Coretec VCX-2400-E, VCX-2400-ER, VCX-2400-DR, VCX-2400-D Installation And Operating Instructions Manual
Page 1

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Revision Date: March 3, 2010
VCX-2400-E MPEG-2 Encoder, IP
VCX-2400-ER MPEG-2 Encoder, IP Rack Mount
VCX-2400-D MPEG-2 Decoder, IP
VCX-2400-DR MPEG-2 Decoder, IP Rack Mount
Core Tec Communications, LLC
2950 Lake Emma Rd
Suite 1030
Lake Mary, FL 32746 USA
Phone (407) 331-0547
Fax (407) 331 0656
www.coretec.com
Technical Support:
U.S. 877-331-0547
(Toll Free)
Elsewhere: 407-331-0547
Page 2

TableofContents
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 3
Familiarization with the VCX2400-E ......................................................................................... 4
Com Port Data Interface ............................................................................................................. 5
Video Input Interface .................................................................................................................. 5
Ethernet Interface ........................................................................................................................ 5
Audio Interface ........................................................................................................................... 5
Power .......................................................................................................................................... 5
Display ........................................................................................................................................ 6
Mounting the Encoder ................................................................................................................. 6
Quick Start ...................................................................................................................................... 7
If user wishes to test video using the VCX-2400-E and VCX-2400–D: .................................... 7
If user wishes to configure settings of VCX2400-E via COM Port or Network: ....................... 8
Updating Firmware using VCXNetBurner ................................................................................... 10
Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 10
Overview ................................................................................................................................... 10
Screenshots ............................................................................................................................... 10
Menu Bar .................................................................................................................................. 13
Instructions for Use ................................................................................................................... 16
IP Configuration............................................................................................................................ 16
Overview ................................................................................................................................... 16
Initial IP Addressing ................................................................................................................. 16
Connecting to Unit ........................................................................................................................ 18
Program Commands...................................................................................................................... 28
Network Setup .......................................................................................................................... 28
Comm Port Setup .................................................................................................................. 30
Encoder Commands .............................................................................................................. 32
Decoder Commands .............................................................................................................. 35
Common Commands ............................................................................................................ 38
SAP Settings ......................................................................................................................... 40
Page 3

MISCALLANEOUS SETTINGS ......................................................................................... 42
Specifications ................................................................................................................................ 42
Model Numbers ............................................................................................................................ 44
Appendix A ................................................................................................................................... 45
Pinouts....................................................................................................................................... 45
Com Port Data Interface Pin Out (uses RJ-45 Plug)............................................................. 45
Standard Ethernet Pin Out .................................................................................................... 46
RJ-11 to Serial Interface Adaptor Pinout .............................................................................. 47
Introduction
The VCX-2400-E and VCX-2400-D are the chassis versions of the Core Tec stand-alone VCX2400 MPEG-2 IP product series. These units are fully compatible with the “-R” card cage versions of the
product series.
The VCX-2400 Digital Video Codec system consists of a video encoder/decoder pair providing
the capability for one-way end-end transmission of compressed digital video in IP packets at data rates in
the 1.2 to 6.0 Mbps range.
The system employs MPEG-2 MPEG2 standard ISO/IEC 13818-2 (ITU-T H.262) encoding. The
encoding-decoding process is applied to an NTSC (or PAL) video input, selected in software.
The video encoder converts the analog video to a serial digital signal, which is multiplexed with
any data sub-channels present. The stream is then formatted into a series of IP packets sent to the
network through a standard Ethernet connection.
Modification of video format and resolution, data sub-channel characteristics, and basic IP
parameters is achieved through one of the following means:
a) A Terminal Program
b) Telnet through the Ethernet connection
c) Core Tec Watchdog software
d) Web Interface (only available for VCX-2400-E)
The video decoder receives the IP packets, separates the video data from the data sub-channels,
and converts the video data to analog form, providing an NTSC (or PAL) output.
The units feature two bi-directional data sub-channels (programmable for RS-232 or RS-422). Data
bits are multiplexed with the digital data stream.
Page 4

FamiliarizationwiththeVCX2400E
The VCX-2400-E Video Encoder accepts one video and two data signals. The output from the
encoder is a stream of IP packets. It also contains a fluorescent LED display to allow monitoring of unit
performance and to facilitate troubleshooting. The encoder has a programmable reset, which prompts the
re-initiation of the video stream.
The VCX-2400-D Video Decoder accepts the signal from the network originally generated by a
VCX-2400-E video encoder. The unit effectively decompresses this data stream and re-creates an analog
waveform in NTSC (or PAL) video format. The unit supports the bi-directional data transmission of two
data sub-channels, corresponding to the encoder. The unit also features an LED display. The encoder has
a programmable reset, which prompts the re-initiation of the video stream, as well as a reboot command.
The decoder also has a programmable reset command, tied to errors in the incoming video stream, as well
as a reboot command.
Front Panel
Control Port
-Used to directly
communicate with
encoder to configure
settings
Power
switch
-controls
unit power
the
VCX2400-E-H, Full Size Encoder
Back Panel
Power Supply
Refer to “Power
Interface” in
Table of Contents
VCX2400-E-H, Half Size Encoder
Video Input
Please refer to
“Video Interface” in
table of
contents
Ethernet
Refer to “Ethernet
Interface” in Table
of Contents
2 Data Subchannels
Refer to “Com Port
Data Interfaces” in
Table of Contents
Page 5

ComPortDataInterface
There are 2 bi-directional data interfaces, RS-232 and RS-422 selectable, on the encoder and
decoder assemblies. Each interface uses RJ-45 connectors. Refer to Appendix A for the correct pin out.
When using the RS-232 configuration pin 7 is ground.
system software.
Refer to Appendix A for the correct pin out
.
Com Port parameters are configured through the
VideoInputInterface
Connect a BNC-terminated coaxial cable from a composite video source (e.g., CCTV camera) to
the BNC connector labeled “VIDEO IN” (encoder). The composite video input should be in NTSC or
PAL format. The maximum length of cable that should be interfaced to the encoder or decoder is 100
feet, although the specific installation environment will dictate the actual permissible length.
EthernetInterface
There is one Ethernet interface for encoder and decoder, which uses a standard RJ-45 connector.
Refer to Appendix A for the correct pin out.
Refer to Appendix A for the Straight Through and Crossover Ethernet Pin Out.
AudioInterface
There is an optional stereo audio Interface for each assembly, which uses the standard RCA-type
audio connector. This is contained on units equipped with the “-A” option. Stereo audio connection is
made via the two stacked (red – right channel; white – left channel) RCA type audio connectors. These
connectors are located next to the video (BNC) connector.
Audio levels are standard line level (1 v p-p) levels.
Note that the audio is uni-directional, in the same direction as the video.
Power
Power is applied through a standard IEC type detachable line cord at the rear of the unit. The unit
automatically senses 110 VAC or 220 VAC supply and will operate with either.
Note that the LED display will be illuminated when power is applied. The display will show
parameters upon activation of the ON/Off switch.
Page 6

