Page 1

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Revision Date: August 26, 2011
VCX-7401 Dual H.264/MPEG-4 Encoder with H.264 Decoder
Core Tec Communications, LLC
2950 Lake Emma Rd
Suite 1030
Lake Mary, FL 32746 USA
Phone (407) 331-0547
Fax (407) 331 0656
www. coretec.com
Technical Support:
U.S. 877-331-0547
(Toll Free)
Elsewhere: 407-331-0547
1
Page 2

2
Page 3

Introduction
The model VCX-7401 is the stand-alone H.264/MPEG4 version of the VCX
family and is housed in a 8.5-inch 1U rack mount case with a control port and a
universal AC power supply.
The VCX Digital Video transport system consists of two video encoders, H.264
and MPEG4, and a decoder. This makes up the encoder(selectable)/decoder pair
providing the capability for one-way end-end transmission of the compressed
digital video stream in the H.264 format. The encoding-decoding process is
applied to an NTSC (or PAL) video input, selected in software.
Modification of video format and resolution, data sub-channel characteristics, and
basic IP parameters is achieved through one of the following means:
a) Terminal Program
b) Telnet through the Ethernet connection
c) Web Interface Applet
d) SNMP
NOTE: The VCX7401 is optimized for encoder or decode operation. While both
the encoders and decoder can be used simultaneously, it is not recommended as
perfomance issues may occur. The exception is using the decoder to view it's
own H.264 stream, as this has minimal affect on performance.
3
Page 4

Familiarization with the VCX-7401
The VCX-7401 Video Encoder accepts one BNC video in, one BNC Video Out
and one data sub-channel. The encoder has a programmable reset, which prompts
the re-initiation of the video stream. The decoder also has a programmable reset
command, tied to errors in the incoming video stream, as well as a reboot
command.
Birds Eye view of the VCX-7401
Front Panel
Front view of the VCX-7401
4
Page 5
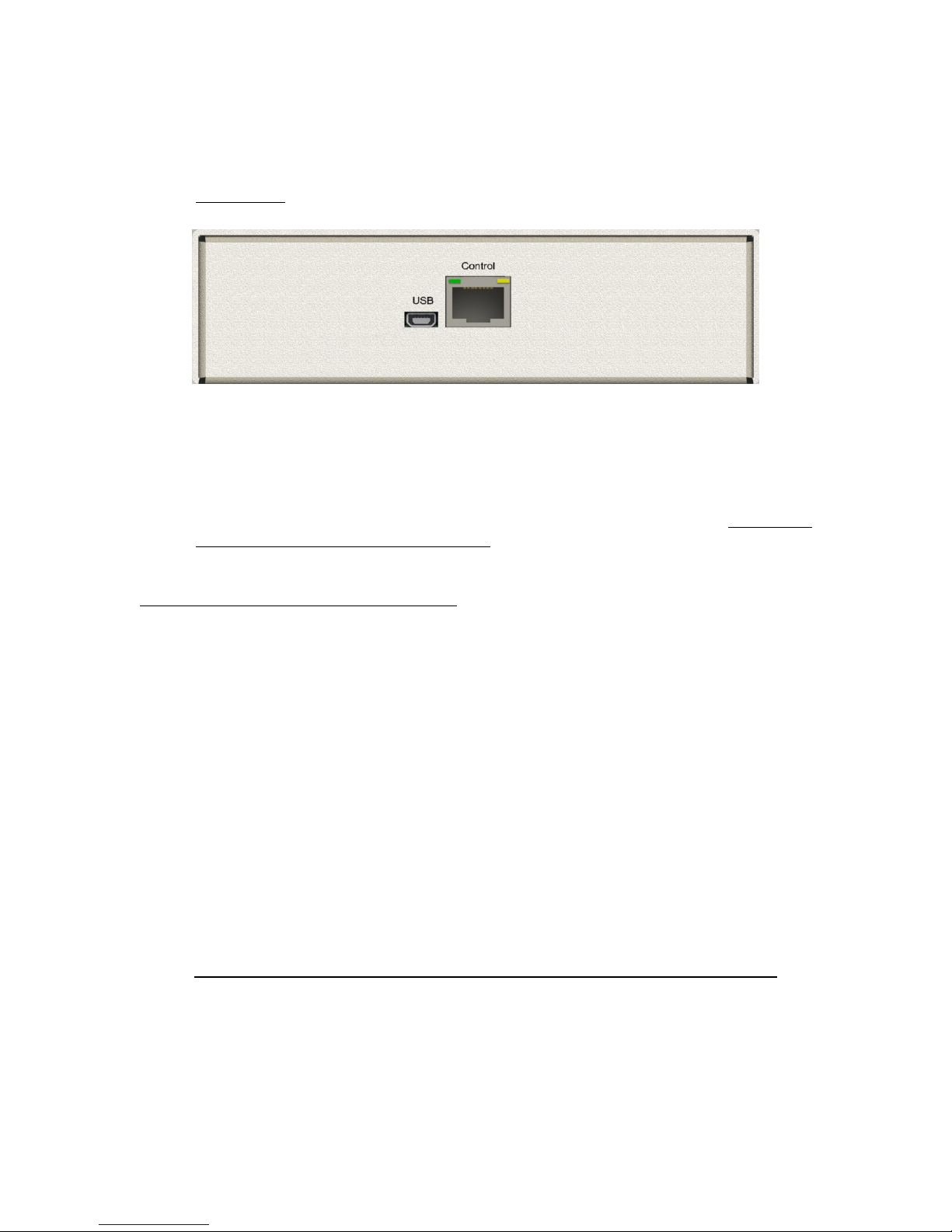
Back Panel
Rear view of the VCX-7401
Com Port Data Interface
There is one bi-directional data interface, RS-232 and RS-422 selectable, on the encoder,
which uses a RJ-45 connector. Refer to Table below for the correct pin out. When using
the RS-232 configuration pin 4 is ground. Com Port parameters are configured through
the system software.
Refer to Appendix A for the correct pin out.
Video Input Interface
Connect a BNC-terminated coaxial cable from a composite video source (e.g., CCTV
camera) to the BNC connector labeled “VIDEO IN” (encoder). The composite video
input should be in NTSC or PAL format. The maximum length of cable that should be
interfaced to the encoder or decoder is 100 feet, although the specific installation
environment will dictate the actual permissible length.
Ethernet Interface
There is one Ethernet interface for encoder or decoder, which uses a standard RJ-45
connector. The standard method of terminating an ETHERNET cable reflects the
TIA568A standard (Telecommunications Industry Association standard).
Refer to Appendix A for the Straight Through and Crossover Ethernet Pin Out.
Power
Power is applied through a standard IEC type detachable line cord at the rear of the unit.
The unit automatically senses 110 VAC or 220 VAC supply and will operate with either.
5
Page 6

