CONEX 20463 Datasheet

Data Sheet (Preliminary)
Conexant Proprietary Information
Doc. No.100444A
December 21, 1999
SmartACFL
Modem
V.90/K56flex/V.34/V.32bis Modem Device Sets with Microcontroller (L2702),
Modem Data Pump (P9373), SmartDAA
(20463), and Optional Voice Codec (20437)
for Low Power Applications
The Conexant SmartACFL V.90/K56flex Modem Device Set with SmartDAA
technology supports analog data up to 56 Kbps, analog fax to 14.4 Kbps,
telephone answering machine (TAM), V.80 synchronous access mode, onboard DSVD, voice/speakerphone (optional), and cellular/GSM operation.
Serial, parallel, or PC Card host interface operation is supported depending on
the selected model (Table 1).
The modem supports ITU-T V.90/K56flex, V.34 and V.32bis data
modulations and is designed to operate with dial-up telephone lines in the U.S.
and worldwide. PC Card and parallel host interface models also support analog
cellular direct connect and GSM direct connect. Low profile, small TQFP
packages and low voltage operation with low power consumption make this
device set ideal for laptop, notebook, and palmtop applications using the
parallel host or serial DTE interface with the MCU, or the PC Card interface
with the MCUP.
The SmartACFL device set consists of a Microcontroller (MCU or MCUP) in a
128-pin TQFP, a Modem Data Pump (MDP) in a 100-pin TQFP, and a Line
Side Device (LSD) (SmartDAA device) in a 32-pin TQFP. The optional Voice
Codec (VC), in a 32-pin TQFP, supports voice/full-duplex speakerphone
(FDSP) operation with interfaces to a microphone and speaker and to a
telephone handset/headset. Figure 1 identifies the major hardware signal
interfaces. The MCUP supports two peripheral channels, one channel for the
modem and a second channel for an optional user-defined function
(Function 2).
Conexant's SmartDAA technology (patent pending) eliminates the need for a
costly line transformer, relays, and opto-isolators typically used in discrete DAA
(Data Access Arrangement) implementations. The SmartDAA architecture also
simplifies product implementation by eliminating the need for country-specific
components enabling worldwide homologation of a single modem board design
and a single bill of materials (BOM).
The SmartDAA system-powered DAA operates reliably without drawing power
from the line, unlike line-powered DAAs that operate poorly when line current is
insufficient due to long lines or poor line conditions. Enhanced features, such
as monitoring of local extension status without going off-hook, are also
supported.
Incorporating Conexant’s proprietary Digital Isolation Barrier (DIB) design
(patent pending) and other innovative DAA features, the SmartDAA
architecture simplifies application design, minimizes layout area, and reduces
component cost.
Features
•
V.90 data/V.17 fax modem
•
SmartDAA technology
−
System side powered DAA operates
under poor line current supply
conditions
−
Wake-on-ring
−
Ring detection
−
Line polarity reversal detection
−
Line current loss detection
−
Pulse dialing
−
Call waiting detection
−
Digital PBX line protection
−
Meets world-wide DC VI Masks
requirements
−
Caller ID detection
•
Data/Fax/Voice call discrimination
•
Hardware-based modem controller
•
Hardware-based digital signal
processor (DSP)
•
Voice/full-duplex speakerphone mode
(S models)
•
V.70 DSVD using optional RCDSVD
SCP (S models)
•
World-wide operation
•
Industry standard communication
commands
•
Selectable parallel/serial interface with
speeds up to 230.4 kbps
−
Parallel 16550A UART-compatible
interface
−
Serial ITU-T V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E)
•
V.80 synchronous access mode
•
Direct mode (serial interface)
•
Synchronous data mode
(serial interface)
•
V.22 bis fast connect
•
Analog cellular direct connect
•
GSM direct connect
•
Sleep mode
•
Thin packages support low profile
designs
•
+3.3V operation with +5V tolerant
digital inputs

SmartACFL
V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications
2
Conexant
Doc. No. 100444A
Proprietary Information
Table 1. SmartACFL Modem Models and Functions
Model/Order/Part Numbers Supported Functions
Marketing Name Device Set
Order No.
MCU
[128-Pin
TQFP]
Part No.
MDP
[100-Pin
TQFP]
Part No.
LSD
[32-Pin
TQFP]
Part No.
Optional
Voice Codec
(VC)
[32-Pin TQFP]
Part No.
