Page 1

Committed
to Quality
DaqLink 4 Channel Multi-probe Data Logger
4 external inputs + internal humidity and temperature sensors
User Guide
For DBSA710 and DBSA720
Page 2

DaqLink
User Guide
Supporting DaqLink v1.2.2.1
November 2009
© Fourier Systems Ltd.
Page 3

Contacting Fourier Systems technical support:
Email:
Web:
support@fouriersystems.com
www.fouriersystems.com/support/contact_support.php
Telephone: USA 1-866-771-6682 (toll-free within USA only)
For Troubleshooting and FAQs visit the website at:
http://www.fouriersystems.com/support/faq/
To download updated versions of the DaqLink User Guide
and DaqLink software/firmware visit:
www.fouriersystems.com/support/download_center.php.
Information in this document is subject to change without
notice.
© 2009 Fourier Systems Ltd. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this document in any manner without the prior
written consent of Fourier Systems Ltd. is strictly forbidden.
Page 4

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1: DAQLINK OVERVIEW 1
1.1. DaqLink Introduction 1
1.2. The DaqLink System 2
1.2.1. The Data Logger 3
1.2.2. Hardware Accessories 4
1.2.3. DaqLink Software 5
CHAPTER 2: DAQLINK IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE 6
2.1. Pre-setup Requirements 6
2.2. Launching the Software 7
2.3. Connecting the Logger 8
2.4. Charging DaqLink Loggers 9
2.5. Loading Map View Background 10
2.6. Configuring the Logger 11
2.7. Viewing Data 13
2.7.1. Online Data Views 13
2.7.2. Logger Tooltip 15
2.7.3. Sensor View 15
2.8. Downloading Data 16
CHAPTER 3: DAQLINK HARDWARE OVERVIEW 17
3.1. Data Logger Front Panel Layout 17
3.1.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 17
Page 5

3.2. Data Logger External Connections 18
3.2.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 18
3.3. Data Logger Sensor Overview 19
3.3.1. Internal Sensor Types 19
3.3.2. External Sensor Types 20
3.3.3. Sensor Connection 21
3.3.4. External PT-100 Sensor Connection 22
3.3.5. Programming Limitations for DBSA710 and
DBSA720
22
3.3.6. External Alarm Output 23
3.3.7. Polarity 25
3.3.8. Frequency/Pulse Counter 25
3.3.9. User Defined Sensors 25
3.3.10. Sensor Alarms 26
3.3.11. Sensor Calibration 26
3.4. Unit Serial Number and Comment 27
3.5. Power Supply 27
3.5.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 Data Loggers 27
3.5.2. Power Adapter 29
3.5.3. Data Logger Battery Life 29
3.6. USB Communication Cable 29
3.7. DaqLink Keypad Overview 30
3.7.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 Keypad 30
3.8. Operating the DBSA710 and DBSA720 31
3.8.1. Turning on the Unit 31
3.8.2. Display Shutdown 32
3.8.3. Main Menu Options 32
3.8.4. Additional Logger Screens 36
CHAPTER 4: USING THE DAQLINK SOFTWARE 38
4.1. Installing DaqLink Software 38
Page 6

4.1.1. System Requirements 38
4.1.2. Installation Procedure 39
4.1.3. Installation Troubleshooting 42
4.2. DaqLink Software Layout 42
4.2.1. Map View 43
4.2.2. Viewing Sensor Data in Map View 44
4.2.3. History View 45
4.2.4. Data Map 46
4.2.5. DaqLink Toolbar Icons 47
4.3. File Menu Items 52
4.3.1. Open 52
4.3.2. Open Project File 52
4.3.3. Save Project 53
4.3.4. Save Project As 53
4.3.5. Exit 53
4.4. Logger Menu Items 53
4.4.1. Display Data 53
4.4.2. Download Data 53
4.4.3. Cancel Download 54
4.4.4. Reset Alarm 54
4.4.5. Calibration 54
4.4.6. Cancel Firmware Update 54
4.4.7. Setup 55
4.4.8. Stop 55
4.4.9. Run 55
4.4.10. Detect Logger 55
4.5. Tools Menu Items 55
4.5.1. Define Sensor 55
4.5.2. Lock Map View 57
4.5.3. Options Menu 57
4.5.4. Email Alarm Notifications 57
4.5.5. SMS Alarm Notifications 57
4.6. Tools > Options Menu Items 58
4.6.1. Preferences Tab 58
Page 7

4.6.2. Email Settings Tab 60
4.6.3. SMS Settings Tab 61
4.6.4. Analysis Menu Items 63
4.7. Saving Data 64
4.8. Viewing Archived (Offline) Data 64
4.9. Viewing Online Data 66
4.9.1. Showing/Hiding the Data Sets 68
4.10. Working in Map View 69
4.10.1. Loading Map View Wallpaper 69
4.10.2. Moving Icons around the Screen 69
4.10.3. Logger Icon Context Menu 70
4.10.4. Viewing Logger Status 70
4.11. Configuring the Logger 72
4.11.1. Device Setup Tab 72
4.11.2. Alarm Setup Tab 76
4.12. Alarm Notifications Setup 78
4.12.1. Contacts Tab 80
4.12.2. Groups Tab 81
4.12.3. Notifications Setup Tab 82
4.12.4. Email and SMS Notification Formats 84
4.13. Calibration 85
4.13.1. Introduction to DaqLink Calibration 86
4.13.2. Calibrating the Data Logger 88
4.13.3. Performing a Two-point Calibration 89
4.13.4. Performing an Offset Calibration 91
4.13.5. Setting the Offset to a Specific Input 91
4.13.6. Calibrating the Internal Temperature Sensor on
the DBSA910
92
4.13.7. Calibrating the External PT-100 Sensor Input 92
4.13.8. Saving Calibration Settings 93
4.13.9. Loading Calibration Settings 93
Page 8

4.14. Analyzing the Data 93
4.14.1. Using the Graph Features 94
4.14.2. Statistical Analysis 100
4.15. Exporting Data to Excel or CSV Formats 100
4.16. Printing the Data 101
4.17. System Password 102
CHAPTER 5: UPDATING DAQLINK SOFTWARE AND
FIRMWARE
104
5.1. Using the Uptodata Client 104
5.2. Updating DaqLink Firmware 107
5.2.1. Downloading the Firmware File 107
5.2.2. Firmware Update from the Map View Icon 108
APPENDIX A: DAQLINK SPECIFICATIONS 109
A.1. Data Logger Input Types 109
A.2. DBSA710 and DBSA720 Outputs 110
A.3. Logger Input Specifications DBSA710 and
DBSA720
110
A.4. General Specifications 112
A.5. System Requirements 113
APPENDIX B: SAFETY INFORMATION 114
APPENDIX C: ORDERING INFORMATION 116
Page 9

APPENDIX D: FIGURES AND TABLES 118
Page 10

Chapter 1:
DaqLink Overview
This chapter provides a general overview of the DaqLink
system.
1.1. DaqLink Introduction
Light, Portable and Independent Logging
With built-in temperature and humidity sensors, plus four
external probe inputs the DaqLink standalone data logger
ensures a low cost, reliable and accurate solution. The
DaqLink logger is a 16-bit, mobile data acquisition device for
continuous indoor or outdoor data monitoring.
The DaqLink system is comprised of two data logger models,
measuring a broad range of parameters on four external
inputs for direct measurement and recording of PT-100,
thermocouple, 0 to 1 V, 4 to 20 mA, contact, frequency and
pulse sensors, as well as internal temperature and relative
humidity sensors.
With its high resolution and fast Analog to Digital converter
(ADC), DaqLink data loggers meet the majority of data
acquisition requirements in most industrial applications. Every
DaqLink logger unit is embedded with a unique serial number
and can be loaded with a descriptive comment for safe
identification. An internal clock and calendar keeps track of the
time and date of every sample measured.
DaqLink loggers can automatically activate external alarm
events when data is outside a specified range. Email and SMS
notifications can be sent to predefined contacts.
1
Page 11

The DaqLink system is powered by the powerful DaqLink
software. The Windows ™ based software is the central
management interface of the DaqLink network. When
connected via USB cable to the PC, DaqLink data can be
monitored online and displayed in real-time graphs or tables.
Analyze data with various mathematical tools, or export data
to a spreadsheet.
The software also enables you to configure, calibrate or
update the firmware of DaqLink units via direct USB
connection.
Key DaqLink benefits include:
• Real-time logging - Online operation with data results on
screen
• Independence - Manual or PC operation with on-site
monitoring via two-row LCD display
• Intuitively - Simple keypad and easy-to-navigate menus
• Long life - Low-power consumption and rechargeable
battery lasting up to six months
• Flexibility - Four alarm levels with visual LCD, and audible
alarms
• Non-stop logging - Continuous data storage to large
onboard memory and periodic USB downloads
1.2. The DaqLink System
The basic DaqLink system will contain at least one of the
following units:
• DaqLink data logger – Part Number DBSA710 or
DBSA720
• Mini-USB communication cable
• Power adapter (one per DaqLink unit ordered)
2
Page 12

• DaqLink software CD containing user guide
1.2.1. The Data Logger
There are two data logger models compatible with the
DaqLink system. These loggers support up to four external
sensors and two internal sensors, temperature and humidity,
depending on the specific model. Data is recorded and stored
to the logger’s internal memory and transmitted over the
network to the DaqLink software running on the PC.
The data logger is programmed to consume as little power as
possible during operation, in order to conserve the battery life.
When not transmitting or recording data the units are in sleep
mode and they wake up when needed.
The battery for the DBSA710 and DBSA720 is rechargeable
and can run up to several months on one charge, depending
on the logger configuration.
Refer to section
Note: Battery life depends on the logger sampling rate,
transmission rate, type of sensor, and number of measured
sensors.
3.5.3 for more information.
3
Page 13

DaqLink Data Loggers
Part Number: DBSA720 Part Number: DBSA710
Four external channel data logger with
two internal sensors, Humidity and
Temperature
Memory Capacity: ~59,000 samples
Power supply: AC or battery operated
Four external channel data logger with
internal Temperature sensor
Memory Capacity: ~59,000 samples
Power supply: AC or battery operated
1.2.2. Hardware Accessories
The DaqLink system includes the following accessories:
• Mini-USB cable for connecting data logger to PC
• Power adapter to power the data logger
4
Page 14

1.2.3. DaqLink Software
The user interface for the DaqLink system, the DaqLink
software CD is provided together with the DaqLink hardware
and includes the following features:
• Data display, management, storage and data diagnostics
• Alarm settings: Email and SMS notifications, visual and
audible alarms
• Sensor definition
• Sensor calibration
• Firmware update
• Automatic software update (via Fourier server)
The software interface is described in detail in Chapter 4.
5
Page 15
Chapter 2: DaqLink Implementation Guide
Fourier Systems suggests first time users of the DaqLink
system read this chapter before drilling down into the many
features of the system described later in the user guide. The
Implementation Guide will give you a clear understanding of
the basic aspects of setting up the system, and getting the
data logger up and running.
2.1. Pre-setup Requirements
Prior to commencing with the DaqLink implementation you
must have the following requirements in place:
PC
• 24/7 availability, if online data monitoring is required
• Reliable AC power
• Sufficient hard disk space to store loggers’ data
• One free USB port
DaqLink devices
At least one DaqLink logger DBSA710 or DBSA720
Mini-USB cable
The mini-USB cable connects the data logger to the PC for
logger configuration and data download (and is supplied with
the PC Suite software kit).
6
Page 16
2.2. Launching the Software
1. Install the DaqLink software on the PC workstation. Refer
to section
more details.
2. Once the software and associated components have
been installed, launch DaqLink from your DaqLink
4.1: Installing DaqLink Software on page 38 for
desktop shortcut
3. The main DaqLink window is launched. The default view
is called Map View.
Figure 1: Main DaqLink window
.
7
Page 17

