Corken Z Series, Z4200, Z2000, Z4500, Z3200 Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual
...Page 1

ORIGINAL INSTRUCTIONS ID105K
Installation, Operation
& Maintenance Manual
Z-Series Sliding Vane Pumps
Truck and Stationary
Model Z2000 Truck Pump
Model Z3200 Truck Pump
Model Z3500 Truck and
Stationary Pump
Model Z4200 Truck Pump
Warning: (1) Periodic inspection and maintenance of Corken products is essential. (2) Inspection, maintenance and installation of Corken products
must be made only by experienced, trained and qualied personnel. (3) Maintenance, use and installation of Corken products must comply with
Corken instructions, applicable laws and safety standards (such as NFPA Pamphlet 58 for LP-Gas and ANSI K61.1-1972 for Anhydrous Ammonia).
(4) Transfer of toxic, dangerous, ammable or explosive substances using Corken products is at user’s risk and equipment should be operated
only by qualied personnel according to applicable laws and safety standards.
Model Z4500 Stationary Pump
Solutions beyond products...
Page 2

Warning
Install, use and maintain this equipment according to Corken’s instructions and all applicable federal, state, local laws
and codes. Periodic inspection and maintenance is essential.
Corken One Year Warranty
CORKEN, INC. warrants that its products will be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of one
year from date of installation, provided that the warranty shall not extend beyond twenty-four (24) months from the date
of shipment from CORKEN. If a warranty dispute occurs, the DISTRIBUTOR may be required to provide CORKEN
with proof of date of sale. The minimum requirement would be a copy of the DISTRIBUTOR’S invoice to the customer.
CORKEN products which fail within the warrant period due to defects in material or workmanship will be repaired or
replaced at CORKEN’s option, when returned, freight prepaid to CORKEN, INC., 3805 N.W. 36th St., Oklahoma City,
Ok l a h o m a 73112 .
Parts subject to wear or abuse, such as mechanical seals, blades, piston rings, valves and packing, and other parts
showing signs of abuse, neglect or failure to be properly maintained are not covered by this limited warranty. Also,
equipment, parts and accessories not manufactured by CORKEN but furnished with CORKEN products are not
covered by this limited warranty and the purchaser must look to the original manufacturer’s warranty, if any. This limited
warranty is void if the CORKEN product has been altered or repaired without the consent of CORKEN.
All implied warranties, including any implied warranty of merchantability or tness for a particular purpose, are
expressly negated to the extent permitted by law and shall in no event extend beyond the expressed warrantee period.
CORKEN DISCLAIMS ANY LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES DUE TO BREACH OF ANY WRITTEN OR
IMPLIED WARRANTY ON CORKEN PRODUCTS. Transfer of toxic, dangerous, ammable or explosive substances
using CORKEN products is at the user’s risk. Experienced, trained personnel in compliance with governmental and
industrial safety standards should handle such substances.
Important notes relating to the European Union (EU) Machinery Directive
Pumps delivered without electric motors are not considered as machines in the EU Machinery Directive. These pumps
will be delivered with a Declaration of Incorporation. The fabricator of the machinery must assure and declare full
compliance with this Directive before the machine in which the pump will be incorporated, or of which it is a part, is
put into service.
Contacting the Factory
Before you contact the factory, note the model number and serial number of your pump. The serial number directs us to
a le containing all information on material specications and test data applying to your specic pump. When ordering
parts, the Corken service manual or Operations, Installation and Maintenance (IOM) manual should be consulted for
the proper part numbers. ALWAYS INCLUDE THE MODEL NUMBER AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING
PARTS.
The model and serial numbers are shown on the nameplate of the unit. Record this information for future reference.
Model No.
Serial No.
Date Purchased
Date Installed
Purchased From
Installed By
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
APPLICABLE NOTICES FOR ATEX 94/9/EC CONFORMITY ...........................................4
PRINCIPLES OF THE Z-SERIES SLIDING VANE PUMP (CORO-VANE®) .................................5
EXCLUSIVE FEATURES OF THE Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® PUMP ......................................5
CHAPTER 1—INSTALLATION OF THE Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® TRUCK PUMP ..........................5
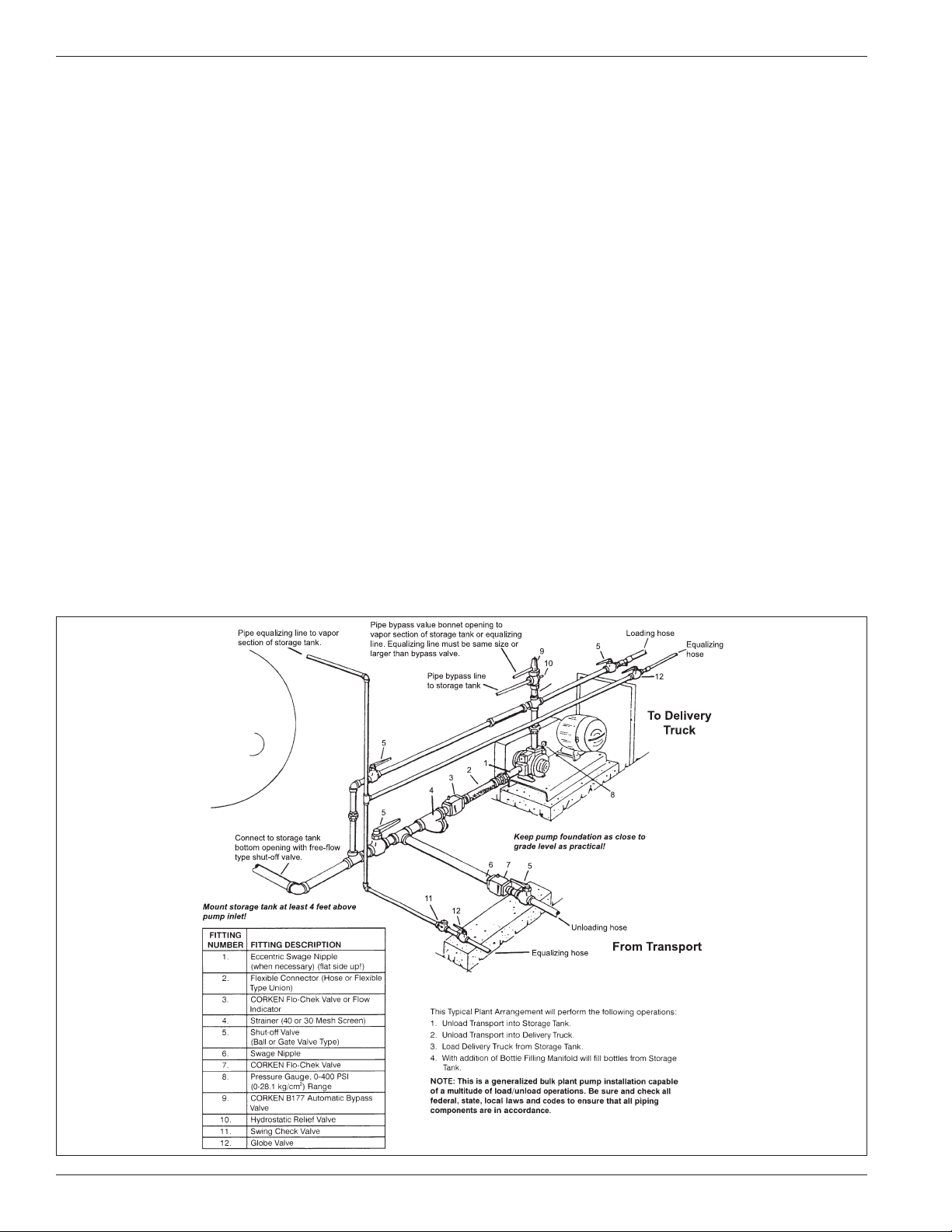
1.1 The Outlet Piping Should Include the Following ..................................................6
1.2 The Bypass System ........................................................................6
1.3 Power Take-off (PTO) Drive Systems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.4 Hydraulic Drive Systems ....................................................................7
CHAPTER 2—OPERATION OF THE Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® TRUCK PUMP ............................7
2.1 How to Transfer From the Truck Tank at Full Capacity ..............................................7
CHAPTER 3—INSTALLATION OF THE Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® STATIONARY PUMP .....................8
3.1 The Inlet Piping Should Include the Following ....................................................8
3.2 The Outlet Piping Should Include the Following ..................................................8
3.3 The Bypass System Must Include the Following ..................................................9
3.4 A Vapor Equalizing System Should be Included ..................................................9
3.5 Driver Installation ..........................................................................9
CHAPTER 4—OPERATION OF THE Z-SERIES STATIONARY CORO-VANE® PUMP ......................10
CHAPTER 5—MAINTENANCE OF THE Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® PUMP ...............................11
5.1 Purpose ................................................................................11
5.2 Scope ..................................................................................11
5.3 Procedures .............................................................................. 11
CHAPTER 6—Z-SERIES CORO-VANE® SEAL REPLACEMENT INSTRUCTIONS ........................13
6.1 Repair/Rebuild Kits with Iron Seal Seat ........................................................16
6.2 Repair/Rebuild Kits with Silicon Carbide Seal Seat ...............................................17
6.3 Assembly Instructions For All Z-Series Repair and Rebuild Kits .....................................18
APPENDICES
A. Model Number Identication Code and Available Options ..........................................19
B. Specications ............................................................................21
C. Performance .............................................................................22
D. Outline Dimensions ........................................................................28
E. Parts Details .............................................................................38
F. V-Belt Selection ...........................................................................45
G. Troubleshooting Guide .....................................................................46
H. Extended Storage .........................................................................48
I. Hydraulic Motor Specications ................................................................48
3
Page 4
Applicable Notices for ATEX 94/9/EC Conformity
Product Type:
Sliding Vane Pump (Coro-Vane®)
Training Instructions:
Instructions for the safe application and use of this
product are provided in this manual. Read this manual
completely prior to installation and use of this product.
Only qualied and properly trained personnel should be
allowed to install, operate, and maintain this equipment.
Models Covered:
Z/ZH2000, ZX/ZXH2000, Z/ZH3200, Z3500, Z/ZH4200,
and Z4500
Intended Application:
The pump models covered by this manual conform to the
European Union ATEX 94/9/EC Directive for explosive
gas atmospheres and transfer of liqueed gases such as
Liqueed Petroleum Gas, anhydrous ammonia, freons,
etc. Electric motors for these pumps in the assembly must
comply with all applicable requirements for local, federal,
and regional codes and regulations.
Possible Misuse Warning:
The designated pump models must only be installed
in systems designed for its intended use, similar to the
examples presented in this manual.
ATEX Classication:
Group II; Category 2; G; Temperature Class T4 – T5
These products are classied under the ATEX directive
as Equipment – Group II – Category 2 – equipment is
intended for use in areas where explosive atmospheres
caused by gases or vapors (G) may be present. The
surface Temperature Class rating is a range between T4
275°F (135°C) and T5 212°F (100°C).
Nameplate:
ATEX directive 94/9/EC marking
Explosive
protection
Equipment classified as
Group II— Catagory 2
Explosive gas
atmosphere high level
Maximum surface temperature
T4 275°F (135°C)
File number
ATE X a nd
machinery directive
Mechanical Ignition Sources:
This equipment may be direct driven through a coupling by an
electric motor or belt driven by an electric motor. Guards for
the drive mechanism in the assembly intended for personal
protection are to be supplied by the customer. The pump
assembly including the drive system must be grounded to
prevent possible electrostatic discharge. Internal parts of the
pump require uid (product being pumped) or damage may
occur. Do not run the pump dry (without liquid in the pump).
The application of liquid level controls in the pump system
is recommended. Preventive Maintenance guidelines are
provided in this manual and are to be followed for the proper
operation and performance of the pump.
Sound Levels:
When properly installed and operated, these pumps do
not exceed 85 dBA noise levels at a distance of one
meter (3.281 ft) from the surface of the pump. This value
is highly dependent upon the installation and may vary
from installation to installation.
Piping Forces and Moments:
Maximum Allowable Pipe Torque
Z/ZH/ZX/ZXH2000
Inlet Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Outlet Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Z/ZH3200 and Z3500
Inlet Size 3 in. (80 mm)
Torque 1,800 in•lbs (203 N•m)
Outlet Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Auxiliary
Inlet
Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Z/ZH4200
Inlet Size 4 in. (100 mm)
Torque 1,900 in•lbs (215 N•m)
Outlet Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Auxiliary
Inlet
Size 2 in. (50 mm)
Torque 1,650 in•lbs (186 N•m)
Preventative Maintenance
Pump Maintenance Schedule:
Daily Monthly 3 Months
Lubricate bearings X
Inspect drive couplings X
Clean inlet strainer X
Check for leaks X
Inspect hose and ttings X
4
Page 5

