Page 1

FCP
Fiberglass Blowers
INSTALLATION, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
This publication contains the installation, operation and
maintenance instructions for standard units of the FCP
Fiberglass Blowers.
Carefully read this publication and any
supplemental documents prior to any
installation or maintenance procedure.
Loren Cook Company’s Fiberglass Catalog provides
additional information describing the equipment, fan
performance, available accessories, and specification data.
For additional safety information, refer to AMCA
publication 410-96, Safety Practices for Users and Installers
of Industrial and Commercial Fans.
All of the publications listed above can be obtained from
Loren Cook Company by phoning (417)869-6474, extension
166; by FAX at (417)832-9431; or by e-mail at
info@lorencook.com.
For information on special equipment, contact Loren Cook
Company Customer Service Department at (417)869-6474.
Rotating Parts & Electrical Shock Hazard:
Disconnect electric power before working on unit.
Follow proper lockout / tagout procedures to ensure
the unit cannot be energized while being installed or
serviced.
A disconnect switch should be placed near the fan in
order that the power can be swiftly cut off, in case of
an emergency and in order that maintenance
personnel are provided complete control of the power
source.
Grounding is required. All field-installed wiring must
be completed by qualified personnel. All fieldinstalled wiring must comply with National Electric
Code (NFPA 70) and all applicable local codes.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in
death or serious injury.
Storage
If the fan is stored for any length of time prior to
installation, completely fill the bearings with grease or
moisture-inhibiting oil (refer to Lubricants on page 6).
Rotate the wheel several revolutions every three to five
days to keep a coating of grease on all internal bearing
parts.
Store the fan in its original crate and protect it from dust,
debris and the weather.
To maintain good working condition of the fan when it is
stored outdoors, follow the additional instructions below.
• Coat the shaft with grease or a rust preventative
compound.
• Wrap bearings for weather protection.
• Cover the inlet and outlet to prevent the accumulation of
dirt and moisture in the housing.
• Periodically rotate the wheel and operate dampers (if
