Page 1

AlphaPC 164SX Motherboard
DIGITAL UNIX
User’s Manual
Order Number: EC–R8P7B–TE
Revision/Update Information:
This is a revised document. It supersedes
the AlphaPC 164SX Motherboard
DIGITAL UNIX User’s Manual,
EC–R8P7A–TE.
Page 2

October 1998
The information in this publication is subje c t to change without noti ce .
COMPAQ COMPUTER CORPORATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR TECHNICAL OR EDITORIAL
ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED HEREIN, NOR FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESUL TING FROM THE FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL. THIS
INFORMATIO N IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND COM PAQ COMPUTER CORPORATION DISC LA IMS ANY
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR P ARTICULAR PURPOSE, GOOD TITLE AND AGAINST
INFRINGEMENT.
This publication contains information protec ted by copyright. No part of this publication may be photocopied or
reproduced in any form wit hout prior written consent from Compaq Computer Cor pora tion.
©1998 Compaq Compute r Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
AlphaPC, COMPAQ, DECnet, DIGITAL, DIGITAL UNIX, OpenVMS, the Compaq logo, and the DIGITAL logo
registered in United States Patent and Trademark Office.
Cypress and hyperCache are trademarks of Cyp re ss Se miconductor Corporati on.
GRAFOIL is a registered trademark of Union Carbide Corporation.
Linux is a registered tra dem ark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, and Windows are registered trademarks and Windows NT is a trademark of Microsoft
Corporation.
SMC is a registered tradem ark of Standard Microsystems Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed ex cl usively through X/Open
Company Limited .
Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Page 3

Contents
1 About This Manual
1.1 Manual Conventions and Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
2 Features
2.1 Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.2 Environmental Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.3 Physical Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.3.1 ATX Hole Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.3.2 ATX I/O Shield Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
3 AlphaPC 164SX Switch Configuration
3.1 Mini-Debugger (CF3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 CPU Speed Selection (CF[6:4]) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.3 Fail-Safe Booter (CF7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
4 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
4.1 PCI Bus Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 ISA Expansion Bus Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.3 SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.4 EIDE Drive Bus Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.5 Diskette (Floppy) Drive Bus Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4.6 Parallel Bus Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4.7 COM1/COM2 Serial Line Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.8 Keyboard/Mouse Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.9 SROM Test Data Input Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.10 Input Power Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.11 Enclosure Fan Power Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
iii
Page 4

4.12 Microprocessor Fan Power Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.13 Soft Power Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4.14 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
5 Memory and Microprocessor Configuration
5.1 Configuring SDRAM Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.2 Upgrading SDRAM Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.3 Increasing Microprocessor Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.3.1 Preparatory Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.3.2 Required Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.3.3 Removing the 21164PC Microprocessor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
5.3.4 Installing the 21164PC Microprocessor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
6 Interrupts and ISA Bus Addresses
6.1 Interrupts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.2 ISA I/O Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
7 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
7.1 Alpha SRM Console Firmware Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.2 Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.3 Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
7.3.1 Environment Variable Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
7.3.1.1 Architecture-Required Environment Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
7.3.1.2 System-Defined Environment Variables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
7.4 Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM . . . . . . 7-22
7.4.1 AlphaBIOS Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
7.4.2 Starting the AlphaBIOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
7.4.3 Installing Alpha SRM Console Using AlphaBIOS Setup Program. . . . . . . . . 7-24
7.5 Installing the DIGITAL UNIX Operating System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-29
7.5.1 Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-29
8 Troubleshooting
8.1 Hardware Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.2 Beep Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.3 Post Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.4 Fail-Safe Booter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
iv
Page 5

9 Battery Recycle/Disposal Information
A Support, Products, and Documentation
A.1 Customer Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
A.2 Supporting Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
A.2.1 Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
A.2.2 Thermal Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
A.2.3 Power Supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
A.2.4 Enclosure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
A.3 Associated Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
v
Page 6

Figures
2–1 AlphaPC 164SX Switch/Connector/Component Location. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2–2 ATX Hole Specification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2–3 ATX I/O Shield Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
3–1 AlphaPC 164SX Configuration Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
4–1 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
5–1 Fan/Heat-Sink Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
7–1 AlphaBIOS Boot Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
7–2 AlphaBIOS Setup Screen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-24
7–3 AlphaBIOS Upgrade Options Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
7–4 AlphaBIOS Warning Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-26
7–5 AlphaBIOS Upgrade SRM Console Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-27
7–6 AlphaBIOS Upgrade Complete Screen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-28
vi
Page 7

Tables
2–1 AlphaPC 164SX Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2–2 AlphaPC 164SX Switch/Connector/Component List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2–3 Power Supply DC Current Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2–4 AlphaPC 164SX Motherboard Envi ronmental Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
4–1 PCI Bus Connector Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4–2 ISA Expansion Bus Connector Pinouts (J22, J23) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4–3 SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts (J7 through J10). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4–4 EIDE Drive Bus Connector Pinouts (J5, J6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4–5 Diskette (Floppy) Drive Bus Connector Pinouts (J11). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4–6 Parallel Bus Connector Pinouts (J13). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
4–7 COM1/COM2 Serial Line Connector Pinouts (J3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4–8 Keyboard/Mouse Connector Pinouts (J4). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4–9 SROM Test Data Input Connector Pinouts (J21) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4–10 Input Power Connector Pinouts (J2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4–11 Enclosure Fan (+12 V dc) Power Connector Pinouts (J16) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4–12 Microprocessor Fan Power Connector Pinouts (J14). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4–13 Soft Power Connector Pinouts (J1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
4–14 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts (J20) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
5–1 AlphaPC 164SX SDRAM Memory Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
6–1 ISA Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6–2 ISA I/O Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
7–1 AlphaBIOS Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
8–1 Beep Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8–2 Post Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
vii
Page 8

Page 9
About This Manual
This manual describes the AlphaPC 164SX motherboard, a board for computing
systems based on the Alp ha 21 16 4PC microproc essor and the companio n 21 174 core
logic chip. It describes the motherboard’s features and how to set its configuration
switches. This manual helps users to install and populate the AlphaPC 164SX
motherboard with memory boards and peripheral cards.
1.1 Manual Conventions and Term in ology
The following conventions are used in this manual.
Caution: Cautions indicate potential damage to equipment, software, or data.
Note: Notes provide additional information about a topic.
Numbering: All numbers a re dec imal or hexade cimal un less otherwi se ind icate d. In
case of ambiguity, a subscript indicates the radix of nondecimal numbers. For
example, 19 is a decimal number, but 19
Extents: Extents are specified by a single number or a pair of numbers in brackets
([ ]) separated by a colon (:), and are incl usive. For example, bits [7:3] specify an
extent including bits 7, 6, 5, 4, and 3. Multiple bit fields are shown as extents.
and 19A are hexadecimal numbers.
16
1
Register Figures: Register figures have bit and field position numbering starting at
the right (low-order ) and increasing to the left (high-order).
Signal Names: All signal names are printed in boldface type. Signal names that
originate in an indu stry- stand ard spe cifi catio n, such a s PCI or IDE, are p rint ed in t he
case as found in the spe cificat ion ( usuall y upper case) . Acti ve low s ignal s have e ither
a pound sign “#” appended, or a “not” overscore bar; for example, DEVSEL# and
RESET
Italic Type: Italic type emphasizes important information and indicates complete
titles of documents.
.
About This Manual 1–1
Page 10

