Page 1
USER MANUAL
CANpro/104
CTIM-00043 (0.02) - January 15, 2010
Page 2

CANpro/104 User Manual
Table of Contents
Copyright Notice ................................................................................................................................................ 4
Trademark Acknowledgement ............................................................................................................................ 4
Revision History ................................................................................................................................................. 4
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................................ 5
Features............................................................................................................................................................... 5
Hardware Installation – Rev C & Later .............................................................................................................. 6
Memory vs I/O Spaces ................................................................................................................................... 6
Memory Space .......................................................................................................................................... 6
I/O Space ................................................................................................................................................... 7
CTI CANpro/104 Spaces ............................................................................................................................... 7
Memory Space .......................................................................................................................................... 7
I/O Space ................................................................................................................................................... 7
Memory Space Enabling ........................................................................................................................... 7
Base Address Decoding ................................................................................................................................. 8
PeliCAN vs BasicCAN Addressing Modes ............................................................................................ 10
Addressing Examples .............................................................................................................................. 10
CAN Controller Addressing Table .......................................................................................................... 12
Common Memory Space Address Selections ......................................................................................... 13
Performance Enhancement .......................................................................................................................... 14
CAN Bus Options ........................................................................................................................................ 14
Termination ............................................................................................................................................. 14
9D Connector Shell Ground ................................................................ .................................................... 14
Interrupt Mode and Selections ..................................................................................................................... 14
Single Interrupt Mode ............................................................................................................................. 15
Dual Interrupt Mode ................................................................................................................................ 15
Shared Interrupt Mode ............................................................................................................................ 15
Shared Interrupt Pull-Down .................................................................................................................... 15
Interrupt Selection ................................................................................................................................... 15
CAN Bus Dominant Timeout and Minimum Speed ............................................................................... 15
Security ID Feature ................................................................................................................................. 16
Jumper Summaries ....................................................................................................................................... 16
J1 ............................................................................................................................................................. 16
J2 ............................................................................................................................................................. 16
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 2
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 3

CANpro/104 User Manual
J3A .......................................................................................................................................................... 16
J3B .......................................................................................................................................................... 17
J3C .......................................................................................................................................................... 17
J4 and J5 .................................................................................................................................................. 17
Hardware Installation – Rev A & B .................................................................................................................. 18
CANpro/104 Opto Diagrams ....................................................................................................................... 18
Interrupts and Memory I/O Range Selection ............................................................................................... 19
Interrupt Selection ................................................................................................................................... 19
Unique Interrupt Lines ............................................................................................................................ 19
Sharing a Single Interrupt Line ............................................................................................................... 19
No Interrupts ........................................................................................................................................... 19
Address Mode and Range Selection ........................................................................................................ 20
Interrupt Sharing ..................................................................................................................................... 21
Other On-board Jumper Selection ................................................................................................................ 22
Connector Pinouts ............................................................................................................................................. 23
Specifications .................................................................................................................................................... 24
Operating Environment ........................................................................................................................... 24
Power Requirements ............................................................................................................................... 24
PC Bus Interface ..................................................................................................................................... 24
Optical/Power Isolation (CANpro/104 Opto models only) ..................................................................... 24
Dimensions .............................................................................................................................................. 24
Connectors/Interface ............................................................................................................................... 24
Certification ...................................................................................................................................................... 24
Certification for CANpro/104 ...................................................................................................................... 24
Limited Lifetime Warranty ............................................................................................................................... 25
Customer Support Overview ............................................................................................................................ 25
Contact Information .......................................................................................................................................... 25
3 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 4
CANpro/104 User Manual
Copyright Notice
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Connect Tech Inc. shall not
be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material. This document contains proprietary information that is protected by
copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated
to another language without the prior written consent of Connect Tech, Inc.
Copyright © 2009 by Connect Tech Inc.
Trademark Acknowledgement
Connect Tech Inc. acknowledges all trademarks, registered trademarks and/or copyrights referred to in this
document as the property of their respective owners.
Not listing all possible trademarks or copyright acknowledgments does not constitute a lack of
acknowledgment to the rightful owners of the trademarks and copyrights mentioned in this document.
Revision History
Revision 0.02 January 15, 2010
Updated manual with Rev.C (or later) Boards
Revision 0.01 December 22, 2008
Updated manual to new format
Updated Table 3
Revision 0.00 Original Document
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 4
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 5

