Page 1

SSB Transceiver
2110
H F R A D I O C O M M U N I C A T I O N S
GETTING STARTED GUIDE
Page 2

No part of this guide may be reproduced, transcribed,
translated into any language or transmitted in any form
whatsoever without the prior written consent of Codan
Limited.
© Copyright 2004 Codan Limited.
Codan part number 15-04136-EN Issue 1, November 2004
®
CALM
is a registered trademark of Codan Limited. Other
brand, product, and company names mentioned in this
document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
The English version takes precedence over any translated
versions.
Page 3

Table of contents
CODAN
Introduction
Overview of this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Accessing the CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1 2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
European Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Electromagnetic compatibility and safety notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
C-tick approval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Care and safety information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2 Your 2110 SSB Transceiver
3 Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Charging a battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting a battery to the transceiver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Inserting the transceiver into a backpack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Selecting an appropriate antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4 The front panel
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
User controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Interface connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Antennas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Hot keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
The channel screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Battery status indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
The handset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide i
Page 4

Table of contents
5 Getting started
Switching on the transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Switching off the transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Setting up basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Selecting a channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Making a basic voice call . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Making a Selective call . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Scanning channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Switching scanning on or off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Pausing scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6 Troubleshooting
Appendix A—Entering and editing text
Editing a screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Entering text. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Changing between alpha and numerical characters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Moving the cursor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Inserting text . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Deleting text. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Saving text changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Appendix B—Using Quick Start
Appendix C—Using the GPS receiver
Appendix D—Transceiver specifications
Appendix E—HF radio transmission
Frequency, distance and time of day . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Antenna selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Channels and modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Networks and scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Etiquette for the use of HF radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
ii 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 5

Appendix F—Definitions
Standards and icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Acronyms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Unit multipliers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
About this issue. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Appendix G—Warranties
Index
Table of contents
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide iii
Page 6

Table of contents
This page has been left blank intentionally.
iv 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 7

List of figures
Figure 1: Typical front panel of a battery charger . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 2: Transceiver with battery pack connected . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 3: The front panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 4: The channel screen in the Channel List . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 5: Battery status indicator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 6: The handset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 7: The reflective properties of the ionosphere . . . . . . . . . . 60
CODAN
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide v
Page 8

List of figures
This page has been left blank intentionally.
vi 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 9

List of tables
Table 1: Earth symbol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 2: Battery storage times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 3: Selection guide for antennas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 4: Standard hot keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 5: General troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 6: Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 7: Examples of channels and modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 8: The phonetic alphabet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
CODAN
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide vii
Page 10

List of tables
This page has been left blank intentionally.
viii 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 11

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing a Codan 2110 SSB Transceiver.
With this great product and Codan’s supreme after-sales
support, you can look forward to many years of clear and
reliable HF communication. Please read this guide thoroughly
and retain it for future reference.
The 2110 SSB Transceiver is a self-contained, lightweight,
waterproof and rugged communication system.
Overview of this guide
This guide provides instructions on how to get started with
your 2110 SSB Transceiver. It assumes that you have limited
knowledge of HF communication and of using an HF radio.
This guide contains the following sections:
Section 1 2110 SSB Transceiver compliance—provides
CODAN
compliance information and safety notices, and
information on specific care and safety
requirements for your transceiver
Section 2 Your 2110 SSB Transceiver—explains briefly
the components that make up your transceiver
Section 3 Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use—
explains briefly how to check that the
transceiver and battery are ready for use
Section 4 The front panel—describes the front panel and
the function of items on the front panel
Section 5 Getting started—explains how to use the basic
operating features of your transceiver
Section 6 Troubleshooting—provides solutions for
common operational issues for the 2110 SSB
Transceiver
Appendix A Entering and editing text—explains how to
enter and edit text in editable screens
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 1
Page 12

Introduction
Appendix B Using Quick Start—explains how to use the
Quick Start feature, if enabled
Appendix C Using the GPS receiver—explains the
information provided by the GPS receiver, if
fitted
Appendix D Transceiver specifications—provides the
common operational specifications of the
transceiver
Appendix E HF radio transmission—describes the medium
of HF communication and how to use it
effectively
Appendix F Definitions—explains the terms and
abbreviations used in this guide
Appendix G Warranties—explains the warranties associated
with the components of the 2110 SSB
Transceiver
There is an index at the end of this guide and a CD containing
extensive reference material.
Accessing the CD
To access the CD:
1 Place the CD in the CD drive of your computer.
The CD will automatically launch the
2110 SSB Transceiver Reference Manual as a fully textsearchable HTML help file.
2 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 13

1 2110 SSB Transceiver
compliance
This section contains the following topics:
Introduction (4)
European Radio and Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment Directive (5)
Electromagnetic compatibility and safety notices (7)
C-tick approval (9)
Care and safety information (10)
CODAN
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 3
Page 14

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Introduction
This section describes how to ensure the 2110 SSB
Transceiver complies with the European Electromagnetic
Compatibility Directive 89/336/EEC and the European Low
Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC as called up in the European
Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
Directive 1999/5/EC.
The CE Declaration of Conformity and Expert Letter of
Opinion for the product is listed on page 73, Associated
documents. This document can be made available upon
request to Codan or a Codan-authorised supplier.
This section also contains the requirements for C-tick.
4 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 15

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
European Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
The 2110 SSB Transceiver has been tested and complies with
the following standards and requirements (articles of the
R&TTE Directive):
• Article 3.1b: ETSI EN 301 489-1
• Article 3.1b: ETSI EN 301 489-15
• Article 3.2: Australian type approval according to
AZ/NZS 4770:2003
• Article 3.1a: assessed against ICNIRP requirements
• Article 3.1a: EN 60950
Compliance with these standards is deemed sufficient to fulfil
the requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC.
Product marking and labelling
Any equipment supplied by Codan that satisfies these
requirements is identified by the , or
markings on the model label of the product.
Declaration of Conformity and Expert Letter of Opinion
The CE Declaration of Conformity and Expert Letter of
Opinion for this product is listed on page 73, Associated
documents. This document can be made available upon
request to Codan or a Codan-authorised supplier.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 5
0191 0191
Page 16

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Protection of the radio spectrum
CAUTION
Most countries restrict the use of HF radio
communications equipment to certain frequency
bands and/or require such equipment to be
licensed. It is the user’s responsibility to check
the specific requirements with the appropriate
communications authorities. If necessary,
contact Codan for more information.
6 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 17

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Electromagnetic compatibility and safety notices
Radiation safety
To ensure optimal transceiver performance and to avoid
exposure to excessive electromagnetic fields, the antenna
system must be installed according to the instructions
provided.
High voltages exist on the antenna during
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
transmission and tuning. Do not touch the
antenna during these activities. RF burns may
result.
Install the grounding system or counterpoise as
directed to prevent RF burns from any metal
part of the transceiver.
You should not transmit from your transceiver
or tune the antenna unless people are beyond the
safe working distance of:
• 0.2 m (8 in) from a long wire, end-fed
broadband, broadband dipole, or wire dipole
antenna
• 0.6 m (2 ft) from any whip antenna
Safe working distance is based on continuous exposure to CW
type transmissions, as set out in the ICNIRP Exposure
Guidelines 1998 for occupational exposure. Safe working
distance can be reduced with normal voice communication.
Electromagnetic compatibility
To ensure compliance with the EMC Directive is maintained,
you must:
1 Cover unused connectors with the protective caps
supplied to prevent electrostatic discharge passing
through your equipment.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 7
Page 18