Display
The fluorescent LED display provides a scrolling list of key parameters when the unit is in its active (nonstand-by) state.
The display is a two-line display. Each parameter is displayed, in turn, for three seconds on the
bottom line. It then moves to the top line while the next parameter is displayed on the bottom line.
The parameters displayed are as follows:
Name of unit
Software version
Device IP address
Sub-net mask
Video IP (multi-cast group)
Maximum Bit Rate (encoder only)
Audio On or Off
Com 1 On or Off
Com 1 Bit Rate
Com 1 IP
Com 2 On or Off
Com 2 Bit Rate
Com 2 IP
MountingtheEncoder
The VCX-2400-E Encoder and VCX-2400-D Decoder mount in an identical fashion. The 1RU
high units are furnished with mounting ears allowing installation in a 19” rack frame.
All signal connections are from the rear, eliminating any need for setback from the front plane of
the rack. The user programming port on the front panel is used to alter system parameters via Hyper
Terminal.
A circulation fan is located on the side of the unit.
Page 7

QuickStart
IfuserwishestotestvideousingtheVCX2400EandVCX2400–D:
1. Unpack the VCX-2400-E Video Encoder.
2. Connect a BNC-terminated coaxial cable from a composite NTSC (or PAL) video source
(e.g., CCTV camera) to the BNC connector labeled “VIDEO IN” on the VCX-2400-E Video
Encoder.
3. Connect a BNC-terminated coaxial cable to a composite NTSC (or PAL) video output (e.g.,
CCTV monitor) to the BNC connector labeled “VIDEO OUT” on the VCX-2400-D Video
Decoder.
4. Connect the VCX-2400-E Video Encoder to the VCX-2400-D Video Decoder via the
Ethernet port (RJ-45), located to the left of the two RJ-45 sub channel-ports on the rear of
each unit, using a Cat 5 Ethernet cross over cable (the send and receive pairs are swapped
end-to end). Normally, when units are connected to an Ethernet Switch, straight through
cables are used, unless connecting to a crossover port on the Ethernet Switch.
Refer to Appendix A for Ethernet Straight through and Cross Over Pin Outs.
5. Insert the detachable line cord into the receptacle on the rear of the VCX-2400-E Encoder and
VCX-2400-D Decoder. The unit automatically senses 110 VAC or 220VAC supply and will
operate with either.
6. The LED display will be illuminated when power is applied.
7. The display will scroll through the parameters currently programmed in the unit.
8. After a few moments, video should appear on the output of the VCX-2400-D Video Decoder.
9. If no video is present on the VCX-2400-D decoder verify the following:
a. Both the Encoder and Decoder LED display are in the operate mode. Display should
indicate “Core Tec Communications Initializing”.
b. The link light on the Ethernet port (RJ-45), located on the upper left of the port
connector is lit on both the Encoder and Decoder. If not the Ethernet cross over cable
may be defective.
c. If the above are correct, please read the network setup installation instructions
included in the manual. Note: the setting in default network setup may have been
changed.
Page 8

IfuserwishestoconfiguresettingsofVCX2400EviaCOMPortorNetwork:
Set up for COM Port:
User may configure VCX2400-E setting using a PC connected to the encoder control port
at the front of the unit. A simple 6-wire phone cable (PCA-2400 programming cable) with the
RJ-11 adaptor described in Appendix A will supply the proper RS-232 connection to the PC’s
serial port. Note: This is not the same as the “Sub-Channel” interface. Do not use the RJ-11
adaptor for this channel.
This configuration will permit the unit configuration by a terminal program running on a PC.
Once you have connected the encoder to the PC’s serial port open your terminal program. The
encoder will boot up then ask for a password. The default password is: admin.
The PC should have its Com Port configured as:
Baud rate 38,400 kbps
Data bits 8 bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit
Flow control None
Refer to Appendix A for pin layout for RJ-11 connector.
Set up for network:
If the operator wishes to configure the unit through the network the user may accomplish
this by the following procedure. Note: The operator must be sure that the VCX-2400-E is
accessible on their SUBNET. Before completing this step, please refer to the Programming
Configuration Section of this Manual. Here you will set the IP address and SUBNET Mask of
the VCX-2400-E so that it is accessible on your SUBNET and has a valid IP address. (An
example IP address is being used in the following example.):
Open a “cmd” window and enter the following commands:
Telnet192.168.0.253 <enter>
The encoder will reply asking for a password. Default password is “admin”.
Password: admin
Having used either of these methods, the encoder is ready to receive configuration commands.
Main unit configuration
The VCX-2400-E units incorporate support for one form of encoding from two different input
channels. It is important the operator understand this to be able to configure the unit properly. All
commands follow this simple format:
(command<space>parameter<enter>)
Page 9

From the command prompt, the operator may view the current configuration by entering the
“display” command. This will dump the entire configuration status for the selected encoder. Remember
there are two encoders in one unit. Enter the following configuration for each of the encoder channels.
Take note the IP address must be of valid encoders on the network. The IP addresses below are just used
as an example. Locate a VCX-2400-E (MPEG2 encoder).
Connection Configuration
ip 192.168.5.150 (use a valid IP on your network)
ipmask 255.255.240.0
name CoreTec Encoder
com1 1
com1ip 192.168.5.151 (IP address of the decoder that is sending sub-channel commands)
com1tcp 1 (assume a universal decoder)
com1server 0
com1timeout 10
com1baud 38400
MPEG2 Configuration
The MPEG2 encoder requires the following parameters be configured to your network:
videoip 239.5.5.151 (use a valid IP on your network)
port 4570
bitrate 1000
res cif
fps 15
Saving Configuration
When all the configuration parameters have been entered, they must be saved to memory and the unit
restarted by entering the following command:
Commit<enter> (please wait a moment until the following prompt appears:)
COMMIT
DONE
Reboot<enter>
Page 10

UpdatingFirmwareusingVCXNetBurner
Introduction
VcxNetburner is a Windows 2000/XP application that allows updating of the VCX-2400
Encoder/Decoder firmware (as well as the VCX4400E and VCX6400E.) VcxNetBurner can
simultaneously update the firmware of all VCX-2400 devices that can be accessed on your network. If
you can telnet to the device then VcxNetBurner can update the firmware. The only exception is that the
device’s current firmware version must be v1.5 or higher. Firmware v1.4 does not contain the update
feature.
Overview
VcxNetBurner has a few interface features that the user should be familiar with before attempting to
update a device. The basic steps are… 1) import the firmware description, 2) broadcast the server IP, and
then 3) initiate the update. However the user needs to be aware of the general process, optional steps,
potential problems, and what to do in the case of an error. We will start with an overview of the user
interface.
Screenshots
The Activity Screen
The Activity screen contains a list of the current activity and a history of past update operations.
A VCX-2400 device that has finished updating will indicate either 1) Complete, 2) Version Current, or 3)
Failed. The Device column lists the serial number of each unit that is responding to the update command.
NOTE: It is important that a VCX-2400 device that has a Failed status NOT be turned off or rebooted.
At the point that the failure occurs the device will not be in a bootable state. If power is cycled or the
firmware cannot be updated without failure after repeated attempts then the firmware chip will need to be
Page 11

