Page 1

Chapter 1: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
SCOPE
This document describes the functional specifications for the Compal NoteBook personal
computer ACY25 series. The system is hardware and software compatible with the IBM
PC/AT personal computer.
SYSTEM
• Intel Mobile P4 1.4G/1.5G/1.6G/1.7G/1.8G/1.9G/2.0GHz (μFCPGA CPU)
• SIS650(SIS315 VGA embedded)
• SB SIS961 for system controller, PCI controller, LPC, AC_link interface, IDE controller &
USB interface.
• SMSC LPC47N227 for FDC, one Serial ports and one Parallel port
• NS87591 for Keyboard Controller, Keyboard Scanner and Battery management Unit
• ENE CB1420 for Card Bus PCMCIA controller.
• Realtech ALC202A for AC97 codec
• Realtech 8100BL for On Board LAN controller
Memory
• Two 200-pin +2.5V DDR SO-DIMM connector, supporting PC1600/PC2100 DDR SDRM
memory card. Maximum upgradable to 1GMB by two 512MB DDR SO-DIMM modules.
128MB, 256MB, 512MB DDR SDRM RAM module.
• 512KB L2 Cache on CPU
BIOS
• 512KB Flash ROM for system and Keyboard BIOS (Bootblock)
a) Suspend to Disk
b) Password protection for System and HDD
c) PC99 and windows WinXP/W2K ready with PnP
d) ACPI compliant BIOS
e) Support windowXP
f) Various hot key for system control
Power
• The charging time from empty to full capacity 3hrs typical (system off), 6.0hrs typical
(system on) at room temperature. based on system loading.
• More than 300 charging / discharging cycles.
• 2.5hr battery mark operation time with PMU disable, APCI enabled and backlight adjusted
to 3/7 Maximum brightness.
• 8-cell Li-Ion of 18650 size battery pack with 57.7wh capacity
Chapter 1-1
Page 2

One 2.5" (9.5mm) up to 40GB Hard Disk
• Bus Master IDE
• Removable
• Support Ultra 100 synchronous DMA(ATA-100)
LAN on board 3COM Realtech 8100BL
Options
• Removable 2.5" IDE HDD, upto 40GB
• Removable Module : CD-ROM, DVD, CDRW, CDRW/DVD COMBO.
• MINI-PCI AC-Link soft modem
• 128MB/256MB/512MB PC1600/PC2100 DDR SO-DIMM modules
• LiIon Main Battery Pack
Touch Pad with two buttons(Standards Compliance)
• ACPI compliance
• Win XP and W2K hardware compliance
I/O Ports
• One 25 pins Parallel port, EPP/ECP Capability
• One 15 pins CRT port
• One 6 pins external PS2/AT full keyboard connector
• One Audio Microphone in, Line out port (with Digital volume control)
• Build in Microphone
• One 3 pins AC Adapter Jack
• One type III/Two type II PCMCIA Card Bus slots
• Three 4 pins USB port
• One RJ11/RJ45 for modem and LAN
PCMCIA Controller
• PC card 95 supported with one type III/two type II card sockets
• SRAM, OTPROM, FLASH ROM, mask ROM memory card up to 64MB
• MODEM/LAN card
• 32bit PCI bus
• Card bus card
Chapter 1-2
Page 3

Excellent Power Management Function
• Standby mode or Hibernation mode, by time out or by hot key
• Speedstep option
• HDD Local Stand-By mode by time out
• LCD Local Stand-By mode by time out
• Low battery alarm by beep and system window (power state indication using the 2 LED on
the palm rest add detail here)
• System status indicators
a) LED system window by 3 LED′s for Num Lock, Caps Lock, Scroll Lock display
b) 4 LED’S indicators
1) POWER: System Active - LED is solid green
Suspend - LED is solid amber
2) IDE : Action - LED flashes green as accessed
3) BATTERY: Charging - LED is blinking green per four seconds
Fully charged - LED is solid green
Discharging - LED is off
Low batt. (10%) - LED is sold amber;
Critical low (5%) - LED is fast blinking amber per second
system beeps when critical low first reached.
4) Wireless: LED is solid green
• Auto-backlight off when LCD cover closed
• ACPI 1.0B supported
Switch
• Power switch
• LCD Lid switch
• Internet switch
• Wireless ON/OFF switch
• E-mail switch
AC Adapter
• Universal AC adapter module. 90-265VAC, 47-63HZ, 70W.
Security
• Boot-up password protection
• Single level password architecture. (Supervisor)
• HDD Password
Memory Card & DDR SO-DIMM Socket
• 128MB, 256MB, 512MB +2.5V PC1600/PC2100 200-Pin DDR SO-DIMM Memory Card
Ready.
Chapter 1-3
Page 4

Electrical specifications
Mother Board
Microprocessor
• Intel μFCPGA
• Design for Mobile, Northwood, PENTIUM 4
• Level 2 Cache controller supported
• Level 1 Write-Back Cache supported
System Logic
• SIS
• Host Bridge/ controller processor host Bus support
• Integrated DRAM controller
• VB BUS Interface
• Power management Functions
• Hyber Link Interface
Memory
• System SDRAM
128MB,256MB,512MB PC1600 /PC2100 DDR SO-DIMM memory modules upgradable to
1GMB extended memory maximum
• System + EC ROM BIOS
512KB Flash ROM
Fixed Disk Interface
• PCI IDE supported
• ATA-5 supported
• PIO MODE 4 Timing supported
• Ultra 100 synchronous DMA mode supported
Video Subsystem
• Graphics Controller embedded in NB SIS650
• 256 bit graphics core
• Texture mapped 3D with point sampled, Bilinear, Trilinear, and Anisotropic filtering
• Hardware setup with support for strips and fans
• Hardware motion compensation assist for software MPEG/DVD decode
• PC 99 and PC 2001 Compliant
Chapter 1-4
Page 5

Super I/O Controller
• SMSC LPC47N227
• Outstanding Features
• LPC bus interface, based on Intel’s LPC Interface Specification Revision 1.01, February
1999 (supports CLKRUN and LPCPD signals)
• PC99 and ACPI compliant
• Serial IRQ support (15 options)
• Interrupt Serializer (4 Parallel IRQs to Serial IRQ)
• Intermal FDD signal support
• 5V tolerant and back-drive protected pins (except LPC bus pins)
• 100-pin TQFP Package
Keyboard Controller
• NS87591
• KBC standard interface
• Support three independent PS/2 devices ( K/B, mouse and internal pointing device )
• Real Time Clock (RTC )
DS1287,MC146818 and PC87911 compatible
• Four on chip times
16-bit programmable timer base counter with 5 bit prescaler
8-bit WATCHDOG timer
16-bit timer with 30-us resolution
16-bit general purpose timer with PWM and Capture Capabilities
• Support AMP1.2
• Active mode operating frequency 4-10 MHz
Chapter 1-5
Page 6

ACPI CarBus Controller ENE CB1420
• ACPI-PCI Bus Power Management Interface specification Rev 1.1 Compliant
• Supports OnNow LAN wakeup, OnNow Ring Indicate, PCI CLKRUN#, and PME#, AND
CardBus CCLKRUN#
• Compliant with PCI specification v2.2, PC Card Standard 7.0 and JEIDA 4.1
• Yenta
TM
PCI to PCMCIA CardBus Bridge register compatible
• ExCA (Exchangeable Card Architeture) compatible registers mappable in memory and I/O
space
• Intel
TM
82365SL PCIC Register Compatible
• Supports PCMCIA_ATA Specification
• Supports 5V/3.3V PC Cards and 3.3V CardBus cards
• Supports single PC Card or CarBus slot with hot insertion and removal
• Supports multiple FIFOs for PCI/CardBus data transfer
• Supports Direct Memory Access for PC/PCI and PCI/Way on PC Card socket
• Programmable interrupt protocol: PCI, PCI+ISA, PCI/Way or PC/PCI interrupt signaling
modes
• Win’98 IRQ and PC-98/99 compliant
• D3
cold
state PME# wakeup support
• 3.3Vaux Power Support
• Integrated PC 98-Subsystem Vendor ID support, with auto lock bit
Floppy Disk Drive
• 3.5"1.44MB, 3 mode as an I/O module
Hard Disk Drive
• 2.5" up to 40 GB, 9.5mm height
CD-ROM Module
• 12.7mm height module
• CD-ROM, DVD, CDRW,COMBO
• 24X CD_ROM
Audio Port
MIC IN
• AC-coupled input,100mVP-P maximum
Line out
• 1V
P-P
Built-in Microphone
• Sensitivity-45dB
• S/N:58dB
Built-in Speakers
• 8Ω, 1W (resonant frequency 460HZ) speakerX2
Built-in Speakers
• 8Ω, 1W (resonant frequency 460HZ) speakerX2
Chapter 1-6
Page 7

Display Device
• COLOR TFT/XGA LCD (CPT CLAA141XF01)
Dimensions : 298.5 (W) X 227.5 (H) X 5.5 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 285.7(W) X 214.3(H) mm, 14.1"
1024 X 768 XGA Resolution
Response time: 30 (max)
Contrast ratio 200:1 (Typ)
Brightness 150 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/XGA LCD (AU B150XN01)
Dimensions : 315.8 (W) X 240.5 (H) X 6.5 (D)mm (max)
Active area : 304.1(W) X 228.1(H)mm, 15”
1024 X 768 XGA Resolution
Response time: 40ms(max)
Contrast ratio 250:1 (Typ)
Brightness 200 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/XGA LCD (LG LP150X04)
Dimensions : 315.8(W) X 240.5 (H) X 6.8(D)mm (max)
Active area : 304.1(W)X228.1(H)mm,15.0”
1024 X 768 XGA Resolution
Response time: 30ms(max)
Contrast ratio 250:1 (Typ)
Brightness 200 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/SXGA+ LCD (IBM ITSX95C)
Dimensions : 317.3 (W) X 242. (H) X 6.3 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 304.5(W) X 228.3(H) mm, 15.0"
1400 X 1050 SXGA Resolution
Response time: 60 (max)
Contrast ratio 200:1 (Typ)
Brightness 140 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/SXGA+ LCD (LG LP150E01-A2M2)
Dimensions : 317.3(W) X 241.5(H) X 6.6 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 304.5(W) X 228.375(H) mm, 15"
1400 X 1050 SXGA+ Resolution
Response time: 50 (max)
Contrast ratio 200:1 (Typ)
Brightness 180 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/XGA LCD (AU UB141X03)
Dimensions : 298.5(W) X 226.7(H) X 5.5 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 285.696(W) X 214.272(H) mm, 14.1"
1024 X 768 XGA Resolution
Response time: 50 (max)
Contrast ratio 250:1 (Typ)
Brightness 150 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/XGA LCD (Hitachi TX38D85VC1CAB)
Dimensions : 315.5(W) X 240.5(H) X 6.8 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 304.1(W) X 228.1(H) mm, 15"
1024 X 768 XGA Resolution
Response time: 60 (max)
Contrast ratio 100:1 (Typ)
Brightness 150 Nit (Typ)
• COLOR TFT/SXGA+ LCD (CPT CLAA150PA01)
Dimensions : 317.3(W) X 242(H) X 6.8 (D) mm (max)
Active area : 304.1(W) X 228.1(H) mm, 15"
1400 X 1050 SXGA+ Resolution
Response time: 40ms (max)
Contrast ratio 200:1 (Typ)
Brightness 150 Nit (Typ)
Chapter 1-7
Page 8

Keyboard
• 86 /90 keys with 101/102 key emulation
• 3.0±0.15mm full stroke keys, operating force 60±10g
• Phantom key auto detect
• Overlay numeric keypad
• Support independent pgdn/pgup/home/end keys
• Support reverse T cursor keys
• Factory-configurable different languages by OEM customer
• Window key supported
Mechanical Specification
• FOR 14.1"
12.7"(W)x10.8"(D)x1.5"(H)[322.0mm(W)x274mm(D)x38.0mm(H)]
6.7lb~7.2lb(including: HDD, CD-ROM, FDD and BATT module)
• FOR 15.0"
12.9"(W)x10.8"(D)x1.5"(H)[327mm(W)x274mm(D)x38.5mm(H)]
6.78lb~7.5lb(including: HDD, CD-ROM, FDD and BATT module)
Option Pack:
• AC adapter : 444g
• HDD Pack : 160g(9.5mm)
• BATT (Li-ion) : 414g(8cell)
• CD-ROM module : 259g
• FDD module : 202g
• Memory card reader module
Mechanical Function
• Removable HDD.
• Module (CD-ROM , BATT , DVD , FDD)
• Battery changeable (Li-ion).
• For security can use Kensington Lock.
• Scissor type key board standard pitch 3.0 m/m travel length.
• PCMCIA sockets supported with one type II cards.
Mechanical Material
• Plastic PC+ABS(Bayer, FR2000)
Environment Specification
Operating
Temperature +5°C to +35°C
Relative Humidity 10% to 90% without condensation
Altitude sea level to 10000FL
Chapter 1-8
Page 9

Storage or Shipment
Temperature -20°C to +50°C
Relative Humidity 10% to 90% without condensation
Altitude sea level to 40,000ft
Chapter 1-9
Page 10
Chapter 2-1
Chapter 2: Software Specification For System BIOS
System Component Summary
Platform
CY25
Processor
Intel® Mobile P4 uFCBGA/uFCPGA
FSB
400MHz
Core Logic
- SIS 650 + SIS961(SB)
- PC 133 compliant
- Integrated VGA
- SpeedStep support
- IMVP support
- DDR 266 support
System Memory
- PC1600/PC2100 DDR SDRAM memory interface design
- 0MB DDR RAM on board
- Two DDR SODIMM (200-pin/2.5V/1.25V) connectors
- Maximum memory up to 1GB with two 512MB SODIMM
- One on Bottom/RAM Door, easily removable to allow easy upgrade
System ROM
512KB flash BIOS ROM
Video Chip
- Integrated VGA chip in SiS650 North Bridge
- SMA (Shared Memory Architecture)
- 16MB VGA memory default setting, up to 64MB
Display
- 1024 x 768 XGA TFT color LCD, display area 14”
- 1024 x 768 XGA TFT color LCD, display area 15”
- 1400 x 1050 SXGA+ TFT color LCD, display area 15”
PCMCIA
- ENE CB1420 CardBus controller
- PC card 95 supported with two Type II or one Type III
- PCI Card Bus
- No ZV(Zoom Video) support
Audio Controller
- Integrated Software Audio in SiS961 South Bridge
with Realtek ALC202A AC97 Codec (No SPDIF)
- Internal microphone
Super I/O
Controller
SMC LPC47N227
Keyboard
Controller
NS PC87591 K/B Controller
Pointing Device
- ALPS Touch pad with two buttons, scroll up/down buttons.
Keyboard
- Support Windows key, Application key
- 19 mm pitch, 3.0 mm travel length
- Full size keyboard with localization, key layouts for US, Europe and Japan required
- Spill-proof
HDD
- 9.5mm height, 2.5" HDD
- Easily removable (Configurable)
- PCI Bus Master Enhanced IDE
- Support Ultra DMA-66/100
FDD
- Internal standard square type FDD drive,
- 12.7mm,
- 1.44MB, 3 mode support
Module Bay
- 12.7mm, 24X CD-ROM drive, easily configurable design
- 12.7mm, 8X CD-RW drive (Manufacture option)
- 12.7mm, 8X DVD-ROM drive (Manufacture option)
- 12.7mm, 8X DVD/CDRW COMBO (Manufacture option)
Power
70W universal AC adapter, 90-264V AC, 47-63Hz
Page 11
Chapter 2-2
Status
- Power status LEDs
(Green/Amber)
- Caps/Num/Scroll lock
LEDs
- HDD activity LEDs (Green)
- Battery status/charging
LED
Controls
- Power button,
- Lid switch,
- 2 user-programmable one-touch
buttons,
- Touch pad Left/Right
- Scroll up/down button,
I/O Ports
- Parallel port,
- VGA port,
- PS/2 port,
- Microphone-in jack,
- Headphone out jack,
- Serial port
- Three USB ports,
- S-Video
- DC-in jack,
- MODEM port w/ RJ-11
connector
- LAN port w/RJ- 45
connector
- Two branded audio
speakers,
- Internal microphone,
- Composite TV-out,
- One Mini-PCI socket
LAN
- Realtek 8100 on board LAN
Mini-PCI
- Option 1: Modem only - AC Link software Modem
- Option 2: Combo - AC Link software Modem + Intersil 802.11b
- Option 3: No Modem - TBD
1394
- VIA chipset: VT6306 (Option)
- PCI single chip solution, PCI 2.2 compliant.
- OHCI v1.1
- IEEE1394.A
System Controls
Hot Keys
All Fn Key will support Sticky key mode.
Fn+ F5 Force Switching Display Mode(LCD->CRT->Simulataneous)
Fn + F10 Cursor keypad on/off.
Pressing this hot key can enable/disable the embedded cursor keypad.
Numeric lock state is logically disable.
Fn + F11 Num keypad on/off
Pressing this hot key can enable/disable the embedded Numeric keypad.
Numeric lock state is logically enable.
Fn + F12 Scroll Lock on/off
Fn + ↑
Increase Brightness (total 10 levels)
Fn + ↓
Decrease Brightness (total 10 levels)
- After rebooting, pad lock is set to off and Num lock is set to on. In this state, the embedded
cursor/number pad is not enabled on the notebook keyboard.
Note: Hot keys for brightness/contrast/Volumn up/down adjustment are in repeat mode, others
will only be updated once for each key depression.
When the embedded cursor/number pad is on, holding down Fn will turn the embedded
cursor/number pad off.
Page 12

