CONEX CX88168SCM, CX20437VC, CX20463LSD Datasheet

Doc. No. 100490C
June 16, 2000
SmartSCM
Modem
V.90/K56flex
/V.34/V.32bis CX88168 Single Chip Modem
with CX20463 SmartDAA
and Optional CX20437 Voice
Codec for Embedded Applications
Data Sheet
Conexant Proprietary Information
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
ii
Conexant
100490C
Revision Record
Revision Date Comments
C 6/16/2000 Revision B release. Supersedes 100490B.
B 6/2/2000 Revision B release. Supersedes 100490A and 100491A.
A 1/26/2000 Initial release.
© 2000,
Conexant Systems, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Conexant Systems, Inc. (“Conexant”) products. These materials are provided by
Conexant as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only. Conexant assumes no responsibility for errors or
omissions in these materials. Conexant may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Conexant
makes no commitment to update the information and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from
future changes to its specifications and product descriptions.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in
Conexant’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Conexant assumes no liability whatsoever.
THESE MATERIALS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, RELATING TO
SALE AND/OR USE OF CONEXANT PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT,
COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. CONEXANT FURTHER DOES NOT WARRANT THE ACCURACY OR
COMPLETENESS OF THE INFORMATION, TEXT, GRAPHICS OR OTHER ITEMS CONTAINED WITHIN THESE MATERIALS.
CONEXANT SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST REVENUES OR LOST PROFITS, WHICH MAY RESULT FROM THE USE OF THESE MATERIALS.
Conexant products are not intended for use in medical, lifesaving or life sustaining applications. Conexant customers using or selling
Conexant products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Conexant for any damages resulting from
such improper use or sale.
The following are trademarks of Conexant Systems, Inc.: Conexant™, the Conexant C symbol, “What’s Next in Communications
Technologies”™, ConfigurACE™, K56flex™, SmartDAA™, and SmartSCM™. Product names or services listed in this publication are for
identification purposes only, and may be trademarks of third parties. Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective
owners.
For additional disclaimer information, please consult Conexant’s Legal Information posted at www.conexant.com, which is incorporated by
reference.
Reader Response:
Conexant strives to produce quality documentation and welcomes your feedback. Please send comments and
suggestions to tech.pubs@conexant.com. For technical questions, contact your local Conexant sales office or field applications engineer.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
iii
Contents
1 INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................................. 1-1
1.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Features ................................................................................................................................................... 1-4
1.2.1 General Modem Features .......................................................................................................... 1-4
1.2.2 SmartDAA Features ................................................................................................................... 1-5
1.2.3 Applications................................................................................................................................ 1-5
1.3 Technical Overview .................................................................................................................................. 1-5
1.3.1 General Description ................................................................................................................... 1-5
1.3.2 MCU Firmware ........................................................................................................................... 1-5
1.3.3 Operating Modes........................................................................................................................ 1-6
Data/Fax Modes................................................................................................................ 1-6
Synchronous Access Mode (SAM) - Video Conferencing................................................. 1-6
Worldwide Operation ........................................................................................................ 1-6
TAM Mode......................................................................................................................... 1-7
Voice/Speakerphone Mode (S Models)............................................................................. 1-7
1.3.4 Reference Design ...................................................................................................................... 1-7
1.3.5 GSM (Parallel Host Interface) .................................................................................................... 1-7
1.4 Hardware Description............................................................................................................................... 1-7
1.4.1 CX88168 Single Chip Modem.................................................................................................... 1-7
1.4.2 Digital Isolation Barrier............................................................................................................... 1-8
1.4.3 CX20463 SmartDAA Line Side Device ...................................................................................... 1-8
1.4.4 CX20437 Voice Codec............................................................................................................... 1-8
1.5 Commands ............................................................................................................................................... 1-8
2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Serial DTE Interface Operation ................................................................................................................ 2-1
2.1.1 Automatic Speed/Format Sensing .............................................................................................2-1
2.2 Parallel Host Bus Interface Operation ...................................................................................................... 2-1
2.3 Establishing Data Modem Connections ................................................................................................... 2-1
Telephone Number Directory ............................................................................................ 2-1
Dialing ............................................................................................................................... 2-1
Modem Handshaking Protocol.......................................................................................... 2-2
Call Progress Tone Detection ........................................................................................... 2-2
Answer Tone Detection..................................................................................................... 2-2
Ring Detection................................................................................................................... 2-2
Billing Protection ............................................................................................................... 2-2
Connection Speeds........................................................................................................... 2-2
Automode.......................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.4 Data Mode................................................................................................................................................ 2-3
Speed Buffering (Normal Mode) ....................................................................................... 2-3
Flow Control ...................................................................................................................... 2-3
Escape Sequence Detection............................................................................................. 2-3
BREAK Detection.............................................................................................................. 2-3
Telephone Line Monitoring................................................................................................ 2-3
Send SPACE on Disconnect (V.22 bis and Below)........................................................... 2-3
Fall Forward/Fallback (V.90/K56flex/V.34/V.32 bis/V.32) ................................................. 2-3
Retrain............................................................................................................................... 2-3
Programmable Inactivity Timer ......................................................................................... 2-3
DTE Signal Monitoring (Serial DTE Interface Only) .......................................................... 2-4
2.5 Error Correction and Data Compression .................................................................................................. 2-4
V.42 Error Correction ........................................................................................................ 2-4
MNP 2-4 Error Correction.................................................................................................. 2-4
V.42 bis Data Compression .............................................................................................. 2-4
MNP 5 Data Compression ................................................................................................ 2-4