V.90/K56fle
x Data
V.34
Data
V.32 bis
Data,
V.17 Fax,
Fax Cl 1,
Fax Cl 2,
TAM,
W-W, V.80
Voice/
FDSP
SmartACFL/56S-PCC DS56-L492-001 L2702-12 P9373-11 20463-11 20437-11 Y Y Y Y
SmartACFL/56-PCC DS56-L492-011 L2702-12 P9373-11 20463-11 — Y Y Y —
SmartACFL/56S DS56-L492-021 L2702-15 P9373-11 20463-11 20437-11 Y Y Y Y
SmartACFL/56 DS56-L492-031 L2702-15 P9373-11 20463-11 — Y Y Y —
Notes:
1. Model options:
S Voice and speakerphone
PCC PC Card host interface (serial DTE/parallel host if not PCC)
56 56 kbps max. rate per V.90
33 33.6 kbps max. rate per V.34
14 14.4 kbps max. rate per V.32bis
2. Supported functions (Y = Supported; — = Not supported):
TAM Telephone answering machine support (handset support requires S model)
Fax Cl 1 and Cl 2 Fax Class 1 and Fax Class 2 support
FDSP Full-duplex speakerphone
Revision History
Revision Date Comments
A 12/21/99 Initial public release of document
Copyright © Conexant Systems, Inc., 1999. All Rights Reserved.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Conexant Systems, Inc. ("Conexant") products. These materials are provided by
Conexant as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only. Conexant assumes no responsibility for errors or
omissions in these materials. Conexant may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Conexant
makes no commitment to update the information contained herein. Conexant shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to its specifications and product descriptions.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in
Conexant’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Conexant assumes no liability whatsoever.
THESE MATERIALS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, RELATING TO
SALE AND/OR USE OF CONEXANT PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL
PROPERTY RIGHT. Conexant further does not warrant the accuracy or completeness of the information, text, graphics or other items
contained within these materials. Conexant shall not be liable for any special, indirect, incidental, or consequential damages, including without
limitation, lost revenues or lost profits, which may result from the use of these materials.
Conexant products are not intended for use in medical, life saving or life sustaining applications. Conexant customers using or selling
Conexant products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Conexant for any damages resulting from
such improper use or sale.
The following are trademarks of Conexant Systems, Inc.: Conexant, the Conexant C symbol, “What’s Next in Communications Technologies”,
SmartDAA, SmartHSF, and SmartACFL. Product names or services listed in this publication are for identification purposes only, and may be
trademarks of third parties. Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Reader Response:
Conexant strives to produce quality documentation and welcomes your feedback. Please send
comments and suggestions to conexant.tech.pubs@conexant.com. For technical questions, contact your local Conexant
sales office or field applications engineer.
V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications SmartACFL
Doc. No. 100444A
Conexant
3
Proprietary Information
Introduction
(continued)
The optional Voice Codec (VC) supports voice/fullduplex speakerphone (FDSP) operation with
interfaces to a microphone and speaker and to a
telephone handset/headset. The optional RCDSVD
Speech Codec Processor (SCP) supports DSVD.
The modem operates by executing firmware from
external 1 Mbit (128k X 8) RAM and 2 Mbit (256k X
8) ROM/Flash ROM. The 33S and 14S models can
alternatively use external 1 Mbit or 2 Mbit
ROM/Flash ROM and the MCU’s internal 32K X 8
RAM. For GSM support the ROM size is doubled.
Accelerator kits and reference designs are available
in electronic form to minimize application design time
and costs. The design package includes schematics,
bill of materials (BOM), board layout files in Gerber
format, and complete documentation. The design is
pretested to pass FCC Part 15, Part 68, and CTR 21
for immediate manufacturing.
