Page 1

No part of this handbook may be reproduced,
transcribed, translated into any language or transmitted
in any form whatsoever without the prior written
consent of Codan Pty Ltd.
© Copyright 1997 Codan Pty Ltd.
Codan part number 15-04076 Issue 1, 1997
No part of this handbook may be reproduced,
transcribed, translated into any language or transmitted
in any form whatsoever without the prior written
consent of Codan Pty Ltd.
© Copyright 1997 Codan Pty Ltd.
Codan part number 15-04076 Issue 1, 1997
Page 2

Page 3

HF SSB transceiver reference manual i
Contents
1 About this manual
2 Installation
Type of station....................................................................2-2
Mounting the transceiver .................................................... 2-5
Mounting the control head and loudspeaker........................2-8
Power supply..................................................................... 2-11
Grounding ........................................................................ 2-12
Ancillary equipment ......................................................... 2-13
3 Channel and scan table setup
Channel creation and editing .............................................. 3-2
Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode..................3-17
Channel deletion...............................................................3-21
Scan table creation............................................................ 3-22
Scan table deletion............................................................3-27
Telephone directory creation.............................................3-29
4 Using Setup mode procedures
Using Setup mode............................................................... 4-2
List of Setup mode procedures.............................................4-3
Advanced users...................................................................4-7
5 Setup procedures—part 1
ALE alphanumeric address setup........................................5-2
ALE option reset.................................................................5-4
HF SSB transceiver reference manual i
Contents
1 About this manual
2 Installation
Type of station....................................................................2-2
Mounting the transceiver .................................................... 2-5
Mounting the control head and loudspeaker........................2-8
Power supply..................................................................... 2-11
Grounding ........................................................................ 2-12
Ancillary equipment ......................................................... 2-13
3 Channel and scan table setup
Channel creation and editing .............................................. 3-2
Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode..................3-17
Channel deletion...............................................................3-21
Scan table creation............................................................ 3-22
Scan table deletion............................................................3-27
Telephone directory creation.............................................3-29
4 Using Setup mode procedures
Using Setup mode............................................................... 4-2
List of Setup mode procedures.............................................4-3
Advanced users...................................................................4-7
5 Setup procedures—part 1
ALE alphanumeric address setup........................................5-2
ALE option reset.................................................................5-4
Page 4

Contents
ii HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option settings ............................................................ 5-6
ALE sounding interval......................................................5-13
Beep loudness...................................................................5-15
Call preamble length......................................................... 5-17
Call privacy on/off ............................................................ 5-19
Clock calibration............................................................... 5-21
Clock setting..................................................................... 5-23
Clone a transceiver ...........................................................5-28
6 Setup procedures—part 2
Display brightness............................................................... 6-2
Display contrast..................................................................6-4
Display diagnostics on/off...................................................6-6
Display frequency ............................................................... 6-8
Emergency selcall receive setup ........................................ 6-11
Emergency selcall transmit setup ...................................... 6-15
Free-Tune Receiver mode availability on/off ..................... 6-19
GPS display on/off............................................................6-21
GPS timeout on/off ...........................................................6-23
7 Setup procedures—part 3
Page call canned message setup ..........................................7-2
Password entry to enable transceiver options....................... 7-5
Power up message on/off................................................... 7-10
Power up mute setting....................................................... 7-13
Power up address display on/off ........................................ 7-16
PTT release beep on/off..................................................... 7-18
PTT transmit cutout.......................................................... 7-20
Recall channels by frequency on/off .................................. 7-22
RF gain on/off................................................................... 7-24
RS-232 connected equipment............................................ 7-26
RS-232 connection baud rate............................................. 7-29
Contents
ii HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option settings ............................................................ 5-6
ALE sounding interval......................................................5-13
Beep loudness...................................................................5-15
Call preamble length......................................................... 5-17
Call privacy on/off ............................................................ 5-19
Clock calibration............................................................... 5-21
Clock setting..................................................................... 5-23
Clone a transceiver ...........................................................5-28
6 Setup procedures—part 2
Display brightness............................................................... 6-2
Display contrast..................................................................6-4
Display diagnostics on/off...................................................6-6
Display frequency ............................................................... 6-8
Emergency selcall receive setup ........................................ 6-11
Emergency selcall transmit setup ...................................... 6-15
Free-Tune Receiver mode availability on/off ..................... 6-19
GPS display on/off............................................................6-21
GPS timeout on/off ...........................................................6-23
7 Setup procedures—part 3
Page call canned message setup ..........................................7-2
Password entry to enable transceiver options....................... 7-5
Power up message on/off................................................... 7-10
Power up mute setting....................................................... 7-13
Power up address display on/off ........................................ 7-16
PTT release beep on/off..................................................... 7-18
PTT transmit cutout.......................................................... 7-20
Recall channels by frequency on/off .................................. 7-22
RF gain on/off................................................................... 7-24
RS-232 connected equipment............................................ 7-26
RS-232 connection baud rate............................................. 7-29
Page 5

Contents
HF SSB transceiver reference manual iii
8 Setup procedures—part 4
Scan table automatic scanning start..................................... 8-2
Scan table editing on/off .....................................................8-4
Selcall address setup ........................................................... 8-6
Selcall address size compatibility......................................8-13
Selcall lockout on/off ........................................................8-16
Selcall mute availability on/off.......................................... 8-18
Status call availability on/off............................................. 8-20
Telcall availability on/off .................................................. 8-22
Tone call setup.................................................................. 8-24
99-beacon call response on/off ..........................................8-27
9 Link Setup mode
Link Setup mode enter/exit ................................................. 9-2
Antenna band or channel control ........................................ 9-5
PIN setup............................................................................ 9-8
Setup mode availability on/off........................................... 9-11
Transceiver reset to factory settings................................... 9-13
10 Display messages
11 Appendix
Connectors........................................................................11-2
Connecting ancillary equipment........................................ 11-8
Using the optional RS-232/I2C Interface ......................... 11-10
Specifications.................................................................. 11-14
Accessories..................................................................... 11-15
Index
Contents
HF SSB transceiver reference manual iii
8 Setup procedures—part 4
Scan table automatic scanning start..................................... 8-2
Scan table editing on/off .....................................................8-4
Selcall address setup ........................................................... 8-6
Selcall address size compatibility......................................8-13
Selcall lockout on/off ........................................................8-16
Selcall mute availability on/off.......................................... 8-18
Status call availability on/off............................................. 8-20
Telcall availability on/off .................................................. 8-22
Tone call setup.................................................................. 8-24
99-beacon call response on/off ..........................................8-27
9 Link Setup mode
Link Setup mode enter/exit ................................................. 9-2
Antenna band or channel control ........................................ 9-5
PIN setup............................................................................ 9-8
Setup mode availability on/off........................................... 9-11
Transceiver reset to factory settings................................... 9-13
10 Display messages
11 Appendix
Connectors........................................................................11-2
Connecting ancillary equipment........................................ 11-8
Using the optional RS-232/I2C Interface ......................... 11-10
Specifications.................................................................. 11-14
Accessories..................................................................... 11-15
Index
Page 6

Contents
iv HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Figures
Figure 2.1 A typical fixed base station.............................. 2-2
Figure 2.2 A typical mobile station...................................2-3
Figure 2.3 Rear view of control head without cover..........2-8
Figure 4.1 The Setup mode tree........................................ 4-9
Figure 9.1 Moving the link for Link Setup mode .............. 9-2
Contents
iv HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Figures
Figure 2.1 A typical fixed base station.............................. 2-2
Figure 2.2 A typical mobile station...................................2-3
Figure 2.3 Rear view of control head without cover..........2-8
Figure 4.1 The Setup mode tree........................................ 4-9
Figure 9.1 Moving the link for Link Setup mode .............. 9-2
Page 7

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-1
1 About this manual
This manual describes how you set up your Codan HF SSB
transceiver.
This issue of the manual incorporates operating information
for software versions from:
• transceiver (main) 4.00
• head (control) panel 4.00.
You should refer to this manual when you want to:
• set up the transceiver for the first time
• change how the transceiver operates
• use options or ancillary equipment with the transceiver.
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-1
1 About this manual
This manual describes how you set up your Codan HF SSB
transceiver.
This issue of the manual incorporates operating information
for software versions from:
• transceiver (main) 4.00
• head (control) panel 4.00.
You should refer to this manual when you want to:
• set up the transceiver for the first time
• change how the transceiver operates
• use options or ancillary equipment with the transceiver.
Page 8

About this manual
1-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
The manual contains 11 chapters.
Chapter 1 explains how to use the manual.
Chapter 2 explains how to install your transceiver and
connect the components that make up your station.
Chapter 3 explains how to set up channels, scan tables and
the telephone directory.
Chapter 4 explains how to use Setup mode. You should read
this before following any Setup mode procedure described in
Chapters 5–8.
Chapters 5–8 contain the Setup mode procedures that have
been separated into four parts for ease of reference.
Chapter 9 contains Link Setup mode procedures.
Chapter 10 lists all information and error messages output to
the transceiver display.
Chapter 11 covers technical information such as the
connector pin arrangements, ancillary equipment settings,
transceiver specifications, options and accessories.
We recommend that only Codan approved service agents
perform maintenance on the transceiver.
About this manual
1-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
The manual contains 11 chapters.
Chapter 1 explains how to use the manual.
Chapter 2 explains how to install your transceiver and
connect the components that make up your station.
Chapter 3 explains how to set up channels, scan tables and
the telephone directory.
Chapter 4 explains how to use Setup mode. You should read
this before following any Setup mode procedure described in
Chapters 5–8.
Chapters 5–8 contain the Setup mode procedures that have
been separated into four parts for ease of reference.
Chapter 9 contains Link Setup mode procedures.
Chapter 10 lists all information and error messages output to
the transceiver display.
Chapter 11 covers technical information such as the
connector pin arrangements, ancillary equipment settings,
transceiver specifications, options and accessories.
We recommend that only Codan approved service agents
perform maintenance on the transceiver.
Page 9
About this manual
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-3
Standards and icons
In this manual, Arial typeface is used for text shown on the
transceiver display. For example:
If
no response
was displayed, send the call again.
Arial typeface in bold is used for the names of buttons, knobs
and connectors. For example:
Press the
On/Off
button.
This icon... Means...
the end of a subject.
a warning.
On/Off
the transceiver button or knob that
you need to operate (the
On/Off
button in this example). The solid
area in the picture of the control head
on the left shows you where to find
the button or knob.
Call
the microphone button that you need
to operate (the
Call
button in this
example). The solid area in the
picture of the microphone on the left
shows you where to find the button.
About this manual
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-3
Standards and icons
In this manual, Arial typeface is used for text shown on the
transceiver display. For example:
If
no response
was displayed, send the call again.
Arial typeface in bold is used for the names of buttons, knobs
and connectors. For example:
Press the
On/Off
button.
This icon... Means...
the end of a subject.
a warning.
On/Off
the transceiver button or knob that
you need to operate (the
On/Off
button in this example). The solid
area in the picture of the control head
on the left shows you where to find
the button or knob.
Call
the microphone button that you need
to operate (the
Call
button in this
example). The solid area in the
picture of the microphone on the left
shows you where to find the button.
Page 10

About this manual
1-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Glossary
This term... Means...
µV Microvolt.
BER Bit Error Rate.
A Ampere.
AC Alternating Current.
ALE Automatic Link Establishment.
AM Amplitude Modulation.
Baud Binary transfer rate.
Call memory a list containing details of the last ten
calls you have received.
CICS Computer Interface Command Set.
D Depth.
dB Decibel.
DC Direct Current.
EPROM
EEPROM
BBPROM
SEEPROM
types of Programmable Read-Only
Memory.
GPS Global Positioning System.
H Height.
HF High Frequency.
kg Kilogram.
kHz Kilohertz.
L/S Loudspeaker.
LCD Liquid Crystal Display.
LSB Lower Sideband.
LU Lower/Upper sideband selectable.
About this manual
1-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Glossary
This term... Means...
µV Microvolt.
BER Bit Error Rate.
A Ampere.
AC Alternating Current.
ALE Automatic Link Establishment.
AM Amplitude Modulation.
Baud Binary transfer rate.
Call memory a list containing details of the last ten
calls you have received.
CICS Computer Interface Command Set.
D Depth.
dB Decibel.
DC Direct Current.
EPROM
EEPROM
BBPROM
SEEPROM
types of Programmable Read-Only
Memory.
GPS Global Positioning System.
H Height.
HF High Frequency.
kg Kilogram.
kHz Kilohertz.
L/S Loudspeaker.
LCD Liquid Crystal Display.
LSB Lower Sideband.
LU Lower/Upper sideband selectable.
Page 11

About this manual
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-5
This term... Means...
MHz Megahertz.
mm Millimetre.
PA Power Amplifier.
PCB Printed Circuit Board.
PIN Personal Identification Number.
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network.
PTT button Press-To-Talk button.
RAM Random Access Memory.
RDD Radphone Direct Dial.
Receive-only
channel
a channel that allows you to receive calls
but not send calls.
Revertive signal an acknowledgment signal automatically
transmitted from a station receiving a
call.
RF Radio Frequency.
RFDS Royal Flying Doctor Service.
Rx Receive.
Scan table a list of channels used when scanning for
incoming calls.
Selcall the simplest type of selective call.
Selective call a call to a specific station using the
station’s address. Selective calls include
beacon calls, selcalls, group calls, telcalls,
GPS calls, page calls, ALE calls and
status calls.
SSB Single Sideband transmission format.
SWR Standing Wave Ratio.
About this manual
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 1-5
This term... Means...
MHz Megahertz.
mm Millimetre.
PA Power Amplifier.
PCB Printed Circuit Board.
PIN Personal Identification Number.
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network.
PTT button Press-To-Talk button.
RAM Random Access Memory.
RDD Radphone Direct Dial.
Receive-only
channel
a channel that allows you to receive calls
but not send calls.
Revertive signal an acknowledgment signal automatically
transmitted from a station receiving a
call.
RF Radio Frequency.
RFDS Royal Flying Doctor Service.
Rx Receive.
Scan table a list of channels used when scanning for
incoming calls.
Selcall the simplest type of selective call.
Selective call a call to a specific station using the
station’s address. Selective calls include
beacon calls, selcalls, group calls, telcalls,
GPS calls, page calls, ALE calls and
status calls.
SSB Single Sideband transmission format.
SWR Standing Wave Ratio.
Page 12

About this manual
1-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
This term... Means...
Transceiver ID a factory set 16-character alphanumeric
code that uniquely identifies your
transceiver.
Transmit channel a channel that allows you to receive and
send calls.
Two-frequency
simplex
a channel that has different transmit and
receive frequencies but does not allow
simultaneous transmit and receive.
Tx Transmit.
TXE Transmit Enabled—allows you to set up
new transmit frequencies.
USB Upper Sideband.
V Volt.
W Width.
Other documents
For information on how you use the transceiver to send and
receive calls, refer to the HF SSB transceiver user guide
(Codan part number 15-04073).
For information on the features fitted to your transceiver,
refer to the front of your HF SSB transceiver user guide for
the list of factory fitted transceiver options.
For information on ALE calling, refer to the 9300 ALE
controller user guide (Codan part number 15-04046).
For information on Telstra radiophone services within
Australia, refer to the Radphone Direct Dial User Guide and
Radphone User Guide produced by Telstra.
About this manual
1-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
This term... Means...
Transceiver ID a factory set 16-character alphanumeric
code that uniquely identifies your
transceiver.
Transmit channel a channel that allows you to receive and
send calls.
Two-frequency
simplex
a channel that has different transmit and
receive frequencies but does not allow
simultaneous transmit and receive.
Tx Transmit.
TXE Transmit Enabled—allows you to set up
new transmit frequencies.
USB Upper Sideband.
V Volt.
W Width.
Other documents
For information on how you use the transceiver to send and
receive calls, refer to the HF SSB transceiver user guide
(Codan part number 15-04073).
For information on the features fitted to your transceiver,
refer to the front of your HF SSB transceiver user guide for
the list of factory fitted transceiver options.
For information on ALE calling, refer to the 9300 ALE
controller user guide (Codan part number 15-04046).
For information on Telstra radiophone services within
Australia, refer to the Radphone Direct Dial User Guide and
Radphone User Guide produced by Telstra.
Page 13