The typical current is 1.2 amps from a 110VAC line and drops to 0.9 amps from a 230
VAC line source.
Mounting the Device
The VCX-7401 Encoder is a 8.5 inch wide device and provides holes for
mounting onto a chassi. The unit can be mounted in any orientation.
Updating Firmware with TFTP
TFTP is a simple and reliable way of updating the firmware on any device. All that is
required is to have access to a TFTP server which will be used as the host and contain the
update file, which is named vcx7401.tgz.
Via Telnet, enter the following command in order to update the firmware for the device
that is being used.
TFTP <Server IP Address>
IP Configuration
Overview
The commands contained in this section provide the means to configure
critical network, com ports, encoder, and decoder parameters. The user should
consult the factory if specific functions of interest do not appear to be supported.
Initial IP Addressing
To set the device parameters properly, encoder and decoder units must be
given appropriate IP addresses, compatible with the network on which they are to
be connected. The software module VXNETCONFIG was developed to allow a
network administrator to set the IP and Subnet in the VCX-7401.
• Installation
To load VXNETCONFIG insert the CORE TEC CD into your CD drive. Select
VXNETCONFIG by double clicking on the program. The following window will
open:
6
Page 7
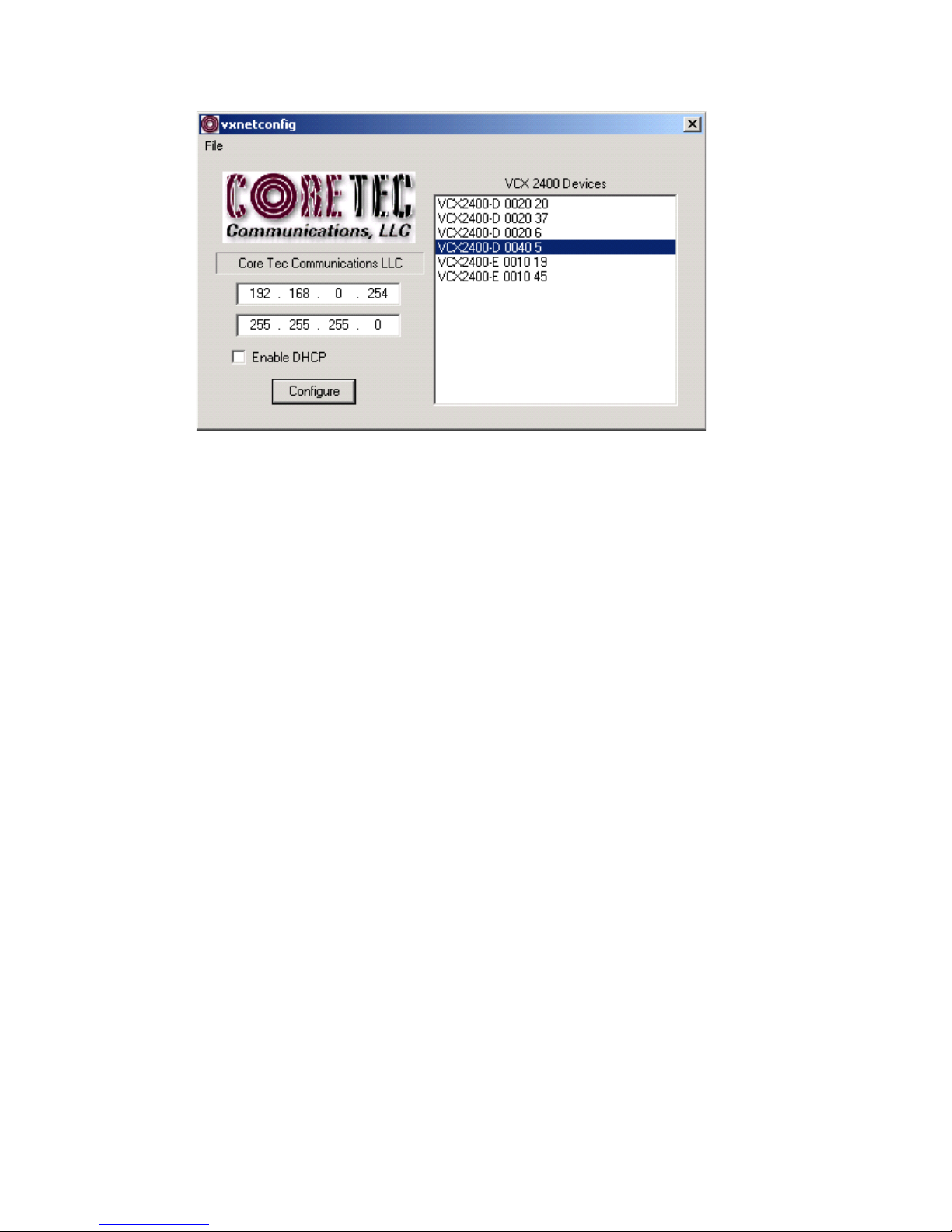
VCXNETCONFIG Window
7
Page 8

