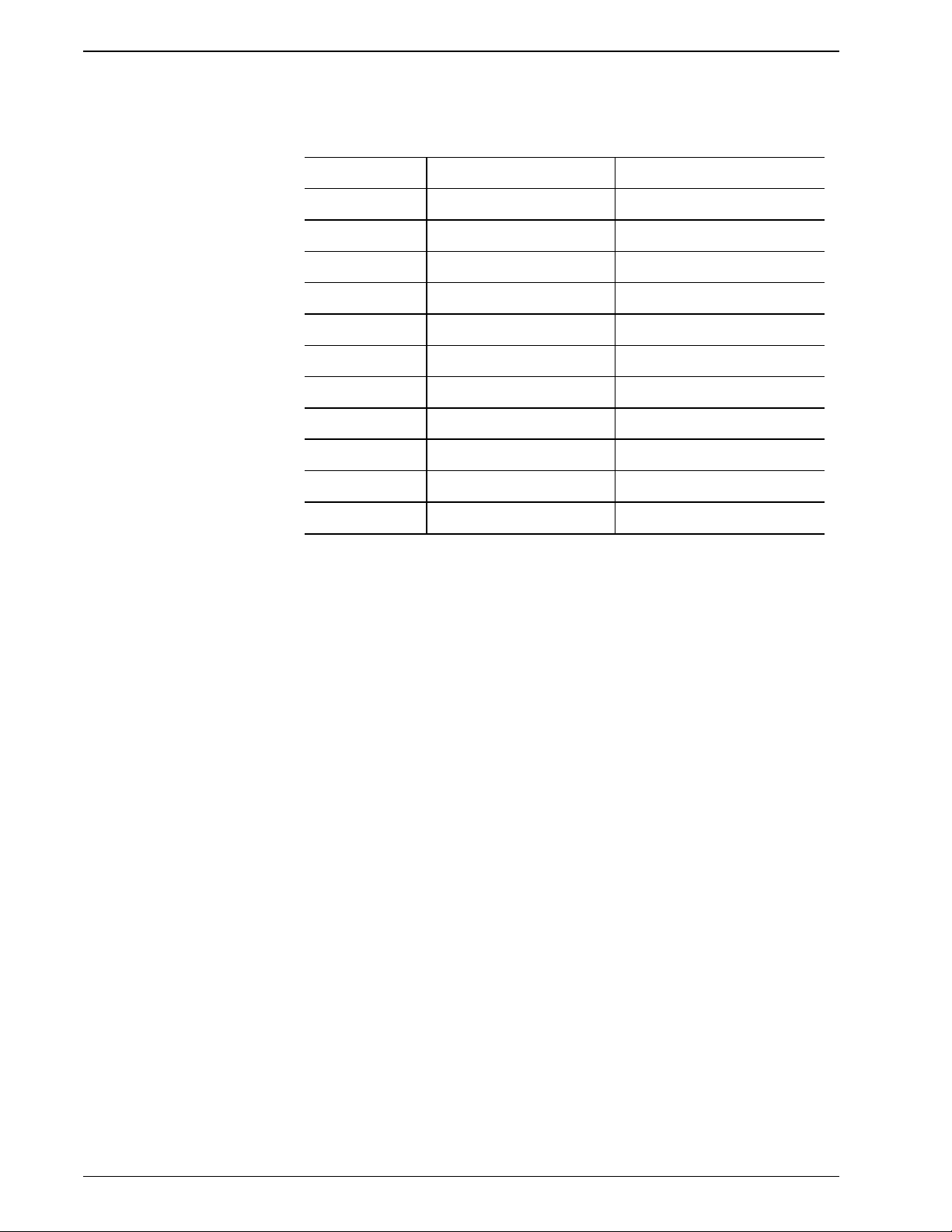
INSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
Table 2.2 Stepper Motor Driver Card Test Points
Test Points Driver 1 Driver 2
TP3 Ground Ground
TP4 Not Used Aspirate Syringe Opto
TP5 Lyse Level Sense Diluent Syringe Opto
TP6 - TP13 Stepper Motor Phases Stepper Motor Phases
TP14 Not Used Diluent Valve Opto
TP15 Diluent Level Sense Not Used
TP16 - TP23 Stepper Motor Phases Stepper Motor Phases
TP24 Not Used Count Valve Opto
TP25 Not Used Traverse Opto
TP26 - TP33 Stepper Motor Phases Stepper Motor Phases
TP34 +24 Volts +24 Volts
2.6 VENT VALVE VACUUM SENSE CARD
The Vent Valve Vacuum Sense Card (VVVS) is responsible for
monitoring the 6-in. Hg of vacuum used for count, venting the isolator
chamber when in drains, and venting the vacuum transducer to obtain
an atmosphere offset.