Manual Conventions and Terminology
Terms: The following terms are used in this manual:
This term... Refers to...
Alpha SRM console The Alpha SRM Console firmware
DIGITAL UNIX installation guide The DIGITAL UNIX Installation Guide
DIGITAL UNIX The DIGITAL UNIX operating system
1–2 About This Manual
Page 11
2
Features
Table 2–1 provides an overview of the AlphaPC 164SX motherboard’s features.
Table 2–1 AlphaPC 164SX Features
Feature Description
Microprocessor Alpha 21164PC microprocessor (64-bit RISC)
Core logic chip 21174 core logic chip, comprising a single control chip that pro-
vides an interface to system memory and the PCI bus
Synchronous DRAM
(SDRAM) memory
Caching
L1 Icache 16KB, direct-mapped, instruction cache on the CPU chip
L1 Dcache 8KB, direct-mapped, data cache on the CPU chip
L2 backup cache Onboard 1MB, direct-mapped, synchronous SSRAM backup
I/O and miscellaneous
support
Firmware Alpha SRM Console firmware
32MB to 512MB memory ar ray -- Two banks of 128-bit memory;
168-pin unbuffered SDRAM DIMMs.
cache with 128-bit data path
• 32-bit and 64-bit, 33-MHz PCI
• Two 64-bit and two 32-bit PCI expansion slots
• Cypress CY82C693U–NC chip with a PCI-to-ISA bridge,
PCI EIDE, keyboard, mouse, and time-of-year clock
• Two dedicated ISA expansion slots
• SMC FDC37C669 combination controller chip provides
control for diskettes, two UARTs with modem control, and
parallel port
• 1MB flash ROM
Features 2–1
Page 12
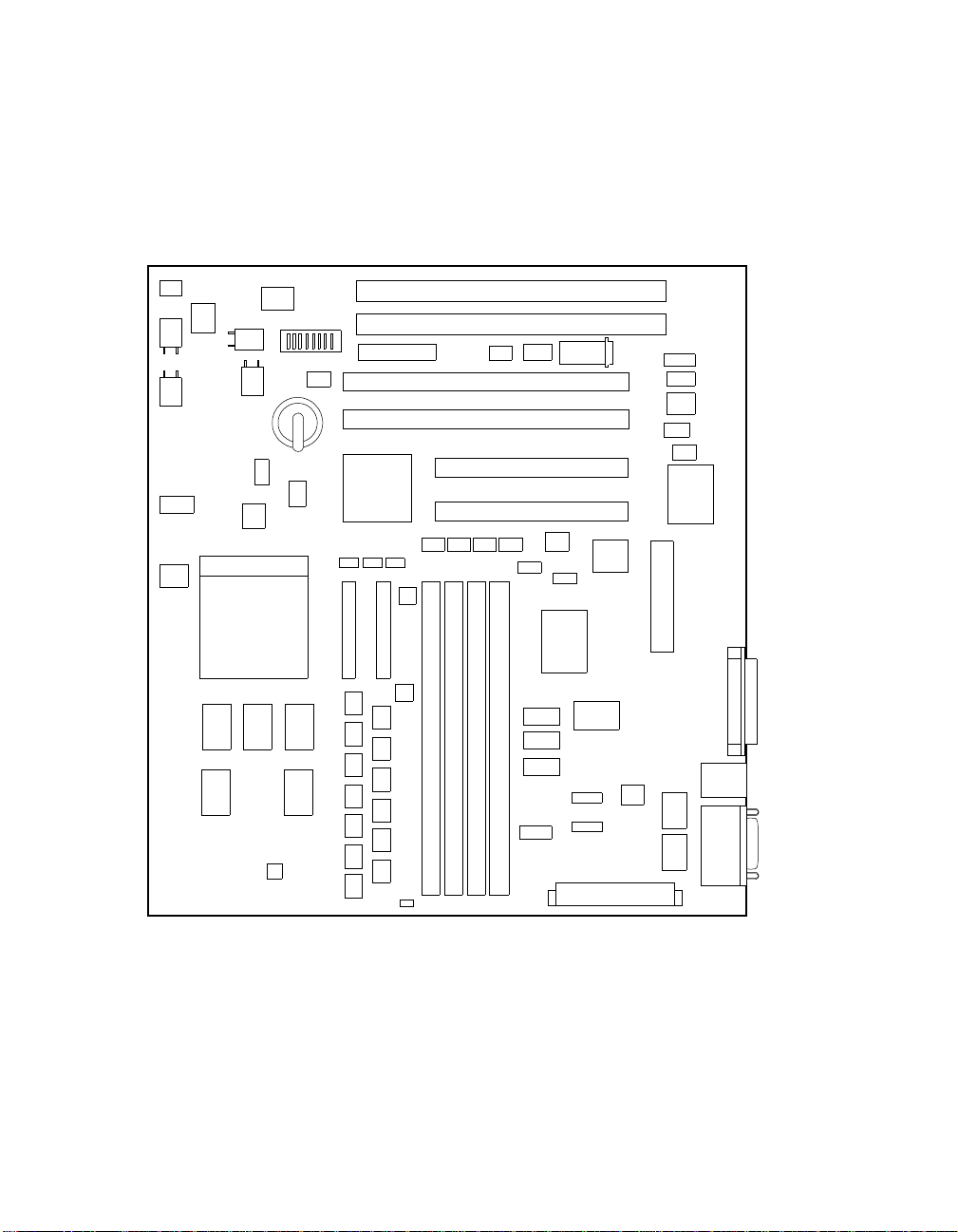
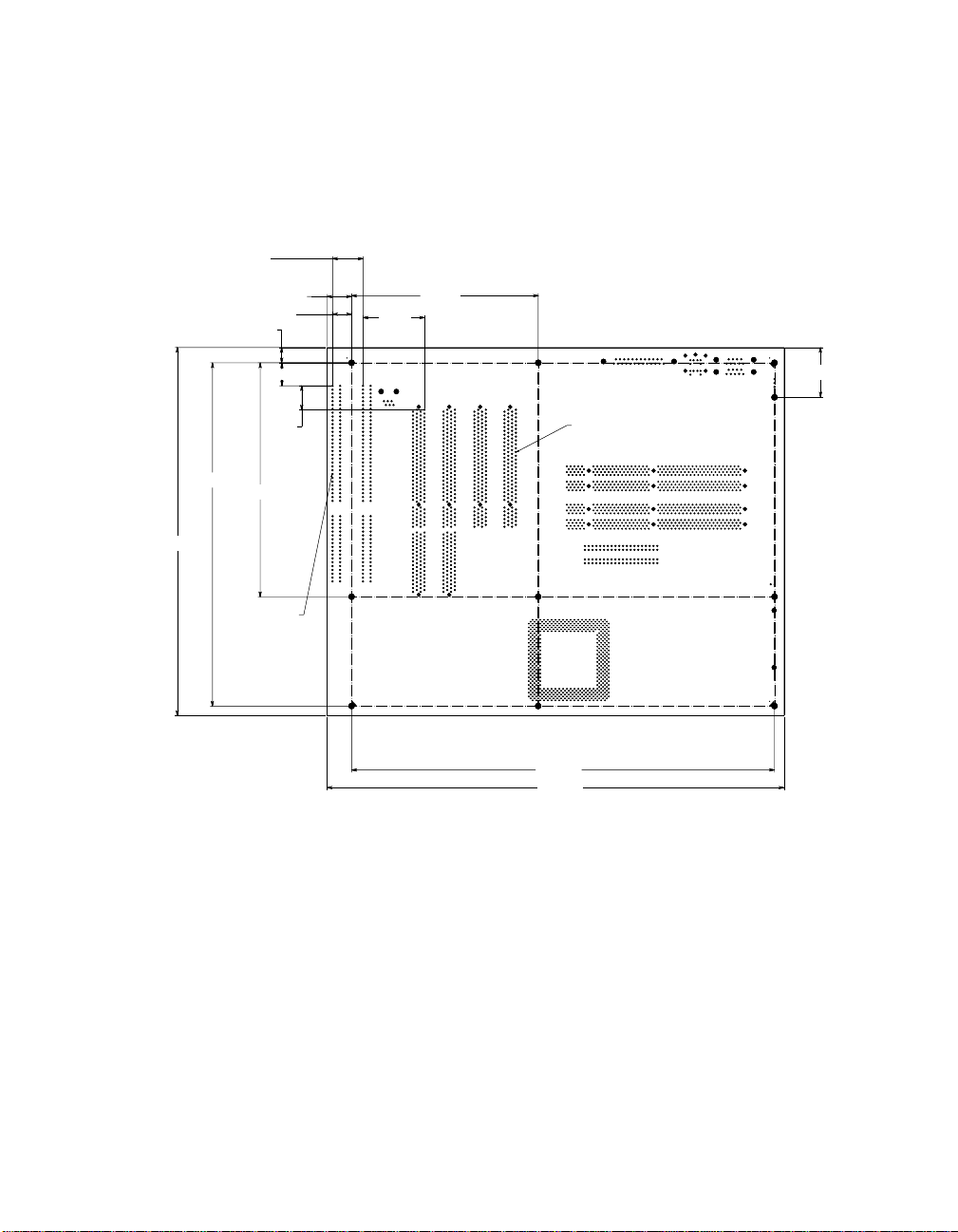
Figure 2–1 shows the AlphaPC 164SX motherboard and its components, and
Table 2–2 describes these components.
Figure 2–1 AlphaPC 164SX Switch/Connector/Component Location
U56
U55
Q7
Q4
J16
J14
XU59
Q8
Q5
XB1
X2
X1
U45
21164PC
U31
U20 U21 U22
U10 U11
U2
J23
SW1 J22
J20
U51
U53
J19
J18
U46
U41 U42
U36
U37
U40
U38
U32
J5 J6
U28
U27
U25
U23
U17
U12
U7
U3
U1
U24
U18
U13
J7 J8 J9
U5
U4
J10
J1
U43
U35
U54
J17
J15
U8
U29
U26
U19
U44
U34
21174
U33
J21
U14
U9
U30
U39
U52
U50
U49
X3
U48
U47
J11
J13
U16
J4
J3
U6
U15
J2
2–2 Features
Page 13

Table 2–2 AlphaPC 164SX Switch/Connector/Component List
Item No. Description Item No. Description
XB1 RTC battery (CR2032) J20 LEDs/speaker/buttons connectors
J1 Soft power connector J21 SROM test port connector
J2 Input power (+3 V, +5 V, -5 V, +12 V,
J22 ISA slot 1
-12 V)
J3 COM1/COM2 (DB9) connectors J23 ISA slot 0
J4 Keyboard/mouse connectors SW1 Configuration switchpack
J5 EIDE drive 2/3 connector U48 System clock PLL (CY2081)
J6 EIDE drive 0/1 connector U10, U11,
L2 cache data SRAMs
U20, U22
J7 SDRAM DIMM 0 [0:63] connector U21 L2 cache tag SRAM
J8 SDRAM DIMM 1 [64:128] connector U33 21174 core logic chip
J9 SDRAM DIMM 2 [0:63] connector U19, U26,
Memory address/control buffers
U29
J10 SDRAM DIMM 3 [64:128] connector U1, U3, U4,
Data switches
U5, U7,
U12, U13,
U17, U18,
U23, U24,
U25, U27
J11 Diskette (floppy) drive connector U40 to U43 Interrupt shift registers
J13 Parallel I/O connector U30 Flash ROM (1MB)
J14 Microprocessor fan/fan sense connector U46 PCI-ISA Bridge (CY82C693U-NC)
J15 PCI slot 3 (32-bit) U36 to U38 IDE buffers
J16 Fan power, enclosure (+12 V) U47 Combination controller
(FDC37C669)
J17 PCI slot 2 (32-bit) U2, U28,
Reg-reg cache isolate logic
U32
J18 PCI slot 1 (64-bit) U31 Microprocessor, socketed
(Alpha 21164PC)
J19 PCI slot 0 (64-bit) U45 Microprocessor clock synthesizer
(MC12439)
Features 2–3
Page 14
Power Requirements
2.1 Power Requirements
The AlphaPC 164SX motherboard has a total power dissipation of 90 W, excluding
any plug-in PCI and ISA devices. Table 2–3 lists the power requirement for each dc
supply voltage.
The power supply must be ATX-compliant.
Table 2–3 Power Supply DC Current Requirements
Voltage/Tolerance Current
+3.3 V dc, ±5% 5.0 A
1
+5 V dc,
–5 V dc,
+12 V dc,
–12 V dc,
1
Caution: Fan sensor required. The 21164PC microprocessor cooling fan must
±5% 12.0 A
±5% 0.0 A
±5% 1.0 A
±5% 100.0 mA
Values indicated are for an AlphaPC 164SX motherboard with an Alpha 21164PC microprocessor
operating at 400 MHz, with 128MB SDRAM, excluding adapter cards and di sk drives.
drive an RPM indicator signal. If the airflow stops, the sensor on the
motherboard detects that the RPM has stopped, and resets the system.
2.2 Environmental Requirements
The 21164PC microprocessor is cooled by a small fan blowing directly into the
chip’s heat sink. The AlphaPC 164SX motherboard is designed to run efficiently by
using only this fan. Add it ion al fa ns may be necessary depending upon cabinetry and
the requirements of plug-in cards.
The AlphaPC 164SX motherboard is specified to run within the environment listed
in Table 2–4.
2–4 Features
Page 15

Physical Parameters
Table 2–4 AlphaPC 164SX Motherboard Environmental Requirements
Parameter Specification
Operating temperature 10°C to 40°C (50°F to 104°F)
Storage temperature –55°C to 125°C (–67°F to 257°F)
Relative humidity 10% to 90% with maximum wet bulb temperature
28°C (82°F) and minimum dew point 2°C (36°F)
Rate of (dry bulb) temperature change 11°C/hour
2.3 Physical Parameters
The AlphaPC 164SX motherboard is an ATX-size printed-wiring board (PWB) with
the following dimensions:
• Length: 30.48 cm (12.0 in ±0.0005 in)
• Width: 24.38 cm (9.6 in ±0.0005 in)
• Height: 6.00 cm (2.4 in)
±2°C/hour (20°F/hour ±4°F/hour)
Features 2–5
Page 16
Physical Parameters
2.3.1 ATX Hole Specification
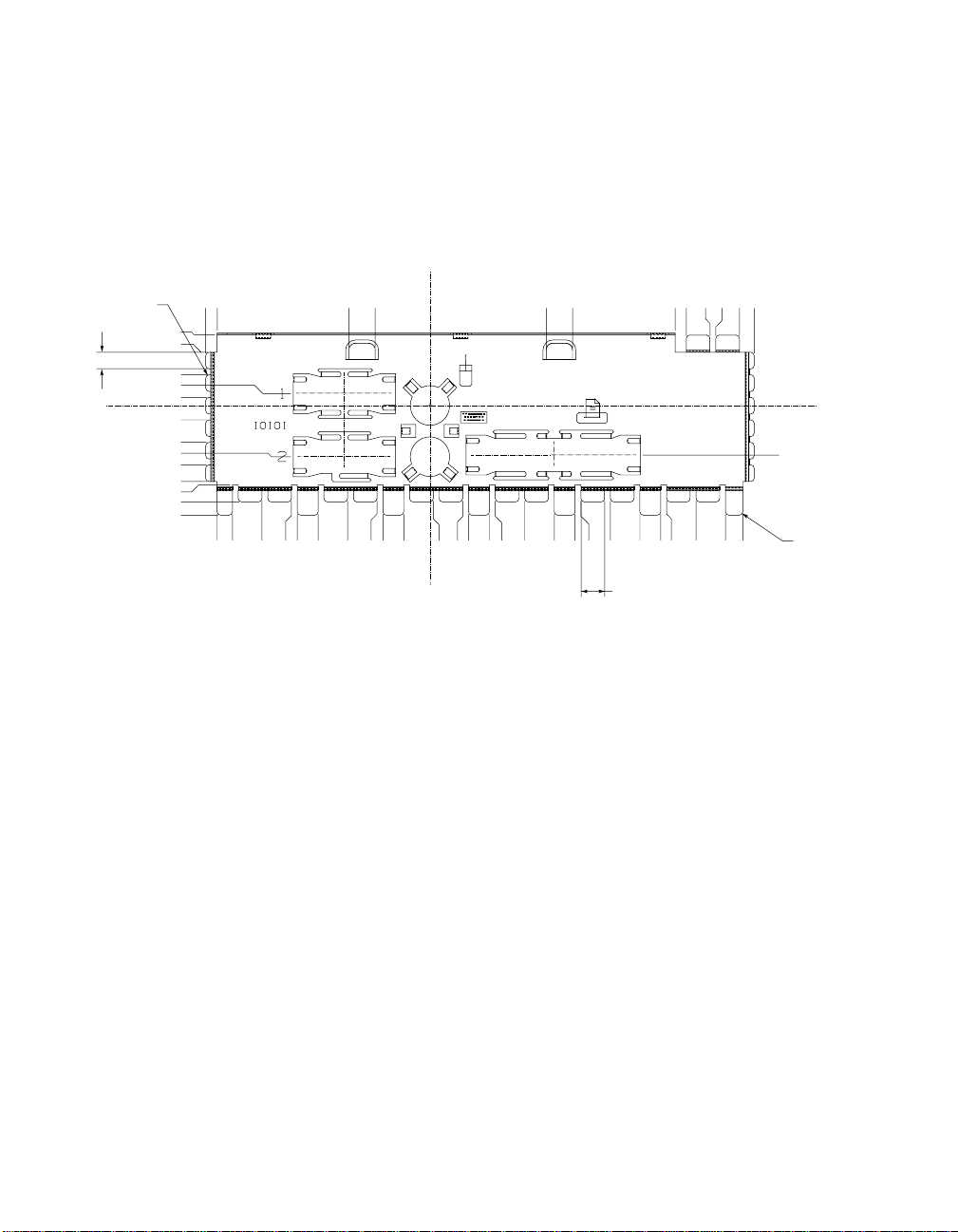
Figure 2–2 shows the ATX hole specification for the AlphaPC 164SX.
Figure 2–2 ATX Hole Specification
.800
TYP Between
Connectors
.650
.500
.400
4.900
1.612
9.600
8.950
ISA Connector
(2 Places)
6.100
.600
.625
11.100
12.000
PCI Connector
(4 Places)
1.300
FM-06122.AI4
2–6 Features
Page 17
2.3.2 ATX I/O Shield Requirements
Figure 2–3 shows the ATX I/O shield dimensions for the AlphaPC 164SX.
Figure 2–3 ATX I/O Shield Dimensions
Physical Parameters
R 1.00
5.00 TYP
21.36
16.05
9.25
3.58
2.45
4.35
11.15
15.47
17.95
22.95
23.96
29.10
33.10
68.4
64.9
64.91
60.26
51.27
42.28
40.48
34.13
24.7
25.14
16.7
16.15
14.35
8.00
0.99
9.98
11.78
18.13
19.93
28.92
35.5
37.91
43.5
44.26
46.06
55.05
64.04
7.19 TYP
74.8
70.39
72.19
78.2
81.18
85.4
87.2
90.17
94.4
98.9
95.40
FM-05986.AI4
14.96
R 1.00
Features 2–7
Page 18