Principles of the Z-Series Sliding
Chapter 1—Installation of the
Vane Pump (Coro-Vane®)
The Z-Series truck pump is a special type of rotary positive
displacement pump, known as a sliding vane pump.
The sliding vane pump has many of the positive displacement
advantages of the gear pump, plus the ability to compensate
for wear, and operate at a lower noise level.
The sliding vane pump consists of a rotor turning in a
cam (liner) machined eccentrically in relation to the rotor;
thereby displacing the liquid trapped between the rotor,
cam and vanes. The Z-Series pumps are made with vanes
produced from advanced polymers which exhibit extremely
low coefficients of friction. The vanes are self-adjusting for
wear which gives the pump long life.
Exclusive Features of the Z-Series Coro-Vane® Pump
The pumping of volatile liquids is one of the most difficult of all
pumping jobs, and pumping from a delivery truck makes it even
more difficult, so more attention must be given to the design and
manufacture of the pump and to its installation and operation.
Z-Series Coro-Vane® Truck Pump
Before installing of your pump, remove all temporary
plastic plugs.
The installation of the Z-Series pump is simple. However,
in order for the pump to deliver optimum performance, the
principles discussed in this book should be followed. The piping
details are furnished to illustrate methods proved by hundreds
of installations. Your own needs may require slight variations,
but every effort should be made to follow the recommendations
identied in this manual.
For the transfer of ammable liquids like LPG, the pump
must be installed according to the applicable local safety
and health regulations. The installer and/or the user must
take into account the following:
• Potential risk due to local conditions regarding the
installation and operation (e.g. poor ventilation and
additional risks due to other elements in the vicinity, etc.).
• Qualication of the personnel.
• Type of liquid being transferred.
In addition to being especially suited for handling volatile
liquids, the Z-Series pump has a number of features to help
make it more easily operated and maintained.
This model has been registered and listed by the
UNDERWRITERS’ LABORATORIES, INC. for use in the
handling of LP-Gas and Ammonia.
The CASE AND HEADS are made of ductile iron for extra
strength and toughness.
The VANES are manufactured of advanced polymers to
provide excellent life and quiet operation. After long service, the
vanes are simply and inexpensively replaced.
Both the CAM and the SIDEPLATES are easily replaced should
the need arise. Sideplates may be reversed for extended
service life.
The MECHANICAL SEAL is designed for longer life under greater
loads and may be inspected or replaced without disturbing the
piping of the pump. No special tools are needed.
BEARINGS are heavy-duty roller type for long bearing life.
PRESSURE GAUGE connections, 1/4 in. pipe thread, are provided.
• Specic safety measures to be applied (e.g. gas
detection, automatic shut-off valves, personal protection
equipment, etc.).
See Appendix A for shipping weight and Appendix D for
outline dimensions.
A rotation arrow is located on the side of the pump so
check the Power Take-off (PTO) to determine its direction
of rotation. The Z-Series pump will match either PTO
rotation. Connect the drive shaft to the pump shaft that
turns the pump in the direction of the arrow.
The PTO selection is important. The pump requires a
PTO with an average output speed of 420 to 800 RPM
when the truck engine is operating at the proper speed to
maintain oil pressure and water circulation.
The DRIVESHAFT connecting the pump to the PTO should
be of the “splined” or slip type. This type driveshaft permits
the shaft to adjust for PTO movement and twisting of the truck
frame. A xed driveshaft transfers the forces directly into the
pump and PTO and will shorten the life of both considerably.
The yokes of the driveshaft universal joints must be positioned
as shown. Improper positioning will soon wear them out and
potentially destroy the bearings in the pump and PTO.
The RELIEF VALVE is built-in and nonadjustable. The
valve is preset at the factory.
NOTE: EVEN WITH THIS INTERNAL SAFETY VALVE,
AN EXTERNAL BYPASS VALVE MUST BE INSTALLED.
INLET PIPING should be as short as possible with
minimum restrictions so that the pressure drop is limited.
Inlet piping is not generally required on the Z3200 or
Z4200. These pumps are bolted directly to the tank
internal valve and must be installed in accordance with
the valve manufacturer’s instructions.
5
Page 6

Figure 1.1: Shaft Alignment
Correct assembly
Incorrect assembly
1.1 The Outlet Piping Should Include the Following
1. A liquid lled pressure gauge should be installed in the
pump outlet or near it. A pressure gauge is necessary
to determine the efficiency of your pumping system.
2. A hydrostatic relief valve is required by most state laws
and for your own safety.
Figure 1.2: Universal Joint Alignment
3. If a meter with a vapor eliminator is installed, pipe the
eliminator outlet to the top of your tank. Never pipe the
eliminator into the pump inlet piping or into the liquid
part of the system at any point.
4. The meter back-pressure valve may be piped into the
tank top or into the pump inlet piping.
5. The discharge piping should be at least the same size
as the meter.
1.2 The Bypass System
The internal safety relief valve is intended as a safety
device and not as an operational bypass valve. The
external bypass valve should be set at a differential
pressure lower than the internal relief valve and may be
connected to the tank at any convenient point, liquid or
vapor. All Z-Series pumps (except ZX2000, which is set
at 175 psid) are set near 150 psid.
ZH2000 Foot mounted hydraulic drive with NPT
connections
ZX2000 Foot mounted with NPT connections and high
pressure internal relief valve spring (175 psid
rather than the standard 150 psid)
ZHX2000 Foot mounted hydraulic drive with NPT
connections and high pressure internal relief
valve spring (175 psid rather than the standard
150 psid)
1.3 Power Take-off (PTO) Drive Systems
Proper pump operation and long life are directly dependent
upon a good drive system. Many truck pumps utilize a
power train consisting of shafts and universal joints from
a power take-off shaft on the truck engine to the pump.
There are several basic principles that should be followed
in laying out a PTO drive. These principles should not be
violated. Following them will produce a workable power train
that results in long pump life and reduced drive wear.
First, the driver shaft and the driven shaft must be parallel
to one another within plus or minus one degree. Improper
alignment will cause jerking and back and forth “whip” to the
pump shaft, thereby imparting a surging pulsation to the liquid
ow, which results in noise, vibration, and abnormal wear.
Second, the angle of the “oating” shaft should be within
the limits for the particular equipment being used (usually
a maximum of 15° at pump speeds up to 800 RPM). To
ensure that shaft expansion or contraction does not distort
the drive system, a splined slip joint should be placed
between the two universal joints. The drive shaft should
be of the “splined” or slip type to permit the shaft to adjust
for PTO movement and twisting of the truck frame. A xed
drive shaft transmits the forces directly to the pump and
PTO which will shorten the life of both considerably.
Third, the yokes of the drive shaft universal joints must be
in a parallel position. Figures one and two illustrate the
proper arrangement.
6
Page 7

Improper installation of the U-joints will soon destroy
them along with the bearings in the pump and PTO.
Properly mounted, the second universal gives uniform
motion to the drive shaft by compensating for the
rotational error introduced by the rst U-joint. An even
number of universal joints (two, four, six, etc.) should
always be used. An odd number of U-joints will cause
unbalanced pump shaft rotation. This problem becomes
greater with increased angularity.
Other points to consider include the proper sizing of the
shaft components with a maximum horsepower load to be
expected, good alignment of hanger bearings and proper
pump coupling alignment. Improper PTO systems count for
a high percentage of truck pump failures. Always remember
to disengage the clutch before shifting the PTO into gear.
Shifting the PTO into gear without disengaging the clutch
imparts an enormous shock on the PTO, drive shaft, pump,
and meter and will soon damage one or all of them.
performance charts in Appendix C. Information on the CharLynn hydraulic motor is found in Appendix I.
Chapter 2—Operation of the Z-Series Coro-Vane® Truck Pump
Performance curves and charts are provided in Appendix C.
The following steps should be performed for the initial
pumping operation:
1. Close the shutoff valve on the end of the delivery hose.
2. Follow the instruction s of the internal valve manufacturer
for putting the valve into operation.
3. Start the pump and circulate liquid through the external
bypass system.
For proper installation of pump drives, follow the rules
listed below:
1. Driver shaft and pump shaft must be parallel, plus or
minus one degree.
2. Operating angle of the “oating” shaft must be 15
degrees maximum.
3. Universal yokes must be in line and parallel.
4. Splined slip joints must be used where needed.
5. Use an even number of universal joints.
6. Always use the least practical number of shafts.
PTO selection and drive system design is extremely
important. The PTO should have an average output speed
of 420 to 800 RPM when the truck engine is operating at
the recommended speed.
The designer of the drive system must select a PTO drive
shaft capable of meeting the torque requirements of the
pumping system.
4. If your system has a Corken bypass valve, adjust the valve
by turning the adjusting screw counter clockwise until the
pump discharge pressure gauge shows nearly the same
pressure it did before you started the pump. Turn the
adjusting screw clockwise until the gauge indicates about
90 to 115 psid above the tank pressure. If a bypass valve
of another make is used, follow the instructions provided
for adjusting the valve.
5. You may increase the speed of your pump as long as
it increases the capacity of the pump and does not
exceed the excess ow valve or external bypass valve
setting. The one exception occurs when the pump is
used to “Pump On” or to load the truck tank. In this
case, the pump inlet conditions are poor at best so the
pump should be operated at a slower RPM.
NOTE: IF PUMP SPEED IS INCREASED, BE
CERTAIN THE METERING SYSTEM WILL
HANDLE THE INCREASED FLOW.
WHEN PROPERLY INSTALLED AND OPERATED, Z-SERIES
CORO-VANE® TRUCK PUMPS DO NOT EXCEED AN 88
dBA NOISE LEVEL AT A DISTANCE OF ONE METER
(3.281 ft) FROM THE SURFACE OF THE PUMP.
1.4 Hydraulic Drive Systems
Truck pumps are also driven by hydraulic systems, consisting
of an adaptor, motor, pump, cooler, and connecting hoses.
The truck pump’s shaft must be properly aligned with the
hydraulic motor’s shaft to avoid excessive stress on the
truck pump’s main and thrust absorbing bearings. See
Appendix D for outline dimensions.
The sizing of the hydraulic motor, hydraulic pump, and hydraulic
oil cooler must be done using the operational requirements
of the truck pump (e.g. ow rate, differential pressure, pump
speed, and required torque and power). These data are on the
2.1 How to Transfer From the Truck
Tank at Full Capacity
To move volatile liquids rapidly from a truck tank requires that
a condition be maintained within the truck tank that keeps the
liquid and the vapors above the liquid in equilibrium . As liquid is
removed from the tank, some of the liquid boils to form vapor to
ll the space created as the liquid leaves. If this action becomes
too violent, the pump will begin to make noise, and the capacity
will be reduced. Truck pumps can lower the truck tank pressure
from 5 psi to 10 psi (below the starting tank pressure). If there
is no means provided for equalizing, then the trouble starts! As
the weather gets colder, the worse this condition will become.
7
Page 8

You can detect this “pull down” in pressure by observing your
truck tank pressure gauge as the pump is operating.
To prevent this violent liquid boiling, pressure in some form
must be introduced into the truck tank. The simple way to
accomplish this is to “equalize” between the truck tank and
the receiving tank. Equalizing takes the higher pressure
vapors from the receiving tank and returns them to the truck
tank. As a result, the void left by the receding liquid is lled.
This in turn lessens the need for the liquid to boil excessively.
The equalizing principle is necessary for volatile liquids.
1/2" x 8" anchor bolt
Pump base
Concrete
Fig u re 3 .1
• Potential risk due to local conditions regarding the
installation and operation (e.g. poor ventilation and
additional risks due to other elements in the vicinity, etc.).
NOTE: Z4500
baseplate should be
filled with grout.
Metal shim
Large washer
NOTE: EQUALIZING BETWEEN TANKS OR THE
ADDITION OF PRESSURE IS NOT A LEGAL
TRANSFER IN MOST STATES. IF EQUALIZING LINES
ARE NOT PERMITTED REMEMBER THAT A QUIET PUMP IS
AN EFFICIENT PUMP. A NOISY PUMP IS NOT EFFICIENT
AND THE CONDITIONS THAT CAUSE THE NOISE ALSO
CAUSE WEAR TO INTERNAL PARTS. OPERATE THE PUMP
AT SPEEDS THAT RESULT IN A “QUIET” TRANSFER.
NOTE: EVEN WITH THIS INTERNAL SAFETY VALVE,
AN EXTERNAL BYPASS VALVE MUST BE INSTALLED.
Chapter 3—Installation of the Z-Series Coro-Vane® Stationary Pump
NOTE: All pumps should be installed in a well ventilated area.
The installation of the Coro-Vane® pump is simple. However,
in order for the pump to deliver optimum performance, the
principles discussed in this book should be followed. The
piping details are furnished to illustrate methods proved
by hundreds of installations. Your own needs may require
slight variations, but every effort should be made to follow
the recommendations identied in this manual.
No pump can discharge more liquid than it receives, so
the pump location and the inlet piping must be given
careful attention. If the inlet piping is inadequate to supply
the demand of the pump, you may expect trouble.
For the transfer of ammable liquids like LPG, the pump
must be installed according to the applicable local safety
and health regulations. The installer and/or the user must
take into account the following:
• The pump must be located as near the storage tank as
possible. For best results the pump inlet line including
the vertical line from the tank should not exceed 12 feet
(3.7 m) in length.
• The bottom of the tank should be at least two feet (0.6
m) above the pump center line. For best results four feet
(1.2 m) is preferred.
• Qualication of the personnel.
• Type of liquid being transferred.
• Specic safety measures to be applied (e.g. gas
detection, automatic shut-off valves, personal protective
equipment, etc.).
Appendix A shows the weight of the bare pump for each
model. For handling a bare pump, lifting slings should be
used. Web slings are preferred over metal slings to minimize
damage to the paint. See Appendix D for outline dimensions.
3.1 The Inlet Piping Should Include
the Following
1. The tank excess ow valve (EFV) should have a ow
rate of 1-1/2 to 2 times the capacity of he pump. Do not
use an EFV without knowing its ow capacity.
2. The tank shut-off valve should be a free-ow type and
not a standard globe valve.
3. A strainer of the “Y” type, with 30 to 40 mesh screen,
must be on the inlet line of the pump. (Mesh size
indicates the number of openings per lineal inch). A
10x pipe diameter before the pump is recommended.
4. Use a exible connection in the pump inlet and outlet
piping to compensate for piping strains.
5. Use an eccentric swage at the pump inlet nozzle to
change the line size (at side up).
6. Make the inlet line level or slope it downward to the pump.
3.2 The Outlet Piping Should
Include the Following
1. A liquid lled pressure gauge should be installed in the
pump outlet or near it. A pressure gauge is necessary
to determine the efficiency of your pumping system.
• The foundation for the pump is important. The foundation
must be rm, level and preferably made of concrete. The
suggestions in gure three should be observed.
2. A hydrostatic relief valve is required by most state laws
and for your own safety.
8
Page 9