supplied).
• Periodically inspect the unit to prevent damaging
conditions.
Installation
Motor Installation
Most motors are shipped mounted on the fans with belts
and drives installed. However, extremely heavy motors and
drives are shipped separately . These motors and drives will
require field installation.
Foundation
This fan requires a strong, level foundation of reinforced
poured concrete. A correctly designed concrete foundation
provides the best means for mounting floor units. The
foundation’s size is determined by fan size and
arrangement, motor size and position, and the specific
location of the installation.
Receiving and Inspection
Carefully inspect the fan and accessories for any damage
and shortage immediately upon receipt of the fan.
• Turn the wheel by hand to ensure it turns freely and
does not bind.
• Inspect dampers (if supplied) for free operation of all
moving parts.
• Record on the delivery receipt any visible sign of
damage.
Handling
Lift the fan by the base or lifting eyes. NOTICE! Never lift
by the shaft, motor, or housing.
Page 2
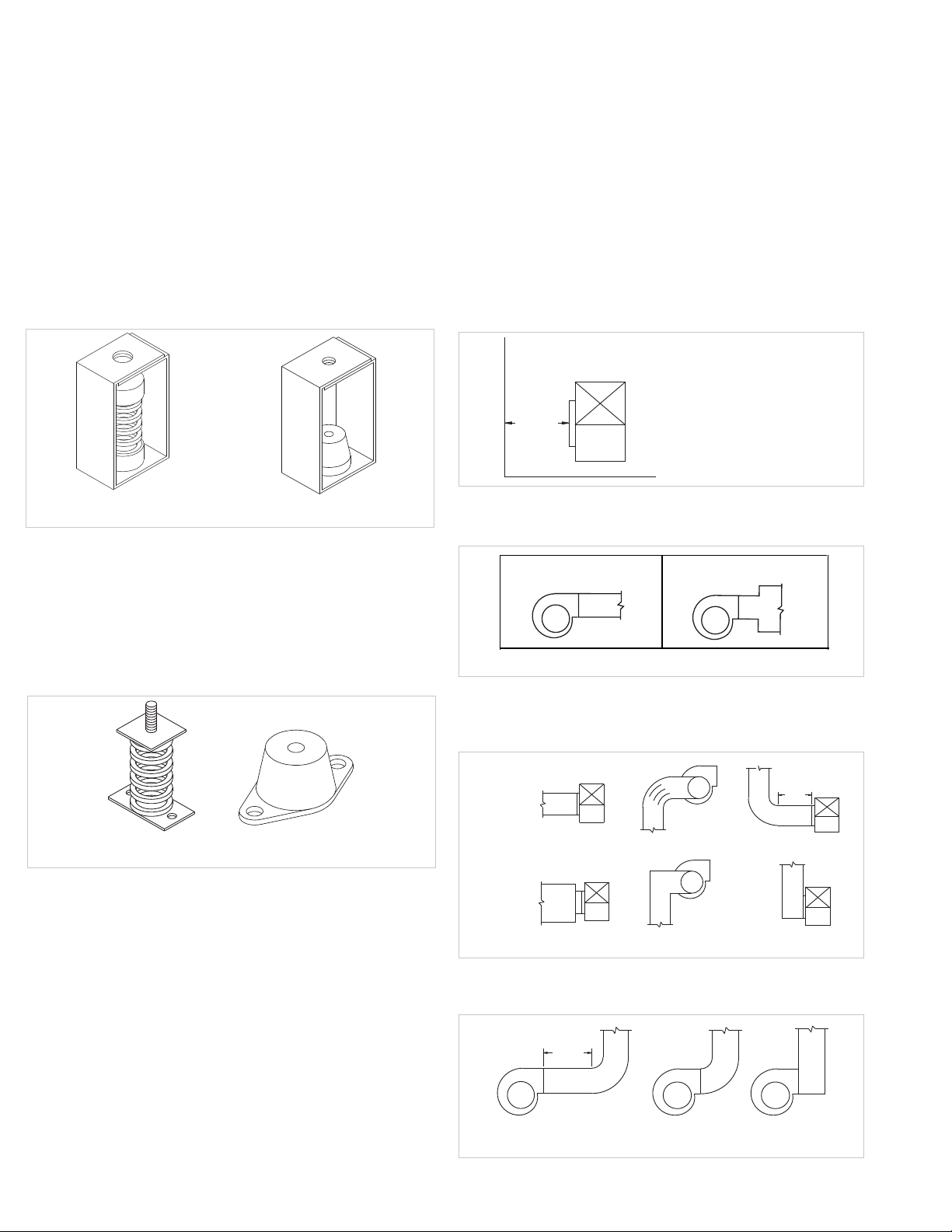
Use the following guidelines to calculate foundation size:
• The overall dimensions of the foundation should
extend at least 6 inches beyond the outline of the fan
and its motor.
• The weight of the foundation should be 2 to 3 times the
weight of the unit and its motor.
Isolation
NOTICE! Although a certain amount of vibration is
inherent in operating centrifugal fans, extreme
vibration is a serious problem that may cause
structural and mechanical failure.
Isolation Base: To prevent vibration and noise from being
transferred to the building isolators are recommended.
Isolators should be located between the fan system and the
support structure.
Floor Mounted Rubber-In-Shear (RIS) Isolators
1. Mount fan and motor on an isolation base (if supplied).
2. Elevate fan to provide room to insert isolators between
the base and foundation and block in position.
3. Position isolators under fan and secure bolts.
4. Remove blocks and allow fan to rest on floor. Isolators
must be installed on a level surface (leveling should
not be required).
5. Secure isolators to mounting surface.
Duct Installation
Efficient fan performance relies on the proper installation
of inlet and discharge ducts. Be sure your fan conforms to
the following guidelines.