Page 19

AlphaPC 164SX Switch Configuration
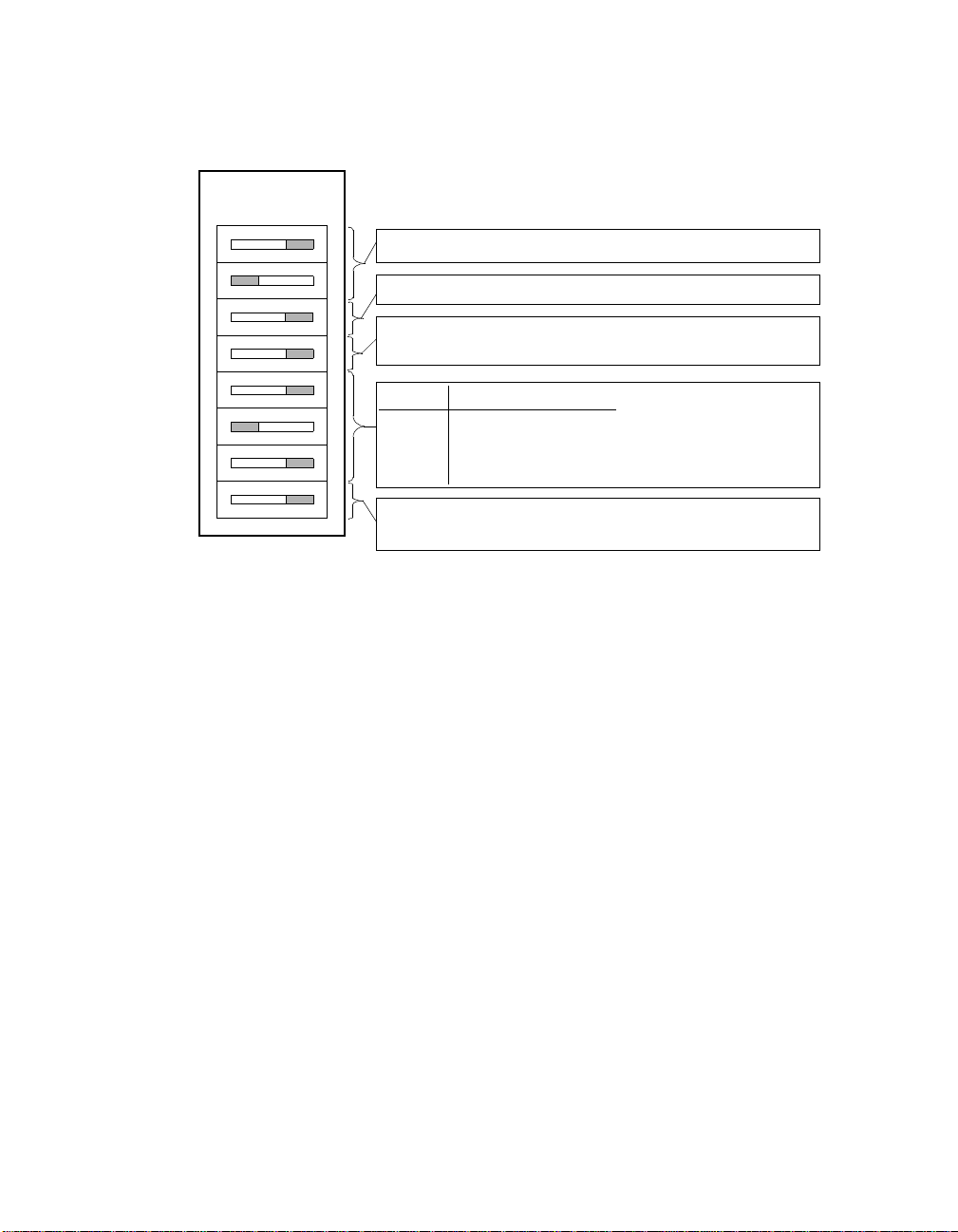
The AlphaPC 164SX motherboard has a switchpack located at SW1, as shown
previously in Figure 2–1. These switches set the hardware conf igu ra ti on. Fi gur e 3 –1
shows these switch configura ti ons .
3.1 Mini-Debugger (CF3)
The Alpha SROM Mini-Debugger is stored in the flash ROM and is enabled/
disabled by switch CF3. The default position for this switch is on (see Figure 3–1).
When this switch is off, it causes the SROM initialization to trap to the MiniDebugger after all initialization is complete, but before starting the execution of the
system flash ROM code.
3.2 CPU Speed Selection (CF[6:4])
The clock synthesizer at U45 makes it possible to change the frequency of the
microprocessor’s clock output. The switch configuration is set in SW1, CF[6:4].
These three switches set the speed at power-up as listed in Figure 3–1. The
microprocessor frequency divided by the ratio determines the system clock
frequency.
3
3.3 Fail-Safe Booter (CF7)
The fail-safe booter provides an emergency recovery mechanism when the primary
firmware image cont ai ned i n f la sh me mo ry has been corrupted. When flash memory
has been corrupted, and no image can be loaded safely from the flash, you can run
the fail-safe booter and boot another image from a diskette that is capable of reprogramming the flash.
Refer to Sect ion 8.4 for more information.
AlphaPC 164SX Switch Configuration 3–1
Page 20
Fail-Safe Booter (CF7)
Figure 3–1 AlphaPC 164SX Configuration Switches
CF0
CF1
CF2
CF3
CF4
CF5
CF6
CF7
01
Note: Switch defaults are in bold.
Reserved. This must remain CF0=1, CF1=0.
Reserved.
Mini-Debugger: 0 enables Mini-Debugger
1 disables Mini-Debugger
CF Bit: 400 MHz 533 MHz
41 1
51 0
61 1
Fail-Safe Booter: 0: Fail Safe
1: Alpha SRM Console
Note:
All other combinations
are reserved.
3–2 AlphaPC 164SX Switch Configuration
Page 21

AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
This chapter lists the pinouts of the AlphaPC 164SX connectors (see Table 4–1
through Table 4–14). See Figure 2–1 for connector locations.
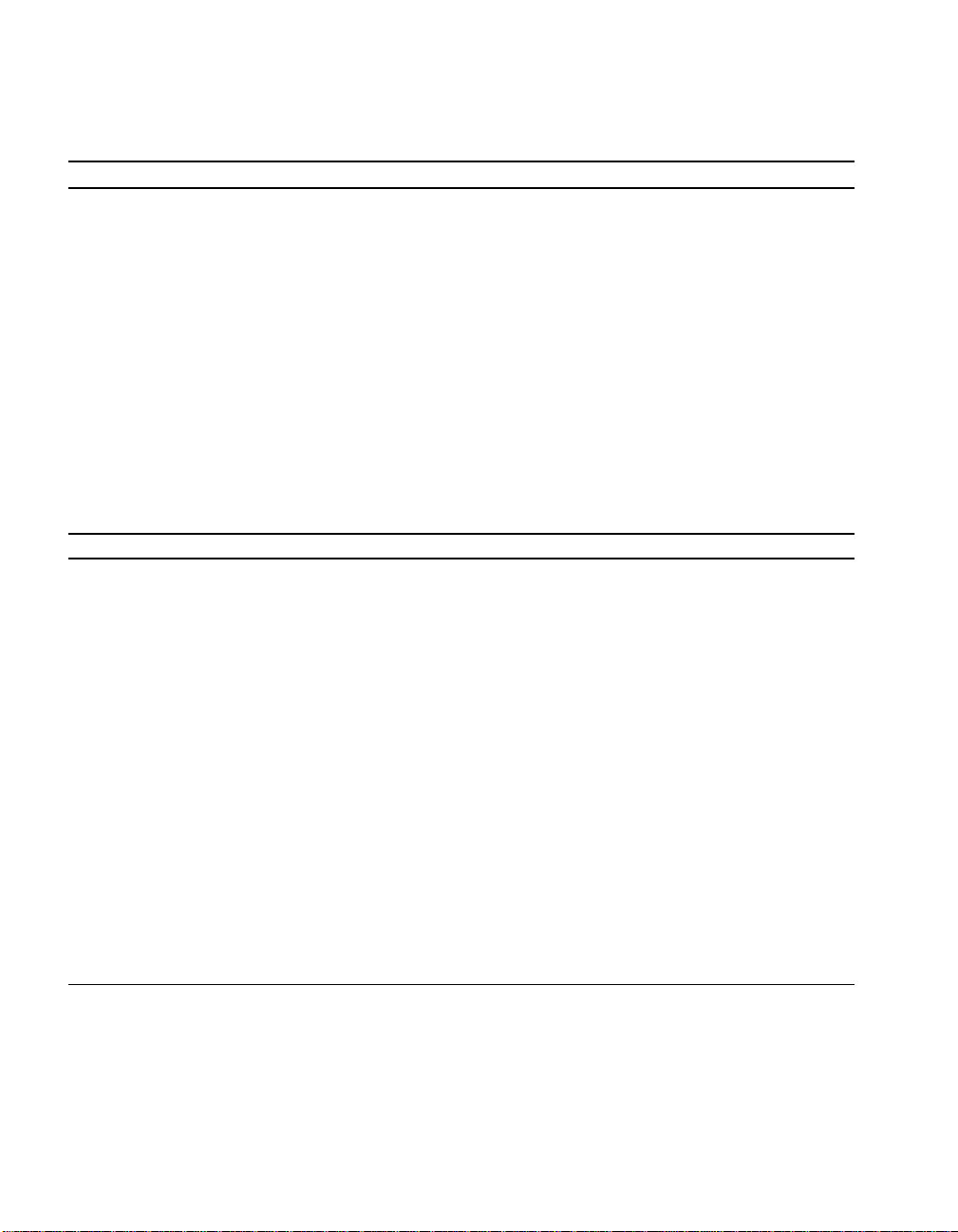
4.1 PCI Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–1 shows the PCI bus connector pinouts.
4
Table 4–1 PCI Bus Connector Pinouts
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
32-Bit and 64-Bit PCI Connectors (J15 , J17, J18, J19)
A1 TRST# A2 +12V A3 TMS A4 TDI
A5 Vdd A6 INTA A7 INTC A8 Vdd
A9 —A10Vdd A11 — A12 Gnd
A13 Gnd A14 — A15 RST# A16 Vdd
A17 GNT# A18 Gnd A19 — A20 AD[30]
A21 +3V A22 AD[28] A23 AD[26] A24 Gnd
A25 AD[24] A26 IDSEL A27 +3V A28 AD[22]
A29 AD[20] A30 Gnd A31 AD[18] A32 AD[16]
A33 +3V A34 FRAME# A35 Gnd A36 TRDY#
A37 STOP# A38 STOP# A39 +3V A40 SDONE
A41 SBO# A42 Gnd A43 PAR A44 AD[15]
A45 +3V A46 AD[13] A47 AD[11] A48 Gnd
A49 AD[09] A5 0 Not used A51 Not used A52 C/BE#[0]
A53 +3V A54 AD[06] A55 AD[04] A56 Gnd
A57 AD[02] A58 AD[00] A59 Vdd A60 REQ64#
A61 Vdd A62 Vdd B1 -12V B2 TCK
B3 Gnd B4 TDO B5 Vdd B6 Vdd
B7 INTB B8 INTD B9 PRSNT1# B10 —
(Sheet 1 of 2)
AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts 4–1
Page 22
PCI Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–1 PCI Bus Connector Pinouts
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
(Sheet 2 of 2)
B11 PRSNT2# B12 Gnd B13 Gnd B14 —
B15 Gnd B16 CLK B17 Gnd B18 REQ#
B19 Vdd B20 AD[31] B21 AD[29] B22 Gnd
B23 AD[27] B24 AD[25] B25 +3V B26 C/BE#[3]
B27 AD[23] B28 Gnd B29 AD[21] B30 AD[19]
B31 +3V B32 AD[17] B33 C/BE#[2] B34 Gnd
B35 IRDY# B36 +3V B37 DEVSEL# B38 Gnd
B39 LOCK# B40 PERR# B41 +3V B42 SERR#
B43 +3V B44 C/BE#[1] B45 AD[14] B46 Gnd
B47 AD[12] B48 AD[10] B49 Gnd B50 Not used
B51 Not used B52 AD[08] B53 AD[07] B54 +3V
B55 AD[05] B56 AD[03] B57 Gnd B58 AD[01]
B59 Vdd B60 ACK64# B61 Vdd B62 Vdd
64-Bit PCI Connectors Only (J18, J19)
A63 Gnd A64 C/BE#[7] A65 C/BE#[5] A66 Vdd
A67 PAR64 A68 D[62] A69 Gnd A70 D[60]
A71 D[58] A72 Gnd A73 D[56] A74 D[54]
A75 Vdd A76 D[52] A77 D[50] A78 Gnd
A79 D[48] A80 D[46] A81 Gnd A82 D[44]
A83 D[42] A84 Vdd A85 D[40] A86 D[38]
A87 Gnd A88 D[36] A89 D[34] A90 Gnd
A91 D[32] A92 — A93 Gnd A94 —
B63 — B64 Gnd B65 C/BE#[6] B66 C/BE#[4]
B67 Gnd B68 D[63] B69 D[61] B70 Vdd
B71 D[59] B72 D[57] B73 Gnd B74 D[55]
B75 D[53] B76 Gnd B77 D[51] B78 D[49]
B79 Vdd B80 D[47] B81 D[45] B82 Gnd
B83 D[43] B84 D[41] B85 Gnd B86 D[39]
B87 D[37] B88 Vdd B89 D[35] B90 D[33]
B91 Gnd B92 — B93 — B94 Gnd
4–2 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
Page 23

ISA Expansion Bus Connector Pinouts
4.2 ISA Expansion Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–2 shows the ISA expansion bus connector pinouts.
Table 4–2 ISA Expansion Bus Connector Pinouts (J22, J23)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Gnd 2 IOCHCK# 3 RSTDRV 4 SD7
5 Vdd 6 SD6 7 IRQ9 8 SD5
9 –5V 10 SD4 11 DRQ2 12 SD3
13 –12V 14 SD2 15 ZEROWS# 16 SD1
17 +12V 18 SD0 19 Gnd 20 IOCHRDY
21 SMEMW# 22 AEN 23 SMEMR# 24 SA19
25 IOW# 26 SA18 27 IOR# 28 SA17
29 DACK3# 30 SA16 31 DRQ3 32 SA15
33 DACK1# 34 SA14 35 DRQ1 36 SA13
37 REFRESH# 38 SA12 39 SYSCLK 40 SA11
41 IRQ7 42 SA10 43 IRQ6 44 SA9
45 IRQ5 46 SA8 47 IRQ4 48 SA7
49 IRQ3 50 SA6 51 DACK2# 52 SA5
53 TC 54 SA4 55 BALE 56 SA3
57 Vdd 58 SA2 59 OSC 60 SA1
61 Gnd 62 SA0 63 MEMCS16# 64 SBHE#
65 IOCS16# 66 LA23 67 IRQ10 68 LA22
69 IRQ11 70 LA21 71 IRQ12 72 LA20
73 IRQ15 74 LA19 75 IRQ14 76 LA18
77 DACK0# 78 LA17 79 DRQ0 80 MEMR#
81 DACK5# 82 MEMW# 83 DRQ5 84 SD8
85 DACK6# 86 SD9 87 DRQ6 88 SD10
89 DACK7# 90 SD11 91 DRQ7 92 SD12
93 Vdd 94 SD13 95 MASTER# 96 SD14
97 Gnd 98 SD15 —— ——
AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts 4–3
Page 24

SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts
4.3 SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts
Table 4–3 shows the SDRAM DIMM connector pinouts.
Table 4–3 SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts (J7 through J10)1
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Gnd 2 DQ0 3 DQ1 4 DQ2
5 DQ3 6 +3V 7 DQ4 8 DQ5
9 DQ6 10 DQ7 11 DQ8 12 Gnd
13 DQ9 14 DQ10 15 DQ11 16 DQ12
17 DQ13 18 +3V 19 DQ14 20 DQ15
21 CB0 22 CB1 23 Gnd 24 NC
25 NC 26 +3V 27 WE
29 DQMB1 30 S0
33 A0 34 A2 35 A4 36 A6
37 A8 38 A10 39 A12 40 +3V
41 +3V 42 CK0 43 Gnd 44 NC
45 S2
49 +3V 50 NC 51 NC 52 CB2
53 CB3 54 Gnd 55 DQ16 56 DQ17
57 DQ18 58 DQ19 59 +3V 60 DQ20
61 NC 62 NC 63 CKE1 64 Gnd
65 DQ21 66 DQ22 67 DQ23 68 Gnd
69 DQ24 70 DQ25 71 DQ26 72 DQ27
73 +3V 74 DQ28 75 DQ29 76 DQ30
77 DQ31 78 Gnd 79 CK2 80 NC
81 NC 82 SDA 83 SCL 84 +3V
85 Gnd 86 DQ32 87 DQ33 88 DQ34
89 DQ35 90 +3V 91 DQ36 92 DQ37
93 DQ38 94 DQ39 95 DQ40 96 Gnd
97 DQ41 98 DQ42 99 DQ43 100 DQ44
101 DQ45 102 +3V 103 DQ46 104 DQ47
105 CB4 106 CB5 107 Gnd 108 NC
109 NC 110 +3V 111 CAS
113 DQMB5 114 S1 115 RAS
117 A1 118 A3 119 A5 120 A7
121 A9 122 BA0 123 A13 124 +3V
46 DQMB2 47 DQMB3 48 NC
31 NC 32 Gnd
28 DQMB0
112 DQMB4
116 Gnd
(Sheet 1 of 2)
4–4 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
Page 25

EIDE Drive Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–3 SDRAM DIMM Connector Pinouts (J7 through J10)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
125 CK1 126 BA1
129 S3
130 DQMB6 131 DQMB7 132 PD
2
127 Gnd 128 CKE0
1
(Sheet 2 of 2)
3
133 +3V 134 NC 135 NC 136 CB6
137 CB7 138 Gnd 139 DQ48 140 DQ49
141 DQ50 142 DQ51 143 +3V 144 DQ52
145 NC 146 NC 147 PD 148 Gnd
149 DQ53 150 DQ54 151 DQ55 152 Gnd
153 DQ56 154 DQ57 155 DQ58 156 DQ59
157 +3V 158 DQ60 159 DQ61 160 DQ62
161 DQ63 162 Gnd 163 CK3 164 NC
165 SA0 166 SA1 167 SA2 168 +3V
1
Pins 1 through 84 are on the front side and pins 85 through 168 are on the back side.
2
The AlphaPC 164SX uses BA1 as both BA1 and ADDR12. Therefore, four-bank DIMMs using ADDR[11:0]
are the maximum size. (Two-bank DIMMs can use ADDR[12:0].)
3
Pull-down.
4.4 EIDE Drive Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–4 shows the EIDE drive bus connector pinouts.
Table 4–4 EIDE Drive Bus Connector Pinouts (J5, J6)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 RESET 2 Gnd 3 IDE_D7 4 IDE_D8
5 IDE_D6 6 IDE_D9 7 IDE_D5 8 IDE_D10
9 IDE_D4 10 IDE_D11 11 IDE_D3 12 IDE_D12
13 IDE_D2 14 IDE_D13 15 IDE_D1 16 IDE_D14
17 IDE_D0 18 IDE_D15 19 Gnd 20 NC (key pin)
21 MARQ 22 Gnd 23 IOW
25 IOR
26 Gnd 27 CHRDY 28 BALE
24 Gnd
29 MACK 30 Gnd 31 IRQ 32 IOCS16
33 ADDR1 34 NC 35 ADDR0 36 ADDR2
37 CS0
38 CS1 39 ACT 40 Gnd
AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts 4–5
Page 26

Diskette (Floppy) Drive Bus Connector Pinouts
4.5 Diskette (Floppy) Drive Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–5 shows the diskette (floppy) drive bus connector pinouts.
Table 4–5 Diskette (Floppy) Drive Bus Connector Pinouts (J11)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Gnd 2 DEN0 3 Gnd 4NC
5 Gnd 6 DEN1 7 Gnd 8 INDEX
9 Gnd 10 MTR0 11 Gnd 12 DR1
13 Gnd 14 DR0 15 Gnd 16 MTR1
17 Gnd 18 DIR 19 Gnd 20 STEP
21 Gnd 22 WDATA 23 Gnd 24 WGATE
25 Gnd 26 TRK0 27 Gnd 28 WRTPRT
29 ID0 30 RDATA 31 Gnd 32 HDSEL
33 ID1 34 DSKCHG —— ——
4.6 Parallel Bus Connector Pinouts
Table 4–6 shows the parallel bus connector pinouts.
Table 4–6 Parallel Bus Connector Pinouts (J13)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 STB 2 PD0 3 PD1 4 PD2
5 PD3 6 PD4 7 PD5 8 PD6
9 PD7 10 ACK 11 BUSY 12 PE
13 SLCT 14 AFD 15 ERR 16 INIT
17 SLIN 18 Gnd 19 Gnd 20 Gnd
21 Gnd 22 Gnd 23 Gnd 24 Gnd
25 Gnd — — —— ——
4–6 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
Page 27