3. If the outlet piping exceeds 50 ft (15.2 m) in length, a
check valve should be installed in the discharge line
near the pump outlet.
3.3 The Bypass System Must
Include the Following
1. If the pump discharge is shut off before the driver has
stopped, a dangerously high pressure can develop;
therefore, an external bypass valve must be installed. The
installation of an external bypass valve permits the pump
to discharge its full capacity back to the supply tank at a
predetermined pressure. NOTE: Even though the pump
may have an internal relief valve, it is not a substitute for an
external bypass valve. The internal relief valve is a safety
relief valve for the pump only and not the entire system.
2. Always install a Corken ZV200 or B177 external
bypass valve in the discharge line of pump. The
bypass valve may discharge into the supply tank at
any convenient liquid or vapor opening; however, it
should not connect to the pump inlet piping.
3.4 A Vapor Equalizing System
Should be Included
To obtain maximum performance from your Coro-Vane® pump,
a vapor equalizing system should be installed. This system is
simply a pipe connecting the vapor sections of the tank being
unloaded and the tank being lled. This equalizing line allows
vapor to move freely between the two tanks (in either direction)
and assures that both tanks remain at the same pressure.
As liquid is withdrawn from a tank, it must be replaced by an
equal amount of vapor or the pressure in the tank will drop.
If an equalizing line is not present, this vapor is formed by
“boiling” of the liquid and a reduction of the tank’s pressure.
Meanwhile, the tank being lled experiences a pressure
increase as the rising uid levels compresses the vapor
space above it. A vapor equalizing line will eliminate both of
these problems and will reduce pumping time, differential
pressure, noise and wear on the entire system. Slow transfer
rates will minimize these effects, and reduce the need for a
vapor equalizing line. However, today’s high transfer rates
require that a vapor equalizing line be installed.
Another way to consider this principle is to remember that it
takes two holes in an oil can for oil to be poured smoothly from
the can; one for the oil to exit and the other for the air to enter.
3.5 Driver Installation
The wiring of your electric motor is extremely important and
must be done by a competent electrical contractor. The
following wire sizing chart indicates the minimum standards
for wire sizes.
Improper motor wiring will cause expensive motor
difficulties from low voltage. If you suspect you have low
voltage, call your power company. Connecting your motor
for the voltage you have available is important too. The
motors furnished with the stationary pumps are usually
dual voltage, so you must be sure of the voltage your power
company is supplying you. Your motor will be completely
ruined if it is connected to the wrong voltage.
A humid climate can cause problems, particularly in explosion
proof motor applications. The normal breathing of the motor,
and alternating between being warm when running and cool
when stopped, often will cause moist air to be drawn into
the motor housing. This moist air will condense, and may
eventually add enough free water to the inside of the motor
to cause it to fail. To prevent this, make a practice of running
the motor and pump at least once a week on a bright, dry
day for an hour or so (pumping through the bypass system).
In this period the motor will heat up and vaporize the
condensed moisture, and drive it out of the motor. No motor
manufacturer will guarantee an explosion-proof or totally
enclosed motor against damage from moisture.
Engine drivers pose a special consideration. The
manufacturer’s instructions must be followed. When the
stationary pump is equipped with an engine from the factory,
the engine speed should normally not exceed 1,800 RPM.
Excessive engine speed will overload the engine and cause
early failure. The engine loses 3% of its power for every
1,000 ft (305 m) above sea level, so if your installation is at a
higher altitude than normal, consult the factory.
Motor
Motor
Hp
phase
3 1 115 34.0 6 4 2
3 230 9.6 12 12 12
5 1 115 56.0 4 1 1/0
3 230 15. 2 12 12 10
7-1/2 1 230 40.0 8 6 4
3 230 22.0 10 10 8
10 3 230 28.0 8 8 8
15 3 230 42.0 6 6 6
20 3 230 54.0 4 4 4
25 3 230 68.0 2 2 2
30 3 230 80.0 1 1 1
40 3 230 10 0.0 2/0 2/0 2/0
50 3 230 130.0 3/0 3/0 3/0
1
Based upon 3% voltage loss copper wire type TW. Single phase
motor calculations are based on two times distance.
Approximate
Volts
220 17.0 12 8 8
460 4.8 12 12 12
230 28.0 10 6 4
460 7.6 12 12 12
450 11.0 12 12 12
460 14 .0 12 12 12
460 21.0 10 10 10
460 27.0 8 8 8
460 34.0 6 6 6
460 40.0 6 6 6
460 52.0 4 4 4
460 65.0 2 2 2
full load
amperes
Recommended
wire size, AWG
Length of run (ft)
0–100 to 200 to 300
1
9
Page 10
Chapter 4—Operation of the Z-Series Stationary Coro-Vane® Pump
Performance curves and charts are provided in Appendix C.
The following steps should be performed for the initial
pumping operation:
1. Verify the strainer screen is clean.
8. Open any shut-off valves between the bypass valve
and the storage tank.
9. Make a note of all pressure gauge readings, especially
the pressure gauge located at the discharge of the
pump. Start the pump and circulate the liquid through
the bypass system back to the storage tank.
10. Verify the proper pump rotation direction. There is an
arrow cast in the pump case.
2. Rotate the pump by hand.
3. Check V-belt drive or direct drive coupling alignment.
Misalignment will cause accelerated wear of the drive
system, motor bearings, and pump.
4. Check motor for proper wiring.
5. Review complete system to make certain the function
of every valve and piece of equipment is clearly
understood. Everyone operating this system must be
properly trained in normal operating procedures and
emergency procedures in event of a malfunction.
6. Close all hose valves.
7. Slowly open the storage tank bottom shut-off valve
(suction line to the pump). Immediately check the
system for leaks.
11. An ampmeter may be used by adjusting the bypass valve
until the ampmeter indicates the full load motor amperage
rating shown on the motor nameplate or maximum rated
differential, whichever comes rst. Permit the pump
to circulate liquid for half an hour or more. If the motor
overload protection device stops the motor in this period
the bypass valve setting is too high and should be
readjusted until the motor will run for half an hour. After a
satisfactory setting is achieved, “seal” the valve adjusting
stem to prevent tampering with the adjustment. See
Important Instructions (IH102) and Installation, Operation
and Maintenance (IOM) Manual (IH106) for more details
on the use of the Corken bypass valves.
12. Your pump has an internal relief valve, it must be set
higher than the external bypass setting. The internal
relief valve is factory preset.
13. After initial operation, re-check the strainer screen.
Fig u re 4 .1
10
Page 11
Chapter 5—Maintenance of the Z-Series Coro-Vane® Pump
5.1 Purpose
By following an effective maintenance program,
unscheduled downtime can be eliminated. This program
should be used by the Operation Manager to get a
maximum utilization of manpower and equipment as
well as to prevent possible unsafe situations and/or
production delays due to equipment breakdown.
Your Corken Z-Series Pump requires regular maintenance
and care like all mechanical equipment. A neglected
or improperly repaired pump will result in premature
failure and cause unsafe conditions. To promote product
longevity and safety, maintenance must be performed by
properly trained technicians. Make sure all safety systems
are in place and the system pressure has been relieved
before attempting ANY maintenance.
Make sure the transfer hoses are not “kinked” which can
cause excessive pump discharge pressure. Always make
sure your hoses are not out of date.
Normal wear parts are the mechanical seals, bearings,
vanes, and sideplates. All of these parts, plus O-rings
and grease seals, are offered in the Corken “repair kit”
listed in this manual directly after the Seal Replacement
Instructions. Use only genuine Corken replacement parts
when repairing the Z-Series pump. Follow the instructions
provided with the parts.
5.2 Scope
The Pump Maintenance Schedule table below includes
the items to be regularly checked and inspected with
a recommended time schedule. These are basic
maintenance recommendations, and each company
should develop their own comprehensive preventive
maintenance program schedule, tailor-made to their
individual operational procedures and requirements.
Pump Maintenance Schedule
Daily Monthly 3 Months
Lubricate bearings X
Inspect drive coupling X
Clean inlet strainer X
Check for leaks X
Inspect hose and ttings X
When it becomes necessary to repair your pump or
remove it from the system, you must be absolutely certain
that all propane, anhydrous ammonia, or whatever product
being pumped is bled from the pump and connecting
piping. Once all the product has safely been bled from the
pump and connecting piping, make certain no pressure
is left in the system. SPECIAL CARE MUST BE TAKEN
DURING THE BLEED DOWN PROCESS TO AVOID
DANGER TO PERSONNEL AND PROPERTY IN THE
AREA. Bleeding a system too fast is a common mistake
and may result in “refrigerated” liquid being left in the
pump and piping even though the pressure gauge shows
no pressure. As the “refrigerated” liquid begins to warm,
more gas will escape causing a dangerous condition.
Take your time in bleeding your system and make proper
provisions to vent or capture the gas in accordance with
local regulations.
NOTE: ONLY A PROPERLY TRAINED
INDIVIDUAL SHOULD BE ALLOWED TO BLEED
A PUMPING SYSTEM.
1. Visual Inspection:
This includes checking for leaks, corroded areas,
condition of hoses, piping and ttings, and any unsafe
condition which may hinder the safety of the personnel
and/or the facility.
Maintenance must only be performed by a properly trained
and qualied individual that follows all the applicable
safety procedures.
5.3 Procedures
ALL REPAIRS TO THE PUMP MUST BE
PERFORMED BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL IN
A SAFE MANNER, UTILIZING TOOLS AND/OR
EQUIPMENT THAT ARE FREE OF HAZARDS, AND
FOLLOWS THE APPLICABLE SAFETY CODES OF
PRACTICE SET BY THE LOCAL AUTHORITIES
HAVING JURISDICTION. MAKE SURE THE SYSTEM
PRESSURE HAS BEEN RELIEVED BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY REPAIR TO THE PUMP.
11
2. Clean Inlet Strainer Screen:
A clogged strainer screen will create too much ow
restriction and vapor will be formed causing the pump
to cavitate. This reduces the pump’s capacity and
accelerates the wear of the internal parts.
3. Inspect Drive Coupling and Driveline:
Check the coupling alignment and the condition of the
union for cuts, broken sections and wear.
4. Lubricate Pump Bearings:
There are two lubrication points on the Z-Series
pumps. A grease zerk is located on the top of each
bearing cap. To prevent over greasing the bearings,
a grease relief tting is located on the bottom of each
Page 12

bearing cap. Always clean each grease zerk and relief
tting before lubricating the bearings. This practice
helps prevent foreign material from reaching the
bearings through the grease zerk and ensures the
grease relief tting is not blocked. If the grease relief
tting is blocked, the excessive grease that cannot
be relieved may cause premature seal failure. If you
use a hand grease gun, put the grease in slowly
and stop as soon as the relief tting opens. Grease
the U-joints and the spline of the drive shaft when
greasing the pump.
NOTE: Always use ball bearing grease (MIL-G-10924C)
with a temperature rating of -65°F.
b. While transferring liquid with the pump, close the
discharge valve(s) so the full ow will be directed
back to the storage tank through the bypass valve.
Then slowly close the valve downstream of the
bypass valves. The discharge pressure of the
pump should increase to the maximum differential
pressure of the pump at no ow conditions (see
Appendix C: Performance Curves).
c. If the maximum differential pressure is not obtained,
the pump must be serviced. See Appendix G
Troubleshooting Guide for additional help.
d. Replace vanes or sideplates if worn.
5. Lubricate Motor Bearing:
If lubrication is required, follow the recommendations
of the electric motor manufacturer for the type of
grease to use and the lubrication frequency.
6. Performance Test:
a. While transferring liquid with the pump, check the
pressure at the pump’s inlet port. The pressure drop
in the inlet piping should not be greater than 3 psi.
7. Tighten all holddown bolts.
8. Inspect motor starter contact points.
This must be performed by an authorized and qualied
electrician, based on the electric motors manufacturer’s
guidelines.
12
Page 13