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-1
2 Installation
This chapter describes how to install your transceiver and
connect the components that make up your station.
It covers:
• type of station (2-2)
• mounting the transceiver (2-5)
• mounting the control head and loudspeaker (2-8)
• power supply (2-11)
• grounding (2-12)
• ancillary equipment (2-13).
On receiving your transceiver, check the contents against the
packing list. Make sure that nothing is missing before
starting installation.
The procedures for installing your transceiver are not
comprehensive. They are to be used as a guide only. We
recommend that installation be carried out by qualified and
experienced personnel.
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-1
2 Installation
This chapter describes how to install your transceiver and
connect the components that make up your station.
It covers:
• type of station (2-2)
• mounting the transceiver (2-5)
• mounting the control head and loudspeaker (2-8)
• power supply (2-11)
• grounding (2-12)
• ancillary equipment (2-13).
On receiving your transceiver, check the contents against the
packing list. Make sure that nothing is missing before
starting installation.
The procedures for installing your transceiver are not
comprehensive. They are to be used as a guide only. We
recommend that installation be carried out by qualified and
experienced personnel.
Page 14

Installation
2-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Type of station
There are two versions of the transceiver. The front control
version has the controls on the front panel of the transceiver.
The extended control version has the controls on a separate
control head.
There are two types of station:
• fixed base station
• mobile station.
Fixed base station
A fixed base station typically consists of an AC power supply
connected directly to the mains. DC output from the power
supply is connected to the transceiver, which in turn is
connected to an antenna.
AC power supply
Coaxial cable
Broadband antenna
system
Microphone
Earth point
AC mains
Chan1 Chan
1
XXXX Power Supply
CODAN
On/Off
Select
Mode
Scan
Emgcy
Call
S'Call
Mute
Voice
Mute
On/Off Mode
Tune
USB/LSB
F2F1
Volume
93XX SSB Transceiver
CODAN
Front control
transceiver
Figure 2.1
A typical fixed base station
Installation
2-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Type of station
There are two versions of the transceiver. The front control
version has the controls on the front panel of the transceiver.
The extended control version has the controls on a separate
control head.
There are two types of station:
• fixed base station
• mobile station.
Fixed base station
A fixed base station typically consists of an AC power supply
connected directly to the mains. DC output from the power
supply is connected to the transceiver, which in turn is
connected to an antenna.
AC power supply
Coaxial cable
Broadband antenna
system
Microphone
Earth point
AC mains
Chan1 Chan
1
XXXX Power Supply
CODAN
On/Off
Select
Mode
Scan
Emgcy
Call
S'Call
Mute
Voice
Mute
On/Off Mode
Tune
USB/LSB
F2F1
Volume
93XX SSB Transceiver
CODAN
Front control
transceiver
Figure 2.1
A typical fixed base station
Page 15
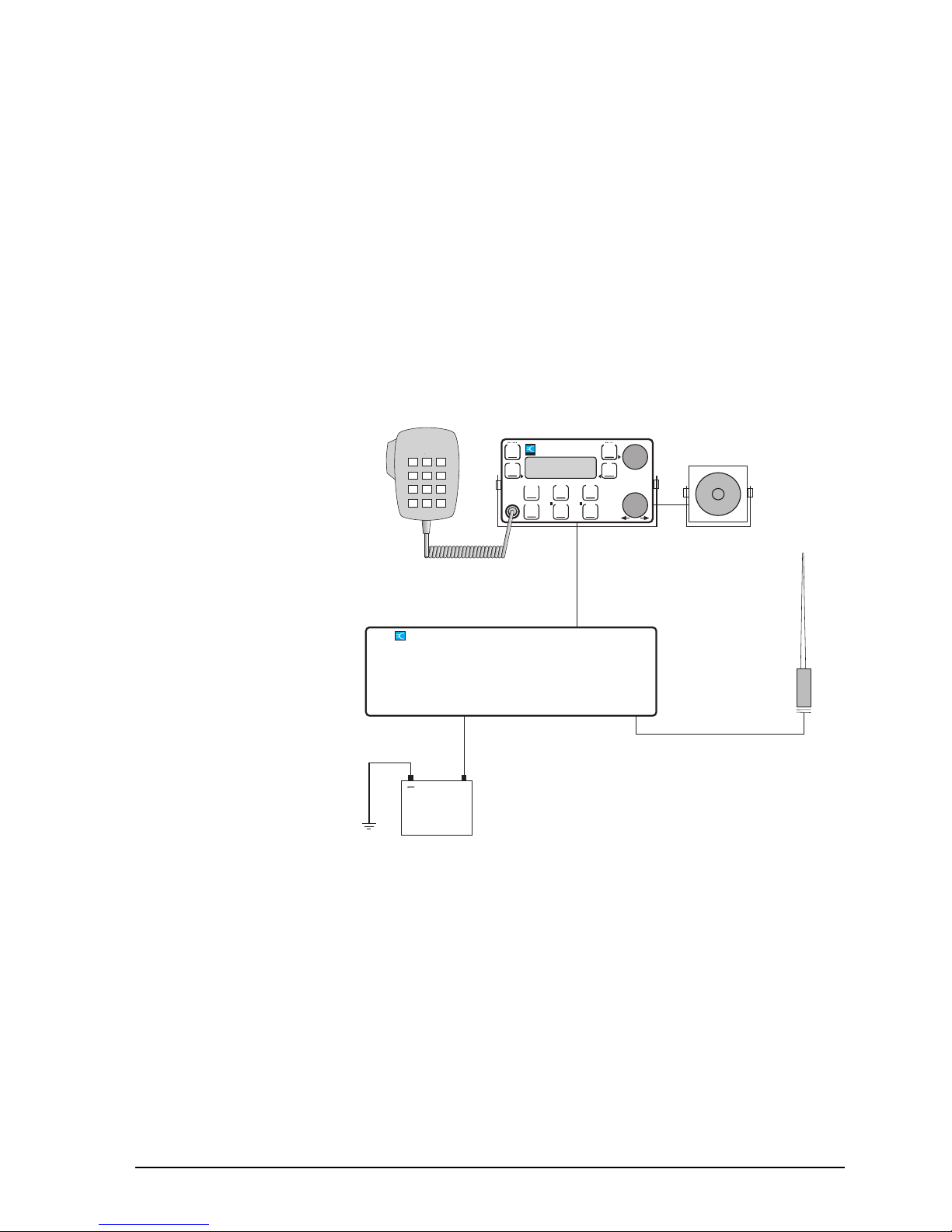
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-3
Mobile station
A mobile station typically consists of a 12V DC power
supply (battery) connected to the transceiver. A coaxial cable
connects the antenna to the transceiver. Automatic tuning
antennas are also connected to the transceiver by a control
cable.
The control head and microphone should be mounted in
such a way as to be easily accessible to the operator.
Coaxial and
control cable
Extended control
transceiver
Microphone
Control Head
Speaker
Automatic tuning
whip antenna
On/Off
CODAN
Select
Mode
Scan
Emgcy
Call
S'Call
Mute
Voice
Mute
On/Off Mode
Tune
USB/LSB
F2F1
Volume
HF SSB Transceiver
12V
Battery
+
Chan1 Chan
1
SSB Transceiver
CODAN
Figure 2.2
A typical mobile station
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-3
Mobile station
A mobile station typically consists of a 12V DC power
supply (battery) connected to the transceiver. A coaxial cable
connects the antenna to the transceiver. Automatic tuning
antennas are also connected to the transceiver by a control
cable.
The control head and microphone should be mounted in
such a way as to be easily accessible to the operator.
Coaxial and
control cable
Extended control
transceiver
Microphone
Control Head
Speaker
Automatic tuning
whip antenna
On/Off
CODAN
Select
Mode
Scan
Emgcy
Call
S'Call
Mute
Voice
Mute
On/Off Mode
Tune
USB/LSB
F2F1
Volume
HF SSB Transceiver
12V
Battery
+
Chan1 Chan
1
SSB Transceiver
CODAN
Figure 2.2
A typical mobile station
Page 16

Installation
2-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Where cables must pass through bulkheads with sharp edges,
the insulation of the cables should be protected by grommets.
Holes in the bulkhead need only be large enough to allow the
end of the cable with the smaller connector to pass through
(for example, the control cable between the control head and
the transceiver).
If the power and control cables are long and follow a
common path, keep the cables separated by a minimum
of 200mm. The cables can be closer together for short
distances, for example, to pass through the same hole in
the bulkhead.
Failure to observe this warning will cause distortion of
the transmitted audio signals.
Installation
2-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Where cables must pass through bulkheads with sharp edges,
the insulation of the cables should be protected by grommets.
Holes in the bulkhead need only be large enough to allow the
end of the cable with the smaller connector to pass through
(for example, the control cable between the control head and
the transceiver).
If the power and control cables are long and follow a
common path, keep the cables separated by a minimum
of 200mm. The cables can be closer together for short
distances, for example, to pass through the same hole in
the bulkhead.
Failure to observe this warning will cause distortion of
the transmitted audio signals.
Page 17

Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-5
Mounting the transceiver
The transceiver must be mounted in a position that:
•
allows easy access to the controls
•
allows a free flow of air through the rear cooling fins
•
is not exposed to direct sunlight
•
will not cause injury to occupants in the event of a
motor vehicle accident.
There are two types of mounting cradles that can be used
when installing your transceiver:
• code 117 mounting cradle—front entry
• code 118 mounting cradle—top/bottom entry.
Both types of cradle (supplied with six metres of DC power
cable) can be used to mount the transceiver. You must
determine the mounting position to best suit your needs.
Code 117 mounting cradle—front entry
This cradle is suitable for locations where there is enough
space available to slide the transceiver in and out.
To mount the cradle:
1. Secure the mounting cradle in position with the rotating
cam catches to the front. Ensure there is sufficient space
at the rear of the cradle to clear the transceiver heat sink
and connectors.
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-5
Mounting the transceiver
The transceiver must be mounted in a position that:
•
allows easy access to the controls
•
allows a free flow of air through the rear cooling fins
•
is not exposed to direct sunlight
•
will not cause injury to occupants in the event of a
motor vehicle accident.
There are two types of mounting cradles that can be used
when installing your transceiver:
• code 117 mounting cradle—front entry
• code 118 mounting cradle—top/bottom entry.
Both types of cradle (supplied with six metres of DC power
cable) can be used to mount the transceiver. You must
determine the mounting position to best suit your needs.
Code 117 mounting cradle—front entry
This cradle is suitable for locations where there is enough
space available to slide the transceiver in and out.
To mount the cradle:
1. Secure the mounting cradle in position with the rotating
cam catches to the front. Ensure there is sufficient space
at the rear of the cradle to clear the transceiver heat sink
and connectors.
Page 18

Installation
2-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
2. Align both cam catch slots with the T-section slides.
Cam catch
(Slot in line
with T slide)
Front section
3. Insert the transceiver side rails into the T-section slides
and push the transceiver fully into the cradle.
4. Apply gentle pressure to the front of the transceiver and
lock it into the cradle by using a flat blade screwdriver to
turn the cam catches one quarter of a turn in either
direction.
Code 118 mounting cradle—top/bottom entry
To mount the cradle:
1. Secure the mounting cradle into position with its spring
clips nearest the front. Ensure there is sufficient space at
the rear of the cradle to take the transceiver heat sink
and connectors.
2. Remove the front and rear fixing screws of the
transceiver side rails (the centre screw to be left
untouched).
Note that adaptor plates have to be fitted to the
transceiver side rails to secure the transceiver to the
cradle.
3. Secure the adaptor plates flush to the transceiver side
rails with the new screws provided, and fit one ‘O’ ring
over each projecting stud. The projecting studs on the
adaptor plates fit into the slides in the cradle.
Installation
2-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
2. Align both cam catch slots with the T-section slides.
Cam catch
(Slot in line
with T slide)
Front section
3. Insert the transceiver side rails into the T-section slides
and push the transceiver fully into the cradle.
4. Apply gentle pressure to the front of the transceiver and
lock it into the cradle by using a flat blade screwdriver to
turn the cam catches one quarter of a turn in either
direction.
Code 118 mounting cradle—top/bottom entry
To mount the cradle:
1. Secure the mounting cradle into position with its spring
clips nearest the front. Ensure there is sufficient space at
the rear of the cradle to take the transceiver heat sink
and connectors.
2. Remove the front and rear fixing screws of the
transceiver side rails (the centre screw to be left
untouched).
Note that adaptor plates have to be fitted to the
transceiver side rails to secure the transceiver to the
cradle.
3. Secure the adaptor plates flush to the transceiver side
rails with the new screws provided, and fit one ‘O’ ring
over each projecting stud. The projecting studs on the
adaptor plates fit into the slides in the cradle.
Page 19

Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-7
4. Insert the transceiver adaptor plates into the cradle slides
and push fully into the cradle.
5. Secure the transceiver into the cradle with the spring
clips.
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-7
4. Insert the transceiver adaptor plates into the cradle slides
and push fully into the cradle.
5. Secure the transceiver into the cradle with the spring
clips.
Page 20
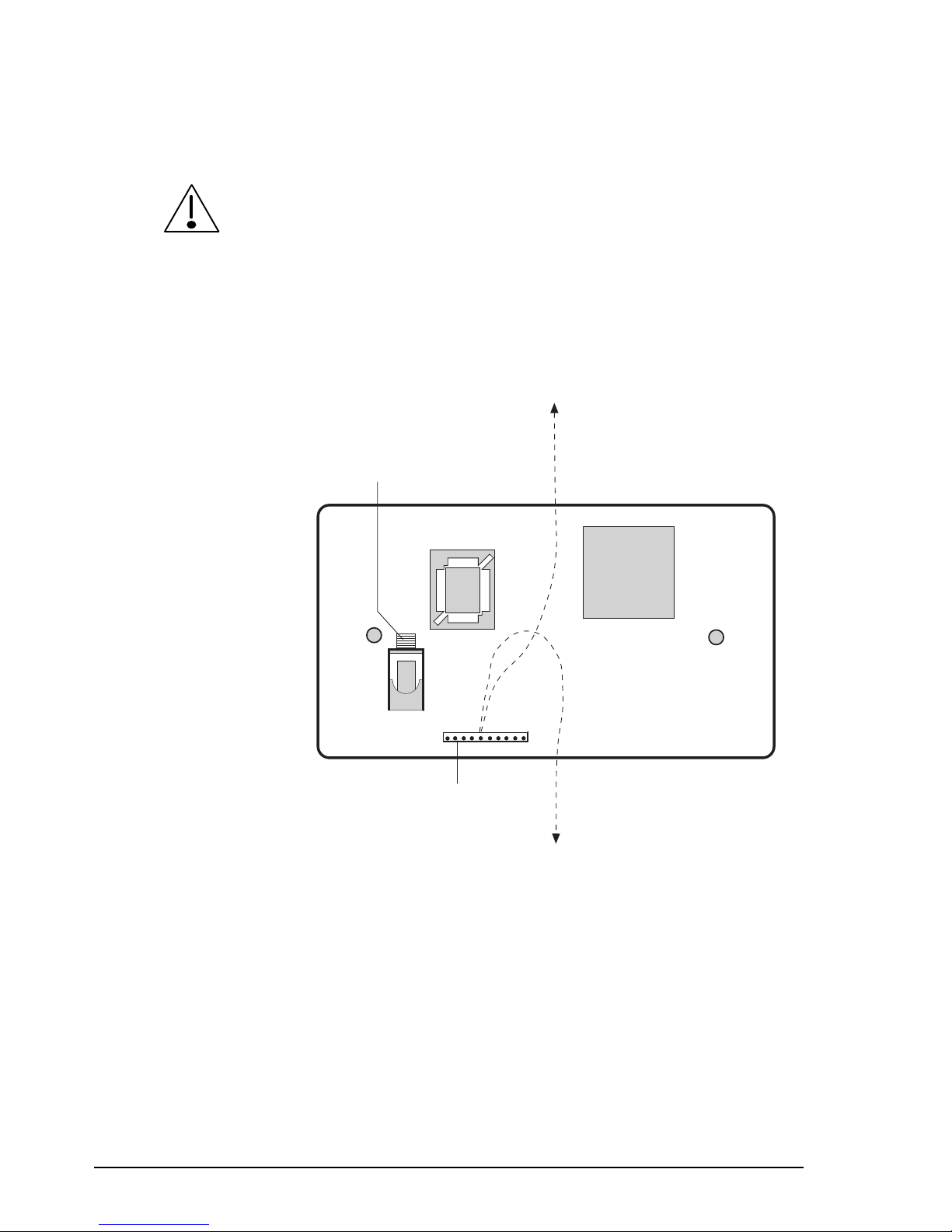
Installation
2-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Mounting the control head and loudspeaker
Make sure that the transceiver is disconnected from the DC
power source before connecting the control head to the
Remote Control
connector on the transceiver.
Select a suitable location to mount the control head and
loudspeaker. Avoid places exposed to direct sunlight such as
the car dashboard close to the windscreen.
L/S loudspeaker socket
10-pin control cable
connector
Bottom entry
cable path
Top entry
cable path
Figure 2.3
Rear view of control head without cover
Installation
2-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Mounting the control head and loudspeaker
Make sure that the transceiver is disconnected from the DC
power source before connecting the control head to the
Remote Control
connector on the transceiver.
Select a suitable location to mount the control head and
loudspeaker. Avoid places exposed to direct sunlight such as
the car dashboard close to the windscreen.
L/S loudspeaker socket
10-pin control cable
connector
Bottom entry
cable path
Top entry
cable path
Figure 2.3
Rear view of control head without cover
Page 21

Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-9
To connect the control cable and loudspeaker cable to the
control head:
1. Remove the two screws on the rear of the control head
and remove the cover. Figure 2.3 shows the rear of the
control head with the cover removed.
2. Feed the loudspeaker cable through the foam grommet
near the control head end of the control cable.
3. Fit the cable clamp to the control cable and attach the
cable clamp to the inside of the rear cover of the control
head (as shown in the diagram on the inside of the rear
cover).
4. Plug the control cable into the 10-pin connector (the
cable only fits one way).
5. Plug the loudspeaker cable into the L/S loudspeaker
socket.
6. Place the foam grommet into the slot on the rear cover.
7. To make sure that the cover will not pinch the cable,
position the cable between the shaded areas in Figure
2.3.
8. Replace the rear cover of the control head and its two
screws carefully. Note that the rear cover of the control
head can be rotated to give you either top or bottom
entry of the cables.
The loudspeaker and the control head have similar mounting
brackets. The procedure for installing them is the same.
To install the brackets:
1. Remove the two cradle screws and washers securing the
mounting cradle to the equipment.
2. Secure the mounting cradle into position. Ensure that
there is sufficient space at the rear for the cables.
3. Secure the equipment to the mounting cradle with the
two screws and washers.
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-9
To connect the control cable and loudspeaker cable to the
control head:
1. Remove the two screws on the rear of the control head
and remove the cover. Figure 2.3 shows the rear of the
control head with the cover removed.
2. Feed the loudspeaker cable through the foam grommet
near the control head end of the control cable.
3. Fit the cable clamp to the control cable and attach the
cable clamp to the inside of the rear cover of the control
head (as shown in the diagram on the inside of the rear
cover).
4. Plug the control cable into the 10-pin connector (the
cable only fits one way).
5. Plug the loudspeaker cable into the L/S loudspeaker
socket.
6. Place the foam grommet into the slot on the rear cover.
7. To make sure that the cover will not pinch the cable,
position the cable between the shaded areas in Figure
2.3.
8. Replace the rear cover of the control head and its two
screws carefully. Note that the rear cover of the control
head can be rotated to give you either top or bottom
entry of the cables.
The loudspeaker and the control head have similar mounting
brackets. The procedure for installing them is the same.
To install the brackets:
1. Remove the two cradle screws and washers securing the
mounting cradle to the equipment.
2. Secure the mounting cradle into position. Ensure that
there is sufficient space at the rear for the cables.
3. Secure the equipment to the mounting cradle with the
two screws and washers.
Page 22

Installation
2-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
4. Plug in the control cable at the Remote Control
connector on the transceiver. Ensure that it is securely
fastened.
The control cable is six metres long. Do not cut the control
or loudspeaker cable. If either cable is too long, gather the
excess neatly and secure it out of the way.
When connecting the microphone, gently rotate the plug in
the microphone socket until the pins locate. Push the plug
home and fasten the locking ring until finger-tight. Do not
over tighten.
Installation
2-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
4. Plug in the control cable at the Remote Control
connector on the transceiver. Ensure that it is securely
fastened.
The control cable is six metres long. Do not cut the control
or loudspeaker cable. If either cable is too long, gather the
excess neatly and secure it out of the way.
When connecting the microphone, gently rotate the plug in
the microphone socket until the pins locate. Push the plug
home and fasten the locking ring until finger-tight. Do not
over tighten.
Page 23

Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-11
Power supply
Ensure that the power supply to operate your transceiver is
12V DC.
Power can be provided by either a 12V battery (for mobile
stations) or a suitable power supply connected directly to the
mains (for fixed base stations).
All installations should be checked by a qualified technician
before power is applied to the transceiver.
The heavy duty six metre length of power cable, which is
supplied with the vehicle mounting cradle for mobile
stations, minimises the voltage drop between the battery and
transceiver during transmission. Do not use a thinner cable
than this.
Protect all cables from sharp edges and mechanical
abrasions.
We recommend that a suitable cartridge fuse (32 Amp—
accessory code 711) is fitted in the active wire, close to the
battery. This will protect the power cable from risk of fire
should damaged insulation touch the vehicle chassis. Do not
use normal glass in-line automotive fuses. The transceiver is
fitted with adequate internal protection.
Connect the power cable between the transceiver and the
battery or the AC power supply.
In extended control installations where the power and
control cables are long and follow a common path, keep
the cables separated by a minimum of 200mm. The
cables can be closer together for short distances, for
example, to pass through the same hole in the bulkhead.
Failure to observe this warning will cause distortion of
the transmitted audio signals.
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-11
Power supply
Ensure that the power supply to operate your transceiver is
12V DC.
Power can be provided by either a 12V battery (for mobile
stations) or a suitable power supply connected directly to the
mains (for fixed base stations).
All installations should be checked by a qualified technician
before power is applied to the transceiver.
The heavy duty six metre length of power cable, which is
supplied with the vehicle mounting cradle for mobile
stations, minimises the voltage drop between the battery and
transceiver during transmission. Do not use a thinner cable
than this.
Protect all cables from sharp edges and mechanical
abrasions.
We recommend that a suitable cartridge fuse (32 Amp—
accessory code 711) is fitted in the active wire, close to the
battery. This will protect the power cable from risk of fire
should damaged insulation touch the vehicle chassis. Do not
use normal glass in-line automotive fuses. The transceiver is
fitted with adequate internal protection.
Connect the power cable between the transceiver and the
battery or the AC power supply.
In extended control installations where the power and
control cables are long and follow a common path, keep
the cables separated by a minimum of 200mm. The
cables can be closer together for short distances, for
example, to pass through the same hole in the bulkhead.
Failure to observe this warning will cause distortion of
the transmitted audio signals.
Page 24

Installation
2-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Grounding
A good ground (RF earth) is essential for efficient
transceiver operation. A chassis ground is provided on the
rear panel of the transceiver.
Use a copper braid of at least 12mm width to ground the
transceiver.
The control head may also require earthing to prevent RF
interference corrupting its data and audio circuits. To do
this, check that the mounting bracket is earthed by ensuring
that the screws holding the mounting bracket are not
insulated. It may be necessary to remove paint from around
the mounting screws to ensure a good contact.
Installation
2-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Grounding
A good ground (RF earth) is essential for efficient
transceiver operation. A chassis ground is provided on the
rear panel of the transceiver.
Use a copper braid of at least 12mm width to ground the
transceiver.
The control head may also require earthing to prevent RF
interference corrupting its data and audio circuits. To do
this, check that the mounting bracket is earthed by ensuring
that the screws holding the mounting bracket are not
insulated. It may be necessary to remove paint from around
the mounting screws to ensure a good contact.
Page 25

Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-13
Ancillary equipment
There is a range of ancillary equipment you can connect to
the transceiver. For details, see Chapter 11, Connecting
ancillary equipment.
Antennas and antenna tuners
Correct installation of the antenna and antenna tuner is
important for good transceiver operation.
To obtain optimal performance and good radiation efficiency
from your transceiver, consider the following for the antenna
and antenna tuner:
• physical location
• distance from the transceiver
• grounding.
Follow the installation instructions provided with each
antenna and antenna tuner to achieve the best possible
performance.
Installation
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 2-13
Ancillary equipment
There is a range of ancillary equipment you can connect to
the transceiver. For details, see Chapter 11, Connecting
ancillary equipment.
Antennas and antenna tuners
Correct installation of the antenna and antenna tuner is
important for good transceiver operation.
To obtain optimal performance and good radiation efficiency
from your transceiver, consider the following for the antenna
and antenna tuner:
• physical location
• distance from the transceiver
• grounding.
Follow the installation instructions provided with each
antenna and antenna tuner to achieve the best possible
performance.
Page 26

Installation
2-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Installation
2-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Page 27

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-1
3 Channel and scan table setup
This chapter covers:
• Channel creation and editing (3-2)
• Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode (3-17)
• Channel deletion (3-21)
• Scan table creation (3-22)
• Scan table deletion (3-27)
• Telephone directory creation (3-29).
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-1
3 Channel and scan table setup
This chapter covers:
• Channel creation and editing (3-2)
• Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode (3-17)
• Channel deletion (3-21)
• Scan table creation (3-22)
• Scan table deletion (3-27)
• Telephone directory creation (3-29).
Page 28

Channel and scan table setup
3-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Channel creation and editing
These procedures are used to:
• create receive-only channels by copying and editing
existing channels
• edit unprotected channels
• create transmit channels (if option TXE is fitted to your
transceiver).
When you send a call, the channel frequency and sideband
have to be the same for both stations. The channel number is
unimportant.
You cannot change the transmit frequencies used by your
transceiver unless your transceiver is fitted with option TXE.
If you edit a transmit channel and change its frequency, it
automatically becomes a receive-only channel.
You can change channel comments to describe how each
channel is used.
If you regularly use certain channels, grouping them together
may be helpful. You do this by copying channels to new
channel numbers. For example, you could create a group of
10 channels with channel numbers 201 to 210.
Unless your transceiver has option TXE, the changes you
can make to a channel depends on whether the channel is:
• protected or unprotected
• a transmit or receive-only channel.
You can change any unprotected channel setting. The only
protected channel setting you can change is the channel
comment. If you want to change the settings of a protected
channel, make an unprotected copy of the channel and edit
this copy.
Channel and scan table setup
3-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Channel creation and editing
These procedures are used to:
• create receive-only channels by copying and editing
existing channels
• edit unprotected channels
• create transmit channels (if option TXE is fitted to your
transceiver).
When you send a call, the channel frequency and sideband
have to be the same for both stations. The channel number is
unimportant.
You cannot change the transmit frequencies used by your
transceiver unless your transceiver is fitted with option TXE.
If you edit a transmit channel and change its frequency, it
automatically becomes a receive-only channel.
You can change channel comments to describe how each
channel is used.
If you regularly use certain channels, grouping them together
may be helpful. You do this by copying channels to new
channel numbers. For example, you could create a group of
10 channels with channel numbers 201 to 210.
Unless your transceiver has option TXE, the changes you
can make to a channel depends on whether the channel is:
• protected or unprotected
• a transmit or receive-only channel.
You can change any unprotected channel setting. The only
protected channel setting you can change is the channel
comment. If you want to change the settings of a protected
channel, make an unprotected copy of the channel and edit
this copy.
Page 29

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-3
Transmit channel settings consist of:
• channel frequency
• sideband (upper/lower/selectable)
• tone call group (1–4 or none)
• selcall group (1–5 or none)
• channel protection (on/off)
• channel comment (description of channel).
Receive-only channel settings consist of:
• channel frequency
• sideband (upper/ lower/selectable)
• channel protection (on/off)
• channel comment (description of channel).
The number of channels available in the transceiver depends
on how much of the transceiver’s memory is used to hold
channel comments. 400 channels are available if only a few
channel comments are used. 200 channels may be available
if all channels have channel comments.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-3
Transmit channel settings consist of:
• channel frequency
• sideband (upper/lower/selectable)
• tone call group (1–4 or none)
• selcall group (1–5 or none)
• channel protection (on/off)
• channel comment (description of channel).
Receive-only channel settings consist of:
• channel frequency
• sideband (upper/ lower/selectable)
• channel protection (on/off)
• channel comment (description of channel).
The number of channels available in the transceiver depends
on how much of the transceiver’s memory is used to hold
channel comments. 400 channels are available if only a few
channel comments are used. 200 channels may be available
if all channels have channel comments.
Page 30
Channel and scan table setup
3-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Creating or editing a channel
This procedure is used to create and edit channels. It does
not allow you to create transmit channels with new transmit
frequencies. Option TXE is required for this.
If you have option TXE fitted to your transceiver, follow the
procedure in Creating a transmit channel on page 3-11.
To create or edit a channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select the channel
frequency that you
want to copy or edit.
If you want to create a receiveonly channel, you can select
any channel.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Do you want to create a
channel with a new
channel number?
Yes
Step 4.
No
Step 6.
Answer:
• Yes if you want to create a
channel by copying or
changing information from
this channel
• No if you want to edit this
channel (that is, save your
changes to this channel).
Channel and scan table setup
3-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Creating or editing a channel
This procedure is used to create and edit channels. It does
not allow you to create transmit channels with new transmit
frequencies. Option TXE is required for this.
If you have option TXE fitted to your transceiver, follow the
procedure in Creating a transmit channel on page 3-11.
To create or edit a channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select the channel
frequency that you
want to copy or edit.
If you want to create a receive-
only channel, you can select
any channel.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Do you want to create a
channel with a new
channel number?
Yes
Step 4.
No
Step 6.
Answer:
• Yes if you want to create a
channel by copying or
changing information from
this channel
• No if you want to edit this
channel (that is, save your
changes to this channel).
Page 31

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-5
Action Notes
4.
Enter the number of
the new channel
numeral
button
Do not enter the number of a
channel that already exists.
5.
Press
Enter
R'call
Continue
Step 9.
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq.
RX 4,0100
.
If you entered the number of a
channel that already exists, the
transceiver beeps. Start the
procedure again by pressing
PTT
6.
(From Step 3.)
To edit this channel,
press
Enter
R'call
If this channel is protected, the
display looks like this:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
If this channel is unprotected,
the display looks like this:
EXIT
ENTER
Channel used
Enter to continue.
– 208
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-5
Action Notes
4.
Enter the number of
the new channel
numeral
button
Do not enter the number of a
channel that already exists.
5.
Press
Enter
R'call
Continue
Step 9.
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq.
RX 4,0100
.
If you entered the number of a
channel that already exists, the
transceiver beeps. Start the
procedure again by pressing
PTT
6.
(From Step 3.)
To edit this channel,
press
Enter
R'call
If this channel is protected, the
display looks like this:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
If this channel is unprotected,
the display looks like this:
EXIT
ENTER
Channel used
Enter to continue.
– 208
Page 32

