Page 1

The information contained in this document has been carefully researched and is, to the best
of our knowledge, accurate. However, we assume no liability for any product failures or
damages, immediate or consequential, resulting from the use of the information provided
herein. Our products are not intended for use in systems in which failures of product could
result in personal injury. All trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective
owners. All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Instruction Manual
CBS-Series
Cosel
Our company network supports you worldwide with offices in Germany, Austria,
Switzerland, Great Britain and the USA. For more information please contact:
FORTEC Elektronik AG
Hauptniederlassung
Lechwiesenstr. 9
86899 Landsberg am Lech
Telefon: +49 (0) 8191 91172-0
Telefax: +49 (0) 8191 21770
E-Mail: sales@fortecag.de
Internet: www.fortecag.de
FORTEC Elektronik AG
Büro Nord
Am Hasenkamp 36
22457 Hamburg
Telefon: +49 (0) 40 54 80 56 11
Telefax: +49 (0) 40 54 80 56 13
E-Mail: nord@fortecag.de
Internet: www.fortecag.de
FORTEC Elektronik AG
Büro West
Hohenstaufenring 55
50674 Köln
Telefon: +49 (0) 221 272 273-0
Telefax: +49 (0) 221 272 273-10
E-Mail: west@fortecag.de
Internet: www.fortecag.de
FORTEC Elektronik AG
Büro Wien
Nuschinggasse 12
A-1230 Wien
Telefon: +43 1 8673492-0
Telefax: +43 1 8673492-26
E-Mail: office@fortec.at
Internet: www.fortec.at
ALTRAC AG
(Tochter der FORTEC):
Bahnhofstraße 3
CH-5436 Würenlos
Telefon: +41 (0) 44 7446111
Telefax: +41 (0) 44 7446161
E-Mail: info@altrac.ch
Internet: www.altrac.ch
Page 2
CBS
Basic Characteristics Data
CBS50 310 - - Yes Yes
*
1
CBS100 370
-
- Ye s Ye s
*
1
CBS200 - Yes Yes
*
1
CBS350 - Yes Yes
*
1
1
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
-
-
370
370
Forward
converter
Forward
converter
Forward
converter
Forward
converter
CBS450 - Yes Yes
*
Aluminum-370Forward converter
table No.1
Refer