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
iv
Conexant
100490C
2.6 MNP 10 Data Throughput Enhancement ................................................................................................. 2-4
2.7 MNP 10EC™ Enhanced Cellular Connection .......................................................................................... 2-4
2.8 Telephony Extensions .............................................................................................................................. 2-5
2.8.1 Line In Use Detection................................................................................................................. 2-5
2.8.2 Extension Pickup Detection ....................................................................................................... 2-5
2.8.3 Remote Hangup Detection......................................................................................................... 2-5
2.9 Fax Class 1, Fax Class 1.0, and Fax Class 2 Operation.......................................................................... 2-5
2.10 Voice/Audio Mode .................................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.10.1 Online Voice Command Mode ................................................................................................... 2-5
2.10.2 Voice Receive Mode .................................................................................................................. 2-5
2.10.3 Voice Transmit Mode ................................................................................................................. 2-6
2.10.4 Audio Mode................................................................................................................................ 2-6
2.10.5 Tone Detectors........................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.10.6 Speakerphone Modes................................................................................................................ 2-6
2.11 Full-Duplex Speakerphone (FDSP) Mode (S Models).............................................................................. 2-6
2.12 Caller ID ................................................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.13 Worldwide Country Support ..................................................................................................................... 2-7
2.14 Diagnostics............................................................................................................................................... 2-7
2.14.1 Commanded Tests..................................................................................................................... 2-7
2.14.2 Power On Reset Tests............................................................................................................... 2-7
2.15 Low Power Sleep Mode............................................................................................................................ 2-7
2.16 GSM Operation......................................................................................................................................... 2-8
3 HARDWARE INTERFACE.................................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.1 CX88168 SCM Hardware Pins and Signals ............................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.1 Common to Parallel and Serial Interface Configurations ........................................................... 3-1
LSD Interface (Through DIB) ............................................................................................ 3-1
Call Progress Speaker Interface ....................................................................................... 3-1
Voice Relay Interface (S Models)...................................................................................... 3-1
Serial EEPROM Interface.................................................................................................. 3-1
External Bus Interface....................................................................................................... 3-1
Analog Cellular Phone Interface ....................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 Serial Interface Configuration Only ............................................................................................ 3-2
Serial DTE Interface and Indicator Outputs (PARIF = Low).............................................. 3-2
3.1.3 Parallel Interface Configuration Only (PARIF = High)................................................................ 3-2
Parallel Host Bus Interface................................................................................................ 3-2
GSM Interface...................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.4 CX88168 SCM Interface Signals ............................................................................................... 3-2
3.2 CX20463 SmartDAA LSD Hardware Pins and Signals .......................................................................... 3-21
3.2.1 General .................................................................................................................................... 3-21
3.2.2 SCM Interface (Through DIB)................................................................................................... 3-21
3.2.3 Telephone Line Interface ......................................................................................................... 3-21
3.2.4 CX20463 LSD Pin Assignments and Signal Definitions........................................................... 3-21
3.3 CX20437 VC Hardware Pins and Signals (S Models)............................................................................ 3-26
3.3.1 General .................................................................................................................................... 3-26
Speakerphone Interface.................................................................................................. 3-26
Telephone Handset/Headset Interface (In Lieu of Analog Cellular Connection)............. 3-26
Analog Cellular Phone Interface (In Lieu of Telephone Handset/Headset
Connection).....................................................................................................................3-26
SCM Interface ................................................................................................................. 3-26
Host Interface..................................................................................................................3-26
3.3.2 CX20437 VC Pin Assignments and Signal Definitions............................................................. 3-26
3.4 Electrical and Environmental Specifications........................................................................................... 3-32
3.4.1 Operating Conditions, Absolute Maximum Ratings, and Power Requirements ....................... 3-32
3.4.2 Interface and Timing Waveforms .............................................................................................3-33
External Memory Bus Timing .......................................................................................... 3-33
Parallel Host Bus Timing................................................................................................. 3-35
Serial DTE Interface........................................................................................................ 3-37
4 PACKAGE DIMENSIONS................................................................................................................................... 4-1

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
v
5 PARALLEL HOST INTERFACE......................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 Register Signal Definitions ....................................................................................................................... 5-3
5.2.1 IER - Interrupt Enable Register (Addr = 1, DLAB = 0) ............................................................... 5-3
5.2.2 FCR - FIFO Control Register (Addr = 2, Write Only) ................................................................. 5-4
5.2.3 IIR - Interrupt Identifier Register (Addr = 2)................................................................................ 5-5
5.2.4 LCR - Line Control Register (Addr = 3)...................................................................................... 5-6
5.2.5 MCR - Modem Control Register (Addr = 4)................................................................................ 5-7
5.2.6 LSR - Line Status Register (Addr = 5) ....................................................................................... 5-8
5.2.7 MSR - Modem Status Register (Addr = 6) ................................................................................. 5-9
5.2.8 RBR - RX Buffer (Receiver Buffer Register) (Addr = 0, DLAB = 0)............................................ 5-9
5.2.9 THR - TX Buffer (Transmitter Holding Register) (Addr = 0, DLAB = 0)...................................... 5-9
5.2.10 Divisor Registers (Addr = 0 and 1, DLAB = 1) ........................................................................... 5-9
5.2.11 SCR - Scratch Register (Addr = 7)............................................................................................. 5-9
5.3 Receiver FIFO Interrupt Operation......................................................................................................... 5-10
5.3.1 Receiver Data Available Interrupt ............................................................................................ 5-10
5.3.2 Receiver Character Timeout Interrupts.................................................................................... 5-10