CANpro/104 User Manual
Introduction
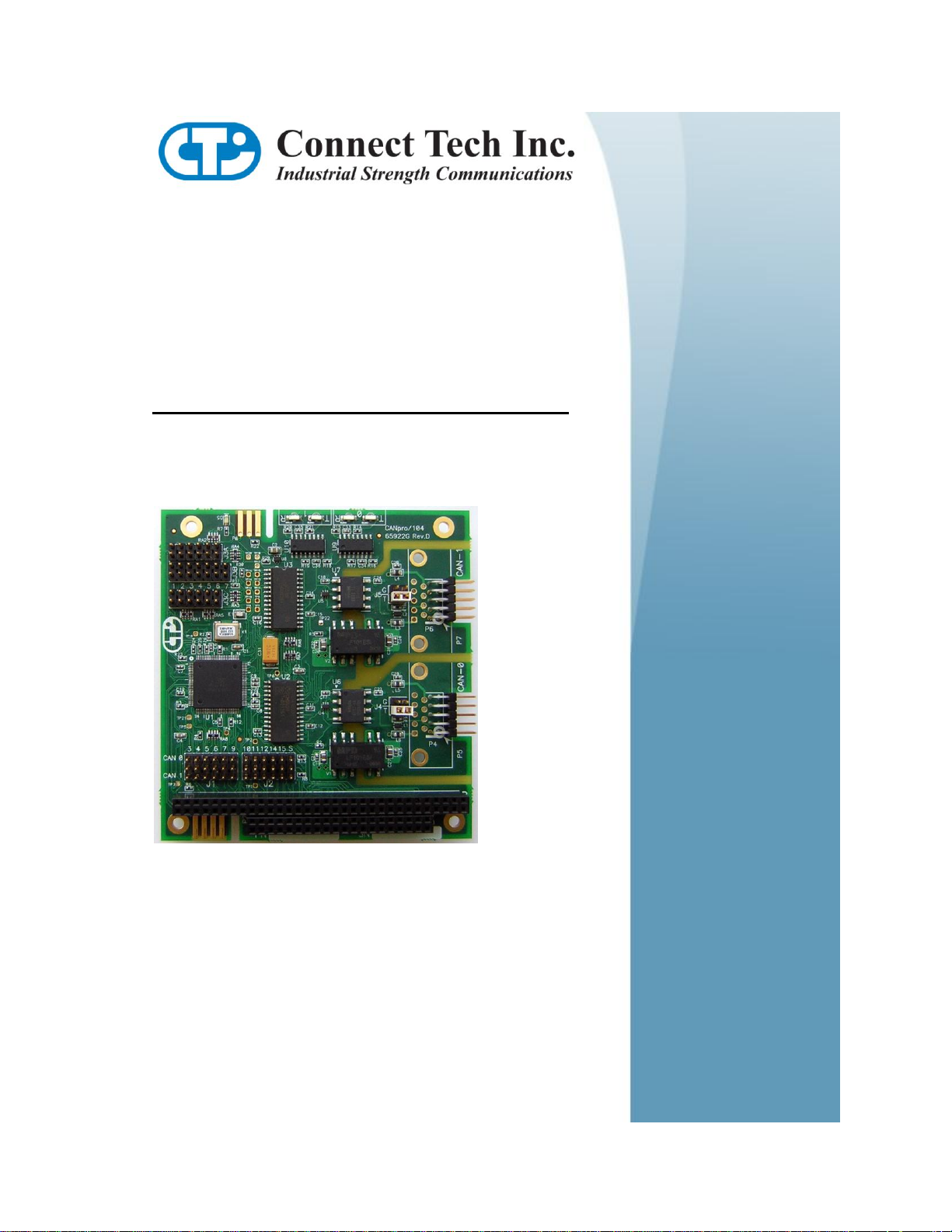
CANpro/104 combines the power of two independent NXP SJA1000 CAN controllers with the compact size
and rugged stability of PC/104. CANpro/104 is ideal for industrial control applications exposed to harsh
conditions or environments. CANpro/104 Opto models feature 2.5 kV of data and power isolation.
Features
● Two independent, industry standard NXP SJA1000 CAN controllers
● PC/104 compliant
● 16MHz input clock (24MHz build option available)
● Fail-safe power-up/power-down using on-board impendence transceivers to maximize nodes on the bus
and ensure glitch-free operation.
● Supports up to 1.0 Mbps operation and over 120 nodes on the bus
● 2000 V(AC) 50/60 Hz sine wave, 2500 V (peak) signal and power isolation for each port from the host
system (on CANpro/104 Opto models only)
● Jumper configurable:
● address range and interrupt sharing
● output slew rate limiting for lower radiated emissions
● -120 Ohm CAN bus termination
● Decoded address range is configurable for BasicCAN and PeliCAN modes
● Ten pin right angled header standard as an I/O connector (DB-9 option available)
● Operating temperature range of -40°C to +85°C
● +5V power output on some models
RoHS compliant
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 5
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 6
CANpro/104 User Manual
Hardware Installation – Rev C & Later
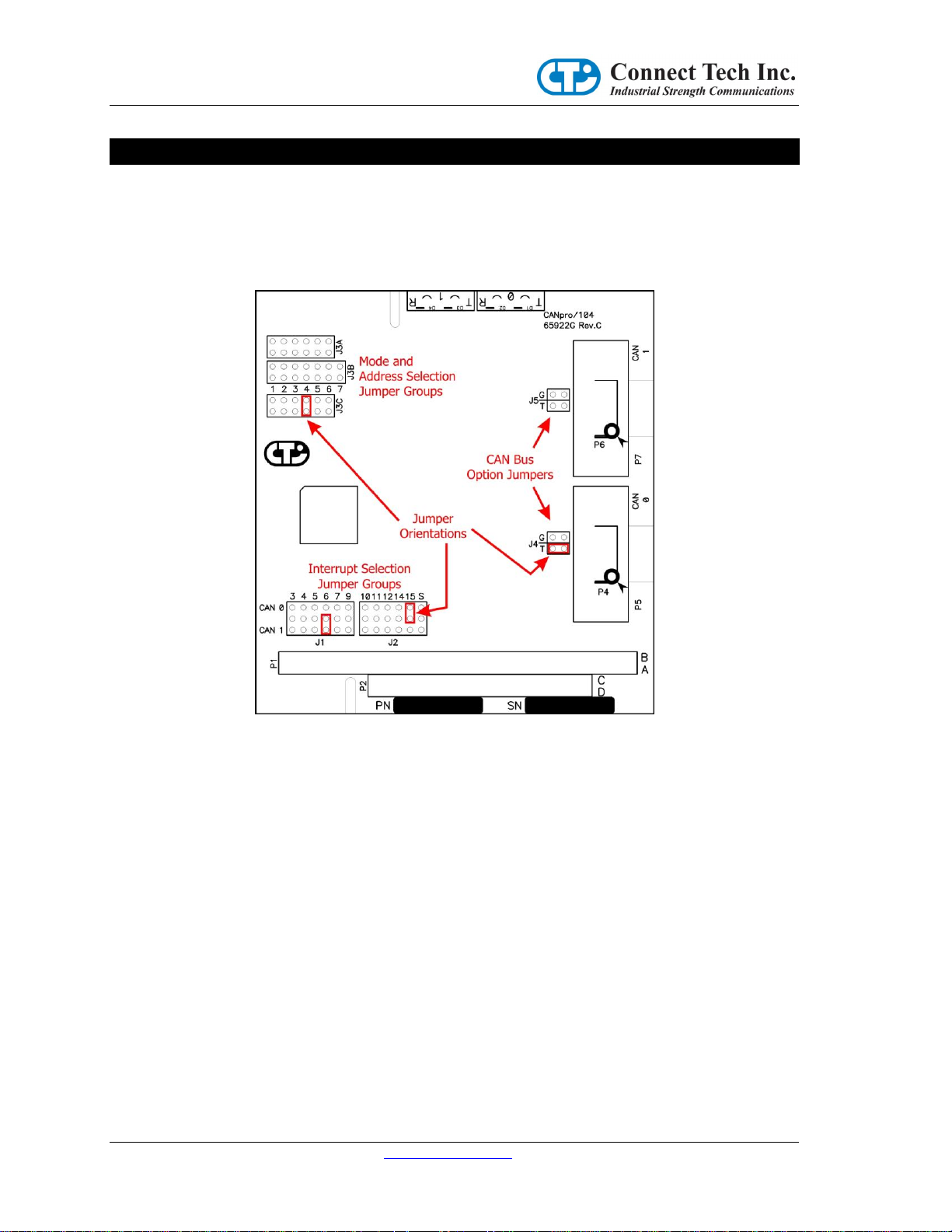
The Connect Tech CANpro/104 board provides two (2) industry standard SJA1000 CAN Bus controllers in
a PC/104 board format which supports both I/O and Memory mapping configurability.
All the configuration options are setup with jumpers, identified as J1, J2, J3A, J3B, J3C, J4 and J5.
Jumpers are always oriented as indicated in the drawing below.
The jumper positions are numbered on the PCB (and are shown in the above drawing). J1 and J2 are
Interrupt Selection jumpers, and the numbers (3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14 and 15) refer to the actual
interrupt number being selected. J3A, J3B and J3C positions are numbered sequentially from left to right.
J3A and J3C have 6 positions, J3B has 7 positions. J4 and J5 positions are labeled “T” and “G”.
Memory vs I/O Spaces
The first decision to make when configuring this board, it to select whether the board will operate within the
Memory or I/O address Space of the computer system in which the board is installed. First a quick
description of the two different Spaces.
Memory Space
Most (but not all) PC/104 CPU System board vendors provide one or more regions of Memory
Addresses that can be configured (or allocated) to the PC/104 Expansion bus connector(s) on CPU
System board. This setup may be performed via the BIOS setup or via jumpers or switches on the
System board. This memory region is usually located at addresses below the 1-Meg CPU memory
address (commonly referred to as the Upper Memory addresses), although some System boards
allow the PC/104 Expansion Bus to be allocated to blocks of addresses within the first 16-Meg of
memory.
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 6
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 7
J3A Position #1
Function
Removed
Memory Space operation enabled
Installed
I/O Space operation enabled
J3C Position #1
Function
Removed
Memory Space is always enabled
Installed
Memory Space powers-up (or resets) as disabled
I/O Space
This region is supported by all PC/104 CPU System board vendors, and commonly consists of I/O
Addresses from 0x000 to 0x3FF, although some System boards support I/O addresses beyond 0x3FF.
(Note: Some I/O mapped PC/104 expansion boards only decode the lowest 10 bits of the I/O address,
therefore these boards restrict the usable I/O space to 0x3FF).
CTI CANpro/104 Spaces
Memory Space
The CTI CANpro/104 board can be configured to operate in the CPU Memory Address Space
between addresses 0x000000 and 0xCFE000. The board decodes an 8192/0x2000 byte block of
memory selectable at numerous address locations throughout the first 16-Meg of CPU address range.
The selection is always on an 8192/0x2000 byte address boundary.
I/O Space
The CTI CANpro/104 board can be configured to operate in the CPU I/O Address Space between
addresses 0x000 and 0x7C0. The board decodes either a 256/0x100 byte block or a 64/x40 byte
sized block depending on the selection of either the PeliCAN or BasicCAN mode (more on this
selection later).
When the PeliCAN mode is selected, the board decodes a 256/0x100 byte block (on a
256/0x100 byte address boundary) at I/O addresses from 0x000 to 0x700.
When the BasicCAN mode is selected, the board decodes a 64/0x40 byte block (on a 64/0x40
byte address boundary) at I/O addresses from 0x000 to 0x7C0.
The selection of either Memory or I/O space is made with Jumper J3A Position #1.
CANpro/104 User Manual
Table 1
Memory Space Enabling
Some CPU System board BIOS’s will scan certain regions of the CPU memory below the 1-Meg
boundary looking for ROM’s to boot from, and if the CTI CANpro/104 board is setup to operate
within these memory regions, the BIOS might accidently confuse this board as being a ROM. To
prevent this, this board has the ability to power-up (or after a system reset) with the Memory Space
disabled.
There are 2 ways to enable the Memory Space. First, it can be enabled permanently by using
Jumper J3C Position #1.
Table 2
7 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 8
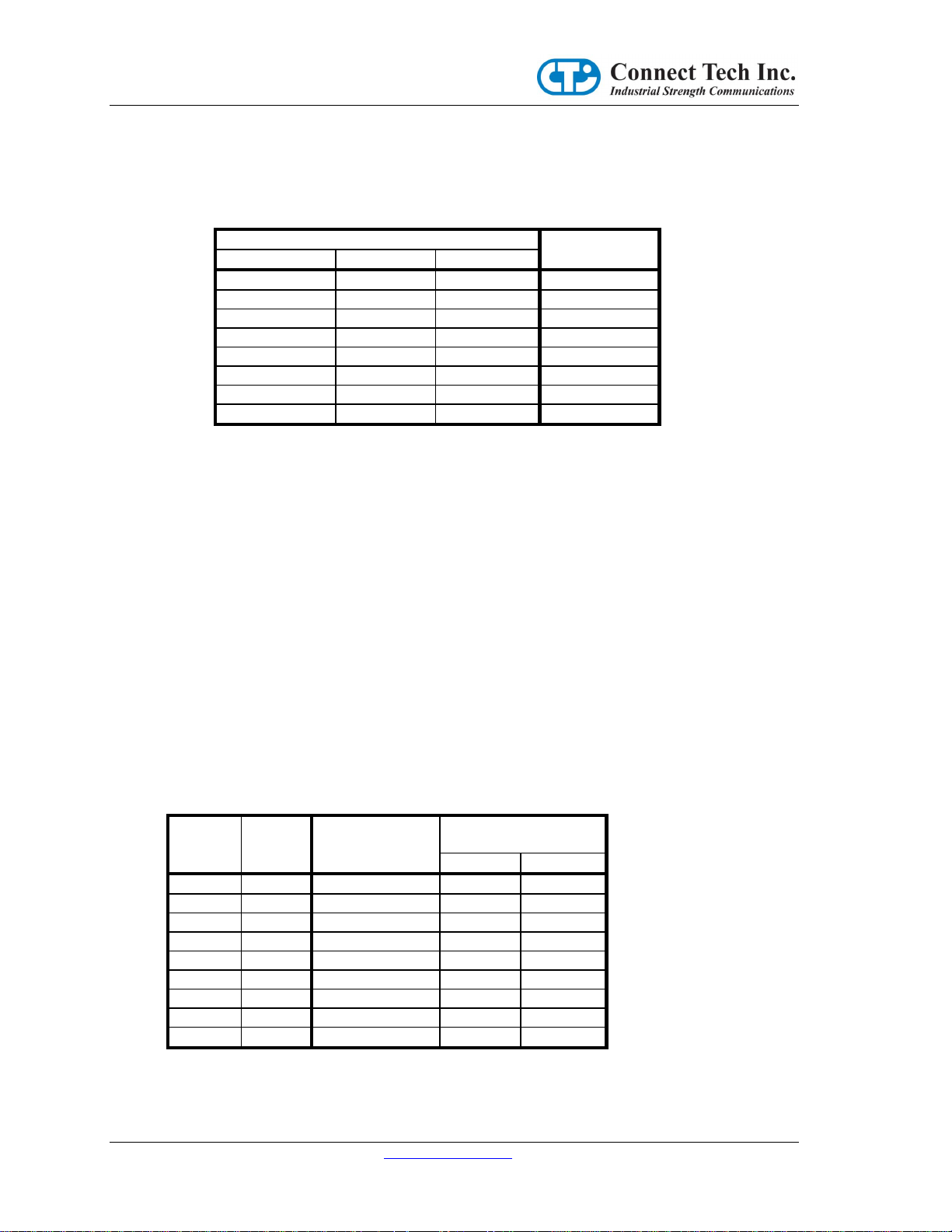
CANpro/104 User Manual
J3B
I/O Address
Position #5
Position #6
Position #7
Removed
Removed
Removed
0x200
Removed
Removed
Installed
0x240
Removed
Installed
Removed
0x280
Removed
Installed
Installed
0x2C0
Installed
Removed
Removed
0x300
Installed
Removed
Installed
0x340
Installed
Installed
Removed
0x380
Installed
Installed
Installed
0x3C0
Jumper
Group
Position
Memory Space
Address Bit
I/O Space
Address Bit
PeliCAN
BasicCAN
J3A 2 23
X
X
3 22
X X 4 19
X X 5 18
X X 6 17
10
10
J3B 1 16
9 9 2 15
8 8 3 14
X 7 4 13
X
6
Secondly, the Memory Space can be enabled by Application or Driver software, after the Operating
system has started. This can be accomplished by writing a data value to an I/O Space Address which
is decoded by the following J3B Jumper settings. Only one byte of the I/O Space is decoded at this
I/O Address, and the location is Write Only.
Table 3
Notes:
1. These I/O address choices do NOT access the CAN Controllers, they are used in
Memory Mode to enable the Memory Space address decoding.
2. Writing a data value of 0xA5 will enable the Memory Space, and a data value of 0x5A
will disable the Memory Space. All other data values written will be ignored.
3. When the Memory Space is permanently enabled (when J3C-1 is removed), any data
value written to the “Memory Enable” I/O address will be ignored.
Base Address Decoding
The CTI CANpro/104 board decodes its Base Address setting (in either Memory or I/O Spaces) by
comparing (matching) various Jumper settings with PC/104 Bus Address bits.
If a Jumper is installed, then the corresponding Address Bit will be matched as a logical “1”.
If a Jumper is removed, then the corresponding Address Bit will be matched as a logical “0”.
The matching of Jumper settings to Address bits depends on whether the board is operated in Memory or I/O
Spaces, and whether PeliCAN or BasicCAN mode is selected.
Table 4
Notes:
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 8
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 9

