Consumer Microcircuits Limited FX829P4, FX829D5, FX829D2 Datasheet
CML Semiconductor Products
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
D/829/4 September 1997
1.0 Features Provisional Issue
•• Rx Audio Processing •• Multi-standard Modem Formats
•• Tx Audio Processing •• ETS/MPT/PAA Standards Compatible
•• 1200/2400 Baud Modem •• Low Voltage Operation
•• DTMF Encoder •• 24-pin Small Form Package
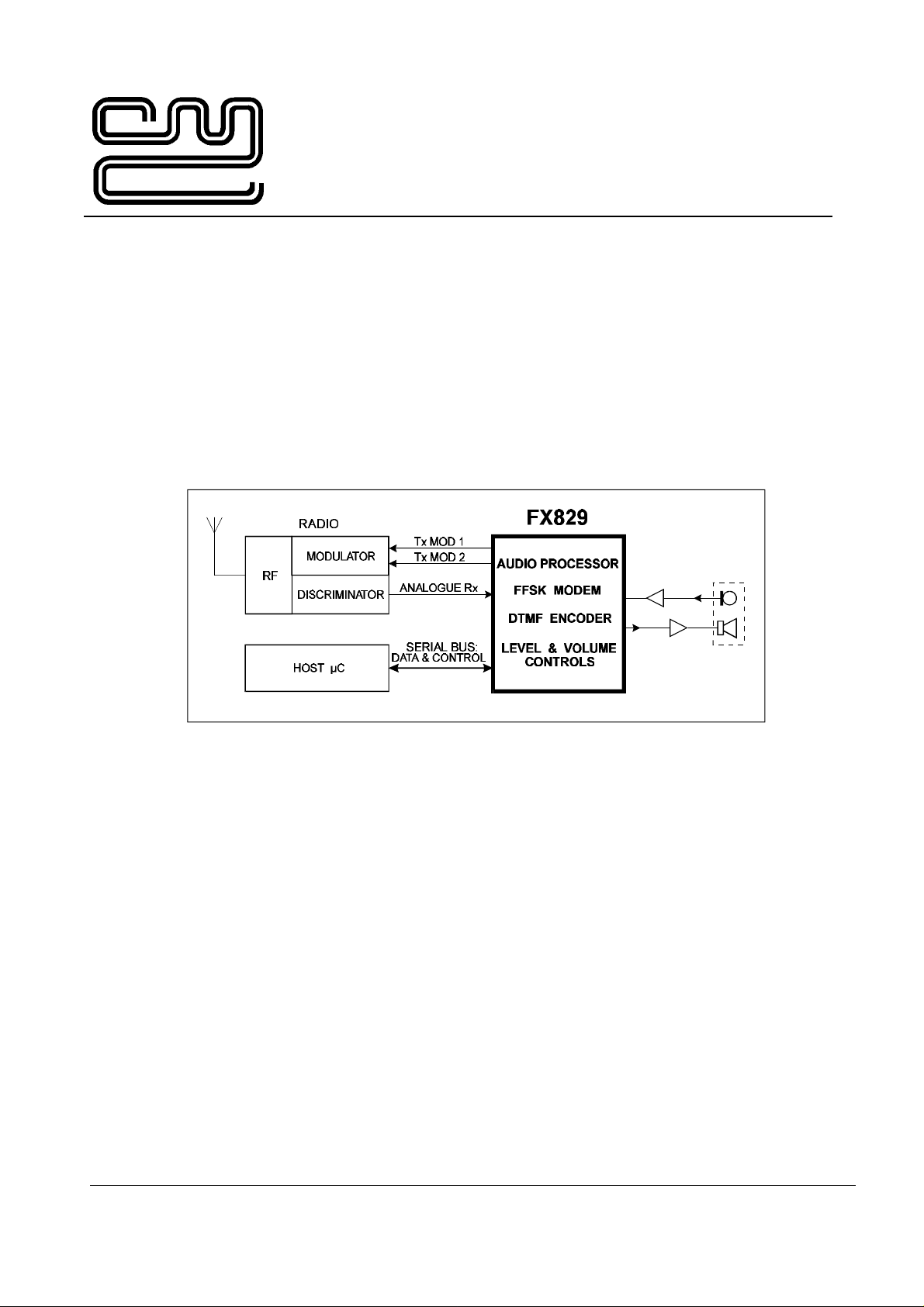
1.1 Brief Description
The FX829 is a low voltage CMOS integrated circuit, designed to provide the baseband audio and
system signal-processing functions required for PAMR or PMR trunked radio applications. It operates
in half-duplex mode under serial-bus control of the host µC.
