Page 1

Comet Labs NFPS2 / WFPS2
2 USB 2.0 Hi-Speed-Port MFP Server
User’s Manual
Version 1.21
1
Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER1 INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................................................5
1.1 About this Manual...........................................................................................5
1.2 Customer Support...........................................................................................5
CHAPTER2 PRODUCT OVERVIEW...............................................................................................6
2.1 Package Contents ...........................................................................................6
2.2 Product CD.....................................................................................................6
2.2.1 Start-up Procedures........................................................................................6
2.3 Physical Description.......................................................................................6
2.4 Installation Procedures...................................................................................7
2.4.1 Installation and Integration............................................................................7
2.4.2 Configuration and Management.....................................................................7
2.5 Features and Benefits.....................................................................................7
CHAPTER3 BASIC INSTALLATION...............................................................................................9
3.1 Connecting the Hardware...............................................................................9
3.2 Wireless connection........................................................................................9
3.2.1 Preliminary.....................................................................................................9
3.2.2 Set Wi r eless Configuration Using MFP Server Control Center.....................9
3.2.3 Set Wireless Configuration Using Server’s Web Pages ................................13
3.3 Assigning an IP Address to the Server..........................................................17
3.3.1 Preliminary...................................................................................................17
3.3.2 Ethernet Address...........................................................................................18
3.3.3 IP Addr ess.....................................................................................................18
3.3.4 Methods for Setting the IP Address...............................................................18
3.3.5 Host Names and Host Name Rules...............................................................18
3.3.6 Setting the IP Address Using DHCP.............................................................18
3.3.7 Setting the IP Address Using the Control Center.........................................18
3.3.8 Setting the IP Address Using the Server’s Web Pages..................................20
3.4 Naming Your USB Devices ...........................................................................22
3.4.1 Printer Names...............................................................................................22
3.4.2 Storage Names..............................................................................................24
3.4.3 Scanner Names .............................................................................................24
CHAPTER4 PRINT SERVER IN WINDOWS................................................................................25
4.1 Overview of Installation Methods.................................................................25
4.2 Connecting the Server...................................................................................25
4.2.1 The Server and Windows PC on Same LAN .................................................26
4.2.2 The Server and Windows PC on Different LANs..........................................26
4.3 Setting up Local Windows Printer Driver.....................................................26
4.4 Adding Network Printers in Windows...........................................................27
4.4.1 Using Standard Windows Methods for LPR Printing Protocol....................27
4.4.2 Using the Control Center for LPR Printing..................................................31
4.4.3 Using Standard Windows Method for Raw TCP Printing ............................32
4.4.4 Using the Control Center for Raw TCP/JetDirect Printing .........................34
4.4.5 Using Standard Windows Methods for SMB/CIFS Printing.........................35
4.4.6 Using the Control Center for SMB/CIFS Printing.......................................36
4.4.7 Using Standard Windows Method for IPP Printing......................................38
CHAPTER5 PRINT SERVER IN UNIX/LINUX .........................................................................41
2
Page 3

5.1 Configuring Host File...................................................................................41
5.2 Printing by LPD/LPR ...................................................................................41
5.3 Using the Server on BSD UNIX/Linux..........................................................41
5.4 Using the Server on RedHat Linux (Fedora Core).......................................42
CHAPTER6 FILE SERVER..............................................................................................................49
6.1 Preliminary...................................................................................................49
6.2 Storage Names..............................................................................................49
6.3 Connecting USB Mass Storage to the Server ...............................................49
6.4 Supported Codepages...................................................................................50
6.5 Adding Your USB Mass Storages to Network with Security.........................52
6.5.1 Setting up File Server Using the Control Center..........................................52
6.5.2 Setting up File Server Using Web Pages .........................................................54
6.5.3 Using Shared Storages by SMB/CIFS Method for Windows ........................55
6.5.4 Using Shared Storage by FTP Methods for Windows...................................56
CHAPTER7 SCAN SERVER............................................................................................................58
7.1 Connecting HP All-In-One to the Server......................................................58
7.2 Using the Shared Scanner in Windows .........................................................58
7.2.1 Using the Control Center..............................................................................58
7.2.2 Using Windows Applications........................................................................60
7.3 Using the Shared Scanner in Linux..............................................................61
7.3.1 Using XSane in RedHat Linux......................................................................61
CHAPTER8 THE CONTROL CENTER .........................................................................................64
8.1 Installing Control Center..............................................................................64
8.2 Using the Control Center..............................................................................64
8.2.1 Using Tools of Control Center......................................................................64
8.2.2 Displaying Server Status...............................................................................65
8.2.3 Setting up Server Configuration...................................................................65
CHAPTER9 REMOTE CONNECT CENTER................................................................................72
9.1 Introduction .................................................................................................72
9.2 Link & Unlink..............................................................................................72
9.3 How to Use ..................................................................................................72
9.4 Auto Link/Unlink..........................................................................................75
9.5 Limitations...................................................................................................78
CHAPTER10 THE SERVER’S WEB P AGES...................................................................................79
10.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................79
10.2 Using the Server’s Web Pages ......................................................................79
10.2.1 Displaying Server Status...............................................................................79
10.2.2 Setting up Server Configuration ...................................................................80
CHAPTER11 EMAIL ALERTING.....................................................................................................85
CHAPTER12 SNMP.............................................................................................................................85
CHAPTER13 TROUBLESHOOTING...............................................................................................86
13.1 LED Indicators .............................................................................................86
CHAPTER14 RESTORE FACTORY DEFAULTS............................................................................87
14.1 Using the Control Center..............................................................................87
14.2 Using the Server’s Web Pages ......................................................................87
3
Page 4

14.3 Using Init Button...........................................................................................88
14.4 Default Parameters List................................................................................88
CHAPTER15 UPGRADE FIRMWARE.............................................................................................90
CHAPTER16 THE INIT BUTTON.....................................................................................................93
4
Page 5

Chapter1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing this Comet Labs NFPS2 / WFPS2 USB MFP Server (in the
following referred to as “Server”). This Server is designed to connect your AIO/MFPs
(All-In-One/Multifunction Peripher al), printers, USB mass storages (hard drives, flash
drives, and memory card readers), and scanners, to your network, allowing all
network users access to these shared USB devices resources.
1.1 About this Manual
This manual provides introductory information as well as detailed instructions on how
to set up and manage Comet Labs NFPS2 and WFPS2 in various network
environments. Compared with NFPS2, WFPS2 has an additional wireless module
(802.11b/g). Except for the wireless-related configuration and operations, all other
configuration and operations are almost the same for NFPS2 and WFPS2. Unless
explicitly specified, all instructions apply to both NFPS2 and WFPS2.
To fully benefit from this document, you should be familiar with basic networking
principles. The instructions described in this manual are based on the settings in a new
Server. To reload the Factory Parameters, you can reset this Server back to Factory
Default, which will restore most of the settings. For details, please refer to the chapter
“Restore Factory Defaults”.
1.2 Customer Support
Should you require any technical assistance, please contact your product reseller. Or
you can visit our website at http://www.cometlabs.com for latest product information.
This document is subject to changes without prior notice.
5
Page 6

Chapter2 Product Overview
2.1 Package Contents
Verify that nothing is missing from the package by using the checking list below.
Please contact your dealer if anything is missing or damaged. All packing materials are
recyclable. Please confirm the items in the package below:
This Server (NFPS2 or WFPS2)
CD (Control Center and User’s Manual)
Power Adaptor
Quick Installation Guide
2.2 Product CD
This CD provides easy-to-use Control Center software, and the User’s Manual.
2.2.1 Start-up Procedures
If your computer is configured to auto start CDs, this CD will start automatically when
inserted. Y ou can also navigate to the CD and start the autorun.exe file from within the
Windows file manager.
2.3 Physical Description
1. Power Adaptor Connector: DC IN 5V/2A adaptor
2. Init Button: print the configuration page and initialize this Server
3. Ethernet Connector: a twisted pair category 5 cable
4. Wireless Station (only for WFPS2): IEEE 802.11 b/g wireless station with antenna
inside
5. USB Host Ports: USB 1.1/2.0 low, full, and Hi-Speed compliant
6. Indicators
Power Indicator is lit while power is applied. If it is not lit, or if it blinks, there is a
problem with this Server or power adapter.
Link Status (only for NFPS2) is lit while network is applied. If it is not lit, it
indicates that this server does not connect to the network.
Status Indicator (only for NFPS2) blinks to indicate network activity.
LAN Indicator (only for WFPS2) blinks to indicate wired network activity. If it is
lit, it indicates the wired network is applied. If it is not lit, it indicates that the
server does not connect to the wired network.
WLAN Indicator (only for WFPS2) blinks to indicate wireless network activity. If
it is lit, it indicates the wireless network is applied. If it is not lit, it indicates that
the server does not connect to the wireless network.
USB1 Indicator is lit while a USB device connects to USB1 Port of this Server. If it
is not lit, or if it blinks, there is a problem with the USB device or this Server.
USB2 Indicator is lit while a USB device connects to USB2 Port of this Server. If it
is not lit, or if it blinks, there is a problem with the USB device or this Server.
6
Page 7
2.4 Installation Procedures
2.4.1 Installation and Integration
Please refer to the table below to select the appropriate installation method. The
Control Center is available on the CD.
Functi
on
Print
Server
OS Method Description
Windows
Standard
Windows Add
Printer Wizard
Control Center
Tool
Installation of LPR, Raw TCP
(JetDirect), Local Port Using
SMB, and IPP
Installation of LPR, Raw TCP,
Local Port Using SMB
Apple MAC OS x Printer Setup
Tool
Unix/Linux
File
Server
Scan
Server
2.4.2 Configuration and Management
Windows None Don’t need installation
Apple MAC OS X None
Unix/Linux Samba Use smbclient in Samba
Windows The Control
Apple MAC OS X Download and
Unix/Linux Download and
Edit
/etc/printcap
File
RedHat Linux
Printer System
Manager
Center
install SANE
install SANE
Frontends
LPR, Raw TCP (JetDirect)
SMB, IPP
Using vi or other editors to
edit the printcap file
Using X-Windows Interface
to operate
Installation of SANE Client
and SANE-Twain Driver
Use terminal
Use SANE Applications such
as XSANE
This Server can be configured and managed from its internal web pages or from the
Control Center. These web pages or PC tools offer you a management tool suitable for
all supported network environments.
2.5 Features and Benefits
This Server provides the following features and benefits:
1. Reliability: The Server provides high performance and reliability combined
with low power consumption.
2. Flexibility: The Server supports print/File/Scan sharing in all major
7
Page 8

computer systems and environments.
3. Easy to Install: The Server installs, operates, and is managed in a reliable
and easy fashion.
4. Security: Y ou can assign administrator name and password to restrict login.
5. Monitoring: The Server’s web pages and user software allow you to
continuously monitor the status of connected USB devices.
6. Future Proof: The firmware stored in the Server’s Flash memory can be
upgraded over the network. This allows y ou to quickly update and enhance its
operational features when new Server software becomes available.
8
Page 9