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Electrical safety
To ensure compliance with the European Low Voltage
Directive is maintained, you must deploy and use the
2110 SSB Transceiver and antennas in accordance with the
instructions in the 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started
Guide, the Quick Reference Cards supplied with each antenna,
and the 2110 SSB Transceiver Reference Manual.
When using equipment that is connected directly to the AC
mains these precautions must be followed and checked before
applying AC power to the unit:
1 Use the standard AC mains cable supplied.
1 Ensure the covers for the equipment are fitted correctly.
The 3121 AC Battery Charger is double insulated and
marked with .
CAUTION
If it is necessary to remove the covers
during service by a qualified electronics
technician, they must be refitted correctly
before using the equipment.
The protective cover must always be fitted
WARNING
Batteries
Battery cells are electrically live at all times and must be
treated with extreme caution. They may supply high shortcircuit currents even if they appear to be damaged or
inoperable.
Batteries should be used to provide power to the transceiver
only, using the supplied connectors.
The batteries will not charge at temperatures higher than 40°C.
8 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
when the 3121 AC Battery Charger is
connected to the AC mains.
Page 19
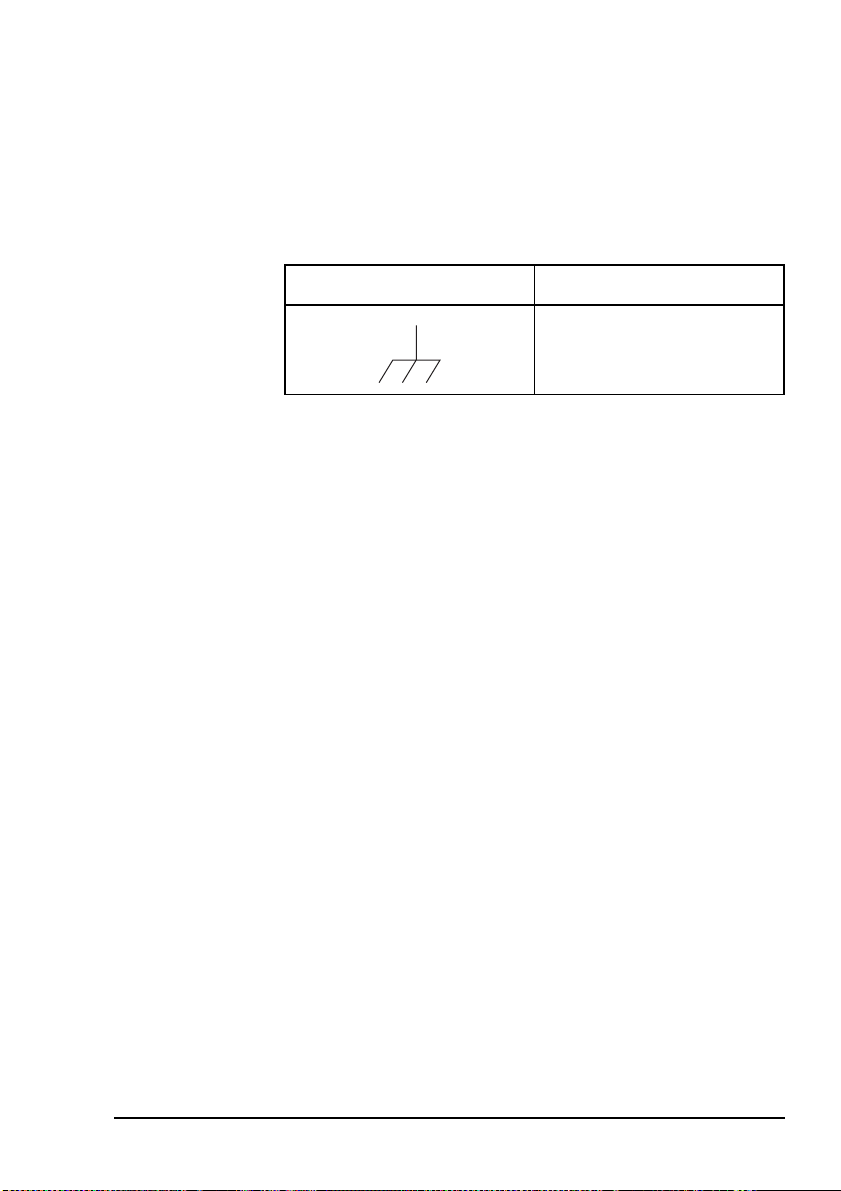
Earth symbol
An antenna earth connection point is provided on the
2110 SSB Transceiver. The symbol shown in Table 1 is used
to identify the earth on the equipment.
Table 1: Earth symbol
Symbol Meaning
C-tick approval
The 2110 SSB Transceiver meets the requirements of the
Australian Communications Authority Radiocommunications
(MF and HF Radiotelephone equipment—Land Mobile
Services) Standard 2003 (AS/NZS 4770).
2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Antenna earth
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 9
Page 20
2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
Care and safety information
Storage of batteries
Codan recommends that batteries are fully charged prior to
storage. The length of time that they can be stored before
recharging is necessary is dependent on the type of battery and
the average storage temperature.
Table 2: Battery storage times
Type Storage time @ 20°C
(70°F)
NiMh 12 months 6 months
SLA 15 months 10 months
Disposal of batteries
Batteries must be recycled. They should not be burnt or
disposed of in landfill.
Immersion of the transceiver in water
The transceiver unit and battery pack are designed to be
waterproof to IP68. The units can withstand immersion in 1 m
(3 ft) of water for up to 1 h. Prolonged immersion may cause
damage to the units.
If the units are immersed in water, drain any water from the
front panel speaker and keypad, then wipe and air dry the
connectors on the units prior to use or charging the battery.
If the units are exposed to salt water, they should be washed
with fresh water as soon as possible.
Storage time @ 30°C
(85°F)
WARNING
10 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Do not expose the connector on the battery pack
to salt water. This will damage the connector.
Page 21

Deploying antennas
2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
WARNING
WARNING
Do not deploy the antenna at sites with
overhead power cables.
Do not deploy or use any antenna if there is
lightning in the area.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 11
Page 22

2110 SSB Transceiver compliance
This page has been left blank intentionally.
12 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 23

2 Your 2110 SSB Transceiver
The 2110 SSB Transceiver system has a range of accessories
that are used in different situations. The following
photographs may help you to identify the transceiver and its
typical accessories.
Transceiver with handset Battery pack Backpack
Whip antenna Counterpoise Wire antenna/halyard
CODAN
Earth stake Balun Battery charger
Coaxial cable Earth lead with
clip and plug
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 13
Configuration software and
programming cable
Page 24

Your 2110 SSB Transceiver
This page has been left blank intentionally.
14 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 25