The output of the VVVS goes to the IORA card. the voltage for 6 in. Hg
of vacuum is 4.286 volts plus the measured atmosphere offset voltage.
2.7 ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY
General
The Electronics Assembly of the MicroDiff is contained in a hinged
compartment at the top of the instrument. It consists of the following
subassemblies:
• Motherboard with 80386 microprocessor
• 200 watt switching power supply
• Front panel with keypad and LCD display
• 1.44 MB 3½in. floppy disk drive
• Data Acquisition Board (DAC)
• Multi Stepper Motor Controller Card (MSMC)
• Analog/Peripheral Board (IORA)
• Vacuum Sensor Amp Board (PVAC)
2-8 PN 4237161B (April 1993)
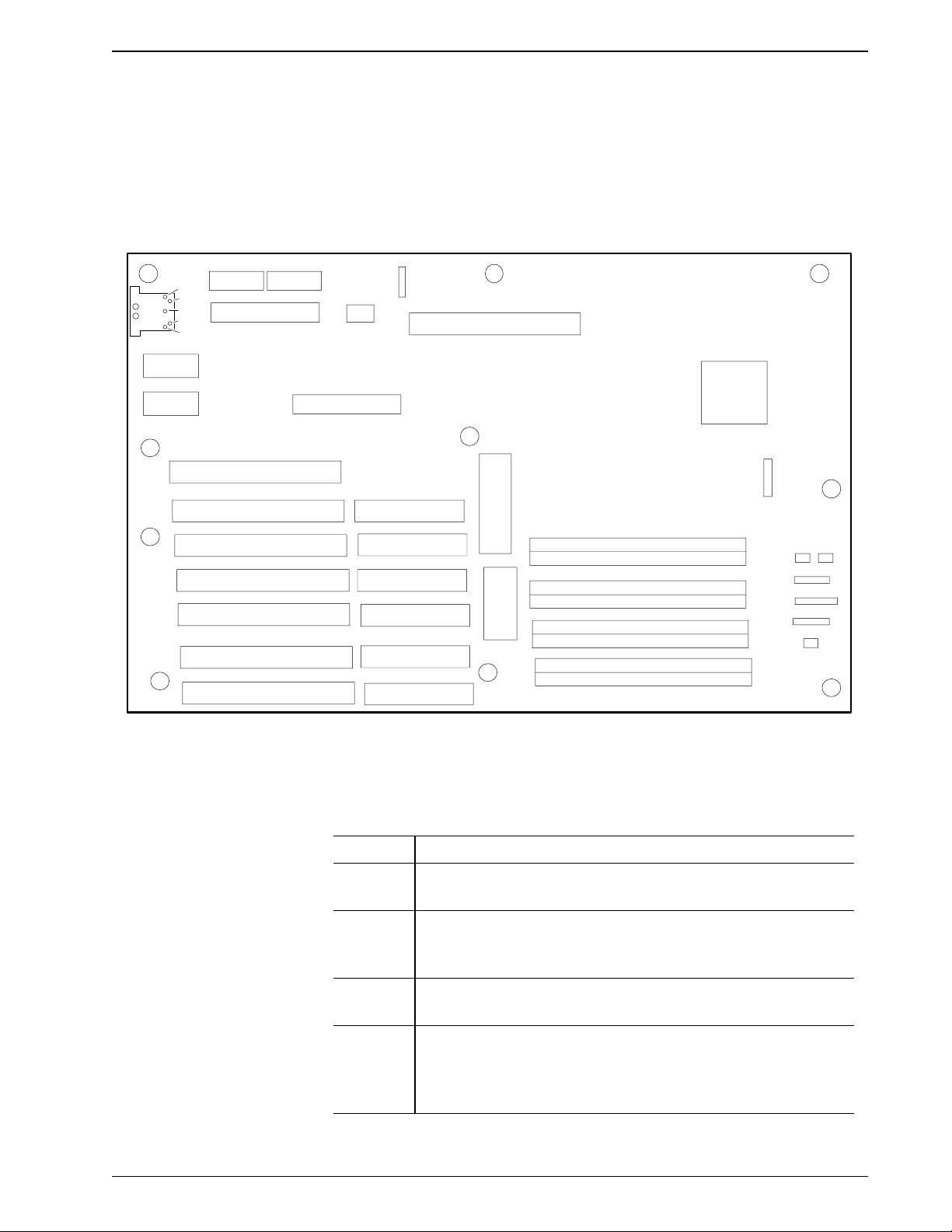
Motherboard
SERIAL 1
SERIAL 2
3
5
2
4
1 PARALLEL
FLOPPY DISK
SWITCH
BATTERY
IDE HARD DISK
80387SX
4
1
4MX9 SIM M
SUPPORT
JUMPER
8742
27512
RESET
SPEAKER
KEYLOCK
IDE ACTIVITY
SXCAT DIAGRAM
7161016A
TURBO
LED
TURBO
SWIT CH
ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY
The Motherboard (Figure 2.3) is an AT compatible 80386 computer. The
disk controller and serial I/O port are resident on the board. Program
software is not resident in EPROMs on the motherboard. The program is
loaded from the diskette drive into the computer’s memory.
Figure 2.3 Motherboard
Switch |Description |
SW1-1 |Close (On) to enable Onboard Battery. |
Open (Off) to enable Offboard Battery. |
SW1-2 |Close (On) to Enable Battery. |
Open (Off) to Disable Battery. |
Must be closed for normal system operation. |
SW1-3 |Close (On) for additional wait states on IDE interface. |
Open (Off) for no additional wait states. |
SW1-4 |Close (On) for Color Adapter. |