Channel and scan table setup
3-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
7.
Is this channel
protected?
Yes
Step 22.
No
Step 8.
If this channel is protected, you
can only change its channel
comment.
8.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq.
RX 4,0100
.
9.
Are you changing the
receive frequency or is
this a receive-only
channel?
Yes
Step 10.
No
Step 13.
Answer yes if either or both of
these questions are true.
10.
To change the
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places. For example,
to enter 2040kHz, enter
204000.
Entering a frequency
automatically makes this a
receive-only channel.
11.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
Channel and scan table setup
3-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
7.
Is this channel
protected?
Yes
Step 22.
No
Step 8.
If this channel is protected, you
can only change its channel
comment.
8.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq.
RX 4,0100
.
9.
Are you changing the
receive frequency or is
this a receive-only
channel?
Yes
Step 10.
No
Step 13.
Answer yes if either or both of
these questions are true.
10.
To change the
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places. For example,
to enter 2040kHz, enter
204000.
Entering a frequency
automatically makes this a
receive-only channel.
11.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
Page 33

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-7
Action Notes
12.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Continue
Step 19.
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
13.
(From Step 9.)
Press
Enter
R'call
The display shows the channel
options:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U T1 S1 NP
If you finish changing channel
options at any time in steps
13–20, you can go to step 21.
14.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
15.
To move to the tone
call group setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Hi: 1320 Lo: 880
U T1 S1 NP
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-7
Action Notes
12.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Continue
Step 19.
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
13.
(From Step 9.)
Press
Enter
R'call
The display shows the channel
options:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U T1 S1 NP
If you finish changing channel
options at any time in steps
13–20, you can go to step 21.
14.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
15.
To move to the tone
call group setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Hi: 1320 Lo: 880
U T1 S1 NP
Page 34

Channel and scan table setup
3-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
16.
To change the tone call
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
T1 to T4
to use this
channel for tone calls
•
T-
to disallow tone calls on
this channel.
17.
To move to the selcall
group setting, rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Self Id: – – – – – – Codan
U T1 S1 NP
18.
To change the selcall
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
S1 to S5
to use this
channel for selcalls
•
S-
to disallow selcalls on
this channel.
19.
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U T1 S1 NP
or
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
Channel and scan table setup
3-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
16.
To change the tone call
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
T1 to T4
to use this
channel for tone calls
•
T-
to disallow tone calls on
this channel.
17.
To move to the selcall
group setting, rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Self Id: – – – – – – Codan
U T1 S1 NP
18.
To change the selcall
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
S1 to S5
to use this
channel for selcalls
•
S-
to disallow selcalls on
this channel.
19.
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U T1 S1 NP
or
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
Page 35

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-9
Action Notes
20.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected.
• P to protect this channel
from all changes
Caution! Once you protect a
channel, only a Codan agent
can change or delete this
channel without deleting all
channels from the transceiver
unless option TXE has been
enabled.
21.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
22.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-9
Action Notes
20.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected.
• P to protect this channel
from all changes
Caution! Once you protect a
channel, only a Codan agent
can change or delete this
channel without deleting all
channels from the transceiver
unless option TXE has been
enabled.
21.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
22.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
Page 36

Channel and scan table setup
3-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
23.
To save all changes for
the edited or copied
channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Channel and scan table setup
3-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
23.
To save all changes for
the edited or copied
channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 37

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-11
Creating a transmit channel
This procedure is used to create transmit channels with new
transmit frequencies when your transceiver has option TXE
(Transmit Enable). Under special circumstances TXE may
be fitted at the time of purchase where local licensing
authorities permit.
To create a transmit channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select any channel.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Enter the number of
the channel
numeral
button
Leave the number unchanged
if you want to edit channel
information for this channel
number instead of saving
changes under a new channel
number.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-11
Creating a transmit channel
This procedure is used to create transmit channels with new
transmit frequencies when your transceiver has option TXE
(Transmit Enable). Under special circumstances TXE may
be fitted at the time of purchase where local licensing
authorities permit.
To create a transmit channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select any channel.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Enter the number of
the channel
numeral
button
Leave the number unchanged
if you want to edit channel
information for this channel
number instead of saving
changes under a new channel
number.
Page 38

Channel and scan table setup
3-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
Enter
R'call
If the channel already exists,
the transceiver beeps. To edit
this channel, press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq
RX 4,010.0
5.
To change the receive
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places. For example,
to enter 2040kHz, enter
204000.
6.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Transmit Freq
RX 2,040.0
TX 2,040.0
7.
To change the transmit
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places.
To inhibit transmission on this
channel, enter 0.
Channel and scan table setup
3-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
Enter
R'call
If the channel already exists,
the transceiver beeps. To edit
this channel, press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Receive Freq
RX 4,010.0
5.
To change the receive
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places. For example,
to enter 2040kHz, enter
204000.
6.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Transmit Freq
RX 2,040.0
TX 2,040.0
7.
To change the transmit
frequency, enter the
new value
numeral
button
Enter the kHz frequency to two
decimal places.
To inhibit transmission on this
channel, enter 0.
Page 39

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-13
Action Notes
8.
Is transmission
inhibited on this
channel?
Yes
Step 9.
No
Step 11.
9.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
10.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Continue
Step 17.
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
11.
(From Step 8.)
Press
Enter
R'call
The display shows the channel
options:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U T1 S1 NP
If you finish changing channel
options at any time in steps
11–18, you can go to step 19.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-13
Action Notes
8.
Is transmission
inhibited on this
channel?
Yes
Step 9.
No
Step 11.
9.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
10.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Continue
Step 17.
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
11.
(From Step 8.)
Press
Enter
R'call
The display shows the channel
options:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U T1 S1 NP
If you finish changing channel
options at any time in steps
11–18, you can go to step 19.
Page 40

Channel and scan table setup
3-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
12.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
13.
To move to the tone
call group setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Hi: 1320 Lo: 880
U T1 S1 NP
14.
To change the tone call
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
T1 to T4
to use this
channel for tone calls
•
T-
to disallow tone calls on
this channel.
15.
To move to the selcall
group setting, rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Self Id: – – – – – – Codan
U T1 S1 NP
Channel and scan table setup
3-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
12.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
13.
To move to the tone
call group setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Hi: 1320 Lo: 880
U T1 S1 NP
14.
To change the tone call
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
T1 to T4
to use this
channel for tone calls
•
T-
to disallow tone calls on
this channel.
15.
To move to the selcall
group setting, rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT
ENTER
Enter Options
Self Id: – – – – – – Codan
U T1 S1 NP
Page 41

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-15
Action Notes
16.
To change the selcall
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
S1 to S5
to use this
channel for selcalls
•
S-
to disallow selcalls on
this channel.
17.
(From Step 10.)
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U T1 S1 NP
or
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
18.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected
• P to protect this channel
from all changes.
Protection only applies when
TXE is disabled.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-15
Action Notes
16.
To change the selcall
group setting, rotate
Select
Select:
•
S1 to S5
to use this
channel for selcalls
•
S-
to disallow selcalls on
this channel.
17.
(From Step 10.)
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U T1 S1 NP
or
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
18.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected
• P to protect this channel
from all changes.
Protection only applies when
TXE is disabled.
Page 42
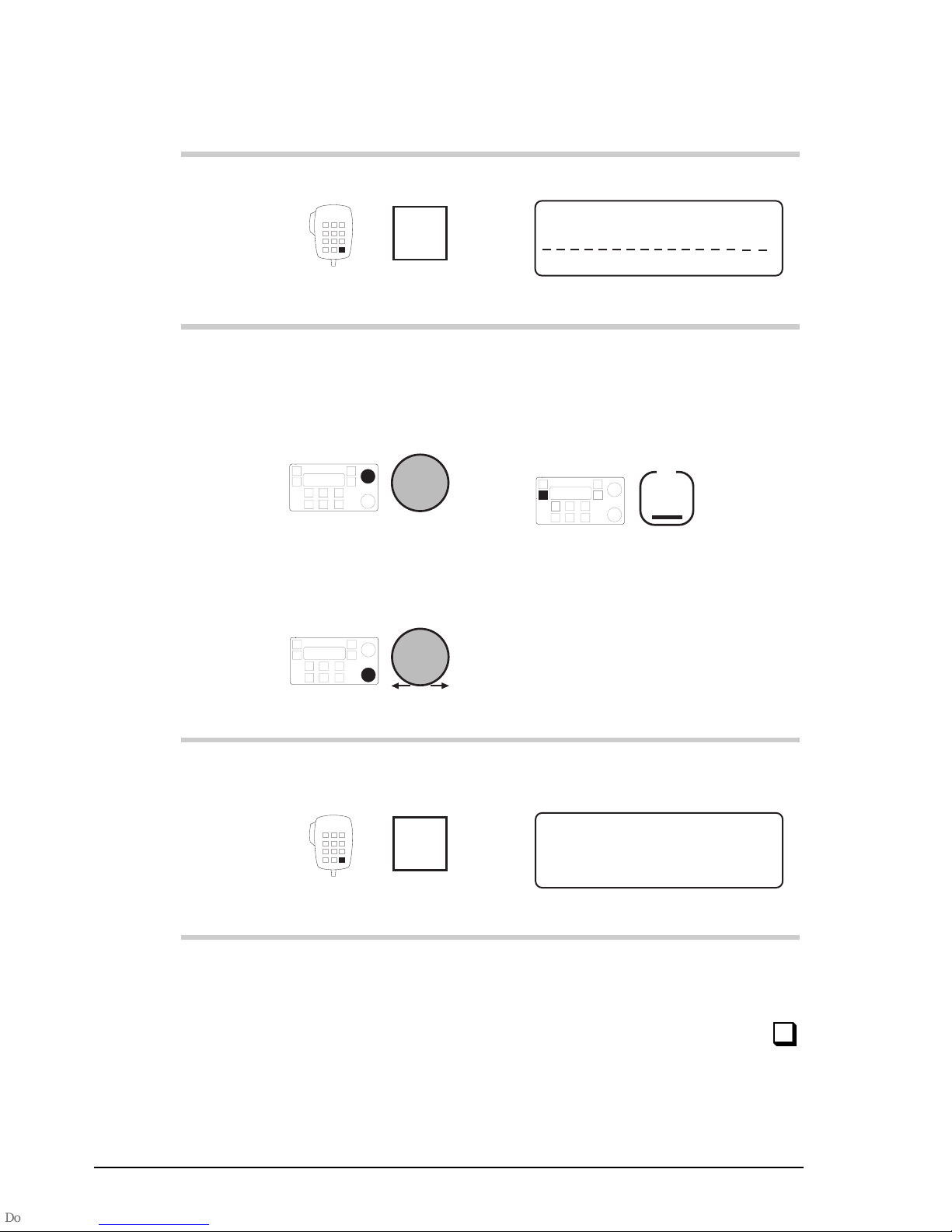
Channel and scan table setup
3-16 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
19.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
20.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
21.
To save all changes for
the channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Channel and scan table setup
3-16 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
19.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
20.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
21.
To save all changes for
the channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 43
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-17
Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode
This procedure is used to create receive-only channels in
Free-Tune Receiver mode.
This procedure is similar to Channel creation and editing
(see page 3-2 for details) except that you cannot create
transmit channels.
After using Free-Tune Receiver mode to tune the transceiver
to a new channel frequency, this procedure is useful for
saving the frequency under a new channel number.
To create a receive-only channel in Free-Tune Receiver
mode:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Free-Tune
Receiver mode.
Example of the display:
USB
HI
Rx.
4,01000
.
Free Tune Receiver
2.
Make any changes to
the frequency.
Refer to the HF SSB
transceiver user guide,
Chapter 3, Using Free-Tune
Receiver mode.
3.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
Rx.
.
Free Tune Receiver
PROG
ENTER
4,83500
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-17
Channel creation in Free-Tune Receiver mode
This procedure is used to create receive-only channels in
Free-Tune Receiver mode.
This procedure is similar to Channel creation and editing
(see page 3-2 for details) except that you cannot create
transmit channels.
After using Free-Tune Receiver mode to tune the transceiver
to a new channel frequency, this procedure is useful for
saving the frequency under a new channel number.
To create a receive-only channel in Free-Tune Receiver
mode:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Free-Tune
Receiver mode.
Example of the display:
USB
HI
Rx.
4,01000
.
Free Tune Receiver
2.
Make any changes to
the frequency.
Refer to the HF SSB
transceiver user guide,
Chapter 3, Using Free-Tune
Receiver mode.
3.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
Rx.
.
Free Tune Receiver
PROG
ENTER
4,83500
Page 44

Channel and scan table setup
3-18 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
5.
Enter the number of
the new channel
numeral
button
Do not enter the number of a
channel that already exists.
6.
Press
Enter
R'call
The display should look like
this:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
If you entered the number of a
channel that already exists, the
transceiver beeps. Start the
procedure again by pressing
PTT
Channel and scan table setup
3-18 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
5.
Enter the number of
the new channel
numeral
button
Do not enter the number of a
channel that already exists.
6.
Press
Enter
R'call
The display should look like
this:
1
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Upper sideband
U NP
If you entered the number of a
channel that already exists, the
transceiver beeps. Start the
procedure again by pressing
PTT
Page 45
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-19
Action Notes
7.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
8.
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
9.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected
• P to protect this channel
from all changes.
Caution! Once you protect a
channel, only a Codan agent
can change or delete this
channel without deleting all
channels from the transceiver.
10.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-19
Action Notes
7.
To change the sideband
setting, rotate
Select
Select
:
• U for upper sideband
• L for lower sideband
•
LU
for either sideband to be
selectable.
8.
To move to the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Volume
Example of the display:
EXIT ENTER
Enter Options
Not protected
U NP
9.
To change the channel
protection setting,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
NP
to leave this channel
unprotected
• P to protect this channel
from all changes.
Caution! Once you protect a
channel, only a Codan agent
can change or delete this
channel without deleting all
channels from the transceiver.
10.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CLEAR ENTER
Enter channel text
Page 46
Channel and scan table setup
3-20 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
11.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
12.
To return to Channel
mode saving the new
channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
USB
HI
Rx.
501
4835
Radio Australia
Channel and scan table setup
3-20 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
11.
To enter a comment to
describe this channel,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network
).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
12.
To return to Channel
mode saving the new
channel, press
Enter
R'call
There is a pause before the
display looks like this example:
USB
HI
Rx.
501
4835
Radio Australia
Page 47

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-21
Channel deletion
This procedure is used to delete unprotected channels.
Only a Codan agent can change or delete a protected channel
unless you have option TXE fitted.
To delete an unprotected channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select the channel that
you want to delete.
Unprotected channels show the
unprotected marker (small dot)
at the bottom left of the
display.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
YES
NO
DELETE CHANNEL?
– 208
4.
Press
F1
The transceiver beeps after the
channel has been deleted.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-21
Channel deletion
This procedure is used to delete unprotected channels.
Only a Codan agent can change or delete a protected channel
unless you have option TXE fitted.
To delete an unprotected channel:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select the channel that
you want to delete.
Unprotected channels show the
unprotected marker (small dot)
at the bottom left of the
display.
2.
Press twice
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
208
DELETE ENTER
Enter Channel No.
3.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
YES
NO
DELETE CHANNEL?
– 208
4.
Press
F1
The transceiver beeps after the
channel has been deleted.
Page 48

Channel and scan table setup
3-22 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Scan table creation
This procedure is used to set up any of the three scan tables.
You can only make changes to scan tables if scan table
editing is switched on (see Chapter 8, Scan table editing
on/off).
Each scan table can hold up to ten receive frequency
channels. You can add a channel to the scan table more than
once if you want the channel to be scanned several times in
each scan cycle.
You can select one of five scan types as displayed:
Selcall
Selcall scanning is the normal setting if you
expect to receive selcalls. Mute is on so that no
voice transmissions are heard. (Use of selcall
mute needs to be on. See Chapter 8, Selcall
mute availability on/off.)
Each channel is scanned for 0.6 seconds.
Scanning only stops for selcalls.
Cont
Use Continuous scanning if you want to listen to
voice traffic as the channels are scanned.
Each channel is scanned for 0.6 seconds.
Scanning only stops for selcalls. Mute is off.
Pause
Use Pause scanning if you expect voice calls and
want scanning to pause for five seconds when
voice is detected on the channel.
Each channel is scanned for one second.
Scanning also stops for selcalls.
Channel and scan table setup
3-22 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Scan table creation
This procedure is used to set up any of the three scan tables.
You can only make changes to scan tables if scan table
editing is switched on (see Chapter 8, Scan table editing
on/off).
Each scan table can hold up to ten receive frequency
channels. You can add a channel to the scan table more than
once if you want the channel to be scanned several times in
each scan cycle.
You can select one of five scan types as displayed:
Selcall
Selcall scanning is the normal setting if you
expect to receive selcalls. Mute is on so that no
voice transmissions are heard. (Use of selcall
mute needs to be on. See Chapter 8, Selcall
mute availability on/off.)
Each channel is scanned for 0.6 seconds.
Scanning only stops for selcalls.
Cont
Use Continuous scanning if you want to listen to
voice traffic as the channels are scanned.
Each channel is scanned for 0.6 seconds.
Scanning only stops for selcalls. Mute is off.
Pause
Use Pause scanning if you expect voice calls and
want scanning to pause for five seconds when
voice is detected on the channel.
Each channel is scanned for one second.
Scanning also stops for selcalls.
Page 49