3 Preparing the 2110 SSB
Transceiver for use
This section contains the following topics:
Charging a battery (16)
Connecting a battery to the transceiver (19)
Inserting the transceiver into a backpack (20)
Selecting an appropriate antenna (21)
CODAN
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 15
Page 26
Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Charging a battery
Before using your transceiver, you must ensure that the
supplied battery is fully charged. You may use an AC–DC or
DC–DC charger with the battery. The AC–DC charger (Type
3121) uses a universal AC mains input of 90–264 VAC. The
DC–DC battery charger (Type 3122) may be powered from
any 12–60 V DC source, for example, from a vehicle 12 V DC
outlet, or from a 24 V vehicle battery.
The Codan battery chargers are specially designed for lownoise operation, so receiver performance remains optimal
while charging the battery via the front panel. You can
continue to use your transceiver during battery charging.
Charging is recommended between 0 and 40°C.
The battery will not commence charging if the
CAUTION
CAUTION
temperature is at or above 40°C. If charging is
already in progress, and the temperature rises to
50°C, charging will be stopped automatically.
To prevent damage to the battery, Codan
recommends the use of the Codan battery
chargers to charge the battery pack.
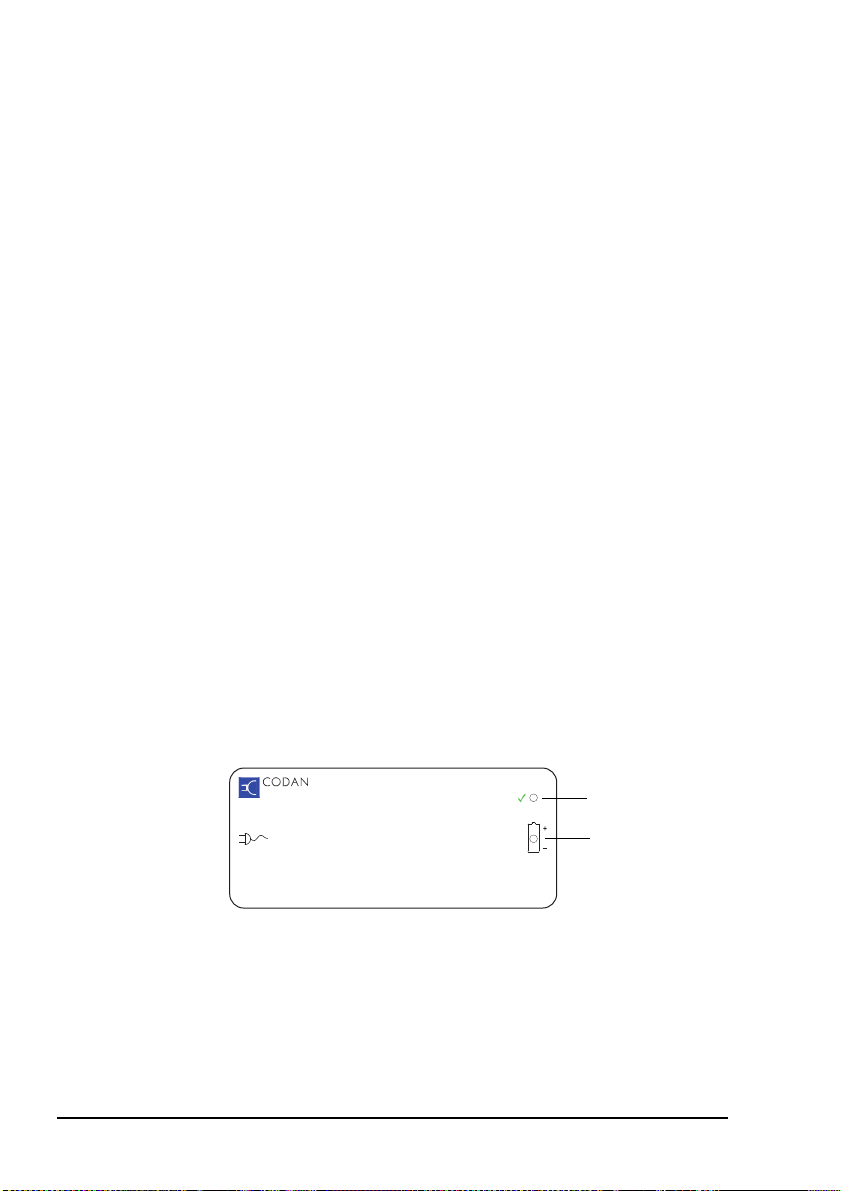
Figure 1: Typical front panel of a battery charger
power on
3121 AC Battery Charger
INPUT
OUTPUT
(green)
charging
(orange, off when
charging complete)
The battery pack should be charged with the
WARNING
connector facing upward and the vents clear of
obstructions so that any gas created during the
charging process is released.
16 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 27

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Provide clear notification that charging is
CAUTION
To charge a battery:
underway. Ensure there is adequate ventilation
around the battery during charging.
1 Do one of the following:
• If the battery is attached to the transceiver, use cable
08-06215-001 to connect the output of the charger to
the 19-way connector on the front panel of the
transceiver.
• If the battery is detached from the transceiver, use cable
08-06214-001 to connect the output of the charger to
the 6-way connector on the top of the battery pack.
1 Connect the charger to an appropriate power source.
If the transceiver is operational during charging, the
battery status indicator on the screen will show that the
battery is charging. When charging is complete, the
battery status indicator will be full.
NOTE
Requirements for alternative chargers
The Codan battery packs may be charged using alternative
supplies, for example, solar panels or hand-crank generators.
In this situation, the voltage level must not exceed 15.5 V and
the current must be within 1–3 A. These chargers must be
connected between pin B (charge in) and pin A (ground) on
the connector on the battery pack.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 17
It will take approximately 16 seconds for
charging to start.
Page 28

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Notes on charging batteries
A battery will require 3–5 discharge/recharge cycles when
new before it reaches its full capacity. In order to increase the
battery service life, it is recommended that the battery is not
fully discharged during each cycle. Full discharge should only
be carried out periodically as follows:
Type Full discharge
NiMh Two full discharge/recharge cycles every 20 charge
cycles
SLA One full discharge/recharge cycle every 20 charge
cycles
For the periodic full discharge cycle, run the battery down to
zero capacity using the transceiver. The transceiver will switch
off automatically when the battery is fully discharged.
If you are using alternative means to discharge
WARNING
the battery, the battery voltage must not go
below 10 V.
WARNING
18 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
An SLA battery must be charged immediately
after discharge to prevent damage to the battery.
Page 29

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Connecting a battery to the transceiver
The battery is connected to the bottom of the transceiver. It is
held in place by clips with locking key latches (see Figure 2).
The battery connector on the base of the
NOTE
Figure 2: Transceiver with battery pack connected
transceiver
battery pack
transceiver is on the same side of the transceiver
as the antenna connectors on the front panel.
clip
key
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 19
Page 30

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Inserting the transceiver into a backpack
All backpacks come with adjustable straps that hold the
transceiver firmly in position. Some backpacks have an
internal mounting frame.
To insert the transceiver into a backpack with an internal
mounting frame:
1 Open the rear of the backpack to expose the mounting
frame.
1 Push the transceiver between the foam mounts on the
frame.
1 Secure the transceiver with the two adjustable straps.
1 Close the rear of the backpack.
To insert the transceiver into the soft backpack:
1 Slide the transceiver into the backpack.
1 Secure the transceiver with the adjustable strap on the
outside of the backpack.
20 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 31

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
Selecting an appropriate antenna
Use the following table as a guide to selecting an antenna that
is appropriate for your communication requirements.
Table 3: Selection guide for antennas
Antenna Communication distance
(km)
Tape ,
Knock-down
whip
3m (10ft)
collapsible
whip
Long wire
and adaptor
End-fed
broadband
Broadband
dipole
Wire dipole
0–100 100–
500
!
!!
!!!
!!!
!!!!
!!!!
up to
2000
up to
5000
Effort to
install
Minimum Adequate
Maximum Superior
Antenna
performance
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 21
Page 32

Preparing the 2110 SSB Transceiver for use
This page has been left blank intentionally.
22 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 33

4 The front panel
Overview
The front panel has three main areas: user controls, connectors
and antennas, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: The front panel
CODAN
interface
connectorsuser controlsantennas
CLAR
2
5
SEC
8
VIEW
MODE
DEF
ABC
3
Tx
PWR
JKL
6
GPS
TUV
9
CALL
LOGS
0
internal
speaker
earth
terminal
location of
internal
TUNE
QZ
1
FREE
Rx
GHI
4
PRS
7
EASI
TALK
infrared
window
GPS
antenna
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 23
Page 34

