
Convision V100/V200 Series
Version 5.1
english

Manual
1
Convision V100/V200 Series
User Manual
Version 5.1
November 2003
© Convision Technology GmbH
All rights reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form without the prior
written permission of Convision Technology GmbH.
All the information and descriptions have been compiled with great care on the basis
of thorough research. Despite our great care, we cannot completely rule out errors or
altered applications that may lead to changed operational sequences or different
results. Convision Technology GmbH can accept neither legal responsibility nor any
other liability for any consequences arising from this or from unintentional errors.
Convision und Convision V100/V200 Series are trademarks of Convision Technology
GmbH.
Microsoft and MS-Internet Explorer are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation. Netscape and Netscape Navigator are registered
trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation. Any other trade names and
product names are the trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective
owners.
Convision Technology GmbH cannot accept liability for increased call charges,
including costs arising from accidental connection set up.
Convision Technology GmbH has created this manual to the best of its ability but
cannot guarantee that the programs / systems will serve the purpose aspired by the
user.
Convision Technology GmbH reserves the right to modify the content of the User
Manual without accepting the obligation of informing third parties.
We reserve the right to make technical modifications.
Convision V100/V200 Series
2
General
Congratulations on purchasing a unit of the Convision V100/V200 Series.
The Convision V100/V200 Series is available in the following versions:
♦= Convision 100 LAN Convision 200 LAN
♦= Convision 100 LAN/ISDN Convision V200 LAN/ISDN
All the descriptions and instructions contained in this manual apply to both versions.
Therefore, the name "Convision V100/V200" is used.
This manual intends to convey the knowledge required to connect and handle your
Convision V100/V200 Series. General information on configuring the required
software on your computer you will find in the document “Convision System
Configuration. You do not need any special software to operate the Convision
V100/V200 Series since all the components are generally included in the standard
software package supplied with the computer.
Please read this manual before connecting your Convision V100/V200.
You can download the latest update of the Convision V100/V200 manual and the
Convision V100/V200 firmware free of charge from the Convision Website
(www.convision.de).
Operate the Convision V100/V200 exclusively with 12 V DC.
Step by Step Procedures
Meeting the System Requirements – refer to Chapter 3
Connecting the Components – refer to Chapter 5
Configuring the System – refer to document “Convision System Configuration“
Setting up Your Browser – refer to document “Convision System Configuration“
Configuring Your Convision V100/V200 – refer to Chapter 6 and 9

Manual
3
Contents
1 General Information .....................................................6
1.1 Scope of Delivery..........................................................................6
1.2 Safety Instructions .......................................................................6
2 Product Variations ........................................................7
3 System Requirements ...................................................8
3.1 Requirements for Operation in an ISDN Telephone Network ........8
3.2 Requirements for Operation in a Local Area Network (LAN) .........8
3.3 Software Requirements ................................................................8
4 Controls, Connectors and Indicators .............................9
4.1 Front View ....................................................................................9
4.2 Rear View ...................................................................................10
4.2.1 Convision V100.............................................................................. 10
4.2.2 Convision V200.............................................................................. 11
5 Connecting the Convision V100/V200.........................12
5.1 Connecting the Unit to the Power Supply....................................12
5.2 Connecting the Unit to the LAN...................................................12
5.3 Connecting the Unit to the ISDN.................................................13
5.4 Connecting the Unit via Modem ..................................................14
5.5 Connecting the Cameras .............................................................14
5.5.1 Convision V100.............................................................................. 14
5.5.2 Convision V200.............................................................................. 15
5.6 Input Connections ......................................................................16
6 Initial Configuration of the Convision V100/V200 ......18
6.1 MSN Configuration via ISDN (Convision V100/V200 LAN/ISDN
only)...........................................................................................18
6.2 IP Configuration in a Local Area Network ...................................19
6.3 IP Configuration via a Direct Connection Using a Cross-Connect
Cable...........................................................................................19
6.4 Deleting the Configuration..........................................................20
7 The HTML Pages – Operation and Configuration .........21
8 Operation....................................................................22
8.1 Cameras......................................................................................22
8.1.1 Controllable Camera....................................................................... 23
8.1.2 MPEG........................................................................................... 26
8.1.3 Sequencer (Convision V200 only) .................................................... 26
8.2 Frame Buffer Display ..................................................................27
8.3 Applications................................................................................28

Convision V100/V200 Series
4
8.3.1 Sockets........................................................................................ 28
8.3.2 Weather Station ............................................................................ 28
8.4 Applets .......................................................................................28
8.5 Modules ......................................................................................29
8.6 Information ................................................................................29
9 Configuration ............................................................. 30
9.1 System Settings..........................................................................30
9.1.1 LAN/Ethernet Connection Data ........................................................ 30
9.1.2 ISDN/Modem Connection Data (Convision V100/V200 LAN/ISDN
only).......................................................................................... 32
9.1.3 Language ..................................................................................... 39
9.1.4 Applets......................................................................................... 40
9.1.5 Modules........................................................................................ 41
9.1.6 Configuration – Saving and Uploading .............................................. 41
9.1.7 Update – Uploading New Firmware................................................... 42
9.1.8 Security Settings........................................................................... 43
9.1.9 Setting the Time and Date.............................................................. 44
9.1.10 Activating the FTP Server ............................................................... 45
9.1.11 Assignment of Devices to the Serial Port........................................... 46
9.1.12 Event Log ..................................................................................... 47
9.2 Camera Settings .........................................................................48
9.2.1 General – Settings for the Image Display.......................................... 48
9.2.2 Name – Renaming Cameras............................................................ 48
9.2.3 Pan/Tilt ........................................................................................ 49
9.2.4 MPEG Parameters.......................................................................... 49
9.2.5 Setting the Camera Properties......................................................... 50
9.3 Events – Actions When an Alarm Is Triggered ............................51
9.3.1 Inputs.......................................................................................... 52
9.3.2 Time Control – Time-Dependent Actions........................................... 53
9.4 Actions .......................................................................................55
9.4.1 Configuring the Frame Buffers......................................................... 55
9.4.2 Transferring Data via FTP (Upload) .................................................. 56
9.4.3 Notification via E-Mail..................................................................... 58
9.4.4 E-Mail State (eMail State)............................................................... 59
9.4.5 Notification via SMS (Short Message Service).................................... 59
9.4.6 VdS 2465 ..................................................................................... 60
9.4.7 Further action with no configuration page ......................................... 60
10 General Descriptions .................................................. 61
10.1 Using the Convision V100/V200 as a Video Server.....................61
10.2 Live optimized and Live compatible ............................................61
10.3 FTP .............................................................................................61
10.4 Password Encryption ..................................................................61
10.5 Channel Bundling........................................................................62
10.6 SMTP or Mail Server....................................................................62
10.7 Control via CGI Parameters ........................................................62
10.8 The TCP/IP Protocol Group.........................................................63
11 Technical Data............................................................ 67

Manual
5
Appendix A FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions /
Troubleshooting..........................................................68
Appendix B Declaration of Conformity ...................................74
Appendix C List of Figures.....................................................75
Appendix D List of Keywords.................................................76

Convision V100/V200 Series
6
1 General Information
1.1 Scope of Delivery
After unpacking, make sure that all the parts have been delivered.
Convision V100/V200
Power pack DC 12 V/4 A
Power cable
ISDN cable
Mounting bracket kit
CD-ROM with Convision
IPSetup Tool
Manual
Adapter mini DIN8 to D-Sub9
The device type and the serial number are on an adhesive label underneath the
Convision V100/V200. This information is also included on the HTML pages in the
"Information" menu (refer to chapter 8.6). In the "Information" menu, you can also
check the current software version of your Convision V100/V200.
1.2 Safety Instructions
The Convision V100/V200 is a high-quality electronic product. Please follow the
safety instructions below to prevent damage:
Never place the Convision V100/V200 near a heating source e.g.
furnace or heaters or expose it to direct sunlight.
Do not cover the Convision V100/V200.
Only clean your Convision V100/V200 using a moist cloth without
abrasive cleaning agents.
Never open the Convision V100/V200 yourself. In the event of a
malfunction or defect, please contact the Convision Technology
GmbH support service or your dealer.
Opening the unit invalidates the warranty

Manual
7
2 Product Variations
With the Convision V100/V200 product range, it is possible to connect 1 or 2
cameras and then access them simply via LAN and ISDN using a standard Internet
browser. The Convision V100/V200 IP video servers transmit very high quality and
high resolution images which ensures that no detail is overlooked. These images can
then be viewed, depending on requirements and transmission method, using a
standard browser from any computer.
In the case of an alarm, the Convision V100/V200 stores up to 32 pre and post alarm
images which can then be sent as an e-mail attachment. Afterwards, the frame buffer
is available for use again immediately.
The Convision V100/V200 offers various compression methods (JPEG, MPEG) in
order that the required image quality is always available for every application. For
example, when monitoring areas where cash is handled, the image quality needs to
be much higher than when viewing an entrance door. During live surveillance, it is
possible to view 25 images per second (PAL norm) from the Convision V100/V200
using MPEG.
The video resolution is 352x288 pixels, which corresponds to full VHS quality. The
Convision V200 can transmit full photo quality images in JPEG video mode with an
outstanding resolution of 704x576 pixels. Only with this transmission quality from
Convision Technology are high resolution cameras really used to their full advantage.
Convision V100 LAN
♦= 1 Camera input
♦= 1 12 Volt DC Output (Power Out)
Convision V100 LAN/ISDN
♦= as Convision V100 LAN, but including ISDN terminal adapter
Convision V200 LAN
♦= 2 Camera inputs
♦= no Power Out
Convision V200 LAN/ISDN
♦= as Convision V200 LAN, but including ISDN terminal adapter

Convision V100/V200 Series
8
3 System Requirements
3.1 Requirements for Operation in an ISDN
Telephone Network
For configuring and operating the Convision V100/V200 via ISDN, you need an basic
ISDN access.
The Convision V100/V200 is completely ready for connection via ISDN, which means
the user need not perform any installation. The Convision V100/V200 has been
equipped with an ISDN card and the required ISDN software has been installed. For
configuring the connections that are to be established via the ISDN interface, please
refer to document “Convision System Configuration“.
If you want to make further settings for the Convision V100/V200 (e.g. TCP/IP,
camera settings etc.) via the ISDN interface, you need a computer with ISDN
capabilities. For more information, please refer to Ch apter 6.1.
3.2 Requirements for Operation in a Local Area
Network (LAN)
For configuring and operating the Convision V100/V200 in a local area network
(LAN), you need a computer with an Ethernet interface. The Convision V100/V200 is
designed for a 10/100 Mbit/s autosensing twisted-pair (TP) connection.
For detailed information on cabling, please refer to Chapter 5.2.
3.3 Software Requirements
To be able to configure the Convision V100/V200, you need an Internet browser that
supports Java such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or Netscape Navigator 4.x.
You do not need any special software to operate the Convision V100/V200 since all
the components are generally included in the standard software package supplied
with the computer.
On computers with an MS operating system, you can configure the system by using
Convision IPSetup directly in the form of an .exe file. In the case of other operating
systems, you have to install a "JVM" (Java Virtual Machine), if not yet installed.
Manual
9
4 Controls, Connectors and
Indicators
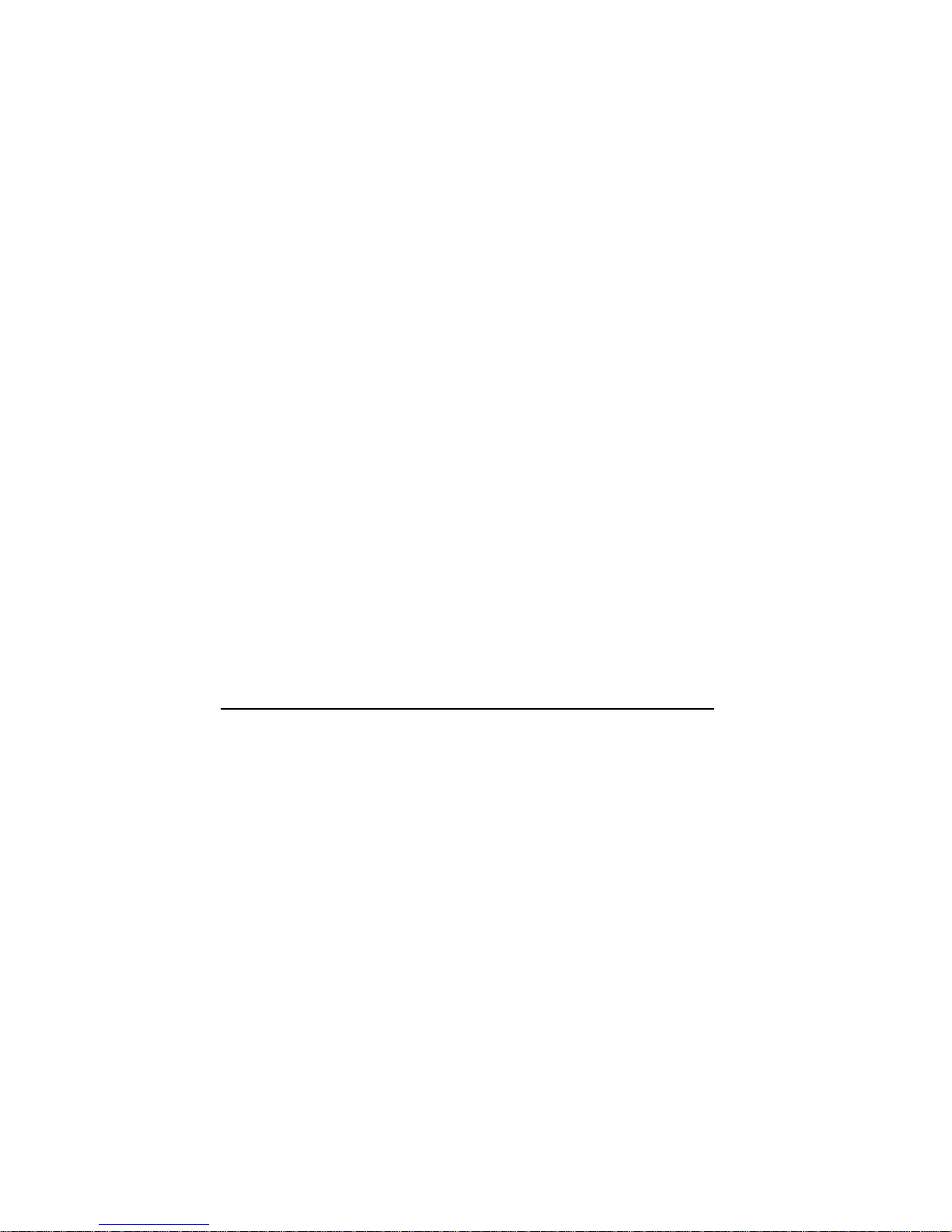
4.1 Front View
Figure 1: Front view of the Convision V100/V200
On the front of the Convision V100/V200 there are four indicator lamps which
indicate the status. These include the following:
♦= Cam: This indicator lamp lights up when a camera is connected to the Convision
V100/V200.
♦= Online: lights up when the Convision V100/V200 has completed an active ISDN
connection, flashes when data is transferred.
♦= Link/Activity: lights up when a connection is present to the Ethernet,
flashes when data is transferred.
♦= Power: lights up as soon as the Convision V100/V200 is connected to the line
power and switched on.
Convision V100/V200 Series
10
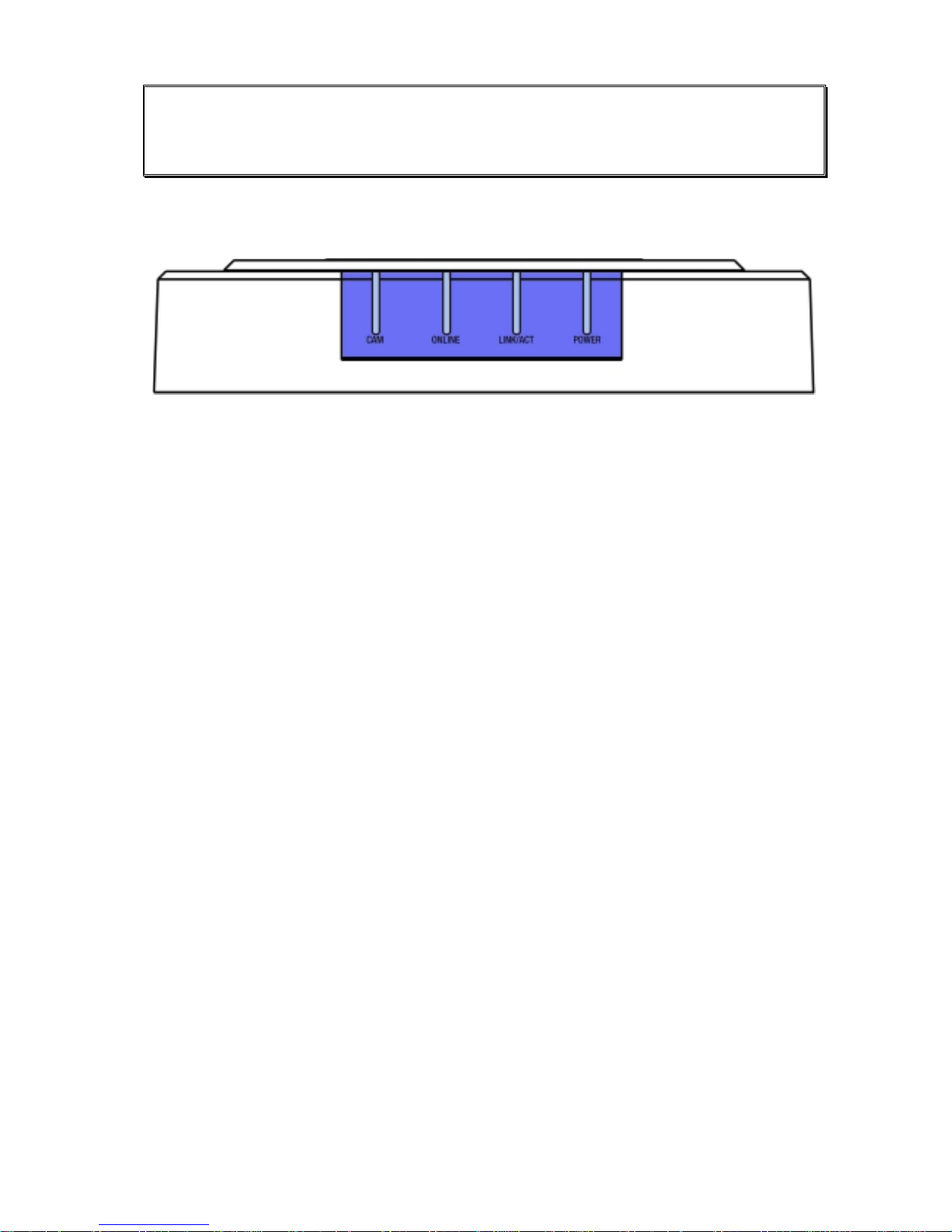
4.2 Rear View
4.2.1 Convision V100
Figure 2: Rear view of the Convision V100
1. ISDN: connection for operating the Convision V100/V200 using an ISDN multi-
device connection.
2. ETHERNET: 10/100 Base T connection for using the Convision V100/V200 in a
LAN.
3. Power out: 12V DC power supply for the camera
4. CAM: BNC Video Connector for a camera
5. SERIAL: (Mini Din 8) serial interface: used to control external devices, e.g. swivel
camera, weather station etc. Convision provides a list of all available devices on
its website www.convision.de (also see Chapter 9.1.11).
6. M-Switch: For deleting configuration
7. ON/OFF: pressing this button switches the device on and off.
8. Input connections: used to connect additional devices, e.g. smoke and motion
detectors. (see Chapter 8.3)
9. POWER IN: socket for the power supply supplied with the unit

