Page 1

Octal V.35 - 10/100 RIOP Installation Guide
Compatible Systems Corporation
4730 Walnut Street
Suite 102
Boulder, Colorad o 80301
303-444-9532
800-356-0283
http://www.compatible.com
Page 2

Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP Installation Guide, Version 1.0
Copyright© 1999, Compatible Systems Corporation
All rights reserved. VSR, VSR-2, MicroRouter and CompatiView are trademarks of Compatible
Systems Corporation. Other trademarks are the property of their respective holders.
FCC Notice: This product has been certified to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device,
pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules. It is designed to provide reasonable protection against
radio or television communication interference in a commercial environment. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area could cause interference with radio or television communication.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction to the Octal V.35-10/10 0 RIOP 1
Chapter 1 - Network Installation 2
Connecting the Octal V.35-10/100 to the Ethernet 2
Telco Line Connection Requirements 3
Connecting a Line Device to the V.35 Interfaces 3
Connecting a Management Console 3
Powering Up the Router 3
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 4
ETHERNET INTERFACE CONFIGURATION 4
IP Protocol 4
Required for IP 4
Suggested for IP 5
IPX Protocol 5
Required for IPX 5
Suggested for IPX 5
AppleTalk Protocol 5
Required for Apple Talk 5
Suggested for AppleTalk 5
DECnet Protocol 5
Required for DECnet 5
Suggested for DECnet 6
WAN INTERFACE CONFIGURATION 6
Physical Communications Setting s 6
PPP Configuration 6
WAN Link Configuration 6
Required for Dedicated/Leased Line Operation 6
Suggested for Dedicated Line Operation 6
IP Protocol 6
Required for IP 6
Suggested for IP 6
IPX Protocol 7
Required for IPX 7
AppleTalk Protocol 7
Required for Apple Talk 7
DECnet Protocol 7
Required for DECnet 7
Suggested for DECnet 7
Frame Relay Configuration 7
WAN Link Configuration 8
Required for Dedicated Line Operation 8
Suggested for Dedicated Line Operation 8
Frame Relay DLCI Mappings 8
IP Protocol 8
Required for IP Numbered Interface 8
i
Page 4
Table of Contents
Required for IP Unnumbered Interface 8
Suggested for IP 9
IPX Protocol 9
Required for IPX 9
Suggested for IPX 9
AppleTalk Protocol 9
Required for Apple Talk 9
Suggested for AppleTalk 9
DECnet Protocol 10
Required for DECnet 10
SMDS Config ur ation 10
Link Configuration 10
SMDS Addressing 10
SAVING A CONFIGURATION FILE TO FLASH ROM 10
Chapter 3 - Shipping Defaults 11
Ethernet Interface 11
IP Routing Defaults 11
IPX Routing Defaults 11
AppleTalk Routing Defaults 11
DECnet Defaults 11
WAN Interfaces 11
Chapter 4 - LED Patterns 12
Over Temp 12
Sys Ready 12
General Indicators 12
Ethernet Traffic Indicators 12
V.35 Traffic Indicators 12
Ethernet Connection Indicators 12
Appendix A - Connector and Cable Pin Outs 13
Pin Outs for HD D-Sub Male to V.35 Male Cable 13
ii
Page 5

