Page 1

PC-HELPER
IEEE-488.2 Interface Board for PCI
GP-IB(PCI)
GP-IB(PCI)L
User’s Guide
CONTEC CO.,LTD.
Page 2
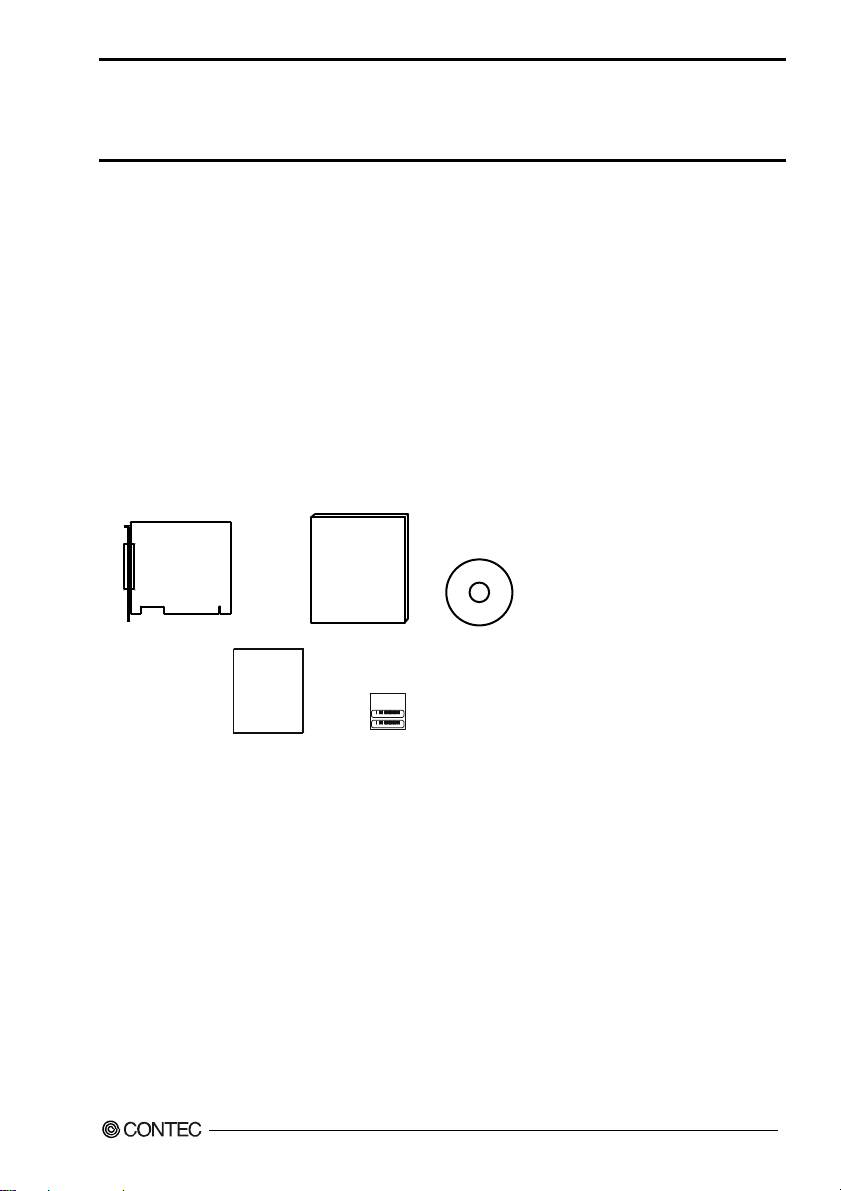
Check Your Package
Thank you for purchasing the CONTEC product.
The product consists of the items listed below.
Check, with the following list, that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or missing
items, contact your retailer.
Product Configuration List
- Board
[GP-IB(PCI)L or GP-IB(PCI)] …1
- This User’s Guide…1
- CD-ROM[API-PAC(W32)] …1
- Warranty Certificate…1
- Serial number label…1
User’s Manual
Board
War ra nty
Certificate
Warranty Certificate
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
User’s Manual
XXXXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXX
Serial number label
CD-ROM
[API-PAC(W32)]
i
Page 3

Copyright
Copyright 2013 CONTEC Co., LTD. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form by any means without prior written
consent of CONTEC Co., LTD.
CONTEC Co., LTD. makes no commitment to update or keep current the information contained in this
document. The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
All relevant issues have been considered in the preparation of this document. Should you notice an
omission or any questionable item in this document, please feel free to notify CONTEC Co., LTD.
Regardless of the foregoing statement, CONTEC assumes no responsibility for any errors that may
appear in this document or for results obtained by the user as a result of using this product.
Trademarks
MS, Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Other brand and product names
are trademarks of their respective holder.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
ii
Page 4
Table of Contents
Check Your P ackage................................................................................................................................ i
Copyright .................................................................................................................................................ii
Trademarks ..............................................................................................................................................ii
Table of Contents ...................................................................................................................................iii
Copyright.................................................................................................................................................
Trademarks..............................................................................................................................................ii
Table of Contents ...................................................................................................................................iii
1. BEFORE USING THE PRODUCT 1
About the Board...................................................................................................................................... 1
Features ............................................................................................................................................1
Support Softwar e..............................................................................................................................2
Cable & Connector (Option)........................................................................................................ 2
Customer Support....................................................................................................................................3
Web Site...........................................................................................................................................3
Limited Three-Years Warranty...............................................................................................................3
How to Obtain Service ............................................................................................................................ 3
Liability ...................................................................................................................................................3
Safety Precautions ...................................................................................................................................4
Safety Information........................................................................................................................... 4
Handling Precautions....................................................................................................................... 5
Environment..................................................................................................................................... 6
Inspection .........................................................................................................................................6
Storage.............................................................................................................................................. 6
ii
2. SETUP 7
What is Setup?......................................................................................................................................... 7
Using the Board under Windows Using the Driver Library API-PAC(W32)...............................7
Using the Board under Window Using Software Other than the Driver Library
API-PAC(W32)................................................................................................................................8
Using the Board under an OS Other than Windows.......................................................................8
Step 1 Installing the Software.................................................................................................................9
About the driver to be used..............................................................................................................9
Starting the Install Program........................................................................................................... 10
For using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx..................................................................................................... 11
For using API-GPLV(W32) ..........................................................................................................13
Step 2 Setting the Hardware................................................................................................................. 14
Parts of the Board and Factory Defaults....................................................................................... 14
Setting the Board ID ......................................................................................................................15
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
iii
Page 5
Plugging the Board.........................................................................................................................16
Step 3 Installing the Hardware..............................................................................................................17
Turning on the PC ..........................................................................................................................17
Setting with the Add New Hardware Wizard................................................................................17
Step 4 Initializing the Software.............................................................................................................20
Invoking API-TOOL Configuration..............................................................................................20
Updating the Settings.....................................................................................................................20
For using API-GPLV(W32)...........................................................................................................21
Step 5 Checking Operations with the Diagnosis Program...................................................................22
What is the Diagnosis Program?....................................................................................................22
Check Method.................................................................................................................................22
Using the Diagnosis Program for Using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx ....................................................22
Using the Diagnosis Program for Using API-GPLV(W32) .........................................................25
Setup Troubleshooting...........................................................................................................................28
Symptoms and Actions...................................................................................................................28
If your problem cannot be resolved...............................................................................................28
3. EXTERNAL CONNECTION 29
Using the On-board Connectors............................................................................................................29
Connecting a Device to a Connector.............................................................................................29
Connector Pin Assignment.............................................................................................................29
Notes on cable connection .............................................................................................................30
4. FUNCTIONS 33
Basic GPIB Functions...........................................................................................................................33
Master/slave function.....................................................................................................................33
Communication function................................................................................................................33
Serial poll/parallel poll/SRQ send functions.................................................................................33
My address setting..........................................................................................................................33
Additional Functions.............................................................................................................................34
Line monitor function.....................................................................................................................34
Communication using FIFO memory (Only GP-IB(PCI))...........................................................34
Analyzer function (Only GP-IB(PCI)) ..........................................................................................35
5. ABOUT SOFTWARE 39
For using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx.............................................................................................................39
Accessing the Help File..................................................................................................................39
Using Sample Programs.................................................................................................................40
For using API-GPLV(W32)..................................................................................................................42
Accessing the Help File..................................................................................................................42
Function List...................................................................................................................................43
Using Sample Programs.................................................................................................................46
Uninstalling the API Function Libraries...............................................................................................47
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
iv
Page 6

CD-ROM Directory Structure ..............................................................................................................48
6. ABOUT HARDWARE 49
Hardware specification .........................................................................................................................49
Different in the specification................................................................................................................ 51
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
v
Page 7

GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
vi
Page 8

1. Before Using the Product
1. Before Using the Product
About the Board
This board is PCI-compliant expansion card to control GPIB devices. You can use it installing in
PCI-compliant slot of your computer.
Using the bundled API function library package [API-PAC(W32)], you can create Windows application
software for this board in your favorite programming language supporting Win32 API functions, such as
Visual Basic or Visual C/C++.
Features
< Common >
- Conforming to the IEEE 488.2 standard, this board can control a variety of compliant external
devices.
- The product is available over an extended period of time as it uses a uPD7210-compatible GPIB
controller developed by CONTEC.
- All of GPIB features can be configured by software.
- The IFC/SRQ line read feature (with IFC latch capability) is available to application programs.
< Feature of GP-IB(PCI)L>
- The timer function is available on application programs, capable of monitoring the time accurately
in the Windows environment.
< Feature of GP-IB(PCI)>
- Communication can be performed at a maximum transfer rate of 1.2 megabytes per second.
- One megabyte of on-board FIFO memory for data transmission and reception allows a large amount
of data to be exchanged at high speed while minimizing the effect of the PC’s CPU speed.
- As FIFO memory can be used to send commands (multiline messages), a small amount of data can
be exchanged at high speed as well.
- The GPIB bus analyzer function is provided to analyze data on the line.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
1
Page 9

