Page 1

The user is responsible for operating this product wisely.
The product is intended for use only as a navigational aid
and should not be used when precise measurement of
direction, location, distance or topography is required.
GPS (Global Positioning System) is operated by the U.S.
government, which is solely responsible for its accuracy and
maintenance. The system is subject to changes, which could
affect the accuracy and performance of GPS equipment.
Remove the batteries from the unit if you do not expect to
use it for months at a time. As with any batteries, leakage
can occur. When re-installing batteries, observe proper polarity.
Warning: If you choose to use this device in a vehicle, it
is the sole responsibility of the operator of the vehicle to use
this device in a safe manner. Be careful to avoid being
distracted from safe and proper driving practices.
Warning: If you choose to use this device in a vehicle, it
is the sole responsibility of the operator to secure the GPS
unit so that it will not cause damage or personal injury in the
event of an accident.
DO NOT mount the GPS receiver over airbag panels or in a
place where the driver or passengers are likely to have an
impact with the device in an accident or collision.
Cobra Electronics Corporation reserves the right to change or
improve information in this manual without notice. Please
visit www.cobra.com for updates or questions.
Customer Support
In this user's manual, you should find all the information you
need to operate your GPS 100. If you require further
assistance after reading through this manual, Cobra
®
Electronics offers the following customer support services:
In the USA:
Automated Help Desk is available in English
24 hours a day, 7 days a week at 773-889-3087.
Customer Service Operators are available in
English and Spanish at 773-889-3087 Monday
to Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. CST.
Questions can be faxed to 773-622-2269.
Automated Technical Assistance is available
in English or Spanish 24 hours, 7 days a week via
e-mail at: productinfo@cobra.com
On-line answers to frequently asked questions
(in English only) can be found at: www.cobra.com.
Outside the U.S.A., please contact your local dealer.
Non-English Manuals
The GPS 100 is equipped to communicate in the language
of your choice: English, Dutch, French, German, Italian,
Portuguese, Spanish or Swedish, (see “System PageSettings: Languages,” page 36).
For operating instructions in Dutch, French, German,
Italian, Portuguese, Spanish or Swedish please visit
www.cobra.com/gps-manuals.html.
A1
Important Information
FCC Compliance
This device complies with Class B of the FCC rules.
Operation is subject to the condition that this device
does not cause harmful interference. It must accept any
interference received, including that which may cause
undesirable operation.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
WARNING
WARNING
Nothing comes close to a Cobra
®
Operating Instructions for Your
GPS 100
GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM RECEIVER
ENGLISH
Go to Table of Contents
Page 2
Congratulations!
You’ve made a smart choice by purchasing the GPS 100
Global Positioning System receiver from Cobra
®
. Designed to
give you access to the most advanced satellite navigation
technology available, your GPS 100 offers you these
sophisticated features and capabilities:
Features:
• Cobra®EXCLUSIVE 18-channel technology gives you
the quickest acquisition time of any handheld recreational
GPS receiver available
• Locks on to signals from satellites. Delivers accurate
positioning within as little as 3 meters
• Indicates direction of travel to your destination with a
compass pointer
• Displays current position, altitude, bearing, time of day, current
speed of travel, average speed throughout your trip and
estimated time of arrival at your destination
• Stores up to 500 navigational waypoints
• Lets you program and store a navigational route using up to
50 waypoints
• Displays the route to your destination and your progress
along that route
• Automatically tracks your travel, and shows you how to return
along the same track (up to 10 separate tracks can be stored)
• Up to 100 map datums to choose from
• Display screen can be backlit for maximum visibility
• Is waterproof to IXP7 (submerged 1 meter for 30 minutes)
standards and can operate in temperatures from 5˚F to 158˚F
(-15˚C to 70˚C)
A3
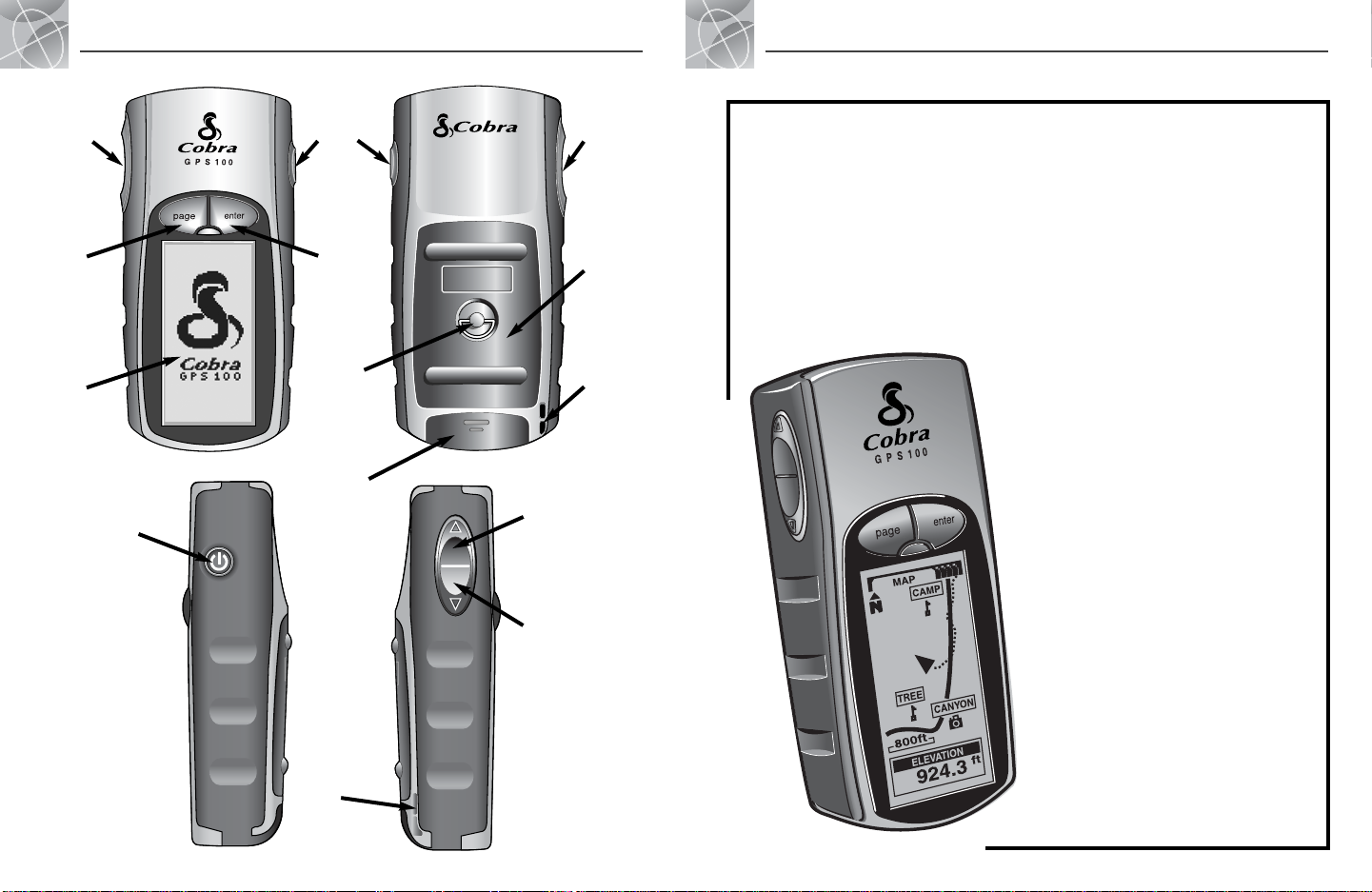
GPS 100
A2
PAGE
button
ZOOM OUT
button
ZOOM IN
button
POWER and
Backlight
button
D-Ring
Fastener
Battery
Compartment
door
External
power
connector
cover
Lanyard
connector
loop
ENTER
button
Backlit
display
screen
Lanyard
connector
loop
GPS 100
Global Positioning System
ZOOM
IN/OUT
buttons
POWER and
Backlight
button
ZOOM
IN/OUT
buttons
Go to Table of Contents
Page 3

Important Information........................................................................................................ A1
Product Features ............................................................................................................... A2–A3
Welcome.......................................................................................................................... 1
GPS General Information .................................................................................................... 2–4
Basic Operation................................................................................................................. 5–7
Installing Batteries...................................................................................................... 5
Using the Buttons....................................................................................................... 5–6
Tur ning the Power On ................................................................................................. 6
Powersaver Mode....................................................................................................... 6
Navigating with the GPS 100 ...................................................................................... 7
The Five Main Pages.......................................................................................................... 8
2.1 Map Page.................................................................................................................. 9–10
2.2 Gauges Page.............................................................................................................. 11–12
2.3 Trip Meter Page.......................................................................................................... 13–14
2.4 Nav Data Page........................................................................................................... 15–30
Waypoints................................................................................................................. 15–18
Tracks....................................................................................................................... 19–20
Route ....................................................................................................................... 21–25
Delete Options........................................................................................................... 26–28
Editing Text ............................................................................................................... 29
Sort or Search ........................................................................................................... 30
2.5 System Page ............................................................................................................. 31–38
Alert................................................................................................................................ 39
GPS General Information .................................................................................................... 40–42
Specifications.................................................................................................................... 43
Maintenance and Service.................................................................................................... 44
Index............................................................................................................................... 45–46
Accessories....................................................................................................................... 47
Declaration of Conformity ................................................................................................... 47
Warranty.......................................................................................................................... 47
Order Form....................................................................................................................... 48
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TABLE OF CONTENTS
9
Page 4

GPS GENERAL INFORMATION
2
GPS Basics
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based radionavigation system. It consists of 24 satellites, which orbit the
Earth at an altitude of approximately 11,000 miles, and
ground stations. GPS provides users with accurate information
on position, velocity and time. This is available anywhere in
the world and in most weather conditions.
GPS was initiated in 1973 to reduce the proliferation of
navigation aids by the United States Department of Defense.