The front panel
User controls
The user control area comprises:
•an LCD
• navigation keys (
• volume controls (
• soft function keys (F1, F2, F3) corresponding to the
function displayed above the key on the front panel
screen
• alphanumeric keys (0–9,
• emergency key ( )
• power key ( )
There are two ways to use the keys on the front panel. You
can:
•press a key, briefly
• hold a key for 2 seconds
The and keys
Press to:
• select the item on the active line in the list
• save changes
• answer ‘yes’ to prompts
, , , , )
, )
, #)
*
Hold to edit settings.
Press to:
• navigate up from settings to entries
• backspace over text
• remove messages on the screen
• cancel changes
• answer ‘no’ to prompts
24 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 35

Hold to go from any location to the home screen. If you
have entered text into a setting and want to discard the
changes you made, hold .
The scroll keys
The and keys are the scroll keys. Use these keys to scroll
up or down through any list, to scroll left or right over text,
and to increase or decrease a value.
Interface connectors
The interface connector area comprises:
• the 6-way handset connector ( )
• the 19-way GPIO connector ( )
Antennas
The front panel
The antenna area comprises:
• the antenna stud ( ) for whip antennas and the long wire
antenna adaptor
•the 50Ω connector ( ) for broadband and dipole
antennas
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 25
Page 36

The front panel
Hot keys
Hot keys enable you to perform a task quickly. The transceiver
comes with some standard hot keys programmed; the keys are
labelled with the corresponding task performed. You can also
create your own hot keys (see the reference material on the
enclosed CD).
Table 4: Standard hot keys
Hot key Function
F1 Pressing F1 performs the macro assigned to this soft function
key. By default, MUTE is assigned to this key, so pressing F1
toggles mute on or off.
F2 Pressing F2 performs the macro assigned to this soft function
key. By default, CALL is assigned to this key, so pressing F2
starts a call.
F3 Pressing F3 performs the macro assigned to this soft function
key. By default, SCAN is assigned to this key, so pressing F3
switches off scanning, or if you were in a call, ends the call and
switches scanning on.
Hold MUTE Holding MUTE toggles the front panel speaker on or off.
TUNE Pressing TUNE displays the PTT tunes screen so you can
manually tune the antenna.
CLAR Pressing CLAR enables you to adjust the receive frequency to
compensate for any frequency offset between your transceiver
and the remote transceiver.
MODE Pressing MODE selects the next allowable mode programmed
for the channel, usually USB or LSB.
FREE Rx Pressing FREE Rx enters Free Tune mode in which you can
adjust or enter a receive frequency.
Tx PWR Pressing Tx PWR toggles the transmission power of the
transceiver between Hi (25 W) and Lo (5 W).
26 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 37

The front panel
Table 4: Standard hot keys (cont.)
Hot key Function
V/S Pressing V/S toggles the mute type between Voice mute and
Selcall mute.
SEC Pressing or holding SEC enters Secure mode, if the hardware
option is fitted, and special firmware is programmed into the
transceiver and enabled.
GPS Pressing GPS displays your current GPS position, if the
hardware option is fitted and enabled.
EASITALK Pressing EASITALK toggles the DSP noise reduction algorithm
on or off.
VIEW Pressing VIEW toggles between the channel screen and the
Address List.
CALL LOGS Pressing CALL LOGS repeatedly steps through a number of
call logs: Calls Out, Calls In, Last Heard, then back to the screen
from which you began. In these logs, you can view the details of
the calls or detected stations.
The Last Heard log is only available if you have the MIL-STD188-141B ALE option installed.
(Emergency) Holding begins an automatic Emergency call transmission
using call information contained in the Emergency entries in the
Address List.
(Power) Pressing cycles the screen and keypad backlighting through
the brightness settings.
+ 9 Pressing + 9 enables you to change the default setting for the
screen contrast.
+ 0 Pressing + 0 enables you to change the default setting for the
screen and keypad backlighting.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 27
Page 38

The front panel
The channel screen
The channel screen is displayed when you press or VIEW.
Figure 4: The channel screen in the Channel List
signal
strength
indicator
Rx/Tx indicator
channel name
Tx freq (kHz)
(not shown if Tx/Rx
are the same)
mute type
indicator
highlighted
when mute
Tx power
indicator
(Hi/Lo)
(V/S,
is on)
call
type
icon
mode
Rx freq (kHz)
battery status
indicator
internal speaker
icon (shown when
speaker enabled)
antenna
selection icon
(internal
50 ohm )
soft function keys
When the transceiver is scanning, the call type icon is replaced
by the scanning icon and the channel information is
replaced by Scanning.
28 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 39

Battery status indicator
The channel screen displays a battery status indicator. The
indicator graphically shows the:
• state of charge
• state of health
Figure 5: Battery status indicator
The front panel
State of charge State of health
32h
16h
100%
50%
16h
8h
State of charge
The state of charge indicates graphically how much charge is
remaining in the battery. The battery continuously monitors
the current consumption of the transceiver and calculates the
remaining hours of use assuming a Tx to Rx ratio of 1:9.
State of health
Rechargeable batteries have a limited lifetime and a limited
number of times that they may be charged and discharged.
Over time, the total amount of charge that a battery may hold
decreases. The state of health indicates graphically how much
charge a battery can still hold, relative to when it was new.
50% 50%
100%
100%
50%100%
A low state of health indicates that the battery may need
replacing.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 29
Page 40

The front panel
NOTE
When charging a new battery it may show a low
state of health until it has been fully charged and
discharged several times.
30 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 41

The handset
The 2110 SSB Transceiver supports standard audio
accessories using H-229 type connectors. The handset is a
standard issue, lightweight, tactical H-250/U type, with builtin earphone, noise-cancelling microphone, and PTT button. It
is connected to the 6-way connector on the front panel of the
transceiver.
Figure 6: The handset
The front panel
earphone
PTT
microphone
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 31
Page 42

The front panel
This page has been left blank intentionally.
32 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 43

5 Getting started
This section contains the following topics:
Switching on the transceiver (34)
Setting up basics (35)
Selecting a channel (36)
Making a basic voice call (37)
Making a Selective call (38)
Scanning channels (41)
You should not transmit from your transceiver
or tune the antenna unless people are beyond the
safe working distance of:
WARNING
• 0.2 m (8 in) from a long wire, end-fed
broadband, broadband dipole, or wire dipole
antenna
• 0.6 m (2 ft) from any whip antenna
CODAN
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 33
Page 44

Getting started
Switching on the transceiver
Prior to operational use, you should connect an
NOTE
To switch on the transceiver:
antenna to the transceiver (see page 21,
Selecting an appropriate antenna, and the Quick
Reference Card supplied with the antenna).
1 Press .
If you are prompted to enter a password, enter your user
or administrator password, then press .
If you enter an incorrect password it is automatically
erased. If you enter an incorrect password three times the
transceiver automatically switches off.
When the transceiver is switched on, it runs a self-test
that checks the memory, hardware, LCD and keys.
Switching off the transceiver
To switch off the transceiver:
1 Hold .
The transceiver is switched off.
34 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 45

Setting up basics
NOTE
Getting started
Basic information for the transceiver, such as
channels, self addresses, time and date, and
enabling channels for scanning, should be set up
by your system administrator using the NGT
System Programmer. If Quick Start is enabled
you can enter some of this information (see
page 49, Using Quick Start).
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 35
Page 46

Getting started
Selecting a channel
To select a channel:
1 Press VIEW until the channel screen is displayed.
If scanning is on, press SCAN to switch it off.
1 Scroll through the channels in the list. Stop scrolling
when the channel you want is displayed.
The channel is selected.
1 If you want to change the sideband or IF filter settings,
press MODE.
If the mode does not change there is only one mode for
the channel.
NOTE
If you have an automatic antenna fitted,
press PTT to tune the antenna to the
currently selected channel.
36 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 47