The FX829 incorporates a dual-rate 1200/2400bps FFSK modem, with a software-flexible choice of
synchronisation codewords, data run-length and CRC checking to suit a wide range of applications.
These features allow very flexible handling of non-prescribed data on traffic channels in addition to the
network signalling sent on control channels. A 16 character DTMF encoder is available in the transmit
mode. The two-point modulation output has software programmable level-adjustment.
The audio processing stages include transmit and receive filtering, to the standards specified for
12.5kHz and 25kHz PAMR/PMR channel operation, plus transmit deviation limiting and a
programmable Rx volume control. Power saving is automatic when audio functions are deselected.
The FX829 is designed for use in radios compatible with MPT1327, PAA1382 and ETS 300 086
trunking standards. Its features and flexibility ensure that it is equally suitable for use with modified or
proprietary standards.
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited

Baseband Signal Processor FX829
CONTENTS
Section Page
1.1 Brief Description.........................................................................................1
1.2 Block Diagram ............................................................................................3
1.3 Signal List...................................................................................................4
1.4 External Components.................................................................................7
1.5 General Description....................................................................................8
1.5.1 Software Description ..................................................................9
1.5.2 FFSK Checksum Generation and Checking............................ 18
1.6 Application Notes.....................................................................................20
1.7 Performance Specification.......................................................................25
1.7.1 Electrical Performance..............................................................25
1.7.2 Packaging..................................................................................32
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 2 D/829/4
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
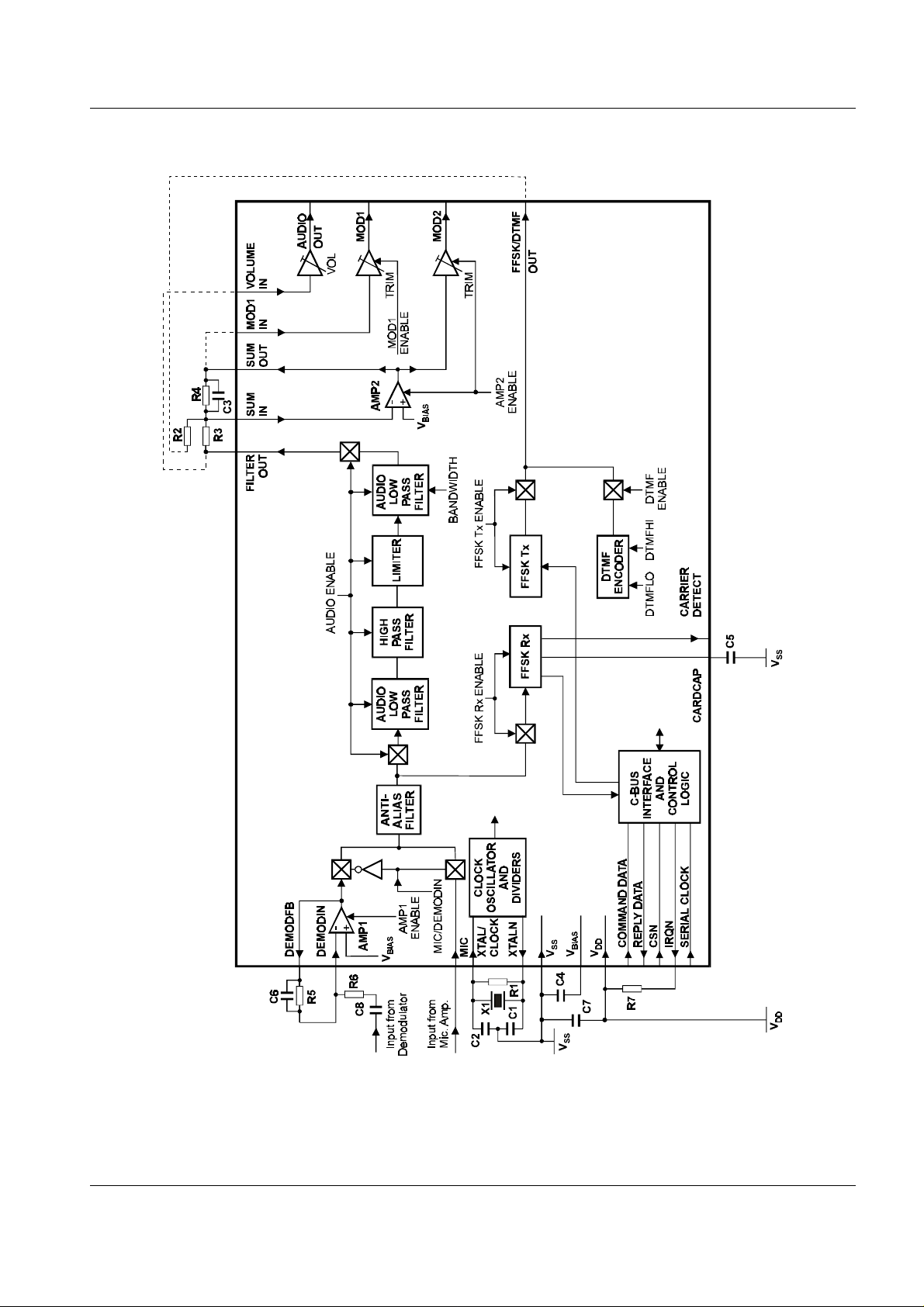
1.2 Block Diagram
Figure 1 Block Diagram
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 3 D/829/4
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.3 Signal List
Package
D2/D5
Signal Description
Pin No. Name Type
1 XTALN O/P The inverted output of the on-chip oscillator.
2 XTAL/CLOCK I/P The input to the on-chip oscillator, for external
