Page 1

M
-
0
p
SN
Installation and O
100
Node Control Modem
eration Manual
Part Number MN/SNM1000.OM Revision 3
Page 2

Page 3

SNM-1000
Comtech EF Data is an ISO 9001
Registered Company.
Node Control Modem
Installation and Operation Manual
Part Number MN/SNM1000.OM
Revision 3
March 31, 2002
Copyright © Comtech EF Data, 2000. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA.
Comtech EF Data, 2114 West 7th Street, Tempe, Arizona 85281 USA, 480.333.2200, FAX: 480.333.2161
.
Page 4

Network Customer Support
The Network Customer Support Plan identifies the steps to be followed in resolving the
Customer’s concern.
The resolution efforts will follow these levels of contact:
• Level One Contact – Factory Authorized Service Center.
• Level Two Contact – Comtech EF Data Customer Support.
• Level Three Contact – Network Test and Field Support
Procedural Steps
Step Procedure
1
2
The Customer raises a concern with the Level One Contact.
The Level One Contact will perform Hardware repairs and Network Operations
troubleshooting in accordance with the Comtech EF Data Service Center
agreement.
3
4
5
6
7
8
If the Level One Contact is unable to resolve the concern, then the Level One
Contact will inform the Level Two Contact of the concern in accordance with the
instructions found within the attached Comtech EF Data Customer Support
Department’s document.
The Level Two Contact will enter the concern into the Comtech EF Data database
and determine whether the concern is a Hardware concern or a Network
Operations concern
The Level Two Contact will interface with the Level One Contact and provide
the appropriate hardware support and enter all correspondence into the Comtech EF
Data database.
If the Level Two Contact determines that the concern is a Network Operations
concern, then the Level Two Contact will inform the Level Three Contact.
The Level Three Contact will interface with the Level One Contact and provide
the appropriate support and enter all correspondence into the Comtech EF Data
database.
If the Level Three Contact determines that there is a Hardware failure then the
Level Three Contact will inform the Level Two Contact. Go to Step 5.
ii
Page 5

Network Support Customer Plan
SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Customer
Yes
Midas Network is functioning
properly?
No
Level One Contact is notified
Authorized Factory Service
Center
Resolved by Hardware repair
or Network Operations
troubleshooting?
No
Level Two Contact is notified
CEFD Customer Support
*Note: If equipment was purchased
directly from Comtech EFData (not
through a Factory Authorized
Service Center), then CEFD
Customer Support will be the initial
point of contact.
Yes
CEFD Customer Support
provides HW support
Hardware
Hardware or Network
Operations issue?
Network Operations
Level Three Contact is notified
CEFD Network Test and Field
Support
Hardware or Network
Operations issue?
Hardware
CEFD Network Test and Field
Support
provides Network Operations
support
iii
iii
Page 6

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
See the Comtech EF Data website at http://www.comtechefdata.com
Authorized Service Center. Contact the Factory Authorized Service Center for:
for contact information for a Factory
• Product support
• Information on upgrading or returning a product
Contact the Comtech EF Data Customer Support Department for:
• Product support or training
• Information on upgrading or returning a product
A Customer Support representative may be reached at:
Comtech EF Data
Attention: Customer Support Department
2114 West 7th Street
Tempe, Arizona 85281 USA
480.333.2200 (Main Comtech EF Data Number)
480.333.4357 (Customer Support Desk)
480.333.2500 FAX
or, E-Mail can be sent to the Customer Support Department at:
service@comtechefdata.com
1. To return a Comtech EF Data product (in-warranty and out-of-warranty) for repair or replacement:
2. Request a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from the Comtech EF Data Customer
Support Department.
3. Be prepared to supply the Customer Support representative with the model number, serial number,
and a description of the problem.
4. To ensure that the product is not damaged during shipping, pack the product in its original shipping
carton/packaging.
5. Ship the product back to Comtech EF Data. (Shipping charges should be prepaid.)
iv
Page 7

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION......................................................................................1–1
1.1 Overview............................................................................................................................................................1–2
1.1.1 Additional Features....................................................................................................................................1–2
1.1.2 Mode of Operation.....................................................................................................................................1–3
1.2 Description........................................................................................................................................................1–4
1.3 Options ..............................................................................................................................................................1–4
1.4 General Specifications......................................................................................................................................1–5
1.4.1 Environmental and Physical ......................................................................................................................1–6
1.4.2 DAC Specifications...................................................................................................................................1–6
1.4.3 Burst Mode Specifications.........................................................................................................................1–7
1.4.4 Continuous Mode Specifications...............................................................................................................1–7
1.5 Viterbi Performance with Noise, Closed Network.........................................................................................1–7
1.6 Typical Spectral Occupancy............................................................................................................................1–8
1.7 Dimensional Envelope......................................................................................................................................1–9
CHAPTER 2. INSTALLATION......................................................................................... 2–1
2.1 Unpacking.........................................................................................................................................................2–1
2.2 Installation ........................................................................................................................................................2–2
2.3 Rear Panel Connections...................................................................................................................................2–4
2.3.1 EFBUS1/2 Port (J6) ...................................................................................................................................2–5
2.3.2 Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)...............................................................................................................2–6
2.3.3 User Port....................................................................................................................................................2–7
2.3.4 Auxiliary 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9).....................................................................................................2–8
2.3.5 Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10).........................................................................................................2–9
2.3.6 AC Power .................................................................................................................................................. 2–10
2.3.7 DC Power .................................................................................................................................................. 2–10
2.3.8 TX IF Output Connector (CP1) .................................................................................................................2–11
2.3.9 RX IF Output Connector (CP2).................................................................................................................2–11
2.3.10 External Reference (CP3)......................................................................................................................2–11
2.3.11 Ground Connector (GND).....................................................................................................................2–11
v
Page 8

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
CHAPTER 3. OPERATION.............................................................................................. 3–1
3.1 Front Panel........................................................................................................................................................3–1
3.1.1 LED Indicators........................................................................................................................................... 3–2
3.1.2 Front Panel Keypad ...................................................................................................................................3–3
3.2 Menu System.....................................................................................................................................................3–4
3.3 Front Panel Menu.............................................................................................................................................3–5
3.4 OPENING SCREEN........................................................................................................................................3–6
3.4.1 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................3–6
3.4.1.1 CONFIGURATION:MODULATOR ...............................................................................................3–6
3.4.1.1.1 MODULATOR:TX-X..................................................................................................................3–6
3.4.1.1.2 MODULATOR:TX-IF FREQUENCY.........................................................................................3–7
3.4.1.1.3 MODULATOR:TX-IF OUTPUT.................................................................................................3–7
3.4.1.1.4 MODULATOR:TX POWER LEVEL..........................................................................................3–7
3.4.1.1.5 MODULATOR:SCRAMBLER....................................................................................................3–8
3.4.1.1.6 MODULATOR:DIFF.ENCODER...............................................................................................3–8
3.4.1.1.7 MODULATOR:CARRIER MODE..............................................................................................3–8
3.4.1.1.8 MODULATOR:MODEM REFERENCE.....................................................................................3–9
3.4.1.1.9 MODULATOR:RS ENCODER...................................................................................................3–9
3.4.1.2 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:DEMODULATOR..................................................................................3–10
3.4.1.2.1 DEMODULATOR:ASSIGNED FILTERS..................................................................................3–10
3.4.1.2.2 DEMODULATOR:RX-IF FREQUENCY...................................................................................3–10
3.4.1.2.3 DEMODULATOR:DESCRAMBLER.........................................................................................3–11
3.4.1.2.4 DEMODULATOR:DIFF. DECODER.........................................................................................3–11
3.4.1.2.5 DEMODULATOR:RF LOOP BACK..........................................................................................3–11
3.4.1.2.6 DEMODULATOR:IF LOOP BACK...........................................................................................3–11
3.4.1.2.7 DEMODULATOR:BER THRESHOLD......................................................................................3–12
3.4.1.2.8 DEMODULATOR:SWEEP CENTER.........................................................................................3–12
3.4.1.2.9 DEMODULATOR:SWEEP RANGE...........................................................................................3–12
3.4.1.2.10 DEMODULATOR:REACQUISITION........................................................................................3–13
3.4.1.2.11 DEMODULATOR:RS DECODER..............................................................................................3–13
3.4.1.3 CONFIGURATION:INTERFACE...................................................................................................3–14
3.4.1.3.1 INTERFACE:TX CLOCK SOURCE...........................................................................................3–14
3.4.1.3.2 INTERFACE:TX CLOCK PHASE..............................................................................................3–14
3.4.1.3.3 INTERFACE:EXT-CLK FREQ...................................................................................................3–15
3.4.1.3.4 INTERFACE:BUFFER CLOCK..................................................................................................3–16
3.4.1.3.5 INTERFACE:RX CLOCK PHASE..............................................................................................3–16
3.4.1.3.6 INTERFACE:B-BAND LOOP BACK.........................................................................................3–17
3.4.1.3.7 INTERFACE:BUFFER SIZE.......................................................................................................3–18
3.4.1.3.8 INTERFACE:BUFFER CENTER................................................................................................3–18
3.4.1.3.9 INTERFACE:LOOP TIMING .....................................................................................................3–19
3.4.1.4 CONFIGURATION:SAVE..............................................................................................................3–19
3.4.1.5 CONFIGURATION:RECALL.........................................................................................................3–19
vi
Page 9

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.2 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:MONITOR.......................................................................................................3–20
3.4.2.1 MONITOR:RAW BER.....................................................................................................................3–20
3.4.2.2 MONITOR:CORRECTED BER ......................................................................................................3–20
3.4.2.3 MONITOR:EB/NO...........................................................................................................................3–21
3.4.2.4 MONITOR:RECEIVE SIGNAL ......................................................................................................3–21
3.4.2.5 MONITOR:SWEEP FREQUENCY.................................................................................................3–21
3.4.2.6 MONITOR:BUFFER FILL ..............................................................................................................3–21
3.4.3 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:FAULTS AND ALARMS...............................................................................3–22
3.4.3.1 FAULTS AND ALARMS:MODULATOR......................................................................................3–23
3.4.3.2 FAULTS AND ALARMS:DEMODULATOR.................................................................................3–23
3.4.3.3 FAULTS AND ALARMS:TX INTERFACE...................................................................................3–24
3.4.3.4 FAULTS AND ALARMS:RX INTERFACE...................................................................................3–25
3.4.3.5 FAULTS AND ALARMS:COMMON.............................................................................................3–26
3.4.4 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS...............................................................3–27
3.4.4.1 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:MODULATOR.....................................................................3–28
3.4.4.2 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:DEMODULATOR................................................................3–28
3.4.4.3 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:TX INTERFACE...................................................................3–29
3.4.4.4 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:RX INTERFACE ..................................................................3–29
3.4.4.5 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:COMMON ............................................................................3–30
3.4.4.6 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:UNAVAL SECONDS...........................................................3–30
3.4.4.7 STORED FAULTS AND ALARMS:CLEAR..................................................................................3–30
3.4.5 FUNCTIONAL SELECT:UTILITY .........................................................................................................3–31
3.4.5.1 UTILITY:MODULATOR................................................................................................................3–32
3.4.5.1.1 MODULATOR:ASSIGN TRANSMIT FILTERS .......................................................................3–32
3.4.5.1.2 MODULATOR:MOD POWER OFFSET....................................................................................3–32
3.4.5.1.3 MODULATOR:MODULATOR TYPE .......................................................................................3–33
3.4.5.1.4 MODULATOR:ENCODER TYPE..............................................................................................3–33
3.4.5.1.5 MODULATOR:TX BPSK ORDERING......................................................................................3–34
3.4.5.1.6 MODULATOR:MOD SPECTRUM ............................................................................................3–34
3.4.5.1.7 MODULATOR:TX-RS INTERLEAVE ......................................................................................3–34
3.4.5.1.8 MODULATOR:TX MODE..........................................................................................................3–34
3.4.5.1.9 MODULATOR:TX SYMBOL RATE.........................................................................................3–35
3.4.5.2 UTILITY:DEMODULATOR...........................................................................................................3–35
3.4.5.2.1 DEMODULATOR:ASSIGN TRANSMIT FILTERS..................................................................3–35
3.4.5.2.2 DEMODULATOR:DEMODULATOR TYPE.............................................................................3–36
3.4.5.2.3 DEMODULATOR:DECODER TYPE.........................................................................................3–36
3.4.5.2.4 DEMODULATOR:RX BPSK ORDERING................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.2.5 DEMODULATOR:DEMOD SPECTRUM..................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.2.6 DEMODULATOR:RX-RS INTERLEAVE.................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.2.7 DEMODULATOR:RX MODE....................................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.2.8 DEMODULATOR:RX SYMBOL RATE....................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.3 UTILITY:INTERFACE....................................................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.3.1 INTERFACE:TX OVERHEAD TYPE........................................................................................3–37
3.4.5.3.2 INTERFACE:RX OVERHEAD TYPE........................................................................................3–38
3.4.5.3.3 INTERFACE:TX TERR INTERFACE........................................................................................3–38
3.4.5.3.4 INTERFACE:RX TERR INTERFACE........................................................................................3–38
3.4.5.3.5 INTERFACE:BUFFER PROGRAM ...........................................................................................3–38
3.4.5.3.6 INTERFACE:FRAMING STRUCTURE.....................................................................................3–40
3.4.5.3.7 INTERFACE:RTS TX-IF CNTRL...............................................................................................3–40
3.4.5.3.8 INTERFACE:TX DATA PHASE ................................................................................................3–40
3.4.5.3.9 INTERFACE:RX DATA PHASE................................................................................................3–41
3.4.5.3.10 INTERFACE:CTS DELAY .........................................................................................................3–41
vii
Page 10