Chapter3 Basic Installation
3.1 Connecting the Hardware
1. Make sure that your USB devices are switched off and that the Server’s Power
Adapter is disconnected.
2. Connect the USB devices to the USB ports with the USB cables.
3. Connect the Server to the network with a twisted-pair category 5 cable,
10baseT or 100baseTX.
4. Turn on the USB devices and make sure it is ready for use.
5. Connect the Power Adapter to the Server. The power indicator will light up and
USB1 and USB2 indicators will flash in turn. When the Link indicator lights up,
the Server is correctly connected to the network. When USB1 and USB2
indicators do not flash, the Server starts to work normally.
6. If you connect USB HP printers to the Server, please press the Init button for 3
seconds on the Server once to print a page of Server configuration report.
3.2 Wireless connection
This section only applies to WFPS2.
3.2.1 Preliminary
Before you can access wireless network, wireless parameters should be set
correctly. You have to setup the first wireless parameter set through LAN
(wired) connection.
Wireless access can be set as 1. Infrastructure (station) mode, which need an
access point to route network messages, or 2. Ad-hoc mode, which connect
nearby wireless PC/devices with the same SSID (Service Set ID).
Wireless access can be secured by WEP64, WEP128, or WPA-PSK/TKIP.
In infrastructure mode, if network administrator wants to change any security
related parameters, WFPS2 should be changed first, and then access point.
If parameters mismatch causes wireless access is not allowed, you have to
modify those parameters through LAN connection.
In infrastructure mode, the maximal transfer rate is 54 MBits depending on
access point’s capability. In ad-hoc mode, only 802.11b (the maximal
transfer rate is 11 MBits) is allowed by specification.
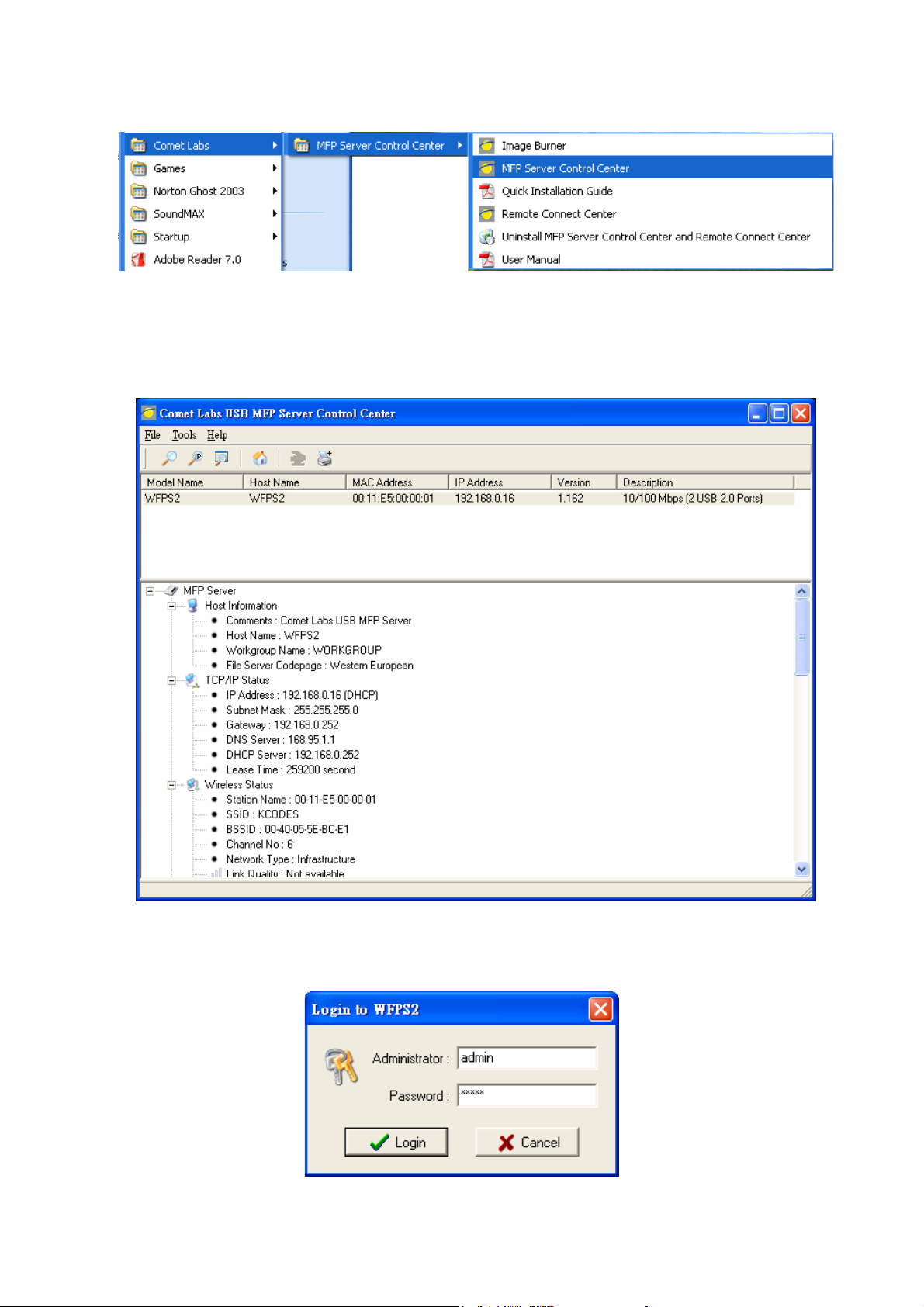
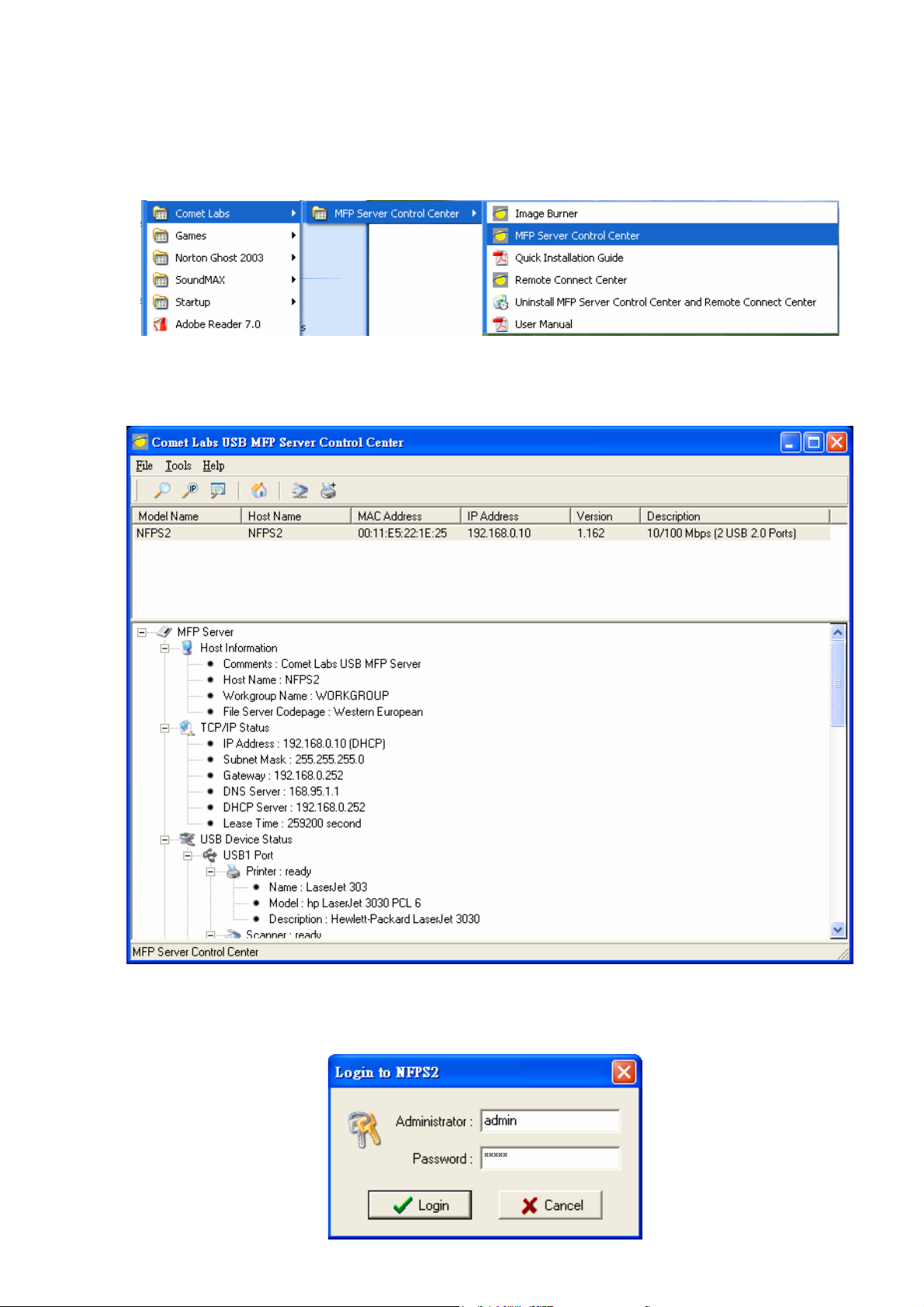
3.2.2 Set Wireless Configuration Using MFP Server Control Center
1. Install MFP Server Control Center. MFP Server Control Center is av ailable in the
Comet Labs WFPS2 USB MFP Server Product CD.
2. Start MFP Server Control Center and Auto-searching MFP server window will
appear.
9
Page 10
# If the wireless parameters are not correct or not set yet, you have to use LAN to access
MFP Server Control Center.
3. If the tool finds MFP servers in y our local area network, then you hav e to select
a MFP server from the server list.
4. Double click the highlight list and type the server’s administrator (default:
admin) and password (default: admin).
5. After you login successfully, from the Server menu, select wireless. The set
10
Page 11
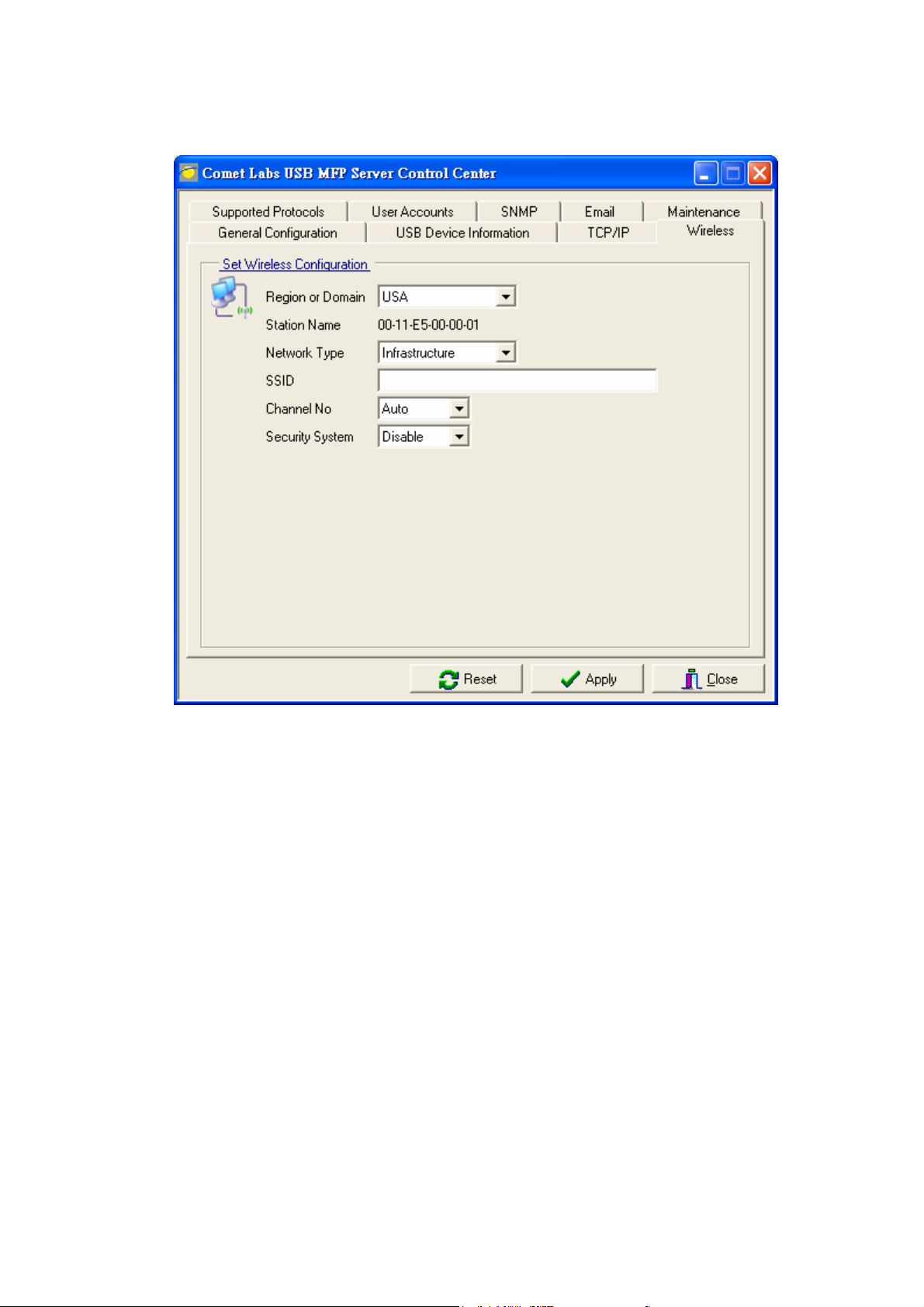
Wireless dialog appears.
6. In order to join an existing wireless network, you have to set the correct
network type (infrastructure or ad-hoc), SSID , and the correct security method
with the correct key information.
7. If the wireless network is secured by WEP64 or WEP128, authentication method,
key index, and WEP key must be set correctly.
11
Page 12
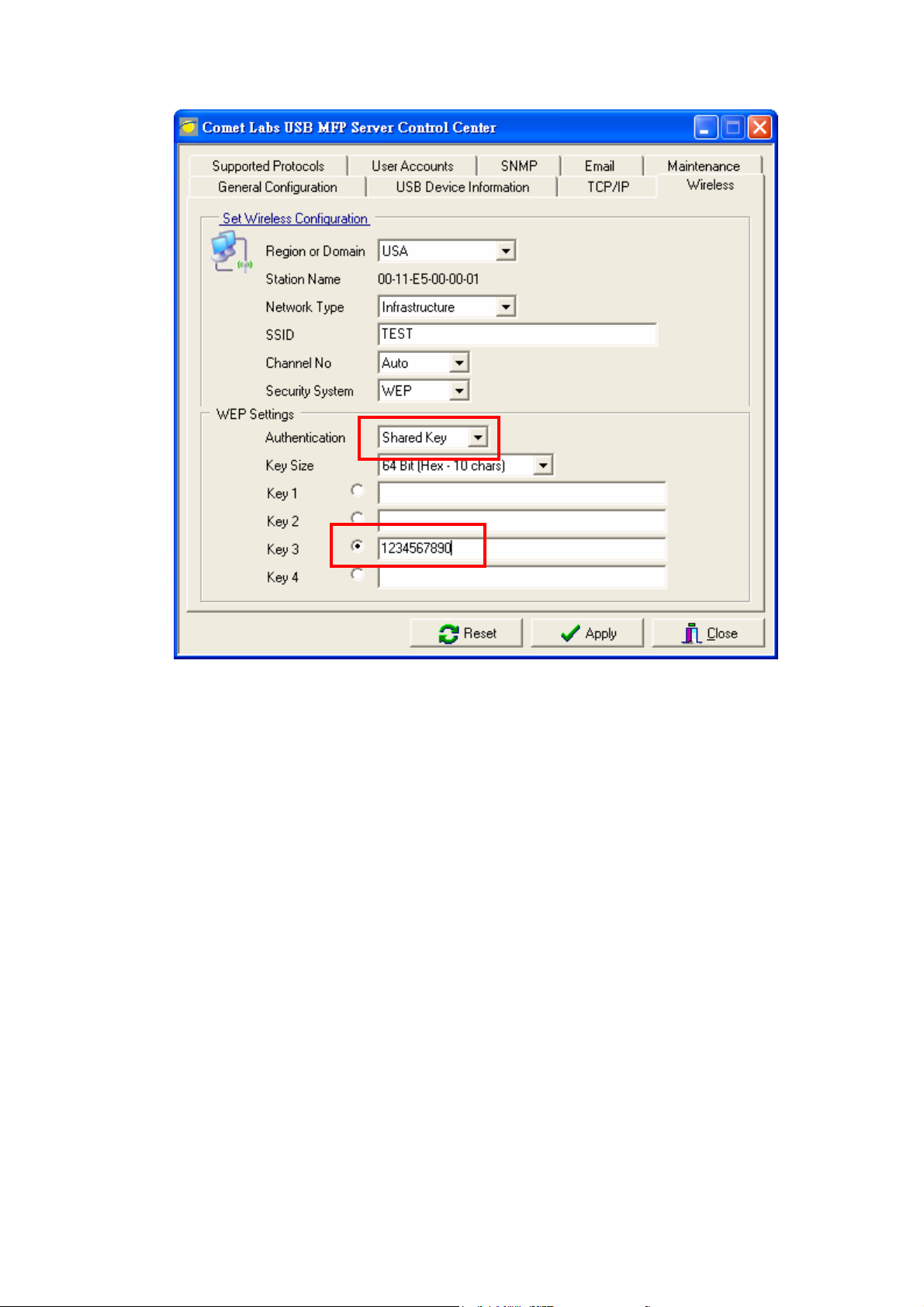
8. If the wireless network is secured by WPA -PSK/TKIP , the shared key must be set