replaced. The 10Mbps revision 2.5 devices (in current production) have removable chips that can be
replaced in the field. The 100Mbps revision 3.0 devices must be reprogrammed at the factory. Since
revision 3.0 is not yet in production there may be other safeguards, such as automatic firmware backup
that may modify these instructions.
When a device is in the process of upgrading, the Activity screen will show the progress as a percent of
complete for each stage. There are four stages.. 1) Erasing, 2) Startup Code, 3) Application Code, and 4)
FPGA. When erasing the progress may not update but erasure will compete in a few seconds. The startup
code frequently completes so quickly that you don’t see it in the Status column.
After the FPGA status reaches completion you should see the Status column change to
Complete. If it changes to Failed at any time during the firmware update you will need to retry updating
the firmware for that unit before cycling power or rebooting.
The Clear Complete button will clear the list display of any operations that did not fail. The Clear Failed
button will clear the list display of any failed operations. The Initiate Update will Broadcast a command
to all online units to connect to the update server to perform a firmware update. Normally the update
server will be the computer that is running VcxNetBurner. However it would be possible to have VCX2400 devices configured to use a different server. When Initiate Update is pressed, all of the VCX-2400
devices within range of multicast packets will connect to its preset update server.
The VCX-2400-D Screen
The VCX2400D is accessed through the VCX-2400D tab and displays the parameters used to select the
version of the firmware sent to VCX-2400 decoder devices. This information is imported from a
import.ini file that is provided with each firmware update. This screen allows the operator to see what
update is selected. It is important to confirm that the files indicated in the file selection boxes are located
on your computer. The import file is selected using the menu’s File- >Import option. This is explained
later in this document. The Apply button saves the current setting on this screen so that when
VcxNetBurner is loaded these parameters are restored. The Revert button will reload the currently saved
parameter set. So if you have modified this screen it can be restored if you haven’t used apply.
Page 12
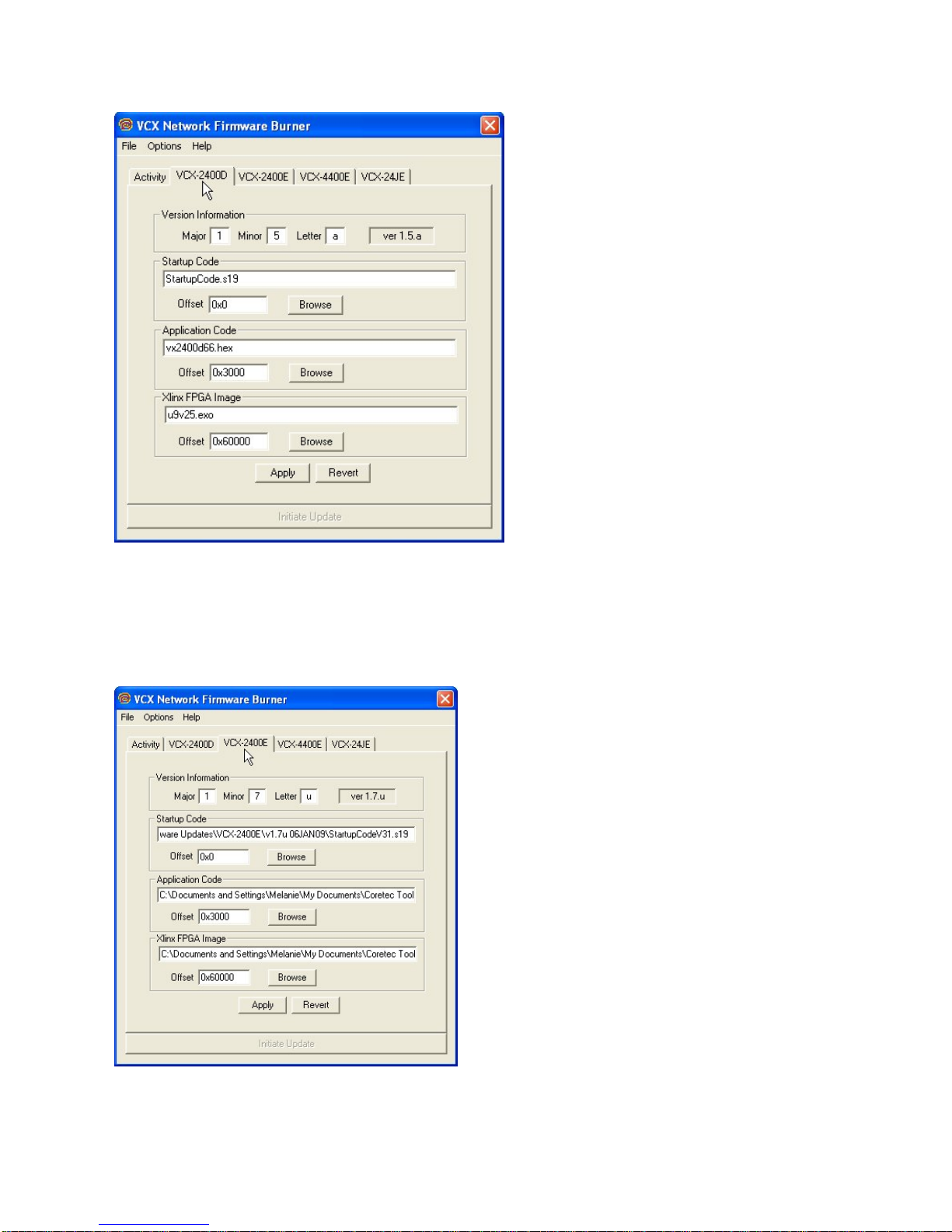
The Encoder Screens
The Encoder screens are accessed through the VCX2400E, VCX440E, & 2/4/J-E tabs and work
identically the same as the VCX-2400D, except that the parameters are applied to the firmware sent to the
VCX-2400, 4400, or 2/4/J Encoder devices.
Page 13
MenuBar
The File Menu
The menu contains selections for 1) File, 2) Options, and 3) Help. The File menu selection presents the
following drop down menu:
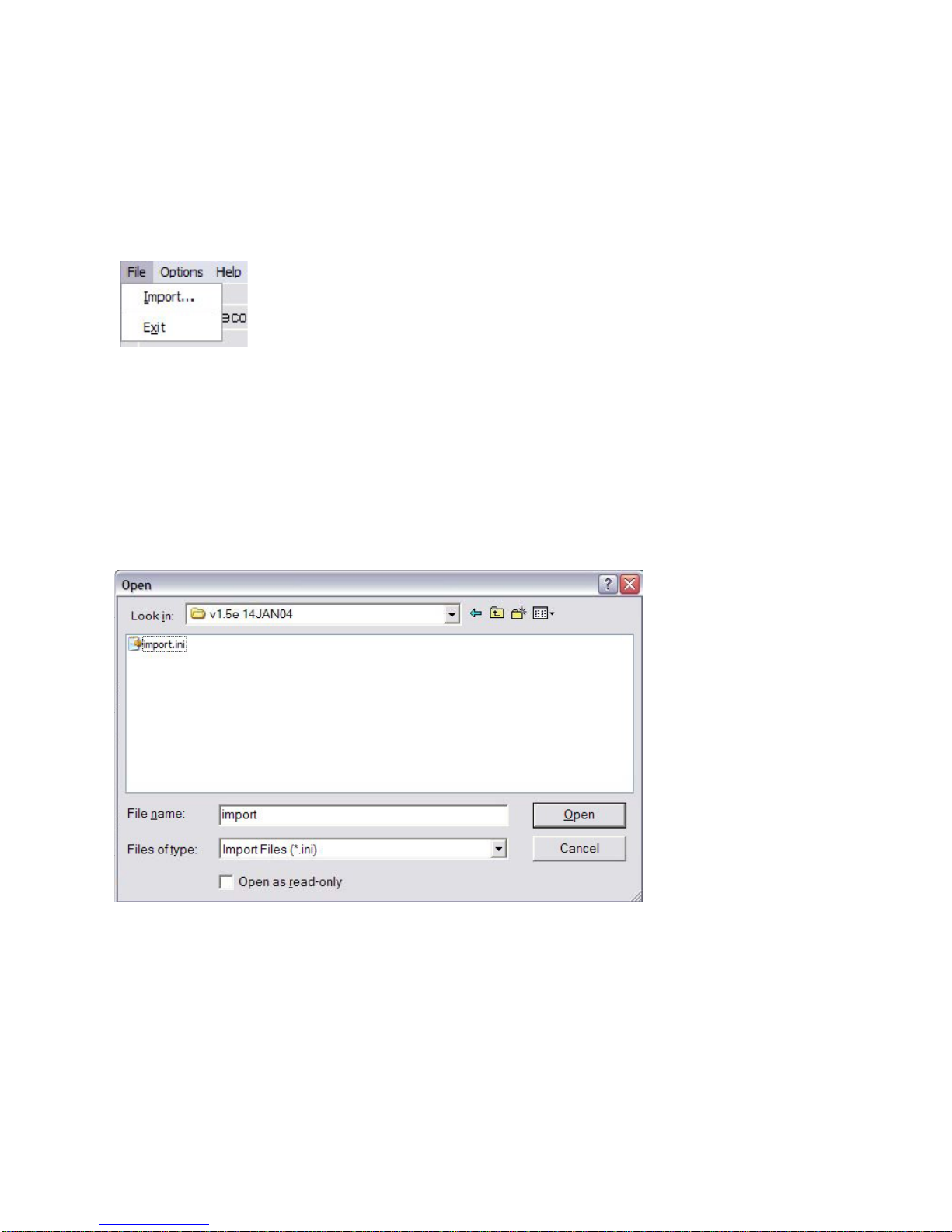
The Exit option will close the application. The Import selection is used to select and configure
VcxNetBurner for a particular firmware update version. Each firmware update will come with an
import.ini file that contains the necessary information and is accessed though the Import menu selection.
The import files are normally separate for both the decoder and encoder, and the supplied updates should
each be stored in a unique directory so that the various update files are not overwritten. When the operator
selects Import, a file selection dialog will be presented. The operator should navigate to the directory were
the firmware update is located and the import.ini file well be selected by default as shown in the
following picture:
After pressing the Open button the following dialog will be displayed.
Page 14
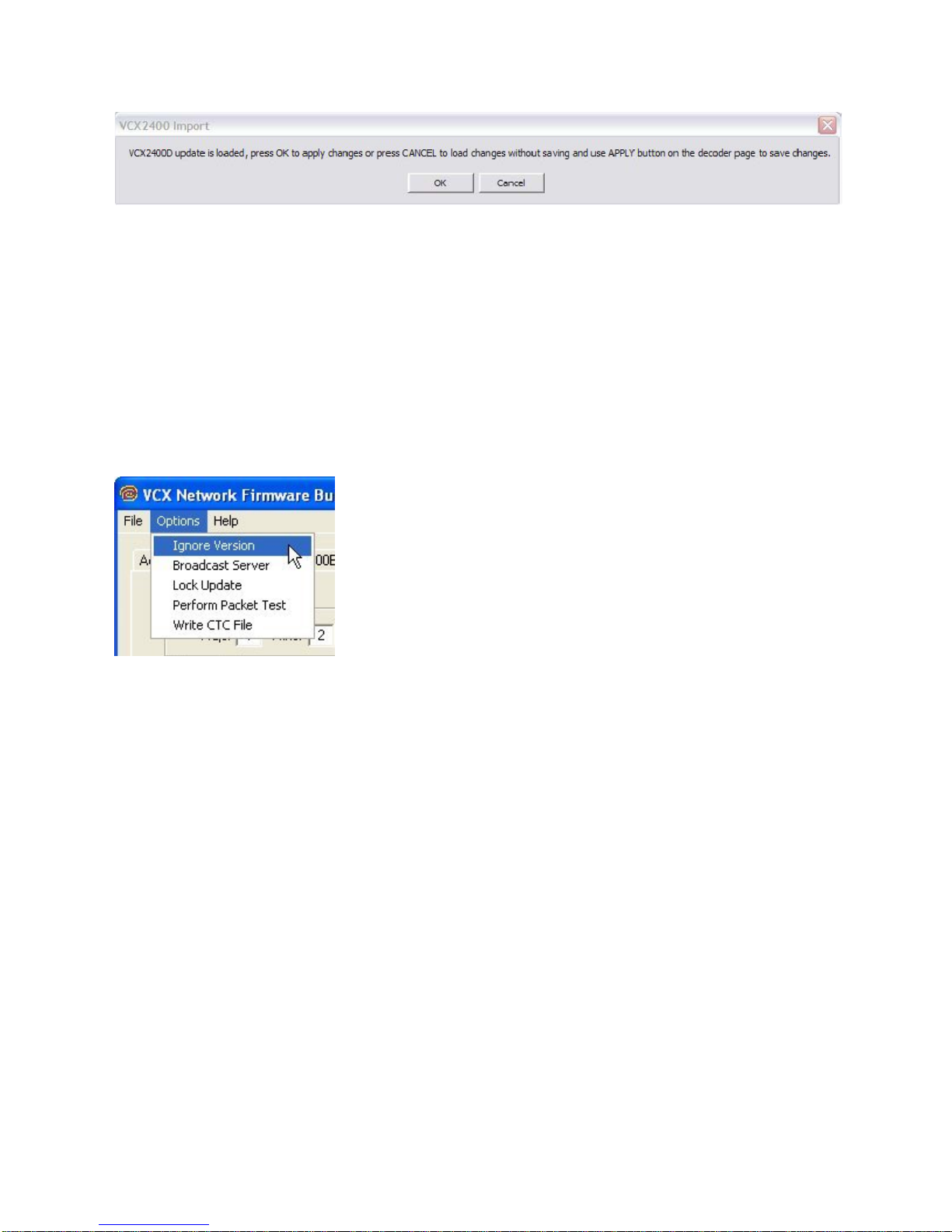
This dialog is telling you that you can save the imported parameters by pressing OK. Or by pressing
Cancel just use the parameters until the application is closed. If you press Cancel the parameters are still
loaded but the old parameters will be loaded then next time VcxNetBurner is used. Selecting OK is the
same as selecting Cancel and then Apply.
NOTE: If you have both encoder and decoder devices you will need to perform the Import operation
twice. One import should be performed for each type of device.
The Options Menu
The Options menu selection will provide the following dropdown menu.
There are five selections in the Options menu… 1) Ignore Version, 2) Broadcast Server, 3) Lock Update
4) Perform Packet Test & 5) Write CTC File.
The Ignore Version selection toggles between on and off. It normally should not be checked. It will
cause a device to update using the current parameters regardless of the current version. It can be used to
change a device to an older version, or even re-update the current version. Devices will normally update
only if the current device firmware version is less than the version listed in VcxNetBurner. For example if
the current device firmware version is 1.5a and the new version is 1.5a or below, an update command will
return the status “Version Current”. See the Activity screen in this document for an example. If the
Ignore Version selection is checked then you will never get a “Version Current” status.
The second option is Broadcast Server. When the operator makes this selection it causes
VcxNetBurner to multicast a command to all devices to set their Update Server IP to the
computer running VcxNetBurner. The devices will only remember the Update Server IP until the next
reboot or power cycle. Reboots automaticall occur after a successful firmware update. It is not necessary
to perform a Broadcast Server operation if the devices have already been programmed with an Update
Server IP. This can be done with Telnet using the command:
UPDATEIP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
It is also possible to configure a device to use a hostname (or URL) to address the server if a DNS server
is also configured. The following are example Telnet commands for this operation.
Page 15