COM1/COM2 Serial Line Connector Pinouts
4.7 COM1/COM2 Serial Line Connector Pinouts
Table 4–7 shows the COM1/COM2 serial line connector pinouts.
Table 4–7 COM1/COM2 Serial Line Connector Pinouts (J3)
COM1 Pin
(Top) COM1 Signal
1 DCD1 1 DCD2
2 RxD1 2 RxD2
3 TxD1 3 TxD2
4 DTR1 4 DTR2
5 SG1 5 SG2
6 DSR1 6 DSR2
7 RTS1 7 RTS2
8 CTS1 8 CTS2
9 RI1 9 RI2
COM2 Pin
(Bottom) COM2 Signal
4.8 Keyboard/Mouse Connector Pinouts
Table 4–8 shows the keyboard/mouse connector pinouts.
Table 4–8 Keyboard/Mouse Connector Pinouts (J4)
Keyboard Pin
(Top) Keyboard Signal
1 KBDATA 1 MSDATA
2NC 2NC
3Gnd 3 Gnd
4 Vdd 4 Vdd
5 KBCLK 5 MSCLK
6NC 6NC
Mouse Pin
(Bottom) Mouse Signal
AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts 4–7
Page 28

SROM Test Data Input Connector Pinouts
4.9 SROM Test Data Input Connector Pinouts
Table 4–9 shows the SROM test data input connector pinouts.
Table 4–9 SROM Test Data Input Connector Pinouts (J21)
Pin Signal Description
1NC —
2SROM_CLK_L Clock out
3 Gnd —
4NC —
5TEST_SROM_D_L SROM serial data in
6NC —
4.10 Input Power Connector Pinouts
Table 4–10 shows the input power connector pinouts.
Table 4–10 Input Power Connector Pinouts (J2)
Pin Voltage Pin Voltage Pin Voltage Pin Voltage
1 +3.3 V dc 2 +3.3 V dc 3 Gnd 4+5 V dc
5Gnd 6+5 V dc 7Gnd 8 P_DCOK
9 5 V SB 10 +12 V dc 11 +3.3 V dc 12 –12 V dc
13 Gnd 14 PS_ON 15 Gnd 16 Gnd
17 Gnd 18 –5 V dc 19 +5 V dc 20 +5 V dc
1
This pinout is ATX-compliant.
1
4.11 Enclosure Fan Power Conn ector Pinouts
Table 4–11 shows the enclosure fan power connector pinouts.
Table 4–11 Enclosure Fan (+12 V dc) Power Connector Pinouts (J16)
Pin Voltage
1 Gnd
2 +12 V dc
3 Gnd
4–8 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
Page 29

Microprocessor Fan Power Connector Pinouts
4.12 Microprocessor Fan Power Connector Pinouts
Table 4–12 shows the microprocessor fan power connector pinouts.
Table 4–12 Microprocessor Fan Power Connector Pinouts (J14)
Pin Signal Description
1 +12 V dc —
2 FAN_CONN_L Fan connected
3 Gnd —
4.13 Soft Power Connector Pinouts
Table 4–13 shows the soft power connector pinouts.
Table 4–13 Soft Power Connector Pinouts (J1)
Pin Signal Description
1 Input System power on/off
2 Gnd —
4.14 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts
J20 is a multipurpose connector that provides pins for the following functions:
• System speaker
• LEDs for power and the EIDE drive
• Buttons for reset and halt
Table 4–14 shows the multipurpose connector pinouts, and Figure 4–1 shows the
connector layout.
Table 4–14 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts (J20)
Pin Signal Description
1 Gnd —
2 HALT_BUTTON Halt system
3 Gnd —
4 RESET_BUTTON Reset system
AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts 4–9
(Sheet 1 of 2)
Page 30

Multipurpose Connector Pinouts
Table 4–14 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts (J20)
Pin Signal Description
5 HD_PU Hard drive power-up
6 HD_LED Pull-up to Vdd
7 — No connection
8 POWER_LED_L Pull-up to Vdd
10, 12, 14, 16 Gnd —
9 SPKR Speaker output
15 Vdd —
11, 13 — No connection
Figure 4–1 Multipurpose Connector Pinouts
J20
HD_PU
12
3
56
78
4
HALT_BUTTON
RESET_BUTTON
HD_LED
POWER_LED_L
(Sheet 2 of 2)
SPKR
Vdd
4–10 AlphaPC 164SX Connector Pinouts
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
Page 31

Memory and Microprocessor Configuration
For higher system speed or greater throughput, SDRAM memory can be upgraded
by replacing DIMMs with those of greater si ze.
When configuring or upgrading SDRAM, observe the following rules:
• Each DIMM must be a 168-bit unbuf fered version and have a frequency of
100 MHz.
• Each bank consists of two DIMMs and must be fully populated.
• Both DIMMs in the same bank must be of equal size.
5.1 Configuring SDRAM Memory
Although not an exhaustive list, Table 5–1 lists the tested SDRAM memory
configurations avail able. As additional conf igurations become available, they will be
posted in online revi sions of this manual on the Alpha OEM World Wide Web
Internet site. See Appendix A for the URL.
For a list of vendors who supply components and accessories for the
AlphaPC 164SX, see Appendix A.
5
Refer to Figure 2–1 for DIMM connector locations.
Note: 1Mb × 72 and 1Mb × 64 DIMMs are not supported.
Memory and Microprocessor Configuration 5–1
Page 32

Upgrading SDRAM Memory
Table 5–1 AlphaPC 164SX SDRAM Memory Configurations
Total Memory J7 J8 J9 J10
32MB 2Mb × 72 2Mb × 72 ——
Bank 0
1
Bank 1
1
64MB 2Mb
96MB 4Mb
128MB 4Mb
160MB 8Mb
192MB 8Mb
256MB 8Mb
512MB 16Mb
1
64-bit-wide DIMMs can also be used.
× 72 2Mb × 72 2Mb × 72 2Mb × 72
4Mb
× 72 4Mb × 72 ——
× 72 4Mb × 72 2Mb × 72 2Mb × 72
× 72 4Mb × 72 4Mb × 72 4Mb × 72
8Mb
× 72 8Mb × 72 ——
× 72 8Mb × 72 2Mb × 72 2Mb × 72
× 72 8Mb × 72 4Mb × 72 4Mb × 72
× 72 8Mb × 72 8Mb × 72 8Mb × 72
16Mb
× 72 16Mb × 72 ——
× 72 16Mb × 72 16Mb × 72 16Mb × 72
5.2 Upgrading SDRAM Memory
You can upgrade memory in the AlphaPC 164SX by adding more DIMMs or
replacing the ones you have with a greater size. Refer to Figure 2–1 for DIMM
connector locations.
Use the following general guidelines:
1. Observe antistatic precautions. Handle DIMMs only at the edges to prevent
damage.
2. Remove power from the system.
5–2 Memory and Microprocessor Configuration
Page 33

Increasing Microprocessor Speed
3. Align the DIMM so that the notch in the DIMM matches the key in the socket.
4. Firmly push the DIMM st ra igh t into the connector. Ens ur e t hat t he DIMM snaps
into the plastic locking levers on both ends.
5. Restore power to the system.
5.3 Increasing Microprocessor Speed
This section describes how to complete the following actions to increase
microprocessor speed:
• Replace the Alpha 21 164PC mi croproces sor wit h an Alpha chip t hat has a higher
speed rating.
• Reconfigure the clock divisor switches.
5.3.1 Preparatory Information
Caution: Static-Sensitive Component – Due to the sensitive nature of electronic
components to static electricity, anyone handling the microprocessor
must wear a properly grounded antistatic wriststrap. Use of antistatic
mats, ESD approved workstations, or exercising other good ESD practices is recommended.
An Alpha 21164PC mic roprocess or with a higher speed rating is ava ilable from your
local distributor. See Appendix A for information about supporting products.
When replacing the microprocessor chip, also replace the thermal conducting
GRAFOIL pad. See Appendix A for information about the parts kit, which includes
the heat sink, GRAFOIL pad, two hex nuts, heat-sink clips, 52-mm fan, and four
screws.
5.3.2 Required Tools
The following tools are required when replacing the microprocessor chip:
A TS30 manual nut/torque driver (or equivalent) with the following attachments is
required to affix the heat sink and fan to the microprocessor’s IPGA package:
• 1/4-inch hex bit
• 3/8-inch socket with 1/4-inch hex drive
• #2 Phillips-head screwdriver bit
Memory and Microprocessor Configuration 5–3
Page 34

Increasing Microprocessor Speed
5.3.3 Removing the 21164PC Microprocessor
Remove the microprocessor currently in place at location U31 by performing the
following st eps:
1. Unplug the fan power/sensor cable from connector J14 (see Figure 2–1).
2. Remove the four 6–32 × 0.625-inch screws that secure the fan to the heat sink.
3. Remove the fan.
4. If the sink/chip/fan cl ip is used, r emove it by unhookin g its ends fr om around the
ZIF socket retainers.
5. Using a 3/8-inch socket, re move the two nu ts secu ring th e heat si nk to the microprocessor studs.
6. Remove the heat sink by gently lifting it off the microprocessor.
7. Remove and discard the GRAFOIL heat conduction pad.
8. Thoroughly clean the bottom surface of the heat sink before affixing it to the
new microprocessor.
9. Lift the ZIF socket actuator handle to a full 90° angle.
10. Remove the microprocessor chip by lifting it straight out of the socket.
5.3.4 Installing the 21164PC Microprocessor
Install the new microprocessor in location U31 by performing the following steps:
Note: Install the heat sink on ly aft er t he micro pro cessor has be en ass emble d to
the ZIF socket.
1. Observe antistatic precautions.
2. Lift the ZIF socket actuator handle to a full 90° angle.
3. Ensure that all the pins on the microprocessor package are straight.
4. The ZIF socket and microprocessor are keyed to al low for proper installation.
Align the microprocessor, with its missing AD01 pin, with the corresponding
plugged AD01 position on the ZIF socket. Gently lower into position.
5. Close the ZIF socket actuator handle to its locked position.
6. Install the heat sink and heat-sink fan as directed in the following steps. A heatsink/fan kit is available from the vendor listed in Appendix A. Refer to
Figure 5–1 for heat-sink and fan assembly details.
5–4 Memory and Microprocessor Configuration
Page 35

Figure 5–1 Fan/Heat-Sink Assembly
Increasing Microprocessor Speed
Screw, 6–32 × 0.625 in
Qty 4
Torque to 3
Fan
Clip, Heat-Sink/Chip/Fan
Nut, Hex,
Aluminum
Flats, Qty 2
Torque to15
Heat Sink, with Fan
Mounting Holes
±1 in-lb
±2 in-lb
Airflow
Thermal Pad
Alpha 21164PC
a. Put the GRAFOIL thermal pad in place. The GRAFOIL pad is used to
improve the thermal conductivity between the chip package and the heat
sink by replacing micro air pockets with a less insulative material. Perform
the following steps to position the GRAFOIL pad:
1. Perform a visual inspection of the package slug to ensure that it is free of
contamination.
2. Wearing clean gloves, pick up the GRAFOIL pad. Do not perform this
with bare hands because skin oils can be transferred to the pad.
3. Place the GRAFOIL pad on the gold-plated slug surface and align it with
the threaded studs.
Memory and Microprocessor Configuration 5–5
Page 36