Applications
•
PC Cards
•
Embedded systems
•
Serial box modems
•
Set top boxes
•
Point of sales terminals
•
Remote monitoring and data collection systems
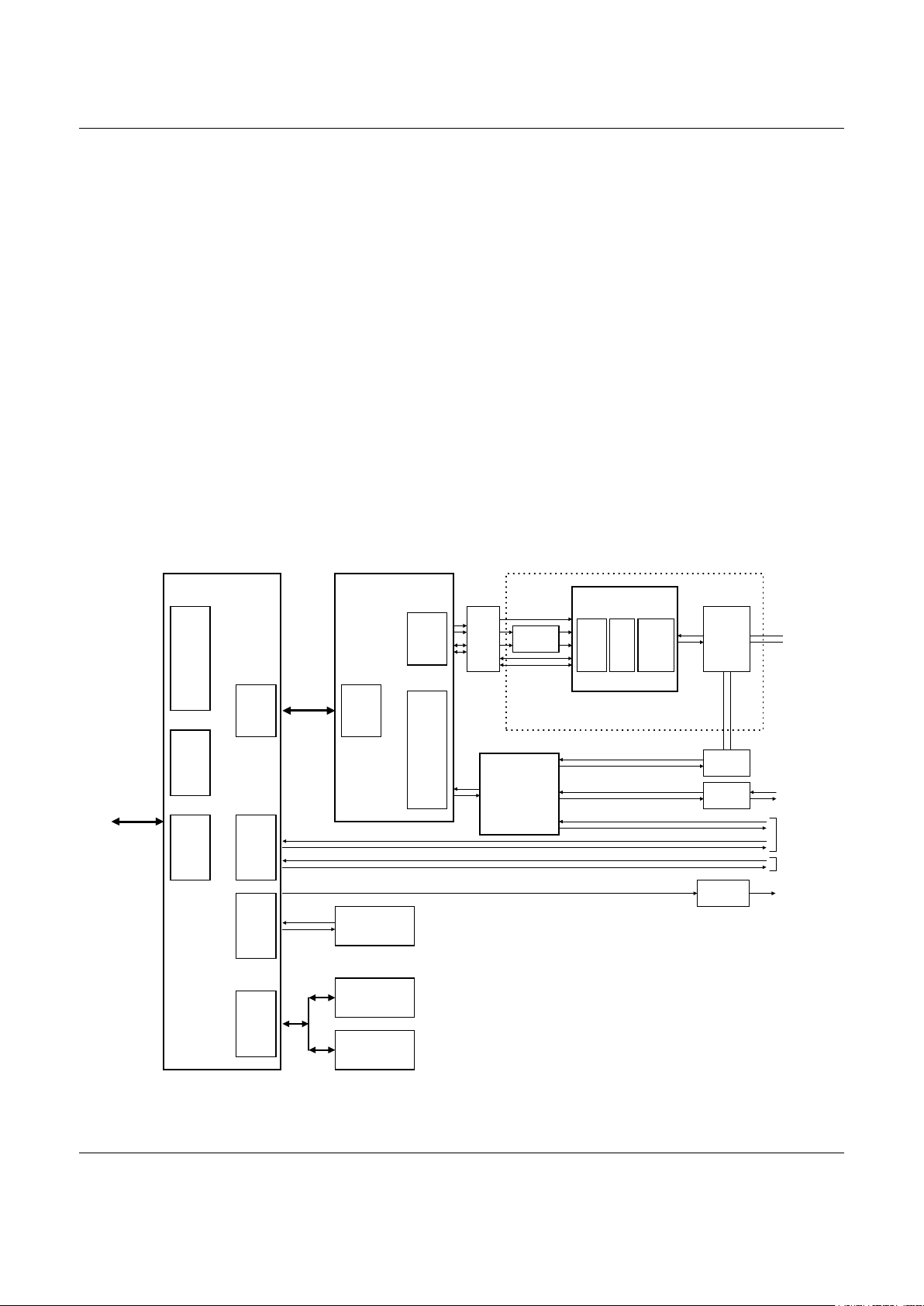
Modem Data Pump (MDP)
P9373: 100-Pin TQFP
Voice Codec (VC)
20437: 32-Pin TQFP
(Optional)
SPEAKER
(Mic/Speaker)
Interface
(Optional)
TIP
RING
Electronic
Inductor,
Diode Bridge,
Protection &
EMI,
Impedance
Components
SmartDAA
Interface
Modem
Data Pump
(MDP)
Telephone
Line
Digital Speaker
Circuit (Optional)
PCCard/Parallel/
Serial DTE
Interface
MIC
SPEAKER
MD251F2_FID
SOUNDUCER
Digital
Isolation
Barrier
(DIB)
(OEM
supplied)
Line Side Device (LSD)
20463: 32-Pin TQFP
Line
Side
DIB
Interface
(LSDI)
Codec
Telephone
Line
Interface
DAA Hardware
HS Hybrid
Components
(Optional)
Cellular
Interface
GSM
Interface
RAM
1M (128K x 8)
Central
Processor
Unit (MCU)
SPEAKER
Serial EEPROM
2K (256 x 8) to
32K (4K x 8)
(Optional)
ROM/Flash ROM
2M (256K x 8)
4M (512K X 8)*
* = GSM Support
MCU
Interface
MDP
Interface
Internal
RAM
Serial
EEPROM
Interface
Expansion
Memory
Bus
Interface
Cellular and
GSM
Interface
Host
Interface
Microcontroller Unit (MCU)
L2702: 128-Pin TQFP
Rectifier and
Filter
Components
Figure 1. SmartACFL Modem Major Interfaces

SmartACFL
V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications
4
Conexant
Doc. No. 100444A
Proprietary Information
Detailed Features
General Modem Features
•
Downloadable Architecture
−
Downloadable MCU firmware from the host/DTE
−
Downloadable MDP code modules from the
MCU, transparent to the host
•
V.90 data modem with receive rates up to 56k bps
and send rates up to V.34 rates
−
ITU-T V.90, K56flex, V.34 (33.6 kbps), V.32 bis,
V.32, V.22 bis, V.22, V.23, and V.21; Bell 212A
and 103
−
V.42 LAPM and MNP 2-4 error correction
−
V.42 bis and MNP 5 data compression
−
MNP 10EC™ enhanced cellular performance
−
V.250 (ex V.25 ter) and V.251 (ex V.25 ter
Annex A) commands
•
V.22 bis fast connect
•
Analog cellular direct connect
•
GSM direct connect
•
V.17 fax modem with send and receive rates up to
14.4 kbps
−
ITU-T V.17, V.29, V.27 ter, and V.21 ch. 2
−
EIA/TIA 578 Class 1 and T.30 Class 1.0
commands
•
V.80 synchronous access mode supports hostcontrolled communication protocols with H.324
interface support
•
Data/Fax/Voice call discrimination
•