UPDATENAME www.myupdateserver.com
DNSIP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
However, unless you have specific reasons for setting up your update server in the device, the Broadcast
Server command will suffice for updating your VCX-2400 device.
The Lock Update allows you to update all VCX-Devices of one type (i.e.- all VCX-2400E connected to
the network) simultaneously. We do not recommend this if you are just beginning to use the software, due
to the risk of overlooking a failure of one particular device.
Rather than this, it is suggested to update only one device at a time. This is done by following the first 6
steps of the instructions listed above and then Telnet into the unit you wish to update and issue the
following command:
UPDATEFIRMWARE
OR
UF
You should monitor the Activity screen for progress. The Telnet session will also provide some text
display that indicates completion. If the operation is successful then the device will automatically reboot
and the Telnet session will be dropped. If the operation failed then you should retry the
UPDATEFIRMWARE command.
TIPS: If using Telnet, use the DISPLAY IP command to verify that an update server IP is listed. Also
ensure that the update server IP is reachable. This would be true if the update server is the same as the
computer in the Telnet session.
The Perform Packet Tests tests to see if the firmware can be downloaded successfully without actually
being burnt into the unit.
The Write CTC File is for Coretecs internal use only.
The Help Menu
The Help menu selection will present the following dropdown menu.
At this time the only option is the About box selection. The about box will display the current version of
VcxNetConfigure. The current version in this example is V1.1 as shown.
Page 16