Description of Program Functions
(a) The first box on the left hand side of the window displays the current IP
address of the CORE TEC device being interrogated. Type the new IP
address into this space
(b) The second box is used to change the SUBNET address. Note that the address
displayed is always 255.255.255.0. Type the new SUBNET address into this
space.
(c) The Enable DHCP box is checked when DHCP is to be enabled.
NOTE: DHCP is not currently enabled on the VCX-7401. Selecting DHCP
Will have no affect.
NOTE: Do not enable DHCP if sub-channels are being used of if there is no
DHCP server. Check with the Network Administrator, or call Core Tec
Tech Support if further assistance is needed.
(d) The Configure button is to execute the requested changes to the IP and
SUBNET information. Note that future queries of the SUBNET will indicate
255.255.255.0. Therefore, the correct SUBNET address should always be
entered prior to using the Configure button.
(e) The box on the right hand of the window displays all VCX-7401 devices
(encoders and decoders) on the network.
(f) To make a change to the equipment addressing perform the following
steps:
(g) Select the Core Tec device address from the list in the box on the right side of
the window.
(h) Move the cursor to the IP box and select the first octet by highlighting the
octet. Enter the new IP data for the selected octet. As the 3 digits are entered,
the software will automatically highlight the next octet for change. Complete
entering the IP address and then switch to the SUBNET data.
(i) Move the cursor to the SUBNET box and select the first octet by highlighting
the octet. Enter the new SUBNET data for the selected octet. As the 3 digits
are entered, the software will automatically highlight the next octet for
change. Complete entering the SUBNET data.
(j) To execute the change press the configure button. The IP address and the
SUBNET will be updated in the selected Core Tec equipment. The new IP
8
Page 9