Hardware-based modem controller
•
Worldwide operation
−
US/Japan/Canada/TBR21 and other countries
−
Caller ID and distinctive ring detection
−
Call progress, blacklisting
•
Telephony/TAM
−
V.253 commands
−
8-bit µ-Law/A-Law coding (G.711)
−
8-bit/16-bit linear coding
−
8 kHz sample rate
−
Concurrent DTMF, ring, and Caller ID detection
•
Full-duplex speakerphone mode (S models)
−
Microphone and speaker interface
−
Telephone handset or headset interface
−
Acoustic and line echo cancellation
−
Microphone gain and muting
−
Speaker volume control and muting
•
PC Card interface (MCUP only) supports two
functions with programmable I/O and window size
•
JTAG Boundary Scan support
•
Built-in host/DTE interface with speeds up to 230.4
kbps
−
Parallel 16550A UART-compatible interface
(MCU)
−
Serial ITU-T V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E) (MCU)
−
PC Card (MCUP)
•
Flow control and speed buffering
•
Automatic format/speed sensing
•
Serial sync/async data; parallel async data
•
Sleep mode
•
Thin packages support low profile designs (1.6 mm
max. height)
•
MCU (L2702): 128-pin TQFP
•
MDP (P9373): 100-pin TQFP
•
LSD (20463): 32-pin TQFP
•
VC (20437): 32-pin TQFP
Description
General
The SmartACFL device set, comprised of separate
microcontroller (MCU), modem data pump (MDP),
and line side device (LSD) devices, provides the
processing core for a complete modem design. The
optional Voice Codec (VC) supports voice/full-duplex
speakerphone (FDSP) operation with interfaces to a
microphone and speaker and to a telephone
handset/headset (S models). The S model can also
be ordered with an RCDSVD Speech Codec
Processor (SCP) in a 100-pin PQFP to support
DSVD.
Modem operation, including dialing, call progress,
telephone line interface, telephone handset interface,
voice/speakerphone interface, and host interface
functions are supported and controlled through the
V.250, V.251, and V.253-compatible command set.
The modem hardware connects to the host via a
parallel, serial, or PC Card interface. The OEM adds
discrete components as required by the modem
model and the application to complete the system
(Table 1). These components may include a crystal
circuit, EEPROM, DIB components, telephone line
interface, optional voice/speakerphone interface, and
optional cellular/GSM interface.
