Page 1
CCP
Centrifugal Plug Fans
INSTALLATION, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
This publication contains the installation, operation and
maintenance instructions for standard units of the CCP
Centrifugal Plug Fans.
Carefully read this publication and any
supplemental documents prior to any
installation or maintenance procedure.
Loren Cook catalog CCP provides additional information
describing the equipment, fan performance, available
accessories, and specification data.
For additional safety information, refer to AMCA publication 410-96, Safety Practices for Users and Installers of
Industrial and Commercial Fans.
All of the publications listed above can be obtained from
Loren Cook Company by phoning 417/869-6474, extension
166; by FAX at 417/832-9431; or by e-mail at info@lorencook.com.
For information on special equipment, contact Loren
Cook Company Customer Service Department at 417/869-
6474.
Rotating Parts & Electrical Shock Hazard:
Disconnect electric power before working on unit.
Follow proper lockout / tagout procedures to ensure
the unit cannot be energized while being installed or
serviced.
A disconnect switch should be placed near the fan in
order that the power can be swiftly cut off, in case of
an emergency and in order that maintenance
personnel are provided complete control of the power
source.
Grounding is required. All field-installed wiring must
be completed by qualified personnel. All fieldinstalled wiring must comply with National Electric
Code (NFPA 70) and all applicable local codes.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in
death or serious injury.
Storage
If the fan is stored for any length of time prior to installation, completely fill the bearings with grease or moistureinhibiting oil (refer to Lubricants on page 5). Rotate the
wheel several revolutions every three to five days to keep a
coating of grease on all internal bearing parts.
Store the fan in its original crate and protect it from dust,
debris and the weather.
Outdoor Storage
To maintain good working condition of the fan when it is
stored outdoors, follow the additional instructions below.
• Coat the shaft with grease or a rust preventative compound.
• Wrap bearings for weather protection.
• Cover the inlet and outlet to prevent the accumulation of
dirt and moisture in the housing.
• Periodically rotate the wheel and operate dampers (if