correctly.
12
Page 13
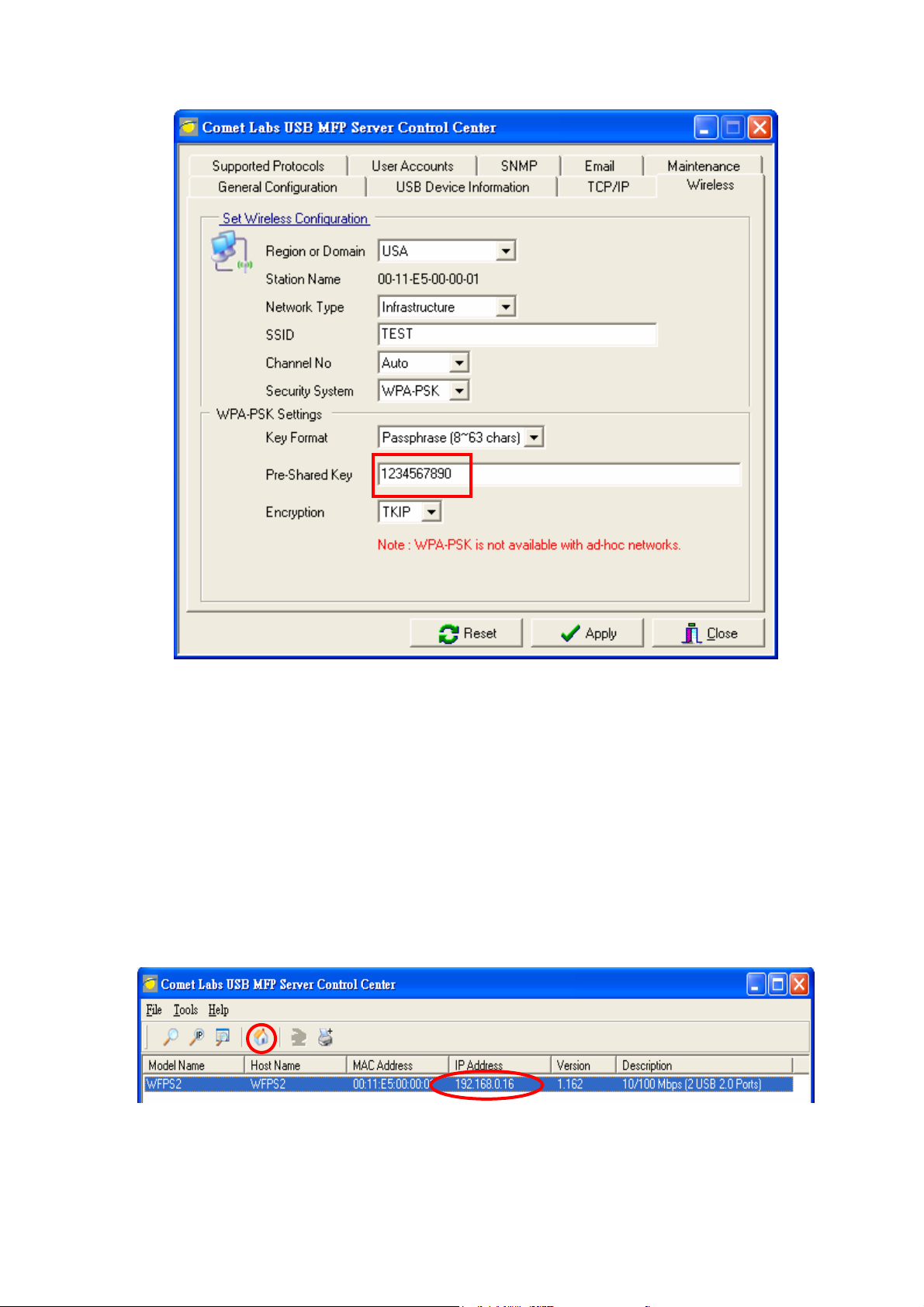
9. Click Apply to save your settings. And the server will reboot.
10. You have now finished the procedure of setting the wireless parameters.
# In infrastructure mode, WFPS2 searches all channels to join the matched wireless service
set. In ad-hoc mode, WFPS2 searches all channels to join the matched wireless ad-hoc
service set too, however, if none are found, WFPS2 creates that service set in the assigned
channel.
# In ad-hoc mode, WPA-PSK/TKIP is not allowed.
3.2.3 Set Wireless Configuration Using Server’s Web Pages
1. You can see the IP address of MFP serv er in the server list. Open IE Browser and
type server’s IP address or click the Home Icon of MFP Server Control Center.
13
Page 14
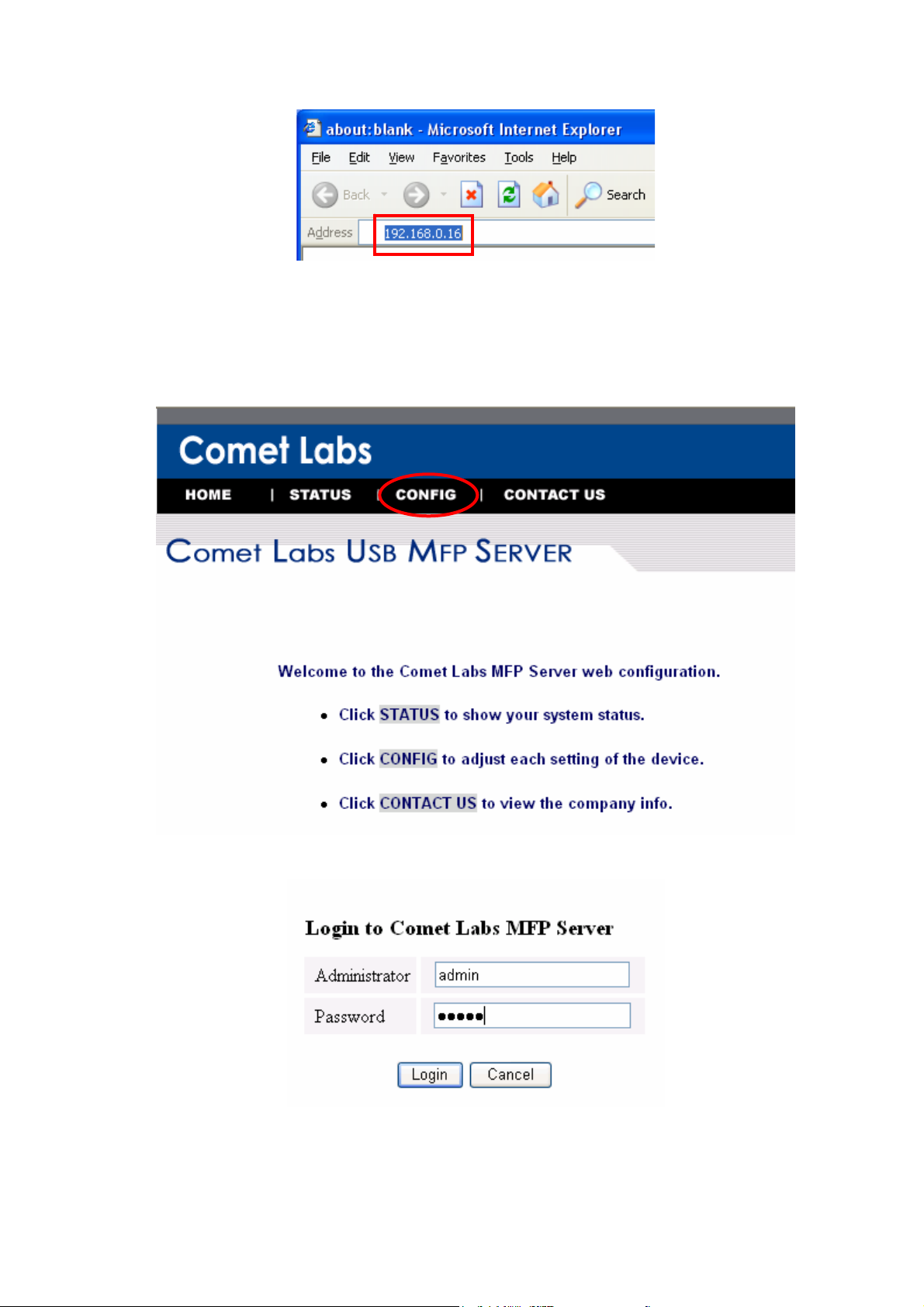
# If the wireless parameters are not correct or not set yet, you have to use LAN to access
Web Pages.
# If the TCP/IP parameters of WFPS2 are not correct, you have to use MFP Serv er Control
Center to set the TCP/IP parameters first.
2. Go to the web page and click CONFIG icon.
3. Login your administrator (default: admin) and password (default: admin).
4. Click Wireless icon.
14
Page 15
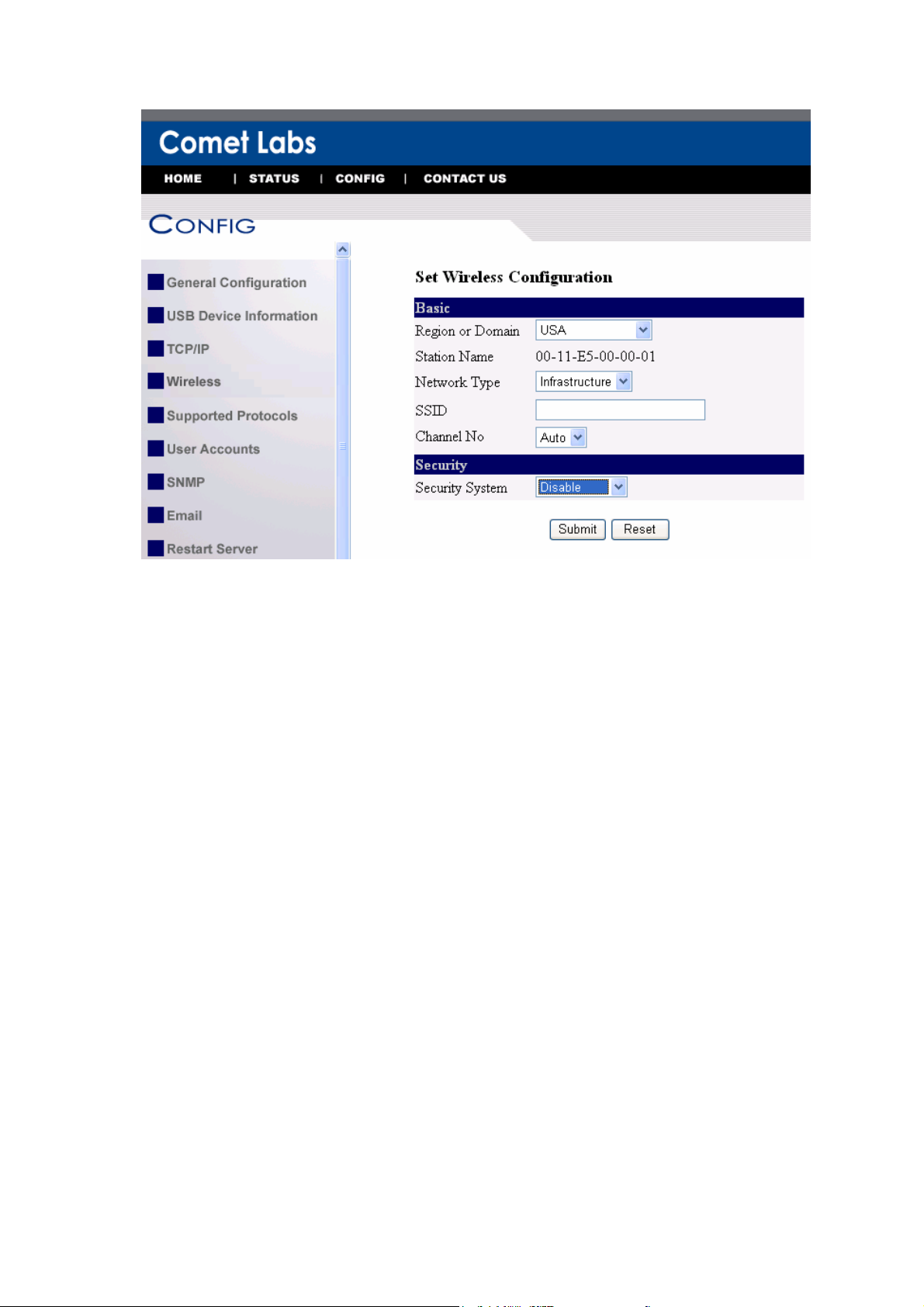
5. In order to join an existing wireless network, you have to set the correct
network type (infrastructure or ad-hoc), SSID , and the correct security method
with the correct key information.
6. If the wireless network is secured by WEP64 or WEP128, key index and WEP key
must be set correctly.
15
Page 16
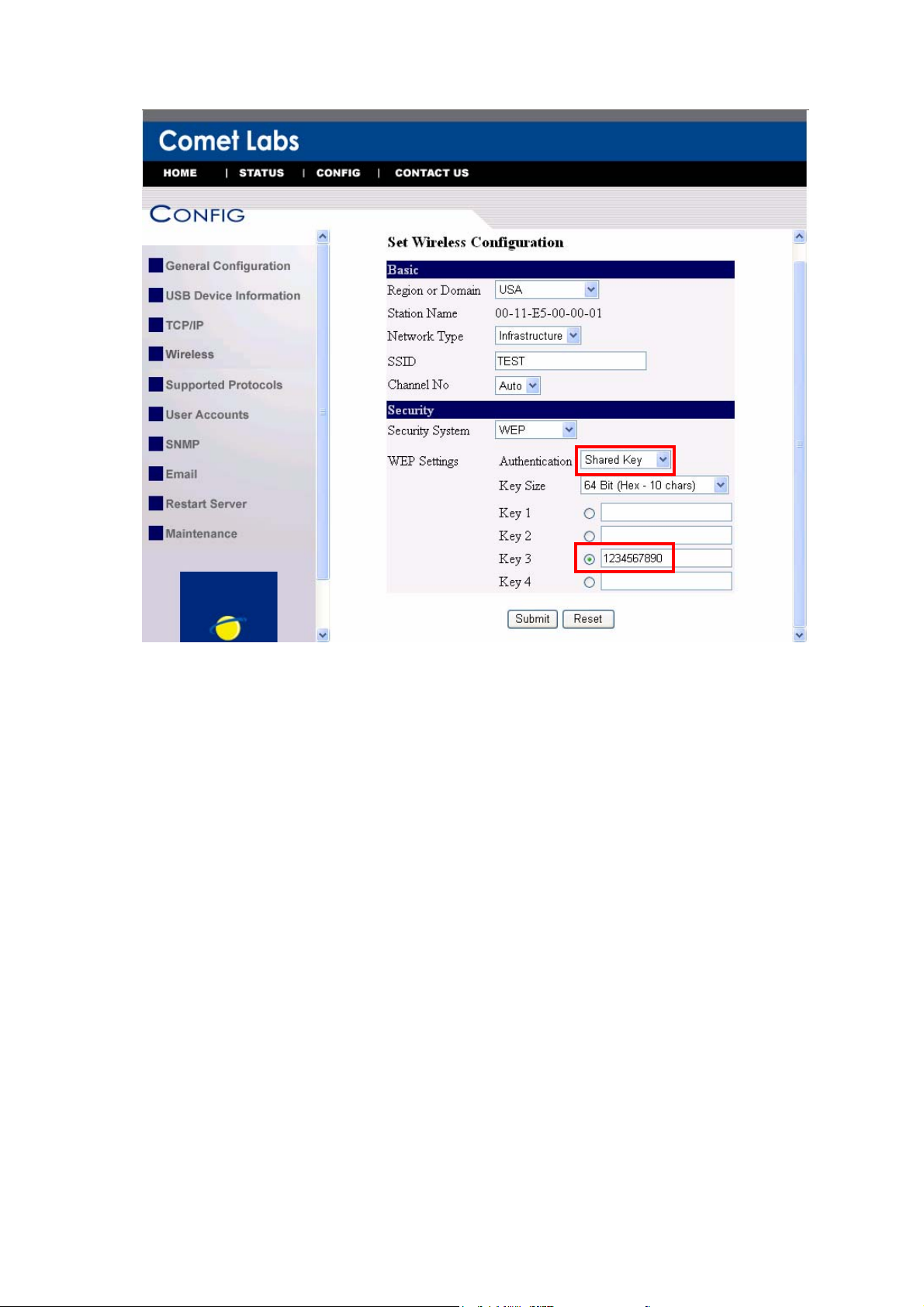
7. If the wireless network is secured by WPA-PSK/TKIP, the shared key must be set
correctly.
16
Page 17
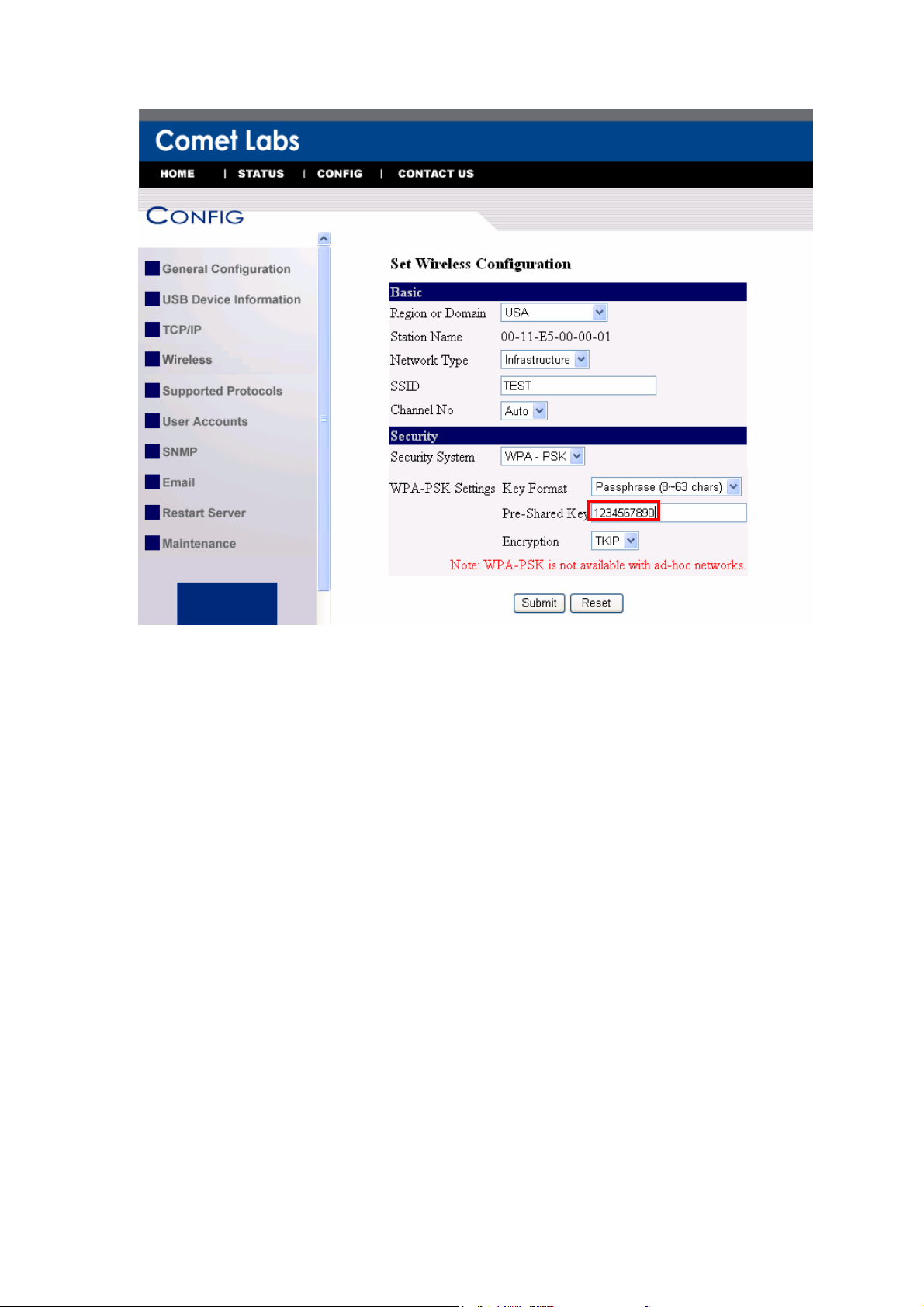
8. Click Submit to save your settings. And the server will reboot.
9. You have now finished the procedure of setting the wireless parameters.
# In infrastructure mode, WFPS2 searches all channels to join the matched wireless service
set. In ad-hoc mode, WFPS2 searches all channels to join the matched wireless ad-hoc
service set too, however, if none are found, WFPS2 creates that service set in the assigned
channel.
# In ad-hoc mode, WPA-PSK/TKIP is not allowed.
After properly configuring the wireless parameters, you can remove the network
cable and reboot the WFPS2. WFPS2 will then connect to your wireless network.
WFPS2 will detect if a network cable is plugged-in or not. If a network cable is
plugged-in, WFPS2 will always connect to the network through the network cable.
Otherwise it will always connect to the network through wireless module. Once
WFPS2 connects to the network, either by network cable or by wireless module, all
operations of print / scan / file server are exactly the same.
3.3 Assigning an IP Address to the Server
3.3.1 Preliminary
If you have a DHCP server on your network, your Server will receive an IP
address automatically. The IP address will then appear on the Control Center
or on the page of configuration report that you printed earlier. If your DHCP
server does not give an IP address to the Server, the Server will use the
default IP address: 192.168.0.2.
17
Page 18

