Comnet RLFDX232S2-24DC, RLFDX232S2-48DC, RLFDX232S2-HV, RLFDX232M2-24DC, RLFDX232M2-HV User Manual
...Page 1

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL
RLFDX232 Series
SUBSTATION-RATED RS-232 & TTL LOGIC DATA
LINK/REPEATER FOR REPLACEMENT OF
GARRETTCOM/DYMEC 5843 & 5844 SERIES
This manual serves the following
ComNet Model Numbers:
RLFDX232M2/24DC
RLFDX232M2/HV
RLFDX232M2/48DC
RLFDX232S2/24DC
RLFDX232S2/HV
RLFDX232S2/48DC
The ComNet™ RLFDX series of serial data link/repeaters are substation-rated and
industrially hardened form, fit, function and completely backwards-compatible
replacements for the popular Garrettcom/Dymec 5843 & 5844 series of RS-232
serial data link/repeaters. They are designed for deployment in environments where
high levels of electromagnetic noise and interference (EMI) and severe voltage
transients and surges are routinely encountered, such as electrical utility substations
and switchyards, heavy manufacturing facilities, trackside and roadside electronic
equipment, and other difficult out-of-plant applications. Optical connectivity provides
significantly extended transmission distances compared to copper media; high levels
of electrical isolation; enhanced reliability and protection for peripheral IEDs, RTUs,
and other equipment; and operational safety.
The RLFDX series of serial data link/repeaters are easily field-configurable for pointto-point, point-to-multipoint/Local-Remote, loop, or bus topologies. They may be also
used for electrical data protocol translation: an RLFDX232-series RS-232 modem and
IED/RTU can communicate directly with an RLFDX485-series RS-422/RS-485 modem
and IED/RTU.
The extremely versatile and simple-to-install RLFDX series is ideal for any missioncritical application where very high levels of reliability and network availability are of
the utmost importance.
Rev. 3.17.15
Page 2

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Contents
FCC/CE Regulation 4
Warranty 4
Disclaimer 4
Safety Information 4
ComNet / Garretcom Interoperability / Compatibility Listing 5
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes Used in this Publication 6
1. Introduction 7
1.1 Definitions 8
1.2 Model RLFDX232 Series Link/Repeaters 11
1.2.1 9 Pin Data Port D-connector 13
1.2.2 DTE/DCE Switch (Two Position Switch) 13
1.2.3 Data Coupling Switch 13
1.2.4 Repeat Switch 14
1.2.5 Handshaking Switch 4B 14
1.2.6 Pin 8 Current Output Option Switch 5B 14
1.2.7 Test Mode Option Switch 3B 15
1.2.8 Optical Ports 15
1.2.9 Diagnostic LEDs 16
1.2.10 Power Connections 16
1.2.10.1 Powering the 24DC Models 16
1.2.10.2 Powering the 48DC Models 17
1.2.10.3 Powering the HV Models 17
1.2.11 Peripheral Equipment 18
1. 2.11.1 IED 18
1.2.11.2 Fiber Optic Cable (FOC) 18
2. Configurations, Operation, and Installation 19
3. Applications 28
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
2.1 Point-To-Point Configuration 20
2.1.1 Installation 21
2.2 LOOP OPERATION - Local/Remote CONFIGURATION 22
2.2.1 Installation 24
2.3 Loop Operation - Peer-To-Peer Configuration 25
2.3.1 Installation 27
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 2
Page 3

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
3.1 Data Rate 28
3.2 Optical Budget 28
3.2.1 Cable Attenuation Factors 29
3.2.1.1 Diameter 29
3.2.1.2 Fittings 29
3.2.1.3 Aging 29
3.2.2 Extending the Distance 30
3.3 Number Of Repeats 30
3.3.1 Effects of Data Rate 31
3.3.2 Pulse Width Distortion 31
3.3.3 Temperature Effect 31
3.4 Types Of Communication 32
4. Testing And Troubleshooting 33
4.1 Testing 33
4.2 Troubleshooting 34
5. Specifications 36
5.1 Electrical and Optical Specifications 36
5.2 Outline Configuration & Mechanical Dimensions for
Models RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC 39
5.3 Outline Configuration & Mechanical Dimensions
for Models RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC,
RLFDX232M2/HV, and RLFDX232S2/HV 40
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 3
Page 4

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
FCC/CE Regulation
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the users will be required to correct the interference at their own
expense.
Warranty
ComNet warrants that all ComNet products are free from defects in material and workmanship
for a specified warranty period from the invoice date for the life of the installation. ComNet will
repair or replace products found by ComNet to be defective within this warranty period, with
shipment expenses apportioned by ComNet and the distributor. This warranty does not cover
product modifications or repairs done by persons other than ComNet-approved personnel, and
this warranty does not apply to ComNet products that are misused, abused, improperly installed,
or damaged by accidents.
Please refer to the product’s data sheet for the actual warranty period(s) of the product(s) associated
with this publication. Data sheets can be found at http://www.comnet.net/comnet-products/
Disclaimer
Information in this publication is intended to be accurate. ComNet shall not be responsible for its
use or infringements on third-parties as a result of its use. There may occasionally be unintentional
errors on this publication. ComNet reserves the right to revise the contents of this publication
without notice.
Safety Information
» Only ComNet service personnel can service the equipment. Please contact ComNet Technical
Support.
» Do not attempt to disasemble the link/repeaters as there are no serviceable parts within. This
action will void the warranty.
» The equipment should be installed in locations with controlled access, or other means of
security, and controlled by persons of authority.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 4
Page 5
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
ComNet / Garretcom Interoperability / Compatibility Listing
Equivalent
Model Data Format Fiber Type Input Power
RLFDX232M2/24DC RS-232/ T TL Multimode 9 to 36 VDC 5843HRT
RLFDX232M2/HV RS-232/ T TL Multimode 88 to 300 VDC / 85 to 264 VAC 5844HRT-H
RLFDX232M2/48DC RS-232/TTL Multimode 36 to 59 VDC 5844HRT- L
RLFDX232S2/24DC RS-232/TTL Single Mode 9 to 36 VDC 5843SHRT
RLFDX232S2/HV RS-232/ T TL Single Mode 88 to 300 VDC / 85 to 264 VAC 5844SHRT-H
RLFDX232S2/48DC RS-232/TTL Single Mode 36 to 59 VDC 5844SHRT-L
Dymec Model
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 5
Page 6

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes Used in this Publication
WARNING
Warning notices are used in this publication to emphasize that hazardous voltages, currents, or
other conditions that could cause personal injury exist in this equipment or may be associated
with its use.
In situations where inattention could cause either injury or damage to equipment, a Warning
notice is used.
CAUTION
Caution notices are used where equipment malfunction is possible if care is not taken.
NOTE / APPLICATION NOTE
Notes and Application Notes call attention to information that is especially significant to
understanding and operating the equipment.
This document is based on information available at the time of its publication. While efforts
have been made to be accurate, the information contained herein does not purport to cover all
details or variations, or to provide for every possible contingency in connection with installation,
operation, or maintenance.
ComNet assumes no obligation of notice to holders of this document with respect to changes
subsequently made.
ComNet makes no representation or warranty, expressed, implied, or statutory with respect to,
and assumes no responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, sufficiency, or usefulness of the
information contained herein. No warranties of merchantability or fitness for purpose shall apply.
Permission is granted to make a reasonable number of copies of this document for the use within
the organization that has purchased the equipment.
“Link/Repeater” is used exclusively to describe this family of Fiber Optic Data Links.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 6
Page 7

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1. Introduction
ComNet Models RLFDX232M2/24DC, RLFDX232S2/24DC, RLFDX232M2/48DC,
RLFDX232S2/48DC, RLFDX232M2/HV and RLFDX232S2/HV are data communications Link/
Repeaters, which allow the replacement of copper wire media with fiber optic cable. Link/
Repeaters simply convert electrical signals to light for transmission, and when received, convert
the light signals back to an electrical format. This is done for RS-232 or TTL protocols.
These Link/Repeaters are passive to software protocols. They are not addressable in
communication protocols, and do not provide any control logic capability to support
communication protocols. Link/Repeaters are designed with several features that allow for easy
installation and flexibility in configuring for various communication systems.
The multimode RLFDX232M2/XX and singlemode RLFDX232S2/XX series are functionally
identical, with the exception of the operating voltage requirements.
NOTE
This manual makes reference to the multimode Model RLFDX232M2/24DC, RLFDX232M2/48DC,
and Model RLFDX232M2/HV when describing features and functionality of the Link/
Repeaters. These descriptions generally apply to the singlemode Model RLFDX232S2/24DC,
RLFDX232S2/48DC, and Model RLFDX232S2/HV as well. When different, a specific reference
is made identifying the particular model(s) and their variation(s). The User should read this
manual to fully understand how to use the many features of the Link/Repeaters in an effective
communication system.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 7
Page 8

