Consumer Microcircuits Limited FX375LS, FX375LG, FX375J Datasheet
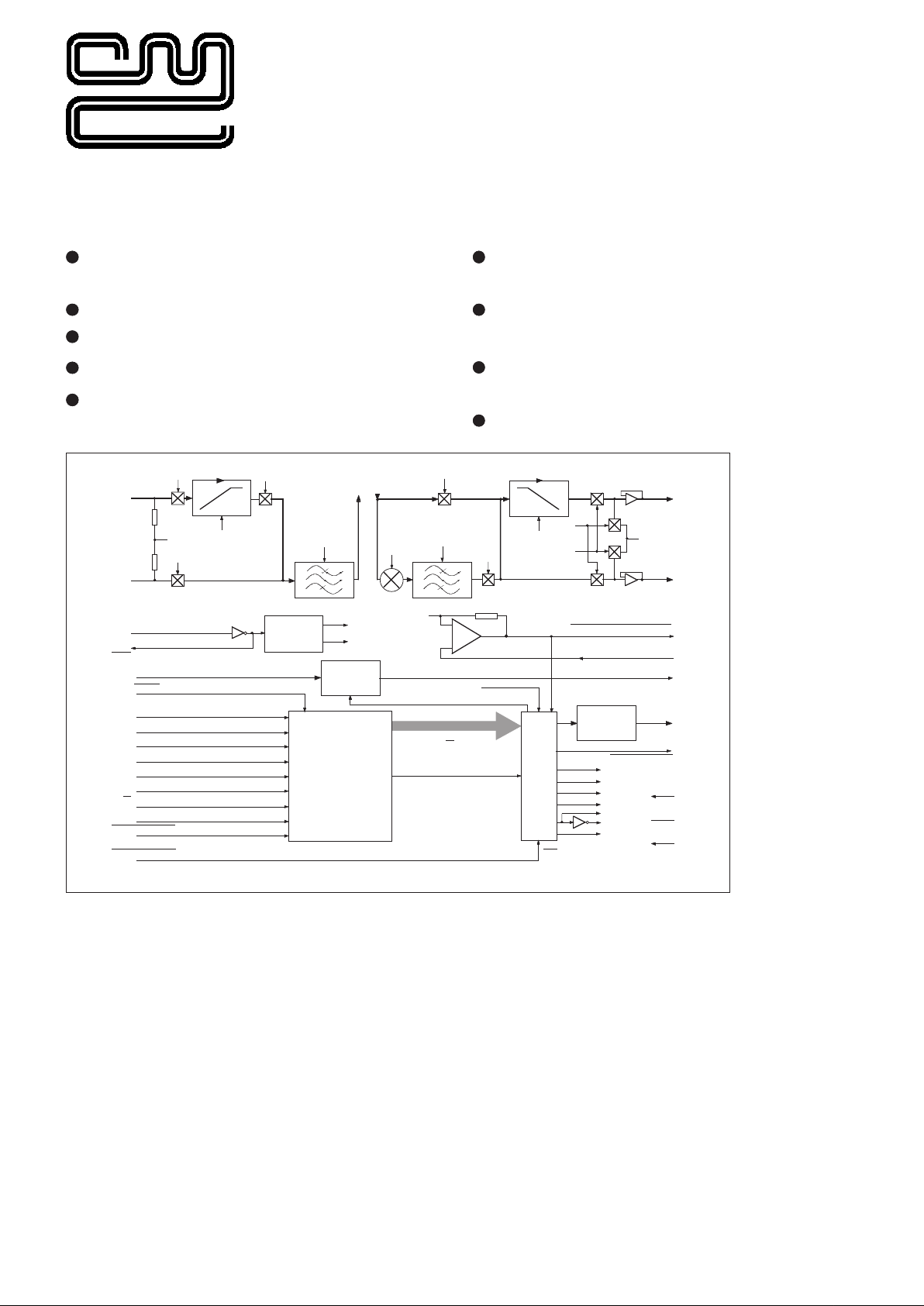
FX375 Private Squelch Circuit
CML Semiconductor Products
PRODUCT INFORMATION
Publication D/375/4 July 1994
Fig.1 Internal Block Diagram
Brief Description
The FX375 is a Low-Power CMOS LSI microcircuit
designed for Tone Operated Voice Privacy in
communication systems.