InstructionsforUse
The following steps should be performed to update your VCX-2400 devices.
1) Obtain the latest update from Core Tec Communications.
2) Place the updates into unique directories for each the decoder and encoder. The
updates will be provided on the FTP server in separate directories.
3) Use the Import menu command to load each update’s import.ini file and use the OK
button to save the current setting.
4) Go to both the Encoder and Decoder screens and verify that the file directories and
version match the latest desired update.
5) Select the Activity screen so that the update process status can be viewed.
6) Use the menu option Options->Broadcast Server to set the current update server to
your computer (optional if configured in the devices).
7) Press the Initiate Update button to multicast the update command to all devices.
8) Monitor the update process on the Activity screen to verify that all units have updated
successfully.
IPConfiguration
Overview
The commands contained in this section provide the means to configure critical network, com ports,
encoder, and decoder parameters. The user should consult the factory if specific functions of interest do
not appear to be supported.
InitialIPAddressing
In order to properly set the device parameters, encoder and decoder units must be given appropriate
IP addresses, compatible with the network on which they are to be connected. A software module,
VXNETCONFIG has been developed to allow a network administrator to set the IP and Subnet in the
VCX-2400 series encoders and decoders.
1) Installation
To load VXNETCONFIG insert the CORE TEC CD into your CD drive. Select
VXNETCONFIG by double clicking on the program. The following window will open:
Page 17

VCXNETCONFIG Window
Page 18

Description of Program Functions
(a) The first box on the left hand side of the window displays the current IP address of the
CORE TEC device being interrogated. Type the new IP address into this space
(b) The second box is used to change the SUBNET address. Note that the address displayed
is always 255.255.255.0. Type the new SUBNET address into this space.
(c) The Enable DHCP box is checked when DHCP is to be enabled.
NOTE: Do not enable DHCP if sub-channels are being used of if there is no DHCP
server. Check with the Network Administrator, or call Core Tec Tech Support if
further assistance is needed.
(d) The Configure
information. Note that future queries of the SUBNET will indicate 255.255.255.0.
Therefore, the correct SUBNET address should always be entered prior to using the
Configure button.
(e) The box on the right hand of the window displays all VCX-2400 devices (encoders and
decoders) on the network.
1) To make a change to the equipment addressing perform the following steps:
(a) Select the Core Tec device address from the list in the box on the right side of the
window.
(b) Move the cursor to the IP box and select the first octet by highlighting the octet. Enter
the new IP data for the selected octet. As the 3 digits are entered, the software will
automatically highlight the next octet for change. Complete entering the IP address and
then switch to the SUBNET data.
(c) Move the cursor to the SUBNET box and select the first octet by highlighting the octet.
Enter the new SUBNET data for the selected octet. As the 3 digits are entered, the
software will automatically highlight the next octet for change. Complete entering the
SUBNET data.
(d) To execute the change press the configure button. The IP address and the SUBNET will
be updated in the selected Core Tec equipment. The new IP address will be displayed.
The SUBNET will display a default class C- SUBNET there is no read back of the
changed SUBNET displayed.
(e) Repeat this process for all the CORE TEC equipment requiring change.
button is to execute the requested changes to the IP and SUBNET
ConnectingtoUnit
There are currently four ways to connect to the VCX-2400-E.
1) Telnet
Page 19

Password: admin (default)
To change the default password perform the following:
Type: PASSWORD <followed by your password (up to 11 characters)>
Where <your password> equals the new password.
For configuration using an Ethernet connection, activate the Telnet function by the following:
a. Initiating from the Command Prompt - Telnet nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
b. Use the MS Windows – START – RUN Telnet nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
(where nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn is the IP address of the unit being configured)
Employ the command set as described below.
Note that the initial IP addresses (factory default) are:
Encoder 192.168.0.253
Decoder 192.168.0.254
Sub net Mask 255.255.255.0
(Alternatively, the end user software SW-2400 is usable when an Ethernet connection is established.)
Page 20

2) Terminal Program
NOTE: The following procedure is valid for standalone units only and is not applicable to rack
mount units.
The Terminal Program, such as HyperTerminal, configuration procedure uses the serial connection on
the front of the unit.
Using the PCA-2400 programming cable, connect to the control port. This cable should be attached to
the serial port of an attached PC and the Hyper Terminal program launched. The PC should have its
Com Port configured as:
Baud rate 38,400 kbps
Data bits 8 bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit
Flow control None
Activate the HyperTerminal function, normally found in a sub-menu under ACCESSORIES. Employ
the command set as described in the following section.
Password: admin (default)
To change the default password perform the following:
Type: PASSWORD <followed by your password (up to 11 characters)>
Where <your password> equals the new password
3) Web Interface
When the unit accepts the log in (default password: admin), the following web page will be
displayed. The header identifies the type of unit followed by the page control bar. The basic
network configuration is displayed in the appropriate fields giving the operator the option to
modify them if needed. There are eight (7) pages to select from each giving the operator
control over the unit operation. General, Video, Network, Subchannel1 and Subchannel2
provide all the parameters that an operator may modify grouped as labeled. There are two (2)
options to the far right, “Log Out” and “Commit/Reboot”, which will terminate the session.
Log Out will log the operator out without committing to the changes made in the previous
pages and the last will perform the commit function, writing the changes to the unit and
performing a reboot. Both operations will log the operator off and close the communications
channel. The web page may or may not report the termination of the communications
channel. The login process must be performed to access the unit again.
The following pictures show the various parameters available to the operator. The definitions
are described below in the command sections.
Open a new Internet Explorer window and enter the IP address of the unit into the explorer
address frame. (Review the section INITIAL IP ADDRESSING to obtain this address)
Page 21