Open (Off) for Monochrome Adapter. |
This switch setting does not matter when using VGA or |
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-9
EGA adapters. |

Linear Power Supply
ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLYINSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
The Linear Power Supply (Figure 2.4) is a self contained unit located
below the Computer Chassis at the bottom of the Main Chassis
Assembly. The unit is accessible with the hinged electronics
compartment open. The Power Supply provides all the necessary dc and
ac voltages to operate the unit. The supplied voltages are:
• ±15 Vdc for the analog circuitry
• +24 Vdc for the stepper motors and pneumatic solenoids
• +240 Vdc to generate aperture current and zap volts
• 0.02 amp constant current source for the Hgb LED.
The unit supplies dc power to the following assemblies:
• DATA ACQ and IORA Boards located in the electronics
compartment.
• PVAC Board, and the Hgb LED assembly located in the diluter
panel.
• Motor Driver boards located in the Main Chassis.
The unit also supplies the ac power for the Vacuum Pump, Switching
Power Supply, and the 24-volt Power Supply.
Power Supply Components
Power Supply Board: This board consists of rectifiers; filters and
regulators for ±15 V and +240 V; a constant current source for the Hgb
LED; connectors for all inputs, outputs and test points.
Power Transformer T1: T1 provides stepped down ac power to the power
supply board for the +15 volt supply, the -15 volt supply, the 240 volt
supply and the constant current source for the Hgb LED supply which is
driven from the +15 volt supply.