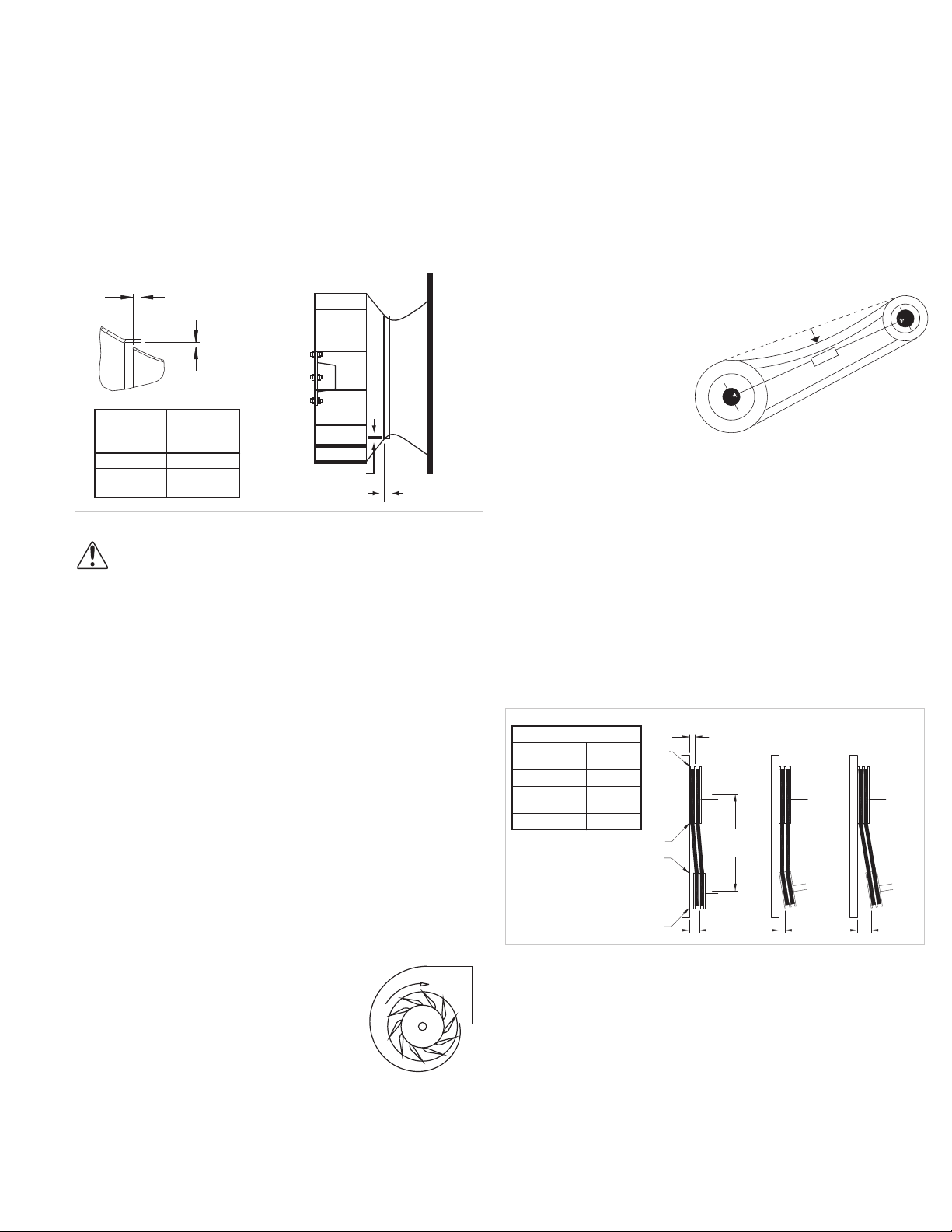
Non-Ducted Inlet Clearance: If your fan has an open inlet
(no duct work), the fan must be placed 1 fan wheel diameter
away from walls and bulkheads.
Non-ducted Inlet
Clearance
MIN 1 DIA
Ceiling Mounted Spring Isolator
Figure 1 - Ceiling Mount Isolators
Rubber-In-Shear Ceiling Isolators
Ceiling Mounted Isolators: Some applications require fan
systems designed for floor mounting to be suspended from
ceiling supports. In such cases, all fans should be installed
on either rails or bases in the classical orientation. T ypically ,
these systems are hung from the corners by rods, which
include isolation hangers of either spring or rubber-in-shear
design. NOTICE! Under no circumstances is the fan to
be inverted and hung by its base angles.
Spring Isolator
Figure 2 -Floor Mount Isolators
Rubber-In-Shear Isolator
Floor Mounted Spring Isolators
1. Mount fan and motor on isolation base (if supplied).
2. Elevate fan (or isolation base) to operating height and
insert blocks to hold in position.
3. Position isolators under the fan and vertically align by
inserting leveling bolt through mounting holes in the
fan or the base. The isolator must be installed on a
level surface.