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.4 UTILITY:NETWORK......................................................................................................................3–41
3.4.5.4.1 NETWORK:RELEASE................................................................................................................3–41
3.4.5.4.2 NETWORK:CHANNELS 1 - 15..................................................................................................3–42
3.4.5.4.3 NETWORK:CHANNELS 16 - 31................................................................................................3–42
3.4.5.5 UTILITY:SYSTEM..........................................................................................................................3–42
3.4.5.5.1 SYSTEM:TIME/DATE................................................................................................................3–42
3.4.5.5.2 SYSTEM:REMOTE BAUD RATE.............................................................................................3–43
3.4.5.5.3 SYSTEM:REMOTE ADDRESS..................................................................................................3–43
3.4.5.5.4 SYSTEM:REMOTE TYPE..........................................................................................................3–43
3.4.5.5.5 SYSTEM:OPERATION MODE..................................................................................................3–44
3.4.5.5.6 SYSTEM:YEAR DISPLAY.........................................................................................................3–44
3.4.5.5.7 SYSTEM:TEST MODE STATUS...............................................................................................3–44
3.4.5.5.8 SYSTEM:LAMP TEST................................................................................................................ 3–45
3.4.5.5.9 SYSTEM:SELF TEST..................................................................................................................3–45
3.4.5.5.10 SYSTEM:DISPLAY CONTRAST...............................................................................................3–45
3.4.5.5.11 SYSTEM:M&C FIRMWARE......................................................................................................3–45
3.4.5.5.12 SYSTEM:BOOT FIRMWARE....................................................................................................3–46
3.4.5.5.13 SYSTEM:FPGA FIRMWARE.....................................................................................................3–46
3.4.5.5.14 SYSTEM:EXT AGC:MAX PWR ................................................................................................3–46
3.4.5.5.15 SYSTEM:EXT AGC:MIN PWR..................................................................................................3–47
3.4.5.5.16 SYSTEM:MASTER.....................................................................................................................3–47
3.4.5.6 UTILITY:MODEM TYPE................................................................................................................3–48
3.4.5.6.1 MODEM TYPE: MODEM TYPE................................................................................................3–48
3.4.5.6.2 MODEM TYPE: MODEM EMULATION..................................................................................3–49
3.4.5.6.3 MODEM TYPE:REVISION EMULATION................................................................................3–49
3.4.5.6.4 MODEM TYPE:MODEM OPTIONS..........................................................................................3–50
3.4.5.6.5 MODEM TYPE:CARD #1 TYPE................................................................................................3–51
3.4.5.6.6 MODEM TYPE:CARD #2 TYPE................................................................................................3–51
3.4.5.6.7 MODEM TYPE:CARD #3 TYPE................................................................................................3–51
3.4.5.6.8 MODEM TYPE:LOCAL MODEM AUPC..................................................................................3–51
3.4.5.6.9 MODEM TYPE:MODEM SERIAL.............................................................................................3–51
3.4.5.6.10 MODEM TYPE:CONFIGURATION CODE - MODEM............................................................3–52
3.4.5.7 UTILITY:FACTORY SETUP..........................................................................................................3–52
3.5 User Port Operation.........................................................................................................................................3–53
3.6 Remote Dial-Up Capability..............................................................................................................................3–54
3.6.1 User Port Modem.......................................................................................................................................3–54
3.6.2 Remote Site Modem..................................................................................................................................3–54
3.7 SNM-1000 Commands .....................................................................................................................................3–55
3.7.1 Character Set..............................................................................................................................................3–55
3.7.2 Status Lines and Flow Control...................................................................................................................3–55
3.7.3 Message Structure......................................................................................................................................3–55
3.7.4 Node Address (NA)...................................................................................................................................3–57
3.7.5 Receive Control Channel Frequency (ICF) ...............................................................................................3–58
3.7.6 Transmit Control Channel Frequency (OFC)............................................................................................3–58
3.7.7 Transmitter On (RF_ON)...........................................................................................................................3–59
3.7.8 Transmitter Off (RF_OFF)........................................................................................................................3–59
3.7.9 Transmit Power (TX).................................................................................................................................3–59
3.7.10 Current SNM-1000 DAC Software Revision (VER).................................................................................3–60
3.7.11 Node to NMS Service Messages (NMS_MSG).........................................................................................3–60
viii
Page 11

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.12 SNM-1000 Mode (MD).............................................................................................................................3–61
3.7.13 Built-In Diagnostic Tests (EFD_DIAG)....................................................................................................3–61
3.7.14 Echo (ECHO).............................................................................................................................................3–64
3.7.15 Setup Override (SETUP)...........................................................................................................................3–64
3.7.16 Channel Type (CT)....................................................................................................................................3–65
3.7.17 Modem Command Sequence (MC)...........................................................................................................3–66
3.7.18 Data Call....................................................................................................................................................3–67
3.7.19 Terminate (TE) ..........................................................................................................................................3–69
3.7.20 Initiate Multipoint Data Call (MI) .............................................................................................................3–70
3.7.21 Add Multipoint Data Circuit (MA)............................................................................................................3–72
3.7.22 Drop Multipoint Data Circuit (MT)...........................................................................................................3–73
3.7.23 Change Forward Channel for Multipoint Data Circuit (MF).....................................................................3–74
3.7.24 Change Return Channel for Multipoint Data Circuit (MR).......................................................................3–75
3.7.25 Send Message to Multipoint Data Circuit Originator (MO)......................................................................3–76
3.7.26 Send Message to Multipoint Data Circuit Listeners (ML).........................................................................3–77
3.7.27 Port Redirection.........................................................................................................................................3–77
3.7.28 Debugging with the User Port....................................................................................................................3–78
CHAPTER 4. THEORY OF OPERATION........................................................................ 4–1
4.1 Demand Assignment Controller (DAC)..........................................................................................................4–1
4.1.1 Specifications.............................................................................................................................................4–3
4.1.2 Theory of Operation ..................................................................................................................................4–3
4.1.3 EFBUS1/2 Port (External).........................................................................................................................4–4
4.1.4 Monitor and Control..................................................................................................................................4–4
4.1.5 Non-Volatile Memory................................................................................................................................4–5
4.1.6 User Port....................................................................................................................................................4–5
4.1.7 M&C Theory of Operation ........................................................................................................................4–5
4.2 Modulator..........................................................................................................................................................4–6
4.2.1 Theory of Operation ..................................................................................................................................4–8
4.2.2 Theory of Modulation Types.....................................................................................................................4–9
4.2.3 Modulator Specifications...........................................................................................................................4–10
4.3 Demodulator.....................................................................................................................................................4–11
4.3.1 Theory of Operation ..................................................................................................................................4–12
4.3.2 Demodulator Specifications.......................................................................................................................4–12
CHAPTER 5. MAINTENANCE ........................................................................................ 5–1
5.1 Fault Isolation...................................................................................................................................................5–1
5.1.1 System Faults/Alarms................................................................................................................................5–2
5.1.2 Faults/Alarms Display...............................................................................................................................5–6
5.1.3 Faults/Alarms Analysis..............................................................................................................................5–6
APPENDIX A. REMOTE CONTROL OPERATION.......................................................... A–1
ix
Page 12

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Figures
Figure 1-1. SNM-1000 Block Diagram.................................................................................................................1–2
Figure 1-2. Typical Installation..............................................................................................................................1–3
Figure 1-3. Typical Spectral Occupancy................................................................................................................1–9
Figure 1-4. SNM-1000 Dimensional Envelope .....................................................................................................1–10
Figure 2-1. Installation of the Mounting Bracket...................................................................................................2–3
Figure 2-2. SNM-1000 Rear Panel ........................................................................................................................2–5
Figure 3-1. SNM-1000 Front Panel View..............................................................................................................3–1
Figure 3-2. Keypad................................................................................................................................................3–3
Figure 3-3. Main Menu..........................................................................................................................................3–5
Figure 3-4. Baseband Loopback............................................................................................................................3–17
Figure 4-1. DAC Block Diagram...........................................................................................................................4–2
Figure 4-2. Modulator Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................4–7
Figure 4-3. Demodulator Block Diagram..............................................................................................................4–11
Figure 5-1. Typical Output Spectrum (with Noise) ...............................................................................................5–10
Figure 5-2. Typical Output Spectrum (Without Noise)......................................................................................... 5–10
Figure 5-3. Typical Eye Constellations..................................................................................................................5–13
Tables
Table 1-1. System Specifications...........................................................................................................................1–5
Table 1-2. Environmental and Physical.................................................................................................................1–6
Table 1-3. Burst Mode Operating Specifications...................................................................................................1–7
Table 1-4. Continuous Mode Operating Specifications.........................................................................................1–7
Table 1-5. Viterbi Performance .............................................................................................................................1–7
Table 2-1. Rear Panel Connectors..........................................................................................................................2–4
Table 2-2. Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7) .........................................................................................................2–6
Table 2-3. SNM-1000 User Port Pinout and Signals.............................................................................................2–7
Table 2-4. AUX 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9)......................................................................................................2–8
Table 2-5. Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10) .....................................................................................................2–9
Table 3-1. SNM-1000 Front Panel Indicators........................................................................................................3–2
Table 4-1. Modulator Specifications......................................................................................................................4–10
Table 4-2. Demodulator Specification...................................................................................................................4–13
Table 5-1. SNM-1000 Faul Tree............................................................................................................................5–3
Table 5-2. Conversion to S/N and E
................................................................................................................5–9
b/N0
x
Page 13

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3 Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
About this Manual
This manual describes the operation and maintenance of the Comtech EF Data
SNM-1000 Node Control Modem. This is a technical document intended for earth station
engineers, technicians, and operators responsible for the operation and maintenance of
the Comtech EF Data SNM-1000 Node Control Modem.
Related Documents
The following document is referenced in this manual:
• Comtech EF Data Specification, SP/5747 DAMA Control Channel Messaging
Conventions and References
Cautions and Warnings
CAUTION indicates a hazardous situation that, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury. CAUTION may also be used to indicate other
CAUTION
WARNING
IMPORTANT
unsafe practices or risks of property damage.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
IMPORTANT indicates a statement that is associated with the task
being performed. .
xi
Page 14

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Metric Conversion
Metric conversion information is located on the inside back cover of this manual. This
information is provided to assist the operator in cross-referencing English to Metric
conversions.
Recommended Standard Designations
Recommended Standard (RS) Designations have been superseded by the new designation
of the Electronic Industries Association (EIA). References to the old designations are
shown only when depicting actual text displayed on the screen of the unit (RS-232, RS485, etc.). All other references in the manual will be shown with the EIA designations
(EIA-232, EIA-485, etc.) only.
Trademarks
Intel is a registered trademark of the Intel Corporation.
Sportster is a registered trademark of US Robotics Incorporated.
Product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged.
Reporting Comments or Suggestions Concerning this Manual
Comments and suggestions regarding the content and design of this manual will be
appreciated. To submit comments, please contact the:
Comtech EF Data Technical Publications Department: techpub@comtechefdata.com
Overview of Changes to Previous Revisions
xii
Page 15

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Electrical Safety
The SNM-1000 Modem has been shown to comply with the following safety standard:
• EN 60950: Safety of Information Technology Equipment, including
electrical business machines
The equipment is rated for operation over the range 100 - 240 volts AC. It has a
maximum power consumption of 40 watts, and draws a maximum of 400 mA.
The user should observe the following instructions:
Fuses
The SNM-1000 is fitted with two fuses - one each for line and neutral connections. These
are contained within the body of the IEC power inlet connector, behind a small plastic
flap.
• For 230 volt AC operation, use T0.75A, 20mm fuses.
• For 115 volt AC operation, use T1.25A fuses, 20mm fuses.
FOR CONTINUED OPERATOR SAFETY, ALWAYS REPLACE THE FUSES
WITH THE CORRECT TYPE AND RATING.
Environmental
The SNM-1000 must not be operated in an environment where the unit is exposed to
extremes of temperature outside the ambient range 0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F), precipitation,
condensation, or humid atmospheres above 95% RH, altitudes (un-pressurised) greater
than 2000 metres, excessive dust or vibration, flammable gases, corrosive or explosive
atmospheres.
Operation in vehicles or other transportable installations that are equipped to provide a
stable environment is permitted. If such vehicles do not provide a stable environment,
safety of the equipment to EN60950 may not be guaranteed.
xiii
Page 16

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Installation
The installation and connection to the line supply must be made in compliance to local or
national wiring codes and regulations.
The SNM-1000 is designed for connection to a power system that has separate ground,
line and neutral conductors. The equipment is not designed for connection to power
system that has no direct connection to ground.
The SNM-1000 is shipped with a line inlet cable suitable for use in the country of
operation. If it is necessary to replace this cable, ensure the replacement has an equivalent
specification.
Examples of acceptable ratings for the cable include HAR, BASEC and HOXXX-X.
Examples of acceptable connector ratings include VDE, NF-USE, UL, CSA, OVE,
CEBEC, NEMKO, DEMKO, BS1636A, BSI, SETI, IMQ, KEMA-KEUR and SEV.
International Symbols:
Symbol Definition Symbol Definition
~
Alternating Current
Fuse
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
In accordance with the Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive 91/263/EEC,
this equipment should not be directly connected to the Public Telecommunications
Network.
Protective Earth
Chassis Ground
xiv
Page 17

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
In accordance with European Directive 89/336/EEC, the SNM-1000 Modem has been
shown, by independent testing, to comply with the following standards:
Emissions: EN 55022 Class B - Limits and methods of measurement of radio
interference characteristics of Information Technology Equipment.
(Also tested to FCC Part 15 Class B)
Immunity: EN 50082 Part 1 - Generic immunity standard, Part 1: Domestic,
commercial and light industrial environment.
Additionally, the SNM-1000 has been shown to comply with the following standards:
EN 61000-3-2 Harmonic Currents Emission
EN 61000-3-3 Voltage Fluctuations and Flicker
EN 61000-4-2 ESD Immunity
EN 61000-4-4 EFT Burst Immunity
EN 61000-4-5 Surge Immunity
EN 61000-4-6 RF Conducted Immunity
EN 61000-4-8 Power frequency Magnetic Field Immunity
EN 61000-4-9 Pulse Magnetic Field Immunity
EN 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips, Interruptions, and Variations Immunity
EN 61000-4-13 Immunity to Harmonics
In order that the Modem continues to comply with these standards, observe
the following instructions:
IMPORTANT
• Connections to the transmit and receive IF ports (BNC female connectors) should
be made using a good quality coaxial cable - for example RG58/U (50 Ω or
RG59/U (75 Ω).
• All 'D' type connectors attached to the rear panel must have back-shells that
provide continuous metallic shielding. Cable with a continuous outer shield
(either foil or braid, or both) must be used, and the shield must be bonded to the
back-shell.
• The equipment must be operated with its cover on at all times. If it becomes
necessary to remove the cover, the user should ensure that the cover is correctly
re-fitted before normal operation commences
xv
Page 18

