Consumer Microcircuits Limited CMX589AP4, CMX589AE2, CMX589AD5, CMX589AD2 Datasheet
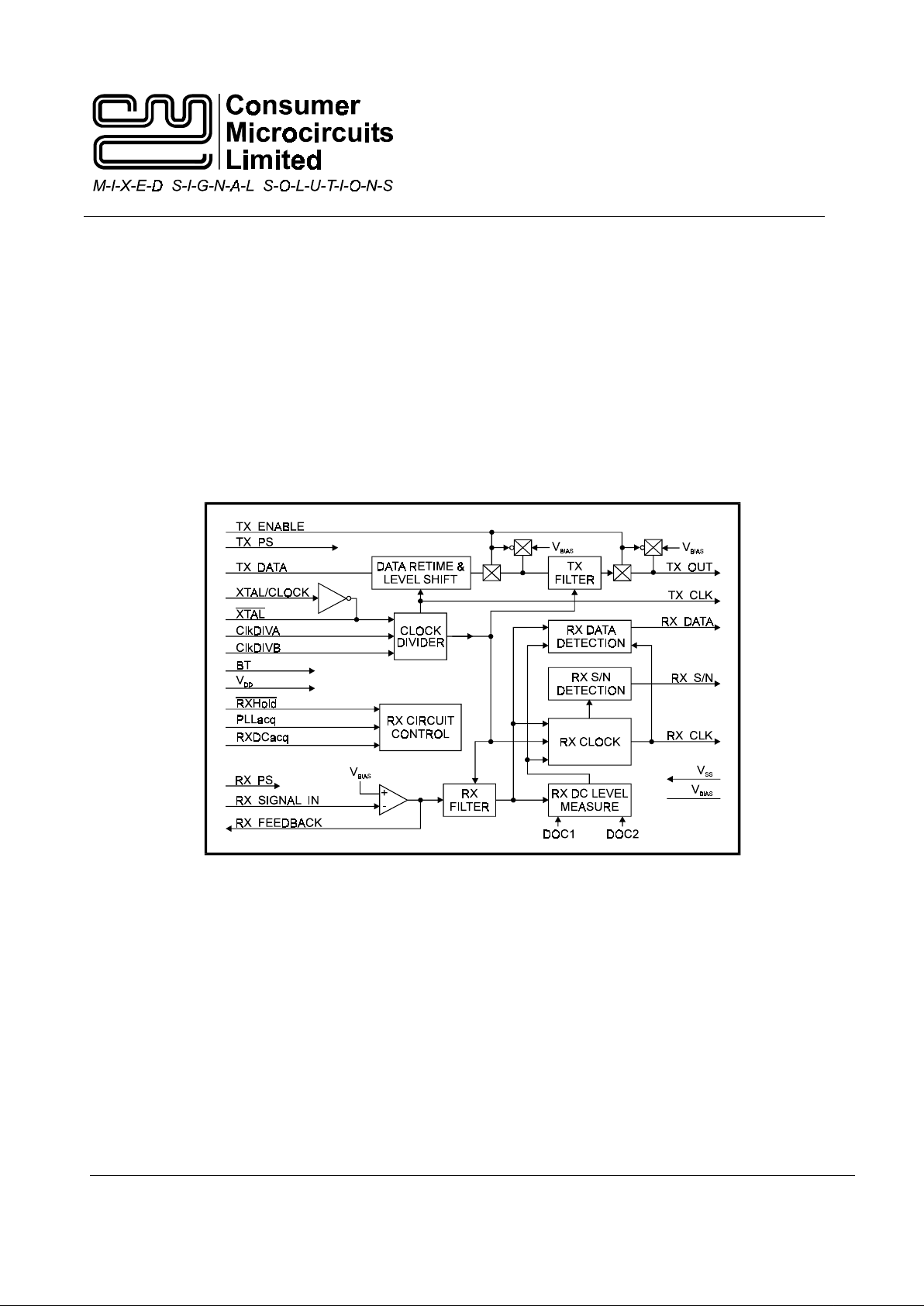
CMX589A
GMSK Modem
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited
D/589A/3 September 1998 Provisional Information
Features and Applications
• Data Rates from 4kbps to 200kbps
• Full or Half Duplex Gaussian Filter and Data
Recovery for Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) Designs
• Selectable BT: (0.3 or 0.5)
• Low Power
3.0V, 20kbps, 1.5mA typ.