5.4 Transmitter FIFO Interrupt Operation..................................................................................................... 5-10
5.4.1 Transmitter Empty Interrupt ..................................................................................................... 5-10

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
vi
Conexant
100490C
Figures
Figure 1-1. SmartSCM Modem Simplified Interface Diagram................................................................................................... 1-2
Figure 1-2. SmartSCM Modem Major Interfaces...................................................................................................................... 1-3
Figure 3-1. CX88168 SCM Hardware Signals for Parallel Interface (PARIF = High) ............................................................... 3-3
Figure 3-2. CX88168 SCM 128-Pin TQFP Pin Signals for Parallel Interface (PARIF = High) .................................................. 3-4
Figure 3-3. CX88168 SCM Hardware Signals for Serial Interface (PARIF = Low) ................................................................. 3-11
Figure 3-4. CX88168 SCM 128-Pin TQFP Pin Signals for Serial Interface (PARIF = Low).................................................... 3-12
Figure 3-5. CX20463 LSD Hardware Interface Signals.......................................................................................................... 3-22
Figure 3-6. CX20463 LSD 32-Pin TQFP Pin Signals ............................................................................................................. 3-22
Figure 3-7. CX20437 VC Hardware Interface Signals............................................................................................................ 3-27
Figure 3-8. CX20437 VC 32-Pin TQFP Pin Signals ............................................................................................................... 3-27
Figure 3-9. Waveforms - External Memory Bus ..................................................................................................................... 3-34
Figure 3-10. Waveforms - Parallel Host Bus .......................................................................................................................... 3-36
Figure 3-11. Waveforms - Serial DTE Interface ..................................................................................................................... 3-37
Figure 4-1. Package Dimensions - 128-Pin TQFP ................................................................................................................... 4-1
Figure 4-2. Package Dimensions - 32-pin TQFP...................................................................................................................... 4-2
Tables
Table 1-1. SmartSCM Modem Models and Functions.............................................................................................................. 1-2
Table 2-1. +MS Command Automode Connectivity ................................................................................................................. 2-2
Table 3-1. CX88168 SCM 128-Pin TQFP Pin Signals for Parallel Interface (PARIF = High) ................................................... 3-5
Table 3-2. CX88168 SCM Pin Signal Definitions for Parallel Interface (PARIF = High)........................................................... 3-7
Table 3-3. CX88168 SCM 128-Pin TQFP Pin Signals for Serial Interface (PARIF = Low)..................................................... 3-13
Table 3-4. CX88168 SCM Pin Signal Definitions for Serial Interface (PARIF = Low)............................................................. 3-15
Table 3-5. CX88168 SCM I/O Type Definitions ...................................................................................................................... 3-20
Table 3-6. CX88168 SCM DC Electrical Characteristics........................................................................................................ 3-20
Table 3-7. CX20463 LSD 32-Pin TQFP Pin Signals............................................................................................................... 3-23
Table 3-8. CX20463 LSD Pin Signal Definitions .................................................................................................................... 3-24
Table 3-9. CX20463 LSD DC Electrical Characteristics......................................................................................................... 3-25
Table 3-10. CX20437 VC 32-Pin TQFP Pin Signals............................................................................................................... 3-28
Table 3-11. CX20437 VC Pin Signal Definitions .................................................................................................................... 3-29
Table 3-12. CX20437 VC DC Electrical Characteristics......................................................................................................... 3-31
Table 3-13. CX20437 VC Analog Electrical Characteristics................................................................................................... 3-31
Table 3-14. Operating Conditions........................................................................................................................................... 3-32
Table 3-15. Absolute Maximum Ratings................................................................................................................................. 3-32
Table 3-16. Current and Power Requirements....................................................................................................................... 3-32
Table 3-17. Timing - External Memory Bus ............................................................................................................................ 3-33
Table 3-18. Timing - Parallel Host Bus................................................................................................................................... 3-35
Table 5-1. Parallel Interface Registers ..................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Table 5-2. Interrupt Sources and Reset Control....................................................................................................................... 5-5
Table 5-3. Programmable Baud Rates ................................................................................................................................... 5-10

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
1-1
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview
The Conexant SmartSCM V.90/K56flex Modem Device Set with SmartDAA technology supports analog data up to 56
kbps, analog fax to 14.4 kbps, telephone answering machine (TAM)/telephony extensions, voice/speakerphone (optional),
GSM, analog cellular (optional), and parallel/serial host interface operation depending on model. Table 1-1 lists the available
models.
The modem operates with PSTN telephone lines worldwide and supports optional direct connect to an AMPS analog cellular
phone. The parallel host interface model also supports direct connect to a GSM phone.
Conexant's SmartDAA technology (patent pending) eliminates the need for a costly analog transformer, relays, and optoisolators typically used in discrete DAA (Data Access Arrangement) implementations The SmartDAA architecture also
simplifies product implementation by eliminating the need for country-specific board configurations enabling worldwide
homologation of a single modem board design and a single bill of materials (BOM).
The SmartDAA system-powered DAA operates reliably without drawing power from the line, unlike line-powered DAAs which
operate poorly when line current is insufficient due to long lines or poor line conditions. Enhanced features, such as
monitoring of local extension status without going off-hook, are also supported.
Incorporating Conexant’s proprietary Digital Isolation Barrier (DIB) design (patent pending) and other innovative DAA
features, the SmartDAA architecture simplifies application design, minimizes layout area, and reduces component cost.
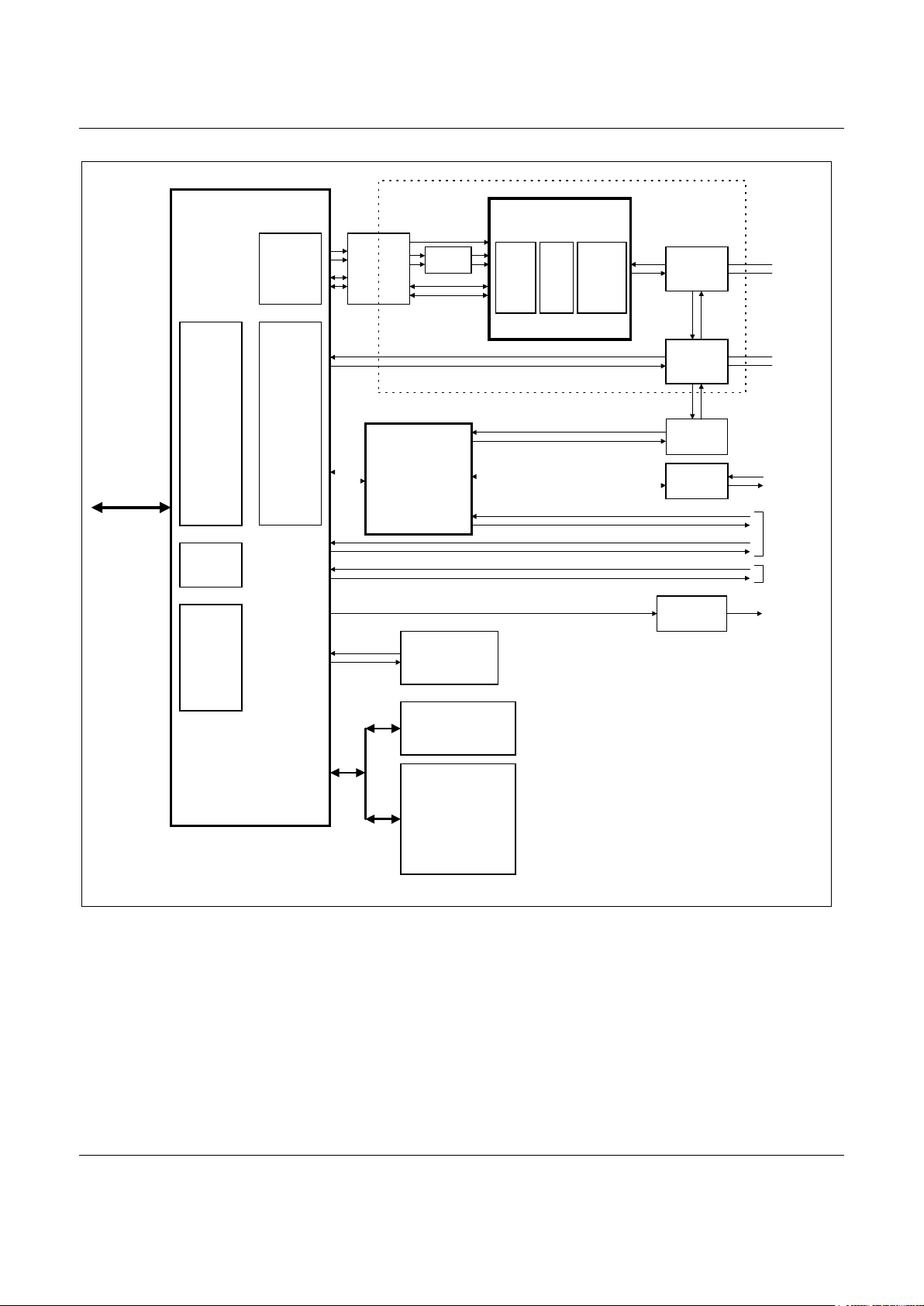
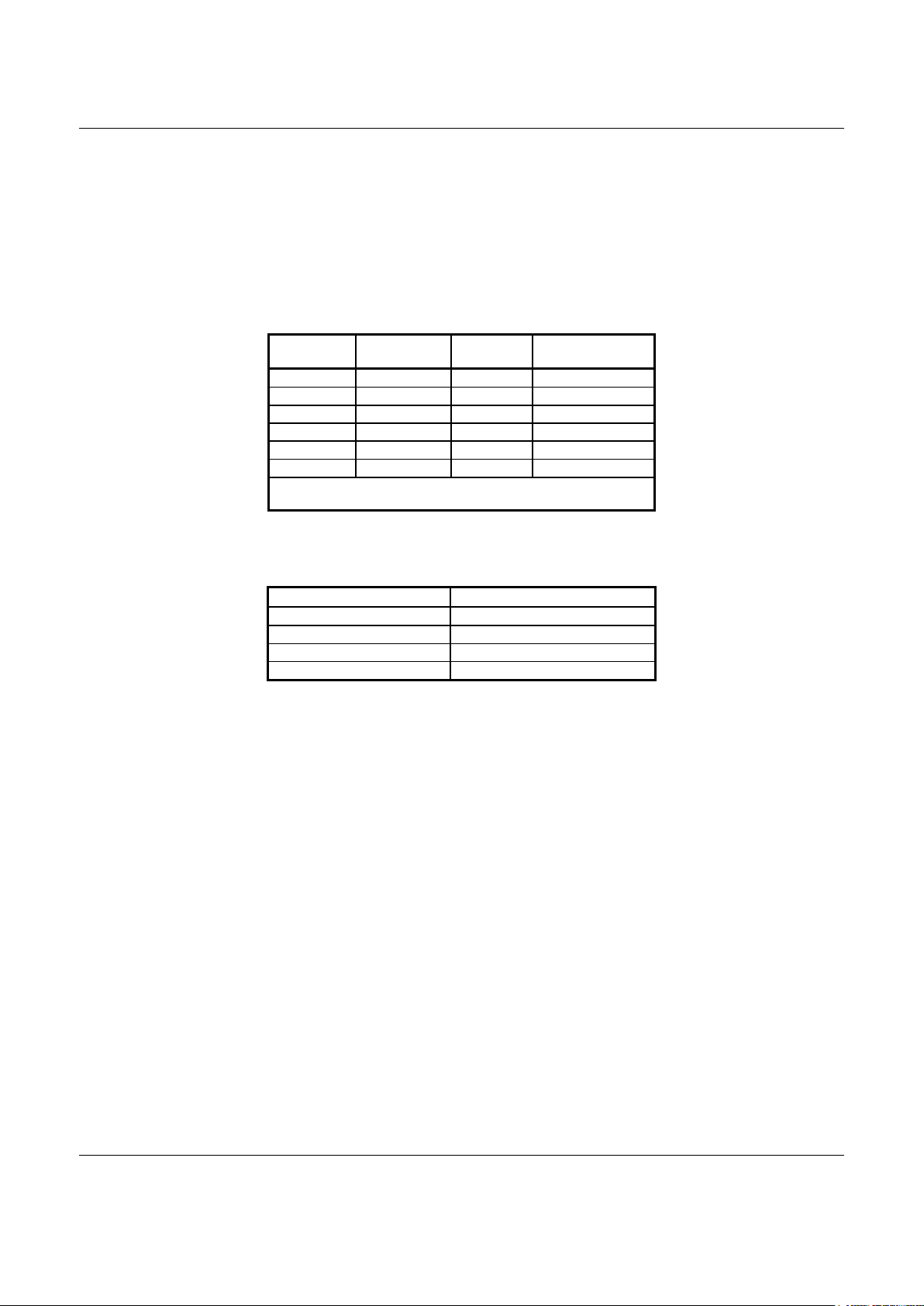
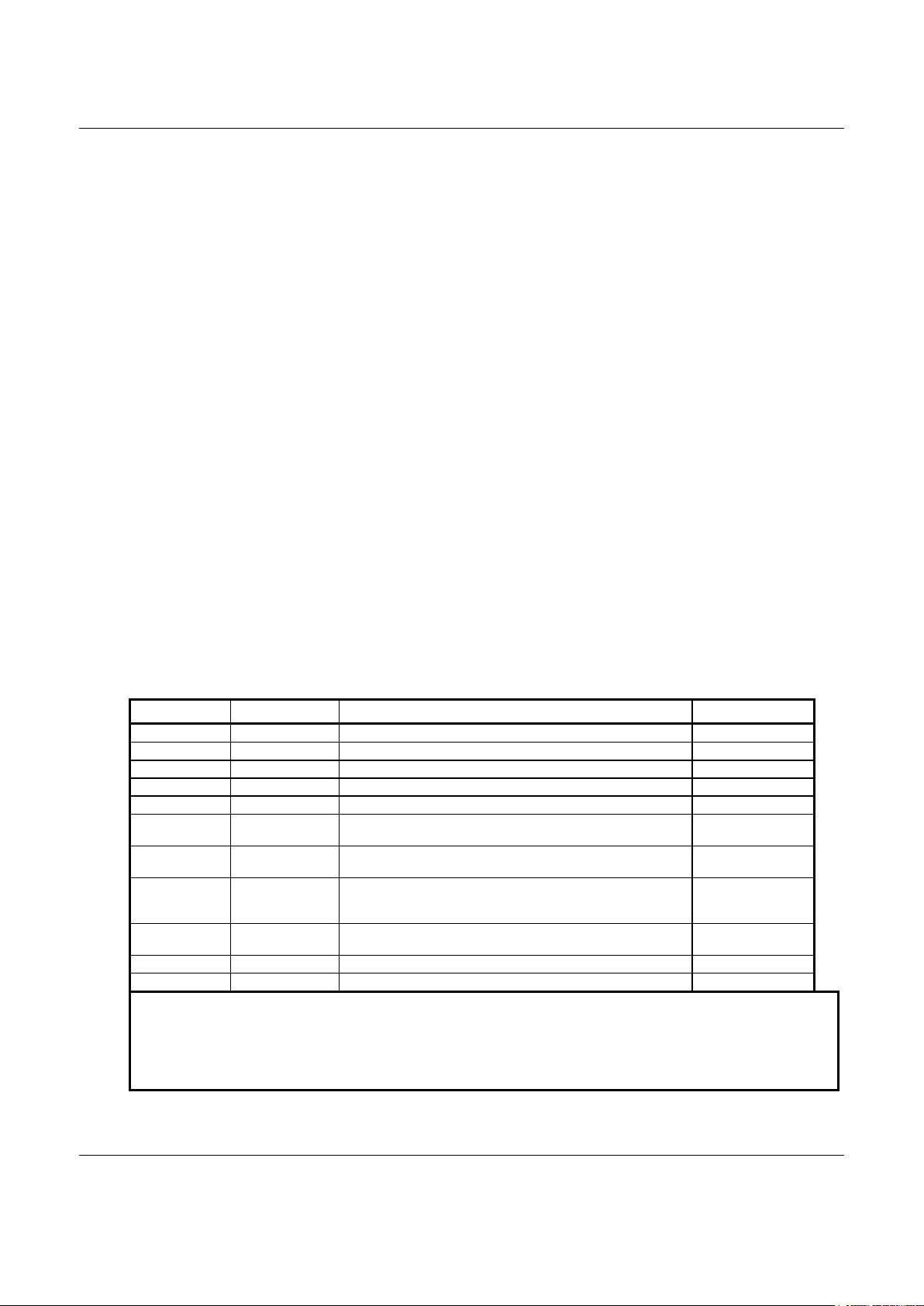
The SmartSCM device set, consisting of a CX88168 Single Chip Modem (SCM) in a 128-pin TQFP and a CX20463
SmartDAA™ Line Side Device (LSD) in a 32-pin TQFP, supports data/fax/TAM operation with hardware-based modem
controller, digital signal processing, and DAA/telephone line interface functions (Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2).
The SCM device integrates modem controller (MCU), modem data pump (MDP), 256k bytes ROM, 32k bytes RAM, and
SmartDAA system side device (SSD) functions onto a single die.
Modem functions for both parallel and serial interface configurations operate using only internal memory with the exception of
GSM which requires external memory. The external memory interface can also be used for customized modem code and
added/modified country profiles.
Low profile, small TQFP packages and low voltage operation with low power consumption make this device set ideal for
embedded and palmtop applications using parallel host or serial DTE interface.
The modem operates by executing firmware from internal ROM and RAM. Customized modem firmware can be executed
from optional external memory, either from ROM/flash ROM or from serial EEPROM and RAM. GSM operation requires an
external 1 Mbit (128k x 8) ROM/flash ROM.
In V.90/K56flex data mode (/56 models), the modem can receive data at line speeds up to 56 kbps from a digitally connected
V.90 or K56flex-compatible central site modem. In this mode, the modem can transmit data at line speeds up to V.34 rates.