Introduction to the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP 1
Introduction to the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP
The Octal V.35-10/100 Routing Input/Output Processor (RIOP), as part of the VSR multigigabit switching router, allows yo u to con nect a local Ethern et and up to eight r emote co rpo rate
networks. Each of the V.35 interfaces has a data capacity of up to 2.048 Mbps, while the
Ethernet interface can operate at either 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
This section of the manual contains information specific to the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP. It is
divided into the following sections:
Chapter 1: Network Installation
Here you will find step-by-s tep instr uctions on how to ph ysically i nstal l the Octal V.35-10/100
and connect it to your network.
Chapter 2: Quickstart Configuration
The Quickstart section provides a basic list of parameters that must be entered into the Octal
V.35-10/100 for proper operation.
Chapter 3: Shipping Defaults
This section of the manual lists factory defaults for the interfaces.
Chapter 4: LED Patterns
This section of the manual describes the LED indicators for the Octal V.35-10/100.
Appendix A: Cable Pin Outs
This section of the manual describes the pin-outs for the V.35 connector cables.
Page 6
Chapter 1 - Network Installation 2
Chapter 1 - Network Installation
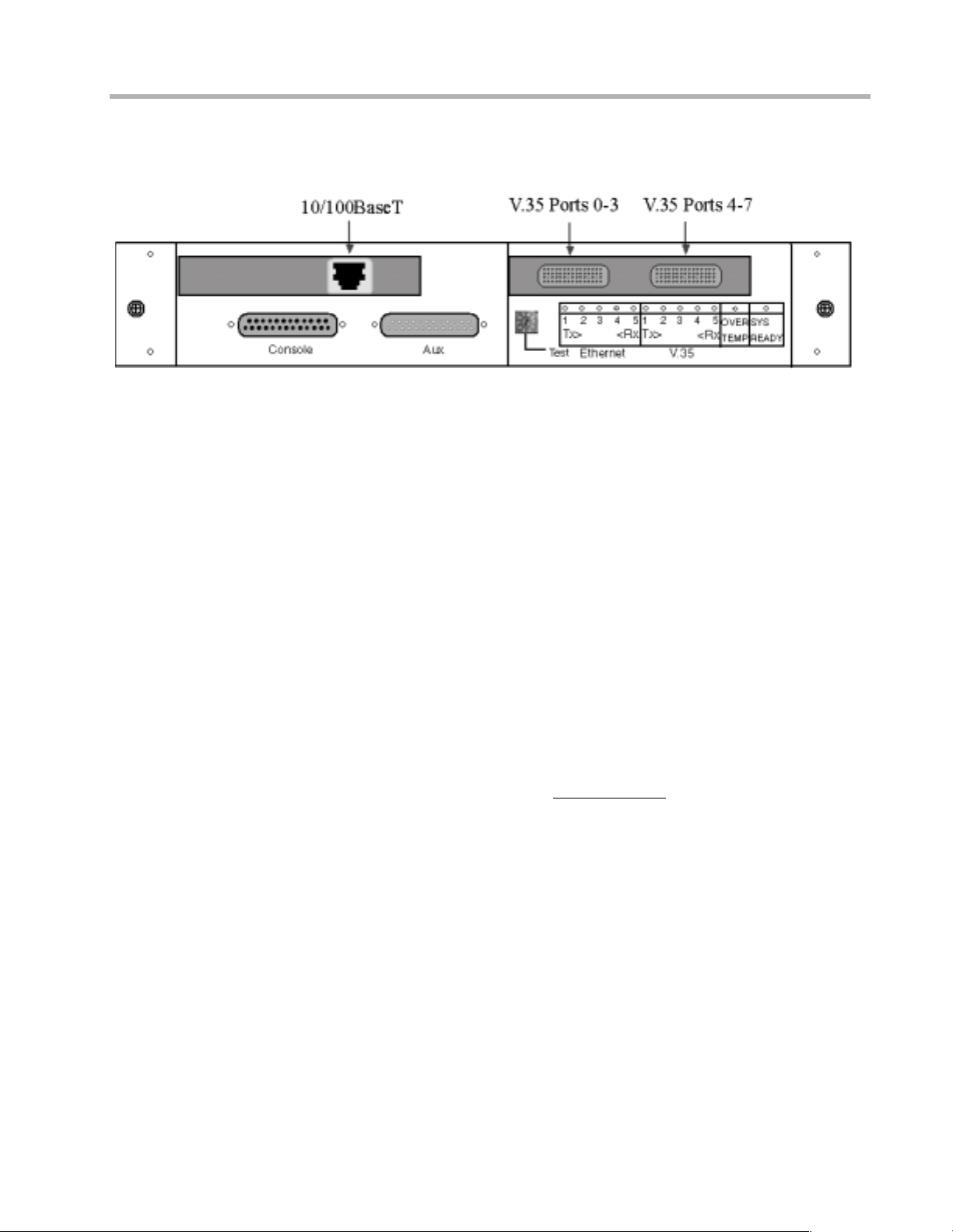
Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP Front Panel
This section of the manual will help you install the Octal V .35-10/100 RIOP to connect a local
Ethernet and up to eight remote corporate networks. These connections can be made to other
Compatible Systems devices or internetworking equipment from other vendors.
In summary, the steps for installation are:
1. After mounting the router or placing it on a desktop, make sure it is not connected to
any power source.
2. Connect the router to the Ethernet network.
3. Connect the router to the wide area communications device(s).
4. Connect a management console to the router (optional).
5. Power up the communications device(s).
6. Plug in the power cable and power up the router.
Connecting the Octal V.35-10/100 to the Ethernet
The 10/100 Ethernet interface direc tly supp orts 1 00B as eTx or 10B as eT twisted-pair Ether net.
To connect the router’s Ethernet interface to twisted-pair Ethernet cabling, you will need an
unshielded twisted-pair station cable that is already connected
twisted-pair hub (for a transmit speed of 10 Mbps) or a 100Mbps Fast Ethernet hub (for a
transmit speed of 100 Mbps).
v
Note: Ethernet cables and cable connectors are not supplied with the Octal V.35-10/100
RIOP product. Category 5 cabling is required for 100 BaseT operation. Please contact your
reseller or your Compatible Systems representative for information on obtaining the correct
Ethernet cabling supplies .
To connect the router to the twisted-pair network, simply plug the twisted-pair cable into the
RJ-45 Ethernet connector on the front of the unit.
to a 10BaseT-compatible
Page 7