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.1 Definitions
The following terms are used in this manual:
IED An IED is any intelligent electrical device capable of RS-232 and/or TTL data
communications, such as; a computer, RTU, PLC, “smart” meter, relay, etc. The IED
must have resident software or firmware that manages the data communication
logic, including protocol (formatting and timing), addressing capability (if required),
control logic software “handshaking”, and scheduling.
Point-to-Point
Two Link/Repeaters directly connected to each other.
Configuration
Local/Remote Loop
Configuration
More than two Link/Repeaters connected together where the fiber optic cable
connects the T optical port of one device to the R optical port of the next unit in
the loop. One IED is designated as the Local and controls all the communication
and the other IEDs act as Remotes and respond only when specifically polled by
the Local.
Peer-to-Peer Loop
Configuration
More than two Link/Repeaters connected together where the fiber optic cable
connects the T optical port of one device to the R optical port of the next unit in
the loop. Each IED has the capability of becoming loop Local as allowed by the
controlling software.
Echo The return of the Local’s transmission back to the Local after traveling around the
optical loop.
Optical Bus
Configuration
More than two Link/Repeaters connected together in a manner where the Local’s
transmission is heard by all IEDs and there is no returning echo of this transmission.
Local The Local is the IED that controls the loop in a Local/Remote loop. This IED is
responsible for the control of the loop, the polling of the Remotes for information,
and the prevention of data collisions. All loop communication is echoed back to
and stops at the Local. The Local’s Repeat Switch is always in the “OFF” position.
Remote A Remote is an IED that is passive in a Local/Remote loop. A Remote’s
communication is under the control of the Local, and should be controlled to
prevent data collision in the loop. All communication generated by the Local will be
repeated through each Remote and back to the Local. A Remote’s Repeat Switch is
always in the “ON” position.
Peer Peers are IEDs that have equal status and each may Local the loop when allowed by
the software. A Peer’s Repeat Switch is always in the “OFF” position and a Peer IED
controls pin 8 of its Link/Repeater in order to obtain status as loop Local.
FOC Fiber Optic Cable.
Single-mode Single-mode fibers generally have diameters of 5μm to 13μm. Because of this
small core, only one axial path for light propagation is available through the fiber.
The optics required to drive single-mode fiber have to be highly focused so that
minimum dispersion occurs. Although more costly optical emitters are required,
the major benefit is that longer transmission distances (< 35 km) can be achieved.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 8
Page 9

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Multi-mode Multi-mode fibers have core diameters of 50μm and larger. This larger core allows the
light rays to be propagated along several different paths down the fiber. The different
paths include an axial component as well as reflected components. Multi-mode units
are economical and effective for optical transmission over distances up to 6 km.
Repeat Switch The Repeat Switch enables (REP) or disables (OFF) the repeater function of the
Link/Repeater.
DTE/DCE Switch Each Link/Repeater is provided with this switch (2 position) to easily adapt the
device to either the DTE or DCE configuration of the equipment which it connects.
Data Coupling Switch Each Link/Repeater is provided with this switch to easily adapt the device for either
DC or AC electrical Input data coupling. With AC data coupling the minimum input
data rate is 1200 baud with DC data coupling there is no minimum input data rate
but a signal stuck on the input will lock up a loop, bussed or star network.
Pin 8 Output Option
Switch
(Switch 5B) RS-232 RLFDX232 Links are provided with this switch to allow users who
require more drive current on the TTL output pin (pin 8) to accomplish this. Selections
are High or Low. Consideration should be given that the current value selected is
appropriate for the input of the device being connected to this data channel.
Test Mode Switch RS-232 Link/Repeaters are provided with this switch to allow users who wish to test
the fiber connections of the link with a built in diagnostic mode. This mode sends a
100Hz signal out the transmit port as well as looping back the copper port (pins 2
and 3) for diagnostic purposes.
Handshaking Switch Each RS-232 Link/Repeater is provided with this switch to easily adapt the device
for use where the connected IED needs to see active electrical levels on certain
handshaking pins but does not require full handshaking implementation.
Simplex
Transmit only or receive only communications.
Communication
Half Duplex
Sequential transmit and receive communications.
Communication
Full Duplex
Simultaneous transmit and receive communications.
Communication
T Transmit optical port.
TE Diagnostic LED that illuminates when the Link/Repeater is receiving an electrical
transmit from its IED.
TO Diagnostic LED that illuminates when the Link/Repeater is transmitting a signal optically.
R Receive optical port.
RE Diagnostic LED that illuminates when the Link/Repeater is delivering a received
optical signal electrically to the IED.
RO Diagnostic LED that illuminates when the Link/Repeater is receiving a signal optically.
Optical Budget The optical budget is expressed in dB, and is the maximum amount of light loss that
can be tolerated for reliable communications. The maximum usable optical distance
between two devices that a signal can be transmitted is determined by subtracting
all of the losses within the optical path from the optical budget. Various factors in the
optical path attenuate the light transmission and must be accounted for, to ensure a
reliable optical path. Key factors include fiber optic cable attenuation (expressed as
dB per unit length), cable aging, and cable fittings (terminations, splitters, etc.).
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 9
Page 10