In V.34 data mode (/56 and /33 models), the modem operates at line speeds up to 33.6 kbps. When applicable, error
correction (V.42/MNP 2-4) and data compression (V.42 bis/MNP 5) maximize data transfer integrity and boost average data
throughput. Non-error-correcting mode is also supported.
In V.32 bis data mode, the modem operates at lines speeds up to 14.4 kbps.
In V.22 bis fast connect mode, the modem can connect at 2400 bps with a very short training time, which is very efficient for
small data transfers.
Fax Group 3 send and receive rates are supported up to 14.4 kbps with T.30 protocol.
V.80 synchronous access mode supports host-controlled communication protocols, e. g., H.324 video conferencing.
In TAM mode, enhanced 2-bit or 4-bit per sample coding schemes at 8 kHz sample rate provide flexible format compatibility
and allows efficient digital storage of voice/audio. Also supported are 8-bit linear and IMA 4-bit ADPCM coding. This mode
supports applications such as digital telephone answering machine (TAM), voice annotation, and recording from and playback
to the telephone line.
S models, using the optional CX20437 Voice Codec (VC) in a 32-pin TQFP, support position independent, full-duplex
speakerphone (FDSP) operation using microphone and speaker, as well as other voice/TAM applications using handset or
headset. S models can also support analog cellular operation with direct connection to an analog cellular phone (in lieu of a
telephone handset/headset connection).
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
1-2
Conexant
100490C
GSM operation supports data services offered by the Global System for Mobile Communications network: data transmissions
to PSTN, ISDN or GSM users. GSM data operation allows data and fax transfer, and connection to videotex.
Analog cellular and GSM direct connect operation is supported by licensed firmware for specific phone types.
This data sheet describes the modem capabilities. Commands and parameters are defined in the Commands Reference
Manual (Doc. No. 100722).
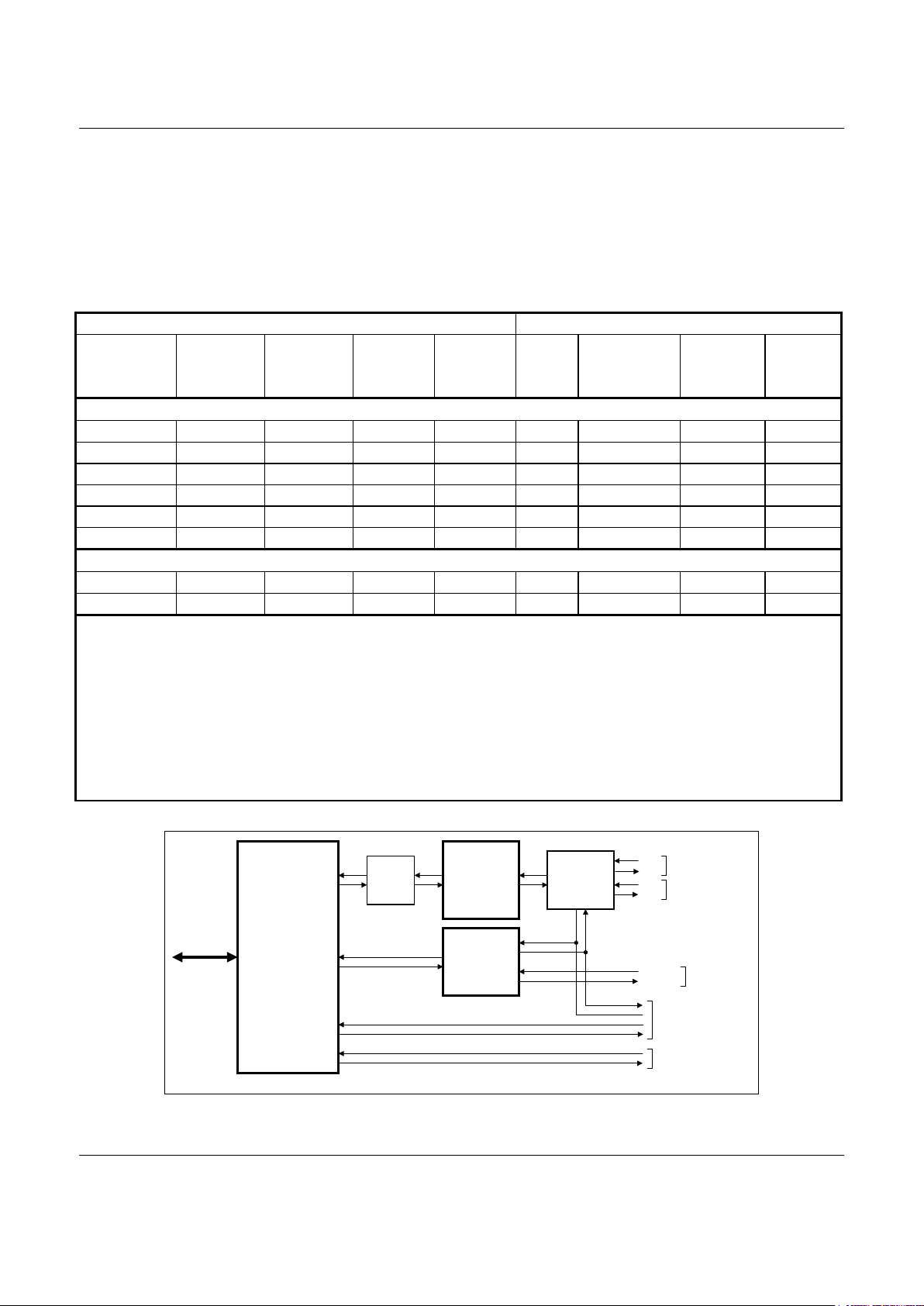
Table 1-1. SmartSCM Modem Models and Functions
Model/Order/Part Numbers Supported Functions
Marketing Name Device Set
Order No.
Single Chip
Modem (SCM)
[128-Pin TQFP]
Part No.
Line Side
Device (LSD)
[32-Pin TQFP]
Part No.
Voice Codec
(VC)
[32-Pin TQFP]
Part No.
V.90 and
K56flex
Data
V.34 Data V.32 bis Data,
V.17 Fax,
TAM,
Worldwide
Voice/FDSP,
Analog
Cellular
EMBEDDED APPLICATIONS
SmartSCM/56 DS56-L145-061 CX88168-11 20463-11 — Y Y Y —
SmartSCM/56S DS56-L145-071 CX88168-11 20463-11 20437-11 Y Y Y Y
SmartSCM/33 DS28-L189-061 CX88168-12 20463-11 — — Y Y —
SmartSCM/33S DS28-L189-071 CX88168-12 20463-11 20437-11 — Y Y Y
SmartSCM/14 DS96-L853-041 CX88168-13 20463-11 — — — Y —
SmartSCM/14S DS96-L853-051 CX88168-13 20463-11 20437-11 — — Y Y
AFTERMAR KET APP LICATIONS
SmartSCM/56 DS56-L144-121 CX88168-11 20463-11 — Y Y Y —
SmartSCM/56S DS56-L144-131 CX88168-11 20463-11 20437-11 Y Y Y Y
Notes:
1. Model options:
S Voice/full-duplex speakerphone (FDSP) and analog cellular
56 56 kbps max. rate per V.90
33 33.6 kbps max. rate per V.34
14 14.4 kbps max. rate per V.32 bis.
2. Supported functions (Y = Supported; – = Not supported).
TAM Telephone answering machine (Voice playback and record through telephone line)
FDSP Full-duplex speakerphone and voice playback and record through telephone line, handset, and mic/speaker
3. For ordering purposes, the CX prefix may not be included in the part number for some devices. Also, the CX prefix may not appear in the part number as branded on
some devices.