4. Adjust the isolators by turning the leveling nut counter
clockwise several turns at a time alternately on each
isolator until the fan weight is transferred onto the
isolators and the fan raises uniformly off the blocks.
Then remove the blocks.
5. Turn lock nut onto leveling bolt and secure firmly in
place against the top of the mounting flange or frame.
6. Secure isolators to mounting surface.
Free Discharge: Avoid a free discharge into the plenum.
This will result in lost efficiency because it doesn’t allow for
a static regain.
Correct
Free Discharge
Incorrect
Inlet Duct Turns: For ducted inlets, allow at least 3 fan
wheel diameters between duct turns or elbows and the fan
inlet.
MIN 3
Correct
Incorrect
Inlet Duct Turns
DIA
Discharge Duct Turns: Where possible, allow 3 duct diameters between duct turns or elbows and the fan outlet. Refer
to figure above.
MIN 3
DIA
Correct
Discharge Duct Turns
Incorrect
2
Page 3
Wheel-to-Inlet Clearance
1 foot
1/4 inch
The correct wheel-to-inlet clearance is critical to proper
fan performance. This clearance should be verified before
initial start-up since rough handling during shipment could
cause a shift in fan components. Refer to wheel/inlet drawing for correct overlap.
Adjust the overlap by loosening the wheel hub and moving the wheel along the shaft to obtain the correct value.
A uniform radial gap (space between the edge of the
cone and the edge of the inlet) is obtained by loosening the
inlet cone bolts and repositioning the inlet cone.
Wheel/Inlet Overlap
DETAIL A
OVERLAP
RADIAL
GAP
Size
120 - 180 5/8”
225 - 270 3/4”
300 - 365 1”
Maximum
Overlap
Radial Clearance
Overlap
Wiring Installation
NOTICE! All wiring should be in accordance
with local ordinances and the National Electrical
Code, NFPA 70. Ensure the power supply
(voltage, frequency, and current carrying
capacity of wires) is in accordance with the
motor nameplate.
(See page 5 for diagram)
NOTICE! Fan must be grounded to prevent electrical
discharge.
Leave enough slack in the wiring to allow for motor
movement when adjusting belt tension. Some fractional
motors have to be removed in order to make the connection
with the terminal box at the end of the motor. To remove
motor, remove bolts securing motor base to power
assembly. Do not remove motor mounting bolts.
Follow the wiring diagram in the disconnect switch and
the wiring diagram provided with the motor. Correctly label
the circuit on the main power box and always identify a
closed switch to promote safety (i.e., red tape over a closed
switch).
Wheel Rotation
Test the fan to ensure the rotation of
the wheel is the same as indicated by
the arrow marked Rotation.
For 115 and 230 Single Phase
Motors: Fan wheel rotation is set
correctly at the factory. Changing the
rotation of this type of motor should only
be attempted by a qualified electrician.
are electrically reversible by switching two of the supply
leads. For this reason, the rotation of the fan cannot be
For 208, 230, and 460, 3 Phase Motors: These motors
restricted to one direction at the factory. See Wiring
Diagrams above for specific information on reversing wheel
direction.
NOTICE! Do not allow the fan to run in the wrong
direction. This will overheat the motor and cause
serious damage. For 3-phase motors, if the fan is
running in the wrong direction, check the control
switch. It is possible to interchange two leads at this
location so that the fan is operating in the correct
direction.
Belt and Pulley Installation
Belt tension is determined by
the sound the belts make when
the fan is first started. Belts will
produce a loud squeal which
dissipates after the fan is
operating at full capacity. If
the belt tension is too tight
or too loose, lost
efficiency and possible
damage can occur.
Do not change the pulley
pitch diameter to change tension.
This will result in a different fan speed
than desired.
1. Loosen motor plate adjustment nuts on L-bolts and
move motor plate in order that the belts can easily slip into
the grooves on the pulleys. Never pry , roll, or force the belts
over the rim of the pulley.
2. Slide the motor plate back until proper tension is
reached. For proper tension a deflection of approximately 1/
4” per foot of center distance should be obtained by firmly
pressing the belt. Refer to Figure 3.