5.0V, 64kbps, 4.0mA typ.
• Low Current Non-DSP Solution
• Small TSSOP Packs fit PCMCIA/PC Cards
• Portable Wireless Data Applications
Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD)
Mobitex Mobile Data System
• Spread Spectrum Data Links
• GPS/Differential GPS Wireless Links
• Point-of-Sale Terminals
• Low Power Wireless Data Link for PCs,
Laptops, and Printers
Brief Description
The CMX589A is a single-chip synchronous data pump/modem designed for Wireless Data Applications.
Employing Gaussian filtering for Minimum shift Keying (GMSK) baseband modulation applications, the
CMX589A features a wide range of available data rates from 4k to 200k bps. Data Rates and the choice of
BT (0.3 or 0.5) are pin programmable to provide for different system requirements.
The Tx and Rx digital data interfaces are bit serial, synchronized to generated Tx and Rx data clocks.
Separate Tx and Rx Powersave inputs allow full or half-duplex operation. Rx input levels can be set by
suitable AC and DC level adjusting circuitry built with external components around an on-chip Rx Input
Amplifier.
Acquisition, Lock, and Hold of Rx data signals are made easier and faster by the use of Rx Control Inputs to
clamp, detect, and /or hold input data levels and can be set by the µProcessor as required. The Rx S/N output
provides an indication of the quality of the received signal.
The CMX589A may be used with a 3.0V to 5.5V power supply and is available in the following packages:
24-pin TSSOP (CMX589AE2), 24-pin SSOP (CMX589AD5), 24-pin SOIC (CMX589AD2), and 24-pin PDIP
(CMX589AP4).

GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 2 D/589A/3
Contents
Section Page
Features and Applications .................................................................................................1
Brief Description .................................................................................................................1
Block Diagram.....................................................................................................................2
2 Signal List.........................................................................................................................4
3 External Components......................................................................................................6
4 General Description.........................................................................................................8
4.1 Clock Oscillator Divider.........................................................................................................8
4.2 Receive ................................................................................................................................8
4.2.1 Rx Signal Path Description..........................................................................................................8
4.2.2 Rx Circuit Control Modes.............................................................................................................9
4.2.3 Rx Clock Extraction...................................................................................................................10