Making a basic voice call
To make a basic voice call:
1 Select the channel that you want to use (see page 36,
Selecting a channel).
1 Hold down PTT then speak, releasing PTT when you
have finished speaking.
Muting the transceiver
If you do not want to listen to on-air noise, you can mute the
transceiver so that you will only hear voice traffic on the
channel.
To switch mute on or off:
1 Press MUTE.
When the channel screen is displayed, the mute status is
indicated by a V (Voice) or S (Selcall) at the top centre of
the screen. If the letter is highlighted, mute is on. If the
letter is not highlighted, mute is off.
Getting started
1 Press V/S until V is displayed on the channel screen.
The transceiver will remain muted until it detects voice
traffic on the channel.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 37
Page 48

Getting started
Making a Selective call
NOTE
To make a Selective call:
The call types available will depend on the
options installed in your transceiver.
1 Press CALL.
1 Enter the address of the station you want to call, scroll to
the type of call you want to make, then press CALL.
Call type Icon Used for...
Channel Test Testing the audible quality of a channel in a
Codan Selcall network.
Replacing LQA information for an
ALE/CALM network (if you have the MILSTD-188-141B ALE option installed).
Emergency Sending an emergency alert tone with a call.
Get Position Requesting the location of a remote transceiver
with a GPS receiver connected and enabled.
Get Status Requesting diagnostic or configuration
information from a remote transceiver.
Message Sending a message to a remote transceiver.
Phone Sending a call to a radio/telephone
interconnect unit, which connects the call to
the public telephone network.
RFDS Emgcy Sending an emergency call to an RFDS base
station (Australia only).
38 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 49

Getting started
Call type Icon Used for...
Selective Sending a selective call to a remote transceiver.
Send Position Sending your GPS position to a remote
transceiver. A GPS receiver must be fitted and
enabled in your transceiver.
1 If you are prompted for details about the call, use the
information in the following table to enter them, then
press CALL.
If this prompt is
displayed...
Select network • select the network in which you want to make the call
My address? • select or enter the self address from which you want to send
Select chan/mode In an ALE/CALM network:
Do this...
the call
• select <auto> if you want the transceiver to select the best
channel/mode for the call, starting with the channel on
which the most recent successful link was established, or
• select the channel/mode you want to use to make the call, or
• if you have the MIL-STD-188-141B ALE option installed,
press to select the best channel/mode combination from
the LQA database
In a Codan Selcall network:
• select the channel/mode you want to use to make the call
and check that it is clear of voice and data traffic
NOTE
To abort the call before a connection to the
other station is made, press PTT.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 39
Page 50

Getting started
1 If you made the call in:
• an ALE/CALM network, wait until a message informs
you that the call has been successful (this means your
call has been automatically answered by the other
station)
• a Codan Selcall network, wait until a message informs
you that the call has been sent and listen for audible
beeps transmitted from the other station
1 Hold down PTT then speak.
Release PTT when you have finished speaking.
If you have the MIL-STD-188-141B ALE
option installed and made the call using a
NOTE
special ALE address syntax, you will be
able to send data within the established link
by pressing CALL and following the
prompts.
1 To end the call, press SCAN.
If the transceiver was scanning prior to the call it
resumes scanning.
40 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 51

Scanning channels
Before you can switch scanning on, you need to allocate some
channels to be scanned. If you have Quick Start enabled you
can create a scan list from channels programmed into the
transceiver (see page 49, Using Quick Start). If this feature is
disabled, your system administrator will allocate some
channels to a network, then enable scanning of this network.
Switching scanning on or off
To switch scanning on or off:
1 Press SCAN.
Scanning is toggled on or off.
NOTE
Getting started
SCAN is also used to end a call.
If the transceiver was scanning before the
call was sent or received, it resumes
scanning. If the transceiver was not
scanning before the call, press SCAN to
switch scanning on.
When scanning is switched on, mute is also switched on.
You cannot use PTT while the transceiver is scanning.
Pausing scanning
To pause scanning:
1 Do one of the following:
• to pause scanning on the current channel/mode,
press
• to pause scanning and scroll to another channel/mode,
press or
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 41
Page 52

Getting started
The channel/modes through which you can scroll are
those in the networks that were being scanned. They are
not listed alphabetically but in the order in which they
were being scanned.
If you do not press a key within 30 seconds the
transceiver automatically resumes scanning.
1 While scanning is paused, do one or more of the
following:
• to converse, hold down PTT
• to resume scanning immediately, press
42 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 53

6 Troubleshooting
Below is a checklist for basic troubleshooting.
Check that:
• all connectors are dry and free of dirt
• all connections are sound
• the battery is connected to the transceiver and has some
charge
• the selected antenna is appropriate for the distance over
which you want to communicate
• the antenna is deployed correctly, oriented in a suitable
direction, and connected to the transceiver
• the grounding system is adequate as per instructions
provided with the antenna
• the antenna selection icon on the front panel screen
matches the type of antenna you are using
If required, restart your transceiver to invoke self-testing. The
self-test checks the memory, hardware, LCD and keys.
CODAN
If a serious fault is reported, contact your Codan
representative.
Tabl e 5 contains some general tips for troubleshooting your
transceiver.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 43
Page 54

Troubleshooting
Table 5: General troubleshooting
Problem Solution
The sound from
the front panel
speaker is muffled
Communications
are not clear
There are no
supports for a
wire antenna
available
I get a burn from
the handset when
I press PTT
Drain any moisture from the front panel of the transceiver by
turning it upside down.
Try another channel.
Press PTT.
If you are using a whip or long wire antenna, check that the
antenna selection icon is ATU or ATU / 5 0 (see Figure 4 on
page 28).
If you are communicating over a short distance, try laying the
whip horizontally for near vertical incident skywave operation.
Change to a long wire antenna.
If communications are still not clear, change to a dipole or
broadband antenna and check that the antenna selection icon is
50 or ATU/50 (see Figure 4 on page 28).
Lay the antenna wire on the ground. Lay the earth lead or
counterpoise in the opposite direction.
The transceiver is not adequately earthed. Attach an earth lead
or counterpoise as per the instructions provided with the
antenna.
GPS is not
working
Ensure that the front panel of the transceiver, and hence the
GPS antenna, is facing the sky so that it can receive signals
from satellites.
44 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 55

Appendix A—Entering and editing text
Editing a screen
To gain access to an editable screen:
1 Hold .
1 Do one of the following:
CODAN
A question mark is displayed at the end of the heading to
show that you can now enter and/or edit text in the
setting.
NOTE
If text has already been entered on the line
it is highlighted.
• To use the text displayed, press .
• To enter new text, start typing. When you have entered
the text, press .
• To edit the text displayed, press . The cursor is
placed at the end of the line so you can backspace over
characters and/or enter new text. When the text is
correct, press .
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 45
Page 56

Entering and editing text
Entering text
To enter text in an editable screen:
1 To enter one of the letters on a key, press the key
repeatedly until the letter is displayed.
NOTE
You can also hold the key until the letter
you want is displayed, then release the key.
1 To enter another letter on the same key, wait until the
cursor moves to the next space...
...then press the key repeatedly until the letter you want is
displayed.
1 To enter a letter on another key, press the key for the
letter.
You do not need to wait until the cursor moves to the
next space.
46 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 57

Entering and editing text
Changing between alpha and numerical characters
To change between upper-case and lower-case letters and
numbers in an editable screen:
1 Press # to change the character/case indicator at the
bottom right of the screen from A to a to #.
When you are prompted to enter a call
NOTE
address, the characters that you can enter
are determined by the call systems installed
in the transceiver.
Moving the cursor
To move the cursor across the text:
1 Use and to move the cursor left and right
respectively.
Inserting text
To ins e rt text :
1 Use and to move the cursor to the point where you
want to insert text (or a space), then press the required
character key.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 47
Page 58