to
input fuse
Circuit method
operation availability
Rated
Model
frequency
Switching
[A]
current
Input
Series/Redundancy
Redundancy
operation
PCB/Pattern
current
protection
Inrush
Material
Double
sidedsided
Single
Series
operation
Basic Characteristics Data
[kHz]
*1 Refer to Instruction Manual.
[A]
Model
3.3V 5V
Output Voltage
12V 15V 24V 28V
CBS5024
CBS5048
CBS10024
CBS10048
CBS20024
CBS20048
2.0
1.0
4.1
2.0
6.1
3.0
2.5
1.3
5.0
2.5
7.6
3.8
2.4
1.2
4.8
2.4
9.6
4.8
2.4
1.2
4.8
2.4
9.6
4.8
2.4
1.2
4.8
2.4
9.7
4.8
2.4
1.2
4.8
2.4
9.7
4.8
Table1. The value of input current(at rated input voltage and rated load
)
4.8
48V
-
-
-
-
-
32V
-
-
-
-
-
-
CBS35024
CBS35048
17
8.2
14
8.2
1.8V 2.5V
1.2
0.6
2.5
1.2
3.8
1.9
1.6
0.8
3.2
1.6
4.8
2.4
-
-
-
-
-
-
CBS45048 - - -
-
-
-
-8.4
---
15 17
8.1
17
8.2
-9.310.510.6
CBS-12
Page 3

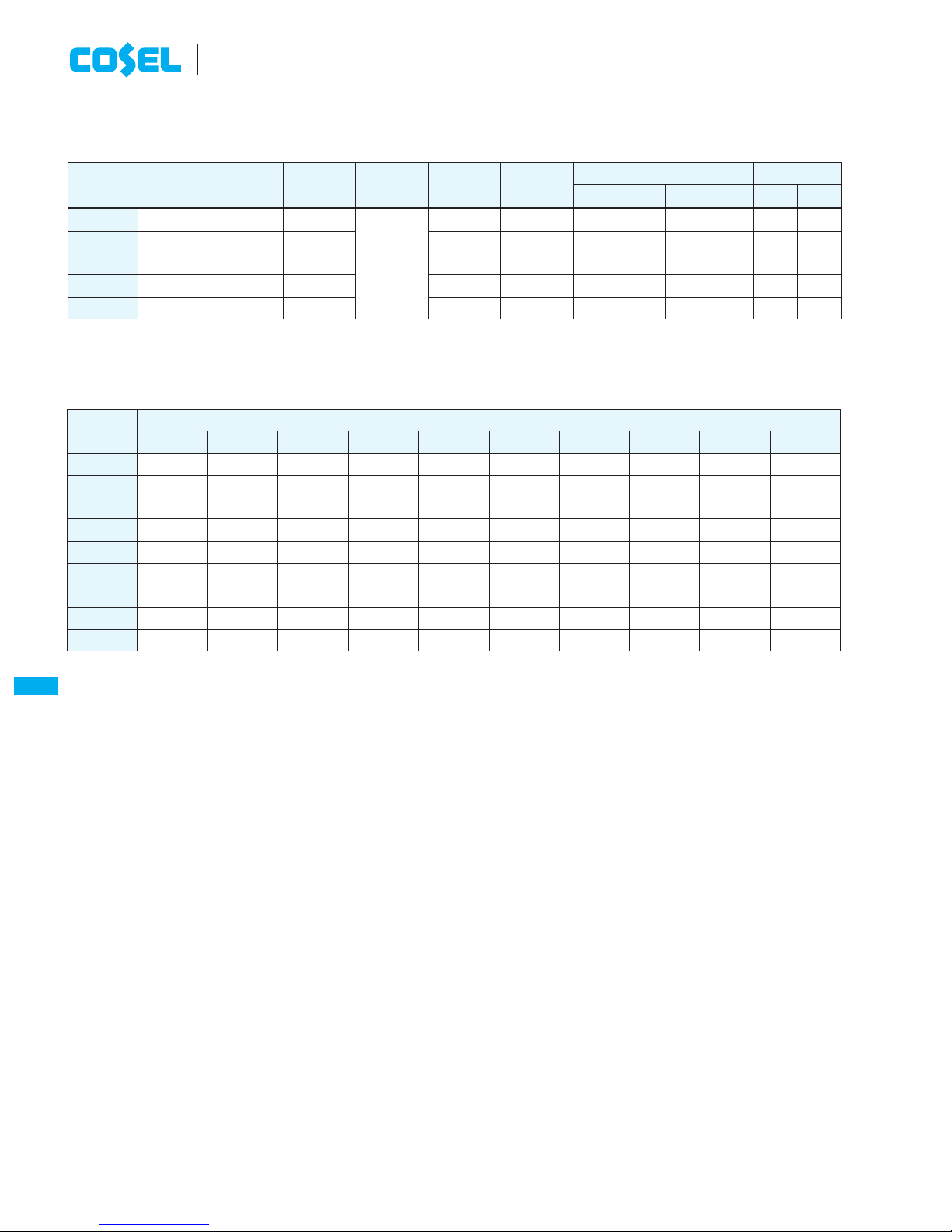
1 Pin Confi guration
CBS-14
2 Connection for Standard Use
CBS-14
6.1 Mounting method
6.2 Stress onto the pins
6.3 Cleaning
6.4 Soldering temperature
6.5 Derating
6.6 Heat sink(Optional parts)
6.7 Addition of a Heat sink(Optional:FO)
CBS-18
CBS-18
CBS-19
CBS-19
CBS-19
CBS-19
CBS-20
4.1 Overcurrent protection
4.2 Overvoltage protection
4.3 Thermal protection
4.4 Remote ON/OFF
4.5 Remote sensing
4.6 Adjustable voltage range
4.7 Withstanding Voltage / Isolation Voltage
5 Series and Parallel Operation
CBS-18
5.1 Series operation
5.2 Redundancy operation
6 Implementation-Mounting Method
CBS-18
7 Safety Considerations
CBS-21
CBS-16
CBS-16
CBS-16
CBS-16
CBS-16
CBS-17
CBS-18
CBS-18
CBS-18
3 Wiring Input/Output Pin
CBS-14
3.1 Wiring input pin
3.2 Wiring output pin
CBS-14
CBS-15
4 Function
CBS-16
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
CBS-13
CBS
Instruction Manual
Page 4
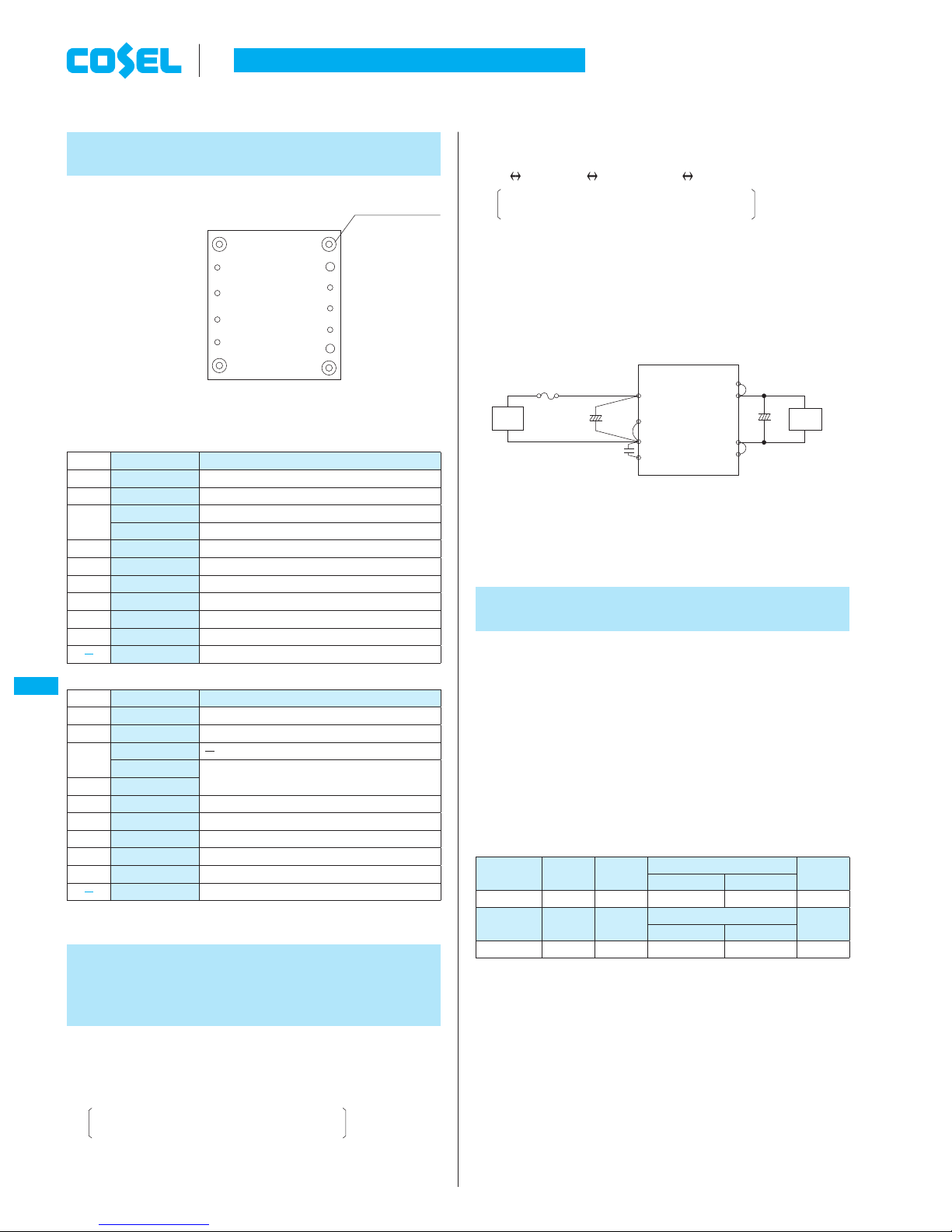
1 Pin Confi guration
3.1 Wiring input pin
(1) External fuse
¡
The input circuit of CBS Series does not come with a built-in fuse.