Increasing Microprocessor Speed
b. Attach the microprocessor heat sink. The heat-sink material is clear
anodized, hot-water -sealed, 60 61-T6 aluminum. The nut mat erial is 201 1-T3
aluminum (this grade is critical). Perform the following steps to attach the
heat sink:
1. Observe antistatic precautions.
2. Align the heat-sink holes with the threaded studs on the ceramic package.
3. Handle the heat sink by the edges and lower it onto the chip package,
taking care not to damage the stud threads.
4. Set a calibrated torque driver to 15 in-lb, ±2 in-lb, (2.3 Nm, ±0.2 Nm).
The torque driver should have a mounted 3/8-inch socket.
5. Insert a nut into the 3/8-inch socket, place on on e of t he studs, and tighten
to the specified torque. Repeat for the second nut.
6. If the sink/chip/fan clip is used, properly install it by positioning it over
the assembly and hooking its ends around the ZIF socket retainers.
c. Attach the heat-sink fan assembly:
1. Place the fan assembly on top of the heat sink, aligning the fan mounting
holes with the corresponding threaded heat-s ink holes. Align the fan so
that the fan power/sensor wires exit the fan closest to connector J14 (see
Figure 2–1). Fan airflow must be directed into the heat sink (fan label facing down toward the heat sink).
2. Using a calibrated torque driver set to 3 in-lb, ±1 in-lb, secure the fan to
the heat sink with four 6–32 × 0.625-inch screws.
3. Plug the fan power/sensor cable into connect or J14.
Note: When installing the microprocessor, you must change the frequency of
its clock output by setting the system clock divisor switches, as
described in Section 3.2.
5–6 Memory and Microprocessor Configuration
Page 37

This section lists the system and I/O interrupt assignments. It also lists the physical
AlphaPC 164SX I/O space assignments.
6.1 Interrupts
Table 6–1 lists each AlphaPC 164SX ISA interrupt and its source.
6
Interrupts and ISA Bus Addresses
Table 6–1 ISA Interrupts
Interrupt Number Interrupt Source
IRQ0 Internal timer 1
IRQ1 Keyboard
IRQ2 Interrupt from controller 2
IRQ3 COM2
IRQ4 COM1
IRQ5 Available
IRQ6 Diskette (floppy)
IRQ7 Parallel port
1
IRQ8#
IRQ9 Available
IRQ10 USB
IRQ11 Available
IRQ12 Mouse
Reserved
(Sheet 1 of 2)
Interrupts and ISA Bus Addresses 6–1
Page 38

ISA I/O Address Map
Table 6–1 ISA Interrupts
Interrupt Number Interrupt Source
IRQ13 Available
IRQ14 EIDE
IRQ15 EIDE
1
The # symbol indicates an active low signal.
6.2 ISA I/O Address Map
Table 6–2 lists the AlphaPC 164SX ISA I/O space address mapping.
Table 6–2 ISA I/O Address Map
Range (hex) Usage
000-00F 8237 DMA #1
020-021 8259 PIC #1
040-043 8253 timer
060-061 Ubus IRQ12 and NMI control
070 CMOS RAM address and NMI mask register
080-08F DMA page registers
(Sheet 2 of 2)
0A0-0A1 8259 PIC #2
0C0-0DF 8237 DMA #2
2F8-2FF Serial port—COM2
370-377 Secondary diskette (floppy)
3BC-3BF Parallel port—LPT1
3F0-3F7 Primary diskette (floppy)
3F8-3FF Serial port—CO M1
6–2 Interrupts and ISA Bus Addresses
Page 39

Alpha SRM Console Firmware
The Alpha SRM Console firmware initializes the system and enables you to install
and boot the DIGITAL UNIX operating system. This firmware resides in the flash
ROM on the AlphaPC 164SX motherboard.
7.1 Alpha SRM Console Firmware Conventions
The following conventions are used in this section:
Convention Description
7
>>>
Backslash (\) at the end of a line Continuation symbol to continue lo ng commands
_>
Maximum command length 255 characters.
Multiple contiguous spaces or tabs Treated as a single space.
Command abbreviations Allowed, if not ambiguous.
Command qualifiers or options Prefix with a space and a dash (-).
Numbers Hexadecimal, unless otherwise specified.
Alpha SRM Console prompt.
on the next line.
Continuation line prompt.
(Registers, such as R0–R31, are shown in
decimal notation.)
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–1
Page 40

Alpha SRM Console Firmware Conventions
The following table lists Alpha SRM Cons ole speci al keys and thei r funct ions. These
special keys, also referred to as shortcut keys, provide command recall, line editing,
and basic input/output control flow.
Shortcut Key Function
Enter
Backspace or
Delete
Ctrl/A
Ctrl/B
Up arrow
Down arrow
Ctrl/C
Ctrl/D
Left arrow
Ctrl/E
Ctrl/F
Right arrow
Ctrl/H
Ctrl/O
Ctrl/Q
Ctrl/R
Ctrl/S
Ctrl/U
Terminate the command line input.
Delete one character to the left of the cursor.
Toggles insert/overstrike mode. (Overstrike is the defau lt.)
Recall previous commands. (The last 16 commands are
stored.)
Terminate the foreground process.
Move the cursor one position to the left.
Move the cursor to the end of the line.
Move the cursor one position to the right.
Move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
Suppress or resume (toggle) console output.
Resume the flow (XON) of data to the console.
Retype the current command line.
Stop the flow (XOFF) of data to the console.
Delete the entire line.
7–2 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 41

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
7.2 Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
This section describes the following basic Alpha SRM Console commands that are
necessary to boot the DIGITAL UNIX operating system:
• arc
• boot
• deposit
• examine
• fwupdate
• set
• show
The Alpha SRM Console offers additional commands. For a complete list of Alpha
SRM Console commands, enter
help at the Alpha SRM Console prompt (>>>).
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–3
Page 42

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
arc
Loads and runs the AlphaBIOS fi rmware update utility from a
diskette.
Syntax
arc
nt
Arguments
None
Options
None
Description
None
Examples
Either of the following commands load and run the AlphaBIOS
firmware update utility from a diskette:
>>>arc
or
>>>nt
7–4 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 43

boot
Syntax
Arguments
Options
Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Initializes the processor, loads a program image fr om the specified
boot device, and transfers control to the loaded image.
boot [-file <filename>] [-flags
<longword>[,<longword>]]
[-protocols <enet_protocol>] [-halt]
[<boot_device>]
<boot_device>
A device path or list of devices from which the fir mware will att empt
to boot. Use the set bootdef_dev command to set an
environment variable that specifies a default boot device.
boot Command Option Description
-file <filename>
-flags
<longword> [,<longword>]
-protocols
<enet_protocol>
-halt
Specifies the name of a file to load into the system. Use
the set boot_file command to set the
environment variable that specifies a default boot file.
Specifies additional information for the operating
system. For DIGITAL UNIX systems, the following
values may be used:
Use the set boot_osflags command to set an
environment variable that specifies a default boot flag
value.
Specifies the Ethernet protocols that will be used for a
network boot. Values may be mop or bootp.
Forces the bootstrap operation to halt and invoke the
console program after the image is loaded and the p age
tables and other data structures are set up.
i = Interactive boot
s = Boot to single user
a = Autoboot to multiuser
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–5
Page 44

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Description
The boot command init ializes the processor, loa ds a program image
from the specified boot device, and transfers control to tha t image. If
you do not specify a boot device in the command line, the default
boot device is used. The default boot device is determined by the
value of the bootdef_dev environment variable.
If you specify a list of devices, a bootstrap is attempted from each
device in th e order in wh ich the device is listed. Then control p asses
to the first successfully booted image. In a list, always enter network
devices last because network bootstraps terminat e o nly if a fata l erro r
occurs or if an image is successfully loaded.
The -flags option can pass additional information to the operating
system about the boot that you are requesting. On an OpenVMS
system, the -flags option specifies the system root number and
boot flags. If you do not spec ify a boot flag qualifier, the default boot
flag’s value specified by the boot_osflags environment variable is
used.
The -protocols option allows selection of either the DECnet
MOP or the TCP/IP BOOTP network protocols. The keywords mop
and bootp are valid arguments for this option. It is possible to set the
default protocol for a port by setting the environment variable
ewa0_protocols or era0_protocols to the appropriate protocol.
Explicitly stating the boot flags or the boot device overrides the
current default valu e for the curr ent boo t req uest , but does not c hange
the corresponding environment variable.
See the Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands
section in this chapter for more information about environment
variables.
7–6 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 45

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Examples
boot Command Example Description
>>>boot
>>>boot ewa0
>>>boot -file dec2.sys ewa0
>>>boot -protocol bootp ewa0
>>>boot -flags 0,1
>>>boot -halt dka0
Boots the system from the d e fault boo t devi ce.
Boots the system from Ethernet port ewa0.
Boots the file named dec2.sys from Ethernet
port ewa0.
Boots the system using th e T CP/IP BOOTP
protocol from Ethernet port ewa0.
Boots the system from t he defau lt boot device
using flag setting 0,1.
Loads the bootstrap image from disk dka0,
halts the bootstrap operation, and invokes the
console program. Subsequently, you can enter
continue to transfer control to the operating
system.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–7
Page 46

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
deposit
Writes data to the specified address.
Syntax
deposit [-{b,w,l,q,o,h}] [{physical, virtual, gpr,
fpr, ipr}] [-n <count>] [-s <step>]
[<device>:]<address> <data>
Arguments
<device>:
The optional device name (or address space) selects the device to
access. The following platform-independent devices are supported:
• pmem
Physical memory.
• vmem
Virtual memory. All access and protection checking occur.
If the access is not allowed to a progr am running with the
current processor status (PS), the console issues an error
message. If memory mapping is not enabled, virtual
addresses are equal to physic al addr esses.
<address>
An address that specifies the offset within a device into which data is
deposited. The address may be any legal symbolic address.
Valid symbolic addresses are shown in the following table.
Symbolic
Address Description
gpr-name
ipr-name
PC
+
7–8 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Represents general-purpose register.
Represents internal processor register.
Program counter.
The location immediately following the last location referenced by
examine or deposit.
Page 47

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Symbolic
Address Description
-
The location immediately preceding the last location referenced by
examine or deposit.
*
@
The location last referenced by examine or deposit.
The location addressed by the last location referenced by examine or
deposit.
<data>
The data to be deposited.
Options
deposit Command Option Description
-b
-w
-l
-q
-o
-h
Specifies data type is byte.
Specifies data type is word.
Specifies data type is longword.
Specifies data type is quadword.
Specifies data type is octaword.
Specifies data type is hexword.
-physical
-virtual
-gpr
-fpr
-ipr
-n <count>
-s <step>
References physical address space.
References virtual address space.
References general-purpose register address space.
References floating-point register address space.
References internal processor register address space.
Specifies the number of consecutive locations to
examine.
Specifies the address increment as a hexadecimal value.
This option allows you to override the increment that is
normally derived from the data size.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–9
Page 48