Chapter 2-3
Buttons
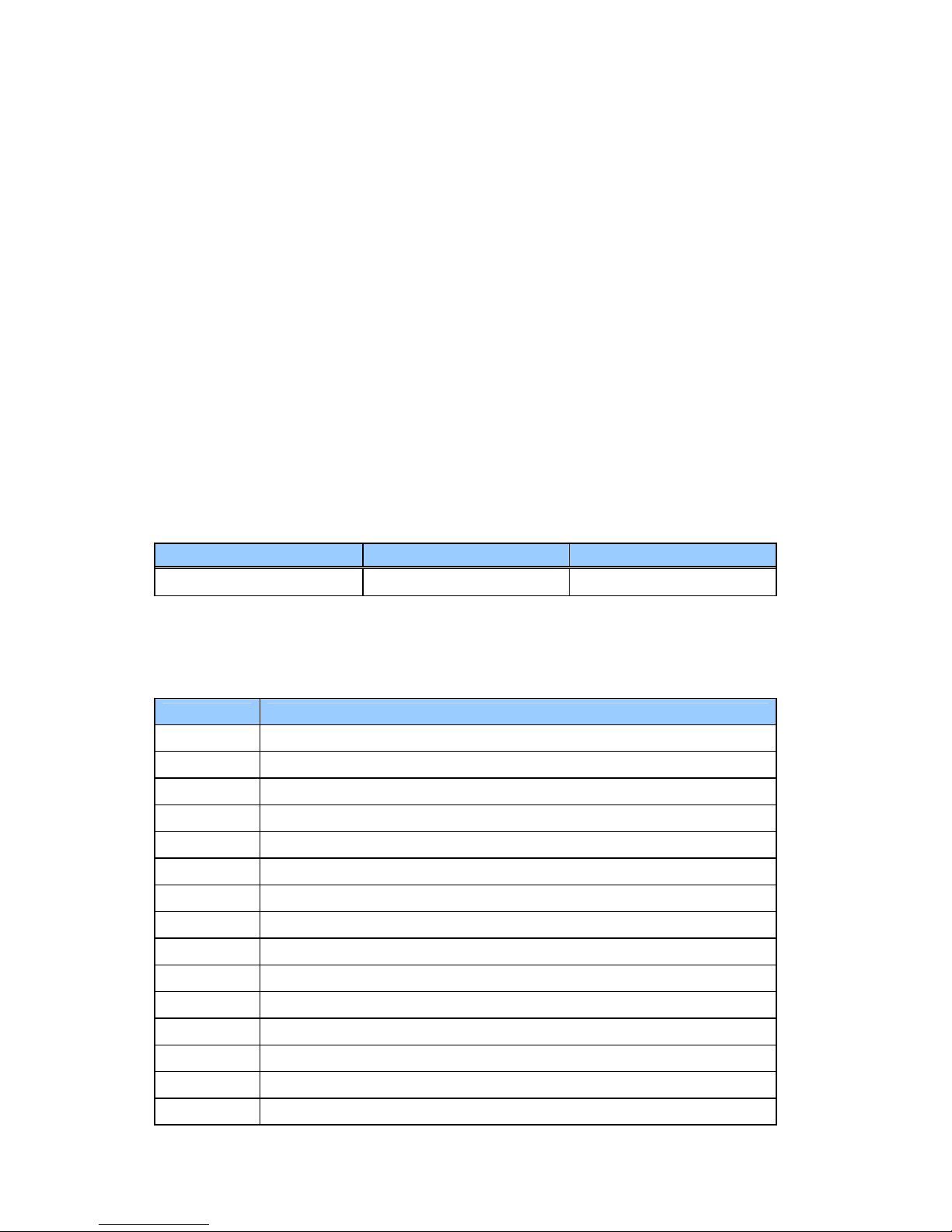
Power Button
Under ACPI, the power button action is under the control of the operation system.
• The following is a table of the state transitions in ACPI mode.
Initial Final Comments
Off On Does a normal reboot. Prompts for password if required.
Standby On Restores device states from RAM. Prompts for password if required.
Hibernate On Restores RAM and device states from disk. Prompts for password if
required.
On Standby,
Hibernate(
default) or
Off
. Action depends on OS setting. Can be set to Standby, Hibernate, or
Off(default).
. Note that the Off option is done under the control of the OS, so it is
functionally the same as doing a Start-Shut down but probably quicker.
Power Button Over-ride
Holding down the Power Button for 4 seconds will cause an unconditional transfer to the Off
state without notifying the operating system.
If press power button for less than 4 seconds, the system will enter suspend to RAM or OFF
state according to OS UI setting.
Lid Switch
This section describes the expected behavior of the system when the lid is opened or closed
by the user.
If the system is running under legacy mode:
• Closing the lid will turn off LCD backlight.
If the system is running under ACPI mode:
• The function of lid switch will follow the OS setting in power management (Nothing,
standby, Hibernate or Power off). If standby, the system wakes up when the lid opens. If
nothing, the backlight must still turn off when the lid is closed.
System status indicators
Please refer to Keyboard BIOS specification.
Core BIOS Features
Enhanced IDE Disk Drive Support (EDD)
In addition to AT standard disk drive support, the Phoenix NoteBIOS 4.06 also supports:
• Auto-detection and sizing of all IDE drives.
• Logical Block Addressing(LBA)
• Fast DMA support
• Ultra DMA-33/66/100 support
The CHS translation mode will be used.
Page 13

Chapter 2-4
Multi Boot
The notebook can support Multi Boot for selecting the boot sequence of hard disk, floppy, CD
ROM, Network Boot in Setup. It identifies all IPL (Initial Program Load) devices in the system
and attempts to boot them in the order specified in Setup.
Quiet Boot
Quiet Boot replaces the customary technical messages during POST with a more visually
pleasing and comfortable display (OEM Logo screen). During POST, right after the
initialization of VGA, The notebook displays an illustration called the OEM screen during
system boot instead of the traditional POST screen that displays the normal diagnostic
messages.
The OEM Logo screen stays up until just before the operating system loads unless:
• Press <Esc> to change the boot order.
• Press <F2> to enter Setup. (When pressed, need to show “Entering Setup…”)
• Press <F12> to boot from LAN (When pressed, need to show “Booting from LAN…”)
• Whenever POST detects a non-terminal error, it switches to the POST screen near the
end of POST, just prior to prompting for a password.
• If the BIOS or an option ROM requests keyboard input, the system switches over to the
POST screen with prompts for entering the information. POST continues from there with
the regular POST screen.
New Interrupt 15h extensions
The BIOS must support the recently defined standard INT 15 extensions:
Big Memory
Big memory support that can reporting greater than 64 megabytes of RAM. The notebook
supports the INT 15h big-memory reporting functions of E801h, E881h, and E820h. This
feature reports all available extended memory (both below and above the 64MB limit) using
both a real mode (E801h) and a 32-bit protected mode (E881h) interface. Operating systems
can access the real-mode interface through the standard INT 15h call. They can access the
protected-mode interface through a 32-bit interrupt call, much like the EISA protected-mode
interface. The Microsoft-defined E820h function returns a complete memory map through a
series of repeated calls.
Boot Block
The Flash ROM used in many systems today offer the customer the advantage of
electronically reprogramming the BIOS without physically replacing the BIOS ROM. This
advantage, however, does create a possible hazard: power failures or fluctuations that occur
during updating the Flash ROM can damage the BIOS code, making the system unbootable.
To prevent this possible hazard, many Flash ROM include a special non-volatile region that
can never be erased. This region, called the boot block, contains a fail-safe recovery routine.
If the boot block finds corrupted BIOS, it prompts the end user to insert a diskette, from which
it loads several files that replace the corrupted BIOS on the Flash ROM with an uncorrupted
one.
Plug-n-Play (PnP) Support
To achieve the goal of PnP, a POST conflict detection and resolution (CDR) module, and a
run-time services module will be integrated into the system BIOS.
The PnP runtime service module includes multiple interfaces so that the system can support
the current DOS/Win3.1 non-PnP drivers, as well as Win95 operating system that include
specific support for the PnP BIOS specification.
Page 14

Chapter 2-5
Security Features
Security features to be supported are passwords, electronic serial number, PC identification
string.
The Electronic Serial Number provides a unique way of identifying an individual notebook.
PC Identification strings allow the user or administrator to personalize the notebook for asset
tracking or identification if it is lost.
The Passwords, Serial Number, and PC Identification strings are to be stored in EEPROM.
2 Level Passwords
The notebook supports two levels of password protection. The password support consists of a
User Password and an Administrator Password. They each contain up to eight characters,
and are stored in EEPROM. Using the administration password to enter the setup utility allows
the user to access all the configurable fields. Whereas using the user password only allows
the user to configure a limited number of fields.
When the password is enabled, the notebook may display a suitable password prompt on the
main display in the following situations:.
• Turning on from off states. (No BIOS suspend/resume password)
• Entering to Setup.
The User will attempt to enter a password, then press ENTER. If the User fails to enter the
password in three tries the system will be halt.
User Password
The user can choose:
• The password will never be required
• Be required to boot.
• The user password may not be set unless the administrator password is set. If the user
wishes to only have one password then the administrator password is used.
Administrator Password
There are three primary uses for the Administrator Password:
• Protect users from changing system configuration that could cause the notebook to
malfunction.
• As the users password if only a single password is desired.
Passwords and Setup
There are individual checkbox items in Setup to allow the user to specify when to require a
password. The wording of these options should be:
Password Required to:
Boot [Enabled]
The following table lists the items in the Setup utility which can be modified by the User.
Time & Date
User password
While setting new password, three failures to enter the old password will result in the system
turning off.
Valid Password Characters
Valid Password Characters
Page 15

Chapter 2-6
• The numbers 0 to 9.
• The letters A to Z (not case sensitive).
The password is stored as scan codes.
Electronic Serial Number
The electronic serial number is a ten (10) byte string which matches the manufacturing serial
number on the bottom of the notebook. The BIOS must display the electronic serial number in
the boot screen and in Setup. The format of the line should be
Serial Number: SSSSSSSSSS
where SSSSSSSSSS is the electronic serial number. The format of the serial number is:
CCYWWNNNNN
Where
CC is a two character country code (TW for Taiwan).
Y is the year of manufacture (7 = 1997, 8 = 1998, etc.)
WW is the week of manufacture (1 to 52)
NNNNN is the unit number (see below).
Unit number is a number from 00000 to 99999 and is incremented for each unit produced.
The unit number is reset at the beginning of each week. Before displaying the serial number,
the BIOS must check for the special
′
invalid′ serial number (INVALID000). If this special serial
number is detected, the BIOS should display the message:
INVALID ELECTRONIC SERIAL NUMBER
ENTER THE SERIAL NUMBER NOW:
The BIOS must then force the user to enter the serial number and program the entered serial
number into the EEPROM. The BIOS must perform validity checks on the serial number
entered.
System boards sent to service must be preprogrammed with this invalid serial number. This is
to insure that when a service technician swaps a new main board into a system that he/she
sets the serial number to match the serial number of the system.
This same electronic serial number is used for the serial number returned by the SM BIOS.
Software Password Backdoor
Because users occasionally forget their password we need a method of removing the
password for them. This method must involve little risk to the security of the password system
in general.
The method is that the User calls up Customer Support, Support tells them to press some
*special key combination which causes a
′
secret code′ to be displayed, the user describes this
to support representative who then use their secret decoder ring to generate a
′
super-
password
′
which they tell the user to type in. This removes (deletes) all passwords (user and
administrator).
During the password request process, three failed attempts to enter the backdoor password
will also cause system turning off.
The back door password process can only be held on the cold boot.
Thermal management
There are two types of cooling techniques used for thermal management. The first type is
passive cooling where the CPU speed is reduced or other devices power consumption is
Page 16
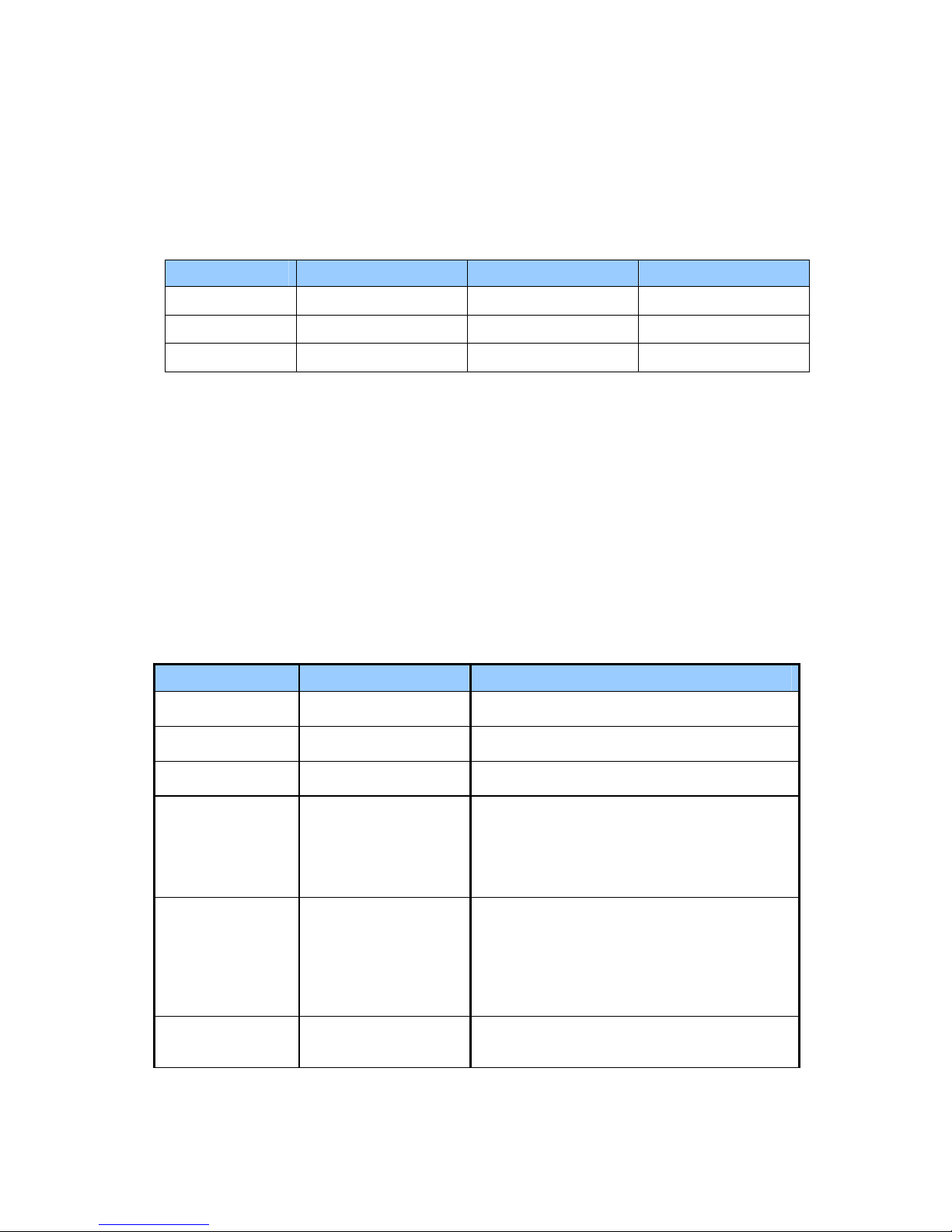
Chapter 2-7
reduced in an effort to reduce heat generation. The second type is active cooling where a fan
is turned on to cool the system.
In non-ACPI mode(Legacy Mode), the thermal management is achieved by controlling the fan
depend on the temperature. Besides turning the fan on and off. The system may also be
shut off whenever the temperature can’t be reduced even the fan are spinning in the full
speed. The system will be turned off immediately when it’s over-heating (over 85°C). The fan
will be turned off when temperature is under 65°C. The table below listed the control point of
temperature changes:
Temperature Fan Off Fan on(100%) System Off
< 62℃
X
65℃
X
> 85℃
X
Power Management
Introduction
The notebook supports ACPI power management modes. The system will dynamically switch
to ACPI mode for configuration and power management when an ACPI OS is loaded.
System Time-outs
The system Time-outs include the Standby time-out, the Suspend time-out, and the Hibernate
time-out.
System Time-outs are handled by the operating system in ACPI mode. BIOS time-outs must
be disabled. System time-outs are set using the control panel power applet.
System Power Management
The overall system can be in one of five system power states as described below:
Legacy Mode ACPI mode Power Management
Off Mech. Off (G3) All devices in the system are turned off
completely.
Soft Off (G2/S5) OS initiated shutdown. All devices in the system
are turned off completely.
On Working (G0/S0) Individual devices such as the CPU and hard
disk may be power managed in this state.
Standby (S1) CPU in Stop Clock state
VGA Standby, turn off backlite
PCMCIA Standby
Audio Power Down
Hard Disk Spin Down motor
Super I/O Low Power Mode
Suspend to RAM (S3) CPU set power down
VGA Suspend
PCMCIA Suspend
Audio Power Down
Hard Disk Power Down
CD-ROM Power Down
Super I/O Low Power mode
Save to Disk (S4) Also called Hibernate state. System Saves all
system states and data onto disk prior to power
off the whole system.
Page 17
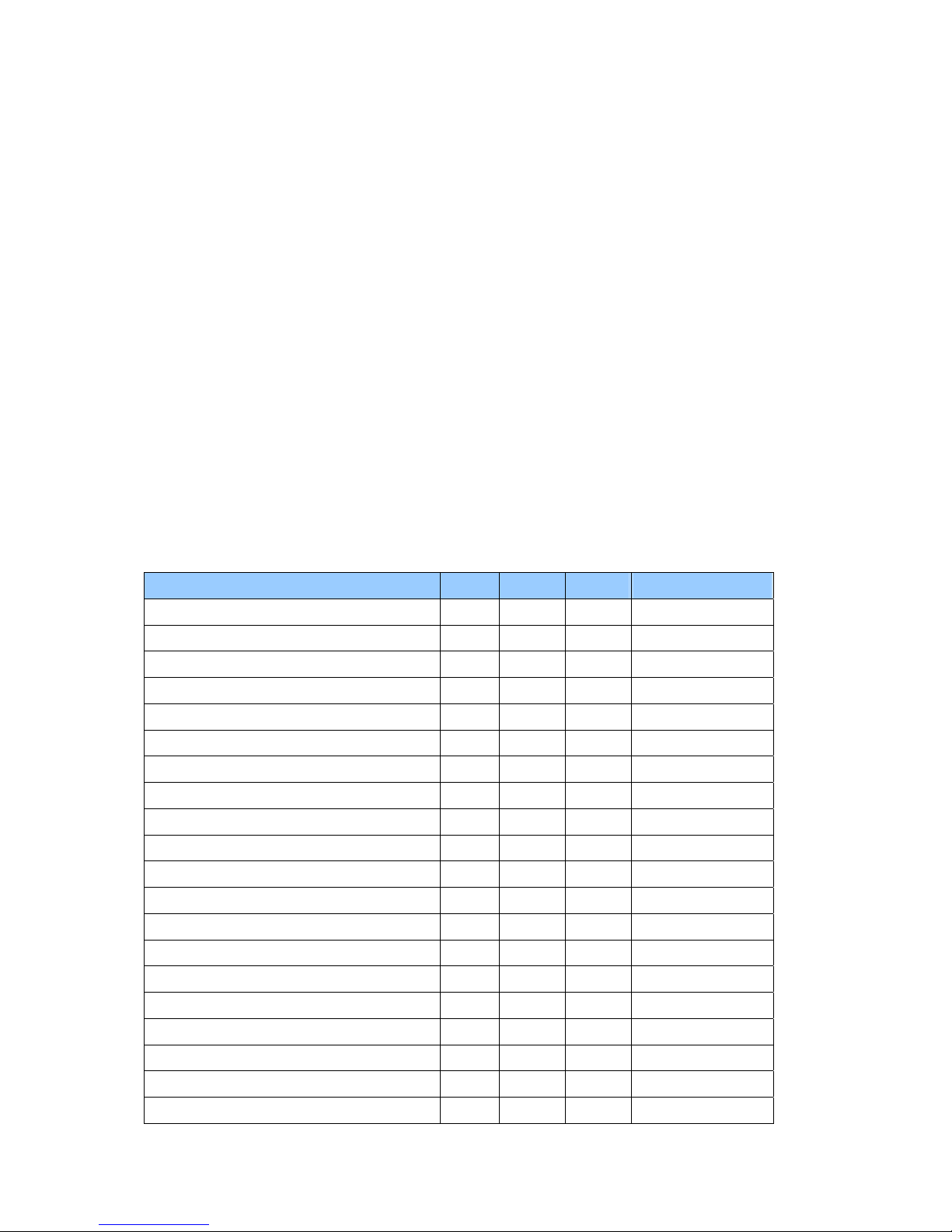
Chapter 2-8
Device Power Management
The device specific power management supported by this notebook includes the CPU and the
hard disk.
CPU power management
• ACPI mode
The operating system detects when the system is idle and places the CPU in one of the 3
CPU low power states (C1, C2 or C3) depending on how much latency it believes the
system can afford.
The C1 state is simply the CPU halt instruction. The C2 state is the CPU stop grant state.
The C3 state is the CPU stop clock state. The CPU stays in this state until an interrupt
occurs.
Hard Disk
• ACPI mode
Newer OSes use the spin down timer of the hard drive to set time-outs. The user can sets
the hard disk spin down time-out in the control panel power applet.
System Wake Up Sources
The table below lists the wake up events for all low power states:
Events S1 S3 S4 Process required
Hot Key(*1) - - - Power button V V V Lid open V V - Lid close - - - Modem Ring (Mini-PCI Modem) V V - Modem Ring (USB/PCMCIA Modem) - - - Modem Ring (Serial Port Modem) - - - LAN (Mini-PCI NIC) V V - LAN (USB/PCMCIA NIC) - - - AC/Battery - - - V
Thermal - - - V
RTC V V - COM/LPT/KB/Mouse/FDD/HDD - - - Audio/Video activity - - - PCMCIA - - - Driver
USB(*2) - - - Driver
Module swap---Battery - - - V
Module swap---non Battery - - - V
CRT(no event) plug/unplug - - - V
Hot Plug PS/2 devices - - - KB only
Page 18