Parallel interface operation, including cellular and
GSM support, is selected by PARIF input high. Serial
interface operation is selected by PARIF input low.
Cellular operation is selected by LINE/CELL input
low. GSM operation is selected by LINE/GSM input
low.

V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications SmartACFL
Doc. No. 100444A
Conexant
5
Proprietary Information
Data/Fax Modes
In V.90/K56flex data modem mode, the modem can
receive data from a digitally connected central site
modem (CSM) at line speeds up to 56 kbps.
Asymmetrical data transmission supports sending
data up to V.34 rates; this mode can fallback to fullduplex V.34 mode, and to lower rates as dictated by
line conditions.
In V.34 data mode, the modem operates at line
speeds up to 33.6 kbps. Error correction (V.42/MNP
2-4) and data compression (V.42 bis/MNP 5)
maximize data transfer integrity and boost average
data throughput up to 230.4 kbps. Non-errorcorrecting mode is also supported.
Data modem modes perform complete handshake
and data rate negotiations. Using V.34 modulation to
optimize modem configuration for line conditions, the
modem can connect at the highest data rate that the
channel can support from 33600 bps down to 2400
bps with automatic fallback. Automode operation in
V.34 is provided in accordance with PN3320 and in
V.32 bis in accordance with PN2330. All tone and
pattern detection functions required by the applicable
ITU or Bell standard are supported.
In V.32 bis mode, the modem operates at line
speeds up to 14.4 kbps.
In V.22 bis fast connect mode, the modem can
connect at 2400 bps with a very short training time,
which is very efficient for small data transfers.
In fax modem mode, the modem can operate in 2wire, half-duplex, synchronous mode and can
support Group 3 facsimile send and receive speeds
of 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800, and 2400 bps.
Fax data transmission and reception performed by
the modem are controlled and monitored through the
EIA/TIA-578 Fax Class 1, T.30 Fax Class 1.0, or Fax
Class 2 command interface. Full HDLC formatting,
zero insertion/deletion, and CRC
generation/checking are provided. Both transmit and
receive fax data are buffered within the modem. Data
transfer to and from DTE is flow controlled by
XON/XOFF and RTS/CTS.
Synchronous Access Mode (SAM) - Video
Conferencing
V.80 Synchronous Access Mode between the
modem and the host/DTE is provided for hostcontrolled communication protocols, e.g., H.324
video conferencing applications.
Voice-call-first (VCF) before switching to a
videophone call is also supported.
Worldwide Operation
The modem operates in US/Japan/Canada/TBR21
and other countries. Country dependent parameters
for functions such as dialing, carrier transmit level,
calling tone, call progress tone detection, answer
tone detection, blacklisting, and relay control are
programmable by ConfigurACE II for Windows.
SmartDAA technology allows a single PCB design
and single BOM to be homologated worldwide.
Advanced features such as digital PBX protection
are also supported.
TAM Mode
TAM Mode features include 8-bit µ-Law, A-Law, and
linear coding at 8 kHz sample rate. Full-duplex voice
supports concurrent voice receive and transmit.
Tone detection and generation, call discrimination,
and concurrent DTMF detection are also supported.
ADPCM (4-bit IMA) coding is supported to meet
Microsoft WHQL logo requirements.
TAM Mode is supported by three submodes:
1. Online Voice Command Mode supports
connection to the telephone line or, for the S
model, a handset.
2. Voice Receive Mode supports recording voice or
audio data input from the telephone line or, for
the S model, a microphone/handset.
3. Voice Transmit Mode supports playback of voice
or audio data to the telephone line or, for the S
model, a speaker/handset.

SmartACFL
V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications
6
Conexant
Doc. No. 100444A
Proprietary Information
Voice/Speakerphone Mode (S Models)
S models include additional telephone handset,
external microphone, and external speaker
interfaces that support voice and full-duplex
speakerphone operation.
Hands-free full-duplex telephone operation is
supported in Speakerphone Mode under host
control. Speakerphone Mode features an advanced
proprietary speakerphone algorithm which supports
full-duplex voice conversation with acoustic, line, and
handset echo cancellation. Parameters are
constantly adjusted to maintain stability with
automatic fallback from full-duplex to pseudo-duplex
operation. The speakerphone algorithm allows
position independent placement of microphone and
speaker. The host can separately control volume,
muting, and AGC in microphone and speaker
channels.