Manual
11
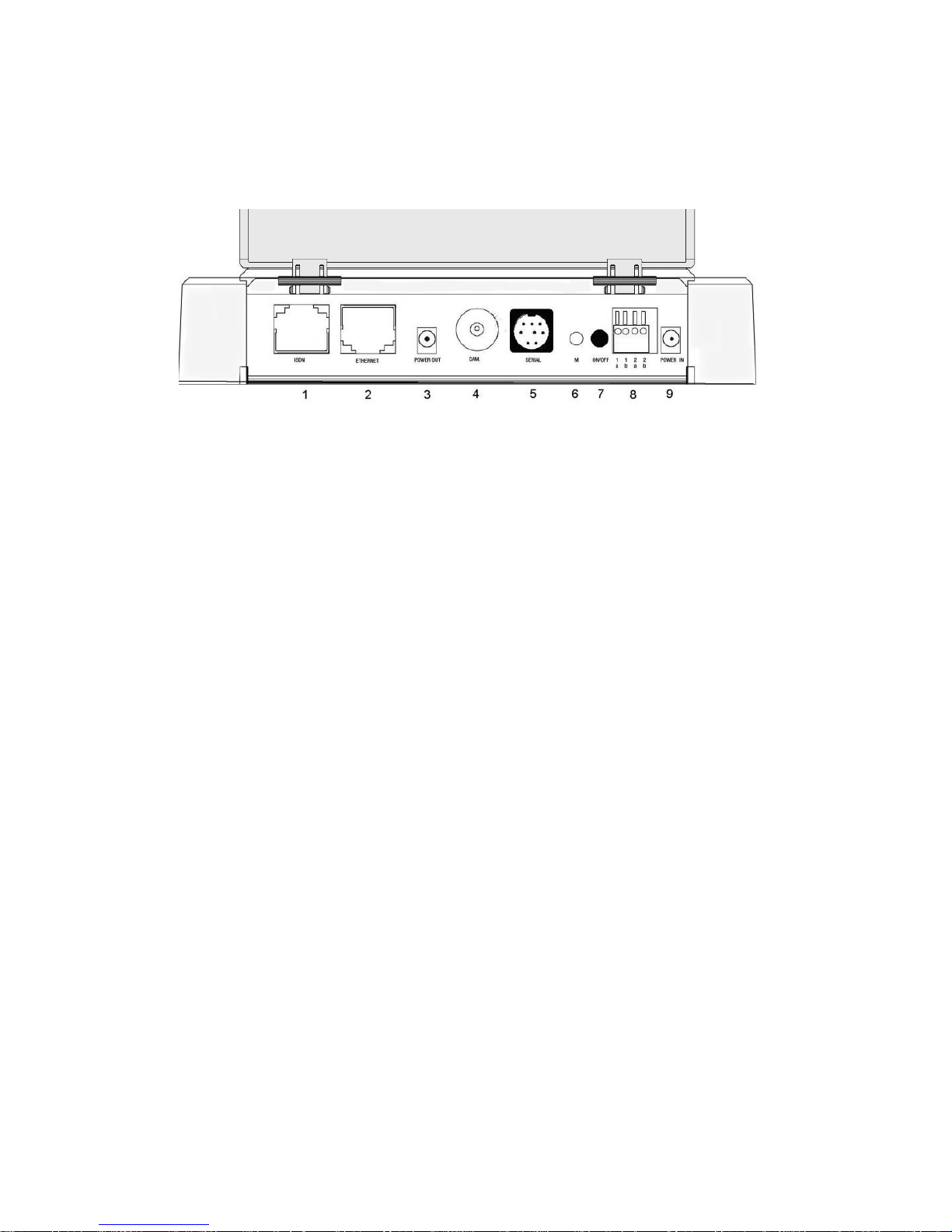
4.2.2 Convision V200
Figure 3: Rear view of the Convision V200
1. ISDN: connection for operating the Convision V100/V200 using an ISDN multidevice connection. .
2. ETHERNET: 10/100 Base T connection for using the Convision V100/V200 in a
LAN.
3. CAM2: BNC Video Connector for a camera
4. CAM1: BNC Video Connector for a camera
5. SERIAL: (Mini Din 8) serial interface: used to control external devices, e.g. swivel
camera, weather station etc. Convision provides a list of all available devices on
its website www.convision.de (also see Chapter 9.1.11).
6. M-Switch: For deleting configuration
7. ON/OFF: pressing this button switches the device on and off.
8. Input connections: used to connect additional devices, e.g. smoke and motion
detectors. (see Chapter 8.3)
♦= POWER IN: socket for the power supply supplied with the unit
Convision V100/V200 Series
12
5 Connecting the Convision
V100/V200
5.1 Connecting the Unit to the Power Supply
Plug the 12-V connector of the power pack cable into the power socket of your
Convision V100/V200. Connect the power pack to the power supply socket using the
power cable. Activate the on/off switch on the rear of the unit. The power LED will
light up.
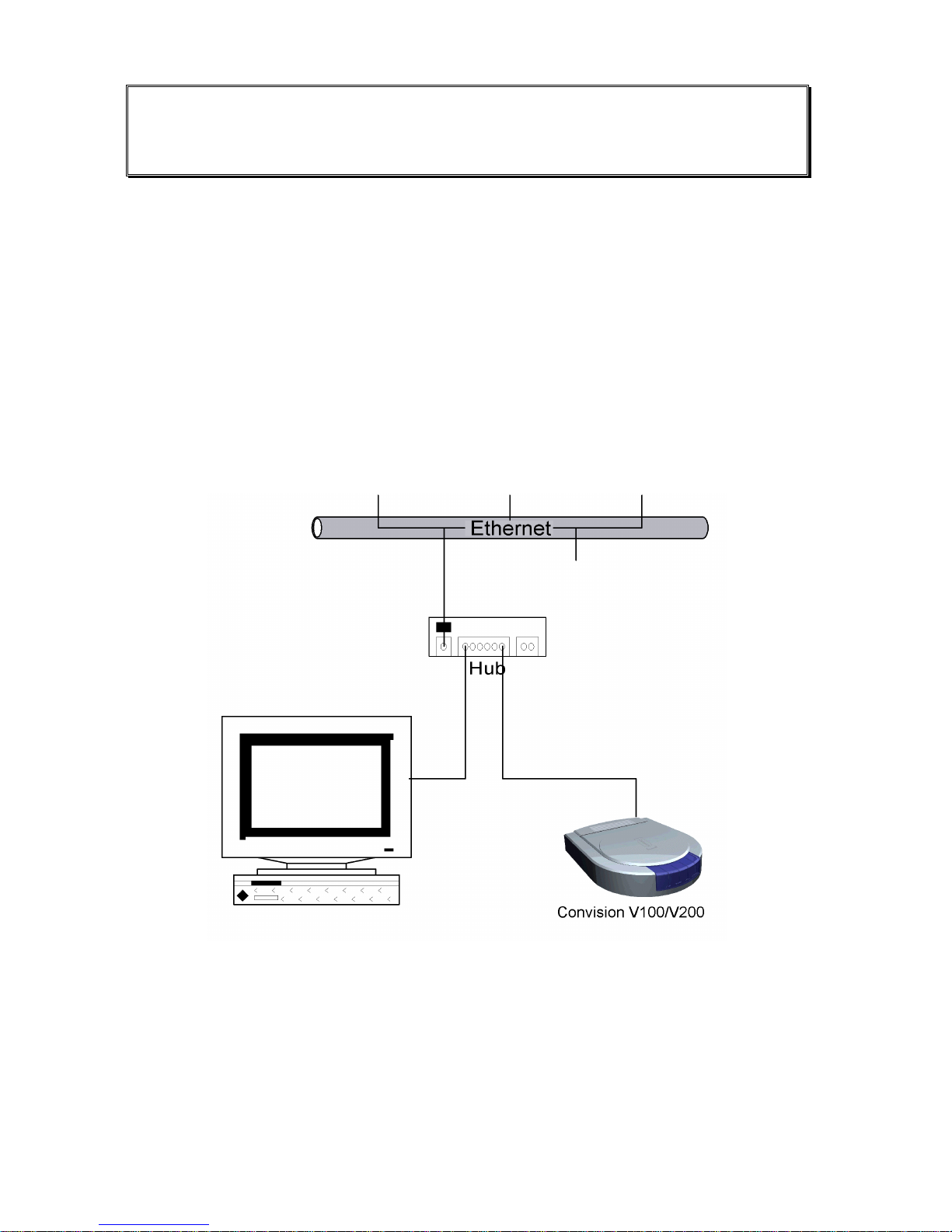
5.2 Connecting the Unit to the LAN
In a LAN, you have to establish a connection between the Convision V100/V200 and
your computer via a hub or switch using a twisted-pair cable with an RJ-45
connector.
Figure 4: LAN connection
1. Connect one end of the TP cable to the Ethernet output on the rear of the
Convision V100/V200 (refer to Figure 2: Rear view of the Convision V100 or
Figure 3: Rear view of the Convision V200).
2. Connect the other end of the TP cable to one of the inputs on the hub.
Manual
13
3. The Link/Active LED next to the Ethernet interface will light up. For information on
setting the IP addresses, please refer to Chapter 6.2. For detailed information on
IP addresses, please refer to Chapter 10.8.
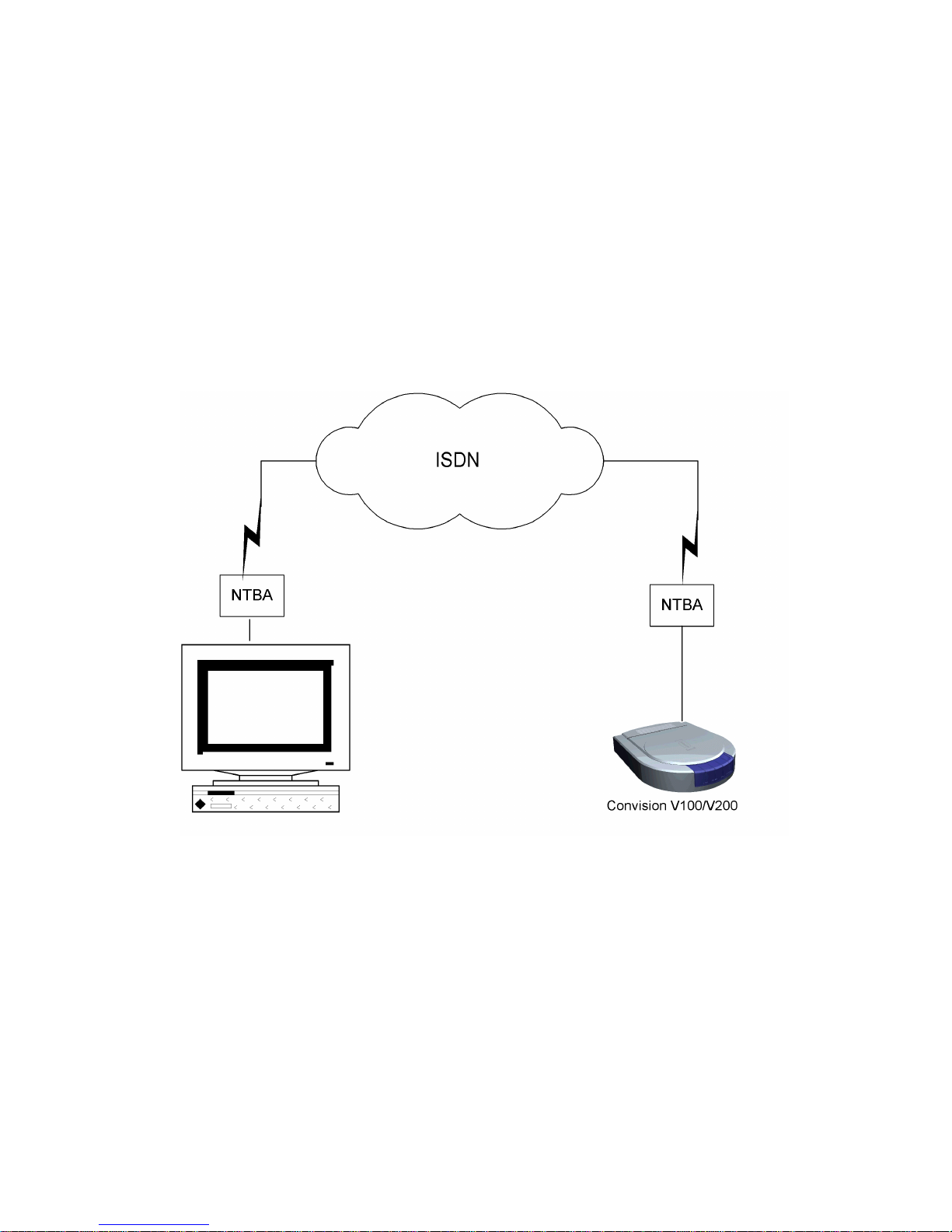
5.3 Connecting the Unit to the ISDN
Your telecommunications network operator provides ISDN access via a network
terminator (NT).
1. Plug one end of the ISDN cable provided (labelled "ISDN") into the ISDN port on
the rear of the device (refer to to Figure 2: Rear view of the Convision V100 or
Figure 3: Rear view of the Convision V200).
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the RJ-45-socket of the ISDN network
terminator.
Figure 5: Connection via ISDN
To be able to communicate with your Convision V100/V200 via ISDN, your computer
must be equipped with the appropriate ISDN hardware (e.g. ISDN card). For
information on installing ISDN hardware, please review the respective manuals of
your computer and of the device to be installed. In addition, you have to configure a
dial-up networking on your computer (refer to document ”Convision System
Configuration“).
Convision V100/V200 Series
14
Operating the Unit Connected to Telecommunications
Equipment
If you want to operate your Convision V100/V200 connected to telecommunications
equipment, you have to connect the Convision V100/V200 to the S0-bus in parallel to
an ISDN telephone that can be accessed from your computer.
For the initial configuration, dial the telephone number assigned to the telephone
connected. Since this is a data call, the phone will not answer (i.e. the pho ne will not
ring) but the Convision V100/V200 will answer the call.
Note: In the case of telecommunications equipment it may be necessary to
enable data transmission for the access. For this purpose, contact the manufacturer
of the telecommunications equipment.
5.4 Connecting the Unit via Modem
To operate the Convision V100/V200 via an analogue modem, connect the modem
to the serial interface (Serial) of your Convision V100/V200 using a serial cable.
Connect the modem to the telephone socket using the telephone cable and to the
power supply via the power pack. For information on configuring the unit, refer to
Chapter 9.1.2.
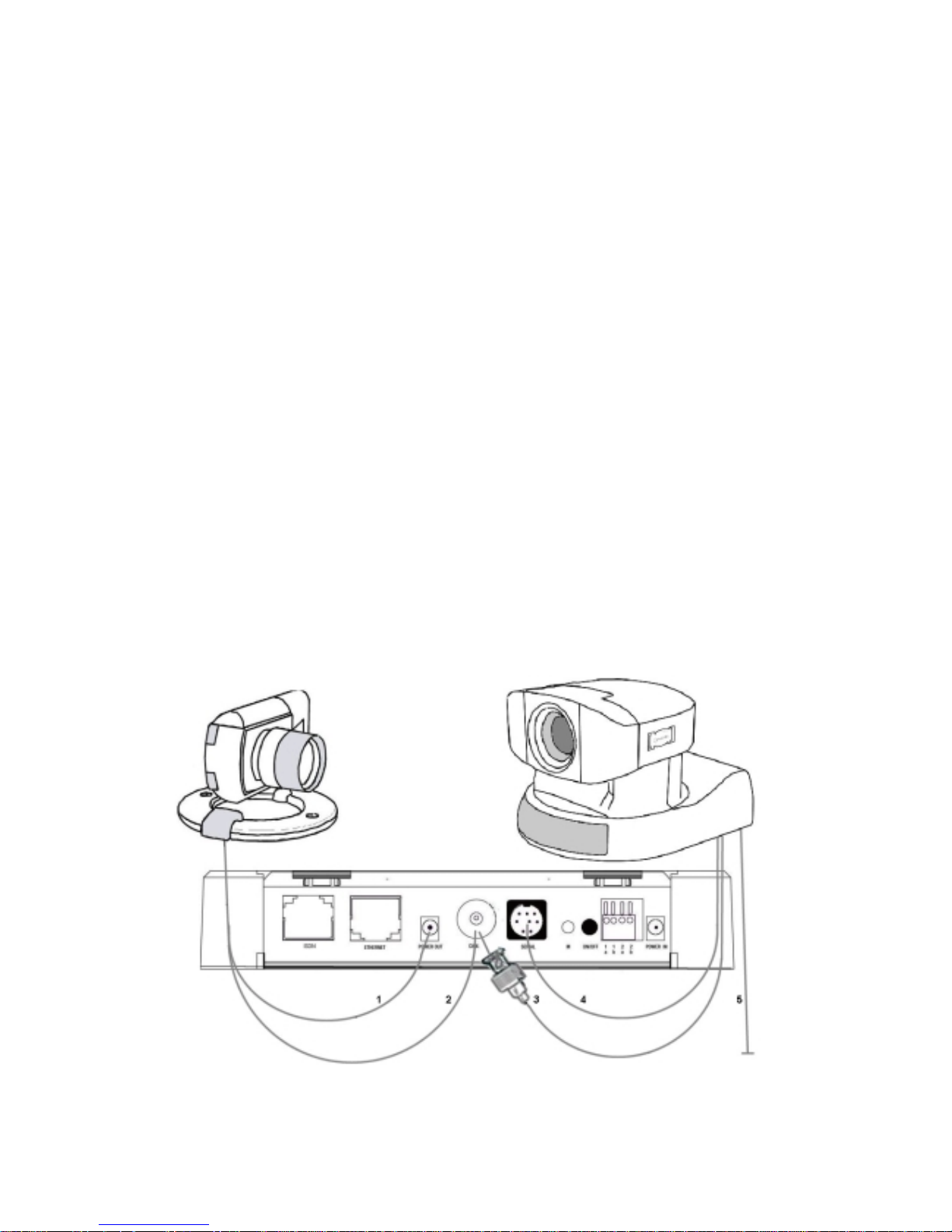
5.5 Connecting the Cameras
5.5.1 Convision V100
Figure 6: Camera connection to Convision V100
Manual
15
1. To supply the camera with 12V DC, connect the power supply of the camera to
the Power out socket next to the Video connection on the rear. The camera can
also be supplied with power externally by a separate power supply.
2. Connect the BNC connector to a camera input on the rear of the Convision
V100/V200.
Connecting a controllable Camera
3. Connect the video cable via the adapter supplied (Cinch to BNC) to the first
camera input of the Convision V100/V200.
4. Connect the control cable (9pin Sub-D to 8pin mini DIN) to the serial input (Serial)
of the Convision V100/V200.
5. The camera is supplied with power via the power pack delivered together with the
camera.
Define the serial input used on the Configuration / System / Device page (refer to
Chapter 9.1).
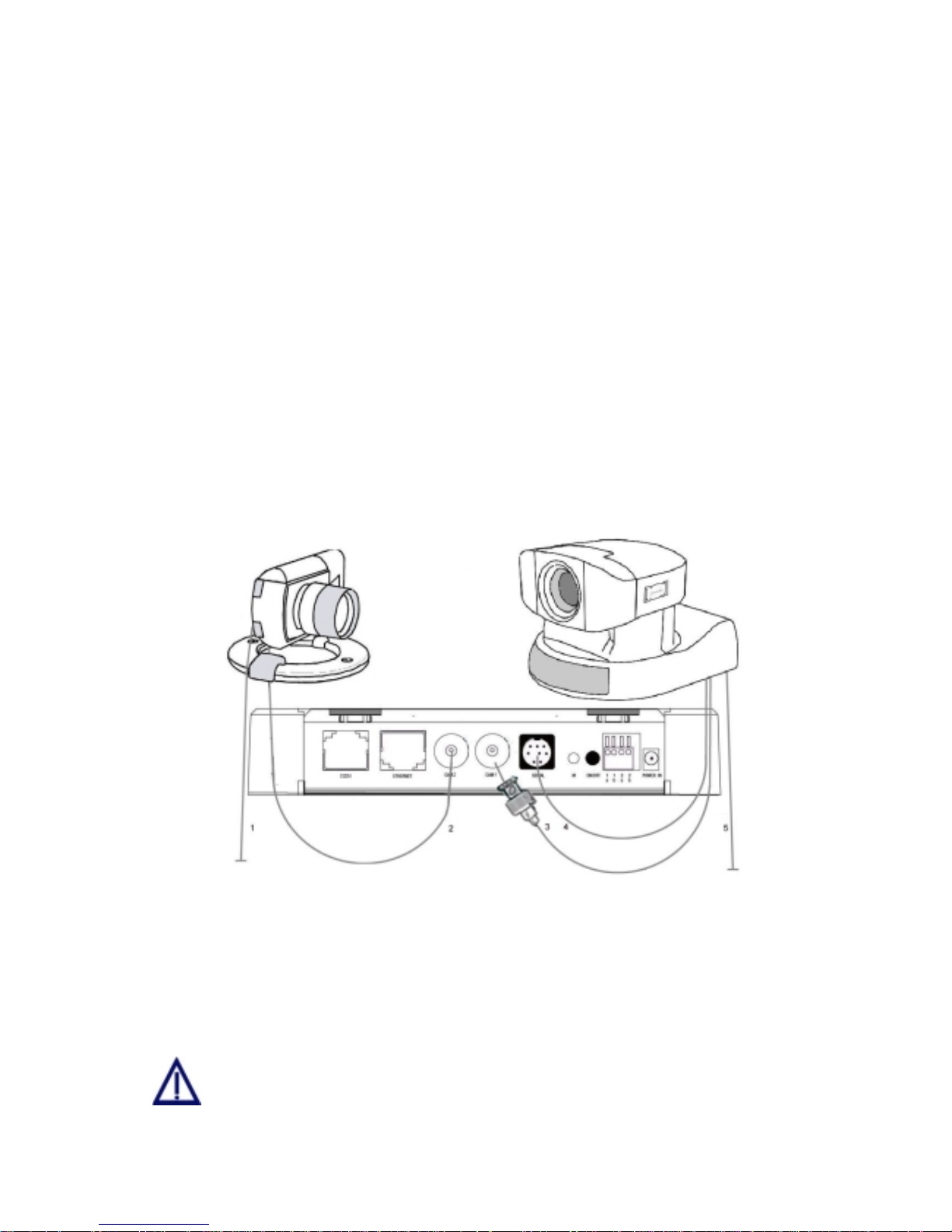
5.5.2 Convision V200
Figure 7: Camera connection to Convision V200
Cameras are connected in the same way as with the Convision V100, but the power
is always supplied separately by the power pack included with the cameras.
If you want to connect several controllable cameras to a Convision V100/V200, all
the cameras following the first one are controlled via series cable connections of the
individual cameras (8pin mini DIN connectors).
You cannot operate 2 different types of controllable cameras simultaneously
via the Convision V100/V200.
Convision V100/V200 Series
16
In some controllable cameras you have to set an internal control address. For
this purpose, please use the addresses starting with "1".
For controlling a camera not supported by the Convision V100/V200 you have to
enable the "Serial-URL-Port" option on the Configuration/System/Device page. For
more information on this topic, please read Chapter 9.1.11 – Serial-URL-Port. The
unit is controlled via a separate applet that can be uploaded to the Convision
V100/V200 (refer to Chapter 8.4 and 9.1.4).
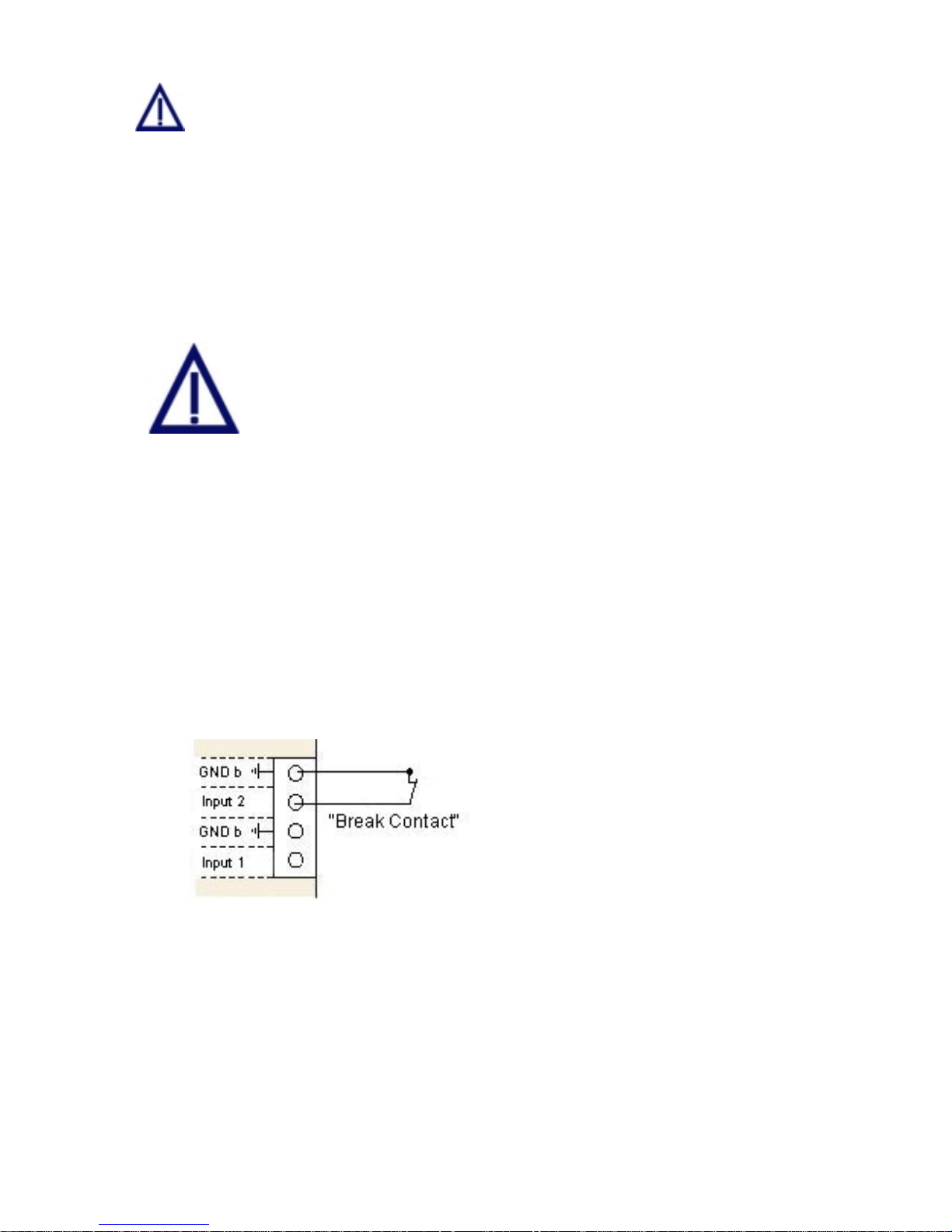
5.6 Input Connections
Connect only devices that have been designed for 12V to your
Convision V100/V200.
Never use 230 Volts on your Convision V100/V200!
Connecting the Lines to the Terminal Strip
1. Remove approx. 10 to 13 mm of the cable insulation.
2. Using a small screwdriver, press against the clamping device above the
receptacle and push the twisted cable into the receptacle.
3. After releasin g the clamping device, it retains the cable. Check by pullin g gently
on the cable.
Input Connections
Alarm devices for various purposes can be connected to the six inputs. Please
observe that only 12 V devices may be connected to the inputs.
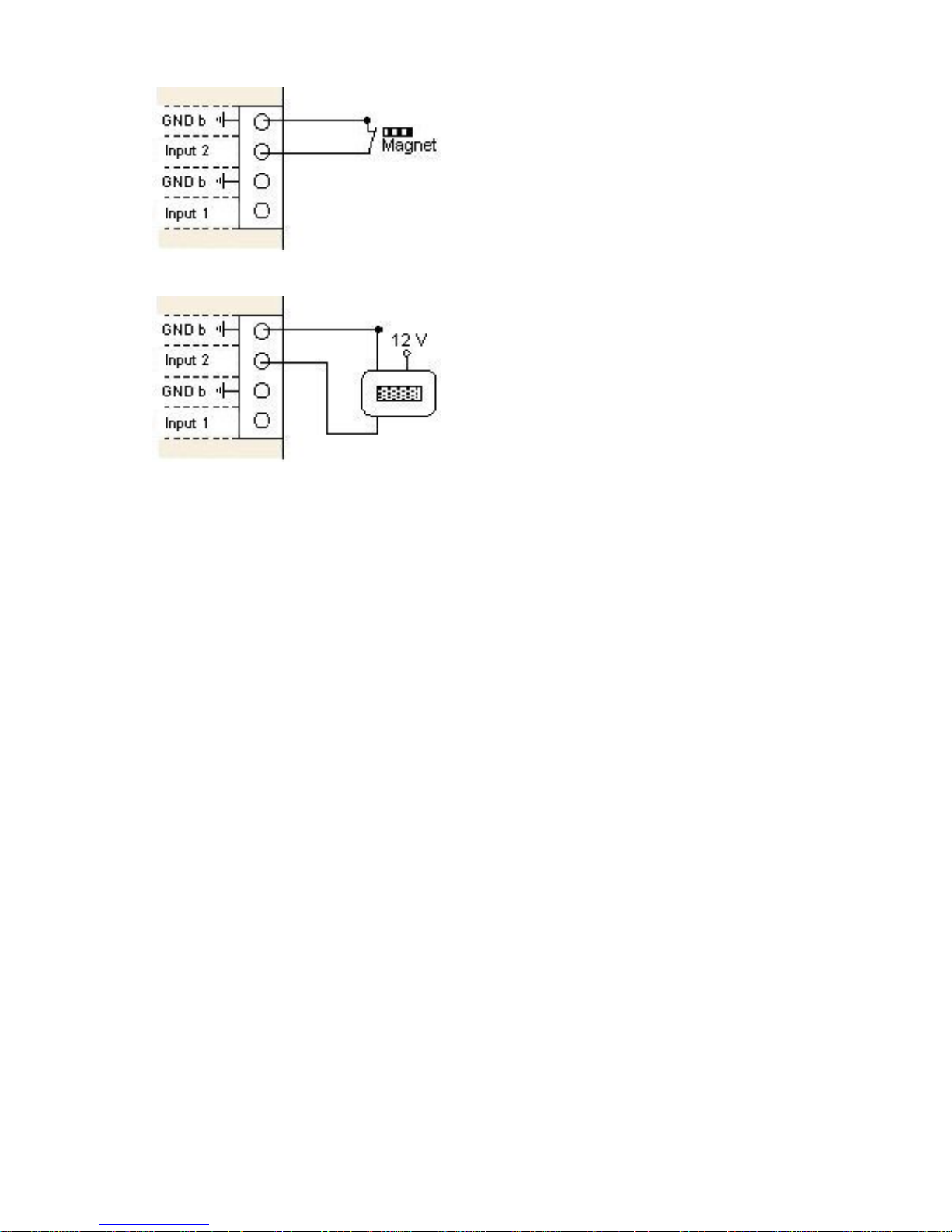
Fig. 8: Example 1 Input Connection
Connection of a switch
Type NC (Normally Closed)
break contact
Manual
17
Fig. 9: Example 2 Input Connection
Connection of a magnetic switch
Type NC (Normally Closed)
break contact
Fig. 10: Example 3 Input Connection
Connection of a motion detector
for alarm units
with own power supply
Type NC (Normally Closed)
break contact