By creating a robust system that overcame the limitations of
many previously existing navigation systems, GPS became
attractive to a broader spectrum of users. GPS has been
successful in classic applications such as aviation and marine
navigation since it was first developed. Since then, it has
become useful for a wide range of people because its
capabilities are accessible using small, affordable equipment.
What was once available only in very expensive equipment,
Cobra
®
brings to you with our high-quality line of affordable
handheld GPS receivers
How GPS Works
GPS uses a global network of 24 satellites that transmit radio
signals to earth from high earth orbit. Thankfully for users,
the United States has offered free use of the system to the
international community. Many international user groups have
accepted GPS as the core for an international civil satellite
navigation capability.
GPS service provides users with extremely accurate
positioning information anywhere on or near the surface of
the earth. To accomplish this, each of the 24 satellites emits
signals to receivers below. GPS determines location by
computing the difference between the time that a signal is
sent and the time it is received. GPS satellites carry atomic
clocks that provide extremely accurate time information. The
time information is placed in the codes broadcast by the
satellite so that a receiver can continuously determine the
time the signal was broadcast. The signal contains data
that your Cobra
®
GPS receiver uses to compute the locations
of the satellites and to make other adjustments needed for
accurate positioning. Your Cobra
®
GPS receiver uses the time
difference between the time of signal reception and the
broadcast time to compute the distance, or range, from the
receiver to the satellite. With information about the ranges
to four satellites and the location of each satellite when
the signal was sent, your Cobra
®
receiver can compute its
own three-dimensional position: latitude, longitude, and
altitude. People think of GPS as having three segments:
the control, space and user segments. What follows is
a little information about each segment.
Control Segment
The Control Segment of GPS consists of the Master Control
Station, Monitor Stations and Ground Antennas.
The one master control station, located at Falcon Air Force
Base in Colorado Springs, Colorado, USA is responsible for
overall management of the remote monitoring and
transmission sites. As the center for support operations, it
calculates any position or clock errors for each individual
satellite, based on information received from the monitor
stations. Then it "orders" the appropriate ground antennas to
relay the corrective information back to that satellite.
Five monitor stations are located at Falcon Air Force Base in
Colorado, Hawaii, Ascension Island in the Atlantic Ocean,
Diego Garcia Atoll in the Indian Ocean and Kwajalein Island in
the South Pacific Ocean. Each of the monitor stations checks
the exact altitude, position, speed and overall health of the
orbiting satellites. The control segment uses measurements
collected by the monitor stations to predict each satellite's
orbit and clock. The prediction data is up-linked, or
transmitted, to the satellites for transmission back to the
continued
WELCOME TO THE COBRA®GPS 100
“GoTo” on
Map Page
“GoTo” on
Gauges Page
Navigate
Route On
Map Page
Navigate
Route on
Gauges Page
Making Travel Easier
Your Cobra®GPS 100 receiver makes travel easier through three
major ways:
GoTo a Waypoint – The GPS 100 guides you in a straight line
to a single point. (See and )
Navigate a Route – The GPS 100 gives you the opportunity to
select two or more waypoints to create a route. You can then use
your GPS 100 to guide you in a straight line from point to point
through your stored route. (See and )
Navigate a Track – The GPS 100 automatically keeps a record
of your progress as you travel and gives you a graphic representation or
“track log” of the path or track you have taken. You can use the track
log to create a track that you can recall for navigation. The track can be
navigated in the forward or the reverse direction of the original travel.
(See and )
This manual is designed to help you take advantage of these and our
many other features. We suggest that you begin by reading the “General
Information” and “System Sections” first. If you are not familiar with the
satellite navigation technology, these will help you understand the basics.
Then, take your Cobra
®
GPS receiver outside and practice while you read the
sections on how to operate it.
Navigate
Track on
Map Page
Navigate
Track on
Gauges Page
1
Go to Table of Contents
Page 5

3
GPS GENERAL INFORMATION
users. The control segment also ensures that the
GPS satellite orbits and clocks remain as designed. A
station can track up to 11 satellites at a time. Each station
performs this "check-up" twice a day, as the satellites
complete their journeys around the earth. Noted variations,
such as those caused by the gravity of the moon and sun and
the pressure of solar radiation, are passed along to the
master control station.
The last of the three pieces of the control segment of GPS
are the ground antennas. Ground antennas monitor and track
the satellites from horizon to horizon. They also transmit
correction information to individual satellites.
Space Segment
The space segment includes the satellites and the Delta
rockets that launch the satellites from Cape Canaveral in
Florida. GPS satellites fly in circular orbits at an altitude of
10,900 miles (17,500 km) and with a period of 12 hours.
The orbits are tilted to the earth's equator by 55 degrees to
ensure coverage of the polar regions. Powered by solar cells,
the satellites continuously orient themselves to point their
solar panels toward the sun and their antenna toward the
earth. Each of the 24 satellites, positioned in 6 orbital
planes, circles the earth twice a day.
The satellites are composed of three major subsystems: Solar
Panels, Internal Components and External Components.
Solar Panels
Each satellite is equipped with solar array panels. These
panels capture energy from the sun, which provides
power for the satellite throughout its life.
Inter
nal Components
Internal components are subsystems such as atomic
clocks and radio transmitters. Each satellite contains four
atomic clocks. These clocks are accurate to a nanosecond
or a billionth of a second. The atomic clocks within the
satellites are so accurate because even an extremely
small time inaccuracy would translate into a extremely
large position difference (1/100 of a second inaccuracy
translates to a position difference of 1,860 miles to any
GPS receiver).
Exter
nal Components
The exterior of the GPS satellite has a variety of
antennas. The signals generated by the radio transmitter
are sent to your Cobra
®
GPS receiver via L-band
antennas. Another component of the satellite is the radio
transmitter, which generates the signal. Each of the 24
satellites transmits its own unique code in the signal.
User Segment
You and your Cobra
®
GPS receiver are a part of the user
segment along with many other private individuals and
military personnel and their GPS receivers. Military GPS
equipment has been integrated into fighters, bombers,
tankers, helicopters, ships, submarines, tanks, jeeps and
soldiers' equipment. GPS is also used on Space Shuttles.
Cutting-edge Satellite navigation technology coupled with
your Cobra®GPS receiver can help overcome many of the
hardships and hazards associated with recreation. Your
Cobra
®
GPS receiver allows you to go practically anywhere
with confidence knowing precisely where you are at all times.
With your Cobra
®
GPS receiver, you will be able to record
accurately any location and return to that precise spot time
and again, any time, anywhere.
GPS GENERAL INFORMATION
Data Field Choices Descriptions
Your Cobra®GPS 100 has the ability to display various types
of information to you. In order to take advantage of the rich
information available to you, it is important that you
understand the meaning of certain terms. Below is a list of
terms that will aid you in using your Cobra
®
GPS 100.
Accuracy - the distance within which the unit can accurately
locate a position
Avg Speed - average speed throughout the current
navigation
Bearing - the direction you are currently heading
Date - the current date
Destination - the destination is the last point on a route, or
the end of a track
Elevation - your current elevation above sea level
ETA - Estimated Time of Arrival, based on the average speed
you have traveled over the course of your entire route or track
Location - your current location shown in degrees/minutes
of latitude and longitude
Max Speed - the highest speed that you have traveled
during the current navigation
Odometer - total cumulative distance traveled since the last
time the odometer was reset
Power - power icon showing power source (external or
battery), battery charge level, and backlight On or Off
Speed - your current speed
Time - the current time in your selected time zone
Trip Odom - the distance traveled since the last time the trip
odometer was reset
Trip Time - the trip time is the total time that has elapsed
during your current navigation since your last reset
4
Set Data Display
Map Page
Set Data Display
Gauges Page
Set Data Display
Trip Meter Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 6
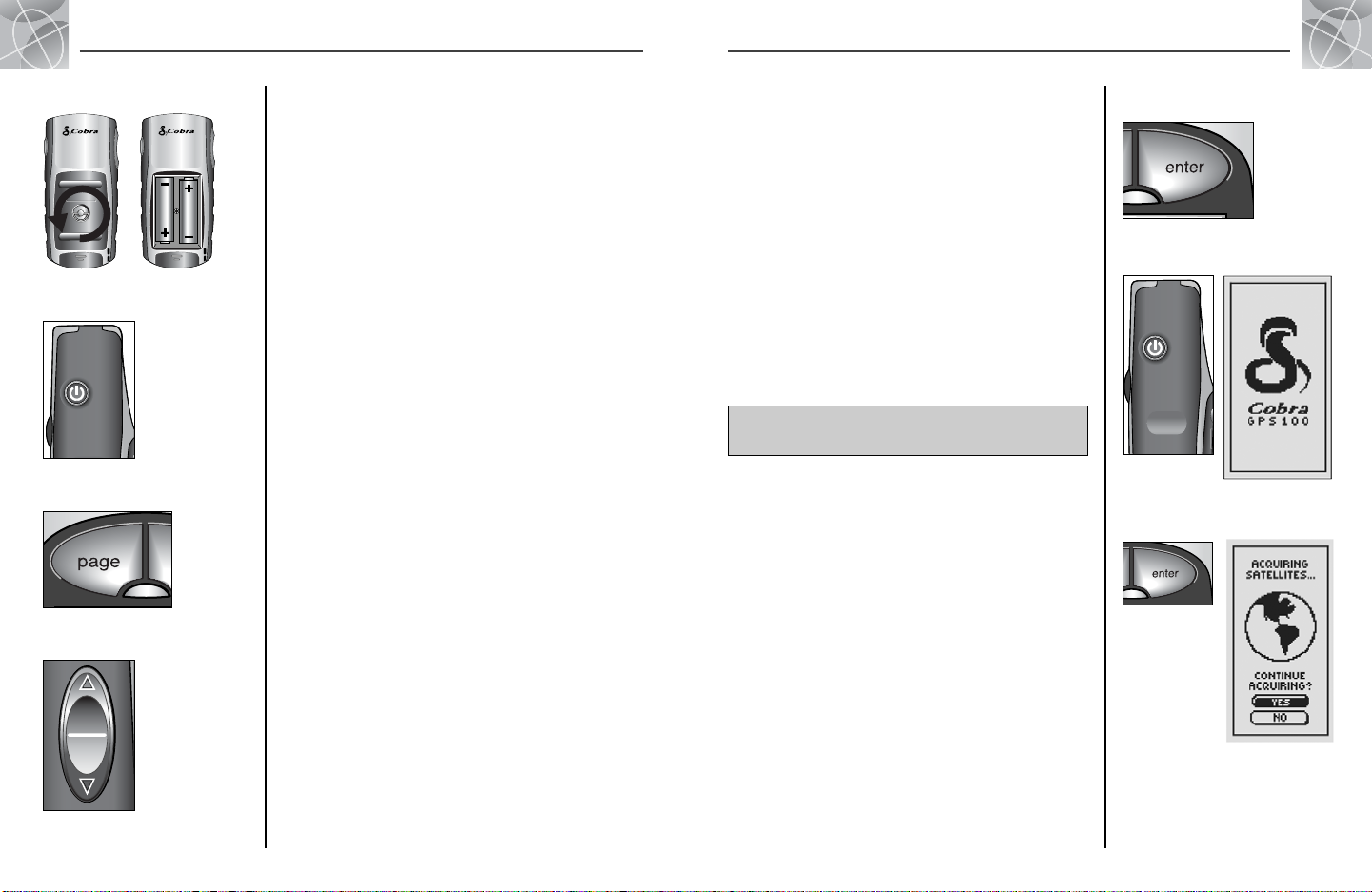
Installing Batteries
Your GPS 100 operates on two standard AA batteries (not included). Always
use high-quality alkaline batteries. To install batteries, twist the D-ring
connector counterclockwise (anticlockwise) and remove the battery
compartment cover. Insert two AA batteries ensuring correct polarity
alignment. Replace the battery compartment cover and twist the D-ring
clockwise to lock.