24V Power Transformer T2: T2 provides stepped down ac voltage for the
+24v Power Supply.
2-10 PN 4237161B (April 1993)
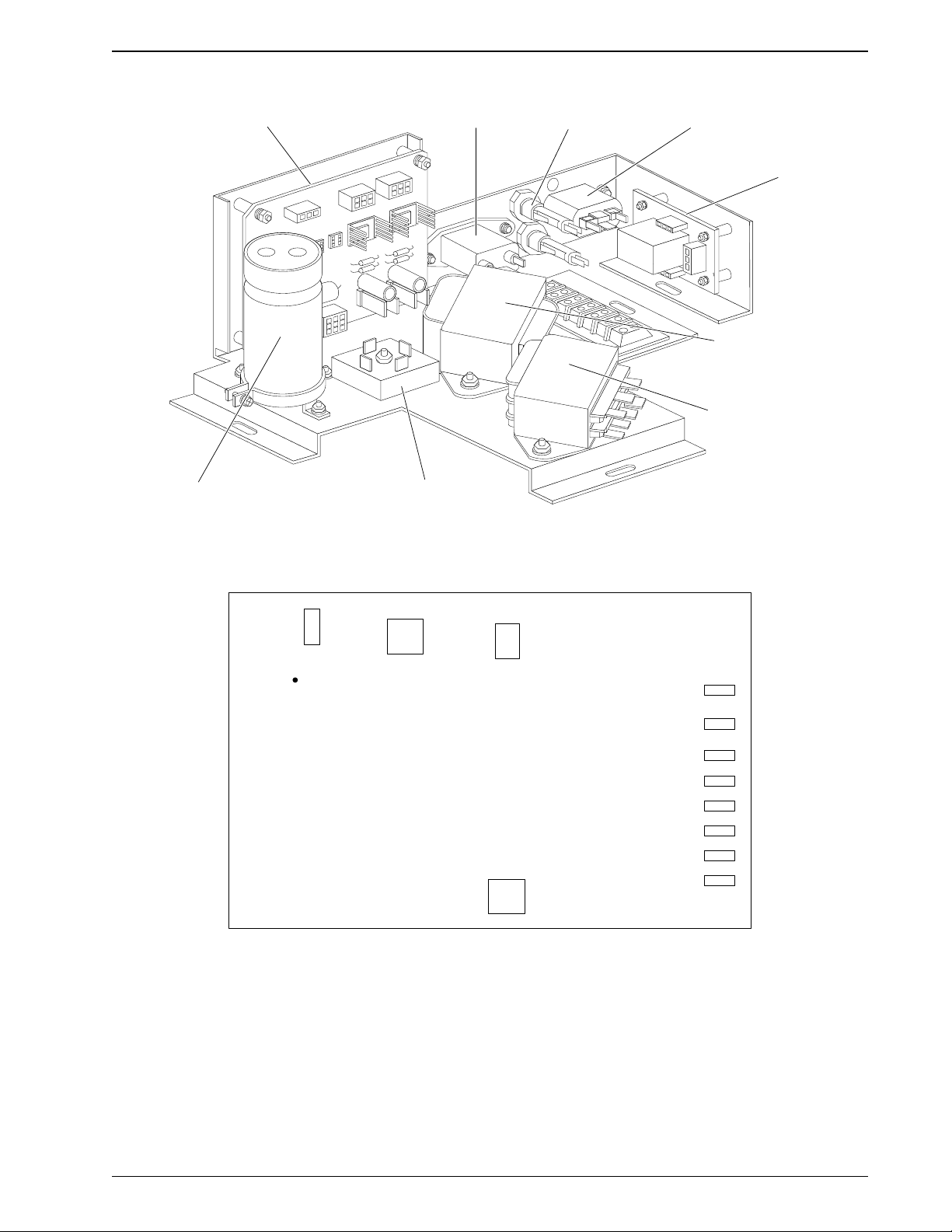
ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY
FUSE HOLDERREGULATOR CARD
LINE FILT ER
OUTLET
RELAY CA RD
24V TRANSFORMER
MAIN TRANSFORMER
BRIDGE RECTIFIER
24V FILTER CAPACITOR
7161-04
J
2
TP9
APP C URRE NT
Figure 2.4 Linear Power Supply
J3
J4
J1
Figure 2.5 Regulator Card
Hgb
Hgb Ref.