3. Lock the motor plate adjustment nuts in place.
4. Ensure pulleys are properly aligned. Refer to Figure 4.
GAP
Figure 3
GAP
Tolerance
Center
Distance
Up thru 12” 1/16”
12” up through
48”
Over 48” 1/4”
Maximum
Figure 4
Gap
1/8”
OFFSET ANGULAR OFFSET/ANGULAR
A
W
B
CENTER
DISTANCE
(CD)
X
Y
Z
3
Page 4

Pulley Alignment
Pulley alignment is adjusted by
loosening the motor pulley setscrew and
by moving the motor pulley on the motor
shaft.
Figure 4 indicates where to measure
the allowable gap for the drive alignment
tolerance. All contact points (indicated
by WXYZ) are to have a gap less than
the tolerance shown in the table. When
the pulleys are not the same width, the
Figure 5
allowable gap must be adjusted by half of the difference in
width (As shown in A & B of Figure 4). Figure 5 illustrates
using a carpenter’s square to adjust the position of the
motor pulley until the belt is parallel to the longer leg of the
square.
Final Installation Steps
1. Inspect fasteners and setscrews, particularly fan
mounting and bearing fasteners, and tighten according
to the recommended torque shown in the following
table.
2. Inspect for correct voltage with voltmeter.
3. Ensure all accessories are installed.
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts on metal (IN-LB)
Setscrews
Size
No.10 3/32” 28 33 3/8”-16 240
1/4” 1/8” 66 80 1/2”-13 600
5/16” 5/32” 126 156 5/8”-11 1200
3/8” 3/16” 228 275 3/4”-10 2100
7/16” 7/32” 29 348 7/8”-9 2040
1/2” 1/4” 42 504
5/8” 5/16” 92 1104
3/4” 3/8” 120 1440
Key Hex
Across
Flats
Recommended
Torque
Min. Max. Size
Hold Down Bolts
Wrench
Torque
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts on FRP (FT-LB)
Size 18-8 SST Hardware Torque
No 10 7
1/4” 12
5/16” 20
3/8” 30
7/16” 41
1/2” 54
5/8” 86
3/4” 128
Operation
Pre-Start Checks
1. Lock out all the primary and secondary power sources.
2. Ensure fasteners and setscrews, particularly those
used for mounting the fan, are tightened.
3. Inspect belt tension and pulley alignment.
4. Inspect motor wiring.
5. Ensure belt touches only the pulleys.
6. Ensure fan and ductwork are clean and free of debris.
7. Inspect wheel-to-inlet clearance. The correct wheel-toinlet clearance is critical to proper fan performance.
8. Close and secure all access doors.
9. Restore power to the fan.
Start Up
Turn the fan on. In variable speed units, set the fan to its
lowest speed and inspect for the following:
• Direction of rotation.
• Excessive vibration.
• Unusual noise.
• Bearing noise.
• Improper belt alignment or tension (listen for
squealing).
• Improper motor amperage or voltage.
NOTICE! If a problem is discovered, immediately
shut the fan off. Lock out all electrical power and check
for the cause of the trouble. See Troubleshooting.
Use of Variable Frequency Drives
Motors:
Motors that are to be operated using a Variable Frequency
Drive (VFD) must be VFD compatible. At a minimum, this
must be a Premium Efficiency motor with Class F
insulation. Motors that are not supplied by Loren Cook
Company should have the recommendation of the motor
manufacturer for use with a VFD.
Grounding:
The fan frame, motor and VFD must be connected to a
common earth ground to prevent transient voltages from
damaging rotating elements.
Wiring:
Line reactors may be required to reduce over-voltage
spikes in the motors. The motor manufacturer should be
consulted for recommended line impedence and usage of
line reactors or filters, if the lead length between the VFD
and the motor exceeds 10 feet (3m).
Fan:
It is the responsibility of the installing body to perform
coast-down tests and identify any resonant frequencies
after the equipment is fully installed. These resonant
frequencies are to be removed from the operating range of
the fan by using the “skip frequency” function in the VFD
programming. Failure to remove resonant frequencies from
the operating range will decrease the operating life of the
fan and void the warranty.
Inspection
Inspection of the fan should be conducted at the first 30
minute, 8 hour and 24 hour intervals of satisfactory
operation. During the inspections, stop the fan and inspect
as per the Conditions Chart.