supplied).
• Periodically inspect the unit to prevent damaging condi-
tions.
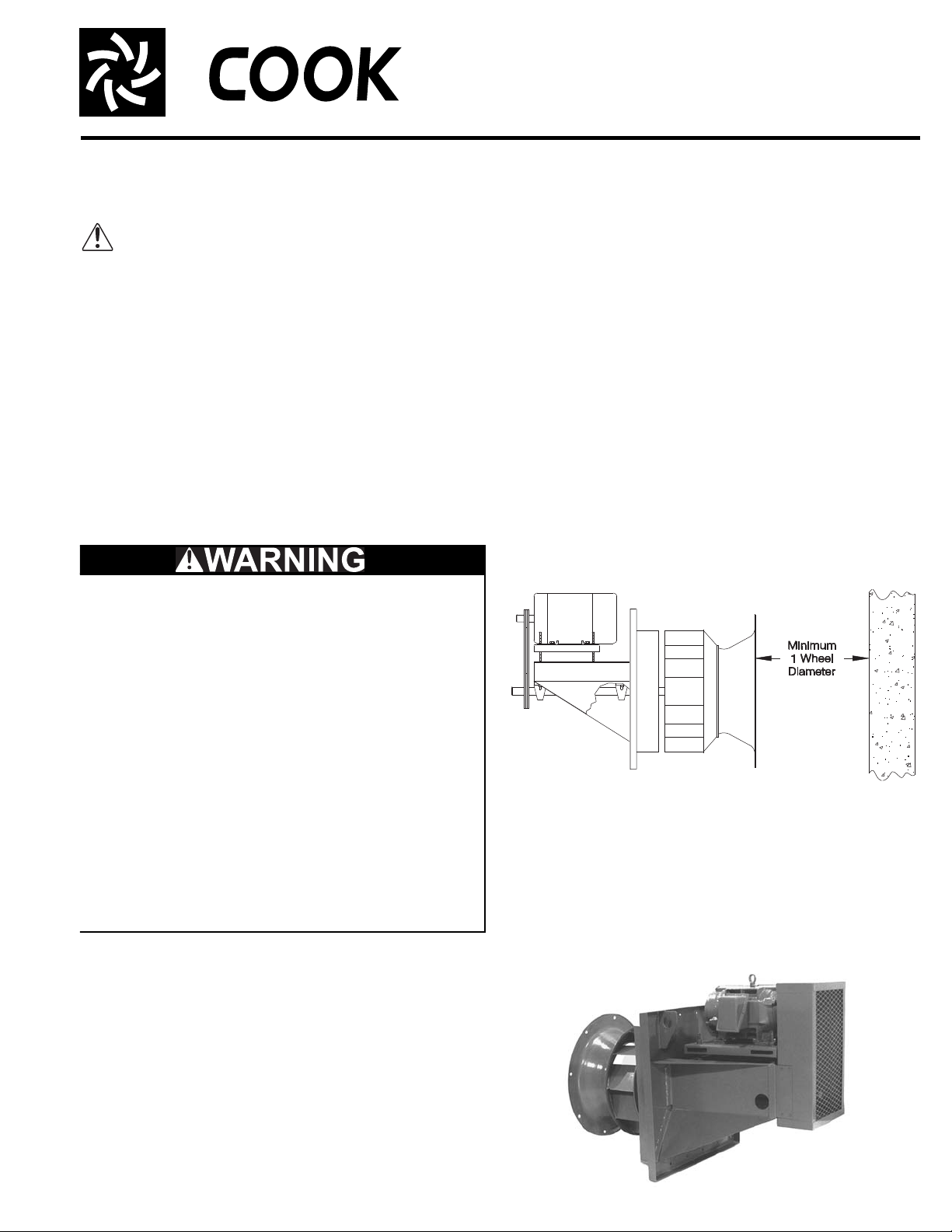
Installation
Figure 2 - Non-ducted Inlet Clearance
When mounting the fan, be sure that the structure of the
wall is rigid enough to support the weight of the fan and its
motor.
Consult the specific fan type submittal for the exact fan
dimensions needed to determine the size of your wall opening. The wall opening should be just large enough for the
Receiving and Inspection
Carefully inspect the fan and accessories for any dam-
age and shortage immediately upon receipt of the fan.
• Turn the wheel by hand to ensure it turns freely and
does not bind.
• Inspect dampers (if supplied) for free operation of all
moving parts.
• Record on the Delivery Receipt any visible sign of
damage.
Handling
Lift the fan by the base or lifting eyes on the housing.
NOTICE! Never lift by the shaft, wheel, or motor.
CCP
Page 2
1 foot
1/4 inch
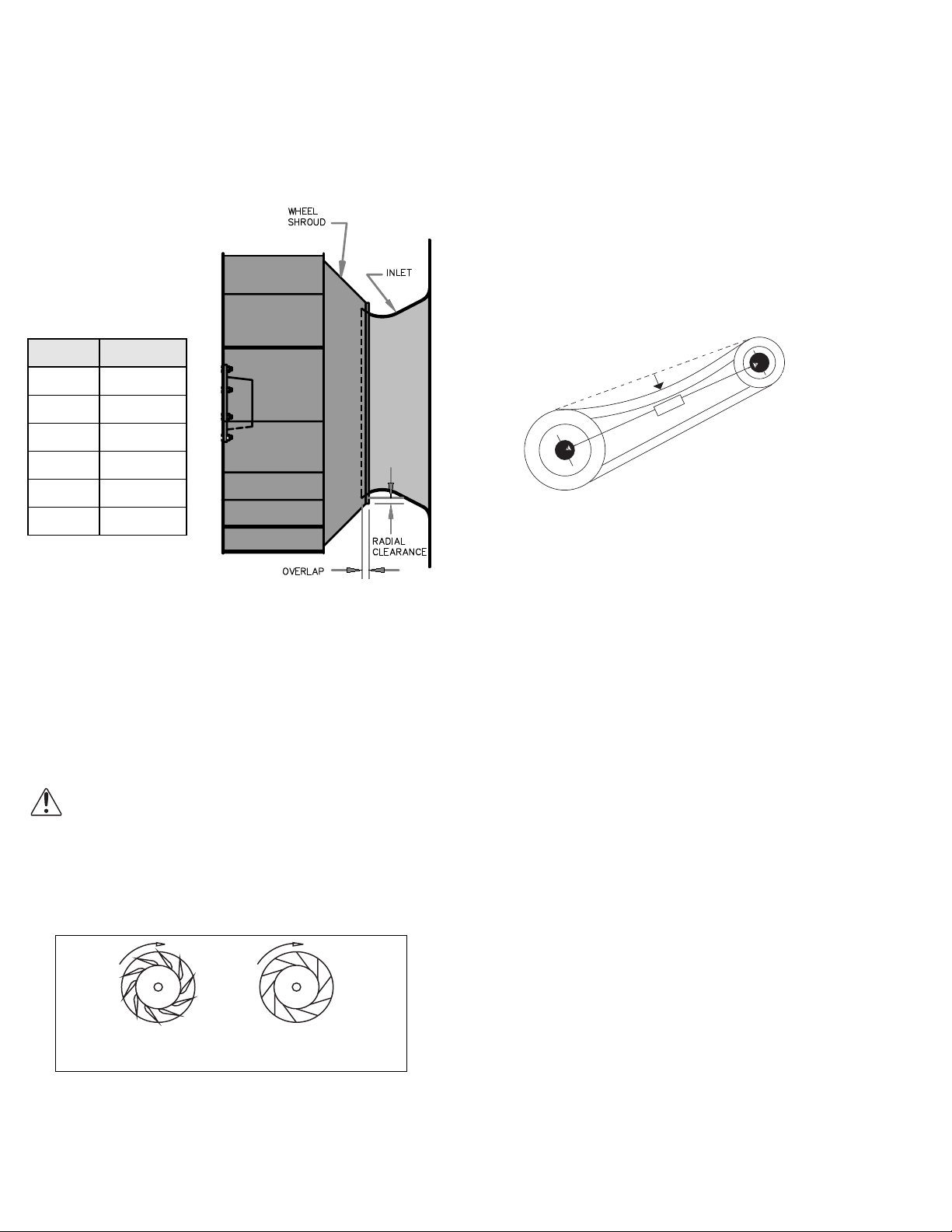
Wheel-to-Inlet Clearance
The correct wheel-to-inlet clearance is critical to proper
fan performance. This clearance should be verified before
initial start-up since rough handling during shipment could
cause a shift in fan components. Refer to wheel/inlet drawing for correct overlap.
Adjust the overlap by loosening the wheel hub and moving the wheel along the shaft to obtain the correct value.
A uniform radial gap
(space between the edge of
the cone and the edge of
the inlet) is obtained by
loosening the inlet cone
bolts and repositioning the
inlet cone.
Size Overlap
100 - 165 3/16”
180 - 245 1/4”
270 - 300 5/16”
330 - 365 3/8”
115 and 230 Single Phase Motors
Fan wheel rotation is set correctly at the factory. Changing the rotation of this type of motor should only be
attempted by a qualified electrician.
208, 230, and 460, 3 Phase Motors
These motors are electrically reversible by switching two
of the supply leads. For this reason, the rotation of the fan
cannot be restricted to one direction at the factory. See
Wiring Diagrams on page 3 for specific information on
reversing wheel direction.
NOTICE! Do not allow the fan to run in the wrong
direction. This will overheat the motor and cause serious damage. For 3-phase motors, if the fan is running
in the wrong direction, check the control switch. It is
possible to interchange two leads at this location so