Convision V100/V200 Series
18
6 Initial Configuration of the
Convision V100/V200
For information on the local configuration of your computer, please refer to document
“Convision System Configuration“. For information on setting up the browser, please
refer to document “Convision System Configuration“.
To establish the first connection with the Convision V100/V200, please follow the
configuration procedure in this chapter. If you have already succeeded in establishing
a connection with the Convision V100/V200, you can skip this chapter. To customize
the configuration of your Convision V100/V200, refer to the detailed description of the
configuration options in Chapter 9. There, you will find a description of the menus
and buttons together with their functions.
When delivere d, the Convision V100/V200 is not configured, i.e. it has not been
assigned an IP address or MSN (multiple subscriber number). This is indicated by the
slowly flashing Online LED following the booting procedure. For this reason, the unit
must be configured. The configuration software "IP Setup" is on the "Products +
Partners" CD in the "Software" folder.
There are four different ways to set up the Convision V100/V200 depending on your
connection.
1. MSN configura tion via ISDN
2. IP Configurat ion in a Local Area Network
3. IP configuration via a direct link between the PC and the Convision V100/V200
using a cross-connect cable
6.1 MSN Configuration via ISDN (Convision
V100/V200 LAN/ISDN only)
To set up the Convision V100/V200 via ISDN, you have to install a dial-up networking
on your computer. For information on this topic, please refer to document “Convision
System Configuration“.
Once dial-up networking has been configured for establishing a connection to the
Convision V100/V200, you can set up the unit. To connect to the Convision
V100/V200, establish a dial-up connection. Do not enter a username or password
(refer to PPP Password, Chapter 9.1.2) and click the "Connect" button. The ISDN
connection to the Convision V100/V200 will be established.
For operation via ISDN, the IP address 10.0.0.10 has been preset for your Convision
V100/V200 but you can change it.
1. Start your browser and enter http://10.0.0.10 as the URL. Your browser will
display the homepage of the Convision V100/V200.
2. Click on "Configuration / System / ISDN/Modem", and then "ISDN”
Manual
19
3. Enter the multiple subscriber number (MSN) assigned.
4. If defined, enter the PPP password to prevent unauthorized connection.
5. Save the data.
If you operate more than one piece of ISDN equipment on one ISDN
connection, you have to assign each unit a separate MSN number to prevent
conflicts.
6.2 IP Configuration in a Local Area Network
Follow the installation procedure below to set up the Convision V100/V200 in the
LAN:
1. Install and configure your LAN network (refer to document “Convision System
Configuration“).
2. Integrate the Convision V100/V200 into your LAN network as described in
Chapter 5.2.
3. Copy the configuration software "IP Setup" from the CD into a directory on your
computer.
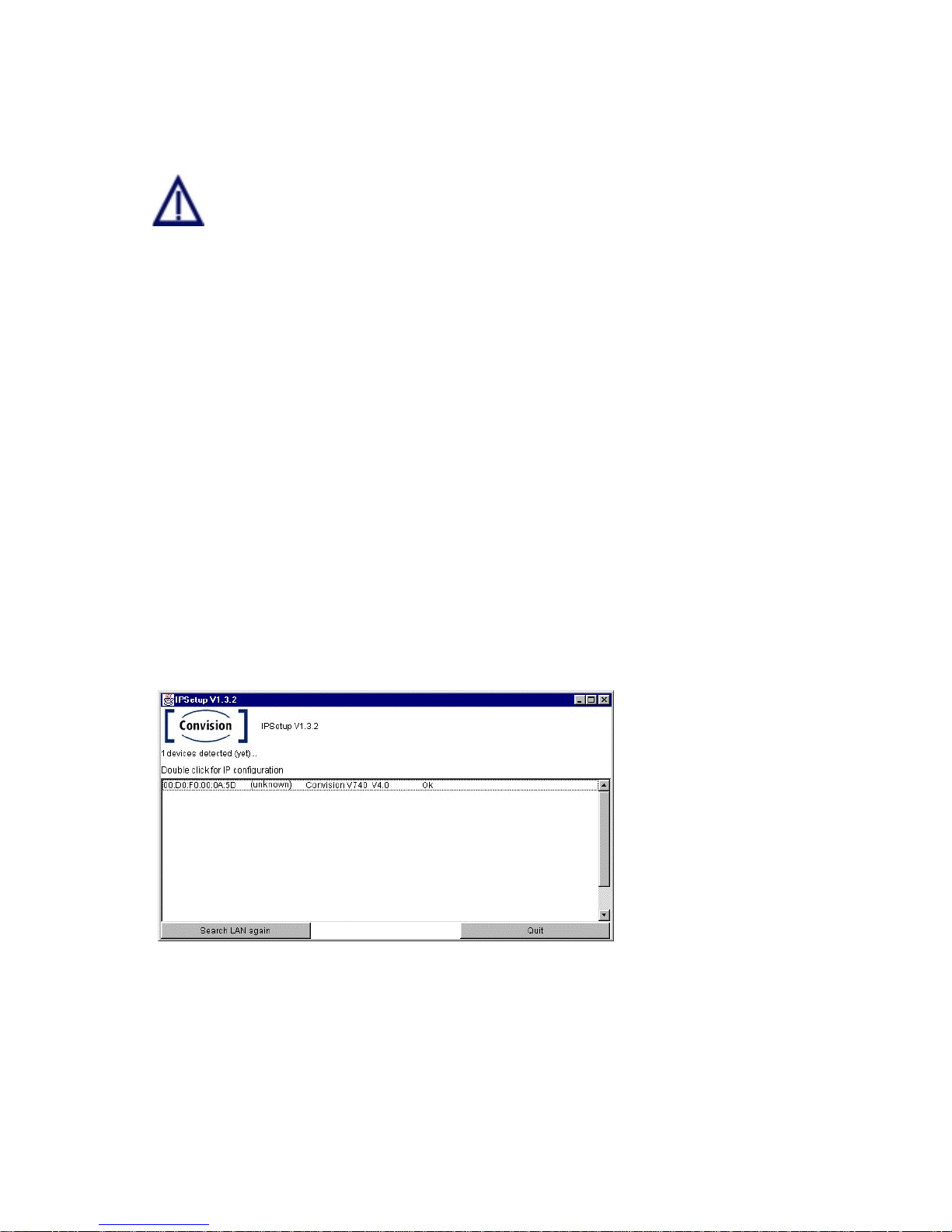
4. Open the Convision IPSetup program. For this purpose, the computer must be in
the same network segment (defined by the network mask) as the Convision
V100/V200. In Windows, the program is launched using "IPSETUP.EXE".
As this is a Java program, it can also be started by opening "java IPSetup".
5. After a few moments (max. 1 min) the program will display the Convision
V100/V200. If the program is not automatically started, double-click the entry and
then enter the IP address and the network mask. (For more information about IP
addresses and network masks refer to Chapter 10.8).
Figure 11:
Initial configuration
with IPSetup
6.3 IP Configuration via a Direct Connection
Using a Cross-Connect Cable
The following hardware and software is required to set up the Convision V100/V200
via a cross-connect cable:

Convision V100/V200 Series
20
♦= an Ethernet cross-connect cable
♦= a computer with an Ethernet network access
♦= the CD containing the IP Setup software for the Convision V100/V200
Next follow the instructions below:
Connect the Convision V100/V200 directly to the LAN card in your computer using a
cross-connect cable.
1. Copy the configuration software "IP Setup" from the CD to a directory on your
computer.
2. Open the Convision IPSetup program. In Windows, the program is launched
using "IPSETUP.EXE".
As this is a Java program, calling “java IPSetup” can also start it.
3. After a few moments (max. 1 min) the program will display the Convision
V100/V200. Double-click the entry and enter the IP address and network mask.
(For more information about IP addresses and network masks refer to Chapter
10.8).
6.4 Deleting the Configuration
If you made a mistake in programming the IP address or network mask or if you have
forgotten your password; you can no longer contact your Convision V100/V200.
However, in this case you can delete the configuration by performing a factory reset.
Once the Convision V100/V200 has been reset, it will be in the initial state, i.e.
neither the IP address nor the MSN have been saved yet.
To delete the configuration of the Convision V100/V200 follow the instructions below:
1. Switch off the Convision V100/V200.
2. Switch it back on and hold down the M button on the rear.
3. When the Cam-LED and the Online-LED flash alternately, release the M but ton.
The configuration is deleted.
4. If you hold down the M button further until the Cam-LED and the Online-LED flash
simultaneously and then release it, are also modules and applets deleted.
5. The configuration has been deleted when the Online LED starts blinking in
intervals of one second after the rebooting procedure. The initial configuration
procedure then needs to be repeated.
Manual
21
7 The HTML Pages – Operation and
Configuration
After the first successful connection, enter the IP address of your Convision
V100/V200 in the address line of your browser.
The Homepage
The homepage of the Convision V100/V200 will be displayed. From this page, you
can access all the viewing and configuration pages.
On the left-hand side you can see the navigation menus for opening the various
pages. At the bottom of this section you will find all the available languages.
On the right you can see the image from the first camera.
Selecting the Language
The language selected upon delivery is either the default language set in the browser
or English. If you want the menus to be displayed in a different language, you have to
select this language at the bottom of the homepage.
In the Configuration / System / Language menu (refer to Chapter 9.1.3) you can
change the default settings and load additional languages.
Useful Notes on Navigation
In the left-hand bar of the browser window, you can see a field with the entry
"Cameras". Click on the arrow to the right of this field to display a list of various menu
items. If you click on one of the menu items, the submenu items will be displayed.
A small square to the left of a list item means that this entry is not
subdivided further. Clicking on this list entry will display the associated
page in the right-hand area.
A triangle to the left of the list entry means that there are more submenu
items that can be displayed by clicking with the mouse. Clicking on
these items displays the associated pages.
For the "Configuration" menu, there is another drop down menu below the first one.
This drop down menu contains the items of the individual configuration menus. To be
able to use of all the possibilities provided by the Convision V100/V200, you have to
configure it first. For this purpose, please read Chapter 9 – Configuration.

Convision V100/V200 Series
22
8 Operation
8.1 Cameras
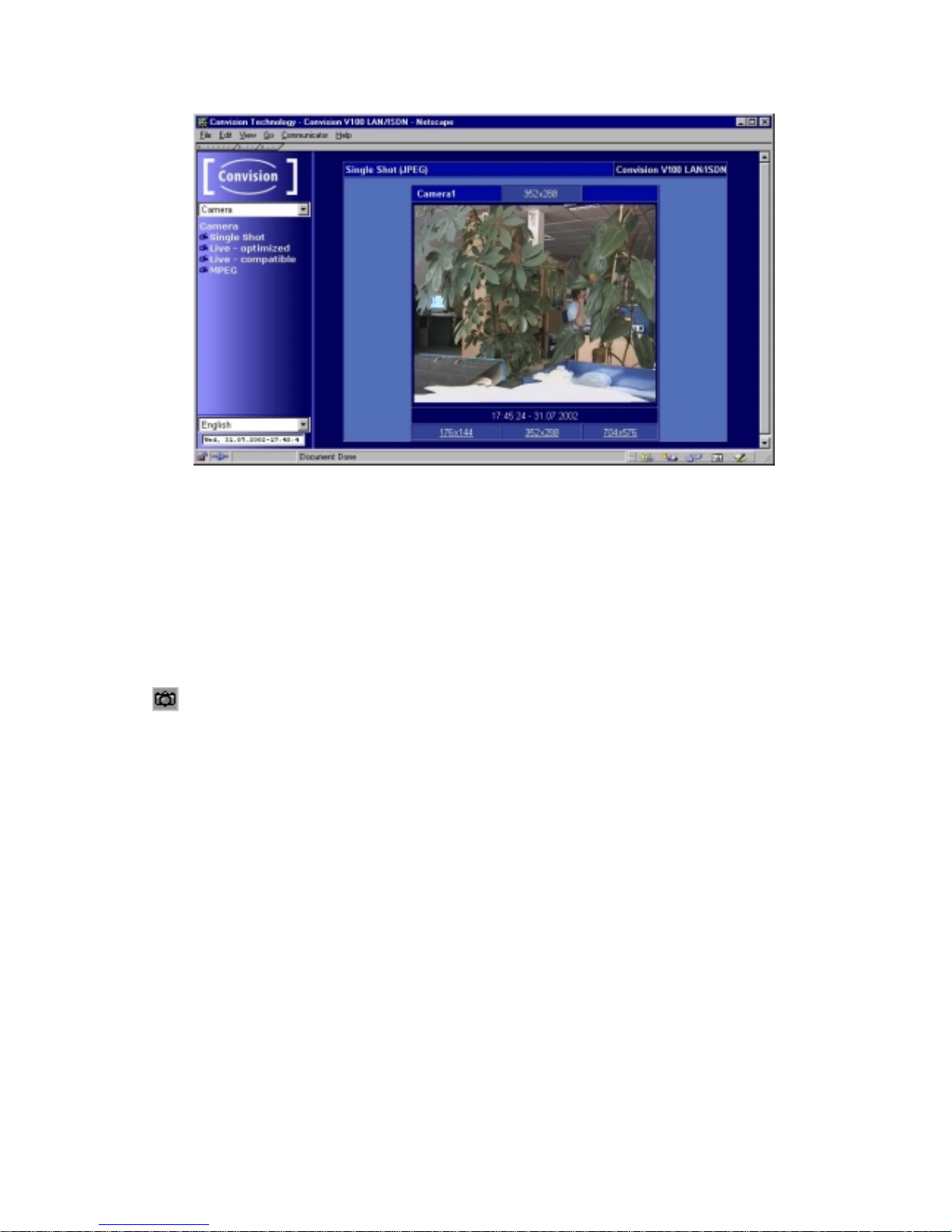
In this menu you can view the images from the connected cameras.
Selecting the Viewing Mode
There are various modes for viewing the camera images. Select on the viewing mode
by clicking on it:
♦= Single Shot (JPEG)
♦= Live-optimized with Server Push (Netscape only)
with ActiveX (Internet Explorer only)
♦= Live-compatible with the Java applet developed by Convision Technology
♦= MPEG
A list of the cameras and multiple views is displayed.
Note: A signed Convision Technology ActiveX Plugin for displaying live streams
in Internet Explorer is available (for more information refer to document “Convision
System Configuration“, Internet Explorer.
Selecting the Camera
Select one of the individual cameras or "View of two cameras" (views of 2 cameras
simultaneously). On the right-hand side, the current image is displayed as
384x288(fullsize). The camera name is displayed inside the frame, provided you
assigned a name under "Configuration / Cameras / Name".
This icon is displayed if one of the inputs is not connected to a
camera.
Selecting the Image Size
Select the image size by clicking one of the three image sizes displayed underneath
the image:
♦= 176 x 144 (halfsize)
♦= 352 x 288 (fullsize); this is the default size.
♦= 768 x 576 (hugesize)
When select ing views of multiple cameras, it is not possible to c hange the size.
Note: The loading time for a large image is longer than for a small image.
Manual
23
Display
Figure 12: Camera display
When the images are displayed using Live-optimized with ActiveX plugin or Livecompatible, you can access a pop-up menu (to display it, click the image using the
right mouse button). This pop-up menu provides options for showing/hiding the date
and time and for starting/stopping the image stream. When using Live-compatible,
you can also flip the image horizontally and vertically and show the camera name
and FPS (frames per second) rate.
Snapshot
In the upper left hand corner of the image in the stream ing section you will find
the Snapshot icon. Clicking on this during the streaming will result in a JPEG single
image being taken. With the right mouse button you can save this in the context
menu of your browser.
8.1.1 Controllable Camera
You can connect various controllable cameras to the Convision V100/V200, which
can be operated directly via the user interface. Depending on their design, these
cameras have different functions. For this reason, the user interface of the Convision
V100/V200 varies, depending on the camera connected.
The user interface of a fully controllable camera is shown in Figure 13.
Note: The camera control is always displayed as a live stream with a fullsize
image from a single camera.

Convision V100/V200 Series
24
In some controllable cameras you have to set an internal control address..
For this purpose, please use the addresses starting with "1".
Figure 13: View of a fully controllable camera
1 Snapshot - Clicking on this during the streaming will result in a JPEG single
image being taken. With the right mouse button you can save this in the
context menu of your browser.
2 Preset Tour - The camera can be pre programmed for up to 6 different position
presets which will be displayed sequentially.
3 Camera presets– storage spaces for selected image sections.
Click on the previously stored preset values to focus the camera on those
sections.
4 Save button– opens a dialog box for storing the preset sections.
5 Current camera image – Click a point in the image to focus the camera on the
selected point.
6 Horizontal pan range – infinitely variable panning
Stepwise panning left/right, depending on the zoom factor
Panning to the left/right end position
7 Panoramic view of the entire pan/tilt area.
8 Clicking on "Refresh" reconstructs the panoramic view using updated frames.
9 Vertical pan range – infinitely variable panning
Stepwise panning up/down, depending on the zoom factor
Panning to the upper/lower end position

Manual
25
10 Zoom – infinitely variable zooming
Zoom in stepwise/Zoom out stepwise
Maximum Zoom/minimum Zoom
11 Travel to the home position of the camera.
Depending on the type of camera connected, some of the following controls will be
displayed instead of the user interface shown in Figure 13:
By clicking on the triangles the camera swivels 1 to 10 steps in
the direction of the arrow. The angle depends on the zoom factor.
By clicking on the double arrow, the camera will be moved 10
times further in one movement than with the single arrow.
Adjusting the zoom factor
Zoom in/Zoom out
Setting the image sharpness range for cameras without auto
focus.
Close-up focus / remote focus
Adjustment of the light incidence in the lens.
Closed iris/open iris
Saving Presets
Note: If the configuration protection function is activated, administrator rights are
required for the storage process.
1. For some controllable cameras you can save specific image sections as preset
sections (Presets). For this purpose, focus on the desired point within the pan
area of the camera.
2. Set the desired zoom factor.
3. Click on the diskette icon. A dialog box for saving the current image section
related to a position number is displayed.
4. Click the desired position and assign it a name.
5. Save the data. The dialog box is closed.
Now you can always focus on that point by clicking the respective position number.
The names will be displayed as a tool tip whenever the mouse cursor is positioned
on the number. The preset sections can also be addressed due to an event (refer to
Chapter 9.3).
Preset Tour
1. Configure the desired presets.
2. Click on the icon . This opens a dialogue box.
3. Click on the desired number position and input the desired amount of time.