The selected device will respond by opening the following page. Note all internet
communication pages will apply while the thread is open.
Type password XXXXXXXXXXX
Where XXXXXXXXXXX is the new password.
The password can be anything up to eleven (11) characters in length.
Page 22

Page 23

Page 24

Page 25

Page 26

Page 27

Logging off
Commit/Reboot
This process will write all the parameters into nonvolatile memory and then reboot the unit. The reboot
process will stop all current operations and restart with the new parameters.
Note: The Commit/Reboot operation, in most cases, will not give the operator an indication the operation
has started, in progress or has finished.
Page 28

4) Core Tec Watchdog Software
Please refer to the Watchdog Manuals.
ProgramCommands
IMPORTANT NOTES:
1. After entering one or more commands, it is necessary to enter COMMIT and REBOOT for
the new settings to take effect.
2. Typing “?” displays a listing of all commands.
NetworkSetup
IP (IP Address)
The IP address setup is in the form of decimal dotted notation. The selection of an IP should
come from the person who administrates the network. The current IP selection is static. A dynamic IP
setting using DHCP is planned for future enhancement.
Default:
Encoder - 192.168.0.253
Decoder - 192.168.0.254
Example command: IP 192.168.0.10 (sets IP address to 192.168.0.10)
IPMASK (IP Subnet Mask)
mask should come from the network administrator. It is used to represent the number of bits in the
current IP subnet.
Default: 255.255.255.0
Example command: IPMASK 255.255.255.128
The IP Subnet Mask is in the form of decimal dotted notation. The selection of an IP subnet
GATEWAY
The GATEWAY command can have either one or three parameters. The first parameter is the IP
address of the host that is the gateway. Optionally you may include the IP address and the subnet mask of
the subnet you want to route through the gateway. You can program up to five gateway entries.
Default: No Gateways
Example command: GATEWAY 192.168.0.1
Page 29

The following example indicates that all packets sent to hosts on the 62.41.10.xxx subnet should be
routed though the gateway at 192.168.100.2
Example command: GATEWAY 192.168.100.2 62.41.100.0 255.255.255.0
CLEARGATEWAY
Clears the gateway table. There are no parameters. This command clears all entries.
CMDPORT (TCP Command Port)
The TCP command port selection is configurable. However the default setting should be
adequate for normal operation. The command port is used by software that can operate the VCX-2400
devices programmatically. For example, a Microsoft Windows GUI based application.
Default: 5000
Example Command: CMDPORT 5010 (sets TCP command port to 5010)
VIDEOIP (Video Destination IP)
The video destination IP is an address that allows the reception of the MPEG-2 stream by a single
(unicast) or multiple (multicase) device(s).
NOTE: Class D IP addresses, in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 are called multicast addresses.
The range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for local purposes and the range 239.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255 is reserved for administrative scooping. Both the encoder and decoder should be set to
the same Video IP for correct operation together.
Default: 239.5.6.8
Example Command: VIDEOIP 234.5.6.10 (sets multicast IP to 234.5.6.10)
VIDEOPORT (Video Multicast Port)
The video multicast port selection is configurable. However the default setting should be
adequate for normal operation.
Default: 4568
Example Command: VIDEOPORT 4569 (sets multicast port to 4569)
Page 30

Comm Port Setup
The VCX-2400 supports two sub-channels that allow the two way transmission of serial data to
selected target devices. The sub-channel can be configured for either RS232 or RS422 operation. It is
not necessary for both ends to use the same configuration. The following is a list of the configuration
items for the sub-channel:
Channel Enable
Baud rate
Parity
IP address of target
TCP port for operation
RS422 or RS232
Certain VCX-2400 devices can be delivered with either one or two comm ports. The ports are designated
as 1 and 2. The commands for configuring the settings use the A or B designation to indicate the port
being configured.
Example(s): COM1xxx for comm port 1 (selects comm port 1)
COM2xxx for comm port 2 (selects comm port 2)
Note: Communications port 2 is also the control port for programming. If this port is also needed for
non-programming related data purposes, the user should program the necessary parameters with the
jumper in place if using the Hyper Terminal method. Upon completion of programming, removal of the
jumper will result in port 2 operating as programmed. If not using Hyper Terminal to program, jumper
should be removed if comm port 2 is to be used.
COM1, COM2 (Comm Port Enable)
This command sets the active state of the comm port. The parameter is “0” or “1”, where “1”
enables and “0” disables the comm port function. At this time the comm port is always enabled and this
command has no effect.
Default: 0 (OFF)
Example Commands: COM1 1 (enables comm port 1)
COM1BAUD, COM2BAUD (Comm Port Baud Rate)
This command sets the baud rate for the comm port. Valid values are 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200,
and 38400. Other data rates may be functional but are not tested.
Default: 9600
Example Command: COM1BAUD 4800
(sets baud rate for comm port 1 at 4800 bps)
Page 31

COM1PARITY, COM2PARITY (Comm Port Parity)
The parity for the comm port can be set to Odd, Even, or None. The parameters for the
COM[1|2]PARITY command are N,O,E, which correspond respectively to None, Odd, Even.
Default: None
Example Command: COM2PARITY N (sets comm port 2 to no parity)
COM1IP, COM2IP (Comm Port IP)
The IP address of the destination for the comm port data is set by this command. A typical setup
would have an encoder and a decoder. The decoder would have a comm port IP address that is the same
as the encoder. And, likewise, the encoder’s comm port IP would be the same as the decoder. Notice that
the default comm ports IP’s are the opposite of the default device IP’s.
Default:
Encoder comm ports - 192.168.0.253
Decoder comm ports- 192.168.0.254
Example Command: COM2IP 192.168.0.10 (points the comm port data to an
encoder, decoder, or other device whose IP address is 192.168.0.10)
COM1PORT, COM2PORT (Comm Port Port)
The comm port port selection is configurable. However the default setting should be adequate for
normal operation.
Default:
Comm port 1 - 5002
Comm port 2 – 5004
Example Command: COM1PORT 5010 (sets comm port 1 to port 5010)
Page 32

COM1RS422, COM2RS422 (RS-232, RS-422 Data Format)
The comm port data format is configurable. The parameter is “0” or “1”, where “1” enables RS-422
and “0” enables RS-232 format.
Default: 0 (RS-232)
Example Command: COM1RS422 0 (sets comm port 1 for RS-232)
Comm port Command – Further Examples
The following examples set up comm port 1:
COM1 1 – Enable comm port 1
COM1BAUD 9600 – Set comm port 1 baud rate to 9600
COM1RS422 1 – Set comm port 1 mode to RS422
COM1PORT 5002 – Set comm port 1 port to 5002
COM1PARITY E – Set comm port 1 parity to even
COM1IP 192.168.0.10 – Set destination address for data to 192.168.0.10
Encoder Commands
PROFILE
Used to select a desired resolution for the encoded video. It also sets the optimal defaults for
other parameters, such as bit rate. The allowable settings are SIF ½, 2/3, D1. The half and two thirds
settings are relative to the full D1 resolution.
Default: SIF
Example Command: PROFILE ½ (sets resolution to ½ D1)
Note: Since the Profile command selects defaults for other settings, it should be issued before any
other commands relating to the encoded MPEG stream.
BRIGHT
Adjusts image brightness. The acceptable range is from 0 to 255, where a higher number
provides more brightness.
Default: 128
Example Command: BRIGHT 170 (increases brightness from default setting)
Page 33