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
European EMC Directive
In order to meet the European Electro-Magnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive
(EN55022, EN50082-1), properly shielded cables for DATA I/O are required. More
specifically, these cables must be shielded from end-to-end, ensuring a continuous
ground shield.
The following information is applicable for the European Low Voltage Directive
(EN60950):
<HAR> Type of power cord required for use in the European Community.
CAUTION: Double-pole/Neutral Fusing
!
International Symbols:
ACHTUNG: Zweipolige bzw. Neutralleiter-Sicherung
Alternating Current.
Fuse.
Safety Ground.
Chassis Ground.
Note: For additional symbols, refer to “Cautions and Warnings” listed earlier in this
preface.
xvi
Page 19

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
Warranty Policy
This Comtech EF Data product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship
for a period of two year from the date of shipment. During the warranty period, Comtech
EF Data will, at its option, repair or replace products that prove to be defective.
For equipment under warranty, the customer is responsible for freight to Comtech EF
Data and all related custom, taxes, tariffs, insurance, etc. Comtech EF Data is responsible
for the freight charges only for return of the equipment from the factory to the customer.
Comtech EF Data will return the equipment by the same method (i.e., Air, Express,
Surface) as the equipment was sent to Comtech EF Data.
Limitations of Warranty
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper installation or
maintenance, abuse, unauthorized modification, or operation outside of environmental
specifications for the product, or, for damages that occur due to improper repackaging of
equipment for return to Comtech EF Data.
No other warranty is expressed or implied. Comtech EF Data specifically disclaims the
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for particular purpose.
Exclusive Remedies
The remedies provided herein are the buyer's sole and exclusive remedies. Comtech EF
Data shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential
damages, whether based on contract, tort, or any other legal theory.
Disclaimer
Comtech EF Data has reviewed this manual thoroughly in order that it will be an easy-touse guide to your equipment. All statements, technical information, and
recommendations in this manual and in any guides or related documents are believed
reliable, but the accuracy and completeness thereof are not guaranteed or warranted, and
they are not intended to be, nor should they be understood to be, representations or
warranties concerning the products described. Further, Comtech EF Data reserves the
right to make changes in the specifications of the products described in this manual at any
time without notice and without obligation to notify any person of such changes.
If you have any questions regarding your equipment or the information in this manual,
please contact the Comtech EF Data Customer Support Department.
xvii
Page 20

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Preface MN/SNM1000.IOM
This page is intentionally left blank.
xviii
Page 21

Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides an overview of the SNM-1000 Node Control modem, referred to in
this manual as “the node control modem” and “node controller.”
The node controller contains the following components:
Modem
DAMA
The modem is a fully digital. Integrated satellite modem and Demand Assigned
Multiple Access (DAMA) controller. The modem is designed to function as
the traffic node controller within Comtech EF Data’s Bandwi dth On-Dem and
(BOD) Multimedia Integrated Digital Access System (MIDAS).
DAMA control is provided by a DAMA Assignment Cont rolle r (DAC)
daughter board.
SNM-1000 Node
Control Modem
1-1
Page 22

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.1 Overview
The SNM-1000 Node Control Modem is a fully integrated digital satellite modem and
DAMA controller. Utilizing the latest digital signal processing techniques, it is designed
to function as a self-contained indoor unit that operates within Comtech EF Data's
Bandwidth-on-Demand (BOD) Multimedia Integrated Digital Access System (MIDAS).
1.1.1 Additional Features
The modem contains the following additional features:
• Integrated DAMA controller in a 1RU package
• Burst mode modulator
• Continuous mode demodulator
• Fast acquisition
• Operational parameters stored in EEPROM
• 50/180 MHz operation
• Software stored in flash for easy update
1-2
Page 23
SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
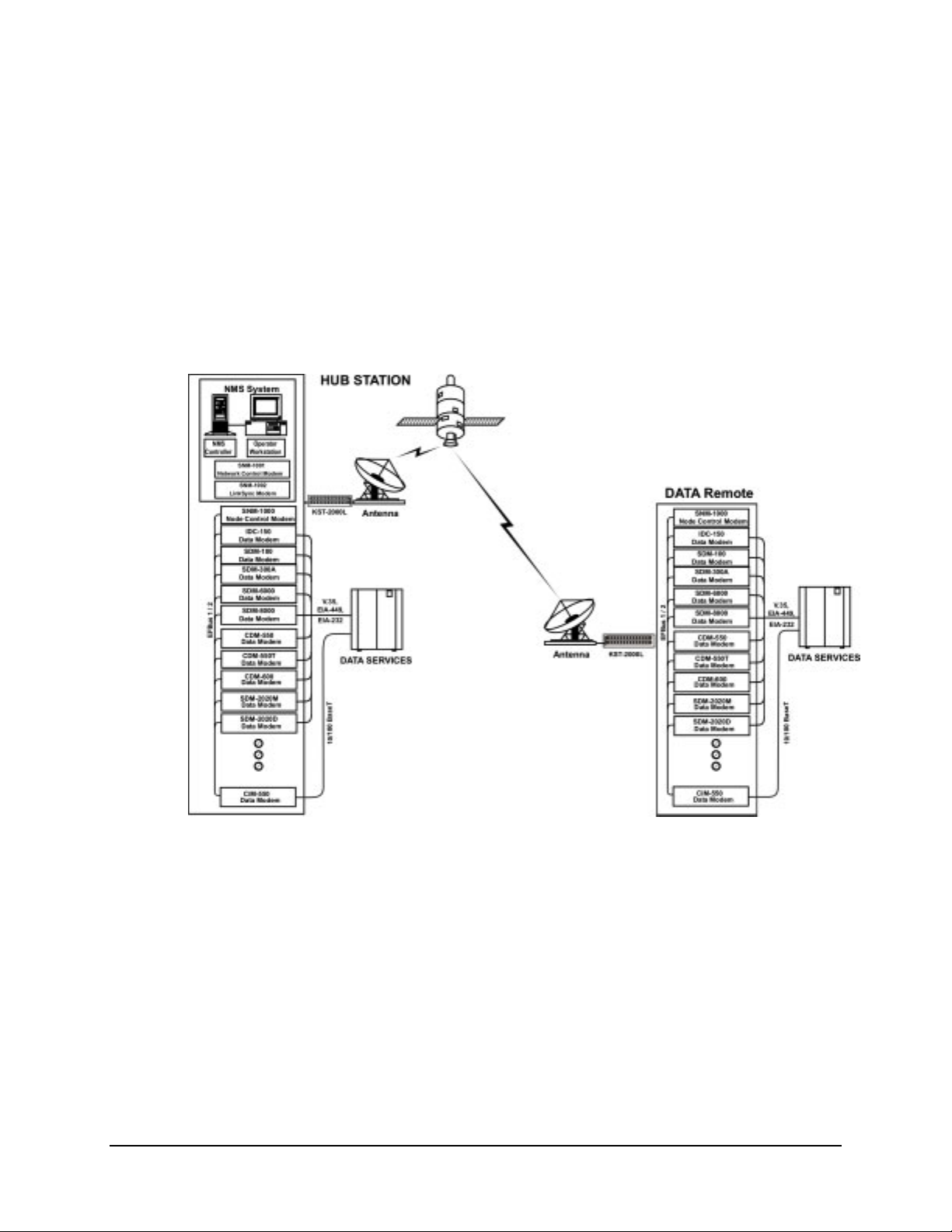
1.1.2 Mode of Operation
The SNM-1000 operates as a dedicated node controller at the HUB and REMOTE sites,
receiving the continuous outbound control channel from the hub station and transmitting
to the hub station on the inbound control channel in burst mode. The node control modem
manages traffic modems utilizing EFBUS1 connecting to the M&C port of the traffic
modems (Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1. Typical Installation
1-3
Page 24

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.2 Description
The SNM-1000 is housed in a 1-Rack Unit (1RU) rack-mountable chassis. Cooling is
provided by a fan mounted on the rear panel. The SNM-1000 operates in burst transmit
with continuous receive mode.
• Burst mode is used by the SNM-1000 to transmit to the NMS over the inbound
control channel. The burst mode data rate is shown below.
Burst Mode Data Rates
19.2 kbit/s at FEC rate 1/2 QPSK
• Continuous mode is used to receive the outbound control channel at the remote.
The continuous mode data rate is shown below.
Continuous Mode Data Rates
19.2 kbit/s Viterbi rate 1/2 QPSK
Figure 1-2. SNM-1000 Block Diagram
1-4
Page 25

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.3 Options
The following options are available for the SNM-1000:
Option
90-264 VAC
-48 VDC
50Ω
75Ω
Part No.
KT/8000-3
KT/8000-4
PL/6093-3
PL/6093-1
1-5
Page 26

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.4 Specifications
This section includes the following specifications:
• General Specifications
• Environmental and Physical Specifications
• DAC
• Burst mode operating specifications
• Continuous mode operating specifications
• Bit Error Rate (BER) specifications
1.4.1 General Specifications
Table 1-1. General Specifications
Parameter Specification
Operating IF Range 50 to 180 MHz, in 1 Hz steps
Digital Data:
Burst Mode Transmit (Slotted Aloha)
TX Data Rate
Continuous Mode Receive
RX Data Rate
Symbol Rate 19.2 kHz
Modulation QPSK
Forward Error Correction Viterbi, K=7, 1/2 rate
Data Scrambling IESS-308 (V.35), IESS-309, or None
External Reference 1, 5, 10, 20 MHz
Plesiochronous Buffer 16 bits to 256 kbps, in 16 bit steps
Modulator
Output Power -5 to –30 dBm, adjustable in 0.1 dB steps
Output Spurious < -55 dBc, 0 to 500 MHz (4 kHz in-band)
Output Harmonics < -55 dBc, 0 to 500 MHz (4 kHz out-of-band)
Output Spectrum Meets IESS-308/309 power spectral mask
Output Return Loss > 20 dB
Output Impedance
Output Frequency Stability
Data Clock Source Internal or External
Internal Stability
TDMA
19.2 kbps
TDM
19.2 kbps
2 to 98 ms, in 2 ms steps
75 Ω (Optional: 50 Ω)
± 10 PPM
External Clock: ± 100 PPM and < 5% jitter
Internal Clock: ± 10 PPM
± 1 x 10
-5
1-6
Page 27

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
Table 1-1. General Specifications (Continued)
Demodulator
Input Power:
Desired Carrier
Maximum Composite
Input Impedance
Input Return Loss > 20 dB
Carrier Acquisition Range
Acquisition Time: 19.2 bps, R=1/2 < 2 seconds
Sweep Reacquisition 0 to 999 seconds, in 1 second steps
Data Clock Internal, External, Transmit, Recovered RX
Outbound (from NMS) Continuous transmission, Time Division Multiplex
Inbound (to NMS) Burst transmission, (TDMA) Slotted Aloha,
Processor
M&C Processor Single processor for node control EEPROM variable
User Port Interface
Interface Type EIA-232
Data Rate 19.2 kbps
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Application Remote circuit initiation and termination via command
Control Interface
EFBUS1:
Interface Type EIA-485
Data Rate 9.6 or 19.2 kbps
Application Multi-drop bus used to control external data traffic
Compatibility Standard Comtech EF Data remote commands
Modems Supported
(Not limited to-)
-30 to –55 dBm
-5 dBm or +40 dBc
75Ω (Optional: 50Ω)
± 35 kHz from 100 Hz to 35 kHz, in 1 Hz steps
(TDM), 19.2 kbps, QPSK, R=1/2
19.2 kbps, QPSK, R=1/2
storage Memory life without power for 10 years.
interface; Transmits and receives service terminal
messages.
modems
SDM-100, SDM-300/300A, SDM-2020M/D,
SDM-6000, SDM-8000, SDM-9000, CDM-550/550T,
CDM-600, CiM-550
1-7
Page 28

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.4.2 Environmental and Physical
Table 1-2. Environmental and Physical
Parameter Specification
Prime Power 90 to 264 VAC, 47 to 63 Hz
Optional: 38 to 64 VDC
Power Dissipation 30 Watt
Size 1.75H x 19.0W x 14.0D inch (1 RU)
(4.4H x 48W x 36D cm)
Weight < 11 lbs (< 5 kg)
Temperature:
Operating
Storage
Humidity Up to 95%, non-condensing
Shipping Container Dimensions 22W x 20D x 12H inches
Shipping Weight 15 lbs (7 kg)
0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F)
-55 to 70°C (-67 to 158°F)
(56W x 51D x 31H cm)
1.4.3 DAC Specification
The DAC performs all of the DAMA control functions. The DAC provides a set of
interface for communicating with an operator, controlling external traffic modems, etc.
The DAC communicates with the NMS for call control and M&C.
1.4.4 Burst Mode Specification
Table 1-3. Burst Mode Operating Specifications
Modulator Specifications
Operating Frequency Range 50 to 180 MHz
Type of Modulation QPSK
Operating Channel Spacing Less than 0.5 dB degradation operating with 2 adjacent-like
channels, each 10 dB higher at 1.3 times the symbol rate, or a
minimum of 1.2 times t he specified acqui siti on range
Phase Noise In accordance with IESS-308
Digital Data Rate:
QPSK, 1/2 Rate
Forward Error Correction Convolution encoding, soft-decision K=7 Viterbi decoding
Data Scrambling Selectable or none, 215-1, synchronous
19.2 kbit/s
1-8
Page 29

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.4.5 Continuous Mode Specifications
Table 1-4. Continuous Mode Operating Specifications
Demodulator Specifications
Input Power (Desired Carrier) -30 to -55 dBm (composite) +30 dB power within 2 MHz from
desired carrier
+40 dB power outside of 2 MHz from desired carrier
-5 dBm maximum composite
Carrier Acquisition Range
Clock Acquisition Range
Acquisition Time < 1 second at all data rates
Directed Sweep:
Sweep Range
Sweep Center
± 35 kHz
± 100 PPM
0 to 70000 Hz
-35000 to +35000 Hz
1.4.6 Viterbi Performance with Noise, Closed Network
Table 1-5 lists the Viterbi decoder specifications with noise, closed network, for the Eb/N0
required to achieve 10
-5
to 10-8 BER.
Table 1-5. Viterbi Performance
Eb/N0 (dB) Specification
BER 1/2 Rate
10-5 4.6
10-6 5.3
10-7 5.9
10-8 6.4
1-9
Page 30

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.5 Typical Spectral Occupancy
Figure 1-3. Typical Spectral Occupancy
1-10
Page 31

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
(36)
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
1.6 Dimensional Envelope
14.0
Figure 1-4. SNM-1000 Dimensional Envelope
1-11
Page 32

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Introduction MN/SNM1000.IOM
This page is intentionally left blank.
1-12
Page 33