CX88168
Single Chip Modem
(SCM)
128-Pin TQFP
CX20463
SmartDAA
Line Side
Device (LSD)
32-Pin TQFP
CX20437
Voice Codec
(VC)
32-Pin TQFP
(Optional)
MIC
SPEAKER
TIP
RING
Telephone
Line
Interface
Discrete
Components
100491_F1-1_SID
Digital
Isolation
Barrier
(DIB)
TIP
RING
HANDSET (OPTIONAL)
TELEPHONE LINE
(OPTIONAL)
PARALLEL
HOST BUS OR
SERIAL DTE
INTERFACE
ANALOG CELL PHONE
(OPTIONAL)
GSM PHONE
(OPTIONAL)
l
Figure 1-1. SmartSCM Modem Simplified Interface Diagram
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
1-3
CX88168
Single Chip Modem (SCM)
128-Pin TQFP
CX20437
Voice Codec (VC)
32-Pin TQFP
(Optional)
SmartDAA
Interface
Modem Data
Pump (MDP)
Digital Speaker
Circuit (Optional)
Paralle Host
or Serial DTE
Interface
MIC
SPEAKER
100491_F1-2_FID
SOUNDUCER
HS Hybrid
Components
(Optional)
RAM
(32K x 8)
ROM
(256k x 8)
Cellular
Interface
GSM Interface
(Parallel host
interface only)
Optional RAM
Up to 1M (128K x 8)
Optional Flash ROM
Up to 4M (512K x 8)
[1M (128K x 8) required for
GSM with Base Modem Code
in Internal Flash ROM]
[4M (512K x 8) required for
GSM with Base Modem Code
in External Flash ROM]
Microcontroller
Unit (MCU)
Serial EEPROM
2K (256 x 8) to
256K (32K x 8)
(Optional)
TIP
RING
Telephone
Line Interface
Discrete
Components
TIP
RING
Voice Relay,
HS Pickup
Detector
(Optional)
TELEPHONE
LINE
TELEPHONE
HANDSET
Digital
Isolation
Barrier (DIB)
Components
CX20463 SmartDAA
Line Side Device (LSD)
32-Pin TQFP
Line
Side
DIB
Interface
(LSDI)
Codec
Telephone
Line
Interface
DAA Hardware
Rectifier
and Filter
Components
(Mic/Speaker)
Interface
(Optional)
Figure 1-2. SmartSCM Modem Major Interfaces

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
1-4
Conexant
100490C
1.2 Features
1.2.1 General Modem Features
•
Data modem
−
ITU-T V.90/K56flex (/56 models)/V.34 (/56 and /33 models), V.32bis, V.32, V.22 bis, V.22, V.23, and V.21;
Bell 212A and Bell 103
−
V.42 LAPM and MNP 2-4 error correction
−
V.42 bis and MNP 5 data compression
−
MNP 10EC™ enhanced cellular performance
−
V.250 and V.251 commands
•
V.22 bis fast connect
•
Analog cellular direct connect using optional CX20437 Voice Codec (S models)
•
GSM cellular direct connect (parallel interface only)
•
Fax modem send and receive rates up to 14.4 kbps
−
V.17, V.29, V.27 ter, and V.21 channel 2
−
EIA/TIA 578 Class 1 and T.31 Class 1.0, and EIA/TIA 578 Class 2 commands
•
V.80 synchronous access mode supports host-controlled communication protocols with H.324 interface support
•
Interfaces to optional external ROM/flash ROM and/or to optional external serial EEPROM and RAM for customized modem
firmware
•
Downloadable Architecture
−
Downloadable MCU firmware from the host/DTE to optional external flash ROM
−
Downloadable MDP code modules from the MCU transparent to the host
•
Data/Fax/Voice call discrimination
•
Hardware-based modem controller
•
Hardware-based digital signal processor (DSP)
•
Worldwide operation
−
Complies to TBR21 and other country requirements
−
Caller ID detection
−
Call progress, blacklisting
−
Internal ROM includes default values for 29 countries
•
Caller ID and distinctive ring detect
•
Telephony/TAM
−
V.253 commands
−
2-bit and 4-bit Conexant ADPCM, 8-bit linear PCM, and 4-bit IMA coding
−
8 kHz sample rate
−
Concurrent DTMF, ring, and Caller ID detection
•
Full-duplex speakerphone (FDSP) mode using optional CX20437 Voice Codec (S models)
−
Microphone and speaker interface
−
Telephone handset or headset interface
−
Acoustic and line echo cancellation
−
Microphone gain and muting
−
Speaker volume control and muting
•
Built-in host/DTE interface with speeds up to 230.4 kbps
−
Parallel 16550A UART-compatible interface
−
Serial ITU-T V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E) logical interface
•
Direct mode (serial DTE interface)
•
Flow control and speed buffering
•
Automatic format/speed sensing
•
Serial async data; parallel async data
•
Thin packages support low profile designs (1.6 mm max. height)
−
CX88168 SCM: 128-pin TQFP
−
CX20463 LSD: 32-pin TQFP
−
CX20437 VC: 32-pin TQFP
•
+3.3V operation with +5V tolerant digital inputs
•
Typical power use
SCM and LSD: 470 mW (Normal Mode); 140 mW (Sleep Mode)
VC: 5 mW (Normal Mode)

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
1-5
1.2.2 SmartDAA Features
•
System side powered DAA operates under poor line current supply conditions
•
Wake-on-ring
•
Ring detection
•
Line polarity reversal detection
•
Line current loss detection
•
Pulse dialing
•
Line-in-use detection – detects even while on-hook
•
Remote hang-up detect – for efficient call termination
•
Extension pickup detect
•
Call waiting detection
•
Digital PBX line protection
•
Meets worldwide DC VI Masks requirements
1.2.3 Applications
•
Handheld computers
•
Gaming devices
•
Point of sales terminals
•
Remote monitoring and data collection systems
1.3 Technical Overview
1.3.1 General Description
Modem operation, including dialing, call progress, telephone line interface, telephone handset interface, optional
voice/speakerphone interface, optional analog cellular phone interface, GSM interface, and host interface functions are
supported and controlled through the V.250, V.251, and V.253-compatible command set.
The modem hardware connects to the host via a parallel or serial interface as selected by the PARIF input. The OEM adds a
crystal circuit, DIB components, telephone line interface, telephone handset/telephony extension interface,
voice/speakerphone interface, cellular interface, GSM interface, optional external serial EEPROM, optional external
ROM/flash ROM, optional external RAM, and other supporting discrete components as supported by the modem model
(Table 1-1) and required by the application to complete the system.
Customized modem firmware can be supported by the use of external memory in various combinations, e.g., either external
ROM/flash ROM (up to 256k bytes), or external serial EEPROM (256 to 32k bytes) and external RAM (up to 128k bytes). To
support country profile addition or modification, external serial EEPROM (256 to 32k bytes) can be installed. Customized code
can include OEM-defined commands, i.e., identification codes (I3), identifier string (I4), manufacturer identification (+GMI),
model identification (+GMM), and revision identification (+GMR), as well as code modification.
Parallel interface operation is selected by PARIF input high. Telephone line, cellular (AMPS) phone, or GSM phone interface
operation is selected by the LINE/CELL and LINE/GSM inputs. Installation of cellular phone driver is also required for cellular
phone interface operation. Installation of GSM firmware is also required for GSM phone interface operation.
Serial interface operation is selected by PARIF input low. Telephone line or cellular (AMPS) phone interface operation is
selected by the LINE/CELL input. Installation of cellular phone driver is also required for cellular phone interface operation.
1.3.2 MCU Firmware
MCU firmware performs processing of general modem control, command sets, data modem, error correction and data
compression (ECC), fax class 1, fax class 1.0, fax class 2, voice/audio/TAM/speakerphone, worldwide, V.80, and serial
DTE/parallel host interface functions according to modem models (Table 1-1).
MCU firmware can be customized to include OEM-defined commands, i.e., identification codes (I3), identifier string (I4),
manufacturer identification (+GMI), model identification (+GMM), and revision identification (+GMR), as well as code
modification.
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
1-6
Conexant
100490C
1.3.3 Operating Modes
Data/Fax Modes
In V.90/K56flex data modem mode (/56 models), the modem can receive data from a digital source using a V.90- or K56flexcompatible central site modem at line speeds up to 56 kbps. Asymmetrical data transmission supports sending data at line
speeds up to V.34 rates. This mode can fallback to full-duplex V.34 mode and to lower rates as dictated by line conditions.
In V.34 data modem mode (/56 and /33 models), the modem can operate in 2-wire, full-duplex, asynchronous modes at line
rates up to 33.6 kbps. Data modem modes perform complete handshake and data rate negotiations. Using V.34 modulation
to optimize modem configuration for line conditions, the modem can connect at the highest data rate that the channel can
support from 33600 bps down to 2400 bps with automatic fallback. Automode operation in V.34 is provided in accordance
with PN3320 and in V.32 bis in accordance with PN2330. All tone and pattern detection functions required by the applicable
ITU or Bell standards are supported.
In V.32 bis data modem mode, the modem can operate at line speeds up to 14.4 kbps.
In V.22 bis fast connect data mode, the modem can connect at 2400 bps with a very short training time, which is very efficient
for small data transfers.
In fax modem mode, the modem can operate in 2-wire, half-duplex, synchronous modes and can support Group 3 facsimile
send and receive speeds of 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800, and 2400 bps. Fax data transmission and reception performed
by the modem are controlled and monitored through the EIA/TIA-578 Fax Class 1, T.31 Fax Class 1.0, or Fax Class 2
command interface. Full HDLC formatting, zero insertion/deletion, and CRC generation/checking are provided.
Synchronous Access Mode (SAM) - Video Conferencing
V.80 Synchronous Access Mode between the modem and the host/DTE is provided for host-controlled communication
protocols, e.g., H.324 video conferencing applications.
Voice-call-first (VCF) before switching to a videophone call is also supported.
Worldwide Operation
The modem operates in TBR21-compliant and other countries. Country-dependent modem parameters for functions such as
dialing, carrier transmit level, calling tone, call progress tone detection, answer tone detection, blacklisting, caller ID, and relay
control are programmable (see Section 2.13).
SmartDAA technology allows a single PCB design and single BOM to be homologated worldwide. Advanced features such as
extension pickup detection, remote hang-up detection, line-in-use detection, and digital PBX detection are supported.
Country code IDs are defined by ITU-T T.35.