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-23
Hold
Use Hold scanning if you expect voice calls and
want scanning to hold for as long as the voice is
detected on the channel.
Each channel is scanned for one second.
Scanning also stops for selcalls.
ALE
Use ALE scanning if you are using an ALE
controller and expect ALE calls.
Scanning stops for both selcall and ALE calls.
Mute is on.
To set up a scan table:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
press
Scan
Example of the display:
EXIT
PROGRAM
Press SCAN to Scan
Scan Table: 1
2.
To select one of the
three scan tables, rotate
Select
Select scan table 1, 2 or 3.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-23
Hold
Use Hold scanning if you expect voice calls and
want scanning to hold for as long as the voice is
detected on the channel.
Each channel is scanned for one second.
Scanning also stops for selcalls.
ALE
Use ALE scanning if you are using an ALE
controller and expect ALE calls.
Scanning stops for both selcall and ALE calls.
Mute is on.
To set up a scan table:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
press
Scan
Example of the display:
EXIT
PROGRAM
Press SCAN to Scan
Scan Table: 1
2.
To select one of the
three scan tables, rotate
Select
Select scan table 1, 2 or 3.
Page 50

Channel and scan table setup
3-24 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Press
F2
For example, scan table 2
looks like this:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
F1 to delete table
F2 to program table
4.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
CLEAR
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Enter Scan name
5.
To enter a comment to
describe this scan table,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network)
.
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
6.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
Continuous scan
Default Scan: Cont
Channel and scan table setup
3-24 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Press
F2
For example, scan table 2
looks like this:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
F1 to delete table
F2 to program table
4.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
CLEAR
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Enter Scan name
5.
To enter a comment to
describe this scan table,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters (for
example,
Local Network)
.
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
6.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
Continuous scan
Default Scan: Cont
Page 51
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-25
Action Notes
7.
To switch between the
types of scanning,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
Selcall
—for normal selcall
scanning
•
Cont
—for selcall scanning
without muting channel
traffic
•
Pause
—for voice call
scanning to pause five
seconds on voice detection
•
Hold
—for voice call
scanning to hold on voice
detection
•
ALE
—for ALE call
scanning
.
8.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
PROGRAM
USB
215 2,500.0
Local Network
9.
To select the channel
to add to the scan table,
rotate
Select
You can add up to ten
channels to the scan table.
To delete a channel already
added to the scan table, press
F1
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-25
Action Notes
7.
To switch between the
types of scanning,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
Selcall
—for normal selcall
scanning
•
Cont
—for selcall scanning
without muting channel
traffic
•
Pause
—for voice call
scanning to pause five
seconds on voice detection
•
Hold
—for voice call
scanning to hold on voice
detection
•
ALE
—for ALE call
scanning
.
8.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
PROGRAM
USB
215 2,500.0
Local Network
9.
To select the channel
to add to the scan table,
rotate
Select
You can add up to ten
channels to the scan table.
To delete a channel already
added to the scan table, press
F1
Page 52

Channel and scan table setup
3-26 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
10.
To add the displayed
channel to the scan
table, press
F2
Prog x1
indicates that this
channel is now entered once in
the scan table:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2 Prog x1
PROGRAM
USB
149 2,040.0
Local Network
11.
Do you want to add
another channel to the
scan table?
Yes
Step 9.
No
Step 12.
12.
To save your changes,
press
Scan
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Return to Step 2 to program
another scan table.
Channel and scan table setup
3-26 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
10.
To add the displayed
channel to the scan
table, press
F2
Prog x1
indicates that this
channel is now entered once in
the scan table:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2 Prog x1
PROGRAM
USB
149 2,040.0
Local Network
11.
Do you want to add
another channel to the
scan table?
Yes
Step 9.
No
Step 12.
12.
To save your changes,
press
Scan
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Return to Step 2 to program
another scan table.
Page 53

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-27
Scan table deletion
This procedure is used to delete any of the three scan tables.
You can only delete scan tables if scan table editing is
switched on (see Chapter 8, Scan table editing on/off).
To delete a scan table:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode, press
Scan
Example of the display:
EXIT
PROGRAM
Press SCAN to Scan
Scan Table: 1
2.
To select one of the
three scan tables for
deletion, rotate
Select
Select scan table 1, 2 or 3.
3.
Press
F2
For example, scan table 2 looks
like this:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
F1 to delete table
F2 to program table
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-27
Scan table deletion
This procedure is used to delete any of the three scan tables.
You can only delete scan tables if scan table editing is
switched on (see Chapter 8, Scan table editing on/off).
To delete a scan table:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode, press
Scan
Example of the display:
EXIT
PROGRAM
Press SCAN to Scan
Scan Table: 1
2.
To select one of the
three scan tables for
deletion, rotate
Select
Select scan table 1, 2 or 3.
3.
Press
F2
For example, scan table 2 looks
like this:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
ENTER
F1 to delete table
F2 to program table
Page 54

Channel and scan table setup
3-28 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
EXIT
Local Network
F1 to delete table
5.
To delete the scan
table, press
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Channel and scan table setup
3-28 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
F1
Example of the display:
DELETE
Scan Table: 2
EXIT
Local Network
F1 to delete table
5.
To delete the scan
table, press
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 55

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-29
Telephone directory creation
This procedure is used to set up the telephone directory for
sending telcalls.
The telephone directory operates like a telephone book. It
can hold ten telephone entries (numbered 0–9). Each entry
consists of a telephone number and a comment.
You can only access the telephone directory from channels
that allow selcalling (channels attached to a selcall group).
To check the selcall group setting for a channel, refer to the
HF SSB transceiver user guide, Chapter 3, Using View
Channel Options mode.
To add or clear entries from the telephone directory:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select a channel that is
set up for selcalling.
You can only access the
telephone directory from a
selcall channel.
2.
Press
Call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
CALL
Rx.
149
2040
TYPE
Selcall: 894477
3.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
CALL
Rx.
149
2040
ENDCALL
Tel:
– – – – – – –
029712233
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-29
Telephone directory creation
This procedure is used to set up the telephone directory for
sending telcalls.
The telephone directory operates like a telephone book. It
can hold ten telephone entries (numbered 0–9). Each entry
consists of a telephone number and a comment.
You can only access the telephone directory from channels
that allow selcalling (channels attached to a selcall group).
To check the selcall group setting for a channel, refer to the
HF SSB transceiver user guide, Chapter 3, Using View
Channel Options mode.
To add or clear entries from the telephone directory:
Action Notes
1.
In Channel mode,
select a channel that is
set up for selcalling.
You can only access the
telephone directory from a
selcall channel.
2.
Press
Call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
CALL
Rx.
149
2040
TYPE
Selcall: 894477
3.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
USB
HI
CALL
Rx.
149
2040
ENDCALL
Tel:
– – – – – – –
029712233
Page 56

Channel and scan table setup
3-30 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CALL
Rx.
PROG
Tel:
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Ch: 149 Tel-Dir:0
5.
To select one of the ten
entries, rotate
Select
Select an entry from 0 to 9.
6.
Press
F2
For example, entry 3 looks like
this:
EXIT
Rx.
ENTER
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Edit Tel Tel-Dir:3
Tel:
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
7.
Enter the telephone
number
numeral
button
To cancel an existing number
and leave this entry unused,
enter 0.
8.
Press
F2
For example, number
083050311 looks like this:
CLEAR
Rx.
ENTER
Edit Text Tel-Dir:3
Tel:
– – – – – – – –
083050311
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Channel and scan table setup
3-30 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
4.
Press
Enter
R'call
Example of the display:
CALL
Rx.
PROG
Tel:
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Ch: 149 Tel-Dir:0
5.
To select one of the ten
entries, rotate
Select
Select an entry from 0 to 9.
6.
Press
F2
For example, entry 3 looks like
this:
EXIT
Rx.
ENTER
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Edit Tel Tel-Dir:3
Tel:
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
7.
Enter the telephone
number
numeral
button
To cancel an existing number
and leave this entry unused,
enter 0.
8.
Press
F2
For example, number
083050311 looks like this:
CLEAR
Rx.
ENTER
Edit Text Tel-Dir:3
Tel:
– – – – – – – –
083050311
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Page 57

Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-31
Action Notes
9.
To enter a comment,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters to
describe the number (for
example, person’s name and
location).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
10.
To save your changes,
press
F2
Example of the display:
CALL
Rx.
PROG
Tel:
083050311
Codan Adelaide
Ch: 149 Tel-Dir:3
11.
Do you want to add
another telephone
number?
Yes
Return to
Step 5.
No
Step 12.
Channel and scan table setup
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 3-31
Action Notes
9.
To enter a comment,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 20 characters to
describe the number (for
example, person’s name and
location).
To clear any existing text,
press
F1
10.
To save your changes,
press
F2
Example of the display:
CALL
Rx.
PROG
Tel:
083050311
Codan Adelaide
Ch: 149 Tel-Dir:3
11.
Do you want to add
another telephone
number?
Yes
Return to
Step 5.
No
Step 12.
Page 58

Channel and scan table setup
3-32 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
12.
To return to Channel
mode, press
PTT
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Channel and scan table setup
3-32 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
12.
To return to Channel
mode, press
PTT
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 59

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-1
4 Using Setup mode procedures
Setup mode allows you to view and change settings that
control transceiver operation.
This chapter:
• explains how to use Setup mode (4-2)
• lists the procedures available in Setup mode (4-3)
• gives some tips on using Setup mode for advanced users
(4-7).
You should read this chapter before running any of the Setup
mode procedures. Chapters 5–8 cover in detail the Setup
mode procedures for the full range of HF SSB series
transceivers. Not all of these procedures may be available in
your transceiver.
You can only use the Setup mode procedures that:
• are standard for all HF SSB series transceivers (see List
of Setup mode procedures on page 4-3)
• correspond to transceiver options factory fitted for your
version of the transceiver in the HF SSB series range
(refer to the front of your HF SSB transceiver user guide
for the list of factory fitted transceiver options)
• correspond to transceiver options that you have
additionally enabled in your transceiver by using
passwords (see Chapter 7, Password entry to enable
transceiver options).
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-1
4 Using Setup mode procedures
Setup mode allows you to view and change settings that
control transceiver operation.
This chapter:
• explains how to use Setup mode (4-2)
• lists the procedures available in Setup mode (4-3)
• gives some tips on using Setup mode for advanced users
(4-7).
You should read this chapter before running any of the Setup
mode procedures. Chapters 5–8 cover in detail the Setup
mode procedures for the full range of HF SSB series
transceivers. Not all of these procedures may be available in
your transceiver.
You can only use the Setup mode procedures that:
• are standard for all HF SSB series transceivers (see List
of Setup mode procedures on page 4-3)
• correspond to transceiver options factory fitted for your
version of the transceiver in the HF SSB series range
(refer to the front of your HF SSB transceiver user guide
for the list of factory fitted transceiver options)
• correspond to transceiver options that you have
additionally enabled in your transceiver by using
passwords (see Chapter 7, Password entry to enable
transceiver options).
Page 60

Using Setup mode procedures
4-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Using Setup mode
You enter Setup mode by pressing the
Mode
button on the
control panel four times starting from the Channel mode
setting.
Setup mode only displays the names of Setup mode
procedures fitted or enabled for your transceiver. The names
of unavailable procedures are blanked out.
The easiest way to use Setup mode is to find the procedure
you want from the following list and turn to the description
of the procedure for further details and step by step guidance.
Procedures are listed alphabetically in Chapters 5–8.
You start each transceiver procedure by entering a setup
code.
If you make a mistake in setting a value and want to avoid
saving your changes, press the F1 button on the control
panel or
PTT
on the microphone to return to an earlier step
in the procedure. Repeated pressing of either button
progresses you back to Channel mode.
If you do not touch any button or knob for 60 seconds while
in Setup mode, the transceiver automatically reverts to
Channel mode. If this happens while you are in the middle
of a procedure, start the procedure again.
The descriptions for the procedures show examples of
channel and frequency numbers. You must enter your own
values.
Using Setup mode procedures
4-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Using Setup mode
You enter Setup mode by pressing the
Mode
button on the
control panel four times starting from the Channel mode
setting.
Setup mode only displays the names of Setup mode
procedures fitted or enabled for your transceiver. The names
of unavailable procedures are blanked out.
The easiest way to use Setup mode is to find the procedure
you want from the following list and turn to the description
of the procedure for further details and step by step guidance.
Procedures are listed alphabetically in Chapters 5–8.
You start each transceiver procedure by entering a setup
code.
If you make a mistake in setting a value and want to avoid
saving your changes, press the F1 button on the control
panel or
PTT
on the microphone to return to an earlier step
in the procedure. Repeated pressing of either button
progresses you back to Channel mode.
If you do not touch any button or knob for 60 seconds while
in Setup mode, the transceiver automatically reverts to
Channel mode. If this happens while you are in the middle
of a procedure, start the procedure again.
The descriptions for the procedures show examples of
channel and frequency numbers. You must enter your own
values.
Page 61
Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-3
List of Setup mode procedures
Procedures labelled standard are available in all HF SSB
series transceivers.
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
ALE alphanumeric
address
5-2 2434 Sets the alphanumeric address of your
transceiver.
ALE option reset 5-4 2432 Resets 9 of the 17 ALE option settings 0–16
to their factory values.
ALE option
settings
5-6 2431 Changes how the ALE controller works.
ALE sounding
interval
5-13 2433 Changes the ALE sounding time interval.
Beep loudness
(standard)
5-15 33 Changes the volume of beeps made by the
transceiver.
Call preamble
length
5-17 242 Sets the length of the preamble transmitted at
the start of a selective call.
Call privacy on/off 5-19 2443 Limits the stations that can receive your
transmissions of GPS, page and status call
information.
Clock calibration
(standard)
5-21 412 Calibrates the transceiver clock against an
external standard.
Clock setting
(standard)
5-23 411 Sets the time and date of the transceiver
clock.
Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-3
List of Setup mode procedures
Procedures labelled standard are available in all HF SSB
series transceivers.
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
ALE alphanumeric
address
5-2 2434 Sets the alphanumeric address of your
transceiver.
ALE option reset 5-4 2432 Resets 9 of the 17 ALE option settings 0–16
to their factory values.
ALE option
settings
5-6 2431 Changes how the ALE controller works.
ALE sounding
interval
5-13 2433 Changes the ALE sounding time interval.
Beep loudness
(standard)
5-15 33 Changes the volume of beeps made by the
transceiver.
Call preamble
length
5-17 242 Sets the length of the preamble transmitted at
the start of a selective call.
Call privacy on/off 5-19 2443 Limits the stations that can receive your
transmissions of GPS, page and status call
information.
Clock calibration
(standard)
5-21 412 Calibrates the transceiver clock against an
external standard.
Clock setting
(standard)
5-23 411 Sets the time and date of the transceiver
clock.
Page 62