4.2.4 Rx Data Extraction.....................................................................................................................10
4.2.6 Rx Signal Quality.......................................................................................................................12
4.3 Transmit ............................................................................................................................. 12
4.3.1 Tx Signal Path Description........................................................................................................12
4.4 Data Formats...................................................................................................................... 15
4.5 Acquisition and Hold Modes ...............................................................................................15
5 Application......................................................................................................................16
5.1 Radio Channel Requirements.............................................................................................16
5.1.1 Bit Rate, BT, and Bandwidth .....................................................................................................16
5.1.2 FM Modulator, Demodulator and IF...........................................................................................16
5.1.3 Two-Point Modulation................................................................................................................17
5.2 AC Coupling of Tx and Rx Signals...................................................................................... 18
6 Performance Specifications.......................................................................................... 19
6.1 Electrical Specifications......................................................................................................19
6.1.1 Absolute Maximum Limits..........................................................................................................19
6.1.2 Operating Limits ........................................................................................................................20
6.1.3 Operating Characteristics..........................................................................................................21
6.2 Packages............................................................................................................................23
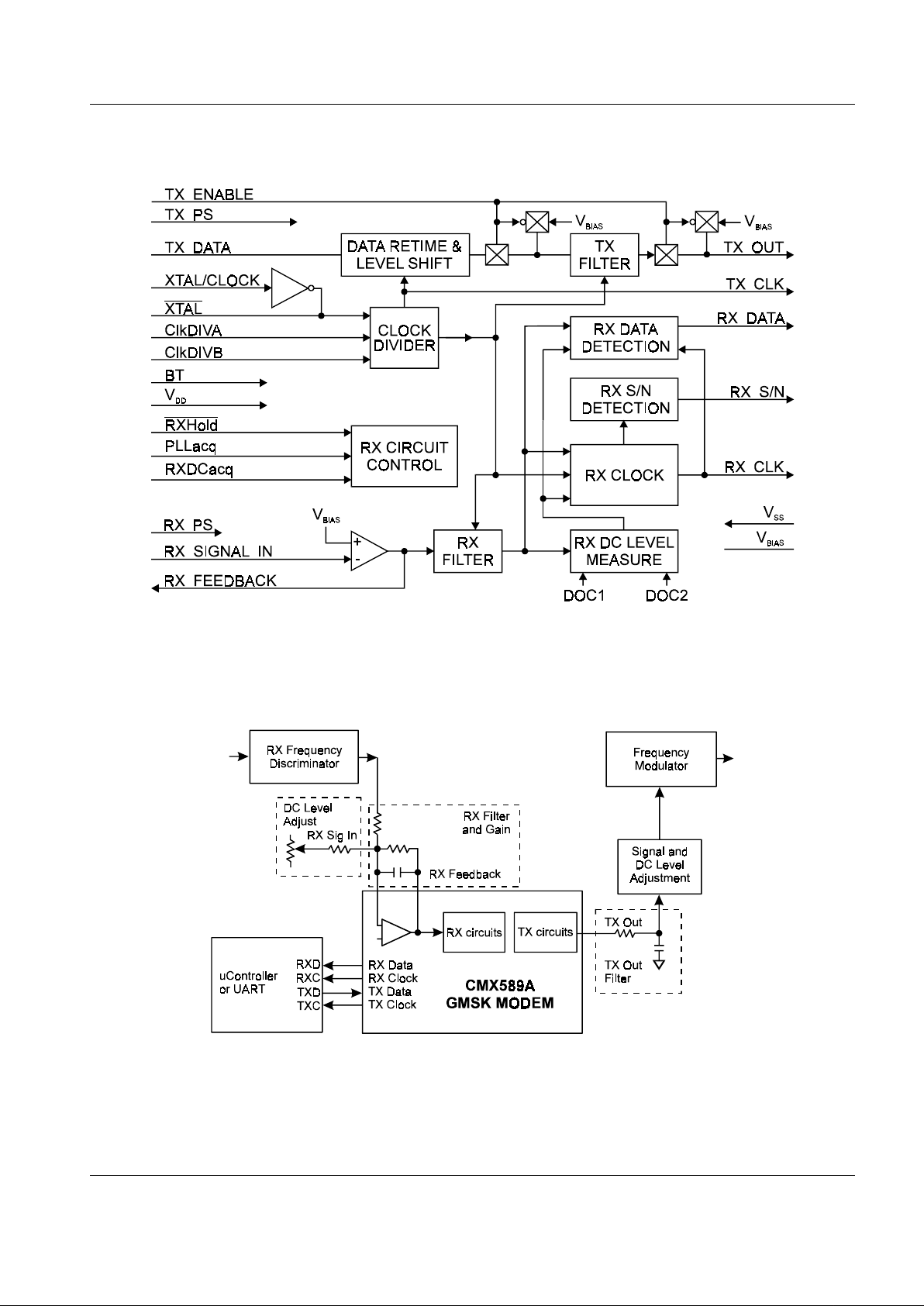
GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 3 D/589A/3
Block Diagram
Figure 1: Block Diagram
Figure 2: System Block Diagram
GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 4 D/589A/3
2 Signal List
Pin No.
E2/D5/
D2/P4
Signal Type Description
1 XTALN O/P The output of the on-chip clock oscillator.
2 XTAL/CLOCK I/P The input to the on-chip Xtal oscillator. A Xtal, or externally derived clock
(f
XTAL
) pulse input should be connected here. If an externally generated
clock is to be used, it should be connected to this pin and the XTALN pin
left unconnected. Note: Operation without a suitable Xtal or clock input
may cause device damage.