+15
Gnd
-15
Gnd
240V Gnd
240V
TP7
TP6
TP5
TP4
TP3
TP8
TP2
TP1
7161-05
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-11
ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLYINSTRUMENT DESCRIPTION
+24 Rectifier and Filter: Provides +24 Vdc for motors and solenoids.
Vacuum Pump Solid State Relay: Connects the input ac voltage to the
vacuum pump.
+24-V Relay: Connects the input ac voltage to the +24-Volt power
transformer. The signal to operate the relay comes from the MSMC Card
through the motor driver.
AC Line Filter: Filters the input ac voltage before going to the
transformers and switching power supply.
Fuses: Control the ac line voltage to the input of the instrument.
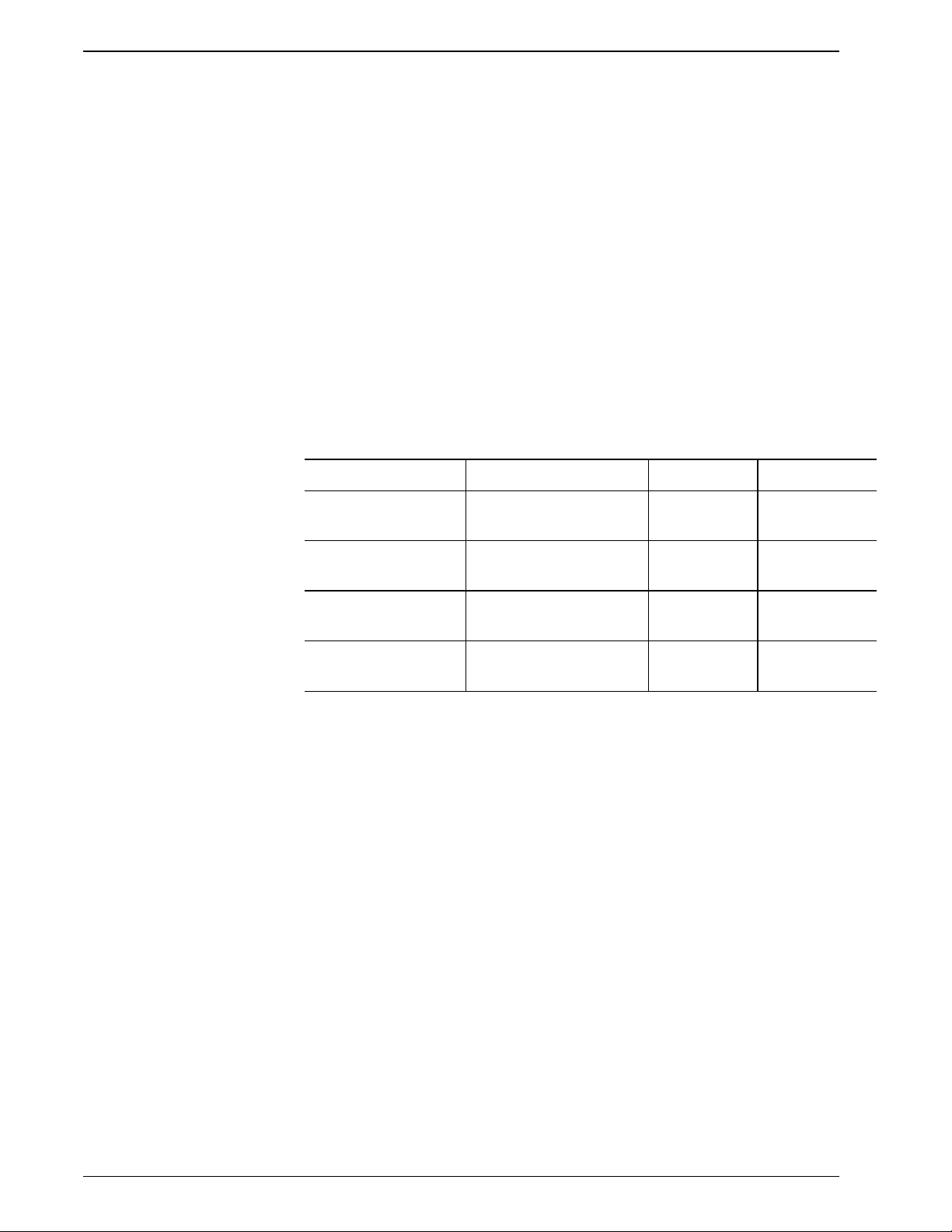
Terminal Block: Provides ac line voltage selection (see Table 2.3).