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Non Return to Zero
(NRZ)
This type of encoding scheme does not require the voltage potential of each data bit
to return to the zero potential. No clock or timing recovery is provided with this type
of communication except in the start and stop bits usually found on each data word.
Return to Zero (RZ) This type of encoding scheme requires the voltage potential of each data bit to
return to the zero potential. This allows timing recovery with each bit instead of just
the start and stop bits of the data word.
Number of Repeats The Number of Repeats is the maximum number of Link/Repeaters that may be
connected in a loop configuration. The sum of the Remote units in a Local/Remote
loop is the number of repeats for that type of loop. The number of Peers minus one
is the number of repeats in a Peer-to-Peer loop.
Asynchronous
Communication
This type of communication does not transmit a separate clock signal in
conjunction with the data signal. Link/Repeaters only support asynchronous
communication. A communication scheme where the clock needs to be transmitted
(Synchronous Communication) is not supported unless the data and clock signals
are transmitted together on the same pin.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 10
Page 11
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
E
C
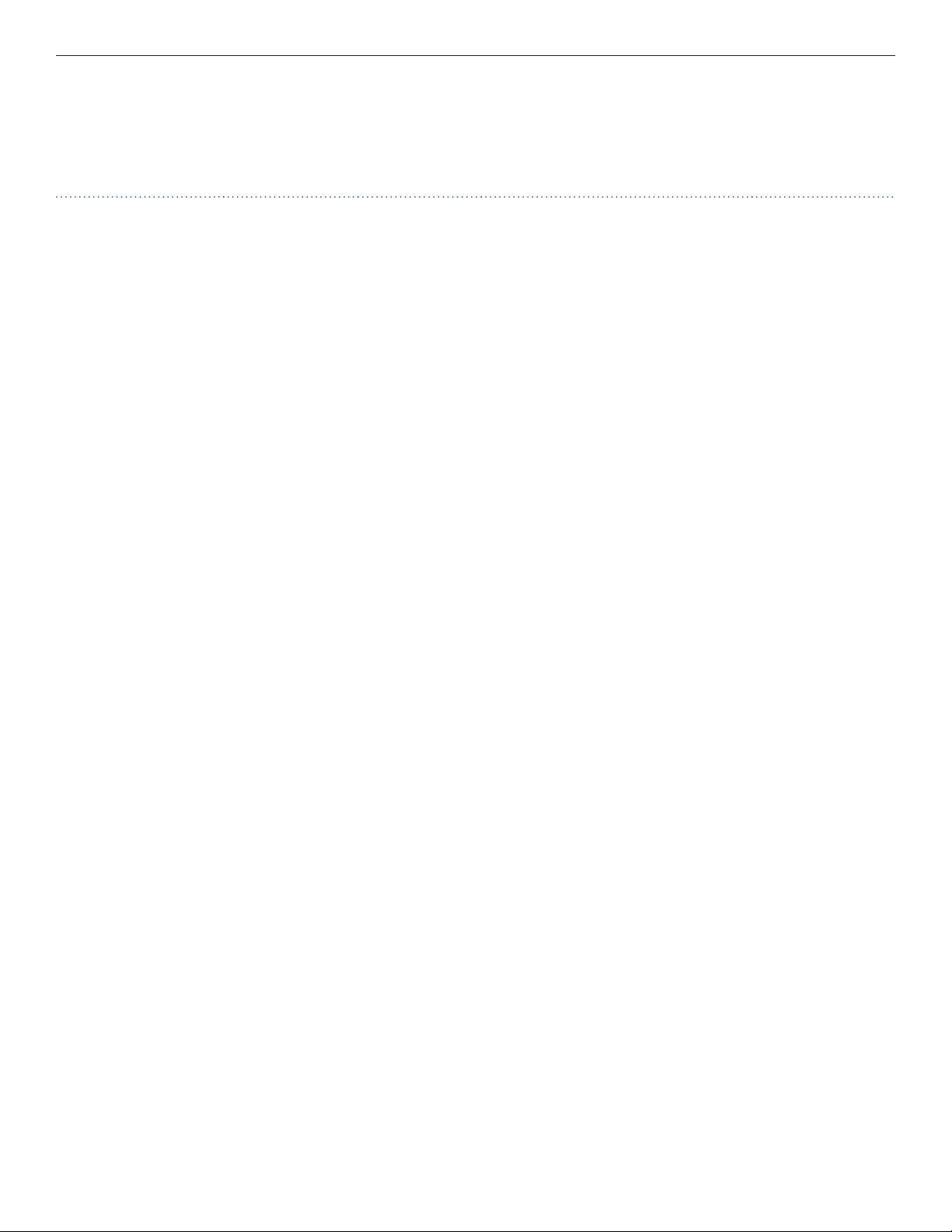
1.2 Model RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC Link/Repeaters
NOTE: Link/Repeaters contain no serviceable parts. Opening the unit will void the warranty.
Each RLFDX232M2/24DC or RLFDX232S2/24DC Link/Repeater consists of the following elements.
+9 TO +36 VDC INPUT
#6-32 THREAD SST REMOVABLE
SWITCH ACCESS PLAT
TYPE ST
FIBER OPTIC
ONNECTOR
9 PIN D-CONNECTOR WITH
#4-40 STANDOFFS
Figure 1 Elements of the Link/Repeater
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 11
Page 12
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
+/– 88 to 300
WITH
5.13 in
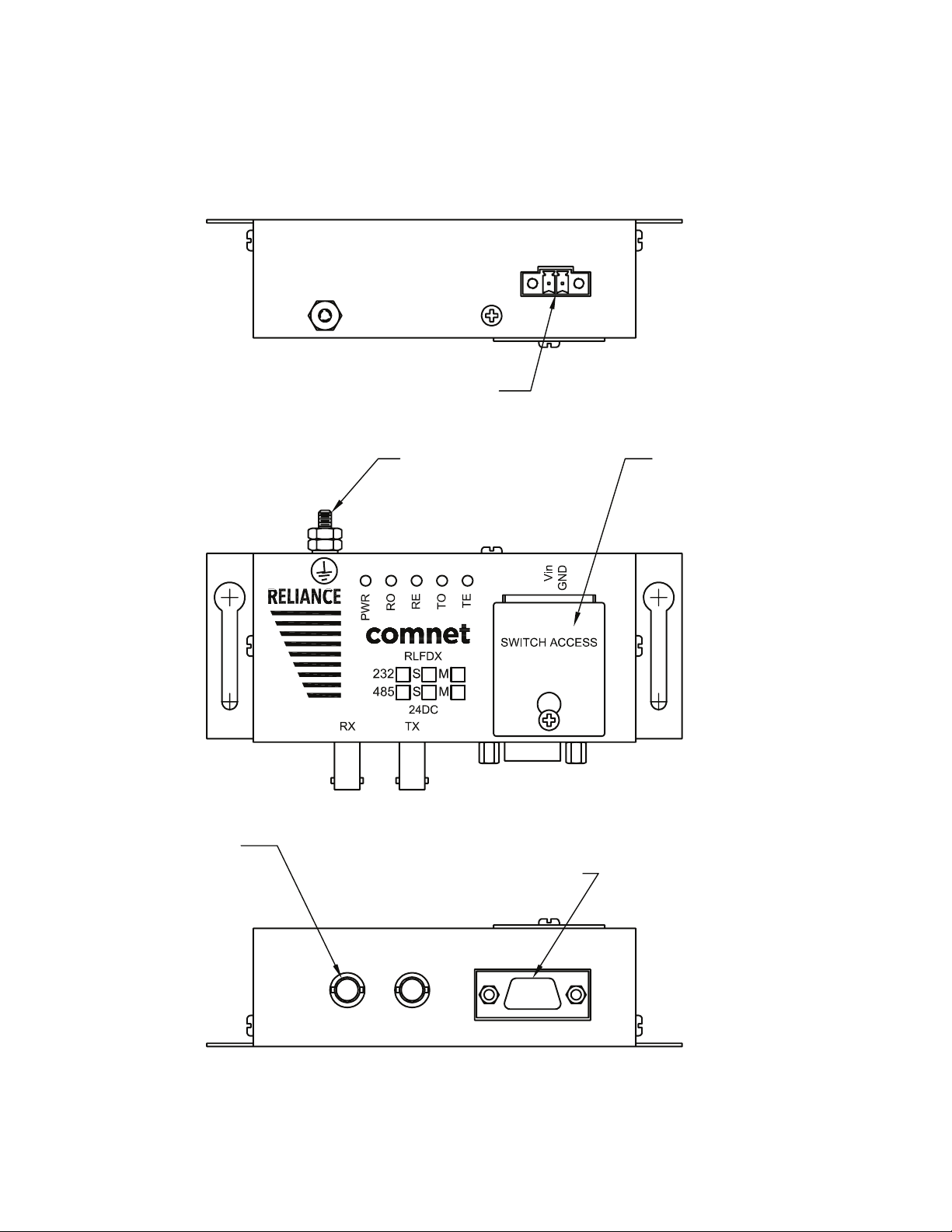
Each RLFDX232(M,S)/(48DC,HV) Link/Repeater consists of the following elements.
13.03 cm
#6-32 THREAD SST
INPUT:
VDC
85 to 264 VAC
OR
+/– 36 to 59 VDC
4.63 in
11.76 cm
4.13 in
10.41 cm
4.15 in
10.54 cm
0.51 in
1.29 cm
2.0 in
5.08 cm
0.46 in
1.16 cm
TYPE ST
FIBER OPTIC
CONNECTOR
REMOVABLE
SWITCH ACCESS PLATE
9 PIN D-CONNECTOR
#4-40 STANDOFFS
1.28 in
3.25 cm
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
Figure 1 Elements of the Link/Repeater
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 12
Page 13

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.2.1 9 Pin Data Port D-connector
The Link/Repeater connects directly to an IED’s RS-232 or TTL communication port. The pin-out
configuration of the Link/Repeater is shown in Figure 2. If the IEDs port is not a 9-Pin Dconnector,
or if the IEDs pin-out configuration differs, a suitable adapter is required. Note: The operating
voltages specified in the table below for Pin 9 are applicable only to models RLFDX232M2/24DC
& RLFDX232S2D/24DC
DTE MODE (Switches Down) DCE MODE (Switches Up)
• 1 Chassis Ground • 1 Chassis Ground
• 2 Transmitted Data (Link Input) • 2 Received Data (Link Output)
• 3 Received Data (Link Output) • 3 Transmitted Data (Link Input)
• 4 No Connection • 4 No Connection
• 5 Signal Common • 5 Signal Common
• 6 (+5 Vdc Output) • 6 (+5 Vdc Output)
• 7 Repeat Enable / Disable • 7 Repeat Enable / Disable
• 8 TTL Output • 8 TTL Output
• 9 +9 to +36 VDC Input • 9 +9 to +36 VDC Input
Figure 2 Data Port Pin Assignments
1.2.2 DTE/DCE Switch (Two Position Switch)
The DTE/DCE Switch on the Link/Repeater switches the functions of pins 2 and 3 to accommodate
the IED configuration as DTE or DCE. This is a 2 position switch and both poles must be set for the
Link/Repeater to work properly.
DTE: Data Terminal Equipment. By RS-232 standards, equipment designed as DTE transmits data out of
pin 2 on a 9 Pin D-connector and receives data on pin 3.
DCE: Data Communication Equipment. By RS-232 standards, equipment designed as DCE transmits data
out of pin 3 on a 9 Pin D-connector and receives data on pin 2.
1.2.3 Data Coupling Switch
The Data Coupling switch selects the electrical input conditioning, the AC position selects
capacitively-coupled data. The DC position is directly coupled.
AC: AC coupling has a minimum incoming data requirement of 1200 baud due to the capacitive coupling.
This option blocks DC electrical levels should the device connected fail and ‘stick in a high level’.
There is a 35 mS timeout for “stuck” output pins, after this time out the link returns to LED off state.
DC: DC coupling allows DC logic levels to be transmitted over the fiber network. Care must be taken
to guarantee that when any device stops transmitting packets that the input level returns to a state
that allows the T receptacle (emitter) to turn off. If it does not and the IED is part of a loop, bus or
star network, the first device to transmit blocks all other devices on the network from transmitting.
*Single-Mode units cannot be DC coupled.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 13
Page 14