If you are not working in a DHCP network, you need to manually set the
Server’s IP address.
3.3.2 Ethernet Address
You do not need to know the Ethernet address of your Server for assigning an IP
address to it. The Control Center can automatically search Servers and list their
Ethernet addresses. Besides, you can find Ethernet address that is located on the
backside label of the Server.
3.3.3 IP Address
Unless you are assigning an IP address using DHCP, you must obtain an unused IP
address from your network administrator.
3.3.4 Methods for Setting the IP Address
You can set the IP address of your Server using one of the following methods,
depending on your network operating environment:
Automatic IP Address Assignment
Manual IP Address Assignment
3.3.5 Host Names and Host Name Rules
The Host Name of the Server defaults to be “NFPS2” (for NFPS2) or “WFPS2” (for
WFPS2). If you put two or more Servers in yo ur local area network, to avoid using the
same Host Names you have to change the Host Names by using the Control Center or
the Server’s web pages. If your Host Name is longer than 15 characters, the Server
uses only the first 15 characters.
3.3.6 Setting the IP Address Using DHCP
Follow the instructions below to get an IP address using DHCP:
1. Edit or create a scope in the DHCP manager of the DHCP daemon. The entries
included in this scope should contain the following parameters:
y range of IP addresses
y subnet mask
y default router IP address
y DNS server IP address
y lease duration
2. Activate the scope. The Serv er automatically gets the DHCP par ameters. If you
are using DNS, you may include at least one DNS server IP address in the DHCP
scope or manually set the DNS server IP address using Server’s web pages or
the Control Center.
3.3.7 Setting the IP Address Using the Control Center
18
Page 19
11. Install the Control Center. The Control Center is available on the Product CD.
12. Start the Control Center and Auto-searching Server window will appear.
13. If the tool finds multiple Servers in your local area network, then you have to
select one Server from the Server List.
14. Double click the highlight list and enter the Server’s administrator (default:
admin) and password (default: admin).
19
Page 20
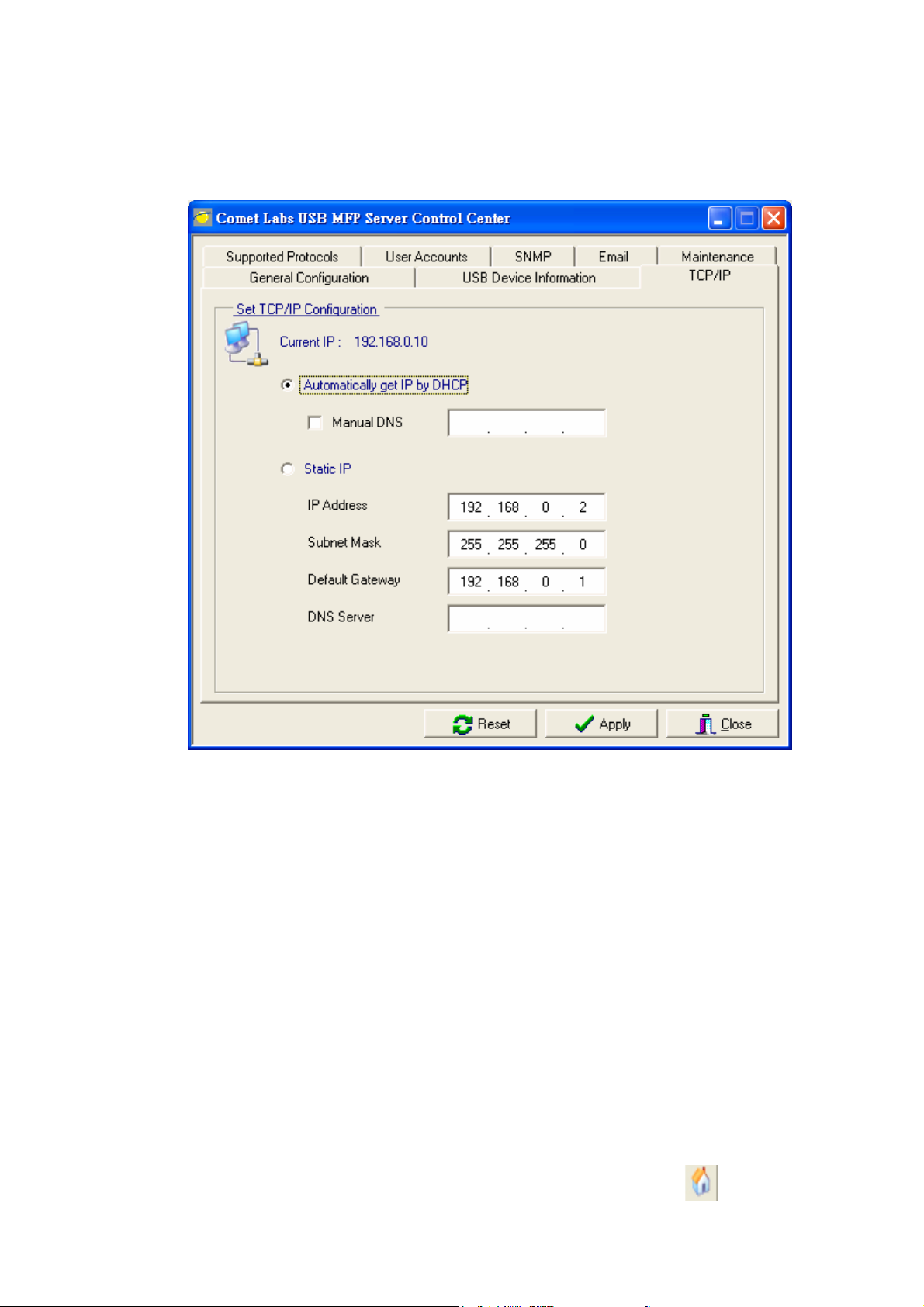
15. After you have logged in successfully, select TCP/IP from the Server’s menu.
The Set IP Address dialog appears.
16. Click the button corresponding to your choice of IP setting method (static or
dynamic using DHCP). When assigning a static IP address you also have to
define Subnet Mask and Default Gateway. If you choose Automatically get
IP by DHCP, you can use desired DNS by clicking the Manual DNS button
and manually assigning a DNS.
17. Click Apply to save your settings. And the Server will reboot.
18. You have now finished the procedure of setting the IP address.
3.3.8 Setting the IP Address Using the Server’s Web Pages
1. If you don’t know the current IP of you Server, you have to do the Step1~Step4
of Set the IP Address Using the Control Center.
2. You can see the IP address of you Server in the Server List. Open IE Browser
and enter the Server’s IP address or click the Home Icon of the Control
Center.
20
Page 21
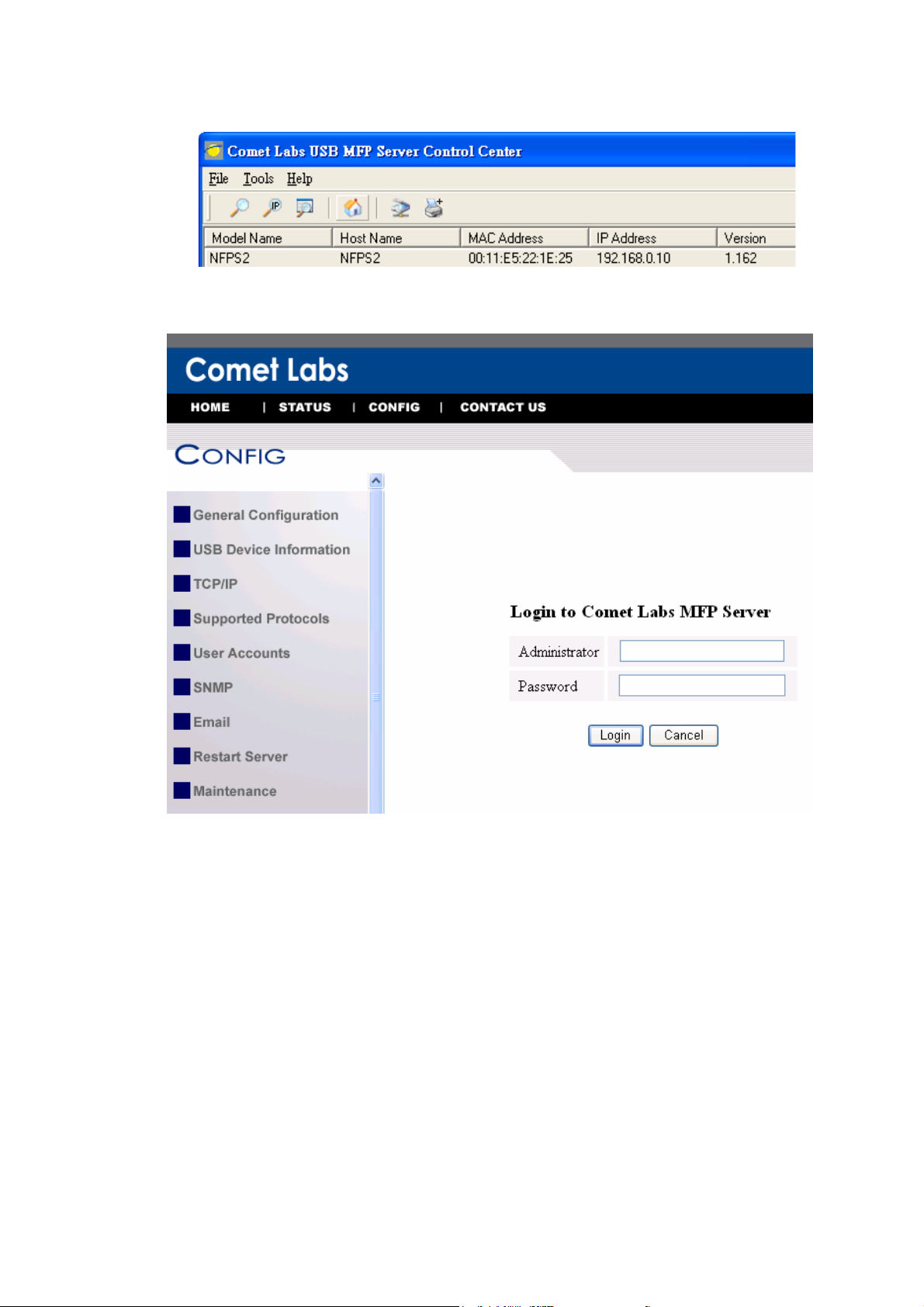
3. Go to the web page and click CONFIG icon.
4. Enter administrator (default: admin) and password (default: admin).
5. Click TCP/IP icon.
21
Page 22
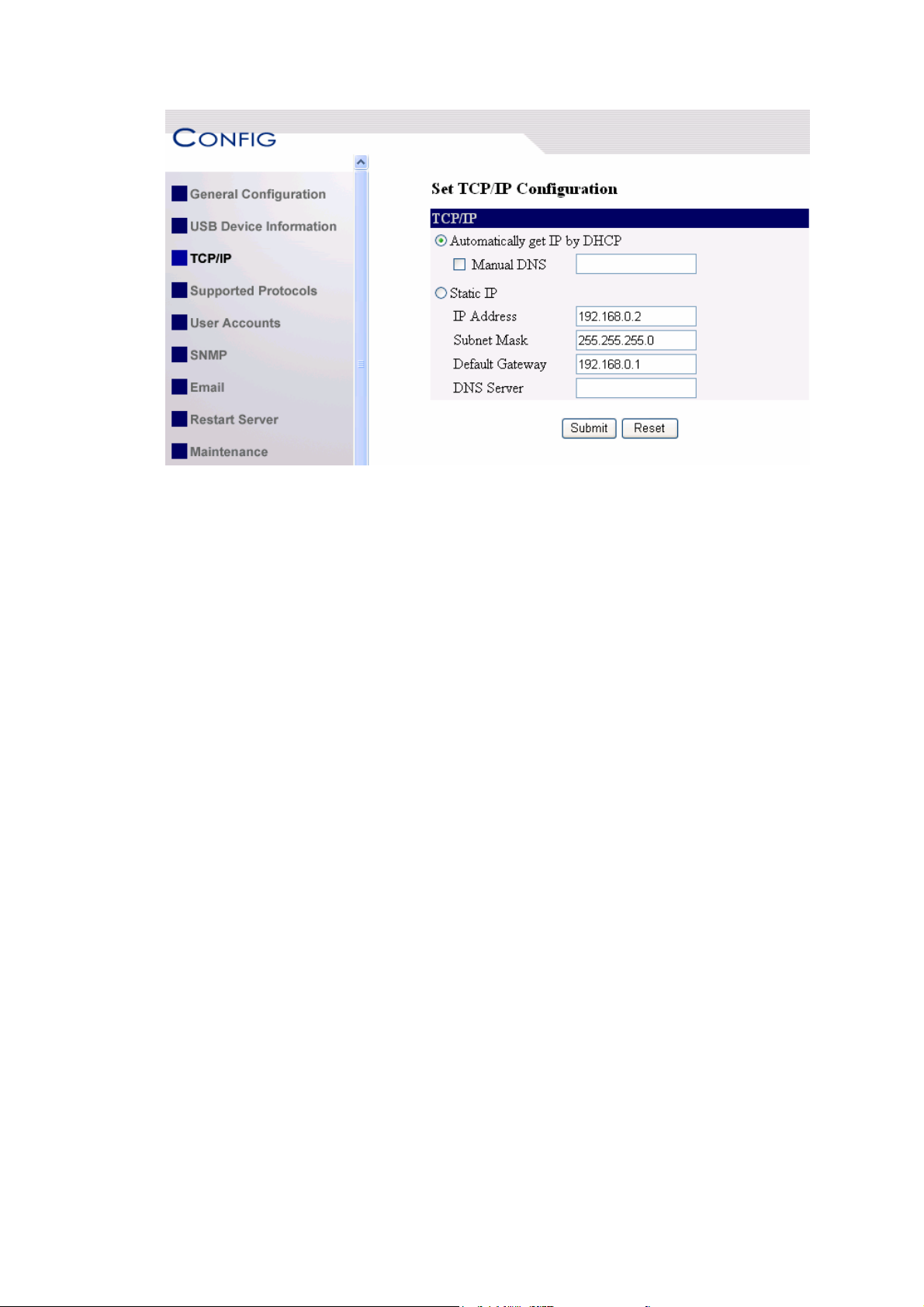
6. Click the button corresponding to your choice of IP setting methods (static or
dynamic using DHCP). When assigning a static IP address you also have to
define Subnet Mask and Default Gateway.
7. Click Submit to save your settings. And the Server will reboot. You have now
finished the procedure of setting the IP address.
3.4 Naming Your USB Devices
3.4.1 Printer Names
Default Printer Name
1. The system will set the printer model names as the default printer names.
The system only allows a 12-character long USB device name. For
example, the printer model name is “hp LaserJet 3030 PCL 6” and then the
default printer name will be set as “LaserJet 303”.
2. If system cannot get the printer model (For example, you use some
parallel printers and use Parallel-to-USB cables to connect the printers),
the default printer names are set as: USB1_Printer and USB2_Printer
with respect to USB1 port and USB2 port.
Set Printer Name
You can set printer names with the Control Center or Server’s web pages.
A. Using the Control Center
1. Start the Control Center and Auto-searching Server window will
appear.
2. If the tool finds multiple Servers in your local area network, then
you have to select one Server from the Server List.
22
Page 23
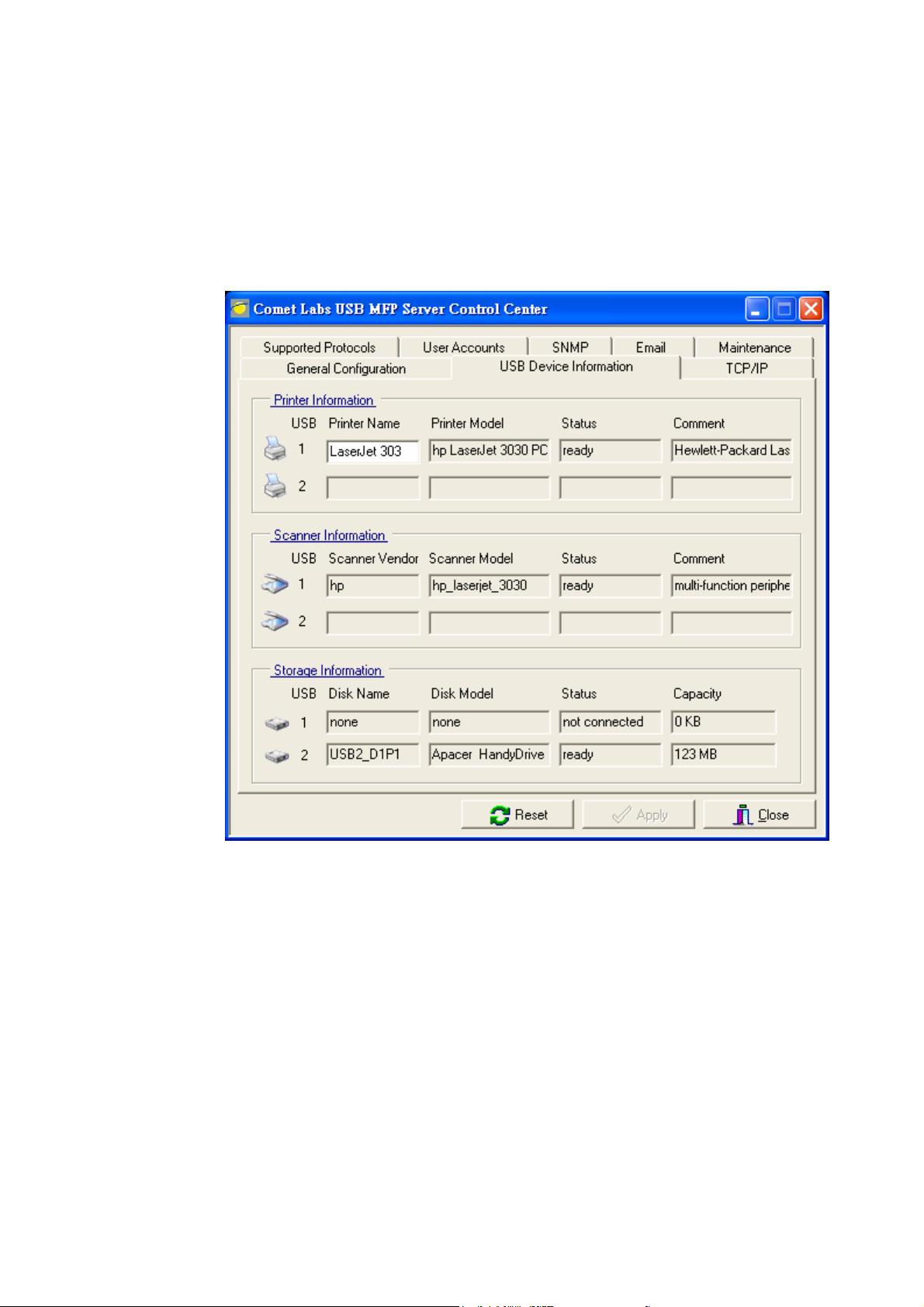
3. Double click the highlight list and enter the Server’s administrator
(default: admin) and password (default: admin).
4. After you have logged in successfully, select USB Device
Information from the Server menu. The Set USB Device
Information dialog appears.
5. Set your printer names in Printer Name box and then click Apply.
B. Using the Server’s Web Pages
1. Go to the web page and click CONFIG icon.
2. Enter administrator (default: admin) and password (default:
admin).
3. Click USB Device Information
23
Page 24
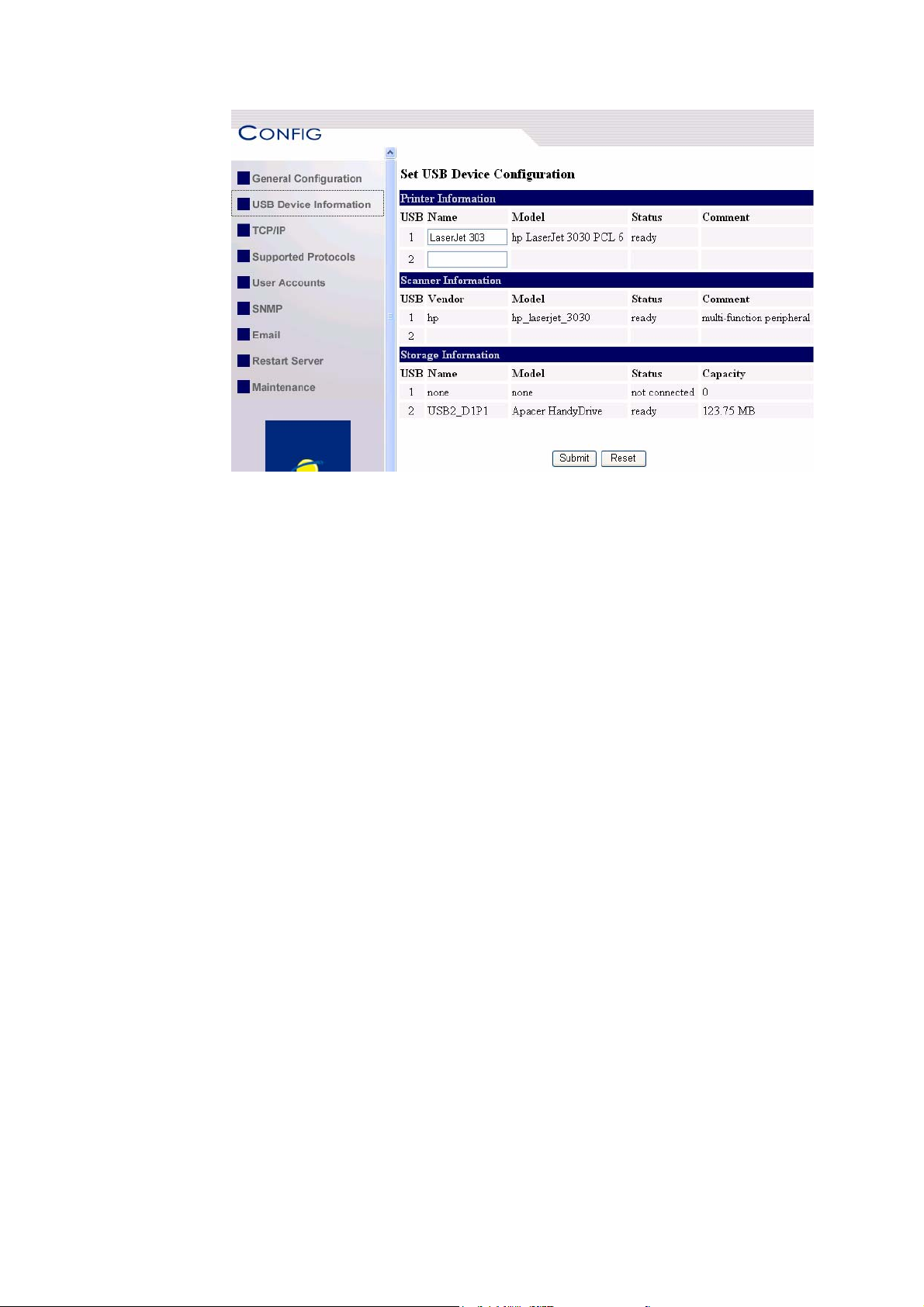
4. Set your printer names in Printer Name box and then click Apply.
3.4.2 Storage Names
The local drives of the two storages in USB1 port and USB2 port are named as
USBx_DyPz, where USBx represents the USBx port, Dy represents the y-th Disk (in
particular to card reader plugging in multiple cards) and Pz represents the z-th
partition.
3.4.3 Scanner Names
The name of connected scanner of HP office jet series consists of the “vender” +
“model” . F or example, the scanner name of HP PSC 1300 series office jet is named as
“HP PSC 1300 series”.
24
Page 25
Chapter4 Print Server in Windows
4.1 Overview of Installation Methods
This chapter describes how to add network printers.
Table List for Installing Network Printer
Windows
Platform
Windows 98, ME,
2000,XP and
2003
Windows 2000,
XP and 2003
Printing
Protocols
SMB/CIFS Printing
IPP Printing Standard Windows Add Printer
LPR Printing
Raw TCP/JetDi r ect
Printing
Method
Standard Windows Add Printer
Wizard
The Control Center’s Add Printer
Wizard
Standard Windows Add Printer
Wizard
The Control Center’s Add Printer
Standard Windows Add Printer
Wizard
The Control Center’s Add Printer
Steps for Installing Network Printer
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Set up Local
Windows Printer
Driver
Connect Your Printer to
the Server and Connect
the Server to Network
Turn on Your
Printer and the
Server
Step 6
Turn on “Online Use
Printer” in Installed
Windows Printer
Driver
Add Network Printer by
- Windows Standard
Method
- Control Center
Step 4 Step 5
Configure Your
Server
4.2 Connecting the Server
To configure your Server correctly, you should know which type of network topology
that your Server is connecting to.
25
Page 26
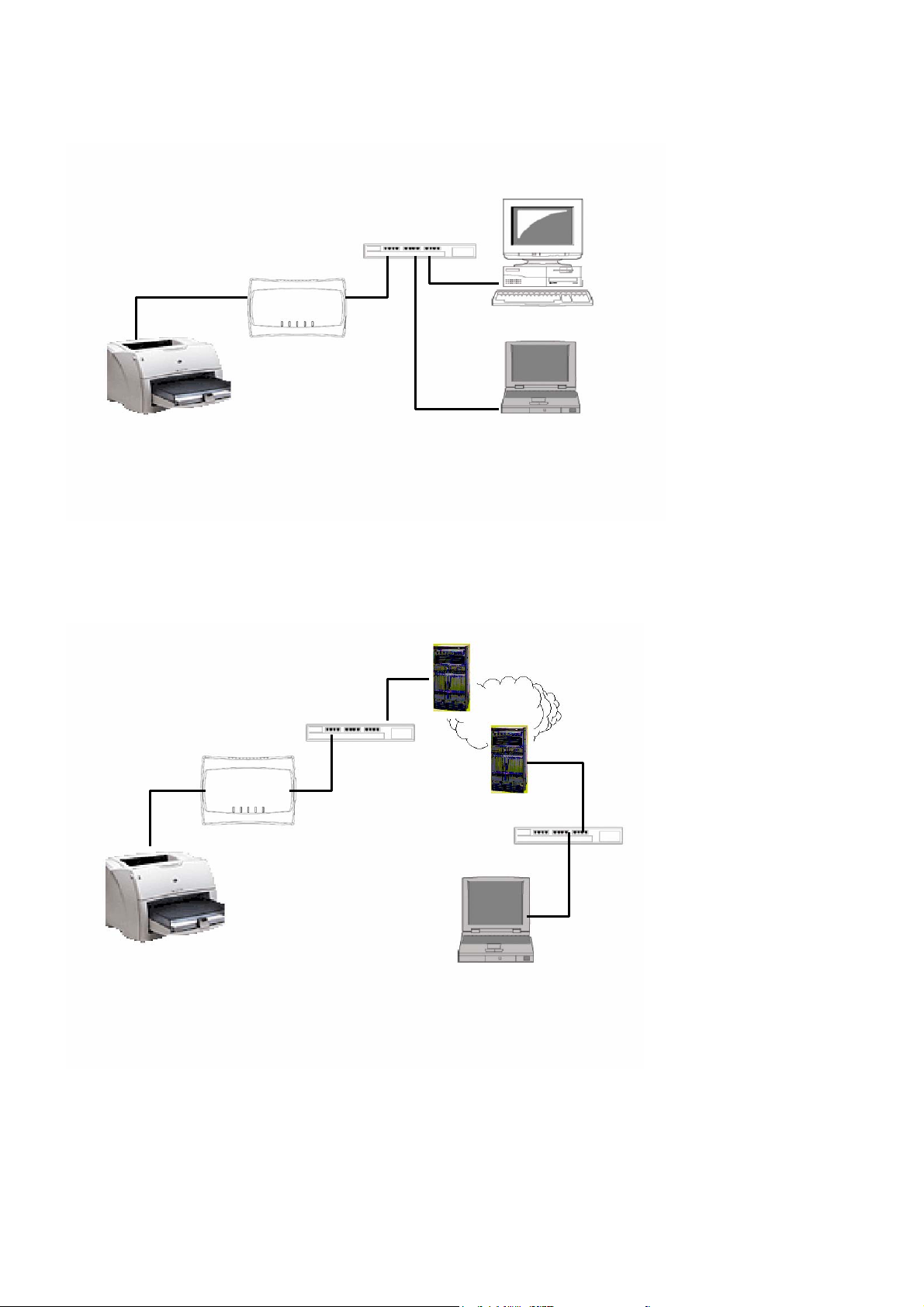
PC
PC
4.2.1 The Server and Windows PC on Same LAN
LAN HUB/Switch
Server
USB Printer
PC
4.2.2 The Server and Windows PC on Different LANs
Example: Wired Windows PC across Internet
Router
LAN HUB/Switch
Server
USB Printer
Internet
Router
LAN HUB/Switch
4.3 Setting up Local Windows Printer Driver
You are advised to install your Windows printer driver in advance. For most printers,
you can install the printer drivers with the following procedure:
26
Page 27