As an optional power source, an Automotive Power Adapter (not included,
see “Optional Accessories”, page 47) can be used with your GPS 100.
Using the Buttons
You can access all features of your GPS 100 by using three buttons. After
reading the general explanations below, please refer to “Using the Map
Page,” page 9, to begin using the buttons to operate your unit.
The POWER Button
Pressing and holding the POWER button for 2 seconds will turn the device
on or off.
With the unit turned on, pressing and releasing the POWER button will turn
on the display backlight. The display will remain lit until no buttons have
been pushed for 15 seconds (for more details, see page 31).
The PAGE Button
Pressing and releasing the PAGE button allows you to cycle through the five
main pages (described in the next section). If you have proceeded to one of
the menus (described later in this manual), the PAGE button is an “escape”
key, allowing you to exit the menu and return to the main page. At any
time, press and hold the PAGE button for 2 seconds to display the Page List
menu. From this menu you can go directly to any main page.
The ZOOM IN/OUT Button
When a map is displayed, you can use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to zoom in
or zoom out on the image of the map. Also, whenever you see a menu of
selections, using the ZOOM IN/OUT button allows you to scroll through the
selections displayed. A side scroll bar next to a menu indicates that more
selections can be viewed by scrolling beyond the bottom or top of the list
that is currently visible.
continued
6
1
BASIC OPERATION
ZOOM IN/OUT Button
PAGE Button
POWER Button
5
1
BASIC OPERATION
The ENTER Button
Pressing and releasing the ENTER button accepts a highlighted selection.
The ENTER button can also be used as a Waypoint
shortcut. To mark a new waypoint using current location, press and
hold the ENTER button for 2 seconds. A confirmation window will pop up.
Turning the Power On
To turn on your GPS 100, press and hold the POWER button for 2 seconds.
A start-up screen appears for a few seconds, followed by a screen that shows
that the unit is attempting to lock onto signals from GPS satellites. Once
three satellite signals have been acquired, the screen will automatically
switch to the Map page and the unit is ready to use.
NOTE: The unit must be outside with a clear view of the sky to acquire
satellite signals for navigation.
To turn the power off, press and hold the POWER button for 2 seconds.
Powersaver Mode
If you wish to save battery power while using just the non-navigational
features of your unit, you can turn GPS navigation off. To do so, select “No”
and press the ENTER button before the screen automatically changes to the
Map page.
In Powersaver Mode, no GPS functions will be available until you turn GPS
back on. To do so, please refer to page 33 of this manual.
NOTE: You can turn GPS off at any time. Please see “Turning GPS Off and
On,” page 33.
ENTER Button
ENTER
Button
Power
Button
GPS Status
Screen
Startup Screen
NOTE: When you use the GPS 100 for the first time, it will take up to
approximately 50 seconds to lock on to the GPS satellites.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 7
1
BASIC OPERATION
7
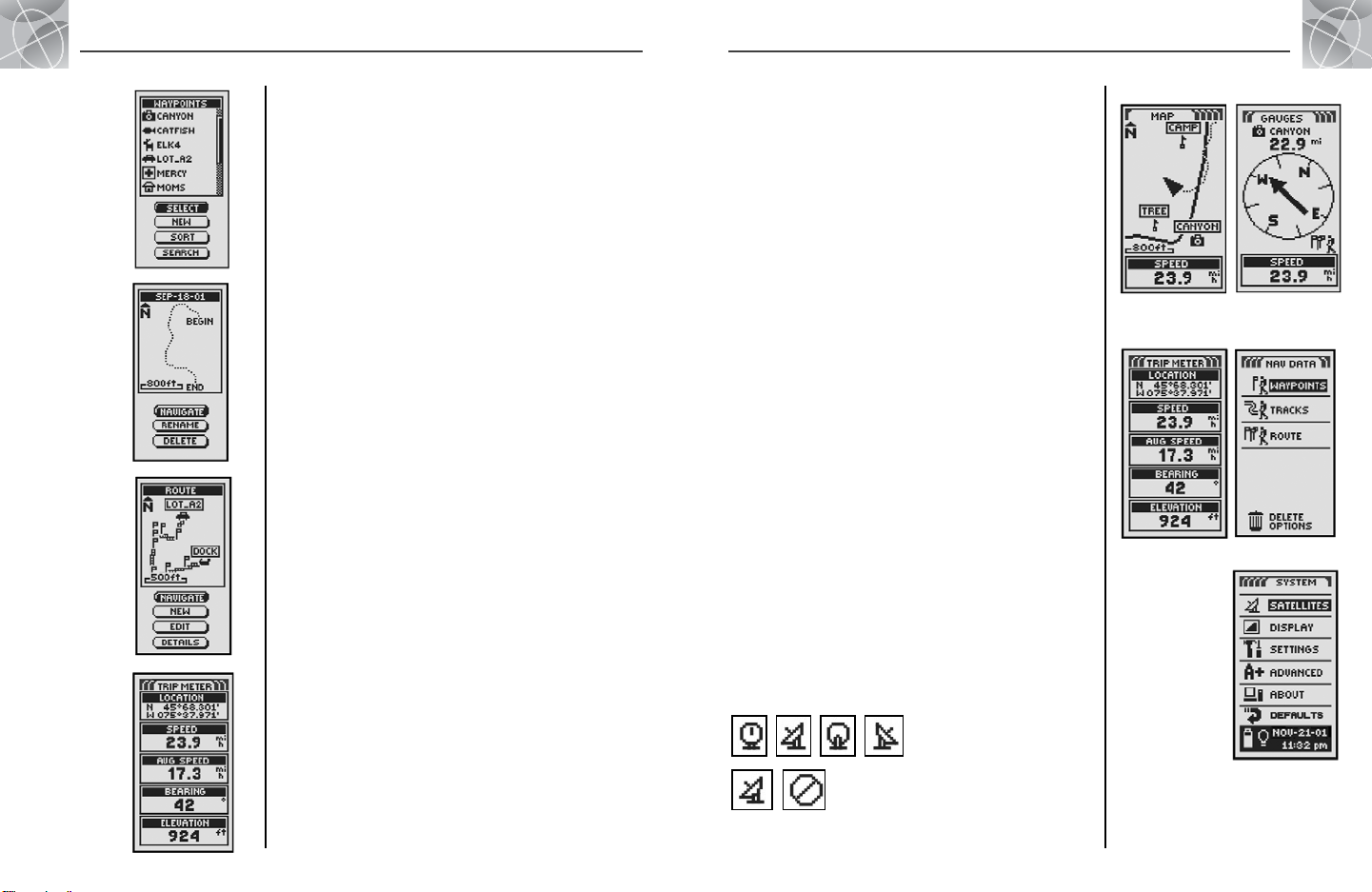
Navigating with the GPS 100
Your GPS 100 receives signals from Global Positioning System satellites that
are in fixed orbits (stationary relative to the ground) around the earth. By
acquiring – or locking onto – the signals from at least three satellites, your
unit can use triangulation to precisely determine your current position, elevation
above sea level and bearing (the direction you are traveling). As you travel,
the unit automatically acquires the strongest satellite signals available at your
current location. By becoming familiar with the unit’s basic operating features,
you will be able to use its powerful navigational capabilities.
Waypoint
A waypoint is a specific location that you ask the unit to record. In this
manual, you will learn how to mark your current location as a waypoint, or
set the coordinates for a waypoint anywhere in the world. You can create
and store up to 500 waypoints. You can have
the unit show you the direction of travel to an individual waypoint, or
how to navigate along a series of waypoints.
Track
Your GPS 100 automatically keeps a record of your travel, called a track. The
unit shows you a map-like picture of your track. You can create and store up
to 10 different tracks. Each track can be recalled and used for navigation as
the unit shows you how to retrace the track again, either forward or in the
reverse direction. When traveling in unfamiliar territory, this is a quick and easy
way to make sure you always know how to get back to your starting point.
Route
A route is a series of waypoints which you choose to navigate in a specific
sequence. Up to 50 waypoints may be stored in a route. Once you have created
a route, your GPS 100 will guide you from waypoint to waypoint. As you reach
each waypoint, the unit automatically begins navigating to the next one.