Chapter 1 - Network Installation 3
Telco Line Connection Requirements
The Octal V.35-10/100 is not a line communications device. In order to connect each V.35 port
to a wide area transmission line, you must use a 56K CSU/DSU, ISDN Terminal Adapter, or
T1/E1 CSU/DSU. Which of these devices you use depends on the type of telco line you are
connecting to.
v
Note: Before attempting to connect the Octal V.35-1 0/100 to a leased telco line, use the
loopback features of your CSU/DSUs to check the line. This can save you a considerable
amount of time, since the more equipment you have on the line, the more difficult it becomes to
determine where a problem is occurring.
The Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP is shipped with two “Quad” cables. These cables have a single
Very High Density D-Sub connector which plugs into one of the Quad V.35 interface ports on
the front of the device and then divides into four separate High Density D-Sub (HD D-Sub)
female interface cables.
v
Note: Port numbers 0 - 3 are stamped on both sets of Quad cables. For ports 4 -7, the
connector marked “Port 0” is Port 4, the connector marked “Port 1” is Port 5, etc.
In addition, there are eight HD D-Sub male to V.35 male adapter cables. The V.35 male
connector plugs into the female V.35 connector on the chassis of the V.35 line communications
device. The pin outs for this cable are shown in Appendix A.
v
Note: Please use only the supplied cables when connecting your V.35 line communication
device to the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP’s interfaces. The cables provided with other equipment
will generally not have the same internal connections.
Connecting a Line Device to the V.35 Interfaces
These interfaces can be used to connect to a wide variety of line communications devices,
including those which support either leased or dialed operation. Examples include leased 56 K
CSU/DSU’s, switched 56K CSU/DSU’s, fractional T1 CSU/DSU’s, ISDN terminal adapters,
and full T1/E1 rate CSU/DSU’s.
Make sure that both units are powered of f. First connect on e of the eight V.35 adapter cables to
the line communications device. Then connect one of the Quad cables to on e of the V.35 in terfaces on the front of the router. Lastly, connect the two cable ends together. With each connection, make sure to fasten the captive screws into the jack screws on either side of the connectors.
Connecting a Management Console
If you wish to connect an out-of-band management console, use the supplied DB-25 male to
DB-25 female console cable and connect to the Console interface on the Octal V.35-10/100
RIOP. You can use a dumb terminal or a computer equipped with VT100 terminal emulation.
The default settings for the Console interface are VT100 terminal emulation, 9600 bps, 8 bits,
no parity, 1 stop bit and no Flow Control.
v
Note: The Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP also has an AUX interface. This is a modem connection
which should only be used in consultation with Compatible Systems Technical Support staff,
who will provide instruction on its use.
Powering Up the Router
Connect the supplied power cord to the front of the VSR and set the power switch to “On.” At
power-up, the router will take approximately one minute to become visible to CompatiView.
v
Note: If you want to use Telnet as a management method, you must first configure an IP
address into the router with an out-of-band console, or reconfigure the IP address on an IP
host or workstation on the same Ethernet segment as the router. See the appropriate VSR
chassis section of the manual for more information on Command Line Management.
Page 8

Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 4
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions
This Quickstart chapter briefly discusses the major parameters that must be set in order to use
the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP as part of your VSR multigigabit switching router.
Detailed information on the meaning of the router’s parameters is provided in the Compa-
tiView Management Software Reference Guide and the Text-Based Configuration and
Command Line Management Reference Guide. You should use this chapter as a starting point
to look up more specific information in the other document s.
If you need more general information on IP, IPX, AppleTalk or wide area protocols, see the
Appendices in the CompatiView Management Software Reference Guide.
There are a number of parameter settings which are optional, in the sense that they are not
required for all installations. These settings are not covered in this chapter.
In this chapter:
CV = CompatiView
TB = Text-Based Configuration
In order to successfully connect to an Internet Service Provider (ISP), you must use router
configuration parameters which will be provided by the technical staff of the ISP. These
parameters must include all IP addresses, WAN settings and any applicable authorization
routines. Please check with your ISP before changing the configuration of your Octal V.3510/100 RIOP.
v
Note: This Quickstart does not include information on setting up packet filters for using the
router as a Firewall. Se e the CompatiView Management Software Reference Guide or Text-
Based Configuration and Command Line Management Reference Guide regarding IP
packet filters for more information.
Ethernet Interface Confi guration
Ethernet interfaces are considerably easier to set up than wide area interfaces since there are
fewer choices that need to be made regarding communications protocols and parameters. We
recommend that you begin by configuring any Ethernet interf ace parameters before proceeding
to configure WAN interface parameters.
IP Protocol
Required for IP
These parameters set the basic address characteristics of the interface. They provide enough
information for another IP node to find the interface (such as a Telnet client), but not enough
information for routing to take place.
• IP address
• IP subnet mask
• IP broadcast address
CV: Use the TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet 0 Dialog Box to set these parameters.
TB: Use the configure command and set the IPAddress, SubnetMask, and IPBroadcast
keywords in the IP Ethernet 0 section.
Page 9

IPX Protocol
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 5
Suggested for IP
These parameters help supply information a bout the segment that the interface is connected to.
With this information, routing can take place.
• Set IP RIP 1, IP RIP 2 or OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
• IP static routes
CV: Use the TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet 0 Dialog Box to set RIP, and the IP Static Routing
Dialog Box (under Global/IP Static Routes) to set static routes. OSPF can only be configured
using text-based configuration.
TB: Use configure and set either the RIPVersion keyword or the OSPFEnabled keyword for
the IP Ethernet 0 section. Use edit config and add static routes in the IP Static section.
Required for IPX
Generally, there are no required changes from the shipping Ethernet configuration for IPX.
The Ethernet interface will autoconfigure to use the two most common IPX frame types, and
will adapt to conditions on the Ethernet.
Suggested for IPX
You may want to s et yo ur ow n n etwo rk n umb ers , rat her t han using the autoconfigured val ues.
You may also want to turn off unused frame types.
CV: Use the IPX Routing: Ethernet 0 Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set keywords in the IPX Ethernet 0 section.
AppleTalk Protocol
Required for AppleTalk
Generally, there are no required changes from the shipping Ethernet configuration for AppleTalk. The Ethernet interface will autoconfigure to use AppleTalk Phase 2, and will adapt to
conditions on the Ethernet.
Suggested for AppleTalk
You may want to s et yo ur ow n n etwo rk n umb ers , rat her t han using the autoconfigured val ues.
You may also want to use more meaningful zone names.
CV: Use the AppleTalk Routing: Ethernet 0 Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set keywords in the AppleTalk Phase 2 Ethernet 0 section.
DECnet Protocol
Required for DECnet
The router’s shipping configuration does not have DECnet turned on. In order to be used,
DECnet must be turned on both globally and for a particular port.
• Set DECnet on (globally, and for this port)
• Set DECnet area
• Set DECnet node
CV: Use the DECnet Routing Dialog Box (under Global/DECne t Routing) and the DECnet:
Ethernet 0 Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set the Mode keyword in the DECnet Ethernet 0 section. Use
configure and set the Enabled, Area, and Node keywords in the DECnet Global section.
v
Note: Setting DECnet on for any port with the command line also sets DECnet on globally.
Page 10

Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 6
In CompatiView you must set a global parameter and a port-specific parameter.
Suggested for DECnet
Setting the parameters above should be adequate for most installations.
WAN Interface Configuration
The default setting for all WAN interfaces on your Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP is Off for all
protocols and for the link configuration. In order to use a WAN interface, you must first set
some physical parameters and then set up the link and protocol parameters.
Physical Communications Settings
You may need to set the baud rate or other physical communications parameters for the WAN
interface. These parameters will depend on the line communications device you are using.
CV: Use the Physical Configuration: WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and the V. 35 Interface WAN 0 (and/or an y other port you wish to
configure) section.
PPP Configuration
This section covers the settings requi red for PPP (point-t o-point) protoco l operation of the V.35
WAN interfaces.
WAN Link Configuration
Required for Dedicated/Leased Line Operation
Dedicated line operation is the simplest to set up.
• Set Dedicated connection
• Set PPP connection
CV: Use the Link Configuration: WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and then set the Mode and ConnectMode keywords in the Link Config
WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
Suggested for Dedicated Line Operation
Dedicated line operation generally does not require additional parameters for operation.
IP Protocol
Required for IP
WAN interfaces which are set for PPP operation do not generally use an IP address. They are
set to act as an “unnumbered interface.” In this mode of operation, there are no required
settings.
Suggested for IP
These parameters help supply information a bout the segment that the interface is connected to.
With this information, routing can take place.
• Set IP RIP 1, IP RIP 2, OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) or BGP (Border Gateway
Protocol)
• Set IP static routes
CV: Use the TCP/IP Routing: WAN Dialog Box to set RIP, and the IP Static Routing Dialog
Box (under Global/IP Static Routes) to set static routes. OSPF and BGP can only be config-
Page 11

ured using text-based configuration.
TB: Use configure and set either the RIPVersion keyword or th e OSPFEnabled keyword in
the IP WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section. Add static routes and a
default router using the edit config IP Static command.
v
Note: Due to the complexity of BGP, configuration parameters for BGP are not given in this
Quickstart. For help with BGP configuration parameters, and other configuration questions,
refer to the Tech Sup port pages on the Compatible Systems Web site at:
http://www.compatible.com/.
IPX Protocol
Required for IPX
WAN interfaces which are set for PPP operation do not gen erally use an IPX address. They are
set to act as an “unnumbered interface.” In this mode of operation, there are no required
settings.
AppleTalk Protocol
Required for AppleTalk
WAN interfaces which are set for PPP operation do not generally use an AppleTalk address.
They are set to act as an “unnumbered interface.” In this mode of operation, there are no
required settings.
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 7
DECnet Protocol
Required for DECnet
The router’s shipping configuration does not have DECnet turned on. In order to be used,
DECnet must be turned on both globally and for a particular port.
• Set DECnet on (globally, and for a port)
• Set DECnet area
• Set DECnet node
CV: Use the DECnet Routing Dialog Box (under Global/DECne t Routing) and the DECnet:
WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set the Mode keyword in the DECnet WAN 0 (and/or any other port
you wish to configure) section. Use configure and set the Enabled, Area, and Node keywords
in the DECnet Global section.
v
Note: Setting DECnet on for any port with the command line also sets DECnet on globally.
In CompatiView you must set a global parameter and a port-specific parameter.
Suggested for DECnet
Setting the parameters above should be adequate for most installations.
Frame Relay Configuration
This section covers the settings required for Frame Relay operation of the V.35 WAN interfaces. In general, the parameters listed here should be set for each WAN interface on which
you plan to use Frame Relay. Note that some WAN interfaces can be running Frame Relay
while others are running PPP.
The V.35 interfaces can only be run synchronously, at rates up to 2 Mb per second.
Page 12

WAN Link Configuration
Required for Dedicated Line Operation
Frame Relay is presently sup po rt ed i n t he Oct al V.35-10/100 RIOP only via syn chro nou s dedicated line operation.
• Set Dedicated connection
• Set Frame Relay connection
CV: Use the Link Configuration: WAN Dialog Box.
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 8
TB: Use configure and then set the Mode
WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
Suggested for Dedicated Line Operation
Dedicated line operation generally does not require additional parameters for operation.
Frame Relay DLCI Mappings
If you are connecting to another Compatible Systems router, this information is not required
for Frame Relay operation. Compatible Systems uses IARP (Inverse Address Resolution
Protocol) to dynamically generate this information. To connect to other vendors’ routers
which do not support IARP, you must provide DLCI-to-protocol mapping information.
v
Note: Many Internet Service Providers (ISP’s) do not support IARP as a default. If your
WAN interface will be connected to an ISP via Frame Relay, check with your ISP technical
staff on whether or not you must manually enter DLCI information.
CV: Use the DLCI Mapping Database (under WAN/Link Configuration/DLCI button).
TB: Use configure and set the DLCI keyword in the Frame Relay WAN 0 (and/or any o ther
port you wish to configure) section.
IP Protocol
There are two ways to set up Frame Relay. One is to set the WAN interface as a “numbered
interface.” This means that the interface (and thus the Frame Relay network) will have an IP
address, subnet mask, etc. The other is to set it as an unnumbered interface and specify that the
link is point-to-point Frame Relay and set the local DLCI. Unnumbered Frame Relay can only
be configured using text-based configuration. Instructions are provided for both options.
and ConnectMode keywords in the Link Config
Required for IP Numbered Interface
• IP numbered interface
• IP address
• IP subnet mask
• IP broadcast address
CV: Use the TCP/IP Routing: WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use the configure command and the Numbered, IPAddress, SubnetMask, and
IPBroadcast keywords in the IP WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure)
section.
Required for IP Unnumbered Interface
• IP unnumbered interface
• Point-to-Point Frame Relay
• Local DLCI
TB: Use the configure command and the Numbered, PointToPointFrame, and InterfaceDLCI keywords in the IP WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
Page 13