Entering and editing text
NOTE
If you want to insert a space, make sure
that A or a is displayed at the bottom right
of the screen before you press 0 otherwise
you will enter a zero.
NOTE
Deleting text
To delete text:
1 Use and to move the cursor one position to the right
of the character that you want to delete, then press .
Saving text changes
To save the changes you have made:
1 Press .
The question mark is removed from the heading.
If you do not want to save the text, hold to discard the
changes.
You can enter a special character using
or with and .
,
*
48 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 59

Appendix B—Using Quick Start
Quick Start provides simple methods to configure your
transceiver to a basic operating state.
Quick Start will be available if your transceiver contains only
one station self address and network names from this default
list:
•*Voice
• *Selcall
•*CALM
•!Default
When you hold , you should see the Quick
Start entries, for example, Add/Edit channel,
Set scan list etc. If these entries are not
displayed, then Quick Start is not available to
you.
CODAN
NOTE
Opening and closing Quick Start
To open Quick Start:
Quick Start is not available in countries that do
not permit programming of transmit frequencies
using the front panel, for example, the United
States of America and Australia.
For detailed information on programming your
transceiver without Quick Start see the
reference material on the enclosed CD.
1 Hold .
To close Quick Start:
1 Press or hold .
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 49
Page 60

Using Quick Start
Adding/Editing a channel
To add or edit a channel:
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Add/Edit channel, then press .
1 Enter the name of the channel that you want to use, then
press .
NOTE
If you want to use an existing channel, scroll to the
channel, then press .
For help with entering text see page 45,
Entering and editing text.
1 Enter the receive frequency in kilohertz, then press .
You can enter the frequency to three
NOTE
decimal places. Press
point, then continue with entering the
frequency.
to enter a decimal
*
1 Enter the transmit frequency in kilohertz, then press .
1 Scroll to the mode combination you want to use, then
press .
The transceiver will return to Quick Start.
1 If you want to add more channels to your transceiver,
scroll to Add/Edit channel and repeat this process.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
If you want to make or receive calls on this
NOTE
new channel, you must add it to your scan
list.
50 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 61

Using Quick Start
Setting up a scan list
To set up a scan list:
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Set scan list, then press .
The first channel in the transceiver is displayed.
1 If you want to add this channel to the scan list, press .
If you do not want to add this channel to the scan list,
press .
When all the channels have been viewed or you have
added 20 channels to your scan list, the transceiver will
return to Quick Start.
If you do not want to scroll through all the channels in
your scan list, hold to return to Quick Start.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
Each time you enter Set scan list, the
CAUTION
resulting scan list will overwrite the
existing scan list.
Setting the time and date
To set the time and date:
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Set time/date, then press .
The display will appear with a line under the day of the
month.
1 Use or to change the current setting to the correct
value, then press .
The line will appear under the month.
1 Repeat the previous step until you have made all of the
changes to the time and date.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 51
Page 62

Using Quick Start
When all the changes have been made, the transceiver
will return to Quick Start.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
Setting your station self address
When Quick Start is available, any self address
that you enter using this method will replace the
NOTE
To set your station self address:
previous self address. If you want to enter more
than one self address, and hence disable the
Quick Start features, see the reference material
on the enclosed CD.
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Set my address, then press .
1 Enter your station self address (maximum of 6 numeric
digits for Codan Selcall, or 15 upper-case/numeric digits
if you have the MIL-STD-188-141B ALE option
installed), then press .
NOTE
For help with entering text see page 45,
Entering and editing text.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
52 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 63

Using Quick Start
Adding/Editing an entry in the Address List or Call Book
To add or edit an address that you call frequently:
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Address/CallBk, then press .
1 Enter the name of the station or person that you want to
add to the list, or use and to select an existing entry,
then press .
NOTE
For help with entering text see page 45,
Entering and editing text.
1 Scroll to the type of call that you want to make, enter the
station address that you want to call, then press .
1 If you selected Message? or No call type, enter the
message, then press .
If you do not want to select a message, press .
1 Scroll to the call system that you want to use to make the
call, then press .
1 If you selected Phone? or No call type, select
<blank> for the phone link that you want to use, then
press .
When all the changes have been made to the call address,
the transceiver will return to Quick Start.
1 If you want to add more call addresses to your Address
List or Call Book, scroll to Address/CallBk and repeat
this process.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 53
Page 64

Using Quick Start
Deleting an entry
To delete addresses, channels or phone links:
1 Open Quick Start.
1 Scroll to Delete..., then press .
1 Scroll to the list from which you want to delete an item,
then press .
1 Scroll to the item you want to delete, then press .
If you delete a channel from the Channel
NOTE
List, it is deleted automatically from the
scan list.
1 Close Quick Start, if required.
54 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 65

Appendix C—Using the GPS receiver
CODAN
The GPS antenna is located behind the front panel of the
transceiver (see Figure 3 on page 23). In order to obtain
reliable and accurate GPS information, you should ensure that
the front panel of the transceiver is pointed toward the sky and
is not shadowed by overhead obstructions.
To access GPS information:
1 Press GPS to see the GPS screen.
To calculate distance and bearing to another transceiver:
1 Go to an Address List or Call Log entry containing a
GPS position of the other station.
The transceiver calculates the distance to the other
transceiver and its bearing from true north with respect to
your current location.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 55
Page 66

Using the GPS receiver
This page has been left blank intentionally.
56 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 67

Appendix D—Transceiver specifications
Table 6: Specifications
Item Specification
Frequency range Transmit: 1.6 to 30 MHz
Receive: 250 kHz to 30 MHz
Channel capacity 400 channels
Operating modes Single sideband (J3E) USB and LSB or switched USB/LSB,
AM H3E (optional)
Sensitivity Frequency:
0.25 to 30 MHz
Frequency:
1.6 to 30 MHz
For 10 dB SINAD with greater than 50 mW audio output
Power output 25 W PEP ±0.5 dB (high power)
5 W PEP ±0.5 dB (low power)
RF amp off:
0.28 µV PD, –118 dBm
RF amp on:
0.14 µV PD, –124 dBm
CODAN
Antenna tuning
times
Approximate
battery life
Environment Ambient temperature: –30 to 60°C
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 57
First time tuning 2.5 s typical
Memory tuning 50 ms typical
13 Ah NiMh: 50 h
8Ah NiMh: 30h
7 Ah SLA: 15 h
Relative humidity: 95% non-condensing
Derate upper ambient temperature by 1°C per 330 m (360 yd)
above sea level
Page 68

Transceiver specifications
Table 6: Specifications
Item Specification
Size 2110 including battery: 245 mm W × 350 mm D × 92 mm H
(9.8 in W × 14.0 in D × 3.7 in H)
2110 only: 245 mm W × 250 mm D × 92 mm H
(9.8 in W × 10.0 in D × 3.7 in H)
Weight 2110 only: 2.5 kg (5.5 lb)
13 Ah NiMh battery 2.9 kg (6.4 lb)
8 Ah NiMh battery 2.1 kg (4.6 lb)
7 Ah SLA battery 3.2 kg (7.1 lb)
Sealing IP68; immersion for 1 h at a depth of 1 m (3 ft)
58 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 69