Chapter 2. INSTALLATION
This chapter provides unpacking and installation instructions, and a description of
external connections information.
The equipment contains parts and assemblies sensitive to damage by
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD). Use ESD precautionary procedures when
CAUTION
touching, removing, or inserting PCBs.
2.1 Unpacking
The modem and manual are packaged in pre-formed, reusable, cardboard cartons
containing foam spacing for maximum shipping protection.
Do not use any cutting tool that will extend more than 1 inch (2.54 cm) into
the container. This can cause damage to the modem.
CAUTION
Unpack the modem as follows:
1. Cut the tape at the top of the carton indicated by OPEN THIS END.
2. Remove the cardboard/foam space covering the modem.
3. Remove the modem, manual, and power cord from the carton.
4. Save the packing material for storage or reshipment purposes.
5. Inspect the equipment for any possible damage incurred during shipment.
6. Check the equipment against the packing list to ensure the shipment is correct.
7. Refer to Section 2.2 for installation instructions.
2–1
Page 34

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.2 Installation
The modem arrives fully assembled from the factory. After unpacking the modem, install
the modem as follows:
1. If required, install the mounting bracket in equipment rack (Figure 2-1). Install
and tighten the bracket bolts.
2. Loosen the screw with flat washer located on the left side of modem chassis.
Mount the modem chassis into the equipment rack and slide the screw with flat
washer through the slot of the mounting bracket. Tighten the screw sufficiently to
allow the modem chassis to slide in the bracket.
3. Connect the cables to the proper locations on the rear panel. Refer to Section 2.4
for connector pinouts, placement, and function.
4. Connect the primary power cable to the power source. Before turning on the
power switch, become familiar with the front panel operation in Chapter 3.
5. If problems exist with the installation, refer to Chapter 5 for troubleshooting
information.
2–2
Page 35

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
Figure 2-1. Installation of the Mounting Bracket
2–3
Page 36

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3 Rear Panel Connections
The rear panel connectors provide all necessary external connections between the node
control modem and other equipment. Figure 2-1 provides a layout of the SNM-1000 rear
panel, and Table 2-1 lists these connectors.
USER
PORT J9
J6
EF BUS 1/2
AUX 1
FAULT ALARM S
J7 J10
EX REF
RX/IF IN PUT
CP3
TX/IF OUTPUT
CP1CP2
Figure 2-2. SNM-1000 Rear Panel
Table 2-1. Rear Panel Connectors
Connection Description
GROUND CONNECTOR The GROUND CONNECTOR (GRN), provides a common chassis ground
connection among all of the equipment, via a #10-32 stud.
AC POWER
The AC POWER accepts input power for the SNM-1000. (+48 VDC optional)
USER PORT The USER PORT allows the user to configure setup parameters, and to
initiate/terminate remotely initiated calls.
EFBUS1/2 The EFBUS1/2 in used by the Node Control Modem to control up to 30 Comtech
EF Data/MIDAS modems.
AUXILIARY 1 The AUXILIARY 1 connector (J9), provides MOD and DEMOD (TTL) faults,
satellite clock, satellite I&Q, and Automatic Gain Control (AGC) output voltage.
FAULT The FAULT connector (J7), provides Form C contact closures for fault reporting.
ALARM
OUTPUT
Not currently used.
The ALARM OUTPUT (J10), provides FORM C contact closures for the purpose
of fault reporting.
EXTERNAL
REFERENCE
RX IF INPUT
CONNECTOR
TX IF OUTPUT
CONNECTOR
The EXTERNAL REFERENCE (CP3), is a BNC connector for an external
reference. The input impedance is 75Ω
The RX IF INPUT CONNECTOR (CP2), is a BNC jack that provides a
connection for the receive IF signal.
The TX IF OUTPUT CONNECTOR (CP1), is a BNC jack that provides a
connection for the transmit IF signal.
Note: The European EMC Directive (EN55022, EN50082-1) requires using properly shielded
cables for DATA I/O. These cables must be double-shielded from end-to-end, ensuring a
continuous ground shield.
2–4
Page 37

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.1 EFBUS1/2 Port (J6)
The EFBUS port provides two separate 2-wire EIA-485 interfaces wired to a common
9-pin D female connector located on the rear of the MIDAS Node Control Modem.
IF Modulator and IF Demodulator status is also presented for external use.
The Modem Control serial port, EFBUS1, is used for control of other Comtech EF Data
traffic modems.
having the MC prefix.
The signals are described in the following table, with signal names
The interface is ASYNC, EIA-485/2 wire, and 19.2 kbps.
The EFBUS2 port is reserved for communication with future MIDAS traffic modems.
Signal Function Name
Ground MCGND - 1 Demodulator fault BP_DF I/O 2 TTL
Modulator fault BP_MF I/O 3 TTL
Receive/Transmit + MS_RD/SD+(EFBUS2) I/O 4 EIA-485
Receive/Transmit - MS_RD/SD-(EFBUS2) I/O 5 EIA-485
Receive/Transmit+ MC_RD/SD+(EFBUS1) I/O 6 EIA-485
Receive/Transmit- MC_RD/SD-(EFBUS1) I/O 7 EIA-485
Ground MSGND - 8 Not used - - 9 Not used - - - -
I/O
MIDAS
Conn Pin #
Signal
Level
The
2–5
Page 38

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.2 Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)
The fault connector provides Form C contact closures for fault reporting. The three Form C
summary fault contacts, ratings 1A maximum at 24 VDC, 0.5A at 120 VAC, are
Modulator, Demodulator, and Common Equipment.
The fault interface connection is a 9-pin subminiature female D connector (J7) located on
the rear panel of the modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the
mating connector. Refer to Table 2-2 for pinout information.
Table 2-2. Fault Connector and Pinouts (J7)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Common equipment is not faulted NO
2 COM
3 Common equipment is faulted NC
4 Modulator is not faulted NO
5 COM
6 Modulator is faulted NC
7 Demodulator is not faulted NO
8 COM
9 Demodulator is faulted NC
Note: A connection between the common (COM) and normally open (NO)
contacts indicates no fault.
Refer to Chapter 5 for a discussion of monitored faults. To obtain a system summary
fault, connect all the Form C contacts in parallel.
2–6
Page 39

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.3 User Port
The User Port provides for serial communications with the modem to allow configuration
of setup parameters and user requests for traffic channel assignments. The interface is
provided on a 9-pin MINI-DIN female connector (DCE) located on the rear panel of the
SNM-1000. Refer to the following listing for User Port s pecifications.
Connector Type 9-pin MINI-DIN
Signal Type EIA-232
Rate 19.2 kbit/s, 8 bits-no parity-1stop
Note: Refer to Appendix A for a description of the software communications parameters
and for detailed message format information.
Pinout and signal levels are described in Table 2-3.
Table 2-3. SNM-1000 User Port Pinout and Signals
Signal Function Name Pin # I/O Signal Level
Receiver Ready RR 1 O EIA-232
Receive Data RD 2 O EIA-232
Send Data SD 3 I EIA-232
Terminal Ready TR 4 I EIA-232
Signal Ground SG 5
Data Mode DM 6 O EIA-232
Request to Send RS 7 I EIA-232
Clear to Send CS 8 O EIA-232
Incoming Call IC 9 O EIA-232
2–7
Page 40

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.4 Auxiliary 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9)
The auxiliary 1 (AUX 1) connector provides:
• MOD and DEMOD (TTL) faults
• Satellite clock
• Satellite I&Q
• Automatic Gain Control (AGC) output voltage
The faults are open collector levels that indicate a modulator or demodulator failure. A logic
“1” indicates the faulted condition.
AGC_OUT is a programmable voltage, 0 to 10V, for a receive signal level between -25 and
-60 dBm.
AUX 1 connection is a 9-pin female D connector (J9) located on the rear panel of the
modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the mating connector. Refer to
Table 2-4 for pinout information
Table 2-4. AUX 1 Connector and Pinouts (J9)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Satellite Clock - SAT_CLK2 No Connection NC
3 Satellite Clock + SAT_CLK+
4 MODULATOR TTL Fault MDFLTTTL
5 Ground GRN
6 RX Q Channel Eye RX_Q
7 DEMODULATOR TTL Fault DFFLTTTL
8 RX 1 Channel Eye Rx_1
9 Agc Output AGC
2–8
Page 41

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.5 Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10)
The alarms connector provides Form C contact closures for alarm reporting. The two Form
C summary fault contacts are Modulator and Demodulator.
The alarms connection is a 9-pin female D connector (J10) located on the rear panel of the
modem. Screw locks are provided for mechanical security on the mating connector. Refer to
Table 2-5 for pinout information.
Table 2-5. Alarms Connector and Pinouts (J10)
Pin # Signal Function Name
1 Alarm 1 is faulted NO
2 COM
3 Alarm 1 is not faulted NC
4 Alarm 2 is faulted NO
5 COM
6 Alarm 2 is not faulted NC
7 Alarm 3 is faulted NO
8 COM
9 Alarm 3 is not faulted NC
• Alarm 1 = Not used
• Alarm 2 = TX
• Alarm 3 = RX
2–9
Page 42

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Installation MN/SNM1000.IOM
2.3.6 AC Power
The AC power is supplied to the SNM-1000 by a standard, d etachab le, non-locking,
3-prong power cord. Refer to the following listing for AC power specifications.
Input power 50W max.
Input voltage 90 to 264 VAC, 47 to 63Hz.
Note: Unit switches ranges automatically.
Connector type IEC
Fuse protection 1A slo-blo line and neutral fusing 5 mm type fuses.
2.3.7 DC Power
For DC supplied units, the DC Power is supplied by terminal lugs installed on the back
panel. Refer to the following table for specifications
Input power 50W max.
Input voltage 38 to 64 VDC.
Connector type Terminal Lug
Fuse protection 1A slo-blo 5 mm type fuses.
2.3.8 TX IF Output Connector (CP1)
CP1 is a BNC connector for the transmit IF signal. The standard output impedance is
75Ω (50 Ω optional ), and the output power level is -5 to -30 dBm. In normal operation, the
output will be a 8PSK, QPSK/OQPSK, or BPSK-modulated result of the data connector
between 50 and 180 MHz, in 1 Hz steps.
2.3.9 RX IF Input Connector (CP2)
CP2 is a BNC connector for the RX-IF signal. The standard input impedance is
75Ω (50Ω optional). For normal operation, the desired carrier signal level should be
between -30 and -55 dBm. Signals between 50 and 180 MHz are selected and demodulated
to produce clock and data.
2.3.10 External Reference (CP3)
CP3 is a BNC connector for an EX REF. The input impedance is 75Ω.For normal
operation, the reference signal is
≥ 0 dBm.
2.3.11 Ground Connector (GND)
A #10-32 stud on the rear panel of the modem is used for connecting a common chassis
ground among all equipment. The AC power connector provides the safety ground.
2–10
Page 43

Chapter 3. OPERATION
A
A
A
This chapter describes the operation of the SNM-1000.
3.1 Front Panel
The front panel of the SNM-1000 (Figure 3-1) provides for monitoring modem
configuration and status.
NMS
NMSEF BUS 1 OPWER ON
NODE
CH
NNEL
FAULT EST MODE
SNM-1010 Data Control Modem
SNM-1000 Data Control Modem
Figure 3-1. SNM-1000 Front Panel View
The front panel features include:
• 32- character, two-line LCD display
• Six-button keypad for local control
• Eight LED's to provide overall status at a glance
These functions are accessible at the front panel by entering on of five pre-defined
function select categories or levels:
• Configuration
• Monitor
• Faults/Alarms
• Stored Faults/Alarms
• Utility
FAULT
POWER ON
TRAN SMITTER ON
TNODEEF BUS 2 RANSMITTER ON
CARRIE R DET ECT
CCHANNEL ARRIER DETECT
TEST MODE
ENTER
ENTER
CLE
CLE
R
R
3–1
Page 44

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.1.1 LED Indicators
In addition to the LCD, the LED’s provides the modem status. The DAC board controls
LEDs 6 through 10. The LED’s support three states:
• ON
• OFF
• Flashing
Table 3-1. SNM-1000 Front Panel Indicators
LED Color Description
POWER ON Green Power is applied to the modem.
FAULT Red A fault condition exists.
TEST MODE Yellow Flashes when the unit is in a test configuration.
TRANSMITTER ON Green Transmitter is currently ON.
Indicates the actual condition of the transmitter, as opposed to the
programmed condition.
In control mode, the indicator blinks since the transmitter is operating in
the burst mode.
In traffic mode, the indicator is solid green.
CARRIER DETECT Green D e c o der is loc k ed .
NODE Green Indicates the node has been enabled or disabled by the NMS. It is ON
if the node is enabled, OFF if the node is disabled.
NMS Green (OFF) Node did not receive timing or ACKNOWLEDGE messages
from the NMS.
(FLASHING) Node received timing message from the NMS, but no
ACKNOWLEDGE message was received.
(ON) Node received timing and ACKNOWLEDGE from the NMS.
CHANNEL Green (OFF) Not used on SNM-1000.
EFBUS1 Green (OFF) Indicates operational status of externally connected traffic
modems.
(ON) OK
(FLASHING) Fault indication.
EFBUS2 Green (OFF) Indicates operational status of externally connected traffic
modems.
(ON) OK
(FLASHING) Fault indication.
3–2
Page 45

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.1.2 Front Panel Keypad
The front panel keypad operates in monitor mode only, and permits local operation of the
modem. The keypad consists of six keys (Figure 3-2).
ENTER
CLEAR
Figure 3-2. Keypad
Each key provides one or more logical functions. These functions are defined in the
following table.
ENTER This key is used to select a displayed function or to execute a modem
configuration change.
CLEAR This key is used to back out of a selection or to cancel a configuration change
which has not been executed using [ENTER]. Pressing [CLEAR] generally returns
the display to the previous selection.
Left and Right
Diamond Keys
Top and Bottom
Diamond Keys
These keys are used to move to the next selection or to move the cursor for certain
functions.
Note: Throughout this chapter, [
diamond keys.
These keys are used primarily to change configuration data (numbers). At times,
they are also used to move from one section to another.
Note: Throughout this chapter, [
diamond keys.
←] and [→] are used to indicate left and right
↑] and [↓] are used to indicate top and bottom
The modem responds by beeping whenever a key is pressed:
• A single beep indicates a valid entry and the appropriate action was taken.
• A double beep indicates an invalid entry or a parameter is not available for
operation.
3–3
Page 46