Chapter 6—Z-Series Coro-Vane® Seal Replacement Instructions
Please Note: The photos listed below contain a Z2000;
however, all Z-Series pumps use the same procedures for
seal replacement.
To determine the parts needed for repair, refer to
Appendix A—Model Number and Identication Code,
and Appendix E—Parts Details.
CAUTION! BLEED ALL PRESSURE FROM THE
PUMP AND PIPING BEFORE STARTING TO
INSTALL YOUR SEAL ASSEMBLY.
Cleanliness
Even the smallest amount of dirt on your new seal can cause
early failure. Keep all parts, tools and your hands clean while
installing the seal. Never touch the smooth lapped faces
of the carbon rotor or seal seat. For LP-Gas, anhydrous
ammonia and similar liquids, you are trying to seal a uid
that is 5 to 10 times thinner than water! Your new seal needs
every chance it can get, so keep it clean.
Workmanship
Your Corken pump is a precision piece of equipment with
very close clearances. Treat it as such. Never use force
during assembly or disassembly (see steps 1 through 10).
Step 1
Depressurize and open the pump
Loosen the head bolts and remove one head with the
bearing cap attached, while holding in on the shaft.
Step 2
Remove the seal seat and grease seal
the workbench as shown in the photo. When replacing the
seal assembly, there is no need to remove the bearings.
With a long screwdriver, reach through the opening of the
bearing cap and lightly tap the seal seat until it falls out
of the head. The seal seat is located at the bottom of the
head. Next, remove the grease seal using same process.
The old seal seat and grease seal will not be reused.
Step 3
Install the new grease seal
NOTE: The photo above is using a cutaway view for
better details.
After the head has been removed from the pump, remove
the head O-ring and place to the side. Place the head on
NOTE: The photo above is using a cutaway view for
better details.
Turn the head over as shown in the photo and install the new
grease seal smooth side up by pressing into the bore next to
the main bearing. To assist with the installation of the grease
seal, place the old seal seat without the O-ring over the top of
the grease seal and press into place as show in the photo. The
grease seal should t ush with the shoulder of the bore (see
Figure 6.1 for details).
13
Page 14
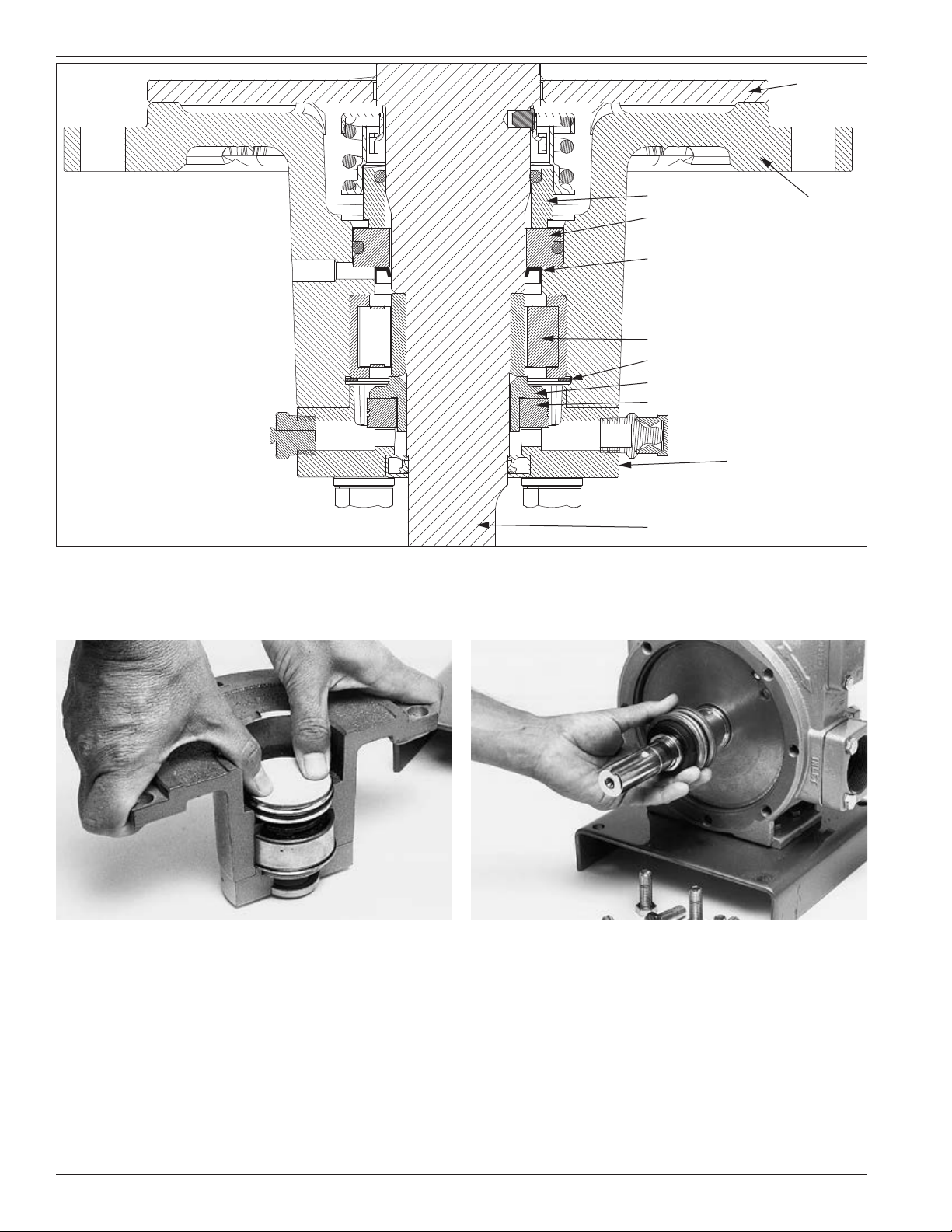
Sideplate
Step 4
Install the new seal seat
Carbon seal
Seal seat
Grease seal
NOTE ORIENTATION: The grease
seal is inserted with smooth side
up, flush with the shoulder of the
head, and directly beneath the seal
seat as shown in this illustration.
Roller bearings
Retainer ring
Thrust bearing mounting ring
Thrust bearings
Bearing cap
Rotor shaft
Fig u re 6 .1
Step 5
Remove the old seal assembly (carbon seal and retainer)
Head
NOTE: The photo above is using a cutaway view for
better details.
Be careful not to touch the smooth, shiny surfaces of the
seal seat. The smooth shiny surfaces must stay clean at all
times. Foreign material on these surfaces can cause seal
failure. Before installing the new seal seat, spray or apply a
generous amount of light oil to the new seal seat and O-ring.
This will allow the O-ring on the outside of the seal seat to
easily slide into place during installation. Before you press
the seal seat in place, make sure you cover the seal seat
with the protective cardboard disc as shown in the photo.
Remove the old seal assembly from the pump shaft while
holding the sideplate against the pump casing. This will
allow the seal retainer assembly to be removed without
pulling the rotor-shaft out of the pump. Inspect the rotor
shaft for burrs or scratches. If present remove with an
emery or polishing cloth.
14
Page 15

Step 6
Install the new seal assembly (retainer and carbon)
Clean the pump shaft and apply a generous amount of light
oil to the shaft and seal assembly.
Step 8
Completing installation
Torque the head bolts in a crossing pattern. There is no
need to disassemble or re-shim the bearing caps. Repeat
all of the above steps when replacing the seal assembly
on the opposite side.
Install the new seal assembly by aligning the seal retainer
slot with the seal drive pin on the shaft.
Step 7
Mechanical seal installation
Install the new case O-ring onto the head.
Apply a generous amount of light oil to each seal face and
carefully install the head assembly over the pump shaft.
Step 9
Lubrication and re-pressurizing
Note: Both sides of the pump are identical; duplicate
procedure to change the seal on the opposite side.
Lubrication
There are two lubrication points on the Z-Series pumps.
A grease zerk is located on each bearing cap. To prevent
over greasing the bearings, a grease relief tting is
located on the opposite side of each bearing cap. Always
clean each grease zerk and relief tting before lubricating
the bearings. This practice helps prevent foreign material
from reaching the bearings through the grease zerk and
ensures the grease relief tting is not blocked. If the
grease relief tting is blocked, the excessive grease that
cannot be relieved may cause premature seal failure.
If you use a hand grease gun, put the grease in slowly
and stop as soon as the relief tting opens. Grease the
U-joints and the spline of the drive shaft when greasing
the pump.
NOTE: Always use ball bearing grease (MIL-G-10924C)
with a temperature rating of -65°F.
Re-pressurize
For best results, slowly pressurize with vapor pressure.
Please Note: If you pressurize with liquid, it will sometimes
refrigerate even though it enters the pump slowly. As a
result, the seal elastomers will not seal properly thereby
causing them to leak.
15
Page 16

6.1 Repair/Rebuild Kits with Iron Seal Seat
Repair Kit 3193-X1 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, ZXH2000)
2-224A O-ring, Buna-N 1
2-231A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
426 2-X Vane driver 3
4428 Vane 6
4431-XA2 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3195-X1 (Z3200, ZH3200)
2-224A O-ring, Buna-N 1
2-234A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
426 2-X Vane driver 3
4232 Va ne 6
4431-XA2 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3195-X2 (Z3500)
2-228A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
5554-X Vane driver 6
3936 Vane 6
6660-XA2 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3197-X1 (Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
2-231A O-ring, Buna-N 2
2-234A O-ring, Buna-N 1
4460 -X Roller bearing 2
4449-X Vane driver 5
4448 Vane 6
4464-XA 2 Seal assembly 2
4453 Thrust bearing 2
4454 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4458 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 58-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4458-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4463 Grease seal 2
4459 Shaft key 1
Rebuild Kit 3194-X1 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, ZXH2000)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4414 Cam 1
4427 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3196-X1 (Z3200, ZH3200)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4242 Cam 1
4231 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3196-X2 (Z3500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
5539 Cam 1
3935 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3198-X1 (Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4443 Cam 1
4446 Sideplate 2
Full Rebuild Kit 3194-X3 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000,
ZXH2000)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4414 Cam 1
4427 Sideplate 2
4430-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3196-X3 (Z3200, ZH3200)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4242 Cam 1
4231 Sideplate 2
4495-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3196-X4 (Z3500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
5539 Cam 1
3935 Sideplate 2
1208-1X6R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3198-X3 (Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4443 Cam 1
4446 Sideplate 2
4444-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
All repair and rebuild kits have Buna-N O-rings which are suitable for
both LPG and NH3 applications.
16
Page 17

6.2 Repair/Rebuild Kits with Silicon Carbide Seal Seat
Repair Kit 3193-X16 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, ZXH2000)
2-224A O-ring, Buna-N 1
2-231A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
426 2-X Vane driver 3
4428 Vane 6
4431-XA6 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3195-X16 (Z3200, ZH3200)
2-224A O-ring, Buna-N 1
2-234A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
426 2-X Vane driver 3
4232 Va ne 6
4431-XA6 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3195-X26 (Z3500)
2-228A O-ring, Buna-N 2
275 4-X Roller bearing 2
5554-X Vane driver 6
3936 Vane 6
6660-XA6 Seal assembly 2
4432 Thrust bearing 2
4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 39-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4441 Grease seal 2
2270 Shaft key 1
Repair Kit 3197-X16 (Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
2-231A O-ring, Buna-N 2
2-234A O-ring, Buna-N 1
4460 -X Roller bearing 2
4449-X Vane driver 5
4448 Vane 6
4464-XA6 Seal assembly 2
4453 Thrust bearing 2
4454 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
4458 Bearing cap shim (0.002) 8
44 58-1 Bearing cap shim (0.010) 2
4458-2 Bearing cap shim (0.020) 2
4463 Grease seal 2
4459 Shaft key 1
Rebuild Kit 3194-X16 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, ZXH2000)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4414 Cam 1
4427 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3196-X16 (Z3200, ZH3200)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4242 Cam 1
4231 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3196-X26 (Z3500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
5539 Cam 1
3935 Sideplate 2
Rebuild Kit 3198-X16 (Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4443 Cam 1
4446 Sideplate 2
Full Rebuild Kit 3194-X36 (Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000,
ZXH2000)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4414 Cam 1
4427 Sideplate 2
4430-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3196-X36 (Z3200, ZH3200)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4242 Cam 1
4231 Sideplate 2
4495-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3196-X46 (Z3500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
5539 Cam 1
3935 Sideplate 2
1208-1X6R Rotor shaft assembly 1
Full Rebuild Kit 3198-X36 Z4200, ZH4200, Z4500)
Includes all items in the Repair Kit plus the following:
4443 Cam 1
4446 Sideplate 2
4444-X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
All repair and rebuild kits have Buna-N O-rings which are suitable for
both LPG and NH3 applications.
17
Page 18

6.3 Assembly Instructions For All Z-Series Repair and Rebuild Kits
1. Place the pump head on a clean work surface with the
bolting ange down.
2. Press the inner grease seal in through the main
bearing cavity until ush with the bottom of the bore.
Seal lips must be oriented down as shown in each
parts detail drawing. (See Figure 6.1)
3. Press the main bearing into the head and install the
retainer ring.
4. Install the relief tting into 1/8 in. NPT threaded hole
and turn the head over.
5. After lubricating the mechanical seal seat with light oil,
press the seal seat into the head using your ngers.
Make sure the seal seat is fully seated and the shiny
side faces up. Apply a generous amount of light oil
to the seal seat to remove any remaining debris and
ngerprints. Install the case O-ring around the pilot OD
of the head.
6. Press the outer grease seals into each of the
bearing caps.
7. Press the spring pins into each of the cam key holes.
8. Install the cam key into the pump case. Slide the cam
into the pump case aligning the long inlet slots to the
inlet portion of the case.
9. Install one sideplate and bolt one head into place with
two bolts.
14. Carefully install the head over the pump shaft and seal
assembly and torque the bolts in accordance with the
appropriate bolt torque pattern drawing. This pattern
ensures even bolting of the head into the case without
deforming the cam inlet port. This is done by bolting
those bolts over the solid portion of the cam port.
15. Turn the pump over and remove the rst head.
16. Install the seal retainer assembly and carbon as
outlined in step 13 above.
17. Bolt head to case as described in step 14 above.
Ensure the rotor shaft turns freely in either direction.
18. Slide the bearing race mounting ring onto one end
of the shaft until contact with the main bearing
inner race. Mount the thrust bearing assembly
onto the bearing race mounting ring and install the
bearing cap.
19. Lightly tighten the bearing cap with two opposed bolts
until the rotor shaft cannot be freely turned. Measure
the gap between the head and bearing cap at four
points around the bearing cap. Adjustment may be
necessary to contain the gap within .001 inch. Round
up the average measurement to the nearest even
number. This is the measured amount of bearing cap
shims. Refer to parts pages for shim measurements.
20. Remove the two bearing cap bolts and install the
measured amount of shims plus .006 inch. Install the four
bearing cap bolts and torque in a crossing pattern.
10. Turn the pump onto the assembled head. Ensure there
is enough room to allow the shaft to extend through
the assembled head by six inches.
11. While holding the rotor-shaft vertical, install the vane
drivers. Vertically install the rotor-shaft into the unit.
Slide the vanes into each rotor slot ensuring the
rounded tip contacts the cam and the vane slots face
into the direction of rotation as shown in each parts
detail drawing.
12. Install the remaining sideplate.
13. Lubricate the pump shaft and seal carbon with light
oil. Install the seal retainer assembly by aligning the
retainer slot onto the seal alignment pin. Carefully
press the seal carbon into the retainer assembly with
the polished face oriented outward by aligning the
carbon notches to the retainer pins. Again, apply a
generous amount of light oil to remove any remaining
debris and ngerprints.
21. Install the remaining bearing race mounting ring and
thrust bearing assembly on the opposite side of the
pump.
22. Perform step 19 again on the opposite side and install
the measured shims plus .002 inch. Install the four
bearing cap bolts and torque in a crossing pattern.
23. Install the shaft key and ensure shaft rotates smoothly.
18
Page 19