address will be displayed. The SUBNET will display a default class CSUBNET there is no read back of the changed SUBNET displayed.
(k) Repeat this process for all the CORE TEC equipment requiring change.
Connecting to the Unit
There are currently three ways to connect to the VCX-7401.
1. Telnet
Password: admin (default)
To change the default password perform the following:
Type: PASSWORD <followed by your password (up to 11 characters)>
Where <your password> equals the new password.
For configuration using an Ethernet connection, activate the Telnet function by
the following:
• Initiating from the Command Prompt - Telnet nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
• Use the MS Windows – START – RUN Telnet nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
(where nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn is the IP address of the unit being configured)
Employ the command set as described below.
Note that the initial IP addresses (factory default) are:
Encoder 192.168.0.253
Decoder 192.168.0.254
Sub net Mask 255.255.255.0
2. Terminal Program
NOTE: The following procedure is valid for standalone units only and is not
applicable to rack mount units.
The Terminal Program, such as HyperTerminal, configuration procedure uses the
serial connection on the front of the unit.
9
Page 10

Using the PCA-2400 programming cable, connect to the control port. This cable
should be attached to the serial port of an attached PC and the Hyper Terminal
program launched. The PC should have its Com Port configured as:
Baud rate 115,200 kbps
Data bits 8 bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit
Flow control None
Activate the HyperTerminal function, normally found in a sub-menu under
ACCESSORIES. Employ the command set as described in the following section.
Password: admin (default)
To change the default password perform the following:
Type: PASSWORD <followed by your password (up to 11 characters)>
Where <your password> equals the new password
3. Web Interface
To get to the Login Page of the web interface applet, the user needs to type in the
IP adress of the device into a URL. On the Login Page, shown below, the user will
need to type in the password to login successfully.
10
Page 11

Login Page of Web Interface Applet
When the unit accepts the log in (default password: admin), the following web
page will be displayed.
11
Page 12

On the top of the screen is a front view image of the device. If you click on any of
these ports the associated tab will appear below the image inside the tabbed pane.
Also an animation will appear for a few seconds on the bottom right corner. The user
may click here in order to to be sent to tutorial page. The user will find here, all the
associated documents to the VCX-7401, such as the manual, as well as video tutorials
on how to use the device and the web applet. Aside from clicking on the ports inteh
image of the device at the top of the applet, they can click directly on the tabs below.
There are currently nine tabs to choose from: Main, Network, Subchannel, OSD,
Video, MPEG4, H264, Decoder and Miscallaneous. To the right the user will see 7
buttons: Logout, Commit, Commit/Reboot, Reboot, Open Manual and two other
buttons that allow you to view either the H264 or MPEG4 video stream on a new web
page.
12
Page 13

Main Tab
13
Page 14

Network Tab
14
Page 15

Subchannel Tab
15
Page 16

OSD Tab
16
Page 17

Video Tab
17
Page 18

MPEG4 Tab
18
Page 19

H264 Tab
19
Page 20

Decoder Tab
20
Page 21

Miscallaneous Tab
Logout Button
The logout button will log the user out with out commiting any changes
that may have been made during the current session. Any changes that were made
will stay until the device has been rebooted.
Commit Button
The commit button will commit any changes that may have been
configured in the current seesion. If you reboot after pressing the commit button,
then all changes will be commited and saved and viewable upon reboot.
Commit/Reboot Button
The commit/reboot button will also log out the user and also commit any
changes that may have been configured in the current seesion. This means that
when the devices shuts down and reboot the changes that were made will still be
in effect.
21
Page 22