1. Click Start, click Control Panel, click Printers and Other Hardware, and
then click Printers and Faxes.
2. Double click Add Printer to start the Add Printer Wizard, and then click Next.
3. Click Local printer, clear the Automatically detect and install my
Plug-n-Play printer check box to avoid having to wait for the completion of
another printer search, and then click Next. If you leave this option selected,
Windows will attempt to find the printer itself and figure out what kind it is. If
Windows does not find the printer, the wizard will continue as described in this
task.
4. Select a Windows driver for your printer. Click Next.
5. Choose whether you want to share the printer with other network users. Do
you want to print a test page? Select the appropriate radio button and click
Next and Finish.
4.4 Adding Network Printers in Windows
Follow the instructions below to use the standard Windows Add Printer Wizard and the
Control Center for adding a network printer in Windows 98 SE, ME, 2000, XP and
2003.
# Note:
1. Before adding a network printer, you are advised to install the local Windows
printer driver in advance.
2. Before using network printer, you have to turn on “Use Printer Online” in
installed network printer driver and then you can use the printer.
4.4.1 Using Standard Windows Methods for LPR Printing Protocol
Windows Platform: Windows 2000, XP and 2003
1. Open Printers and Faxes
2. Right-click the printer for which you want to change settings, and then click
Properties/ports
3. Clear Enable bidirectional support and click Add port, and then click
Standard TCP/IP Port from the dropdown and click New port.
4. The "Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard" will pop up and click Next.
27
Page 28
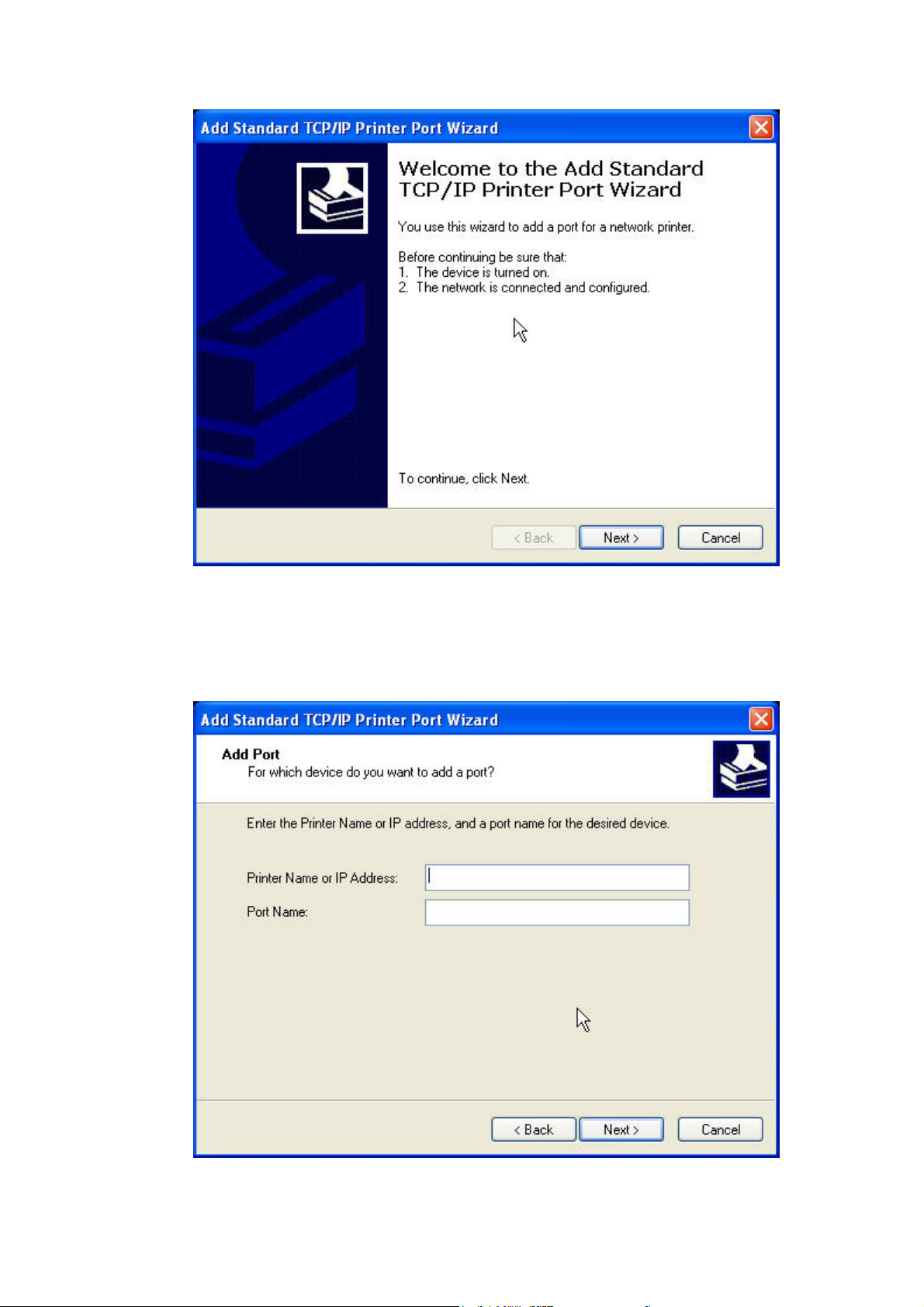
5. In the Printer Name or IP Address box, enter the Host Name of the Server
(default: NFPS2 or WFPS2) or IP address of the Server. In the Port Name box,
enter your desired names or USB1_LPR or USB2_LPR for printer connected
to USB1 port and USB2 port, respectively.
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your Windows PC such as
Internet PC, you must enter Server’s IP address in Printer Name or IP
28
Page 29