CANpro/104 User Manual
PC/104 Bus
Address Bit
SJA1000 Selection
or Register Address Bit
12
Address bit is ignored
11
Address bit is ignored
10
Address bit is ignored
9
Address bit is ignored
8
Address bit is ignored
7
Select SJA1000 device
=0, selects the CAN-0 Port
=1, selects the CAN-1 Port
6 6 5
5
4 4 3
3
2 2 1 1 0
0
PC/104 Bus
Address Bit
SJA1000 Selection
or Register Address Bit
PeliCAN Addressing Mode
BasicCAN Addressing Mode
10
Decoded (see Table 4)
Decoded (see Table 4)
9
Decoded (see Table 4)
Decoded (see Table 4)
8
Decoded (see Table 4)
Decoded (see Table 4)
7
Select SJA1000 device
=0, selects the CAN-0 Port
=1, selects the CAN-1 Port
Decoded (see Table 4)
6 6 Decoded (see Table 4)
5 5 Select SJA1000 device
=0, selects the CAN-0 Port
=1, selects the CAN-1 Port
4
4
4 3 3
3
2
2
2 1 1
1
0
0
0
1. X = Address bit is ignored (and the corresponding Jumper is Not Used).
2. When Memory Space is selected, PC/104 Address bits 20 and 21 are always decoded as logical
“0”.
To determine which Jumpers to install and which to remove, the desired Address needs to be broken down
into a binary number, all the Jumpers that correspond to “1-bits” must be installed, and all Jumpers
corresponding to “0-bits” must be removed.
The remaining lower bits of the PC/104 Bus Address are either, ignored, or are used to select and address the
Registers of the SJA1000 CAN controllers, in the following manner.
When Memory Space is selected
Table 5
When I/O Space is selected
Table 6
9 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 10