Using Setup mode procedures
4-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Clone a transceiver
(standard)
5-28 Copies the settings from one transceiver to
another by a process called cloning.
Display brightness
(standard)
6-2 311 Changes the brightness of the display.
Display contrast
(standard)
6-4 312 Changes the contrast of the display.
Display diagnostics
on/off (standard)
6-6 314 Switches on or off the display of diagnostic
information about your transceiver.
Display frequency
(standard)
6-8 313 Sets how the frequency is displayed for each
channel.
Emergency selcall
receive setup
6-11 24422 Sets up the transceiver for receiving
emergency selcalls.
Emergency selcall
transmit setup
6-15 24421 Sets up the transceiver for sending
emergency selcalls.
Free-Tune Receiver
mode availability
on/off (standard)
6-19 3442 Switches on or off the availability of Free-
Tune Receiver mode.
GPS display on/off 6-21 3421 Switches on or off the display of your
transceiver’s GPS location.
GPS timeout on/off 6-23 3422 Switches on or off the GPS timeout warning.
Page call canned
message setup
7-2 24441 Prepares and stores up to three messages
ready for sending in a page call.
Using Setup mode procedures
4-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Clone a transceiver
(standard)
5-28 Copies the settings from one transceiver to
another by a process called cloning.
Display brightness
(standard)
6-2 311 Changes the brightness of the display.
Display contrast
(standard)
6-4 312 Changes the contrast of the display.
Display diagnostics
on/off (standard)
6-6 314 Switches on or off the display of diagnostic
information about your transceiver.
Display frequency
(standard)
6-8 313 Sets how the frequency is displayed for each
channel.
Emergency selcall
receive setup
6-11 24422 Sets up the transceiver for receiving
emergency selcalls.
Emergency selcall
transmit setup
6-15 24421 Sets up the transceiver for sending
emergency selcalls.
Free-Tune Receiver
mode availability
on/off (standard)
6-19 3442 Switches on or off the availability of Free-
Tune Receiver mode.
GPS display on/off 6-21 3421 Switches on or off the display of your
transceiver’s GPS location.
GPS timeout on/off 6-23 3422 Switches on or off the GPS timeout warning.
Page call canned
message setup
7-2 24441 Prepares and stores up to three messages
ready for sending in a page call.
Page 63

Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-5
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Password entry to
enable transceiver
options (standard)
7-5 42 Enables transceiver options that are built into
the transceiver and deletes forgotten PINs.
Power up message
on/off (standard)
7-10 34411 Allows you to set up a message that is
displayed for several seconds when the
transceiver is first switched on.
Power up mute
setting (standard)
7-13 34412 Selects the initial mute setting that is used
when the transceiver is first switched on.
Power up address
display on/off
7-16 34413 Selects whether or not your address, set up in
selcall group 1, is briefly displayed when the
transceiver is first switched on.
PTT release beep
on/off (standard)
7-18 3432 Switches on or off PTT release beeping.
PTT transmit
cut-out (standard)
7-20 3431 Prevents the transceiver from being left on in
the transmit state by mistake.
Recall channels by
frequency on/off
(standard)
7-22 32 Selects whether or not you can recall
channels by frequency.
RF gain on/off
(standard)
7-24 3443 Switches on or off the RF gain.
RS-232 connected
equipment
(standard)
7-26 3411 Identifies the equipment connected to either
the RS-232 socket or GP connector on the
transceiver rear panel.
RS-232 connection
baud rate
(standard)
7-29 3412 Sets the speed of information transfer for
equipment connected to the transceiver rear
panel.
Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-5
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Password entry to
enable transceiver
options (standard)
7-5 42 Enables transceiver options that are built into
the transceiver and deletes forgotten PINs.
Power up message
on/off (standard)
7-10 34411 Allows you to set up a message that is
displayed for several seconds when the
transceiver is first switched on.
Power up mute
setting (standard)
7-13 34412 Selects the initial mute setting that is used
when the transceiver is first switched on.
Power up address
display on/off
7-16 34413 Selects whether or not your address, set up in
selcall group 1, is briefly displayed when the
transceiver is first switched on.
PTT release beep
on/off (standard)
7-18 3432 Switches on or off PTT release beeping.
PTT transmit
cut-out (standard)
7-20 3431 Prevents the transceiver from being left on in
the transmit state by mistake.
Recall channels by
frequency on/off
(standard)
7-22 32 Selects whether or not you can recall
channels by frequency.
RF gain on/off
(standard)
7-24 3443 Switches on or off the RF gain.
RS-232 connected
equipment
(standard)
7-26 3411 Identifies the equipment connected to either
the RS-232 socket or GP connector on the
transceiver rear panel.
RS-232 connection
baud rate
(standard)
7-29 3412 Sets the speed of information transfer for
equipment connected to the transceiver rear
panel.
Page 64

Using Setup mode procedures
4-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Scan table
automatic scanning
start (standard)
8-2 11 Sets the time delay between finishing a call
and resuming automatic scanning.
Scan table editing
on/off (standard)
8-4 12 Switches on or off scan table editing.
Selcall address
setup
8-6 211 Sets up your address for any of your
transceiver’s five selcall groups S1–S5.
Selcall address size
compatibility
8-13 213 Selects how you communicate with stations
that are incapable of using addresses longer
than four digits.
Selcall lockout
on/off
8-16 2441 Switches on or off selcall lockout.
Selcall mute
availability on/off
8-18 212 Switches on or off the availability of selcall
mute on the control panel (the S’Call Mute
button).
Status call
availability on/off
8-20 24442 Switches on or off the ability to send the
three types of status call—remote diagnostics
call, remote config call and user status call.
Telcall availability
on/off
8-22 22 Switches on or off the ability to send telcalls.
Tone call setup
(standard)
8-24 23 Sets up the high and low frequency pairs for
any of the four tone call groups T1–T4.
99-beacon call
response on/off
8-27 241 Switches on or off the ability to respond to
received 99-beacon calls (selcalls ending in
99).
Using Setup mode procedures
4-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Procedure Page Setup
code
Description
Scan table
automatic scanning
start (standard)
8-2 11 Sets the time delay between finishing a call
and resuming automatic scanning.
Scan table editing
on/off (standard)
8-4 12 Switches on or off scan table editing.
Selcall address
setup
8-6 211 Sets up your address for any of your
transceiver’s five selcall groups S1–S5.
Selcall address size
compatibility
8-13 213 Selects how you communicate with stations
that are incapable of using addresses longer
than four digits.
Selcall lockout
on/off
8-16 2441 Switches on or off selcall lockout.
Selcall mute
availability on/off
8-18 212 Switches on or off the availability of selcall
mute on the control panel (the S’Call Mute
button).
Status call
availability on/off
8-20 24442 Switches on or off the ability to send the
three types of status call—remote diagnostics
call, remote config call and user status call.
Telcall availability
on/off
8-22 22 Switches on or off the ability to send telcalls.
Tone call setup
(standard)
8-24 23 Sets up the high and low frequency pairs for
any of the four tone call groups T1–T4.
99-beacon call
response on/off
8-27 241 Switches on or off the ability to respond to
received 99-beacon calls (selcalls ending in
99).
Page 65

Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-7
Advanced users
This section explains how Setup mode procedures are
arranged in the transceiver. You do not need to understand
this to use Setup mode, but some readers may find this
knowledge useful.
The Setup mode tree in Figure 4.1 shows how Setup mode
procedures are accessed. Each menu of options displayed by
the transceiver is represented by a branch in this tree.
Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-7
Advanced users
This section explains how Setup mode procedures are
arranged in the transceiver. You do not need to understand
this to use Setup mode, but some readers may find this
knowledge useful.
The Setup mode tree in Figure 4.1 shows how Setup mode
procedures are accessed. Each menu of options displayed by
the transceiver is represented by a branch in this tree.
Page 66

Using Setup mode procedures
4-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Bright*
Display
brightness
(311)
Selcall ALE
Display*
Emgcy
Privacy
Call
privacy
on/off
(2443)
Call*Scan* Config*
Auto*
Scan table
automatic
scanning
start (11)
Enable*
Scan table
editing
on/off (12)
Clone*
Clone a
transceiver
Setup mode menus
Telcall
Telcall
availability
on/off (22)
Tone*
Tone call
setup
(23)
Beacon
99-Beacon
call
response
on/off (241)
Preamble
Call preamble
length (242)
Lockout
Selcall
lockout
on/off (2441)
Sound
ALE
sounding
interval
(2433)
Default
ALE option
reset (2432)
Options
ALE option
settings
(2431)
Beeps*
Beep
loudness
(33)
Recall*
Recall
channels by
frequency
on/off (32)
Page
Page call
availability
on/off
(24441)
Status
Status call
availability
on/off
(24442)
Alpha ID
ALE
alphanumeric
address setup
(2434)
GPS PTT*
Timeout
GPS timeout
on/off (3422)
Display
GPS display
on/off (3421)
PTT
Beep*
PTT release
beep on/off
(3432)
Timer*
PTT
transmit
cutout
(3431)
Power Up*
Show ID
Power up
address display
on/off (34413)
Mute*
Power up
mute
setting
(34412)
Message*
Power up
message
on/off (34411)
RF
Gain*
RF gain
on/off
(3443)
Receiver*
Free-Tune
Receiver
mode
availability
on/off (3442)
ID
Selcall
address
setup
(211)
Mute
Selcall
mute
availability
on/off
(212)
ID size
Selcall
address size
compatibility
(213)
Contrast*
Display
contrast
(312)
Format*
Display
frequency
(313)
dB Volt*
Display
diagnostics
on/off
(314)
RS232*
Config*
RS-232
connection
baud rate
(3412)
Mode*
RS-232
connected
equipment
(3411)
Transmit
Emergency
selcall
transmit setup
(24421)
Receive
Emergency
selcall
receive setup
(24422)
Time*
Calib*
Clock
calibration
(412)
Set*
Clock
setting
(411)
Password*
Password entry
to enable
transceiver
options (42)
Indicates
standard
feature for
all HF SSB
transceivers
*
Figure 4.1
The Setup mode tree
Using Setup mode procedures
4-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Bright*
Display
brightness
(311)
Selcall ALE
Display*
Emgcy
Privacy
Call
privacy
on/off
(2443)
Call*Scan* Config*
Auto*
Scan table
automatic
scanning
start (11)
Enable*
Scan table
editing
on/off (12)
Clone*
Clone a
transceiver
Setup mode menus
Telcall
Telcall
availability
on/off (22)
Tone*
Tone call
setup
(23)
Beacon
99-Beacon
call
response
on/off (241)
Preamble
Call preamble
length (242)
Lockout
Selcall
lockout
on/off (2441)
Sound
ALE
sounding
interval
(2433)
Default
ALE option
reset (2432)
Options
ALE option
settings
(2431)
Beeps*
Beep
loudness
(33)
Recall*
Recall
channels by
frequency
on/off (32)
Page
Page call
availability
on/off
(24441)
Status
Status call
availability
on/off
(24442)
Alpha ID
ALE
alphanumeric
address setup
(2434)
GPS PTT*
Timeout
GPS timeout
on/off (3422)
Display
GPS display
on/off (3421)
PTT
Beep*
PTT release
beep on/off
(3432)
Timer*
PTT
transmit
cutout
(3431)
Power Up*
Show ID
Power up
address display
on/off (34413)
Mute*
Power up
mute
setting
(34412)
Message*
Power up
message
on/off (34411)
RF
Gain*
RF gain
on/off
(3443)
Receiver*
Free-Tune
Receiver
mode
availability
on/off (3442)
ID
Selcall
address
setup
(211)
Mute
Selcall
mute
availability
on/off
(212)
ID size
Selcall
address size
compatibility
(213)
Contrast*
Display
contrast
(312)
Format*
Display
frequency
(313)
dB Volt*
Display
diagnostics
on/off
(314)
RS232*
Config*
RS-232
connection
baud rate
(3412)
Mode*
RS-232
connected
equipment
(3411)
Transmit
Emergency
selcall
transmit setup
(24421)
Receive
Emergency
selcall
receive setup
(24422)
Time*
Calib*
Clock
calibration
(412)
Set*
Clock
setting
(411)
Password*
Password entry
to enable
transceiver
options (42)
Indicates
standard
feature for
all HF SSB
transceivers
*
Figure 4.1
The Setup mode tree
Page 67

Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-9
If you are comfortable using menus and selecting menu
options, you can refer to the Setup mode tree instead of
entering setup codes to access each procedure. This allows
you to use Setup mode by directly following the guidance
shown on the transceiver display.
Each branch in the menu tree shows:
• the name of the menu item shown on the display
• the name in small print of the equivalent procedure in
this manual, if any, for this menu item
• the setup code in parentheses.
To navigate around the Setup mode tree, use front panel
button:
• F2 to select a highlighted menu option and advance
down the tree
• F1 to go back up the tree to the previous menu.
For example, you could branch down to the
Power Up
menu
and view each of the
Power Up
menu options,
Message
,
Mute
and
Show ID
, in turn making any changes to settings
as necessary.
Using Setup mode procedures
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 4-9
If you are comfortable using menus and selecting menu
options, you can refer to the Setup mode tree instead of
entering setup codes to access each procedure. This allows
you to use Setup mode by directly following the guidance
shown on the transceiver display.
Each branch in the menu tree shows:
• the name of the menu item shown on the display
• the name in small print of the equivalent procedure in
this manual, if any, for this menu item
• the setup code in parentheses.
To navigate around the Setup mode tree, use front panel
button:
• F2 to select a highlighted menu option and advance
down the tree
• F1 to go back up the tree to the previous menu.
For example, you could branch down to the
Power Up
menu
and view each of the
Power Up
menu options,
Message
,
Mute
and
Show ID
, in turn making any changes to settings
as necessary.
Page 68

Using Setup mode procedures
4-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Using Setup mode procedures
4-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Page 69

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-1
5 Setup procedures—part 1
This chapter contains the following Setup mode procedures:
• ALE alphanumeric address setup (5-2)
• ALE option reset (5-4)
• ALE option settings (5-6)
• ALE sounding interval (5-13)
• Beep loudness* (5-15)
• Call preamble length (5-17)
• Call privacy on/off (5-19)
• Clock calibration* (5-21)
• Clock setting* (5-23)
• Clone a transceiver* (5-28).
* indicates a standard procedure available in all HF SSB
series transceivers (see Chapter 4, Using Setup mode
procedures).
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-1
5 Setup procedures—part 1
This chapter contains the following Setup mode procedures:
• ALE alphanumeric address setup (5-2)
• ALE option reset (5-4)
• ALE option settings (5-6)
• ALE sounding interval (5-13)
• Beep loudness* (5-15)
• Call preamble length (5-17)
• Call privacy on/off (5-19)
• Clock calibration* (5-21)
• Clock setting* (5-23)
• Clone a transceiver* (5-28).
* indicates a standard procedure available in all HF SSB
series transceivers (see Chapter 4, Using Setup mode
procedures).
Page 70

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE alphanumeric address setup
Setup code 2434
This procedure is used to set the alphanumeric address of
your transceiver.
This address is needed in ALE (Automatic Link
Establishment) calls that use alphanumeric station addresses.
An alphanumeric address is either a 7–15 digit number or an
address containing one or more of the characters ‘A–Z’, ‘@’
and ‘?’.
Your alphanumeric address is valid for all channels and
ALE scan tables.
To set your alphanumeric address:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2434
numeral
buttons
Example of the display:
CLEAR
Enter ALE ID
Alpha ALE ID
PROGRAM
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE alphanumeric address setup
Setup code 2434
This procedure is used to set the alphanumeric address of
your transceiver.
This address is needed in ALE (Automatic Link
Establishment) calls that use alphanumeric station addresses.
An alphanumeric address is either a 7–15 digit number or an
address containing one or more of the characters ‘A–Z’, ‘@’
and ‘?’.
Your alphanumeric address is valid for all channels and
ALE scan tables.
To set your alphanumeric address:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2434
numeral
buttons
Example of the display:
CLEAR
Enter ALE ID
Alpha ALE ID
PROGRAM
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Page 71