Appendix E—HF radio transmission
The HF band is the range of frequencies between 3 and
30 MHz. HF transceivers usually cover a frequency range of
1.6 to 30 MHz.
Codan HF transceivers transmit on single sidebands. This
reduces the power required to send HF signals and increases
the number of channels available within the HF spectrum.
HF transceivers are primarily used for long-range
communication where distances of 3000 km (1800 mi) and
more are possible. Obstructions such as buildings and
mountains have little effect on long-range communication. HF
radio can cover such large distances because of the way the
transmitted radio signal propagates.
HF radio waves propagate in three ways simultaneously:
• ground wave
• direct wave
• sky wave
CODAN
Ground wave
The ground wave travels near the ground for short distances,
typically up to 100 km (60 mi) over land and 300 km (190 mi)
over sea. The distance covered depends upon the operating
frequency, transmission power, and type of terrain.
Direct wave
The direct wave travels in a direct line-of-sight from the
transmitter to the receiver.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 59
Page 70

HF radio transmission
Sky wave
The sky wave is the most important form of HF propagation.
The radio wave is transmitted toward the sky and is reflected
by the ionosphere to a distant receiver on earth.
The reflective properties of the ionosphere change throughout
the day, from season to season, and yearly.
Figure 7: The reflective properties of the ionosphere
ionosphere
emitted
HF wave
transmitter
Frequency, distance and time of day
The extent to which a radio wave is reflected depends on the
frequency that is used. If the frequency is too low, the signal is
absorbed by the ionosphere. If the frequency is too high, the
signal passes straight through the ionosphere. Within the HF
band, low frequencies are generally considered to be in the
range of 2 to 10 MHz. High frequencies are above 10 MHz.
A frequency chosen for daytime transmission may not
necessarily be suitable for night-time use. During the day, the
layers of the ionosphere are thick. The layers absorb lower
frequencies and reflect higher frequencies. At night, the
ionosphere becomes very thin. The low frequencies that were
absorbed during the day are reflected and the high frequencies
that were reflected during the day pass straight through.
Summer HF communications usually operate on higher
frequencies than those used in winter over the same distance.
reflected
HF wave
receiver
60 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 71

Solar activity varies over an 11 year cycle. Higher frequencies
need to be used during periods of peak activity.
It is important to remember that you may need to change the
frequency you are using to achieve the best communication.
The general rules of thumb for HF communication are:
• the higher the sun, the higher the frequency
• the further the distance, the higher the frequency
Antenna selection
The selection of an appropriate antenna is critical to the
success of your communications (see page 21, Selecting an
appropriate antenna).
Channels and modes
A channel is a name that is given to a frequency or a pair of
frequencies, e.g. ‘Channel 1’, ‘4500’ and ‘Headquarters’. The
frequencies may be any frequencies within the HF range.
HF radio transmission
Each channel has one or more modes associated with it. Each
mode indicates a sideband that can be used with the channel,
such as USB or LSB. When you make a call you need to
specify the channel and the mode you want to use.
Tabl e 7 shows examples of channels and the information
associated with them.
Table 7: Examples of channels and modes
Channel Receive frequency
(kHz)
Channel 1 10600 10600 LSB, USB
4500 4500 – AM
Headquarters 22 758 23 000 USB
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 61
Transmit frequency
(kHz)
Modes
Page 72

HF radio transmission
Networks and scanning
A network is two or more stations that use the same
frequencies and call system to communicate.
The frequencies are allocated by a government authority and
enable the network to maintain HF communication throughout
the day and night.
The call system is the method the network uses to make and
receive calls. For example, in networks that use the Codan
Selcall call system to make calls, the user enters the address of
the station they want to call, then selects the channel/mode on
which to make the call. In networks that use the ALE/CALM
call system, the transceiver selects the best channel/mode for
the call.
The transceiver can be set to scan the channel/modes used by
your network to detect incoming calls. It is recommended that
when you are not using the transceiver to communicate you
switch scanning on. This ensures that you can receive calls
from stations in your network.
Etiquette for the use of HF radio
There is a standard procedure for communicating over HF
radio. Before you begin transmitting, switch off scanning,
select a channel, then press PTT on the handset to initiate
tuning of the antenna. Listen to the channel that you are going
to use and ensure that there is no voice or data communication
taking place. You may need to wait until the channel is clear or
select another channel.
When you first establish communication with another station
it is customary to state their call sign and then your own using
the phonetic alphabet (see Table 8 on page 63). For example:
‘Alpha Bravo One, this is Alpha Bravo Two. Do you receive
me? Over.’
62 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 73
HF radio transmission
In this example your call sign is AB2 and you are calling a
station with the call sign AB1. A call sign is a group of letters
and numbers issued by a government authority to identify a
station. The phonetic alphabet is used to ensure that your call
sign is understood.
The word ‘over’ is used to signify the end of your
transmission. The transceiver may be set up to transmit a short
beep when you release the PTT button on the handset. When
your conversation with the other party is finished, the party
that speaks last should say ‘out’.
Swearing or foul language should not be used—heavy
penalties can apply.
Keep communication as short as possible.
Table 8: The phonetic alphabet
Letter Word Letter Word
A Alpha N November
B Bravo O Oscar
C Charlie P Papa
DDeltaQQuebec
EEchoRRomeo
F Foxtrot S Sierra
GGolfT Tango
HHotelUUniform
I India V Victor
J Juliet W Whiskey
KKiloXX-ray
L Lima Y Yankee
M Mike Z Zulu
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 63
Page 74

HF radio transmission
This page has been left blank intentionally.
64 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 75

Appendix F—Definitions
Standards and icons
The following standards and icons are used in this guide:
This typeface Means...
Italic a cross-reference or text requiring emphasis
This icon Means...
" a step within a task
CODAN
NOTE
CAUTION
WARNING
the text provided next to this icon may be of
interest to you
proceed with caution as your actions may
lead to loss of data, privacy or signal quality
your actions may cause harm to yourself or
the equipment
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 65
Page 76

Definitions
Acronyms and abbreviations
This term Means...
ALE automatic link establishment
AM amplitude modulation
BER bit error rate
CALM Codan automated link management
CW carrier wave
DC direct current
DSP digital signal processor
ETSI European Telecommunications Standards
Institute
GPIO general purpose input/output
GPS global positioning system
HF high frequency
ID identification
ICNIRP International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection
IF intermediate frequency
LBT listen before transmit
LCD liquid crystal display
LED light emitting diode
LSB lower sideband
LQA link quality analysis
NiMh nickel metal hydride
NSP NGT system programmer
66 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 77

Definitions
This term Means...
PA power amplifier
PC personal computer
PTT press-to-talk
RF radio frequency
R&TTE radio and telecommunications terminal
equipment
Rx receive
SB sideband
SINAD (signal + noise + distortion)-to-(noise +
distortion) ratio
SLA sealed lead acid
tcvr transceiver
Tx transmit
USB upper sideband
V firmware/software version
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 67
Page 78

Definitions
Glossary
This term Means...
active line The line below the title of a list on the front
panel screen. Items in the active line are
selected by pressing .
address The HF transceiver equivalent of a
telephone number. Your station self address
is used by other stations to call you, and it is
sent when you make calls to identify you as
the caller. It is sometimes referred to as an
ID, a station ID, or a self ID.
MIL-STD-188141B ALE
option
call detect time The length of time during scanning that the
channel Frequencies programmed in the transceiver
Channel Test
call
Emergency call A call that enables you to trigger an
An option that enables you to make ALE
ALL, ANY, Group Selective, NET and
Wildcard calls, and perform LQA reporting
and AMD messaging.
transceiver pauses on each channel in order
to detect an incoming call. It is the inverse
of the scan rate.
to transmit and receive signals on air.
A call that enables you to test the quality of
a channel. It is sometimes referred to as a
Beacon call. Channel Test calls may be
made in an ALE/CALM network to replace
information in the LQA database, and to
perform a manual sounding operation (if
you have the MIL-STD-188-141B ALE
option installed).
emergency alarm at a specific station then
speak to an operator there.
frequency The number of cycles per second of a radio
wave, usually expressed in kilohertz.
68 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 79