CANpro/104 User Manual
J3C Position #2
Function
Removed
PeliCAN Addressing mode enabled
Installed
BasicCAN Addressing mode enabled
Address
Bit
Bit
Value
J3A or J3B
Position
Installed
or Removed
23 0 J3A-2
Removed
22 1 J3A-3
Installed
21 0 Address Bit always decoded as “0”
20 0 Address Bit always decoded as “0”
19 1 J3A-4
Installed
18 0 J3A-5
Removed
17 1 J3A-6
Installed
16 0 J3B-1
Removed
15 0 J3B-2
Removed
14 1 J3B-3
Installed
13 1 J3B-4
Installed
PeliCAN vs BasicCAN Addressing Modes
The SJA1000 can operate in 2 different modes, the PeliCAN mode which has extended features and
additional registers and which consume 128 bytes of address space per device (there are 2 devices on
this board). And, the BasicCAN mode which has reduced functionality but only consumes 32 bytes
of register space per device.
Note: The mode of operation of the SJA1000 is performed by changing Bit-7 of the Clock
Divider Register (which defaults to BasicCAN mode whenever a PC/104 Bus Reset occurs).
When the SJA1000’s are operated in BasicCAN mode, it is desirable to accommodate the smaller
number of registers by decoding a smaller amount of I/O Space (because the I/O Space region is
limited in total size).
The selection of Addressing Mode is done with Jumper J3C Position #2. This selection has no
meaning when Memory Space operation is enabled (see Jumper J3A above).
Table 7
Addressing Examples
Example #1: Memory Address 0x4A6000 (this address is above the 1-Meg boundary)
0x4A6000 = 0100.1010.011X.XXXX.CJJJ.JJJJ (binary)
Address bits in red are matched against their respective Jumper settings.
X = Address bits that are ignored by the board.
C = Address bit that is used to select the SJA1000 controller.
J = Address bits that are used to select the SJA1000 registers.
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 10
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Table 8
Page 11