Appendix A—Z-Series Truck Pumps Model Number and Identication Code
Base Model Z2000/ZH2000 ZX2000/ZXH2000 Z/ZH3200 Z/ZH4200
Inlet 2" NPT 2" NPT 3" ANSI 4" ANSI
Outlet 2" NPT 2" NPT 2" ell Dual 2" NPT
Auxiliary Inlet None None 2" NPT 2" NPT
Internal Relief 150 psi 175 p si 150 psi 150 psi
Weight Bare
Pump lb (kg)
Vane
Type
Vanes GCB-50 Standard G
O-ring
Material
1
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
Seal Seat
Flange Options WF=Slip-on weld ange ell = Elbow All ANSI anges are 300# • indicates available ange connections
Inlet Flange
Standard
Extra Cost
Options
6 Vanes with
Vane Drivers
Buna-N Standard A
Neoprene
Cast Iron No charge option —
Silicon Carbide Standard 6
®1
2" NPT • • E
3" ANSI • P
4" ANSI • S
2" WF • • F
100
(45)
100
(45)
Standard H
No charge option B
140
(64)
275
(125)
Model Number
Base X X X X X X X
Outlet Flange
Standard
No Cost
Options
Extra Cost
Options
Auxiliary Flange
Standard
No Cost
Options
Extra Cost
Options
Part Number Test—Options
3000-X1 Hydrostatic test
2" NPT • • • E
2" NPT ell • G
1-1/2" NP T • C
2" NPT • E
1-1/2" WF • D
2" WF • • • • F
2" weld ell • H
2" NPT • • E
None • • U
1-1/2" NP T • C
Blind Flange • • T
1-1/2" WF • D
2" WF • • F
2" NPT ell • G
2" weld ell • H
19
Page 20

Appendix A—Z-Series Stationary Pump Model Number and
Identication Code
Base Model Z3500 Z4500
Inlet 3" NPT (Standard) 4" 300# ANSI
Outlet 3" NPT Elongated (Standard) 3" 300# ANSI
Weight—bare
pump lb (kg)
Vane
Type
Vanes GCB-50 Standard G
O-ring
Material
1
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
Seal Seat
Flange Options WF=Slip-on weld ange ell = Elbow All ANSI anges are 300# • indicates available ange connections
Inlet Flange
Standard
No Cost
Option
Extra Cost
Options
6 Vanes with
Vane Drivers
Buna-N Standard A
Neoprene
Cast Iron No charge option —
Silicon Carbide Standard 6
®1
4" ANSI • S
3" NPT • M
4" NPT • Q
3" WF • N
4" WF • R
160
(73)
265
(120)
Standard H
No charge option B
Model Number
Base X X X X X X
Outlet Flange
3" ANSI • P
Standard
Extra Cost
Options
Mounting Options
Description Model Part Number Maximum Driver (hp) Ship Weight (mounting only) lb
Mounting set up for V-belt drive. Includes steel baseplate,
adjustable motor slid base, V-belt drive and enclosed belt
guard
Part Number Test—Options
3000-X1 Hydrostatic test
3" NPT
Elongated
3" WF
Elongated
• T
• V
Z4500 103 -15 - 25 630
Z3500 103 -10- 20 560
20
Page 21

Appendix B—Specications
Equipment Type & Options
Truck sliding vane pump
Multiple connection options
Optional auxiliary inlet
Applications
Propane bulk transfer Auto-fuel pumping
NH3 nurse tanks Carousel cylinder lling
LPG cylinders
Features & Benets
Sliding vane: Positive displacement
Heavy duty bearings: Long bearing life
Single mechanical seal: Very easy seal replacement and maintenance
Built in relief valve (NPT models only): Factory pre-set—added protection
Pressure gauge connections: Suction and discharge to reduce piping needs
Reversible side plates: Longer service life
Operating Specications
RPM range: 420–800 RPM Max. differential pressure: 125 psid (8.6 bar d)
for Z/ZH2000, Z/ZH3200, Z/ZH4200, and Z4500
150 psid (10.3 bar d) for ZX/ZXH2000 and Z3500
Maximum working pressure: 350 psig (24.1 bar)
Temperature range: -25°F–225°F (-32°C–107°C) Flow range: 41–400 gpm (155–1,514 L/min)
Internal relief valve: Yes
Material Specications
Part Model Standard Material Optional Material
Case, head, rotor, reliefvalve cap, bearing cap
Cam All Gray iron ASTM A48, Class 50
Sideplate All Gray iron ASTM A48, Class 30
Welding ange All Steel
Seal seat All Silicon carbide
Seal metal parts
All Ductile iron ASTM A536
Z/ZH/ZX/ZXH2000,
Z/ZH3200, Z3500,
Z/ZH4200, Z4500
Steel
Stainless steel, Ni-Resist,
gray iron
Shaft All 8620 steel
Vanes and vane drivers All Advanced polymers
Z/ZH3200 Steel, cadmium plated
Relief valve spring
Relief valve
Bearing All Steel
Thrust bearing All Steel
O-rings All Buna-N
Retainer rings All Steel
1
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
Z/ZH/ZX/ZXH2000, Z3500,
Z/ZH4200, Z4500
Z/ZH3200, Z3500 Steel
Z/ZH/ZX/ZXH2000,
Z/ZH4200, Z4500
Stainless steel
Stainless steel
21
Kalrez®1, Neoprene®1,
®1
Viton
Page 22

Appendix C—Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, and ZXH2000
150125
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100755025
Differential Pressure (psid)
Capacity (gpm)
1
500 RPM
600 RPM
650 RPM
750 RPM
Performance Curves
1
The chart shows approximate deliver y rates as seen in vapor equalized propane systems at 70°F (21°C) with no pressure loss in pump suction piping.
The following will cause increased vaporization of the liquid in the pump suction, adversely af fecting the deliver y:
1. Restrictions in the suction piping such as internal valves, excess flow valves, elbows, etc.
2. Restriction or lack of a vapor return line
3. Temperatures below 70°F (21°C)
This loss of delivery is not caused by the pump but is a result of the natural thermodynamic properties of liquefied petroleum gases. See the
“GUIDE TO CORKEN LIQUEFIED GAS TRANSFER EQUIPMENT” (CP226) for additional information.
22
Page 23

Appendix C—Z3200 and ZH3200 Performance Curves
125
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
100755025
Differential Pressure (psid)
Capacity (gpm)
1
500 RPM
600 RPM
650 RPM
750 RPM
1
The chart shows approximate deliver y rates as seen in vapor equalized propane systems at 70°F (21°C) with no pressure loss in pump suction piping.
The following will cause increased vaporization of the liquid in the pump suction, adversely af fecting the deliver y:
1. Restrictions in the suction piping such as internal valves, excess flow valves, elbows, etc.
2. Restriction or lack of a vapor return line
3. Temperatures below 70°F (21°C)
This loss of delivery is not caused by the pump but is a result of the natural thermodynamic properties of liquefied petroleum gases. See the
“GUIDE TO CORKEN LIQUEFIED GAS TRANSFER EQUIPMENT” (CP226) for additional information.
23
Page 24

Appendix C—Z4200 and ZH4200 Performance Curves
125
180
200
220
240
260
280
300
320
340
360
100755025
400
380
Differential Pressure (psid)
Capacity (gpm)
1
500 RPM
600 RPM
650 RPM
750 RPM
1
The chart shows approximate deliver y rates as seen in vapor equalized propane systems at 70°F (21°C) with no pressure loss in pump suction piping.
The following will cause increased vaporization of the liquid in the pump suction, adversely af fecting the deliver y:
1. Restrictions in the suction piping such as internal valves, excess flow valves, elbows, etc.
2. Restriction or lack of a vapor return line
3. Temperatures below 70°F (21°C)
This loss of delivery is not caused by the pump but is a result of the natural thermodynamic properties of liquefied petroleum gases. See the
“GUIDE TO CORKEN LIQUEFIED GAS TRANSFER EQUIPMENT” (CP226) for additional information.
24
Page 25

Appendix C—Performance Charts
Z2000, ZH2000, ZX2000, and ZXH2000 Coro-Vane® Truck Pumps
Pump
Speed
Differential
Pressure
Approximate Delivery of
Propane
1
Brake hp
Required
Pump Torque
Required
RPM psid (kPa) gpm (L/min) bhp (kW) ft•lb (N•M)
750 50 (345) 82 (309) 2.9 (2.2) 2 0 .4 (27.7)
750 100 (689) 7 7 (2 91) 5.8 (4.3) 40.8 (55.3)
750 1502 (1,034) 75 (284) 8.9 (6.63) 62.2 (84.3)
650 50 (345) 69 (261) 2. 5 (1.9) 20.4 (27.7)
650 100 (689) 64 (242) 5.1 (3.8 ) 40.8 (55.3)
650 1502 (1,034) 63 (238) 7.7 (5.7) 62.2 (84.3)
600 50 (345) 63 (238) 2.3 (1.7) 2 0 . 4 ( 2 7.7 )
600 100 (689) 58 (219) 4.6 (3.5) 40.8 (55.3)
600 1502 (1,034) 56 (212) 7.1 (5.3) 62.2 (84.3)
500 50 (345) 52 (197 ) 1.9 (1.4) 20.4 (27.7)
500 100 (689) 4 6 (174) 3.9 (2.9) 40.8 (55.3)
500 1502 (1,034) 4 4 (166) 5.9 (4.4) 62.2 (84.3)
Z3200 and ZH3200 Coro-Vane® Truck Pumps
Pump
Speed
RPM psid (kPa) gpm (L/min) bhp (kW) ft•lb (N•M)
750 50 (345) 112 (424) 6.2 (4.6) 43.4 (58.9)
750 100 (689) 99 (375) 9.9 (7.4) 69.3 (94.0)
650 50 (345) 95 (360) 5.2 (3.9) 42.0 (57.0)
650 100 (689) 84 (318) 8.2 (6.1) 66.3 (89.9)
600 50 (345) 86 (326) 5.0 (3.7) 41.3 (56.0)
600 100 (689) 76 (288) 7. 8 ( 5 . 9) 6 4.8 (87. 9 )
500 50 (345) 70 (265) 3.8 (2.8) 39. 9 (54.1)
500 100 (689) 62 (235) 5.8 (4.3) 60.9 (82.6)
Differential
Pressure
Approximate Delivery of
Propane
1
Brake hp
Required
Pump Torque
Required
Z4200, ZH4200, and Z4500 Coro-Vane® Truck Pumps
Pump
Speed
RPM psid (kPa) gpm (L/min) bhp (kW) ft•lb (N•M)
750 50 (345) 369 (1,397) 12.5 (9.3) 87 (118.0)
750 100 (689) 325 (1,230) 2 5 .1 (18.6) 175 (237.3)
650 50 (345) 316 (1,19 6) 10.8 (8.0) 87 (118.0)
650 100 (689) 278 (1,052) 21.7 (16.1) 175 (237.3)
600 50 (345) 289 (1,09 4) 9.9 (7.3) 8 7 (118 . 0)
600 100 (689) 254 (961) 20.0 (14.8) 175 (237. 3)
500 50 (345) 236 (893) 8.3 (6.2) 8 7 (118 . 0)
500 100 (689) 208 (787) 16.7 (12.4) 175 (237.3)
1
Delivery times are approximate—see note on page 22 for further explanation.
2
Applies to ZX/ZXH2000 models only.
Differential
Pressure
Approximate Delivery of
Propane
1
Brake hp
Required
25
Pump Torque
Required
Page 26

Appendix C—Performance Curves
Z3500
26
Page 27

Appendix C—Performance Curves
Z4500
27
Page 28

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model Z2000
1/4" x 1-9/16" square key
INTERNAL RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLER TO PROVIDE
NOT FOR RECIRCULATING
SET AT 125 P.S.I. MAXIMUM
CORKEN, INC.
A Unit Of IDEX Corp.
SET AT 150 P.S.I.
SEPARATE BY-PASS VALVE
3-1/4
(8.25)
16
(40.61)
1-1/8
(2.85)
2-1/8
(5.40)
2-1/8
(5.40)
3/4
(1.9)
Inltet: 2" NPT
1/2
(1.2 7)
7/16
(1.11)
5-15/16
(15.08)
2-1/ 2
(6.35)
4
(10 .16)
9-1 /4
(23.5)
2-3/8
(6.03)
2-1/ 2
(6.35)
4- 9/16
(11. 59)
(10 .16)
4
Outlet: 2" NPT
5-1/2
(13.97)
4- 9/16
(11. 59)
1/4" NPT
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
28
Page 29

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model Z3200
Eight 7/8" (2.22) diameter holes
2" NPT auxillary inlet
2" NPT
discharge
1/4"
NPT
1/4" NPT
Internal
relief
valve
3" 300 lb ANSI flange inlet
1/4" square keyway
INTERNAL RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLER TO PROVIDE
NOT FOR RECIRCULATING
SET AT 125 P.S.I. MAXIMUM
CORKEN, INC.
A Unit Of IDEX Corp.
SET AT 150 P.S.I.
SEPARATE BY-PASS VALVE
8-3/4
(22.23)
6-3/4
(17.14)
5
(12.70)
3-7/8
(9.84)
14-15/16
(37.94)
10-15/16
(27.78)
4-15/16
(12.47)
1-1/8
(2.86)
17-1/2
(44.43)
1-5/8 (4.13)
3-7/16
(8.73)
5-11/32
(13.57)
2-7/16
(6.24)
1-1/8
(2.86)
8-1/4 D
(20.95)
6-5/8 BC
(16.83)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
29
Page 30