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Description
The deposit command writes data t o the s pecifi ed addr ess, s uch as
a memory location, register, device, or file. The defaults for address
space, data size, and address are the last specified values. After
initializat ion, the default for address space is physical memory; for
data size, the default is a quadword; and for address, the default is
zero.
An address or device can be specified by concatenating the device
name with the address. For example, use pmem:0 and specify the
size of the address space to be written. If a conflicting device,
address, or data size is specified, the console ignores the command
and issues an error response.
Examples
deposit Command Example Description
>>>d -n 1ff pmem:0 0
>>>d -l -n 3 pmem:1234 5
>>>d -n 8 r0 ffffffff
>>>d -l -n 10 -s 200 pmem:0 8
7–10 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Clears the first 512 bytes of physical
memory.
Writes the value 5 into four longwords,
starting at physical memory address 1234.
Loads GPRs R0 through R8 with -1.
Writes the value 8 in the first longword of
the first 17 pages in physical memory.
Page 49

examine
Syntax
Arguments
Options
Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Displays the contents of the specified address.
examine [-{b,w,l,q,o,h,d}] [-{physical, virtual,
gpr, fpr, ipr}] [-n <count>] [-s <step>]
[<device>:]<address>
<device>:
The optional device name (or address space) selects the device to
access.
<address>
The address specifies the first location to examine within the current
device. The address can be any legal address specified.
examine Command Option Description
-b
-w
-l
-q
-o
-h
-d
-physical
-virtual
-gpr
-fpr
Specifies data type is byte.
Specifies data type is word.
Specifies data type is longword.
Specifies data type is quadword.
Specifies data type is octaword.
Specifies data type is hexword.
Specifies the data displayed is the decoded macro
instruction. The Alpha instruction decode (-d) does not
recognize machine-specific PALcode instructions.
References physical address space.
References virtual address space.
References general-purpose register address space.
References floating-point register address space.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–11
Page 50

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
examine Command Option Description
-ipr
-n <count>
-s <step>
Description
References internal processor register address space.
Specifies the number of consecutive locations to
examine.
Specifies the address increment as a hexadecimal value.
This option allows you to override the increment that is
normally derived from the data size.
The examine command disp lays the contents of the s pecified
address, such as a memory location, register, device, or file. The
defaults for addres s space, data siz e, and addre ss are the last specifie d
values. After initialization, the default for address space is physical
memory; for data size, the default is a quadword; and for address, the
default is zero.
An address or device can be specified by concatenating the device
name with the address. For example, use pmem:0 and specify the
size of the address space to be displayed. If a conflicting device,
address, or data size is specified, the console ignores the command
and issues an error response.
The display line cons ists of the devic e name, the he xadecimal address
(or offset within the device), and the examined data (also in
hexadecimal).
The examine command supp orts t he same o ptions as the deposit
command. Additionally , the examine command supports inst ruction
decoding with the -d option, which disassembles instructions
beginning at the current address.
7–12 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 51

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Examples
examine Command
Example Display Description
>>>e r0 gpr: 0 (R0) 0000000000000002
>>>e -g 0 gpr: 0 (R0) 0000000000000002
>>>e grp:0 gpr: 0 (R0) 0000000000000002
>>>examine -n 5 r7 gpr: 38 (R7) 0000000000000000
gpr: 40 (R8) 0000000000000000
gpr: 48 (R9) 0000000000000000
gpr: 50 (R10) 000000007FFBF800
gpr: 58 (R11) 000000007FF781A2
gpr: 60 (R12) 0000000000000000
>>>examine ipr:11 ipr 11 (KSP) FFFFFFFF8228DFD0
Examines the
contents of R0,
using a symbolic
address.
Examines the
contents of R0,
using address
space.
Examines the
contents of R0,
using a device
name.
Examines the
contents of R7
and the next five
registers.
Examines the
contents of
internal
processor
register 11.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–13
Page 52

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
fwupdate
Loads and runs the AlphaBIOS fi rmware update utility from a
diskette.
Syntax
fwupdate
Arguments
None
Options
None
Description
The fwupdate command script is used to load and run the
AlphaBIOS firmware update utility from a diskette. The file
fwupdate.exe is extracted from a diskette with a FAT file structure.
This executable is then loaded to physical address 900000 and is
executed in PALmode.
Examples
The following fwupdate command script loads and runs the
AlphaBIOS firmware update utility from a diskette:
>>>fwupdate
7–14 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 53

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
set
Sets or modifies the value of an environment variable.
Syntax
set <envar> <value> [-default] [-integer] [-string]
Arguments
<envar>
The environment variable to be assigned a new value.
<value>
The value that is assigne d to the environmen t varia ble. It can be e ither
a numeric value or an ASCII string.
Options
set Command Option Description
-default
-integer
-string
Description
Restores an environment variable to its default value.
Creates an environment variable as an integer.
Creates an environment variable as a string.
The set command is used to set or modify the value of an
environment variable. Environment variables are used to pass
configuration information between the console and the operating
system. See Section 7.3 for more information about environment
variables.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–15
Page 54

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
Examples
set Command Example Description
>>>set bootdef_dev ewa0
>>>set auto_action boot
>>>set boot_osflags 0,1
>>>set foobar 5
Modifies the default boot device to ewa0.
Attempts to boot the operating system following an
error, halt, or power-up.
Modifies the default boot flags to 0,1.
Creates an environment variable called foobar and
gives it a value of 5.
7–16 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 55

Basic Alpha SRM Console Command Descriptions
show
Displays the current value of the specified environment variable or
information about the system.
Syntax
show [{config, device [device_name], iobq, hwrpb,
map, memory, pal, version, <envar>...}]
Arguments
show Command Argument Description
config
device [device name]
iobq
hwrpb
map
memory
pal
version
<envar>
Options
None
Description
Displays the current memory configuration, PCI logical
slots, and ISA logical slots.
Displays the devices and controllers in the system.
Specifying a device name returns information on that
device only.
Displays the input/outpu t counter blocks.
Displays the hardware restart parameter block.
Displays the system virtual m e mory map.
Displays the memory module config uration.
Displays the version of DIGITAL UNIX PALcode.
Displays the version of the console.
Displays the current value of a specified environment
variable.
The show command displays information about the system and the
current value of a specified environment variable. See
Section 7.3
for more information about environment variables.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–17
Page 56

Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands
Examples
show Command Example Description
>>>show device
dka0.0.0.6.0 DKA0 RZ26L 441A
dka400.4.0.6.0 DKA400 RRD43 3213
dva0.0.0.0.1 DVA0
ewa0.0.0.12.0 EWA0 08-00-2B-E2-1C-25
pka0.7.0.6.0 PKA0 SCSI Bus ID 7
>>>show memory
48 Meg of System Memory
>>>show *
(refer to Section 7.3)
>>>show boot*
(refer to Section 7.3)
Lists device information, such as
system designation, drive model,
or Ethernet address.
Lists system random-access
memory (RAM) size.
Lists all environment variables
and their settings.
Lists all environment variables,
beginning with boot.
7.3 Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console
Commands
This section describes environment variables that are used to define the system
operational stat e and to pass information between the firmware and the operating
system.
7.3.1 Environment Variable Descriptions
Environment variables are classified as either Alpha SRM Console architecturerequired or system-defined.
7–18 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 57

Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands
7.3.1.1 Architecture-Required Environment Variables
The following table shows common Alpha SRM Console architecture-required
environmen t variables and their descriptions. For a complete list, en ter show * at
the Alpha SRM Console prompt.
Architecture-Required Environment
Variable Description
auto_action
boot_file
boot_osflags
bootdef_dev
When used with the set or show command, this
variable modifies or displays the console action
that follows an error, halt, or power-up. The
action can be halt, boot, or restart. The default is
halt.
When used with the set or show command, this
variable modifies or displays the file name to be
used when a bootstrap requires a file name. The
default is null.
When used with the set or show command, this
variable modifies or displays the additional
parameters to be passed to system software. The
default is 0.
When used with the set or show command, this
variable modifies or displays the default device
or device list from which the system will attempt
to boot. If the system software is preloaded, the
variable is preset to point to the dev ice containing
the preloaded software. The default is null.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–19
Page 58

Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands
7.3.1.2 System-Defined Environment Variables
The following table shows common Alpha SRM Console system-defined
environmen t variables and their descriptions. For a complete list, en ter show * at
the Alpha SRM Console prompt.
System-Defined
Environment Variable Description
console
control_scsi_term
ewa0_mode
os_type
pci_parity
oem_string
When used with the set command, this variable modifies
the console output to either the serial port or the graphics
controller.
This variable is unused in the motherboard system.
This variable determines if the AUI (ThinWire) or the
twisted-pair Ethernet ports will be enabled. AUI is the
default. (Autosensing is not supported.)
When used with the set or show command, this variable
modifies or displays the specified firmware that will be
loaded on the next power cycle. Specify the value osf or
UNIX to select the Alpha SRM Console.
This variable controls PCI parity checking. The possible
values are:
on = Parity checking is enabled.
off = Parity checking is disabled; this is the
default.
sniff = Parity checking is enabled or disabled
depending on the PCI device.
When used with the set or show command, this variable
modifies or displays a text string that identifies the product
name in the Alpha SRM Console banner.
7–20 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 59

Environment Variables for Alpha SRM Console Commands
System-Defined
Environment Variable Description
language n
The language environment variable assigns language n to
the system (wher e n is the option number of a language listed
in the menu that follows). Use the following procedure to
select the language:
1. At the Alpha SRM Console prompt, enter the following
commands:
>>>set language 0
>>>init
The following menu and prompt are displayed :
n
Language
n
Language
=======================================
0 none (display menu) 40 Français (Suisse Romande)
30 Dansk 42 Italiano
32 Deutsch 44 Nederlands
34 Deutsch (Schweiz) 46 Norsk
36 English (American) 48 Portugues
38 English (British/Irish) 4A Suo mi
3A Español 4C Svenska
3C Français 4E Vlaams
3E Français (Canadian)
(1..16):
2. Enter the number that corresponds to the language that you
want to use. The following example shows how to assign
the English (American) language to the system:
(1..16):36
3. When you receive a message to reset the system, power
cycle the system.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–21
Page 60

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
7.4 Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update
the Flash ROM
Use the AlphaBIOS firmware update utility to update the fi rmware in a flash ROM.
7.4.1 AlphaBIOS Conventions
AlphaBIOS uses universally accepted keys and key combinations for navi gating the
interface and selecting items. If you are familiar with MS-DOS or Microsoft
Windows key board conventions, navigating AlphaBIOS is simple. Use the keys and
key combinations shown in Table 7–1 when navigating and selecting items in
AlphaBIOS.
Table 7–1 AlphaBIOS Keys
Key or Key Combination Description
Tab Move highlight forward between fields of a dialog.
Shift + Tab Move highlight backwards between fields of a dialog.
↓ or ↑ Move highlight within a menu, or cycle through available field
values in a dialog window.
Alt + ↓ Drop down a menu of choices from a drop-down listbox. A
Home Move to the beginning of a text-entry field.
End Move to the end of a text-entry field.
← or → Move to the left or right in a text-entry field.
Esc Discard changes and back up to previous screen.
Two levels of keyboard help are available:
• Press F1 once to display explanations of the keystrokes available for the
currently displayed part of AlphaBIOS.
• Press F1 twice to display e xplanat ions of the keys tr okes ava ilabl e for na vig ating
throughout AlphaBIOS.
7–22 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
drop-down listbox can be recognized by the symbo l ⇓.
Page 61

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
7.4.2 Starting the AlphaBIOS
To start the AlphaBIOS, follow this procedure:
1. Insert the AlphaBIOS diskette into diskette drive A.
2. At the Alpha SRM Console prompt, enter the following command:
>>>fwupdate
Note:
Because the firmware update utility reinitializes some system components, it may appear as if your system is restarting.
Figure 7–1 shows an example of the AlphaBIOS Boot screen with the “Press
<F2> to enter SETUP” message at the bottom.
Figure 7–1 AlphaBIOS Boot Screen
AlphaBIOS Version 5.60
Please select the operating system to start:
Windows NT Workstation 4.00
Press Enter to choose.
digital
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
3. Press F2 to start the AlphaBIOS setup program.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–23
Page 62

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
7.4.3 Installing Alpha SRM Console Using AlphaBIOS Setup Program
Figure 7–2 shows an example of the AlphaBIOS Setup screen. Select the
AlphaBIOS Upgrade... option by using the arrow or Tab keys.
Figure 7–2 AlphaBIOS Setup Screen
Press Enter to begin installing the SRM Console firmware image.
7–24 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 63