In order to protect the power module, a normal-blow fuse should
be installed to +VIN.
¡
When multiple modules get input voltage from a single front-end
power supply, a normal-blow fuse must be installed to each mod-
ule.
Model
CBS5024 CBS10024
CBS20024
CBS35024
1R8/2R5/03/05
12/15/24/28
Rated current
6A 12A 20A 25A 30A
Model
CBS5048 CBS10048
CBS20048
CBS35048
CBS45048
1R8/2R5/03/05
12/15/24/28/48
Rated current
3A 6A 10A 12A 20A
(2) Noise Filter/Grounding Capacitor
¡
A grounding capacitor C
Y
must be used to reduce the line noise
on the input line and stabilize the power module operation (Fig.
2.1). Note that resonance and inductance from the input line fi lter
may cause the power module to become unstable.
¡
An appropriate fi lter must be used if conformance to the conduct-
ed noise regulation is required or if surge voltage may be applied
to the unit. Please consult us for more details.
¡
Install a grounding capacitor C
Y
of at least 4700 pF as close to the
input pins as possible (within 50mm of the pins).
2 Connection for
Standard Use
¡
The power module needs input and output connections as shown
in Fig. 2.1.
Reference: 3 ”Wiring Input/Output Pin”
6.5 ”Derating”
¡
Short the following pins to turn on the power module.
-VIN
RC, +VOUT +S, and -VOUT -S
Reference: 4.4 ”Remote ON/OFF”
4.5 ”Remote sensing”
¡
Only DC voltage can be applied to CBS Series. Applying AC volt-
age will damage the power module.
¡
The power module is designed for conduction cooling. Make
sure that heat sinks, fans, etc. are used for heat dissipation.
Refer to 6.5 ”Derating”
3
Wiring Input/Output Pin
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-14
CBS
Table 1.1 Pin Assignment
No. Pin Name Function
1
+VIN +DC input
2
RC Remote ON/OFF
3
NC No connection (CBS350/450)
CASE Wiring base plate (CBS50/100/200)
4
-VIN -DC input
5
+VOUT +DC output
6
+S +Remote sensing
7
TRM Adjustment of output voltage
8
-S -Remote sensing
9
-VOUT -DC output
Mounting hole Mounting hole
No. Pin Name Reference
1
+VIN 3.1 ”Wiring input pin”
2
RC 4.4 ”Remote ON/OFF”
3
NC
CASE
3.1 ”Wiring input pin”
4
-VIN
5
+VOUT 3.2 ”Wiring output pin”
6
+S 4.5 ”Remote sensing”
7
TRM 4.6 ”Adjustable voltage range”
8
-S 4.5 ”Remote sensing”
9
-VOUT 3.2 ”Wiring output pin”
Mounting hole 6.1 ”Mounting method”
Fig.2.1 Connection for Standard Use
Table 3.1 Recommended Fuses (Normal-Blow Type)
Fig.1.1 Pin Confi guration (bottom view)
5 +VOUT
9 -VOUT
8 -S
7 TRM
6 +S
-VIN 4
3
RC 2
+VIN 1
4-Mounting hole
(CBS50/100/200) CASE
(CBS350/450)NC
+
Co
Load
+VIN
-VIN
+VOUT
-VOUT
RC
Fuse
DC
input
Cin
+
CY
+S
-S
CASE (CBS50/100/200)
Mounting hole (CBS350/450)
Cin : External capacitor on the input side
Co : External capacitor on the output side
C
Y
: Primary decoupling capacitor
Page 5

(5) Reverse Input Voltage Protection
¡
Avoid applying reversed-polarity voltage to the power module as it
will damage the power module. To protect the power module from
reversed polarity voltage, installing an external diode as shown in
Fig. 3.3 is recommended.
¡
If the total capacitance of the grounding capacitor exceeds 15000
pF, the specifi ed isolation voltage between input and output may
not be satisfi ed. In this case, either reduce the capacitance of the
grounding capacitor at the input or install a grounding capacitor to
the output.
There is no maximum limit to capacitance C
Y
when the power
module is used with an isolation voltage of less than 500VAC (1
min.) between input and output.
(3) External Capacitor on the Input
¡
An external capacitor Cin must be installed between +VIN and
-VIN to reduce line noise and stabilize the power module opera-
tion (Fig. 2.1).
¡
The capacitor must be installed less than 50mm of the power
module. As ripple current will fl ow through this capacitor, pay at-
tention to the ripple current rating of the capacitor.