Chapter 2-9
Critical low battery - - - -
Field ‘Process Required’ identifies that further process for the occurred events must be
processed during wake up or resume procedure.
*1: Hot keys are not wake up source of standby, suspend to RAM and Hibernate states.
*2: Activity of the USB device is dependent on the driver support.
Power Button
The power button will wake the system from any low power state as described in the Power
Button section.
Real Time Clock Alarm
The Real Time Clock alarm interrupt will wake the system from standby, suspend.
Power Management – ACPI
Introductions
The Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is a well-specified power
management and configuration mechanism. It evolves the existing collection of power
management codes, APM, PnP BIOS, ..etc.
Power State Transition Diagram
The state transition diagram is identical to the one in APM mode.
Time-outs while On AC Power
OS determines the behavior of the feature.
Embedded controller
The keyboard controller will act as the ACPI embedded controller and support the ACPI EC
protocol and interface.
SCI/SMI events
All ACPI OS controllable events will be triggered as SCI. Otherwise SMI will be triggered.
PC2001
The notebook must meet Microsoft Logo requirements in accordance with the PC2001 Design
Guide and the Microsoft Logo test programs.
Miscellaneous Features
Single BIOS ROM
The system BIOS and Keyboard BIOS share one single flash ROM. The size of the flash
ROM is 512KB.
USB Support
This feature allows the use of a USB keyboard to access BIOS Setup and to be used in DOS
without additional drivers.
IDE interface
The IDE device supported master channel.
Flash utility – one BIOS ROM only
The flash utility can be used to program both system and keyboard BIOS at the same time.
Page 19

Chapter 2-10
EEPROM
There is one EEPROM which is used to store many important system and user data in the
notebook The size of the EEPROM is 2K bytes.
Password Protection
Password and Security support will be implemented in this model. See the PhoenixBIOS 4.0
User Manual for sample screen and the description of Password and Security support.
VGA Support
This section describes the expected behavior when a video monitor is connected to the VGA
port on the notebook or port replicator.
The BIOS will use both of the RGB and pin 11 methods to determine the presence of an
external VGA monitor. Either case meet will indicate an external VGA monitor is present.
The BIOS setup utility will have a menu for setting up the behavior of the external VGA port
according to user preference. There are two settings:
Setting 1, AUTO: Auto-select External VGA if attached(CRT only), LCD if external not
attached.
Setting 2, BOTH: Both External VGA and LCD always on.
When setting 1 is selected the BIOS will automatically turn the internal display off and the
external monitor on, whenever an external monitor is detected. Otherwise it will enter LCD
only mode (with the backlite off if the cover lid is closed). This means that the BIOS must
check for the external video being present during POST; on resume from standby, on resume
from suspend to RAM, on resume from hibernate; on warm dock, on hot dock, on hot undock,
and on warm undock.
When setting 2 is selected, the BIOS will always turn on both the internal display and external
monitor regardless of whether an external monitor is detected.
The hot key for switching the external video (Fn + F5) must only make a temporary change. It
must not change the user
′
s preference in CMOS, it will just change the current state of the
external video port. Also the hot key must not check to see if an external monitor is detected
before switching to external only mode. It should just toggle between internal only, both, and
external only (without regard to monitor detect). The hot key setting will not survive suspend
to RAM, hibernate. In these cases the mode should be set back to the setting stored in
CMOS.
Internal Pointing Device Support
Added a new BIOS setup to enhance the PS/2 pointing devices
PS/2 Pointing Devices:
Auto-Selected: Disable internal pointing devices if external PS/2 mouse is present.
Simultaneous:
The internal pointing device is always enabled. Any external pointing device
connected will also be enabled at the same time.
• If an external PS/2 mouse is detected, it will be enabled. If USB mice are detected, they
will be enabled as well. If an external mouse contains a third mouse button, it will function
as expected.
• Double click the Mouse icon in the Windows2000/XP Control Panel to adjust pointer
speed, double click speed, right-handed versus left-handed button settings, and pointer
appearance. The settings in this applet apply to all the external and internal pointing
devices in the system. Except as described below, there are no individual pointing device
adjustments available.
• Tapping (or double tapping) on the TouchPad is equivalent to a single (or double) left
mouse click. The Synaptics TouchPad driver will be available on the hard drive and the
Page 20
Chapter 2-11
customer may choose to manually install it. The Synaptics TouchPad driver should only be
installed after first selecting Touch pad only in BIOS Setup.
• Hold down center button of external PS/2 mouse: While holding down the center button of
an external mouse, move the mouse. This will cause the window to move. If the center
button is not held down, all pointing devices function normally.
• Use TouchPad: The TouchPad is locked in as the Scrolling or Magnifying Glass device.
Sweeping across the TouchPad causes the window to move. The other pointing devices
function normally.
BIOS Version and Resource Allocated
BIOS version number
The BIOS version string is in below format:
pppp.x.yy
Where:
pppp Four letter platform descriptor.
x One digit BIOS major revision number.
yy Two digit BIOS minor revision number
Below lists the BIOS version numbers that will be assigned to this platform.
Platform QA Releases Production Release
CY25 CY25_0.xx CY25_1.00
NOTE: yy starts at 0 and is incremented with each release of the specific type. During the
development and testing of the second release the engineering and QA release will
Configuration Requirements
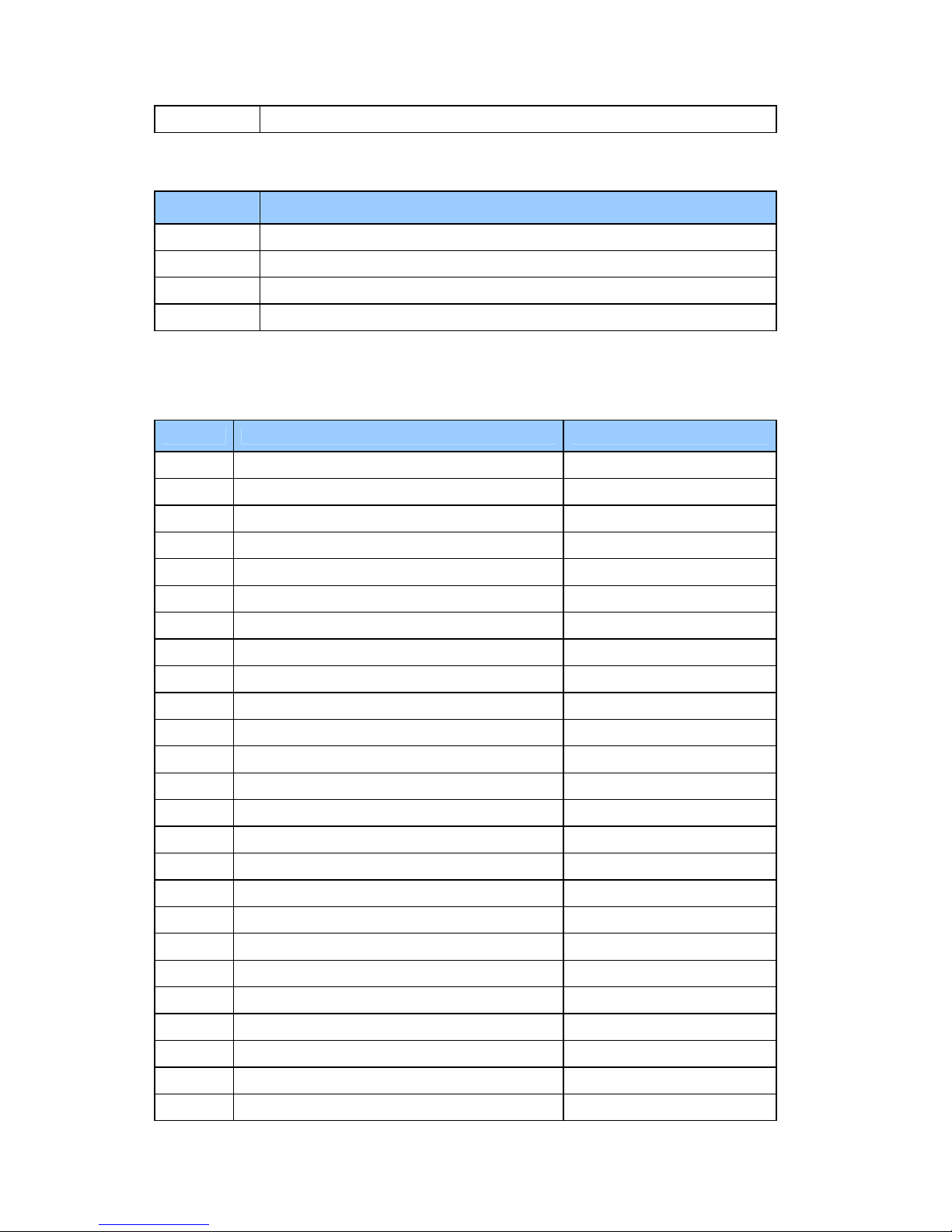
The table below lists the possible usage of the system resources:
IRQ Hardware
00 System Timer
01 Keyboard
02 Programmable Interrupt Controller
03 Free by default or Generic
04 Communications Port (COM1)
05 PCI AUDIO/MODEM
06 Standard Floppy Disk Controller
07 ECP Printer Port (LPT1)
08 Real Time Clock
09 SCI
10 LAN / Universal Serial Bus
11 PCMCIA/VGA
12 Mouse
13 Numeric data processor
14 Primary IDE controller (hard disk)
Page 21
Chapter 2-12
15 Secondary IDE controller (CD ROM)
DMA Hardware
00 PnP Audio System CODEC
01 Free
02 Standard Floppy Disk Controller
03 ECP Printer Port (default)
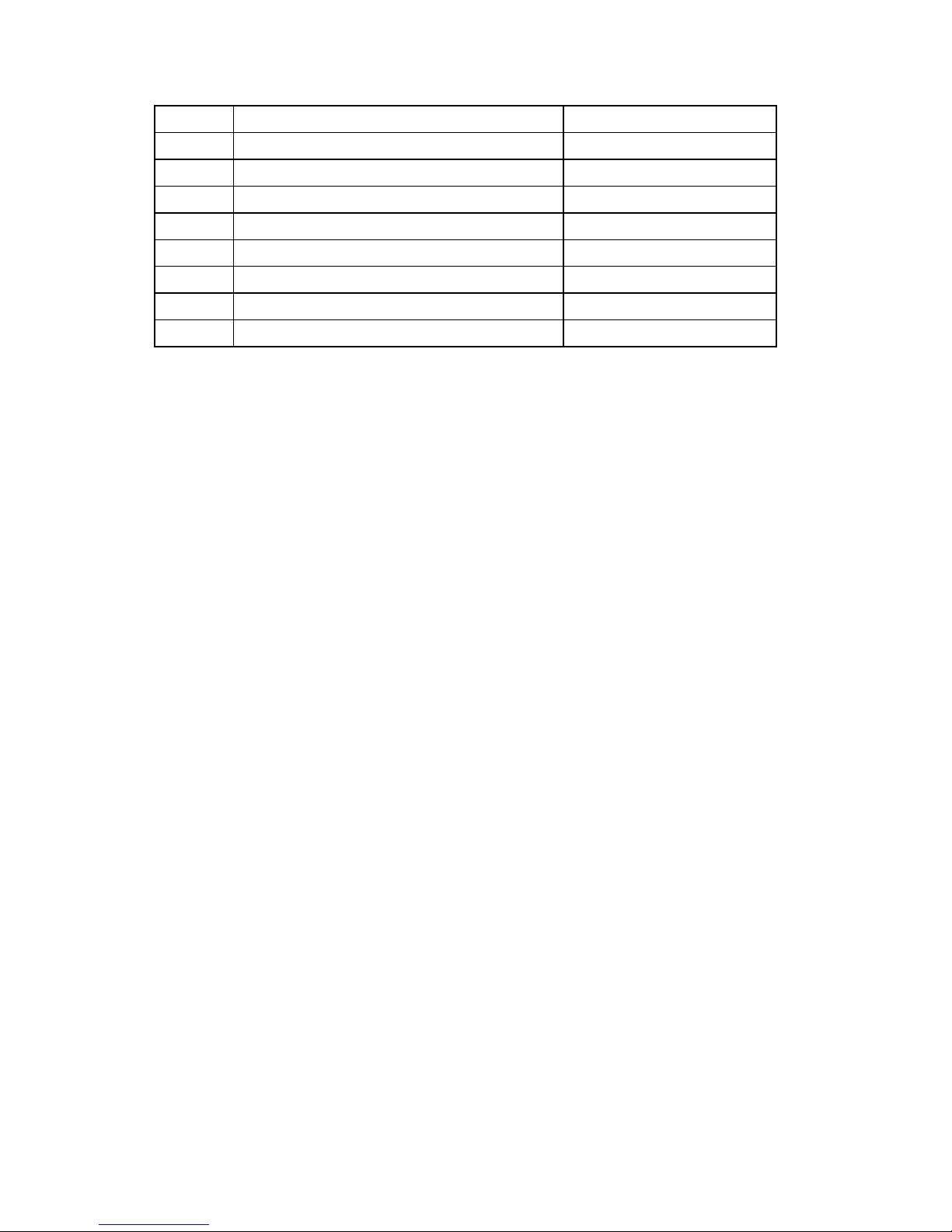
System Management BIOS(SM BIOS) version 2.3.1 or greater
This product require that SMB 2.3.1 BIOS sub-structures be supported as follows:
TYPE Structure Type Required?
0 BIOS Information YES
1 System Information (Component ID) YES
2 Motherboard Information YES
3 System Enclosure YES
4 Processor Information YES
5 Memory Controller YES
6 Memory Information YES
7 Cache Information YES
8 Port Connector Information YES
9 System Slots YES
10 On Board Devices YES
11 OEM Strings YES
12 System Configuration YES
13 BIOS Language Information NO
14 Group Associations NO
15 System Event Log NO
16 Physical Memory Array YES
17 Memory Devices YES
18 Memory Error Information NO
19 Memory Array Mapped Address YES
20 Memory Device Mapped Address YES
21 Built-in Pointing Device YES
22 Portable Battery YES
23 System Reset NO
24 Hardware Security NO
Page 22
Chapter 2-13
25 System Power Control NO
26 Voltage Probe NO
27 Cooling Device NO
28 Temperature Probe NO
29 Electrical Curretn Probe NO
30 Out-of-Band Remote Access NO
32 BIOS Intergrity Service YES
126 Inactive NO
127 End-of-Table YES
This product require that the Serial Number field, which is a string at offset 7 of the Type 1
(System Information) sub-structure, is to be filled in with the unit
′
s Electronic Serial Number.
This would be filled in at boot time. Please see section 5.4.2 for information on the Electronic
Serial Number.
POST summary screen
The Post summary screen is a screen that appears at the end of the POST processing if quiet
boot is disabled or the user presses the Esc key during POST. The screen must contain the
information listing below:
• A copyright message
• Electronic Serial Number
• UUID number
• The BIOS revision number and model name in customer format
At the bottom of the screen, the screen should have the following messages:
Press ESC to change boot order
Press <F2> to enter setup, <F12> to boot from LAN
CMOS RAM management
The BIOS will automatically update certain information in CMOS on each boot. This
information includes:
• DRAM size and configuration
• Hard disk configuration
• Always report the existence of one FDD.
If the CMOS RAM fails checksum or a power lost on CMOS battery is detected during boot, an
appropriate error message will be displayed:
System CMOS checksum bad – Default configuration used
The system BIOS must automatically load default values defined in the setup menu during
POST when encounter these problems. The user must not be required to take any action to
continue the rest of POST(or entering SETUP).
Diskless Boot
This feature allows the system to boot off of a LAN when the hard disk is absent or has not
been loaded with the operating system. It is utilized by the software download process in
manufacturing. This product will use PXE since this is a PC2001 requirement.
Page 23

Chapter 2-14
System Setup
Invoking setup
The setup function can only be invoked by pressing F2 when ″ Press <F2> to enter Setup″
message is prompted on the bottom of screen during POST.
The setup uses a menu driven interface to allow the user to configure their system. The
features are divided into 6 parts as follows:
Main Allows the user to specify standard IBM PC AT system parameters.
System Devices Provides advanced settings of the system.
Security Provides security settings of the system.
Boot Allows the user to specify the boot options.
Info. Display the system informations.
Exit Allows the user to save CMOS setting and exit Setup.
During setup, all Fn function keys and power saving functions are disabled.
Setup screens
Main Menu
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
System Time: [09:00:00]
System Date: [01/01/2002] <Tab>, <Shift-Tab>, or
Floppy Disk Drive 1.44 MB Floppy disk size
Internal Hard Disk: [ xxxxx MB] Disk Size
ATAPI Device : [ Model Name]
Boot Display Device: [Both]
Screen Expansion: [Enabled]
Television Type: [NTSC] Select NTSL or PAL standard
VGA Memory: [32MB] VGA Memory Size Configuration
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
System Time and System Date
The hours is displayed with 24 hour format. The values set in these two fields take effect
immediately.
Floppy Disk Drive
Page 24