Xtal circuit or clock.
3 SERIAL CLOCK I/P The "C-BUS" serial clock input. This clock,
produced by the µController, is used for transfer
timing of commands and data to and from the
device. See "C-BUS" Timing Diagram.
4 COMMAND DATA I/P The "C-BUS" serial data input from the
µController. Data is loaded into this device in
8-bit bytes, MSB (B7) first, and LSB (B0) last,
synchronised to the SERIAL CLOCK. See
"C-BUS" Timing Diagram.
5 REPLY DATA O/P The "C-BUS" serial data output to the
µController. The transmission of REPLY DATA
bytes is synchronised to the SERIAL CLOCK
under the control of the CSN input. This 3-state
output is held at high impedance when not
sending data to the µController. See "C-BUS"
Timing Diagram.
6 CSN I/P The "C-BUS" data loading control function: this
input is provided by the µController. Data
transfer sequences are initiated, completed or
aborted by the CSN signal. See "C-BUS"
Timing Diagram.
7 IRQN O/P This output indicates an interrupt condition to
the µController by going to a logic "0". This is a
"wire-ORable" output, enabling the connection of
up to 8 peripherals to 1 interrupt port on the
µController. This pin has a low impedance
pulldown to logic "0" when active and a highimpedance when inactive. An external pullup
resistor is required.
The conditions that cause interrupts are
indicated in the STATUS register and are
effective if not masked out by a corresponding
bit in the CONTROL register.
8 CARRIER DETECT O/P The carrier detect output for the FFSK Rx.
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 4 D/829/4

Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.3 Signal List (continued)
Package
D2/D5
Signal Description
Pin No. Name Type
9 CARDCAP O/P The carrier detect integrating capacitor.
10 V
BIAS
O/P A bias line for the internal circuitry, held at
. This pin must be decoupled by a
½ V
DD
capacitor mounted close to the device pins.
11 MIC I/P The ac coupled Tx audio input (external
amplification is required for use as a microphone
input).
12 V
ss
Power The negative supply rail (ground).
13 DEMODIN I/P The ac coupled inverting input to the Rx input
amplifier (AMP1).
14 DEMODFB O/P The output of the Rx input amplifier (AMP1) and
the input to the audio filter/limiter section.
15 FILTER OUT O/P Output of the audio filter/limiter section. In
powersave mode this output is connected to
via a 500kΩ resistor.
V
BIAS
16 FFSK/DTMFOUT O/P The 1200 or 2400 baud FFSK Tx output and the
DTMF encoder output. When enabled but not
transmitting FFSK or DTMF signals, or when in
powersave mode, this output is connected to
via a 500kΩ resistor.
V
BIAS
On power-up, this output can be any level: a
General Reset command is required to ensure
that this output attains V
BIAS
initially.