Trip Meter
Along with the navigational features, the trip meter in your GPS 100 keeps
accurate time, allowing it to precisely calculate your speed of travel,
average speed throughout your trip and estimated time of arrival (ETA) if
you have chosen a destination.
8
2
THE FIVE MAIN PAGES
Waypoint
Track
Route
Trip Meter
The Five Main Pages
In the following sections of this manual, you will learn how to use five main
pages to access all the features of your GPS 100:
Map Page
The Map page displays a map of your current position in relation to any
waypoints that you have selected. It can show you the direction of travel to
a selected destination. The Map page also shows you the track that you
have traveled along. If you have created a route, the map can show you
that route and your current position on it. (See page 9)
Gauges Page
The Gauges page displays a compass that shows your current direction of
travel or the direction to your next waypoint. The data field currently showing
“speed” is user-selectable. (See page 11)
Trip Meter Page
The Trip Meter page displays a number of user-selectable fields with information
about your current location, the progress you have made, your direction of
travel, your speed of travel and the time of your trip. (See page 13)
Nav Data Page
The Nav Data page allows you to store and select waypoints for navigation,
use the unit’s automatic tracking feature and program and recall a route to
selected destinations. (See page 15)
System Page
The System page allows you to choose the various settings and formats that
the unit uses to navigate and display information. (See page 31)
NOTE: Whenever satellite lock is lost or GPS is turned OFF, certain
animation icons (below) appear on screen and continue to loop until GPS is
ON and/or satellite lock is re-acquired. (See page 41)
Animation sequence that appears
when satellite lock is lost
Animation sequence that appears when GPS is
turned OFF
Map Page Gauges Page
Trip Meter
Page
Nav Data
Page
System Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 8
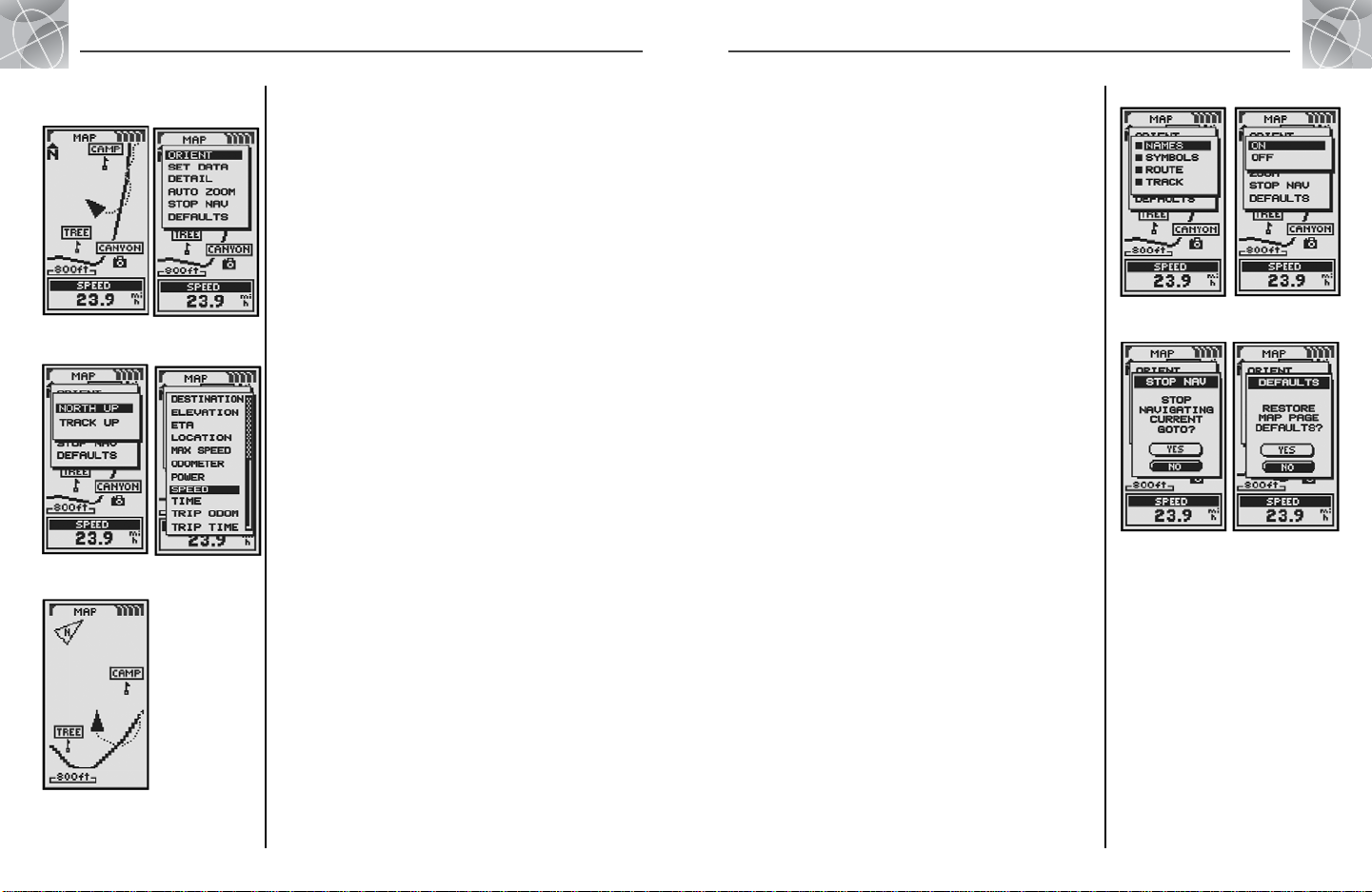
2.1
MAP PAGE
9
10
2.1
MAP PAGE
Map Page
The Map page displays a graphic representation of the navigation currently
in progress. Any waypoints, routes or tracks that you are using will be
displayed. A black ▲ (triangle) in the middle points to the direction you are
currently traveling. A data field at the bottom of the screen shows you
information of your choosing about your position or navigation. You can
zoom in and out on the map image by using the ZOOM IN/OUT button. You
have a number of options for customizing the display, (details below).
Selecting Options
From the Map page, press and release the ENTER button to display the Map
Page Options menu. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through the
menu sections, then press the ENTER button to go to the highlighted option.
Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight your choice, then press the
ENTER button to select it. Press the PAGE button to return to the main page.
Orient Option
Highlight and select ORIENT to designate the orientation of the map display.
To make the screen always represent magnetic north, highlight and select
NORTH UP (see ). To make the screen always represent the direction
of travel, highlight and select TRACK UP (see ).
Set Data Option
Highlight and select SET DATA to choose the information about your current
position or navigation that you want to be displayed at the bottom of the
Map page. Highlight and select FULL MAP to show the entire image of the
map currently in use (see ). Highlight and select from the following for
display at the bottom of the page: Accuracy, Average Speed, Bearing, Date,
Destination, Elevation, ETA, Location, Maximum Speed, Odometer, Power,
Speed, Time, Trip Odometer,Trip Time (see ). (For more information about
the optional data selections, see “Data Descriptions,” page 4)
continued
Map Page
(North Up)
Select Options
Orient Map
Display
Set Data
Display
Using the Map Page
Full Map
(Track Up)
Using the Map Page
Set Auto Zoom Map Details
Defaults
On/Off
Stop Nav
On/Off
Map Detail Option
Highlight and select DETAIL to show/hide any or all of the details to be
displayed on the map. These details include names of waypoints, waypoint
symbols, your navigational route and travel completed so far (track).*
Auto Zoom Option
Highlight and select AUTO ZOOM to turn this feature on or off. When this
feature is on, the scale of the map adjusts automatically to show the entire
navigation currently in progress. When this feature is off, you adjust the
scale of the map manually using the ZOOM IN/OUT button.*
Stop Nav Option
To stop the current navigation (GoTo, Route or Track), highlight and select
STOP NAV. Highlight and select YES to stop. Highlight and select NO to
make the current navigation continue.*
Defaults Option
Highlight and Select DEFAULTS to restore all original default Map page
settings. Highlight and select YES to restore original settings to map
Orientation = North Up; Data field information = Speed; map Details
shown = Names, Symbols, Route, Track; Auto Zoom = On. Highlight
and select NO to maintain all current settings.