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.2 Menu System
Use the Main menu in Figure 3-3 as a quick reference for accessing the modem functions.
When the modem power is applied, the base level of the menu system displays the
sign-on message:
• Line 1 of the sign-on message is the modem type.
• Line 2 is the node address.
The main level of the menu system is Function Select. To access this level from the
sign-on message, press the [←] or [→] keys. From the Function Select menu, select one
of the functional categories:
• Configuration
• Monitor
• Faults/Alarms
• Stored Faults/Alarms
• Utility
Press [←] or [→] to move from one selection to another. When line 2 displays the desired
function, select that level by pressing [ENTER]. After entering the appropriate functional
level, press [←] or [→] to move to the desired function.
To view the modem’s configuration, enter the Configuration level from the Function
Select menu. Once in the Configuration menu, press [←] or [→] to scroll through the
Configuration menu selection:
• Modulator
• Demodulator
• Interface
• Save
• Recall
Press [ENTER] to select the desired Configuration menu option. To view the options for
the selected configuration parameters, press [←] or [→].
Notes:
1. Menus or commands that are specific to certain modem configurations are only
accessible after selecting the appropriate modem configuration. This prevents
incompatible parameters from accidentally being selected.
3. All of the windows are accessible in the Custom mode. Take caution not to select
incompatible parameters, as the modem does not shut out incompatible command
choices in the Custom mode.
3–4
Page 47

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.3 Front Panel Menu
SELECT
CONFIGURATION
MONITOR
FAULTS/ALARMS
STORED FLTS/ALMS
UTILITY
FACTORY SETUP (NOT APPLICABLE)
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
INTERFACE
SAVE
RECALL
RAW BER
CORRECTED BER
EB/NO
RECEIVE SIGNAL
SWEEP FREQUENCY
BUFFER FILL
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
TX INTERFACE
RX INTERFACE
COMMON
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
TX INTERFACE
RX INTERFACE
COMMON
UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
CLEAR
MODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
INTERFACE
NETWORK
SYSTEM
MODEM TYPE
ASSIGNED TRANSMI T FILTERS
TX-IF FREQUENCY
TX-IF OUTPUT
TX POWER LEVEL
SCRAMBLER
DIFF ENCODER
CARRIER MODE
MODEM REFERENCE
ASSIGNED RECEIVE FREQUENCY
RX-IF FREQUENCY
DESCRAMBLER
DIFF DECODER
RF LOOP BACK
IF LOOP BACK
BER THRESHOLD
SWEEP CENT ER
SWEEP RANGE
REACQUISITION
TX CLOCK SOURCE
TX CLOCK PHASE
EXT-CLK FREQ
BUFFER CLOCK
RX CLOCK PHASE
B-BAND LOOP BACK
BUFFER SIZE
BUFFER CENTER
LOOP TIMING
ASSIGNED TRANSMI T FILTERS
MOD POWER OFFSET
MODULATOR TYPE
ENCODER TYPE
TX BPSK OREDERING
MOD SPECTRUM
TX MODE
TX SYMBOL RATE
ASSIGNED RECEIVE FILTERS
DEMODULATOR TYPE
DECODER TYPE
RX BPSK ORDERING
DEMOD SPECTRUM
RX MODE
RX SYMBOL RATE
TX OVERHEAD TYPE
RX OVERHEAD TYPE
TX TERR INTERFACE
RX TERR INTERFACE
BUFFER PROGRAM
FRAMING STRUCTURE
RTS TX-IF CNTRL
TX DATA PHASE
RX DATA PHASE
CTS DELAY
RELEASE
CHANNELS 1-15
CHANNELS 16-31
TIME/DATE
REMOTE BAUD RATE
REMOTE ADDRESS
REMOTE TYPE
OPERATION MODE
YEAR DISPLAY
TEST MODE STATUS
LAMP TEST
SELF TEST
DISPLAY CONTRAST
M&C FIRMWARE
BOOT FIRMWARE
FPGA FIRMWARE
EXT AGC: MAX PWR
EXT AGC: MIN PWR
MASTER RESET
MODEM TYPE
MODEM EMULATION
REV EMULATION
MODEM OPTIONS
CARD #1
CARD #2
CARD #3
LOCAL MODEM AUPC
MODEM SERIAL
CONFIGURATION
(NOT APPLICABLE)
(NOT APPLICABLE)
(NOT APPLICABLE)
Figure 3-3. Main Menu
3–5
Page 48

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
Note: The following menus show the modem functions that are available operating as a
DAMA Controller (DAC). The default settings for the DAMA Controller are shown
underlined.
3.4 OPENING SCREEN
SNM 1000
NA 2000
3.4.1 FUNCTION SELECT:CONFIGURATION
FUNCTION SELECT
CONFIGURATION
3.4.1.1 CONFIGURATION:MODULATOR
CONFIGURATION
MODULATOR
3.4.1.1.1 MODULATOR: CODE RATE/TYPE
TX-X QPSK 1/2
19.200 kbps
Transmit code rate/type as follows:
TX-A QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-B QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-C QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-D QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-V QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed.
3–6
Page 49

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.1.2 MODULATOR:TX-IF FREQENCY
TX-IF FREQUENCY
70.000000 MHz
Displays the modulator TX IF frequency between 50 and 180 MHz, in 1 Hz steps.
Upon entry, the current transmitter frequency is displayed with the flashing cursor on the
first character. Press [← ] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑ ] or [↓ ] to increase
or decrease the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
3.4.1.1.3 MODULATOR:TX-IF OUTPUT
TX-IF OUTPUT
ON
Displays the modulator output status, either On
or Off.
3.4.1.1.4 MODULATOR:TX POWER LEVEL
TX POWER LEVEL
-20.0 dBm
Displays the modulator output level from:
• -5.0 to –30.0 dBm (Normal Range)
Upon entry, the current output power level is displayed with the flashing cursor on the
first character. Press [← ] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑ ] or [↓ ] to increase
or decrease the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
3–7
Page 50

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.1.5 MODULATOR:SCRAMBLER
SCRAMBLER
ON
Displays the scrambler status, either On
or Off.
3.4.1.1.6 MODULATOR:DIFF. ENCODER
DIFF. ENCODER
OFF
Displays the differential encoder status, either On or Off
.
3.4.1.1.7 MODULATOR:CARRIER MODE
CARRIER MODE
NORMAL-MODULATED
Displays the carrier mode of operation as follows:
Normal-Modulated
Center-CW
Offset-CW
Dual-CW
Upon entry, the current carrier mode is displayed with the flashing cursor on the first
character. Press [↑ ] or [↓ ] to change the carrier mode. Press <ENTER> to execute the
change.
The carrier mode in normally in this Off position.
Generates a carrier at the current modulator frequency. This can be used to
measure the output frequency.
Generates a single, upper, side-band-suppressed carrier signal. The upper side-
band is at one-quarter of the symbol rate from the carrier. When inverted
spectrum is selected, this generates a single, lower, side-band-suppressed
carrier.
Generates a dual side-band suppressed carrier signal. Side-bands are at one-half
of the symbol rate from the carrier. This is used to check the channel balance and
carrier null.
3–8
Page 51

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.1.8 MODULATOR:MODEM REFERENCE
MODEM REFERENCE
INTERNAL
Displays the following references to the modulator:
• INTERNAL
• EXT1, EXT5, EXT10 and EXT20 MHz EXT REF (CP3)
Note: If any EXT REF is selected for the modem reference and there is no input to CP3,
the modem will detect an alarm and switch to the INTERNAL clock.
Upon entry, the current modem reference is displayed with the flashing cursor on the first
character. Press [↑ ] or [↓ ] change the modem reference. Press <ENTER> to execute the
change.
3.4.1.2 CONFIGURATION:DEMODULATOR
CONFIGURATION
DEMODULATOR
3.4.1.2.1 DEMODULATOR:CODE RATE/TYPE
RX-X QPSK 1/2
19.200 kbps
Receive code rate/type as follows:
RX-A QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-B QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-C QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-D QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-V QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed. Press [↑ ] or [↓ ] change the
assigned filter. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
3–9
Page 52

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.2.2 DEMODULATOR:RX-IF FREQUENCY
RX-IF FREQUENCY
70.000000 MHZ
Displays the demodulator receive frequency, between 50 and 180 MHz, in 1 Hz steps.
3.4.1.2.3 DEMODULATOR:DESCRAMBLER
DESCRAMBLER
ON
Displays the descrambler status, either On
or Off.
3.4.1.2.4 DEMODULATOR:DIFF.DECODER
DIFF. DECODER
ON
Displays the differential decoder status, either On
3.4.1.2.5 DEMODULATOR:RF LOOP BACK
RF LOOP BACK
OFF
Displays the RF loop back status, either On or Off
3.4.1.2.6 DEMODULATOR:IF LOOP BACK
IF LOOP BACK
OFF
Displays the IF loop back status, either On or Off
.
or Off.
.
3–10
Page 53

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.2.7 DEMODULATOR:BER THRESHOLD
BER THRESHOLD
NONE
Displays the BER threshold .
If the BER threshold set is exceeded, a receive fault will be indicated by the modem
status indicators. BER threshold may be set from 1.0 E-3 to 1.0 E-8, or may be disabled
by specifying NONE.
3.4.1.2.8 DEMODULATOR:SWEEP CENTER
SWEEP CENTER
+ 0 HZ
Displays the sweep center frequency for the directed sweep function. When in directed
sweep, the value from the sweep monitor screen (when the modem was last locked)
should be entered for the sweep center frequency. The sweep center frequency can be set
in the range from –35000 to +35000 Hz. Default: 0 Hz
Upon entry, the current sweep center frequency is displayed with the flashing cursor on
the first character. Press [← ] or [→] to move the flashing cursor, and [↑ ] or [↓ ] t o
increase or decrease the digit at the flashing cursor. Press <ENTER> to execute the
change.
.
3.4.1.2.9 DEMODULATOR:SWEEP RANGE
SWEEP RANGE
30000 HZ
Displays the overall travel of the sweep width range during acquisition in the directed
sweep mode. The sweep width may be set from 0 to 70000 Hz. Default: 30000 Hz
When set at 70000 Hz, the modem is in Normal acquisition mode. The smaller the range,
the faster the modem will lock, provided the receive carrier center frequency is within the
RX-IF frequency sweep range.
3–11
.
Page 54

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.2.10 DEMODULATOR:REACQUISITION
REACQUISITION
0 SECONDS
Displays the sweep reacquisition mode time duration. This is the time that the modem
will remain in a narrow sweep after loss of acquisition. After this timer runs out, the
modem will return to the normal acquisition sweep. The reacquisition time is 0 to 999
seconds. Default: 0 seconds
.
3.4.1.3 CONFIGURATION:INTERFACE
CONFIGURATION
INTERFACE
3.4.1.3.1 INTERFACE:TX CLOCK SOURCE
TX CLOCK SOURCE
SCT (INTERNAL)
Programs the clock source for the modem transmitter clock to the following
configurations:
TX Terrestrial
SCT (INTERNAL)
EXT CLOCK
Upon entry, the current TX clock source is displayed. Press [↑ ] or [↓ ] to make the
selection. Press <ENTER> to execute the change.
Sets the TX clock to recover timing from the incoming clock/data.
Sets the TX clock to operate from the modem internal clock (this also is the
fallback clock).
Note: When loop timing is enabled, SCT (LOOP) is displayed instead of
SCT (INTERNAL).
Sets the TX clock to operate from the EXT-CLK clock. Transmit clock source
must be phase/frequency locked to the data that is being transmitted. The
correct frequency must be programmed into EXT-CLK FREQ.
3–12
Page 55

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.3.2 INTERFACE:TX CLOCK PHASE
TX CLOCK PHASE
NORMAL
Programs the TX clock phase to AUTO, NORMAL
Upon entry, the current TX clock phase is displayed. Press [↑ ] or [↓ ] to make the
selection. When AUTO is s elected, the modem will automatically select NORMAL or
INVERT to properly phase the TX clock with the TX data. Press <ENTER> to execute
the change.
, INVERT.
3.4.1.3.3 INTERFACE:EXT-CLK FREQ
EXT-CLK FREQ
1544.000 KHZ
Programs the external reference clock input frequency between 8.0 kHz and 10.0 MHz.
Default: 1544 kHz
Note: The clock rate must be equal to the data rate unless the asymmetrical loop timing
option is present.
This clock frequency can be any multiple of 600 Hz from 2.4 to 64 kHz, and can be any
multiple of 8 kHz from 64 kHz to 4.376 MHz.
This can be used for the Doppler/plesiochronous buffer reference. It can be a reference to
SCT. Use the master clock input on J8 for the external master reference. The EXT REF
on CP3 only allows for 1, 5, 10, and 20 MHz external reference input.
Upon entry, the current setting for the external reference is displayed. Press [←] or [→]
to increment or decrement the digit at the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
.
3–13
Page 56

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.3.4 INTERFACE:BUFFER CLOCK
BUFFER CLOCK
RX (SATELLITE)
Programs the interface buffer output clock to one of the following modes:
RX (SATELLITE)
SCT (INTERNAL)
EXT. CLOCK
TX TERRESTRIAL
INSERT CLOCK
Upon entry, the current setting of the plesiochronous buffer clock is displayed. Press [↑] or
[↓] to make the selection. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
Sets the output buffer clock to the satellite clock. (This is a Bypass.)
Sets the buffer clock to operate from the modem internal clock. This is
also the fallback clock.
Sets this clock source to the external clock.
Sets the buffer output clock to recover timing from the incoming TX data
clock.
Selects the recovered clock from the insert send data input received from
the terrestrial equipment.
3.4.1.3.5 INTERFACE:RX CLOCK PHASE
RX CLOCK PHASE
NORMAL
Programs the RX clock phase to Normal
Upon entry, the status of the RX Clock is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection.
Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
or Inverted.
3–14
Page 57