17 SUM IN I/P Input to the audio summing amplifier (AMP2).
18 SUM OUT O/P Output of the audio summing amplifier (AMP2).
19 MOD1 IN I/P Input to MOD1 audio gain control.
20 VOL IN I/P Input to the audio volume control.
21 AUDIO OUT O/P Output of the audio volume control.
22 MOD1 O/P Output of MOD1 audio gain control.
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 5 D/829/4
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.3 Signal List (continued)
Package
D2/D5
Signal Description
Pin No. Name Type
23 MOD2 O/P Output of MOD2 audio gain control.
24 V
DD
Power The positive supply rail. Levels and voltages are
dependent upon this supply. This pin should be
decoupled to V
by a capacitor.
SS
Notes: I/P = Input
O/P = Output
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 6 D/829/4
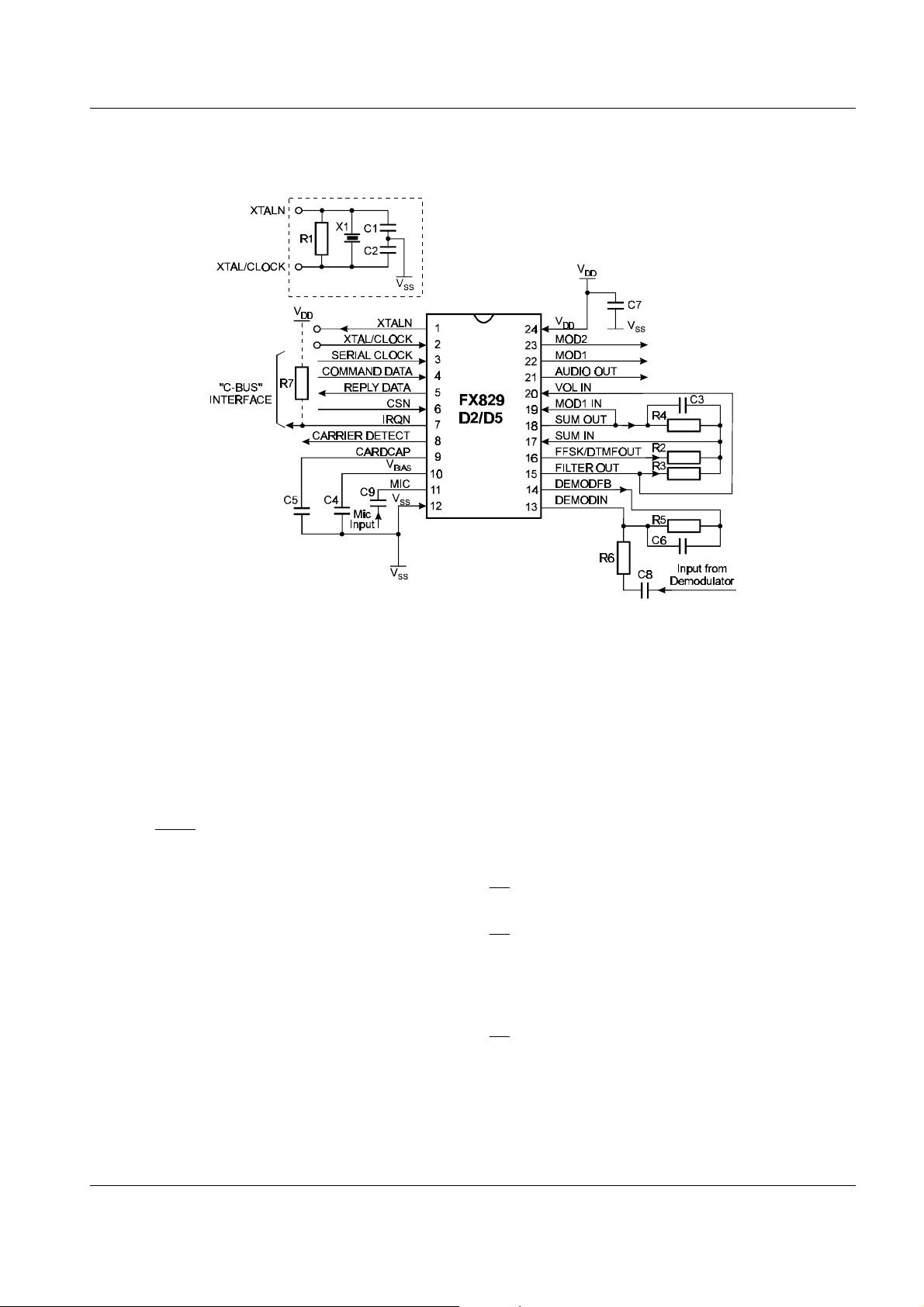
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.4 External Components
C1 22pF ±20% R1 1MW ±5% X1 4.032MHz ±100ppm
C2 22pF ±20% R2 Note 1 ±10%
C3 68pF ±20% R3 Note 1 ±10%
C4 0.1µF ±20% R4 100k
C5 0.1µF ±10% R5 100k
W ±10%
W ±10%
C6 100pF ±20% R6 Note 2 ±10%
C7 0.1µF ±20% R7 22k
W ±10%
C8 Note 2 ±20%
C9 5.6nF ±20%
Notes: 1. R2, R3, R4 and C3 form the gain components for the Summing Amplifier (AMP2).