*See “Using the Nav Data Page,” page 15, to learn about this feature.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 9
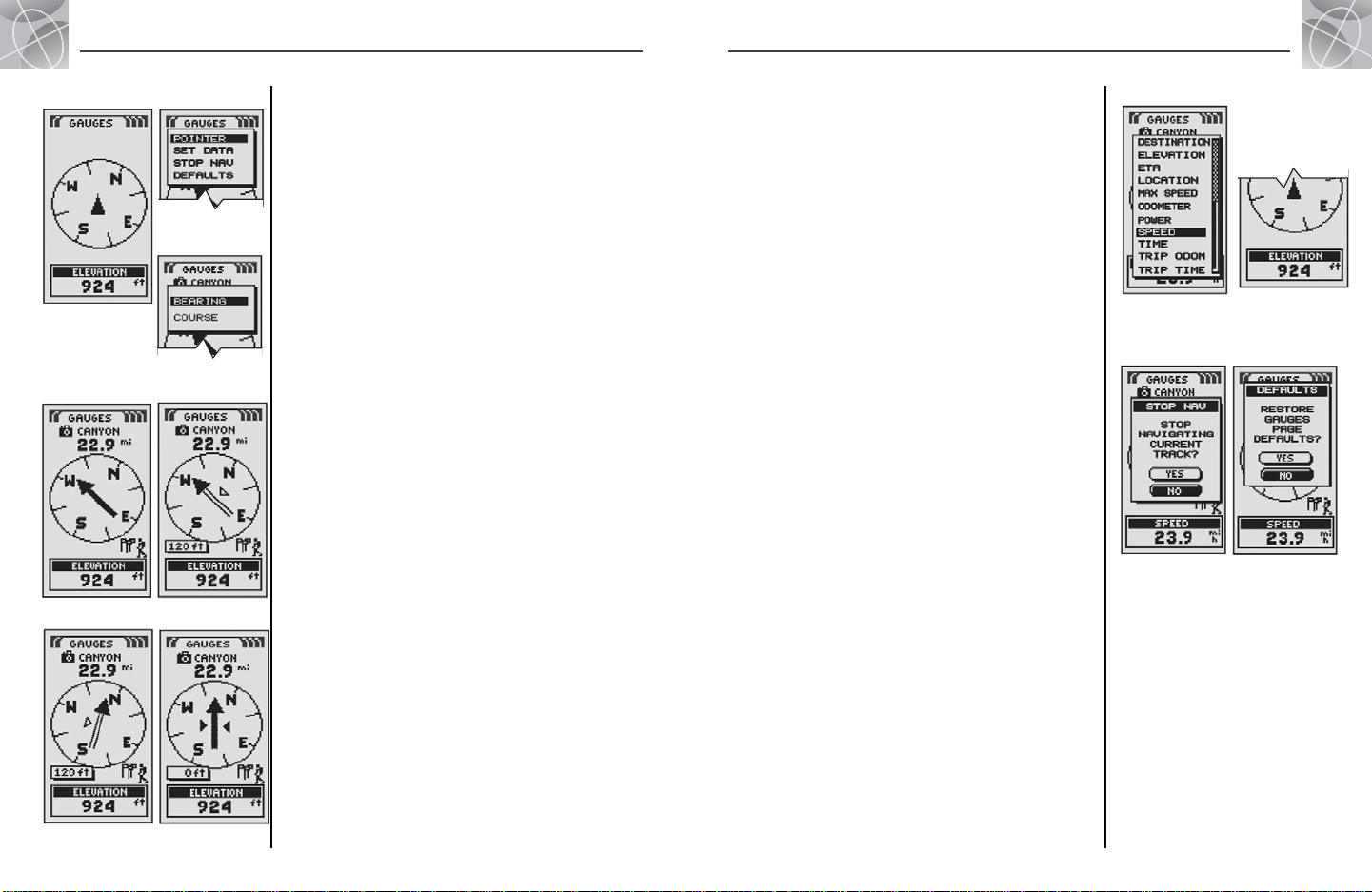
2.2
GAUGES PAGE
11
12
2.2
GAUGES PAGE
Using the Gauges Page
Compass
Select Options
Bearing
Pointer
Settings
Gauges Page
The Gauges page displays a compass that indicates direction of travel. It can
show the direction you are currently traveling or the direction from your current
position to the next waypoint in your navigation.
Selecting Options
From the Gauges page, press and release the ENTER button to display the
Gauges Page Options menu. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through
the menu sections, then press the ENTER button to go to the highlighted
option. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight your choice, then
press the ENTER button to select it. Press the PAGE button to return to the
main page.
Pointer Options
Highlight and select POINTER to designate the compass display information
about your course . Highlight and select BEARING to make the compass
indicate the direction to your next waypoint . Highlight and select COURSE
to make the compass indicate direction to your next waypoint with arrows
that show if you are on course or left or right of course. This
display also shows how many feet or meters off course you are currently.*
Right of
Course
Left of Course On Course
continued
*See “Using the Nav Data Page,” page 15, to learn about this feature.
Using the Gauges Page
Set Data Option
Highlight and select SET DATA to choose information about your current
position or navigation that you want displayed at the bottom of the Gauges
page. You may highlight and select from the following: Accuracy, Average
Speed, Bearing, Date, Destination, Elevation, ETA, Location, Maximum
Speed, Odometer, Power, Speed, Time, Trip Odometer, Trip Time. (For more
information about the optional data selections, see “Data Descriptions,”
page 4)
Stop Nav Option
To stop the current navigation (GoTo, Route or Track), highlight and select
STOP NAV. Highlight and select YES to stop. Highlight and select NO to
make the current navigation continue.*
Defaults Option
Highlight and Select DEFAULTS to restore all original default Gauges page
settings. Highlight and select YES to restore original settings to Pointer =
Bearing; Data field information = Speed. Highlight and select NO to
maintain all current settings.
*See “Using the Nav Data Page,” page 15, to learn about this feature.
Set Data List
Stop Nav
Yes/No
Restore
Defaults
Yes/No
Data from
Set Data List
Displays on
Gauges Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 10
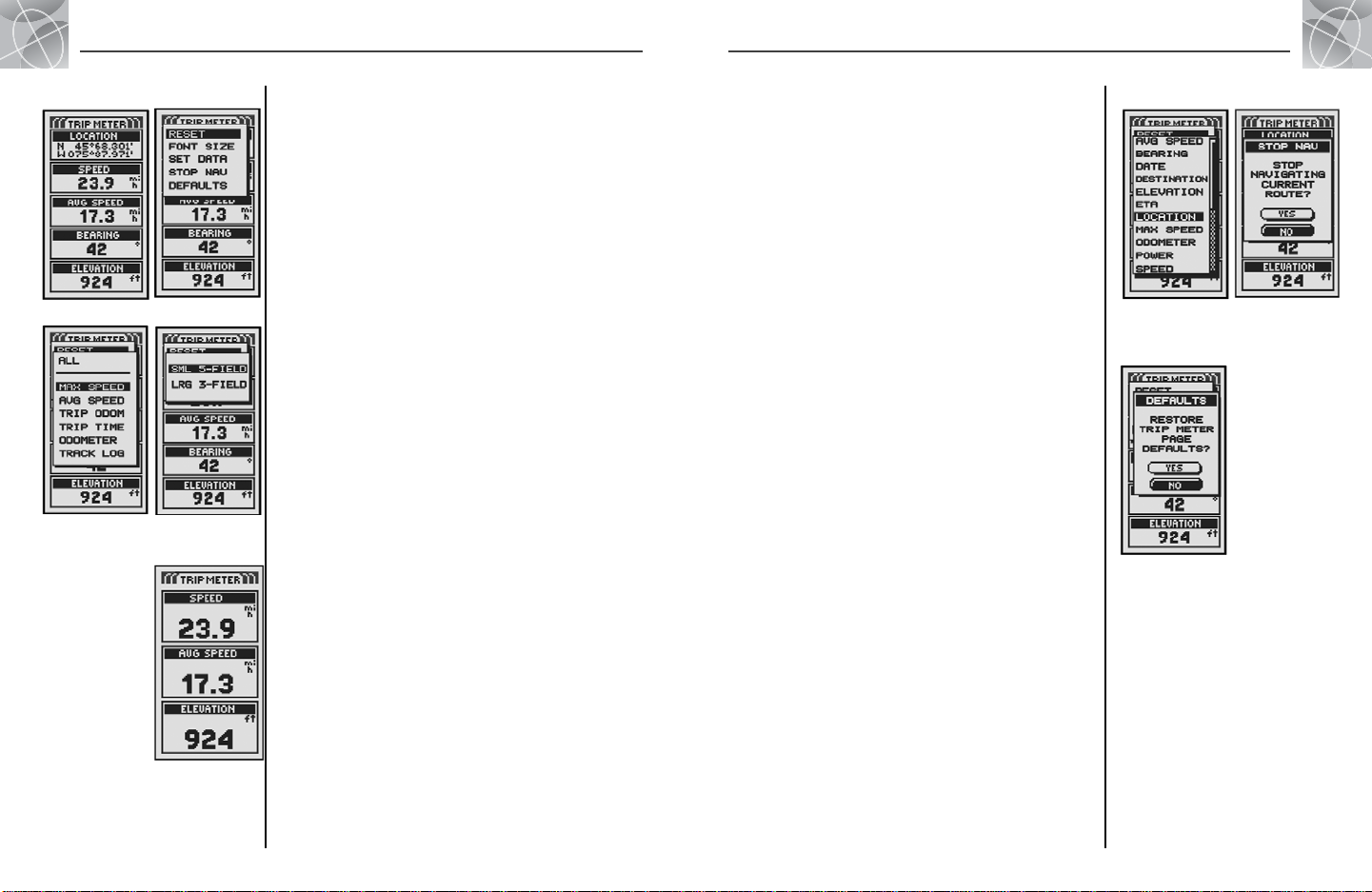
2.3
TRIP METER PAGE
2.3
TRIP METER PAGE
Using the Trip Meter Page
Trip Meter Info
Option Settings
Reset Values
Trip Meter Page
The Trip Meter page displays information about your current position, the
navigation in progress and other available data. It can display up to 5 fields
that you can select from a total of 15 choices.
Selecting Options
From the Trip Meter page, press and release the ENTER button to display the
Trip Meter Page Options menu. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll
through the menu sections, then press the ENTER button to go to the
highlighted option. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight your
choice, then press the ENTER button to select it. Press the PAGE button to
return to the main page.
Reset Option
Highlight and select RESET to reset any or all of the Trip Meter values to 0.
Highlight and select ALL to reset all values to 0, or highlight and select
individual values: Maximum Speed, Average Speed, Trip Odometer, Trip
Time, Odometer, Track Log.
Font Size Option
Highlight and select FONT SIZE to increase or reduce the size of the text
displayed in each field. Highlight and select SML 5-FIELD for smaller text
with 5 data fields displayed or highlight and select LRG 3-FIELD for larger
text with 3 data fields displayed.
NOTE: The lower two fields from 5-field screen will be hidden when
switching to 3-field.
continued
Font Size
13
Using the Trip Meter Page
14
LRG 3–FIELD
Option
Data Options Stopping Nav
Restore
Defaults
Yes/No
Set Data Option
Highlight and select SET DATA to choose the fields you want displayed on
the Trip Meter page. (Highlight and select the field you want to change –
the highlighted field will blink – then highlight and select the new field
from the menu.) Menu includes: Accuracy, Average Speed, Bearing, Date,
Destination, Elevation, ETA, Location, Maximum Speed, Odometer, Power,
Speed, Time, Trip Odometer, Trip Time. (For more information about the
optional data selections, see “Data Descriptions,” page 4)
Stop Nav Option
To stop the current navigation, highlight and select STOP NAV.