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-3
Action Notes
3.
To enter your
alphanumeric address,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 15 ‘0–9’, ‘A–Z’,
‘@’ and ‘?’ characters. Any
space is automatically replaced
by ‘0’.
To clear an existing address,
press
F1
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
4–Alpha ID
2–Default
3–Sound
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-3
Action Notes
3.
To enter your
alphanumeric address,
select each character
using
Select
and move between
characters using
Volume
Enter up to 15 ‘0–9’, ‘A–Z’,
‘@’ and ‘?’ characters. Any
space is automatically replaced
by ‘0’.
To clear an existing address,
press
F1
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
4–Alpha ID
2–Default
3–Sound
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 72

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option reset
Setup code 2432
This procedure is used to reset 9 of the 17 ALE option
settings 0–16 to their factory values.
To reset the ALE option settings:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2432
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Press ENTER to reset
ALE system options
3.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Press ENTER again to
reset ALE options
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-4 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option reset
Setup code 2432
This procedure is used to reset 9 of the 17 ALE option
settings 0–16 to their factory values.
To reset the ALE option settings:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2432
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Press ENTER to reset
ALE system options
3.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Press ENTER again to
reset ALE options
Page 73

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-5
Action Notes
4.
To confirm resetting,
press
F2
The transceiver beeps after
resetting all ALE options.
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
3–Sound
2–Default
4–Alpha ID
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-5
Action Notes
4.
To confirm resetting,
press
F2
The transceiver beeps after
resetting all ALE options.
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
3–Sound
2–Default
4–Alpha ID
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 74

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option settings
Setup code 2431
This procedure is used to change how the Automatic Link
Establishment (ALE) controller works.
There are 17 ALE system settings numbered 0–16. These
settings control ALE call performance and do not usually
require changing. You can change nine. The remaining
eight are not displayed since their values are fixed.
Setting No. Description
0 Sounding On/Off
2 Channel Quality Decay Time
3 Sounding Signal Length
5 BER Threshold
6 Golay Threshold
7 Error Threshold
11 ALE Silent Mode
13 Call Retry Limit
14 Channel Quality Averaging
For further information, this manual should be read in
conjunction with the 9300 ALE controller user guide (Codan
part number 15-04046).
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-6 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
ALE option settings
Setup code 2431
This procedure is used to change how the Automatic Link
Establishment (ALE) controller works.
There are 17 ALE system settings numbered 0–16. These
settings control ALE call performance and do not usually
require changing. You can change nine. The remaining
eight are not displayed since their values are fixed.
Setting No. Description
0 Sounding On/Off
2 Channel Quality Decay Time
3 Sounding Signal Length
5 BER Threshold
6 Golay Threshold
7 Error Threshold
11 ALE Silent Mode
13 Call Retry Limit
14 Channel Quality Averaging
For further information, this manual should be read in
conjunction with the 9300 ALE controller user guide (Codan
part number 15-04046).
Page 75

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-7
Sounding On/Off (ALE option 0)
This ALE option switches on or off sounding.
When sounding is switched off, your transceiver no longer
sends or receives ALE sounding signals. For correct ALE
operation, you should leave sounding on all the time.
If ALE Silent Mode (ALE option 11) is switched on, the
Sounding On/Off option setting is ignored and your station
does not send or receive ALE sounding signals. To set the
sounding interval, see ALE Sounding Interval on page 5-13.
Channel Quality Decay Time (ALE option 2)
This ALE option sets the artificial decay time for the record
of channel quality that is stored in the channel quality table
in ALE controller memory.
You can switch off decay or set a decay time in the range
1–8 hours.
For example, switching the sounding off and setting a decay
time of four hours would result in the record of a perfect
channel (100% channel quality) decaying to an unusable
channel (0% channel quality) over a period of four hours.
Sounding Signal Length (ALE option 3)
This ALE option sets the length in seconds of the sounding
transmission for each channel in the scan group.
When an ALE station sends sounding signals, a separate
signal is transmitted for each channel in the scan group. The
ALE station sends these signals sequentially. The total
length of the sounding transmission is the product of the
sounding signal length and the number of channels.
For example, if the sounding signal length is set to 10
seconds and the scan group contains seven channels, the
ALE station takes 70 seconds to complete sounding
transmission.
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-7
Sounding On/Off (ALE option 0)
This ALE option switches on or off sounding.
When sounding is switched off, your transceiver no longer
sends or receives ALE sounding signals. For correct ALE
operation, you should leave sounding on all the time.
If ALE Silent Mode (ALE option 11) is switched on, the
Sounding On/Off option setting is ignored and your station
does not send or receive ALE sounding signals. To set the
sounding interval, see ALE Sounding Interval on page 5-13.
Channel Quality Decay Time (ALE option 2)
This ALE option sets the artificial decay time for the record
of channel quality that is stored in the channel quality table
in ALE controller memory.
You can switch off decay or set a decay time in the range
1–8 hours.
For example, switching the sounding off and setting a decay
time of four hours would result in the record of a perfect
channel (100% channel quality) decaying to an unusable
channel (0% channel quality) over a period of four hours.
Sounding Signal Length (ALE option 3)
This ALE option sets the length in seconds of the sounding
transmission for each channel in the scan group.
When an ALE station sends sounding signals, a separate
signal is transmitted for each channel in the scan group. The
ALE station sends these signals sequentially. The total
length of the sounding transmission is the product of the
sounding signal length and the number of channels.
For example, if the sounding signal length is set to 10
seconds and the scan group contains seven channels, the
ALE station takes 70 seconds to complete sounding
transmission.
Page 76

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
The maximum setting of the sounding signal length is 100
seconds.
Bit Error Rate (BER) Threshold (ALE option 5)
This ALE option sets the value of the BER Threshold used
in BER testing.
You can set a value in the range 0–48.
BER testing is a method of error detection for ALE word
transmission. ALE stations send and receive ALE link
controlling information in blocks of data called ALE words.
An ALE word consists of a 3-bit preamble and a 21-bit data
field.
The result of BER error testing is used in the process of
determining whether or not the ALE link can be established
using the selected channel.
The higher the BER value of a transmitted ALE word, the
greater the error. A BER value of 0 indicates perfect
reception of an ALE word. The maximum BER value of 48
indicates that all bits of the ALE word were bad.
If a received ALE word contains more errors than the BER
Threshold, the ALE controller rejects the word. The lower
you set the BER Threshold, the greater the likelihood of
rejecting words with errors.
Golay Threshold (ALE option 6)
This ALE option sets the value of the Golay Threshold used
in Golay testing.
You can set a value in the range 0–4.
Golay testing is an additional method of error detection for
ALE word transmission. The result of Golay error testing is
used in the process of determining whether or not the ALE
link can be established using the selected channel.
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-8 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
The maximum setting of the sounding signal length is 100
seconds.
Bit Error Rate (BER) Threshold (ALE option 5)
This ALE option sets the value of the BER Threshold used
in BER testing.
You can set a value in the range 0–48.
BER testing is a method of error detection for ALE word
transmission. ALE stations send and receive ALE link
controlling information in blocks of data called ALE words.
An ALE word consists of a 3-bit preamble and a 21-bit data
field.
The result of BER error testing is used in the process of
determining whether or not the ALE link can be established
using the selected channel.
The higher the BER value of a transmitted ALE word, the
greater the error. A BER value of 0 indicates perfect
reception of an ALE word. The maximum BER value of 48
indicates that all bits of the ALE word were bad.
If a received ALE word contains more errors than the BER
Threshold, the ALE controller rejects the word. The lower
you set the BER Threshold, the greater the likelihood of
rejecting words with errors.
Golay Threshold (ALE option 6)
This ALE option sets the value of the Golay Threshold used
in Golay testing.
You can set a value in the range 0–4.
Golay testing is an additional method of error detection for
ALE word transmission. The result of Golay error testing is
used in the process of determining whether or not the ALE
link can be established using the selected channel.
Page 77

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-9
The higher the Golay value calculated for a received ALE
word, the greater the error.
If a received ALE word contains more errors than the Golay
Threshold, the ALE controller rejects the word. The lower
you set the Golay Threshold, the greater the likelihood of
rejecting words with errors.
Error Threshold (ALE option 7)
This ALE option sets the maximum number of sequentially
received bad ALE words that are allowed before the ALE
controller decides that the quality of the current channel is
too poor to establish an ALE link. A bad word is a word that
has exceeded either the BER or Golay Threshold.
You can set a value in the range 0–4.
If the test fails during the process of establishing the ALE
link, the call aborts and the transceiver returns to Scan
mode.
ALE Silent Mode (ALE option 11)
This ALE option switches on or off ALE Silent mode.
When ALE Silent mode is switched off, the station runs as a
normal ALE station.
When ALE Silent mode is switched on, the station will not:
• recognise any incoming ALE calls
• send or receive sounding signals even if Sounding
On/Off (ALE option 0) is switched on.
You can still send ALE calls in ALE Silent mode.
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-9
The higher the Golay value calculated for a received ALE
word, the greater the error.
If a received ALE word contains more errors than the Golay
Threshold, the ALE controller rejects the word. The lower
you set the Golay Threshold, the greater the likelihood of
rejecting words with errors.
Error Threshold (ALE option 7)
This ALE option sets the maximum number of sequentially
received bad ALE words that are allowed before the ALE
controller decides that the quality of the current channel is
too poor to establish an ALE link. A bad word is a word that
has exceeded either the BER or Golay Threshold.
You can set a value in the range 0–4.
If the test fails during the process of establishing the ALE
link, the call aborts and the transceiver returns to Scan
mode.
ALE Silent Mode (ALE option 11)
This ALE option switches on or off ALE Silent mode.
When ALE Silent mode is switched off, the station runs as a
normal ALE station.
When ALE Silent mode is switched on, the station will not:
• recognise any incoming ALE calls
• send or receive sounding signals even if Sounding
On/Off (ALE option 0) is switched on.
You can still send ALE calls in ALE Silent mode.
Page 78

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Call Retry Limit (ALE option 13)
This ALE option controls the number of times the ALE
station tries to establish an ALE link using each channel in
turn from the scan group.
You can set 99 for no limit to the number of tries or a value
in the range 0–98.
On each selected channel, two attempts are made to establish
a link before trying the next preferred channel, where two
more attempts are made and so on, until all channels in the
scan table have been tried (unless a link is established).
The sequence is then repeated dependent upon the number
set in the Call Retry Limit.
If a link is not established, the display shows
LINK FAILED
accompanied by error beeps. Retry duration can be up to one
minute per channel.
Channel Quality Averaging (ALE option 14)
This ALE option sets the method used to update an existing
channel quality value stored in ALE controller memory
when the new channel quality reading is worse than the
stored value.
You can replace old values with:
• new readings
• different weighted averages of the old values and new
readings.
Averaging reduces the effect that one bad reading may have
on a perfect channel. If a new reading is better than an old
value, the old value is replaced by the new reading.
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-10 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Call Retry Limit (ALE option 13)
This ALE option controls the number of times the ALE
station tries to establish an ALE link using each channel in
turn from the scan group.
You can set 99 for no limit to the number of tries or a value
in the range 0–98.
On each selected channel, two attempts are made to establish
a link before trying the next preferred channel, where two
more attempts are made and so on, until all channels in the
scan table have been tried (unless a link is established).
The sequence is then repeated dependent upon the number
set in the Call Retry Limit.
If a link is not established, the display shows
LINK FAILED
accompanied by error beeps. Retry duration can be up to one
minute per channel.
Channel Quality Averaging (ALE option 14)
This ALE option sets the method used to update an existing
channel quality value stored in ALE controller memory
when the new channel quality reading is worse than the
stored value.
You can replace old values with:
• new readings
• different weighted averages of the old values and new
readings.
Averaging reduces the effect that one bad reading may have
on a perfect channel. If a new reading is better than an old
value, the old value is replaced by the new reading.
Page 79

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-11
Changing an ALE option setting
To change an ALE option setting:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2431
numeral
button
Example of the display:
EXIT
ALE Sounding on
ENTER
ENABLED
ALE System Option: 0
3.
To find the ALE option
you want to change,
rotate
Select
The name of the option setting
is shown on the third line of
each display.
You can only display and
change nine of the 17 ALE
options (numbered 0–16).
4.
To select this ALE
option, press
F2
For example, option 13 (Call
Retry Limit) looks like this:
EXIT
Call retry limit
ENTER
0
ALE System Option: 13
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-11
Changing an ALE option setting
To change an ALE option setting:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2431
numeral
button
Example of the display:
EXIT
ALE Sounding on
ENTER
ENABLED
ALE System Option: 0
3.
To find the ALE option
you want to change,
rotate
Select
The name of the option setting
is shown on the third line of
each display.
You can only display and
change nine of the 17 ALE
options (numbered 0–16).
4.
To select this ALE
option, press
F2
For example, option 13 (Call
Retry Limit) looks like this:
EXIT
Call retry limit
ENTER
0
ALE System Option: 13
Page 80

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
5.
To change the setting,
rotate
Select
6.
To save your change,
press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
Call retry limit
ENTER
1
ALE System Option: 13
7.
Do you want to change
another ALE option?
Yes
Return to
Step 3.
No
Step 8.
8.
To return to Channel
mode, press four times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-12 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
5.
To change the setting,
rotate
Select
6.
To save your change,
press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
Call retry limit
ENTER
1
ALE System Option: 13
7.
Do you want to change
another ALE option?
Yes
Return to
Step 3.
No
Step 8.
8.
To return to Channel
mode, press four times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 81

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-13
ALE sounding interval
Setup code 2433
This procedure is used to change the ALE sounding time
interval.
ALE stations repeatedly send sounding signals to determine
how good each channel is for transmission. The ALE
sounding interval is the time between signal transmissions.
You can select:
•
30 Mins
•
45 Mins
•
1 Hour
•
2 Hours
•
4 Hours
•
8 Hours
•
16 Hours
.
To change the ALE sounding time interval:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-13
ALE sounding interval
Setup code 2433
This procedure is used to change the ALE sounding time
interval.
ALE stations repeatedly send sounding signals to determine
how good each channel is for transmission. The ALE
sounding interval is the time between signal transmissions.
You can select:
•
30 Mins
•
45 Mins
•
1 Hour
•
2 Hours
•
4 Hours
•
8 Hours
•
16 Hours
.
To change the ALE sounding time interval:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
Page 82

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
2.
Enter 2433
numeral
button
Example of the display:
EXIT
Sounding Interval
ENTER
2 Hours
Set ALE Sounding
3.
To change the ALE
sounding interval,
rotate
Select
Select a time in the range 30
minutes to 16 hours.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
3–Sound
2–Default
4–Alpha ID
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-14 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
2.
Enter 2433
numeral
button
Example of the display:
EXIT
Sounding Interval
ENTER
2 Hours
Set ALE Sounding
3.
To change the ALE
sounding interval,
rotate
Select
Select a time in the range 30
minutes to 16 hours.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
ALE MENU
1–Options
ENTER
3–Sound
2–Default
4–Alpha ID
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press three times
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 83

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-15
Beep loudness
Setup code 33 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to change the volume of beeps made
by the transceiver.
You can select:
•
NORMAL
(error beeps loud and acceptance beeps soft)
•
SOFT
(all beeps soft)
•
LOUD
(all beeps loud).
To change the beep loudness:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 33
numeral
button
The display looks like one of
the following:
EXIT
Soft and loud beeps
ENTER
NORMAL
Adjust Beep Volume
EXIT
Always soft beeps
ENTER
SOFT
Adjust Beep Volume
EXIT
Always loud beeps
ENTER
LOUD
Adjust Beep Volume
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-15
Beep loudness
Setup code 33 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to change the volume of beeps made
by the transceiver.
You can select:
•
NORMAL
(error beeps loud and acceptance beeps soft)
•
SOFT
(all beeps soft)
•
LOUD
(all beeps loud).
To change the beep loudness:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 33
numeral
button
The display looks like one of
the following:
EXIT
Soft and loud beeps
ENTER
NORMAL
Adjust Beep Volume
EXIT
Always soft beeps
ENTER
SOFT
Adjust Beep Volume
EXIT
Always loud beeps
ENTER
LOUD
Adjust Beep Volume
Page 84