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
A
/
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.3.6 INTERFACE:B-BAND LOOP BACK
B-BAND LOOP BACK
OFF
Programs the modem for baseband loopback operation, On or Off
When baseband loopback is turned on, the data and timing signals are switched from the
demodulator to the modulator on the modem side of the interface. The DTE baseband
signals are also looped back from the transmitter data and clock to receiver data and clock
on the customer side of the interface. This is a bi-directional loopback of the baseband data.
Refer to figure 3-4 for a block diagram of baseband loopback operation.
Upon entry, the status is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press [ENTER]
to execute the change.
.
CUSTOMER
DAT A
REMOTE SERIAL
INTERFACE
FAULT INDICATORS
IBS OR IDR
INTERFACE
SATELLITE MODEM
ENCODER/
MODULATOR
MICRO-
COMPUTER
DEMODULATOR
DECODER
POWER SUPPLY
TRANSMIT RF
EQUIPMENT
CPOWER
RECEIVE RF
EQUIPMENT
ANTENNA
Figure 3-4. Baseband Loopback
Note: When baseband loopback is turned on, data is looped back on the customer side of the interface.
This is a bi-directional loopback of the baseband data. This test mode will verify the customer equipment
and cabling between the modem and the customer equipment. The baseband loopback is not bi-directional
in D&I.
3–15
Page 58

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.3.7 INTERFACE:BUFFER SIZE
BUFFER SIZE
384 BITS
Sets the size of the buffer, 32 to 262144 bits, 1 to 99 mS , or 0 (Bypass)
Upon entry, the current buffer length is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to select the desired
buffer size. The buffer size is displayed in seconds or bits. Enter the Utility Interface menu
to change the buffer units to seconds or bits.
• If selecting seconds, choose from 1 to 99 ms, in increments of 1 ms,
or 0 (Bypass).
• If selecting bits, choose from 32 to 262144 bits, in increments of 16 bits.
• Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
Note: To have the modem calculate the plesiochronous shift, set the buffer units to ms.
When a specific buffer depth is desired, set the buffer units to bits. Select bits or ms from
the Utility Interface menu.
3.4.1.3.8 INTERFACE:BUFFER CENTER
BUFFER CENTER
YES/NO
This configuration function is used to center the buffer. Choosing YES centers the buffer.
Press <ENTER> twice to center the buffer.
3–16
Page 59

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.1.3.9 INTERFACE:LOOP TIMING
LOOP TIMING
OFF
The SCT output will become phase-locked to the RX satellite clock.
TX and RX data rates must be equal unless the asymmetrical loop timing option is On or
Off
.
• Upon entry, the status is displayed.
• Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection.
• Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
3.4.1.4 CONFIGURATION:SAVE
CONFIGURATION
SAVE
The Configuration Save menu allows programming of configuration parameters into
memory on the M&C. There are five memory locations that may be used to store specific
configuration setups that are used frequently. After changing the configuration
parameters to the desired settings, enter the Configuration Save menu and select memory
location 1 through 5.
Press [ENTER] to execute the save.
3.4.1.5 CONFIGURATION:RECALL
CONFIGURATION
RECALL
The Configuration Recall menu allows the user to recall a previously saved configuration
setup. Upon entry, select memory location 1 through 5 by pressing [↑] or [↓].
Press [ENTER] to execute the recall.
3–17
Page 60

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.2 FUNCTION SELECT:MONITOR
FUNCTION SELECT
MONITOR
3.4.2.1 MONITOR:RAW BER
RAW BER
NO DATA
Displays the current BER or “No Data
Range: < m.m E-e to > m.m E-e.
Note: Low limit is based on performance. High limit is based on data/code rate.
” (if carrier is not locked).
3.4.2.2 MONITOR:CORRECTED BER
CORRECTED BER
NO DATA
Displays the current corrected BER or “No Data
Range: 1.0 E-3 to 1.0 E-12.
Note: Low limit is based on performance. High limit is 1.0 E-12.
” (if carrier is not locked).
3–18
Page 61

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.2.3 MONITOR:EB/NO
EB/NO
16.0
Displays the current Eb/N0 or “No Data” (if carrier is not locked).
Range: 2.0 to 16.0 dB.
Note: Low limit is based on the data rate. High limit is 16.0 dB.
3.4.2.4 MONITOR:RECEIVE SIGNAL
RECEIVE SIGNAL
-60.0 DBM
Displays the current receive signal level.
Range: -25.0 to -60.0
dBm.
3.4.2.5 MONITOR:SWEEP FREQUENCY
SWEEP FREQUENCY
+ 0 HZ
Displays the current offset frequency or “No Data” (if carrier is not locked).
Range: -35,000 to +35,000 Hz.
3.4.2.6 MONITOR:BUFFER FILL
BUFFER FILL
50%
Displays the current plesiochronous buffer fill status percent.
Range: 1 to 99%.
3–19
Page 62

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.3 FUNCTION SELECT:FAULTS/ALARMS
FUNCTION SELECT
FAULTS/ALARMS
The Faults/Alarms menu is accessible from the Function Select menu. The Faults/Alarms
are similar to monitor functions, as they display the current fault status of the group being
displayed.
Press [←] or [→] to move between the following Faults/Alarms groups:
• Modulator
• Demodulator
• Transmit Interface
• Receive Interface
• Common Equipment
Line 2 of the display shows the current Faults/Alarms status in real time. For each
parameter monitored, fault status is displayed as one of the following:
• “–” indicates that no fault or alarm exists.
• “+” indicates that a fault exists, and will cause switching in a redundant system.
• Reversed contrast “+” indicates an active alarm.
Unlike faults, alarms do not cause switching to occur. To display labels for individual
faults or alarms, press [ENTER].
Press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor to make the selection. The label for that
Fault/Alarm is then displayed on line 1 of the display. Press [CLEAR] to exit this level of
operation and return to the previous level.
The following sections outline the faults and alarms monitored and displayed in each
group.
3–20
Page 63

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.3.1 FA ULTS AND ALARMS:MODULA TOR
MODULATOR
+--------
IF SYNTHESIZER
DATA CLOCK SYN
I CHANNEL
Q CHANNEL
AGC LEVEL
MODEM REF ACT
MODEM REF PLL
MODULE
CONFIGURATION
Modulator IF synthesizer fault.
Transmit clock synthesizer fault. Indicates the internal Voltage
Controlled Oscillator (VCO) has not locked to the incoming data
clock.
I channel data activity fault.
Q channel data activity fault.
TX IF AGC level fault.
MODEM REF activity alarm.
MODEM REF PLL not locked.
Modulator module fault.
Modulator configuration fault.
3.4.3.2 FAULTS AND ALARMS:DEMODULATOR
DEMODULATOR
+-++-----
CARRIER DETECT
IF SYNTHESIZER
I CHANNEL
Q CHANNEL
BER THRESHOLD
MODULE
CONFIGURATION
Carrier detect fault. Indicates the decoder is not locked.
Demodulator IF synthesizer fault. Indicates the IF synthesizer is
not locked.
I channel activity fault. Indicates a loss of activity in the I channel
of the quadrature demodulator.
Q channel activity fault. Indicates a loss of activity in the
Q channel of the quadrature demodulator.
Secondary alarm result of the BER threshold set in the DEMOD
Configuration menu.
Demodulator/decoder module fault.
Demodulator/decoder configuration fault.
3–21
Page 64

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.3.3 FA ULTS AND ALARMS:TX INTERFACE
TX INTERFACE
---------
TX DROP
TX DATA/AIS
TX CLK PLL
TX CLK ACTIVITY
TX AUDIO 1 CLIP
TX AUDIO 2 CLIP
CONFIGURATION
Not Applicable.
Data or AIS. When data fault is selected in the Interface Configuration
menu, the fault indicates a data stable condition. This indicates the
data is all 1s or 0s (i.e., data is not transitioning). When AIS is
selected, the alarm indicates the data is all 1s from customer data input
to the modem. When None is selected in the Interface Configuration
menu, the TX Data/AIS Fault/Alarm is not activated.
Note: AIS is an alarm, not a switching fault.
Transmitter phase-locked loop fault. Indicates the transmitter
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) is not locked.
Activity detector alarm of the selected interface transmit clock.
The interface will fall back to the internal clock when this alarm
is active.
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable.
TX interface configuration fault.
Indicates the TX interface cannot execute a programmed
configuration parameter.
3–22
Page 65

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.3.4 FA ULTS AND ALARMS:RX INTERFACE
RX INTERFACE
---------
BUFFER UNDERFLOW
BUFFER OVERFLOW
RX DATA/AIS
FRAME BER
BACKWARD ALARM
BUFFER CLK PLL
BUFFER CLK ACT
DEMUX LOCK
RX 2047 LOCK
BUFFER FULL
RX INSERT
RX AUDIO 1 CLIP
RX AUDIO 2 CLIP
CONFIGURATION
Buffer underflow alarm. Indicates that a buffer underflow has
occurred.
Buffer overflow alarm. Indicates that a buffer overflow has
occurred.
Data or AIS. When data fault is selected in the Configuration
Interface menu, the fault indicates a data stable condition. This
indicates the data coming from the satellite is all 1s or 0s (i.e.,
data is not transitioning). When AIS is selected, the Alarm
indicates the data is all 1s from the satellite. When None is
selected in the Configuration Interface menu, the RX Data/AIS
Fault/Alarm is not activated.
Note: AIS is an alarm, not a switching fault.
Frame BER fault. Indicates that the frame BER exceeds 1-3.
Not Applicable.
Buffer clock phase-locked loop fault. Indicates the buffer clock
PLL is not locked.
Activity detector alarm of the selected interface receive clock.
The interface will fall back to the satellite clock when this fault is
active.
DEMUX lock fault. Indicates that the DEMUX is not locked.
RX 2047 lock alarm. Indicates the RX 2047 data pattern is not
locked.
Note: This alarm is only active if RX 2047 is ON.
Buffer full alarm. Indicates the buffer is less than 10% or greater
than 90% full.
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable.
Configuration alarm.
3–23
Page 66

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.3.5 FA ULTS AND ALARMS:COMMON
COMMON
---------
BATTERY/CLOCK
-12V SUPPLY
+12V SUPPLY
+5V SUPPLY
SELF TEST
CONTROLLER
INTERFACE MODULE
Battery or clock fault.
-12V power supply fault.
+12V power supply fault.
+5V power supply fault.
Not Applicable.
Controller fault. Typically indicates the controller has gone
through a power on/off cycle.
Interface module fault. Typically indicates that the interface
module is missing or will not program.
3–24
Page 67

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.4 FUNCTION SELECT:STORED FLTS/ALMS
FUNCTION SELECT
STORED FLTS/ALAMS
The modem stores the first 10 (Flt0 through Flt9) occurrences of fault status changes in
each of the following major fault categories:
• Modulator
• Demodulator
• Transmit Interface
• Receive Interface
• Common Equipment
Each fault status change is stored with the time and date of the occurrence of the fault.
Stored faults may be viewed by entering the stored faults level from the Select menu.
Stored faults are not maintained through controller power-on reset cycle. However, the
last known time is maintained in nonvolatile Random Access Memory (RAM). On
power-up, a common equipment fault is logged (Flt0) with that last known time and date.
In addition, on power-up, an additional common equipment fault is logged (Flt1) to
indicate the power-up time and date. The power-down and power-up times are logged as
common equipment fault 0 and common equipment fault 1, respectively.
On entering the stored faults level, press [←] or [→] to move between the fault groups
and the “Clear Stored Faults ?” selections. The time and date of the first stored fault
status (Flt0) for the selected group will be displayed alternately on line 2 of the display.
Press [↑] or [↓] to cycle through the selected group has stored fault status (Flt0 through
Flt9). To display the fault status associated with the displayed time and date, press
[ENTER]. To identify the fault, press [←] or [→] to move the flashing cursor. To clear
the currently logged stored faults, press [ENTER] when the “Clear Stored Faults/Yes?”
selection is displayed.
Note: Faults are stored in time sequence, with the oldest fault status change stored in
Flt0, and the most recent in Flt9. Only the first 10 fault status changes are stored. All
stored faults, which have not been used, indicate “No Fault” on the display.
3–25
Page 68

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.4.1 STORED FLTS/ALMS:MODULATOR
MODULATOR X
STORED TIME/DATE
(FAULT LABEL)
---------
IF Synthesizer
DATA CLOCK SYN
I CHANNEL
Q CHANNEL
AGC LEVEL
MODEM REF ACT
MODEM REF PLL
MODULE CONFIGURATION
3.4.4.2 STORED FLTS/ALMS:DEMODULATOR
DEMODULATOR X
STORED TIME/DATE
(FAULT LABEL)
---------
CARRIER DETECT
IF SYNTHESIZER
I CHANNEL
Q CHANNEL
BER THRESHOLD
MODEL
CONFIGURATION
3–26
Page 69

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.4.3 STORED FLTS/ALMS:TX INTERFACE
TX INTERFACE X
STORED TIME/DATE
(FAULT LABEL)
---------
TX DROP (Not Applicable)
TX DATA/AIS
TX CLK PLL
TX CLK ACTIVITY
TX AUDIO 1 CLIP (Not Applicable)
TX AUDIO 2 CLIP (Not Applicable)
CONFIGURATION
3.4.4.4 STORED FLTS/ALMS:RX INTERFACE
RX INTERFACE X
STORED TIME/DATE
(FAULT LABEL)
---------
BUFFER UNDERFLOW
BUFFER OVERFLOW
RX DATA/AIS
FRAME BER
BACKWARE ALARM (Not Applicable)
BUFFER CLK PLL
BUFER CLK ACT
DEMUX LOCK
RX 2047 LOCK
BUFFER FULL
RX INSERT (Not Applicable)
RX AUDIO 1 CLIP (Not Applicable)
RX AUDIO 2 CLIP (Not Applicable)
CONFIGURATION
3–27
Page 70

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.4.5 STORED FLTS/ALMS:COMMON
COMMON X
STORED TIME/DATE
(FAULT LABEL)
---------
BATTERY/CLOCK
-12 VOLT SUPPLY
+12 VOLT SUPPLY
+5 VOLT SUPPLY
SELF TEST (Not Applicable)
CONTROLLER
INTERFACE MODULE
3.4.4.6 STORED FLTS/ALMS:UNAVL SECONDS
UNAVAL SECONDS X
STORED TIME/DATE
Note: Reed-Solomon option only.
A fault is indicated if the Reed-Solomon Codec could not correct bit errors in one block
of serialized data in any given second.
3.4.4.7 STORED FLTS/ALMS:CLEAR
CLEAR ??
STORED FAULTS
3–28
Page 71

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5 FUNCTION SELECT:UTILITY
FUNCTION SELECT
UTILITY
The Function Select Utility menu is divided into the following categories:
• Modulator
• Demodulator
• Interface
• Network
• System
• Modem Type
• Factory Setup
The menu information includes:
• Filter Types
• Terrestrial Interface Types
• Mod/Demod Types
• Time/Date
• Encoder/Decoder Types
• Modem Types
• Current Firmware
• Test Mode Status
• Overhead Type
• Revision Emulation
• Lamp Test
Provisions are also made for assigning data and code rates to the modulator and
demodulator.
After entering the Utility menu, press [←] or [→] to select the desired sub-menu, and
press [ENTER].
Notes:
1. The Utility Factory Setup menu is for Comtech EF Data service personnel only.
Entering this menu without authorization may cause the modem to operate
incorrectly.
2. Changes in the Utility menu may cause changes in other front panel menus.
3–29
Page 72