Address box.
6. Click Next.
7. Click Custom/settings.
8. Click Settings and confirm that the settings are as below. The queue names are
USB1_LQ, USB2_LQ for USB1 port 1 and USB2 port, respectively. Click OK.
29
Page 30

9. Click Finish
30
Page 31

4.4.2 Using the Control Center for LPR Printing
Windows Platform: Windows 2000, XP and 2003
1. Start the Control Center, select your Server and click Add Printer.
2. Select USB1 Port or USB2 Port to add the printer in Add the printer box,
choose to use Host Name or IP address to represent the Server in Select IP
address or Host Name in printer port box, and select the network printing
protocol of Printing with LPR (Line Printer Remote).
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your Windows PC such as
Internet PC, you must choose IP address in Select IP address or Host Name
in printer port box.
3. Click Apply.
4. Select the desired printer driver and click Set Port to Printer.
31
Page 32

5. If you cannot find any printer driver in Printer List, please install your printer
driver first or click Add New Printer to install the printer driver.
4.4.3 Using Standard Windows Method for Raw TCP Printing
Windows Platform: Windows 2000, XP and 2003
1. Open Printers and Faxes
2. Right-click the printer for which you want to change settings, and then click
Properties
3. Clear Enable bidirectional support and click Add port, and then click
Standard TCP/IP Port from the dropdown and click New port.
4. The "Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard" will pop up and click Next.
5. In the Printer Name or IP Address box, enter the Host Name of the Server
(default: NFPS2 or WFPS2) or IP address of the Server. In the Port Name box,
enter USB1_RAW or USB2_RAW for printer connected to USB1 port and
USB2 port, respectively.
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your Windows PC such
Internet PC, you must enter the Server’s IP address in Printer Name or IP
Address box.
6. Click Next.
7. Click Custom/settings.
8. The click Settings and confirm that the settings are as below. The default Port
Number values are 9100, 9101 for USB port 1 and USB port 2, respectively.
Refer to the Server’ s web pages or the Control Center , you can get exact values.
Click OK.
32
Page 33

9. Click Finish.
33
Page 34

4.4.4 Using the Control Center for Raw TCP/JetDirect Printing
Windows Platform: Windows 2000, XP and 2003
1. Start the Control Center, select your Server and click Add Printer.
2. Select USB1 Port or USB2 Port to add the printer in Add the printer box,
choose to use or IP address to represent the Server in Select IP Address or
Host Name in printer port box, and select the network printing protocol of
Print with Raw TCP Mode.
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your Windows PC such as
Internet PC, you must choose IP address in Select IP Address or Host
Name in printer port box.
3. Click Apply.
34
Page 35

4. Select the desired printer driver and click Set Port to Printer.
5. If you cannot find any printer driver in Printer List, please install your printer
driver first or click Add New Printer to install the printer driver.
4.4.5 Using Standard Windows Methods for SMB/CIFS Printing
# Before using SMB/CIFS printing, you have to login the SMB/CIF Print/File
server in advance and then you may use it; otherwise you have to disable
SMB/CIFS Print/File Server Authentication.
# If you use SMB on Windows 98 SE/ME with Server Authentication, you must
login to your Windows 98 SE/ME using the same user name as in the Server’s
User Account.
Windows Platform: Windows 98SE, ME, 2000, XP and 2003
1. Open Printers and Faxes
2. Right-click the printer for which you want to change settings, and then click
Properties.
3. Click the Ports tab.
4. Clear Enable bidirectional support and click add port, and click Local Port,
and then click New Port… in the Printer Ports box.
35
Page 36

5. In the Port Name box, enter the path to the printer with the following
format: ”\\ Server’s Host Name\printer name” or ”\\ Server’s IP
address\printer name” (Please refer to the Server’s web pages or the Control
Center to know exact path). For example: if you set the Server’s Host Name
as “NFPS2” and printer name (USB1 port) as LaserJet 303, then the network
path is expressed as: \\NFPS2\LaserJet 303.
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your windows PC such as
Internet PC, you must enter IP address in Port Name box.
6. Click OK, and then select a Windows driver for your printer. If you already have
the printer’s driver installed, you will be ask ed whether to keep it or to replace
it. Click Next.
7. Choose whether you want to share the printer with other network users. Do you
want to print a test page? Select the appropriate radio button and click Next
and Finish.
4.4.6 Using the Control Center for SMB/CIFS Printing
# Before using SMB/CIFS printing, you have to login the SMB/CIF Print/File
server in advance and then you may use it; otherwise you have to disable
SMB/CIFS Print/File Server authentication.
# If you use SMB on Windows 98 SE/ME with Server Authentication, you must
login to your Windows 98 SE/ME using the same user name as in the Server’s
User Account.
Windows Platform: Windows 98, ME, 2000, XP and 2003
1. Start the Control Center, select your Server and click Add Printer.
36
Page 37

2. Select USB1 Port or USB2 Port to add the printer in Add the printer box,
choose to use Host Name or IP address to represent the Server in Select IP
Address or Host Name in printer port box, and select the network printing
protocol of Printing with Network Path (SMB).
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your Windows PC such as
Internet PC, you must choose IP address in Select IP address or Host
Name in printer port box.
3. Click Apply.
4. Select the desired printer driver and click Set Port to Printer.
37
Page 38

5. If you cannot find any printer driver in Printer List, please install your printer
driver first or click Add New Printer to install the printer driver.
4.4.7 Using Standard Windows Method for IPP Printing
Windows Platform: Windows 98 SE, ME, 2000, XP and 2003
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, click Printers and Other Hardware, and then
click Printers and Faxes.
2. Double click Add Printer to start the Add Printer Wizard, and then click Next.
3. In this window, select A network printer, or a printer attached to
another computer and click Next.
38
Page 39

4. Click the Next button. On the next window , select Connect to a printer on the
Internet or on a home or office network. In the URL: field, enter the following
to connect to the Server: http://Server’s Host Name /printer name or
http:/Server’s IP address /printer name.
For example, http://NFPS2/LaserJet 303.
# If your Server is running on a different LAN than your windows PC such
as Internet PC, you must enter IP address in URL: Field.
39
Page 40

5. Click Next and then continue Windows Add Printer Wizard.
40
Page 41

Chapter5 Print Server in Unix/Linux
This chapter describes how to add network printers to Unix/Linux PC.
5.1 Configuring Host File
If using IP administration system like DNS, manually registering the Host Name and IP
address may be not required. Otherwise, you hav e to edit hosts file and contact your
network administrator.
1. Log in to Linux machine by “root”.
# login root
2. Register the Server’s Host Name and IP address into /etc/hosts file.
To edit host file, use an editor, e.g. “vi”.
Example: The IP address is “192.168.1.100”, Host Name is “NFPS2”
192.168.1.1 dns # DNS Server
192.168.1.2 mail # Mail Server
192.168.1.100 NFPS2 # Server
3. Switch on the Server. Verify the network connection by using the ping
command.
# ping NFPS2
If there is no response or error occurs, there may be problems with IP address
configuration, host file editing or network status. Please contact your network
administrator.
5.2 Printing by LPD/LPR
This section explains how to print using LPD protocol of TCP/IP.
For further information on “lpr” and “lp” commands, refer to your workstation manual.
LPD Protocol: LPD (Line Printer Daemon) is a protocol that enables you to execute
printing to a printer on the network.
Remote-Printer Queue: The Server has two remote printer queues: USB1_LQ and
USB2_LQ with respect to USB port 1 and UB port2.
To print files using a printer driver, use “lp” or “lpr”.
5.3 Using the Server on BSD UNIX/Linux
1. Log in to the BSD Unix machine through “root”.
# login root
2. Register the Server into /etc/printcap file.
Example: To register the printer of USB1 port by the printer name “Printer1”.
Printer1:\ ---(A)
:lp=:rm=NFPS2:rp=USB1_LQ:\ ---(B)
41
Page 42

:sd=/var/spool/lpd/Printer1:\ ---(C)
:lf=/var/spool/lpd/Printer1/Printer1_errs: ---(D)
where
(A) Describes the printer name.
(B) lp: Device file name to connect printer. No name designation required on the
network.
rm: Host Name for the remote printer. Enter the Host Name registered to
/etc/hosts file.
rp: Remote printer name. Please input the remote printer queue name.
(C) sd: Spool directory name. It must be the absolute path.
(D) lf: Error log file name. It must be the absolute path.
3. Create the spool directory and error log file registered to /etc/printcap file.
Example: To create the spool directory “Printer1” and error log file
“Printer1_errs”.
# mkdir /var/spool/lpd/Printer1 Create the spool directory
# touch /var/spool/lpd/Printer1/Printer1_errs Create the error log file
# chown -R daemon /var/spool/lpd/Printer1 Change the owner to daemon
# chgrp -R daemon /var/spool/lpd/Printer1 Change the group to daemon
4. Start Printing.
A. Use the "lp" command.
- # lp -d Printer1 <Print file name>
- # lp -d Printer2 <Print file name>
B. Use the “lpr” command.
- # lpr -P Printer1 <print file name>
- # lpr -P Printer2 <Print file name>
5.4 Using the Server on RedHat Linux (Fedora Core)
In the RedHat (Fedora Core) x-window user interface, follow these steps:
1. To start the application, select Main Menu button (on the Panel)->
Applications->System Settings -> Printing.
42
Page 43

2. Click on the New button in the Printer configuration window.
3. Click on the Forward button in the Add a new print queue window.
43
Page 44

4. Fill in your desired printer name and description (optional) in Queue name
window and then click on the Forward button.
5. In Queue type window, you will now be asked to specify which Printer Queue
type you are using, select the one option form Networked Unix (LPD),
Networked CUPS (IPP), Networked Windows (SMB) and Networked
JetDirect options. Click on the Forward button.
6. Fill in parameters for Queue type window:
A. Networked Unix (LPD): Fill in the Server’s IP address and queue name
and then click the Forward button. Example: If your Server’s IP address is
44
Page 45

192.168.1.100 and it connects to HP PSC 1300 MFP via USB1 port. You can
enter IP address in the Server box as 192.168.1.100 and Queue name in
Queue box as USB1_LQ.
B. Networked JetDirect: Fill in the Server’s IP address and protocol’s TCP
port and then click the Forward button. Example: If your Server’s IP
address is 192.168.1.100 and it connects HP PSC 1300 MFP via USB1 port.
You can enter IP address in the Server box as 192.168.1.100 and TCP Port
in Port box as 9100.
C. Networked Windows (SMB):
i. Click on the Specify button to specify SMB server Authentication.
45
Page 46

ii. Fill in the Workgroup, Host Name, User name and Password in
Authentication window and then click on the OK button.
iii. Click on the Forward button.
46
Page 47

D. Networked CUPS (IPP): Fill in the Server’s IP address and printer name
then click the Forward button. Example: If your Server’s IP address is
192.168.1.100 and its printer name is psc 1300 ser. You can enter IP
address in Server box as 192.168.1.100 and printer name in Path box as
psc 1300 ser.
7. Select your printer driver. Click on the Forward button. Windows will display
the Finish, and create the new print queue folder.
47
Page 48

8. Click Finish button.
48
Page 49

Chapter6 File Server
This chapter describes the file server function of the Server which allows USB storage
devices to be shared across a network by using SMB: NetBIOS over TCP/IP and FTP
protocol.
6.1 Preliminary
1. This product supports a file format of FAT12/16/32. It will not support a drive
formatted by NTFS, etc.
2. Comet Labs is not responsible for the loss or corruption of data in memory
devices, including hard disk; Comet Labs is not responsible for the leak,
manipulation, loss, or corruption of data in memory devices connected to the
Server after unauthorized access.
3. In order to use the USB Mass Storage device connected to the Server, the SMB
protocol or FTP protocol must be set up.
4. This product does not support to magnet optical drive devices such as CD/DVD.
5. This product allows shared two USB storage devices over the network in
Windows through the USB ports.
6. This product does not support the USB devices through USB hub.
6.2 Storage Names
The local drives of the two storages in USB1 port and USB2 port are named as
USBx_DxPx, where USBx represents the USBx port, Dx represents the the x-th Disk
and Px represents the x-th partition.
6.3 Connecting USB Mass Storage to the Server
Storage
The Server
LAN HUB/Switch
49
Page 50

6.4 Supported Codepages
- What is codepage?
Used by the system to encode and interpret string characters. Codepage formats
are not the same for each language. Some languages, such as Japanese have
multibyte characters, while others, such as English and German, need only one byte
to represent each character.
- Filename Encoding of FAT File System
This is known as an 8.3 file name, a short file name using codepage encoding. The
FAT file system also supports file names that can be up to 255 characters long. This
is known as a long file name using Unicode (UTF-16) encoding.
- When do you need to configure codepage?
The Server supports Windows codepages. If users want to communicate files using
FTP client tool or SMB on Windows 98/Me/2000 with the Server, they have to set
their Server codepage to be same as the codepage that their Windows PC is using.
1. FTP
2. SMB on Windows 98/Me/2000
- Configuring the Server’s Codepages
Users can use the following methods to set the Server’s codepage.
A. Using Control Center
1. Start Control Center and Auto-searching Server window will appear.
2. If the tool finds the Servers in your local area network, then you have to select
one Server from the Server List.
3. Double click the highlight list and enter the Server’s administrator (default:
admin) and password (default: admin).
4. After you have logged in successfully, setting General Configuration dialog
appears.
50
Page 51

5. Select your codepage form File Server Codepage box and click Apply.
B. Using Server’s Web Pages
1. Go to the web page, click CONFIG
2. Login your administrator (default: admin) and password (default: admin).
3. After you have logged in successfully, setting General Configuration dialog
appears.
51
Page 52

4. Select your codepage form File Server Codepage box and click Apply.
6.5 Adding Your USB Mass Storages to Network with Security
You can use the following protocols to share your USB Mass Storages with user level
security in network:
SMB/CIFS: NetBIOS over TCP/IP
FTP
The protocols are shown in Supported Protocols box of the Control Center or the
Server’s web pages.
6.5.1 Setting up File Server Using the Control Center
1. Start the Control Center and Auto-searching Server window will appear.
2. If the tool finds multiple Servers in your local area network, then you have to
select one Server from the Server List.
3. Double click the highlight list and enter the Server’s administrator (default:
admin) and password (default: admin).
4. After you have logged in successfully, click Supported Protocols.
52
Page 53

5. Set up File Server Configuration:
A. Set SMB/CIFS Print/File Server
Enable SMB/CIFS Print/File Server: select the item, if you want to
support SMB/CIFS print/File server.
Enable Internet Access: clear the item, if you do not allow that users
can access your SMB/CIFS server via Internet. If you select the item,
you allow Internet users can access your storage using the SMB/CIFS
protocol.
Enable Server Authentication: select the item, if you want to share
your storage with user level security which requires user name and
password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be shared
without security.
B. Set FTP Server:
Enable FTP Server: select the item, if you want to support FTP server.
FTP port: enter the desired FTP port. The default value is 21.
Maximum Session Number: select the item and fill in desired
53
Page 54

number.
Enable Passive Mode: select the item, if you want to allow that your
FTP server can accept passive mode command.
Enable Server Authentication: select the item, if you want t o sh ar e
your storage with user level security which requires user name and
password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be shared
without security.
Allow Anonymous Login: select the item, if you want to allow the
user “anonymous” to login your FTP server with read-only permission
and the Server will not check the password. If you clear the item, your
FTP server will not support anonymous login function.
6.5.2 Setting up File Server Using Web Pages
1. Go to the web page, click CONFIG
2. Login your administrator (default: admin) and password (default: admin).
3. After you have logged in successfully, click Supported Protocols.
4. Set up File Server Configuration:
54
Page 55