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
Figure 7–3 shows an example of the AlphaBIOS Upgrade Options screen. If more
than one image is found, the new image's name is displayed. If the name of the new
image is not SRM Console, use the down arrow key to cycle through the available
field values until SRM Console is displayed.
Figure 7–3 AlphaBIOS Upgrade Options Screen
Press Enter to continue the installation.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–25
Page 64

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
Figure 7–4 shows an example of th e AlphaBIOS screen that warn s you that you ha ve
selected to switch the operating system.
Figure 7–4 AlphaBIOS Warning Screen
Press Enter to continue the installation.
7–26 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 65

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
A screen similar to Figure 7–5 is displayed. The version numbers shown on your
screen may be different than those shown in Figure 7–5.
Figure 7–5 AlphaBIOS Upgrade SRM Console Screen
Press F10 to continue the installation.
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–27
Page 66

Using the AlphaBIOS Firmware Update Utility to Update the Flash ROM
Figure 7–6 shows an example of the AlphaBIOS Upgrade Complete screen.
Figure 7–6 AlphaBIOS Upgrade Complete Screen
To load the SRM Console, power-cycle the system.
7–28 Alpha SRM Console Firmware
Page 67

Installing the DIGITAL UNIX Operating System
7.5 Installing the DIGITAL UNIX Operating System
Note: DIGITAL UNIX Version 4.0D is the minimum revision required for the
AlphaPC 164SX motherboard system.
This section supplements the DIGITAL UNIX Installation Guide for installing the
DIGITAL UNIX operating system on an AlphaPC 164SX motherboard system.
Note: If you already have a previo us version of DIGITAL UNI X ins ta ll ed, s ee
the DIGITAL UNIX Installation Guide for information on h ow to
upgrade to a new version of the operat ing syste m. Be sure to revi ew the
preinstallation tasks, which are covered in the DIGITAL UNIX
Installation Guide.
7.5.1 Requirements
You need the followin g hardware and software to install the DIGITAL UNIX
operating system on an AlphaPC 164SX motherboard system:
• A minimum of 32MB of main memory; 64MB is recommended
• A 1GB (or larger) SCSI or EIDE hard disk capable of storing the supported
software su bsets
• Supported load devices
– SCSI CD–ROM drive capable of reliably reading in 512-byte block mode
or
– EIDE (ATAPI) CD–ROM drive
or
– A network inte rface
• A console terminal with ASCII capabili ty or a supported graphics display
console
• DIGITAL UNIX Version 4.0D or higher Operating System Volume 1 compact
disc
• Alpha SRM Console Version 4.9 or higher
Alpha SRM Console Firmware 7–29
Page 68

Page 69

This chapter contains information about troubleshooting hardware and software
during AlphaPC 164SX startup.
8.1 Hardware Startup
Use the following troubleshooting steps if video is not working on your system. If
you still have no video after reviewing these steps, please call your system vendor.
Troubleshooting Steps: No Video
1. Check t he connectio n to the ac ou tlet.
2. Check the voltage setting on the power supply (115 V ac in the U.S.).
3. Check that the frequency/switch selection matches the speed of the Alpha chip.
4. Check that the CPU fan is connected and spinning.
5. Ensure that the flash ROM update procedure was performed correctly. If you
have a terminal attached to COM1, check the output for error messages after
verifying that the flash ROM update procedure was performed correctly.
8
Troubleshooting
6. Reseat the video card and ensure that it is connected to the monitor.
7. Reseat the DIMMs.
8. Replace the DIMMs.
Troubleshooting 8–1
Page 70

Beep Codes
8.2 Beep Codes
The beep codes provide error information about the AlphaPC 164SX system.
Table 8–1 lists and describes the beep codes.
Table 8–1 Beep Codes
Beep Code Description
1–2–31 This sequence represents the fail-safe booter startup.
4 No valid header found in ROM; loading entire ROM.
5 No memory found.
6 Checksum error detected when image was read back from memory.
1
One beep and a pause, followed by two beeps and a pause, followed by three beeps.
8.3 Post Codes
The post codes indicate the progress of the SROM and SRM Console firmware.
Table 8–2 lists and describes the post codes.
Table 8–2 Post Codes
Source
SROM 00 Firmware initialization is complete
8–2 Troubleshooting
(Sheet 1 of 3)
Post Code
(hex) Description
01 CPU speed detected
02 CPU speed converted
03 Configuration jumpers read
04 Bcache configuration value computed
05 Bcache control value computed
0C Memory sized and memory bank 0 written
0D Enable Dcache
13 All of memory rewritten (good data parity written)
14 Memory errors cleared; start reading system ROM
15 Loading ROM without SROM decompression
16 Loading ROM using SROM decom pression
17 System ROM loaded to memory
18 Icache flush code written to memory
19 CPU errors cleared; jump to system code
20 ISA bus reset
Page 71

Post Codes
Table 8–2 Post Codes
Post Code
Source
(hex) Description
3A Jump to Mini-Debugger
3F Fatal error. Second code identifies source of error:
SRM
Console
FF
FE
FD Sem a phore initialization
FC Heap initialization
FB Heap initialization
FA Heap initialization
F9 Driver structure initialization
F8 Idle process PID initialization
F7 File system initialization
F6 Timer data structures initialization
F5 Lowering IPL
F4 Entering idle loop
F3 Creating task to deallocate dead PCBs
F2 Creating polling task
F1 Creating timer task
F0 Creating power-up task
EF Configuring memory
EE Phase 1 driver startup
ED Configuring the PCI/ISA bus
EC Phase 3 driver startup
EB Switchin g stdin/out/err to console terminal device
EA Phase 4 driver startup
E9 Building per CPU slot in the HWRPB
E8 SCSI class driver initialization
E7 Phase 5 driver startup
(Sheet 2 of 3)
05 = No memory found
06 = Checksum error detected when image was read back
from memory
Starting console
Idle PCB initialization
Fail-safe
booter
FD
FC
I/O bus initialization
I/O initialization complete
FB UART initialization
Troubleshooting 8–3
Page 72

Fail-Safe Booter
Table 8–2 Post Codes
Post Code
Source
(hex) Description
BF Fail-safe booter is scanning the diskette
1 Fail-safe booter is loading the AlphaBIOS
2 Fail-safe booter is loading the Debug Monitor
3 Fail-safe booter is loading the SRM console
4 Fail-safe booter is loading the Linux mini-loader
8.4 Fail-Safe Booter
The fail-safe booter provides an emergency recovery mechanism when the primary
firmware image cont ai ned i n f la sh me mo ry has been corrupted. When flash memory
has been corrupted, and no image can be loaded safely from the flash, you can run
the fail-safe booter and boot another image from a diskette that is capable of reprogramming the flash.
Starting the Fail-Safe Booter
You can start the fail-safe booter in one of two ways:
• If the primary firmware image is unavailable when the system is powered on or
reset, the fail-safe booter runs automatically. When the fail-safe booter runs, the
system emits a series of beeps through the speaker as beep code 1-2-3; that is,
one beep and a pause, followed by two beeps and a pause, followed by three
beeps. After the diskette activity light flashes, insert the AlphaPC 164SX SRM
Console Firmware diskette. The fail-safe booter will load and run the
AlphaBIOS firmware update utility from this diskette. Proceed to Section 7.4
and follow the procedur e for updating your flash ROM.
(Sheet 3 of 3)
• You can also start the fail-safe booter manually as follows:
1. Power off your system.
2. Slide switch CF7 to off, as described in Section 3.3.
3. Power on your system.
4. Insert the Al phaPC 16 4SX SRM Con sol e Fi rmware diskette into the diske tt e
drive.
5. Proceed to Section 7.4 and follow the procedures.
8–4 Troubleshooting
Page 73

9
Battery Recycle/Disposal Information
NOTICE
Recycle or dispose of batteries promptly in accordance with your organization’s
environmental policies. If this is a LITHIUM battery, the following additional
precautions may apply:
• Replace batteries correctly to prevent possible explosion.
• Replace batteries with the same or equivalent type.
• Prior to disposal or recycling, protect all batteries against accidental short cir-
cuiting by affi xing nonconductive tape across battery te rminals or conductive
surfaces.
• Keep batteries away from small children.
Battery Recycle/Disposal Information 9–1
Page 74

Page 75

Support, Products, and Document ation
A.1 Customer Support
The Alpha OEM website provides the following information for customer support.
URL Description
http://www.digital.com/alphaoem
Contains the following links:
• Developers’ Area: Development tools, code examples,
driver developers’ information, and technical white
papers
• Motherboard Products: Motherboard details and
performance information
• Microprocessor Products: Microprocessor details and
performance information
• News: Press releases
• Technical Informa tion: Motherboard firmware and
drivers, hardware compatibility lists, and product
documentation library
A
• Customer Support: Feedback form
Support, Products, and Documentation A–1
Page 76

Supporting Products
A.2 Supporting Products
This section lists sources for components and accessories that are not included with
the AlphaPC 164SX.
A.2.1 Memory
Dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) ar e available f rom a variety of vendors . For a
list of the qualified vendors, visit the Alpha OEM World Wide Web Internet site at
http://www.digital.com/alphaoem
Click on Technical Information.
Then click on
A.2.2 Thermal Products
Components included in this heat-sink and fan solution are heat sink, GRAFOIL
pad, two hex nuts, heat-sink clips, 52-mm fan, and four screws. These are available
from:
United Machine and Tool Design Company, Inc.
Alpha OEM Hardware Compatibility List.
18 River Road
P.O. Box 168
Fremont, NH 03044
Phone: 603-642-5040
Fax: 603-642-5819
PN 70-33148-01
A.2.3 Power Supply
An ATX form-factor power supply, suitable for use with the AlphaPC 164SX
(+3.3 V, +5 V, –5 V, +12 V, –12 V), is available from:
Quantum Power Labs, Inc.
1410 Gail Borden Place C-4
El Paso, TX 79935
Phone: 915-599-2688
Fax: 915-599-2699
PN AP2-5300FRV (300 W)
A–2 Support, Products, and Documentation
Page 77

Antec, Inc.
2859 Bayview Drive
Fremont, CA 94538
Phone: 510-770-1200, ext. 313
PN PP-253V (250 W)
A.2.4 Enclosure
An enclosure, suitable for housing the AlphaPC 164SX and its power supply, is
available from:
Delta Axxion Technology
1550 Northwestern
El Paso, TX 79912
Phone: 915-877-5288
PN DL17
A.3 Associated Documentation
You can order the following associated documentation directly from the vendor.
Associated Documentation
If you have feedback about the Alpha technical documentation, please send your
comments to
Title Vendor
Alpha Architecture Reference Manual
EY–W938E–DP
Alpha Architecture Handbook
EC–QD2KB–TE
Alpha 21164PC Microprocessor
Hardware Reference Manual
EC–R2W0A–TE
Alpha 21164PC Microprocessor Data Sheet
EC–R2W1A–TE
alpha.techdoc@compaq.com.
Call your sales office or call
Butterworth-Heinemann (DIGITAL Press)
at 1-800-366-266 5
Order online:
http://www.digital.com/alphaoem
See previous entry
See previous entry
Support, Products, and Documentation A–3
Page 78

Associated Documentation
Title Vendor
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.1
PCI Multimedia Design Guide, Revision 1.0
PCI System Design Guide
PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification,
Revision 1.0
PCI BIOS Spec ification, Revision 2.1
CY82C693U hyperCache/Stand-Alone PCI
Peripheral Controller with USB Data Sheet
Super I/O Floppy Disk Controller with Infrared
Support (FDC37C669) Data Sheet
PCI Special Interest Group
U.S. 1–800–433–5177
International 1–503–797–4207
Fax 1–503–234–6762
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation
3901 North First Street
San Jose, CA 95134
Phone: 1-800-858-1810
Standard Micros ystems Corporation
80 Arkay Drive
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Phone: 1-800-443-7364
Fax: 1-516-231-6004
A–4 Support, Products, and Documentation
 Loading...
Loading...