¡
If the power module is to be turned ON/OFF directly with a switch,
inductance from the input line will induce a surge voltage several
times that of the input voltage and it may damage the power mod-
ule. Make sure that the surge is absorbed, for example, by con-
necting an electrolytic capacitor between the input pins.
(4) Input Voltage Range/Input Current Range
¡
Keep the input voltage ripple within the specifi cations below. Out-
put ripple voltage will increase as these values increase.
¡
Make sure that the peak input voltage stays within the specifi ed
input voltage range of the power module.
¡
Choose a front end power supply that can supply enough current
Ip (Fig. 3.2) for starting up the power module.
3.2 Wiring output pin
¡
Install an external capacitor Co between +VOUT and -VOUT to
increase stability of output (Fig. 2.1).
Recommended capacitance of Co is shown in Table 3.2.
¡
Choose a high frequency type electrolytic capacitor for Co. Output
ripple and rise time will be infl uenced by the capacitor’s ESR and
ESL and the wiring impedance.
¡
As ripple current will fl ow through capacitor Co, pay attention to
the ripple current rating of the capacitor.
¡
Install capacitor Co as close to the power module as possible
(within 50mm).
This is useful for reducing radiated noise and increasing stability
of the power module operation.
Base plate temperature : Tc=-20 to +100
C
VOUT 1.8V/2.5V/3.3V/5V 12V 15V 24V 28V 32V 48V
CBS50 2200 470 220
CBS100 2200 470 220
CBS200 2200 1000 470 330
CBS350
470 220
CBS450
220
Base plate temperature : Tc=-40 to +100
C
VOUT 1.8V/2.5V/3.3V/5V 12V 15V 24V 28V 32V 48V
CBS50 2200
X
2 470X2 220X2
CBS100 2200X2 470X2 220X2
CBS200 2200X2 1000X2 470X2
330X3
CBS350
470X3
220X3
CBS450
220X3
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-15
CBS
Ripple
voltage
Input voltage [V]
Input voltage range
Time t
Fig.3.1 Input Voltage Ripple
Fig.3.2 Input Current Characteristics
+VIN
-VIN
DC IN
+VIN
-VIN
DC IN
(a) (b)
Fig.3.3 Reverse Input Voltage Protection
Table 3.2 Recommended Capacitance for External Output Capacitor Co ( F)
lp
Input current [A]
Input voltage [V]
Input voltage range
Ripple voltage CBS50/100/200/35024:less than 2Vp-p
CBS50/100/200/35048:less than 4Vp-p
CBS45048:less than 4Vp-p
Capacitance CBS50/100/20024:at least 68 F
CBS50/100/20048:at least 33 F
CBS35024:at least 220 FX2
CBS45048:at least 68 FX2
Tc=-20 to +100C Electrolytic or Ceramic capacitor
Tc=-40 to +100C Ceramic capacitor
CBS35048:at least 68 FX2
Page 6
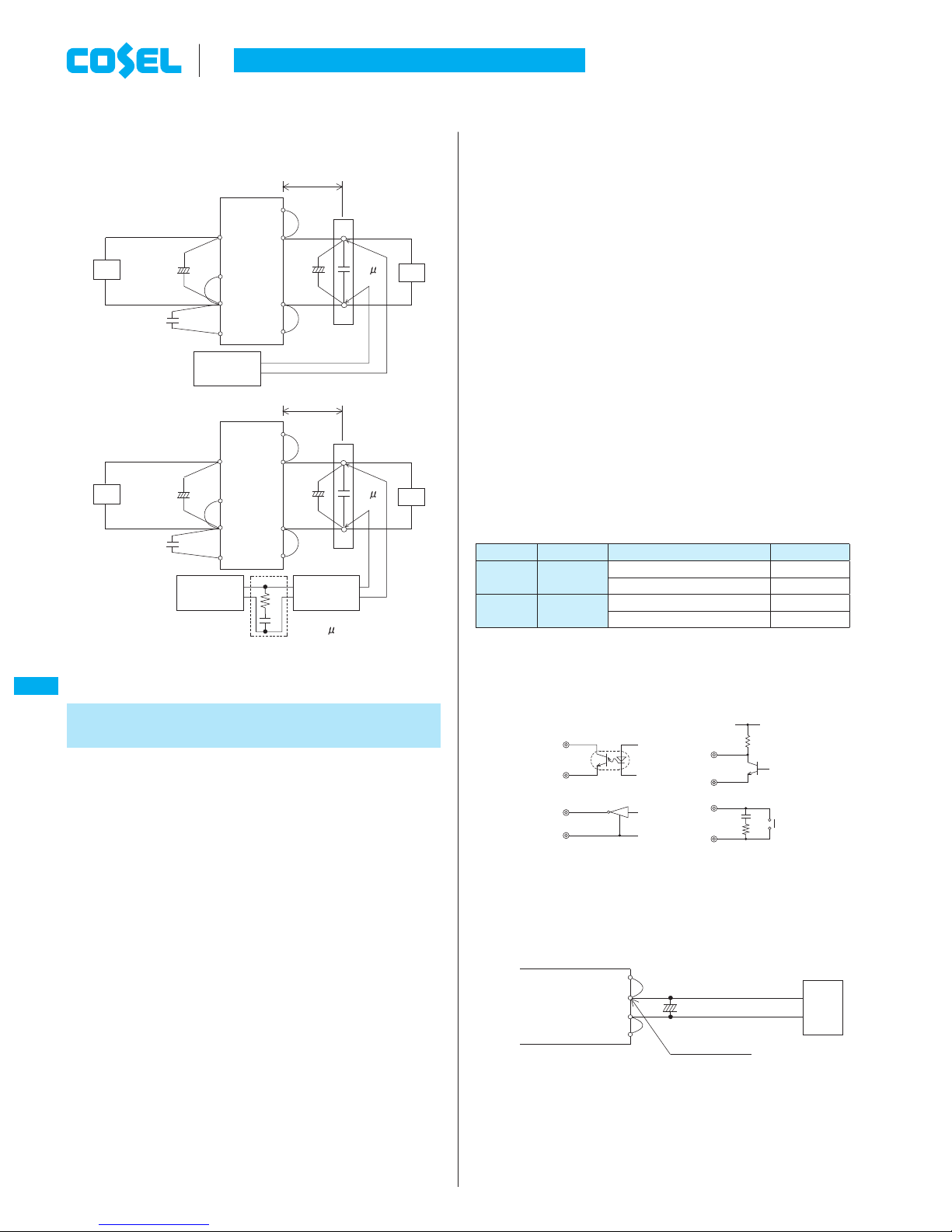
4 Function
4.1 Overcurrent protection
¡
Over Current Protection (OCP) is built in and works at 105% of
the rated current or higher. However, use in an over current situa-
tion must be avoided whenever possible. The output voltage of the
power module will recover automatically if the fault causing over
current is corrected.