This half-duplex device consists of a Fixed Frequency
Voice Band Inverter interfaced with a Continuous Tone
Controlled Squelch System (CTCSS) Encoder/
Decoder, whose allocated tone is used for voice
privacy and audio squelch operation.
Frequency Inversion is achieved by modulating the
input audio with a fixed carrier frequency to exchange
the high and low frequencies of the voice band, making
the resulting audio output unintelligible to receivers not
equipped with a compatible system.
The on-chip CTCSS Dencoder is capable of encoding
and decoding any one of 38 sub-audio tones in the
range 67.0Hz to 250.3Hz, these Xtal derived tones are
selected by a 6-bit binary word that can be loaded to
the device in either a serial or parallel format.
The Privacy function is exclusive only to units using the
same tone set, other intercepted signals remain "as
transmitted."
A 'Press to Listen' facility allows monitoring of the
channel prior to transmitting.
This device has separate, switched Rx and Tx voice,
and tone audio paths. Voice paths use switched
capacitor bandpass filters for the attenuation of subaudio tones and unwanted modulation products.
6dB/octave pre- and de-emphasis filtering in the Tx
path maintains natural sounding audio from this device
when embodied in communication transceivers.
The FX375, which is available in DIL and SMT
packages, can be simply controlled by switches, or
interfaced to a µProcessor.
External requirements are a single 5-volt supply, an
external 4.0MHz Xtal or clock input and signal coupling
components.
FX375
On-Chip Pre- and De-Emphasis
Filtering in the Tx Path
38 Programmable Tones
+ 'NoTone' Facility
Audio Path Filtering
(300Hz – 3033Hz)
Low Power 5V CMOS
Tone Operated Private/Clear
Switching
CTCSS Tone Encode/Decode
Separate Rx/Tx Speech Paths
Fixed Frequency Speech Inversion
µP Compatible Interface with Serial
or Parallel Control Loading
Tx AUDIO OUTPUT
Rx AUDIO OUTPUT
BIAS
Rx
Tx
BIAS
Rx
Tx
Tx
PRIVATE
CLEAR
6dB/OCTAVE
– 6dB/OCTAVE
Tx AUDIO INPUT
Rx AUDIO INPUT
FILTER
OUTPUT
BALANCED
MODULATOR
INPUT
f
CLK2
f
CARRIER
f
EMPH
f
EMPH
f
CLK1
Rx TONE DETECT OUTPUT
Rx TONE DECODER OUTPUT
CONTROL
PRIVATE ENABLE
LOGIC
Rx PATH
Tx PATH
PRIVATE
TX
TONE
OUTPUT
–
+
CTCSS
TONE
DETECT
HYSTERESIS
REFERENCE
LOAD/LATCH
f
CARRIER
f
CLK1
f
CLK2
LD5LD
0
XTAL
Rx TONE INPUT
Rx/Tx
CONTROL
PRESS TO LISTEN
V
SS
V
DD
V
BIAS
PTL
DECODE COMPARATOR INPUT
3333Hz
D INPUT
0
D INPUT
1
D or SERIAL CLOCK INPUT
2
D or SERIAL DATA INPUT
3
D or SERIAL ENABLE 2
4
D or SERIAL ENABLE 1
5
8-BIT
SHIFT
REGISTER
AND
LATCHES
XTAL
3333Hz
FILTERS
f
EMPH
CLOCKS
NOTONE OUTPUT
Features

2
Pin Number Function
FX375J
FX375LH
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Xtal/Clock: The input to the clock oscillator inverter. An external 4MHz Xtal or clock
input is to be applied at this pin. See Figure 2.
Xtal: The 4MHz output of the clock oscillator inverter. See Figure 2.
Load/Latch: This input regulates the operation of the eight input latches : D0, D1, D2,
D3, D4, D5, Rx/Tx and Private Enable for both parallel and serial input load modes.
Rx/Tx and Private Enable inputs can be used independently in either mode by the use
of Load/Latch and Control inputs configured as shown in Table 3, the data format
(D0 – D5), remains as set. This input has an internal 1MΩ pullup resistor.