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model Z3500
18.750
(47.6)
1.750
(4.4)
1.750
(4.4)
1.250
(3.2)
1.250
(3.2)
8.435
(21.4)
7.188
(18.3)
5.375
(13.7)
4.125
(10.5)
4.125
(10.5)
3.000
(7.6)
3.000
(7.6)
1.758
(4.5)
1.125
(2.9)
3" NPT
inlet
1/4"
keyway
5.500
(14.0)
7.188
(18.3)
6.813
(17.3)
6.046
(15.4)
3" NPT
outlet
3.25
(8.18)
7.688
(19.5)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
30
Page 31

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model Z4200
2-1/8
(5.40)
C
O
R
K
E
N
C
O
R
K
E
N
2" NPT
auxillary
inlet
Internal relief valve
1/4" NPT
1/4" NPT
INLET
OUTLET
Eight 7/8 (2.22)
diameter holes
Outlet: 2" NPT
Outlet: 2" NPT
5/16" square key
5/16" square key
Inlet:
4" 300 lb ANSI
flange
13-13/16
(35.08)
7
(17.78)
7-3/4
(19.69)
8
(20.32)
3-1/4
(8.26)
16-31/32
(43.08)
2-5/8
(6.67)
1-3/16
(3.01)
4
(10.16)
4
(10.16)
19-1/2
(49.53)
1-1/4
(3.17)
10-1/8 D
(25.72)
7-7/8 BC
(20.00)
1-1/4 (3.18)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
31
Page 32

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model Z4500
8-Ø .875 (2.2)
on a 6-5/8" B.C.
Outlet
3" R.F. 300#
ANSI flange
21.121
(53.6)
2.875
(7.3)
2.875
(7.3)
Inlet
4" R.F. 300#
ANSI flange
8-Ø .875 (2.2)
on a 7-7/8" B.C.
5/16"
square key
10.75
(27.3)
1. 0
(2.5)
6.5
(16.5)
4-5/8 (1.587)
mounting holes
8.469
(21.5)
4.688
(11.9)
1.875
(4.8)
4.688
(11.9)
6.125
(15.6)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
32
Page 33

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model ZH2000
Hydraulic motor
Hydraulic drive adapter assembly
1/4" square keyway
INTERNAL RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLER TO PROVIDE
NOT FOR RECIRCULATING
SET AT 125 P.S.I. MAXIMUM
CORKEN, INC.
A Unit Of IDEX Corp.
SET AT 150 P.S.I.
SEPARATE BY-PASS VALVE
4248
Char-Lynn Hydraulics, Inc.
A Division of EATON
6.2 Cubic Inch / Rev
Disc Valve Hydraulic Motor
Model No. 104-1002
8
(20.30)
1-1/8 D
(2.85)
17-11/16
(44.90)
10-1/2
(26.63)
3-1/4
(8.25)
13/16
(2.06)
2-1/8
(5.40)
Inltet: 2" NPT
3/4
(1.9)
5-15/16
(15.08)
1/2
(1.2 7)
7/16
(1.11)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
4
(10 .16)
2-1/ 2
(6.35)
9-1 /4
(23.5)
33
2-3/8
(6.03)
2-1/ 2
(6.35)
4- 9/16
(11. 59)
(10 .16)
4
Outlet: 2" NPT
5-1/2
(13.97)
4- 9/16
(11. 59)
1/4" NPT
Page 34

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model ZH3200
Char-Lynn Hydraulics, Inc.
A Division of EATON
6.2 Cubic Inch / Rev
Disc Valve Hydraulic Motor
Model No. 104-1002
INTERNAL RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLER TO PROVIDE
NOT FOR RECIRCULATING
SET AT 125 P.S.I. MAXIMUM
CORKEN, INC.
A Unit Of IDEX Corp.
SET AT 150 P.S.I.
SEPARATE BY-PASS VALVE
1/4" square keyway
3" 300 lb ANSI flange inlet
Hydraulic drive
adapter assembly
Hydraulic motor
1/4" NPT
2" NPT
discharge
Internal relief valve
1/4" NPT
Eight 8-7/8 (2.22)
diameter holes
1-1/8
(2.87)
6-3/4
(17.15)
5-5/16
(13.57)
14-15/16
(37.94)
5
(12.70)
1-5/8 (4.13)
10-15/16 (27.78)
4-15/16 (12.47)
8-3/4 (22.22)
18-1/8 (46.02)
10-15/16 (27.75)
3-7/15
(8.73)
8-1/4D
(20.96)
3-7/8
(9.84)
6-5/8 D B.C.
(16.83)
2-7/16
(6.24)
1-1/8 (2.86)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
34
Page 35

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Model ZH4200
Hydraulic motor
2" NPT
auxillary
inlet
1/4" NPT
1/4" NPT
Inlet: 4" 300 lb
ANSI flange
5/16" square keyway
Eight 7/8 (2.22)
diameter holes
Outlet: 2" NPT Outlet: 2" NPT
Internal relief valve
Hydraulic drive
adapter assembly
19-9/16
(49.69)
9-3/4
(24.77)
12-3/8
(31.43)
4
(10.16)
8
(20.32)
3-1/4
(8.26)
10-1/8 D
(25.72)
7-7/8 B.C.
(20.00)
7-3/4 (19.69)
16-31/32 (43.08)
7 (17.78)
13-13/16
(35.08)
2-5/8
(6.67)
1-3/16
(3.01)
4
(10.16)
C
C
O
O
R
R
K
K
E
E
N
N
INLET
OUTLET
Char-Lynn Hydraulics, Inc.
A Division of EATON
6.2 Cubic Inch / Rev
Disc Valve Hydraulic Motor
Model No. 104-1002
MODEL
SERIAL
NO.
LISTED 656L
PAT. NOS. 3,072,066 AND 3,392,677
POWER OPERATED PUMP FOR LPG OR ANHYDROUS NH
READ CORKEN INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING
OKLAHOMA CITY,OKLAHOMA MADE IN U.S.A.
CORKEN,INC. A Unit Of IDEX Corp.
CORO-VANE
R
2-1/8
(5.40)
1-1/4 (3.18)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
35
Page 36

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Z3500–103 Mounting
15 (38.1)
12 (30.5)
1-1/2 (3.8)
4-1/2
(11.4)
5-3/16
(13.2)
3
(7.62)
18-1/8
(46)
3" NPT inlet3" NPT outlet
34 (86)
7-1/2 (19)
7-3/16 (18)
31-1/2 (80)
1-1/4 (3)
7-3/16
(18)
8-1/2
(22)
1/4" pipe plug Electric motor
Adjustable motor slidebase
Use four 1/2" anchor bolts
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
36
Page 37

Appendix D—Outline Dimensions for Z4500–103 Mounting
20 (50.80)
17 (43.18)
12-1/4 (31.12)
4 (10.16)
5-5/8
(14.30)
8-1/2
(21.59)
10-3/4
(27.31)
10-1/2
(26.67)
9-1/2
(24.13)
1-1/4
(3.18)
1-7/8
(4.76)
1-1/2
(3.81)
Baseplate web
Discharge
3" - 300# ANSI
Adjustable motor slide base
Use for 1/2"
anchor bolts
Electric motor
Beltguard
Inlet
4" - 300# ANSI
9-5/16 (23.65)
30-7/8 (78.44)
39-1/2 (100.33)
42 (106.68)
All dimensions are in inches (centimeters).
37
Page 38

Appendix E—Parts Details for Models Z/ZH/ZX/ZXH2000
36 (25 ft•lb)
Inlet
Outlet
37 (45 ft•lb)
37 (45 ft•lb)
35 (15 ft•lb)
36 (25 ft•lb)
36 (25 ft•lb)
34
14
36 (25 ft•lb)
14
40
41
O-ring Code
A Buna-N
B Neoprene
D Viton
E Tef l on
®a
®a
®a
Note: Hydraulic motor is not shown.
See pages 16 and 17 for repair/rebuild kits.
CAUTION: Always relieve pressure in the unit before attempting
any repairs.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 4413 Case 1
2. 4414 Cam 1
3. 4416 Head 2
4. 4417 Bearing cap 2
5. 1174 - 3 Relief valve cap 1
6. 4282
7. 4424 Cam key 1
8. 4425 Relief valve 1
9.
4426
1240
Shim (Z2000, ZH2000) 1
Shim (ZX2000, ZXH2000) 3
Relief valve spring (Z2000,
ZH2000)
Relief valve spring (ZX2000,
ZXH2000)
10. 4427 Sideplate 2
11. 4428
12. 4262-X Vane driver 3
13. 44 30-X 2R Rotor—shaft assembly 1
14.
15. 4432 Thrust bearing assembly 2
16. 4435 Bearing race mounting ring 2
b
4431-X_2
4431-X_6
c
c
Vane 6
Mech seal assy—cast iron 2
Mech seal assy—silicon carbide
17. 4438 Grease seal 2
4439 Bearing cap shim (.002) red
18.
443 9 -1 Bearing cap shim (.010) brown
4439-2 Bearing cap shim (.020) yellow
19. 275 4-X Roller bearing 2
20. 3253 Cam key pin 2
1
1
2
As
req.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
21. 2760-244 Retainer ring 2
22. 4441 Grease seal 2
23. 2270 Shaft key—1/4" x 1-9/16" 2
4479-2 Flange–2" NPT 2
24.
4479-2S Flange–2" welded
25. 2649 Nameplate 1
4248
26.
4248-1
Relief valve nameplate
(Z2000, ZH2000)
Relief valve nameplate
(ZX2000, ZXH2000)
27. 1359 Lubrication instruction plate 2
28. 134 3 1/8" NPT relief tting 2
29. 2158 1/8" NPT grease zerk 2
30. 2159 Lubricap 2
31. 3442 1/4" NPT pipe plug 2
32. 2-231_
33. 2-224_
34. 2-261_
35. 7001-031-NC125A Bolt—hexagon head 4
c
c
c
O-ring—ange 2
O-ring—relief valve cap 1
O-ring—case 2
36. 7001- 037-NC150A Bolt—hexagon head 16
37. 7001-0 43- NC125A Bolt—hexagon head 16
38. 7012-006-SF025E Screw 8
39. 720 6 - 0 37A Lockwasher 8
40. 4985 Shaft protector 1
41. 7012-010SF050E Screw 2
a
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
b
Slots in vanes must face TOWARDS the direction of rotation.
c
_ denotes O-ring code. See chart above.
38
1
1
Page 39

29 (15 ft•lb)
(25 f t•l b)
28 (60 ft•lb)
28 (60 ft•lb)
25 (25 ft•lb)
22
12
4
Inlet
Outlet
4
43
44
Appendix E—Parts Details for Models Z/ZH3200
O-ring Code
A Buna-N
B Neoprene
D Viton
E Tef l on
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
®a
®a
®a
1. 4495 -X2R Rotor shaft assembly 1
2. 4242 Cam 1
3. 4232
c
Vane 6
4. 4231 Sideplate 2
5. 4488 Head 2
6. 4239 Case 1
7. 4417 Bearing cap 2
8. 4438 Grease seal 2
9. 4435 Mounting ring 2
4439 Bearing shim (.002) red
10.
443 9 -1 Bearing shim (.010) brown
4439-2 Bearing shim (.020) yellow
11. 2270 Shaft key 2
12.
4431-X_2
4431-X_6
b
b
Mechanical seal assembly—
cast iron
Mechanical seal assembly—
silicon carbide
13. 2754 Bearing outer race 2
14. 4432 Thrust bearing assembly 2
15. 2760 -244 Retainer ring 2
16. 1174 - 2 Relief valve cap 1
17. 13 59 Lubrication instruction plate 2
18. 4441 Grease seal 2
19. 7012-0 06SF019E Screw 8
20. — Not shown –
21. — Not shown –
22. 2-262_
23. 2-224_
b
b
O-ring—case 2
O-ring—relief valve cap 1
24. 1240 Relief valve spring 1
a
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
b
_ denotes O-ring code. See chart above.
c
Slots in vanes must face TOWARDS the direction of rotation
As
req.
Note: Hydraulic motor is not shown.
See pages 16 and 17 for repair/rebuild kits.
CAUTION: Always relieve pressure in the unit before attempting
any repairs.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
25. 7001-037NC150A Bolt—3/8-16 x 1-1/2" hex head 16
26. 2158 1/8" NPT grease zerk 2
27. 1343 1/8" NPT relief tting 2
28. 7001-050NC150A Bolt—1/2-13 x 1-1/2" hex head 16
29. 70 01- 031NC125A Bolt—5/16-16 x 1-1/4" hex head 4
30. 1241 Relief valve 1
1172-1.5 Outlet ange—1.5" NPT 1
1172-1.5 S Outlet ange—1.5" WF 1
117 2-2 Outlet ange—2" NPT 1
31.
117 2-2S Outlet ange—2" WF 1
1947 Outlet ange—1.5" NPT ell 1
4243 Outlet ange—2" NPT ell 1
5520 Outlet ange—2" steel WF
2
2
32. 4241 Cam key 1
33. 3253 Cam key pin 1
34. 3442 1/4" NPT pipe plug 1
35. 4262-X Vane driver 3
36. 2-234_
37. 2159 Lubricap 2
1172-1.5 Aux. inlet ange—1.5" NPT 1
1172-15S Aux. inlet ange—1.5" WF 1
117 2-2 Aux. inlet ange—2" NPT 1
38.
117 2-2S Aux. inlet ange—2" WF 1
1920-3 Aux. inlet ange—blind 1
4243 Aux. inlet ange—2" NPT ell 1
39. 2649 Nameplate 1
40. 4248 Relief valve nameplate 1
41. 4282 Relief valve shim
42. 72 0 6 - 037A 3/8" lockwasher 8
43. 4985 Shaft protector 1
44. 7012-010SF050E Screw 2
b
O-ring—ange 1
As
req.
39
Page 40