Chapter 2-15
The Floppy Drive status is auto detected by system.
1.44MB, 3
1/2
“ If there exists floppy drive.
Not installed If there is no floppy drive.
Internal Hard Disk
The hard disk types and capacity are auto detected and set by the system. If there is no hard
disk present or unknown type, ″None″ should be shown on this field, otherwise the capacity
must be shown.
ATAPI Device
The CD-ROM, DVD-ROM or CD-RW are auto detected and set by the system. If there is no
ATAPI Device present or unknown type, ″None″ should be shown on this field, otherwise the
model name must be shown.
Boot Display Device
Both: Simultaneously enable both the integrated LCD screen and the system’s external
video port (for an external CRT or projector).
Auto-Selected: During power on process, the system will detect if any display device is
connected on external video port. If any external display device is connected,
the power on display will be in CRT (or projector) only mode. Otherwise it will
be in LCD only mode.
Screen Expansion:
Enabled:
Disabled:
VGA Memory
VGA Memory size = 16/32
/64 MB.
The default value is set to 32 MB.
Television Type:
NTSC: TV is NTSC standard
PAL: TV is PAL standard
Intel® SpeedStep™ Technology:
Automatic:
, / Maximum Performance / Battery Optimized / Reversed
NOTE: The sub-items under each device will not be shown if the device control is set to
disable or auto. This is because the user is not allowed to control the settings in these cases.
Page 25
Chapter 2-16
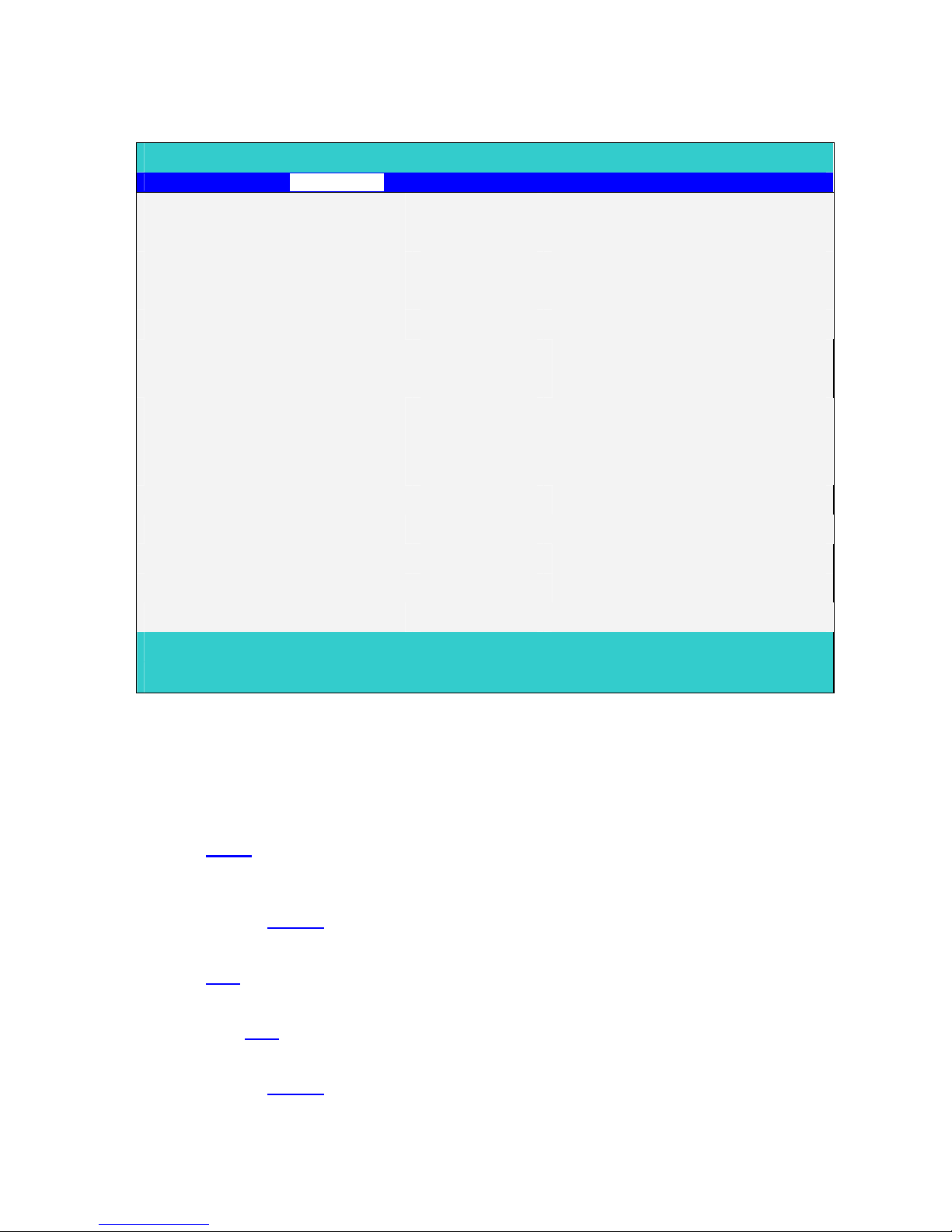
System Devices
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
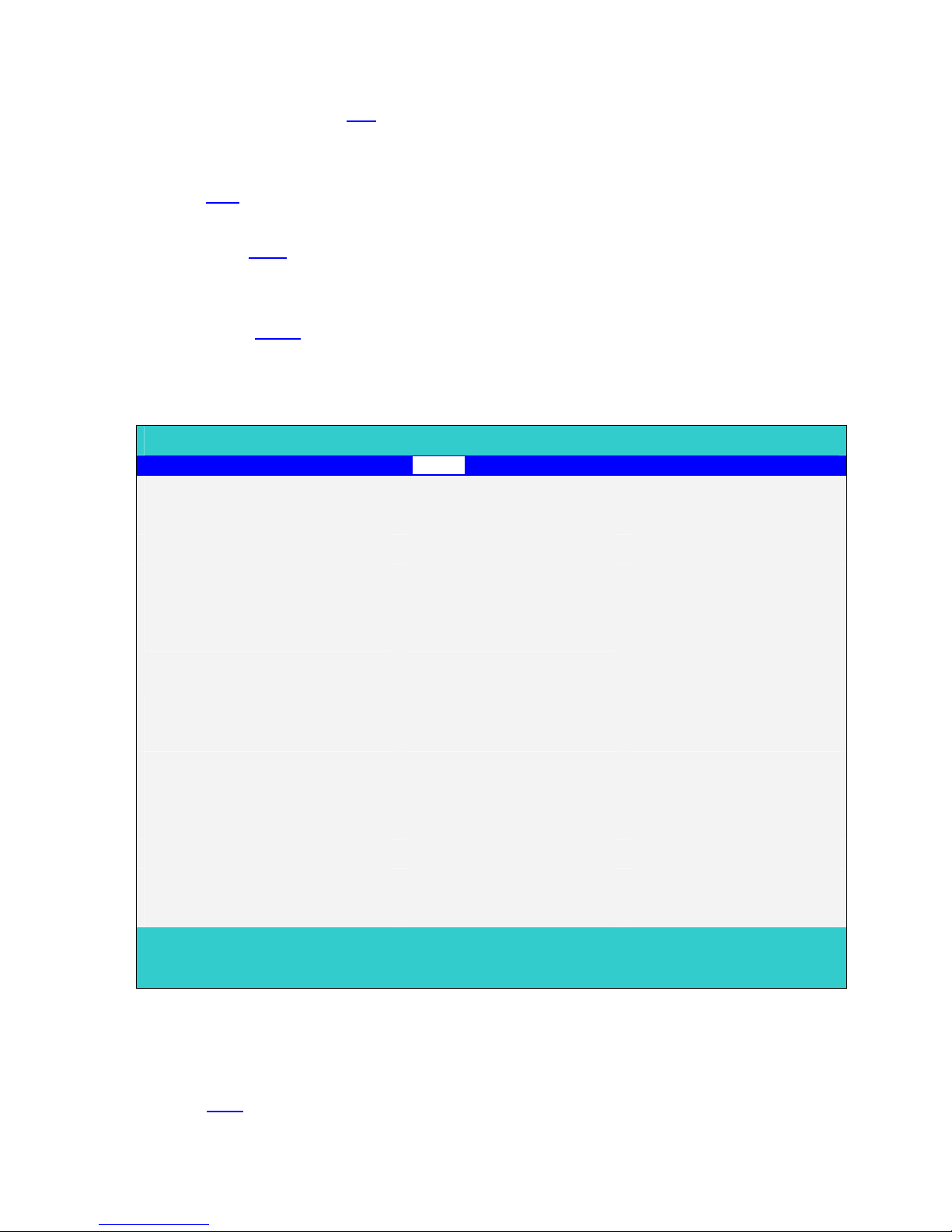
PS/2 Pointing Device [Both]
Serial Port: [Enabled]
Base I/O address [3F8h]
Interrupt [IRQ4]
Parallel Port: [Enabled]
Mode: [ECP]
Base I/O address: [378h]
Interrupt [IRQ7]
ECP DMA channel: [DMA1]
Intel® SpeedStep™ Technology [ Automatic]
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
PS/2 Pointing Device
Configures the integrated internal pointing device using options:
Auto-Selected: If an external PS/2 mouse is connected to the system, then disable the
internal pointing device. Otherwise enable the onboard pointing device.
When an external PS/2 mouse is warm/hot plugged into the PS/2 mouse
port, the internal pointing device will be disabled.
Both: The internal pointing device is always enabled. Any external pointing
device connected will also be enabled at the same time.
Serial Port
Disabled/Enabled/Auto
Base I/O address
3F8h/2F8h/3E8h/2E8h
Interrupt
IRQ3/IRQ4
Parallel Port
Disabled/Enabled/Auto
Mode
Page 26
Chapter 2-17
Normal/Bi-directional/ECP/EPP
Base I/O address
378h/278h/3BCh
Interrupt
IRQ 5/IRQ 7
ECP DMA channel:
This field is hidden if Mode is not ECP
DMA 1/DMA 3
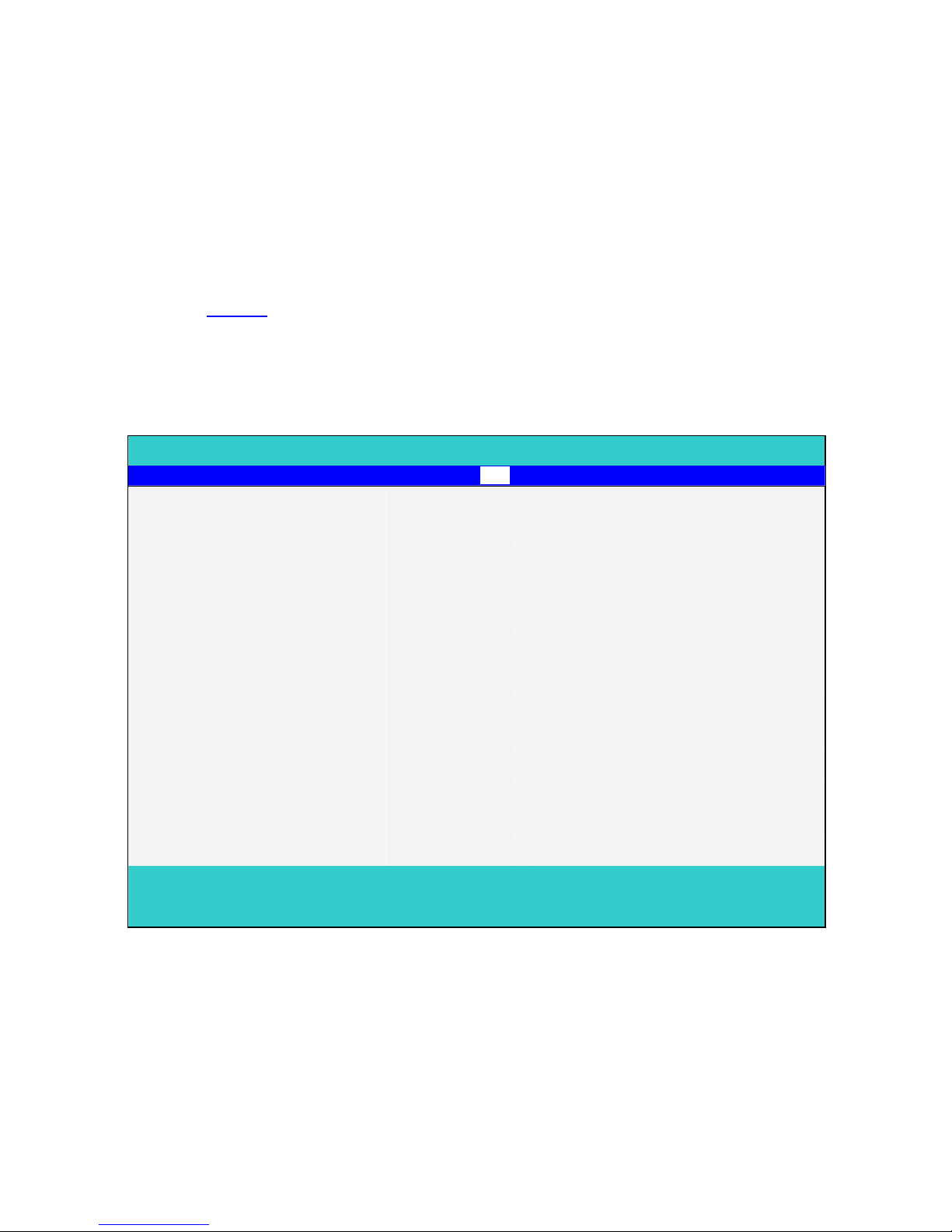
Security Menu
The following is Security menu if both of password is disabled, or enter Supervisor password
when password is enabled:
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
User Password is Clear
Administrator Password is Clear
Set User Password [Enter]
Set Administrator Password [Enter] Supervisor Password
controls access to the
setup utility
Password Required to:
Boot: [Enabled]
Processor Serial Number : [Enabled]
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
User Password is / Administrator Password is
These two fields shows that Administrator/User Passwords are set or not.
Set System Password is set.
Clear
System Password is not set.
Page 27

Chapter 2-18
Set User Password / Set Administrator Password
Enter This field always shows the message.
While these fields are highlighted and press ′Enter′, a window similar to the following is
shown:
Set Administrator Password
Enter New Password [ ]
Confirm New Password [ ]
If there is an old password then setup will prompt with the following window instead and a
current password will be required to be entered at first:
Set Administrator Password
Enter current password [ ]
Enter New Password [ ]
Confirm New Password [ ]
User can now type password in field ″Enter New Password″, and re-enter password in field ″
Confirm New Password ″ for verification.
If the verification is OK:
Setup Notice
Changes have been saved.
[ continue]
The password setting is complete after user presses enter.
If the current password entered does not match the actual current password:
Setup Warning
Invalid password
Re-enter Password
[ continue]
If the new password and confirm new password strings do not match:
Setup Warning
Password do not match
Re-enter Password
The format of the password is as follows:
Length No more than 8 characters.
Page 28
Chapter 2-19
Characters 0-9, A-Z (not case sensitive)
Password Required to
Defines whether a password is required or not while the events defined in this group
happened. The following sub-options are all requires the Administrator password for changes
and should be grayed out if the user password was used to enter setup.
Boot
Allows the user to specify whether or not a password is required to boot.
Disabled
/Enabled
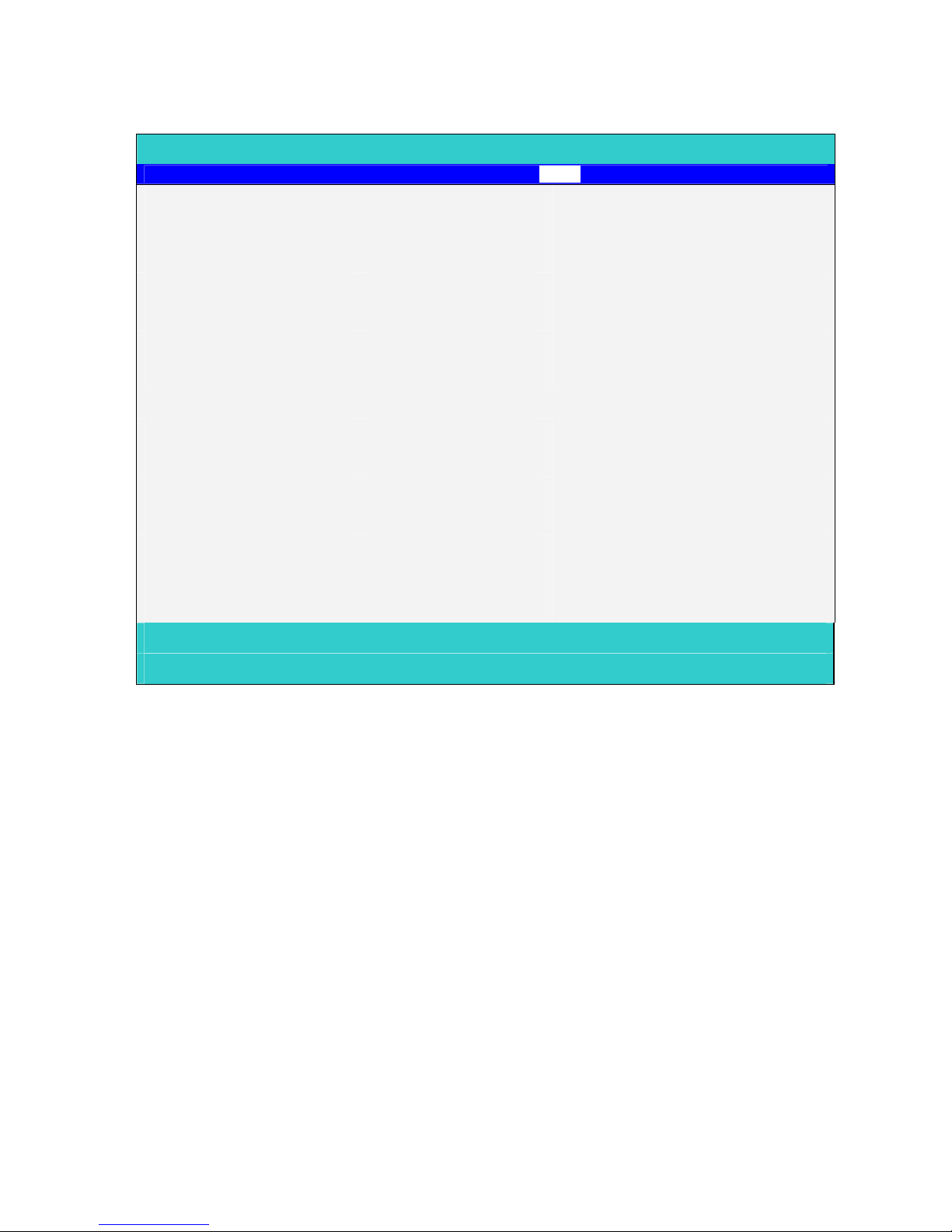
Boot Menu
This menu allows the user to decide the order of boot devices to load the operating system.
Bootable devices includes the diskette drive in module bay, the onboard hard disk drive and
the CD-ROM in module bay.
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
1. Hard Disk
2. CD-ROM/DVD Drive
3. Floppy
4. Network Boot
Use <↑> or <↓> to select a device,
then press <F6> to move it up the
List, or <F5> to move it down the list.
Press <Esc> to escape the menu
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 29
Chapter 2-20
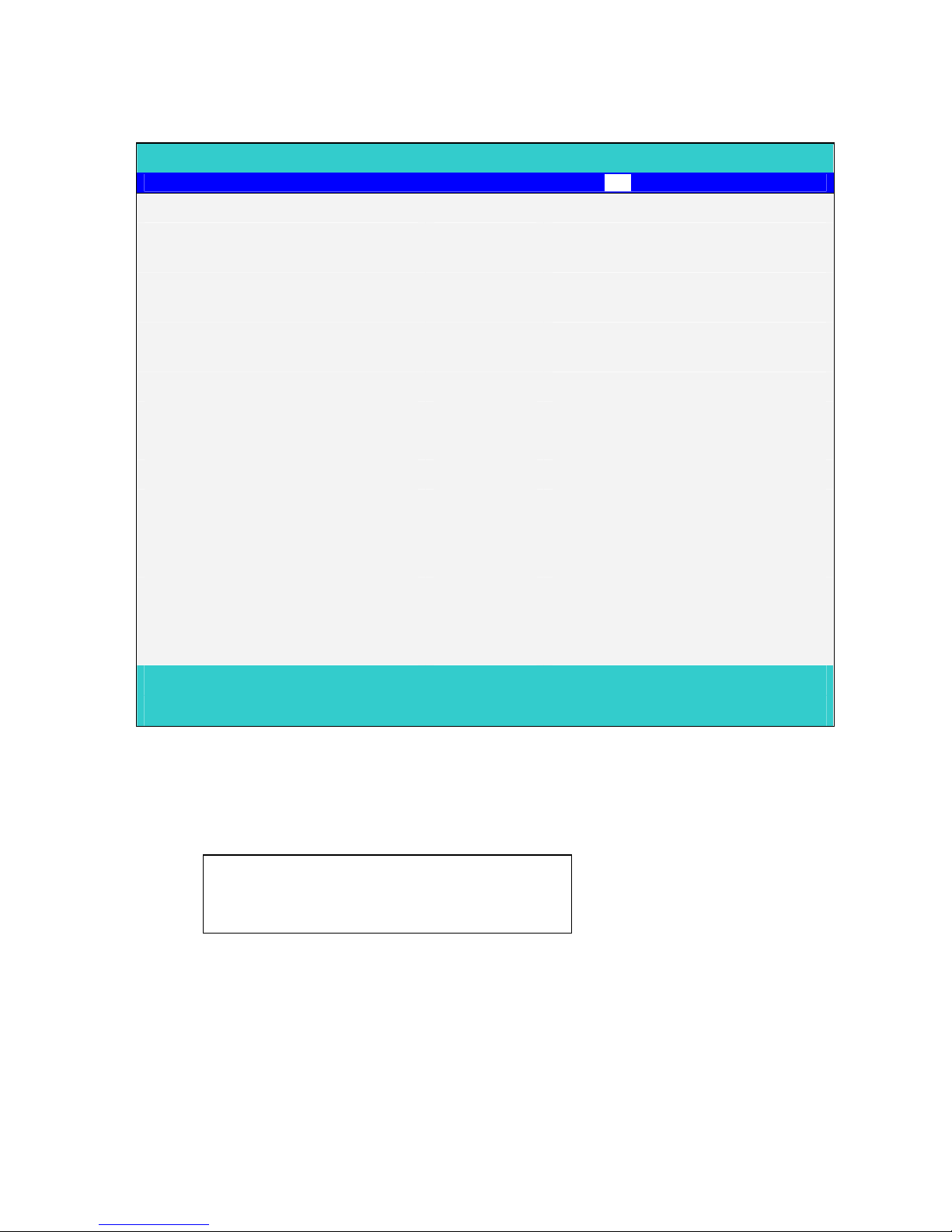
Informations Menu
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
System BIOS Version: CY25_1.00
VGA BIOS Version: SiS 1.07.xx
Serial Number: xxxxxxxxxx
UUID Number: xxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxx
System Memory: 640 KB Show System Memory Size
Extended Memory: 127 MB Show Extened Memory Size
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
UUID Number
UUID = 16 bytes
System Memory
This field reports the memory size of system base memory. The size is fixed to 640KB.
Extended Memory
This field reports the memory size of the extended memory in the system.
Extended Memory size = Total memory size - 1 MB
Page 30
Chapter 2-21
Exit Menu
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
Main System Devices Security Boot Info. Exit
Item specific Help
Saving Changes and Exit Exit System Setup and save your
changes to CMOS
Discarding Changes and Exit Exit utility without saving Setup data
to CMOS.
Get Default Values Load default values for all SETUP
item.
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item F5/F6 Change Values F9 Setup defaults
Esc Exit ←→ Select Menu Enter Select4Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Saving Changes and Exit
Allows the user to save changes to CMOS and reboot the system. The following message is
shown when user presses ″Enter″ on the item.
Setup Confirmation
Save configuration changes and exit now
[ Yes] [No]
System will reboot if Yes is selected and will stay in Setup if No is selected.
Page 31