CANpro/104 User Manual
Address
Bit
Bit
Value
J3A or J3B
Position
Installed
or Removed
23 0 J3A-2
Removed
22 0 J3A-3
Removed
21 0 Address Bit always decoded as “0”
20 0 Address Bit always decoded as “0”
19 1 J3A-4
Installed
18 1 J3A-5
Installed
17 0 J3A-6
Removed
16 0 J3B-1
Removed
15 1 J3B-2
Installed
14 0 J3B-3
Removed
13 0 J3B-4
Removed
Address
Bit
Bit
Value
J3A or J3B
Position
Installed
or Removed
23 -> 11 X ---
---
10 0 J3A-6
Removed
9 1 J3B-1
Installed
8 1 J3B-2
Installed
7 0 J3B-3
Removed
6 1 J3B-4
Installed
Address
Bit
Bit
Value
J3A or J3B
Position
Installed
or Removed
23 -> 11 X ---
---
10 1 J3A-6
Installed
9 1 J3B-1
Installed
8 0 J3B-2
Removed
Example #2: Memory Address 0x0C8000 (this address is below the 1-Meg boundary)
0x0C8000 = 0000.1100.100X.XXXX.CJJJ.JJJJ (binary)
Table 9
Example #3: I/O Address 0x340 (BasicCAN mode)
0x340 = XXXX.XXXX.XXXX.X011.01CJ.JJJJ (binary)
Table 10
Example #4: I/O Address 0x600 (PeliCAN mode)
0x600 = XXXX.XXXX.XXXX.X110.CJJJ.JJJJ (binary)
Table 11
11 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 12

CANpro/104 User Manual
Accessed Resource
Offset from Base Address
Memory Space
I/O Space
BasicCAN mode
PeliCAN mode
CAN-0 Port (SJA1000)
0x000 0x07F
0x000 0x01F
0x000 0x07F
CAN-1 Port (SJA1000)
0x080 0x0FF
0x020 0x03F
0x080 0x0FF
Memory Enable Bit
At the I/O Address setup
with JB3 Positions 5,6,7
N/A
N/A
CAN Controller Addressing Table
Once the Base Memory or I/O Address is setup, the 2 SJA1000 CAN controllers are accessed at the
following address offsets.
Table 12
The SJA1000 Register offsets can be found in the documentation from NXP Semiconductor
(formerly Philips). www.nxp.com (enter SJA1000 into their search tool).
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 12
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 13

CANpro/104 User Manual
Base
Memory
Address
J3A
J3B
2
[23]
3
[22] 4 [19] 5 [18] 6 [17] 1 [16] 2 [15] 3 [14] 4 [13]
0x0C0000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
Out
Out
Out
0x0C2000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
Out
Out
In
0x0C4000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
Out
In
Out
0x0C6000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
Out
In
In
0x0C8000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
In
Out
Out
0x0CA000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
In
Out
In
0x0CC000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
In
In
Out
0x0CE000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
In
In
In
0x0D0000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
Out
Out
Out
0x0D2000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
Out
Out
In
0x0D4000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
Out
In
Out
0x0D6000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
Out
In
In
0x0D8000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
In
Out
Out
0x0DA000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
In
Out
In
0x0DC000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
In
In
Out
0x0DE000
Out
Out
In
In
Out
In
In
In
In
0x0E0000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
Out
Out
Out
0x0E2000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
Out
Out
In
0x0E4000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
Out
In
Out
0x0E6000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
Out
In
In
0x0E8000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
In
Out
Out
0x0EA000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
In
Out
In
0x0EC000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
In
In
Out
0x0EE000
Out
Out
In
In
In
Out
In
In
In
0x0F0000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
Out
Out
Out
0x0F2000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
Out
Out
In
0x0F4000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
Out
In
Out
0x0F6000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
Out
In
In
0x0F8000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
In
Out
Out
0x0FA000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
In
Out
In
0x0FC000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
In
In
Out
0x0FE000
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
In
In
In
Common Memory Space Address Selections
Most System boards allow the PC/104 Bus stack to be allocated a portion of the memory address
located in the 256K region of memory just below the 1-Meg address boundary (Addresses
0x0C0000 to 0x0FFFFF). Different BIOS’s allow different sized regions to the allocated. The
CANpro/104 board requires 8K (8192 bytes) of memory space.
The following table shows the Jumpers required to set up the Base Memory Address within this
256K region.
In = Jumper installed (Corresponding Memory Address bit is = “1”)
Out = Jumper removed (Corresponding Memory Address bit is = “0”)
[xx] = Corresponding Memory Address bit number
Table 13
13 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 14