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.2.4 Repeat Switch
The Repeat Switch enables the repeater function in the “ON” position and disables it in the “OFF”
position.
ON: The repeater function available in the Link/Repeater is enabled. This function converts the optical
signal received on the R optical port to an electrical signal, and delivers this signal to the appropriate
pin of the 9-Pin connector, and re-transmits the signal optically out the Link/Repeater’s T optical port.
OFF: The repeater function available in the Link/Repeater is disabled. The Link/Repeater converts the
optical signal received on the R optical port to an electrical signal, and delivers this signal to the
appropriate pin of the 9-Pin connector. It does not re-transmit the signal optically out the Link/
Repeater’s T optical port.
1.2.5 Handshaking Switch 4B
The Handshaking Switch outputs +5 VDC on a standard handshaking pin in the “ON” position,
and disconnects the pins in the “OFF” position.
ON: Pin 6 (Data Set Ready) of the Link/Repeater output is held at +5 VDC. This signal is used by devices
requiring handshaking signals to indicate the readiness of the connected devices to receive data.
OFF: Pin 6 of the Link/Repeater is not connected.
1.2.6 Pin 8 Current Output Option Switch 5B
RLFDX232 Link/Repeaters are provided with this switch to allow users select one of 2 output
source drive current values for the TTL output pin (pin 8). Selections are 10ma (207 ohms) or 20ma
(67 ohms).
Consideration should be given that the current value selected is appropriate for the input of the
device being connected to this data channel.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 14
Page 15

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
R
T
9 Pin D Sub
Pin 1
1.2.7 Test Mode Option Switch 3B
RLFDX232 Series Link/Repeaters are provided with this switch to allow users who wish to test the
fiber connections of the link with a built in diagnostic mode. This mode sends a 100Hz signal out
the transmit port as well as looping back the copper port (pins 2 and 3) for diagnostic purposes.
High / Low
Handshaking D8R/OFF
3 4 5
2
1
Test Mode ON/OFF
Data Coupling DC/AC
Repeat Mode ON/OFF
2
DCE/DTE
1
FIGURE 4. Switch Settings
1.2.8 Optical Ports
There are two optical ports: T and R. The T optical port transmits data signals optically to the next
Link/Repeater. The R port receives the optical data signal from another Link/Repeater’s T optical
port. Each optical port is fitted with a type-ST connector for connecting to the fiber optic cable.
Fiber Connector
Fiber Connector
Connector
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
Figure 3 Optical Ports and Electrical Port
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 15
Page 16

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.2.9 Diagnostic LEDs
Each Link/Repeater is equipped with four diagnostic/status indicating LEDs. They represent the
electrical transmit (TE), optical transmit (TO), electrical receive (RE), and optical receive (RO)
paths. These LEDs, when illuminated, indicate that the appropriate path is active. When the Link/
Repeater is transmitting, both TE and TO LEDs will illuminate to indicate the transmit path is
active. When the Link/Repeater is receiving light signals, both RO and RE LEDs will illuminate. If
the unit is in the repeat mode and receiving light, the RO, RE and TO LEDs will illuminate, as the
signal is being retransmitted out of the optical port, as well as being outputted to the electrical
data D-connector. LEDs only illuminate when the path is active; powering on the unit does not
illuminate the LEDs unless their path is active. When data is present on the paths, the LEDs may
flicker; this is a normal condition. The diagnostic LEDs may also be used for troubleshooting, by
observing that the illumination of the LEDs corresponds with activity in the unit. See Figure 5 for
LED patterns and signal paths.
2 2 23
PWR
RO
RE
TO
TE
Normal Transmission Normal Receive Normal Repeat
FIGURE 5. Diagnostic LED patterns and signal paths
3 3
PWR
RO
RE
TO
TE
PWR
RO
RE
TO
TE
NOTE: The LEDs only illuminate when there is data traffic, and are not illuminated during signal
quiet times. The LEDs may flicker; this is normal operation.
1.2.10 Power Connections
1.2.10.1 Powering Models RLFDX232M2/24DC & RLFDX232S2/24DC
Model RLFDX232M2/24DC may be powered either through pin 9(+) and pin 5 (Ground) of the
9-Pin D connector, or the external power connector located on the rear of the unit:
1. When powering the RLFDX232M2/24DC via pin 9 of the D-connector, the IED must supply at
least 250 mA, or 340mA for the RLFDX232S2/24DC. This voltage should be regulated, and
within a range of +9 to +36 Vdc.
2. When powered from the external power connector located on the rear of the unit, the
operating voltage may be unregulated.
CAUTION: Regardless of the power connection used, Model RLFDX232M2/24DC requires 250
mA, and 340 mA for the RLFDX232S2/24DC, within a range of +9 to +36 VDC. A power supply
not capable of supplying 250 mA over the entire operating temperature range may cause the
Link/Repeater to malfunction.
Note: Connection of the no. 6-32 ground stud located on the rear of the unit to station ground is
optional for models RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 16
Page 17

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.2.10.2 Powering Models RLFDX232M2/48DC & RLFDX232S2/48DC
48 Volt DC Models RLFDX232M2/48DC and RLFDX232S2/48DC operate from any source of
36 to 59 VDC. These units include an internal regulated power supply. The supply voltage may
be unregulated, but the circuit must be capable of providing a minimum of 250 mA for the
RLFDX232M2/48DC, and 340 mA for the RLFDX232S2/48DC .
WARNING: Both models provide a no. 6-32 screw ground stud and a power connector on the
side of the housing. Be certain to connect a suitable earth ground to the grounding stud on
the side of the Link/Repeater. Remove the power plug from the power connector of the Link/
Repeater. Connect the power lines to the power plug, being careful not to leave any wire strands
exposed, and replace the power plug.
As the DC input is isolated from ground, these units may be operated from either positive or
negative DC sources.
1.2.10.3 Powering Models RLFDX232M2/HV and RLFDX232S2/HV
Models RLFDX232M2/HV and RLFDX232S2/HV operate from any source of 85 to 264 VAC (50/60
Hz), or 88 to 300 VDC. They include an internal voltage regulated power supply, and may be
connected directly to the AC line, or station battery bus power. The station battery bus voltage
may be unregulated, but the circuit must be capable of providing a minimum of 35mA for model
RLFDX232M2/HV, or 50mA for the RLFDX232S2/HV.
Both models provide a no. 6-32 ground stud and a power connector on the side of the housing.
Be certain to connect a suitable earth ground to the grounding stud on the side of the Link/
Repeater. Remove the power plug from the power connector of the Link/Repeater. Connect the
power lines to the power plug, being careful not to leave any wire strands exposed, and replace
the power plug.
As the high-voltage DC input is isolated from ground, these units may be operated from either
positive or negative DC sources.
This power input to the RLFDX232-series is Surge Withstand Protected to IEC 61000-4-4,
EN61000-4-5 Standard and ANSI/IEEE C37.90.1-1989.
WARNING: When installing a Model RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, RLFDX232M2/HV
or a RLFDX232S2/HV Link/Repeater, an earth ground must be attached to the ground stud on
the side of the case before connecting to operating power. Failure to follow this procedure may
result in an electrical shock hazard to personnel.
Note: Connection of the no. 6-32 ground stud located on the rear of the unit to station ground is
optional for models RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 17
Page 18

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
1.2.11 Peripheral Equipment
1. 2.11.1 IED
An IED is any intelligent electrical device such as a computer, RTU, PLC, “smart” meter, protective
relay, etc., that has the ability to communicate data via an RS-232 or TTL format. The IED should
have a communication port for the connection of the Link/Repeater. If the IEDs communication
port connector will not permit the Link/Repeater to be plugged in directly, a suitable adapter must
be made to accommodate the connection. Care should be taken to ensure that the correct signals
are connected to each other. See Figure 2 for the Link/Repeater pin signal assignments. Check
your IEDs equipment manual for its signal assignments.
The IED must also have intelligent software to execute the data communication. This intelligence
needs to logically manage the data and signal traffic, including any addressing, token passing,
handshaking, data formatting, and scheduling.
1.2.11.2 Fiber Optic Cable (FOC)
The selection of the fiber optic cable is important. High quality cable will ensure the maximum
performance of the Link/Repeater. Important factors to consider are the manufacturer’s
specification on optical attenuation per unit length, optical attenuation due to aging, diameter,
and tensile strength. Choosing the best quality FOC for your installation is important.
Model RLFDX232M2/24DC, RLFDX232M2/48DC, and RLFDX232M2/HV Link/Repeater units
are designed for use with type-ST cable terminations, and are compatible with multimode FOC
ranging from 50 μm to 200 μm.
Model RLFDX232S2/24DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, and RLFDX232S2/HV Link/Repeater units are
designed for type-ST cable terminations, and are compatible with single-mode FOC ranging from
5 μm to 13 μm.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 18
Page 19