Chapter 2-22
Discarding Changes and Exit
Allows the user to not save changes before exiting Setup. The following message is shown
when user presses ″Enter″ on this item.
Warning
Configuration has not been saved!
Save before exiting?
[Yes] [No]
System will reboot after either selection.
Get Default Values
Allows the user to load default values in CMOS Setup. The following message is shown when
user presses ″Enter″ on this item:
Setup Confirmation
Load default configuration now?
[ Yes] [No]
It still stay in Setup after either selection.
OS Compatibility
OS Retail Support
MS-DOS Minimal (Diagnostics and Manufacturing utilities)
Microsoft XP Home Edition Full
Microsoft XP Professional Edition Full
Microsoft Windows 2000 Not supported
Microsoft Windows Millennium Not supported
Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition
(ACPI only)
Not supported
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 SP5+ Not supported
Page 32

Chapter 2-23
Software Specification for KB-BIOS
General purpose
This document define the EC specification with standard interface and also define the special
feature for OEM function .It’s useful for software engineer to access EC status,and for SA test
guide.
Features
•
Advanced Power Management 1.2 support
• ACPI1.0 b and PC2001 compliant
• Support SMBus specification V1.0
• Hot keys for system control
• Audio volume output control
• External LED control
• Battery scope report and control
• Battery learning support
• Sticky key support
• Power switch control
• Speaker control
• Port replicator
• Extra key emulation
• Two host interface channels support
• Supports three independent devices
• Devices Hot Plug-and Play/Hot swapping configuration
• Internal Keyboard country selection
Types of KB-BIOS provided
• Standard version
Support for US(87)/UK(88)/Japanese(90) keyboard.
KB-BIOS command support with SYSTEM-BIOS
Command set 40h-4Fh for OEM defined through Port60/64 and Port62/66
Command Set (from system's point of view) via 60/64 and 62/66
CMD DATA Description return
40h
Boot fail restart
0x01-0x7F Boot fail restart, write in a byte to EC and enable the timer.
This command called by BIOS and will cause the system
reboot after the byte count down to zero if system still no
reset the counter. It could make sure the system success
boot up.
None
Page 33

Chapter 2-24
CMD DATA Description return
41h EC state notification
A0h Return core code version number One byte
A1h Return platform id ‘COMPAL’
42h Bank assign for EEPROM None
0x00-0x07 Bank assign for EEPROM,work with 4D/4E command
replace 4B/4C command
None
43h 00h - FFh Get RAM value from EC, Host can use this command to
send address to get OEM RAM value. The address range
are from 00h to DFh.
1 WORD
0x19 Get PANEL ID Panel id
44h None Get project ID 0x12
45h
Hook for every projects
NONE
46h fan speed read
01h fan speed 1
N = 60M/return value( rotate one circle 4 pulses)
N = 120M/return value( rotate one circle 2 pulses)
2 bytes
(high byte,
low byte)
02h Fan speed 2
N = 60M/return value( rotate one circle 4 pulses)
N = 120M/return value( rotate one circle 2 pulses)
2 bytes
(high byte
low byte)
47h Speaker mute On/Off
A7h Mute off None
A8h Mute on None
48h Reserved for docking control None
49h Thermal control notification
A0h Fan off None
A1h Fan speed level 1 None
A2h Fan speed level 2 None
A3h HCT enable None
49h A5h Fan speed level 4 None
4Ah
A
uto into S2R(Delay about 4 Secs) or S2D and resume by
timeout, This command provided engineer to verify S2R or
S2D and resume function is OK or not
Resume count(second base ), Range is from 0x02 to 0x7F
Bit7 = 0 -> Enabled S2R function
1 -> Enabled S2D function
0x02-0x7F Enabled S2R function None
0x80-0xFF Enabled S2D function None
Page 34

Chapter 2-25
CMD DATA Description return
4Bh Write the data to device through SMBus interface
1 00h-FFh Slave address of device
2 00h-FFh Lo byte address if device is EEPROM otherwise is command
or register
3 00h-FFh Hi byte address if device is EEPROM, otherwise is zero
data byte to write 0=Write
OK
0xFE =
Fail
4Ch Read data from devices through SMBus
1 00h-FFh Slave address of device
2 00h-FFh Lo byte address if device is EEPROM otherwise is command
or register
3 00h-FFh Hi byte address if device is EEPROM, otherwise is zero data byte
(00h-FFh)
4Dh Write byte into EEPROM
1 00h-FFh EEPROM address
2 00h-FFh Data byte for write byte 0=Write
OK
0xFE =
Fail
4Eh Read byte from EEPROM
00h-FFh EEPROM address Data byte
0xFE =
Fail
4Fh Reserved for R591 utility None
Page 35

Chapter 2-26
Command set 50h-5Fh for OEM defined through Port60/64 and Port62/66
Command Set (from system's point of view) via 60/64 and 62/66
CMD DATA Description return
50h None Get Docking status. A0h = No dock
A6h = simple docked
51h None Get revision number of KB-BIOS BIOS Rev. 3 bytes
byte0 :
bit0-bit2 = major number(0-
7)
bit3-bit7 = type of KB-BIOS
e.g. 0 = A, 1=B and so on..
byte1
minor revision number(0-9)
byte2
If it is 00h then system
display “ROM”,other It is
“T01” if it is 01h and so
on.. .
52h None Hook for every projects(Get platform ID) 5Bytes “ACY25”
53h None Reserved None
54h 0x00-0xFF EC CMOS RAM read Data byte from CMOS
55h EC CMOS RAM write
0x00-0xFF CMOS address offset
0x00-0xFF data byte 0x00 => pass
0x01 => fail
56h Get SMI trigger source One byte
Battery status change 80h
Ask suspend(On mode) A0h
brightness level update A1h
contrast level update A2h
audio volume decreased A3h
audio volume increased A4h
Lid open A5h
Lid closed A6h
External device plugged A7h
External device removed A8h
Page 36

Chapter 2-27
CMD DATA Description return
Bluetooth wake up event A9h
Bluetooth switch event Aah
Scr expand event Abh
56h Cpu fast event Adh
Cpu slow event Aeh
Pop up event Afh
Resume request from suspend B0h
Ask time out event B1h
Battery life in critical low state B2h
Battery life in low power state B3h
Standby request B4h
Battery Plug-In B5h
Battery Plug-Out B6h
Reserved B7h
Suspend to RAM request B8h
Save to DISK request B9h
Docked request Bah
Undock request Bbh
Reserved Bch
Thermal change event Bdh
Write LM75 event Beh
SMBus event Bfh
Password event C0h
mute function toggle C1h
Power button pressed C2h
TV out toggle C3h
Beep Alarm event C4h
Reserved C5h
Change use battery C6h
AC power plug-in C7h
AC power plug-out C8h
IR toggle event C9h
Modem Ring In Cah
Unload OS Ultra Base Devices Cbh
Surprise undock event Cch
Battery polling Cdh
PME signal active Ceh
Page 37

Chapter 2-28
CMD DATA Description return
Mouse hot plug event Cfh
56h CRT plug in/out event D0h
Sleep button event D1h
RTC date/time update event D2h
Device change event F0h
Bluetooth lan event F1h
no event FFh
57h None Module identification One byte
bit0 : Ext. FDD exis
bit1 : Int. FDD exist
bit2 : IDE exist
other bit : Reserved
58h 0x00-0xFF Set flat panel type None
59h System state notification None
70h Sticky key mode enable None
71h Sticky key mode disable None
80h start to get LCD status panel information
from EEPROM
None
90h One touch button application allow to
send scan code(user button) if user
pressed
None
91h One touch button application don’t allow
to send scan code(user button) if user
pressed
None
92h Mail message is waiting(no support in
Hurricane)
None
93h Mail message end of waiting(no support in
Hurricane)
None
94h Mute on None
95h Mute off None
9Ah Ac off(cut off AC power) None
9bh Ac on None
A2h System enter S2D(S4) state None
A3h System enter beep mode for battery LB
state in CMOS setup
None
A4h System enter quiet mode for battery LB
state in CMOS setup
None
A5h Fan control by EC None
A8h Fan control by OS None
A9h external PS2 only None
Page 38

Chapter 2-29
CMD DATA Description return
Aah Both enable external PS2 and internal
touch pad
None
Ach Auto enable/disable external PS2 and
internal touch pad
None
B1h System into standby None
B2h Resume from standby None
B5h VGA suspend enable None
B6h VGA suspend disable None
B8h Modem ring disable None
B9h PME enable None
Bah PME disable None
Bbh S4 status bit clear None
Bch S4 status bit set None
C1h force battery pack auto learning None
C2h disable battery pack learning None
C3h SMI/SCI Trigger event enable None
C4h SMI/SCI Trigger event disable None
Cbh PCMCIA suspend disable None
Cch PCMCIA suspend enable None
Cdh Wake up LAN disable None
Ceh Wake up LAN enable None
D0h Disable IRQ1 None
D1h Enable IRQ 1
D2h Beep alarm 100mS None
D5h PCMCIA reset off None
D6h PCMCIA reset on None
E1h Turn LCD back-light on None
E2h Turn LCD back-light off None
E5h Select US keyboard Matrix None
E6h Select JP keyboard Matrix None
E7h Select UK keyboard Matrix None
E8h EC into ACPI mode None
E9h Non-ACPI mode (EC default) None
F2h disable watchdog None
F3h enable watchdog None
F4h enable RTC access by EC None
F5h disable RTC access by EC None
F6h Clear header of Boot code None
Page 39

Chapter 2-30
CMD DATA Description return
F7h Restart system and Clear header of Boot
code
None
F8h Shut down system and Clear header of
Boot code
None
F9h Clear header of Boot code None
5Ah RTC update
1 A0h Update Year of RTC ,Year(00-99) BCD
format
2 00-99 Year which want to display None
1 A1h Update Month of RTC ,Month ( 1..12) BCD
format
2 01-12 Month which want to display None
1 A2h Update DAY of RTC ,Day(01-07) BCD
format
2 01-07 Day which want to display None
1 A3h Update HOUR of RTC ,Hour(00-23) BCD
format
2 00-23 Hour which want to display None
1 A4h Update Minute of RTC ,Minute (0..59),
BCD format
2 00-59 Minutes which want to display None
1 A5h Update Second of RTC ,Second (0..59),
BCD format
2 00-59 Seconds which want to display None
5Bh Reserved
5Ch None Get brightness level current brightness level
(0x00-0x0a)
5Dh Set brightness level
0x00h-
0x0ah
new brightness level None
5Eh None Get contrast level Current contrast level
(0x00-0x40)
5Fh Set contrast level
0x00h-
0x40h
new contrast level None
Hot keys for system control
•
Definitions
All Fn Key will support Sticky key mode.
Fn + F5 Force Switching Display Mode(LCD->CRT->Simulataneous)
Fn + F10 Cursor keypad on/off.
Page 40

Chapter 2-31
Pressing this hot key can enable/disable the embedded cursor keypad.
Numeric lock state is logically disable.
Fn + F11 Num keypad on/off
Pressing this hot key can enable/disable the embedded Numeric keypad.
Numeric lock state is logically enable.
Fn + F12 Scroll Lock on/off
Fn + ↑
Increase Brightness (total 10 levels)
Fn + ↓
Decrease Brightness (total 10 levels)
After rebooting, pad lock is set to off and Num lock is set to on. In this state, the embedded
cursor/number pad is not enabled on the notebook keyboard.
Note: Hot keys for brightness/contrast adjustment are in repeat mode, others will only be
updated once for each key depression.
Audio volume output control
Use Volumn Up/Down Button for Increasing/Decreasing respectively, it controls the volume
output of the audio chip.
External Buttons status report and control
Define the function of buttons which is controlled by EC.
Power Switch
• If system is Off/S2D : System will be turned on while Power switch is depressed by more
than 500 ms with or without AC insert
• If system is in S2R/Standby state : System will resume while Power switch is depressed by
more than 100 ms
Mechanical off button
• It will reset KB-BIOS then turn off system.This signal connect to 591 LREST to do
hardware reset.
Wireless on/off switch
It will enable/disable wireless function.
One touch Button
• Support 2 one touch buttons, it will launch homologous application.
User Button 1: press this button can launch default defined Internet application.
User Button2 : press this button can launch default defined E-mail browser application.
External LEDs status report and control
Define the Led display status.
Definitions of Lock LEDs
• Caps lock LED: Caps Lock State of Keyboard
• Num Lock LED: Num Lock State of Keyboard
Page 41

Chapter 2-32
Definitions of System state LED
• There is one dual-color LED indicator both of Green and Amber color
• Green color support for System state. The definition is in below:
Green color activity : System On.
Green color off : System Off.
• Amber color support for power management state. The definition is below:
• Amber color activity : System in sleep(S1 state) or S2R mode(S3 state).
Color off : Not in power management mode.
Definitions of DC-DC state LED
• Green color : for battery charging state.
Green color activility:Battery charging with AC(green LED on for 1sec per 4
sec)
Green color on : Battery full by AC charge.
Green color off : Battery full/discharge
• Amber color(Green and Red) : for battery discharge state.
Amber color activility : batterywithin low state(remain 12 minutes left)
Amber color blinking : battery in critical low state( remain 3 minutes left).
LED flash once per second.
Amber color off : Battery charging
• Red color : Stop charge by battery Bad cell, Over temperature or charging protection.
Definitions of Wireless on/off State LED
• Blue color: Wireless power on.
• Off: Wireless power off.
Battery status report and control
Define the battery type spec and battery protection function.
Battery status
• There are four battery states for each battery pack depend on getting the battery state
through SMBus protocol from Smart battery pack: full, normal, low, critical low.
• The battery gas-gauge and level of low power states should base on ‘current’ system
configuration.
• Battery turn on system condition : gasgauge > 5%
Page 42

Chapter 2-33
Battery discharge/charging control
Charging Dischargung Action
Charging :0℃<T<50℃
Stop charging:T>60
℃
Stop charging
&
Red Led on
T>73℃ T>73℃
T>73
℃
Shut down
R.S.O.C.
≦
10% LB(Beeping)
R.S.O.C. < 3%
LLB
Dependent on OS
TBD
LLC
Shut down
System
R.S.O.C < 5%
during system is in S2R mode.
S2D
Fast Charge Time
out: 8 Hours
Trickle Charge Time Out:
1 Hour.
Battery BAD
&
Red Led on
TBD
OverVoltage
&
Red Led on
In ACPI mode
• System should 'Save to Disk'(S2D) or beeping(Low condition) depend on OS setting .
Battery type
• The KB-BIOS will support for smart battery pack by SMBus protocol.
• ACPI1.0b and PC2001 Compliant,with PC2001 spec “A mobile system must use a Smart
Battery or an ACPI control method battery”,our currently design is ACPI control method
battery.
Li-ion Battery :
14.8V/3900mAH (4S2P)
14.8V/4000mAH(4S2P)
Ni-MH Battery : No Support
• Compatible with Intel’s SMBus and Philip’s I2C bus protocol.
KB-BIOS Power management support
EC will support S1(sleep mode),S3(standby mode),S4(suspend to disk) mode to save the
power comsumption.
Page 43

Chapter 2-34
Power states
• Sleep mode
LCD panel back-light off
• Save to RAM
keyboard(int./ext.) scanning off
• Save to DISK
no actions except turning off system with AC exist or turn off KBC without AC.
SMI/SCI/SWI/SBS/SPB events(To be Changed)
• Following list is which events(SMI/SCI/SWI/SBS) will be generated under different OS.
APM Mode ACPI mode
Function Description ON
mode
S2R
mode
S2D
mode
Trigge
r event
S0
status
S1,S2,
S3
status
S4
status
S5
status
SCI
event
SWI
event
Brightness level changed
SMI - - A1h SCI - - - 11h -
Contrast level changed
SMI - - A2h SMI - - - 12h -
CoverLid close
SMI - - A6h SCI - - - 16h -
Display toggle
SMI - - Ach SCI - - - 1ch -
Battery in critical low
SMI SMI - B2h SCI SCI - - 22h -
Battery in low state
SMI - - B3h SCI - - - 23h -
Standby request
SMI - - B4h - - - - 24h -
Battery pack plugin
SMI - - B5h SBS - - - 25h -
Battery pack removed
SMI - - B6h SBS - - - 25h -
Suspend To RAM request
SMI - - B8h SCI - - - 28h -
Save To DISK request
SMI - - B9h - - - - 29h -
Docking in
SMI - - Bah SCI SPB - - 2ah -
Undock
SMI - - BBh SCI - - - 2bh -
AC plugin
SMI - - C7h SBS - - - 37h -
AC removed
SMI - - C8h SBS - - - 38h -
Modem ringin
SMI - - Cah - SPB - - 3ah 04
PME signal active
SMI SMI - Ceh SCI SPB - - 3eh 02
CRT plugin/out
SMI D0h SCI 40h
RTC Update
SMI D2h SCI 42h
Thermal Status Report and Fan Control
EC will control fan on/off function according to the CPU temperature(EC can get temperature
from thermal sensor through SMBus) .In currently spec,Fan will be off when temperature below
Page 44

Chapter 2-35
55℃50℃ ,and if temperature over 92℃85℃ five times,EC will auto turn off system to protect
CPU.For detail data please reference follows table.
Fan State & System State Temperature
Fan Off
55
℃
50
℃
Fan on 3.5V
70
℃
60
℃
Fan on 5V
76
℃
65
℃
Throttling on
78
℃
Throttling off
65
℃
Turn off Fan & shut down
92
℃
85
℃
Port replicator and Docking station
Button control
• The power switch and power kill button on docking station was identical to the one on the
NoteBook PC.
• Software controlled mechanical interlock and eject button.
Docked and undock control
• Support for cold dock ,warm dock ,hot dock and hot undock .
• Support for Software and Hardware eject with AC power source exist.
LEDs indicator
There are two LED indicators in SPR: System state LED and DC-DC state LED.
Extra keyboard emulation
Windows key emulation
• Left/Right windows keys both depressed: Fn and Application key depressed
simultaneously.
• Right window key : press Fn+Left window key.
Fn Key emulation (Not support)
• External keyboard Fn-key emulation except Pad-Lock by pressing both Left Ctrl and Left
Alt of external keyboard. It will not work on USB keyboard.
Internal Key-Pad mode control
Number lock on Key pad on Number lock
and Key pad
both on
Number lock
and Key pad
both off
U 4 Left key 4 U
J 1 End key 1 J
Single key
: : : : :
U U U U Left key
J J J J End key
Fn +
: : : : :
We have several keys support keypad mode. List as below:
Page 45