A. Set SMB/CIFS Print/File Server
Enable SMB/CIFS Print/File Server: select the item, if you want to
support SMB/CIFS print/File server.
Enable Internet Access: clear the item, if you do not allow that users
can access your SMB/CIFS server via Internet. If you select the item,
you allow Internet users can access your storage using the SMB/CIFS
protocol.
Enable Server Authentication: select the item, if you want to share
your storage or printer with user level security which requires user
name and password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be
shared without security.
B. Set FTP Server:
Enable FTP Server: select the item, if you want to support FTP server.
FTP port: enter the desired FTP port. The default value is 21.
Maximum Session Number: select the item and fill in desired
number.
Enable Passive Mode: select the item, if you want to allow that your
FTP server can accept passive mode command.
Enable Server Authentication: select the item, if you want t o sh ar e
your storage with user level security which requires user name and
password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be shared
without security.
Allow Anonymous Login: select the item, if you want to allow the
user “anonymous” to login your FTP server with read-only permission
and the Server will not check the password. If you clear the item, your
FTP server will not support anonymous login function.
6.5.3 Using Shared Storages by SMB/CIFS Method for Windows
1. Connect a USB storage device to this product.
2. Select My Network Places
3. Click Display the Computers of Workgroup
4. Double click Microsoft Windows Network icon.
55
Page 56

5. Double click the Workgroup that the Server belongs to. The default
Workgroup name is “WORKGROUP”. You can refer to Control Center or the
Server’s web pages to get it. You will see that the Server will be displayed as
the default Host Name "NFPS2" or the Host Name that you have set.
6. If you cannot find Workgroup name of the Server in Microsoft Windows
Network, you can select Search for Computer… in My Network Places and
enter the Host Name of the Server (For example, default Host Name “NFPS2”
or the Server’s IP address) to find it.
7. Double click this Host Name icon.
8. If you clear Enable SMB/CIFS Print/File Server Authentication in
Supported Protocols, you login to the SMB server without requiring
authentication; otherwise you have to enter user name and password to login
to the Server. You can add user name and password in User Account box by
the Control Center or the Server’s Web page.
# Note:
If you use SMB on Windows 98 SE/ME, you must login to your Windows 98
SE/ME using the same user name as in the Server’s User Account.
9. The shared folders will be listed as USB1_DyPz, and USB2_DyPz where Dy
represents the y-th disk and Pz represents the z-th partition with respect to
USB1 port and USB2 port.
10. Perform Open, Paste, Remove or Copy the files to the shared folders.
6.5.4 Using Shared Storage by FTP Methods for Windows
A. Use Microsoft IE to the shared USB Mass Storages
1. Open Microsoft IE
2. In Web Address List, enter command: “ftp://Server’s Host Name“ or
“ftp://Server’s IP address”. If you have changed the default FTP port : 21 to
the new value, you hav e to add the new port number in the tail of command as
“ftp://Server’s Host Name: ftp port” or “ftp://Server’s IP address: ftp port”.
3. If you set Enable Server Authentication in FTP server protocol settings
you have to enter user name and password to login to the Server; if you set
Allow Anonymous Login, you can use the user name “anonymous” to login
with Read-only permission. If you clear Server authentication, you do not
need username or password to login to the Server. Y ou can add user name and
password in User Account box by the Control Center or the Server’s Web
pages.
4. The shared folders will be listed in IE.
5. Perform Paste, Remove or Copy the files to the shared folders.
56
Page 57

B. Use Microsoft Dos’s FTP client
1. Enter Dos command as “ftp”
2. Enter “open server’s Host Name” or “open server’s IP address”. If you have
changed the default FTP port : 21 to the new value, you hav e to add the new
port number in the tail of command as “open server’s Host Name ftp port” or
“open server’s IP address ftp port” .
3. If you set Enable Server Authentication in FTP server protocol settings
you have to enter user name and password to login to the Server; if you set
Allow Anonymous Login, you can use the user name “anonymous” to login
with Read-only permission. If you clear Server authentication, you do not
need username or password to login to the Server. Y ou can add user name and
password in User Account box the Control Center or the Server’s W eb pages.
4. Perform FTP commands to use this FTP server.
57
Page 58

Chapter7 Scan Server
This chapter explains how to use the scan server function of this product. The scan
server function enables a USB scanner of HP all-in-one series, connected to this
product, to be shared as a network scanner. The scan server function is available in
any platform that can use SANE client.
7.1 Connecting HP All-In-One to the Server
HP MFP
Scanner
7.2 Using the Shared Scanner in Windows
7.2.1 Using the Control Center
NFPS2
LAN HUB/Switch
1. Start the Control Center, select your Server, and click Network Scanner.
2. Select your scanner for USB1 port or USB2 port.
58
Page 59

3. Set the options. The options are defined as follows:
- Source: choose flatbed scanning or scrollfed scanning
- Mode: choose lineart (black/white), Gray and color mode
- Resolution: choose the image resolution
- Contrast: tune the contrast of the image
- Brightness: tune the brightness of the image
- Range: define the scanning range of the image
Note: Not all the MFP scanners support the options above. In such a case, the
options will be grayed out and not accessible.
4. Click Preview button.
5. Adjust the window size to be scanned.
6. Click Scan button.
7. Save as your images to the file.
59
Page 60

7.2.2 Using Windows Applications
Prior to using scanning functions in Windows applications such as MS Word,
Photoshop …etc, you have to install network scanner’s TWAIN driver in advance.
When you install the Control Center, it will also install this TWAIN driver.
Example: Using Photoshop
1. Start Photoshop, click File ->Import->Comet Labs Network Scanner
2. Select a Server’s IP address or enter a Server IP address in Server Information
box. You can click Search Server button to search existing Servers in your
network.
3. Click Connect to Network Scanner button in Server Information box.
60
Page 61

4. Select your scanner in Server Information box.
5. Click Preview button.
6. Adjust the window size to be scanned.
7. Click Scan button.
7.3 Using the Shared Scanner in Linux
7.3.1 Using XSane in RedHat Linux
1. Download SANE-Backends from
2. Download and install SANE-frontends: XSane (UNIX binary) from
http://www.xsane.org.
3. Edit \etc\sane.d\net.conf and put the IP address of the Server where the
scanner is connected into one line, for example:
http://www.sane-project.org.
61
Page 62

192.168.0.2.
4. To start the application, select Main Menu button (on the Panel)->
Applications->Graphics -> Scanning.
5. Perform scan function.
62
Page 63

63
Page 64

Chapter8 The Control Center
This chapter describes how to use the Control Center.
8.1 Installing Control Center
1. Insert the included CD into the personal computer. The Autorun screen as in the
following should appear.
2. Click Install Application button.
3. Click Next, if you see any Next button in installation windows.
4. Click Finish.
8.2 Using the Control Center
8.2.1 Using Tools of Control Center
You can use the following tools to help you use the Server:
Auto Search : renew to auto search the existing Servers in the network
IP Search : search the Server by IP address
Refresh : refresh the highlight list’s Server status
Go to web : go to the web pages of the highlighted Server
64
Page 65

Network Scanning : perform network scanner function of the highlighted
Server
Add Printer : perform add printer function of the highlighted Server
8.2.2 Displaying Server Status
You can start the Control Center and select your Server to see its status which includes
Host Information, TCP/IP, USB Devices Status, and Supported Protocols.
8.2.3 Setting up Server Configuration
General Configuration
Set Host Information: You hav e to set some information for using SMB
protocol:
5 Comment: optionally set to describe the Server
5 Host Name: the name to represent the Server for using SMB/CIFS
protocol
5 Workgroup: the SMB/CIFS workgroup name that the Server belongs
to.
File Server Codepage: If users want to communicate files using FTP
client tool or SMB on Windows 98 SE/Me/2000 with the Server, they have
to set their Server codepage to be same as the codepage that their
Windows PC is using. Generally, the criteria of choosing codepage are
based on your Windows codepage. For example, if your Windows
codepage is Traditional Chinese, you have to select Traditional Chinese
(Big5) in the Server. Please refer to the chapter “File Server”.
USB Device Information: You can set printer names and display some
information of USB mass storages and scanners. Please refer to the chapter
“Print Server”, the chapter “File Server”, and the chapter “Scan Server”.
TCP/IP: Y ou hav e to set the Server’ s T CP/IP configur ation to connect T CP/IP
network. Please see the chapter on Basic Installation for more details.
Supported Protocols: The Server supports the following TCP/IP protocols:
TCP/IP
5 Enable LPR (Line Printer Remote) Printing: select or clear Enable LPR
Printing support. It is enabled in Factory Default.
5 Enable IPP Printing: select or clear Enable IPP Printing support. It is
enabled in Factory Default.
5 Enable Raw TCP Printing: select or clear Enable Raw TCP Printing
support. It is enabled in Factory Default and users may set the
protocol’s TCP ports as following boxes:
- TCP Port 1: set TCP port for the printer of USB1 port (default: 9100)
- TCP Port 2: set TCP port for the printer of USB2 port (default: 9101)
5 Enable SMB/CIFS Print/File Server: select or clear Enable
65
Page 66

SMB/CIFS Print/File Server support. It is enabled in Factory
Default.
- Enable Internet Access: select or clear Enable Internet Access
support. If you clear the item, you do not allow that users can
access your SMB/CIFS server via Internet. If you select the item,
you allow Internet users can access your storage using the
SMB/CIFS protocol.
- Enable Server Authentication: select or clear Enable Server
Authentication support. Select the item, if yo u want to s hare your
storage or printer with user level security which requires user name
and password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be
shared without security.
5 Enable FTP Server: select or clear Enable FTP Server support. It is
enabled in Factory Default and users may set some parameters as
follows:
- FTP Port: Enter an integer number to set FTP server’s TCP port
(default: 21)
- Set Maximum Session Number: select or clear Set Maximum
Session Number support. Y ou can limit the FTP session number by
selecting the support and enter an integer to set the allowable
maximum session number. If you clear this field it means that FTP
server will have no limitation in session number.
- Set Passive Mode: select or clear Set Passive Mode support that
FTP server can accept passive mode.
- Enable Server Authentication: select or clear Enable Server
Authentication support. If you select the support, you need to
enter user name and password to login to the Server. If you clear
the support, you do not need user name and password to enter the
Server.
- Allow Anonymous Login: select the item, if you want to allow the
user “anonymous” to login to your FTP server with Read-Only
permission and FTP server will not check the password. If you clear
the item, your FTP server will not support anonymous login
function.
5 Enable SANE (Scanner Access Now Easy) Server: select or clear
Enable SANE Server support. It is enabled in Factory Default and
users may set the TCP port as follows:
- SANE Port: set SANE server’s TCP port (default: 6566)
5 Enable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play): select or clear Enable UPnP
support. It is enabled in Factory Default.
66
Page 67

User Accounts: You can change administrator name and password or add a
user account for SMB/CIFS Print/File server and FTP File server. If you forgot
administrator name and password, you must to perform Restore Factory
Default action by plugging in the power adaptor while pressing the Init button.
Please refer to the chapter “Restore F actory Defaults”. Administrator owns the
Read-Write Permission for File servers.
Set Administrator
5 New Administrator: enter your desired administrator name.
5 New Password: enter your desired password.
5 Retype Password: confirm your previous password typing.
User Accounts list
5 User name: add a new user account for accessing the storage
attached to the Server.
5 Password: set a password for added user.
5 Permission: select Read-Only or Read-W rite permission to access File
servers.
5 Add: click Add button, after entering the user name, corresponding
password, and Permission selection. The account will take effect once
shown in the blank below.
5 Delete: delete the existing user account.
67
Page 68

SNMP: Yo u can set community and some parameters for SNMP server.
Furthermore, you can enable SNMP v3 for more security.
Set SNMP Configuration
5 Authentic Community: set Community name of SNMP server.
5 Trap Community: set Trap Community name for SNMP server to send trap
packets.
5 Trap Address: enter an IP address to send the Trap packet.
5 SysContact: enter some letters for variable of SysContact that represents
the name of system contact.
5 SysName: enter some letters for variable of SysName that represents the
name of system.
5 SysLocation: enter some letters for variable of SysLocation that represents
the location of system.
5 EnableAuthenTrap: enter 1 or 2 for the variable of EnableAuthenTrap that
represents to enable (1) or disable (2) to send Trap pack ets receiving the
wrong Community name.
SNMP V3
5 Enable SNMP V3: select or clear Enable SnmpV3 support
5 User Security name: set user security name of SNMP v3
5 Auth Password: set authentication password of SNMP v3.
5 Privacy Password: set privacy password of SNMP v3.
68
Page 69

Email: If you w ant to receive some alerting mail from the Server, you have to
enable SMTP Protocol, and set Email configuration. Y ou can set new SMTP port
number (default: 25).
Set Email Configuration
5 SMTP Protocol: select or clear Enable SMTP support
5 SMTP Server Name: enter your SMTP server’s Host Name or IP
address.
5 SMTP Port Number: set new SMTP server’ s TCP port number (default:
25).
5 Subject: enter the subject of the e-mail.
5 From Address: enter the sender’s e-mail address.
5 To Address: enter an e-mail address to send that mail to a person.
5 Cc: stands for carbon copy; enter an e-mail address to send that mail
to a second person.
5 SMTP Server requires authentication: login to remote SMTP server
which requires authentication.
5 Account Name: enter account name for remote SMTP server.
5 Password: enter account’s password for remote SMTP server.
69
Page 70

70
Page 71

Maintenance: If you want to restart the Server, restore the Server to factory
defaults, download new firmware file from product’s public website and
upgrade new firmware, you can use the Maintenance tool.
Restart Server: click this button, the Server will restart.
Factory Default: click this button, the Server will restore factory default
values.
Download New Firmware: click this button to download new firmware
or user software from this product’s public website.
Upgrade Firmware: click Open to find the firmware file to be upgraded.
Click Upgrade to upload the firmware into the Server.
71
Page 72

Chapter9 Remote Connect Center
9.1 Introduction
The goal of Comet Labs NFPS2 / WFPS2 USB MFP server is to provide the
print/scan/file server in a single product. For printers and scanners, there is no
industrial standard. In order to support many different models of printers and
scanners from various vendors, you must put so man y printer/scanner driv ers into a
single product. Obviously this is very hard and not practical. We have developed a new
technology , called “USB device server”, to solve this problem. With USB device server
technology, it is not necessary to implement printer/scanner drivers in Comet Labs
NFPS2 / WFPS2. Actually, NFPS2 / WFPS2 relies on printer/scanner drivers that are
installed on PCs. By the way, in the field of traditional network print server, the
common protocols used are, for example, SMB/CIFS, LPR, raw TCP, and IPP . However,
in order to reduce cost, many printer vendors produce so-called GDI or host-based
printers. For technical reasons, these kinds of printers can not work with the
traditional network printer protocols. The USB device server technology can also deal
with the problem. The “Remote Connect Center” is a Windows application that exploits
the USB device server technology to provide the functionality of print/scan/file server.
The basic concept of USB device server and the usage of the “Remote Connect Center”
will be introduced in the following chapters.
In summary, NFPS2/WFPS2 has a totally different technology , USB device server, to
deal with printers and scanners (MFPs).
A. For printers, some special kinds of printers, such as GDI printers or host-based
printers, can not work well with traditional print server technology as described in
the previous chapters. Users should use the Remote Connect Center to deal with
these kinds of printers.
B. For MFPs or scanners, the operations described in chapter 7 are only workable for
HP’s MFPs. Users should use the Remote Connect Center to deal with non-HP
MFPs.
9.2 Link & Unlink
“Remote Connect Center” allows you to use USB printers or USB MFPs as if they were
connected directly to your PC although they are actually connected to the NFPS2 /
WFPS2 USB MFP server. The “link” operation is a software operation that simulates an
actual USB device plug-in. That is to say, when you do a “link” operation from “Remote
Connect Center”, PC can then detect a USB device’ s plug-in, although actually you do
not plug in any USB device. Similarly, the “unlink” operation is a software operation
that simulates the disconnection of the USB device.
9.3 How to Use
Here we will describe how to use “Remote Connect Center” to do network printer
72
Page 73

installation. Before following the steps listed below, you must first make sure that
your Windows PC can access USB MFP server via TCP/IP. The simplest way to do this
is using “Control Center” to search for the USB MFP server on the network and change
its IP address to be the same subnet as the Windows PC.
A. T urn on NFPS2 / WFPS2 and the printer.
B. Connect the printer to NFPS2. The LED of the USB port will light-on.
C. Run the “Remote Connect Center” program. In the “USB Device Server List”
window, you can see the host names and IP addresses all of the NFPS2 /
WFPS2 servers on the network, as the following figure.
D. In the “Remote Connect Center”, in order to connect the USB MFP server on
which the printer is attached, please click the server.
E. If there is any printer or MFP attached on the server, then you can see the
USB device tree as the following figure. The window at the bottom will show
some additional information of the server.
73
Page 74

F. Please follow the installation manual of the printer to do the installation.
G. When you are asked to plug in the printer into PC’s USB port, either before
running the printer driver setup program or during the execution of the
printer driver setup program, click the desired printer in the “Remote
Connect Center” and then click the “Link” button to do the link operation and
get the ownership of the printer, as the following figure. The computer name
of the printer owner will be shown at the end of the printer.
74
Page 75