CANpro/104 User Manual
J3C Position #6
Function
Removed
Normal PC/104 Bus Cycle length
Installed
Shortened PC/104 Bus Cycle length
Performance Enhancement
PC/104 Memory and I/O Bus cycles are typically about 700 nS long in total, but the access speed of the
SJA1000 is considerably faster. The PC/104 Bus allows Memory and I/O Bus cycles to be shortened by the
assertion of the SRDY* signal at the appropriate time in the Bus Cycle. This shortening of the PC/104 Bus
Cycle can yield some significant performance improvements is some applications.
The CTI CANpro/104 board allows the PC/104 Bus cycle to be shortened by about 30% with Jumper J3C
Position #6.
Table 14
Note: Not all System boards will support Bus Cycle shortening via the PC/104 SRDY* signal.
Consult with the manufacturer of your System board to determine if this feature is supported.
CAN Bus Options
The board supports 2 CAN Bus Options with Jumper J4 and J5.
J4 is associated with CAN Port-0, and J5 is for CAN Port-1.
CAN Bus Termination
Ground the Shell of the 9D Connector
Termination
A 120 ohm termination resistor is placed across the CAN Bus signals (CANH and CANL), by
placing a jumper on Position “T” of either J4 or J5. It is desirable to place a termination resistor at
each physical end on a CAN Bus segment.
9D Connector Shell Ground
On CANpro/104 boards equipped with a 9D CAN Bus connector, the Metal Shell of that connector
can be connected to the Isolated Ground of the board (each CAN Port has a separate Ground), by
placing a jumper on Position “G” of either J4 or J5. This might be useful in some installations to
reduce noise.
Interrupt Mode and Selections
The board can be operated with either one or two interrupts, the interrupt(s) can be shared with another
PC/104 board (which supports shared interrupts), and the Pull-down resistor, which is required for shared
interrupts, can be enabled on this board.
The Jumper Blocks consist of 2 groups of Interrupt Selections, one group for the CAN-0 controller (red box)
and the other for the CAN-1 controller (blue box).
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 14
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 15

CANpro/104 User Manual
J1/J2 Position “S”
Function
Removed
Dual Interrupt Mode
Installed
Single Interrupt Mode
J3C Position
Function
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
3
CAN-1 Interrupt Shared
CAN-1 Interrupt Not Shared
4
CAN-0 Interrupt Shared
CAN-0 Interrupt Not Shared
J3C Position #5
Function
Removed
Shared Interrupt(s) Pull-Down disabled
Installed
Shared Interrupt(s) Pull-Down enabled
Single Interrupt Mode
This mode routes the interrupt signal from both SJA1000 CAN controllers to one PC/104 Bus
Interrupt signal. This mode is set up by installing Jumper J1/J2 Position “S” (either the CAN-0 or
the CAN-1 “S” position can be used). When this jumper is installed, the Interrupt signal occurs on
the “CAN-0 row” of J1 and J2 (red box).
Dual Interrupt Mode
This mode routes the interrupt signal from the CAN-0 SJA1000 CAN controller to the CAN-0
PC/104 Bus Interrupt signal and the CAN-1 SJA1000 CAN controller to the CAN-1 PC/104 Bus
Interrupt signal. This mode is set up by removing Jumper J1/J2 Position “S”.
Table 15
Shared Interrupt Mode
In either the Single or Dual interrupt modes, the PC/104 Bus Interrupt Signal can be shared with a
similarly selected interrupt on another PC/104 board (which supports shared interrupts). There are 2
jumpers which control this sharing on J3C Positions #3 and #4.
Table 16
Shared Interrupt Pull-Down
When shared interrupts are employed, there MUST be one board (among the boards that share the
same interrupt) that MUST be setup to activate a Pull-Down resistor on the Interrupt signal. This is
accomplished by Jumper J3C Position #5.
Table 17
Interrupt Selection
In either of the CAN-0 or CAN-1 groups there is 11 possible interrupts that can be selected. The
jumpers are numbered by the PC/104 Bus Interrupt number (3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14 or 15).
Only one jumper should be installed in the appropriate group.
CAN Bus Dominant Timeout and Minimum Speed
The CANpro/104 board implements a CAN Bus transceiver which has a “Dominant State timeout
feature”. This feature prevents the board from permanently holding the CAN bus in the “Dominant
state”. Due to this feature, the minimum CAN Bus data rate supported is 20K bps.
15 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 16

CANpro/104 User Manual
Position
Function (for either CAN-0 or CAN-1)
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
3
PC/104 Interrupt #3 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #3 Not Selected
4
PC/104 Interrupt #4 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #4 Not Selected
5
PC/104 Interrupt #5 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #5 Not Selected
6
PC/104 Interrupt #6 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #6 Not Selected
7
PC/104 Interrupt #7 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #7 Not Selected
9
PC/104 Interrupt #9 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #9 Not Selected
Position
Function (for either CAN-0 or CAN-1)
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
10
PC/104 Interrupt #10 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #10 Not Selected
11
PC/104 Interrupt #11 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #11 Not Selected
12
PC/104 Interrupt #12 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #12 Not Selected
14
PC/104 Interrupt #14 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #14 Not Selected
15
PC/104 Interrupt #15 Selected
PC/104 Interrupt #15 Not Selected
S
Single Interrupt Mode
Dual Interrupt Mode
Position
Function
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
1
“I/O” Space operation enabled
“Memory” Space operation enabled
2
Mem Addr[23] = 1
Mem Addr[23] = 0
3
Mem Addr[22] = 1
Mem Addr[22] = 0
4
Mem Addr[19] = 1
Mem Addr[19] = 0
5
Mem Addr[18] = 1
Mem Addr[18] = 0
6
Mem Addr[17] or I/O Addr[10] = 1
Mem Addr[17] or I/O Addr[10] = 0
Security ID Feature
Some users may wish to associate the operation of their software with a particular hardware
installation. To support this ability, an ID mechanism is available which uses a simple, somewhat
unusual (but predictable) Write/Read mechanism by which software can determine that the CTI
CANpro/104 board is installed. This feature is only available when the CANpro/104 board is
operated in “Memory Mode”. Contact CTI Technical Support for information about the method and
algorithm required to use this feature.
Jumper Summaries
The following tables of Jumper settings are useful once the user is familiar with the operations performed by
those jumpers.
J1
Table 18
Only one position can be jumpered.
J2
Table 19
Only one interrupt numbered position can be jumpered.
J3A
Table 20
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 16
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 17