1. Before Using the Product
Support Software
You should use CONTEC support software according to your purpose and development environment.
Driver Software Package
API-PAC(W32)
(Bundled)
API-PAC(W32) is the library software that provides the commands for CONTEC hardware products in
the form of Windows standard Win32 API functions (DLL). It makes it easy to create high-speed
application software taking advantage of the CONTEC hardware using various programming languages
that support Win32 API functions, such as Visual Basic and Visual C/C++.
It can also be used by the installed diagnosis program to check hardware operations.
CONTEC provides download services to supply the updated drivers and differential files.
For details, read Help on the bundled CD-ROM or visit the CONTEC’s Web site.
< Operating environment >
OS Windows XP, 2000, NT, Me, 98, etc..
Adaptation language Visual C/C++, Visual Basic, Delphi, Builder, etc..
Others Each piece of library software requires 50 megabytes of free hard disk spa ce.
API-GPLV(W32)
API-GPLV(W32) is a driver created according to the National Instruments Corporation’s GPIB function style. The
driver is software to control the CONTEC GPIB board using a LabVIEW-based GPIB system or existing application
program.
library supporting LabVIEW (Bundled)
It can also be used by the installed diagnosis program to check hardware operations.
CONTEC provides download services to supply the updated drivers and differential files.
For details, read Help on the bundled CD-ROM or visit the CONTEC’s Web site.
< Operating environment >
OS Windows XP, 2000, NT, Me, 98, etc..
Adaptation language LabVIEW, Visual C++, Borland C++, Visual Ba sic, etc..
Others Each piece of library software requires 20 megabytes of free hard disk spa ce.
Cable & Connector (Option)
GPIB Cable : PCN-02 (2m)
GPIB Cable : PCN-04 (4m)
GPIB Connector : CN-GP/C
Effective when the cable being plugged into the board interfere
with the PC’s main unit. See the troubleshooting section at the
end of Chapter 2.
Check the CONTEC’s Web site for more information on these options.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
2
Page 10

1. Before Using the Product
Customer Support
CONTEC provides the following support services for you to use CONTEC products more efficiently
and comfortably.
Web Site
Japanese http://www.contec.co.jp/
English http://www.contec.com/
Chinese http://www.contec.com.cn/
Latest product information
CONTEC provides up-to-date information on products.
CONTEC also provides product manuals and various technical documents in the PDF.
Free download
You can download updated driver software and differential files as well as sample programs available in
several languages.
Note! For product information
Contact your retailer if you have any technical question about a CONTEC product or need its price,
delivery time, or estimate information.
Limited Three-Years Warranty
CONTEC Interface boards are warranted by CONTEC Co., LTD. to be free from defects in material and
workmanship for up to three years from the date of purchase by the original purchaser.
Repair will be free of charge only when this device is returned freight prepaid with a copy of the
original invoice and a Return Merchandise Authorization to the distributor or the CONTEC group office,
from which it was purchased.
This warranty is not applicable for scratches or normal wear, but only for the electronic circuitry and
original boards. The warranty is not applicable if the device has been tampered with or damaged
through abuse, mistreatment, neglect, or unreasonable use, or if the original invoice is not included, in
which case repairs will be considered beyond the warranty policy.
How to Obtain Service
For replacement or repair, return the device freight prepaid, with a copy of the original invoice. Please
obtain a Return Merchandise Authorization Number (RMA) from the CONTEC group office where you
purchased before returning any product.
* No product will be accepted by CONTEC group without the RMA number.
Liability
The obligation of the warrantor is solely to repair or replace the product. In no event will the
warrantor be liable for any incidental or consequential damages due to such defect or consequences that
arise from inexperienced usage, misuse, or malfunction of this device.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
3
Page 11
1. Before Using the Product
Safety Precautions
Understand the following definitions and precautions to use the product safely.
Safety Information
This document provides safety information using the following symbols to prevent accidents resulting
in injury or death and the destruction of equipment and resources. Understand the meanings of these
labels to operate the equipment safely.
DANGER
WAR NI NG
CAUTION
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will
result in death or serious injury.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injury or in property damage.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
4
Page 12
1. Before Using the Product
Handling Precautions
DANGER
Do not use the product where it is exposed to flammable or corrosive gas. Doing so may result in
an explosion, fire, electric shock, or failure.
CAUTION
- There are switches on the board that need to be set in advance. Be sure to check these before
installing the board.
- Only set the switches and jumpers on the board to the specified settings.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
- Do not strike or bend the board. Doing so could damage the board.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, cause a failure or breakage.
- Do not touch the board's metal plated terminals (edge connector) with your hands.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
If the terminals are touched by someone's hands, clean the terminals with industrial alcohol.
- Do not install or remove the board to or from the slot while the computer's power is turned on.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
Doing so could cause trouble. Be sure that the personal computer or the I/O expansion unit power is
turned off.
- Make sure that your PC or expansion unit can supply ample power to all the boards installed.
Insufficiently energized boards could malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
- The specifications of this product are subject to change without notice for enhancement and quality
improvement.
Even when using the product continuously, be sure to read the manual and understand the
contents.
- Do not modify the product. CONTEC will bear no responsibility for any problems, etc., resulting
from modifying this product.
- Regardless of the foregoing statements, CONTEC is not liable for any damages whatsoever
(including damages for loss of business profits) arising out of the use or inability to use this
CONTEC product or the information contained herein.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
5
Page 13

1. Before Using the Product
Environment
Use this product in the following environment. If used in an unauthorized environment, the board may
overheat, malfunction, or cause a failure.
Operating temperature
0 to 50ºC
Humidity
10 to 90%RH (No condensation)
Corrosive gases
None
Floating dust particles
Not to be excessive
Inspection
Inspect the product periodically as follows to use it safely.
- Check that the bus connector
of the board and its cable have
been plugged correctly.
- Check that the board has
no dust or foreign matter adhering.
- The gold-plated leads of the bus connector
have no stain or corrosion.
Storage
When storing this product, keep it in its original packing form.
(1) Put the board in the storage bag.
(2) Wrap it in the packing material, then put it in the box.
(3) Store the package at room temperature at a place free from direct sunlight, moisture, shock,
vibration, magnetism, and static electricity.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
6
Page 14

2. Setup
2. Setup
This chapter explains how to set up the board.
What is Setup?
Setup means a series of steps to take before the product can be used.
Different steps are required for software and hardware
The setup procedure varies with the OS and applications used.
Using the Board under Windows
Using the Driver Library API-PAC(W32)
This section describes the setup procedure to be performed before you can start developing application
programs for the board using the bundled CD-ROM “Driver Library API-PAC(W32)”.
Taking the following steps sets up the software and hardware. You can use the diagnosis program later
to check whether the software and hardware function normally.
Step 1 Installing the Software
Step 2 Setting the Hardware
Step 3 Installing the Hardware
Step 4 Initializing the Software
Step 5 Checking Operations with the Diagnosis Program
If Setup fails to be performed normally, see the “Setup Troubleshooting” section at the end of this
chapter.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
7
Page 15

2. Setup
Using the Board under Window
Using Software Other than the Driver Library
API-PAC(W32)
For setting up software other than API-PAC(W32), refer to the manual for that software. See also the
following parts of this manual as required.
This chapter Step 2 Setting the Hardware
This chapter Step 3 Installing the Hardware
Chapter 3 External Connection
Chapter 6 About Hardware
Using the Board under an OS Other than Windows
For using the board under an OS other than Windows, see the following parts of this manual.
This chapter Step 2 Setting the Hardware
Chapter 3 External Connection
Chapter 6 About Hardware
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
8
Page 16
2. Setup
Step 1 Installing the Software
This section describes how to install the API function libraries.
Before installing the hardware on your PC, install the API function libraries from the bundled
API-PAC(W32) CD-ROM.
The following description assumes the operating system as Windows Me. Although some user
interfaces are different depending on the OS used, the basic procedure is the same.
About the driver to be used
Two GPIB communication drivers come with your board: API-GPIB(98/PC)W95/NT and
API-GPLV(W32).
API-GPIB(98/PC)W95/NT provides a CONTEC proprietary function interface.
API-GPLV(W32) provides a function interface equivalent to that from National Instruments
Corporation (hereafter NI), allowing the GPIB488, GPIB488.2, and VISA functions of LabVIEW to be
used directly and application programs created for NI boards to run without modification.
Selection guide
Given below is a guideline for easily selecting the appropriate driver for the board.
driver to be used Purpose
API-GPIB(98/PC)
- Used to use CONTEC functions
- To make the board operate as fast as possible
- To convert (digitize) binary and string data easily
API-GPLV(W32)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
- To use existing applications for NI boards
- To use LabVIEW
- Familiar with NI functions but not with CONTEC functions
9
Page 17