IPX Protocol
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 9
Suggested for IP
These parameters help supply information a bout the segment that the interface is connected to.
With this information, routing can take place.
• Set IP RIP 1, IP RIP 2, OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) or BGP (Border Gateway
Protocol)
• IP static routes
CV: Use the TCP/IP Routing: WAN Dialog Box to set RIP, and the IP Static Routing Dialog
Box (under Global/IP Static Routes) to set static routes. OSPF and BGP can only be configured using text-based configuration.
TB: Use configure and set either the RIPVersion keyword or th e OSPFEnabled keyword in
the IP WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section. Add static routes and a
default router using the edit config IP Static command.
v
Note: Due to the complexity of BGP, configuration parameters for BGP are not given in this
Quickstart. For help with BGP configuration parameters, and other configuration questions,
refer to the Tech Sup port pages on the Compatible Systems Web site at:
http://www.compatible.com/.
Required for IPX
Frame Relay operation requires that the WAN interface be set as a “numbered interface.” This
means that the interface (and thus the Frame Relay network) must have an IPX network
number.
• IPX numbered interface
• IPX network number
CV: Use the IPX Routing: WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set the Numbered and Net keywords in the IPX WAN 0 (and/or any
other port you wish to configure) section.
Suggested for IPX
The settings above are all that is generally required for IPX operation over Frame Relay.
AppleTalk Protocol
Required for AppleTalk
Frame Relay operation requires that the WAN interface be set as a “numbered interface.” This
means that the interface (and thus the Frame Relay network) must have an AppleTalk network
number and the interface must have an AppleTalk node number.
• AppleTalk numbered interface
• AppleTalk network number
• AppleTalk node numbe r
• AppleTalk zone name
CV: Use the AppleTalk Routing: WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set the Numbered, NetLower, and DefZone keywords in the Apple-
Talk WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
Suggested for AppleTalk
You may want to use more meaningful zone names.
CV: Use the AppleTalk Routing: WAN Dialog Box.
Page 14

TB: Use configure and set keywords in the AppleTa lk WAN 0 (and/or any other port you
wish to configure) section.
DECnet Protocol
Required for DECnet
In order to be used, DECnet must be turned on both globally and for a particular port.
WAN interfaces which are set for Frame Relay operation do not need any additional parame-
ters set in order to function.
• Set DECnet on (globally, and for this port)
CV: Use the DECnet Routing Dialog Box (under Global/DECne t Routing) and the DECnet:
WAN Dialog Box.
TB: Use configure and set the Mode keyword in the DECnet WAN 0 (and/or any other port
you wish to configure) section.
v
Note: Setting DECnet on for any port with the command line also sets DECnet on globally.
In CompatiView you must set a global parameter and a port-specific parameter.
SMDS Configuration
This section covers the settings required for SMDS (Switched Multi-megabit Data Service)
operation of the V.35 WAN interfaces (IP only).
service that offers LAN-to-LAN connectivity across a wide area at up to 1.544 Mbps.
addresses and other parameters can only be set using the command line interface.
Chapter 2 - Quickstart Instructions 10
SMDS is a connectionless, packet-switched
SMDS
v
Note: The IP protocol settings and the physical communication settings are the same as they
would be for Frame Relay operation. The only parameters which sh ould be set differently for
SMDS are the Link Configuration and the SMDS addressing section.
Link Configuration
SMDS is presently supported in the Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP only via synchronous dedicated
line operation.
• Set Dedicated connection
• Set SMDS connection
TB: Use configure and then set the Mode
WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
SMDS Addressing
Many of these parameters will be given to you by your service provider.
TB: Use configure and set the StationAddress, IPMulticast and PollingFrequency
keywords in the SMDS WAN 0 (and/or any other port you wish to configure) section.
Saving a Configuration File to Flash ROM
Once a configuration is complete, you can save it to the router’s Flash ROM. Until saved, all
changes are made in a separate buf f e r an d th e actual r outer interfaces co ntinue to r un as before
the changes were made.
and ConnectMode keywords in the Link Config
CV: Use the Save to/Device option from the File menu.
TB: Use the save command.
Page 15