4. Check for DaqLink updates. Go to Help > Check for
Updates from the DaqLink main menu to check for newer
versions of DaqLink software and firmware released since
you purchased your system. For more details on the
Update feature go to
Software and Firmware.
Chapter 5: Updating DaqLink
2.3. Connecting the Logger
Note: Only one DaqLink logger will be detected by the PC at
a time.
1. Only once the DaqLink software and USB driver have
been installed, connect the DaqLink data logger
(DBSA710 or DBSA720) to the Fourier-supplied power
adapter.
Note: Only use adapters provided by Fourier Systems. Use of
the wrong adapter could damage your DaqLink units.
2. Turn on the unit by pressing the Scroll button
the front keypad. The unit will beep when turned on.
3. Connect the mini-USB cable to the computer and to the
data logger’s mini-USB port.
4. From the DaqLink main menu, go to Logger > Detect
Logger. The data logger icon will appear in the Map View
indicating that the logger is detected.
8
on
Page 18
Figure 2: Adding data logger icon to Map View
Note: If the logger is not recognized by the software try
connecting the mini-USB cable to another USB port on the
PC. Or select Logger > Detect Logger again in the main
menu.
Should you disconnect the logger’s USB cable or power
adapter (and the battery eventually dies), the logger icon
will be grayed out:
Note: You can move the logger icon elsewhere on the screen
by going to Tools > Lock Map View and unselecting this
option.
2.4. Charging DaqLink Loggers
This section refers to charging the DBSA710 or DBSA720
loggers.
Note: Only use adapters provided by Fourier Systems. Use of
the wrong adapter could damage your DaqLink units.
If the loggers will run from the battery supply make sure to first
charge each of the loggers for 16 hours before use in order
maximize the battery life. A fully charged battery can last
several months, depending on your logger configuration.
9
Page 19
If the loggers will run from the AC power supply, when first
connected to the AC adapter the logger will always initiate the
16 hour charge cycle.
Note: For loggers measuring data with the internal
temperature sensor, it is critical to note that during the charge
cycle the logger will heat up thereby causing the internal
temperature sensor reading to rise up to 10 ˚C above ambient
temperature. Once the charging process is complete, the
logger will cool down and the internal temperature sensor
readings will return to normal.
For loggers remaining connected to AC power, to prevent the
logger from heating up again following the initial charge cycle,
the logger will receive a one minute trickle charge each day
rather than stay continually charged. This is sufficient to
ensure the logger doesn’t self-discharge and will maintain the
logger’s full charge status.
Refer to section 3.5.1 for more details on the DaqLink loggers’
power supply.
2.5. Loading Map View Background
Load an image into the DaqLink software showing a map of
your facility in order to place the Logger icons in their relative
positions. As you deploy more standalone loggers, this will
prove very helpful.
• Double click the Map View background to browse to the
image directory and load the image. Remember to unlock
the Map View in order to move the icons around.
• Right-click the Map View background and two options will
be available: Load Wallpaper and Reset Wallpaper,
which resets to the default Fourier wallpaper.
10
Page 20
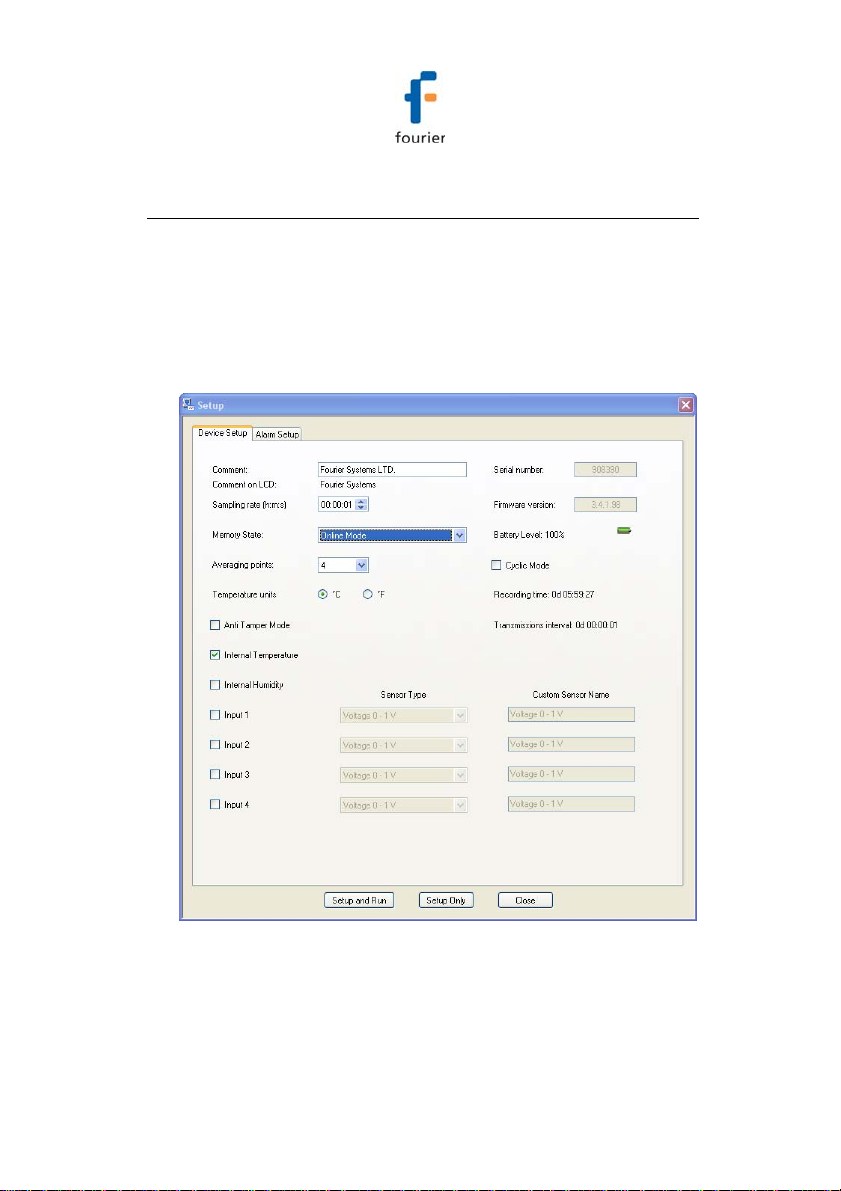
2.6. Configuring the Logger
Once the software has detected the DaqLink logger, you must
configure the unit in order to start acquiring data.
5. Right-click on the Logger icon. Select Setup from the
context menu.
The Setup window will be launched.
Figure 3: Logger Setup window
This dialog provides non-editable information such as the
serial number, battery level, and firmware version of the
current unit.
11
Page 21

On the Device Setup and Alarm Setup tabs, the user is
able to configure the following parameters:
Unit's comment
Sampling rate
Memory State
Averaging points
Temperature units °C/°F (on the logger LCD)
Anti-tamper mode
Active sensors
Custom sensors' names
Alarm levels
Alarm duration
Alarm delay
Alarm pre delay
6. Select the Memory State, Online or Optimized Memory
Modes.
7. Select the sensors you wish to connect to the logger for
data acquisition. It doesn’t matter which order you select
the sensors. You may only have Input 4 selected, for
example, and Inputs 1 to 3 left unselected.
8. Select the sampling rate anywhere from 1 every second
to 1 every 18 hours.
9. Unless you have Alarm levels you wish to edit (see the
Alarms Setup tab), click either Setup and Run (to send
the setup and immediately log data), or Setup Only (to
send the setup but only log data at your command).
10. If you selected Setup Only in step 5, right-click the
Logger icon and select Run from the context menu to
start logging data or click
in the main tool bar.
12
Page 22