Reboot Button
The reboot button will immediately shut down the device and reboot. If any
changes were made during the session and not commited, then they will not stay
in effect after reboot completes.
NOTE: This is good to use if the user has made many new configurations but
doesn't wish to keep them.
Open Manual
The open manual button is just a shorcut to open this manual.
View H264 Video
This button will open a new page where the H.264 video stream may be
viewed.
View MPEG4 Video
This button will open a new page where the MPEG4 video stream may be
viewed.
4. SNMP
Please refer to SNMP Commands for VCX-7401 Document.
Program Commands
IMPORTANT NOTES:
1. After entering one or more commands, it is necessary to enter COMMIT and REBOOT for
the new settings to take effect.
2. Typing “?” displays a listing of all commands.
3. The prompt will tell you if commands related to the encoder and decoder are applied to one
or the other. If the prompt is “Encoder>” then the command applies to the encoder.
Likewise, if the prompt is “Decoder>” then the commans applies to the decoder. The current
mode can be changed by typing MPEG4, H264 or DECODER at the prompt.
22
Page 23

Network Setup
IP (IP Address)
The IP address setup is in the form of decimal dotted notation. The selection of
an IP should come from the person who administrates the network. The current IP
selection is static. A dynamic IP setting using DHCP is planned for future enhancement.
Default:
Example command:
IPMASK (IP Subnet Mask)
The IP Subnet Mask is in the form of decimal dotted notation. The selection of
an IP subnet mask should come from the network administrator. It is used to represent
the number of bits in the current IP subnet.
Encoder - 192.168.0.253
Decoder - 192.168.0.254
IP 192.168.0.10 (sets IP address to 192.168.0.10)
Default: 255.255.255.0
Example command:
IPMASK 255.255.240.0
GATEWAY <ip-address> [<ip-subnet address> <subnet mask>]
The GATEWAY command can have either one or three parameters. The first
parameter is the IP address of the host that is the gateway. Optionally you may include
the IP address and the subnet mask of the subnet you want to route through the gateway.
You can program up to five gateway entries.
Default: No Gateways
Example command:
GATEWAY 192.168.0.1
The following example indicates that all packets sent to hosts on the
62.41.1.0.xxx subnet should be routed though the gateway at 192.168.0.2
Example command:
GATEWAY 192.168.0.2 62.41.1.0 255.255.255.0
CLEARGATEWAY
This command will clear the gateway table. There are no parameters. This
command clears all entries.
23
Page 24

CMDPORT <TCP command port number>
The TCP command port selection is configurable. However, the default setting
should be adequate for normal operation.
Default: 5000
Example Command:
CMDPORT<sp>5010 (sets TCP command port to 5010)
VIDEOIP <video destination IP address>
The video destination IP is an address that allows the reception of the H.264
stream by a single (unicast) or multiple (multicast) device(s).
NOTE: Class D IP addresses, in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 are called
multicast addresses. The range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for local purposes
and the range 239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 is reserved for administrative scooping. Both
the encoder and decoder should be set to the same Video IP for correct operation
together.
Default: 239.5.6.8
Example Command:
VIDEOIP 234.5.6.10 (sets multicast IP to 234.5.6.10)
VIDEOPORT <video multicast port number>
The video multicast port selection is configurable. However, the default setting
should be adequate for normal operation. The port number should use even numbers
only for proper operation with some video playback software.
Default: 4568
Example Command:
VIDEOPORT 4570 (sets multicast port to 4570)
Common Commands
The following commands apply to both encoders and decoders.
COMMIT
This command saves the parameter changes in permanent memory. A commit
command must be issued before a reboot or power cycle if the new device settings are to
be maintained.
24
Page 25

DEATHBLOW
This command causes a reboot of the device. The purpose of this command is to
cause a reboot from the password prompt. If you cannot login into the command, prompt
because of the “Another administrator is logged in.” message, then you can use
DEATHBLOW as the password to return the unit to the power up state.
EXIT
Exits from the command prompt and releases the current login. You may also
use the following alternatives… LO (Log Off) and QUIT.
NTSC
This command sets unit for NTSC video operation.
PAL
This command sets unit for PAL video operation.
REBOOT
This command restarts device from power-up state. Most changes in device
settings require a reboot after a commit.
START
This command starts encoding or playback (video out).
STOP
This command stops encoding or playback (video out).
VER
This command displays the software version/build date, BSP (board support
package) version/build date, and board revision.
Example response:
Version: VCX7401 v1.6a, Date: 29JUN11
25
Page 26