R2 and R3 should be chosen as required from the system specification, using the
following formulae:
Audio Gain =
DTMF Gain=
R4
−
R3
R4
−
R2
2. R5, R6, C6 and C8 form the gain components for the Rx Input Amplifier (AMP1).
R6 should be chosen as required by the signal level, using the following formula:
Gain =
R5
−
R6
C8 x R6 should be chosen so as not to compromise the low frequency performance of
this product.
Figure 2 Recommended External Components
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 7 D/829/4

Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.5 General Description
The FX829 consists of five main sections: the audio filter section, the programmable attenuators, the
DTMF encoder, the FFSK transmitter and the FFSK receiver. All these sections are controlled via a
serial ("C-BUS") interface. The four sections are described below.
Audio Filtering
This consists of an input amplifier and a common audio filter section, which may be switched between
Rx and Tx. The filter section comprises an anti-alias filter followed by low-pass and high-pass filtering
with an amplitude limiter to set the maximum deviation. Three variable attenuation blocks may be
used to set the volume (in Rx) or the modulation level (in Tx). Pre- and de-emphasis can be added
externally using resistors and capacitors around AMP1, AMP2 and the microphone amplifiers, see
Figure 7. The anti-alias filter is designed to reduce aliasing effects above 50kHz which is
approximately half the internal filter's sample rate.
The filtering is designed to meet the ETS 300 086 specification.
Various powersave modes are incorporated.
MOD1 and MOD2 Attenuators
The MOD1 input can be connected directly to SUM OUT, so that the MOD1 and MOD2 outputs can
then be used for two point modulation. Alternatively, the MOD1 attenuator can be used for auxiliary
gain adjustment, in which case the input signal must be ac coupled with a suitable capacitor.
DTMF Encoder
This generates the standard DTMF tones according to the CONTROL 2 Register settings. It also has
a powersave mode.
FFSK Tx
The Tx function of the FFSK modem operates continuously in a free format mode, which means that
the preamble and frame sync have to be programmed like normal data bytes. However, a 2-byte
checksum may be generated automatically by simply marking the beginning and end of the data to be
used. Any number of whole bytes may be used to generate the checksum.
After the last byte has been transmitted one additional "hang bit" is automatically added to the end. All
Tx operations are programmed from the "C-BUS" via an 8-bit buffer. The Tx part of the FFSK modem
has a powersave mode.
The modulation output is one cycle of 1200Hz for a "1" and one and a half cycles of 1800Hz for a "0"
at 1200 baud, or one half cycle of 1200Hz for a "1" and one cycle of 2400Hz for a "0" at 2400 baud.
FFSK Rx
In Rx, the modem automatically achieves bit sync and then recognises the previously selected SYNC
and/or SYNT word of the MPT1327, ETS 300 230 or PAA1382 specifications. At the same time as
the above, it can also recognise a user programmed 16-bit RX SYNC WORD.
On reception of the SYNC, SYNT or RX SYNC WORD, the device will automatically (or manually at
any time) start checking the data and checksum. It provides a 1-bit correct/incorrect result every byte,
so that any number of bytes can be checked.
The Rx part of the FFSK modem operates at 1200 or 2400 baud and has a powersave mode. Both
FFSK Rx and Tx work in half duplex mode.
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 8 D/829/4
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
1.5.1 Software Description
Address/Commands
Instructions and data are transferred, via "C-BUS", in accordance with the timing information given in
Figure 11.