The Logger icon will appear as follows when in Run
mode:
11. To stop the logger, right-click the Logger icon and select
Stop from the context menu.
Note: Running the logger clears the logger memory. All
previously recorded data will be erased when you begin a new
logging session.
.
2.7. Viewing Data
Once you run the logger, you have several ways of viewing
the online data that is being acquired.
• Online graph/table/statistics views
• Logger icon tooltip
• Sensor view
2.7.1. Online Data Views
Double clicking the Logger icon or selecting Display Data in
the Logger icon context menu will open the online graph.
This graph is updated in real-time with the newly recorded
data.
You can switch between Graph, Table and Statistics views to
view the data in different formats.
13
Page 23
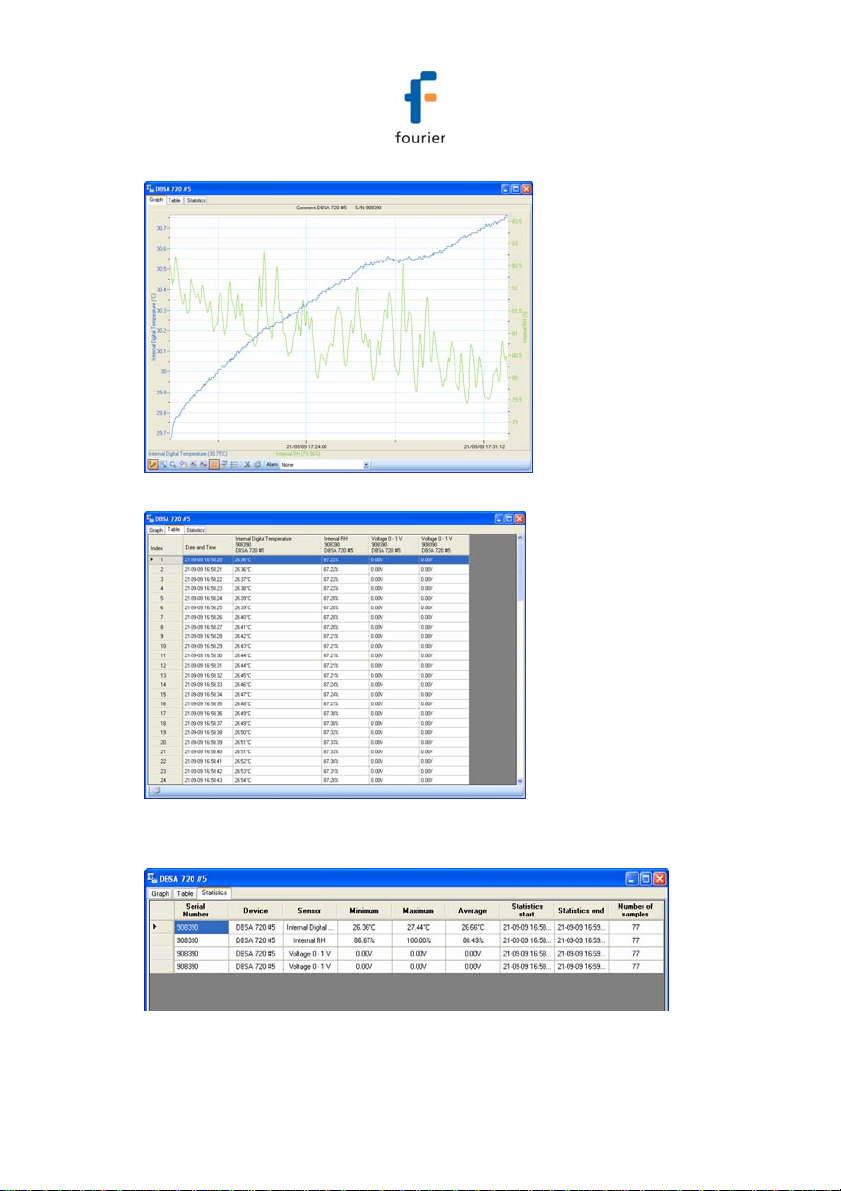
Figure 4: Online data – Graph view
Figure 5: Online data – Table view
Figure 6: Online data – Statistics view
14
Page 24
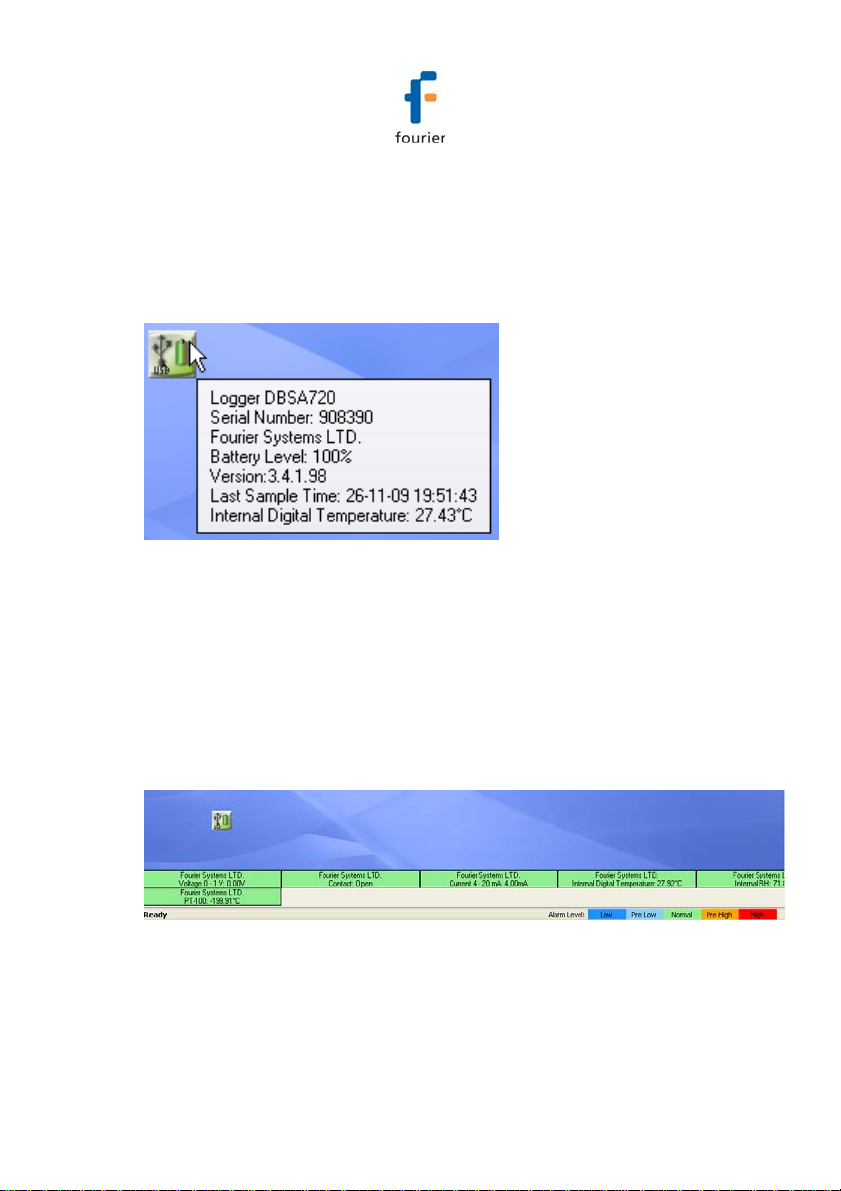
2.7.2. Logger Tooltip
Close the online data window and return to Map View. Scroll
over the Logger icon and you will see a tooltip displaying the
relevant logger information, including real-time data.
Figure 7: Logger tooltip
This tool-tip is updated with every newly recorded sample.
2.7.3. Sensor View
You can monitor data by viewing the data display of each
individual sensor, rather than using the Graph or Table views.
When the logger is running, the individual sensor data is
displayed in a box in the bottom pane of the main Map View.
Figure 8: Sensor view
• If the sensor is in alarm, the sensor box will change color
from green to red (just as the Logger icon would).
15
Page 25
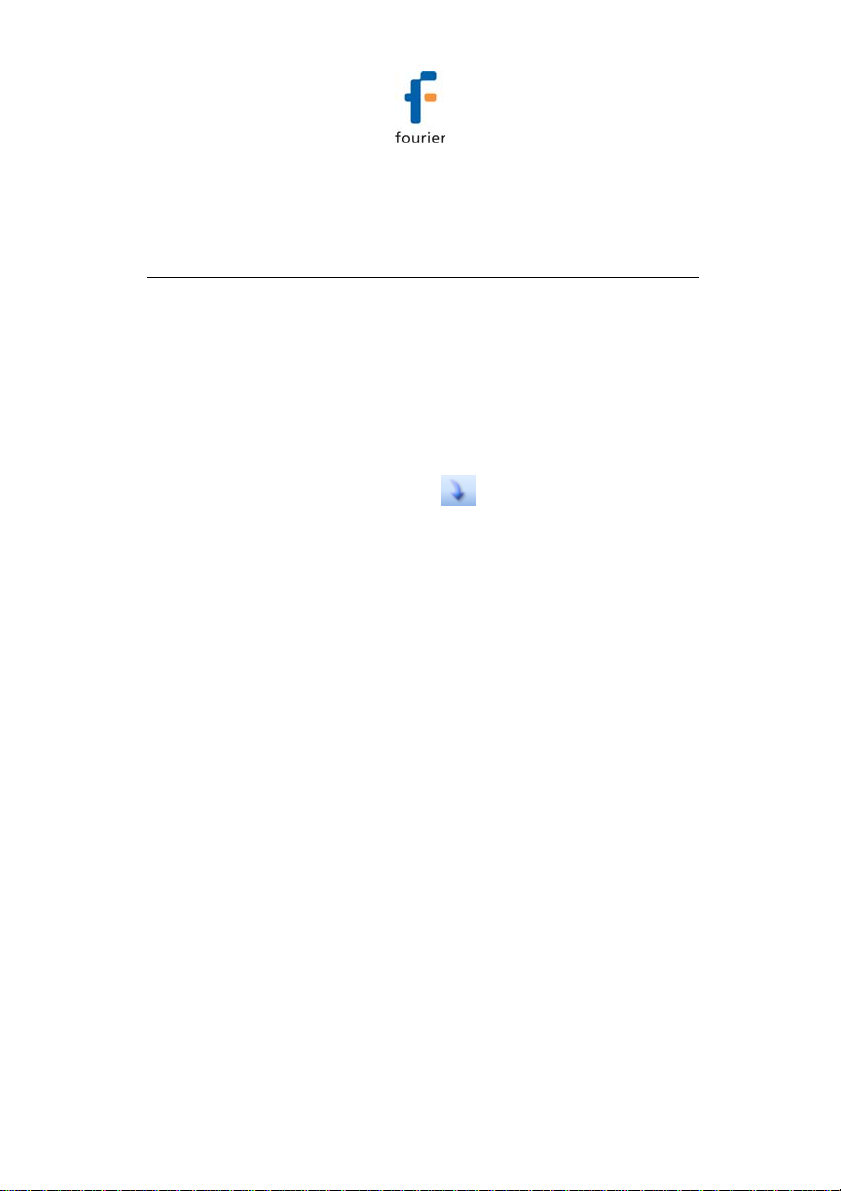
• Double-clicking the individual sensor box will open the
data in the online Graph view.
2.8. Downloading Data
If the logger is being used as a standalone device you will
have to connect it to the computer via USB cable in order to
download the data to the software.
1. Connect logger to PC and go to Logger > Detect Logger
in the main menu.
2. To download data:
• Click the Download icon
• Go to Logger > Download Logger, or
• Right-click the logger icon and select Download Data
3. View the downloaded data by double-clicking the logger
icon.
in the upper toolbar, or
16
Page 26
Chapter 3: DaqLink Hardware Overview
This chapter details the hardware features of the DaqLink
data loggers.
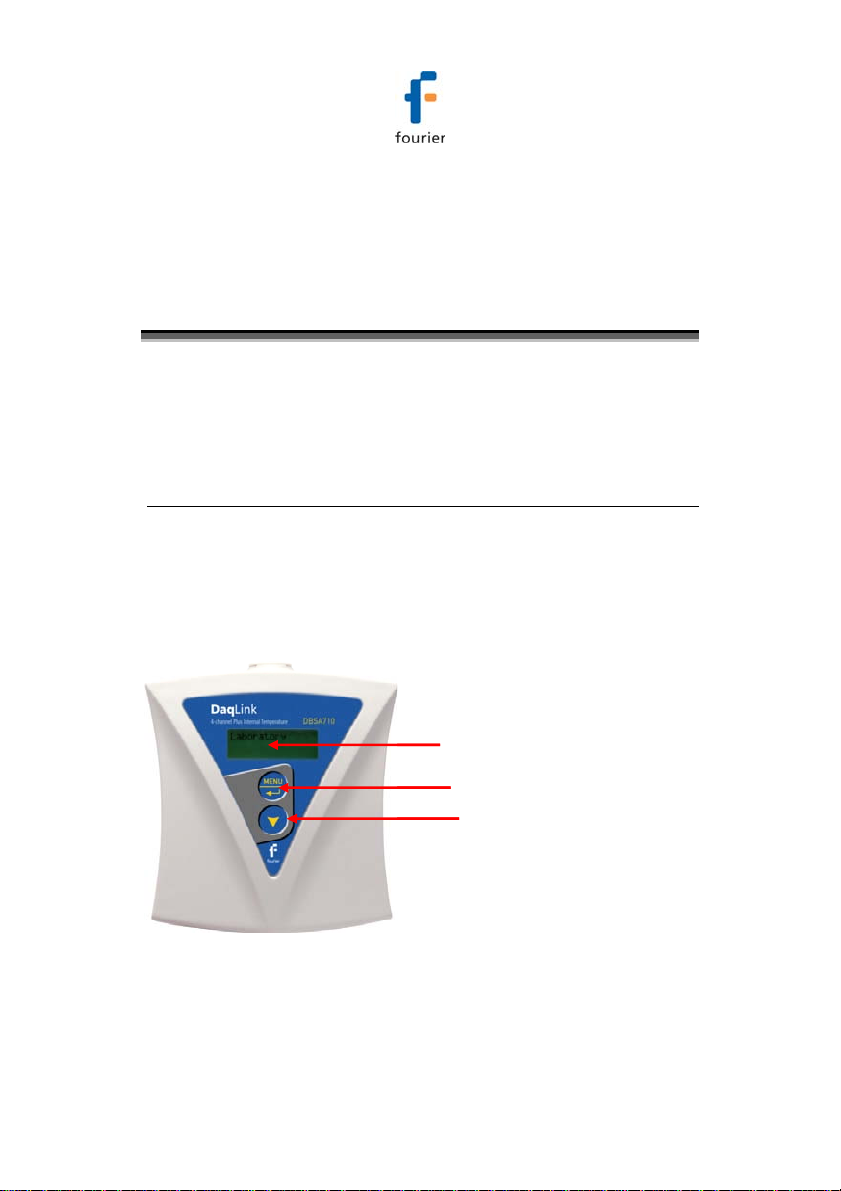
3.1. Data Logger Front Panel Layout
3.1.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720
Apart from the color scheme, the DBSA710 and DBSA720
data logger models have the same front panel design.
LCD screen
LCD screen
Menu/Enter button
Menu/Enter button
Scroll button
Scroll button
Figure 9: DBSA710 data logger front panel
LCD screen
Displays logger status, logger data, and Min/Max values.
17
Page 27
Menu/Enter button
Use to enter logger menu options and to execute logger
commands.
Scroll button
Use to scroll though menu items and to power on unit.
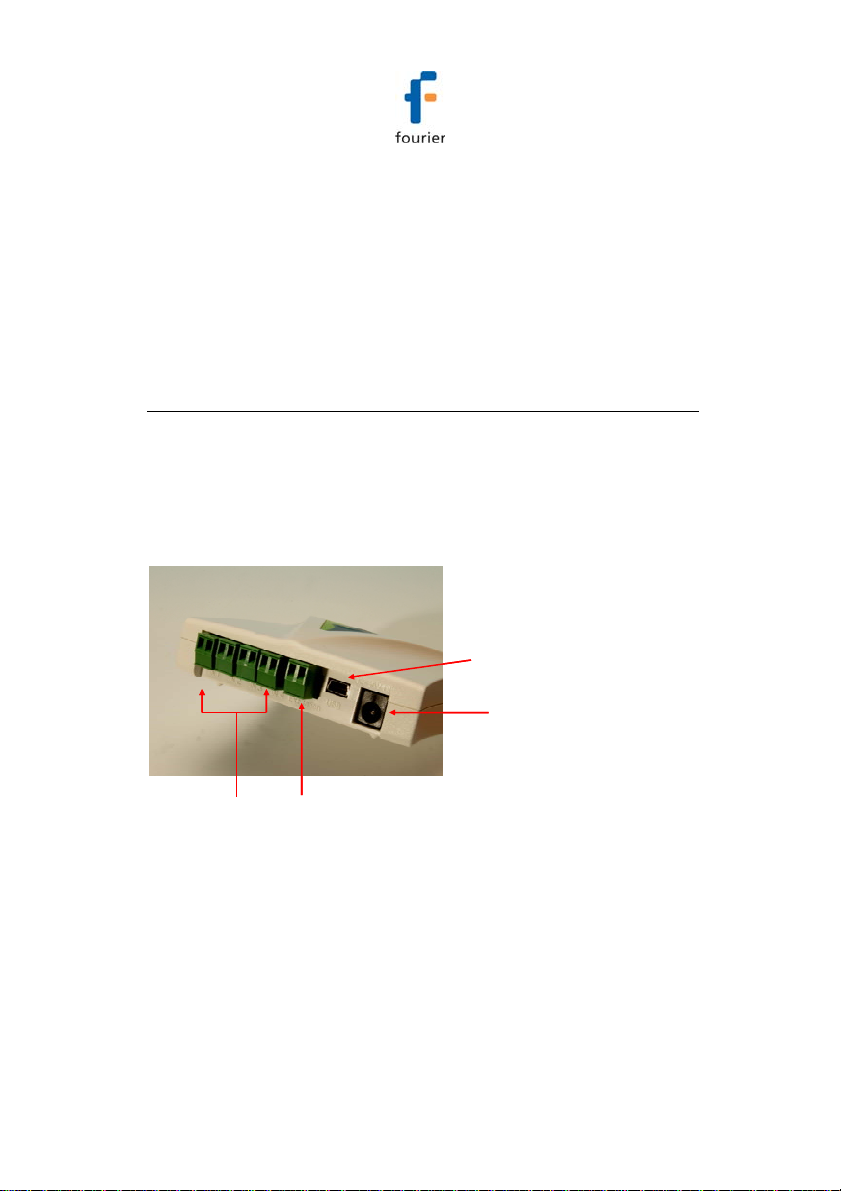
3.2. Data Logger External Connections
3.2.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720
External connections of the DBSA710 and DBSA720 are
exactly the same.
Mini USB port
Mini USB port
12 V power socket
12 V power socket
Negative Center
Negative Center
Excitation
Excitation
Four sensor
Four sensor
inputs
inputs
Figure 10: DBSA720 data logger external connections
Mini USB Port
To enable communication between logger and PC, for
configuration and data download.
12 V Power Socket
18
Page 28
To connect logger to external power supply (negative center).
Sensor Inputs
Pluggable screw terminal blocks marked In-1 to In-4 (from left to
right), to connect wide range of sensor types for data acquisition.
All four inputs can be used simultaneously. Sensors can be
connected in any order.
To connect a sensor to the DaqLink data logger, unplug the
screw terminal, connect the sensor’s wires to the terminals, and
then plug the terminal back to the corresponding socket on the
input block.
Excitation socket
Output power socket used to power external sensors, power
derived directly from the external power supply adaptor.
3.3. Data Logger Sensor Overview
This section provides an overview of the hardware
specifications of the DaqLink data loggers.
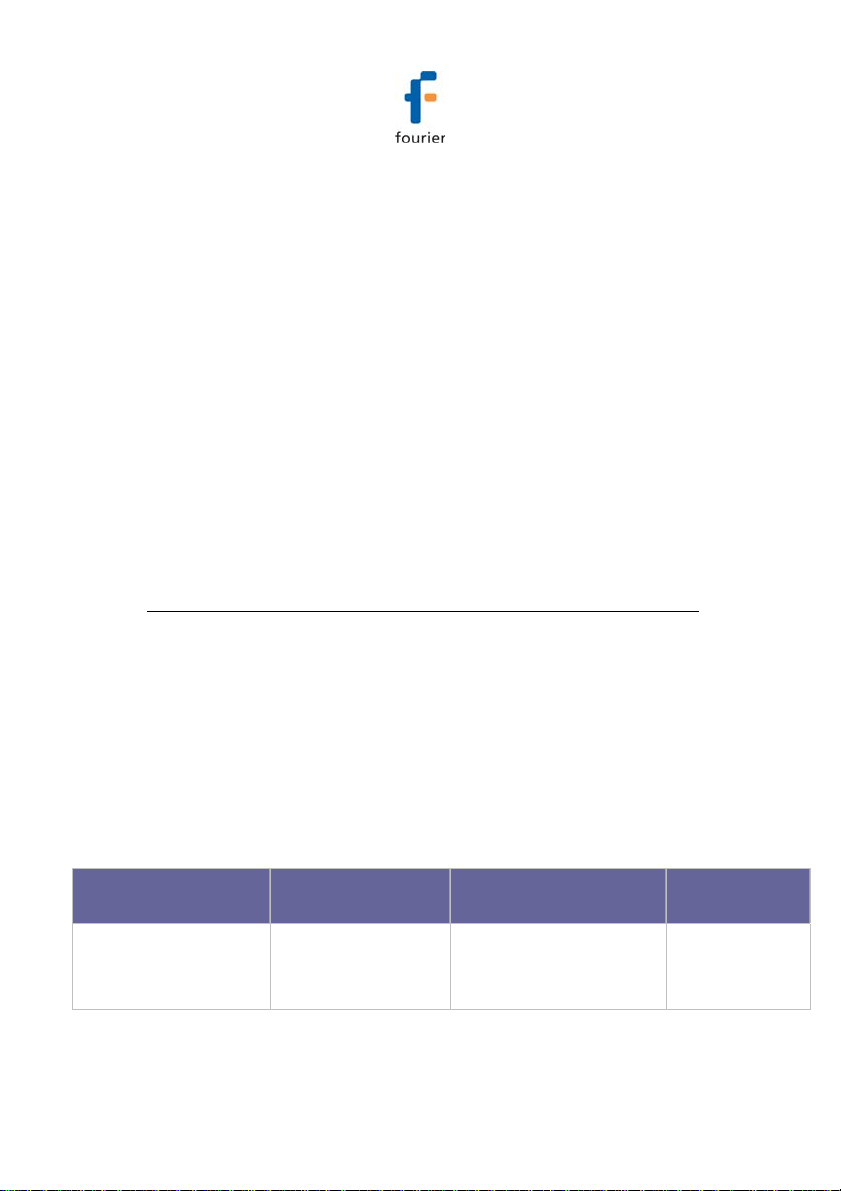
3.3.1. Internal Sensor Types
The DBSA710 and DBSA720 loggers include internal
sensors, depending on the logger model.
Sensor Measurement
Range
Digital Humidity 5% to 95%
Accuracy Logger
±3% (in DaqLink
software)
±4% (on logger LCD)
19
Model
DBSA720
Page 29
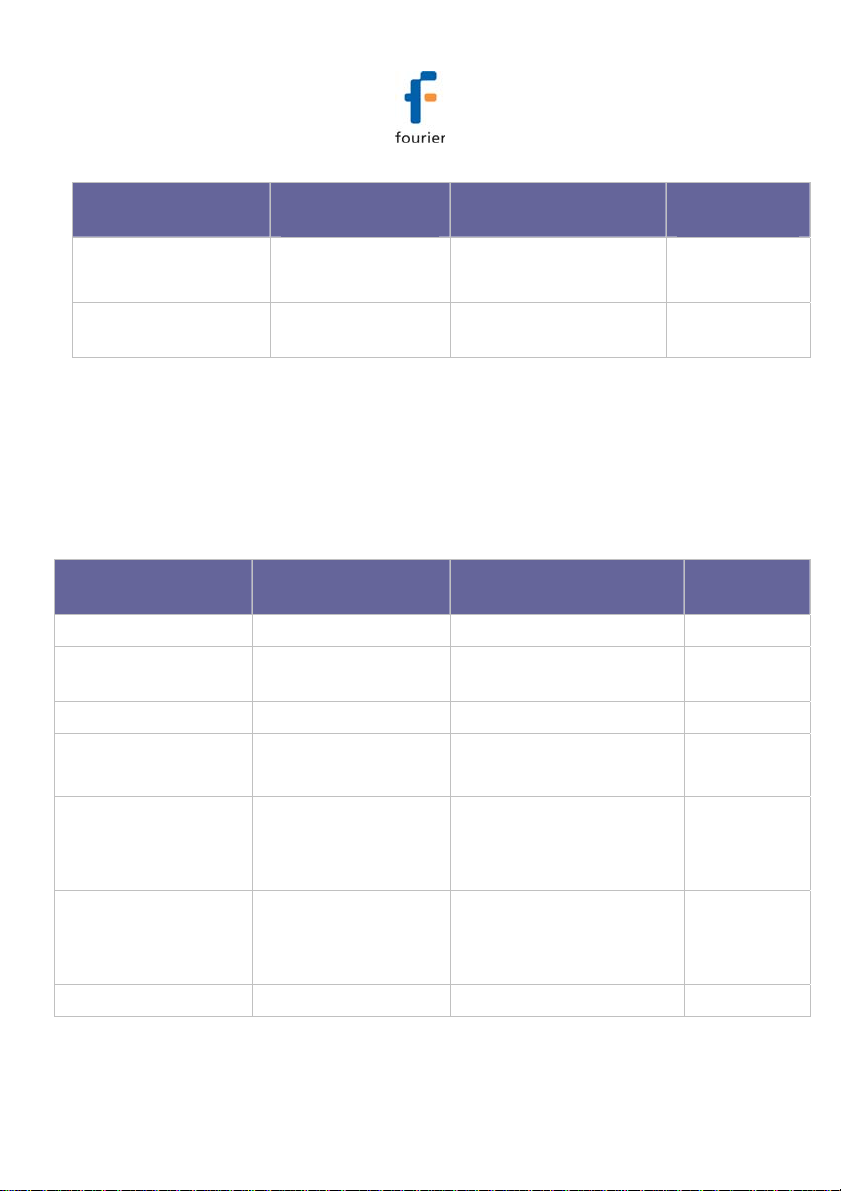
Sensor Measurement
Range
Digital Temperature -20 ºC to 50 ºC ±0.5 ºC DBSA720
Accuracy Logger
Model
Temperature
PT100
-20 ºC to 50 ºC ±0.3 ºC DBSA710
3.3.2. External Sensor Types
DBSA710 and DBSA720
Each of the four input channels of these data logger models
are multi-purpose and can be individually configured to any of
the following types and ranges.
Sensor Measurement
Range
Current 4 to 20 mA ± 0.5 % In-1 to In-4
Contact Open (0) /
Close (1)
Frequency 20 Hz to 4 KHz N/A In-4 only
Pulse Counter 1 to 65,536 pulses
0 to 4 KHz
Temperature
PT100 (2-wire)
Temperature TC-J -200 ºC to 1,000 ºC -200 to -60 ºC ±0.5 %
Temperature TC-K -200 ºC to 1,000 ºC -200 to -60 ºC ±0.5 % In-1 to In-4
-200 to 400 ºC -200 to -60 ºC ±0.5 %
N/A In-1 to In-4
N/A In-4 only
-60 to 60 ºC ±0.3 ˚C
60 to 400 ºC ±0.5 %
-60 to 60 ºC ±0.5 ˚C
60 to 1,000 ºC ±0.5 %
Accuracy Available
Inputs
In-1 to In-4
In-1 to In-4
20
Page 30