CANpro/104 User Manual
Position
Function
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
1
Mem Addr[16] or I/O Addr[9] = 1
Mem Addr[16] or I/O Addr[9] = 0
2
Mem Addr[15] or I/O Addr[8] = 1
Mem Addr[15] or I/O Addr[8] = 0
3
Mem Addr[14] = 1
or
I/O Addr[7] = 1 (BasicCAN mode only)
Mem Addr[14] = 0
or
I/O Addr[7] = 0 (BasicCAN mode only)
4
Mem Addr[13] = 1
or
I/O Addr[6] = 1 (BasicCAN mode only)
Mem Addr[13] = 0
or
I/O Addr[6] = 0 (BasicCAN mode only)
5
Memory Space Enable Bit-2 [Note 1]
6
Memory Space Enable Bit-1 [Note 1]
7
Memory Space Enable Bit-0 [Note 1]
Position
Function
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
1
Memory Space powers-up (or resets)
disabled
Memory Space is always enabled
2
BasicCAN mode enabled
PeliCAN mode enabled
3
CAN-1 Interrupt Shared
CAN-1 Interrupt Not Shared
4
CAN-0 Interrupt Shared
CAN-0 Interrupt Not Shared
5
Shared Interrupt(s) Pull-Down enabled
Shared Interrupt(s) Pull-Down disabled
6
Shorten Memory and I/O Bus Cycles
Normal Memory and I/O Bus Cycles
Position
Function
Jumper Installed
Jumper Removed
T
CAN Bus Termination Resistor enabled
CAN Bus Termination Resistor disabled
G
9D Connector Shell Grounded [Note 1]
9D Connector Shell NOT Grounded
J3B
Table 21
The 3 Memory Space Enable bits select 8 choices of I/O Addresses for the Memory Enable feature.
J3C
Table 22
J4 and J5
Table 23
The 9D Shell is Grounded to the Isolated Ground for the respective CAN Port.
17 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 18

CANpro/104 User Manual
Hardware Installation – Rev A & B
Before you begin, take a minute to ensure that your package includes the required components that should
have shipped with your CANpro/104.
● One CANpro/104 CAN controller board
● One CD containing documentation
If any of these components is missing, contact Connect Tech (See Contact Details) or your reseller. Also,
visit the Download Zone of the Support Center on the Connect Tech website for the latest product manuals,
installation guides, diagnostic utilities and device driver software.
CANpro/104 Opto Diagrams
Figure 1 shows the locations of various hardware components found on the CANpro/104.
Figure 1: CANpro/104 Board Diagram
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 18
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 19

CANpro/104 User Manual
Interrupts and Memory I/O Range Selection
CANpro/104’s interrupt lines and I/O ranges are jumper assignable.
Interrupt Selection
J1 and J2 are used for interrupt selection. Interrupt selection for the first CAN controller is achieved
via the upper and centre rows of pins on the connector. The lower and center rows of pins allow
selection of interrupts for the second CAN controller. Please refer to Figure 1 to locate jumper
blocks J1 and J2.
CANpro/104 offers flexible interrupt configuration. Each CANpro/104 card can use one PC/104
interrupt per controller, share one interrupt across both controllers or use no interrupts at all.
Unique Interrupt Lines
The example below illustrates CANpro/104 configured for two unique interrupts with controller 0
interrupting on IRQ 4 and controller interrupting on IRQ 5.
Sharing a Single Interrupt Line
CANpro/104’s CAN controllers can also interrupt on the same interrupt line. The diagram below
demonstrates both controllers interrupting on line IRQ 11. Please note that the interrupt selection for
the interrupt that both controllers share must be made on the CAN 0 rows.
No Interrupts
To force operation without interrupts, simply leave the interrupt jumper blocks J1 and J2
unpopulated. This requires software polling to determine an interrupt condition.
19 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 20

CANpro/104 User Manual
Jumper Location
Board Mode Selection
ON (BasicCAN)
OFF (PeliCAN)
Addr3
Addr2
Addr1
Addr0
CAN 0
CAN 1
CAN 0
CAN 1
ON
ON
ON
ON
0x000
0x020
0x000
0x080
ON
ON
ON
OFF
0x040
0x060
0x000
0x080
ON
ON
OFF
ON
0x080
0x0A0
0x000
0x080
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
0x0C0
0x0E0
0x000
0x080
ON
OFF
ON
ON
0x100
0x120
0x100
0x180
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
0x140
0x160
0x100
0x180
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
0x180
0x1A0
0x100
0x180
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
0x1C0
0x1E0
0x100
0x180
OFF
ON
ON
ON
0x200
0x220
0x200
0x280
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
0x240
0x260
0x200
0x280
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
0x280
0x2A0
0x200
0x280
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
0x2C0
0x2E0
0x200
0x280
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
0x300
0x320
0x300
0x380
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
0x340
0x360
0x300
0x380
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
0x380
0x3A0
0x300
0x380
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
0x3C0
0x3E0
0x300
0x380
Address Mode and Range Selection
The first five jumper locations of jumper block J3 are used for board address selection. The first
jumper location (Addr Mode) selects the number of address bits to use for the decoding of the board
address. The next four jumpers configure the actual board address.
If you intend to configure both of the board’s controllers in BasicCAN mode, install a jumper in the
Addr Mode location. This configures the board to respond to a 64 byte address range (32 bytes per
controller).
Alternatively, if you intend to operate one or both of the CAN controllers in PeliCAN mode, leave
the Addr Mode location unpopulated. This configures the board to respond to a 256 byte address
range (128 bytes per controller).
The address range for the board itself is directly selected by the Addr3, Addr2, Addr1 and Addr0
jumper locations. The following table describes the base addresses of the controllers 0 and 1 (CAN
0 and CAN 1) for every possible combination of Addr Mode and AddrX jumper locations.
Table 24: CAN 0 and CAN 1 Base Addresses
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 20
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 21

CANpro/104 User Manual
Interrupt Sharing
Jumper block J3 also plays a part in the interrupt sharing. PC/104 supports the sharing of an
interrupt between multiple cards. For example, two separate CANpro/104 cards are able to share the
same interrupt across all four controllers. To accomplish interrupt sharing, the following steps must
be taken:
All cards that share the same interrupt, but are not actively asserting an interrupt, must tri-state their
outputs. On CANpro/104 cards, this is accomplished by installing a jumper on the INTshrX jumper
location of each CAN controller(s) you wish to share interrupts.
One 1K Ohm resistor must also be attached to each shared interrupt. With the example of two
CANpro/104 cards, the INTres jumper would be installed on only one of the cards.
NOTE:
CANpro/104 has the capability to tri-state its interrupt outputs and the 1K Ohm resistor is jumper
configurable. Other cards may not be able to share interrupts. Please check the manual for each
card.
The example below has configured both cards to interrupt on IRQ 11. Both controllers will tri-state
their outputs when not driving the interrupt line active. This example assumes that another card in
the stack has enabled the 1K Ohm pull-down resistor. Only one card in the group of cards sharing
the same interrupt should enable a pull-down resistor.
To enable the resistor, simply install a jumper on the INTres jumper location, as shown below.
Please note that the Interrupt Resistor Enable controls the Interrupt Resistor for all shared CAN
controller interrupts on the card. You cannot enable the Interrupt Termination Resistor for one
controller only if both are configured for interrupt sharing.
If a card has interrupt sharing enabled for only one of its controllers, the resistor will only be enabled
on the interrupt of the controller that is sharing interrupts.
21 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 22