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2. Configurations, Operation, and Installation
The RLFDX232 series of Link/Repeaters may be connected in a Point-to-Point configuration, in a
Local/Remote Loop, in a Peer-to-Peer Loop, or an optical bus, depending upon the requirements
of the overall communication system.
These models are designed to accept electrical inputs per EIA RS-232, and TTL standards.
RS-232 data communication signals are always on pins 2 or 3: transmit or receive pin assignment is
based upon the setting of the DTE/DCE switch of the Link/Repeater’s 9-Pin D-connector.
For TTL data communication, the transmit signal (Link/Repeater receive) is on either pin 2 or 3
depending on the setting of the DTE/DCE switch, and the receive (Link/Repeater transmit) is on
pin 8.
When the Link/Repeater has a high TTL potential (above 2.4 volts) on its transmit pin, it will
transmit optically.
All signal voltage levels on the 9-Pin D-connector are referenced to pin 5 (signal ground) of the
D-connector.
NOTE: Pin 8 always has the TTL data output signal present, even when utilizing RS-232
communications Take care to ensure that the presence of the TTL signal on pin 8 will not
adversely affect the operation of the connected IED.
It is also possible to optically connect the Link/Repeaters together within the same optical network
when IEDs with different electrical data formats are utilized. For example, where one IED is
communicating via RS-232, another IED is communicating with RS-422 or RS-485, etc., the data
format translation between the IEDs is performed automatically in this application.
APPLICATION NOTE:
Fully electrically, mechanically, and optically identical to and backward-compatible with the
Garrettcom/Dymec 5843, 5844, 5845, and 5846 Series, products in the ComNet RLFDX Series
may directly replace a Dymec unit anywhere within the network, and can optically communicate
to each other, eliminating the need for external format translation interface devices, provided all
connected devices are operating at the same data rate.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 19
Page 20

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.1 Point-To-Point Configuration
For Point-to-Point operation, two Link/Repeaters are optically connected to each other.
This configuration permits full-duplex communication (simultaneous transmitting and receiving),
half-duplex communication (sequential transmitting and receiving), and simplex (one device
transmitting or receiving only).
APPLICATION NOTE:
In Point-to-Point operation, the communication logic (control software) of the IEDs must manage:
1. The transmission of data signals.
2. The reception of data signals.
3. Any “handshaking” required must be accomplished through software.
Local Remote
T TR R
COM COM
2 3
3 25 5
DTE
DCE
ON
OFF
FIGURE 6. Point-to-Point Configuration
DTE
DCE
ON
OFF
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 20
Page 21

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.1.1 Installation
1. Set the DTE/DCE Switch to the appropriate position for each Link/Repeater and its respective IED.
2. Set the Repeat Switch on all of the units to the “OFF” position.
3. Connect the Link/Repeater to the IEDs RS-232 or TTL communication port (including any
adapter that may be needed).
4. Connect the Fiber Optic Cables (T of one device to R of the second device).
5. Connect power to the Link/Repeater as follows:
A) If models RLFDX232M2/24DC or RLFDX232S2/24DC are to be powered through the
D-connector (+9 to +36 VDC on pin 9 referenced to Pin 5, signal ground) then the unit is
energized when it is connected to the D-connector (the power LED will illuminate).
B) Connect the power leads to the power connector, and then energize the power source. The
unit is now powered (the power LED will illuminate).
WARNING: When installing a Model RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, RLFDX232M2/
HV, or RLFDX232S2/HV Link/Repeater, an earth ground must be attached to the no. 6-32
ground stud on the side of the housing before connecting to operating power. Failure to
follow this procedure may result in an electrical shock hazard to personnel.
6. Verify operation using the diagnostic/status indicating LEDs. (See Figure 5).
NOTE: Note: Connection of the no. 6-32 ground stud located on the rear of the unit to station
ground is optional for models RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC.
NOTE: The LEDs only illuminate when there is signal traffic and are not illuminated during signal
quiet times. The LEDs may flicker; this is normal operation.
APPLICATION NOTE
The Point-to-Point concept can also be used to create an optical bus network. This can be useful
in those applications where the software in the Local has not been written in such a way that it
can support the return of the transmitted echo that normally occurs in loop networks.
Note that all Remotes receive the Local’s transmission, but only the polled Local hears the
response from the addressed Remote. The Local must always be the first IED within the network.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 21
Page 22

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.2 LOOP OPERATION - LOCAL/REMOTE CONFIGURATION
NOTE Before constructing a loop network, be sure that the software protocol of the Local is
capable of managing the receipt of its own echoed transmission. If it cannot, then use a
Point-to-Point configuration only between devices in an optical bus network topology.
This configuration supports a network that requires more than two IEDs to be communicating. In
a Local/Remote loop system, one IED acts as a Local at all times and addresses or “polls” each of
the other connected IEDs individually. Each Remote receives the same transmission from the Local
IED but only responds when it recognizes its address in the polling message.
Local
ON
OFF
2
COM
5
R
3
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
T
333
TTT
COMCOMCOM
222
555
RRR
RemoteRemoteRemote
FIGURE 7. Local/Remote Loop Configuration
The Local must have its Repeat Switch in the “OFF” position. When it transmits a request from its
T optical port, it will receive the echo of its request at its R optical port. This request has gone
around the loop, and has been repeated by each Remote in the loop. In this mode, the Local does
not repeat (re-transmit) any of these received signals optically around the loop, because its Repeat
Switch is in the “OFF” position.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 22
Page 23

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
NOTE The communication logic and control software of the Local IED must be able to manage
the receipt of its echoed request. The receipt of the echo can be used in conjunction with
a watchdog timer to continuously verify loop integrity.
When addressed, the Remote will transmit an appropriate response. Each Link/Repeater
connected to a Remote IED must have its Repeat Switch set in the “ON” position. In this mode, all
signals received on a Remote’s R optical port are delivered to the IEDs communication port, and at
the same time repeated out the T optical port to the next device in the loop. If an IED determines
that this request requires a response, then the Link/Repeater transmits the IEDs response out the T
optical port. The response is repeated at each Remote device, until it arrives at the Local.
When an IED is a Remote, it should not attempt to initiate a transmission while it is receiving a
signal. Since signals being received are also being repeated at the same time, any attempts to
transmit its response while still receiving can corrupt both transmissions due to a data collision.
CAUTION: If a Remote IED attempts to transmit while receiving a message, a data collision will
occur.
In Local/Remote Loop Operation, half-duplex communication (sequential transmit and receive
functions) is available. Only the Local can communicate full-duplex (simultaneous transmit and
receive) in a Local/Remote loop.
APPLICATION NOTE
In a Local/Remote Loop Operation, the communication logic (control software) and the Local IED
must manage:
1. The transmission to Remotes (including addressing).
2. The receipt of the echo of its transmissions.
3. The receipt of the Remote’s response to its transmission.
4. The control of the Remotes to prevent the initiation of a transmission while receiving a signal.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 23
Page 24

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.2.1 Installation
1. Set the DTE/DCE Switch to the appropriate position for each Link/Repeater and its respective IED.
2. Set the Repeat Switch to the “OFF” position on the Local. Set the Repeat Switch to the “ON”
position on each Remote.
3. Connect the Link/Repeater to the IEDs RS-232 or TTL communication port (Including any
adapter that may be needed).
4. Connect the Fiber Optic Cables (T of one device, to R of the next device in the loop). Continue
around the loop back to the Local, to close the loop.
5. Connect power to the Link/Repeater as follows:
A) If the unit is to be powered through the D-connector (+9 to +36 VDC on pin 9 referenced to
pin 5, signal ground), the unit will energize when it is connected to the D-connector (the power
LED will illuminate).
B) If the unit is to be powered through the power connector: Connect the power leads and the
power connector and then energize the power source. The unit is now powered (the power
LED will illuminate).
WARNING
When installing a Model RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, RLFDX232M2/HV, or
RLFDX232S2/HV Link/Repeater, an earth ground must be attached to the no. 6-32 ground
stud on the side of the housing before connecting to power. Failure to follow this procedure
may result in an electrical shock hazard to personnel.
6. The units are now installed and operating.
7. Verify operation using the diagnostic/status indicating LEDs. (See Figure 5).
NOTE The LEDs only illuminate when there is signal traffic and are not illuminated during signal
quiet times. The LEDs may flicker: This is normal operation.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 24
Page 25

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.3 Loop Operation - Peer-To-Peer Configuration
NOTE Before constructing a loop network, be sure that the software protocol is capable of
managing the receipt of the echo of its own transmission. If it cannot, then use a Point-toPoint configurations only between devices in an optical bus network approach.
A Peer-to-Peer loop configuration is similar to the Local/Remote loop configuration, except that
each IED in the loop is capable of localing the loop in a pseudo-Local/Remote loop. To achieve
this, all models within the RLFDX series provide an electrical means of controlling the “Off/Repeat”
function.
In this application, all Link/Repeaters are connected in a loop with their Repeat Switch in the
“OFF” position. Each IED must be able to control pin 7 of the D-connector, to enable and disable
the “ON” function. When an IED applies a low potential (less than 0.6 Vdc to pin 7), it enables the
repeat function of the Link/Repeaters. This is equivalent to the Repeat Switch being in the “ON”
position. When an IED wishes to become the loop Local, it raises the potential on pin 7 to a high
potential (greater than 2.0 Vdc). This disables the Link/Repeaters’ repeat function as if the Repeat
Switch were in the “OFF” position.
NOTE: The communication logic and control software of the Local IED must be able to manage
the receipt of its echoed request. The receipt of the echo can be used in conjunction with
a watchdog timer to continuously verify loop integrity.
ON
OFF
FIGURE 8. Peer-to-Peer Loop Configuration
ON
OFF
333
TTT RRR
COMCOMCOM
IEDIEDIED
222 555
ON
OFF
When the potential on pin 7 is low, signals received on the R optical port are delivered to the IED,
and are repeated out the T optical port to the next device in the loop. A high potential on pin 7
causes signals received on the R optical port to be delivered to the IED only, and are not repeated
out the T port. It is not necessary for a Remote unit to raise the potential of its pin 7 to transmit.
After an IED has completed its tasks Localing the loop, it must return its pin 7 to a low potential, enabling
its repeater function, and re-establishing loop continuity for the next IED that becomes loop Local.
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
12/20/12 PAGE 25
Page 26