Convision V100/V200 Series
26
4. Save the data.
5. Start the “Tour“ by clicking on start. The black indicator and the ”Tour“ icon will
change to red.
6. End the “Tour“ by clicking o n “stop“. The red indicator and the “Tour” icon will
change to black.
Note: If the configuration protection function is activated, administrator rights are
required for the storage process.
8.1.2 MPEG
The MPEG compression reduces the quantity of data for the image sequences in
comparison to JPEG images considerably. This is made possible by the fact that only
the differences to the last image are transferred, not the entire image. This means
that it is, for example, sufficient to only store each fifteenth image as JPEG and those
in between as differences.
The MPEG standard defines a quantity of 25 images per second. For compensation,
the ratio of JPEG images to difference data is changed at low data transmission
rates. The lower the transmission rate, the lower the number of JPEG images used,
moreover, it is also possible to display one image double instead of two images one
after another in sequence. However, this makes the video stream less fluent.
There are various decoders for playing back MPEG streams which allow streaming,
i.e. play back while the data is being downloaded. Nevertheless, there is a certain
chronological delay between recording of the images and playback in the browser.
Possible decoders include a JAVA-Applet and the Microsoft Windows Media Player
which is based on ActiveX technology.
The simultaneous viewing of two different MPEG-Streams or one MPEGStream and one JPEG-Stream is not possible.
8.1.3 Sequencer (Convision V200 only)
The sequencer allows you to program the cameras to be viewed sequentially for a
specified time, without having to manually shift between the cameras.
Configuration
♦= Click the activation box before each camera you want to view.
♦= Input the time in seconds you want to view the camera for.
♦= Save the data.
You can also set the sequencing configuration in the
“Configuration/Camera/Sequencer“ menu.

Manual
27
Start sequencer
♦= Click on either Live-optimised or Live-compatible. You will see the images,
depending on your browser configuration, either in Live-optimised or Livecompatible mode.
Stop sequencer
♦= Click on “Save“ in the configuration menu
8.2 Frame Buffer Display
Frame buffers are storage spaces in the main memory of the Convision V100/V200.
In these buffers you can store as many as 32 pre and post-event images per camera.
Each camera is assigned one frame buffer. This means, images recorded by camera
1 are exclusively stored in frame buffer 1 etc. Any one event can be stored in several
frame buffers. Each frame buffer can store multiple events.
Requirements
♦= Configure and activate the frame buffers by selecting the Configuration menu in
the first drop down menu and Frame Buffer in the second drop down menu. Then
select Frame Buffer in the menu displayed (refer to Chapter 9.4.1).
♦= An event that you assigned the recording in a frame buffer as an action has
occurred.
If the above requirements have been met, the im ages stored in this buffer will be
displayed.
Figure 14: Displaying the images in the frame buffer

Convision V100/V200 Series
28
1. Select a came ra (frame buffer).
2. The pre-event images are displayed at the top, the first image is displayed
enlarged in the center of the window and the post-event images are displayed at
the bottom.
3. Clicking on an image will enlarge it.
Note: The frame buffers are automatically restarted as soon as your images are
sent by email or VdS 2465. The next pre-event images will then be displayed. A
frame buffer that was activated but not sent will not be restarted. In this case, all the
pre-event and post-event images will be displayed.
State
This menu displays a status overview of the frame buffers (red button = started, black
button = stopped).
8.3 Applications
The Convision V100/V200 supports various devices that can be controlled via the
serial interface, such as weather stations or controllable sockets (not included in the
scope of delivery).
8.3.1 Sockets
Remote controllable sockets with a serial connector supported by Convision
Technology can be controlled using a Convision V100/V200 via the serial port. In this
menu you can switch the sockets on or off.
For this purpose select the socket and the seriel interface (Serial) under
„Configuration / System / Devices“.
8.3.2 Weather Station
If a weather station supported by Convision Technology is connected to your
Convision V100/V200, e.g. the Huger WM918, a list with all the data transferred,
such as temperature, wind speed and wind direction will be displayed. For this
purpose select the weather station and the serial interface (Serial) under
„Configuration / System / Devices“.
The data from the weather station can be sent via FTP Upload or E-Mail. (refer to
Chapter 9.4).
8.4 Applets
To extend the possibilities already provided by your Convision V100/V200, you can
load your own applets with additional controllers for other devices. Applets are
programs executed in the browser. Depending on these applets, the associated
HTML pages will be displayed.

Manual
29
You can upload the applets to the Convision V100/V200 via "Configuration / System /
Applet" (refer to Chapter 9.1.4). Storage for applets is limited. If further applets can
not be uploaded then you will receive the following message „Input error or wrong
file!“.
8.5 Modules
Modules are software programs that perform various functions in the Convision
V100/V200, thus enhancing the firmware. For modules that you can upload to the
device if desired, please visit www.convision.de. Depending on the functions of the
individual modules, module-specific HTML pages will be displayed. Some of the
modules may also be an extension of existing HTML pages.
Each module is supplied together with a PDF document containing a description and
operating instructions.
You can upload the modules to the Convision V100/V200 via "Configuration / System
/ Module / Upload" (refer to Chapter 9.1.5). Storage for modules is limited. If further
modules can not be uploaded then you will receive the following message „Input
error or wrong file!“.
8.6 Information
This menu displays the current firmware version of your Convision V100/V200 and
the creation date of this firmware. If a new software version is available for download
at www.convision.de, you can update your Convision V100/V200 (refer to Chapter
9.1.7).
Below the date is the serial number of your Convision V100/V200. Each unit has its
own serial number. You can use it, for example, as a registration number when
connecting to the ConvisionCall server (refer to Chapter 9.1.2).
The serial number is also printed on a label underneath your Convision V100/V200.

Convision V100/V200 Series
30
9 Configuration
If the configuration protection function is activated, only the administrator is
permitted to change the settings in this menu.
9.1 System Settings
Use these menus for making general system settings. These include the
connections, security settings, uploading various files, activating the FTP server and
assigning the serial interfaces. In addition, this menu also provides the Event log.
The event log records the configurations you made, system processes and errors
that occurred.
9.1.1 LAN/Ethernet Connection Data
If you want to integrate your Convision V100/V200 in a LAN using a permanent IP
address, you can enter various IP addresses via this menu.
IP Addresses
Figure 15: Configuring the IP addresses
During the initial configuration using IPSetup (refer to Chapter 6.2 or 6.3), you have
already assigned an IP address and a network mask. This data is now displayed on
this page. You can change this if des ired. After a change you will be prompted to
reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot" button.
Note: If your Convision V100/V200LAN/ISDN is connected via ISDN only, i.e.
you assigned an MSN at initial configuration (refer to Chapter 6.1), these fields will be
blank. You do not need to enter any data.
If you do not know the individual IP addresses, ask your system administrator.
The IP address must be unique, i.e. it must not be assigned to another computer in
the network. You can use the Ping command to check whether or not an IP address

Manual
31
is still available for the Convision V100/V200
(refer to document “Convision System Configuration“). (For more information about
IP addresses and network masks refer to Chapter 10.8)
Configuration of a Port Number
The default ports for the IP Video Server are 80 (HTTP) and 21 (FTP). You do not
need to specify these ports. If you require another port, click on “Port“ and replace
the default settings with your own data. Save the data and reboot the video server.
Access: Write the IP address with a colon and the new port number in the address
line of the browser.
http://192.168.0.111:8050
Only change this port if you have sufficient TCP/IP knowledge.
The Router Entry
If you are using a default router in your network to connect to the Internet, enter its IP
address in the "Router" field. All the IP addresses outside the LAN will then be
accessed via this router.
The DNS-server entry:
In this field you have to enter the IP address of a DNS (Domain Name Service)
server (a DNS server converts an alphanumeric address to an IP address). In this
case, you should select the DNS server of the provider set in the Convision
V100/V200. For information on this topic, please revert to your provider.
Syslog-Server
A syslog server receives messages and error messages in a LAN. If you are
operating a syslog server in your network, the Convision V100/V200 can send its
messages to this server, similar to the event log. If your network does not include a
syslog server, this field should remain empty.
The default port for a syslog server is 514. If you have set up your syslog server on
another port, you can change this in the “Port” section.
Note: It makes sense to specify a syslog server only if it can be accessed via the
Ethernet.
Mail Server
The mail server must be specified if you are intending to send e-mails or SMS via the
LAN connection to the Internet. If you want to send mail via an ISDN connection, you
have to enter the respective data via the ISDN/Modem item.
1. Enter a DNS server (refer to Chapter 10.8 – The Domain Name System).

Convision V100/V200 Series
32
2. Now enter the SMTP server (mail server) of the LAN or your provider.
3. Enter the address of the sending Convision V100/V200. This address must be
registered with the provider.
4. Select the authentication method as required by the provider.
5. Enter the user name and password. (refer to Chapter 10.6).
Figure 16: Configuring the mail server
9.1.2 ISDN/Modem Connection Data
If the Convision V100/V200 is operated via an ISDN connection or a modem, enter
the connection data via this menu item. The Convision V100/V200 can be connected
either via ISDN or via an analogue modem. It is not possible to operate the two
connections at the same time.
The user can only establish a connection to the Convision V100/V200 if both
the user and the Convision V100/V200 are using either analogue connections
or ISDN connections. Data transmission from an analogue modem to ISDN is
possible only over ConvisionCall.
Note: Please check whether you need to enter additional zeroes for your
telephone system.
General
Every time you change or update something in this menu, you will be asked to restart
the Convision video server to save the changes. Click the “Reboot” button to do this.
Setting the IP Address
The IP address preset for devices accessed via ISDN connections is 10.0.0.10. If you
want to access multiple devices via the same ISDN connection and a router, you can
enter further addresses and network masks. After a change you will be prompted to
reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot" button. (For more information
about IP addresses and network masks refer to Chapter 10.8)

Manual
33
PPP Host Name
As a rule, routers identify IP video servers by the MSN. However, some routers also
use the host name for the device. The default name is “ConvisionVideoWebserver“,
but you can change this here.
Selecting ISDN or Modem
Choose one of these two buttons to specify whether your Convision V100/V200 is
connected via ISDN or a modem.
ISDN Connection to the Convision V100/V200 (Convision
V100/V200 LAN/ISDN only)
1. In the "Phone number (MSN)" field, enter the multiple subscriber number (MSN))
for dialling the Convision V100/V200.
Note: Normally, when using a telephone system, you have to enter only the
extension as the telephone number.
2. Enter the user name in the "Identification for PPP" (point-to-point protocol) field.
3. Enter the password in the "Password for PPP" field.
Note: The data you enter in these fields must also be entered in dial-up
networking when establishing an ISDN connection (refer to document “Convision
System Configuration“).
Note: The PPP login name and password are advisable for security reasons if the
Convision V100/V200 is addressed directly via an ISDN connection because a
connection can be established even if access to the device is protected by the user
password (refer to Chapter 9.1.8).
4. If supported by your provider, activate the password encoding option if desired
(refer to Chapter 10.4).
5. If supported by your provider, activate the channel bundling option if desired (refer
to Chapter 10.5).
When setting up dial-up networking, than you have to enable multi-channel
connection set up (refer to document “Convision System Configuration“).
6. Save the data.
7. You will be prompted to reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot"
button.

Convision V100/V200 Series
34
Figure 17: Configuring the ISDN parameters
Connecting to different Providers
The Convision V100/V200 needs the connection data to be able to establish a
connection via a provider, e.g. to send e-mail,
to perform an FTP upload or
to establish a connection to ConvisionCall.
While connected to a provider, the Convision V100/V200 cannot be accessed
via the default router.
By entering multiple providers, it is possible to establish alternative connections
automatically, if the first attempt at establishing a connection fails. Apart from that,
you can select different connections for different tasks.
1. Select one of the eight connection buttons on the "Connections" button bar.
2. Assign a name.
3. Enter the phone number of the provider.
4. Enter the user name in the "Identification for PPP" (point-to-point protocol) field.
5. Enter the password in the "Password for PPP" field.
6. If supported by your provider, activate the password encoding option if desired
(refer to Chapter 10.4).
7. If supported by your provider, activate the channel bundling option if desired (refer
to Chapter 10.5).
When setting up dial-up networking, you have to enable multi-channel
connection set up (refer to document “Convision System Configuration“).
Note: If your provider does support channel bundling but it is not possible to
bundle the two lines, the connection will be terminated with an error message in the
event log (refer to Chapter 9.1.12).

Manual
35
Figure 18: Configuring connections
8. TimeOut specifies the time period the Convision V100/V200 remains connected
to the provider after the last data has been transferred. 55 seconds is the default
time period. If desired, enter a different time in seconds (max. 99999 seconds).
9. Deactivate the checkbox if you want to terminate the connection immediately after
the last data has been transferred or upon interruption of the data stream.
10. Enter the DNS server of the provider (refer to Chapter 10.8 – The Domain Name
Service) .
The following data needs to be entered only if you want to use this connection for
sending e-mail or SMS!
11. Enter the SMTP server (mail server) of the LAN or your provider.
12. Enter the address of the sending Convision V100/V200. This address must be
registered with the provider.
13. Select the authentication method as required by the provider.
14. Enter the user name and password (refer to Chapter 10.6).
Configuring the Modem
In the "Analog Modem" menu you will find settings for a modem that supports the
extended Hayes command set.
The init strings for initializing the modem depend on the modem used. The init strings
for your device can be found in the operating instructions of your modem.

Convision V100/V200 Series
36
Make sure that you have chosen “Modem” under „Configuration/System/ISDNModem/General”!
1. Enter the login name for identification for PPP.
1. Enter the PPP password.
1. If the values for your modem differ from the settings, please enter the correct
strings.
2. Save the data.
3. You will be prompted to reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot"
button.
4. If you made a mistake, click on "Default" to restore the settings.
After changes to this data, you have to reboot your Convision V100/V200.
ConvisionCall (Convision V100/V200 LAN/ISDN only)
ConvisionCall is a service offered by Convision Technology GmbH so that you can
easily reach your Convision V100/V200 connected via ISDN. Apart from that you
save the costs of an ISDN long-distance call since the Convision V100/V200
connects to the ConvisionCall server via your local Internet provider at an economical
rate and with a dynamic IP address.
Note: The connection costs incur on the Convision V100/V200 side because it
sets up the connection.
Note: Only the connection set up is made via the ConvisionCall server, not the
data transfer.
Note: When selecting a connection with channel bundling to the provider (refer to
Chapter 9.1.2), only one access at a time can be made to the Convision V100/V200.
For setting up another connection, there is no other free B-channel for signaling.
To be able to use this service, you need register with the ConvisionCall server. This
connection can also be set up if the user connects via an analogue modem.
However, the Convision V100/V200 must be connected via ISDN.
1. Turn on ConvisionCall by clicking the "Activate" checkbox.
2. The IP address of the ConvisionCall server and the associated telephone number
has already been entered. If the installation site of your Convision V100/V200 is
not in Germany, you have to enter the country code (0049).
3. Select the connection which you want to use with ConvisionCall. You may also
select a fallback connection, when an error occurs with the first one. Make sure
that the timeout is activated in the connection configuration page.
4. To be able to use this service, you need to register with the ConvisionCall server.

Manual
37
For more information on ConvisionCall, please visit:
http://www.convision.de/convision/_de/convisioncall/call.html. To register, you need
the serial number and the connected ISDN telephone number of the Convision
V100/V200. The serial number is located on a sticker underneath the Convision
V100/V200 and on the HTML pages in the "Information" menu.
Registration and Configuration
1. Use a browser to open the Convision website www.convision.de, click the
"ConvisionCall" button and select "Register to ConvisionCall- Server".
2. Fill in the registration form and save it. You are now registered with the
ConvisionCall server and in future you need only enter your login name and
password to log in.
Note: Please check whether you need to enter additional zeroes for your
telephone system.
3. Click "To Convision IP Video server". Enter your login name and password.
4. Click on the “Add” button; enter the data of your Convision V100/V200. Save your
data. A window containing the data you just saved will be displayed.
Figure 19: Configuring the ConvisionCall server
5. Open a second browser window and position the two browser windows in such a
way that you can access both windows.
6. In the 2nd browser window, open the configuration page of your Convision
V100/V200 (Configuration / ISDN / ConvisionCall) and click the "Control" button.
The Convision V100/V200 will now wait for a call from the ConvisionCall server
(for the set timeout) to learn the phone number of the server.

Convision V100/V200 Series
38
Figure 20: Configuring ConvisionCall in the Convision V100/V200
7. Immediately (within the set timeout, refer to Chapter 9.1.2 Connecting to Different
Providers) select the "Connect" option in the first browser window. The server will
now call your Convision V100/V200. The Convision notices that it is being called
but does not answer the call. Instead, it updates (if applicable) the number of the
ConvisionCall server and establishes a dial connection to the Internet via the
Internet Provider.
8. Once the connection has been successfully established, the "Call received"
message will be displayed.
9. The ConvisionCall telephone number has probably now been corrected
automatically. Save the data again.
Note: If you call the Convision V100/V200 via dial-up networking and there is not
enough free telephone lines, disconnect dial-up networking to your Convision
V100/V200 immediately after you clicked the "Control" button.
Using ConvisionCall
1. Use a browser to call the Convision website www.convision.de .
2. Click the "ConvisionCall" button.
3. Click "To Convision IP Video server".
4. Log in to the ConvisionCall server using your name and password.
5. Select a Convision V100/V200 in the window displayed (refer to Figure 19:
Configuring the ConvisionCall server) and click "Connect".
6. You will be connected to your Convision V100/V200.
The connection will automatically be terminated when data is no longer being
transferred. If a timeout is set, the connection will be terminated after the timeout has
elapsed (refer to Chapter 9.1.2 Connecting to Different Providers).
Click "Connect again" if you want to re-establish the connection to the Convision
V100/V200.