30 Minute Interval
Inspect bolts, setscrews, and motor mounting bolts.
Adjust and tighten as necessary.
8 Hour Interval
Inspect belt alignment and tension. Adjust and tighten as
necessary.
24 Hour Interval
Inspect belt tension, bolts, setscrews, and motor
mounting bolts. Adjust and tighten as necessary.
4
Page 5

Maintenance
Establish a schedule for inspecting all parts of the fan.
The frequency of inspection depends on the operating
conditions and location of the fan.
Inspect fans exhausting corrosive or contaminated air
within the first month of operation. Fans exhausting
contaminated air (airborne abrasives) should be inspected
every three months.
Regular inspections are recommended for fans
exhausting non-contaminated air.
It is recommended the following inspection be
conducted twice per year.
• Inspect bolts and setscrews for tightness. Tighten as
necessary. Worn setscrews should be replaced
immediately.
• Inspect belt wear and alignment. Replace worn belts
with new belts and adjust alignment as needed. See
the Belt and Pulley Installation.
• Bearings should be inspected as recommended in the
Lubrication Conditions Chart.• Inspect variable inlet
vanes for freedom of operation and excessive wear.
The vane position should agree with the position of the
control arm. As the variable inlet vanes close, the
entering air should spin in the same direction as the
wheel.
• Inspect springs and rubber isolators for deterioration
and replace as needed.
• Inspect for cleanliness. Clean exterior surfaces only.
Removing dust and grease on motor housing assures
proper motor cooling. Removing dirt from the wheel
and housing prevent imbalance and damage.
Wiring Diagrams
Single Speed, Single Phase Motor
Ground A
L
T-1
T-4
Ground B
When ground is required, attach to ground A or B with no. 6 thread forming
screw. To reverse, interchange T-1 and T-4.
2 Speed, 2 Winding, Single Phase Motor
Ground A
T-1
T-4
Ground B
When ground required, attach to ground A or B with No. 6 thread forming
screw. To reverse, interchange T-1 and T-4 leads.
Single Speed, Single Phase, Dual Voltage
Ground A
L
Line
L
1
2
T-5
J-10
Ground B
When ground required, attach to ground A or B with No. 6 thread forming
screw. To reverse, interchange T-5 and J-10 leads.
Link A
Link B
Low Voltage
Typical Damper Motor Schematic
Fan
Motor
Transformer**
Line
L
T-5
J-10
Ground B
1
2
High Speed
L
1
L
2
Low Speed
Ground A
L3
L2
L1
Transformer**
Line
L
Line
L
1
2
Link A & B
For 3 phase, damper motor voltage should be the same between L1 and
L2. For single phase application, disregard L3. *Damper motors may be
available in 115, 230 and 460 volt models. The damper motor nameplate
voltage should be verified prior to connection. ** A transformer may be provided in some installations to correct the damper motor voltage to the
specified voltage.
Wiring Diagrams
3 Phase, 9 Lead Motor
Y-Connection
Low Voltage
208/230 Volts
4
5
6
1
728
To reverse, interchange any 2 line leads.
3
9
L2L
L
3
1
High Voltage
460 Volts
456
789
12
L2L
L
1
2 Speed, 1 Winding, 3 Phase Motor
High Speed
1
Together
2
Motor
To reverse, interchange any 2 line leads. Motors require magnetic control.
3
L
4
1
L
5
2
6
Line
L
3
2 Speed, 2 Winding, 3 Phase
To reverse: High Speed-interchange leads T11 and T12.
Low Speed-interchange leads T1 and T2. Both Speeds-interchange any 2
line leads.
3 Phase, 9 Lead Motor
Delta-Connection
Low Voltage
208/230 Volts
8
7
4
6
2
1
3
L
1
3
L
2
Low Speed
Motor
L
High Voltage
9
5
3
3
1
2
3
4
6
460 Volts
789
456
3
12
L
L
L
1
3
2
L
1
L
2
Line
L
3
Open
5
Damper
Motor*
Second
Damper
Motor
5
Page 6

Lubrication - Fan Bearings
Greasable fan bearings are lubricated through a grease
fitting on the bearing.