that the fan is operating in the correct direction.
402 7/16”
445 1/2”
Wiring Installation
All wiring should be in
accordance with local ordinances and the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70. Ensure the power supply (voltage, frequency, and current carrying capacity of wires) is in
accordance with the motor nameplate.
Leave enough slack in the wiring to allow for motor
movement when adjusting belt tension. Some fractional
motors have to be removed in order to make the connection with the terminal box at the end of the motor. To
remove motor, remove bolts securing motor base to power
assembly. Do not remove motor mounting bolts.
Follow the wiring diagram in the disconnect
switch and the wiring diagram provided with the
motor. Correctly label the circuit on the main
power box and always identify a closed switch
to promote safety (i.e., red tape over a closed
switch).
Airfoil Backward
Wheel Rotation
Test the fan to ensure the rotation of the wheel is the
Proper Wheel Rotation
Inclined
same as indicated by the arrow marked Rotation.
Figure 1
Belt and Pulley Installation
Belt tension is determined by the sound the belts make
when the fan is first started. Belts will produce a loud
squeal which dissipates after the fan is operating at full
capacity. If the belt tension is too tight or too loose, lost efficiency and possible damage can occur.
Do not change the pulley pitch diameter to change tension. This will result in a different fan speed than desired.
a. Loosen motor plate adjustment bolts and move motor
plate in order that the belts can easily slip into the
grooves on the pulleys. Never pry, roll, or force the
belts over the rim of the pulley.
b. Slide the motor plate back until proper tension is
reached. For proper tension a deflection of approximately 1/4” per foot of center distance should be
obtained by firmly pressing the belt. Refer to Figure 1.
Use of Variable Frequency Drives
Motors -
Motors that are to be operated using a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) must be VFD compatible. At a minimum, this must be a Premium Efficiency motor with Class F
insulation. Motors that are not supplied by Loren Cook
Company should have the recommendation of the motor
manufacturer for use with a VFD.
Grounding -
The fan frame, motor and VFD must be connected to a
common earth ground to prevent transient voltages from
damaging rotating elements.