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
NOTE Powering and controlling pin 7 is ignored in all configurations except Peer-to-Peer loop
operation.
Half-duplex communication is available with this configuration.
When an IED is in the Remote state, it should not attempt to initiate a transmission while it is
receiving a signal.
Since signals being received are also being repeated at the same time, any attempt to transmit its
response while still receiving, can corrupt both transmissions due to a data collision.
NOTE Any Link/Repeater that has its Repeat Switch in the “OFF” position and has a high
potential on pin 7 will not repeat those signals received on its R optical port through its T
port. Only transmissions initiated by its IED are transmitted through its T optical port.
APPLICATION NOTE
In Peer-to-Peer loop operation, the communication logic (control software) and the Local IED
must manage:
1. The transmission to Remotes.
2. The receipt of the echo of its transmissions.
3. The receipt of the Remote’s response to its transmission.
4. The control of pin 7 of D-connector.
5. The control of the Remotes to prevent the initiation of a transmission while receiving a signal.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 26
Page 27

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
2.3.1 Installation
1. Set the DTE/DCE Switch to the appropriate position for each Link/Repeater and its respective IED.
2. Set the Repeat Switch on all the units to the “OFF” position.
3. Connect the Link/Repeater to the IEDs RS-232 or TTL communication port (Including any
adapter that may be needed).
4. Connect the Fiber Optic Cables (T of one device to R of the second device). Continue around
the loop to complete the loop.
5. Connect power to the Link/Repeater as follows:
A) If the unit is to be powered through the D-connector (+9 to +36 VDC on pin 9, referenced to
pin 5, signal ground), the unit is energized when it is connected to the D-connector (the power
LED will illuminate).
B) If the unit is to be powered through its power connector: Connect the power leads and the
power connector, and then energize the power source. The unit is now powered (the power
LED will illuminate).
WARNING: When installing a Model RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC,
RLFDX232M2/HV or RLFDX232S2HV Link/Repeater, an earth Ground must be
attached to the no. 6-32 ground stud on the side of the case before connecting
to power. Failure to follow this procedure may result in an electrical shock hazard
to personnel.
Note: Connection of the no. 6-32 ground stud located on the rear of the unit to station ground is
optional for models RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC.
6. The units are now installed and operating.
7. Verify operation using the diagnostic LEDs. (See Figure 5).
NOTE The LEDs only illuminate when there is signal traffic and are not illuminated during signal
quiet times. The LEDs may flicker. This is normal operation.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 27
Page 28

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
3. Applications
When planning a system using any RLFDX232-series Link/Repeaters, the following system
parameters should be considered:
» Data Rate
» Optical Budget, and the distance between connected units
» Number of units in a loop configuration
» Powering the Link/Repeaters
» Type of communication, including format
» Selection of Fiber Optic Cable (FOC)
3.1 Data Rate
All RLFDX232-series Link/Repeaters automatically support data rates from 1200 bits per second
(AC-coupled is the factory default setting) to 250 Kilobits per second. No internal baud selection
or setting is required. However, it is necessary that all connected IEDs within the network be set at
the same data rate.
3.2 Optical Budget
The optical budget is a ratio of the receiver sensitivity to transmitter launched optical power;
i.e., the amount of light loss available from the transmitter to the receiver. It is calculated on a
log scale, so that a 3 dB loss is equal to one-half of the original power; 10 dB is one tenth of the
original power; 20 dB is one hundredth, etc. Many different elements in the optical path or circuit
can induce losses to the power of the signal. This attenuation must be taken into account when
determining the maximum distance that the signal can be reliably transmitted. The major factor
is the attenuation of the fiber optic cable. Cable attenuation is expressed as “X” dB per kilometer.
Other factors of attenuation include FOC fittings (connectors/terminations, splitters, etc.) FOC
diameter, and FOC aging over time.
Optical budget is the result of the expression:
Optical Budget [dB] = 10 x log10 Receiver sensitivity [μw]
Launch Power [μw]
Each RLFDX232M2/XX Multimode Link/Repeater has a typical optical budget of 19.5 dB.
Each RLFDX232S2/XX Singlemode Link/Repeater has a typical optical budget of 19 dB.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 28
Page 29

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
3.2.1 Cable Attenuation Factors
The following cable factors must be applied as corrections to the optical budget.
3. 2.1.1 Diam et er
Multimode: FOC of different diameters will limit the available optical budget of a system due to
different FOC core diameters. The 19.5 dB typical optical budget is applicable to
62.5μm diameter multimode FOC. Table 1 shows the correction factors to use on
the available optical budget for different diameter cable.
Table 1
FOC Diameter Factor
50μm -3 dB
100μm +4 dB
200μm +7 dB
Single mode: 19 dB of optical budget is typically available and is essentially consistent for
standard singlemode fiber diameters.
3.2.1.2 Fittings
Adding additional splices, feed-throughs, or patch panels to the fiber optic cable plant will add
losses to the available optical budget. Optical budget loss information is available from the
manufacturer(s) of these components.
3.2.1.3 Aging
As the FOC ages, tiny cracks will form in the glass core of the fiber, resulting in an increase in
the attenuation of the cable. The optical emitters age over time, causing a very slow reduction in
their optical launch power. ComNet suggests that an optical loss margin buffer be applied to the
calculated optical budget, to ensure proper operation due to aging of the network over a 20-year
life span. A 2.5 dB to 3 dB loss factor is suggested to compensate for system aging over this 20
year period.
EXAMPLE: FOC is 62.5/125 μm multimode
100 kpsi rated 3 dB/km and 3 dB for aging
No other attenuating items in the circuit
initial: 19.5 dB Optical Budget
less: 3 dB aging
less: 0 dB for other circuit attenuation fittings
equals: 16.5 dB
divided by: 3 dB/km
equals: 5.5 km maximum distance of FOC between transmitter and receiver
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 29
Page 30

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
NOTE: Fiber optic transmission radically extends transmission distances beyond the normal
copper media RS-232 or TTL standards limits. The maximum usable optical transmission
distance between Link/Repeaters must be calculated using the factors listed above.
3.2.2 Extending the Distance
Should the optical transmission distance between two devices exceed that calculated above, it is
possible to insert a Model RLFDX232M2/XX (for multimode cable plants) or Model RLFDX232S2/
XX (for singlemode cable plants) Link/Repeater to function as a stand-alone repeater. Two Link/
Repeaters would be necessary, one for each direction of the fiber path. When installed as a
repeater only, the 9-Pin D-connector of either Model RLFDX232M2/XX or Model RLFDX232S2/
XX should be installed with a terminator that covers the pins, and connects the transmit pin (2 or
3, depending on the DTE/DCE switch position) to the signal common pin 5, and also connects the
signal common pin 5 to chassis ground pin 1.
3.3 Number Of Repeats
In a loop configuration, the maximum number of units that can be used as repeaters must be
determined. A repeater is any unit that uses the repeat function of the Link/Repeater. All Remotes
in a Local/Remote loop are considered repeaters. Three factors must be considered in calculating
the maximum number of repeaters possible in a loop; the data rate (bits per second); the
minimum required width of the original pulse echoed back to the Local; and the maximum/peak
operating temperature.
Num ber of Repeats in a Loop Configuration*
1000
100
Repeats
10
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
1
0001001011
Data Rates (kbps)
FIGURE 9. Number of Repeats
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 30
Page 31