Highlight and select YES to stop. Highlight and select NO to have current
navigation continue.*
Defaults Option
Highlight and Select DEFAULTS to restore all original default Trip Meter
page settings. Highlight and select YES to restore original settings to
Font Size = Small 5-Field; Data field information = Location, Speed,
Trip Odometer, Odometer, Maximum Speed. Highlight and select NO to
maintain all current settings.
*See “Using the Nav Data Page,” page 15, to learn about this feature.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 11

Nav Data Page
The Nav Data page gives you access to the powerful navigational features of
your GPS 100. From this page, you can create and store up to 500 waypoints.
For each one, you can choose a name and assign a symbol. Using the
navigational features, you can ask the unit to show you the “GoTo” direction
of travel to reach a selected waypoint.
You can also create and store up to 10 tracks. Your GPS 100 automatically
keeps a record of your progress as you travel and gives you a graphic
representation of the track you have taken. You can have the unit guide you
in the reverse direction along the same track.
You can select two or more waypoints to create a route. Your GPS 100 will
then show you the way to follow the route accurately.
Whenever navigation is in progress, a hiker icon will appear in the lower
right hand corner of the Map Page and Gauges Page .
Waypoints
When you select WAYPOINTS from the Nav Data page, (see ), your
GPS 100 will display a list of the waypoints currently stored. You can create,
save and recall up to 500 waypoints. If you want to change the location for a
waypoint, its location coordinates can be edited. You can ask the unit to
show you the “GoTo” direction of travel to reach any waypoint you select.
NOTE: You can store up to 50 waypoints into a route.
NOTE: You can record your current location as a waypoint at any time
simply by pressing the ENTER button for 2 seconds, or by following the
procedure described on page 16, under “New Option.”
Selecting Options
From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select WAYPOINTS by pressing the ENTER button. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT
button to scroll through the menu sections, then press the ENTER button to
go to the highlighted option. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight
your choice, then press the ENTER button to select it. Press the PAGE button
to return to the main page.
continued
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
Using the Nav Data Page
Navigation
on Map
Navigation
On Gauges
Select Stored
Waypoints
View
Direction
Waypoints: Summary
Nav Data
Page Display
Hiker
Icons
Go To
Waypoint
Navigate
Track
Navigate
Route
Select Option
Highlight and choose SELECT to access any waypoint on the list. Highlight
and select GOTO to return to the Map page to navigate to the selected
waypoint (see “GoTo a Selected Waypoint,” page 18). Highlight and select
EDIT to change the name, symbol, location coordinates or elevation of the
selected waypoint . Highlight and select DELETE to delete the selected
waypoint . Highlight and select PREVIEW to view a graphic representation
of the selected waypoint from your current location . The image can be
zoomed in and out.
New Option
Highlight and select NEW to add a new waypoint to the list. Highlight and
select MARK CURRENT to save the coordinates for your current location as a
waypoint. The default name (a 3-digit number) and symbol (a flag) will be
assigned. You can either accept the default name and symbol or rename and
change the symbol of the waypoint (see “Editing Text”, page 29). (You can
use Waypoints/Select/Edit to change them later.) Highlight and select
ENTER MANUAL to enter the location coordinates for a waypoint manually
(see “Editing Text,” page 29). Entering an elevation is optional. The default
name (a 3-digit number) and symbol (a flag) will be assigned. (You can use
Waypoints/Select/Edit to change them later.)
Waypoint shortcut: To mark a new waypoint using current location,
press and hold the ENTER button for 2 seconds. A confirmation window
will pop up.
Sort Option
Highlight and select SORT to sort the list of waypoints according to name,
symbol, nearest waypoint or most recently saved waypoint. Highlight and
select NAME to sort waypoints in alphabetical order by name. Highlight and
select SYMBOL to have waypoints with that symbol displayed first
(waypoints with the same symbol are sorted alphabetically). Highlight and
select NEAREST to have waypoints sorted by distance from your current
location, with the nearest listed first. Highlight and select MOST RECENT to
sort waypoints according to when they were saved, with the most recent
listed first (see “Sort or Search,” page 30).
Search Option
Highlight and select SEARCH to search the list of waypoints for a name that you
entered. Press the ENTER button to begin entering the name you want to search
(see “Editing Text,” page 29). The name of the waypoint containing the letters
you entered is highlighted on the list (see “Sort or Search,” page 30).
Edit Info Delete
Waypoint
15
Preview
Waypoint
Add New
Waypoint
Sort List of
Waypoints
Search Existing
Waypoint List
16
Go to Table of Contents
Page 12

2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
Waypoints: Creating New Waypoints: GoTo
18
“GoTo” a Selected Waypoint
To make the map show the navigational path to a selected waypoint:
1. From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select WAYPOINTS by pressing the ENTER button . Highlight and select
SELECT .
2. Highlight and select the waypoint you want to navigate or “GoTo” .
The waypoint information screen for that waypoint appears with four
selections: GoTo, Edit, Delete and Preview .
3. Highlight and select GOTO to navigate to your selected waypoint .
This will bring up the Map page with the GoTo path between your current
position and the selected “GoTo” waypoint .
NOTE: You can Preview the selected waypoint’s location on the map by
selecting PREVIEW in the waypoint information screen. Selecting OK in the
Preview screen will return you to the waypoint information screen.
While in the Gauges Page, a navigation or “GoTo” is illustrated by a flag and
hiker icon in the bottom right hand corner of the screen. Also, your selected
GoTo waypoint and distance to that waypoint are shown above
the compass .
17
Creating a New Waypoint
To mark your current location as a new waypoint:
Waypoint shortcut: To mark a new waypoint using current location,
press and hold the ENTER button for 2 seconds. A confirmation window
will pop up.
1. From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select WAYPOINTS by pressing the ENTER button Highlight and
select NEW .
2. Highlight and select MARK CURRENT . The waypoint information screen
appears . A default name (a 3-digit number) and symbol (a flag) will
be assigned. You can either accept the default name and symbol or rename
and change the symbol of the waypoint (see "Editing Text", page 29).
3. When you have finished editing your new waypoint, select SAVE to
return to the main Nav Data page . To return to the main Nav Data
Page without saving the new waypoint, press the PAGE button .
To enter any location as a new waypoint manually:
1. From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button
and select WAYPOINTS by pressing the ENTER button Highlight and
select NEW .
2. Highlight and select MANUAL . The waypoint information screen
appears . A default name (a 3-digit number) and symbol (a flag)
will be assigned. You can either accept the default name and symbol or
rename and change the symbol of the waypoint (see "Editing Text,"
page 29). The Location field will blink.
3. Enter the location (latitude and longitude) of your new waypoint,(see
"Editing Text," page 29).
4. Highlight Elevation, the field will blink. Enter the location's elevation
(see "Editing Text," page 29).
NOTE: ELEVATION does not need to be entered to save your new waypoint.
5. When you have finished editing your new waypoint, select SAVE to
return to the main Nav Data page . To return to the main Nav Data
Page without saving the new waypoint, press the Page button .
New
Waypoint
Nav Data
Page
Information
Screen
Current or
Manual
Information
Screen
Return to Nav
Data Page
Selecting Stored
Waypoint
Nav Data
Page
Select
Waypoint
“GoTo” on
Map Page
“GoTo” on
Gauges Page
Waypoint
Information
Go to Table of Contents
Page 13
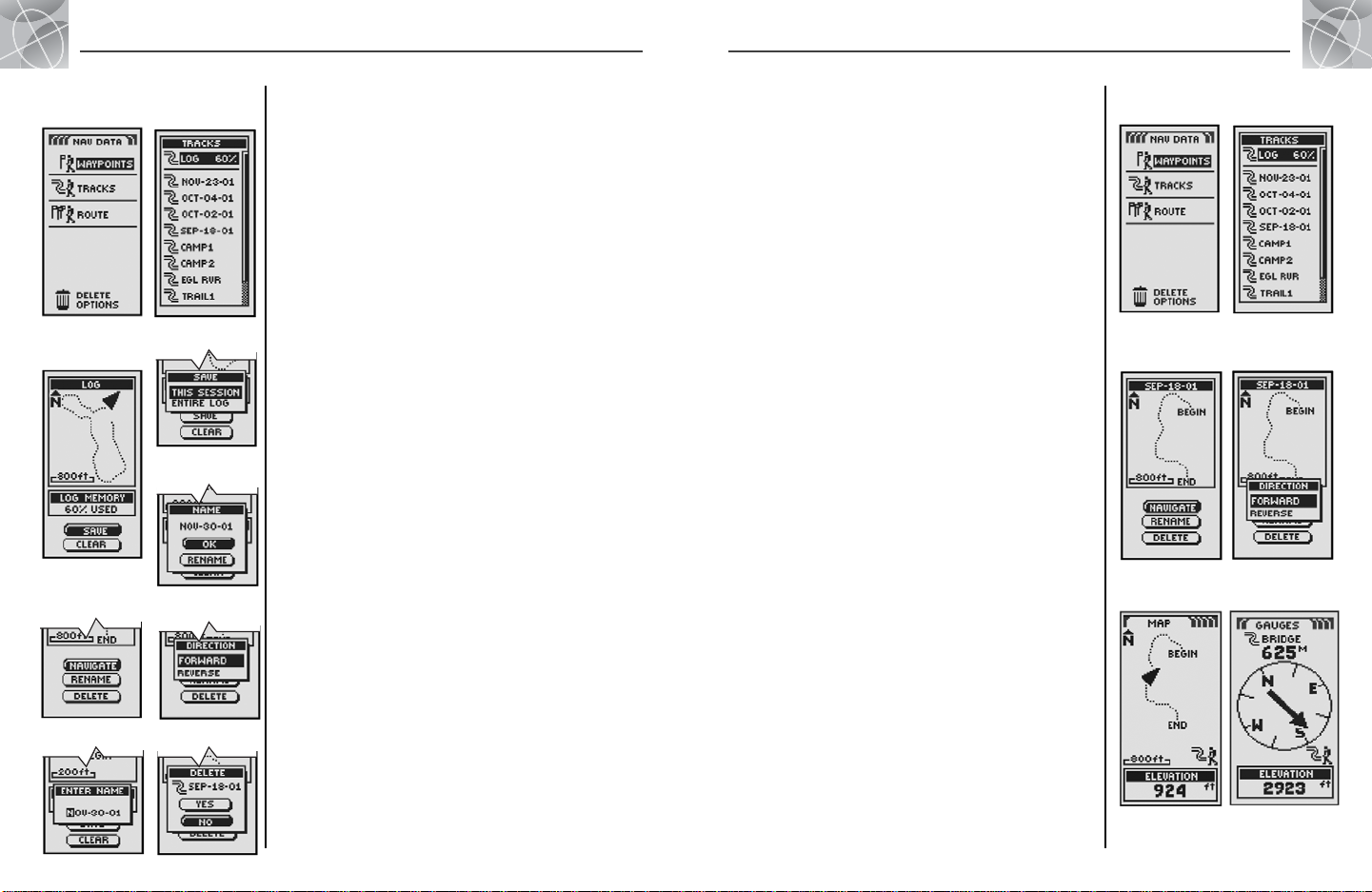
2.4 2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
Tracks
When you select TRACKS from the Nav Data page (see ), your GPS 100
will display a list of the tracks currently stored. Your unit will automatically
record a track as you travel. You can store up to 10 tracks and later recall
any of those tracks to use for navigation. Your unit can guide you along a
selected track in either direction.