Definitions
This term Means...
Get Position call A call that gets the GPS position of a
specific station.
Get Status call A call that gets diagnostic or configuration
information about the transceiver at a
specific station.
front panel The interface that is used to control the
functions of the 2110 SSB Transceiver. It
consists of a display, keypad and connectors
for the handset, antenna, ancillary
equipment, and earthing.
hot key A key on the front panel that is pre-
programmed with a macro that enables you
to perform a task quickly.
Last Heard Log A log of the last 100 on-air transmissions
detected by the current station.
The Last Heard Log is available if the MILSTD-188-141B ALE option is installed.
listen before
transmit
If enabled, the automatic process that the
transceiver uses to detect whether or not
there is traffic on a channel and, when
necessary, select another channel or inform
the user that the channel is busy.
LQA beacon A Channel Test call made in an
ALE/CALM network using a Group
Selective or NET address syntax. On
completion of the beacon, the information
collected replaces the information for the
channel stored in the LQA database. It is
sometimes referred to as an ALE beacon.
The LQA beacon is available if the MILSTD-188-141B ALE option is installed.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 69
Page 80

Definitions
This term Means...
macro A short set of instructions to automate a task
you perform with the transceiver. When a
macro is assigned to a key, the key becomes
a hot key.
manual sounding A Channel Test call made in an
ALE/CALM network using the text
SOUNDING as the call address. The
station performs a sounding operation,
which other stations use to update the
information in their LQA database.
Manual sounding is available if the MILSTD-188-141B ALE option is installed.
Message call A call that enables you to send a message to
a specific station.
mode A type of reception or transmission you can
use with a channel, comprising a sideband
and an IF filter.
network Two or more stations that use the same
frequencies and call system to
communicate.
Phone call A call that enables you to connect to a
public telephone network.
PTT button Press-to-talk button, located on the left side
of the handset. This button enables you to
communicate during voice calls, switch
mute off, cancel voice calls prior to the
point where voice can be transmitted, cancel
calls where data is being transmitted, and
exit out of editable screens without saving
changes.
revertive A signal sent by a station in response to a
call.
70 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 81

Definitions
This term Means...
transceiver unit The device that modulates audio signals
onto radio frequencies that can be
transmitted on air, and that demodulates the
radio frequencies it receives into audio
signals.
Selective call A call that enables you to contact a specific
station then speak to an operator.
Send Position
call
A call that sends your GPS position to a
specific station.
sideband A band of frequencies that is above or
below a modulated carrier frequency.
station A point of communication consisting of a
transceiver, a battery, an antenna, ancillary
equipment, and appropriate connecting
cables.
transceiver A transceiver unit with speaker, handset,
and battery.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 71
Page 82

Definitions
Units
NOTE
Measurement Unit Abbreviation
Length metre
Frequency hertz Hz
Time second s
Voltage volt V
Weigh t gram
Unit multipliers
Imperial dimensions are in United States
Customary Units.
m
(inch/feet/yard/
mile)
hour h
(pound)
(in/ft/yd/mi)
g
(lb)
Units are expressed in accordance with ISO
NOTE
Unit Name Multiplier
Mmega1000000
kkilo1000
m milli 0.001
72 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
1000:1992 ‘SI units and recommendations for
the use of their multiples and of certain other
units’.
Page 83

About this issue
This is the first issue of the 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting
Started Guide.
Associated documents
This guide is one of a series of documents associated with the
2110 SSB Transceiver. The other documents are:
• 2110 SSB Transceiver Reference Manual (Codan part
number 15-04135-EN) supplied on the CD inside the
back cover of this guide
• 2110 SSB Transceiver Technical Service Manual (Codan
part number 15-02071-EN)
• 2110 SSB Transceiver Repair Guide (Codan part number
15-04139-EN)
• Declaration of Conformity for the 2110 SSB Transceiver
(Codan part number 19-40157)
Definitions
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 73
Page 84

Definitions
This page has been left blank intentionally.
74 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 85

Appendix G—Warranties
Codan’s warranty statement is provided on the International
Product Warranty Card (Codan part number 12-50144). This
statement sets out standard use and misuse under the terms of
the warranty.
The following warranties are supplied with the 2110 SSB
Transceiver and accessories:
Item Warranty period
CODAN
2110 SSB
Transceiver
NiMh battery pack 3 years ex-factory
SLA battery pack 1 year ex-factory
Battery chargers 3 years ex-factory
Antennas 1 year ex-factory
Backpacks 1 year ex-factory
NOTE
3 years ex-factory
If the transceiver or battery pack are opened
then care must be taken when re-assembling to
ensure that water tight seals retain integrity.
Inspect all gaskets prior to closing and replace
any that appear damaged. Original screws must
be used. Failure to do so may void a warranty
claim associated with moisture ingress.
Replacement gaskets and screws are available
as spares from your Codan representative.
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide 75
Page 86

Warranties
This page has been left blank intentionally.
76 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 87

Index
CODAN
A
Address List
adding/editing entries 53
calling from 38
alternative charger requirements 17
B
battery discharge regime 18
battery storage 10
C
call sign 62
call systems
ALE/CALM 62
Codan Selcall 62
calls
from Address List 38
channel screen 28
channels
definition 61
manual selection 36
compliance
C-tick approval 9
electromagnetic compatibility and safety
notices 7
earth symbol 9
electrical safety 8
electromagnetic compatibility 7
protection of the radio spectrum 6
European Radio and Telecommunications
Terminal Equipment Directive 5
C-tick approval 9
E
electromagnetic compatibility and safety notices
compliance
earth symbol 9
electrical safety 8
electromagnetic compatibility 7
protection of the radio spectrum 6
entering and editing text
changing between alpha and numerical
characters 47
deleting text 48
editing a screen 45
entering special characters 48
entering text 46
inserting text 47
moving the cursor 47
saving text changes 48
European Radio and Telecommunications
Terminal Equipment Directive
compliance 5
F
frequency selection
depending on distance and time of day 60
front panel keys 23
G
ground wave 59
H
handset 31
HF radio transmission 59
D
deleting entries 54
direct wave 59
discharge regime
battery 18
2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide Index-1
M
modes 36, 61
N
networks 62
Page 88

Index
P
password
entering 34
phonetic alphabet 63
power on/off 34
Q
Quick Start 49
adding/editing a channel 50
adding/editing an entry in the Address List or
Call Book 53
deleting an entry 54
opening and closing 49
setting the time and date 51
setting up a scan list 51
setting your station self address 52
S
safety
radiation 7
scan rate, see call detect time 68
scanning channels 41, 62
pausing channel scanning 41
selecting
an item in a list 24
channel 36
sky wave 60
storage
battery 10
W
wave
direct 59
ground 59
sky 60
Index-2 2110 SSB Transceiver Getting Started Guide
Page 89

www.codan.com.au
Head Office
Codan Limited
ABN 77 007 590 605
81 Graves Street
Newton SA 5074
AUSTRALIA
Telephone +61 8 8305 0311
Facsimile +61 8 8305 0411
asiasales@codan.com.au
Codan (UK) Ltd
Gostrey House
Union Road
Farnham Surrey GU9 7PT
UNITED KINGDOM
Telephone +44 1252 717 272
Facsimile +44 1252 717 337
uksales@codan.com.au
Codan US, Inc.
8430 Kao Circle
Manassas VA 20110
USA
Telephone +1 703 361 2721
Facsimile +1 703 361 3812
ussales@codan.com.au
Codan Limited
ABN 77 007 590 605
105 Factory Road
Oxley Qld 4075
AUSTRALIA
Telephone +61 7 3716 6333
Facsimile +61 7 3716 6350
 Loading...
Loading...