Wiring -
Line reactors may be required to reduce over-voltage
spikes in the motors. The motor manufacturer should be
2
Page 3
consulted for recommended line impedence and usage
of line reactors or filters, if the lead length between the
VFD and the motor exceeds 10 feet (3m).
Fan -
It is the responsibility of the installing body to perform
coast-down tests and identify any resonant frequencies
after the equipment is fully installed. These resonant frequencies are to be removed from the operating range of
the fan by using the “skip frequency” function in the VFD
programming. Failure to remove resonant frequencies
from the operating range will decrease the operating life
of the fan and void the warranty.
Belt and Pulley Installation continued
c. Lock the motor plate adjustment bolts in place.
d. Ensure pulleys are properly aligned. Refer to Figure
2.
Pulley Alignment
Pulley alignment is adjusted by loosening the motor pulley setscrew and by
moving the motor pulley on the motor
shaft.
Figure 2 indicates where to measure the
allowable gap for the drive alignment tolerance. All contact points (indicated by
WXYZ) are to have a gap less than the
tolerance shown in the table. When the
pulleys are not the same width, the
Figure 3
allowable gap must be adjusted by half of the difference in
width (As shown in A & B of Figure 2). Figure 3 illustrates
using a carpenter’s square to adjust the position of the
motor pulley until the belt is parallel to the longer leg of the
square.
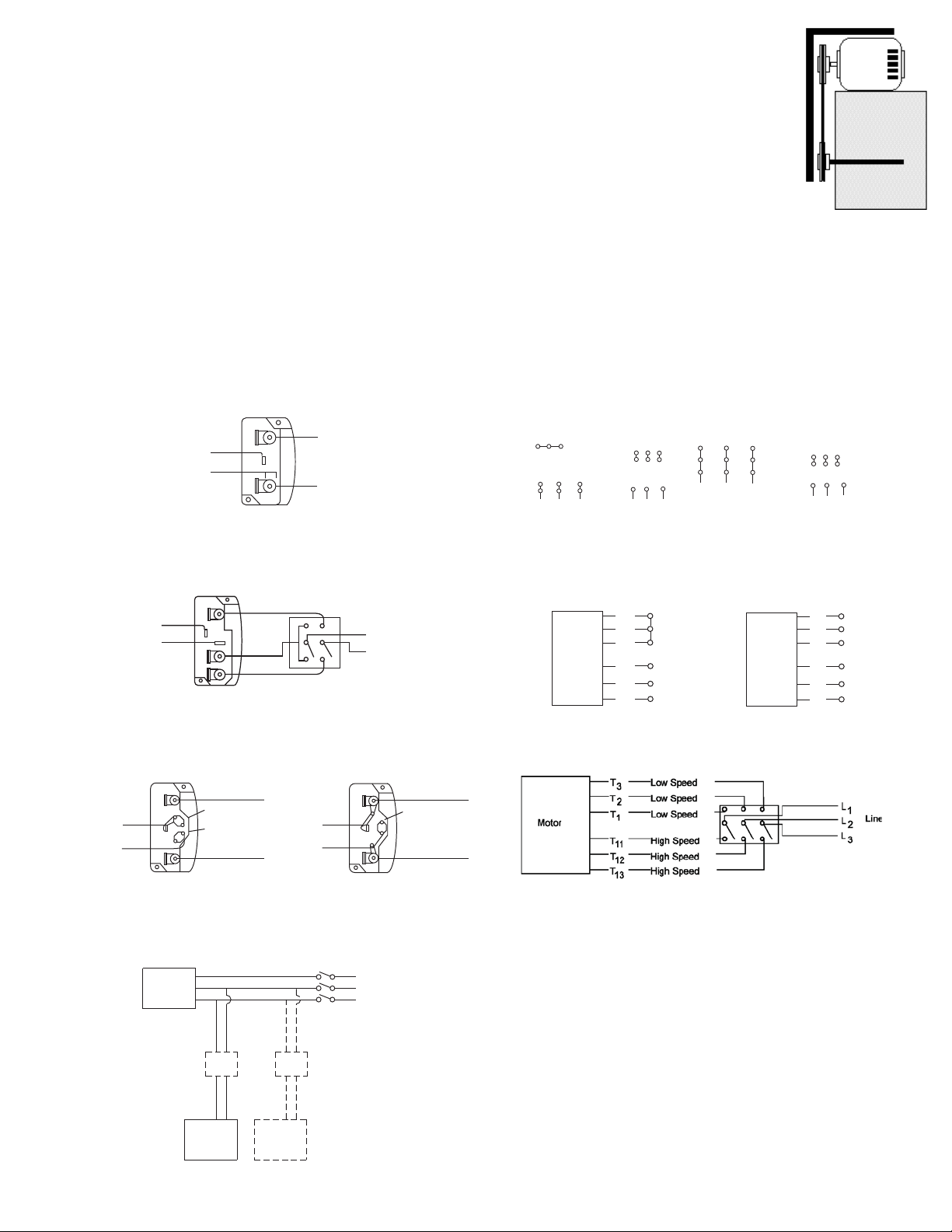
Wiring Diagrams
Single Speed, Single Phase Motor
Ground A
L
T-1
T-4
Ground B
When ground is required, attach to ground A or B with no. 6 thread form-
1
Line
L
2
Wiring Diagrams
3 Phase, 9 Lead Motor
Y-Connection
Low Voltage
208/230 Volts
4
5
6
3
1
9
728
L2L
L
1
3
High Voltage
460 Volts
456
789
12
L2L
L
1
To reverse, interchange any 2 line leads.