When the output voltage drops after OCP works, the power mod-
ule enters a ”hiccup mode” where it repeatedly turns on and off at
a certain frequency.
4.2 Overvoltage protection
¡
Over Voltage Protection (OVP) is built in. When OVP works, out-
put voltage can be recovered by shutting down DC input for at
least one second or by turning off the remote control switch for
one second without shutting down the DC input. The recovery
time varies according to input voltage and input capacitance.
¡
The specifi ed ripple and ripple noise are measured by the method
introduced in Fig. 3.4.
Remarks:
Note that devices inside the power module may fail when a volt-
age greater than the rated output voltage is applied from an exter-
nal power supply to the output terminal of the power module. This
could happen in in-coming inspections that include OVP function
test or when voltage is applied from the load circuit. OVP can be
tested by using the TRM terminal. Consult us for details.
4.3 Thermal protection
¡
Over Temperature Protection (OTP) is built in. If the base plate
temperature exceeds 100C, OTP will work, causing the output
voltage to drop. Output voltage can be recovered by shutting
down DC input for at least one second or by turning RC off for one
second without shutting down the DC input.
4.4 Remote ON/OFF
¡
The remote ON/OFF function is incorporated in the input circuit
and operated with RC and -VIN. If positive logic control is re-
quired, order the power module with ”-R” option.
ON/OFF logic
Between RC and -VIN
Output voltage
Standard Negative
L level(0 - 1.2V) or short ON
H level(3.5 - 7.0V) or open OFF
Optional
-R
Positive
L level(0 - 1.2V) or short OFF
H level(3.5 - 7.0V) or open ON
¡
When RC is at low level, a current of 0.5mA typ will flow out.
When Vcc is used, keep it within the following rage:
3.5 [ VCC [ 7V.
When remote ON/OFF is not used, short RC and -VIN.
4.5 Remote sensing
(1) When Remote Sensing is Not Used
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-16
CBS
Fig.3.4 Method of Measuring Output Ripple and Ripple Noise
Fig. 4.1 RC Connection Example
Table 4.1 Remote ON/OFF Specifi cations
Transistor
IC Relay
Vcc
Opto coupler
RC
-VIN
RC
-VIN
RC
-VIN
RC
-VIN
+S
+VOUT
-S
-VOUT
+
Co
Short at pin root
Load
Fig. 4.2 When Remote Sensing is Not Used
DC
input
Cin
CBS50/100/200
4700pF
+
50mm
+VIN
Oscilloscope
BW : 20MHz
-VIN
CASE
+VOUT
-VOUT
-S
+S
0.1 F
Co
+
Measuring board
Load
RC
DC
input
Cin
4700pF
+
50mm
+VIN
Oscilloscope
BW : 100MHz
-VIN
Mounting
hole
+VOUT
-VOUT
-S
+S
0.1
F
Co
+
Measuring board
Load
RC
1.5m 50W
Coaxial Cable
R=50
W
C=0.01 F
R
C
CBS350
CBS350/450
Page 7

¡
When remote sensing is not used, make sure +VOUT and +S are
shorted, and that -VOUT and -S are shorted as well.
¡
Keep the patterns between +S and +VOUT and between -S and
-VOUT as short as possible. Avoid a looping pattern. If noise en-
ters the loop, the operation of the power module will become un-
stable.
(2) When Remote Sensing is Used
¡
Using remote sensing with long wires may cause output voltage to
become unstable. Consult us if long sensing wiring is necessary.
¡
Sensing patterns or wires should be as short as possible. If wires
are used, use either twisted-pair or shielded wires.
¡
Use wide PCB patterns or thick wires between the power module
and the load. Line drop should be kept less than 0.3V. Make sure
output voltage from the power module stays within the specifi ed
range.
¡
If the sensing patterns are shorted by mistake, a large current may
fl ow and damage the pattern. This can be prevented by installing
fuses or resistors close to the load.
As wiring or load impedance may generate oscillation or large
fluctuations in output voltage, make sure enough evaluation is
given in advance.
4.6 Adjustable voltage range
¡
Output voltage can be adjusted by connecting an external potenti-
ometer (VR1) and resistors (R1 and R2) as shown in Fig. 4.5.
Output voltage will increase if the resistance between 1 and 2 is
reduced by turning the potentiometer clockwise.
Recommended values for external components are shown in
Table 4.2.
Consult us if the power module is used in a different confi guration.
¡
Output voltage between +VOUT and -VOUT can be adjusted by
connecting external resistors to TRM.