Lubrication Conditions Chart
Fan Class Fan Status Shaft Size
Centrifugal
Blower
Class I
Centrifugal
Blower
Class II
Centrifugal
Blower
Class III
Normal Conditions
(Clean, Dry & Smooth)
Extreme Conditions
(Dirty/Wet/Rough)
Normal Conditions
(Clean, Dry & Smooth)
Extreme Conditions
(Dirty/Wet/Rough)
Normal Conditions
(Clean, Dry & Smooth)
Extreme Conditions
(Dirty/Wet/Rough)
> 1-1/2” 10,000
< 1-1/2” 2,000
> 1-1/2” 2,000
< 1-1/2” 400
> 2” 7,500
< 2” 1,000
> 2” 1,500
< 2” 200
> 2” 3,000
< 2” 500
> 2” 500
< 2” 100
Maximum Interval
(operational hrs)
Exceptions to the greasing interval chart:
• Periodic Applications (any break of one week or
more): it is recommended that full lubrication be
performed prior to each break in operation.
• Higher Temperature: it is recommended to halve
the intervals for every 30F increase in operating
temperature above 120F not to exceed 230F
for standard bearings; High Temperature bearings (optional) can operate up to 400F.
• Vertical Shaft: it is recommended that the intervals should be halved.
For best results, lubricate the bearing while the fan is in
operation. Pump grease in slowly until a slight bead forms
around the bearing seals. Excessive grease can burst
seals thus reducing bearing life.
Before lubricating, the grease nipple and immediate
vicinity should be thoroughly cleaned without the use of
high pressure equipment. The grease should be supplied
slowly as the bearing rotates until fresh grease slips past
the seal. Excessive pressure should be avoided to prevent
seal damage.
In the event the bearing cannot be seen, use no more
than three injections with a hand-operated grease gun.
NOTICE! Loren Cook Company uses petroleum
lubricant in a lithium base. Other types of grease
should not be used unless the bearings and lines have
been flushed clean. If another type of grease is used, it
should be a lithium-based grease conforming to NLGI
grade 2 consistency. A NLGI grade 2 grease is a light
viscosity, low-torque, rust-inhibiting lubricant that is
water resistant. Its temperature range is from -30F to
+200F and capable of intermittent highs of +250F. For
temperatures above 250°F Mobiltemp SHC 32 is
recommended.
Lubrication - Motor Bearings
Motors are provided with prelubricated bearings. Any
lubrication instructions shown on the motor nameplate
supersede instructions below.
Motor bearings without provisions for relubrication will
operate up to 10 years under normal conditions with no
maintenance. In severe applications, high temperatures or
excessive contaminates, it is advisable to have the
maintenance department disassemble and lubricate the
bearings after 3 years of operation to prevent interruption
of service.
For motors with provisions for relubrication, follow
intervals of the following table.
Relubrication Intervals
NEMA Frame Size
Up to and
Service
Conditions
Standard 3 yrs. 6 months 2 yrs. 6 months 1 yr. 3 months
Severe 1 yr. 3 months 1 yr. 3 months 6 months 1 months
including 184T
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
213T-365T 404T and larger
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
Motors are provided with a polyurea mineral oil NGLI #2
grease. All additions to the motor bearings are to be with a
compatable grease such as Exxon Mobil Polyrex EM and
Chevron SRI.
The above intervals should be reduced to half for vertical
shaft installations.
Motor Services
Should the motor prove defective within a one-year
period, contact your local Loren Cook representative or
your nearest authorized electric motor service
representative.
Pulley and Belt Replacement
1. Remove pulleys from their respective shafts.
2. Clean the motor and fan shafts.
3. Clean bores of pulleys & coat the bores with heavy oil.
4. Remove grease, rust, or burrs from pulleys & shafts.
5. Remove burrs from shaft by sanding.
6. Place fan pulley on fan shaft and motor pulley on its
shaft. Damage to the pulleys can occur when
excessive force is used in placing the pulleys on their
respective shafts.
7. Tighten in place.
8. Install belts on pulleys and align as described in the
Belt and Pulley Installation section.
Bearing Replacement
1. Follow all local lock-out / tag-out procedures and
unwire the units motor.
2. Loosen the bolts supporting the motor plate and
remove the belt. Inspect the belt for signs of wear and
set aside.