3 Phase, 9 Lead Motor
Delta-Connection
Low Voltage
208/230 Volts
7
6
1
3
L
L
1
3
8
4
2
2
ing screw. To reverse, interchange T-1 and T-4.
2 Speed, 2 Winding, Single Phase Motor 2 Speed, 1 Winding, 3 Phase Motor
Ground A
T-1
T-4
Ground B
High Speed
L
1
L
2
Low Speed
Line
When ground required, attach to ground A or B with No. 6 thread forming
screw. To reverse, interchange T-1 and T-4 leads.
Motor
To reverse, interchange any 2 line leads. Motors require magnetic control.
High Speed
1
Together
2
3
L
4
1
L
5
6
L
2
Line
3
Single Speed, Single Phase, Dual Voltage 2 Speed, 2 Winding, 3 Phase
Ground A
L
T-5
J-10
Link A
Link B
Low Voltage
Ground B
Line
L
1
T-5
J-10
2
Ground B
When ground required, attach to ground A or B with No. 6 thread forming
screw. To reverse, interchange T-5 and J-10 leads.
Ground A
Link A & B
L
Line
L
1
2
To reverse: High Speed-interchange leads T11 and T12.
Low Speed-interchange leads T1 and T2. Both Speeds-interchange any 2
line leads.
Typical Damper Motor Schematic
9
5
3
L
3
Motor
High Voltage
460 Volts
789
456
3
12
L1L
L
2
Low Speed
1
2
3
4
5
6
3
L
L
L
Open
1
2
Line
3
Fan
Motor
Transformer**
Damper
Motor*
Second
Damper
Motor
L3
L2
L1
Transformer**
For 3 phase, damper motor voltage should be the same between L1 and
L2. For single phase application, disregard L3. *Damper motors may be
available in 115, 230 and 460 volt models. The damper motor nameplate
voltage should be verified prior to connection. **A transformer may be provided in some installations to correct the damper motor voltage to the
specified voltage.
3
Page 4

Final Installation Steps
a. Inspect fasteners and setscrews, particularly fan
mounting and bearing fasteners, and tighten according to the recommended torque shown in the table
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts.
b. Inspect for correct voltage with voltmeter.
c. Ensure all accessories are installed.
Field Balancing
Due to the innumerable methods for mounting the CCP
fan, field balancing must be performed after final installation. The fan must be dynamically two-plane balanced to
obtain a maximum vibration velocity of .0785 inches/second. Failure to perform this field balance may result in
excessive vibration levels which can lead to early failure of
the fan and/or mounting structure and will void the warranty.
Operation
Pre-Start Checks
Tolerance
Center Distance
Up thru 12” 1/16”
12” up through 48 1/8”
Over 48” 1/4”
Maximum
Gap
OFFSET ANGULAR OFFSET/ANGULAR
A
W
the Conditions Chart.
30 Minute Interval
Inspect bolts, setscrews, and motor mounting bolts.
Adjust and tighten as necessary.
8 Hour Interval
Inspect belt alignment and tension. Adjust and tighten as
necessary.
24 Hour Interval
Inspect belt tension., bolts, and setscrews and motor
nting bolts. Adjust and tighten as necessary.