H. PC will detect the plug-in of the printer. Continue to follow the installation
manual of the printer to do the rest jobs of installation. If the USB device is
a MFP, the installation will also install scanner driver.
I. After the installation, you can see the ne wly created printer on the PC. If the
USB device is a MFP, you can also see a newly created scanner from the
“Control Panel”. Now you can try to issue a print job to this printer from any
Windows application like Microsoft Word.
J. Once the print job is finished, from the “Remote Connect Center”, click the
“Unlink” button to do the unlink operation and to release the printer
ownership.
K. The “Remote Connect Center” doesn’t really quit if you click the “X” box
(close box) at the top right corner of the window. Instead, the “Remote
Connect Center” just minimizes itself to the system tray. There are two ways
to really close the “Remote Connect Center. The first way is choosing “Exit”
item in the “File” menu in the “Remote Connect Center”. The second way is
right-clicking on the icon in the system tray and choosing the “Exit” item. The
“Remote Connect Center” will automatically “unlink” necessary devices
before really quitting.
9.4 Auto Link/Unlink
It is a little bit tedious to do link and unlink every time before and after a print job,
respectively. The “Remote Connect Center” provides a feature – auto link / unlink so
that users do not need to manually link and unlink printers. Please note that auto link
/ unlink only applies to printers. For scanners, the only solution is manual link / unlink.
To enable auto link / unlink, please follow to steps below.
A. Click the printer you want to do auto link / unlink, as the following figure.
75
Page 76

B. Click the “Set Auto Link” button.
C. The following window will appear. Click the Windows printer (this is a logical
printer) that matches the printer attached on the NFPS2 / WFPS2 (this is a
physical printer). Then click the “ Apply” button.
D. Then, in the “Auto Link Printer List” you can see a newly created item that
describes the association between the Windows printer and the physical
printer on the server.
76
Page 77

E. Then try to issue a print job. You will see the “Remote Connect Center” will
automatically do a link operation and, once the print job finished, it will
automatically do an unlink operation.
F. Even you already properly setup an auto-link printer, the “Remote Connect
Center” must be running while a print job is issued. This means you’d better
run the “Remote Connect Center” every time after you login Windows. In
order to skip this manual operation, you can make the “Remote Connect
Center” be run automatically after you login Windows. T o do this, choose the
“Configure” item in the “T ools” menu. The following window will appear. Click
on the check box and then on the “OK” button.
G. If you would like to break the association between the Windows printer and
the physical printer, just click on the association and click the “Delete” button
in the “Auto Link Printer List”.
77
Page 78

By the way, if the printer is manually linked (owned) by someone else and he forgets
to unlink the printer, you can click the “Force Link” button to forcedly get the
ownership. However, this way is not recommended.
9.5 Limitations
There are some limitations to use “Remote Connect Center” to do network printer
installation.
A. Only supports Windows 2000/XP/2003.
B. Only one PC can get the ownership of the same printer at the same time.
Moreover, once a printer or MFP is “linked” by a Windows PC so that the
Windows PC “owns” that printer, other Windows PCs can not print to this
printer via any network printer protocols. Therefore please remember to do
the “unlink” operation after installation.
C. Only supports USB printers and USB MFPs. Do not support USB storage, like
flash drives. NFPS2 USB MFP server only supports USB storage through
traditional file server protocols like FTP and SMB/CIFS. In the “Remote
Connect Center” , you can see the plugged-in USB stor age in the “USB Device
List” window, but the “Link” button is disabled so that you can not “link” the
USB storage. If you click the plugged-in USB stor age, the “Network Storage”
button will be enabled as the following figure. Then you can click this button
to access the storage via SMB/CIFS protocol.
78
Page 79

Chapter10 The Server’s Web Pages
10.1 Introduction
The Server runs the daemon of http server, httpd on TCP port: 80. Users may use the
web pages to see the Server’s system status and configure the Server.
10.2 Using the Server’s Web Pages
10.2.1 Displaying Server Status
You can see the status of Host Information, TCP/IP and USB devices.
79
Page 80

10.2.2 Setting up Server Configuration
T o set up the Server configur ation, the system will request user to enter administrator
(default: admin) and password (default: admin) to login.
General Configuration
Set Host Information: You have to set some information for networking
using SMB protocol:
5 Comment: optionally set to describe the Server
5 Host Name: the name to represent the Server for using SMB protocol
5 Workgroup: the SMB workgroup name that the Server belongs to.
File Server Codepage: if users want to communicate files using FTP
client tool or SMB on Windows 98 SE/Me/2000 with the Server, they have
to set their Server codepage to be same as the codepage that their
Windows PC is using. Generally, the criteria of choosing codepage are
based on your Windows codepage. For example, if your Windows
codepage is Traditional Chinese, you have to select Traditional Chinese
(Big5) in the Server. Please refer to the chapter “File Server”.
USB Device Information: You can set printer names and displa y some
information of USB mass storages and scanners. Please refer to Chapter 4,
Chapter 6 and Chapter 7.
TCP/IP: You have to set the Server’ s TCP/IP configur ation to connect TCP/IP
network. Please see Chapter 3 Basic Installation for more details.
Supported Protocols: The Server supports the following TCP/IP protocols:
TCP/IP
5 Enable LPR (Line Printer Remote) Printing: select or clear Enable LPR
Printing support. It is enabled in Factory Default.
5 Enable IPP Printing: select or clear Enable IPP Printing support. It is
enabled in Factory Default.
5 Enable Raw TCP Printing: select or clear Enable Raw TCP Printing
support. It is enabled in Factory Default and users may set the
protocol’s TCP ports as following boxes:
- TCP Port 1: set TCP port for the printer of USB1 port (default: 9100)
- TCP Port 2: set TCP port for the printer of USB2 port (default: 9101)
5 Enable SMB/CIFS Print/File Server: select or clear Enable
SMB/CIFS Print/File Server support. It is enabled in Factory
Default.
- Enable Internet Access: select or clear Enable Internet Access
support. If you clear the item, you do not allow that users can
access your SMB/CIFS server via Internet. If you select the item,
you allow Internet users can access your storage using the
SMB/CIFS protocol.
- Enable Server Authentication: select or clear Enable Server
Authentication support. Select the item, if yo u want to s hare your
80
Page 81

storage or printer with user level security which requires user name
and password to login. If you clear the item, your storage will be
shared without security.
5 Enable FTP Server: select or clear Enable FTP Server support. It is
enabled in Factory Default and users may set some parameters as
follows:
- FTP Port: enter an integer number to set FTP server’s TCP port
(default: 21)
- Set Maximum Session Number: select or clear Set Maximum
Session Number support. Y ou can limit the FTP session number by
selecting the support and enter an integer to set the allowable
maximum session number. If you clear the support, it means that
FTP server will have not any limitation in session number.
- Set Passive Mode: select or clear Set Passive Mode support that
FTP server can accept passive mode.
- Enable Server Authentication: select or clear Enable Server
Authentication support. If you select the support, you need to
enter user name and password to login to the Server. If you clear
the support, you do not need user name and password to enter the
Server.
- Allow Anonymous Login: select the item, if you want to allow the
user “anonymous” to login to your FTP server with Read-Only
permission and FTP server will not check the password. If you clear
the item, your FTP server will not support anonymous login
function.
5 Enable SANE (Scanner Access Now Easy) Server: select or clear
Enable SANE Server support. It is enabled in Factory Default and
users may set the TCP port as follows:
- SANE Port: set SANE server’s TCP port (default: 6566)
5 Enable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play): select or clear Enable UPnP
support. It is enabled in Factory Default.
User Accounts: You can change administrator name and password or add a
user account for SMB/CIFS Print/File server and FTP File server. If you forgot
administrator name and password, you must perform R estore F actory Default
action by plugging in the power adaptor while pressing the Init button. Please
refer to the chapter “Restore Factory Defaults”. Administrator owns the
Read-Write Permission for File servers.
Set Administrator
5 New Administrator: enter your desired administrator name.
5 New Password: enter your desired password.
5 Retype Password: confirm your previous password typing.
User Accounts list
5 User name: add a new user account for accessing the storage
attached to the Server.
81
Page 82

5 Password: set a password for added user.
5 Permission: select Read-Only or Read-W rite permission to access File
servers.
5 Add: click Add button, after entering the user name, corresponding
password, and Permission selection. The account will take effect once
shown in the blank below.
5 Delete: delete the existing user account.
SNMP: Yo u can set community and some parameters for SNMP server.
Furthermore, you can enable SNMP v3 for more security.
Set SNMP Configuration
5 Authentic Community: set Community name of SNMP server.
5 Trap Community: set Trap Community name for SNMP server to send
trap packets.
5 Trap Address: enter an IP address to send the Trap packet.
5 SysContact: enter some letters for variable of SysContact that
represents the name of system contact.
5 SysName: enter some letters for variable of SysName that represents
the name of system.
5 SysLocation: enter some letters for variable of SysLocation that
represents the location of system.
5 EnableAuthenTrap: enter 1 or 2 for the variable of EnableAuthenTrap
that represents to enable (1) or disable (2) to send Trap packets
receiving the wrong Community name.
SNMP V3
82
Page 83

5 Enable SNMP V3: select or clear Enable SnmpV3 support
5 User Security name: set user security name of SNMP v3
5 Auth Password: set authentication password of SNMP v3.
5 Privacy Password: set privacy password of SNMP v3.
Restart Server: click this button, the Server will restart.
Maintenance If you want to restore factory default values of the Serv er and
upgrade new firmware, you can use the Maintenance tool.
5 Factory Default: click this button, the Server will restore factory default
values.
83
Page 84

5 Download New Firmware from Website: click this button to download
new firmware or user software from this product’s public website.
5 Upgrade Firmware: click Open to find the firmware file to be upgraded.
Click Upgrade to upload the firmware into the Server.
84
Page 85

Chapter11 Email Alerting
This Server emails a notification to the user at these events:
1. Adding or Removing a USB device.
2. System Error.
Chapter12 SNMP
This Server runs an SNMP daemon supporting SNMP v1, v2c, and v3 protocols (Simple
Network Management Protocol). Users can use SNMP client software such as HP
OpenView to manage the Server. The Server supports all relevant parts of MIB-II and
a private MIB. You can set these MIB variables from the Server’s web pages or by
using the Control Center.
85
Page 86

Chapter13 Troubleshooting
This chapter provides useful information to help you resolve difficulties that you ma y
experience with your Server. Fault symptoms, possible causes, and remedial actions
are provided within a quick reference table. This Server’s USB ports only support MFPs,
printers, scanners, and mass storage.
13.1 LED Indicators
Indicators Color/Behavior Description
Orange Power On Power
Not lit Power off/System error
Green Network connected Link
Not Lit No physical connection to network
Green blinking Activity on network Status
Not lit No activity on network
USB1
USB2
Green USB device connected
Green blinking Connected USB device error
Not lit No physical connection to USB device
Green USB device connected
Green blinking Connected USB device error
Not lit No physical connection to USB device
USB Device Status
Devices Status Description
Printer
Ready Printer is ready.
Printing Printer is printing.
Out of paper Printer is out of paper.
Error There are errors in network printing.
Storage
Scanner
Ready Storage is ready. Mass
Error There are errors in network File server.
Ready Scanner is ready.
Flatbed Scanning Flatbed of scanner is scanning.
Scrollfed
Scanning
Error There are errors in network scanning.
Scrollfed of scanner is scanning.
86
Page 87

Chapter14 Restore Factory Defaults
You may restore the Server’s default parameters by one of the following methods.
14.1 Using the Control Center
1. Start the Control Center.
2. If the tool finds Servers in your local area network, then you have to select a
Server from the Server List.
3. Double click the highlight list and enter the Server’s administrator (default:
admin) and password (default: admin).
4. After you have logged in successfully, from the Server menu, select
Maintenance. The Maintenance dialog appears.
5. Click Factory Default.
14.2 Using the Server’s Web Pages
1. Go to the Server’s web page and click CONFIG
2. Enter administrator (default: admin) and password (default: admin).
3. Click Maintenance.
87
Page 88

4. Click Factory Default.
5. Click Yes to confirm
14.3 Using Init Button
Plug in the power adaptor while pressing the Init button until LED indicators of Power,
USB1 and USB2 blink. After that, plug off the power adaptor and then plug in the
power adapter again to restart the Server. Finally, the Server will operate using the
Factory Default values.
14.4 Default Parameters List
Host Information
z Comment (Optional): Comet Labs USB MFP Server
z Host Name: NFPS2
z Workgroup: WORKGROUP
z Code Page of File Server: Western European
TCP/IP
z Automatically get IP by DHCP: Enabled
- Manual DNS: None (Disabled).
z Static IP: Disabled
- IP Address: 192.168.0.2
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: 192.168.0.1
- DNS Server: none
Supported Protocols
z LPR Printing: Enabled
z IPP Printing: Enabled
z Raw TCP/JetDirect Printing: Enabled
- TCP Port (USB1): 9100
- TCP Port (USB2): 9101
z SMB/CIFS Print/File Server: Enabled
- Internet Access: Disabled
88
Page 89

- Server Authentication: Disabled
z FTP Server: Enabled
- FTP Port: 21
- Set Maximum Session Number: 5 (Enabled)
- Passive Mode: Enabled
- Server Authentication: Enabled
- Allow Anonymous Login: Disabled
z SANE Server: Enabled
- SANE Port: 6566
z UPnP: Enabled
User Accounts
z Administrator: admin
z Password: admin
SNMP
z Authentic Community: public
z Trap Community: public
z Trap Address: 0.0.0.0
z SysContact: sales@cometlabs.com
z SysName: Comet Labs USB MFP Server
z SysLocation: www.cometlabs.com
z EnableAuthenTrap: 2 (disable)
z SNMPv3: Disabled
- User Security Name: None
- Auth Password: None
- Privacy Password: None
Email
z SMTP Protocol: Disabled
z SMTP Server Name: None
z SMTP Port Number: 25
z Subject: None
z From Address: None
z To Address: None
z Cc: None
z SMTP Server requires authentication: Disabled
- Account Name: None
- Password: None
89
Page 90

Chapter15 Upgrade Firmware
This chapter describes how to upgrade firmware. Please follow one of the following
Procedures:
Procedure A: Using the Control Center
1. Open Control Center. It will automatically search the existing Servers and display their
statuses.
2. Select the Server that you want to upgrade the firmware. Double click the selected
Server and enter Administrator (default: admin) and Password (default: admin).
3. Select the Maintenance button.
4. Click Open to find your new firmware file and click Upgrade to start upgrading the
firmware.
5. Wait for 15 seconds for system reboot.
Procedure B: Using the Server’s Web Pages
1. Power on the Server. Suppose that the Server is in DHCP mode.
90
Page 91

2. Check the Server's IP address.
3. First, run Control Center. It will automatically search for Servers on the LAN. Then
Servers’ IP addresses will be shown in Control Center.
4. Run any Web browser, like Microsoft Internet Explorer. Go to “http://Server’s IP
address “or “http://Server’s Host Name” to access the Server's home page.
5. Click CONFIG at the top of the menu.
6. Login the Server with Administrator (default: admin) and Password (default: admin).
7. Click Maintenance.
8. Click Upgrade Firmware.
9. Click Browse button to choose the file of new firmware.
10. Click Upload button to start firmware upgrade.
11. Wait for 15 seconds for system reboot.
Procedure C: Using the Init Button and the TFTP Client
1. Plug in the power adaptor while pressing the Init button until LED indicators of
Power, USB1 and USB2 blink. Please note that after that, the Server will
operate using the factory default values after restarting, i.e., your
Server’s configuration will recover to Factory Default values.
91
Page 92

2. Start the TFTP client Tool: Image Burner
3. Enter the Server’s F allback IP address: 192.168.0.2 and click Open Image to
open your new firmware. Please note that you must configure your PC’ s TCP/IP
such that PC and the Server belong to the same LAN, i.e. PC’s IP is
192.168.0.xxx and subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
4. Click Upload Image.
5. Wait for Image Uploading to finish and then click Close.
6. Plug-off the power adapter and then plug-in the power adapter to restart the
Server.
92
Page 93

Chapter16 The Init Button
The Init button is used for:
1. Print Configuration Report: Press Init button for exceeding 3 seconds and
then the connected HP printer or PCL supported printer will print out the
system configuration.
2. Maintenance: Plugging in the power adapter while pressing the Init button
until USB1 and USB2 LED indicators blink alternately. After that, the Server
will do the following tasks:
A. Reset the Server to factory default, which will restore most of the
parameters and settings to factory default values,
B. Perform a TFTP server. You can upgrade new firmware using the “Image
Burner” utility.
Note: After performing the tasks mentioned above, you have to plug off the
power adaptor and then plug in the power adaptor to restart the Server.
93
 Loading...
Loading...