3 ClkDivA I/P Logic level inputs control the internal clock divider and therefore the
transmit and receive data rate. See Table 4.
4 ClkDivB I/P Logic level inputs control the internal clock divider and therefore the
transmit and receive data rate. See Table 4.
5 RxHOLDN I/P A logic ‘0’ applied to this input will freeze the Clock Extraction and Level
Measurement circuits unless they are in ‘Acquire’ mode.
6 RxDCacq I/P A logic ‘1’ applied to this input will set the Rx Level Measurement circuitry
to the ‘Acquire’ mode. See Table 6.
7 PLLacq I/P A logic ‘1’ applied to this input will set the Rx Clock Extraction circuitry to
the ‘Acquire’ mode. See Table 5.
8 Rx PSAVE I/P A logic ‘1’ applied to this input will powersave all receive circuits except
for Rx CLK output (which will continue at the set bit-rate) and cause the
Rx Data and Rx S/N outputs to go to a logic ‘0’.
9V
BIAS
The internal circuitry bias line, held at VDD/2. This pin must be bypassed
to V
SS
by a capacitor mounted close to the pin.
10 Rx FB O/P Output of the Rx Input Amplifier.
11 Rx Signal In I/P Input to Rx input amplifier.
12 V
SS
power Negative supply (GND).
13 DOC1 Connections to the Rx Level Measurement Circuitry. A capacitor should
be connected from this pin to V
SS
.
14 DOC2 Connections to the Rx Level Measurement Circuitry. A capacitor should
be connected from this pin to V
SS
.
15 BT A logic level to select the modem BT (the ratio of the Tx Filter's -3dB
frequency to the Bit-Rate). A logic ‘1’ = BT of 0.5 and a logic ‘0’ = BT of
0.3.

GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 5 D/589A/3
Pin No.
E2/D5/
D2/P4
Signal Type Description
16 Tx Out I/P Gaussian filtered Tx output signal. In powersave mode the Tx Out pin is
high impedance.
17 Tx Enable I/P A logic ‘1’ applied to this input, enables the transmit data path, through
the Tx Filter to the Tx Out pin. A logic ‘0’ will place the Tx Out pin to
V
BIAS
via a high impedance.
18 Tx PSAVE I/P A logic ‘1’ applied to this input will powersave all transmit circuits except
for the Tx Clock.
19 Tx Data I/P The logic level input for the data to be transmitted. This data should be
synchronous with Tx CLK.
20 Rx Data I/P A logic level output carrying the received data, synchronous with
Rx CLK.
21 Rx CLK I/P A logic level clock output at the received data bit-rate.
22 Tx CLK I/P A logic level clock output at the transmit data bit-rate.
23 Rx S/N O/P A logic level output which may be used as an indication of the quality of
the received signal.
24 V
DD
power Positive supply. Levels and voltages within the device are dependent
upon this supply. This pin should be bypassed to V
SS
by a capacitor
mounted close to the pin.