Chapter 3 - Shipping Defaults 11
Chapter 3 - Shipping Defaults
Ethernet Interface
IP Routing Defaults
• On
• Address: 198.41.12.1
• Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Broadcast Address: 198.41.12.255
• IP RIP off
IPX Routing Defaults
• 802.3 on, autoseeding
• 802.2 on, autoseeding
• Type II on, nonseeding
• 802.2 SNAP on , nonseeding
AppleTalk Routing Defaults
• Phase 1 off
• Phase 2 on, autoseeding
DECnet Defaults
WAN Interfaces
• Off
• Off
Page 16

Chapter 4 - LED Patterns 12
Chapter 4 - LED Patterns
Some of the LEDs on the front of the VSR multigigabit switching router serve dual functions.
In addition to indicating certain router-wide operating conditions, they may also display portspecific information.
v
Note: Any continuous flashing pattern not noted in this chapter may be caused by a hard-
ware failure. Please call Compatible Systems Technical Support if your router shows a hardware failure.
Router LED Patterns
The following LEDs and li ght pat terns provid e info rmation about t he VSR’s physica l state and
operating conditions.
Over Temp
The router is above the proper operating temperature. The filter needs changing. See the
appropriate VSR chassis section of the manual for instructions.
Sys Ready
The router booted properly without detecting any failures.
General Indicators
Ethernet Lights V.35 Lights Indication
5 flashing 1 flashing Router stacks starting up.
3&4 flashi ng 2&3 flashi ng No OS loaded. Running from ROM.
1&4 flashing 2&5 flashing Erasing OS in Flash ROM.
5 flashing 1,2&3 flashing Erasing config in Flash ROM.
1 - 5 scanning 5 - 1 scanning Flash ROM erase due to switch se tting five o r six
Octal V.35-10/100 RIOP LED Patterns
The following LEDs and lig ht patte rns pr ovide informat ion ab out the Oct al V.35-10/100 RIOP
interfaces.
Ethernet Traffic Indicators
Scan from 1 to 3: Ethernet transmit packet
Scan from 5 to 3: Ethernet receive packet
V.35 Traffic Indicators
TX: WAN transmit packet
is complete. Set switch to zero and cycle power.
RX: WAN receive packet
Ethernet Connection Indicators
Link: The Link light indicates that there is a good connection to the hub.
Activity: The Activity light indicates that there is activity across the link.
100: The 100 light indicates that the interface is operating at 100 Mbps.
Page 17

Appendix A - Connector and Cable Pin Outs 13
Appendix A - Connector and Cable Pin Outs
Pin Outs for HD D-Sub Male to V.35 Male Cable
V.35 DTE – DCE Signal
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
AA
1
Unused by the V.35 interface circuitry.
2
Receive Line Signal Detect (RLSD) must be asserted by the CSU/DSU when the WAN line
is operational. The CSU/DSU should be configured to have (RLSD) follow the state of the
link.
3
Data Terminal Ready (DTR) will be asserted by the VSR V.35 circuitry when the VSR is
ready to communicate.
4
Used only when internal clocking has been selected.
↔
↔
→
←
←
←
→
→
←
→
←
→
←
→
←
←
←
Chassis Ground
Signal Ground
Request to Send
Clear to Send
Data Set Ready
Receive Line Signal Detect
Data Terminal Ready
Tx Data +
Rx Data +
Tx Data –
Rx Data –
Tx Clock Out +
Rx Clock In +
Tx Clock Out –
Rx Clock In –
Tx Clock In +
Tx Clock In –
1
1
1
3
4
4
2
 Loading...
Loading...