D5 – (Serial Enable 1) :
D
4
– (Serial Enable 2) :
D3 – (Serial Data Input) :
D2 – (Serial Clock Input) :
D
1
D
0
Rx Tone Decode Output : The output of the decode comparator. In Rx a logic '0'
indicates 'CTCSS tone decoded' above the internal reference level, or Notone
programmed. This action internally enables the Rx audio path and Frequency Inversion
function (when applicable) as shown in Table 1. In Tx this output is a logic '1'.
Decode Comparator Input : A logic '1' at this pin, in Rx, is compared internally with a
fixed reference level, a more positive input value will produce a logic '0' at the Rx Tone
Decode Output. This input should be externally connected to the Rx Tone Detect
Output via external integrator components C7, R2, R3, D1 (see Figure 2).
Rx Tone Detect Output : This output, in Rx, goes to a logic '1' when a valid,
programmed CTCSS tone is received at the Rx Tone Input. This input should be
externally connected to the Decode Comparator Input via external integrator
components C7, R2, R3, D1 (see Figure 2).
Notone Output : Outputs a logic '0' when a " Notone" CTCSS code has been
programmed . It can be used to operate squelch circuitry under receive "Notone"
conditions.
VSS : Negative supply rail (GND).
The FX375LG and LS package styles are configured as a serial-data loading device,
Parallel Programing Inputs D0, D1 and D5, and the NOTONE Output pin functions are not
available.
FX375LG
FX375LS
2
3
4
–
5
6
7
–
–
8
9
10
–
11
The Rx/Tx tone programming and function inputs.
Programmed as shown in Table 2 these inputs will select
the CTCSS tone frequency and parallel or serial loading
function. Notone, when set in receive, enables the Rx
Audio Output and forces the Rx Tone Decode Output to a
logic '0,' in transmit the Tx Tone Output is held at V
BIAS
(Notone). These inputs each have an internal 1MΩ pullup
resistor. If FX375LG or LS package styles are used Pin 5
(Serial Enable 2) should be externally connected to VSS.
3
Pin Number Function
FX375J
FX375LH
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
FX375LG
FX375L
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
1
Tx Tone Output : This is the buffered, programmed CTCSS tone sinewave output in
Tx. During Rx and Notone operation this output is held at V
BIAS
. See note "g," page 7 with
reference to capacitive load limits of this output.
V
BIAS
: This bias pin is set internally to VDD/2. It must be externally decoupled using a
capacitor, C8, of 1.0µF (minimum) to VSS, see Figure 2.
Filter Output : The Input Audio Bandpass Filter output, this pin must be connected to
the Balanced Modulator Input via a capacitor, C6, and decoupled to VSS by C10, see
Figure 2.
Balanced Modulator Input : The input to the Balanced Modulator, this pin must be
connected to the Filter Output via a capacitor, C6, see Figure 2.
Rx Audio Output : Outputs the received audio from a buffered output stage and is held
at V
BIAS
when in Tx.
Tx Audio Output : The output of the audio path in the Tx mode and is held at V
BIAS
when in Rx.
Rx Audio Input : The Audio input pin for the Rx mode. Input signals should be a.c.
coupled via an external capacitor, C4, see Figure 2.
Tx Audio Input : This is the voice input pin for the Tx mode. Signals should be a.c.
coupled via an external capacitor, C3, see Figure 2.
PTL : The "Press To Listen" function input, in the receive mode a logic '0' enables the
Rx Audio Output directly, overriding tone squelch but not intercepting a private
conversation. In the transmit mode a logic '0' reverses the phase of the Tx Tone Output
for "squelch tail" reduction (see Table 1), this function, in Tx, should be accurately
applied by a timing circuit to ensure correct system operation.
Control : This input, with Load/Latch, selects the operational mode of Rx/Tx and
Private Enable functions, see Table 3.
Rx/Tx : Selects the receive or transmit mode (Rx = '1', Tx = '0') and can be loaded by
serial or parallel means, as described in Table 3.
Private Enable : This input selects either Private or Clear modes (Clear = '1',
Private ='0'), and can be loaded by serial or parallel means, as described in Table 3. In
Rx this input could be taken from the Rx Tone Decode Output. This input has an internal
1MΩ pullup resistor.
Rx Tone Input : The received tone input to the on-chip CTCSS decoder and should be
a.c. coupled via capacitor C5, see Figure 2.
V
DD
: Positive supply rail. A single +5V power supply is required.
 Loading...
Loading...