Table 2.3 Terminal Block Connections
Input Voltage Relay Card AC Wire Position Jumper
100 White
Black
120 White
Black
220 White
Black
240 White
Black
1
4
1
6
1
4|
1
6|
1&2
3&4
1&2
5&6
2&5
2&5
The Power Transformer T1 has three secondaries that provide ac voltage
to all the supplies. The high voltage winding is surrounded by an
electrostatic shield to reduce noise induced by the ac line. All the
secondary windings of the transformer are internally fused.
The ac voltage is then distributed to the power supply card where the ac
is full wave rectified, filtered, and regulated. The regulated supplies are
protected against overload and short circuit by current foldback and
thermal shutdown.
Two input signals to the Power Supply Card come from the DAC Card.
These signals are the aperture current ON command and aperture
current control. The aperture current ON command turns on the high
voltage regulator when aperture current is required.
The aperture current control is a signal between 0 and 5 Volts that
controls the output of the high voltage regulator. The output of this
regulator controls the gain of the pre-amp section on the DAC Card.
The Power Supply has two fuses, F1 and F2, rated at 2.0 A for 100 Vac to
120 Vac or 1.0 Amps for 200 Vac to 240 Vac.|
2-12 PN 4237161B (April 1993)

Switching Power Supply
The Switching Power Supply is in the top chassis and provides +5 Vdc
and +12 Vdc to the CPU and associated electronics. The switching
supply also has the POWER ON switch for the system and a cooling fan.
The ac input voltage is switch selectable for 90 Vac to 130 Vac or 180
Vac to 260 Vac. The voltages developed are plus and minus 5 volts and
plus and minus 12 volts.
There are 5 connectors coming from the Switching Power Supply. A label
on the Switching Power Supply list the voltage and current for each
connector and connector pin.
The power connectors P4 and P5 must not be switched!! If they are
reversed the computer motherboard may be damaged. P4 should be
towards the rear of the board and P5 towards the front. Another way to
check proper connection is thatthecommonblackwiresfor each of the
connectors will be next to each other in the middle .
ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY
CAUTION
Data Acquisition Card
The destination of the Switching Power Supply connectors are:
P1 Spare
P2 Spare
P3 Diskette Drive
P4 Computer Motherboard P1
P5 Computer Motherboard P2
The Data Acquisition Card (DAC) (Figure 2.6) performs the following
functions:
• Pre-Amp for RBC/PLT/WBC • Aperture Current Control
• Aperture Cleaning Circuit • RBC/WBC Editing
• Thresholding for RBC/PLT/WBC • PLT Processing
• RBC/WBC Counting • Interface to the AT bus
• Aperture Integrity Monitor • RBC/PLT/WBC Analog to
Digital conversion
PN 4237161B (April 1993) 2-13
 Loading...
Loading...