CANpro/104 User Manual
Other On-board Jumper Selection
Near each I/O connector a 2x2 jumper block (either J4 or J5) will allow the configuration of both bus
termination and slew rate limiting for the transceiver. J4 configures options for CAN controller 0, while J5
configures options for CAN controller 1.
Installing a jumper on the first location of J4 or J5 (the gray area above) will enable a 120 Ohm termination
resistor across the CAN-H and CAN-L lines. Termination is recommended for improved signal integrity in
longer transmission lines. Termination requirements should be evaluated on a case by case basis. Typically
both ends of a CAN bus are terminated, but no termination is enabled on cards that sit in the middle of the
bus.
Installing a jumper on the second location of J4 or J5 (the gray area above) will disable slew rate limiting for
the associated CAN port. Slew rate limiting will reduce the emitted switching noise that is sent out onto the
CAN bus lines and radiated from those lines. Switching noise may cause EMI / EMC incompatibilities
depending on the cabling used to support the system. The use of slew rate limiting may aid in a system that is
close to the limit of emissions already. Properly shielded cabling will dramatically reduce emissions.
Slew rate limiting may only be used on busses operating at slower baud rates. With the jumper installed, full
1Mbps operation is possible.
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 22
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 23

CANpro/104 User Manual
Pin No.
Signal
1
+5V
2
CAN-L
3
CAN GND (isolated or non)
4
N/C 5 N/C 6 CAN GND (isolated or non)
7
CAN-H
8
N/C
9
+5V
Male DB-9 Connector
1
5
6
9
Pin No.
Signal
1
+5V
2
CAN-GND (isolated or non)
3
CAN-L
4
CANH
5
CAN-GND (isolated or non)
6
NC 7 NC 8 +5V
9
NC
10
NC
7 5 3
1
2
4 6 8
Printed circuit board
9
10
10-pin header
View facing 10-pin header
Connector Pinouts
Table 25: DB-9 Cable Connector Pinouts
For boards populated with right angled 2x5 0.100” headers, cable CAG104 will break out from the
onboard 2x5 header to a DB-9 connector.
Table 26: 10-pin Header Pinouts
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 23
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 24

CANpro/104 User Manual
Specifications
Operating Environment
Storage temperature: -40 C to 125 C
Operating temperature: -40 C to 85 C
Humidity: 95%, non-condensing
Power Requirements
+5 VDC @ 500mA (maximum)
380 mA (minimum)
NOTE:
Power output on CAN connectors may draw up to an additional 1A per port (non-isolated models).
190 mA per port (isolated models) given 150mA current draw in the +5V output.
PC Bus Interface
PC/104
Optical/Power Isolation (CANpro/104 Opto models only)
500V for each CAN port from the host system and other isolated CAN ports.
Dimensions
Compliant to PC/104 specification 2.5
Connectors/Interface
Standard: 10-pin, right angled header (+5V power output)
Optional: DB-9
Certification
Certification for CANpro/104
The CANpro/104 product family is to be included into a device ultimately subject to FCC, DOC/IC, and CE
certification. The customer is responsible for bringing the completed device into compliance prior to resale.
Connect Tech has designed CANpro/104 with EMI and EMC considerations such as:
Ground and power planes
Controlled slew-rate signals
EMI/EMC reducing PCB layout
CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010 www.connecttech.com 24
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
Page 25

CANpro/104 User Manual
Limited Lifetime Warranty
Connect Tech Inc. provides a Lifetime Warranty for all Connect Tech Inc. products. Should this product, in
Connect Tech Inc.'s opinion, fail to be in good working order during the warranty period, Connect Tech Inc.
will, at its option, repair or replace this product at no charge, provided that the product has not been subjected
to abuse, misuse, accident, disaster or non Connect Tech Inc. authorized modification or repair.
You may obtain warranty service by delivering this product to an authorized Connect Tech Inc. business
partner or to Connect Tech Inc. along with proof of purchase. Product returned to Connect Tech Inc. must be
pre-authorized by Connect Tech Inc. with an RMA (Return Material Authorization) number marked on the
outside of the package and sent prepaid, insured and packaged for safe shipment. Connect Tech Inc. will
return this product by prepaid shipment service.
The Connect Tech Inc. lifetime warranty is defined as the serviceable life of the product. This is defined as
the period during which all components are available. Should the product prove to be irreparable, Connect
Tech Inc. reserves the right to substitute an equivalent product if available or to retract lifetime warranty if no
replacement is available.
The above warranty is the only warranty authorized by Connect Tech Inc. Under no circumstances will
Connect Tech Inc. be liable in any way for any damages, including any lost profits, lost savings or other
incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use of, or inability to use, such product.
Customer Support Overview
If you experience difficulties after reading the manual and/or using the product, contact the Connect Tech
reseller from which you purchased the product. In most cases the reseller can help you with product
installation and difficulties.
In the event that the reseller is unable to resolve your problem, our highly qualified support staff can assist
you. Our online Support Center is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week on our website at:
www.connecttech.com/sub/support/support.asp. Please go to the Download Zone or the Knowledge Database
for product manuals, installation guides, device driver software and technical tips. Submit your questions to
our technical support engineers at support@connecttech.com. Our technical support is always free.
Contact Information
Telephone/Facsimile
Technical Support representatives are ready to answer your call Monday through Friday, from 8:30 a.m. to
5:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time. Our numbers for calls are:
Toll: 800-426-8979 (North America only) | Tel: 519-836-1291 | Fax: 519-836-4878 (online 24 hours)
Email/Internet
You may contact us through the Internet. Our email and URL addresses are:
sales@connecttech.com | support@connecttech.com | www.connecttech.com
Mail/Courier
Connect Tech Inc.
42 Arrow Road
Guelph, ON N1K 1S6 Canada
25 www.connecttech.com CTIM-00043 (0.01) 1/15/2010
800-426-8979 | 519-836-1291
 Loading...
Loading...