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts (IN/LB)
Setscrews
Size
No.10 3/32” 28 33 3/8”-16 240
1/4” 1/8” 66 80 1/2”-13 600
5/16” 5/32” 126 156 5/8”-11 1200
3/8” 3/16” 228 275 3/4”-10 2100
7/16” 7/32” 348 384 7/8”- 9 2040
1/2” 1/4” 504 600 1”- 8 3000
5/8” 5/16” 1104 1200 1-1/8” - 7 4200
3/4” 3/8” 1440 1800 1-1/4” - 7 6000
Key Hex
Across
Flats
Recommended
Torque
Min. Max. Size
Hold Down Bolts
Wrench
Torque
a. Lock out all the
primary and
X
Y
CENTER
DISTANCE
(CD)
secondary
power sources.
b. Ensure fasten-
ers and set-
Figure 2
Z
B
GAP
GAP
screws,
particularly those used for mounting the fan, are tight-
ened.
c. Inspect belt tension and pulley alignment.
d. Inspect motor wiring.
e. Ensure belt touches only the pulleys.
f. Ensure fan and ductwork are clean and free of debris.
g. Inspect wheel-to-inlet clearance. The correct wheel-
to-inlet clearance is critical to proper fan performance.
h. Close and secure all access doors.
i. Restore power to the fan.
Start Up
Turn the fan on. In variable speed units, set the fan to its
lowest speed and inspect for the following:
• Direction of rotation.
• Excessive vibration.
• Unusual noise.
• Bearing noise.
• Improper belt alignment or tension (listen for squealing).
• Improper motor amperage or voltage.
NOTICE! If a problem is discovered, immediately
shut the fan off. Lock out all electrical power and check
for the cause of the trouble. See Troubleshooting.
Maintenance
Establish a schedule for inspecting all parts of the fan.
The frequency of inspection depends on the operating conditions and location of the fan.
Inspect fans exhausting corrosive or contaminated air
within the first month of operation. Fans exhausting contaminated air (airborne abrasives) should be inspected
every three months.
Regular inspections are recommended for fans exhaust-
ing non-contaminated air.
It is recommended the following inspection be conducted
twice per year.
• Inspect bolts and setscrews for tightness. Tighten as
necessary. Worn setscrews should be replaced immediately.
• Inspect belt wear and alignment. Replace worn belts
with new belts and adjust alignment as needed. Refer
to Belt and Pulley Installation, page 2.
• Bearings should be inspected as recommended in the
Conditions Chart.
• Inspect variable inlet vanes for freedom of operation
and excessive wear. The vane position should agree
with the position of the control arm. As the variable inlet
vanes close, the entering air should spin in the same
direction as the wheel.
• Inspect for cleanliness. Clean exterior surfaces only.
Removing dust and grease on motor housing assures
proper motor cooling. Removing dirt from the wheel
and housing prevent imbalance and damage.
Inspection
Inspection of the fan should be conducted at the first 30
minute, 8 hour and 24 hour intervals of satisfactory opera-
tion. During the inspections, stop the fan and inspect as per
4
Page 5

Lubrication - Fan Bearings
Bearings are lubricated through a grease fitting on the
exterior of the fan housing and should be lubricated by the
schedule, Lubrication Conditions Chart.
For best results, lubricate the bearing while the fan is in
operation. Pump grease in slowly until a slight bead forms
around the bearing seals. Excessive grease can burst
seals thus reducing bearing life.
Before lubricating, the grease nipple and immediate
vicinity should be thoroughly cleaned without the use of
high pressure equipment. The grease should be supplied
slowly as the bearing rotates until fresh grease slips past
the seal. Excessive pressure should be avoided to prevent
seal damage.
Use no more than three injections with a hand-operated
grease gun.
Exceptions to the greasing interval chart:
• Periodic Applications (any break of one week or
more): it is recommended that full lubrication be performed
prior to each break in operation.
• Higher Temperature: it is recommended to halve the
intervals for every 30F increase in operating temperature
above 120F not to exceed 230F for standard bearings;
High Temperature bearings (optional) can operate up to
400F.
• Vertical Shaft: it is recommended that the intervals
should be halved.
Loren Cook Company uses petroleum lubricant in a lithium base. Other types of grease should not be used unless
the bearings and lines have been flushed clean. If another
type of grease is used, it should be a lithium-based grease
conforming to NLGI grade 2 consistency.
A NLGI grade 2 grease is a light viscosity, low-torque,
rust-inhibiting lubricant that is water resistant. Its temperature range is from -30F to +200F and capable of intermittent highs of +250F. For temperatures above 250F
Mobiltemp SHC 32 is recommended.