3. Measure and record the distance of the wheel from
the housing side.
4. Using a putty knife at the wheel hub, scrape the resin
from the safety plate and retaining bolt.
5. Remove the retaining bolt and safety plate and set
aside.
6. Using either a jewelry screw driver or small drill bit,
remove the beeswax from the set screw openings and
set screw heads.
7. Remove the wheel and remove the old bearings and
shaft.
8. Install the new shaft to the wheel, safety plate, and
retaining bolt. Tighten all per the torque values as
stated on page 4.
9. Using a fiberglass resin repair kit, apply resin per the
manufacture instruction over the safety plate, and
retaining bolt. Recommend using a Grainger part
6
Page 7

number 3RAR9 or equal.
10. Reapply beeswax to protect the set screw heads.
11. Install the new shaft by sliding the bearings to the
desired location using the measurement record earlier
and loosely mounting the bearing support. Bearing
bolts and bearing set screws should be loose enough
to allow shaft position later. Please note the wheel to
inlet clear matches as close as possible the diagram
on page 3
12. Tighten all hardware per the torque values as stated
on page 4 and follow the Operation Pre-Start Check
and Start-Up listed in this document.
After 24 hours of operation, retighten the setscrews to
the appropriate torque. This assures full locking of the inner
race to the shaft. Make sure the socket key or driver is in
good condition with no rounded corners. The key should be
fully engaged in the setscrew and held squarely to prevent
rounding out of the setscrew socket when applying
maximum torque.
Maximum Fan RPM
Size
120 4500 4500
150 3600 4300
180 2900 3600
245 2200 2700
270 2000 2400
300 1800 2200
330 1650 2000
365 1500 1800
Maximum RPM
FCP FCP 66
Overheated Motor:
• Motor improperly wired.
• Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor
or belt drive assembly.
• Cooling air diverted or blocked.
• Improper inlet clearance.
• Incorrect fan RPMs.
•Incorrect voltage.
Overheated Bearings
• Improper bearing lubrication
• Excessive belt tension.
Troubleshooting
Low Capacity or Pressure:
• Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor or
belt drive assembly.
• Poor fan inlet conditions. There should be a straight
clear duct at the inlet.
• Improper wheel alignment.
Excessive Vibration and Noise:
• Damaged or unbalanced wheel.
• Belts too loose; worn or oily belts.
• Speed too high.
• Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor or
belt drive assembly.
• Bearings need lubrication or replacement.
• Fan surge or incorrect inlet or outlet condition.
7
Page 8

Limited Warranty
Loren Cook Company warrants that your Loren Cook
fan was manufactured free of defects in materials and
workmanship, to the extent stated herein. For a period
of one (1) year after date of shipment, we will replace
any parts found to be defective without charge, except
for shipping costs which will be paid by you.
This warranty is granted only to the original purchaser
placing the fan in service.
This warranty is void if the fan or any part thereof has
been altered or modified from its original design or has
been abused, misused, damaged or is in worn condition
or if the fan has been used other than for the uses
described in the company manual. This warranty does
not cover defects resulting from normal wear and tear.
To make a warranty claim, notify Loren Cook
Company, General Offices, 2015 East Dale Street,
Springfield, Missouri 65803-4637, explaining in writing,
in detail, your complaint and referring to the specific
model and serial numbers of your fan. Upon receipt by
Loren Cook Company of your written complaint, you will
be notified, within thirty (30) days of our receipt of your
complaint, in writing, as to the manner in which your
claim will be handled. If you are entitled to warranty
relief, a warranty adjustment will be completed within
sixty (60) business days of the receipt of your written
complaint by Loren Cook Company.
This warranty gives only the original purchaser placing
the fan in service specifically the right. You may have
other legal rights which vary from state to state.
For fans provided with motors, the motor
manufacturer warrants motors for a designated period
stated in the manufacturer’s warranty. W arranty periods
vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Should motors
furnished by Loren Cook Company prove defective
during the designated period, they should be returned to
the nearest authorized motor service station. Loren
Cook Company will not be responsible for any removal
or installation costs.
Corporate Offices: 2015 E. Dale Street Springfield, MO 65803 417.869.6474
lorencook.com
8
FCP IOM - June 2013
 Loading...
Loading...