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.1 UTILITY:MODULATOR
UTILITY
MODULATOR
3.4.5.1.1 MODULATOR: ASSIGN TRANSMIT FI LTERS
ASSIGN
TRANSMIT FILTERS
Transmit code rate/type as follows:
TX-A QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-B QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-C QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-D QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
TX-V QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed.
3.4.5.1.2 MODULATOR:MOD POWER OFFSET
MODEM POWER OFFSET
+ 0.0 DB
Modulator power offset adjust. Offsets the modulator output power readout in the
Configuration menu. This feature does not actually change the modulator power level, but
displays an offset value in the monitor.
The modulator power offset range is -99.9 to +99.9 dB, in 0.1 dB steps.
Note: Anything except 0.0 dB will cause ADJ to be displayed for the TX power level.
3–30
Page 73

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.1.3 MODULATOR:MODULATOR TYPE
MODULATOR TYPE
INTELSAT OPEN
Transmit filter type select. Select one of the following for network filtering:
Note: Change in EFD, ASYNC, or Custom modem types only.
INTELSAT OPEN
EFD CLOSED SDM-51 COMPATIBLE
CSC CLOSED
Notes:
1. TX filter type is selectable only when CUSTOM is selected for the modem type in
the Utility Modem Type menu.
2. Code Rate 3/4 is not compatible with a combination of a CSC CLOSED Modulator
Type and Sequential Encoder.
FDC CLOSED
3.4.5.1.4 MODULATOR:ENCODER TYPE
ENCODER TYPE
VITERBI
Encoder type selection. Select VITERBI
Notes:
1. Change in EFD, ASYNC, or Custom modem types only.
2. A Sequential Encoder Type and a 3/4 Code Rate combination is
not compatible with a CSC CLOSED Modulator Type.
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
or SEQUENTIAL encoder type.
3–31
Page 74

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.1.5 MODULATOR:TX BPSK ORDERING
TX BPSK ORDERING
STANDARD
Transmit BPSK bit ordering selection. Select STANDARD
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
or NON-STANDARD
3.4.5.1.6 MODULATOR:MOD SPECTRUM
MOD SPECTRUM
NORMAL
Programmable vector rotation allows the operator to select NORMAL
spectrum reversal of the I and Q baseband channels.
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change
or INVERT for
3.4.5.1.7 MODULATOR:TX MODE
TX MODE
BURST
Selection of BURST
cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
or CONTINUOUS. Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing
3.4.5.1.8 MODULATOR:TX SYMBOL RATE
TX SYMBOL RATE
19.200 KSPS
Status only. Selects TX Symbol Data rate.
3–32
Page 75

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.2 UTILITY:DEMODULATOR
UTILITY
DEMODULATOR
3.4.5.2.1 DEMODULATOR:ASSIGN TRANSMIT FILTERS
ASSIGN
TRANSMIT FILTERS
Receive code rate/type as follows:
RX-A QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-B QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-C QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-D QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
RX-V QPSK 1/2 19.200 kbps
Upon entry, the current transmitter rate is displayed.
3.4.5.2.2 DEMODULATOR: DEMODULATOR TYPE
DEMODULATOR TYPE
INTELSAT OPEN
Transmit filter type select. Select one of the following for network filtering:
Note: Change in EFD, ASYNC, or Custom modem types only.
INTELSAT OPEN
EFD CLOSED SDM-51 COMPATIBLE
CSC CLOSED
Notes:
1. TX filter type is selectable only when CUSTOM is selected for the modem type in
the Utility Modem Type menu.
2. Code Rate 3/4 is not compatible with a combination of a CSC CLOSED
Modulator Type and Sequential Encoder.
FDC CLOSED
3–33
Page 76

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.2.3 DEMODULATOR:DECODER TYPE
DECODER TYPE
VITERBI
Decoder type selection. Select VITERBI
Notes:
1. Change in EFD, ASYNC, or Custom modem types only.
2. A Sequential Decoder Type and a 3/4 Code Rate combination is
not compatible with a CSC CLOSED Modulator Type.
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
or SEQUENTIAL decoder type.
3.4.5.2.4 DEMODULATOR:RX BPSK ORDERING
RX BPSK ORDERING
STANDARD
Receive BPSK bit ordering selection. Select STANDARD
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
3.4.5.2.5 DEMODULATOR:DEMOD SPECTRUM
DEMOD SPECTRUM
NORMAL
Programmable vector rotation allows the operator to select NORMAL
spectrum reversal of the I and Q baseband channels.
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
or NON-STANDARD
or INVERT for
3–34
Page 77

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.2.6 DEMODULATOR:RX MODE
RX MODE
CONTINUOUS
Selection of BURST or CONTINUOUS
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change..
.
3.4.5.2.7 DEMODULATOR:RX SYMBOL RATE
RX SYMBOL RATE
19.200 KSPS
Status only.
Selects RX Symbol Data rate, with 4.800 to 2500.000 ksps.
3.4.5.3 UTILITY:INTERFACE
UTILITY
INTERFACE
3.4.5.3.1 INTERFACE:TX OVERHEAD TYPE
TX OVERHEAD TYPE
NONE
Select None for TX overhead type.
Note: Overhead types are selectable only when Custom is selected for modem type in the
Utility Modem Type menu.
3–35
Page 78

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.3.2 INTERFACE:RX OVERHEAD TYPE
RX OVERHEAD TYPE
NONE
Select None RX overhead type.
Note: Overhead types are selectable only when Custom is selected for modem type in the
Utility Modem Type menu.
3.4.5.3.3 INTERFACE:TX TERR INTERFACE
TX TERR INTERFACE
RS422
Displays the TX interface type RS-232, RS-422, or V.35.
Note: Not applicable since SNM-1000 is not used for User Data Traffic.
3.4.5.3.4 INTERFACE:RX TERR INTERFACE
RX TERR INTERFACE
RS422
Displays the RX interface type RS-232, RS-422, or V.35.
Note: Not applicable since SNM-1000 is not used for User Data Traffic.
3.4.5.3.5 INTERFACE:BUFFER PROGRAM
BUFFER PROGRAM
BITS
Buffer unit program function. Select MILLI-SECONDS or BITS
Note: To have the modem calculate the plesiochronous shift, set the buffer units to MILLISECONDS. For a specific buffer depth, set the buffer units to BITS.
.
3–36
Page 79

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.3.6 INTERFACE:FRAMING STRUCTURE
FRAMING STRUCTURE
T1 FRAMING
STRUCTURE: G.704
E1 FRAMING
STRUCTURE: G.704
Displays the currently selected framing type and structure of the data. This function is used
with the buffer program in ms for plesiochronous buffer slips.
Upon entry, the framing type (T1 or E1) is displayed on Line 1. The framing structure of
each type (None or G.704) is displayed on Line 2. Press [←] or [→] and [↑] or [↓] to select
framing structure and type. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
3.4.5.3.7 INTERFACE:RTS TX-IF CNTRL
RTS TX-IF CNTRL
OFF
Programs the modem to allow a Request To Send (RTS) signal to On or Off
when data is ready for transmission.
Press[←], [→], [↑], or [↓] to move the flashing cursor. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
3.4.5.3.8 INTERFACE:TX DATA PHASE
TX DATA PHASE
NORMAL
TX data phase relationship. Use this option to select NORMAL
data relationship to the selected TX clock.
Upon entry, press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Pre ss [ENTER] to execute the change.
the output
or INVERT for the TX
3–37
Page 80

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.3.9 INTERFACE:RX DATA PHASE
RX DATA PHASE
NORMAL
RX data phase relationship. Use this option to select NORMAL
data relationship to the selected RX clock.
Upon entry, press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Pre ss [ENTER] to execute the change.
or INVERT for the RX
3.4.5.3.10 INTERFACE:CTS DELAY
CTS DELAY
X SECONDS
Sets the delay in seconds (0 to 60) for the Clear To Send (CTS) signal.
Default: 0 Seconds
.
3.4.5.4 UTILITY:NETWORK
SNM 1000
NA 2000
3.4.5.4.1 NETWORK:RELEASE
SNM 1000
REL 4.X.X
Status only.
Shows installed version of DAC code and code ’s CRC in he xa decima l.
e.g. rel 4.3.0 p cc14
3–38
Page 81

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.4.2 NETWORK:CHANNELS 1 -15
CHANNELS 1 – 15
---------------
3.4.5.4.3 NETWORK:CHANNELS 16 - 31
CHANNELS 16 – 31
---------------
Status only.
- = Traffic Modem Not Installed
I = Traffic Modem Idle
O = Traffic Modem Offline
C = Call in Progress
S = Connecting Call
D = Disconnecting Call
3.4.5.5 UTILITY:SYSTEM
UTILITY
SYSTEM
3.4.5.5.1 SYSTEM:TIME/DATE
TIME: 12:00:00AM
DATE: 7/04/1976
Time of day and d a te dis p lay/s e t f unc ti on.
The current time and date in the modem’s memory are displayed when selected.
To change the modem t im e and /o r da te , pr es s [EN TE R] .
• Press [←] or [→] to position the cursor over the parameter to be changed.
• Press [↑] or [↓] to change the parameter.
• Once the parameters are displayed as desired, press [ENTER] to set the time and
date.
3–39
Page 82

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.5.2 SYSTEM:REMOTE BAUD RATE
REMOTE BAUD RATE
19.200 BPS NONE
The parity and baud rate settings of the modem are displayed.
To change the modem pa r i ty, p re ss [E NTER].
• Press [←] or [→] to position the cursor over the parameter to be changed.
• Press [↑] or [↓] to change the parameter.
• Once the parameters are displayed as desired, press [ENTER] to set the baud rate
and parity.
• The parity can be set to EVEN, ODD, or NONE
The baud rate is 19200 bit/s.
.
3.4.5.5.3 SYSTEM:REMOTE ADDRESS
REMOTE ADDRESS
1
The current modem address is displayed (1 to 255).
Note: 0 is reserved as a global address.
To change the remote address, press [ENTER]. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press
[ENTER] to execute the change.
3.4.5.5.4 SYSTEM:REMOTE TYPE
REMOTE TYPE
RS485 (2-WIRE)
Select RS-485 (2-Wire),
RS-485 (4-Wire), or RS-232.
3–40
Page 83

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.5.5 SYSTEM:OPERATION MODE
OPERATION MODE
DUPLEX
Programs the modem for DUPLEX
Upon entry, the operational status may be changed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection.
Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
Note: When TRANSMIT ONLY or RECEIVE ONLY are selected, the appropriate faults
are masked from the Faults and Stored Faults menus.
, TRANSMIT ONLY, or RECEIV E ON LY ope ra ti on.
3.4.5.5.6 SYSTEM:YEAR DISPLAY
YEAR DISPLAY
2 - DIGIT
Selects the display for the year in either 2-digit or 4-digit format.
Upon entry, the year display may be changed. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection. Press
[ENTER] to execute the change
3.4.5.5.7 SYSTEM:TEST MODE STATUS
TEST MODE STATUS
---------
Test mode status indicator. The following modem test points are listed and display a “+”
when a test mode is active:
! RS CORR OFF
! INTRFC LOOP BACK
! B-BAND LOOP BACK
! RF LOOP BACK
! IF LOOP BACK
! CARRIER MODE
• RX 2047 Pattern
• TX 2047 Pattern
To view the test modes, press [ENTER]. Press [↑] or [↓] to make the selection.
3–41
Page 84

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.5.8 SYSTEM:LAMP TEST ??
LAMP TEST ??
PRESS ENTER
Lamp test function. Press [ENTER] to turn the front panel indicators on for 3 seconds.
3.4.5.5.9 SYSTEM:SELF TEST (NOT APPLICABLE)
3.4.5.5.10 SYSTEM:DISPLAY CONTRAST
DISPLAY CONTRAST
LEVEL: 64
Sets the contrast setting of the Front Panel menu.
Press [ENTER] to begin. Press [↑] or [↓] to increment or decrement the number at the
flashing cursor, from 0 to 100. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
3.4.5.5.11 SYSTEM:M&C FIRMWARE
M&C FIRWARE
FW/NNNNNN-DDR
Displays the M&C module firmware version.
The display includes the month, day, and year.
3.4.5.5.12 SYSTEM:BOOT FIRMWARE
BOOT FIRWARE
FW/NNNNNN-DDR
Displays the boot module firmware version.
The display includes the month, day, and year
3–42
Page 85

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.5.13 SYSTEM:FPGA FIRMWARE
FPGA FIRWARE
FW/NNNNNN-DDR
Displays the FPGA module firmware version.
The display includes the month, day, and year
3.4.5.5.14 SYSTEM:EXT AGC: MAX PWR
EXT AGC: MAX PWR
0.0 VOLTS
Sets the AGC voltage for a receive signal level of -60.0 dBm. The voltage range is 0.0
10.0V, in 0.5V steps.
Upon entry, the current external AGC voltage level is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
increment or decrement the AGC voltage level in 0.5V steps. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
Note: For any receive signal level between -25.0 and -60.0 dBm, the software will
interpolate the required AGC voltage.
to
3.4.5.5.15 SYSTEM:EXT AGC: MIN PWR
EXT AGC: MIN PWR
10.0 VOLTS
Sets the AGC voltage for a receive signal level of -25.0 dBm. The voltage range is 0.0 to
10.0V
, in 0.5V steps.
Upon entry, the current external AGC voltage level is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to
increment or decrement the AGC voltage level in 0.5V steps. Press [ENTER] to execute the
change.
Note: For any receive signal level between -25.0 and -60.0 dBm, the software will
interpolate the required AGC voltage.
3–43
Page 86

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.5.16 SYSTEM:MASTER RESET
MASTER RESET
HARD/SOFT
Initiating a hard reset will reset the modem and place the
default configuration settings in ROM. Initiating a soft reset
CAUTION
Select [ENTER] once to access HARD or SOFT.
Press [←] or [→] to make the selection. Press [ENTER].
Press [→] five times to move the cursor to YES. Select YES and press [ENTER] again.
Note: The following parameters do not revert to default settings after a hard reset:
will reset the modem hardware, but saves the current
configuration settings
.
• Address
• Parity
• Baud Rate
• Remote Type
• Ext AGC: Min Pwr
• Ext AGC: Max Pwr
• Display Contrast
3–44
Page 87