2. Setup
Starting the Install Program
(1)
Load the CD-ROM [API-PAC(W32)] on your PC.
(2)
The API-PAC(W32) Installer window appears automatically.
If the panel does not appear, run (CD-ROM drive letter):\AUTORUN.exe.
(3)
Click on the [Install the drivers] button.
CAUTION
Before installing the software in Windows XP, 2000, or NT, log in as a user with administrator
privileges.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
10
Page 18
2. Setup
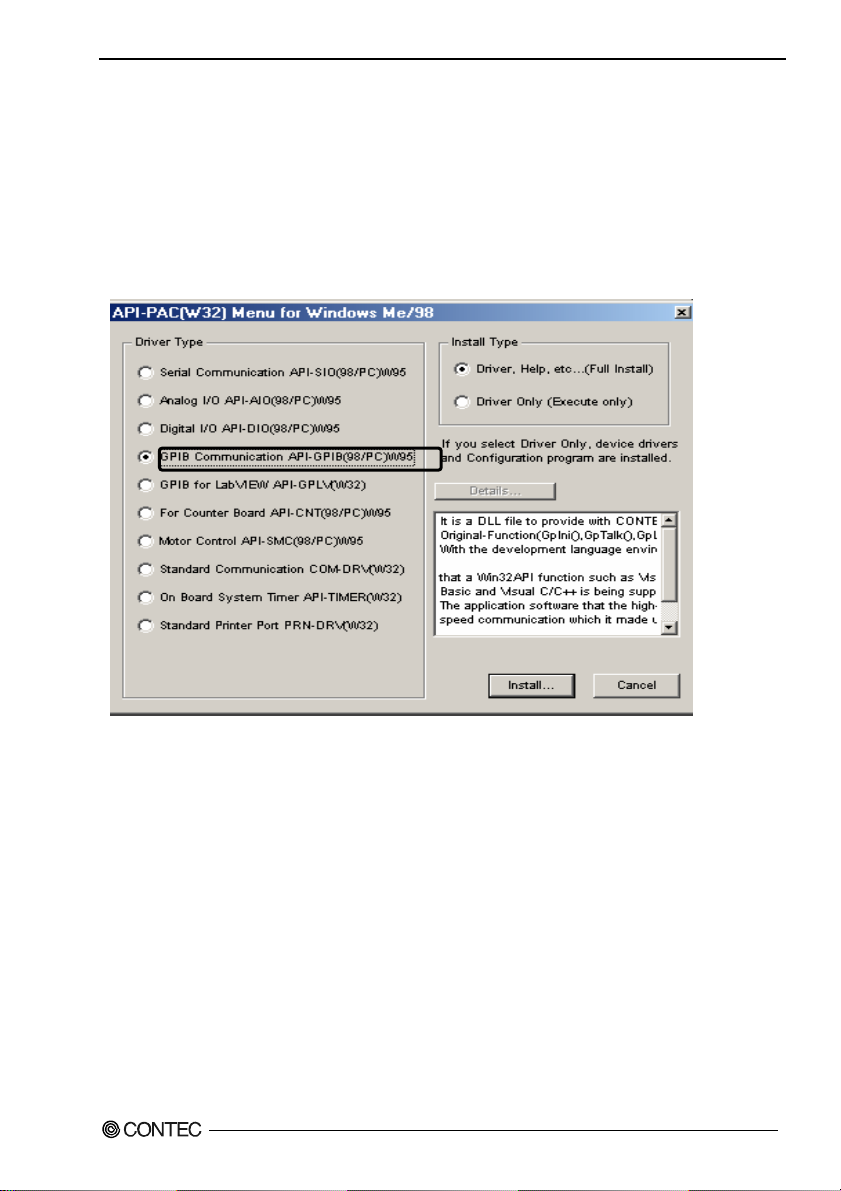
For using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx
Select API- GPIB(98/PC)
(1)
The following dialog box appears to select “Driver Type” and “Install Type”.
(2)
Select “GPIB Communication API-GPIB(98/PC)W95”.
(3)
Select “Driver, Help, etc..(Full Install)”.
(4)
Click on the [Install] button.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
11
Page 19

2. Setup
uting the Installation
Exec
(1) Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed to install.
(2) When the required files have been copied, the “Perform a hardware setup now” and “Show readme
file” check boxes are displayed.
When you are installing the software or hardware for the first time:
1) Uncheck “Perform a hardware setup now”.
2) Click on the [Finish] button. Go to Step 2 to set and plug the hardware.
* When the hardware has already been installed:
Check “Perform a hardware setup now”, then go to Step 4 “Initializing the Software”.
You have now finished installing the software.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
12
Page 20