Table 1: Signal List
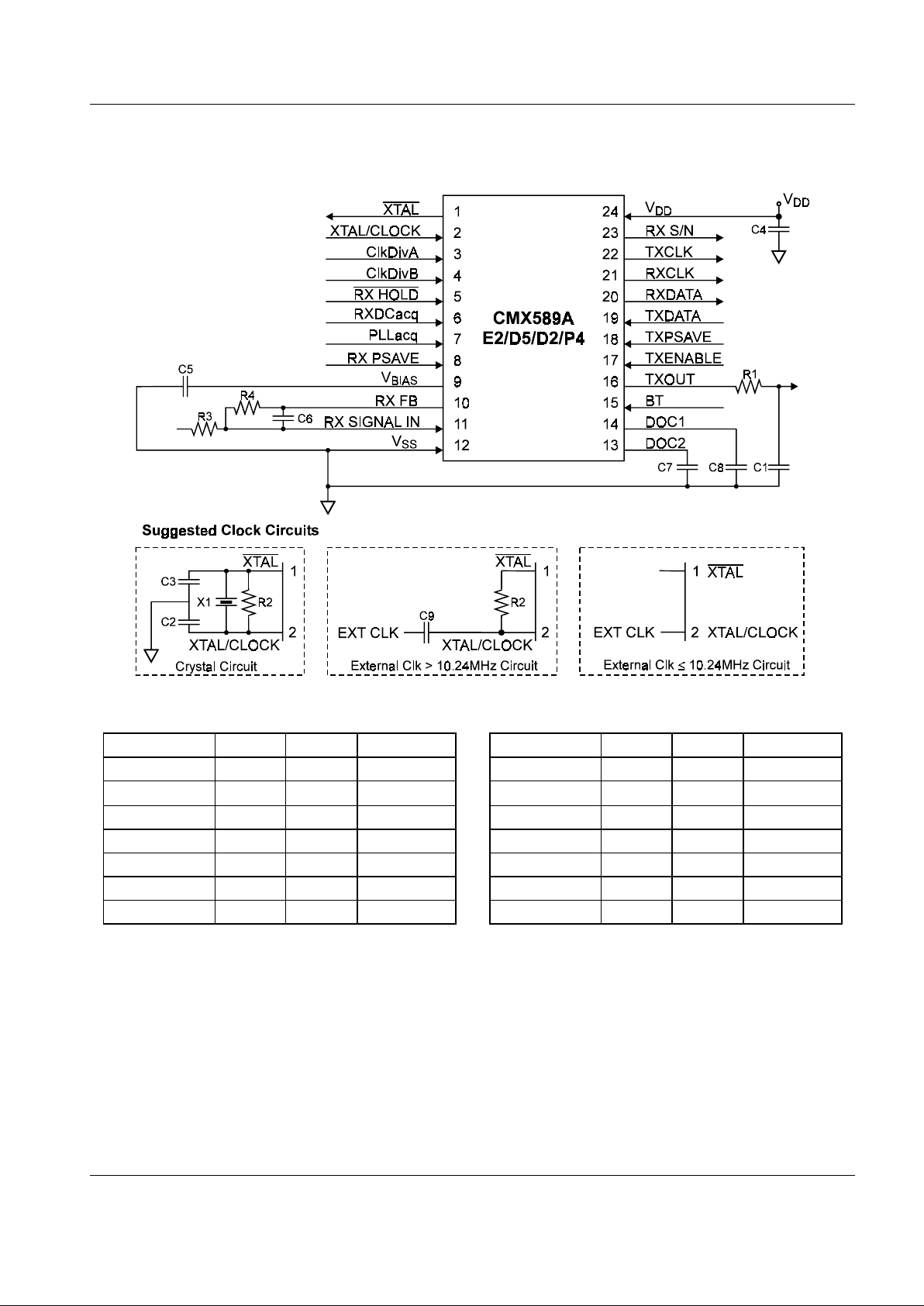
GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 6 D/589A/3
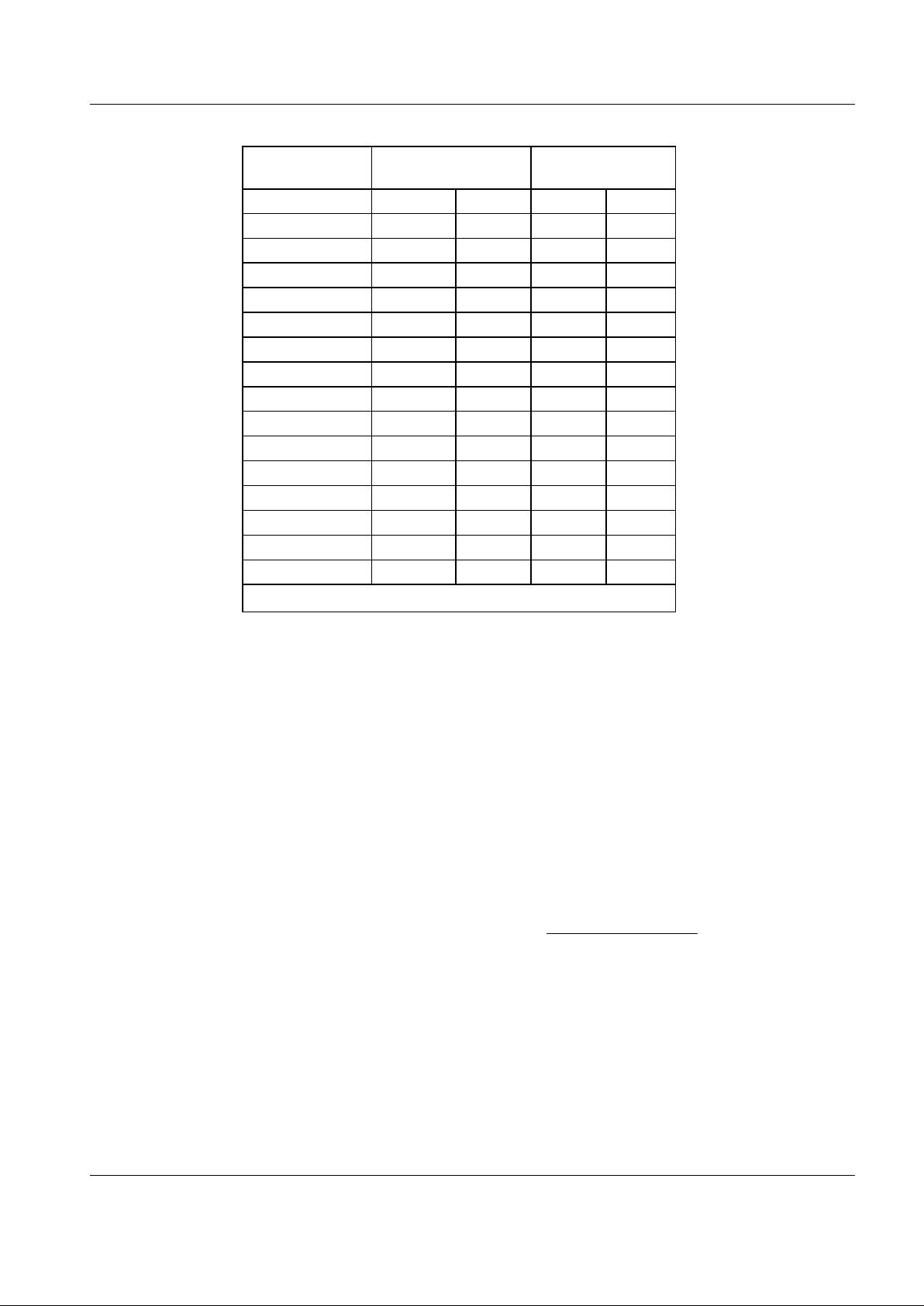
3 External Components
Figure 3: Recommended External Components
Component Notes Value Tolerance Component Notes Value Tolerance
R1 1 ±5% C4 0.1µF ±20%
R2
1.0M
Ω
±10% C5 1.0µF ±20%
R3 2 ±10% C6 5 ±20%
R4 3 ±10% C7 6
C1 1 ±10% C8 6
C2 4
C3 4 X1 8
Table 2: Recommended External Components
Recommended External Component Notes:
1. The RC network formed by R1 and C1 is required between the Tx Out pin and the input to the modulator.
This network, which can form part of any DC level shifting and gain adjustment circuitry, forms an important
part of the transmit signal filtering. The ground connection to the capacitor C1 should be positioned to give
maximum attenuation of high-frequency noise into the modulator.