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-16 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
To switch between
NORMAL, SOFT
and
LOUD
, rotate
Select
Select:
•
NORMAL
if you want loud
error beeps and soft
acceptance beeps
•
SOFT
if you always want
soft beeps
•
LOUD
if you always want
loud beeps.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CONFIG MENU
1–Display
2–Recall
ENTER
3–Beeps
4–More
1/3
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-16 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
To switch between
NORMAL, SOFT
and
LOUD
, rotate
Select
Select:
•
NORMAL
if you want loud
error beeps and soft
acceptance beeps
•
SOFT
if you always want
soft beeps
•
LOUD
if you always want
loud beeps.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CONFIG MENU
1–Display
2–Recall
ENTER
3–Beeps
4–More
1/3
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 85

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-17
Call preamble length
Setup code 242
This procedure is used to set the length of the preamble
transmitted at the start of a selective call.
The preamble is part of the coded message structure that is
transmitted when you send a selective call. The preamble
allows the receiving station sufficient time to scan to the
selected channel and recognise the incoming call.
You can set the preamble for:
•
Selcall
(for all types of selective call except ALE calls)
•
ALE
(for all types of selective call including ALE calls).
If you do not have an ALE controller, you should use the
Selcall
preamble. If your station has an ALE controller and
you want to be able to send ALE calls, you should use the
ALE
preamble.
ALE calls need a longer preamble than other types of
selective call. The
Selcall
preamble lasts six seconds. The
ALE
preamble lasts 12 seconds. Setting the
ALE
preamble
does not stop you from sending other types of selective call
but increases the initial call response time.
To change the preamble length:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-17
Call preamble length
Setup code 242
This procedure is used to set the length of the preamble
transmitted at the start of a selective call.
The preamble is part of the coded message structure that is
transmitted when you send a selective call. The preamble
allows the receiving station sufficient time to scan to the
selected channel and recognise the incoming call.
You can set the preamble for:
•
Selcall
(for all types of selective call except ALE calls)
•
ALE
(for all types of selective call including ALE calls).
If you do not have an ALE controller, you should use the
Selcall
preamble. If your station has an ALE controller and
you want to be able to send ALE calls, you should use the
ALE
preamble.
ALE calls need a longer preamble than other types of
selective call. The
Selcall
preamble lasts six seconds. The
ALE
preamble lasts 12 seconds. Setting the
ALE
preamble
does not stop you from sending other types of selective call
but increases the initial call response time.
To change the preamble length:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
Page 86

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-18 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
2.
Enter 242
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
SELCALL
Setup Call Preamble
Selcall Preamble
or
EXIT ENTER
ALE
Setup Call Preamble
ALE Preamble
3.
To switch between
SELCALL
and
ALE
,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
SELCALL
if you are not
using an ALE controller
•
ALE
if you are using an
ALE controller to send
calls.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CALL MENU
1–Beacon
2–Preamble
ENTER
3–ALE
4–More
2/4
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-18 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
2.
Enter 242
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
SELCALL
Setup Call Preamble
Selcall Preamble
or
EXIT ENTER
ALE
Setup Call Preamble
ALE Preamble
3.
To switch between
SELCALL
and
ALE
,
rotate
Select
Select:
•
SELCALL
if you are not
using an ALE controller
•
ALE
if you are using an
ALE controller to send
calls.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CALL MENU
1–Beacon
2–Preamble
ENTER
3–ALE
4–More
2/4
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 87

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-19
Call privacy on/off
Setup code 2443
This procedure is used to limit the stations that can receive
your transmissions of GPS, page and status call information.
You switch on call privacy by setting a privacy key (a
number up to six digits). This restricts the stations that can
receive your information to those using an identical privacy
key.
To switch on or off call privacy:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2443
numeral
button
If privacy is unset, the privacy
key is shown as 0 like this:
EXIT
Enter Privacy Key
ENTER
Key: – – – – – 0
If privacy is set, the privacy
key is hidden like this:
EXIT ENTER
ALE
Setup Call Preamble
ALE Preamble
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-19
Call privacy on/off
Setup code 2443
This procedure is used to limit the stations that can receive
your transmissions of GPS, page and status call information.
You switch on call privacy by setting a privacy key (a
number up to six digits). This restricts the stations that can
receive your information to those using an identical privacy
key.
To switch on or off call privacy:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 2443
numeral
button
If privacy is unset, the privacy
key is shown as 0 like this:
EXIT
Enter Privacy Key
ENTER
Key: – – – – – 0
If privacy is set, the privacy
key is hidden like this:
EXIT ENTER
ALE
Setup Call Preamble
ALE Preamble
Page 88

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-20 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Enter the privacy key
numeral
button
Enter up to six digits (these are
displayed).
To switch off call privacy,
enter 0 for the privacy key.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CALL MENU
1–Lockout
2–Emgcy
ENTER
3/4
4–More
3–Privacy
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-20 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Enter the privacy key
numeral
button
Enter up to six digits (these are
displayed).
To switch off call privacy,
enter 0 for the privacy key.
4.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
CALL MENU
1–Lockout
2–Emgcy
ENTER
3/4
4–More
3–Privacy
5.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 89

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-21
Clock calibration
Setup code 412 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to calibrate the transceiver clock
against an external standard.
The clock is used for timing incoming selective calls
recorded in call memory.
You can adjust the running of the clock by changing the
number of seconds that the clock gains or loses each month.
The calibration range is -150 to +310 seconds/month in steps
of 10 (approximate values).
The first time you calibrate the clock, set the value to zero
seconds/month. Over a period of a few months, see if the
clock gains or loses time and recalibrate as necessary.
To calibrate the clock:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 412
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT
TIME CALIBRATION
ENTER
Only use to adjust
fast or slow clock
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-21
Clock calibration
Setup code 412 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to calibrate the transceiver clock
against an external standard.
The clock is used for timing incoming selective calls
recorded in call memory.
You can adjust the running of the clock by changing the
number of seconds that the clock gains or loses each month.
The calibration range is -150 to +310 seconds/month in steps
of 10 (approximate values).
The first time you calibrate the clock, set the value to zero
seconds/month. Over a period of a few months, see if the
clock gains or loses time and recalibrate as necessary.
To calibrate the clock:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 412
numeral
button
The display shows:
EXIT
TIME CALIBRATION
ENTER
Only use to adjust
fast or slow clock
Page 90
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-22 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Press
F2
The display shows the day and
time that the calibration was
last set:
EXIT
TIME CALIBRATION
ENTER
Last 04/06/97 18:04
+010 sec/month
+--
4.
To change the
calibration setting,
rotate
Select
The calibration range is -155
to +310 seconds/month in steps
of 10.
As you change the value, the
slider moves at the bottom of
the screen—as displayed
above.
5.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
TIME SETUP MENU
ENTER
1– Set
2–Calib
6.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-22 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Press
F2
The display shows the day and
time that the calibration was
last set:
EXIT
TIME CALIBRATION
ENTER
Last 04/06/97 18:04
+010 sec/month
+--
4.
To change the
calibration setting,
rotate
Select
The calibration range is -155
to +310 seconds/month in steps
of 10.
As you change the value, the
slider moves at the bottom of
the screen—as displayed
above.
5.
To save your change,
press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
TIME SETUP MENU
ENTER
1– Set
2–Calib
6.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 91

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-23
Clock setting
Setup code 411 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to set the time and date of the
transceiver clock.
The time is always shown in 24 hour format. The clock is
used for timing incoming selective calls recorded in call
memory.
To change the clock setting, you must complete the
procedure. If you exit the procedure before the end, all
changes are lost.
The clock stops during the procedure. When you complete
the procedure, it restarts using the new settings.
To set the clock:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 411
numeral
button
The clock stops running.
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter hours
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-23
Clock setting
Setup code 411 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to set the time and date of the
transceiver clock.
The time is always shown in 24 hour format. The clock is
used for timing incoming selective calls recorded in call
memory.
To change the clock setting, you must complete the
procedure. If you exit the procedure before the end, all
changes are lost.
The clock stops during the procedure. When you complete
the procedure, it restarts using the new settings.
To set the clock:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 411
numeral
button
The clock stops running.
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter hours
Page 92
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-24 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Enter the hour if you
want to change the
hour
numeral
button
Use 24-hour format. For
example, enter 18 for 6pm.
4.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter minutes
5.
Enter the minutes if
you want to change the
minutes
numeral
button
6.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Select date format
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-24 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
3.
Enter the hour if you
want to change the
hour
numeral
button
Use 24-hour format. For
example, enter 18 for 6pm.
4.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter minutes
5.
Enter the minutes if
you want to change the
minutes
numeral
button
6.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Select date format
Page 93

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-25
Action Notes
7.
To switch between
D/M/Y
and
M/D/Y
date
formats, rotate
Select
Select:
•
D/M/Y
for day/month/year
•
M/D/Y
for month/day/year.
8.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter days
9.
Enter the day for the
D/M/Y
format if you
want to change the day
(or month for the
M/D/Y
format)
numeral
button
10.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter months
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-25
Action Notes
7.
To switch between
D/M/Y
and
M/D/Y
date
formats, rotate
Select
Select:
•
D/M/Y
for day/month/year
•
M/D/Y
for month/day/year.
8.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter days
9.
Enter the day for the
D/M/Y
format if you
want to change the day
(or month for the
M/D/Y
format)
numeral
button
10.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
ENTER
Enter months
Page 94
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-26 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
11.
Enter the month for the
D/M/Y
format if you
want to change the
month (or day for the
M/D/Y
format)
numeral
button
12.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
SAVE
Enter years
13.
Enter the last two
digits of the year if you
want to change the year
numeral
button
For example, enter 97 for
1997.
14.
To save all changes to
the time and date, press
F2
The clock restarts at the time
the F2 button is pressed. The
display shows:
EXIT
TIME SETUP MENU
2–Calib
ENTER
1– Set
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-26 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
11.
Enter the month for the
D/M/Y
format if you
want to change the
month (or day for the
M/D/Y
format)
numeral
button
12.
Press
F2
Example of the display:
EXIT
TIME SETUP
16:01 D/M/Y 03/05/97
SAVE
Enter years
13.
Enter the last two
digits of the year if you
want to change the year
numeral
button
For example, enter 97 for
1997.
14.
To save all changes to
the time and date, press
F2
The clock restarts at the time
the F2 button is pressed. The
display shows:
EXIT
TIME SETUP MENU
2–Calib
ENTER
1– Set
Page 95

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-27
Action Notes
15.
If you are setting the
clock for the first time,
calibrate the clock.
Set calibration to zero
seconds/month. See Clock
calibration on page 5-21.
16.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-27
Action Notes
15.
If you are setting the
clock for the first time,
calibrate the clock.
Set calibration to zero
seconds/month. See Clock
calibration on page 5-21.
16.
To return to Channel
mode, press twice
F1
Example of the display:
149
2040
CALL
Rx.
USB
HI
Geneva Switzerland
Pwr
Page 96

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-28 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Clone a transceiver
(standard procedure)
This procedure is used to copy the settings from one
transceiver to another by a process called cloning. Cloning
transceivers allows you to set up several transceivers that all
work in exactly the same way.
You clone transceivers by connecting the microphone socket
of the transceiver, which is already set up, to the microphone
socket of a transceiver that is to become a clone.
You can obtain the cable required for this procedure from an
authorised Codan dealer (Codan part no. 08-05138-001).
Except for the PIN, selcall group information and
alphanumeric address, the cloning procedure overwrites all
settings in the transceiver that you are copying to.
To clone a transceiver:
Action Notes
1.
Use the Cloning cable
to join the microphone
sockets of the two
transceivers.
2.
Switch on both
transceivers.
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-28 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Clone a transceiver
(standard procedure)
This procedure is used to copy the settings from one
transceiver to another by a process called cloning. Cloning
transceivers allows you to set up several transceivers that all
work in exactly the same way.
You clone transceivers by connecting the microphone socket
of the transceiver, which is already set up, to the microphone
socket of a transceiver that is to become a clone.
You can obtain the cable required for this procedure from an
authorised Codan dealer (Codan part no. 08-05138-001).
Except for the PIN, selcall group information and
alphanumeric address, the cloning procedure overwrites all
settings in the transceiver that you are copying to.
To clone a transceiver:
Action Notes
1.
Use the Cloning cable
to join the microphone
sockets of the two
transceivers.
2.
Switch on both
transceivers.
Page 97

Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-29
Action Notes
3.
On the master
transceiver you are
cloning from,
repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
4.
Select
4-More
by
rotating
Select
5.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Time
2–Password
ENTER
4–More
2/2
3–Clone
6.
Select
3-Clone
by
rotating
Select
Setup procedures—Part 1
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 5-29
Action Notes
3.
On the master
transceiver you are
cloning from,
repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
4.
Select
4-More
by
rotating
Select
5.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Time
2–Password
ENTER
4–More
2/2
3–Clone
6.
Select
3-Clone
by
rotating
Select
Page 98

Setup procedures—Part 1
5-30 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
7.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Clone transceiver.
Connect cable and
press F2 to begin
8.
To start the transfer of
information, press
F2
The display shows:
Cloning transceiver.
After about two minutes,
cloning finishes and the master
transceiver beeps twice. The
display shows:
Please remove the
cloning cable to
return to the Setup
Menu.
9.
Disconnect the cable
and switch off both
transceivers.
Setup procedures—Part 1
5-30 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Action Notes
7.
Press
F2
The display shows:
EXIT ENTER
Clone transceiver.
Connect cable and
press F2 to begin
8.
To start the transfer of
information, press
F2
The display shows:
Cloning transceiver.
After about two minutes,
cloning finishes and the master
transceiver beeps twice. The
display shows:
Please remove the
cloning cable to
return to the Setup
Menu.
9.
Disconnect the cable
and switch off both
transceivers.
Page 99

HF SSB transceiver reference manual 6-1
6 Setup procedures—part 2
This chapter contains the following Setup mode procedures:
• Display brightness* (6-2)
• Display contrast* (6-4)
• Display diagnostics on/off* (6-6)
• Display frequency* (6-8)
• Emergency selcall receive setup (6-11)
• Emergency selcall transmit setup (6-15)
• Free-Tune Receiver mode availability on/off* (6-19)
• GPS display on/off (6-21)
• GPS timeout on/off (6-23).
* indicates a standard procedure available in all HF SSB
series transceivers (see Chapter 4, Using Setup mode
procedures).
HF SSB transceiver reference manual 6-1
6 Setup procedures—part 2
This chapter contains the following Setup mode procedures:
• Display brightness* (6-2)
• Display contrast* (6-4)
• Display diagnostics on/off* (6-6)
• Display frequency* (6-8)
• Emergency selcall receive setup (6-11)
• Emergency selcall transmit setup (6-15)
• Free-Tune Receiver mode availability on/off* (6-19)
• GPS display on/off (6-21)
• GPS timeout on/off (6-23).
* indicates a standard procedure available in all HF SSB
series transceivers (see Chapter 4, Using Setup mode
procedures).
Page 100

Setup procedures—Part 2
6-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Display brightness
Setup code 311 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to change the brightness of the
display.
You can also adjust the brightness of the display using the
On/Off
button on the control panel (refer to the HF SSB
transceiver user guide, Chapter 3, Adjusting the display
brightness).
To adjust the brightness of the display:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 311
numeral
button
The display shows:
ENTER
LCD Brightness
Adjust Brightness
With Select Knob.
EXIT
3.
To adjust the
brightness, rotate
Select
Setup procedures—Part 2
6-2 HF SSB transceiver reference manual
Display brightness
Setup code 311 (standard procedure)
This procedure is used to change the brightness of the
display.
You can also adjust the brightness of the display using the
On/Off
button on the control panel (refer to the HF SSB
transceiver user guide, Chapter 3, Adjusting the display
brightness).
To adjust the brightness of the display:
Action Notes
1.
Repeatedly press
Mode
until you see the
display for Setup mode.
The display shows:
EXIT
SETUP MENU
1–Scan
2–Call
ENTER
3–Config
4–More
1/2
2.
Enter 311
numeral
button
The display shows:
ENTER
LCD Brightness
Adjust Brightness
With Select Knob.
EXIT
3.
To adjust the
brightness, rotate
Select
 Loading...
Loading...