Sensor Measurement
Range
-60 to 60 ºC ±0.5 ˚C
60 to 1,000 ºC ±0.5 %
Temperature TC-T -200 ºC to 400 ºC -200 to -60 ºC ±0.5 %
-60 to 60 ºC ±0.5 ˚C
60 to 400 ºC ±0.5 %
Voltage 0 to 1 V ± 0.5 % In-1 to In-4
Voltage 0 to 50 mV ± 0.5 % In-1 to In-4
Accuracy Available
Inputs
In-1 to In-4
3.3.3. Sensor Connection
Connect the sensor/s to the terminal block/s at the top of data
logger:
Figure 11: DaqLink logger sensor inputs
Sensors do not have to be added successively. You may only
configure In-4, or configure In-1 and In-3, for example, when
setting up the logger via the software.
21
Page 31

3.3.4. External PT-100 Sensor Connection
The PT-100 sensor, as supplied by Fourier Systems, comes
pre-wired to the data logger’s terminal block.
The PT-100 positive polarity (red) and ground (white) wires
are connected to the + input of the terminal block. The
negative polarity (black) wire is connected to the – input on
the terminal block.
3.3.5. Programming Limitations for DBSA710 and DBSA720
The standard sampling rate for all sensors on all inputs is from
a maximum of one sample every second to a minimum of one
sample every 18 hours. However, there are certain limitations
using a specific combination of sensors, which must be taken
into account when programming the DaqLink data loggers.
Note: The software integrates all programming limitations
automatically when configuring the loggers.
Please refer to the table below for DaqLink programming
limitations, where:
PT100, Thermocouple J, K or T = A
Internal Digital Temperature (on DBSA720) = B
Sensor
Combination
3 x A
4 x A
A + B
Maximum
Sampling Rate
One sample every
three seconds
22
Example Setup
In-1: PT-100
In-2: TC-J
In-3: TC-J
Page 32

Sensor
Combination
(2 x A) + B
(3 x A) + B
(4 x A) + B One sample every
Table 1: Data Logger programming limitations
Maximum
Sampling Rate
One sample every
four seconds
five seconds
Example Setup
Internal: Temp
In-1: TC-T
In-2: PT-100
Internal: Temp
In-1: TC-T
In-2: TC-J
In-3: PT-100
In-4: PT-100
3.3.6. External Alarm Output
The DaqLink system supports connection of an external alarm
e.g. siren, audible alarm, to In-1 of the DBSA710 and
DBSA720 data loggers.
When connected to the logger, the external alarm will be
activated only when that logger is in alarm status.
Once there is no alarm status, the external alarm will be
deactivated.
Data Logger External Alarm
In-1 of the DBSA710 and DBSA720 serves either as a
standard sensor input or as an external alarm output. Ensure
the logger is connected to AC power if connected to an
external alarm.
Configure In-1 as Alarm Normally Open or Alarm Normally
Closed in the logger Setup window in the DaqLink software.
23
Page 33

Normally Open will result in the alarm being activated during
alarm status (the circuit will be closed).
Normally Closed will result in the alarm being activated when
logger is not in alarm and therefore deactivated when there is
an alarm (the circuit will be opened).
Connect In-1 to your external alarm device and connect the
logger to AC power.
Use the Alarm Setup tab in the Setup dialog to define the
logger alarm settings. If these settings are breached then the
alarm will be activated.
External Alarm Schematic
See the schematic below explaining how to hook up an
external alarm to the DaqLink unit.
-
-
+
+
-
-
+
+
+
+
3-4 V battery
-
-
24
3-4 V battery
to power relay
to power relay
Relay
Relay
-
-
+
+
Alarm device
Alarm device
(e.g. siren)
(e.g. siren)
Figure 12: External alarm schematic
Page 34