Lubrication Conditions Chart
Fan Class Fan Status Shaft Size
Normal Conditions
Centrifugal Blower
Class I
Centrifugal Blower
Class II
(Clean, Dry & Smooth)
Extreme Conditions
(Dirty/Wet/Rough)
Normal Conditions
(Clean, Dry & Smooth)
Extreme Conditions
(Dirty/Wet/Rough)
> 1-1/2” 10,000
< 1-1/2” 2,000
> 1-1/2” 2,000
< 1-1/2” 400
> 2” 7,500
< 2” 1,000
> 2” 1,500
< 2” 200
Maximum Interval
(operational hrs)
Lubrication - Motor Bearings
Motors are provided with prelubricated bearings. Any
lubrication instructions shown on the motor nameplate
supersede instructions below.
Motor bearings without provisions for relubrication will
operate up to 10 years under normal conditions with no
maintenance. In severe applications, high temperatures or
excessive contaminates, it is advisable to have the maintenance department disassemble and lubricate the bearings
after 3 years of operation to prevent interruption of service.
For motors with provisions for relubrication, follow intevals of the following table.
Relubrication Intervals
NEMA Frame Size
Service
Conditions
Standard 3 yrs. 6 months 2 yrs. 6 months 1 yr. 3 months
Severe 1 yr. 3 months 1 yr. 3 months 6 months 1 months
Up to and
including 184T
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
213T-365T 404T and larger
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
1800 RPM
and less
Over 1800
RPM
Motors are provided with a polyurea mineral oil NGLI #2
grease. All additions to the motor bearings are to be with a
compatable grease such as Exxon Mobil Polyrex EM and
Chevron SRI.
The above intervals should be reduced to half for vertical
shaft installations.
Motor Services
Should the motor prove defective within a one-year
period, contact your local Loren Cook representative or
your nearest authorized electric motor service representative.
Changing Shaft Speed
All belt driven fans with motors up to and including 5 HP
(184T max.) are equipped with variable pitch pulleys. To
change the fan speed, perform the following:
a. Loosen setscrew on driver (motor) pulley and remove
key, if equipped.
b. Turn the pulley rim to open or close the groove facing.
If the pulley has multiple grooves, all must be adjusted
to the same width.
c. After adjustment, inspect for proper belt tension.
Speed Reduction
Open the pulley in order that the belt rides deeper in
the groove (smaller pitch diameter).
Speed Increase
Close the pulley in order that the belt rides higher in
the groove (larger pitch diameter). Ensure that the RPM
limits of the fan and the horsepower limits of the motor
are maintained.
Maximum RPM
CCP-A
Size
120 3948 5151 120 3692 4817
135 3508 4577 135 2953 3853
150 2749 3587 150 2656 3465
165 2509 3273 165 2414 3150
180 2150 2805 180 2389 3117
195 1987 2592 195 2204 2876
210 1841 2402 210 1786 2330
225 1712 2234 225 1659 2164
245 1608 2098 245 1532 1999
270 1418 1850 270 1391 1815
300 1276 1665 300 1251 1632
330 1162 1516 330 1141 1489
365 1065 1389 365 1022 1333
402 964 1258 402 936 1221
445 873 1139 445 846 1104
Maximum RPM
Class I Class II Class I Class II
CCP-F
Size
Maximum RPM
5
Page 6

RPM Derating Factor
Operating
Temperature (°F)
For elevated airstream temperatures, the maximum fan speed limits must be derated
by the factors above.
Steel Aluminum
Speed Limit
Factor
70 1.00 70 1.00
200 0.98 200 0.93
300 0.96 300 0.79
400 0.94
500 0.91
600 0.87
700 0.81
800 0.75
Operating
Temperature (°F)
Speed Limit
Factor
Pulley and Belt Replacement
a. Remove pulleys from their respective shafts.
b. Clean the motor and fan shafts.
c. Clean bores of pulleys and coat the bores with heavy
oil.
d. Remove grease, rust, or burrs from the pulleys
e. Remove burrs from shaft by sanding.
f. Place fan pulley on fan shaft and motor pulley on its
shaft. Damage to the pulleys can occur when exces-
sive force is used in placing the pulleys on their
respective shafts.
g. Tighten in place.
h. Install belts on pulleys and align as described in the
Belt and Pulley Installation section.
Bearing Replacement
The fan bearings are pillow block ball bearings.
An emery cloth or file may be needed to remove imper-
fections in the shaft left by the setscrews.
a. Mark the location on the shaft of both bearing races,
setscrews, and the wheel and pulley . Mark the location
and orientation of the inlet cone. Note the clearance
between the wheel and inlet cone.
b. Remove the pulley.
c. Remove the inlet cone.
d. Remove the wheel from the shaft. A 2-jaw puller may
be required.
e. Remove bearing hold-down bolts. Remove shaft and
bearings as one unit.
f. Remove the anti-corrosion coating from the shaft with
a suitable degreaser.
g. Remove the bearing from the shaft using a bearing
puller. If a bearing puller is not available, tap on the
bearing with a wood block and hammer to remove it.
h. Smooth and clean the shaft and bearing bore thor-
oughly.
i. Place the bearings into position making sure they are
not on a worn section of the shaft. Tapping the inner
ring face with a soft driver may be required.