Chapter 2-36
“ 7“,” 8“,” 9“,” 0“,” U”,” I”,” O”,” P”,” J”,” K”,” L”,” ;”,” M”,” .”,” /”.
Other Fn key
• Scroll lock :press Fn + F12
• Numeric keypad lock: Fn + F11
• Pad lock: Fn + F10
Two host interface channels support
Keyboard and mouse interface transfer port
• One channel is dedicated for the keyboard and mouse data transfer(host address 60h and
64h). The Keyboard and Mouse channel of KBC is compatible to the legacy 8042 host
interface. It is base on two registers: Command/Data and Status
• The KB-BIOS interrupt generates IRQ1(Keyboard) and IRQ12(Mouse) for system.
Power management interface transfer port
• The other for the power management function(host address 62h and 66h). The Power
Management channel of KBC structure and operation are similar to those of the
Keyboard/Mouse channel.
Support three independent devices
• The KBC provides three data transfer channels. Each channel has two quasi-bidirectional
signals that are used for the direct interface to an external keyboard, mouse or any other
PS/2 compatible pointing device.
• The three channels are identical and thus allow the connector ports to be interchangeable.
Devices PnP configuration
Hot Plug-and-Play support
• The KBC watches both external devices, checking if the devices have recently been
plugged in or unplugged. The Hot pluggability of external PS2 devices feature detects the
attachment or removal of these devices.
Hot swapping control
• When the device is plugged in, the software automatically initializes the state of that
device, checks port swapping, and setup the KBC to handle dual-device operation. In dualdevice operation, the internal device is set in the same state as external device. When the
external device is unplugged, the internal device becomes the primary device.
ACPI EC interface Specification support
ACPI interface support
• The KBC provides support for Advance Configuration and Power Interface
specification(ACPI) Embedded Controller interface.
EC command support
• The 2nd (Power Management) host interface channel of the KBC is dedicated to this
function.
• All EC commands defined in the ACPI specification - Read/Write, Burst Mode
enable/disable and Query command - are supported.
Page 46

Chapter 2-37
Internal keyboard change Configuration
US/UK/JP country option
• The KBC supports three country selection by KBD_SEL application.
• You can key in KBD_SEL get the syntax for your option at DOS prompt.
Sticky key support
• Press shift key 5 times will enable sticky key function.Turns on StickyKeys,which allows
you to press a modifier key(CTRL,ALT,or SHIFT),or the windows logo key, and have it
remain active until the next time you press a key other then CTRL,ALT,SHIFT,or windows
logo key. This is useful for people who have diffculity pressing two keys simultaneously.
EC name space Configuration
SMBus EC interface ACPI RAM definition
Offset Description
60h
SMBus protocol
61h
SMBus statue
Bit0-Bit4 – Status
Bit5 - Reserved
Bit6 - ALARM
Bit7 - DONE
62h
SMBus Address
63h
SMBus Command
64h – 83h
SMBus Data
84h
SMBus BCNT
85h
SMBus alarm address
86h
SMBus alarm data 0
87h
SMBus alarm data 1
Word registers to Emulate smart charge RAM definition
Offset Description
90h – 91h
CHG_MODE0
CHG_MODE1
Bit0 – INHIBIT_CHARGE(0=enabled, 1=inhibit)
Bit1 – ENABLE_POLLING(0=disable, 1=enable)
Bit2 – POR_RESET(0=Mode unchanged, 1=set power on defaults)
Bit3 – RESET_TO_ZERO(0=No change, 1=set charging values to zero)
Bit4-15 – Reserved
92h – 93h
CHG_STAT0
CHG_STAT1
Bit0 – CHARGE_INHIBITED(Status of bit in CHG_MODE register)
Bit1 – MASTER_MODE(Set if HOST controlled & ENABLE_POLL)
Bit2 – VOLTAGE_NOTREG(Set if CHG_VOLT not in regulation )
Bit3 – CURRENT_NOTREG(Set if CHG_CURRENT not in regulation)
Bit4 – LEVEL_2(Set always at least level 2)
Bit5 – LEVEL_3(Set always if level 3 capable)
Page 47

Chapter 2-38
Offset Description
Bit6 – CURRENT_OR(Set if CHG_CURRENT out of range)
Bit7 – VOLTAGE_OR(Set if CHG_VOLT out of range)
Bit8 – THERMISTOR_OR(Set if thermistor R>100K Ohms)(Open)
Bit9 – THERMISTOR_COLD(Set if thermistor R>30K Ohms)(Cold Batt)
Bit10 – THERMISTOR_HOT(Set if thermistor R<3K Ohms)(Hot Batt)
Bit11 – THERMISTOR_UR(Set if thermistor R<500 Ohms)(Under range)
Bit12 – ALARM_INHIBITED(Set if charging inhibited from Alarm)
Bit13 – POWER_FAIL(Set if power fail)
Bit14 – BATTERY_PRESENT(Set if battery present)
Bit15 – AC_PRESENT(Set if charging power source available)
94h –95h
CHG_CURRENT0
CHG_CURRENT1
Bit0-Bit15 – Requested charging current(mA)
0=Turn off charger
65535=Provide maximum safe charger current
96h – 97h
CHG_VOLT0
CHG_VOLT1
Bit0-Bit15 – Requested charging voltage(mV)
0=Turn off charger
65535=Provide maximum safe charger voltage
98h – 99h
CHG_ALARM0
CHG_ALARM1
*** Alarm Bits ***
0x8000 – OVER_CHARGED_ALARM
0x4000 – TERMINATE_CHARGE_ALARM
0x2000 – RESERVED
0x1000 – OVER_TEMP_ALARM
0x0800 – TERMINATE_DISCHARGE_ALARM
0x0400 – RESERVED
0x0200 – REMAINING_CAPACITY_ALARM
0x0100 – REMAINING_TIME_ALARM
*** Status Bits ***
0x0080 – INITIALIZED
0x0040 – DISCHARGING
0x0020 – FULLY_CHARGED
0x0010 – FULLY_DISCHARGED
*** Error Code ***
0x0000 – 0x000F – All bits set hi prior to AlarmWarning() xmit
Page 48

Chapter 2-39
Word registers to Emulate smart selector RAM definition
Offset Description
9Ah
SEL_STATE0
Bit0 – PRESENT_A(Set if 1
st
battery present)
Bit1 – PRESENT_B(Set if 2
nd
battery present)
Bit2 – PRESENT_C(Set if 3
rd
battery present)
Bit3 – PRESENT_D(Set if 4
th
battery present)
Bit4 – CHARGE_A(Set if 1
st
battery be charging)
Bit5 – CHARGE_B(Set if 2
nd
battery be charging)
Bit6 – CHARGE_C(Set if 3
rd
battery be charging)
Bit7 – CHARGE_D(Set if 4
th
battery be charging)
9Bh
SEL_STATE1
Bit0 – PWR_BY_A(Set if system power up by 1
st
)
Bit1 – PWR_BY_B(Set if system power up by 2
nd
)
Bit2 – PWR_BY_C(Set if system power up by 3
rd
)
Bit3 – PWR_BY_D(Set if system power up by 4
th
)
Bit4 – SMB_A(Set if 1
st
battery on SMBus)
Bit5 – SMB_B(Set if 2
nd
battery on SMBus)
Bit6 – SMB_C(Set if 3
rd
battery on SMBus)
Bit7 – SMB_D(Set if 4
th
battery on SMBus)
EC interface OEM common RAM definition
Offset Description
9Ch
ACPI_FLAG0
Bit0 – Primary HDD(1:exist)
Bit1 – Internal FDD(1:exist)
Bit2 – CDROM(1:on)
Bit3 –Secondary HDD(1:exist)
Bit4 – LS120(1:exist)
Bit5 – External FDD(1:exist)
Bit6 –CRT plug in (1:exist)
Bit7 – Reserved
9Dh
ACPI_FLAG1
Bit0 – Sleep button(1:pressed)
Bit1 – Video out button(1:pressed)
Bit2 – Decrease Volume(1:pressed)
Bit3 – Increase Volume(1:pressed)
Bit4 – Mute button(1:pressed)
Bit5 – Contrast button(1:pressed)
Bit6 – Brightness button(1:pressed)
Bit7 – Save to disk button(1:pressed)
9Eh
ACPI_FLAG2
Bit0 - ACPI entry S4 state
Bit1 – Password button status
Bit2 – Spark beep button status
Bit3 – Touchpad button status
Bit4 –Bit7 Reserved.
9Fh
Reserved
A0h
UbStatus: Ultra Base control pin status
Bit0 – DPWR, Turn on Dock PCI power(0=off, 1=on)
Page 49

Chapter 2-40
Offset Description
Bit1 – UDRF, Undock request(0=inactive, 1=undock & flash LED)
Bit2 – UDRS, Undock request(0=inactive, 1=undock & solid LED)
Bit3 – EQBF, Enable Q-Buff(0=disable, 1=enable)
Bit4 – DWELL, Docked well LED(0=LED off, 1=LED on)
Bit5 – QVCCOK, Dock power ready status(0=No, 1=Yes)
Bit7 –CheckEject , (SoftEject request : 0=No 1=Yes )
A1h
DCID: Customer ID
Bit0 –DockType0, Dock on or not(0=off, 1=on)
Bit1 –DockType1, reserved
Bit4 – OS_undock OK
Bit5 – OS dock OK
Bit6 – Safe Undock OK
Bit7 –DockChange, Ultra Base had changed from docked to undock or undock to
dock (0=no, 1=yes)
A2h
Battery Learning steps.
A3h
SYS_STATUS: System indicator
Bit0 – S0LED, S0 state LED(0=LED off, 1=LED on)
Bit1 – S3LED, S3 state LED(0=LED off, 1=LED on)
Bit2 – VGAQ, VGA H/W suspend(0=VGA on, 1=VGA suspend)
Bit3 – PCMQ, PCMCIA H/W suspend(0/1=PCMCIA on/suspend )
Bit4 – PCMR, PCMCIA H/W reset (0=disable, 1=enable)
Bit5 –ADP,Ac adapter (0=offline, 1=online)
Bit6 –SYSR6(reserved)
Bit7 –SYSR7(reserved)
A4h
WAKEUP_ENABLE: Enable wake up function
Bit0 –PMEWAKE(PME Wk Enable:0=Disable, 1=Enable)
Bit1 –MDMWAKE (Modem Wk Enable:0=Disable, 1=Enable)
Bit2 - LANWAKE(LAN wakeup enable:0=Disable, 1=Enable)
Bit3-Bit7 – reserved
A5h
FANOFF_TEMP: Fan off temperature level
A6h
FANSPD1_TEMP: Fan on speed 1t
A7h
FANSPD2_TEMP: Fan on speed 2
A8h
FANSPD3_TEMP: Fan on speed 3
A9h
FANSPD4_TEMP: Fan on speed 4
AAh
FANSPD5_TEMP: Fan on speed 5
ABh
FANSPD6_TEMP: Fan on speed 6
ACh
FANSPD7_TEMP: Fan on speed 7
ADh
Temperature index
AEh
Reserved
AFh
THERMAL_STATUS
Bit0 – MODE (0=Local mode, 1=Remote mode)
Bit1 – FANSPDB0(Fan on/off parameter0)
Bit2 – FANSPDB1(Fan on/off parameter1)
Bit 2 1 ( When control by OS )
0 0 : Fan off
Page 50

Chapter 2-41
Offset Description
0 1 : Fan on speed 1
1 0 : Fan on speed 2
1 1 : Fan on speed 3
Bit3 – INITOK ( 0:Control by OS 1:Control by EC )
Bit4 – Fan1 Active
Bit5 – Fan2 Active
Bit6 – Fan speed timer init OK
B0h
CPU_TEMP: CPU current temperature
B1h
SWI_Events: SWI Event indicators
Bit1 – Lid Open, Lid open event (0= off, 1= on)
Bit2 – PME, PME event (0= off, 1= on)
Bit3 –Power Button, Power button event (0= off, 1= on)
Bit4 –Ring In, Ring In event (0= off, 1= on)
Bit5 – BtWake,Bluetooth wake up event(0=off,1=on)
Bit6 – Dock ,Dock in event(0=off,1=on)
B2h
Percentage : Battery in critical low condition.
B3h
Percentage : Battery in low condition.
B4h
Fan1 pulse width low byte
B5h
Fan1 pulse width high byte
B6h
Fan2 pulse width low byte
B7h
Fan2 pulse width high byte
B8h
Bluetooth Status
Bit0 – Detach(0=Detach,1=Attach)
Bit1 – Power(0=power off,1=power on)
Bit2 – Detach Status(0=Detach OK,1=Attach OK)
Bit3 –Power Status(0=Power off OK,1=Power on OK)
Bit4 – Switch(0=switch off,1=switch ok)
Bit5 –wake up
Bit6 –Bluetooth led(0=led off,1=led on)
B9h
Lcd brightness value (0x00-0x0a)
BAh
Lcd contrast value (0x00-0x1F)
BBh
Reserved
BCh
Project ID
BDh
Reserved
BEh
ITOC timer low byte
BFh
ITOC timer high byte
F9h
Fan1 RPM low byte
FAh
Fan1 RPM high byte
FBh-FFh
Reserved
Page 51

Chapter 2-42
Control method for 1st battery pack RAM definition
Offset Description
C0h
Bit4-6 – Manufacturer
Bit 6 5 4
0 0 1 : Sanyo
0 10 : Sony
1 0 0 : Panasonic
Bit7- Battery type
0 : Ni-MH
1 : Li-ion
C1h
Battery Status
Bit0 – Discharging
Bit1 – Charging
Bit2 – Discharging and Now is critical low
Bit3-7 – Reserved
C2h-C3h
Remaining Capacity
C4h-C5h
Serial Number
C6h-C7h
Present Voltage
C8h-C9h
Design Voltage
CAh-CBh
Design Capacity
CCh-CDh
Full charge capacity
Ceh
Gasgauge
CFh-D8h
Reserved
Control method for 2nd battery pack RAM definition
Offset Description
E0h
Bit4-6 – Manufacturer
Bit 6 5 4
0 0 1 : Sanyo
0 10 : Sony
1 0 0 : Panasonic
Bit7- Battery type
0 : Ni-MH
1 : Li-ion
E1h
Battery Status
Bit0 – Discharging
Bit1 – Charging
Bit2 – Discharging and Now is critical low
Bit3-7 – Reserved
Page 52

Chapter 2-43
Offset Description
E2h-E3h
Remaining Capacity
E4h-E5h
Serial Number
E6h-E7h
Present Voltage
E8h-E9h
Design Voltage
EAh-EBh
Design Capacity
ECh-EDh
Full charge capacity
EEh
Gasgauge
Efh-F8h
Reserved
Page 53

Chapter 3: Hardware
Major Sub-assembly Specification
System interconnection (For BY25)
Chapter 3-1
Page 54

MOTHER BOARD
JP28 KBD/PS2_6.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. KBD_DATA 2. PS2_DATA
3. GND 4. VCC
5. KBD_CLK 6. PS2_CLK
JP24,JP26,JP31 USB _CON..PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. VCC 2. USB(2,0,4)D-
3. USB(2,0,4)D+ 4. GND
JP6 CRT CONN..PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. R_RED 2. R_GREEN
3. R_BLUE 4. C
5. GND 6. GND
7. GND 8. GND
9. CRTVDD 10. GND
11. MSEN# 12. DDCDATA
13. HSYNC 14. VSYNC
15. DDCCLK
JP1 LPTCN-27.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. +5V_PRN 2. FD0
3. FD1 4. FD2
JP28 KBD/PS2_6.PRT JP20 Switch buttom Interface CONN
JP24,JP26,JP31 USB _CON..PRT JP1 CPU FAN CONN.
JP6 CRT CONN..PRT JP14 RJ45-11 CONN.
JP1 LPTCN-27.PRT JP4 DDR 200P SO-DIMM
JP9 HDD JP15 MODEM CONN
PCN2 BATT-B.PRT JP29 Audio M/B
JP19 FDD.PRT JP16 MINI-PCI CONN
PCN1 DC JACK PRT JP7 TV-OUT CONN
JP10 CDROM.PRT JP8 PANEL CONN
JP12 PCMCIA-CONN. 84P.PRT JP30 CARD READER CONN
JP5 DDR-200P.PRT JP11 1394 CONN
JP18 Int. KB Interface CONN
U1 CPU socket
U5 Northbridge
U10 Southbridge
Chapter 3-2
Page 55

5. FD3 6. FD4
7. FD5 8. FD6
9. FD7 10. LPTACK#
11. LPTBUSY 12. LPTPE
13. LPTSLCT 14. LPTAFD#
15. LPTERR# 16. LPT_INIT#
17. SLCTIN# 18. GND
19. GND 20. GND
21. GND 22. GND
23. GND 24. GND
25. GND
JP9 HDD
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. HD_IDERST# 2. GND
3. PD_D7 4. PD_D8
5. PD_D6 6. PD_D9
7. PD_D5 8. PD_D10
9. PD_D4 10. PD_D11
11. PD_D3 12. PD_D12
13. PD_D2 14. PD_D13
15. PD_D1 16. PD_D14
17. PD_D0 18. PD_D15
19. GND 20. NC
21. PD_DREQ 22. NC
23 PD_IOW# 24. GND
25. PD_IOR# 26. GND
27. PD_IORDY 28. PD_CSEL
29. PD_DACK# 30. GND
31. PD_IRQA 32. NC
33. PD_A1 34. CBLIDA
35. PD_A0 36. PD_A2
37. PD_CS#1 38. PD_CS#3
39. HDD_LED# 40. GND
41. +5VS 42. +5VS
43. GND 44. +5VS
PCN2 BATT-B.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. BATT+ 2. LI/NIMH#
Chapter 3-3
Page 56

3. GND 4. BATT_TEMP
5. EEPROMVCC 6. SMB_EC_CK1
7. SMB_EC_DA1 8 GND
JP19 FDD.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. HDSEL# 2 GND
3 RDATA# 4 GND
5 WR# 6 GND
7 TRACK0# 8 GND
9 WGATE# 10 GND
11 WDATA# 12. FDD_DET#
13. STEP# 14. 3MODE
15 FDDIR# 16. NC
17 MTR0# 18. NC
19 NC 20. NC
21 DISKCHG# 22. +5VS
23 DRV0# 24. +5VS
25. INDEX# 26. +5VS
PCN1 DC JACK PRT (70W)
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. VIN 2. GND
JP10 CDROM.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. INT_CD_L 2. INT_CD_R
3. CD_AGND 4. GND
5. CD_IDERST# 6. SD_D8
7 SD_D7 8. SD_D9
9. SD_D6 10. SD_D10
11. SD_D5 12. SD_D11
13. SD_D4 14. SD_D12
15. SD_D3 16. SD_D13
17. SD_D2 18. SD_D14
19. SD_D1 20. SD_D15
21. SD_D0 22. SD_DREQ
23. GND 24. SD_SIOR#
25. SD_SIOW# 26. GND
27. SD_SIORDY 28. SD_DACK#
Chapter 3-4
Page 57

29. SD_IRQ15 30. NC
31. SD_SBA1 32. CBLIDB
33. SD_SBA0 34. SD_SBA2
35. SD_CS1# 36. SD_SCS3#
37. CDLED# 38. +5V_IDE
39. +5V_IDE 40. +5V_IDE
41. +5V_IDE 42. +5V_IDE
43. GND 44. +5VS
45. GND 46. GND
47. SD_CSEL 48. GND
49. NC 50. +5VS
JP12 PCMCIA-CONN. 84P.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
A1. GND A2. GND
A3. S1_D3 A4. S1_CD1#
A5. S1_D4 A6. S1_D11
A7 S1_D5 A8. S1_D12
A9. GND A10. S1_D6
A11. S1_D13 A12. S1_D7
A13. S1_D14 A14. S1_CE1#
A15. S1_D15 A16. GND
A17. S1_A10 A18. S1_CE2#
A19. S1_OE# A20. S1_VS1
A21. S1_A11 A22. GND
A23. S1_IORD# A24. S1_A9
A25. S1_IOWR# A26. S1_A8
A27 S1_A17 A28 GND
A29. S1_A13 A30. S1_A18
A31. S1_A14 A32. S1_A19
A33. S1_WE# A34. S1_A20
A35. S1_RDY# A36. S1_A21
A37 S1_VCC A38 S1_VCC
A39. S1_VPP A40. S1_VPP
A41. S1_A16 A42. GND
A43. S1_A22 A44. S1_A15
A45. S1_A23 A46. S1_A12
A47. S1_A24 A48. S1_A7
A49. GND A50. S1_A25
Chapter 3-5
Page 58