2. Setup
For using API-GPLV(W32)
Select API-GPLV(W32)
(1)
The following dialog box appears to select “Driver Type” and “Install Type”.
(2)
Select “GPIB for LabVIEW API-GPLV(W32)”.
(3)
Select “Driver, Help, etc..(Full Install)”.
(4)
Click on the [Install] button.
Executing the Installation
(1) Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed to install.
(2) The driver installation is completed when the GPIB setup utility is started.
If you are installing the software and hardware for the first time, click on the [Cancel] button in this
step to terminate the installation procedure.
* When the hardware has already been installed:
Go to “For Using API-GPLV(W32)” in Step 4 "Initializing the Software".
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
13
Page 21
2. Setup
Step 2 Setting the Hardware
This section describes how to set the board and plug it on your PC.
The board has some switches and jumper to be preset.
Check the on-board switches and jumpers before plugging the board into an expansion slot.
The board can be set up even with the factory defaults untouched. You can change board settings later.
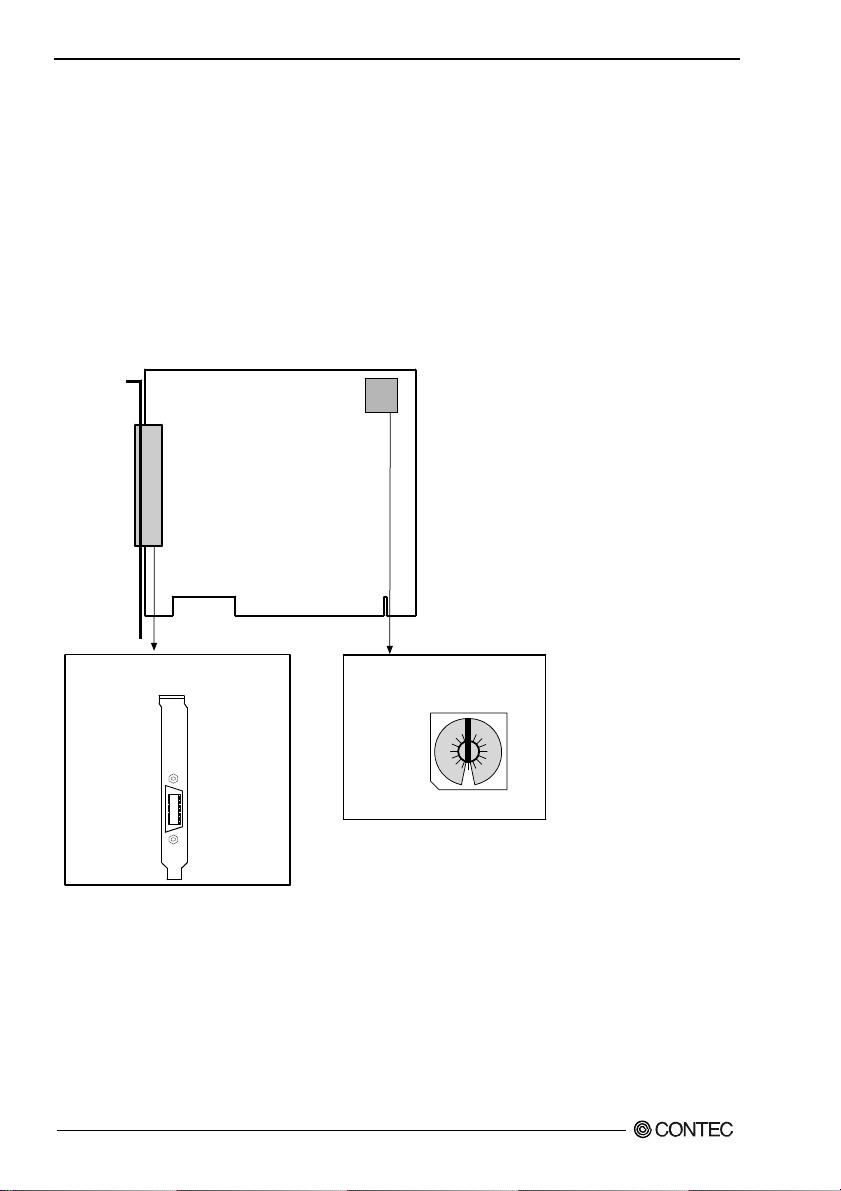
Parts of the Board and Factory Defaults
Figure 2.1. to. show the names of major parts on the board.
Note that the switch setting shown below is the factory default.
GP-IB(PCI)x
- Interface connector
(CN1)
- Board ID setting switch
(SW1)
BOARD ID
8
9
A
7
6
5
4
3
2
F
1
0
SW1
B
C
D
E
Figure 2.1. Part Names
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
14
Page 22
2. Setup
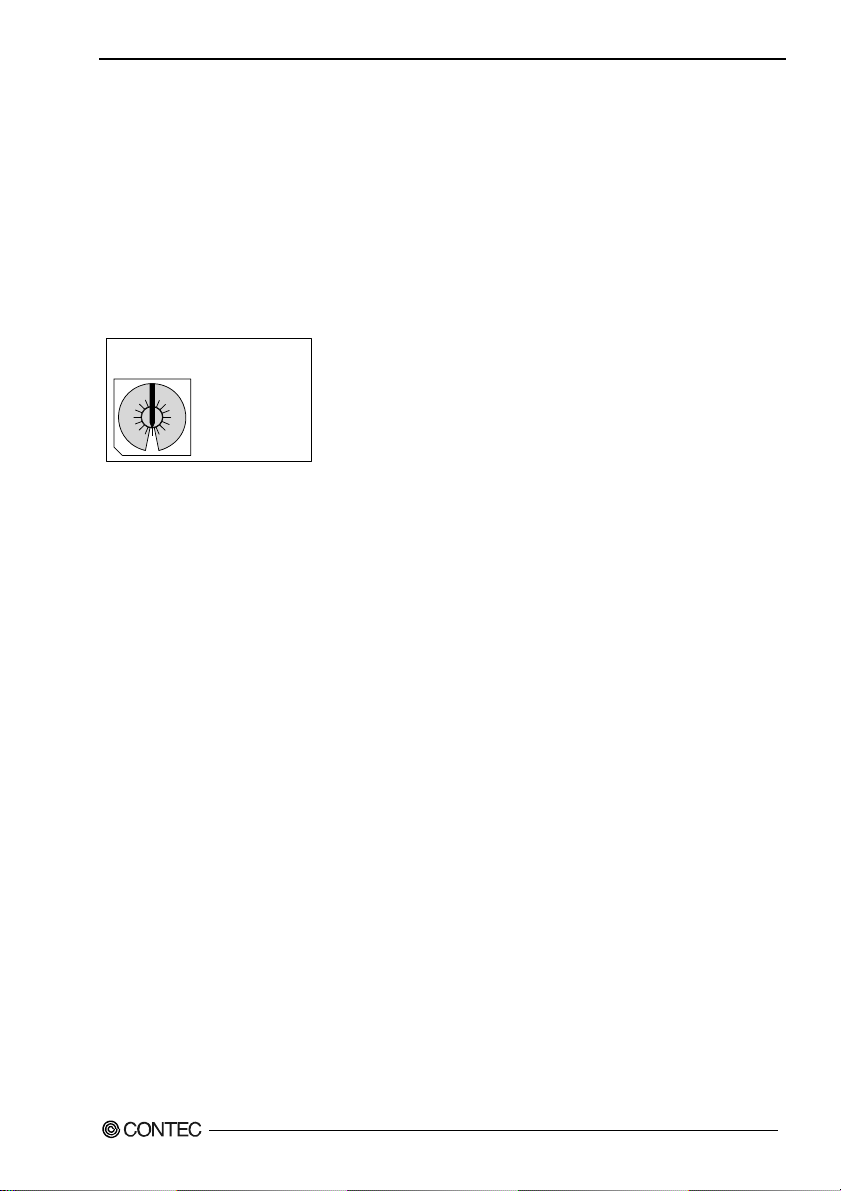
Setting the Board ID
If you install two or more boards on one personal computer, assign a different ID value to each of the
boards to distinguish them.
The board IDs can be set from 0 to Fh to identify up to sixteen boards.
If only one board is used, the original factory setting (Board ID = 0) should be used.
Setting Procedure
To set the board ID, use the rotary switch on the board. Turn the SW1 knob to set the board ID as
shown below.
SW1
BOARD ID
9
A
7
B
6
C
5
D
4
E
3
2
F
Factory setting:
1
0
(Board ID = 0)
Figure 2.2. Board ID Settings (SW1)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
15
Page 23
2. Setup
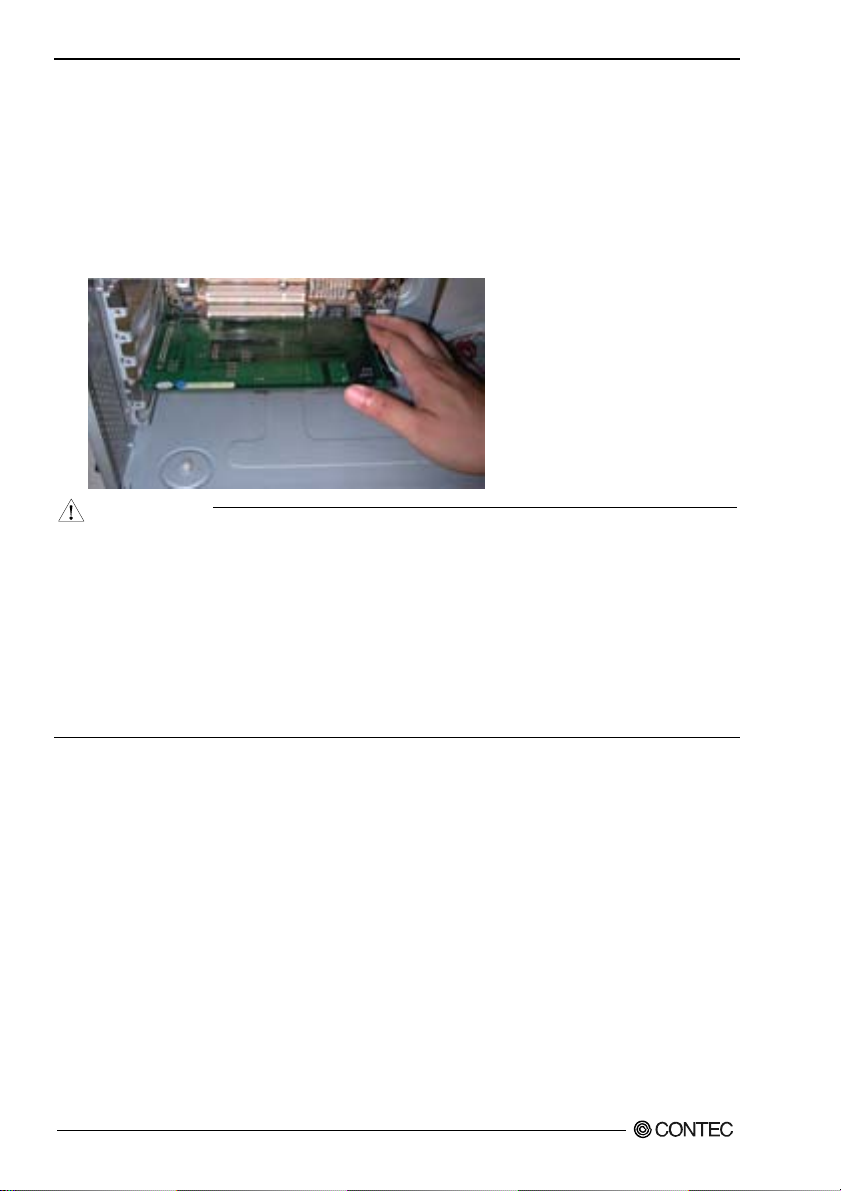
Plugging the Board
(1) Before plugging the board, shut down the system, unplug the power code of your PC.
(2) Remove the cover from the PC so that the board can be mounted.
(3) Plug the board into an expansion slot.
(4) Fasten the board bracket to the PC’s chassis with the removed screw.
(5) Put the cover back into place.
CAUTION
- Do not touch the board's metal plated terminals (edge connector) with your hands.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
If the terminals are touched by someone's hands, clean the terminals with industrial alcohol.
- Do not install or remove the board to or from the slot while the computer's power is turned on.
Otherwise, the board may malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
Doing so could cause trouble. Be sure that the personal computer or the I/O expansion unit power is
turned off.
- Make sure that your PC or expansion unit can supply ample power to all the boards installed.
Insufficiently energized boards could malfunction, overheat, or cause a failure.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
16
Page 24

2. Setup
Step 3 Installing the Hardware
For using an expansion board under Windows, you have to let the OS detect the I/O addresses and IRQ
to be used by the board. The process is referred to as installing the hardware.
In the case of using two or more boards, make sure you install one by one with the Add New Hardware
Wizard.
Turning on the PC
Turn on the power to your PC.
CAUTION
- The board cannot be properly installed unless the resources (I/O addresses and interrupt level) for
the board can be allocated. Before attempting to install the board, first determine what PC
resources are free to use.
- The resources used by each board do not depend on the location of the PCI bus slot or the board
itself. If you remove two or more boards that have already been installed and then remount one of
them on the computer, it is unknown that which one of the sets of resources previously assigned to
the two boards is assigned to the remounted board. In this case, you must check the resource
settings.
Setting with the Add New Hardware Wizard
(1) The “Add New Hardware Wizard” will be started.
Select “Specify the location of the driver”, then click on the [Next] button.
If you are using Windows NT 4.0, the “Add New Hardware Wizard” is not started.
Go to Step 4 “Initializing the Software”.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
17
Page 25

2. Setup
) Specify that folder on the CD-ROM which contains the setup information (INF) file to register the
(2
board.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
ource folder
S
The setup information (INF) file is contained in the following folder on the bundled CD-ROM.
Windows XP, 2000 \INF\Win2000\Gpib\PCI
Windows Me, 98, 95 \INF\Win95\Gpib\PCI
Example of specifying the folder for use under Windows Me
\INF\Win95\Gpib\PCI
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
18
Page 26

2. Setup
CAUTION
In Windows XP, the Hardware Wizard displays the following alert dialog box when you have
located the INF file. This dialog box appears, only indicating that the relevant driver has not
passed Windows Logo testing, and it can be ignored without developing any problem with the
operation of the board.
In this case, click on the [Continue Anyway] button.
You have now finished installing the hardware.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
19
Page 27

2. Setup
Step 4 Initializing the Software
The API function library requires the initial setting to recognize the execution environment. It is called
the initialization of the API function library.
Invoking API-TOOL Configuration
(1) Open the Start Menu, then select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “ API-TOOL
Configuration”
(2) API-TOOL Configuration detects boards automatically.
The detected boards are listed.
Updating the Settings
(1) Select “Save setting to registry…” from the “File” menu.
You have now finished installing the initial setting of Software.
G
20
P-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
Page 28

2. Setup
For using API-GPLV(W32)
Invoking Configuration Utility
(1) Open the Start Menu, then select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPLV” –
“Configuration Utility”
- Select GPIB Board:
Select the board to be used.
- Hard Ware Setting:
Set the I/O address, board ID, and
IRQ.
- IEEE488.2:
Make IEEE 488.2 software settings.
- Interface Name:
From the list, select the board to be
set up.
- GPIB Address:
Set the device address of the board.
The primary address can be set to 0
to 30.
- Termination Methods:
Set the termination format.
- I/O Timeout:
Set the transmit/receive time-out
period.
- System Controller:
Select whether to use the board as a
system controller.
Updating the Settings
(1) Click on the [Refresh] button, then on the [OK] button.
You have now finished installing the initial setting of Software.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
21
Page 29