• + from DBSA710/720 goes to – of the Relay inputs
• + of Relay input goes to battery that powers the Relay
• Load inputs of the Relay go to the Alarm device e.g. siren,
lights, etc.
• - of the battery goes to – of DBSA710/720.
Note: Maximum load of the Relay is 50 mA, 3 V.
Refer to Appendix A: DaqLink Specifications for the full
external alarm output specification.
3.3.7. Polarity
Current, voltage, thermocouples and user defined sensors
have distinct polarity. Be careful to connect them in the right
polarity.
3.3.8. Frequency/Pulse Counter
Connect the signal wires to In-4 terminal blocks, and select
Frequency or Pulse counter for Input 4 from the logger
Setup window in the DaqLink software. Inputs 1 to 3 are still
available for other sensors.
The Frequency/Pulse counter is optically isolated from the
internal circuitry and can simultaneously measure a signal
source, together with another input.
3.3.9. User Defined Sensors
DaqLink provides a simple and straightforward tool for
defining a limited number of custom sensors. Almost any
sensor or transducer with 0 – 1 V or 4 – 20 mA output is
25
Page 35

accepted by the DaqLink logger and its electrical units are
automatically scaled to meaningful user-defined engineering
units.
The sensor definitions are stored in the logger’s memory and
are added to the sensors list. The sensor’s readings are
displayed in the user defined units only in the DaqLink
software. Future versions will also support displaying the user
defined engineering units on the logger LCD.
Refer to section
4.5.1 for more details.
3.3.10. Sensor Alarms
Via the software, users can define minimum and maximum
alarm levels for each input individually. Users can define prelow and pre-high alarm levels, for an additional level of safety
in case the logger is approaching an actual breach of alarm.
The DaqLink logger display indicates when the sensor reading
is in alarm of any type. The symbols AL-H, AL-L, AL-P-H or
AL-P-L are visible next to the corresponding input readings.
Refer to section
4.12 for more details.
3.3.11. Sensor Calibration
The DaqLink data logger is shipped fully calibrated. However,
further calibration can be applied via the DaqLink software.
The calibration parameters are sent to the data loggers via
USB connection and stored in the logger’s memory.
Users may calibrate individual inputs as well as all inputs at
once. Calibration settings may be saved and then loaded into
the logger at a later date if the calibration settings have
changed.
Refer to section
4.12.4 for more details.
26
Page 36

3.4. Unit Serial Number and Comment
Every DaqLink data logger unit is embedded with a unique
serial number.
The data logger only can be loaded with a descriptive
comment to identify its task and location. You may add or edit
the logger comment via the DaqLink software.
Every time data is transferred to the computer it is labeled
both with the logger’s serial number and comment and is
displayed in the graph or data table view.
The unit serial number is also marked on a sticker on the back
of the product.
3.5. Power Supply
3.5.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 Data Loggers
The DBSA710 and DBSA720 data loggers run from an
internal NiMh rechargeable battery as well as from external
AC power supply. Depending on the logger configuration,
from a fully charged battery, the data logger can run for up to
several months. Refer to section
battery life.
Note: Charge the data logger units for 16 hours before using
them for the first time.
When connected to external power supply, the data logger
battery will not be charged when the unit is turned off. This will
allow the system to protect the battery from overheating.
3.5.3 for more details on
27
Page 37

First Time Charging
From a fully drained battery, you must charge the battery for
16 hours to bring it to a full charge. Once the charge cycle is
complete, the logger will run from the external power supply,
without draining (or charging) the internal battery. In order to
maintain a fully charged battery and ensure the battery
doesn’t self-discharge, the battery charger will daily charge
the unit for one minute to maintain the battery capacity.
Note: Before storing the DaqLink units make sure you have
unplugged all the sensors and turned the units off via the
keypad.
Standard Charging
Whenever a logger is reconnected to the charger it will begin
the 16-hour charge cycle, no matter what the status of the
battery. Once the charging cycle is complete the logger will
run from external power supply.
Effect of Charging Battery on Temperature
Sensor
For loggers measuring data with the internal temperature
sensor, it is critical to note that during the charge cycle the
logger will heat up thereby causing the internal temperature
sensor reading to rise by up to 10 ˚C above ambient
temperature. Once the charging process is complete, the
logger will cool down and the internal temperature sensor
readings will return to normal.
For loggers remaining connected to AC power, to prevent the
logger from heating up again following the initial charge cycle,
the logger will receive a one minute trickle charge each day
rather than stay continually charged. This is sufficient to
ensure the logger doesn’t self-discharge and will maintain the
logger’s full charge status.
28
Page 38

3.5.2. Power Adapter
The DaqLink power adapter is used to power the DBSA710
and DBSA720 units. The mains adaptor (AC/DC adaptor)
converts mains power (from a wall outlet) to a voltage suitable
to the DaqLink hardware unit.
• Output: Capacitor filtered 9 to 12 VDC, 300 mA
• Female plug, center negative
Note: Only use Fourier-supplied power adapters to avoid
damaging the units with incorrect power supply.
3.5.3. Data Logger Battery Life
Battery life depends on the logger sampling rate, type of
sensor, and number of measured sensors.
DBSA710 and DBSA720 can last up to six months on a
charged battery depending on logger configuration.
3.6. USB Communication Cable
A mini USB communication cable is supplied as part of the
DaqLink PC Suite. This cable connects the DaqLink data
logger to the DaqLink PC workstation. When connected to the
PC the logger can communicate with the software for
configuration and data download purposes, for example.
The USB cable also powers the logger when connected to the
PC but it does not charge the internal battery.
29
Page 39

Note: The USB driver is installed as part of the software
installation process. Without this driver the PC won’t detect
the logger. To avoid compatibility problems do not connect the
logger to the PC before installing the USB driver.
Type B plug
Connect to PC USB port
Type A plug
Connect to logger USB port
Figure 13: USB communication cable
3.7. DaqLink Keypad Overview
3.7.1. DBSA710 and DBSA720 Keypad
The DBSA710 and DBSA720 units each have two buttons on
the keypad, which are used to navigate through the LCD
menu options, as well as turn on the units.
Refer to section
3.8 to learn how to operate the data loggers.
The Menu button
functionalities:
Navigate to the main menu. When
pressed from within a submenu, the
display will take you back to the main
menu.
Selecting an option from one of the
menus. When pressed on one of the
30
has two
Page 40

main menu items, it will take you to
the sub menu options.
The Scroll button
functionalities:
When the unit is off, pressing this
button will power the unit on.
Scrolls through the menu options.
has two
3.8. Operating the DBSA710 and DBSA720
This section explains how to operate the DBSA710 and
DBSA720 loggers and provides an overview of the menu
options on the units’ LCD screen.
3.8.1. Turning on the Unit
In order to view the logger menu options, the unit must be
powered on by pressing the Scroll button
Ensure the logger is charged or connected to the AC adapter.
Once the unit is switched on it will emit a short beep and the
screen will display a welcome message:
on the keypad.
DaqLink DBSA710
Ready
31
Page 41

3.8.2. Display Shutdown
If the logger screen is inactive for thirty seconds it will turn off.
However the logger will continue to operate in the
background. Press the Scroll button to enable the LCD
screen again. The screen will not turn off during firmware
upgrade.
3.8.3. Main Menu Options
There are three menu categories on the data logger:
• View Data
• Status
• Min/Max Values
Note: If the unit is not in Run mode only the Status menu
options will be available.
Press the Menu
Scroll through the main menu options (View Data, Status and
Min/Max Values) using the Scroll button. Once you reach the
main menu option you need, press Enter to select that option
and enter the sub menus.
button to reach the main menu display.
View Data Menu
View Data
32
Page 42

Note: View Data is the default page when the unit is running.
If there is more than one sensor running, the screen will auto
scroll between the sensors showing the sensor name and
senor value. These are real-time displays.
The display will switch back to the View Data screen after five
minutes if none of logger buttons have been pressed.
If the sensor breached any of the predefined alarm levels,
then the alarm symbol will be displayed alongside the data
reading.
For example:
In-TMP
24˚C AL-Lo
The logger display alarm symbols are:
• AL-HI : Alarm High
• AL-Lo : Alarm Low
• AL-P-H : Pre Alarm High
• AL-P-L : Pre Alarm Low
Status Menu
Status
The Status menu contains the following sub menus, all
reachable by using the Scroll button.
The sub menus are outlined below in the order in which they
appear on the logger display.
33
Page 43

Name and Status
As explained previously, the unit name (or Comment) is
displayed on the first row and the second row indicates the
logger status.
If the logger is running, then the following screen is displayed.
Fourier Systems
Logger running
Batt Level (battery level)
If the power adapter is not connected the battery percentage
will be displayed.
If the power adapter is connected External power will be
displayed.
Batt Level: 67%
Logger Version
This menu informs the user of the logger firmware version.
This is helpful when you need to upgrade the system
firmware, to check the current version. Or when contacting
Fourier technical support, with any technical issues.
Logger version:
2.03.00.01.98.00
The firmware version is commonly referred to by the numbers
in bold in the screen above. For example, the firmware
version which is supported by this user guide is v1.98.
34
Batt Level:
External power
Page 44

S/N
This menu displays the unit’s eight digit SN.
S/N 12345678
Memory Mode
There are two possible device modes:
• Stop when full – when the logger memory is full the logger
will stop logging.
• Cyclic mode – for continuous logging. The logger will
continue to log once the memory is full by writing over the
first recorded samples.
The memory mode is toggled in the Setup dialog, using the
Cyclic Mode checkbox.
When the logger memory is full, the LCD will display Memory
Full.
Press Menu to pause logger (when logger is in Run mode)
By pressing the Menu button, the logger will cease to log data
until the Menu button is pressed again from the same screen.
When in Paused mode, the user can still scroll through the
logger menu screens and use other features. The user must
scroll back to the Pause Logger menu in order to resume the
logger operation.
Reset Unit
When the unit is reset, upon start up it will automatically
reconnect to the DaqLink software if a USB connection is
35
Page 45

established. In addition, if the logger will continue to operate
according to its last set up instruction. For example, if the
logger was in Run mode, then after reset it will continue to run
and record data.
Turn Off Unit / Stop and turn off
Selecting this option will shut the unit down. You can turn the
unit on again by pressing the Scroll button.
If the logger is in Run mode, selecting this option will first stop
the logger, and then turn it off.
It is recommended to turn off the unit when it is not in use.
Min/Max Values Menu
Each sensor’s minimum/maximum readings (taken from the
current logging session) will be displayed on two rows.
The first row indicates the sensor type, along with the
measurement units e.g. V, and the alarm indication if there is
an active alarm on this sensor.
The second row indicates the minimum and maximum
measured value and the units. H and L represent High and
Low values, respectively.
In-TMP ˚C
26.06H 25.61L
3.8.4. Additional Logger Screens
Loading Firmware
When updating the firmware of the data logger via the
software’s Firmware Update Center, the logger screen will
36
Page 46

display the update progress. When complete the main logger
status screen will be displayed.
Also refer to
Firmware.
Loading firmware
Progress: 55%
Note: Logger must be in Stop mode before firmware can be
updated.
Chapter 5: Updating DaqLink Software and
37
Page 47

Chapter 4: Using the DaqLink Software
This chapter provides detailed description of
the DaqLink software features, allowing you to
manage your DaqLink network and perform a
variety of actions on your data loggers, such
as setup, calibration, defining new sensors,
managing Email and SMS notifications,
firmware updates and so on.
4.1. Installing DaqLink Software
Part of your DaqLink package includes a DaqLink software
CD. Follow the software installation instructions provided
below.
4.1.1. System Requirements
To work with DaqLink your system should be configured
according to the following specifications:
Software
• Windows 2000 SP3, Windows 2003, Windows XP SP2,
and Windows Vista
• Internet Explorer 5.01 or higher
• Minimum screen resolution: 1024 x 768 (800 x 600 not
supported)
38
Page 48

Hardware
• Pentium 800 MHz or higher
• 256 MB RAM
• 250 MB available disk space for the DaqLink application
4.1.2. Installation Procedure
Please read these instructions before proceeding with the
installation process.
1. Insert the DaqLink software CD into your computer’s CD
drive. The DaqLink Installation Wizard automatically starts
running.
2. The Wizard first installs Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0.
The DaqLink software requires this platform in order to
run. Follow the installation instructions to install the .NET
Framework on your PC. This step can take up to two
minutes to complete. Click Finish once installation is
complete.
3. The Silicon Laboratories USB driver installation will now
launch. The driver is necessary for the computer to detect
the DaqLink data logger hardware.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to continue the
installation process. The default installation location is
C:\SiLabs.
39
Page 49

Figure 14: Installing Silicon Labs USB driver – Step 1
5. The following window will pop up. Make sure to select the
checkbox to launch the driver installer, and click Finish.
Figure 15: Installing Silicon Labs USB driver – Step 2
40
Page 50