NOTE: Your GPS 100 automatically begins tracking your travel whenever it
is turned on and linked to satellites. It keeps the recorded travel stored in its
log even when the power is turned off, starting a new tracking "session"
when it is turned back on. Old tracks will remain in memory (2,000
tracking points) unless erased by user (see "Deleting Individual Tracks,"
page 28).
Selecting Options
From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select TRACKS by pressing the ENTER button to display the Tracks screen.
Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through the list of tracks, then press
the ENTER button to go to the highlighted track. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT
button again to highlight your choice, then press the ENTER button to select
it. Press the PAGE button to return to the main page.
Log Option
Highlight and select LOG to save the current track or scroll to recall a track
saved previously . Highlight and select SAVE to save either THIS
SESSION (the travel recorded since the unit was last turned on) or the
ENTIRE LOG (all travel recorded since the log was last cleared) (see
CLEAR below). You can either accept the default name (the current date)
or rename the track before saving (see “Editing Text,” page 29).
Highlight and select CLEAR to clear the log of all travel that has been
recorded. The unit automatically restarts recording your travel.
Select Option
Highlight and select any stored track for navigation, renaming or deletion .
Highlight and select NAVIGATE and then FORWARD or REVERSE to
display the map page showing you the direction to travel to follow on the
selected track. Highlight and select RENAME to change the name of a
selected track (see “Editing Text,” page 29). Highlight and select
DELETE to delete the selected track .
View Stored
Tracks
Nav Data
Page
Save or
Recall Track
Save Options
Name Track
Accessing
Tracks
Direction
Enter Name
Delete
NAV DATA PAGE
Tracks: Summary
2019
Navigate a Selected Track
To make the map show the navigational path along a selected track:
1. From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select TRACKS by pressing the ENTER button .
2. Highlight and select the track you want to navigate . A map of the
selected track appears with three selections: Navigate, Rename and
Delete .
3. Highlight and select NAVIGATE to navigate through your selected
track . Highlight and select FORWARD to navigate from the beginning
to the end of the selected track . Highlight and select REVERSE to
navigate from the end to the beginning of the selected track .
4. This will bring up the Map page with the track path shown .
While in the Gauges Page, Track navigation is illustrated by a curved double
line and hiker icon in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. Also, your
selected track and distance to complete the navigation of that track are
shown above the compass .
Stored
Tracks
Nav Data
Page
Track Preview
and Options
Navigation
on Map
Navigation on
Gauges Page
Track: Navigation
Directions
Go to Table of Contents
Page 14

22
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
21
Creating a New Route
To create a new route consisting of up to 50 waypoints:
1. From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select ROUTE , by pressing the ENTER button. Highlight and select
NEW . A screen displaying OVERWRITE EXISTING? appears .
2. Highlight and select YES . A blank NEW ROUTE list appears with the
first field already highlighted .
3. Select that blank field . A list of all the waypoints you currently have
stored appears .
4. Highlight and select SELECT . Highlight the waypoint you want to put
into your route. You can sort or search the list (see "Sort" and "Search,"
page 16).
continued
Routes: Summary
Display
Waypoints
Routes: Creating New
Route Page
Nav Data
Page
Display New
Route List
Overwrite
Existing Route
Route
When you select ROUTE from the Nav Data page (see ), you can use your
GPS 100 to designate a route consisting up of to 50 waypoints. The unit will
then guide you along the route. As you reach each waypoint, the unit will
automatically begin pointing you to the next waypoint, until you reach your
final destination.
Selecting Options
From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select ROUTE by pressing the ENTER button to display the Route screen. Use
the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through the menu sections, then press
the ENTER button to go to the highlighted option. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT
button again to highlight your choice, then press the ENTER button to select
it. Press the PAGE button to return to the main page.
Navigate Option
Highlight and select NAVIGATE to make your GPS 100 guide you along a
route you have created (see “New Option” below). Highlight and select
FORWARD to navigate forward along a route from start to end point or
highlight and select REVERSE to navigate in a reverse direction from end point
to start point.
New Option
Highlight and select NEW to create a new route. When the OVERWRITE
EXISTING? screen appears, highlight and select YES to create your new
route (see “Creating A New Route,” page 22) or NO to cancel creation
of a new route.
Edit Option
Highlight and select EDIT to add or delete any waypoints you have selected
in creating a new route. On the Edit screen highlight and select REMOVE to
delete a waypoint, INSERT to insert a waypoint or DONE to save changes
and return to Route screen .
Details Option
Highlight and select DETAILS to see any or all of the waypoints of a specific
route you have planned. Highlight and select OK to return to main Nav Data page.
Designating
New Route
Creating
New Route
Editing
Waypoints
Nav Data
Page
Navigating
Along Route
Waypoints
Listed
Viewing
Waypoints
Go to Table of Contents
Page 15

24
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
23
Routes: Creating New
Inserting a Waypoint into a Route
To add a waypoint to an existing route:
1. From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button
and select ROUTE by pressing the ENTER button . Highlight and select
EDIT . The Edit Route list of waypoints in your route appears .
2. Highlight and select the waypoint that will come immediately before the
one you want to add . An EDIT menu appears .
3. Highlight and select INSERT . A list of all waypoints appears .
4. Highlight and select SELECT . Highlight the waypoint you want to add
to your route. If you wish, you can sort or search the list (see “Sort” and
“Search,” page 16).
5. Select the highlighted waypoint to add it to your Route . The Edit
Route list appears with the added waypoint displayed.
Repeat the previous steps if you wish to add more waypoints to your route.
6. When you have finished adding waypoints to your route, select DONE to
return to the main Nav Data page .
Nav Data
Page
Access Edit
Menu
Highlight
Waypoint
Return To Nav
Data Page
Routes: Inserting a Waypoint
Edit Route
List
Highlight
Insert
Creating a New Route (continued)
5. Select the highlighted waypoint to add it to to your route . The New
Route list appears with the added waypoint displayed .
Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to highlight the next blank field. Repeat steps
3 to 5 to add more waypoints.
6. When you have finished adding waypoints to your route, press the PAGE
button to return to the main Nav Data page .
Insert/Remove Waypoints in Route
To insert a waypoint into the route, highlight and select the waypoint that
will come immediately before the one you want to add. Highlight and select
INSERT . When the list of all waypoints appears, select the waypoint to
insert as you did in , and above.
To remove a waypoint in the route, highlight and select the waypoint you
want to remove. Highlight and select REMOVE . Your New Route list will
automatically be updated to reflect the waypoint removal.
Change
Waypoint
Return
to Nav
Data
Page
Add
Waypoint
Highlight
Waypoint
Go to Table of Contents
Page 16

26
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
25
Routes: Navigation Delete Options: Summary
Delete Options
When you select DELETE OPTIONS from the Nav Data page (see ), you can
delete waypoints, tracks or routes that you have created or delete all data
currently stored.
Selecting Options
From the Nav Data page, highlight and select DELETE OPTIONS to display
the Delete Options screen. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through
the menu sections, then press the ENTER button to go to the highlighted
option. Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight your choice, then
press the ENTER button to select it. Press the PAGE button to return to the
main page.
Waypoints Option
Highlight and select WAYPOINTS if you wish to delete any or all of the waypoints
you have stored. Highlight and select ONE-BY-ONE to delete waypoints one
at a time (see “Deleting Individual Waypoints,” page 27). Highlight and
select ALL to delete all waypoints currently stored.
Tracks Option
Highlight and select TRACKS if you wish to delete any or all of the tracking
sessions currently in memory. Highlight and select ONE-BY-ONE to delete
track sessions one at a time (see “Deleting Individual Tracks,” page 28).
Highlight and select ALL to delete all tracks currently in memory.
Route Option
Highlight and select ROUTE if you wish to delete the route you currently
have stored. Highlight and select DELETE – YES and the entire route will be
deleted. Highlight and select DELETE – NO to cancel the delete function.
All Option
Highlight and select ALL if you wish to delete all waypoints, tracks and the
route you currently have stored. Highlight and select DELETE ALL NAV DATA –
YES and the data will be deleted. Highlight and select DELETE ALL NAV DATA
– NO to cancel the delete function.