The component values should be chosen so that the product of the resistance and the capacitance is:
For a BT of 0.3 R1C1 = 0.34/bit rate (bps)
For a BT of 0.5 R1C1 = 0.22/bit rate (bps)
GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 7 D/589A/3
Data Rates
(kbps)
BT = 0.3 BT = 0.5
R1 C1 R1 C1
4
120k
Ω
680pF
120k
Ω
470pF
4.8
100k
Ω
680pF
100k
Ω
470pF
8
91k
Ω
470pF
120k
Ω
220pF
9.6
91k
Ω
390pF
47k
Ω
470pF
16
47k
Ω
470pF
91k
Ω
150pF
19.2
100k
Ω
180pF
91k
Ω
120pF
32
47k
Ω
220pF
47k
Ω
150pF
38.4 *
47k
Ω
180pF
47k
Ω
120pF
64 *
56k
Ω
100pF
51k
Ω
68pF
80 *
39k
Ω
68pF
128 *
82k
Ω
22pF
144 *
68k
Ω
22pF
160 *
62k
Ω
22pF
176 *
56k
Ω
22pF
192 *
51k
Ω
22pF
* VDD ≥ 4.5V, external clock
Table 3: Data Rate vs. BT and Selected External Component Values
Note
: In all cases, the value of R1 should not be less than 20.0kΩ, and that the calculated value of C1
includes calculated parasitic capacitance.