2. Setup
Step 5 Checking Operations with the Diagnosis Program
Use the diagnosis program to check that the board and driver software work normally, thereby you can
confirm that they have been set up correctly.
What is the Diagnosis Program?
The diagnosis program diagnoses the states of the board and driver software.
It can also be used as a simple checker when an external device is actually connected.
Using the “Diagnosis Report” feature reports the driver settings, the presence or absence of the board,
I/O status, and interrupt status.
Check Method
Perform the transmit/receive test and check the execution environment with the board connected to the
remote device.
Before diagnosis, check the address of the remote device. Prepare the user’s guide and command
reference for the remote device as required (to perform testing smoothly).
Using the Diagnosis Program for Using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx
Starting the Diagnosis Program
Select the board in the API-TOOL Configuration windows, then run the Diagnosis Program.
* The name of the board you have just added is displayed.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
22
Page 30

2. Setup
heck of GPIB communication
C
The remote device address setting, communication data format setting, and main dialog boxes are
displayed.
(1) Specify the remote device address and
click on the [OK] button.
(3) The main dialog box appears.
(2) Specify the communication format and click on
the [OK] button.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
T
he following commands can be used to check GPIB operations.
“Send”: Sends the typed character string with a delimiter to the remote device.
“Receive”: Receives data from the remote device and displays it along with the number of data items.
“Trigger”: Sends a trigger command to the remote device.
“Poling”: Polls the remote device and displays the obtained status byte.
Note
When communication has been completed successfully, “xxxxx completed normally” is displayed
as the “return value”.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
23
Page 31

2. Setup
gnosis Report
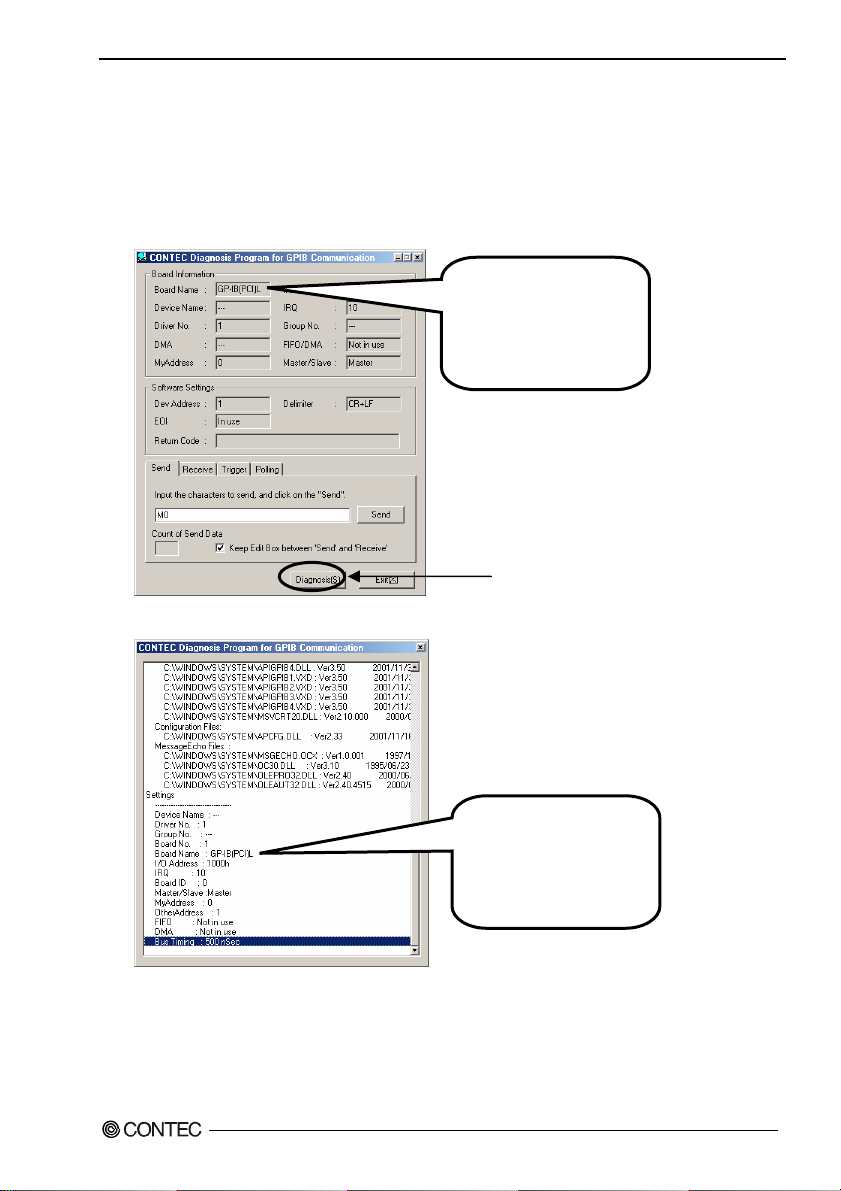
Dia
(1) Clicking on [Diagnosis] displays detailed data including board settings and the diagnosis results
while saving them in text format.
The results are saved and displayed as a text file (GpibRep.txt) in the install folder (Program
Files\CONTEC\API-PAC(W32)).
The diagnosis program performs "board presence/absence check", "driver file test", "board setting
test", and so on.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
Click on [Diagnosis].
2) A diagnosis report is displayed as shown below.
(
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
24
Page 32
2. Setup
Using the Diagnosis Program for Using API-GPLV(W32)
Starting the Diagnosis Program
Open the Start Menu, then select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPLV” – “Diagnosis
Program”. Click on [Start] and follow the on-screen instructions.
* The installed board name is displayed.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
25
Page 33

2. Setup
heck of GPIB communication
C
The remote device address setting, communication data format setting, and main dialog boxes are
displayed.
(1) Specify the remote device address and
click on the [OK] button.
(3) The main dialog box appears.
(2) Specify the communication format and click
on the [OK] button.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
he following commands can be used to check GPIB operations.
T
“Send”: Sends the typed character string with a delimiter to the remote device.
“Receive”: Receives data from the remote device and displays it along with the number of data items.
“Trigger”: Sends a trigger command to the remote device.
“Poling”: Polls the remote device and displays the obtained status byte.
Note
When communication has been completed successfully, “xxxxx completed normally” is displayed
as the “return value”.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
26
Page 34
2. Setup
gnosis Report
Dia
(1) Clicking on [Diagnosis] displays detailed data including board settings and the diagnosis results
while saving them in text format.
The results are saved and displayed as a text file (GpibRep.txt) in the install folder (Program
Files\CONTEC\API-PAC(W32)).
The diagnosis program performs "board presence/absence check", "driver file test", "board setting
test", and so on.
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)L
- GP-IB(PCI)
(2) A diagnosis report is displayed as shown belo w.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
Click on [Diagnosis].
* The name of the board
you have just added is
displayed.
- GP-IB(PCI)
- GP-IB(PCI)
L
27
Page 35