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.6 UTILITY:MODEM TYPE
UTILITY
MODEM TYPE
3.4.5.6.1 MODEM TYPE:MODEM TYPE
MODEM TYPE
CUSTOM
Selects the following types of modem operation:
• CUSTOM
• EFD Closed Network Operation
When the modem is changed from one type of operation to another, the modem will be
reset to the default configurations of the new modem type. The RF-IF Output must be
turned on to get the modem to lock.
• If the existing modem type is the same as the type entered, the modem will not
change any parameters.
• If the modem type is changed to Custom, no parameters will be changed.
• If the modem will not allow the modem type selection, that type of operation
may not be an available option.
• Select MODEM OPTIONS and OVERHEAD OPTIONS to see which modem
operations are allowed.
Note: D&I is designed to work with the G.703 interface only.
Selections are made from the Front Panel menu
3–45
Page 88

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.6.2 MODEM TYPE:MODEM EMULATION
MODEM EMULATION
DISABLED
Selects the following types of modem emulation:
SDM-100 VER: 15.7.1
SDM-300 6.2.2
SDM-308-4 4.03
SDM-308-4 6.05
SDM-308-4 6.08
SDM-308-4 7.03
SDM-309 6.04
SDM-650 4.12A
SDM-650 4.16
SDM-6000 5.1.1
or Disabled
Upon entry, the current modem emulation is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to change the
display. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
3.4.5.6.3 MODEM TYPE:REVISION EMULATION
REV EMULATION
CURRENT VERSION
Programs an emulation mode of a previous functional revision. This allows the user to
select the CURRENT VERSION
Note: The number displayed in the CURRENT VERSION position increases with each
software version change.
Upon entry, the CURRENT VERSION is displayed. Press [↑] or [↓] to select the
FUNCTIONAL version. Press [ENTER] to execute the change.
or FUNCTIONAL X.
3–46
Page 89

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
Notes:
1. Programming a current version (default) allows all features and options (if
installed) to operate normally.
2. Programming a FUNCTIONAL version (X) eliminates any changes that affect
the later version. Only functional changes are affected by the revision emulation
feature.
3. A correction change (e.g., VER 3.1.2) remains fixed in accordance with the latest
version. Since the revision emulation default is the current version, program the
functional version at the start of each operation.
4. The revision emulation feature does not affect some interface changes for the
direct operation of the modem (Configuration save/recall, test mode screen in the
Utility/System, all factory setup modes, etc.).
3.4.5.6.4 MODEM TYPE:MODEM OPTIONS
MODEM OPTIONS
--------------
Displays the installed modem options.
If the option is installed, a “+” symbol is displayed. To view the available options press
[ENTER]. Observe for the flashing cursor. Press the [←] [→] arrows to move from one
symbol to the next. The first line will display the option. The second line will display the
status:
HIGH POWER ( 0 ) 0 = Not Installed, Not Upgradeable
HIGH STABILITY ( 0 ) - = Not Installed
ASLT ( - ) + = Installed
VITERBI ( + ) X = Not Installed, Field Upgradeable
SEQUENTIAL ( - )
SINGLE RATE ( - )
LOW RATE VAR ( - )
FULL RATE VAR ( + )
CARD #1 PCB ( + )
CARD #2 PCB ( x )
CARD #3 PCB ( x )
8PSK 2/3 ( - )
TX ONLY ( - )
RX ONLY ( - )
3–47
Page 90

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.6.5 MODEM TYPE:CARD #1 TYPE
CARD #1 TYPE
DAC 01
Status Only.
Displays either of the following:
• DAC 01
• NOT INSTALLED
3.4.5.6.6 MODEM TYPE:CARD #2 TYPE (NOT INSTALLED)
3.4.5.6.7 MODEM TYPE:CARD #3 TYPE (NOT INSTALLED)
3.4.5.6.8 MODEM TYPE:LOCAL MODEM AUPC
LOCAL MODEM AUPC
OFF
Configures the modem for the self-monitoring Local Modem AUPC mode and for local TX
power control (self-monitoring) due to severe rain fade.
Notes:
1. The self-monitoring Local Modem AUPC mode is not used when the
ASYNC/AUPC is selected as the Modem Type.
2. Used for local control (self-monitoring) due to severe rain fade.
3.4.5.6.9 MODEM TYPE:MODEM SERIAL
MODEM SERIAL
123456789
Status Only
3–48
Page 91

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.4.5.6.10 MODEM TYPE:CONFIGURATION CODE - MODEM
CONFIGURATION
CODE - MODEM
1) AAAAAAAAAA
2) AAAAAAAAAA
If installed, Status Only
Comtech EF Data supplied code.
.
3.4.5.7 UTILITY:FACTORY SETUP (NOT APPLICABLE)
3–49
Page 92

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.5 User Port Operation
The User Port allows the user at the remote site to communicate with the remote control
SNM-1000 to request the setup and termination of circuits, send and receive service
messages, and configure the SNM-1000. The commands configure and control the
SNM-1000 and the traffic modems that have addresses within the range of 1 through 30.
The remote control SNM-1000 modem always utilizes address zero.
The User Port uses a 9-pin mini-DIN female connector on the rear of the SNM-1000. The
port is configured as a DCE with the pin definitions as shown in the following listing.
Signal Function Name Pin # I/O Signal Level
Receiver Ready RR 1 O EIA-232
Receive Data RD 2 O EIA-232
Send Data SD 3 I EIA-232
Terminal Ready TR 4 I EIA-232
Signal Ground SG 5
Data Mode DM 6 O EIA-232
Request to Send RS 7 I EIA-232
Clear to Send CS 8 O EIA-232
Incoming Call IC 9 O EIA-232
The interface operates at 19.2 kbps, 8 data bits, No Parity, and 1 Stop Bit. Levels are in
accordance with EIA-232. The User Port can also be accessed using an optional Public
Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) dial-up modem.
3–50
Page 93

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.6 Remote Dial-Up Capability
The SNM-1000 User Port can be accessed via an external PC modem. A user dials into
an SNM-1000 from a remote location using the following items:
• Personal computer
• Auto-interface speed-detect modem
• Modem terminal software capable of emulating an ANSI terminal
3.6.1 User Port Modem
The remote dial-up was tested using a US Robotics, Inc. external Sportster™ 28.8
modem with V.34 and V.32bis at the User Port. Recommended dip switch settings for
this modem are described in the following listing.
Pin 1 Down Data Terminal Override
Pin 2 Up Verbal Result Codes
Pin 3 Up Suppress Result Codes
Pin 4 Down No Echo, Off-line Commands
Pin 5 Up Auto Answer On
Pin 6 Up Carrier Detect Normal
Pin 7 Up Load NOVRAM Defaults
Pin 8 Up Dumb Mode
The US Robotics, Inc. external Sportster™ 28.8 modem or a similar modem should be
used at the User Port.
3.6.2 Remote Site Modem
The remote dial-up was tested using a US Robotics, Inc. external or internal Sportster™
28.8 modem with V.34 and V.32bis at the remote site. Recommended dipswitch settings
for this modem are the factory default settings.
The US Robotics, Inc. external or internal Sportster™ 28.8 modem or a similar modem
should be used at the remote site.
On the PC, modem setting requirements include the following:
ANSI emulation
19.2, 8, N, 1
Software flow control XON/XOFF
1 ms character pacing for ASCII uploads
3–51
Page 94

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7 SNM-1000 Commands
The commands described in this section are used to set SNM-1000 functional parameters
within a DAMA environment. Refer to Appendix A for commands used to communicate
with external modems attached to an SNM-1000.
3.7.1 Character Set
The interface responds to ASCII characters in the range of 0x00 to 0x7F. The 8th bit
(most significant) is not generated on the transmit side and is ignored on the receive side.
3.7.2 Status Lines and Flow Control
The interface ignores all status inputs.
3.7.3 Message Structure
A message is either a command or a response. Each message is made up of three
elements:
• Prefix
• Message body
• End character
3.7.3.1 Prefix
The prefix consists of the channel number in ASCII decimal, with a valid range of 0
through 30. Leading zeros are ignored. Prefix 0 is valid for an SNM-1000 Node Control
modem and prefixes 1 through 30 are valid for external traffic modems attached to the
SNM-1000 such as SDM-300s, SDM-6000s, etc.
3–52
Page 95

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.3.2 Message Body
The message body is made up of individual commands and fields.
Certain conventions are used to improve the readability of the commands presented in
this document. These conventions do not appear in the commands themselves.
Conventions used in the command names and descriptions include the following
characters.
[...] Square brackets are used to indicate that the enclosed items are optional. (The
square brackets themselves do not appear in the message.)
<...> Angle brackets are used to enclose the names of other syntactical elements.
(When those elements appear in an actual message, the actual element is used
and the angle brackets are omitted.)
‘...’ Single quotes are used to enclose an ASCII character for illustration of syntax
elements. (The single quotes themselves do not appear in the message.)
3.7.3.3 End Character
The end character for both command and response messages is a carriage return
(represented by “cr”).
3.7.3.4 Case Sensitivity
Messages are not case sensitive. However, the DCE generates responses and results in
uppercase text.
3.7.3.5 Delimiters
Commas and semicolons are valid delimiters that may be used interchangeably with no
difference in behavior.
3.7.3.6 End Character
Each message is ended with a single character which signals the end of the message:
“]” End bracket for responses.
3–53
Page 96

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.3.7 Queries
The interface can be queried by issuing a valid command without a value at the end. This
will result in the return of the currently set value.
Example (assume a previously sent command as shown):
ICF 70.4567'cr' — sets inbound control IF frequency to 70.4567 MHz.
Now a query:
ICF'cr'
Response from interface:
ICF 70.4567 — inbound control IF frequency is 70.4567 MHz.
3.7.4 Node Address (NA)
This command sets the node number for the remote control channel mode SNM-1000
controller.
3.7.4.1 Command Format
NA <node_number>'cr'
<node_number> Range of 1 to 9999 and must be unique in the network.
Unpredictable results will occur if two nodes are online and both have been
assigned the same node number.
The node number will generally be defined by the provisioning documents that
establish remote sites and circuits.
3.7.4.2 Local Command Responses
node address = <node_number>
3–54
Page 97

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.5 Receive Control Channel Frequency (ICF)
This command sets the receive (NMS to remote) control channel IF frequency at the
remote node.
3.7.5.1 Command Format
ICF <frequency>'cr'
<frequency> Entered in MHz.
Range of 50 to 90 MHz, or 100 to 180 MHz
Resolution of 100 Hz.
Formatting is pseudo-floating point.
Example:
ICF 70.4567 sets receive control IF frequency to 70.4567 MHz.
3.7.5.2 Local Command Responses
ICF= <frequency>, <control channel offset>, <traffic channel
offset>
3.7.6 Transmit Control Channel Frequency (OCF)
This command sets the transmit (remote to NMS) control channel IF frequency at the
remote node.
3.7.6.1 Command Format
OCF <frequency>'cr'
<frequency> Entered in MHz.
Range of 50 to 90 MHz, or 100 to 180 MHz.
Resolution of 100 Hz.
Formatting is pseudo-floating point.
Example:
OCF 70.1234 sets transmit control IF frequency to 70.1234 MHz.
3.7.6.2 Local Command Responses
OCF= <frequency>, <control channel offset>, <traffic channel
offset>
3–55
Page 98

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.7 Transmitter On (RF_ON)
This command enables the SNM-1000 transmitter.
3.7.7.1 Command Format
RF_ON'cr'
3.7.7.2 Local Command Responses
None.
3.7.8 Transmitter Off (RF_OFF)
This command disables the SNM-1000 transmitter.
3.7.8.1 Command Format
RF_OFF'cr'
3.7.8.2 Local Command Responses
None.
3.7.9 Transmit Power (TX)
This command sets the SNM-1000 transmit power.
3.7.9.1 Command Format
TX <tx_power>'cr'
<tx_power> In the range of +5 to -30 dBm, in 0.1 dBm steps.
The format for TX_power is [+] XX.X with an implied minus sign.
3.7.9.2 Local Command Responses
transmit power = <tx_power>
3–56
Page 99

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.10 Current SNM-1000 DAC Software Revision (VER)
This command queries the SNM-1000 DAC board for its current software revision
number.
3.7.10.1 Command Format
VERSION'cr' or VER’cr’
3.7.10.2 Local Command Responses
DAC VERSION: X.Y.ZZZ.CCCC Where:
X.Y = SNM-1000 DAC software release number.
ZZZ = Revision level for the release.
CCCC = Checksum
3.7.11 Node to NMS Service Messages (NMS_MSG)
This command permits the transmission of up to 28 ASCII text characters to the NMS.
3.7.11.1 Command Format
NMS_MSG 'text string to be transmitted to the NMS''cr'
3.7.11.2 Local Command Responses
None.
3–57
Page 100

SNM-1000 Node Control Modem Revision 3
Operation MN/SNM1000.IOM
3.7.12 SNM-1000 Mode (MD)
This command sets the SNM-1000 mode.
3.7.12.1 Command Format
MD <mode>'cr'
<mode> EXT Remote Control Channel-External Traffic
Remote Control Channel-External Traffic mode — the modem performs control functions
to control external traffic modems..
3.7.12.2 Local Command Responses
mode = <mode>
3.7.13 Built-In Diagnostic Tests (EFD_DIAG)
Note: Qualified personnel shall perform these tests only.
This command starts the SNM-1000 DAC Diagnostic software:
EFD_DIAG'cr'
Wait several seconds. The User Port will display:
Diagnostic Test, Press F1 for Help.
>
Enter an ANSI F1 function key character sequence to display the diagnostic main menu:
F1: Help Screen
F2: Transfer Control to Flash Loader
F3: Transfer Control to PDREM Ram
F4: Restore Area 1 Defaults
F5: Restore Area 2 Defaults
1: Run Ram test
2: Run NOVRAM cycle power test
3: Run Chip Select test
4: Run EFBUS1 to EFBUS2 loopback test
5: Run EFBUS2 to EFBUS1 loopback test
6: Run Service Terminal loopback test
7: Alarm Input Test
To leave the diagnostic tests and return to SNM-1000 operational code, enter an ANSI F4
function key character sequence.
3–58
 Loading...
Loading...