However, when the input voltage is 18 - 20VDC with CBS50/100/
20024 or 36 - 40VDC with CBS50/100/20048, the output voltage
adjustment range is 60 - 105% of the rated output voltage except
for 1.8/2.5/48V output models.
When input voltage is 20 - 22VDC with CBS35024 models or 36
- 40VDC with CBS35048 models, the output voltage adjustment
range becomes as shown in Fig. 4.4-1.
¡
The wiring to the potentiometer should be as short as possible.
As the ambient temperature fl uctuation characteristics deteriorates
depending on the types of resistors and potentiometers used,
please use resistors and potentiometers of the following specifi ca-
tions:
Resistors
.............
Metal fi lm type, coeffi cient less than ±100ppm/
C
Potentiometers
...
Cermet type, coeffi cient less than ±300ppm/
C
¡
When output voltage adjustment is not required, open TRM.
¡
Note that, when adjusting output voltage, setting output voltage
too high may cause OVP to work.
Control Amp. of
rated voltage
VOUT
1.8V
2.5V
3.3 - 48V
RB
1.3kW
1.8kW
3kW
-
+
+S
+VOUT
TRM
-S
-VOUT
2.5V
RA
3kW
RB
RC
1kW
R2
R1
1
VR1
5kW
3
2
The output adjustment range for CBS450 is shown in Fig. 4.4-2.
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-17
CBS
Fig. 4.5 Connecting External Parts
+S
Co
-S
+VOUT
-VOUT
+
Wire as close as possible
Load
Fig. 4.3 When Remote Sensing is Used
Fig. 4.4-1 CBS350 Output Voltage Adjustment Range
Fig. 4.4-2 CBS450 Output Voltage Adjustment Range
OUTPUT VOLTAGE [V]
OUTPUT VOLTAGE [V]
INPUT VOLTAGE [V]
CBS4504828
26.0
25.0
24.0
19.2
0
380
0
040 57
60
32.2
30.8
28.0
16.8
3640 60
76
INPUT VOLTAGE [V]
CBS4504824
ADJUSTMENT RANGE [%]
ADJUSTMENT RANGE [%]
INPUT VOLTAGE [V]
CBS35048
OO
INPUT VOLTAGE [V]
CBS35024
OO
20
100
105
110
21 22 230
00
80
60
32,48
12,24,28
36
100
105
110
115
38 40 420
80
60
32,48
48
12,24,28
35.2
32.0
25.6
0
36040
76
OUTPUT VOLTAGE [V]
INPUT VOLTAGE [V]
CBS4504832
Page 8

5.1 Series operation
¡
Multiple CBS units can be used in series. Keep the output current
less than the smallest specifi ed rated current of the modules con-
nected in series. Make sure the current fl own into the power mod-
ule will not exceed the rated current.
5.2 Redundancy operation
¡
Parallel operation is not possible.
¡
Redundancy operation is available by wiring as shown below.
5 Series and Parallel
Operation
¡
Even a slight difference in output voltage can affect the balance
between the values of I
1
and I2.
Please make sure that the value of I
3
does not exceed the rated
current of a power supply.
I
3
the rated current value
6.1 Mounting method
¡
When multiple power modules are used side by side, position
them with sufficient spaces to allow adequate air ventilation so
that the aluminum base plate temperature of each power module
will remain within the temperature range shown in the derating
curves (Fig. 6.2).
¡
Do not pass the DC input pattern underneath the power module
as this will increase conducted noise. Place the DC input pattern
away from the power module.
Do not pass the DC output pattern underneath the power module
as this will increase output noise. Place the DC output pattern
away from the power module.
¡
High frequency noise is radiated from the power module. When
mounting the power module on a PCB, leave a copper pattern
on the PCB to let it act as a shield and connect this pattern to the
CASE pin (CBS50/100/200) or the mounting hole.
¡
When a heat sink cannot be fi xed on the base plate side, order the
power module with ”-T” option. A heat sink can be mounted by affi x-
ing a M3 tap on the heat sink. In case of CBS350/450, make sure a
mounting hole will be connected to a grounding capacitor C
Y
.
Mounting hole
Standard M3 tapped
Optional : -T
f
3.4 thru
6.2 Stress onto the pins
¡
Applying excessive stress to the input or output pins of the power
module may damage internal connections. Avoid applying stress
in excess of that shown in Fig. 6.1.
¡
Input and output pins are soldered onto the internal PCB. Do not
bend or pull the leads with excessive force.
¡
As unexpected stress may be applied to the pins, set the diameter
of the PCB mounting hole at 3.5mm.
¡
As unexpected stress may be applied to the pins from vibration
or shock, fi x the power module by using the mounting holes with
screws to reduce stress.
¡
Fix the power module to the PCB with the screws before soldering
the input and output pins to prevent the PCB pattern being dam-
aged.
6 Implementation
-
Mounting Method
4.7 Withstanding Voltage / Isolation Voltage
¡
When testing the withstanding voltage, make sure the voltage is
increased gradually. When turning off, reduce the voltage gradual-
ly by using the dial of the hi-pot tester. Do not use a voltage tester
with a timer as it may generate voltage several times as large as
the applied voltage.
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-18
CBS
Fig. 5.1 Examples of Series Operation
Load
Load
Power
Supply
Power
Supply
Load
Power
Supply
Power
Supply
(a) (b)
Fig. 5.2 Example of Redundancy Operation
Table 6.1 Mounting Hole Confi guration
+S
+VOUT
-S
-VOUT
+S
+VOUT
-S
-VOUT
Load
I
I
1 I3
2
Table 4.2 Recommended Values of External Resistors
No. VOUT
Adjustable range
VOUT±5% VOUT±10%
R1 R2 R1 R2
1 1.8V 1.8k
W
6.2k
W
1.6k
W
3.6k
W
2 2.5V 2.7k
W
7.5k
W
2.4k
W
4.7k
W
3 3.3V 2.4k
W
11k
W
2.4k
W
6.8k
W
4 5V 5.6k
W
5.6k
W
5 12V 18k
W
18k
W
6 15V 24k
W
24k
W
7 24V 43k
W
39k
W
8 28V 51k
W
47k
W
9 32V 56k
W
56k
W
10 48V 82k
W
82k
W
Page 9
6.3 Cleaning
¡
Clean the soldered side of the power module with a brush.