Do not hammer on the housing.
j. The outer ring of the bearing is spherical and swivels in
the housing to compensate for misalignment. Secure
hold-down bolts, but do not fully tighten.
k. Align the setscrews on the bearings and tighten one
setscrew on each bearing.
l. Rotate the shaft to allow the bearing outer rings to find
their center of free movement.
m. Install the wheel on the shaft. Install the inlet cone in
its original location. And adjust bearing position and
inlet cone to center the wheel in the inlet cone.
n. Tighten hold-down bolts to proper torque. Refer to
torque chart.
o. Turn the shaft by hand. Resistance should be the
same as it was before hold-down bolts were fully tight-
ened.
p. Tighten bearing setscrews to specified torque.
q. Re-install the pulley and adjust the belt tension.
Refer to Belts and Pulley Installation.
r. Test run and retighten all setscrews and bolts and trim
balance as necessary (.0785 in/sec max.).
After 24 hours of operation, retighten the setscrews to the
appropriate torque. This assures full locking of the inner
race to the shaft. Make sure the socket key or driver is in
good condition with no rounded corners. The key should be
fully engaged in the setscrew and held squarely to prevent
rounding out of the setscrew socket when applying
maximum torque.
Troubleshooting
Problem and Potential Cause
Low Capacity or Pressure
•Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor or belt drive assembly.
•Poor fan inlet conditions. There should be a straight clear duct at the
inlet.
•Improper wheel alignment.
Excessive Vibration and Noise
•Damaged or unbalanced wheel.
•Belts too loose; worn or oily belts.
•Speed too high.
•Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor or belt drive assembly.
•Bearings need lubrication or replacement.
•Fan surge or incorrect inlet or outlet condition.
Overheated Motor
•Motor improperly wired.
•Incorrect direction of rotation. Make sure the fan rotates in same direction as the arrows on the motor or belt drive assembly.
•Cooling air diverted or blocked.
•Improper inlet clearance.
•Incorrect fan RPMs.
•Incorrect voltage.
Overheated Bearings
•Improper bearing lubrication
•Excessive belt tension.
6
Page 7

CCP Parts List
4
3
5
8
2
1
13
Part
No.
1 Fan Sheave
2 Belt Set
3 Motor Sheave
4 Motor
5 Motor Plate
6 Mounting Plate
7 Shaft
8 Insulated Plug (Optional)
9 Inlet Cone
10 Wheel
11 Inboard Bearing
12 Outboard Bearing
13 Scroll (Optional)
6
7
12
Description
Sizes 120 - 445
11
9
10
7
Page 8

Limited Warranty
Loren Cook Company warrants that your Loren Cook fan was manufactured free of defects in materials and workmanship, to the extent stated herein. For a period of one (1)
year after date of shipment, we will replace any parts found to be defective without charge, except for shipping costs which will be paid by you.
This warranty is granted only to the original purchaser placing the fan in service.
This warranty is void if the fan or any part thereof has been altered or modified from its original design or has been abused, misused, damaged or is in worn condition or if the
fan has been used other than for the uses described in the company manual. This warranty does not cover defects resulting from normal wear and tear.
To make a warranty claim, notify Loren Cook Company, General Offices, 2015 East Dale Street, Springfield, Missouri 65803-4637, explaining in writing, in detail, your complaint
and referring to the specific model and serial numbers of your fan. Upon receipt by Loren Cook Company of your written complaint, you will be notified, within thirty (30) days of
our receipt of your complaint, in writing, as to the manner in which your claim will be handled. If you are entitled to warranty relief, a warranty adjustment will be completed within
sixty (60) business days of the receipt of your written complaint by Loren Cook Company.
This warranty gives only the original purchaser placing the fan in service specifically the right. You may have other legal rights which vary from state to state.
For fans provided with motors, the motor manufacturer warrants motors for a designated period stated in the manufacturer’s warranty. Warranty periods vary from manufacturer
to manufacturer. Should motors furnished by Loren Cook Company prove defective during the designated period, they should be returned to the nearest authorized motor service station. Loren Cook Company will not be responsible for any removal or installation costs.
Corporate Offices: 2015 E. Dale Street Springfield, MO 65803 417.869.6474
lorencook.com
8
CCP IOM - Dec 2013
 Loading...
Loading...