Manual
39
VdS – Alarm Notification in Compliance with VdS 2465
(Convision V100/V200 LAN/ISDN only)
Apart from TCP/IP, the Convision V100/V200 can alternatively use a special alarm
protocol (VdS 2465) to send alarm messages. These messages are sent via an ISDN
connection to an alarm center. At the alarm center, special software receives and
decodes these messages so that measures can be taken immediately.
This menu is used to define the parameters for connecting to the alarm center. The
individual messages are defined in the "Action / VdS 2465" submenu (refer to
Chapter 9.4.6).
1. Enter the telephone number of the alarm ce nter that will answer your alarm
message.
2. Enter the VdS identification. Your alarm center provides this ID to identify your
Convision V100/V200.
3. Periodic reporting to the alarm center serves for verifying whether your Convision
V100/V200 is operational.
4. Indicate at which time the monitoring message is to be sent.
5. Indicate the line for the monitoring message
VdS alarm notifications can only be sent to an alarm center with the facilities
to process these messages.
VdS alarm notifications can only be sent via ISDN.. Sending with a modem is
not possible.
9.1.3 Language
Selection
By default, the Convision V100/V200 menus can be displayed in German, English,
Spanish or French. Upon the first access to the Convision V100/V200 user interface,
the current browser setting is used.
Via this menu, you can select the language or you can continue using the default
language of your browser.
For this purpose, activate the associated button.

Convision V100/V200 Series
40
Figure 21: Selecting the language
Upload
You can add a language version by uploading a file containing all the menu texts to
the Convision V100/V200.
Modules with other languages are available on the Convision Website
www.convision.de. Download the desired language module to your computer.
1. To upload the language module to the Convision V100/V200, enter the file name
(extension .lgf) together with the complete path to the directory in which it is
stored.
2. Alternatively you can click the "Browse" button to search for the file. Once you
have located it, double-click to add it to the input line.
3. Then click the "Upload file" button.
Do not switch off the Convision V100/V200 during the upload procedure.
Do not access the Convision V100/V200 in any other way during the
procedure.
9.1.4 Applets
In this menu, you can load your own applets to the Convision V100/V200, e.g. for
controlling other devices via the serial interface. In the "Applets" menu (refer to
Chapter 8.4), you can display the associated HTML page. You can delete an applet
that you do not need any longer.
You can download a sample applet that you can adapt to your needs free of charge
on the Convision Website www.convision.de.
Upload
1. To upload an applet to the Convision V100/V200, enter the file name (extension
.jar) together with the complete path to the directory, in which it is stored.
2. Alternatively you can click the "Browse" button to search for the file. Once you
have located it, double-click to add it to the input line.

Manual
41
3. Then click the "Upload file" button.
Do not switch off the Convision V100/V200 during the upload procedure.
Do not access the Convision V100/V200 in any other way during the
procedure.
Delete
When clicking the delete menu item, a list of all the applets you have already
uploaded will be displayed. If you want to delete one of these modules, select it and
then click the "Delete" button.
For an HTML display of your applet, select the "Applets" menu (refer to Chapter 8.4).
9.1.5 Modules
Modules are software programs that perform various functions in the Convision
V100/V200, thus enhancing the firmware. For modules that you can upload to the
device if desired, please visit www.convision.de.
Via the "Module" item in the "Configuration" menu, you can upload further modules to
the Convision V100/V200, activate modules or delete them.
The HTML page of a module is displayed either via the "Module" menu (refer to
Chapter 8.5) or as an extension to an existing HTML page.
Upload
1. To upload a module to the Convision V100/V200, enter the file name (extension
.mod) together with the complete path to the directory in which it is stored.
2. Alternatively you can click the "Browse" button to search for the file. Once you
have located it, double-click to add it to the input line.
3. Then click the "Upload file" button.
Do not switch off the Convision V100/V200 during the upload procedure.
Do not access the Convision V100/V200 in any other way during the
procedure.
Delete
When clicking the delete menu item, a list of all the modules you have already
uploaded will be displayed. If you want to delete one of these modules, select it and
then click the "Delete" button.
9.1.6 Configuration – Saving and Uploading
You can save all the configuration data of your Convision V100/V200 in a binary
encoded file (default "convision.cfg") on your computer.

Convision V100/V200 Series
42
To save the file, click "Save configuration to file". Select the desired directory in the
dialog box displayed.
You can upload the saved file to other devices of the same type and thus easily
transfer the settings you made. You can also use this file to define the basic
configuration. If you made undesired changes, for example, you can easily restore
the original configuration using this file.
After you transferred the configuration file to other devices, you must assign a new IP
address/MSN.
The device associated with the IP address set in the configuration file
must not be reachable within the LAN when the file is transferred to
another device. As soon as you have transferred the file, change the IP
address if the two devices are to be reachable within the LAN at the
same time. Switch on the other device only after you have made these
changes.
1. To upload the configuration file to the Convision V100/V200, enter the file name
(extension .conf) together with the complete path to the directory in which it is
stored.
2. Alternatively you can click the "Browse" button to search for the file. Once you
have located it, double-click to add it to the input line.
3. Then click the "Upload file" button.
Do not switch off the Convision V100/V200 during the upload
procedure.
Do not access the Convision V100/V200 in any other way during the
procedure.
9.1.7 Update – Uploading Ne w Firmware
Via this submenu you can upload new firmware versions to the Convision
V100/V200.
The software is continuously updated and its performance improved. The latest
version of the software is available for download free of charge as a ZIP file on the
Convision website www.convision.de.
1. To update the software, enter the full path of the directory to which you unzipped
the update file on your computer aft er dow nl o adi ng .
2. Alternatively you can click the "Browse" button to search for the file. Once you
have located it, double-click to add it to the input line.
3. Then click the "Upload file" button.
Do not switch off the Convision V100/V200 during the update procedure.
Do not access the Convision V100/V200 in any other way during the
procedure.

Manual
43
Figure 22: Update dialog box
Note: Following an update, controllable cameras may not be initialized correctly.
In this case, switch off the camera and the Convision V100/V200, and then switch on
the camera first. Wait for the camera self-test to complete and then switch on the
Convision V100/V200.
9.1.8 Security Settings
In this submenu you can define security measures against unauthorized access to
your Convision V100/V200. There are three levels for protecting the Convision
V100/V200 against unauthorized access.
Save your data once you have entered the passwords and activated the respective
levels.
Figure 23: The three security levels

Convision V100/V200 Series
44
Protecting the Configuration against Unauthorized Access
If you want to protect the configuration settings against unauthorized access, enter a
password in the "Administrator password" area and confirm it. Then activate the
"Protect configuration against unauthorized access" checkbox.
Now a prompt for entering the administrator password will be displayed as soon as
the "Configuration" menu is selected. A user with the login name "admin" will always
be granted access to all the areas of the device.
The login name for the administrator is “admin” and cannot be changed.
Protecting the Recording Sector against Unauthorized Access
If you also wish to protect the recording sector, i.e. the access to the frame buffer ,
enter a password in the "Password for recording sector" area and confirm it. Then
activate the "Protection of the recording sector" checkbox.
Now a prompt for entering the password fo r the recording sector will be displayed as
soon as the "Record" menu is selected. A user with the login name "record" always
has access to all the areas. An exception is the "Configuration" menu, provided it has
been password-protected.
The login name for the recording sector is “record” and cannot be changed.
Protecting the Device against any Unauthorized Access
You also have the possibility of protec ting the Convision V100/V200 against
unauthorized access in general. For this purpose, enter a password in the "User
password" area and confirm it. Then activate the "Protect Convision V100/V200
against unauthorized access" checkbox.
Now a prompt to enter the user password will be displayed upon any access to the
Convision V100/V200. A user with the login name “user” cannot access the
"Configuration" and "Frame Buffer" menus, provided these have been passwordprotected.
The login name for the user section is “user” and cannot be changed.
9.1.9 Setting the Time and Date
The date and time are set upon delivery of the Convision V100/V200. If these
settings are not correct due to different time zones, you can change them via this
menu item. Save the data.
These two settings are buffered for a certain period even without an external power
supply via a backup battery.
Your Convision V100/V200 can automatically change from summer to winter time.
The time conversion is done in MESZ (Middle European Summer Time) and is
already configured for the next few years. If you do not require this, simply delete the
pre-configured time.

Manual
45
9.1.10 Activating the FTP Server
Use this menu to activate the Convision V100/V200 as an FTP server. When this
option is activated, the camera images can be downloaded using either HTTP
(Hypertext Transfer Protocol) or FTP (File Transfer Protocol).
After changes to these data, you have to reboot your Convision V100/V200.
Figure 24: FTP-Server dialog box
Permitting Anonymous FTP Access
If the Convision V100/V200 is protected in that the various security levels have been
activated (refer to Chapter 9.1.8), it will not be possible to access it via FTP without
entering a login name and password.
You then have to use the following URL to access the Convision V100/V200:
ftp://login-name:password@IP-address/....
The login name is either "admin" or "user" and the password is the one assigned in
the security settings. Once the page has been opened, the password is no longer
displayed in the address line.
If "Anonymous FTP allowed" has been activated, users are able to access the
images on the Convision V100/V200 with the login name "anonymous" or "ftp" and
any password via an FTP program.
Note: If the FTP protocol is opened using a browser, it is not necessary to enter
the user data. The login name "anonymous" is the default setting for this access.

Convision V100/V200 Series
46
Downloading Images via FTP using a Browser
You can obtain an up-to-date image using the following path:
ftp://IP-address/cameras/camera2/fullsize.jpg
This command addresses camera 2. For other image sizes, you can enter "halfsize"
or "hugesize" instead of "fullsize".
9.1.11 Assignment of Devices to the Serial Port
In the "Device" menu you have to enter the devices connected to the serial interfaces
(Serial) of your Convision V100/V200.
1. In the table displayed, select which device is connected to COM 1 (Serial). If no
devices are connected, select "No device connected!" (default).
2. If several controllable cameras are connected, specify the number of cameras
(Convision V200 only).
3. If you want to operate a device not listed in the table, select "Serial Url Port". You
will control the device with your own applet that you have to upload to the
Convision V100/V200 (refer to Chapter 8.4 and 9.1.4).
4. Save the data.
5. You will be prompted to reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot"
button.
You cannot connect two models of one device type (e.g. cameras) to the two
COM ports.
Figure 25: Assignments of the serial ports

Manual
47
Serial URL port
Once the serial URL port has been activated, it is possible to control devices not
supported by the Convision V100/V200, e.g. other controllable cameras. In this case,
all the parameters required for setting the serial connection and the actual data will
be transferred.
The data that needs to be entered for controlling the device can be obtained from the
device manufacturer.
When programming a website or an applet, you can integrate lin ks or buttons th at
include CGI parameters in addition to the IP address of the Convision V100/V200 in
the URL. These parameters are forwarded to the device to be controlled via the serial
URL port. You can download a manual for programming the Convision Webserver
and a sample applet at www.convision.de.
9.1.12 Event Log
The Convision V100/V200 logs all the system events (information, errors and
warnings). Click on the "Event log" menu item to list all these events.
Click on "Delete events" if you want to delete the list.
Figure 26: Event log
You can change or filter the display by clicking on one of the buttons above the list:
Change the order of the entries
All entries visible and refresh the display
Filter: only events visible
Filter: only warnings visible
Filter: only errors visible

Convision V100/V200 Series
48
9.2 Camera Settings
In the "Configuration/Cameras" menu you can rename the connected cameras, i.e.
assign them individual names (e.g. depending on the position of the camera). In
addition, you can set the camera properties.
9.2.1 General – Settings for the Image Display
Figure 27: Gerneral camera settings
Per default the video norm is PAL. If the cameras do not correspond to the selected
norm the camera images will be shown distorted.
- Select „NTSC“, if your cameras correspond to the NTSC norm.
- Save the data.
- You will be prompted to reboot the device. For this purpose, click the "Reboot"
button.
♦= Activate the checkbox if the camera images are to be stored in the "hard disk
cache" of the browser (not in Internet Explorer).
activated: The individual image displayed in the browser window can be
saved.
n ot activated: When saving an image, an up-to-date image from the camera is
used instead of the one displayed in the browser.
♦= Activate this checkbox to enable the display of date/time in the images viewed
using Live-compatible.
Note: Live-compatible also has a pop-up menu (click the right mouse button on
the image) via which the date can be shown/hidden.
9.2.2 Name – Renaming Cameras
In this menu you can assign each camera a name. It is a good idea to use the name
of the location at which the respective camera is mounted. After entering the names,

Manual
49
click the "Save" button to save the names you assigned in the Convision V100/V200.
The names assigned to the cameras will then be displayed in the camera views.
9.2.3 Pan/Tilt
This menu is displayed only if a controllable camera is connected.
In the associated dialog box you have to enter the maximum time in seconds granted
to a user for controlling a camera. During this time period, any other access to this
camera will be rejected. If a "0" is entered in this field, every access is permitted, i.e.
if several users access a camera simultaneously, one user can change the position
desired by another user.
9.2.4 MPEG Parameters
Here you can select the type of connection for your Convision V100/V200. The
parameters are then set for display of the camera images (JPEG/MPEG), depending
on the setting.
Fig. 28: Connection and parameters
♦= Size of image half/fullsize (see Chapter 8.1)
♦= Quality Fixed minimum quality for an image -> Transmission-
rate varies
♦= RepeatBFrame Instead of transferring a new image, the last image
transferred is displayed again
♦= Bitrate Fixed data transmission rate -> Quality of
individual images varies
By repeatedly displaying images already transferred, the quantity of data to be
transferred is reduced so that a higher quality is possible for the individual images.

Convision V100/V200 Series
50
You can only select one of the parameters either “Quality” or “Bitrate”. When the
band width is small, you should specify a minimum quality with "Quality".
9.2.5 Setting the Camera Properties
1. Select a camera.
This icon is displayed if one of the inputs is not connected to a
camera.
2. Select the property you want to change, i.e. either "Saturation", "Brightness",
"Contrast", "Quality" or "Hue" (for NTSC cameras only).
Note: The hue (for NTSC cameras only) defines the color hue of the image and is
set to 128 by default. If the image does not exhibit a natural hue with this setting, you
can adapt it by slightly changing the default value.
3. Adjust the settings according to your requirements.
♦= Possibility 1: the 6 number buttons above the image represent the various
saturation levels. Click on one of the number buttons to select this level. If you are
satisfied with the setting, click the "Save" button.
Figure 29: Setting the camera properties 1
♦= Possibility 2: if you click on the rectangle made up of six small rectangles in the
upper right-hand corner, images representing all the six levels will be displayed.
You can select the desired level by clicking on the corresponding image.

Manual
51
Figure 30: Setting the camera properties 2
Note: If your Convision V100/V200 is connected via ISDN it is advisable to reduce
the quality and thus the data volume of the images to achieve a smooth image
stream.
9.3 Events – Actions When an Alarm Is Triggered
An event occurs either when an input is activated, time-dependent by timers you
configured, when an internal event occurs or when a camera detects and reports an
activity.
These menu items are used to configure the events. You then assign actions to the
events that are to be triggered as a response. The following actions may be possible:
♦= Camera Presets (at least one controllable camera must be connected)
Activate the preset positions that are to be taken. These
positions will be taken directly one after the other in the order
listed.
♦= Frame Buffer Activate the checkboxes of the frame buffers that are to be filled
but not sent. If you want to append frame buffers to an e-mail or
VdS notification, you must not enter them here.
♦= Camera Tour (at least one controllable camera must be connected) Here you
can start or stop the camera tour that was previously configured
under either Camera/Live Optimized or Live Compatible.
♦= FTP Activate the checkboxes of the FTP uploads that are to be
performed.
♦= eMail Activate the checkboxes of the e-mails that are to be sent.
♦= eMail State An e-mail with informations about the state of the device will be
sent.
♦= SMS Activate the checkboxes of the SMS that are to be sent.
♦= VdS 2465 : Activate the checkboxes of the VdS 2465 notifications that are to
be sent.

Convision V100/V200 Series
52
9.3.1 Inputs
You can connect various signallin g devices to the inputs of the Convision Vide o
Webserver. Use this menu item to assign each input (Input 1 and 2) the actions that
are to be performed when a message is recei ved.
Figure 31: Configuring the alarm inputs– assigning actions
1. Select an input and enter a name for it.
2. Click on an input in the first table column. A page with a weekly schedule is
displayed.
Figure 32: Configuring the inputs – weekly schedule
3. Now define one or two time periods for each day of the week on which this input
is to be active. Enter start and stop times for the respective days of the week.
4. If you want to have a set period of time between two events, click on “Time
between 2 Events“. A window will then pop up where you can enter a time in
seconds fo r each input. Here yo u can also defi ne a minimum time an input signal
must be present, until it is interpreted as a signal. By default "0" each signal will
be interpreted. Save the data.
5. Save the data in the schedule window.

Manual
53
6. Return to the page, on which you can select the inputs. The configured and saved
inputs are now indicated by a clock symbol.
7. Click "Add" to select actions that are to be performed in the selected inputs.
8. A page will be displayed on which you can assign the e vent actions from various
groups.
9. You can assign any number of actions. All the actions assigned will be listed in
the table in the line associated with the respective input.
10. Repeat steps 1 to 9 for the other input, if desired.
11. Save the data.
12. Click "Delete" to cancel the assignment of actions.
Note: All the actions you want to trigger must first be configured. Clicking on the
actions opens the associated configuration pages. Check the status on these pages
to avoid assigning partitions that do not exist or messages that have not been written.
9.3.2 Time Control – Time-Dependent Actions
In this menu you can configure up to eight different points in time (timers 1 – 8) at
which the Convision V100/V200 is to perform actions. Points in time trigger periodical
actions (e.g. every 10 minutes) within defined time periods (e.g. daily between 8 a.m.
and 4 p.m.).
Figure 33: Configuring the points in time – assigning actions
1. Select a timer and enter a name for it.
2. Click on a timer (timers 1 to 8) in the first table column. A page with a weekly
schedule is displayed.