CONTRAST
Adjusts image contrast. The acceptable range is from 0 to 127, where a higher number provides
more contrast.
.
SATURATION
Adjusts color saturation. The acceptable range is from 0 (no color) to 127.
Example Command: SATURATION 75 (increases color saturation from default)
TINT
Adjusts color tint. The acceptable range is from –128 to 127.
Default: 63
Example Command: CONTRAST 90 (increases contrast from default)
Default: 63
Default: 0
Example Command: TINT –10 (adjusts tint)
BITRATE
Adjusts the bit rate (in kbits/sec) of the encoded MPEG-2 video. This sets the maximum rate (of
the variable bit stream) encoded. If audio is in the MPEG-2 stream, then an additional 256 kbits/sec will
be added to the rate set by this command.
Default: The default is set by the Profile command
Example Command: BITRATE 2000 (Sets max bit rate to 2 Mbits/sec)
Note: This command should be issued AFTER the Profile command if the Profile command is used.
AUDIO
The audio command is used to enable or disable audio in the MPEG-2 stream. The parameter is
“0” or “1”, where “1” enables and “0” disables the audio function.
Default: 0
Example Command: AUDIO 1 (enables audio)
Page 34

DISPLAY <VIDEO | COM |IP | SAP>
This command displays current encoder settings. Entering DISPLAY only provides all settings.
Adding the VIDEO, COM, or IP qualifiers displays settings for video, comm port, or IP parameters,
respectively.
Example Command: DISPLAY IP (displays current IP encoder settings)
Page 35

Decoder Commands
T (Onscreen Text)
Allows the placement of a persistent text over the video. The text is placed at the current cursor
position if the text cursor positioning commands are sent beforehand. Otherwise the text is justified and
placed according to the text justification command.
Default: none
Example Command: T say hi for the camera
(enters text “say hi for the camera”)
TX, TY (Onscreen Text Cursor Position)
There are two text cursor position commands. One command (TX) is for the horizontal (X)
position and the other (TY) is for the vertical (Y) position. The text cursor commands will override the
text justification command and vice versa. When text cursor commands are issued, the text will wrap to
the next line and scroll the screen at the bottom.
Default: none
Example Commands: To set the cursor at (0,5)
TX 0
TY 5
TPOS (Onscreen Text Justification)
Overrides cursor positioning commands and causes the text to print at the same location with
justification. There are six justification positions. Three are for vertical justification and the others for
horizontal justification. For the horizontal there is left, center, and right. For the vertical there is top,
center, and bottom. The nine possible combinations are expressed as 0 – 9 as a parameter as follows:
1 = Top left
2 = Top center
3 = Top right
4 = Bottom left (Default)
5 = Bottom center
6 = Bottom right
7 = Center left
8 = Center
9 = Center right
Default: 4
Example Command: TPOS 6 (justifies text at bottom right)
Page 36

CLR (Clear Onscreen Text)
This command clears the screen and erases the persistent storage of the last text command.
Default: N/A
Example Command: CLR
TC xx (Text Color)
Command sets foreground and background text color. The first character defines foreground
color; the second, background color, as follows:
Character
Color
0 Transparent
1 Black
2 White
3 Light Gray
4 Medium Gray
5 Dark Gray (All colors here and below – 75% transparent)
6 Red
7 Blue
8 Green
9 Yellow
A Purple
B Teal
C Orange
D Pink
E Flesh
F Light Blue
Default: 27 (White text on blue background)
Example Command: TC 60 (red text on transparent background)
COLORBAR (Color Bars)
Used to replace the decoded video with a built-in color bar test pattern generator. The allowed
parameters are 0 (color bars off) and 1 (color bars on).
Default: OFF
Example Command: COLORBAR 1 (turns color bars on)
Page 37

BUFFERLOW, BUFFERHIGH
These settings define an acceptable range of video frames in the decoder buffer. If the number of
frames in the decoder exceeds the buffer high setting, then the decoder starts playing back the buffered
frames faster than real time, until the number of frames buffered drops to the buffer low setting. This is
used to limit the latency of the encoded video. If the two setting are too close together then the video
playback will experience frequent dropped frames and a decrease in the smoothness of the frame rate.
Defaults: BUFFERLOW 3
BUFFERHIGH 10
Example Commands: BUFFERLOW 5
BUFFERHIGH 7
(tightens buffer settings from default)
RESTARTLEVEL
Defines the number errors detected in the incoming MPEG stream before a reset of the decoder
will occur. If the decoder encounters a large number of stream errors over any period of time it will often
get into a state where the displayed video is permanently degraded. By resetting the decoder hardware
periodically after the detection of errors, this situation can be managed without user intervention.
Default: 250
Example Command: RESTARTLEVEL 300
(resets the decoder after 300 received errors)
RESTARTTIME
If a situation is encountered where the decoder receives infrequent errors, but, due to the nature of
the errors, gets into a degraded state, then the decoder can be commanded to automatically reset after a set
period of time. The timer is triggered after receiving ten errors in the stream. The parameter for this
command is in units of milliseconds. An entry of zero disables the timer. The timer is reset if a reset
occurs due to the number of errors exceeding the restart level
Default: 300000 (300 seconds)
Example Command: RESTARTTIME 200000
(resets the decoder 200 seconds after receiving 10 errors)
DISPLAY <COM | IP>
This command displays current decoder settings. Entering DISPLAY only provides all settings.
Adding the COM or IP qualifiers displays settings for comm port or IP parameters, respectively.
Example Command: DISPLAY IP (displays current IP decoder settings)
Page 38

Common Commands
The following commands apply to both encoder and decoder.
AUTOREBOOT
Sets a periodic timed reboot of the device. The parameter is the number of seconds between
reboots.
Default: 0 (off)
Example: AUTOREBOOT 3600
AUTOSTART
Sets a periodic timed restart of the video encoder/decoder. The parameter is the number of
seconds between starts.
Default decoder: 0 (off)
Default encoder: 28800 (8 hours)
Example: AUTOSTART 3600
300 seconds equals 5 minutes
3600 seconds equals 1 hour
COMMIT
Saves parameter setttings changes in permanent memory. A commit command must be issued
before a reboot or power cycle if the new device settings are to be maintained.
DEATHBLOW
Causes a reboot of the device. The purpose of this command is to cause a reboot from the
password prompt. If you cannot login into the command prompt because of the “Another administrator is
logged in.” message, then you can use DEATHBLOW as the password to return the unit to the power up
state.
EXIT
Exits from the command prompt and releases the current login. You may also use the following
alternatives… LO (LogOff) and QUIT.
NTSC
Sets unit for NTSC video operation.
Page 39