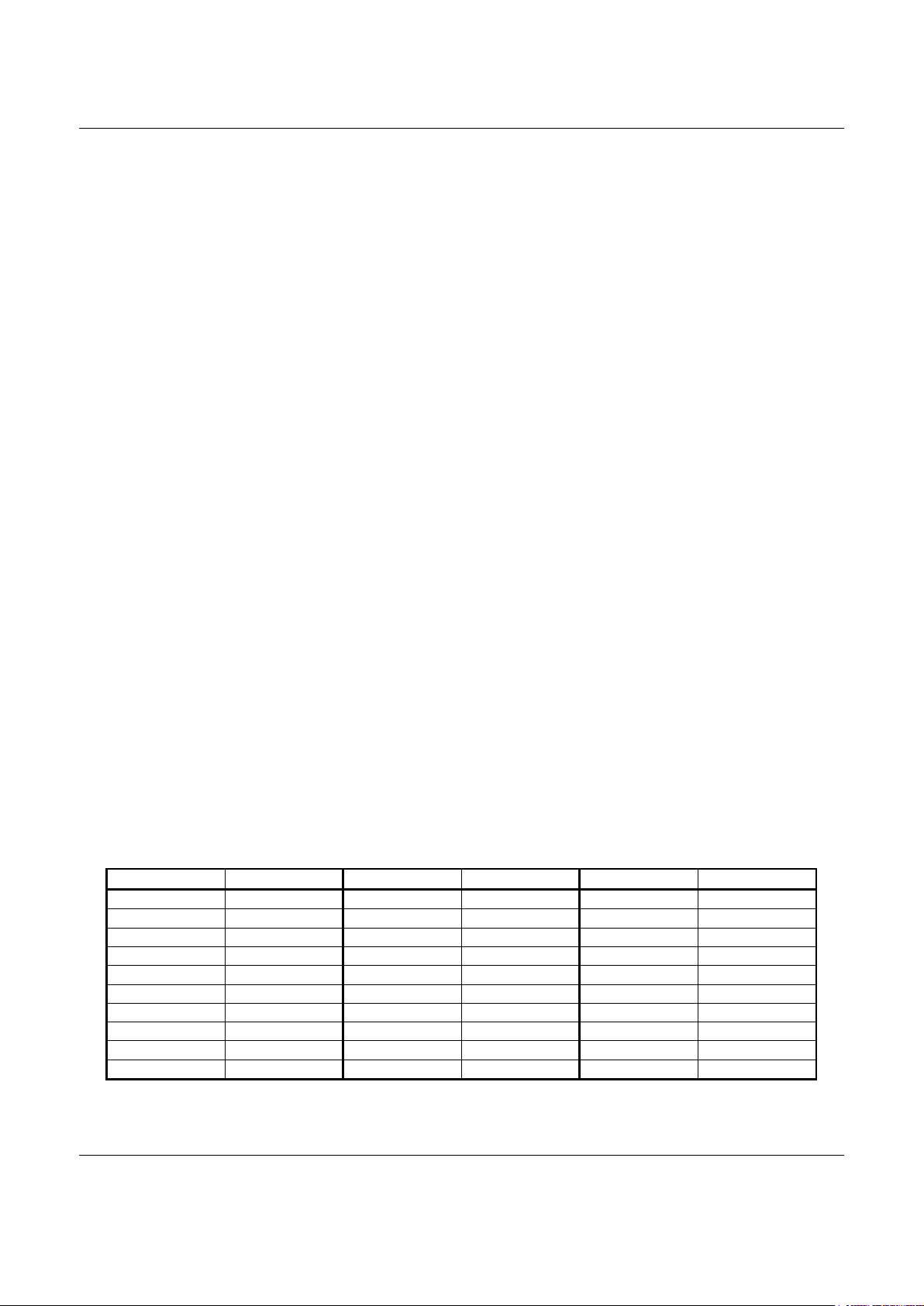
Internal ROM includes default profiles for 29 countries including TBR21-compliant profiles. These profiles can be overridden
by modified values stored in external serial EEPROM. If optional external ROM/flash ROM is used, a maximum of 31 country
profiles can be stored in external ROM/flash ROM. Additional country profiles can also be stored in external serial EEPROM
(request additional country profiles from a Conexant Sales Office). The default countries supported are:
Country Country Code Country Country Code Country Country Code
Australia 09 India 53 Portugal 8B
Austria 0A Ireland 57 Singapore 9C
Belgium 0F Italy 59 South Africa 9F
Brazil 16 Japan 00 Spain A0
China 26 Korea 61 Sweden A5
Denmark 31 Malaysia 6C Switzerland A6
Finland 3C Mexico 73 Taiwan FE
France 3D Netherlands 7B United Kingdom B4
Germany 42 Norway 82 United States B5
Greece 46 Poland 8A

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
1-7
TAM Mode
TAM Mode features include 8-bit linear coding at 8 kHz sample rate. Tone detection/generation, call discrimination, and
concurrent DTMF detection are also supported. ADPCM (4-bit IMA) coding is also supported to meet Microsoft WHQL logo
requirements.
TAM Mode is supported by three submodes:
1. Online Voice Command Mode supports connection to the telephone line or, for S models, a
microphone/speaker/handset/headset.
2. Voice Receive Mode supports recording voice or audio data input from the telephone line or, for S models, a
microphone/handset/headset.
3. Voice Transmit Mode supports playback of voice or audio data to the telephone line or, for S models, a
speaker/handset/headset.
Voice/Speakerphone Mode (S Models)
S models include additional telephone handset, external microphone, and external speaker interfaces which support voice
and full-duplex speakerphone (FDSP) operation.
Hands-free full-duplex telephone operation is supported in Speakerphone Mode under host control. Speakerphone Mode
features an advanced proprietary speakerphone algorithm which supports full-duplex voice conversation with acoustic, line,
and handset echo cancellation. Parameters are constantly adjusted to maintain stability with automatic fallback from fullduplex to pseudo-duplex operation. The speakerphone algorithm allows position independent placement of microphone and
speaker. The host can separately control volume, muting, and AGC in microphone and speaker channels.
1.3.4 Reference Design
A data/fax/TAM/speakerphone reference design for an external modem (RD00-D970) is available to minimize application
design time, reduce development cost, and accelerate market entry.
A design package is available in electronic form. This package includes schematics, bill of materials (BOM), vendor part list
(VPL), board layout files in Gerber format, and complete documentation.
1.3.5 GSM (Parallel Host Interface)
Supported GSM features include:
•
Data modem
−
V.21, V.23, V.22, V.22 bis, V.32
−
ISDN interoperability: 300 bps to 9600 bps
•
Transparent asynchronous mode up to 9600 bps
•
Non-transparent mode (RLP) up to 9600 bps
•
Fax modem send and receive rate up to 9600 bps
•
AT GSM commands (ETSI 07.07)
•
GSM direct connect
•
Firmware interface for OEM-provided phone driver
•
Automatic GSM cable presence detection
•
Built-in parallel host (16550A UART) interface
GSM operation requires an external 1 Mbit (128k x 8) ROM/flash ROM. If optional external ROM/flash ROM is used for the
base modem code, GSM operation requires 1 Mbit of an the external 4 Mbits (512k x 8) ROM/flash ROM.
1.4 Hardware Description
SmartDAA technology (patent pending) eliminates the need for a costly analog transformer, relays, and opto-isolators that
are typically used in discrete DAA implementations. The programmable SmartDAA architecture simplifies product
implementation in worldwide markets by eliminating the need for country-specific components.
1.4.1 CX88168 Single Chip Modem
The CX88168 Single Chip Modem (SCM), packaged in a 128-pin TQFP, includes a Microcontroller (MCU), a Modem Data
Pump (MDP), 256k bytes internal ROM, 32k bytes internal RAM, and SmartDAA interface functions.
The SCM connects to host via a parallel host (PARIF = high) or a logical V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E) serial DTE interface (PARIF =
low).

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
1-8
Conexant
100490C
The SCM performs the command processing and host interface functions. The crystal frequency is 28.224 MHz.
The SCM optionally connects to external OEM-supplied ROM/flash ROM and RAM over a non-multiplexed 19-bit address bus
and 8-bit data bus. GSM operation requires external 1M (128k x 8) ROM/flash ROM.
The SCM optionally connects to an external OEM-supplied serial EEPROM over a dedicated 2-line serial interface. The
capacity of the EEPROM can be 256 bytes up to 32k bytes. The EEPROM can hold information such as firmware
configuration customization, country code parameters, and cellular drivers.
The SCM performs telephone line signal modulation/demodulation in a hardware digital signal processor (DSP) which
reduces computational load on the host processor.
The SmartDAA Interface communicates with, and supplies power and clock to, the LSD through the DIB.
1.4.2 Digital Isolation Barrier
The OEM-supplied Digital Isolation Barrier (DIB) electrically DC isolates the SCM from the LSD and telephone line. The SCM
is connected to a fixed digital ground and operates with standard CMOS logic levels. The LSD is connected to a floating
ground and can tolerate high voltage input (compatible with telephone line and typical surge requirements).
The DIB transformer couples power and clock from the SCM to the LSD.
The DIB data channel supports bidirectional half-duplex serial transfer of data, control, and status information between the
SCM and the LSD over two lines.
1.4.3 CX20463 SmartDAA Line Side Device
The CX20463 SmartDAA Line Side Device (LSD) includes a Line Side DIB Interface (LSDI), a coder/decoder (codec), and a
Telephone Line Interface (TLI).
The LSDI communicates with, and receives power and clock from, the SmartDAA interface in the SCM through the DIB.
LSD power is received from the MDP PWRCLKP and PWRCLKN pins via the DIB through a half-wave rectifying diode and
capacitive power filter circuit connected to the DIB transformer secondary winding.
The CLK input is also accepted from the DIB transformer secondary winding through a capacitor and a resistor in series.
Information is transferred between the LSD and the SCM through the DIB_P and DIB_N pins. These pins connect to the SCM
DIB_DATAP and DIB_DATAN pins, respectively, through the DIB.
The TLI integrates DAA and direct telephone line interface functions and connects directly to the line TIP and RING pins, as
well as to external line protection components.
Direct LSD connection to TIP and RING allows real-time measurement of telephone line parameters, such as the telephone
central office (CO) battery voltage, individual telephone line (copper wire) resistance, and allows dynamic regulation of the offhook TIP and RING voltage and total current drawn from the central office (CO). This allows the modem to maintain
compliance with U.S. and worldwide regulations and to actively control the DAA power dissipation.
1.4.4 CX20437 Voice Codec
The optional CX20437 Voice Codec (VC), packaged in a 32-pin TQFP, supports voice/full-duplex speakerphone (FDSP)
operation with interfaces to a microphone and speaker and to a telephone handset/headset. The VC also supports and
analog cellular operation with direct connect interface to a cellular phone (in lieu of telephone handset/headset connection).
1.5 Commands
The modem supports data modem, fax class 1 modem, fax class 1.0 modem, fax class 2 modem, voice/audio, full-duplex
speakerphone (FDSP), MNP 10/MNP 10EC, and V.80 commands, and S Registers in accordance with modem model
options. See Doc. No. 100722 for a description of the commands.