2. R3, R4 and C6 form the gain components for the Rx Input signal. R3 should be chosen as required by the
signal input level.
3. For bit rate ≤ 64kbps, R4 = 100kΩ. For bit rate > 64kbps, R4 = 10kΩ.
4. The values chosen for C2 and C3 (including stray capacitance), should be suitable for the applied V
DD
and
the frequency of X1.
As a guide: C2 = C3 = 33pF at 1.0MHz falling to 18pF at the maximum frequency.
At 3.0V, C2 = C3 = 33pF falling to 18pF at 5.0MHz the equivalent series resistance of X1 should be less
than 2.0KΩ falling to 150Ω at the maximum frequency. Stray capacitance on the Xtal/Clock circuit pins
must be minimized.
5. For bit rate ≤ 64kbps, C6 = 22pF. For bit rate > 64kbps, C6 =
Ω×π××
10k 2 rate bit 3
1
e.g. for 128kbps, C6 = 41.1pF.
6. C7 and C8 should both be .015µF for a data rate of 8kbps, and inversely proportional to the data rate for
other data rates, e.g. 0.030µF at 4kbps, 1800pF at 64kbps, 680pF at 192kbps.
7. The tolerance of C9 is not very critical because it primarily serves as a dc blocking capacitor.
8. The CMX589A can operate correctly with the Xtal frequencies between 1.0MHz and 16.0MHz
(V
DD
= 5.0V) and 1.0MHz to 5.0MHz (VDD = 3.0V). External clock frequencies up to 25.6MHz (V
DD
≥
4.5V)
are also supported (See Table 4 for examples.) For best results, a crystal oscillator design should drive the
clock inverter input with signal levels of at least 40% of V
DD
, peak to peak. Tuning fork crystals generally
cannot meet this requirement. To obtain crystal oscillator design assistance, consult your crystal
manufacturer. Operation of this device without a Xtal or Clock input may cause device damage.