COM Port Setup
The VCX-7401 supports one sub-channel that allows two-way transmission of
serial data to selected target devices. The sub-channel can be configured for either
RS232 or RS422 operation. It is not necessary for both ends to use the same
configuration. The following is a list of the configuration items for the sub-channel:
Channel Enable
Baud rate
Parity
IP address of target
TCP port for operation
RS422 or RS232
COM <0|1>
This command sets the active state of the com port. The parameter is “0” or “1”, where
“1” enables and “0” disables the com port function. At this time, the com port is always
enabled and this command has no effect.
Default: 0 (OFF)
Example Commands: COM 1 (enables com port 1)
COM BAUD <Comm Port Baud Rate>
This command sets the baud rate for the comm port. Valid values are 2400,
4800, 9600, 19200, and 38400. Other data rates may be functional but are not tested.
Default: 9600
Example Command: COMBAUD 4800
(sets baud rate for com port at 4800 bps)
COM PARITY <O|E|N>
The parity for the com port can be set to Odd, Even, or None. The parameters for
the COM[1|2]PARITY command are N,O,E, which correspond respectively to None,
Odd, Even.
Default: None
Example Command: COMPARITY N (sets com port to no parity)
COM IP <Com Port IP>
The IP address of the destination for the com port data is set by this command. A
typical setup would have an encoder and a decoder. The decoder would have a com port
IP address that is the same as the encoder. In addition, likewise, the encoder’s com port
IP would be the same as the decoder. Notice that the default com ports IP’s are the
opposite of the default device IP’s.
Default:
26
Page 27

Encoder com ports - 192.168.0.253
Decoder com ports- 192.168.0.254
Example Command: COMIP 192.168.0.10 (points the com port data to an
encoder, decoder, or other device whose IP address is 192.168.0.10)
COM PORT (Com Port)
The com port selection is configurable. However, the default setting should be adequate
for normal operation.
Default:
Com port - 5002
Example Command: COMPORT 5010 (sets com port to port 5010)
COM RS422 <0|1>
The com port data-format is configurable. The parameter is “0” or “1”, where
“1” enables RS-422 and “0” enables RS-232 format.
Default: 0 (RS-232)
Example Command: COMRS422 0 (sets com port for RS-232)
COM TCP <0|1>
The Com port can use either TCP or UDP to transfer serial data. TCP
provides more reliable transfer, but requires that the device be configured for
server or client. See the COM SERVER command for this setting.
1= Use TCP, 0=Use UDP
COM SERVER <0|1>
When using TCP to transfer Com serial data the device needs to be configured
for client or server. The recommended convention is to set the Encoder, which is
connected to the camera PTZ to the server.
1 = server, 0 = client
OSD COMMANDS (On Screen Display)
These permit the configuration of the On-Screen-Display(OSD) properties of the
encoder. This section is for labeling the video stream. The OSD is only supported in D1
resolution streams at this time. The same OSD will be on both MPEG-4 and H.264
encoders at D1 resolution.
OSDENABLE <0|1>
27
Page 28

Enables of disables display of the on screen display.
OSD <1…2> <label text>
This command permits up to two lines of text to be configured for display with
the outgoing video stream. The text lines must be assigned from 1 to 2 in order and
unassigned lines between assigned lines are not permitted. All five lines need not be
assigned text strings.
Example:
osd 1 This is the first line of text.
osd 2 This is the second.
This is the first line of text.
This is the second
OSDX <1…2> <x pos=1...60>
This command will locate the line of text associated with the number 1-2 with the
horizontal location defined by the <x pos>.
Example:
osdx 1 50 will set the first character of the line of text 1 to x position 50.
OSDY <1…2> <y pos=1...22>
This command will locate the line of text associated with the number 1-2 with the
horizontal location defined by the <y pos>.
Example:
Note:When using the OSDX and OSDY commands, the screen resolution must be taken
into account. Locating the first character outside the video frame will prevent that entire
line from being displayed. If the first character is within the field but the string is longer
that the video frame the string will be cut short. Characters are 12x20 pixels and relate to
the current resolution set by the “PROFILE” command. The range of coordinates starts
with 0 and continue to the maximum pixel range divided by 16 (character size) and
subtract 1 ( because 0 is the first position).
Example:
D1 resolution in the vertical (Y direction) is 480 and yields 24 line locations
(480/20)-1=24 so line 1 to line 24 are the available Y locations.
OSDCLEAR
This command will clear all the fields configured by the previous commands.
Video Commands
These are associated with the quality of video being encoded. The resolution both
in frame size and in the time domain are supported in this command set.
osdy 1 22 will set the first character of the line of text 1 to y position 22.
ENCODER <1 or 2>
28
Page 29