PAL
Sets unit for PAL video operation.
REBOOT
Restarts device from powerup state. Most changes in device settings require a reboot after a
commit.
START
Starts encoding or playback (video out).
STREAMTYPE
Selects between Program or Transport multiplexing of the video stream. Acceptable parameters
are T or P, where P is Program and T is Transport.
Default: P (program stream)
Example: STREAMTYPE T (transport stream)
STOP
Stops encoding or playback (video out).
VER
Displays the software version/build date, BSP (board support package) version/build date, and
board revision.
Example response:
Version: VCX2400d3 v1.6a, Date: 29JUN04
BSP VCXV73 v1.2, 04JUN04
Board revision: 3.1
WD
The watchdog is a timer that will perform a complete reset of the device if the firmware encounters a
lockup condition. The parameter is “0” or “1”, where “1” enables and “0” disables the watchdog
function. Enabling the watchdog allows the VCX-2400 devices to automatically recover from some
fatal error conditions without user intervention.
Default: 0 (OFF)
Example Command: WD 1 (enables watchdog)
Page 40

SAP Settings
The encoder is capable of multicasting SAP (Session Announcement Protocol RFC-2974) packets with
SDP (Session Description Protocol RFC-2327) content. There are a number of parameter setting for
configuring SAP. They are presented in this section. The user should refer to the referenced RFCs to
understand the significance of the SAP/SDP parameter settings.
SAP
Use to enable or disable the SAP multicast. The allowable parameter is ON or OFF.
Default: OFF
Example: SAP ON
SAPAUTHOR
Used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) author information. The parameter is an ASCII string with a
limitation of 30 characters.
Default: No text
SAPCOPYRIGHT
Used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) copyright information. The parameter is an ASCII string with a
limitation of 30 characters.
Default: No Text
SAPINFO
Used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) info information. The parameter is an ASCII string with a
limitation of 62 characters.
Default: Core Tec VCX2400e
Example: SAPINFO Intersection of 1st and main
SAPINTERVAL
Sets the interval between SAP packet transmission. The parameter is the number of milliseconds
between transmits.
Default: 5000 (5 seconds)
Example: SAPINTERVAL 10000 (10 seconds)
Page 41

SAPIP
Sets the IP address of the destination host for SAP packets. This address is a multicast address
defined in RFC-2974. It is unlikely that the user will need to change this setting.
Default: 224.2.127.254
SAPKEYWORD
Used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) keyword information. The parameter is an ASCII string with a
limitation of 30 characters.
Default: No text
SAPNAME
Used to set the SDP (RFC-2327) name information. The parameter is an ASCII string with a
limitation of 30 characters.
Default: Core Tec Communications, LLC
Example: SAPNAME Main Street Camera #1
SAPPORT
Sets the destination port for SAP packets. The port number is defined in RFC-2974. It is
unlikely that the user will need to change this setting.
Default: 9875
SAPUPDATE
Issue this command after changing the SAP parameters to update all devices listening to SAP
multicasts.
Page 42

MISCALLANEOUS SETTINGS
CAMERA[n]
Store a user defined camera type code 0..255
This is a current list of the Cameras we support:
Cohu = 1
Philips_Bosch = 2
Pelco = 3
Vicon = 4
RVision = 5
Panasonic = 6
CAMERAID [n]
Store a user defined camera ID code 0..255
DISPLAY <VIDEO | COM | IP | SAP | MISC>
This co mmand displays current encoder settings. Entering DISPLAY only provides all settings.
Adding the VIDEO, COM, IP, SAP or MISC displays those respective settings specifically.
Example Command: DISPLAY IP (displays current IP encoder settings)
Specifications
PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL
Dimensions
11.0” x 5.25”
Mounting
R-12 Card Cage Enclosure
Weight
.6 pounds
Temperature
-20 degrees to + 70 degrees Centigrade
(-4 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit)
Page 43

Humidity
0 to 95% non-condensing
POWER REQUIREMENTS
From Enclosure
CONNECTORS
Video
NTSC/PAL BNC
Power
From Back-plane (36 pin Molex)
Data
Network RJ-45
Com ports RJ-45
ELECTRICAL
Video Input (NTSC/PAL)
Impedance: 75 ohm unbalanced, return loss >
30 dB
Dynamic
Range: 0.5 volts to 2.0 volts peak to peak
Video Output (NTSC/PAL)
Impedance: 75 ohm unbalanced, return loss >
30 dB
Output Level: 1.0 volts peak to peak nominal
(.9 volts minimum to 1.1 volts maximum)
Sync Level: 257 mV (36 IRE) to 314 mV (44 IRE)
Bar Level: 642 mV (90 IRE) to 785 mV (110 IRE)
Burst Level: 257 mV (36 IRE) to 314 mV (44 IRE)
Resolution: Full D1: 720h x 480v (NTSC); 720h x 576v (PAL)
1/2 D1: 352h x 480v (NTSC); 480h x 576v (PAL)
CIF: 352h x 240v (NTSC); 352h x 288v (PAL)
QCIF: 160x120
QQCIF: 80x60
Frame Rate: 1 to 30 frames per second maximum
Data (Network)
Format: Ethernet IEEE 802.3; 10/100 Base T
Page 44

Line Rate: down to 64kbps
Data (Sub-channels)
Format: RS-232 or RS-422 (programmable) (2)
Data Rates: 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400 bps
Programming Data
Format: EIA RS-232C (primary data lines)
Rate: 38.4 kbps
Form: 8-bit data, 1 stop bit, no parity
ModelNumbers
BASE MODELS
VCX-2400-E MPEG 2 Video Encoder – IP
VCX-2400-D MPEG 2 Video Decoder – IP
VCX-2400-E-R MPEG 2 Video Encoder – IP (Card Cage Mount)
VCX-2400-D-R MPEG 2 Video Decoder – IP (Card Cage Mount)
*Note: Base models feature two data sub-channels
ACCESSORIES
(see R-12 data sheet for product options and accessories)
SW-2400 Video Watchdog
R-12 Card Cage Enclosure
PCA-2400 Programming Cable Assembly
TM
User Software
Page 45

AppendixA
Pinouts
Com Port Data Interface Pin Out(uses RJ-45 Plug)
Pin Signal Description Signal Type
1 RS-232 Receive Input
2 RS-232 RTS Output
3 RS-232 Transmit Output
4 RS-232 CTS Input
5 RS-422 Receive Data + Input
6 RS-422 Transmit Data - Output
7
8 RS-422 Transmit Data + Output
RS‐422
RS-232
Receive Data Ground
Input
Ground
Page 46

StandardEthernetPinOut
Straight Through Ethernet Pin Out Cross Over Ethernet Pin Out
Page 47

RJ11toSerialInterfaceAdaptorPinout
The PC should have its Com Port configured as:
Baud rate 38,400 kbps
Data bits 8 bits
Parity No Parity
Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit
Flow control None
RJ-11 Adaptor VCX-Encoder Series
Front Panel Serial Interface
5
9
4
8
3
7
2
6
1
WHT
BLK
RED
6
5
4
3
2
1
Manufa ct u rer Supplied Serial Adapt or
Below is the pin layout of the RJ-11:
Pin Function
1 Ground
2 Unused
3 Unused
4 Serial Out
5 Serial In
6 Ground
 Loading...
Loading...