V.70 DSVD Mode using RCDSVD SCP Device
(S Models)
On-board DSVD operation requires installation of the
optional RCDSVD SCP (R6715-14). GSM operation
is not available when the RCDSVD SCP is
connected because MCU port PB5 is used for SCP
chip select output (~SVDSEL) rather than address
line A18 output which is needed to support the 4M
ROM.
DSVD provides full-duplex digital simultaneous voice
and data over a single telephone line. DSVD uses
codecs in the RCDSVD SCP to code (compress)
analog speech signals on the RCDSVD LINEIN pin
or MICIN pin for passing to the modem controller in
digitized form. DSVD also decodes (decompresses)
coded speech received from the modem controller
for routing to the RCDSVD LINEOUT pin or
SPKP/SPKN pins in analog form.
DSVD operates in accordance with ITU-T
interoperable G.729 and G.729 Annex A with
interoperable G.729 Annex B. Voice activity
detection supports speech coding at an average bit
rate significantly lower than 8.0 kbps.
DSVD decoder timing recovery algorithm
compensates for clock skew, asynchronous host-todecoder data transfer delay, intervening variable
length data block transmission delay, and loss of
encoded speech data.
The voice interface can be in the form of a headset,
handset or a microphone and speaker (half-duplex
speakerphone). Handset echo cancellation supports
handset use through a hybrid.
In Handset Mode, the RCDSVD SCP interfaces to
the telephone interface circuit using the Line Input
(LINEIN) and Line Out (LINEOUT) lines. In Headset
or Speakerphone Mode, the RCDSVD SCP
interfaces to the audio interface circuit using the
Microphone Input (MICIN) and Speaker out (SPKR)
lines.
GSM (Parallel Host or PC Card Interface)
GSM operation requires installation of 4M (512k x 8)
ROM (56 models) or 2M ROM (33 and 14 models).
ON-board DSVD is not available when the 4 Mbit
ROM is installed since the MCU port PB5 is used for
address line 18 rather than RCDSVD SCP chip
select output (~SVOSEL).
Features supported in GSM operation include:
•
Data modem
−
V.21, V.23, V.22, V.22 bis, V.32
−
ISDN interoperability: 300 bps to 9600 bps
•
Transparent asynchronous mode up to 9600 bps
•
Non-transparent mode (RLP) up to 9600 bps
•
Fax modem send and receive rate up to 9600 bps
•
AT GSM commands (ETSI 07.07)
•
GSM direct connect
•
Firmware interface for OEM-provided phone driver
•
Automatic GSM cable presence detection
•
Built-in parallel host (16550A UART) interface
Sleep Mode
Sleep mode is supported in the modem device set
and the RCDSVD SCP device.
Additional Information
Additional information is described in the SmartACFL
Modem Device Family with SmartDAA Technology
for Low Power Applications Designer’s Guide (Doc.
No. 100446) and the Command Reference Manual
(Doc. No. 100500).

V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications SmartACFL
Doc. No. 100444A
Conexant
7
Proprietary Information
Hardware Description
SmartDAA technology (patent pending) eliminates
the need for a costly analog transformer, relays, and
opto-isolators that are typically used in discrete DAA
implementations. The programmable SmartDAA
architecture simplifies product implementation in
worldwide markets by eliminating the need for
country-specific components.
Microcontroller (MCU/MCUP)
The microcontroller is a Conexant 8-bit
microcomputer with pins to support serial
DTE/parallel host bus/PC Card, MDP, voice/TAM,
speakerphone, and RCDSVD SCP interface
operation. The operating voltage is +3.3V with +5V
tolerant inputs.
The MCUP incorporates a built-in PC Card interface
and CIS memory allowing the MCUP to directly
connect to the PC Card 68-pin socket without
requiring external PICA and CIS devices.
The MCU connects to the DTE/host via a V.24
(EIA/TIA-232-E) serial DTE interface or a parallel
host bus depending on installed firmware, whereas
the MCUP connects to a PC Card socket via built-in
PC Card interface. Unless otherwise stated,
references to general microcontroller functions
include both the MCUP and MCU.
The MCU performs the command processing and
host interface functions. The crystal frequency is
28.224 MHz. The MCU outputs a 28.224 MHz clock
to the MDP eliminating need for a separate MDP
crystal circuit.