2. Setup
Setup Troubleshooting
Symptoms and Actions
Initialization of a board cannot be performed [Windows NT4.0]
The driver may not yet be activated. If your PC is running under Windows NT 4.0, set the PnP OS
option in the BIOS Setup menu to "NO".
For details on how to set up the BIOS, refer to the manual for your PC.
A GPIB error occurs.
The remote device address may be incorrect or the GPIB cable may not yet be connected.
The GPIB cable cannot be connected.
The GPIB cable may interfere with the chassis of your PC and not be plugged correctly into the
interface connector of the board depending on the structure of your PC, for example, when the slots are
located in the rear panel of the PC too deeply.
You can use the GPIB connector adapter (CN-GP/C) to work around this problem.
Board Board
GPIB
Cable
The OS won't normally get started or detect the board. [Windows XP
Turn off the power to your PC, then unplug the board . Restart the OS and delete the board settings of
API-TOOL Configuration. Turn off the PC again, plug the board, and restart the OS. Let the OS
detect the board and use API-TOOL Configuration to make board settings over again.
CN-GP/C
GPIB
Cable
2000]
,
If your problem cannot be resolved
Refer to the troubleshooting section of API-GPLV HELP.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
28
Page 36
3. External Connection
3. External Connection
This chapter describes the interface connectors on the board and the external I/O circuits.
Check the information available here when connecting an external device.
Using the On-board Connectors
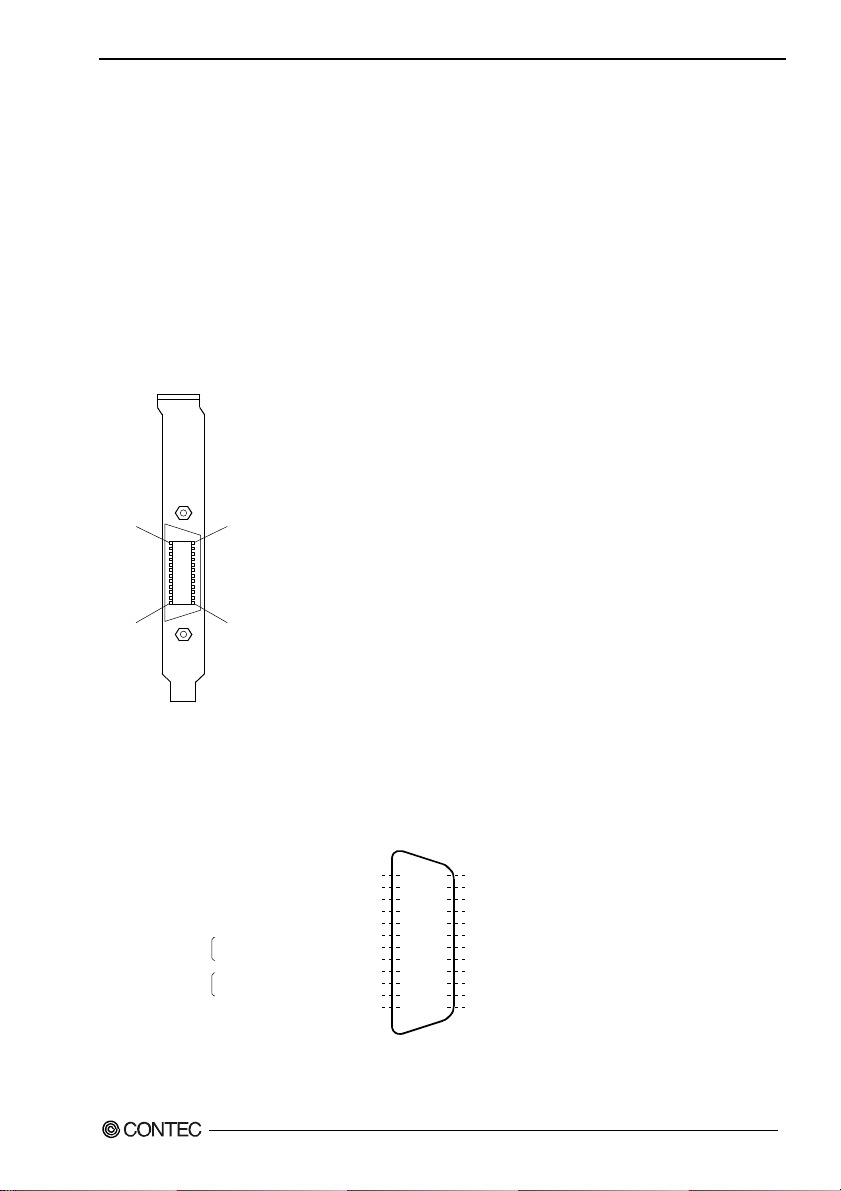
Connecting a Device to a Connector
To connect an external device to this board, plug the cable from the device into the interface connector
(CN1) shown below.
1
CN1
12
On-board connector : 555139-1(AMP)
Applicable connector(cable): GPIB cable(IEEE-488 rated)
13
24
Figure 3.1. Interface Connectors and Mating Connectors
Connector Pin Assignment
Data bus DIO1
Data bus DIO2
Data bus DIO3
Management bus(End or Identify)
Handshake
Management bus
(Not Ready for Data)
bus
(Not Data Accepted)
Data bus DIO4
(Data Valid)
(Interface Clear)
(Service Request)
(Attention)
(Ground)
Figure 3.2. Pin Assignment of CN1
EOI
DAV
NRFD
NDAC
IFC
SRQ
ATN
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DIO5 Data bus
13
DIO6 Data bus
14
DIO7 Data bus
15
DIO8 Data bus
16
REN(Remote Enable)Management bus
17
GND (Ground)
18
GND (Ground)
19
GND (Ground)
20
GND (Ground)
21
GND (Ground)
22
GND (Ground)
23
Logic GND
24
CN1
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
29
Page 37
3. External Connection
Notes on cable connection
The GPIB has restrictions on the number of devices connected and the cable length according to the
standard.
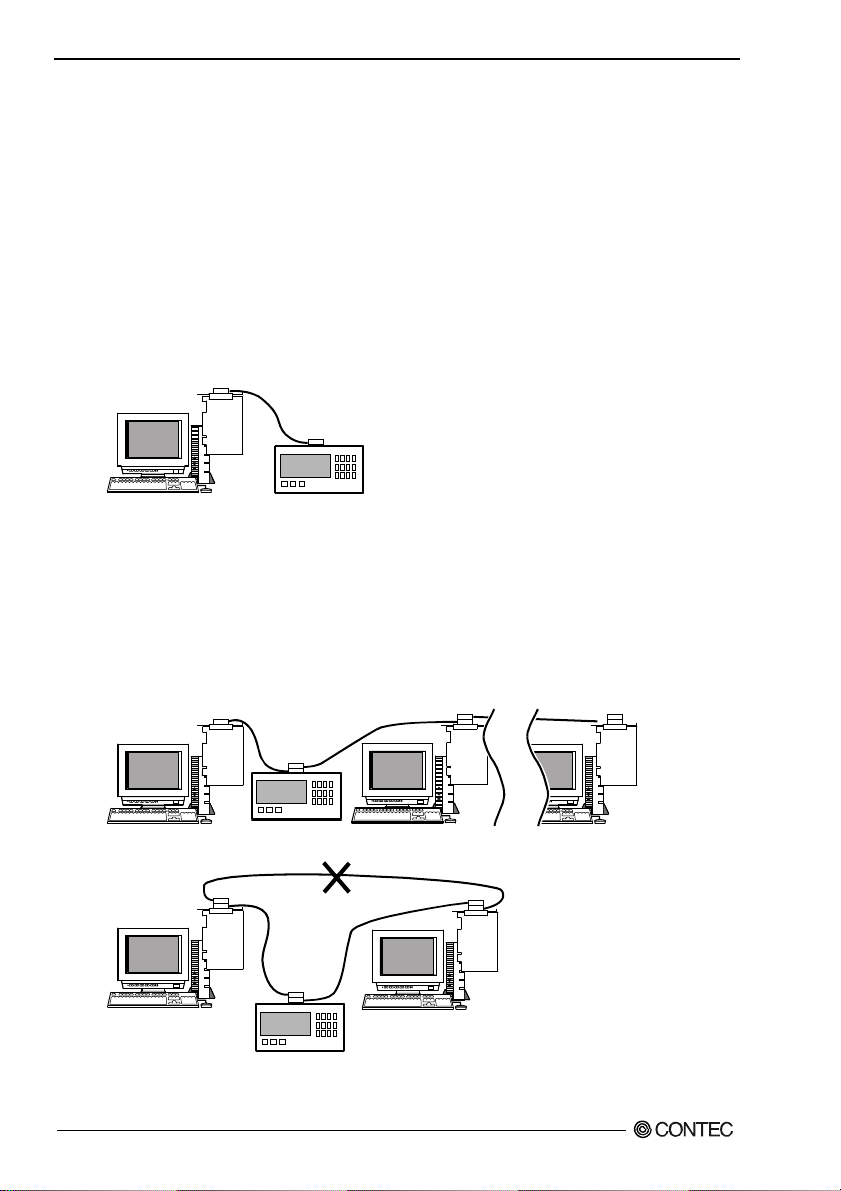
(1) The maximum number of interfaces (external devices) is 15, which can be connected to one system.
(2) The maximum total length of cables that can be used to interconnect a group of devices in one bus
system is “2 m x (the number of devices)” or 20 m, whichever is shorter. (JIS C1901-1987).
Note, however, the individual cables between devices must be within 4 m long. Some examples
are given below.
System with a total of two devices
-
2 m x (Number of devices = 2) < 20 m
The maximum total length of cables for this system is therefore 4 m.
3765
- System with a total of three devices
2 m x (Number of devices = 3) < 20 m
The maximum total length of cables for this system is therefore 6 m. The two cables used in
the system must be [2 m + 4 m] or [2 m + 2 m] in length so that neither is longer than 4 m.
- System with a total of fifteen devices
2 m x (Number of devices = 15) > 20 m
The maximum total length of cables for this system is therefore 20 m.
3765
(3) The cables in the system must not form a loop.
3765
(4) Unplug the cable from any device which is left off for some reason such as a fault.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
30
...
Page 38

3. External Connection
)
(5
When powering the measurement system, turn on the measuring instrument first and then on the
PC.
(6) Neither unplug/plug the cable nor turn on/off the device during communication. Doing so stops
the operation or causes an error, resulting in trouble.
(7) The talker and listener must be addressed to talk and to listen, respectively, by the controller before
the talker can send messages to the listener.
At least two thirds of all the devices connected must be turned on.
(8)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
31
Page 39

3. External Connection
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
32
Page 40

4. Functions
4. Functions
This section describes the functions of the board.
Basic GPIB Functions
Master/slave function
The board can serve as the master (controller) or slave depending on the setting of API-TOOL
Configuration (API-GPIB(98/PC)xx) or Setup Utility (API-GPLV(W32)).
When used as the master, the board can send IFC (InterFace Clear) at any timing and control the REN
(Remote ENable) line.
Communication function
The board can send and receive data in accordance with the IEEE 488 Standard. You can add
delimiters and EOI (End of Identify) to outgoing data depending on the software settings.
Serial poll/parallel poll/SRQ send functions
The following functions can be used depending on the master/slave configuration.
Master
Serial poll
Parallel poll
Slave
Status byte setting
SRQ (Service ReQuest) transmission
Response to parallel polling
My address setting
The GPIB address (my address) of the board can be set by API-TOOL Configuration
(API-GPIB(98/PC)xx) or Configuration Utility (API-GPLV(W32)). No setting is required on the
board.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
33
Page 41
4. Functions
Additional Functions
Line monitor function
The board can read the current status of all control lines and handshake lines (IFC, ATN, SRQ, REN,
EOI, DAV, NRFD, NDAC). It can also read latch data from the IFC line.
GPIB (PCI) can read the latch data on all control lines and the current status of the data line (DIO 1-8).
Current status read Latch data read
GP-IB(PCI)
All Line(IFC, ATN, SRQ, REN, EOI, DAV, NRFD,
NDAC, DIO1 to DIO8)
Control line, Handshake line (IFC, ATN, SRQ,
REN, EOI, DAV, NRFD, NDAC)
GP-IB(PCI)L
Control line, Handshake line (IFC, ATN, SRQ,
REN, EOI, DAV, NRFD, NDAC)
Only IFC line
Communication using FIFO memory (Only GP-IB(PCI))
The board can use on-board FIFO memory for communication. As the board controls this form of
communication, it can be performed at high speed irrelevant to the PC’s CPU speed.
Note, however, that the actual communication speed is set to the speed of the slowest device in
compliance with the GPIB standard.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
34
Page 42