26
27
28
29
23
10
16
17
25
24
13
12
11
30
32
37
38
39
31
4
20
7
41
15
44
21
36
40
42
3
5
8
43
1
19
6
34 (25 ft•lb)
34 (25 ft•lb)
22
2
14
18
35 (45 ft•lb)
9
34 (25 ft•lb)
33 (25 ft•lb)
Appendix E—Parts Details for Models Z3500
O-ring Code
A Buna-N
B Neoprene
D Viton
E Tef l on
®a
®a
®a
CAUTION: Always relieve pressure in the unit before attempting any repairs.
Note: Hydraulic motor is not shown.
See pages 16 and 17 for repair/rebuild kits.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 2-228
2. 2-245
3. 2-259
4. 2-268
b
b
b
b
O-ring 1
O-ring 1
O-ring 1
O-ring 2
1206-3 Inlet flange—3" NPT 1
1206-4 Inlet flange—4" NPT 1
5.
1206-3S Inlet flange—3" WF 1
1206-4S Inlet flange—4" WF 1
6. 1207-2 Relief valve cap 1
7. 1208-1X6 R Rotor shaft assembly 1
8. 1224 Relief valve 1
9. 130 9 Cam key 1
10. 1343 Grease relief fitting 2
11. 1359 Lubrication plate 2
12. 2158 Grease zerk 2
13. 2159 Lubricap 2
14. 2270 S h a f t key—1/4 " 1
15. 2649 Nameplate 1
16. 2754-X Roller bearing 2
17. 2760-244 Retainer ring 2
18. 3253 Cam key pin 2
19. 3442 Pipe plug—1/4" NPT 2
20. 3935 Sideplate 2
21. 3936
22. 4248 Relief valve warning tag 1
a
Registered trademarks of the DuPont company.
b
_ denotes O-ring code. See chart above.
c
Slots in vanes must face TOWARDS the direction of rotation
c
Vane 6
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
23. 4417 Bearing cap 2
24. 4432 Thrust bearing assembly 2
25. 4435 Thrust bearing mounting ring 2
26. 4438 Grease seal / Oil seal 2
27. 4439 Bearing cap shim—0.002" 2
28. 4439 -1 Bearing cap shim—0.010" 2
29. 4439-2 Bearing cap shim—0.020" 2
30. 4441 Grease seal 2
31.
6660-X_2
6660-X_6
32. 4985 Shaft protector 1
33. 7001-037NC125A Hex head bolt 24
b
b
34. 7001-037NC150A Hex head bolt 16
35. 7001-043NC150A Hex head bolt 6
Mechanical seal
assembly—cast iron
Mechanical seal
assembly—silicon carbide
36. 7012-006SF019E Screw 9
37. 7012-010SF050E Screw 2
2
2
38. 7206-037A Lock washer—0.375" 8
39. 5534 Head 2
40. 5537 Case 1
41. 5539 Cam 1
42.
5538
5538-3S
Outlet flange—3" NPT
Elongated
Outlet flange—3" WF
Elongated
1
1
43. 5548 Spring 1
44. 5554-X Vane driver 6
40
Page 41

18
37
(75 f t•l b)
36
(25 f t•l b)
40
36
(25 f t•l b)
36
(25 f t•l b)
36
(25 f t•l b)
41
Appendix E—Parts Details for Models Z/ZH4200
Note: Hydraulic motor is not shown.
See pages 16 and 17 for repair/rebuild kits.
CAUTION: Always relieve pressure in the unit
before attempting any repairs.
O-ring Code
A Buna-N
B Neoprene
D Viton
E Tef l on
®a
®a
®a
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 4442
2. 4443
3. 4444-X2R
4. 4445
b
b
b
b
Case 1
Cam 1
Rotor-shaft assembly 1
Head 2
5. 4446 Sideplate 2
6. 4448
c
Vane 6
7. 4449-X Vane driver 5
8. 4450 Relief valve cap 1
9. 4451 Relief valve spring 1
10. 4452 Shim 1
11. 4453 Thrust bearing assembly 2
12. 4454 Bearing race mounting ring 2
13. 4455 Cam key 1
14. 4456 Bearing cap 2
15. 4457 Relief valve 1
4458 Bearing cap shim (.002) red
16.
445 8-1 Bearing cap shim (.010) brown
4458-2 Bearing cap shim (.020) yellow
17. 4459 Shaft key—5/16 x 1-3/4 1
18. 4460 -X Roller bearing 2
19. 2760-283 Retainer ring 2
20. 3253 Cam key pin 5
21. 4462 Grease seal 2
a
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
b
_ denotes O-ring code. See chart above.
c
Slots in vanes must face TOWARDS the direction of rotation
d
Prior to January 1998.
As
req.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
22. 4463 Grease seal 2
4464 -X_2
b
23.
4464 -X_6
b
117 2-2 Aux. inlet ange—2" NPT 1
24.
117 2-2S Aux. inlet ange—2" WF 1
Mechanical seal
assembly—cast iron
Mechanical seal
assembly—silicon carbide
1920-3 Aux. inlet ange—blind 1
d
4479-2
25.
4981-2 Discharge ange—2" NPT 2
Discharge ange—2" NPT 2
26. 2649 Nameplate 1
27. 4248 Relief valve nameplate 1
28. 1359 Lubrication instruction plate 2
29. 1343 1/8 NPT relief tting 2
30. 2158 1/8 NPT grease zerk 2
31. 2159
32. 3442 1/4 NPT pipe plug 2
33. 2-231_
34. 2-234_
35. 2-270_
b
b
b
b
Lubricap 2
O-ring—discharge ange 2
O-ring—auxiliary inlet ange 1
O-ring—case 2
36. 7001-037NC150A Bolt—hexagon head 24
37. 7001-0 62NC125A Bolt—hexagon head 16
38. 7012-006SF019E Screw 8
39. 720 6 - 0 37A Lockwasher 8
40. 4985 Shaft protector 1
41. 7012-010SF050E Screw 2
2
2
41
Page 42

Appendix E—Parts Details for Model Z4500
O-ring Code
A Buna-N
B Neoprene
D Viton
E Tef l on
Note: Hydraulic motor is not shown.
See pages 16 and 17 for repair/rebuild kits.
CAUTION: Always relieve pressure in
the unit before attempting any repairs.
35
(25 f t• lb)
27
37
®a
®a
®a
39
40
15
9
10
33
8
21
18
19
12
36
14
11
29
22
16
31
30
7
3
23
38
35
(25 f t• lb)
17
5
34
4
20
36
(75 ft•lb)
25
37
26
1
24
32
13
20
32
28
2
6
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 5522 Case 1
2. 4443 Cam 1
3. 4444-X2R Rotor-shaft assembly 1
4. 4445 Head 2
5. 4446 Sideplate 2
6. 4448
c
Vane 6
7. 4449-X Vane driver 5
8. 4450 Relief valve cap 1
9. 4451 Relief valve spring 1
10. 4452 Shim 1
11. 4453 Thrust bearing assembly 2
12. 4454 Bearing race mounting ring 2
13. 4455 Cam key 1
14. 4456 Bearing cap 2
15. 4457 Relief valve 1
4458 Bearing cap shim (.002) red
16.
445 8-1 Bearing cap shim (.010) brown
4458-2 Bearing cap shim (.020) yellow
17. 4459 Shaft key—5/16 x 1-3/4 1
18. 4460 -X Roller bearing 2
19. 2760-283 Retainer ring 2
a
Registered trademark of the DuPont company.
b
_ denotes O-ring code. See chart above.
c
Slots in vanes must face TOWARDS the direction of rotation
As
req.
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
20. 3253 Cam key pin 5
21. 4462 Grease seal 2
22. 4463 Grease seal 2
Mechanical seal
assembly—cast iron
Mechanical seal
assembly—silicon carbide
23.
4464 -X_2
4464 -X_6
b
b
24. —— Inlet ange—4" ANSI 1
25. —— Outlet ange—3" ANSI 1
26. 2649 Nameplate 1
27. 4248 Relief valve nameplate 1
28. 1359 Lubrication instruction plate 2
29. 1343 1/8 NPT relief tting 2
30. 2158 1/8 NPT grease zerk 2
31. 2159 Lubricap 2
32. 3442 1/4 NPT pipe plug 2
33. 2-234_
34. 2-270_
b
b
O-ring—relief valve 1
O-ring—case 2
35. 7001-037NC150A Bolt—hexagon head 16
36. 7001-062NC125A Bolt—hexagon head 16
37. 7012-006SF019E Screw 8
38. 7206-037A Lockwasher 8
39. 4985 Shaft cover 1
40. 7012-010SF050E Screw 2
2
2
42
Page 43

Appendix E—Parts Details for Hydraulic Adapter (4496-X1)
Fits Models Z2000, Z3200, and Z3500 Only
16
13
11
10
5
14
17
15
4
3
16
9
14
17
2
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 134 3 Grease relief tting 1
2. 1359 Lubrication plate 1
3. 2158 Grease zerk 1
4. 2159 Lubricap 1
5. 2270 Shaft key 1
6. 4439 Bearing cap shim—0.002" 1
7. 443 9 -1 Bearing cap shim—0.010" 1
8. 4439-2 Bearing cap shim—0.020" 1
9. 4441 Grease seal 1
10. 4487-1
Hydraulic drive solid
coupling
11. 4496 Hydraulic drive bracket 1
12. 4497 Hydraulic drive bearing cap 1
13. 4499 Hydraulic drive name plate 1
14. 7001- 037NC150A Bolt—hexagon head 8
15. 7006-037NC037A Set screw 2
16. 7012-006SF019E Screw 6
72 0 6 - 037A Lock washer—0.375"
17.
12
16
1
8
6
7
1
8
43
Page 44

Appendix E—Parts Details for Hydraulic Adapter (4496-1X1)
Fits Models Z4200 and Z4500 Only
16
13
11
10
5
14
17
15
4
3
16
9
14
17
2
Ref.
Part No. Description Qty
No.
1. 134 3 Grease relief tting 1
2. 1359 Lubrication plate 1
3. 2158 Grease zerk 1
4. 2159 Lubricap 1
5. 2270 Shaft key 1
6. 4439 Bearing cap shim—0.002" 1
7. 443 9 -1 Bearing cap shim—0.010" 1
8. 4439-2 Bearing cap shim—0.020" 1
9. 4463 Grease seal 1
10. 44 87-2
Hydraulic drive solid
coupling
11. 4 496 -1 Hydraulic drive bracket 1
12. 4939 Hydraulic drive bearing cap 1
13. 4499 Hydraulic drive name plate 1
14. 7001- 037NC150A Bolt—hexagon head 8
15. 7006-037NC037A Set screw 2
16. 7012-006SF019E Screw 6
72 0 6 - 037A Lock washer—0.375"
17.
12
16
1
8
6
7
1
8
44
Page 45