Data Modem Operation.
Data modem functions operate in response to the AT commands when +FCLASS=0. Default
parameters support U.S./Canada operation.
MNP 10 Operation.
MNP 10 functions operate in response to MNP 10 commands.
MNP 10EC Operation
. MNP 10EC is enabled by the -SEC=1 command.
Fax Modem Operation.
Facsimile functions operate in response to fax class 1 commands when +FCLASS=1, fax class 1.0
commands when +FCLASS=1.0, or to fax class 2 commands when +FCLASS=2 is installed.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
1-9
Voice/Audio Operation.
Voice/audio mode functions operate in response to voice/audio commands when +FCLASS=8.
Speakerphone Operation.
FDSP functions operate in response to speakerphone commands when +FCLASS=8 and
+VSP=1 is selected.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
1-10
Conexant
100490C
This page is intentionally blank.
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
2-1
2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 Serial DTE Interface Operation
2.1.1 Automatic Speed/Format Sensing
Command Mode and Data Modem Mode.
The modem can automatically determine the speed and format of the data sent
from the DTE. The modem can sense speeds of 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 7200, 9600, 12000, 14400, 16800, 19200,
21600, 24000, 26400, 28800, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 230400 bps and the following data formats:
Parity
Data Length
(No. of Bits)
No. of
Stop Bits
Character Length
(No. of Bits)
None 7 2 10
Odd 7 1 10
Even 7 1 10
None 8 1 10
Odd 8 1 11*
Even 8 1 11*
*11-bit characters are sensed, but the parity bits are stripped off
during data transmission in Normal and Error Correction modes.
The modem can speed sense data with mark or space parity and configures itself as follows:
DTE Configuration Modem Configuration
7 mark 7 none
7 space 8 none
8 mark 8 none
8 space 8 even
Fax Modem Mode.
In V.17 fax mode, the modem can sense speeds up to 230.4 kbps.
2.2 Parallel Host Bus Interface Operation
Command Mode and Data Modem Mode.
The modem can operate at rates up to 230.4 kbps by programming the Divisor
Latch in the parallel interface registers if supported by communications software and/or driver (a Windows 95/98 driver is
available from Conexant).
Fax Modem Mode.
In V.17 mode, the modem can operate at rates up to 230.4 kbps by programming the Divisor Latch in the
parallel interface registers if supported by communications software and/or driver (a Windows 95/98 driver is available from
Conexant).
2.3 Establishing Data Modem Connections
Telephone Number Directory
The modem supports four telephone number entries in a directory that can be saved in a serial NVRAM. Each telephone
number can be up to 32 characters (including the command line terminating carriage return) in length. A telephone number
can be saved using the &Zn=x command, and a saved telephone number can be dialed using the DS=n command.
Dialing
DTMF Dialing.
DTMF dialing using DTMF tone pairs is supported in accordance with ITU-T Q.23. The transmit tone level
complies with Bell Publication 47001.
Pulse Dialing.
Pulse dialing is supported in accordance with EIA/TIA-496-A.
Blind Dialing.
The modem can blind dial in the absence of a dial tone if enabled by the X0, X1, or X3 command.
SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
2-2
Conexant
100490C
Modem Handshaking Protocol
If a tone is not detected within the time specified in the S7 register after the last digit is dialed, the modem aborts the call
attempt.
Call Progress Tone Detection
Ringback, equipment busy, congested tone, warble tone, and progress tones can be detected in accordance with the
applicable standard.
Answer Tone Detection
Answer tone can be detected over the frequency range of 2100 ± 40 Hz in ITU-T modes and 2225 ± 40 Hz in Bell modes.
Ring Detection
A ring signal can be detected from a TTL-compatible 15.3 Hz to 68 Hz square wave input.
Billing Protection
When the modem goes off-hook to answer an incoming call, both transmission and reception of data are prevented for 2
seconds (data modem) or 4 seconds (fax adaptive answer) to allow transmission of the billing tone signal.
Connection Speeds
The modem functions as a data modem when the +FCLASS=0 command is active.
Line connection can be selected using the +MS command. The +MS command selects modulation, enables/disables
automode, and selects minimum and maximum line speeds (Table 2-1).
Automode
Automode detection can be enabled by the +MS command to allow the modem to connect to a remote modem in accordance
with draft PN-3320 for V.34 (Table 2-1).
Table 2-1. +MS Command Automode Connectivity
<mod> Modulation
Possible Rates (bps)
1Notes
V21 V.21 300
V22 V.22 1200
V22B V.22 bis 2400 or 1200
V23 V.23 1200 See Note 2
V32 V.32 9600 or 4800
V32B V.32 bis 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, or 4800 Default for /14
models
V34 V.34 33600, 31200, 28800, 26400, 24000, 21600, 19200, 16800,
14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800, or 2400
Default for /33
models
V90 V.90 56000, 54667, 53333, 52000, 50667, 49333, 48000, 46667,
45333, 42667, 41333, 40000, 38667, 37333, 36000, 34667,
33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000
Default for /56
models
K56 K56flex 56000, 54000, 52000, 50000, 48000, 46000, 44000, 42000,
40000, 38000, 36000, 34000, 32000
B103 Bell 103 300
B212 Bell 212 1200
Notes:
1. See optional <automode>, <min_rate>, and <max_rate> subparameters for the +MS command.
2. For V.23, originating modes transmit at 75 bps and receive at 1200 bps; answering modes transmit at 1200 bps and receive at
75 bps. The rate is always specified as 1200 bps. V.23 half duplex is not supported.
3. If the DTE speed is set to less than the maximum supported DCE speed in automode, the maximum connection speed is
limited to the DTE speed.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
2-3
2.4 Data Mode
Data mode exists when a telephone line connection has been established between modems and all handshaking has been
completed.
Speed Buffering (Normal Mode)
Speed buffering allows a DTE to send data to, and receive data from, a modem at a speed different than the line speed. The
modem supports speed buffering at all line speeds.
Flow Control
DTE-to-Modem Flow Control.
If the modem-to-line speed is less than the DTE-to-modem speed, the modem supports
XOFF/XON or RTS/CTS flow control with the DTE to ensure data integrity.
Escape Sequence Detection
The +++ escape sequence can be used to return control to the command mode from the data mode. Escape sequence
detection is disabled by an S2 Register value greater than 127.
BREAK Detection
The modem can detect a BREAK signal from either the DTE or the remote modem. The \Kn command determines the
modem response to a received BREAK signal.
Telephone Line Monitoring
GSTN Cleardown (V.90, K56flex, V.34, V.32 bis, V.32).
Upon receiving GSTN Cleardown from the remote modem in a non-
error correcting mode, the modem cleanly terminates the call.
Loss of Carrier (V.22 bis and Below).
If carrier is lost for a time greater than specified by the S10 register, the modem
disconnects (except MNP 10).
Receive Space Disconnect (V.22 bis and Below).
If selected by the Y1 command in non-error-correction mode, the modem
disconnects after receiving 1.6 ± 10% seconds of continuous SPACE.
Send SPACE on Disconnect (V.22 bis and Below)
If selected by the Y1 command in non-error-correction mode, the modem sends 4 ± 10% seconds of continuous SPACE
when a locally commanded hang-up is issued by the &Dn or H command.
Fall Forward/Fallback (V.90/K56flex/V.34/V.32 bis/V.32)
During initial handshake, the modem will fallback to the optimal line connection within V.90/K56flex/V.34/V.32 bis/V.32 mode
depending upon signal quality if automode is enabled by the +MS or N1 command.
When connected in V.90/K56flex/V.34/V.32 bis/V.32 mode, the modem will fall forward or fallback to the optimal line speed
within the current modulation depending upon signal quality if fall forward/fallback is enabled by the %E2 command.
Retrain
The modem may lose synchronization with the received line signal under poor or changing line conditions. If this occurs,
retraining may be initiated to attempt recovery depending on the type of connection.
The modem initiates a retrain if line quality becomes unacceptable if enabled by the %E command. The modem continues to
retrain until an acceptable connection is achieved, or until 30 seconds elapse resulting in line disconnect.
Programmable Inactivity Timer
The modem disconnects from the line if data is not sent or received for a specified length of time. In normal or error-correction
mode, this inactivity timer is reset when data is received from either the DTE or from the line. This timer can be set to a value
between 0 and 255 seconds by using register S30. A value of 0 disables the inactivity timer.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
2-4
Conexant
100490C
DTE Signal Monitoring (Serial DTE Interface Only)
DTR#.
When DTR# is asserted, the modem responds in accordance with the &Dn and &Qn commands.
RTS#.
RTS# is used for flow control if enabled by the &K command in normal or error-correction mode.
2.5 Error Correction and Data Compression
V.42 Error Correction
V.42 supports two methods of error correction: LAPM and, as a fallback, MNP 4. The modem provides a detection and
negotiation technique for determining and establishing the best method of error correction between two modems.
MNP 2-4 Error Correction
MNP 2-4 is a data link protocol that uses error correction algorithms to ensure data integrity. Supporting stream mode, the
modem sends data frames in varying lengths depending on the amount of time between characters coming from the DTE.
V.42 bis Data Compression
V.42 bis data compression mode, enabled by the %Cn command or S46 register, operates when a LAPM or MNP 10
connection is established.
The V.42 bis data compression employs a “string learning” algorithm in which a string of characters from the DTE is encoded
as a fixed length codeword. Two 2k-byte dictionaries are used to store the strings. These dictionaries are dynamically
updated during normal operation.
MNP 5 Data Compression
MNP 5 data compression mode, enabled by the %Cn command, operates during an MNP connection.
In MNP 5, the modem increases its throughput by compressing data into tokens before transmitting it to the remote modem,
and by decompressing encoded received data before sending it to the DTE.