GMSK Modem CMX589A
1998 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 8 D/589A/3
4 General Description
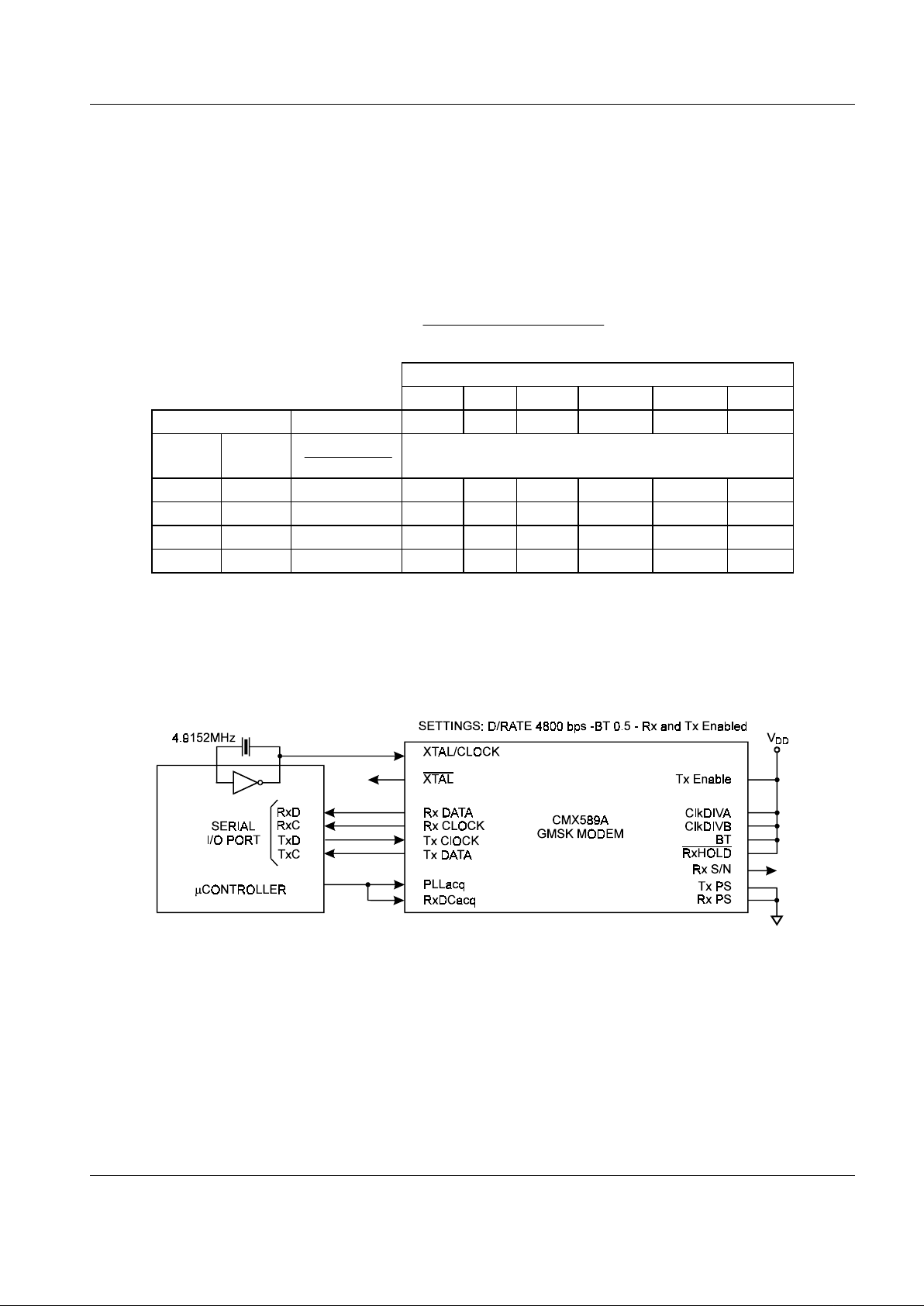
4.1 Clock Oscillator Divider
The Tx and (nominal) Rx data rates are determined by division of the frequency present at the XTALN pin as
generated by the on-chip Xtal oscillator, with external components, or supplied from an external source.
The division ratio is controlled by the logic level inputs on ClkDivA and ClkDivB pins as shown in Table 4,
together with an indication of how various standard data rates may be derived from common µP Xtal
frequencies.
A/B
)
(
ClkDiv Ratio Division
Fre
q
uenc
y
Xtal/Clk
Rate Data
=
Xtal/Clock Frequency (MHz)
24.576* 8.192 4.9152 4.096 2.4576 2.048
Inputs 12.288/3 12.288/5 6.144/3
ClkDivA ClkDivB
Rate Data
Fre
q
Xtal/Clk
Data Rate (kbps)
0 0 128 192* 64* 38.4* 32 19.2 16
0 1 256 96* 32 19.2 16 9.6 8
1 0 512 48* 16 9.6 8 4.8 4
1 1 1024 24* 8 4.8 4
* VDD ≥ 4.5V, external clock
Table 4: Example Clock/Data Rates
Note
: The device operation is not guaranteed above 200kbps or below 4kbps at the relevant supply voltage.
Figure 4: Minimum µController System Connections
4.2 Receive
4.2.1 Rx Signal Path Description
The function of the Rx circuitry is to:
1. Set the incoming signal to a usable level.
2. Clean the signal by filtering.
3. Provide dc level thresholds for clock and data extraction.
4. Provide clock timing information for data extraction and external circuits.
5. Provide Rx data in a binary form.
6. Assess signal quality and provide Signal-to-Noise information.
 Loading...
Loading...