This command switches the command mode to ENCODER. Any video
commands apply to the encoder in this mode. Encoder #1 is the H264 encoder and #2 is
the MPEG-4 encoder. You may also use the command H264 in place of ENCODER 1
and MPEG4 in place of ENCODER 2.
DECODER
This command switches the command mode to the DECODER. Any video
commands apply to the decoder in this mode.
BITRATE [n]
This command adjusts the bit rate (in kbits/sec) of the encoded H.264 video.
Default: The default is set by the Profile command
Example Command: BITRATE 2000 (Sets max bit rate to 2 Mbits/sec)
Notes: This command should be issued AFTER the Profile command if the
Profile command is used.
FPS [n]
Sets encoded frames/second. Where n = frames per second of the video stream
For NTSC: (i.e. 30, 15, 10, 7, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1)
For PAL: (i.e. 25, 12, 8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1)
RES <D1|CIF|QCIF>
Sets encoder resolution. Currently H264 only supports D1. The MPEG-4
encoder supports all listed resolutions.
QCIF - 176x120
CIF - 352x240
D1 - 720x480
BRIGHT [n]
This command adjusts image brightness. The acceptable range is from 0 to 255,
where a higher number provides more brightness.
Default: 128
Example Command: BRIGHT 170 (increases brightness from default setting)
CONTRAST [n]
This command adjusts image contrast. The acceptable range is from 0 to 255,
where a higher number provides more contrast.
Default: 63
Example Command: CONTRAST 90 (increases contrast from default)
SATURATION [n]
Adjusts color saturation. The acceptable range is from 0 (no color) to 255.
29
Page 30

Default: 63
TINT [n]
SAP Settings
The encoder is capable of multicasting SAP (Session Announcement Protocol RFC-
2974) packets with SDP (Session Description Protocol RFC-2327) content. There are a
number of parameter settings for configuring SAP. They are presented in this section.
The user should refer to the referenced RFCs to understand the significance of the
SAP/SDP parameter settings.
SAP
This command is used to enable or disable the SAP multicast. ON or OFF are the
permitted parameters.
Example Command: SATURATION 75 (increases color saturation from default)
Adjusts color tint. The acceptable range is from –128 to 127.
Default: 0
Example Command: TINT 10 (adjusts tint)
Default: OFF
Example: SAP ON
SAPINFO
This command is used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) info information. The
parameter is an ASCII string with a limitation of 62 characters.
Default: Core Tec VCX2400e
Example: SAPINFO Intersection of 1st and main
SAPINTERVAL
This command sets the interval between SAP packet transmissions. The
parameter is the number of milliseconds between transmits.
Default: 5000 ms (5 seconds)
Example: SAPINTERVAL 10000 ms (10 seconds)
SAPIP
This command sets the IP address of the destination host for SAP packets. This
address is a multicast address defined in RFC-2974. It is unlikely that the user will need
to change this setting.
Default: 224.2.127.254
SAPNAME
30
Page 31