4. Functions
Analyzer function (Only GP-IB(PCI))
The state transition of all lines in the GPIB cable can be analyzed by using the on-board FIFO memory.
This function can be used to locate the cause of a failure or to check data flowing on lines.
The function is provided by the analyzer utility (Analyzer.exe).
Open the Start Menu, then select “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPIB” – “GPIB ANALYZER”.
Otherwise, directly execute “Program Files\API-PAC(W32)\GPIB\ANALYZER\Analyzer.exe”.
Running Method
(1) Install the board on your PC according to Step 2 “Setting the Hardware” and Step 3 “Installing the
Hardware” in Chapter 2 “Setup”.
After having installed the board, connect the board to an instrument for analysis. The board can
communicate with the instrument while executing analysis.
Example 1 of Connection:
3765
One board communicating the instrument while analyzing
Example 2 of Connection:
3765
PC1
PC1: Only the analyzer is executed.
PC2: Communicating with the measuring instrument
(2) The analyzer utility is started with the following dialog box. Enter the number of the on-board
SW1 (BOARD ID) in decimal representation, then click on [OK]. The factory default of SW1 is 0.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
PC2
35
Page 43

4. Functions
(3)
Click on the [Start Analyze] button. The analyzer utility analyzes the subsequent changes to lines.
When the communication you want to analyze has been completed, click on the [Stop Analyze]
button. The analysis results will be displayed on the screen.
Convenient usage
(1) Using the start and end triggers
During analysis, the analyzer utility can obtain data only when a specific condition is satisfied in
the entire session of communication. The condition that can be specified is a communication
status (polling, transmit/receive, etc.), a change to the control line (EOL, SRQ, ATN, etc.), a data
line match (specified ASCII code), or a delimiter match.
Select “Set Trigger Condition” from the “Set” menu.
The analyzer utility works as follows with the settings made on the Trigger Set Dialog below.
- The analyzer utility starts analysis the moment IFC changes.
- The analyzer utility ends analysis upon transmit/receive of data “CR” (0DH).
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
36
Page 44

4. Functions
(2
) Saving analysis data
Once saved, obtained analysis data can be opened again with the analyzer utility. Since analysis
data is saved in CSV format as well, you can reference and edit the data using a proper program
such as Excel.
(3) Viewing analysis data in a chart
The analysis utility can display analysis data in a chart.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
37
Page 45

4. Functions
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
38
Page 46

5. About Software
5. About Software
The bundled CD-ROM “Driver Library API-PAC(W32)” contains the functions that provide the
following features:
- All of the master mode, slave mode, and interrupt level can be set by software.
- Three-wire handshaking is employed to assure transfer even between the sending and receiving
devices different in speed.
For details, refer to the help file. The help file provides various items of information such as “Function
Reference”, “Sample Programs”, and “FAQs”. Use them for program development and
troubleshooting.
For using API-GPIB(98/PC)xx
Accessing the Help File
(1) Click on the [Start] button on the Windows taskbar.
(2) From the Start Menu, select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPIB” – “API-GPIB
HELP” to display help information.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
39
Page 47

5. About Software
Using Sample Programs
Bundled sample programs cover basic transmit/receive and polling in master and slave modes and
support ADVANTEST Multimeters, YEW voltage generators, and SONY Tektronix oscilloscopes.
Use these sample programs as references for program development and operation check.
The sample programs are stored in \Program Files\CONTEC\API-PAC(W32)\GPIB\Samples.
Running a Sample Program
(1) Click on the [Start] button on the Windows taskbar.
(2) From the Start Menu, select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPIB” – “SAMPLE…”.
(3) A sample program is invoked.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
40
Page 48

5. About Software
ple Programs - Examples
Sam
-Master Mode : Executes a series of operations in master mode.
-Slave Mode : Executes a series of operations in slave mode.
-Multi-meter : Triggers a multimeter periodically (based on the timer and events) to
sample and display data.
-Voltage Source control : Allows the master to gain control of a digital voltmeter at fixed
-Oscilloscope 1 : Receives screen data from an oscilloscope and displays it in a graph.
-Oscilloscope 2 : Receives screen data from an oscilloscope and saves it in CSV format.
-MultiLine Message : Creates a multiline message for the remote device.
Master Mode
[
Slave Mode
[
] [
] [Oscilloscope
intervals.
MultiLine Me s sa g e
2]
]
[Volta
ge Source control]
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
41
Page 49
5. About Software
For using API-GPLV(W32)
API-GPLV(W32) is a driver created in NI’s GPIB function style as the software for controlling
CONTEC GPIB boards.
When the driver is installed, existing applications such as LabVIEW can operate CONTEC GPIB boards.
For details, refer to the help file. The help file provides information such as “operation specifications”,
“additional information”, and “troubleshooting”.
Accessing the Help File
(1) Click on the [Start] button on the Windows taskbar.
(2) From the Start Menu, select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPLV” – “API-GPLV
HELP” to display help information.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
42
Page 50

5. About Software
Function List
Up to now the NI-488.2 Board-Level Calls
Function Name Action Outline
ibask Return information about software configuration parameters.
ibcac Become Active Controller.
ibcmd Send GPIB commands.
ibcmda Send GPIB commands asynchronously.
ibconfig Change the software configuration parameters.
ibdma Enable or disable DMA.
ibeos Configure the end-of-string (EOS) termination mode or character.
ibeot Enable/disable auto-assertion of GPIB EOI line at the end of write.
ibfind Open and initialize a GPIB board.
ibgts Go from Active Controller to Standby.
ibist Set or clear the board individual status bit for parallel polls.
iblines Return the status of the eight GPIB control lines.
ibln Check for the presence of a device on the bus.
ibloc Go to local.
ibnotify Asynchronously notify user when one or more GPIB events occur.
ibonl Place the device online or offline.
ibpad Change the primary address.
ibppc Parallel poll configure.
ibrd Read data from a device into a user buffer.
ibrda Read data asynchronously from a device into a user buffer.
ibrdf Read data from a device into a file.
ibrpp Conduct a parallel poll.
ibrsc Request or release system control.
ibrsv Request service and change the serial poll status byte.
ibsad Change or disable the secondary address.
ibsic Assert IFC (Interface Clear).
ibsre Set or clear the Remote Enable (REN) line.
ibstop Abort asynchronous I/O operation.
ibtmo Change or disable the I/O timeout period.
ibwait Wait for GPIB events.
ibwrt Write data to a device from a user buffer.
ibwrta Write data asynchronously to a device from a user buffer.
ibwrtf Write data to a device from a file.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
43
Page 51

5. About Software
Up t
o now the Ni-488.2 Device-Level Calls
Function Name Action Outline
ibask Return information about software configuration parameters.
ibbna Change the access board of a device.
ibclr Clear a specific device.
ibconfig Change the software configuration parameters.
ibdev Open and initialize a device
ibeos Configure the end-of-string (EOS) termination mode or character.
ibeot Enable/disable auto-assertion of GPIB EOI line at the end of write.
ibln Check for the presence of a device on the bus.
ibloc Go to local.
ibnotify Asynchronously notify user when one or more GPIB events occur.
ibonl Place the device online or offline.
ibpad Change the primary address.
ibpct Pass control to another GPIB device with Controller capability.
ibppc Parallel poll configure.
ibrd Read data from a device into a user buffer.
ibrda Read data asynchronously from a device into a user buffer.
ibrdf Read data from a device into a file.
ibrpp Conduct a parallel poll.
ibrsp Conduct a serial poll.
ibsad Change or disable the secondary address.
ibstop Abort asynchronous I/O operation.
ibtmo Change or disable the I/O timeout period.
ibtrg Trigger selected device.
ibwait Wait for GPIB events.
ibwrt Write data to a device from a user buffer.
ibwrta Write data asynchronously to a device from a user buffer.
ibwrtf Write data to a device from a file.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
44
Page 52

5. About Software
-488.2 Calls for Multiple Devices
NI
Function Name Action Outline
AllSpoll Serial poll all devices.
DevClear Clear a single device.
DevClearList Clear multiple devices.
EnableLocal Enable operations from the front panel of deceives (leave remote
programming mode).
EnableRemote Enable remote GPIB programming for devices.
FindListn Find listening devices on the GPIB.
FindRQS Determine which device is requesting service.
PassControl Pass control to another device with Controller capability.
PPoll Perform a parallel poll on the GPIB.
PPollConfig Configure a device to respond to parallel polls.
PPollUnconfig Unconfigure devices for parallel polls.
RcvRespMsg Read data bytes from a device that is already addressed to talk.
ReadStatusByte Serial poll a single device.
Receive Read data bytes from a device.
ReceiveSetup Address a device to be a Talker and the interface board to be a Listener in
ResetSys Reset and initialize IEEE 488.2-compliant devices.
Send Send data bytes to a device.
SendCmds Send GPIB command bytes.
SendDataBytes Send data bytes to devices that are already addressed to listen.
SendIFC Reset the GPIB by sending interface clear.
SendList Send data bytes to multiple GPIB devices.
SendLLO Send the Local Lockout (LLO) message to all devices.
SendSetup Set up devices to receive data in preparation for SendDataBytes.
SetRWLS Place devices in Remote With Lockout State.
TestSRQ Determine the current state of the GPIB Service Request (SRQ) line.
TestSys Cause IEEE 488.2-compliant devices to conduct self-test.
Trigger Trigger a device.
TriggerList Trigger multiple devices.
WaitSRQ Wait until a device asserts the GPIB Service Request (SRQ) line.
preparation for RcvRespMsg.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
45
Page 53