Appendix F—V-Belt Selection for Stationary Coro-Vane® Pumps
1,450 RPM Motor
Belt
Number
B64 B15.4 B7.4 2 420 1-3V14.0 1-3V3.35 3V600
B60 B13. 6 B4.2 470 1- 3V10.6 1-3V2.80 3V530
B60 B12.4 B4.2 520 1-3V10.6 1- 3V 3.15 3V530
B55 B 11. 0 B4.2 580 1-3V10.6 1-3V3.65 3V560
B56 B 11. 0 B4.8 640 1-3V8.0 1-3V3.00 3V500
B64 B15.4 B4.4 3 420 2-3V10.6 2-3V2.65 3V530
B64 B15.4 B4.8 470 2- 3V10.6 2-3V2.80 3V530
A55 2A10 .6 2A3.6 520 1-3V14.0 1- 3V4.12 3V630
B55 2B11.0 2B4.2 580 1- 3V14.0 1-3V4.75 3V630
B60 B12.4 B5.4 640 2-3V8.0 2-3V3.00 3V500
B56 B 11. 0 B5.2 710 2-3V6.9 2-3V2.80 3V475
B53 B9.4 B4.8 780 1-3V8.0 1-3V3.65 3V500
B53 B8.6 B5.0 860 2-3V5.3 2-3V2.65 3V450
B51 B 7.4 B4.8 950 1-3V6.5 1-3V3.65 3V475
B64 2B15.4 2B4.4 5 420 3 -A13.2 3-A3.2 A60
B60 2B13.6 2B4.2 470 2-A13.2 2-A3.6 A60
B60 2B12.4 2B4.2 520 2-A12. 0 2-A3.6 A56
B55 2B11.0 2B4.2 580 2-3V10.6 2-3V3.65 3V560
B56 2B11. 0 2B4.8 640 3-3V8.0 3-3V3.00 3V500
B56 2B11. 0 2B5.2 710 2-3V8.0 2-3V3.35 3V500
B53 2B9.4 2B4.8 780 2-3V6.9 2 -3V 3.15 3V475
B53 2B8.6 2B5.0 860 2-3V6.5 2 -3V 3.15 3V475
B51 2 B 7.4 2B4.8 950 2-3V6.0 2-3V3.35 3V475
B64 3B15.4 3B4.4 7-1/2 420 4-A13.2 4-A3.2 A60
B64 2B15.4 2B4.8 470 3-A13. 2 3-A3.6 A60
B60 3 B12.7 3B4.2 520 3-3V14.0 3-3V4 .12 3V630
B55 3B11. 0 3B4.2 580 2- 3V14.0 2-3V4.75 3V630
B56 3B 11. 0 3B4.8 640 2- 3V14.0 2-3V5.30 3V630
B56 3B 11. 0 3B5.2 710 2-3V10.6 2-3V4.50 3V560
B53 3B9.4 3B4.8 780 3-3V6.9 3 - 3V 3.15 3V475
B53 3B8.6 3B5.0 860 3-3V6.5 3 - 3V 3.15 3V475
B51 3 B 7. 4 3B4.8 950 2-3V8.0 2- 3V4.50 3V530
B71 3B18.4 3B5.2 10 420 3-3V19.0 3 -3V4.50 3V710
B71 2B18.4 2B5.8 470 3- 3V19.0 3-3V5.00 3V 710
B60 4B12.4 4B4.2 520 3-3V14.0 3-3V4 .12 3V630
B55 4B11.0 4B4.2 580 3-3V14.0 3 -3V4.50 3V630
B56 4B11. 0 4B4.8 640 2- 3V14.0 2-3V5.30 3V630
B62 3 B12.4 3B5.8 710 2-3V14.0 2-3V5.60 3V630
B56 3B 11. 0 3B5.8 780 2-B12.4 2-B5.6 B60
B62 3 B12.4 3 B 7.0 860 2-3V10.6 2-3V5.30 3V560
B60 3B9.4 3B6.0 950 2- 3V10.6 2-3V5.60 3V560
B71 4B18.4 4B5.2 15 420 4-3V19.0 4-3V4.75 3V710
B71 3B18.4 3B5.8 470 4 -3V19.0 4-3V5.00 3V 710
B62 5B13.6 5B4.8 520 3 -3V19.0 3-3V5.60 3V750
B60 5B12.4 5B4.8 580 4-3V14.0 4 -3V4.75 3V630
B56 5B11. 0 5B4.8 640 3 -3V14. 0 3-3V5.30 3V630
B56 5B11. 0 5B5.2 710 3-3V14.0 3-3V5.60 3V630
B53 5B9.4 5B4.8 780 3-B12.4 3-B5.6 B60
B53 5B8.6 5B5.0 860 2-B12.4 2-B6.0 B60
B51 5 B 7.4 5B4.8 950 2 -B11.0 2-B6.0 B56
B75 4B18.4 4B6.6 20 520 4-3V19.0 4-3V5.60 3V750
B68 4B15.4 4B6.8 640 4 -3V14.0 4-3V5.30 3V630
B64 4B12.4 4B6.6 780 3- B13. 6 3-B6.0 B62
B68 3B13.6 3B8.0 860 4- 3V10.6 4-3V5.30 3V560
B65 3B12.4 3B8.0 950 3-B11. 0 3-B6.0 B56
5VX680 4-5V15.00 4-5V5.50 25 520 4-B18.4 4-B5.2 BX76
5VX700 3- 5V14.0 3-5V6.30 640 4-B16.0 4-B5.6 BX70
5VX680 3-5V12.5 3-5V6.70 780 3 -B15.4 3 - B 7. 4 BX71
5VX660 3 - 5 V11.3 3-5V6.70 860 4-B15.4 4-B6.6 BX70
Sheave Pitch Diameter Sheave Pitch Diameter
Pump Motor Pump Motor
Motor
Hp
Nominal
Pump RPM
1,750 RPM Motor
Belt
Number
45
Page 46

Appendix F—V-Belt Selection for the Z4500
1,450 RPM Motor
Belt
Number
3VX690 QD 3/3V14.0 0 Q D3/3V4.12 7. 5 420 QD3/3V19.0 0 QD3/3V4.75 3/3V800
3VX710 QD3/3V14.00 QD3/3V4.50 470 QD2 /3V19.0 0 QD2/3V5.30 3VX800
3VX710 QD3/3V14.00 QD3/3V5.00 520 Q D3/3V14.00 QD3 /3V4.12 3VX690
3VX630 QD3/3V10.6 0 QD3 / 3V4.12 580 QD 3/3V14.0 0 QD3/3V4.50 3V X710
3VX650 QD 3/3V10.6 0 QD3 /3V4.75 640 QD2/3V14.00 QD2/3V5.30 3VX710
2/3VX 710 Q D2 /3V14.00 QD2/3V6.90 710 Q D3/3V10.60 QD3/3V4.50 3V650
3VX650 QD2/3V10.60 QD2/3V5.60 780 QD2/3V14.00 QD2/3V6.50 2/3VX710
3VX600 QD3/3V8.00 QD 3/ 3V4.75 860 QD2/3V10.60 QD2/3V5.30 3VX650
3VX580 QD3/3V6.90 Q D3/3V4 .5 0 950 QD 2/3V10.60 QD2/3V6.00 3VX670
3VX690 QD 3/3V14.0 0 Q D3/3V4.12 10 420 QD 3/ 3V14 .0 0 QD3/3V3.35 3VX690
3VX710 QD2/3V14.00 QD 2/3V4.75 470 QD3/ 3V14 .0 0 QD3/3V3.65 3VX690
3VX710 QD2/3V14.00 QD2/3V5.00 520 QD3/3V10.60 QD3 / 3V3 .15 3VX616
3VX710 QD2/3V14.00 QD2/3V5.60 580 QD2A15.6/B16.0 QD2A4.8/B5.2 2/B72
3VX650 QD2/3V10.60 Q D2 /3V4.75 640 QD2A15.0/ B15.4 QD2A5.0/B5.4 2/B71
3VX650 QD2/3V10.60 QD2/3V5.30 710 QD1A15.6/B16.0 QD1A6.0/B6.4 B74
3VX570 QD3/3V6.90 QD3/3V3.65 780 Q D2/3V10.60 QD2/ 3V4.75 3VX650
3VX600 QD2/3V8.00 QD 2/3V4.75 860 QD2/3V10.60 QD2/3V5.30 3VX650
3VX580 QD2/3V6.90 Q D2 /3V4.5 0 950 QD3/3V6.00 QD3/3V3.35 3VX550
3/3VX800 QD 3/3V19.00 QD3/3V5.60 15 420 QD3/3V25.00 QD3/3V6.00 3/3V900
3/3VX800 QD 3/3V19.00 QD3/3V6.00 470 QD3 /3V19.00 QD3/3V5.30 3VX800
3V830 QD3/3V19.00 QD3/3V6.90 520 QD3/ 3V19.00 QD3/3V5.60 3/3VX800
3VX710 QD3/3V14.00 QD3/3V5.60 580 QD3/ 3V19.00 QD3/3V6.50 3V810
3V730 QD3 /3V14.00 QD33/3V6.00 640 QD3 /3V14.00 QD3/3V5.30 3/3V710
3/3VX710 Q D3 /3V14. 00 QD3/3V6.90 710 Q D3/3V14.00 QD3/3V5.60 3V X710
3VX650 QD 3/3V10.6 0 QD3/3V5.60 780 QD3/3V10.6 0 Q D3 /3V4.75 3V X650
3/3VX670 QD 3/3V10.6 0 QD3/3V6.50 860 QD3/ 3V10.60 QD3/3V5.30 3VX650
3/3VX670 QD 3/3V10.6 0 QD3/3V6.90 950 Q D3/3V10.60 QD3/3V6.00 3VX670
B78 QD3A18.0/B18.4 QD3A6.0/B6.4 20 520 QD3A18.0/B18.4 QD3A5.0/B5.4 3/B77
B73 Q D3A15.0/ B15.4 QD3A6.2/B6.6 640 QD3A18.0/B18.4 QD3A6.0/B6.4 3/B78
B68 QD 3A12.0/B12.4 QD3A6.2/B6.6 780 QD3A15.0/B15.4 QD3A6.4/B6.8 3/B73
B65 QD3A10.6/B11.0 QD3A6.0/B6.4 860 QD 3A13. 2/B13.6 QDA6.2/B6.6 3/B70
B78 QD4A18.0/B18.4 QD4A6.0/B6.4 25 520 QD3/5V18.70 QD3/5V5.50 3/5VX800
B80 QD3A18.0/B18 .4 QD3A7.6/B8.0 640 QD3A18.0/B18.4 QD3A6.2/B6.6 3/B78
B75 Q D3A15.0/B15.4 QD3A7.6/B8.0 780 QD3/5V10.90 QD 3/ 5V4.90 5VX650
B72 QD3A13.2/B13 .6 QD3A7.6/B8.0 860 QD3A13.2/ B13. 6 QD3A6.2/B6.6 3/B70
Sheave Pitch Diameter Sheave Pitch Diameter
Pump Motor Pump Motor
Motor
Hp
Nominal
Pump RPM
1,750 RPM Motor
Belt
Number
Appendix G—Troubleshooting Guide
In diagnosing pump and system troubles, record the
following data during product transfers:
1. Pressure at pump suction.
2. Pressure at pump discharge.
3. Pressure in truck tank.
Problem Cause Solution
Low capacity Pump speed too slow Check engine speed and PTO on pulley ratio. Consult pump
performance curve. Use tachometer on pump if speed is
questionable.
High differential pressure Restriction in discharge piping or hose too small. Vapor
equalization lines too small or not used.
External bypass valve stuck
Readjust, repair, or replace valve.
open or set too low
Clogged strainer Clean strainer.
4. Pressure in tank being lled.
5. Pipe size and length of suction and discharge lines.
6. Size and length of vapor equalizing line.
7. Pump speed if practical.
46
Page 47

Appendix G—Troubleshooting Guide (continued)
Problem Cause Solution
Low capacity
(continued)
Pump runs but no
ow
Pump will not turn–
locked up
Will not build
pressure
Pump is noisy Cavitation from poor suction
Pump leaks
around shaft
Suction pipe too small or
restricted
Worn vanes Replace.
Pump without vapor return Without vapor equalization, a pump can remove only about 3%
Worn sideplates Reverse or replace sideplates. Check universal drive assembly
Vanes sticking Remove vanes and clean out foreign matter (check strainer).
Valve closed Check valves. Make sure internal tank excess ow valve is
Excess ow valve slugged Stop pump until valve opens. If problem continues, slow pump
Broken shaft Disassemble and inspect pump. Repair if necessary.
Defective meter Service meter.
Foreign matter in pump Clean out the pump —check strainer in suction line.
Vanes broken Clean out pump carefully and replace vanes. Has pump been
Bearing seized Replace pump bearings. Grease monthly. Use ball bearing
Moisture frozen in pump Let thaw and break loose carefully. Add methanol to tank (on
Poor suction conditions Clean inlet strainer. Increase pipe size.
External bypass valve set too
low
Worn vanes and/or sideplates Disassemble, inspect and repair as necessary. Do not run dry!
conditions
Vanes sticking As above.
Bearings worn Replace—grease monthly.
Meter screen clogged Clean
Very high differential pressure Check for restriction in discharge line. Delivery hose too small
PTO shaft vibration Inspect and repair driveline component.
Seal or O-rings failed Inspect seal assembly and replace if necessary. Keep new
Indicated by pump inlet pressure dropping several pounds
when pump is started. Remove restriction or modify piping.
of the truck tank capacity per minute without severe cavitation
and capacity loss.
to make sure angularity is within limits, yokes are parallel and
slip-joint is greased. Check bearings. Check pulley alignment
on belt drive pumps.
Replace vanes if swollen.
open! Refer to manufacturer’s instructions.
down or install a new or larger excess ow valve.
operated dry? Then, check for damage to cam and rotor shaft
assembly.
grease manufactured for intended service.
LP-Gas). Check with product supplier about possibility of water
in gas.
Set valve for higher pressure—see instructions. See IH102 and
IH106 IOM manuals for more information.
As above.
and too long. Slow down pump!
Check vapor release oat assembly on meter and meter
differential valve.
seal very clean when replacing seal. Recommend a light oil
lm on O-rings. Do not run pump dry!
47
Page 48

Appendix H—Storage of the
Z-Series Coro-Vane® Pump
Appendix I—Hydraulic Motor
Specications
1
If your Corken Z-Series pump is to be removed from
service for some time, the pump must be protected
as propane, butane and anhydrous ammonia all leave
the metal “bare” and open to corrosion. Piping and
tanks not in service should also be protected, as the
rust particles can destroy the pump’s seals almost
immediately after startup.
1. Fill or thoroughly ush the pump with a light rust
inhibiting oil. (If the pump is ushed with oil, placing
some desiccant packets inside the pump will provide
added protection.)
2. Plug all pump openings.
3. Store in a dry location.
4. Before placing the pump back into service, drain the
oil and remove any desiccant packets.
5. Refer to the “OPERATION OF YOUR PUMP” section
of this manual.
Operating Specications for Char-Lynn Hydraulic Motor
Mounting ange 2 bolt SAE A
Input shaft
Port ‘A’ 7/8-14 O - ring
Port ‘B’ 7/8-14 O - ring
Pilot diameter
Motor displacement
Maximum speed continuous duty 742 RPM
Flow continuous duty 20 gpm (76 L/min)
Torque continuous duty
Case drain 7/16-20 O -ring
Recommended uids
Minimum viscosity 70 SSU (13 cSt)
Maximum operating temperature 180°F (82°C)
1
Data applies to this particular motor only. Your application may vary,
please consult factory for details.
1 in. diameter
straight keyed
3.250/3.245 in.
(57.15 /57.0 2 m m)
6.2 cubic in. per
revolution
3,500 in•lb
(395.5 N•M)
Premium quality
anti-wear
Solutions beyond products...
CORKEN, INC. • A Unit of IDEX Corporation
3805 N.W. 36th St., Oklahoma City, OK 73112
Phone (405) 946-5576 • Fax (405) 948-7343
Visit our website at http://www.corken.com
or e-mail us at cocsalesdept@idexcorp.com
@CorkenInc
Printed in the U.S.A.
June 2016
 Loading...
Loading...