This command is used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) name information. The
parameter is an ASCII string with a limitation of 30 characters.
Default: Core Tec Communications, LLC
Example: SAPNAME Main Street Camera #1
SAPPORT
This command sets the destination port for SAP packets. The port number is
defined in RFC-2974. It is unlikely that the user will need to change this setting.
Default: 9875
SAPUPDATE
Issue this command after changing the SAP parameters to update all devices listening to
SAP multicasts.
SNMP Settings
This command allows the encoder to set the SNMP trap receiver. You may add or
remove the receiver from the encoder.
Format: SNMPMANAGER [ADD:REMOVE] <n.n.n.n> [abcdef...]
Example: snmpmanager add 192.168.5.66 public
RWCOMMUNITY
This command sets the read/write community name. (The SNMP Manager must
know this Community name in order to “Get” or “Set” messages.) It allows the SNMP
manager to issue “Get” and “Get Next” messages as well as “Set” messages.
Format: RWCOMMUNITY <abcdef…>
Example: rwcommunity private
ROCOMMUNITY
This command sets the read only community name. (The SNMP Manager must
know this Community name in order to “Get” messages.) It allows the SNMP manager to
issue “Get” and “Get Next” messages only.
Format: ROCOMMUNITY <abcdef…>
Example: rocommunity public
31
Page 32

Miscellaneous Settings
DISPLAY <ENCODER|DECODER|COM|IP|SAP|OSD|SNMP|NAME|MISC>
This command displays current encoder settings. Entering DISPLAY only
provides all settings. Adding the the second word displays those respective settings
specifically.
Example Command: DISPLAY IP (displays current IP encoder settings)
JVM (JOIN VIDEO MULTICAST)
This command causes the encoder to join the IGMP multicast group for it's own
stream. It was implemented because some switches will broadcast the video multiple cast
to all ports when no decoder has joined the multicast stream.
Example: JVM [1|0]
1=on
0=off
32
Page 33

Specifications
PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL
Dimensions
8.5” x 5.25”
Mounting
R-12 Card Cage Enclosure
Weight
.6 pounds
Temperature
-20 degrees to + 70 degrees Centigrade
(-4 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit)
Humidity
0 to 95% non-condensing
POWER REQUIREMENTS
From Enclosure
CONNECTORS
Video
NTSC/PAL BNC
Power
From Back-plane (36 pin Molex)
Data
Network RJ-45
Comm ports RJ-45
ELECTRICAL
Video Input (NTSC/PAL)
Impedance: 75 ohm unbalanced, return loss > 30 dB
Dynamic
Range: . 5 volts to 2.0 volts peak to peak
33
Page 34

Video Output (NTSC/PAL)
Impedance: 75 ohm unbalanced, return loss > 30 dB
Output Level: 1.0 volts peak to peak nominal
(.9 volts minimum to 1.1 volts maximum)
Sync Level: 257 mV (36 IRE) to 314 mV (44 IRE)
Bar Level: 642 mV (90 IRE) to 785 mV (110 IRE)
Burst Level: 257 mV (36 IRE) to 314 mV (44 IRE)
Resolution: Full D1: 720h x 480v (NTSC); 720h x 576v (PAL)
Frame Rate: 1 to 30 frames per second maximum
Data (Network)
Format: Ethernet IEEE 802.3; 10/100 Base T
1/2 D1: 352h x 480v (NTSC); 480h x 576v (PAL)
CIF: 352h x 240v (NTSC); 352h x 288v (PAL)
QCIF: 160x120
QQCIF: 80x60
Line Rate: down to 64kbps
Data (Sub-channels)
Format: RS-232 or RS-422 (programmable) (2)
Data Rates: 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400 bps
Programming Data
Format: EIA RS-232C (primary data lines)
Rate: 38.4 kbps
Form: 8-bit data, 1 stop bit, no parity
34
Page 35

Models
BASE MODELS
VCX-7401 H.264 encode and decode, MPEG-4 encode
35
Page 36

Appendix A
Pinouts
RS-422/RS-232 Serial Data Port Pin-out (uses RJ-45 Plug)
RS-232 Programming Port Pin-out (uses RJ-45 Plug)
Pin Description
1 RS-232 Receive (Input)
2 Ground
3 RS-232 Transmit (Output)
4 Ground
5 RS-422 RX+
6 RS-422 TX7 RS-422 RX8 RS-422 TX+
Pin Description
1 Receive (Input)
2 Ground
3 Transmit (Output)
4 Ground
5 Unused
6 Unused
7 Unused
8 Unused
36
Page 37

Straight Through Ethernet Pin Out Cross Over Ethernet Pin Out
Standard Ethernet Pin Out
37
Page 38

38
 Loading...
Loading...