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
3.3.1 Effects of Data Rate
The number of repeaters is a linear inverse function to the data rate (i.e., more possible repeats at
lower data rates). The data rate, or bits per second rate, determines what the original pulse width
of each bit will be. The higher the data rate, the smaller the pulse width of each bit.
As the signal passes through a repeater, any distortion effect on the data signal is greater at
higher data rates, due to smaller pulse widths then lower data rates.
3.3.2 Pulse Width Distortion
As the data signal is passed from repeater to repeater, there is a small change to the pulse width;
this is defined as pulse width distortion. The amount of change that is tolerable corresponds to
the percentage of original pulse width required by a particular communications system design.
Typically, a communication system requires that the data word, or bit stream that each Remote
IED receives, matches the signal originally generated by the Local, within some tolerance of
pulse width distortion. High tolerance systems allow more pulse width distortion; therefore, more
repeats are tolerated. Conversely, low tolerance systems allow fewer repeats in the loop.
Figure 9 shows the maximum number of repeats possible if 70% of the original pulse width is
required by any IED within the loop. The acceptable percentage of the original pulse width is
due to the requirements of the IEDs. If more of the original pulse width is necessary or less is
allowable, then the number found in Figure 9 can be modified. Table 2 shows the factors to be
used to correct the number of repeats found in Figure 10 for such cases.
Table 2
% of Original Pulse Multiply Factor
80% .67
60% 1.33
50% 1.67
3.3.3 Temperature Effect
At peak operating temperatures above 65°C, the maximum number of repeats should be derated
by 20%. At higher temperatures, the distortion caused by each repeat increases, reducing the
maximum number of possible repeaters within the network.
EXAMPLE: Peak temperature of the system will be 70°C
Data Rate: 9600 bps
60% of original pulse width possible
initial: 100 repeats (from Figure 10)
less: 20% de-rate for 70°C
times: 1.33 for 60% pulse width
equals: 100 x 0.8 x 1.33 = 106 repeats
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 31
Page 32

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
3.4 Types Of Communication
The RLFDX-series of Link/Repeaters support the following types of asynchronous communications:
» Simplex - Transmission only or receive only
» Half-duplex - Sequential transmit and receive
» Full-duplex - Simultaneous transmit and receive
Half-
Simplex
Point-to-Point: (Repeat Switch “OFF”) X X X
Local/Save Loop: Local (Repeat Switch “OFF”) X X X
Local/Remote Loop: Remote (Repeat Switch “ON”) X X
Peer-to-Peer Loop: Local (Repeat Switch “OFF” and pin 7 “high”) X X X
Peer-to-Peer Loop: Remote (Repeat Switch “OFF” and pin 7 “low”) X X
Duplex
Full-
Duplex
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 32
Page 33

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
4. Testing And Troubleshooting
4.1 Testing
Models RLFDX232M2/XX and RLFDX232S2/XX lend themselves to easy installation and testing.
Testing the units requires transmitting and receiving data, or setting the Test Mode switch to ON
while observing that the diagnostic/status indicating LEDs are illuminating in the proper sequence.
To test whether a unit is transmitting and receiving correctly, insert a short fiber jumper between
the T and R optical ports, and transmit a signal (or turn the Test Mode Switch ON). Note that all
four diagnostic LEDs should illuminate during communications (refer to Figure 5).
To test the units in a loop configuration, two Link/Repeaters are required. Connect a short fiber
jumper from the T optical port of one Link/Repeater, to the R optical port of the other. Set the
Repeat Switch for one of the units to ON, and the other to OFF. The unit with the Repeat Switch in
the OFF position is the Local. Using the Local, transmit and receive (or use the Test Mode Switch
in the ON position) through the other unit in the repeat mode. Observe that the diagnostic LEDs
illuminate during communications (refer to Figure 5).
When a Link/Repeater is not connected to an IED and is in the “repeat” mode, Transmit (pin 2 or
pin 3, depending on the position of the DCE/DTE switch) and Chassis Ground (pin 1) should be
connected to Signal Common Ground (pin 5). This will prevent any spurious noise from being
induced into the fiber optic loop circuit while servicing an IED.
Single-Mode Models RLFDX232S2/24DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, and RLFDX232S2/HV Only:
When not connected to an IED, and in the repeat mode, the Link/Repeater should have Chassis
Ground (pin 1) connected to Signal Common/Ground (pin 5). If these pins are not tied together,
noise could be induced into the fiber loop. This is also necessary when servicing an IED in order to
keep the fiber loop and the Link/Repeater operational.
WARNING: The jumper connecting Chassis Ground and Signal Common/Ground should be
disconnected before reconnecting Models RLFDX232S2/24DC, RLFDXS2/48DC, or
RLFDX232S2/HV to an IED.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 33
Page 34

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
4.2 Troubleshooting
If the unit does not work properly, refer to the set up instructions in this guide, and use the
following check list:
» Is the unit properly powered?
› Verify the unit is receiving the correct power.
› Is the Power LED on?
› If required, make sure power from D-connector is present on Pin 9.
» Check that the indicating LEDs are responding to the optical and electrical activity.
» Is the unit mated properly to the IED? If an adapter is used, check that pin assignments are
connected correctly.
› Are the fiber cables connected properly? T to R; not R to R, or T to T.
› Are the DTE/DCE and the Repeat switches set to the proper positions for the application?
» Determine that the IED’s originating signal is within standards.
NOTE: If the Link/Repeater is not connected directly to an IED, determine that the electrical
signal received by the Link/Repeater is not corrupt. The Link/Repeater only repeats the
signal it is given, it does not re-clock or re-generate the signal.
» Review the IED’s software and protocols. Does the IED have physical handshaking
requirements, and have the appropriate settings on the IED been made to compensate for
these requirements?
» Consult factory.
NOTE: The LEDs only illuminate when there is signal traffic, and are not illuminated during signal
quiet times. The LEDs may flicker. This is normal operation.
NOTE: Link/Repeaters contain no user-serviceable parts. Opening the unit will void the warranty.
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 34
Page 35

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
PIN Explanation
2 Transmitted Data (Link input)
3 Received Data (Link Output)
5 Signal Common
Pinout for DTE Mode (Normal Functionality)
PIN Explanation
2 Received Data (Link Output)
3 Transmitted Data (Link input)
5 Signal Common
Pinout for DCE Mode (Normal Functionality)
PIN Explanation
1 Chassis (Earth) Ground
6 Data Set Ready (+5 V output)
8 TTL Output
7 Repeat Enable / Disable
9 + 9 to +36 VDC Input (Models
RLFDX232M2/24DC & RLFDX232S2/24DC only)
Pinout for Extended Functionality
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 35
Page 36

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
5. Specifications
5.1 Electrical and Optical Specifications
All Specifications over entire Operating Temperature Range. All Specifications are subject to
change without notice.
Multimode RLFDX232M2/24DC
Optical Budget Typical 19.5 dB 19.5 dB
Output power Typical -10.5 dBm peak -10.5 dBm peak
Receiver Sensitivity Typical -30 dBm peak -30 dBm peak
(62.5/125 Multimode) (62.5/125 Multimode)
Wavelength
Connector Type ST ST
Compatible Fiber Type Multimode Multimode
Configuration (Switches) DTE/DCE DTE/DCE
Data Rate DC to 250K bps DC to 250K bps
850nm 850nm
(50 -200μm) (50 -200μm)
AC/DC Coupled AC/DC Coupled
Link/Repeat Link/Repeat
Pin 8 Drive Current Pin 8 Drive Current
Pin 6 +5 V (DSR or CTS pull-up) Pin 6 +5 V (DSR or CTS pull-up)
Diagnostic Mode Diagnostic Mode
RLFDX232M2/48DC &
RLFDX232M2/HV
Data Transmission Asynchronous, simplex or Full
Duplex
Transmission Distance up to 5000 meters up to 5000 meters
(62.5/125 Cable@3dB/km) (62.5/125 Cable@3dB/km)
Bit Error Rate 10-E9 Max. 10-E9 Max.
Point to Point Latency 4 μsec Max 4 μsec Max
Repeat Latency 400 nsec Max 400 nsec Max
Electrical Parameters
Inputs
I/O Data Format EIA RS232; CCITT v24 EIA RS232; CCITT v24
Data Connector 9 pin D-Type Female 9 pin D-Type Female
Input Impedance >3000 Ohms >3000 Ohms
Input Voltage +/- 30 Volts Max +/- 30 Volts Max
Outputs
Output Impedance >300 Ohms >300 Ohms
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
Asynchronous, simplex or Full
Duplex
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 36
Page 37

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Driver Output +/- 5 V min into 3000 Ohms +/- 5 V min into 3000 Ohms
Pin 8 Output 0 to 5V 0 to 5V
67 or 207 Ohm 67 or 207 Ohm
Source Impedance Source Impedance
Ambient Temperature
Operating Temperatures -40º to +85º C -40º to +85º C
Storage Temperature -40º to +85º C -40º to +85º C
Power Required 3.0 Watts 3.0 Watts
250 mA @ 12 VDC 35 mA @ 88 to 300 V (/HV)
65 mA @ 36 to 59 VDC (/48DC)
Power Dissipation BTU/H 8.2 BTU 10.9 BTU
Weight 9 oz 17 oz
Dimensions (Inches) 2.0W × 5 .1L × 1.3H 4.1W × 5.1L × 1.3H
Indicators Power Power
Transmit Fiber Transmit Fiber
Transmit Electrical Transmit Electrical
Receive Fiber Receive Fiber
Receive Electrical Receive Electrical
Single-mode RLFDX232S2/24DC
RLFDX232S2/48DC &
RLFDX232S2/HV
Optical Budget Typical 19 dB 19 dB
Output power Typical -14.5 dBm peak -14.5 dBm peak
Receiver Sensitivity Typical -33.5 dBm peak -33.5 dBm peak
(9/125 Single-Mode) (9/125 Single-Mode)
Wavelength 1300 nm 13 00nm
Connector Type ST ST
Compatible Fiber Type Single-Mode (9-13 μm) Single-Mode (9-13 μm)
Configuration (Switches) DTE/DCE DTE/DCE
AC/DC Coupled AC/DC Coupled
Link/Repeat Link/Repeat
Pin 8 Drive Current Pin 8 Drive Current
Pin 6 +5 V (DSR or CTS pull-up) Pin 6 +5 V (DSR or CTS pull-up)
Diagnostic Mode Diagnostic Mode
Data Rate DC to 250K bps DC to 250K bps
Data Transmission Asynchronous, simplex or Full
Duplex
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
Asynchronous, simplex or Full
Duplex
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 37
Page 38