2.6 MNP 10 Data Throughput Enhancement
MNP 10 protocol and MNP Extended Services enhance performance under adverse channel conditions such as those found
in rural, long distance, or cellular environments. An MNP 10 connection is established when an MNP 2-4 connection is
negotiated with a remote modem supporting MNP 10.
MNP Extended Services.
The modem can quickly switch to MNP 10 operation when the remote modem supports MNP 10
and both modems are configured to operate in V.42.
V.42 bis/MNP 5 Support.
V.42 bis/MNP 10 can operate with V.42 bis or MNP 5 data compression.
2.7 MNP 10EC™ Enhanced Cellular Connection
A traditional landline modem, when used for high-speed cellular data transmission, typically encounters frequent signal
interference and degradation in the connection due to the characteristics of the analog cellular network. In this case, cellularspecific network impairments, such as non-linear distortion, fading, hand-offs, and high signal-to-noise ratio, contribute to an
unreliable connection and lower data transfer performance. Implementations relying solely on protocol layer methods, such as
MNP 10, generally cannot compensate for the landline modem's degraded cellular channel performance.
The modem achieves higher cellular performance by implementing enhanced cellular connection techniques at both the
physical and protocol layers, depending on modem model. The modem enhances the physical layer within the modulation by
optimizing its responses to sudden changes in the cellular connection. The MNP 10EC protocol layer implemented in the
modem firmware improves data error identification/correction and maximizes data throughput by dynamically adjusting speed
and packet size based on signal quality and data error performance.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
2-5
2.8 Telephony Extensions
The following telephony extension features are supported and can be typically be implemented in designs for set-top box
applications and TAM software applications to enhance end-user experience:
•
Line In Use detection
•
Extension Pickup detection
•
Remote Hang-up detection
2.8.1 Line In Use Detection
The Line In Use Detection feature can stop the modem from disturbing the phone line when the line is already being used.
When an automated system tries to dial using ATDT and the phone line is in use, the modem will not go off hook and will
respond with the message “LINE IN USE”.
2.8.2 Extension Pickup Detection
The Extension Pickup Detection feature (also commonly referred as PPD or Parallel phone detection) allows the modem to
detect when another telephony device (i.e., fax machine, phone, satellite/cable box) is attempting to use the phone line.
This feature can be used to quickly drop a modem connection in the event when a user picks up a extension phone line. For
example, this feature allows set top boxes with an integrated SmartSCM modem to give normal voice users the highest
priority over the telephone line.
This feature can also be used in Telephone Answering Machine applications (TAM). Its main use would be to stop the TAM
operation when a phone is picked up.
2.8.3 Remote Hangup Detection
The Remote Hangup Detection feature will cause the modem go back onhook during a data connection when the remote
modem is disconnected for abnormal termination reasons (remote phone line unplugged, remote server/modem shutdown.
For Voice applications, this method can be used in addition to silence detection to determine when a remote caller has hung
up to terminate a voice recording.
2.9 Fax Class 1, Fax Class 1.0, and Fax Class 2 Operation
Facsimile functions operate in response to fax class 1 commands when +FCLASS=1, fax class 1.0 commands when
+FCLASS=1.0, or to fax class 2 commands when +FCLASS=2 is installed
In the fax mode, the on-line behavior of the modem is different from the data (non-fax) mode. After dialing, modem operation
is controlled by fax commands. Some AT commands are still valid but may operate differently than in data modem mode.
Calling tone is generated in accordance with T.30.
2.10 Voice/Audio Mode
Voice and audio functions are supported by the Voice Mode. Voice Mode includes three submodes: Online Voice Command
Mode, Voice Receive Mode, and Voice Transmit Mode.
2.10.1 Online Voice Command Mode
This mode results from the connection to the telephone line or a voice/audio I/O device (e.g., microphone, speaker, or
handset) through the use of the +FCLASS=8 and +VLS commands. After mode entry, AT commands can be entered without
aborting the connection.
2.10.2 Voice Receive Mode
This mode is entered when the +VRX command is active in order to record voice or audio data input at the RIN pin, typically
from a microphone/handset or the telephone line.
Received analog voice samples are converted to digital form and compressed for reading by the host. AT commands control
the codec bits-per-sample rate.
Received analog mono audio samples are converted to digital form and formatted into 8-bit unsigned linear PCM format for
reading by the host. AT commands control the bit length and sampling rate. Concurrent DTMF/tone detection is available at
the 8 kHz sample rate.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
2-6
Conexant
100490C
2.10.3 Voice Transmit Mode
This mode is entered when the +VTX command is active in order to playback voice or audio data to the TXA output, typically
to a speaker/handset or to the telephone line.
Digitized voice data is decompressed and converted to analog form at the original compression quantization sample-per-bits
rate then output to the TXA output.
Digitized audio data is converted to analog form then output to the TXA output.
2.10.4 Audio Mode
The audio mode enables the host to transmit and receive 8-bit audio signals. In this mode, the modem directly accesses the
internal analog-to-digital (A/D) converter (ADC) and the digital-to-analog (D/A) converter (DAC). Incoming analog audio
signals can then be converted to digital format and digital signals can be converted to analog audio output.
2.10.5 Tone Detectors
The tone detector signal path is separate from the main received signal path thus enabling tone detection to be independent
of the configuration status. In Tone Mode, all three tone detectors are operational.
2.10.6 Speakerphone Modes
Speakerphone modes are controlled in voice mode with the following commands:
Use Speakerphone After Dialing or Answering (+VSP=1).
+VSP=1 selects speakerphone mode while in +FCLASS=8
mode. Speakerphone operation is entered during Voice Online Command mode after completing dialing or answering.
Speakerphone Settings.
The +VGM and +VGS commands can be used to control the microphone gain and speaker volume,
respectively. The VGM and +VGS commands are valid only after the modem has entered the Voice Online mode while in the
+VSP=1 setting.
2.11 Full-Duplex Speakerphone (FDSP) Mode (S Models)
The modem operates in FDSP mode when +FCLASS=8 and +VSP=1 (see Section 2.10.6).
In FDSP Mode, speech from a microphone or handset is converted to digital form, shaped, and output to the telephone line
through the line interface circuit. Speech received from the telephone line is shaped, converted to analog form, and output to
the speaker or handset. Shaping includes both acoustic and line echo cancellation.
2.12 Caller ID
Caller ID can be enabled/disabled using the +VCID command. When enabled, caller ID information (date, time, caller code,
and name) can be passed to the DTE in formatted or unformatted form. Inquiry support allows the current caller ID mode and
mode capabilities of the modem to be retrieved from the modem.

SmartSCM Modem Data Sheet
100490C
Conexant
2-7
2.13 Worldwide Country Support
Internal modem firmware supports 29 country profiles (see Section 1.3.2). These country profiles include the following
country-dependent parameters:
•
Dial tone detection levels and frequency ranges.
•
DTMF dialing parameters: Transmit output level, DTMF signal duration, and DTMF interdigit interval.
•
Pulse dialing parameters: Make/break times, set/clear times, and dial codes are programmable
•
Ring detection frequency range.
•
Blind dialing enabled/disable.
•
Carrier transmit level (through S91 for data and S92 for fax). The maximum, minimum, and default values can be defined
to match specific country and DAA requirements.
•
Calling tone is generated in accordance with V.25. Calling tone may be toggled (enabled/disabled) by inclusion of a “^”
character in a dial string. It may also be disabled.
•
Frequency and cadence of tones for busy, ringback, congested, warble, dial tone 1, and dial tone 2.
•
Answer tone detection period.
•
Blacklist parameters. The modem can operate in accordance with requirements of individual countries to prevent misuse
of the network by limiting repeated calls to the same number when previous call attempts have failed. Call failure can be
detected for reasons such as no dial tone, number busy, no answer, no ringback detected, voice (rather than modem)
detected, and key abort (dial attempt aborted by user). Actions resulting from such failures can include specification of
minimum inter-call delay, extended delay between calls, and maximum numbers of retries before the number is
permanently forbidden ("blacklisted").
These country profiles may be altered or customized by modifying the country-dependent parameters. Additional profiles may
also be included. There are two ways to add or modify profiles:
•
Linking additional or modified profiles from an external serial EEPROM.
•
Incorporating additional or modified profiles into optional external flash ROM containing the entire modem firmware code.
Please contact an FAE at the local Conexant sales office if a country code customization is required.
2.14 Diagnostics
2.14.1 Commanded Tests
Diagnostics are performed in response to &T commands.
Analog Loopback (&T1 Command).
Data from the local DTE is sent to the modem, which loops the data back to the local
DTE.
2.14.2 Power On Reset Tests
Upon power on, the modem performs tests of the modem, internal and external RAM, and NVRAM. If the modem, internal
RAM, or external RAM test fails, the TMIND# output is pulsed (serial interface version) or the DCD bit in the parallel interface
register is pulsed (parallel interface version) as follows:
Internal or external RAM test fails: One pulse cycle (pulse cycle = 0.5 sec. on, 0.5 sec. off) every 1.5 seconds.
Modem device test fails: Three pulse cycles every 1.5 seconds.
If the NVRAM test fails (due to NVRAM failure or if NVRAM is not installed), the test failure is reported by AT commands that
normally use the NVRAM, e.g., the &V command.
2.15 Low Power Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode Entry.
The modem enters the low power sleep mode when no line connection exists and no host activity occurs
for the period of time specified in the S24 register. All modem circuits are turned off except the internal clock circuitry in order
to consume reduced power while being able to immediately wake up and resume normal operation.
Wake-up.
Wake-up occurs when a ring is detected on the telephone line, the host writes to the modem (parallel interface), or
the DTE sends a character to the modem (serial interface).
 Loading...
Loading...