Prevent liquid from getting into the power module. Do not clean by
soaking the power module into liquid.
¡
Do not allow solvent to come in contact with product labels or res-
in cases as this may change the color of the resin case or cause
deletion of the letters printed on the product label.
¡
After cleaning, dry the power modules well.
6.4 Soldering temperature
¡
Flow soldering: 260C for up to 15 seconds.
¡
Soldering iron (26W): 450C for up to 5 seconds.
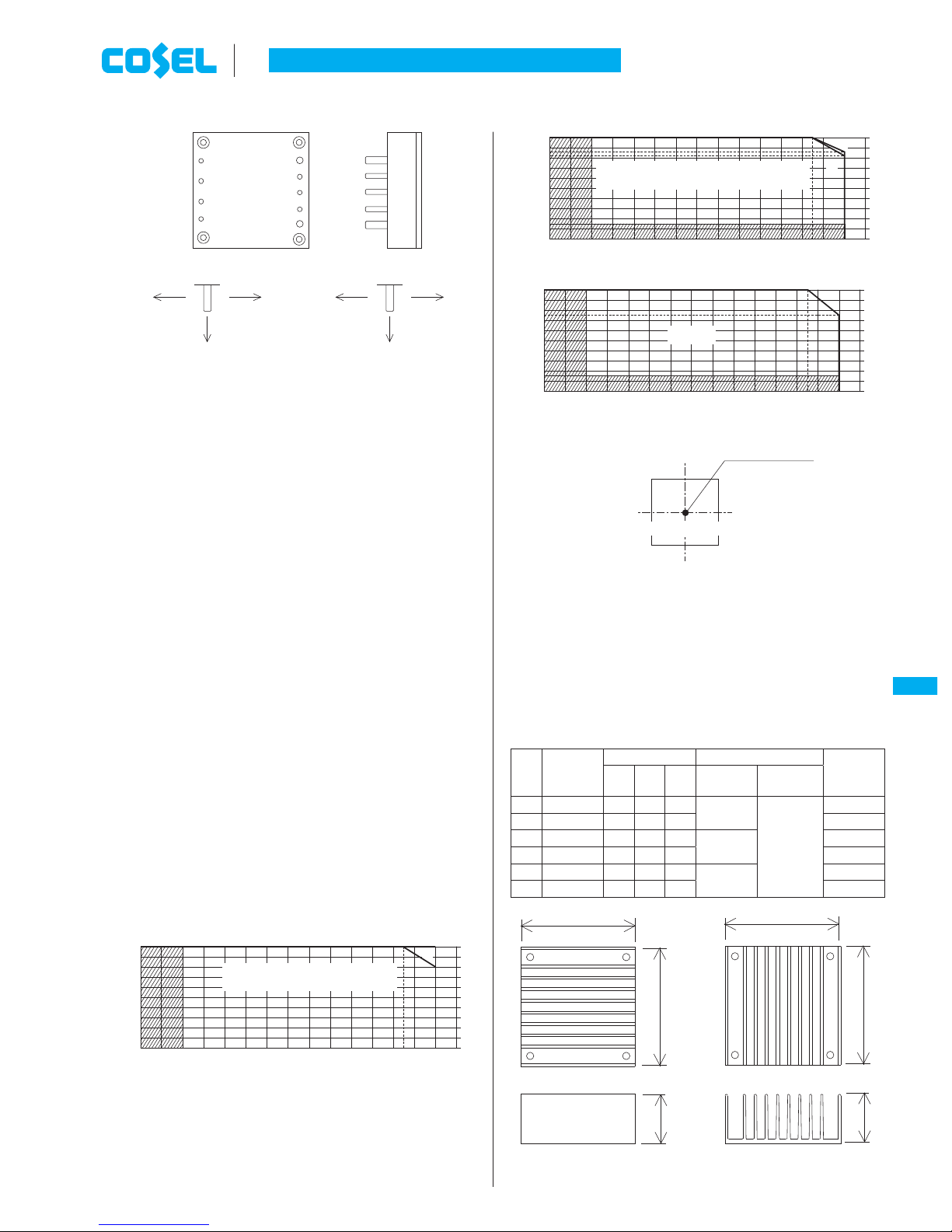
6.5 Derating
¡
Use the power modules with conduction cooling (e.g. heat dissipa-
tion from the aluminum base plate to the attached heat sink).
Fig. 6.2 shows the derating curves with respect to the aluminum
base plate temperature. Note that operation within the hatched ar-
eas will cause a signifi cant level of ripple and ripple noise. Contact
us for more information on cooling methods.
¡
It is necessary to note thermal fatigue life by power cycle.
Please reduce the temperature fl uctuation range as much as pos-
sible when the up and down of temperature are frequently gener-
ated.
Contact for more information on cooling methods.
6.6 Heat sink(Optional parts)
¡
The power module works with conduction cooling and needs heat
dissipation using heat sinks. Optional heat sinks are available for
CBS Series. Refer to Table 6.2 for details on the thermal resis-
tance of heat sinks.