5. About Software
Using Sample Programs
Sample programs can execute basic transmit/receive and polling.
Use these sample programs as references for program development and operation check.
The sample programs are stored in \Program Files\CONTEC\API-PAC(W32)\GPLV\Samples.
Running a Sample Program
(1) Click on the [Start] button on the Windows taskbar.
(2) From the Start Menu, select “Programs” – “CONTEC API-PAC(W32)” – “GPLV” – “SAMPLE
GPLV”.
(3) A sample program is invoked.
Program example
-GpibTest : Executes initialization, transmission, reception, and polling.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
46
Page 54
5. About Software
Uninstalling the API Function Libraries
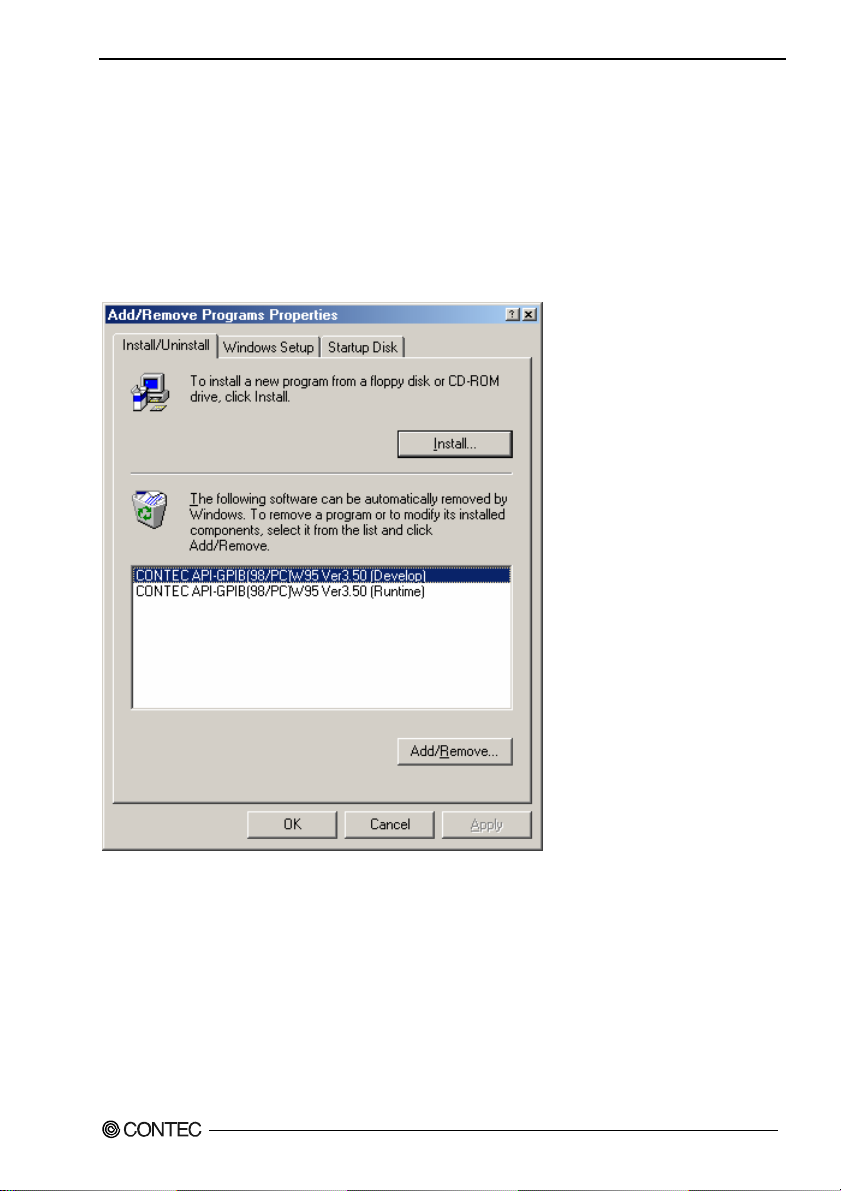
To uninstall API-PAC(W32), follow the procedure below.
(1) Click on the [Start] button on the Windows taskbar. From the Start Menu, select “Settings” –
“Control Panel”.
(2) Double-click on “Add/Remove Programs” in the Control Panel.
(3) Select “CONTEC API-GPIB(98/PC)xx VerX.XX (xxxx)” or
“CONTEC API-GPLV(W32) VerX.XX (xxxx)”.
[Add/Remove] button. Follow the on-screen instructions to uninstall the function libraries.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
47
Page 55

5. About Software
CD-ROM Directory Structure
\
| Autorun.exe Installer Main Window
| Readmeu.htm Version information on each API-TOOL
|– APIPAC
| |– AIO
| | |– Disk 1
| | |– Disk 2
| | |– ……
| | |– Disk N
| |– CNT
| |– ……
|– FreeSamples Sample programs in Delphi and Builder
| |– Builder 1.0
| |– ……
|– HELP HELP file
| |– Aio
| |– Cnt
| |– ……
|– INF OS-specific INF file folder(Windows 9X, 2000)
| |– WDM
| |– Win2000
| |– Win95
|– Manual Reference Manual(PDF type)
|– Readme Driver read me file folder
|– Release Driver file(For creation of a user-specific install program)
|– API_NT
|– API_W95
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
48
Page 56
6. About Hardware
6. About Hardware
This chapter provides hardware specifications and hardware-related supplementary information.
Hardware specification
The following tables list the hardware specifications of the board.
GP-IB(PCI)L
Table 6.1. Specification <GP-IB(PCI)L>
Item Specifications
Number of channel 1 channel
Conforms to IEEE-488.1, 488.2(GPIB)standards
Transfer format 8-bit parallel, 3-wire handshake system
Transfer rate 120Kbyte/sec (Max.)
Signal logic
Interrupt 1 level use
Total cable length 20m or less
Cable length between device 4m or less *1
Connectable number of device 15 devices (Max.)
I/O address Any 32-byte boundary
Consumed current +5VDC 300mA (Max.)
Operating conditions 0 to 50°C, 10 to 90%RH (No condensation)
PCI bus specification 32-bit, 33MHz, 5V
External dimensions (mm) 121.69(L) × 105.68(H) *2
Weight 110g
*1 For details, see item (2) in Chapter3, "Connecting Cables".
*2 Boards with different board numbers are different in these specifications. See Table 6.4 "Different in the
specification" at the end of this document.
Board Dimensions
121.69
Negative logic
L level : 0.8V or less
H level : 2.0V or more
105.68
[mm]
The standard outside dimension (L) is
the distance from the end of the board
to the outer surface of the slot cover.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
49
Page 57

6. About Hardware
GP-IB(PCI)
T
able 6.2. Specification <GP-IB(PCI)>
Item Specifications
Number of channel 1 channel
Conforms to IEEE-488.1, 488.2(GPIB)standards
Transfer format 8-bit parallel, 3-wire handshake system
Transfer rate 1.2Mbyte/sec (Max.)
Capacity of
transmission/receiving data
Signal logic
Interrupt 1 level use
Total cable length 20m or less
Cable length between device 4m or less *1
Connectable number of device 15 devices (Max.)
I/O address Any 16-byte boundary
Consumed current +5VDC 970mA (Max.)
Operating conditions 0 to 50°C, 10 to 90%RH(No condensation)
PCI bus specification 32-bit, 33MHz, 5V
External dimensions (mm) 121.69(L) × 106.68(H)
Weight 130g
*1 For details, see item (2) in Chapter3, "Connecting Cables".
1Mbyte
Negative logic
L level : 0.8V or less
H level : 2.0V or more
Board Dimensions
121.69
106.68
[mm]
The standard outside dimension (L) is
the distance from the end of the board
to the outer surface of the slot cover.
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
50
Page 58

6. About Hardware
Table 6.3. Interface function
Code Function
SH1 Source handshake functions
AH1 Acceptor handshake functions
T6 Basic talker, serial polling, MLA talker release
L4 Basic listener MTA listener release
TE0 No extended talker functions
LE0 No extended listener functions
SR1 Service request function
RL1 Remote function
DC1 Device clear function
DT1 Device trigger function
PP1 Configuration by remote message
C1 System controller function
C2 IFC send, controller in-charge
C3 REN send
C4 Response to SRQ
C26 Interface message send, parallel polling
Different in the specification
The GP-IB(PCI)L is different in specifications, depending on the board number as listed below.
Table 6.4. Different in the specification
■GP-IB(PCI)L
Board No. No.
Dimension (mm) 121.69(L) × 106.68(H) 121.69(L) × 105.68(H)
GP-IB(PCI)L, GP-IB(PCI)
7169 No. 7169A
51
Page 59

GP-IB(PCI)L
GP-IB(PCI)
User’s Guide
CONTEC CO., LTD. December 2013 Edition
3-9-31, Himesato, Nishiyodogawa-ku, Osaka 555-0025, Japan
Japanese http://www.contec.co.jp/
English http://www.contec.com/
Chinese http://www.contec.com.cn/
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form by any means without prior written
consent of CONTEC CO., LTD. [12172013]
[04112000] Management No. A-46-166
[12172013_rev5] Parts No. LZN7082
 Loading...
Loading...