The MCU connects to the MDP via dedicated lines
and the external bus. The external bus also connects
to OEM-supplied RAM (56 models), ROM/flash
ROM, and to the optional RCDSVD SCP.
The MCU connects to a serial EEPROM over a
dedicated serial interface.
Two independent functions are supported; the
modem function and an optional user-defined
Function 2. A Card Option Configuration Register
and a Configuration and Status Register for each
function allow independent configuration/control and
status reporting of the respective function.
The MCUP PC Card interface features include:
•
PC Card interface logic and memory
−
Internal 512-byte Card Information Structure
(CIS) provides the tuple information needed to
define the PC Card functionality.
−
CIS Table is configurable from ROM/flash
memory (default) or from NVRAM (option)
−
Address decode logic
•
Modem Function
−
Decoding for standard COM ports in
Overlapping I/O Address Mode
−
Independent I/O Address Mode support
−
Power-down mode control
−
Digital speaker pass-through
−
Supports two ring handling methods
−
Ring Indicate pass-through to Status Change
−
Six 8-bit Modem Function Card Configuration
Registers
Configuration Option Register (full support)
Configuration and Status Register (full support)
Pin Replacement Register (CREADY and
RREADY)
Extended Status Register (RIEvt and RIEnab)
I/O Base Register 0
I/O Base Register 1
•
Optional User-defined Function 2
−
Reset and chip select control
−
Power-down mode control
−
16-bit data transfer control
−
Disable EEPROM control
−
Interrupt request pass through
−
Four 8-bit Card Configuration Registers
Configuration Option Register (full support)
Configuration and Status Register (full support)
I/O Base Register 0
I/O Base Register 1
•
MCU and MCUP packaged in 128-pin TQFP

SmartACFL
V.90/K56flex Modem Device Sets with SmartDAA Technology for Low Power Applications
8
Conexant
Doc. No. 100444A
Proprietary Information
RCDSVD Speech Codec Processor (SCP)
(Optional)
The RCDSVD SCP (R6715-14), required for onboard DSVD operation, is packaged in a 100-pin
PQFP. The 56.448 MHz crystal frequency is
supplied by the MDP XCLK output.
MCU/MCUP Firmware
MCU/MCUP firmware performs processing of
general modem control, command sets, data
modem, error correction and data compression
(ECC), fax class 1, fax class 2, DSVD,
voice/audio/TAM/speakerphone, W-class, V.80,
analog cellular, GSM, and serial DTE/parallel
host/PC Card interface functions according to
modem models (Table 1).
Configurations of the modem firmware are provided
to support parallel host bus interface (MCU), serial
DTE interface (MCU) or PC Card interface (MCUP)
operation.
The modem firmware is provided in object code form
for the OEM to program into external ROM/flash
ROM. The modem firmware may also be provided in
source code form under a source code addendum
license agreement.
Modem Data Pump (MDP)
The Modem Data Pump (MDP) supports data/fax
modem, voice record from and playback to the
telephone line, and optional voice/full-duplex
speakerphone operation. The MDP communicates
with the MCU via parallel bus, serial data and clock,
and serial voice (optional) signals. Downloadable
architecture allows upgrading of MDP code from the
MCU.
The MDP, packaged in a 100-pin TQFP, includes a
modem controller interface, a digital signal processor
(DSP), a voice codec (VC) interface, and a
SmartDAA Interface.
The MDP performs telephone line signal
modulation/demodulation in a hardware DSP which
reduces computational load on the host processor.
Downloadable architecture allows updating of MDP
executable code.
The SmartDAA Interface communicates with, and
supplies power and clock to, the LSD through the
DIB.
The input clock frequency is 28.224 MHz and is
supplied by the MCU. The operating voltage is +3.3V
with +5V tolerant inputs.
ADPCM voice processing is supported.
Downloading of MDP code from the MCU is
supported.
Digital Isolation Barrier (DIB) (OEM Supplied)
The DIB electrically DC isolates the MDP from the
LSD. The MDP is connected to a fixed digital ground
and operates with standard CMOS logic levels. The
LSD is connected to a floating ground and can
tolerate high voltage input (compatible with
telephone line and typical surge requirements).
A digital transformer (DXFMR) in the DIB power
channel couples power and clock digital waveforms
from the MDP to the LSD.
The DIB data channel supports bidirectional halfduplex serial transfer of data, control, and status
information between the MDP and the LSD over two
lines.
 Loading...
Loading...