A51 S1_A6 A52 S1_VS2
A53 S1_A5 A54 S1_RST
A55 S1_A4 A56 S1_WAIT#
A57 GND A58 S1_A3
A59 S1_INPACK# A60 S1_A2
A61 S1_REG# A62 S1_A1
A63 S1_BVD2 A64 S1_A0
A65 GND A66 S1_BVD1
A67 S1_D0 A68 S1_D8
A69 S1_D1 A70 S1_D9
A71 S1_D2 A72 S1_D10
A73 GND A74 S1_WP
A75 S1_CD2# A76 GND
A77 GND
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
B1. GND B2. GND
B3. S2_D3 B4. S2_CD1#
B5. S2_D4 B6. S2_D11
B7 S2_D5 B8. S2_D12
B9. GND B10. S2_D6
B11. S2_D13 B12. S2_D7
B13. S2_D14 B14. S2_CE1#
B15. S2_D15 B16. GND
B17. S2_A10 B18. S2_CE2#
B19. S2_OE# B20. S2_VS1
B21. S2_A11 B22. GND
B23. S2_IORD# B24. S2_A9
B25. S2_IOWR# B26. S2_A8
B27 S2_A17 B28 GND
B29. S2_A13 B30. S2_A18
B31. S2_A14 B32. S2_A19
B33. S2_WE# B34. S2_A20
B35. S2_RDY# B36. S2_A21
B37 S2_VCC B38 S2_VCC
B39. S2_VPP B40. S2_VPP
B41. S2_A16 B42. GND
B43. S2_A22 B44. S2_A15
Chapter 3-6
Page 59

B45. S2_A23 B46. S2_A12
B47. S2_A24 B48. S2_A7
B49. GND B50. S1_A25
B51 S1_A6 B52 S1_VS2
B53 S1_A5 B54 S1_RST
B55 S1_A4 B56 S1_WAIT#
B57 GND B58 S1_A3
B59 S1_INPACK# B60 S1_A2
B61 S1_REG# B62 S1_A1
B63 S1_BVD2 B64 S1_A0
B65 GND B66 S1_BVD1
B67 S1_D0 B68 S1_D8
B69 S1_D1 B70 S1_D9
B71 S1_D2 B72 S1_D10
B73 GND B74 S1_WP
B75 S1_CD2# B76 GND
B77 GND
JP5 DDR-200P.PRT
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1. MVREF_DIM 2. MVREF_DIM
3. GND 4. GND
5. MD0 6. MD4
7 MD1 8. MD5
9. +2.5V 10. +2.5V
11. RDQS0 12. GND
13. MD6 14. MD3
15. GND 16. GND
17. MD2 18. MD7
19. MD8 20. MD12
21. +2.5V 22. +2.5V
23. MD9 24. MD13
25. RDQS1 26. GND
27 GND 28 GND
29. MD10 30. MD14
31. MD15 32. MD11
33. +2.5V 34. +2.5V
35. DDR_CLK0 36. +2.5V
37 DDR_CLK0# 38 GND
Chapter 3-7
Page 60

39. GND 40. GND
41. MD16 42. MD20
43. MD21 44. MD17
45. +2.5V 46. +2.5V
47. RDQS2 48. GND
49. MD18 50. MD22
51 GND 52 GND
53 MD19 54 MD23
55 MD24 56 MD28
57 +2.5V 58 +2.5V
59 MD25 60 MD29
61 RDQS3 62 GND
63 GND 64 GND
65 MD30 66 MD26
67 MD31 68 MD27
69 +2.5V 70 +2.5V
71 GND 72 GND
73 GND 74 GND
75 GND 76 GND
77 RDQS8 78 GND
79 GND 80 GND
81 +2.5V 82 +2.5V
83 GND 84 GND
85 NC 86 NC
87 GND 88 GND
89 DDRCLK2 90 GND
91 DDRCLK2# 92 +2.5V
93 +2.5V 94 +2.5V
95 CKE3 96 CKE2
97 GND 98 GND
99 MAA12 100 MAA11
101 MAA9 102 MAA8
103 GND 104 GND
105 MAA7 106 MAA6
107 MAA5 108 MAA4
109 MAA3 110 MAA2
111 MAA1 112 MAA0
113 +2.5V 114 +2.5V
Chapter 3-8
Page 61

115 MAA10 116 MAA12
117 MAA11 118 SRAS#
119 SWE# 120 SCAS#
121 RCS0# 122 RCS1#
123 NC 124 NC
125 GND 126 GND
127 MD32 128 MD36
129 MD37 130 MD33
131 +2.5V 132 +2.5V
133 RDQS4 134 GND
135 MD34 136 MD38
137 GND 138 GND
139 MD35 140 MD39
141 MD40 142 MD44
143 +2.5V 144 +2.5V
145 MD41 146 MD45
147 RDQS5 148 GND
149 GND 150 GND
151 MD42 152 MD43
153 MD46 154 MD47
155 +2.5V 156 +2.5V
157 +2.5V 158 DDR_CLK1#
159 GND 160 DDR_CLK1
161 GND 162 GND
163 MD48 164 MD49
165 MD52 166 MD53
167 +2.5V 168 +2.5V
169 RDQS6 170 GND
171 MD50 172 MD54
173 GND 174 GND
175 MD51 176 MD55
177 MD57 178 MD56
179 +2.5V 180 +2.5V
181 MD61 182 MD60
183 RDQS7 184 GND
185 GND 186 GND
187 MD58 188 MD62
189 MD59 190 MD63
Chapter 3-9
Page 62

191 +2.5V 192 +2.5V
193 SMBDAT 194 GND
195 SMBCK 196 GND
197 +3VS 198 GND
199 NC 200 NC
JP18 Int. KB Interface CONN
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1.
ID1
2.
ID
2
3.
GN
D
4.
USER BTN#
5.
LED+
6.
LE
D
-
7
KSO0
8.
KSO1
9.
KSO
2
10.
KSO3
11.
KSO
4
12.
KSO5
13.
KSO
6
14.
KSO7
15.
KSO
8
16.
KSO9
17.
KSO10
18.
KSO11
19.
KSO1
2
20.
KSO13
21.
KSO1
4
22.
KSO15
23.
KSI0
24.
KSI1
25.
KSI
2
26.
KSI3
27
KSI
4
28
KSI5
29.
KSI
6
30.
KSI7
JP20 Switch buttom Interface CONN
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1.
+3VALW
2.
+3V
S
3.
SCROLLLED#
4.
NUMLED#
5.
CAPSLED#
6.
51ON#
7
EC ACT#
8.
GN
D
-MIC
9.
INT MI
C
10.
GN
D
-MIC
11.
USER BTN0#
12.
USER BTN1#
13.
USER BTN2#
14.
USER BTN3#
15.
GN
D
16.
NC
17.
N
C
18.
NC
19.
N
C
20.
GND
JP1 CPU FAN CONN.
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1.
+5VFAN1
2.
FAN1_SPEED1
3.
GND
Chapter 3-10
Page 63

JP14 RJ45-11 CONN.
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1.
R
2.
R
3.
RX
-
4.
R
5.
R
6.
RX+
7
TX
-
8.
TX+
9.
N
C
10.
MOD TIP
11.
MOD RIN
G
12.
NC
13.
GN
D
14.
GND
15.
LED1 GRNP
16.
LED GRNN
17.
LED2 YELP
18.
LED2 YELN
JP4 DDR 200P SO-DIMM
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
1.
MVREF_DIM
2.
MVREF_DIM
3.
GND
4.
GND
5.
MD0
6.
MD4
7
MD1
8.
MD5
9.
+2.5V
10.
+2.5V
11.
RDQS0
12.
GND
13.
MD6
14.
MD3
15.
GND
16.
GND
17.
MD2
18.
MD7
19.
MD8
20.
MD12
21.
+2.5V
22.
+2.5V
23.
MD9
24.
MD13
25.
RDQS1
26.
GND
27
GND
28
GND
29.
MD10
30.
MD14
31.
MD15
32.
MD11
33.
+2.5V
34.
+2.5V
35.
DDR_CLK3
36.
+2.5V
37
DDR_CLK3#
38
GND
39.
GND
40.
GND
41.
MD16
42.
MD20
43.
MD21
44.
MD17
45.
+2.5V
46.
+2.5V
47.
RDQS2
48.
GND
49.
MD18
50.
MD22
51
GND
52
GND
53
MD19
54
MD23
Chapter 3-11
Page 64

55
MD24
56
MD28
57
+2.5V
58
+2.5V
59
MD25
60
MD29
61
RDQS3
62
GND
63
GND
64
GND
65
MD30
66
MD26
67
MD31
68
MD27
69
+2.5V
70
+2.5V
71
GND
72
GND
73
GND
74
GND
75
GND
76
GND
77
RDQS8
78
GND
79
GND
80
GND
81
+2.5V
82
+2.5V
83
GND
84
GND
85
NC
86
NC
87
GND
88
GND
89
DDRCLK5
90
GND
91
DDRCLK5#
92
+2.5V
93
+2.5V
94
+2.5V
95
CKE3
96
CKE2
97
GND
98
GND
99
MAA12
100
MAA11
101
MAA9
102
MAA8
103
GND
104
GND
105
MAA7
106
MAA6
107
MAA5
108
MAA4
109
MAA3
110
MAA2
111
MAA1
112
MAA0
113
+2.5V
114
+2.5V
115
MAA10
116
MAA12
117
MAA11
118
SRAS#
119
SWE#
120
SCAS#
121
RCS2#
122
RCS3#
123
NC
124
NC
125
GND
126
GND
127
MD32
128
MD36
129
MD37
130
MD33
131
+2.5V
132
+2.5V
133
RDQS4
134
GND
135
MD34
136
MD38
Chapter 3-12
Page 65

137
GND
138
GND
139
MD35
140
MD39
141
MD40
142
MD44
143
+2.5V
144
+2.5V
145
MD41
146
MD45
147
RDQS5
148
GND
149
GND
150
GND
151
MD42
152
MD43
153
MD46
154
MD47
155
+2.5V
156
+2.5V
157
+2.5V
158
DDR_CLK4#
159
GND
160
DDR_CLK4
161
GND
162
GND
163
MD48
164
MD49
165
MD52
166
MD53
167
+2.5V
168
+2.5V
169
RDQS6
170
GND
171
MD50
172
MD54
173
GND
174
GND
175
MD51
176
MD55
177
MD57
178
MD56
179
+2.5V
180
+2.5V
181
MD61
182
MD60
183
RDQS7
184
GND
185
GND
186
GND
187
MD58
188
MD62
189
MD59
190
MD63
191
+2.5V
192
+2.5V
193
SMBDAT
194
+3VS
195
SMBCK
196
GND
197
+3VS
198
GND
199
NC
200
NC
P15 MODEM CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1
MOD RING
2
MOD TIP
JP29 Audio M/B
PIN NO SIGNAL PIN NO SIGNAL
Chapter 3-13
Page 66

1 CLK 14M SIO 2 GND
3
A
C97 BCLK 4 HPLUG
5
A
C97 RST# 6
A
C97 SYNC
7
A
C97 SDOUT 8
A
C97 SDIN0
9 MD MIC 10 MONO IN
11 MOD AUDIO MONR 12 +3VS
13 CD AGND 14 CDROM L
15 CDROM R 16 GND MIC
17 INTMIC 18 GND
19 PS2 DATA 20 PS2 CLK
21 EC MUTE 22 FULL LED#
23
A
CT LED# 24 CHARGING LED#
25 POWER1 LED# 26 POWER2 LED#
27 LED2 28 +5VS
29 +5VALW 30 +3VALW
JP16 MINI-PCI CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1.
NC
2.
NC
3.
NC
4.
NC
5.
NC
6.
NC
7
NC
8.
NC
9.
NC
10.
NC
11.
NC
12.
NC
13.
D
14.
NC
15.
NC
16.
NC
17.
PIRQD#
18.
+5VS
19.
+3VS
20.
PIRQB#
21.
REQ#4
22.
GNT#4
23.
GND
24.
+3.3VAU
X
25.
PCLK MINI
26.
PCIRST#
27
GND
28
+3VS
29.
REQ#1
30.
GNT#1
31.
+3VS
32.
GND
33.
A
D31
34.
MINI PME#
35.
A
D29
36.
LAN_PME#
37
GND
38
AD30
39.
A
D27
40.
+3VS
41.
A
D25
42.
AD28
43.
LAN IDSEL
44.
AD26
45.
CBE#3
46.
AD24
Chapter 3-14
Page 67

47.
A
D23
48.
MINI IDSEL
49.
GND
50.
GND
51
A
D21
52
AD22
53
A
D19
54
AD20
55
GND
56
PAR
57
A
D17
58
AD18
59
CBE#2
60
AD16
61
IRDY#
62
GND
63
+3VS
64
FRAME#
65
CLKRUN#
66
TRDY#
67
SERR#
68
STOP#
69
GND
70
+3VS
71
PERR#
72
DEVSEL#
73
CBE#1
74
GND
75
A
D14
76
AD15
77
GND
78
AD13
79
A
D12
80
AD11
81
A
D10
82
GND
83
GND
84
AD9
85
A
D6
86
CBE#0
87
A
D7
88
+3VS
89
+3VS
90
AD6
91
A
D5
92
AD4
93
NC
94
AD2
95
A
D3
96
AD0
97
+5VS
98
NC
99
A
D1
100
NC
101
GND
102
GND
103
A
C97 SYNC
104
NC
105
A
C97 SDIN1
106
AC97 SDOUT
107
A
C97 BCLK
108
NC
109
+3.3
VAUX
110
AC97 RST#
111
MOD AUDIO MON
112
NC
113
GND
114
GND
115
MD MIC
116
MD AUDIO MON
117
GND
118
GND
119
GND
120
GND
121
MODEM RI#
122
NC
123
+5VS
124
+3.3VAU
X
127
GND
129
GND
Chapter 3-15
Page 68

JP7 TV-OUT CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1 GND 2 LUMA
3 GND 4 CRMA
5 GND 6
7 COMPS
JP8 PANEL CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1.
LCDVDD
2.
LCDVDD
3.
DC2
4.
GND
5.
TX0-
6.
TX0+
7
GND
8.
TX1-
9.
TX1+
10.
GND
11.
TX4-
12.
TX4+
13.
GND
14.
TXBCLK-
15.
TXBCLK+
16.
GND
17.
PID3
18.
PID2
19.
PID1
20.
PID0
21.
TX2-
22.
TX2+
23.
GND
24.
TCACLK-
25.
TXACLK+
26.
GND
27
TX5-
28
TX5+
29.
GND
30.
TX6-
31.
TX6+
32.
GND
33.
DD2
34.
LCDVDD
35.
LCDVDD
36.
DAC BRIG
37
INVT PWM
38
DISPOFF#
39.
B+
40.
B+
JP30 CARD READER CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1 +5VS 2 +5VS
3 USB5 D+ 4 USB5 D5 PCIRST# 6 GND
JP11 1394 CONN
PIN No SIGNAL PIN No SIGNAL
1
X
TPA0+ 2 XTPA0-
3
X
TPB0+ 4 XTPB0-
Chapter 3-16
Page 69

Chapter 4: AC-DC CONVERTER
ACY25 series Power System block diagram
Chapter 4-1
Page 70

Description
This specification defines the performance and characteristic ASTEC SA80-3105-2278 AC
adapter power supply. It supplies a constant voltage 19V output source for ACY25 series
notebook computer.
Feature
Accepts universal input from 90V
AC
to 265V
AC
Offers constant Voltage 19.5V output source with 70W max output power capacity.
High efficiency 84% typical after burn in one hour
Compact Size
Electrical Specification
Input Voltage range: universal input, 90VAC TO 265VAC
Inrush current: 188Apk MAX @240V
AC
(cold start)
Input frequency range: 47~63Hz
Input Current: 1.2Amax at 90V
AC ,
70W LOAD
Start-up time:
≦
3sec at all line and load condition
HOLD-UP time:
≧
10m sec at 120VAC.full load condition
OUTPUT Voltage Regulation: 18.5V~20V including the effects of line Voltage
variation, load current, ripple and noise
OUTPUT Current: 0Amin, 3.68Amax continuos
OUTPUT Voltage ripple:≦300mV PK-PK for resistor load
OUTPUT Voltage Dynamic regulation: Output change between 0A and 3.51A,
Appled at 100Hz with 50% duty cycle at 0.5A/us slew Rate. Voltage
overshoot<0.5V.
DC OUTPUT PIN OUT:
Adapter power return
Adapter power + output.
AC SOCKET : 2PIN (L,N,FG) 2.5A 250V UL : 94V-0.
Temperature Range:
Operating temperature: +5℃ TO 40℃
Storage temperature: -100℃ TO +70℃
Chapter 4-2
Page 71

DC-DC CONVERTER
Description
The DC-DC converter is designed to supply the power for ACY25 series notebook computer
of Compal. It supply +5VALWP, +3VALWP, +1.8VALWP, +2.5VP, +CPU_CORE,
+1.25VP,+1.2VP for logical system, and supplies for the built-in NS87591 microprocessor
which handles the keyboard and PMU control functions of the system. The power ON/OFF is
also controlled by NS87591.There is also a charger power source built-in it. It can charge
battery pack whether the computer is ON or OFF.
Features
High efficiency, up to 90%(using battery)
Accept wide range DC input voltage from 8V to 21V
Built-in charger power source
The power ON/OFF is controlled by software
Electrical specification
Input Voltage/Current
10V to 20V at the summing point of AC Adapter and battery
INPUT Current 5A max from battery
INPUT Current 3.5A max from AC Adapter
Temperature Range:
Operating temperature : 0℃ to 40℃
storage temperature range : -20℃ to 65℃
Chapter 4-3
Page 72

DC/DC OUTPUT
Fixed output voltage/Current
Item +5VALWP +1.25VP +1.2VP
nominal voltage +5V +1.25V +1.2V
min. load 0A 0A 0A
max. load 4A 2A 0.2A
peak load 5.5A 3A 0.3A
total regulation 5V±5% 2% static 5%
4% transient
ripple voltage 100mVp-p max. 25mVp-p max. 60mVp-p max.
Item +12VALWP +3VALWP +1.8VALWP
nominal voltage +12V +3.3V +1.8V
min. load 0A 0A 0A
max. load 120mA 4A 1.5A
peak load 200mA 6A 2.5A
total regulation 12V±5% 3.3V±5% 1.8V±5%
ripple voltage 200mVp-p max. 100mVp-p max. 60mVp-p max.
Item +CPU_CORE +2.5VP
Nominal voltage Base on table1 +2.5V
Min load 0mA 0mA
Max load 32A 4A
Peak load 40A 6A
Total regulation -2mV/A with +-45mV 5%
Ripple voltage 60mVp-p max. 60mVp-p max.
Table 1
VID[4..0]
+CPU_CORE
P
VID[4..0]
+CPU_CORE
P
VID[4..0]
+CPU_CORE
P
VID[4..0]
+CPU_CORE
P
00000 1.75 01000 1.35 100000 0.975 11000 0.775
00001 1.70 01001 1.30 10001 0.950 11001 0.750
00010 1.65 01010 1.25 10010 0.925 11010 0.725
00011 1.60 01011 1.20 10011 0.900 11011 0.700
00100 1.55 01100 1.15 10100 0.835 11100 0.675
00101 1.50 01101 1.10 10101 0.850 11101 0.650
00110 1.45 01110 1.05 10110 0.825 11110 0.625
00111 1.40 01111 1.00 10111 0.800 11111 0.600
Chapter 4-4
Page 73