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
Transmission Distance up to ~30K meters up to ~30K meters
(9/125 Cable@0.3dB/km) (9/125 Cable@0.3dB/km)
Bit Error Rate 10-E9 Max. 10- E9 Max.
Point to Point Latency 4 μsec Max 4 μsec Max
Repeat Latency 400 nsec Max 400 nsec Max
Electrical Parameters
Inputs
I/O Data Format EIA RS232; CCITT v24 EIA RS232; CCITT v24
Data Connector 9 pin D-Type Female 9 pin D-Type Female
Input Impedance >3000 Ohms >3000 Ohms
Input Voltage +/- 30 Volts Max +/- 30 Volts Max
Outputs
Output Impedance >300 Ohms >300 Ohms
Driver Output +/- 5 V min into 3000 Ohms +/- 5 V min into 3000 Ohms
Pin 8 Output 0 to 5V 0 to 5V
67 or 207 Ohm Source Impedance 67 or 207 Ohm Source Impedance
Ambient Temperature
Operating Temperatures -40º to +70º C -40º to +70º C
Storage Temperature -40º to +85º C -40º to +85º C
Power Required 3.0 Watts 3.0 Watts
250 mA @ 12V 50 mA @ 88 to 300 V (/HV)
65 mA @ 36 to 59 VDC (/48DC)
Power Dissipation BTU/H 10.2 BTU 12.3 BTU
Weight 9 oz 17 oz
Dimensions (Inches) 2.0W X 5.1L X 1.3H 4.1W X 5.1L X 1.3H
Indicators Power Power
Transmit Fiber Transmit Fiber
Transmit Electrical Transmit Electrical
Receive Fiber Receive Fiber
Receive Electrical Receive Electrical
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 38
Page 39

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
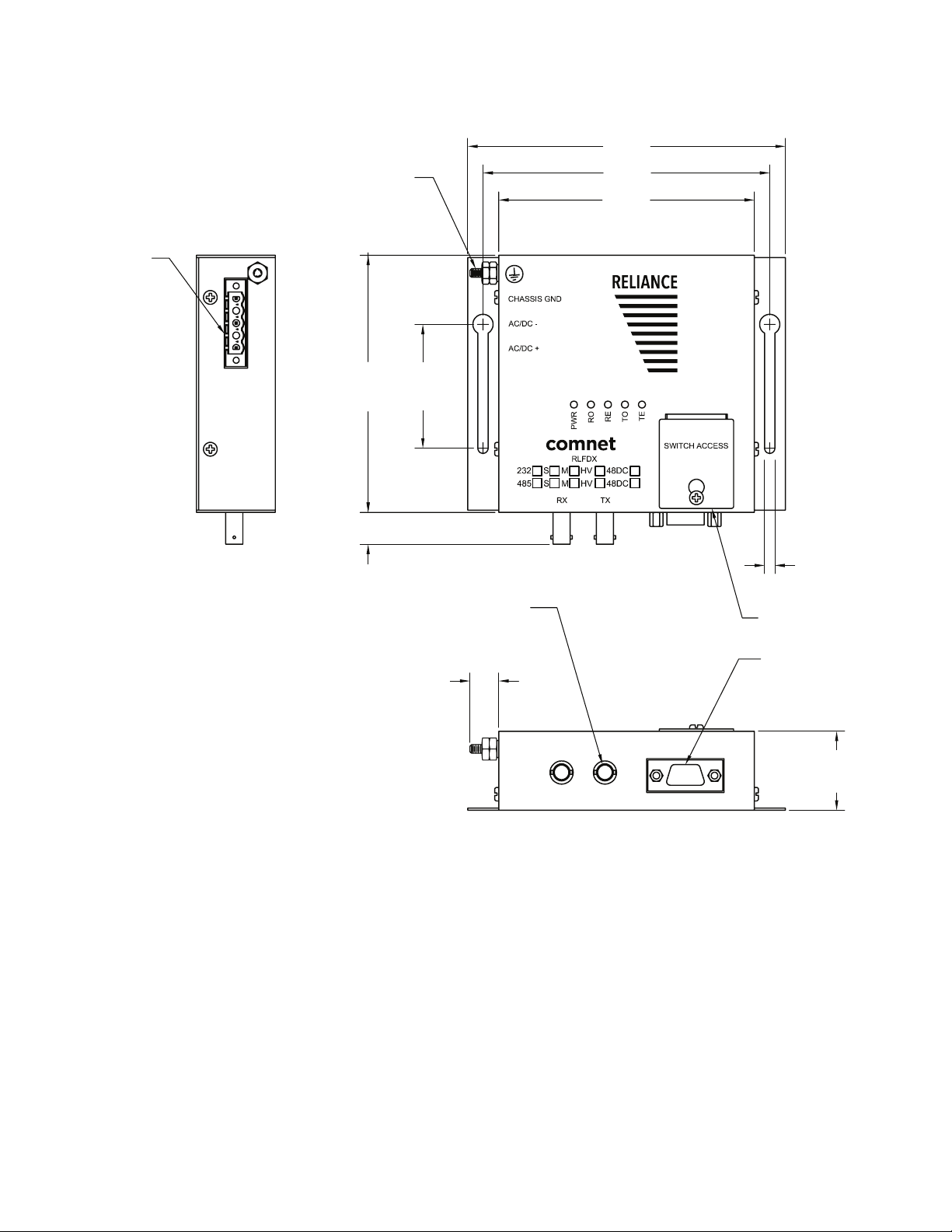
5.18 cm
2.82 cm
5.2 Outline Configuration & Mechanical Dimensions for Models
RLFDX232M2/24DC and RLFDX232S2/24DC
1.28 in
3.25 cm
9 TO 36 VDC INPUT
4.13 in
10.41 cm
5.13 in
13.03 cm
4.63 in
11.76 cm
0.46 in
1.16 cm
#6-32 THREAD SST
1.13 in
0.51 in
1.29 cm
TYPE ST
FIBER OPTIC
CONNECTOR
2.04 in
0.17 in
0.43 cm
REMOVABLE
SWITCH ACCESS PLATE
9 PIN D-CONNECTOR WITH
#4-40 STANDOFFS
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 39
Page 40

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
+/– 88 to 300
WITH
5.13 in
5.3 Outline Configuration & Mechanical Dimensions for Models
RLFDX232M2/48DC, RLFDX232S2/48DC, RLFDX232M2/HV, and
RLFDX232S2/HV
13.03 cm
#6-32 THREAD SST
INPUT:
VDC
85 to 264 VAC
OR
+/– 36 to 59 VDC
4.63 in
11.76 cm
4.13 in
10.41 cm
4.15 in
10.54 cm
0.51 in
1.29 cm
2.0 in
5.08 cm
0.46 in
1.16 cm
TYPE ST
FIBER OPTIC
CONNECTOR
REMOVABLE
SWITCH ACCESS PLATE
9 PIN D-CONNECTOR
#4-40 STANDOFFS
1.28 in
3.25 cm
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 40
Page 41

INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL RLFDX232 SERIES
TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427
INS_RLFDX232_REV–
12/20/12 PAGE 41
Page 42

ComNet Customer Service
Customer Care is ComNet Technology’s global service center, where our
professional staff is ready to answer your questions at any time.
Email ComNet Global Service Center: customercare@comnet.net
3 CORPORATE DRIVE | DANBURY, CT 06810 | USA
T: 203.796.5300 | F: 203.796.5303 | TECH SUPPORT: 1.888.678.9427 | INFO@COMNET.NET
8 TURNBERRY PARK ROAD | GILDERSOME | MORLEY | LEEDS, UK LS27 7LE
T: +44 (0)113 307 6400 | F: +44 (0)113 253 7462 | INFO-EUROPE@COMNET.NET
© 2015 Communications Networks Corporation. A ll Rights Reser ved. “ComNet ” and the “ComNet Logo” are regis tered trademarks of Communication Networks, LLC.
 Loading...
Loading...