6. In the subsequent window, click Install to install the
driver.
Figure 16: Installing Silicon Labs USB driver – Step 3
The installation of the driver could take up to one minute
or more, depending on the system.
Figure 17: Installing Silicon Labs USB driver – Step 4
7. Once installed click Finish to close the USB driver Install
Wizard dialog.
8. The main DaqLink Installation Wizard now resumes.
Follow the installation instructions to install DaqLink on
your computer. Once the installation process is completed
click Finish.
9. The DaqLink software and components have now been
installed. Double click the DaqLink shortcut on your
desktop to launch the software.
10. Connect the DaqLink data logger to a USB port on your
computer. It will automatically detect the logger as new
hardware. After a few seconds you will see a message
41
Page 51

stating that the device is ready for use. You may now
begin to configure your DaqLink units.
4.1.3. Installation Troubleshooting
When connected to the PC USB port the logger was not
detected by the software.
Ensure that the USB driver was installed properly.
Go to Control Panel > Add/Remove Programs (in WinXP),
and check that the driver is installed:
If not, you should run the Silicon Labs setup file to install the
USB driver: CP210x_VCP_Win2K_XP_S2K3.exe setup.exe to
install the driver.
If the driver is installed, ensure that there is no other device
sharing the USB com port with the DaqLink data logger.
If you didn’t select the Launch CP210x VCP Driver Installer
checkbox during step 2 of the driver installation wizard (see
section
again and be sure to select the checkbox.
4.1.2), then the driver wasn’t installed. Run the wizard
4.2. DaqLink Software Layout
This section provides an overview of the default DaqLink
window view as well as a guide to all of the icons available
throughout the software.
The most commonly used tools and commands are displayed
on two toolbars. Tools that relate to all aspects of the program
42
Page 52

are located in the main (upper) toolbar. Tools specific to the
graphs are located on the graph (lower) toolbar.
Refer to section
4.2.5 for a description of these toolbars
4.2.1. Map View
When DaqLink is first launched, the default window that is
opened is the Map View (see screenshot below).
You can also switch to Map View at any time by clicking the
Map View button
This view is used to monitor the location of all of the data
loggers deployed as well as the data recorded by each sensor
input when working in Online mode.
Icons are used to represent each of the DaqLink units, and
using the mouse the user can select specific actions to be
performed on the unit.
Figure 18: Main window - Map View
Refer to section
in the main toolbar.
4.10 for more details on working in Map View.
43
Page 53

4.2.2. Viewing Sensor Data in Map View
When the logger is in Run mode and connected to the
DaqLink software the sensor data is represented in individual
windows at the bottom of the Map View window. All sensors
which are currently online will be displayed in this view. If a
logger is currently offline then its data will not be visible.
Figure 19: Main window – Sensor Data in Map View
Sensor in Alarm
When the sensor data is in alarm, the color of the sensor
window will change according to the alarm type. There is a
legend in the lower right corner of the main window:
For example:
This screenshot indicates that the Internal Digital Temperature
reading is in High alarm, while the other sensors are reading
at normal levels.
Additional Features
• The sensor windows may be dragged and rearranged
anywhere on the lower pane.
44
Page 54

• Double clicking the sensor window will open the Data
Display window, where the real-time sensor data is
displayed in graph or table view.
4.2.3. History View
Clicking the History View button in the main toolbar will
switch the main window to view archived, offline data stored in
the DaqLink directory on the workstation.
You must first open the archived data file by clicking Open
File
will be displayed in the History View, otherwise, the History
View window will be blank.
Refer to section
64 for more details on opening files in History View.
Figure 20: Main window – History View
on the main toolbar. When you open the data file it
4.8: Viewing Archived (Offline) Data on page
45
Page 55

In History View, the user may view the data in graph or table
format by clicking the relevant tabs, as well as view a number
of Statistics taken from the data set.
To learn the functionality of the lower graph toolbar, refer to
section
4.2.5 below.
4.2.4. Data Map
The History View window also includes the Data Map pane,
on the left of the window.
The Data Map displays all data sets opened in History View,
saved in the current project file, and includes nodes for each
sensor in the data set.
Clicking the sensor label removes the data from the graph.
When the label is black, the data is not displayed on the
graph. The sensor data plot color is matched to the color of
the sensor label in the Data Map.
Each data set is preceded by a Logger icon
be expanded or collapsed to display the associated sensor
data.
Clicking the Tree icon
the Data Map pane altogether allowing a full screen graph
view.
in the lower graph toolbar removes
46
, which can
Page 56

Data Map
Figure 21: Data Map
4.2.5. DaqLink Toolbar Icons
This section outlines all of the toolbar icons available in the
software.
Main (Upper) Toolbar Icons
Figure 22: Main toolbar icons
The main toolbar is always available at the top of the DaqLink
application, no matter what window view the user is in.
This toolbar cannot be moved or hidden.
•
•
Open file - Opens archived logger data file
stored on the PC
Map view - Switches main window to Map
view, where the DaqLink units and sensor data
are represented
47
Page 57

•
History view - Switches main window to
History view, where archived logger data can
be viewed and analyzed
•
•
Setup - Launches logger Setup window
Run - When logger is in Stop mode, click Run
to start logging
•
Stop - When logger is in Run mode, click to
stop logging
•
•
Download – Downloads data from logger
Alarm mute/unmute - Mutes or unmutes an
audible alarm in the system when a sensor
reading has breached the user-defined alarm
level
•
Email Alarm Notifications - Configuration
window for Email alarm notifications
•
SMS Alarm Notifications - Configuration
window for SMS alarm notifications
•
GSM Modem - Indicates if GSM modem is
connected (green icon) or disconnected (grey
icon)
•
Temperature unit toggle - Display all data in
Celsius
•
Temperature unit toggle - Display all data in
Fahrenheit
Table 2: Main toolbar icon list
48
Page 58

Map View Icons
The following icons representing the various statuses of the
DaqLink units are viewed in Map View. Using these icons the
user is able to determine the status of the logger e.g. alarm,
power, and connection.
Alarm status is color-coded: Green = Normal ; Red = Alarm
•
Logger which has received its Setup but is in
Stop mode.
Running from internal battery supply.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Logger which has received its Setup but is in
Stop mode.
Running from external power supply.
Logger in Run mode and running on battery
supply.
Green indicates there are no alarms.
Logger in Run mode and running on external
power supply.
Green indicates there are no alarms.
Logger in Run mode with an alarm alert.
Running from internal battery supply.
Logger in Run mode with an alarm alert.
Running from external power supply.
Logger is offline and is no longer detected by
the computer. Its power supply may have failed
or the USB cable was disconnected.
Logger is processing a command sent from the
software.
49
Page 59

•
Table 3: Main toolbar icon list
Logger is downloading data.
Graph (Lower) Toolbar Icons
The graph toolbar is located at the bottom of the open graph
view, when the user is either in Online Data Display:
Or History View:
The toolbar cannot be moved or hidden.
•
Data Map (in History View only) – Hides or
shows the Data Map pane in the History View
window.
•
•
•
•
•
•
Plot Legend (in Display Data View only) –
Hides or shows the sensor labels from the
bottom of the graph.
Autoscale - Returns the data to its default
scale.
Zoom in – Zooms in on the graph data.
Pan graph – Pans the graph along the x or y
axis.
Select first cursor – Adds a cursor to the
designated plot on the graph
Select second cursor – Adds a second cursor
to the designated plot on the graph.
50
Page 60

•
•
Grid – Adds a grid to the graph background
Add Custom View (in History View only) –
adds the open, customized graph view to the
Data Map
•
•
•
•
Table 4: Lower graph toolbar icon list
Copy graph – Copies the graph to your
clipboard, to be copied to a document or
spreadsheet, for example.
Graph properties – Opens the Graph
Properties window.
Export to Excel – Export the open data sets to
Excel format.
Print – Opens the Print dialog. Available for
graph, table and statistics views.
Data Map Icons
•
•
•
•
•
•
Displayed internal Temperature sensor data
set
Hidden internal Temperature sensor data set
Displayed internal Humidity sensor data set
Hidden internal Humidity sensor data set
Displayed external sensor data set
Hidden internal sensor data set
51
Page 61

•
•
•
Displayed graph function
Hidden graph function
Parent node for all logger data sets. Click to
expand or collapse all child nodes.
•
•
•
Table 5: Data Map icons
Logger data set. Click to expand or collapse
the data set containing all measured inputs of
the specific logger.
Parent node for all custom graph views. Click
to expand or collapse all child nodes.
Displayed custom graph view. When hidden
the icon is grayed out.
4.3. File Menu Items
4.3.1. Open
Select Open to access archived data files for each logger you
have configured.
Shortcuts: You can also click the Open icon
Ctrl+O to open archived files.
4.3.2. Open Project File
Opens project files of offline data, containing data from one or
more loggers, as opposed to standard data files containing
data from only one logger.
or press
52
Page 62

4.3.3. Save Project
This feature lets the user save multiple data sets and custom
graph views into a single Project File. Only available in History
View.
4.3.4. Save Project As
Use this feature to save an existing Project file under a
different name.
4.3.5. Exit
Exits the DaqLink application.
4.4. Logger Menu Items
4.4.1. Display Data
Displays the logger’s data in Graph view. The graph displays
the data in real-time. There is also the option to display the
data in Table view or to view the data statistics.
4.4.2. Download Data
Downloads all data in the logger memory to the DaqLink
software. When logger is downloading the data, the Logger
icon in Map View will appear as follows:
53
Page 63

4.4.3. Cancel Download
When logger is downloading data you may cancel the
download per logger by selecting this menu item.
Note: This feature works only if there are no other commands
in the queue following the Download process.
4.4.4. Reset Alarm
When the logger is in a state of alarm, this option will reset the
alarm state to normal on both the logger and the software.
The visual and audible alarms will return to normal. If after
reset the logger is still in alarm conditions, then the visible and
audible alarms will return.
4.4.5. Calibration
Refer to section 4.12.4 on page 84 for an overview of the
Calibration feature.
Note: A logger can’t be calibrated while it is in Run mode.
The option will be grayed out. You must Stop the logger first.
5.2 on page 107 for an overview of how to update the logger
firmware.
4.4.6. Cancel Firmware Update
When a firmware update is in progress, select this option to
cancel the update and continue using the previous firmware
version.
54
Page 64

4.4.7. Setup
Refer to section 4.11 on page 72 for an overview of how to
setup the logger.
4.4.8. Stop
Sends a command to the logger to stop logging data.
4.4.9. Run
Sends a command to the logger to start logging data. This
command will also clear the existing logger memory.
4.4.10. Detect Logger
If the logger is not automatically detected when connected to
the computer via USB, use this option to detect the logger.
4.5. Tools Menu Items
4.5.1. Define Sensor
DaqLink enables the user to define custom sensors. This is a
useful tool for when the data logger is communicating with
many sensor types from different vendors.
Any additional sensor that you would like to connect to the
logger must comply with the following restrictions:
The sensor’s output must be either voltage in the range of 0 to
1 V, 0 to 50 mV, current in the range of 4 to 20 mA or Pulse in
the range of 0 to 65535 pulses.
55
Page 65

1. Click Tools > Define New Sensor and the Define New
Sensor dialog will open.
Figure 23: Define New Sensor dialog
2. Click Add to enable the fields.
3. Select the Base sensor from the drop-down menu
(depending on whether your sensor’s output is 0 to 1
V, 0 to 50 mV, 4 to 20mA, or measuring pulses).
4. Enter the sensor name and sensor unit.
5. Enter two calibration values (two real values and the
corresponding output values of the sensor).
6. Click Close.
56
Page 66

To use the custom defined sensor:
1. Enter the Setup dialog for the data logger you want to
configure.
2. Select the Input you wish to use and from the Sensor
Type drop-down menu, select the custom sensor, which
now appears in this list.
3. Proceed with the setup as you would normally do.
4.5.2. Lock Map View
While in Map View, with Lock Map View selected the Map
View icons are in a fixed position and can’t be moved. You
must unselect this option in order to freely move the icons
anywhere on the screen. This is essential if working with a
custom background image.
4.5.3. Options Menu
Refer to section 4.6 for more details.
4.5.4. Email Alarm Notifications
The Email Alarm Notifications dialog is where the user can
configure all notifications to be sent via Email to a predefined
contact list. Refer to section
4.12 for details.
4.5.5. SMS Alarm Notifications
The SMS Alarm Notifications dialog is where the user can
configure all notifications to be sent via SMS to a predefined
contact list. Refer to section
4.12 for details.
57
Page 67

4.6. Tools > Options Menu Items
The Options dialog is divided into three main tabs:
• Preferences
• Email Settings
• SMS Settings
4.6.1. Preferences Tab
Figure 24: Options > Preferences tab
58
Page 68

The Preferences tab includes the following options:
Minimize application to system tray
When this checkbox is selected, the DaqLink icon
will
appear in the computer’s system tray in the lower right of the
screen when the application is minimized. Simply double-click
the icon to maximize the application to full screen.
Run application on Windows startup
Select this checkbox to have the DaqLink application launch
together with Windows start-up.
Map View background
Use this option to toggle between Stretch and Center views
for the background image used in Map View.
Set decimal places for…
For each DaqLink sensor, internal or external, you may select
between 0 and 6 decimal places to be used when displaying
the data in the software.
Date format
Choose between four date formats to be used throughout the
software when displaying data e.g. in the Graph display.
Ignore regional settings when exporting to CSV
Selecting this option will ensure that data will be corrected
exported to a CSV file and will not use any custom regional
settings in the Windows OS which might adversely affect the
layout of the data in the CSV file.
59
Page 69