Charger
Controlled by NS87591 microprocessor from motherboard
Temperature sense capability for the battery (charge active between 0℃~ 40℃)
fast charge [2.5Amps-8cells(3900mAH), LiIon Battery when system off, approach
30W fast charge when system ON.(depend on system load)
Charging termination: check the Full_charged bit in Battery status of Smart
Battery.
When system turns off, the charging time from empty to full is 3.0 hrs typically
at room temperature.
Other battery services are presented by NS87591 microprocessor include
maximum charging timer, charging temperature range etc.
Charger power:
BATT++ Constant voltage mode: 16.8V±1%
Constant charger current mode:2.5A±10%-8cells(3900mAH)
Constant adapter current mode:3.20A±10%
OVER Current protection:
+5VALWP: 5.67~9.17A
+3.3VALWP: 5.23~8.73A
+CPU_CORE: 40~60A
OVER Voltage protection:
+5VALWP: V0+V0*(4~10%)
+3.3VALWP: V
0+V0
*(4~10%)
+CPU_CORE: V
0+V0
*12%
Short circuit protection:
latch mode for +5VALWP, +3VALWP, +CPU_CORE
auto recovery mode for +12VALWP
I/O
P1:Ac adapter input Jack socket
Pin 1: Adapter power return
Pin 2: Adapter power + input
Chapter 4-5
Page 74

DC/DC Interface
DC/DC
Signals I/O
Voltage
Level
Description
EC_ON# I 0~floating Active Low, NS87591 use this pin to control the system
power on/off.
ACOFF I 0~3.3V Active High, turn off the adaptor power for battery automatic
learning cycle.
ACIN O 0~3.3V Active High, go high when adaptor plug-in.
VGATE O 0~3.3V Active High, go high when +CPU_CORE ready.
VR_ON I 0~3.3V Active High, turn on/off the +CPU_CORE, +1.2VP
VID[0..4] I 0~3.3V CPU VID
FSTCHG I 0~3.3V Active High, NS87591 use this pin to enable charger.
IREF I 0~3.3V NS87591 DAC output, it control the charging current.
SMB_EC_CK1 I/O 0~5V SMBus Clock.
SMB_EC_DA1 I/O 0~5V SMBus data.
BATT_TEMP O 0~3.3V Battery Temperature detect pin
SUSP# O 0~3.3V Active High, NS87591 use this pin to suspend system
BATTERY
Lithium-Ion battery for ACY25 series
18650 2P4S, 14.8V/3900mAH, Lithium-Ion battery
Built-in protection and gas gauge function.
More than 300 charging/discharging cycles.
Modularized battery pack, easy to be replaced.
On board RTC battery: Maxell ML1220/1FC 3V/14mAH Lithium or
Sanyo ML1220-TT28 3V/15mAH Lithium
Chapter 4-6
Page 75

ACY25 14.1” & 15” INVERTER SPECIFICATION
General Description
There are two control signals that come from system to control lamp brightness. One signal is
named DAC_BRIG, which limits current to meet LCD lamp current specification. Another one
is named PWM, which adjusts lamp brightness. This inverter brightness is adjusted by PWM
burst mode. The PWM burst mode is that turning on and off the lamp at a rate of 150Hz. The
effective brightness is a function of the duty cycle.
Features
Wide range 9V to 21V input voltage
Brightness adjustment by PWM burst mode.
Close loop controls lamp current.
Absolute maximum rating
Environment: Temperature:
Operating temperature: 0℃ ~ 55℃
Storage temperature : -20℃ ~ 70℃
Humidity: 0 ~ 90% without condensation
MTBF: 50000 hours.
Electrical characteristic
No Item Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Comment
1 Input voltage INV_PWR 9 14.8 21 V
2 Input current Iin -- 0.33 -- A
3 Lamp current I
L
2.7 -- 6.3 mA *Note 1
4 Frequency F 45 55 65 KHz *Note2
5 Output power Pout -- -- 4.5 W
6 Efficiency
η
80% -- -- --
7 Starting voltage V
s
1600 -- -- V At 0’C
8 Starting time Tvs 1 -- 1.5 Sec
2.8 3.3 3.6 V Backlight on/off signal
9 Dispoff#
0 0.5 0.8 V Low level
10
Limited lamp
aximum current
DAC-BRIG 0 3.3 V *Note 1
Chapter 4-7
Page 76

142 150 158 Hz PWM signal frequency
3.0 3.3 3.6 V PWM signal amplitude
11
PWM signal
*note 4
INV_PWM
30 -- 100 %
Period
Ton
Duty =
12
lamp current
over-shoot
PKZeroI−
-- -- 10 %
Line transient( 10.8V to
21V/100us) and turn on
transient
13
Current
Waveform factor
rms
p
I
I
1.27
2
1.56 Multiple
OR
rms
p
I
I
−
*10
14
Unbalance
Rate
rms
pp
I
II
−
−
-10% 0 +10% Multiple
15 Turn off voltage Voff -- -- 100Vp-p V PWM=40%
16
Voltage Rise
time
Trise -- -- 300us us PWM=40%
17 Voltage fall time Tfall -- -- 300us us PWM=40%
Notes:
*1. Limited lamp maximum current by DAC_BRIG signal:
When DAC_BRIG voltage is 0V and INV_PWM enables (100%), lamp has max. limited
current.
When DAC_BRIG voltage is 3.3V and INV_PWM enables (100%), lamp has min. limited
current.
DAC_BRIG signal comes from system chipset with internal resistance of 3KΩ.
*2. Inverter operating frequency should be within specification (45~65kHz) at max. and min.
brightness load.
*3. INV_PWM enable implies INV_PWM signal is High level (On duty cycle is 100%). It is a
square wave of 150Hz to adjust backlight brightness that is a function of PWM duty cycle.
Backlight brightness is maximum value under INV_PWM at 100% and brightness is
minimum under INV_PWM at 40%.
*4. The system interface signals belong to 3.3V.
*5. Please make sure open lamp output voltage should be within starting voltage specification.
*6. Inverter should pass human body safety test.
*7. Inverter should no smoking by any component open/ short test
*8. Transformer voltage stress should not be over 85% under any condition
( turn on overshoot transient and line transient).
*9. Audio noise should be less than 36dB at 10 cm distance.
Chapter 4-8
Page 77

Electrical specification
No Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Comment
V
oper
. -- 700 -- Vrms Lamp operating voltage
I
L
5.7 6.0 6.3 mArms DAC_BRIG: 0 V, PWM: 100%
I
L
2.7 3.0 3.3 mArms DAC_BRIG: 0 V, PWM:30%
F 45 55 65 KHz
1
η
80% -- -- --
Thermal
All components on inverter board should follow below rules:
Component using conditions (component stress) must be within component specification
including voltage rating, current rating, temperature etc.
Component temperature should follow below:
• Δ T < 30℃ , at 25 , 35℃.
• Component temperature should be less than 70℃ inside system at 35℃.
Connector description
Input Connector:
CN1: ACES 87213-0700; JST SM07B-SRSS-TB
Pin No. Symbol Description
1 INV_PWR Input voltage (9V-21V)
2 INV_PWR Input voltage (9V-21V)
3 INV_PWM Adjust brightness by burst mode(3.3 V 150Hz)
4 DISOFF # Backlight on/off control, active HIGH(3.3V)
5 DAC_BRIG Max. current limit
6 GND Power system return
7 GND Power system return
Chapter 4-9
Page 78

Output Connector:
CN2: JST_SM02B_BHSS-1
Pin No. Symbol Description
1 HV Connected to high voltage of LCD lamp
2 LV Connected to low voltage of LCD lamp
Note : Please mark “ CAUTION HIGH VOL TAGE” around CN2
Safety Protection
Open lamp protection:
When inverter is on open lamp status, any component on inverter should be O.K and inverter
is no damaged, no fire and no arcing. If inverter can’t shunt down during open lamp happen,
inverter must pass below conditions:
Human body test.
Open lamp burning: Inverter burns for 24 hours at open lamp status. No parts damage.
Human body safety test:
Short inverter output, transformer secondary output to GND by a 2KΩ resistor which connects
one end to GND and another one to those outputs. They should meet output current limitation
requirement as follow. Output current I is the current that flows through 2K
Ω
resistor.
Output current I ≦ 0.7mA , if frequency f ≦ 1KHz
Output current I ≦ 0.7mA * f (kHz) , if f ≧ 1KHz.
However, output current should be less than 70mA even frequency is more than 100KHz.
Abnormal test:
Any one component is short or open; inverter should be no fire, no arcing. And result must
meet output current limitation requirement.
Chapter 4-10
Page 79

Chapter 5: Disassembly
General
This chapter provides detailed directions for disassembling the computer. You will require a
medium size screwdriver, small screwdriver and a 6mm nut driver (for the helix screw nuts on
the rear ports).
Before starting to disassemble the computer, refer to the diagram below. This indicates which
modules need to be removed to access the module needing repla c ement. Always start by
removing the battery pack. Then work down through the diagram, removing only those modules
necessary to reach the module to be replaced.
Battery
CPU
Compart-
ment Cover
Expansion Memory
Compartment Cover
Strip cover
Keyboard
FDD
CD-RW/DVD
-ROM or
CD-ROM /
Combo Drive
HDD
Button
board
Wireless LAN /
modem card
Display
Assembly
CPU Fan
PC
Card
Expansion
memory
Top Cover
Audio board
Touch pad
System board
Microphone jack
Speakers
Chapter 5-1
Page 80

The example below shows which modules need to be removed before the audio board
can be removed and repaired or replaced. The audio board is overlapped by the top
cover, which must be removed before the audio board can be reached. The top cover is
in turn overlapped by several other units (shaded gray) and these must be removed
before the top cover can be reached. Always starts the disassembly process by
removing the battery.
Battery
CPU
Compart-
ment Cover
Expansion Memory
Compartment Cover
Strip cover
Keyboard
FDD
CD-RW/DVD
-ROM or
CD-ROM /
Combo Drive
HDD
Button
board
Wireless LAN /
modem card
Display
Assembly
CPU Fan
PC
Card
Expansion
memory
Top Cover
Audio board
Touch pad
System board
Microphone jack
Speakers
Chapter 5-2
Page 81

Safety Precautions
Before you begin disassembly, read the following safety precautions and observe them
carefully as you work.
DANGER:
1. Always use the lithium ion battery pack or backup battery that is authorized by the
manufacturer or compatible with the unit. Since other battery packs have different
specifications, they may be incompatible with the unit, and may burst or explode. Heating or
disassembling the battery pack could cause leakage of alkaline solution. Throwin g the battery
pack into a fire could cause the battery pack to explode.
2. The power supply, FL inverter and other components carry high voltages. To avoid the risk of
electric shock when you need to turn on the power of a partially disassembled computer to
check its operation, be very careful not to touch connectors or components. Also, do not
disassemble individual components in first-level maintenance.
WARNING: To avoid the risk of electric shock or other injury:
1. Always turn the power off and disconnect the AC adaptor from the power source.
2. Remove any metal jewelry or accessories such as necklaces, bracelets, or rings. Batteries in the
computer retain an electrical charge so there is danger of electrical sho ck even when the
computer is disconnected from an AC power source.
3. Never work with wet or damp hands.
4. The computer contains sharp edges and corners: be careful not to injure yourself.
5. Make sure that all replacement components meet the specifications for the computer and that all
cables and connectors are securely fastened.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the computer:
1. When you change a component, be sure the replacement component meets the required
specifications. Never use foreign parts.
2. Metal objects such as screws or paper clips which fall into the unit can cause a short-circuit, fire,
or other internal damage.
3. When assembling the computer, make sure you use the correct screws to secure the various
pieces in place. Screw sizes are listed in their corresponding figure. Make sure all screws are
securely fastened. Loose screws can cause short circuits, resulting in heat, smoke, or fire.
4. Before removing an module or other component, make sure all cables to the component have
been disconnected.
5 . If you use AC power, be sure to use the cable that came with the computer or one recommended
by the manufacturer.
Chapter 5-3
Page 82

Before You Begin
Look over the procedures in this section before you begin disassembling the computer.
Familiarize yourself with the disassembly and reassembly steps. Begin each procedure by
removing the AC adaptor and the battery pack.
1. Do not disassemble the computer unless it is operating abnormally.
2. Use only the correct and approved tools.
3. Make sure the working environment is free from the following elements whether you
are using or storing the computer.
Ö Dust and contaminates
Ö Static electricity
Ö Extreme heat, cold and humidity
4. Do not perform any operations that are not necessary and use only the described
procedures for disassembling and installing modules in the computer.
5. After removing parts from the computer, place them in a safe place away from the
computer so they will not be damaged and will not interfere with your work.
6. You will remove and replace many screws when you disassemble the computer. When
you remove screws, make sure they are placed in a safe place and identified with the
correct parts.
7. When assembling the computer make sure you use the correct screws to secure the
various pieces. Screw sizes are listed in their corresponding figures.
8. The computer contains many sharp edges and corners, so be careful not to injure
yourself.
9. After you have replaced a component, make sure the computer is functioning properly
by performing the appropriate test on the component you have fixed or replaced.
Chapter 5-4
Page 83

Disassembly Procedures
The computer has two basic types of cable connectors:
Pressure Plate Connectors
Standard Pin Connectors
To disconnect a Pressure Plate connector, lift up the tabs on either side of the con nector’s
plastic pressure plate and slide the cable out of the connector. To connect the cable to a
Pressure Plate connector, make sure the pressure plate is fully lifted and slide the cable into the
connector. Secure the cable in place by pushing the sides of the pressure plate down so the
plate is flush with the sides of the connector . Ge ntly pull on the cable to make su re the cable i s
secure. If you pull out the connector , connect it again making sure the connector’s pressure
plate is fully lifted when you insert the cable.
Standard pin connectors are used with all other cables. These connectors can b e connected
and disconnected by simply pulling them apart or pushing them together.
Assembly Procedures
After you have disassembled the computer and fixed or rep aire d th e problem tha t was cau sing
the computer to operate abnormally, you will need to reassemble the computer.
While assembling the computer, remember the following general points:
Take your time. Most problems arise when you get in a hurry assembling the
computer.
Make sure all cables and connectors are securely fastened.
Before securing the module or other parts, make sure that no cables will be pinched
by screws or the module.
Check that all latches are closed securely.
Make sure all the correct screws are used to secure all components. Using the wrong
screw can either damage the threads on the screw or the head of the screw and may
prevent proper seating of a module.
After installing a component in the computer, confirm that the component and the computer are
functioning properly.
Chapter 5-5
Page 84

Tools and Equipment
The use of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) equipment is very important for your safety and the
safety of those around you. Proper use of these devices will increase the success rate of your
repairs and lower the cost for damaged or destroyed parts. The following equipment is
necessary to disassemble and reassemble the computer:
One medium size screwdriver
One small screwdriver
One 6mm nut driver (for the helix screw nuts on the rear ports)
Tweezers, to lift out screws that you cannot grasp with your fingers.
ESD mats for the floor and the table you are working on.
ESD wrist strap or heel grounder.
Anti-static carpeting or flooring.
Air-ionizers in highly static sensitive areas.
Chapter 5-6
Page 85

Battery
1. Place the computer upside down with the front facing toward you.
2. Press the battery release button down and slide the battery latch to the right.
3. The battery pack will pop up slightly. Lever it out by easing up the protruding
edge.
Figure 5-1: Removing the battery
Chapter 5-7
Page 86

PC Card
1. Push the eject button for the card you want to release. The button will pop out
when you release it.
Figure 5-2: Ejecting a PC card (1/2)
2. Push the eject button once more to pop the PC Card out slightly .
3. Grasp the PC Card and remove it.
4. Push the eject button back into place, if necessary.
Figure 5-3: Ejecting a PC card (2/2)
Chapter 5-8
Page 87

Display Assembly
The instructions and figures below are for the 15” display. Differences with the 14” display are indicated
where necessary.
Removing the display assembly
1. Remove two M2.5×5 screws securing the strip cover.
Figure 5-4: Removing two screws securing the strip cover
Chapter 5-9
Page 88

2. Open the display fully so that the display and computer are flat on the table.
3. Insert the end of a small screwdriver between the strip cover and one of the display
assembly hinges. Gently pry off the strip cover.
Figure 5-5: Removing the strip cover
Chapter 5-10
Page 89

4. Lever the LCD display wire set connector off the system board connector . Do not pull on the
wire itself as this may cause damage. Instead, pull on the connector white wire set
connector.
5. Remove two M2.5×5 screws securing the display assembly hinges.
Figure 5-6: Releasing the LCD display wire set and hinges
Chapter 5-11
Page 90

6. Turn the computer over. Remove two M2.5×9 screws from the base and two M2.5×7
screws from the rear panel.
Figure 5-7: Removing two screws securing the display assembly
7. Turn the computer upright. Open the display so that it is perpendicular to the desk, then
gently lift off the display.
Figure 5-8: Lifting off the display assembly
Disassembling the display assembly
1. Remove two mask seals and two M2.5×7 screws securing the LCD bezel. If disassembling
the 14” display, two M2.5×5 screws must also be removed from the top of the LCD bezel.
Chapter 5-12
Page 91

Figure 5-9: Removing two screws securing the LCD bezel
2. Ease the bezel off the display, starting from one of the sides. The bezel is secured by
latches, with four on each of the sides, seven along the bottom edge and six along the top
edge.
Figure 5-10: Removing the LCD bezel
3. Remove the following eight screws securing the LCD module in the LCD cover:
Ö Two M2×3 screws from each side
Ö Two M2.5×5 screws from the upper corners
Ö Two M2.5×5 screws from the bottom corners
Chapter 5-13
Page 92

Figure 5-11: Removing eight screws securing the LCD module
4. Lift the LCD module out of the LCD cover.
Chapter 5-14
Page 93

5. Release the LCD cable from its hook to the left of the FL inverter board.
6. Detach the HV cable from the right of the FL inverter board.
Figure 5-12: Detaching the FL inverter board
7. Remove one M2.5×3 screw securing the FL inverter board.
8. Gently lift out the FL inverter board and detach the FL FPC from its left-hand end.
Figure 5-13: Detaching the FL FPC
9. Remove the LCD array and place face down.
10. Remove two pieces of tape sticking the LCD cable to the LCD array.
11. Detach the LCD cable from its connector
Chapter 5-15
Page 94

Figure 5-14: Removing the LCD cable
12. Remove six M2×2.5 screws securing the LCD bracket to the LCD module (the 14” LCD
module is secured by four screws).
Figure 5-15: Removing the LCD bracket
Chapter 5-16
Page 95

Keyboard / button board
1. Remove four M2.5×3 screws securing the keyboard.
Figure 5-16: Removing four screws securing the keyboard
Chapter 5-17
Page 96

2. Lift the keyboard up and place higher on the computer base unit so that the keyboard cable
connector is exposed.
3. Detach the keyboard cable and remove the keyboard.
Figure 5-17: Removing the keyboard
4. Remove two M2.5×3 screws securing the button bo ard. Remove the button board.
Figure 5-18: Removing the button board
Chapter 5-18
Page 97

Wireless LAN / Modem Unit
1. Remove two M2.5×3 screws securing the wireless LAN card compartment cover .
Remove the cover.
Figure 5-19: Removing the Wireless LAN compartment cover
Chapter 5-19
Page 98

2. Disconnect the modem cable.
3. If you will subsequently remove the top cover, you should peel back the tape
covering the Touch pad FFC and detach the FFC from its connector . If your aim is
solely to remove the Wireless LAN / modem card you do not need to detach the
FFC.
Figure 5-20: Disconnecting the Wireless LAN / modem card
Chapter 5-20
Page 99

4. Push out the two latches securing the wireless LAN /modem card. One end of the
card will pop up.
5. Grasp the wireless LAN /modem card and pull it out.
Figure 5-21: Removing the Wireless LAN / modem card
Chapter 5-21
Page 100

Expansion Memory
1. Remove one M2.5×5 screw securing the expansion memory compartment cover .
Lift off the cover.
Figure 5-22: Removing one screw securing the expansion memory compartment cover
Chapter 5-22
 Loading...
Loading...