No. Model
Size[mm]
Thermal resistance[C/W]
Style
HWD
Convection
(0.1m/s)
Forced Air
1 F-CBS-F1 12.7 57.9 61.5
7.5
Refer Fig.6.4
Horizontal
2 F-CBS-F2 12.7 58.4 61.0 Vertical
3 F-CBS-F3 25.4 57.9 61.5
4.6
Horizontal
4 F-CBS-F4 25.4 58.4 61.0 Vertical
5 F-CBS-F5 38.1 57.9 61.5
3.0
Horizontal
6 F-CBS-F6 38.1 58.4 61.0 Vertical
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-19
CBS
+VOUT
-VOUT
-S
TRM
+S
-VIN
CASE
RC
NC
+VIN
+VOUT, -VOUT
39.2N(4kgf) 39.2N(4kgf)
Less thanLess than
Less than
39.2N(4kgf)
19.6N(2kgf) 19.6N(2kgf)
19.6N(2kgf)
Others
Less thanLess than
Less than
Fig. 6.1 Stress onto Pins
Fig.6.2 Derating Curve
Tc:Measuring point
Table 6.2 Types of Heat Sinks Available
Fig.6.3 Heat Sink Types
Aluminum base plate
Horizontal Vertical
Load factor[%]
Aluminum base plate temperature Tc [C]
-40
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 110
0
(15)
(75)
50
100
CBS450
(85)
Aluminum base plate temperature Tc [C]
Load factor[%]
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 110
0
50
100
2
1
(85)
1CBS200O12,15,24,28 4
2Others (Excluding CBS350/450)
,8
W
D
H
W
D
H
Aluminum base plate temperature Tc [C]
Load factor[%]
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 110
0
(15)
(85.7)
(83.3)
50
100
2
(85)
1CBS3502412,CBS3502448,CBS3504848
2
Others
(CBS350)
1
Page 10

6.7 Addition of a Heat sink(Optional:FO)
¡
Heat sink pre-attached models are also available.
(Except CBS350/450)
Option
Size[mm]
Weight
[g]
Style
Heat sink
type name
HWD
F1 26.5 58.7 62.5
150 or less
Horizontal F-CBS-F1
F2 26.5 59.5 62.0 Vertical F-CBS-F2
F3 39.2 58.7 62.5
170 or less
Horizontal F-CBS-F3
F4 39.2 59.5 62.0 Vertical F-CBS-F4
F5 52.0 58.7 62.5
185 or less
Horizontal F-CBS-F5
F6 52.0 59.5 62.0 Vertical F-CBS-F6
¡
Derating curve characteristics with respect to aluminum base plate
temperature are shown in Fig. 6.6. Measure the temperature of
the base plate in a location away from direct airfl ow (A). Note that
operation within the hatched areas will cause a signifi cant level of
ripple and ripple noise.
¡
Make sure that PCB mounting screws do not touch the heat sink
mounting screws.
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-20
CBS
Fig.6.4 Thermal Resistance of Heat Sink(Forced Air)
Table 6.3 Types of Heat Sink Pre-Attached Models Available
W
D
H
W
D
H
Fig. 6.5 Dimensions of Heat Sink Pre-Attached Models
Fig. 6.6 Derating Curve Characteristics
A
Air
Fig. 6.7 Measuring Point
Fig. 6.8 PCB Mounting Screw Dimensions
Mounting hole
PCB
M3(Mounting screw)
7mm max
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
Wind velocity(m/s)
Thermal resistance( /w)
F-CBS-F1/F2
F-CBS-F3/F4
F-CBS-F5/F6
C
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 110
0
50
(95)
1CBS200 12, 15, 24, 28, 48
2Others (Excluding CBS350/450)
90-40
Aluminum base plate temperature Tc[ ]
C
100
Load factor[%]
1
2
Horizontal Vertical
Page 11

7
Safety Considerations
¡
To apply for safety standard approvals with the power module, the
following conditions must be met. Consult us for more details.
¿
The power modules must be used as a component power supply
in end-use equipment.
¿
Neither basic isolation nor double/reinforced isolation is provided
across input, output and the base plate of the power module. If
the power module is to be used with input voltage of more than
60VDC and needs basic or double/reinforced isolation, the re-
quired isolation must be provided in the construction of the fi nal
product.
¿
Use external fuses that comply with safety standards at the input.
DC-DC Converters Bus Converter
.
Power Module Type
Instruction Manual
CBS-21
CBS
Page 12

Our company network supports you w
and
the USA. For more information pl
F
OR
Haup
Lech
8689
Telef
Telef
E-
Ma
Inter
FORTEC
Elektronik A
Büro Nord
Am Hasenkamp 36
22457 Hamburg
Telefon: +49 (0)
40
Telefax: +49 (0)
40
E-Mail:
nord@forte
Internet:
www.fortec
FORTEC
Elektronik A
Büro Wien
Nuschinggasse 12
A-1230 Wien
Telefon:
+43 1 8673
Telefax:
+43 1 8673
E-Mail:
office@fort
Internet:
www.fortec
Membe
offices in Germany
, Austria, Swit
Elektronik AG
+49 (0) 8191 91172-0
+49 (0) 8191 21770
sales@fortecag.de
www.fortecag.de
56 13
FORTEC
Elektronik AG
Büro West
Hohenstaufenring 55
50674 Köln
Telefon:
+49 (0) 221
Telefax:
+49 (0) 221
E-Mail:
west@forteca
Internet:
www.fortecag
-0
-26
ALTRAC AG
(Tochter der Fortec AG):
Bahnhofstraße 3
CH-5436 Würenlos
Telefon:
+41 (0) 44 7
Telefax: +4
1 (0) 44 7
E-Mail:
info@altrac.c
Internet:
www.altrac.c
of the
Group:
, Great Britain
-0
72 273-10
 Loading...
Loading...