Path for application data files
The default path for saving all data recorded by the data
loggers is:
C:\Program Files\Fourier Systems\DaqLink\DaqLink data files\
Click Browse to change the path e.g. to a network path.
Save text data files
Select this checkbox if you would like DaqLink to also save
the logger data to a text file. The default path is: C:\Program
Files\Fourier Systems\DaqLink\DaqLink data text files\ and
clicking Browse will let you change this path.
Enable automatic data download when DaqLink is
launched
Select this checkbox if you want to have automatic download
of data when the DaqLink software is launched. If a DaqLink
logger is connected to the PC during software launch then
data will be automatically downloaded.
4.6.2. Email Settings Tab
DaqLink’s alarm notification feature enables sending of Emails
to notify the user of any alarm in the system. This feature will
only work when the DaqLink is working in Online mode.
First select the Send Email notifications check box. Fill in
the fields accordingly so that DaqLink will be able to send
Emails to predefined Email contacts when your loggers have
breached certain alarm levels.
Make sure to enter the field correctly e.g. with no extra spaces
or typos.
60
Page 70

Refer to section
and to section
notifications.
Note: DaqLink supports SMTP and MIME encoding, and
POP3 mail protocols.
4.11.2 for setting Alarm levels on the logger
4.12 for managing the Email alarm
Figure 25: Options > Email Settings tab
4.6.3. SMS Settings Tab
DaqLink’s alarm notification feature enables sending of SMS’s
to notify the user of any alarm in the system. This feature will
only work when the DaqLink is working in Online mode.
First select the Send SMS notifications check box. Using the
SMS feature requires connection of a GSM modem and SIM
card to the DaqLink PC, or even just a cellular phone with an
active SIM card.
61
Page 71

You must select the COM port which the GSM modem/cellular
phone is connected to in order for the software to detect it.
Note: When using a cellular phone as a modem, ensure that
the PC software suite is disabled before connecting the phone
to the PC com port. Otherwise the com port will not be
available for the DaqLink software.
Once the configuration is complete, DaqLink will be able to
send SMS’s to predefined SMS contacts when your logger
have breached certain alarm levels.
Refer to section
and to section
4.11.2 for setting Alarm levels on the logger
4.12 for managing the SMS alarm notifications.
Figure 26: Options > SMS Settings tab
Note: Once the GSM modem is online you will see the green
GSM icon appear in the DaqLink upper toolbar.
62
Page 72

4.6.4. Analysis Menu Items
The Analysis menu items are enabled when viewing offline
data in History View.
The Analysis options available are:
• Functions Parameters
• Dew Point
• FO Pasteurization
• Histogram
• Export to Excel
• Export to CSV
Export to Excel
You may export offline data to Excel by selecting this menu
item or by clicking the Export to Excel icon
graph toolbar in History View. The data is opened in an Excel
worksheet and includes pertinent information such as logger
name, SN, sensor names, alarm levels as well as the actual
data readings.
Refer to section
4.15 for more information.
in the lower
Export to CSV
You may export offline data to CSV file format by selecting
this menu item. Upon selecting this option, you will be
prompted to save the file either in the default DaqLink
directory or in directory of your choosing. The data is opened
in CSV file format and includes pertinent information such as
logger name, SN, sensor names, alarm levels as well as the
actual data readings.
Refer to section
4.15 for more information.
63
Page 73

4.7. Saving Data
As soon as a logger starts to record data the software creates
a data file to which it writes the logger data.
Logger data files are stored in the following default location:
C:\Program Files\Fourier Systems\DaqLink\DaqLink data files
A folder is created for each data logger and is named
according to the logger Serial Number. In this folder is stored
the data files. A file is created for each day that the logger is
recording data. The file name format is the date followed by
the file extension e.g. 2007-12-30.dat.
The data is saved automatically by the software. There is no
need for the user to save the data manually. The data is
saved to the data file as follows:
• Every 15 minutes
• When the software is closed
• When the user opens an archived data file, the file is
updated with all data not saved to that point
You can also save the data in a text file format. Refer to
section
4.6.1 for more details.
4.8. Viewing Archived (Offline) Data
The user can view the logger data online or can choose to
open archived data. Archived data is all data that was logged
by a specific logger and recorded by the software into the
DaqLink directory on the PC.
64
Page 74

Follow the instructions below to open archived data.
1. Click the Open icon to launch the Open Data Files
dialog.
2. Select the logger from the list of loggers in the dialog. You
can sort according to logger S/N or Comment.
3. Using the calendar define the date and time period for
which you wish to view your data and click OK. Days for
which data exists appear in bold.
Figure 27: Open Data Files dialog
4. In the Sync Data dialog, you can select the sampling rate
at which you wish to display the data. The default option
is the original rate. Click OK.
65
Page 75

Figure 28: Sync Data dialog
The data is opened in History View. Refer to section
an explanation of the History View.
You may display data sets from more than one logger and
display them all in History View, using the Data Map to
navigate through the data. Refer to section
details regarding the Data Map.
4.2.4 for more
4.2.1 for
4.9. Viewing Online Data
When the logger is connected to the PC and detected by the
DaqLink software you can view its data online in real-time, as
it is being recorded and transmitted to the PC.
• While the logger is running double click the Logger icon
in the Map View.
• While the logger is running open the logger context menu
and select Display Data.
66
Page 76

Figure 29: Online data window
The data displayed in this window is the data that was
transmitted by the logger in the current software session. Data
transmitted during a previous session of the software being
open will not be displayed. For example, when you setup the
logger it creates a new online session. This data can be
viewed by opening archived data. Refer to section
4.8.
You may view the data in a graph or table by clicking the
relevant tabs in the online data window. While in either or
these views, the data is constantly being updated in real-time
in the respective view according to the sampling rate of the
logger.
67
Page 77

4.9.1. Showing/Hiding the Data Sets
In the online graph display, where you have data from only
one logger displayed, you can show or hide the individual
sensor data by using the sensor labels at the bottom of the
graph.
In the screenshot above you can see two labels, Internal
Digital Temperature and Int RH. At present, each label is
active meaning the sensor data corresponding to the label is
shown on the graph.
By clicking any of the sensor labels, you can hide the data
from the graph. The label will then be grayed out. See the
screenshot below:
68
Page 78

Note: You can hide all of the sensor labels (not plots) from the
graph by clicking the Plot Legend icon .
4.10. Working in Map View
The Map View is the main view from which you monitor your
loggers.
Refer to section
and section
4.10.1. Loading Map View Wallpaper
You can load an image file representing a map of your facility
in which the loggers are deployed. You can then move the
unit icons into their actual positions on the map.
• Double-click on the Map View background to go
straight into the Open dialog and locate the image file.
• Right-click on the Map View background to open the
Wallpaper dialog and have the option to either Load or
Reset the wallpaper.
4.2.1 for a quick overview of the Map View
4.2.5 for a list of all the Map View icons.
Note: When deploying the system for the first time it is highly
recommended to use a map of the facility to make the
deployment work efficiently.
4.10.2. Moving Icons around the Screen
Go to Tools > Lock Map View and ensure this menu item is
not selected in order to freely move the unit icons around the
screen. When you have finished placing the icons into
69
Page 79

position you may then lock the Map View so as not to
mistakenly place an icon out of position.
4.10.3. Logger Icon Context Menu
Right clicking the Logger icon will give the following options,
which also appear in the Logger main menu and are detailed
in section ?:
• Display Data
• Download Data
• Cancel Download
• Reset Alarm
• Calibration
• Update Firmware
• Cancel Firmware Update
• Setup
• Stop
• Run
The Remove option only appears in the Logger icon context
menu, and only when the logger is offline. Selecting Remove
will simply remove the logger icon from the Map View.
4.10.4. Viewing Logger Status
When you scroll the mouse cursor over the Logger icon a
tooltip will pop up displaying data relevant to the Logger status
at the time.
70
Page 80

Logger Tooltip
The tooltip will always display the following data, even if
offline:
• Model type
• Serial Number
• Logger Name/Comment
When the logger is online and running the following tooltip is
displayed:
In online mode, the logger also displays:
• Power status (% Battery left or Connected to AC)
• Version number: Firmware version of the logger
• Last sample time: If logger is running, time stamp of last
recorded sample.
• Real-time Sensor values: All sensor values are displayed,
including sensor name and alarm status.
Command Queue Progress
The tooltip is updated with specific commands being
performed by the logger. For example, if the logger is
downloading data to the software you can see the progress in
the tooltip. In addition, the Logger icon has a blue progress
71
Page 81

indicator so you can monitor the progress without using the
tooltip.
Common commands include Download, Setup, Stop, and
Run.
4.11. Configuring the Logger
DaqLink software allows you to configure each logger when
connected to the workstation.
Also refer to section
To configure the logger once it’s detected by the DaqLink
software, right-click the Logger icon in the Map View and
select Setup or go to Logger > Setup from the main menu.
You have two tabs, Device Setup tab and Alarm Setup.
The main logger configuration is performed on the Device
Setup tab. Any alarm levels you wish to configure is
performed on the Alarm Setup tab.
2.6 on how to configure the logger.
4.11.1. Device Setup Tab
Comment
This is the name of the logger. It is advisable to name the
logger according to the location in the facility.
Note: The Comment field in the software and on the logger
display supports all standard alphanumeric characters except
for the following: ', ", ~, &, \
72
Page 82

Sampling Rate
Sampling rate is one sample per second to one sample per 18
hours. However, there are programming limitations you must
be aware of when configuring the loggers. The sampling rate
will vary depending on the number and type of sensors you
setup. Refer to section
3.3.5 on page 22.
Memory State
From the drop-down menu you have the following options:
• Online Mode: For working with logger connected to PC.
Data will be transmitted in real-time i.e. at the same time
as the sampling rate.
• Optimized Memory Mode: For working with the logger
as a standalone device, not connected to the PC. In this
mode, the memory is more efficiently managed as the
data does not need to be transmitted together with the
sampling rate. Use the Transmissions interval
parameter in the Setup window to see the rate at which
the data will be displayed on the logger or in the software.
Note: If used when connected to the PC, the data will not
be transmitted in real-time.
Cyclic Mode
If this checkbox is not selected, the logger will stop recording
data when the memory capacity is filled.
Enabling Cyclic mode will result in the oldest samples in the
memory being overwritten by new samples once the memory
is full. This allows continuous data logging.
73
Page 83

Averaging Points
You can choose have online averaging of up to 10 points
around the real value in order to smooth the data readings, if
they are a little noisy. The recommended averaging is 4
samples.
Note: If configuring Alarm duration with averaging points
selected, the alarm will be counted from the time of the last
sampling point used to calculate the average.
Temperature Units
Toggle between °C and °F. This applies to the readings
displayed on the logger LCD as well as in the software.
Anti Tamper Mode
To prevent tampering with the DaqLink logger, selecting this
option will disable the following features on the logger menu:
• Pause
• Reset
• Stop and turn off unit
Active Sensors
Depending on the logger model, you can activate up to two
internal sensors and four external sensors. Simply select the
inputs you want to use and then select the sensor types from
the adjacent drop-down menu. You don’t have to select the
external sensor input in any order. You may select only Input
4 if you desire.
Note: On the DBSA720 you cannot run the humidity sensor
without running the temperature sensor in parallel.
74
Page 84

This is because when using the DBSA720 data logger and
selecting the internal humidity sensor in the Device Setup
dialog, the internal digital temperature sensor will
automatically be selected as well. This sensor provides the
temperature compensation necessary for the humidity sensor
to reach the 3% accuracy as stated in the sensor
specifications. It is not used for recording temperature. The
internal digital sensor is used to record temperature on the
DBSA720.
Custom Sensor Names
You can also give the sensor a custom name, which will
appear in the software when viewing the data. This is
convenient when using several of the same type of sensors
and you wish to differentiate between them in terms of their
environment or material it is measuring.
Recording Time
This field displays the length of time the logger memory will be
able to record for depending upon the number of sensors
used and sampling rate.
Setup and Run
Clicking Setup and Run will send the setup to the logger and
immediately start logging data.
Setup Only
Clicking Setup Only will send the setup to the logger but it will
not actually start logging data. You will need to select Run
from the Logger context menu or go back into the Setup
dialog.
75
Page 85