Convision V100/V200 Series
54
Figure 34: Configuring the points in time – weekly schedule
3. Define how often this timer is to be activated, e.g. how often an e-mail is to be
sent or an output is to be switched. You can select "Seconds", "Minutes" or
"Hours".
4. Now define one or two time periods for each day of the week on which this period
is to be active. Enter start and stop times for the respective days of the week.
5. Save the data.
6. Start the timer. The black indicator next to the list box in the upper right-hand
corner will change its color to red.
Saving the page again after starting the timer will stop it.
7. Return to the page, on which you can select the timers.
8. Click "Add" to select actions that are to be performed at the selected points in
time.
9. A page will be displayed on which you can assign the event actions from various
groups.
10. You can assign any num ber of actions. All the actions assigned will be listed in
the table in the line associated with the respective timer.
11. Repeat steps 1 to 10 for other timers, if desired.
12. Save the data.
13. Click "Delete" to cancel the assignment of actions.
Note: All the actions you want to trigger must first be configured. Clicking on the
actions opens the associated configuration pages. Check the status on these pages
to avoid assigning partitions that do not exist or messages that have not been written.

Manual
55
9.4 Actions
The Convision V100/V200 performs actions in response to events (at an input or
time-controlled – refer to Chapter 9.3).
9.4.1 Configuring the Frame Buffers
Figure 35: Configuring the frame buffers
Frame buffers are storage spaces in the main memory of the Convision V100/V200.
In these buffers you can store as many as 32 pre and post event images per camera.
Each camera is assigned one frame buffer. Thus, the images from camera 1 are
recorded in frame buffer 1 etc.
Once a frame buffer has been activated, it continuously stores frames. As soon as a
buffer is filled, it is overwritten. If an event occurs (refer to Chapter 9.3), the preset
number of post-event images are stored, then the recording procedure is aborted.
Thus, the remaining storage space contains the pre-event images.
Each event may be stored in several frame buffers. Each frame buffer can store
multiple events. You can attach several frame buffers of your choice to any e-mail or
VdS notification.
For information on displaying frame buffers, please refer to Chapter 8.2.
1. Click on "Configuration/Frame Buffer" and select a frame buffer in the top button
bar of the page displayed.
2. Specify the number of images that are to be recorded before an event.
3. Specify the number of images that are to be recorded following an event. The
maximum permissible total number of pre- and post-event images is 16 or 32.
If the total number you entered exceeds 16 (384x288 pixels) or 32 (196x144
pixels), the number is automatically corrected to 16 or 32.

Convision V100/V200 Series
56
4. Specify the recording speed between the maximum speed (25 images per
second) and 1 image every 2 seconds.
5. Select the image size. The maximum number of images stored is 16 for large
images and 32 for the small images.
6. Save the data.
7. Start recording to the frame buffer by clicking the corresponding option in the
table in the lower part of the page. The black indicator to the right of the option will
change to red.
8. Repeat steps 1 to 7 for the other frame buffer, if desired.
9. Stop recording to the frame buffer by clicking the corresponding option in the
table in the lower part of the page. The red indicator to the right of the option will
change back to black.
To send a frame buffer by e-mail or VdS 2465 notification, open the "Configuration /
Action / eMail or VdS2465 page, select the desired message and activate the
checkbox(es) next to the desired frame buffer(s). After they are sent, frame buffers
are automatically restarted. The images stored in the buffer are overwritten by a new
event.
A frame buffer that was activated but not sent will not be restarted. In this case, all
the pre and post event images will be displayed.
9.4.2 Transferring Data via FTP (Upload)
At predefined points in time or in response to an event, the Convision V100/V200 can
transfer an image (Upload) to a web server directory via FTP.
In this case, the Convision V100/V200 is the FTP client. (For information on
configuring the Convision V100/V200 as the FTP server, please refer to Chapter
9.1.10). You can transfer an up-to-date image recorded by any camera as well as
data of a connected weather station.
Figure 36: FTP upload

Manual
57
Note: The login information can be obtained from your administrator (LAN) or
from your provider.
1. Select one of the 8 FTP uploads in the upper button bar.
2. Enter a name.
3. Specify the name or the IP address of the server to which the images are to be
transferred.
4. Enter a login name and password with access rights to this server.
Note: If an anonymous access to a server is permitted, "anonymous" is often
used as the login name and the password is your own e-mail address.
5. If the images are not to be saved in the default directory of the user, enter the
path to the server directory in which the images are to be stored.
6. Enter a name for the ima ge file. Images will only be transferred if a file name is
entered.
7. Enter a file name for the data from the weather station. The data is transferred as
an HTML file by default. If you enter ".txt" as the file name extension, the data is
transferred as a text file.
8. Specify the connection via which the upload is to be performed.
9. Enter an alternative connection that is to be used if the first on e fails.
10. Repeat steps 1 to 9 for other FTP uploads, if desired.
11. Save the data.
Image Names
The filenames may contain wildcards so that the images can be saved on a server
using consecutive numbers. Using the name "image*.jpg" will copy the images
"image0.jpg" to "image9.jpg" to the server. An additional "*" needs to be entered for
each digit required, i.e. the name "image**.jpg" will copy the images "image00.jpg" to
"image99.jp"” to the server. The image counter is reset to zero once you save the
FTP message.
The following variables can be used in naming the image files:
♦= %DATE% current date
♦= %YEAR% current year
♦= %MONTH% current month
♦= %DAY% current day
♦= %TIME% current time
♦= %IP% IP address of the IP video server
♦= %SERIAL% serial number of the IP video server
The variables will be replaced by their values when saving the pictures on
an ftp server. For example:
Image-%DATE%-%IP%_***.jpg
will become Image-14_05_2002-192.168.0.123_001.jpg

Convision V100/V200 Series
58
9.4.3 Notification via E-Mail
At predefined points in time or in response to an event, the Convision V100/V200 can
send an e-mail to as many as 10 addresses.
You can attach an up-to-date image recorded from any camera, frame buffers as well
as data from a connected weather station to the e-mail.
Figure 37: Configuring e-mail notification
1. Select one of the 8 messages in the top button bar.
2. Enter a name.
3. Enter the e-mail address of the recipient in the "Recipient" field. If the message is
to be sent to multiple recipients (max.10), separate the e-mail addresses using a
semicolon.
4. Enter the reference in the "Subject" field (e.g. alarm).
5. Enter the message in the ”Text” box (e.g. burglary at xxx., address: xxxx etc.).
6. You can attach images recorded by each camera to the e-mail. For this purpose,
activate the checkbox next to the desired cameras.
7. You can attach images stored in the frame buffers to the e-mail. For this purpose,
activate the checkbox next to the desired frame buffers.
If you append images from several frame buffers, the e-mail may become
very large. In this case, it may not reach the recipient at all.
8. To attach data from a connected weather station, activate the corresponding
check box.
9. Specify the connection that is to be used to send this e-mail.
10. Enter an alternative connection that is to be used if the first on e fails.
11. Repeat steps 1 to 10 for other e-mails, if desired.
12. Save the data.

Manual
59
9.4.4 E-Mail State (eMail State)
Basic status reports (cameras and event log) for the IP video server can be sent by
e-mail as an action following an event or time-controlled.
9.4.5 Notification via SMS (Short Message Service)
At predefined points in time or in response to an event, the Convision V100/V200 can
send an SMS to as many as 10 addresses. An SMS can have a maximum length of
160 characters. You cannot attach any other data.
Figur e 38: Conf igurin g SMS
1. Select one of the 8 messages in the top button bar.
2. Enter a name.
3. Enter the e-mail address of the mobile telephone in the "Recipient" field. If the
message is to be sent to multiple recipients (max.10), separate the e-mail
addresses using a semicolon.
Note: Since the messages can be sent via e-mail to a mobile telephone, ask your
mobile network operator for the e-mail address of the mobile telephone (e.g. <phone
number> @d2-message.de, <phone number>@t-d1-sms.de, <phone
number>@smsmail.eplus.de).
4. Enter the message text in the "Text" field (max. 160 characters).
5. Specify the connection that is to be used to send the SMS.
6. Enter an alternative connection that is to be used if the first on e fails.
7. Repeat steps 1 to 6 for other SMS, if desired.
8. Save the data.
SMS messages are sent to the mobile telephone via the e-mail function of the
provider, which means the e-mail/SMS function must be enabled for this
telephone.

Convision V100/V200 Series
60
9.4.6 VdS 2465
In response to an event, the Convision V100/V200 can send a VdS notification to an
alarm center. You can attach several frame buffers to the notification. (For
information on configuring the connection, refer to Chapter 9.1.2, VdS 2465).
Figure 39: Configuring VdS2465
1. Select one of the 8 messages in the top button bar.
2. Enter a name.
3. Enter an alarm type. Ask your alarm center for a list of alarm types you can use.
4. You can attach images stored in the frame buffers to the message. For this
purpose, activate the checkbox next to the desired frame buffers.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 for other messages, if desired.
6. Save the data.
9.4.7 Further action with no configuration page
Camera Tour
Here you can start or stop the camera tour that was previously configured under
either Camera/Live Optimized or Live Compatible (refer to Chapter 8.1.1). This can
be started or stopped or activated by an event, as long as the input is activated
(start/stop).

Manual
61
10 General Descriptions
10.1 Using the Convision V100/V200 as a Video
Server
If the Convision V100/V200 is integrated in your LAN with a fixed IP address, it can
be accessed as a web server directly from the Internet. However, do bear in mind
that the capacity of the video server is limited – with a large number of users, a proxy
server solution is strongly recommended (CGI script and daemon on a powerful web
server).
A great advantage of this connection option is the high image refresh rates.
10.2 Live optimized and Live compatible
There are three options for displaying frame sequences (Motion-JPEG) in your
browser:
Live optimized - Server-Push is a software program executed in the browser for
continuously playing back images without the connection between the server and
browser being interrupted. It is available in Netscape Navigator only.
Live optimized - Convision Technology developed an ActiveX plugin especially for
displaying frame sequences in Internet Explorer. When starting the first frame
sequence using this program, it will be installed as a plugin for the Internet Explorer
on your computer.
Live compatible - A Java applet also developed by Convision Technology GmbH is
available for this and all the other browsers.
10.3 FTP
For transmitting images via FTP (File Transfer Protocol), the Convision V100/V200
can be used either as an FTP server or as an FTP client. It is always the client that
takes the initiative for transferring data.
As a server, the Convision responds to the request of a client, e.g. the browser, and
sends the requested images (FTP download). As a client, the Convision V100/V200
dials up a server and transmits one or more pre-configured images. An FTP upload is
performed.
10.4 Password Encryption
Some providers use the encrypted submission of the registered password as an
additional security feature. If you have defined a password for incoming or outgoing
connections on the Convision V100/V200, you can activate the password encryption
function.
If the provider does not accept the encrypted transfer of the password, the
connection will still be established via the unencrypted transfer of the password.

Convision V100/V200 Series
62
If you did not define a password, this option will be ignored.
Ask your provider whether password encryption is supported or not.
10.5 Channel Bundling
A basic ISDN access provides two transmission channels with a bandwidth of 64 Kbit
each for language or other user data. These channels are referred to as B-channels.
For a standard ISDN connection, only one of the two available B channels is used.
When both the B-channels are used for data transfer, this is referred to as "channel
bundling". This means, twice the data volume can be transferred at the same time.
The charges accrue per channel, which means that they will be doubled during
channel bundling.
Channel bundling can be activated individually for incoming and outgoing
connections to the Convision V100/V200.
Not all providers support this option. If you activated channel bundling but your
provider does not support this option, a single channel connection will be established.
Ask your provider whether channel bundling is supported or not.
Note: If your provider does support channel bundling but it is not possible to
bundle the two lines, the connection will be terminated with an error message in the
event log (refer to Chapter 9.1.12).
10.6 SMTP or Mail Server
An SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server forwards outgoing e-mail messages
to the recipient. The address of the SMTP server can be obtained from the system
administrator for a LAN connection an d fro m y our telecomm uni ca ti ons prov i der for an
ISDN connection.
To be able to access the SMTP server, the e-mail address of the sending Convision
V100/V200 must be registered with the provider.
SMTP Authentication – SMTP-after-POP
Some e-mail providers require authentication to prevent anyone with an unauthorised
or fake e-mail address from using the SMTP server. One authentication method is
SMTP Authentication. You need to enter a user name and password for this.
Another authentication is a registration via POP 3 (Post Office Protocol – Protocol
used to access a server which stores e-mails for other computers).
If the provider requires this method for authentication, just enter the user names and
password in the same way you have to to receive your e-mail.
10.7 Control via CGI Parameters
CGI (Common Gateway Interface) is a way of providing programs that can be
opened by HTML files. The program and the parameters to be used to open the
program is placed in the URL following the IP address. An example is given below:

Manual
63
http://IP address/path/CGI program?Parameter1=value1&Param2=value2&...
This program with its parameters can be opened using a button, a link, a form or the
address line of a web page. CGI programs are used by the ConvisionCall service, for
example, or for controlling non-supported devices via the serial URL port.
10.8 The TCP/IP Protocol Group
TCP/IP is a group of protocols with the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and IP
(Internet Protocol) being the group's most important components. They form the
widest spread solution in the area of internetworking and have established a de facto
market standard.
To integrate a device into your local area network properly, you have to assign an IP
address to the device. This section will describe the structure of IP addresses and
network masks so that you can set them correctly. You will also find information on
the services and protocols of TCP/IP.
The IP Address
Internet addresses are used to identify computers in TCP/IP networks. They form an
integral part of the Internet Protocol and are therefore referred to as IP addresses.
The Structure of an IP Address
The IP address is a binary code with a length of 4 bytes. To make this structure
easier to understand, the individual bytes are separated by full stops and written as
decimal figures. Take a look at the followi ng example:
Assuming a computer has the IP address: 11000000 10101000 01100100 00000010
In decimal notation this address is: 192.168.100.2
Every IP address is made up of a network identification (network ID) and a host
identification (host ID). This structure is similar to that of a telephone number, which
is also divided into a local area code and a subscriber ID. As opposed to a telephone
number, the length of an IP address never changes.
Depending on the length of the host ID and network ID, the IP addresses are
grouped into network classes. The A, B and C network classes primarily used are
presented in the following graphics. The D and E classes are reserved for special
purposes.
As shown in the graphics, the longer the host ID, the shorter the network ID. This
means, the possible number of network IDs per network class and the possible
number of host IDs per network vary.

Convision V100/V200 Series
64
For example, network class B contains 16.384 subnets with 65.534 hosts each, while
network class C contains 2.097.154 subnets with 254 hosts each.
The Domain Name Service (DNS)
Although the decimal notation of the IP address is already simplified, it remains a
rather difficult-to-use method of addressing a computer in the Internet.
This is why the domain name service (DNS) was developed. The domain name
service enables the assignment of a name to each computer in a TCP/IP network.
This name has nothing to do with the IP address of the computer but it is mapped to
this IP address using specific mechanisms. This means that the name can be used to
determine the IP address. In addition, it is possible to structure a TCP/IP network
hierarchically and to group the computers according to geographic or thematic
criteria. These groupings are referred to as domains.
Example:
Assuming a computer has the IP address 192.168.101.16:
It has the assigned name "Computer.organization.de". This is a name for any
computer in any company located in Germany.
The fundamental component of the DNS is a hierarchically organized database that
is managed by a suitable server, referred to as the DNS server. These DNS servers
can be either public or part of a private network.
If a DNS server is not available in your LAN, use a simpler form of name assignment
such as a text file that maps the names of the individual computers to the associated
IP addresses.
Note: This file named Hosts is stored in the Windows directory (Windows 98), in
the WINNT directory (Windows NT) or as /etc/hosts under Unix.

Manual
65
Private IP Space
The IP address is an integral part of the Internet Protocol, which forms the basis for
communication in the Internet and is also often used in a LAN. The network mask is
used to subdivide larger networks. The IP address must be unique across the entire
network, in which it is registered.
If you are not planning a permanent internet access of your own or are not using a
respective filtering system, the IP address of the computer cannot be registered in
the public internet. In this case you should select an IP address from the "private IP
space" .
These are IP addresses designed for local networks that will not be forwarded in the
Internet. Computers with addresses of this kind are not visible outside the local
network. For class C networks there are 256 address spaces, namely from
192.168.0.x to 192.168.255.x.
The only issue to be considered when selecting addresses from this space is the
allocation of IP numbers from the same address space for a class C network. All
computers must have addresses within the range of 192.168.12.1 to 192 168.12.254,
for example. The numbers 0 and 255 are reserved for special functions and must not
be assigned.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Since the length of the IP address has been restricted to 32 bits, the number of IP
addresses available worldwide is rather limited. At the same time, however, the
worldwide demand for IP addresses is increasing, e.g. due to the increased interest
in the World Wide Web.
The dynamic IP addresses provide a solution to this problem. In this case, IP
addresses are assigned for temporary use from an IP address pool, including all the
information on gateways, network masks, DNS servers and the like. After a specific
time, the IP address returns to the pool and is available again.
This system is used when connecting to Internet providers, for example. The IP
addresses assigned within your LAN are not made public in this process.
Static IP Addresses
If your IP address is to be visible in the public Internet, e.g. if you want to maintain
your own web server, this address must be unique worldwide. To obtain an IP
address of this type, please contact your Internet service provider or the German
Network Information Center (DE-NIC).
The Network Mask
The network mask is used to determine which part of the IP address describes the
network and which part identifies the computer in the network. Example:

Convision V100/V200 Series
66
Assuming the IP address of a computer is 192.168.100.3
And assuming the net mask is 255.255.255.0.
Then the network identification is 192.168.100.
The fourth number identifies the computer.
Note: Incorrectly defined IP addresses and network masks very often cause
errors in TCP/IP networks. For this reason, if you are not absolutely sure or if
problems come up, please contact an experienced network administrator.