Instruction and data transactions to and from the FX829 consist of an Address/Command (A/C) byte
followed by either:
(i) a further instruction or data (1 or 2 bytes) or
(ii) a status or Rx data reply (1 byte)
8-bit Write Only Registers
HEX
ADDRESS/
COMMAND
$01 RESET N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
$10 CONTROL 1 AMP1 AMP2 AUDIO FFSKRX FFSKTX UK/F MIC B/W
$11 CONTROL 2 CHKSUM DTMFEN DTMFHI DTMFLO DTMF3 DTMF2 DTMF1 DTMF0
REGISTER
NAME
BIT 7
(D7)
BIT 6
(D6)
BIT 5
(D5)
BIT 4
(D4)
BIT 3
(D3)
BIT 2
(D2)
BIT 1
(D1)
BIT 0
(D0)
$13 AUDIO
ATTENUATION 0 0 0 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
$40 CONTROL 3/
IRQ ENABLE
$43 TXDATA
0 1200/2400 TXIDLEM RXDATAM TXDATAM
<----------------------------------------------- TXDATA ----------------------------------------------->
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
<-------------------------- GAIN -------------------------->
RX SYNC
WORD
PRIME
SYNT
PRIME
16-bit Write Only Registers
HEX
ADDRESS/
COMMAND
$12 MOD LEVELS MOD 1 <-------------------------- MOD 1 -------------------------->
$44 RX SYNC <------------------------------------------- RX SYNC WORD ----------------------------------------->
REGISTER
NAME
(1) 0 0 ENABLE BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
(2) 0 0 0 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
WORD (1) BIT 15 BIT 14 BIT 13 BIT 12 BIT 11 BIT 10 BIT 9 BIT 8
(2) BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
BIT 7
(D7)
<------------------------------------------- RX SYNC WORD ----------------------------------------->
BIT 6
(D6)
BIT 5
(D5)
BIT 4
(D4)
<-------------------------- MOD 2 -------------------------->
BIT 3
(D3)
BIT 2
(D2)
BIT 1
(D1)
SYNC
PRIME
BIT 0
(D0)
Write Only Register Description
RESET Register (Hex address $01)
The reset command has no data attached to it. It sets the device registers into the specific states as listed
below:
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 9 D/829/4
Baseband Signal Processor FX829
REGISTER NAME BIT 7
(D7)
CONTROL 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CONTROL 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CONTROL 3/IRQ ENABLE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
AUDIO ATTENUATION 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TXDATA X X X X X X X X
MOD LEVELS (1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MOD LEVELS (2) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RX SYNC WORD (1) X X X X X X X X
RX SYNC WORD (2) X X X X X X X X
STATUS 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RXDATA X X X X X X X X
BIT 6
(D6)
BIT 5
(D5)
BIT 4
(D4)
BIT 3
(D3)
BIT 2
(D2)
BIT 1
(D1)
X = undefined
CONTROL1 Register (Hex address $10)
This register is used to control the functions of the device as described below:
AMP1
(Bit 7)
AMP2
(Bit 6)
When this bit is "1", AMP1 is enabled.
When this bit is "0", AMP1 is disabled (i.e. powersaved).
When this bit is "1", both AMP2 and MOD2 are enabled.
When this bit is "0", both AMP2 and MOD2 are disabled (i.e. powersaved) and the
MOD2 output is pulled to V
via a 1MW resistor.
BIAS
BIT 0
D0)
AUDIO
(Bit 5)
FFSKRX
(Bit 4)
FFSKTX
(Bit 3)
UK/F
(Bit 2)
When this bit is "1", the audio filter/limiter section is enabled.
When this bit is "0", the audio filter/limiter section is disabled (i.e. powersaved).
When this bit is "1", the FFSK Rx is enabled.
When this bit is "0", the FFSK Rx is disabled (i.e. powersaved).
Note:
1. The FFSK Rx and Tx cannot both be enabled at the same time. If both
FFSKRX and FFSKTX are "1", then they will both be disabled
(i.e. powersaved).
When this bit is "1", the FFSK Tx is enabled.
When this bit is "0", the FFSK Tx is disabled (i.e. powersaved).
Note:
1. The FFSK Tx and Rx cannot both be enabled at the same time. If both
FFSKTX and FFSKRX are "1", then they will both be disabled
(i.e. powersaved).
2. The DTMF Encoder and FFSK Tx cannot both be enabled at the same time.
If both DTMFEN and FFSKTX are "1", then they will both be disabled.
When this bit is "1", the SYNC/SYNT is set to the PAA standard of
"1011010000110011" (SYNC)
When this bit is "0", the SYNC/SYNT is set to the MPT standard of
"1100010011010111" (SYNC)
1997 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 10 D/829/4
 Loading...
Loading...