Close
Clicking Close will close the Setup dialog without saving any
of your configurations.
Note: Running the logger clears the logger memory. All
previously recorded data will be erased when you begin a new
logging session.
4.11.2. Alarm Setup Tab
A major feature of the DaqLink system is the ability to
configure alarm levels into the loggers so any breach of these
levels as recorded on the data logger is monitored by the
software, and the user is notified via Email/SMS/audible and
visual indicators.
The Alarm Setup tab lets you configure each sensor for the
following alarms:
• Low
• Pre-Low
• Pre-High
• High
• Contact Open / Contact Close (when the Contact sensor
is selected)
Using the Pre Alarms gives the user ample warning of a
possible breach of real alarm levels, so necessary measures
can be taken to prevent such a breach.
Simply select the check box for the type of alarm you wish to
be notified. You can select all alarms too. Enter the alarm
value in the text box.
76
Page 86

Figure 30: Alarm Setup tab
Alarm Delay and Pre-alarm Delay
The time until the alarm (or pre-alarm) is activated. You may
not want to have the alarm sound immediately after the alarm
level is breached as you are only interested in a condition
where the alarm level lasted a certain amount of time.
For example, if monitoring change of temperature in a freezer,
you would only be interested in a High alarm which lasted
more than one minute as anything else could just be caused
by the freezer door opening for a few seconds, as opposed to
a power failure leading to rise in temperature.
77
Page 87

Alarm Duration
The duration of the alarm that is set off by one or more
sensors breaching the alarm level.
Note: Ensure Averaging is set to zero when enabling the
Alarm Duration feature.
Sound Alarm during Pre-alarm
You also have the option to sound the alarm in the software
during a pre-alarm scenario, not just for a standard alarm.
Once you have configured your alarms, you may return to the
Device Setup tab or click one of the Setup buttons at the
bottom of the tab.
4.12. Alarm Notifications Setup
Once you have completed the logger alarm setup in section
4.11.2 above, you can now configure DaqLink to send alarm
notifications via Email or SMS.
From the Tools menu select one of the following options,
depending on the type of notifications required:
• Email Alarm Notification
• SMS Alarm Notification
Or click the Email
toolbar in order to launch the notification dialog.
Note: To enable sending of Email or SMS first define the
Email and SMS settings in the Tools > Options dialog.
Connect a GSM modem to the PC if sending SMS’s. Refer to
section 4.6 on page 58 for more details.
or SMS icons located in the upper
78
Page 88

The Alarm Notifications dialog also lets you manage your
contact list of alarm notification recipients.
Figure 31: Alarm Notifications Setup dialog
As the Email and SMS Alarm Notifications must be defined
separately, they each have separate dialogs. However the
interface is identical and the contacts are stored in the same
database.
The Email/SMS Notifications dialog is divided into the
following tabs:
• Notifications Setup
• Contacts tab
• Groups tab
79
Page 89

4.12.1. Contacts Tab
The first step is to create the contacts who shall be receiving
the notifications. The ability to manage contacts is possible
from both the Email and SMS Notifications dialogs.
1. Click the Contacts tab and then click Add Contact.
Figure 32: Adding a contact
2. In this dialog you must first enter the contact name in the
Name field. That is the only mandatory field but if you
don’t enter at least the phone number or Email then they
won’t receive any alarm notifications.
The other fields in the dialog are as follows:
Title: Corporate position
Phone number: The number the DaqLink software
will use to send the SMS notification.
80
Page 90

Note: The phone number field supports the following
characters: 0-9, # , *, -, ( ), +
Email: The address the DaqLink software will use to
send the Email notification.
Workday Start and End: You can define the hours in
which the contact will be eligible to receive the
notifications i.e. so they don’t receive SMS or Email
while in the office, or vice versa.
Vacation: You can define when the contact is on
vacation so they won’t receive any notifications over
this period.
Number of SMS resends: The number of times
DaqLink will send follow-up SMS’s with the alarm
notification. The maximum is nine resends per alarm.
The gap between each resend is five minutes.
Note: In order to stop receiving SMS resends, you can
simply send an SMS with ‘OK’ in the message body to
the GSM SIM card’s phone number.
3. When the contact details have been entered, click OK.
4. The contact will be added to the Contacts tab. You may
choose to add another contact, edit an existing contact or
remove a contact from the list.
4.12.2. Groups Tab
1. Click the Groups tab and then click Add Group. The
Group Details dialog will open.
81
Page 91

Figure 33: Adding a group
2. Enter a Group name and add your existing contacts to the
group by selecting the checkbox next to the Contact
name.
3. Click OK to create the Group. In the Groups tab you may
choose to add a group, edit an existing group or remove a
group from the list.
4.12.3. Notifications Setup Tab
1. Once the contacts have been created you may start
defining which contacts should receive the alarm
notifications.
2. The pane on the left-hand side of the Notifications Setup
tab displays all loggers, which have been configured in
your facility. You must define the alarm notifications for
each unit in turn. Select the first unit you wish to define.
3. The Email or SMS tab is now active for the unit selected
in step 1 above. In this tab, select the type of alarm for
82
Page 92

which the notification should be sent in the event that the
predefined alarm level is breached.
4. Only the sensors which were configured in the logger
Setup, with alarms levels, are enabled in this tab.
5. Select the checkboxes according to the type of sensor
alarm for which notifications should be sent.
You may also select a Normalized alarm. A notification
will be sent when the logger returns to normal levels
having previously been in alarm state.
6. Click the Contact button adjacent to each of the sensors
which have defined alarms. In the Select Contact dialog,
select the contact and/or group that will receive the
notification.
7. You can also click Check All to select all the sensor
alarms for notification.
Note: In Optimized Memory Mode, when the logger
transmission rate is slower than the sampling rate, an
alarm notification is still sent even if the logger
transmission time hasn’t passed. For example, if the
sampling rate is every 5 minutes, and the transmission
rate is every 10 minutes, if a logger reaches a high alarm
after 7 minutes a notification will be sent. The system
won’t wait until the scheduled transmission time.
83
Page 93

4.12.4. Email and SMS Notification Formats
Email Notification Format
When the Email notification is sent the recipient receives the
Email in the following format:
Email Header:
DaqLink Alarm Internal Temperature (Last recorded 25.47C)
Low Alarm
Email Body:
DaqLink Alarm
Comment: Factory 1/F
S/N: 808932
08-07-09 13:53:41
Internal Temperature Low Alarm
Last recorded 25.47 C
The Email header contains the sensor type, last recorded
sample, and alarm type.
In addition the Email body contains the logger comment, serial
number, time stamp of last sample and value of last sample.
SMS Notification Format
When the SMS notification is sent the recipient receives the
SMS in the following format. (The logger comment is
displayed in the first row).
Factory 1/F
Sensor: Internal Digital Temperature – High
Alarm last recorded 29.59 C
84
Page 94

4.13. Calibration
The DaqLink data loggers are shipped fully calibrated with a
calibration certificate. However, DaqLink does provide a
simple and efficient process for users wishing to calibrate the
DaqLink data loggers themselves. The process itself can be
performed when the logger is connected to the PC via USB. A
calibrator or other type of calibration instrument is necessary.
The Calibration options are accessible via the Logger context
menu in the Map View (right-clicking the Logger icon).
Before performing logger calibration, the logger must be in
Stop mode. In addition, all of the calibration options are
accessible with a password making it difficult for nonauthorized users of the system to tamper with the loggers’
calibration settings.
Note: The default password is 1234. The password can be
changed in the password dialog box.
The Calibration option menu options are:
• Calibration: Opens the main Calibration dialog
• Save Calibration: Saves the logger’s current calibration
settings
• Load Calibration: Loads a logger’s previously saved
calibration settings.
• Reset Calibration: Resets the logger’s calibration
settings so that the raw hardware data is obtained,
without any software calibration applied to these values.
• Restore Factory Calibration Default: Restores the
logger’s calibration settings to the factory calibration i.e.
85
Page 95

the calibration settings it received prior to shipment from
Fourier.
4.13.1. Introduction to DaqLink Calibration
Although the DaqLink data loggers come fully calibrated, the
software enables you to calibrate any of the DaqLink sensors,
on any input. The calibration parameters are sent to the data
logger and stored in its memory.
DaqLink employs two different calibration methods: Two-
point calibration and Offset calibration.
Each sensor can be calibrated using the Two-point calibration
method, and then tweaked using offset calibration, except for
the Thermocouples. These sensors require offset calibration
only.
Sensor Type Calibration
Method
Current 4 – 20 mA
Humidity (Internal) Digital
Temperature
(Internal)
Temperature
(Internal)
Temperature PT-100 2-wire
Temperature Thermocouple J Offset calibration
Digital
PT-100
Two-point
calibration
Two-point
calibration
Two-point
calibration
Two-point
calibration and
offset
Two-point
calibration and
offset
86
Page 96

Temperature Thermocouple K Offset calibration
Temperature Thermocouple T Offset calibration
Voltage 0 to 1 V
Voltage 0 to 50 mV
Two-point
calibration
Two-point
calibration
Calibration Tips
Prior to any two-point calibration it is recommended to restore
factory calibration defaults.
Prior to calibrating any of the thermocouple sensor types,
calibrate the Voltage 50 mV sensor as this will set the gain
(slope) of all thermocouple sensor types.
After calibrating 50 mV, TC-J, TC-K or TC-T sensor types for
all inputs you can refine the offset calibration for each input
individually.
You may calibrate all thermocouple sensor types at once, or
individually.
Prior to calibrating the PT-100 input, you must first perform
Reset Calibration in the Calibration dialog.
Two-point Calibration
The two-point calibration sets the gain (slope) and offset
(intercept) of the sensor's conversion function.
Use the two-point calibration to calibrate all DaqLink sensors
except for the Thermocouples. In some cases you may need
to refine your calibration using the fine offset tuning tool.
87
Page 97

Offset Calibration
To calibrate the Thermocouple temperature sensors: TC-J,
TC-K and TC-T, first calibrate the 50 mV sensor type. That will
set the slope for all Thermocouple temperature sensors. Then
proceed to adjust the offset using the Offset calibration
technique.
4.13.2. Calibrating the Data Logger
Figure 34: Calibration dialog
1. From the Map View, open the Logger context menu and
select Stop.
2. Select Calibration > Calibrate and enter the password in
the Password dialog.
88
Page 98

3. Select the sensor you wish to calibrate from the Sensor
drop-down menu.
4. If calibrating an external sensor, select the inputs to
calibrate. Select All or an individual input, 1 to 4.
5. Click Setup to send the sensor setup to the logger.
Note: The calibration process does not delete the logger’s
setup prior to calibration. Once Calibration is complete the
original logger setup will be restored.
6. If you selected All inputs, then by default the logger will
be setup to log data on Input 1 during the calibration
process. Otherwise, if you selected a specific input, it will
setup the logger to calibrate on that input.
Logger Data Pane
The Logger Data pane displays real-time readings on the
logger, at a default sampling rate of one per second. You can
also view the logger’s general status. Use the Logger Data
pane to verify your logger is properly calibrated.
The Calibration dialog will enable either Two-point or Offset
calibration, or both, depending on the sensor selected.
Note: The calibrated sensor parameters will be saved both in
the DaqLink logger and in the software memory, so there is no
need to calibrate the logger every time you run the software.
4.13.3. Performing a Two-point Calibration
To perform a two-point calibration, you must have two
reference points to input against the real logger sensor
values.
89
Page 99

Figure 35: Two-point calibration window
1. In the Point #1 field, enter the first Reference Value and
the corresponding Logger Value.
2. In the Point #2 field, enter the second Reference Value
and the corresponding Logger Value.
Note: If you are using a calibrator and the logger is currently
displaying the real value to be calibrated, press the Copy
button to copy the real value to the Logger Value text box.
3. Press Send Calibration to send these values to the
logger memory.
4. Compare the real value in the Logger Data pane to the
reference value. If the values are within an acceptable
margin of error you may close the Calibration window, or
move on to the next sensor or input.
5. If the values are still not accurate enough, you can
perform Offset calibration to tweak with values further.
Note: Fourier strongly recommends calibrating using the
default Reference values that appear in the two Reference
value text boxes for each sensor.
90
Page 100

4.13.4. Performing an Offset Calibration
If, after the Two-point calibration procedure, the logger still
exhibits some offset value use the Offset calibration tool to
correct it.
The offset value is the difference between the value displayed
by the DaqLink logger and the reference value. For example if
the calibrator is set to 0 °C and the logger reads 1 °C the
offset value is +1, but if the logger reads −1 °C then the offset
value is −1.
To perform an Offset calibration, simply select the Offset
calibration radio button to enable the Offset text box. For
Thermocouples you will only have the option to perform an
Offset calibration.
Enter the offset value in the text box and click Send
Calibration. Continue to adjust the offset accordingly until
satisfied with the readings.
4.13.5. Setting the Offset to a Specific Input
After setting the offset to all inputs simultaneously, you can
set the offset of each input separately for even better
accuracy.
To set the offset of a specific input:
1. Measure two known reference values making sure to use
the input you need to calibrate.
2. Enter the offset value as described in section
above, making sure to select the correct input number
instead of All.
91
4.13.4
 Loading...
Loading...