Manual
67
11 Technical Data
Camera inputs Convision V100: 1 FBAS input, PAL, NTSC, BNC
connector
Convision V200: 2 FBAS inputs, PAL, NTSC, BNC
connector
Adapter Cinch to BNC supplied
Interfaces RS232 with max. 115 KBit/s, mini DIN-8 plug, adapter
to D-Sub9 supplied
Detector inputs 2 NC inputs for motion detectors etc.
Transmission Convision V100/V200 LAN/ISDN: ISDN, LAN 10/100
Base T, Modem
Convision V100/V200 LAN: LAN 10/100 Base T,
Modem
Dome support e.g. Sony EVI-D30/D31, Sensormatic SpeedDome,
Philips G3 AutoDome, Ernitec BDR510/550, Dennard
2050 (>= V4.0 Build 1883), JVC TK-C675B, Lilin PIH7000 Series, Panasonic WV-CS850 Series, SAE
Dragon, Canon VC-C4/C4R, VCL Microspere Orbiter
Gold, Vicon Surveyor 99 and 2000-16/22, Pelco
Spectra II (D-Protocol)
Alarm center support The VdS 2465 protocol is supported.
Compression MPEG stream/JPEG, up to 25 frames/second (PAL),
up to 30 frames/second (NTSC)
Approx. 3-50 KB/frame
Frame size Resolution of 176x144, 352x288, 704x575 pixels
Pre / post alarm frames 32 frames with a resolution of 176 x 144 pixels or 16
frames with a resolution of 352x288 pixels
Protocols TCP/IP, PPP, HTTP Server, FTP, SMTP Client
Configuration Completely with Web browser via HTML
Internet Browser e.g. Netscape Navigator 4.x or higher, Microsoft
Internet Explorer 5.5 or higher
HTTP 1.0 and HTML 3.2, Java Script 1.2, Java 1.4
Power supply External 12V/1.5 A power pack 100-240 V (GS, CE,
UL, CSA)
Power consumption 5 W
Dimensions Width: 140 mm, height: 28 mm, depth: 190 mm
Weight 740 g
Temperature range 0 to +50°C (+32 °F to +122 °F)
Approvals CE0682, EN50081, EN50082, EN50022

Convision V100/V200 Series
68
Appendix A FAQ – Frequently Asked
Questions / Troubleshooting
Connection
Why can't I establish a connection to
the Convision V100/V200 via ISDN?
Is the Convision V100/V200 switched on?
Did you enter the correct MSN for the
Convision V100/V200?
Is the line busy?
When connecting via a telephone system, do
you have to enter "0" or "00" as a prefix?
Check the settings for the proxy server in your
Internet browser. It should be set either to
direct access to the Internet, or - with manual
configuration - the IP address of the Convision
V100/V200 should be entered as an exception.
Tip: Are the Convision V100/V200 and the
computer connected to the same S0 bus?
Try a different S0 bus.
Windows NT only:
Check whether RAS and dial-up networking
are correctly installed.
Why can't I establish a connection to
the Convision V100/V200 via a
LAN?
Is the Convision V100/V200 switched on?
Is the IP address of the Convision V100/V200
correct? If not, assign one using the Convision
IPSetup tool.
Is TCP/IP installed and configured on the
computer?
Check the settings for the proxy server in your
Internet browser. It should be set either to
direct access to the Internet, or - with manual
configuration - the IP address of the Convision
V100/V200 should be entered as an exception.
Does the Convision V100/V200
affect the performance of the LAN?
If the Convision V100/V200 is accessed
frequently, it may affect the transfer rate in the
network.

Manual
69
To what extent does the Convision
V100/V200 affect the performance
of the LAN?
Up to 450 KB per second during image
streaming. If the load is too high, reduce the
refresh rate!
Why can't I establish a connection to
the Convision V100/V200 via a
modem?
Is the Convision V100/V200 switched on?
Is the modem switched on?
Is the modem connected to the serial port of
the Convision V100/V200?
Has "Modem" been selected in the System /
ISDN / General" menu?
Has "Analog Modem” been set in the interface
configuration and was the Convision
V100/V200 rebooted?
Did you enter the correct settings for your
modem?
Only modem to modem connecti ons ar e
possible. Connections to a modem via ISDN is
not possible.
How can I connect the Convision
V100/V200 directly to a computer?
Computer with network card: Connect the
computer and the Convision V100/V200 via a
twisted-pair cable (cross-connect cable).
Windows-based PC via PC direct connection
using a null modem cable.
Why can't I establish a connection to
the provider although I entered the
correct PPP identification and
password?
Have you activated password encryption?
Deactivate this option and repeat the
connection attempt. Some provi der s appear to
accept encoding, but then the submission of
the password fails.
Messages
Which Internet provider can I use? You can use any Internet provider with e-mail
access who supports PPP dial-up with PAP or
CHAP authentication.
What is the maximum permissible
length of an e-mail?
An e-mail message may consist of 256
characters plus images.
To how many recipients can I send
an e-mail?
You can enter as many as 10 recipients
separated by a semicolon.

Convision V100/V200 Series
70
E-mails are not being sent. Incorrect Internet provider data or default
router not entered.
Entry of e-mail sender address missing or
incorrect.
Entry of SMTP server missing or incorrect.
Entry of DNS server missing or incorrect.
The telephone system may not permit calls to
numbers starting with 010… In this case, use a
different Internet-by-call provider or Internet
provider (e.g. T-Online via 0191011...)
Tip: Try entering the IP address of the SMTP
server instead of the name.
How many characters can be sent
via SMS?
The maximum permissible length of an SMS is
160 characters. You cannot attach any images.
Is a dialling pause possible for
telephone systems?
No.
Camera
A camera image is not displayed
although a camera is connected.
The camera is not supplied with voltage.
The camera is not switched on.
The video cable is not connected or defective.
The control panel of a controllable
camera is not displayed on the user
interface (browser window).
The camera was not correctly configured under
System/Device.
The control cable is not connected or defective.
The Convision V100/V200 must be rebooted
after a camera has been connected.
What types of cameras can be
connected to the Convision
V100/V200?
Any camera with a PAL or NTSC output. It is
connected to the Convision V100/V200 via a
BNC connector (male).
What kind of video cable do I need
to connect the cameras?
You should use a high-quality coaxial cable
with a low attenuation factor (75 Ω).
What is the maximum permissible
length of a video cable?
If you supply the camera with voltage via the
video cable, it should not exceed 50 m.
If the video cable is longer, the camera must
be supplied with power via a separate cable.
If the cable is longer than 100 m, the quality of
the video signal may deteriorate. The
maximum length supplied by us is 300 m.

Manual
71
How is a controllable camera
connected?
The control unit is connected via an 8-pin mini
DIN to 9-pin sub-D coupling. The image is
transferred via a cinch cable with BNC adapter.
The power supply is autonomous.
How many controllable cameras can
I connect?
You can connect 2 controllable cameras to the
Convision V200.
The cameras are connected in series; only the
first one is directly connected to the Convision
V100/V200.
Security
How can I protect the Convision
V100/V200 against unauthori zed
access?
The Convision V100/V200 features several
safety levels:
1. The entire Convision V100/V200 can be
secured. The configuration can be secured.
3. The recording sector can be secured.
Apart from these three levels, there is a
password protection for PPP access via ISDN.
Similar to other network topologies, the
operator is responsible for assigning
passwords.
Is external access to the LAN
possible via the Convision
V100/V200 when using ISDN?
No, the Convision V100/V200 is not a router.
What happens to the Convision
V100/V200 in the event of a power
failure?
Without an emergency power supply, the
Convision V100/V200 will be switched off. The
configuration will not be lo st as it is sa ved in a
flash ROM.
After the power failure, the Convision
V100/V200 will reboot and start with the preset
tasks.
Are the former configuration settings
retained after an update?
No, if fundamental changes have been made
to an HTML page, the
original settings will not be saved.
Are the images on the hard disk
retained after an update?
No, if fundamental changes have been made
in the hard disk section, the hard disk will be
reformated when the device is updated.
When I perform an update, will the
ISDN connection be maintained?
No, you have to re-establish the connection.
What is the login name for the
administrator?
The login name for the administrator is
"admin".

Convision V100/V200 Series
72
What is the login name for the user? The login name for the user is "user".
What is the login name for the
recording sector?
The login name for the recording sector is
"record".
The Convision V100/V200 does not
permit any access after the access
protection feature has been
enabled.
Try using the login name "admin" and a blank
password field.
Try using the login name "admin" and the
password you assigned.
The last possibility is to delete the
configuration.
LED indicators
Why does the Online LED flash? The Convision V100/V200 has not yet been
configured.
Why doesn't the Camera LED light
up although a camera is connected?
The LED is updated only when you reboot the
Convision V100/V200 or when a camera image
is displayed.
Browser
In Server Push mode, the Netscape
Browser gets stuck after some time.
Due to an error in Netscape Navigator, the
Server Push connection breaks down after a
while.
To avoid this, use the Java applet for image
streams, which will automatically re-establish a
connection after a breakdown.
When using the HTML user
interface, not all the functions are
available?
Javascript, Java and Cookies must be enabled
in your browser.
What do the terms Server Push and
Java applet mean?
Server Push is a function in Netscape
Navigator for displaying JPEG images as
image streams. For other browsers, the Java
applet must be used.
Former or incorrect parameters are
displayed despite correct setting of
the configuration parameters.
Make sure that the browser does not load
documents from the cache (refer to document
“Convision System Configuration“).
Images are not displayed in ActiveX
mode.
The Convision ActiveX plugin must be loaded.
The security settings of the browser must
permit loading and executing ActiveX plugins.
The processor of your computer must have an
MMX extension.

Manual
73
General
In what temperature range does the
Convision V100/V200 operate?
The Convision V100/V200 operates in a
temperature range of from 0 °C to 50 °C (+32
°F to +122 °F)
Can I perform a remote reset of the
Convision V100/V200 ?
Yes, e.g. select Configuration / System / FTP
and save the settings without any changes.
Then click the "Reboot" button.
How many users can access the
Convision V100/V200
simultaneously via the LAN?
Depending on the task, up to 20 users.
How many users can access the
Convision V100/V200
simultaneously via ISDN?
Two simultaneous connections can be set up,
if channel bundling (also with ConvisionCall) is
enabled, only one.
Via ConvisionCall without channel bundling
the number is theoretically higher but due to
the small bandwidth of the line the
transmission rate is very low.
What is the pin assignment of the DSub9 connector (female) of the
serial interface?
Pins 1 and 9 are not assigned.
What is the pin assignment of a
cross-connect cable?

Convision V100/V200 Series
74
Appendix B Declaration of Conformity
KONFORMITÄTSERKLÄRUNG
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Geräteart:
Micro Web Server
Type of equipment:
Produkt / Product : Convision V100/V200 Series
Das bezeichnete Produkt stimmt mit den Vorschriften folgender EU- Richtlinie(n)
überein:
The aforementioned product complies with the following European Council directive(s):
93/97/EWG EG EMV- Richtlinie / EC EMC directive
1999/5/EG EG Telekommunikationsendei nr i cht ungen - Richtlinie
EC Telecommunications terminal equipment directive
Zur vollständigen Einhaltung der EMV- Richtlinie wurden folgende Normen
herangezogen:
To fully comply with the EMC directive, the following standards have been used:
EN 55022 Class B : 1987
EN 50081-1 : 1995
EN 50082-2 : 1995
Dieser Erklärung liegt zugrunde: Prüfungen im EMV- Prüflabor
This certification is based on: Tests in EMI test laboratory
Aussteller / Holder of certificate :
Convision Technology GmbH
Zuckerbergweg 22
38124 Braunschweig
Germany

Manual 75
Appendix C List of Figures
Front view of the Con vision V100/V200 9
Rear view of the Convision V100 10
Rear view of the Convision V200 11
LAN connection 12
Connection via ISDN 13
Camera connection to Convision V100 14
Camera connection to Convision V200 15
Example 1 Input Connection 16
Example 2 Input Connection 17
Example 3 Input Connection 17
Initial configuration with IPSetup 19
Camera display 23
View of a fully controllable camera 24
Displaying the images in the frame buffer 27
Configuring the IP addresses 30
Configuring the mail server 32
Configuring the ISDN parameters 34
Configuring connections 35
Configuring the ConvisionCall server 37
Configuring Conv isionCall in the Convision V100/V200 38
Selecting the language 40
Update dialog box 43
The three security levels 43
FTP-Server dialog box 45
Assignments of the serial ports 46
Event log 47
Gerneral camera settings 48
Connection and parameters 49
Setting the camera properties 1 50
Setting the camera properties 2 51
Configuring the alarm inputs– assigning actions 52
Configuring th e inputs – weekly s chedule 52
Configuring the points in time – assigning actions 53
Configuring th e points in time – weekly schedule 54
Configuring the frame buffers 55
FTP upload 56
Configuring e-mail notification 58
Configuring SMS 59
Configuring VdS2465 60

Convision V100/V200 Series
76
Appendix D List of Keywords
A
ActiveX......................................................22, 26, 72
Administrator.........................................................30
Administrator password.........................................44
Alarm center..........................................................39
anonymous............................................................45
Applet..............................................................28, 40
Authentication...........................................31, 35, 62
B
Battery...................................................................44
B-channel..............................................................62
BNC.......................................................................70
C
Camera
connection.........................................................15
controllable......................................15, 23, 47, 71
Names...............................................................48
Properties..........................................................50
Settings.............................................................48
Camera Tour...................................................51, 60
CGI Parameters..............................................47, 62
Channel bundling..................................................62
Configuration
ConvisionCall....................................................37
Main ............................................................21, 30
Modem..............................................................35
Configuration file...................................................41
Connection
of the Convision V100 to providers ...................34
via ISDN............................................................32
Connectors......................................................10, 11
ConvisionCall........................................................36
Cross-connect cable.......................................18, 73
D
Delete
Configuration.....................................................20
Devices.................................................................46
Dial-Up Networking.........................................18, 33
Domain Name Service (DNS)...................31, 35, 64
Dynamic IP addresses..........................................65
E
E-mail........................................................58, 59, 70
eMail State............................................................59
Ethernet.....................................................10, 11, 20
Event log...............................................................47
F
Firmware...............................................................42
Frame Buffer...........................27, 44, 51, 55, 58, 60
FTP.......................................................................61
Client.................................................................56
Server................................................................45
H
Host identification..................................................63
HTML pages ...................................................21, 28
Hue .......................................................................50
I
Image size.......................................................22, 56
Image streaming.............................................51, 69
Indicator lamps........................................................9
Information............................................................29
Initial configuration..........................................18, 19
Inputs........................................................16, 51, 52
Internet Browser....................................................18
IP address...................18, 19, 20, 30, 32, 63, 64, 65
IPSetup.................................................................19
Iris.........................................................................25
ISDN ...................................................18, 32, 36, 68
ISDN basic access..................................................8
J
Java Virtual Machine...............................................8
JPEG.....................................................................22
L
LAN...........................................................12, 19, 68
Language........................................................21, 39
Language module.................................................40
LED.......................................................................72
Live-compatible.........................................22, 48, 61
Live-optimized.................................................22, 61
Log........................................................................47
M
Mail Server............................................................31
Media Player.........................................................26
Microsoft Internet Explorer....................................22
Modem......................................................14, 35, 69
Module............................................................29, 41
MPEG ...................................................................26
MSN......................................................................18
Multiple subscriber number (MSN)..................19, 33
N
Netscape Browser...................................................8
Network identification............................................63
Network mask.......................................................65
Network terminator (NT)........................................13
P
Panoramic view.....................................................24
Password..............................................................37
Password encryption.......................................61, 69
Plugin....................................................................72
Point in time..........................................................53

Manual 77
Port.......................................................................31
Power failure.........................................................71
PPP .................................................... 18, 33, 34, 69
PPP Host Name....................................................33
Preset.............................................................24, 25
Preset Tour........................................................... 25
Private IP space....................................................65
R
Reset....................................................................73
Router................................................................... 31
S
Safety Instructions.................................................. 6
Security settings...................................................43
Sequencer............................................................26
Serial interface................................................46, 73
Serial number
of the Convision V100/V200............................. 29
Serial URL port..................................................... 47
Server Push.................................................... 61, 72
SMS (Short Message Service).......................59, 70
SMTP....................................................................62
Snapshot ........................................................23, 24
Sockets
controllable.......................................................28
State
Frame Buffer.....................................................28
Static IP addresses...............................................65
Subnet..................................................................64
Summer Time....................................................... 44
Syslog server........................................................ 31
System settings....................................................30
T
TCP/IP...................................................... 63, 64, 66
Telecommunications equipme nt........................... 14
Telephone system................................................ 70
Time ..................................................................... 44
Time zone............................................................. 44
Tour................................................................ 51, 60
TP cable...............................................................12
U
Updating the firmware.................................... 42, 71
Upload
Applet............................................................... 40
Configuration file...............................................42
FTP................................................................... 56
Language..........................................................40
Module.............................................................. 41
URL...................................................................... 47
User password......................................................44
V
VdS 2465............................................ 39, 51, 56, 60
Video cable........................................................... 70
View of two cameras............................................22
W
Weather station....................................................28
Z
Zoom....................................................................25
 Loading...
Loading...