Access Delete
Options
Delete
Routes
Delete All
Data
Nav Data
Page
Delete
Waypoints
or Tracks
Navigate a Selected Route
To make the map show the navigational path along the route:
1. From the Nav Data Page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select ROUTE by pressing the ENTER button . A map of the selected
route appears with four selections: Navigate, New, Edit and Details .
2. Highlight and select NAVIGATE to navigate through your selected
route . Highlight and select FORWARD to navigate from the beginning
to the end of the selected route . Highlight and select REVERSE to
navigate from the end to the beginning of the selected route .
3. This will bring up the Map page with the route path shown .
NOTE: You can view the list of waypoints in the route by selecting DETAILS
in the route options screen. Selecting OK in the Details screen will return you
to the route options screen.
While in the Gauges Page, Route navigation is illustrated by a group of flags
and hiker icon in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. Also, the next
waypoint on your route navigation and the distance to that waypoint are
shown above the compass .
Navigate
Route
Nav Data
Page
Navigation
On Map
Direction
Navigation on
Gauges Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 17

28
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
27
Delete Options: Individual Waypoints
Delete Options: Individual Tracks
Deleting Individual Tracks
To delete selected tracks one at a time:
1. From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select DELETE OPTIONS by pressing the ENTER button . The Delete
Options menu appears .
2. Highlight and select TRACKS . The Delete menu appears .
3. Highlight and select ONE-BY-ONE .Alist of all saved tracks appears .
4. Highlight and select the track you wish to delete . A Delete
Confirmation menu appears .
5. Highlight and select YES and the list of all tracks will appear with the
selected track deleted . Highlight and select NO to return to the
tracks list . Highlight and select DONE to return to the main Nav
Data Page .
Repeat steps 4 and 5 to delete other tracks.
6. When you have finished deleting, press the PAGE button to return to the
main Nav Data page .
Delete
Track
Access
Delete Menu
Select Deletion
Method
Highlight
Track
Confirm
Deletion
View Revised
Tracks List
Return to Nav
Data Page
Delete a
Waypoint
Access
Delete Menu
Deleting Individual Waypoints
To delete selected waypoints one at a time:
1. From the Nav Data page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select DELETE OPTIONS by pressing the ENTER button . The Delete
Options menu appears .
2. Highlight and select WAYPOINTS . The Delete menu appears .
3. Highlight and select ONE-BY-ONE . A list of all waypoints currently
stored appears . You can sort or search the list (see “Sort” and
“Search,” page 16).
4. Highlight and select SELECT. The first waypoint is highlighted .
5. Highlight the waypoint you wish to delete . A Delete Confirmation
menu appears .
6. Highlight and select YES and the list of all waypoints appears with
the selected waypoint deleted . Highlight and select NO to return
to the list of all waypoints currently stored . Highlight and select
DONE to return to the main Nav Data Page .
Repeat steps 5 and 6 to delete other waypoints.
7. When you have finished deleting, press the PAGE button to return to the
main Nav Data page .
Choose Delete
Method
Highlight
Waypoints
Confirm
Deletion
View Revised
Waypoints List
Return to Nav
Data Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 18

30
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
2.4
NAV DATA PAGE
Editing Text
29
Sort Or Search
Editing Text
To enter or change the information displayed or enter information into a search
field for a waypoint, track or route, use the following procedure:
1. From any screen that allows you to enter letters, numbers or symbols
(names of waypoints/tracks/routes, dates, etc.), use the ZOOM IN/OUT
button to scroll to the field you want to edit and press the ENTER button .
2. Highlight the space where you want to insert a letter or symbol, or the
character you want to change . Press the ENTER button to bring up a
pop-up menu showing the characters to choose from .
3. Scroll through the characters until the one you want is highlighted .
Press the ENTER button to select it. The new character appears in place
and is highlighted.
4. Press the ENTER button again to accept the new character . The
character next to it will be highlighted .
Repeat the same procedure to change the next character if desired. Press the
ZOOM IN/OUT button to skip characters you do not want to change.
To clear a selected character and all characters that follow it, highlight the
Backspacer symbol (at the end of the menu) . Press the ENTER
button to finish editing.
5. When you have finished entering or changing all characters, press the
ENTER button. Highlight the Down character (at the beginning of
the menu) and press the ENTER button .
If necessary, use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll to the next field you
want to edit and follow the same procedure to enter or change characters.
Use ZOOM
IN/OUT
Button
Highlighting
Spaces
Access Menu
of Characters
Next Character
Appears
Accept New
Character
Clear a
Character
Highlight “Down”
Character
Waypoints
List
Sort Menu
Search
Symbols List
Choosing Your
Letter
Sort Option
1. From any screen with the SORT option, highlight and select SORT .
2. Choose from the following choices:
• Alphabetically by name:
a. The list of waypoints and 4 options will be presented: NAME,
SYMBOL, NEAREST, MOST RECENT. Highlight and select NAME .
• By a chosen symbol (with the selected symbol listed first and waypoints
with the same symbol sorted alphabetically):
a. The list of waypoints and 4 options will be presented: NAME,
SYMBOL, NEAREST, MOST RECENT. Highlight and select SYMBOL .
b. A list of waypoint symbols appears. Highlight and select the symbol
you want at the top of the list .
•Nearest waypoint to your current location:
a. The list of waypoints and 4 options will be presented: NAME,
SYMBOL, NEAREST, MOST RECENT. Highlight and select
NEAREST .
• According to when they were saved with the most recently saved
waypoint listed first:
a. The list of waypoints and 4 options will be presented: NAME,
SYMBOL, NEAREST, MOST RECENT. Highlight and select MOST
RECENT .
3. The waypoint list appears sorted. Continue your pervious activities.
Search Option
To search any list of waypoints for a particular name:
1. From any screen with the SEARCH option, highlight and select SEARCH .
2. Select (by pressing the ENTER button) the highlighted blank space to enter
the first letter of the name you are searching for (see “Editing Text,”
page 29) .
3. The waypoints containing that letter first appear at the top of the list.
• Continue to enter letters into the blanks until the waypoint you are
searching for appears highlighted at the top of the list .
• Accept the current highlighted waypoint. Scroll to select the waypoint
you are searching for.
4. Continue your previous activities.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 19

2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
2.5
Using the System Page
3231
SYSTEM PAGE
Using the System Page
Defaults Option
Highlight and Select DEFAULTS to restore all original default settings for the
entire GPS 100 system. Highlight and select YES to restore original settings
(see chart below). Highlight and select NO to maintain all current settings.
Status Bar Indicator
The status bar at the bottom of the System page updates information
automatically. You can see whether the backlight is on or off, as well as the
current date and time. You can also determine the present status of the battery
as the battery symbol increases the amount of black from the top down as it
discharges.
Access
About
Option
Access
Defaults
Option
Status Bar
System Page
The System page gives you various options for changing the system settings
used by your GPS 100. From this page you can turn GPS navigation on and
off and adjust settings for features such as display, sounds, time, compass,
map, method of navigation, activate WAAS, change map datum, etc.
Selecting Options
From the System page, use the ZOOM IN/OUT button to scroll through the
menu sections, then press the ENTER button to go to the highlighted option.
Use the ZOOM IN/OUT button again to highlight your choice, then press the
ENTER button to select it. Use the PAGE button to back up to the main page.
Satellites
To turn GPS navigation on and off, highlight and select SATELLITES, (see
"Turning GPS On and Off," page 33). Highlight and select GPS MODE.
Highlight and select YES or NO in response to the prompt to access your
unit’s navigational features or to disable your unit’s navigational features.
(Turning GPS mode off preserves battery power.)
Display Options
To adjust the display Contrast and Backlight settings, highlight and select
DISPLAY, (see ”Adjusting the Display,” page 34). Highlight and select
CONTRAST to increase or decrease the display contrast. Highlight and select
BACKLIGHT to designate the duration of time the backlight will stay lit.
Settings Option
Highlight and Select SETTINGS to change the following system settings:
Clock Format, Time Zone, Daylight Saving, Language, Units, Sounds (see
"Using the Settings Screen," page 35).
Advanced Option
Highlight and Select ADVANCED to change the following advanced
operational parameters used by your unit: WAAS, Compass, Map Datum,
Position Format, North Reference, Battery Saver (see "Using the Advanced
Screen," page 37).
About Option
Highlight and select ABOUT to display certain system information. Information
displayed includes: percentage of memory used; unit serial number, software
version and applicable patent numbers.
System
Page
Turn GPS
Navigation
On/Off
Access
Navigational
Features
Adjust
Display
Settings
System Page Defaults
Function Default
GPS Status On
Backlight time out 15 seconds
Clock Format 12 Hour
Time Zone Current Location
Daylight Saving Auto
(Summer Time)
Language English
Measurement Units English
Function Default
Sounds On
WAAS On
Compass Cardinal
Map Datum WGS 84
Position Format hddd˚mm.mm
North Reference True
Battery Saver Off
Map Page Defaults
Function Default
Orient North Up
Data Field Speed
Details Shown Names (show)
Symbols
(show)
Route (show)
Track (show)
Auto Zoom On
Trip Meter Defaults
Function Default
Data Field 5 Fields
*
Location
Speed
Trip Odom
Odometer
Max Speed
Data Field 3 Fields
Location
Speed
Trip Odom
*default font size
Gauges Defaults
Function Default
Pointer Bearing
Function Default
Data Field Speed
Settings
Advanced
Settings
Go to Table of Contents
Page 20

2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
GPS Off/On Adjusting the Display
34
Adjusting the Display
You can adjust various settings for your unit’s display.
1. From the System page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select DISPLAY by pressing the ENTER button . CONTRAST and
BACKLIGHT appear .
2. SELECT will be highlighted . To adjust contrast or backlight settings,
press the ENTER button. Contrast field will begin to blink .
3. Choose from the following. You only need to select the settings you
want to change.
• Contrast
Highlight and select CONTRAST . Using the ZOOM IN/OUT button
you will now be able to change the contrast of the display screen .
Press the ENTER button to complete your CONTRAST adjustment.
• Brightness
Highlight and select BACKLIGHT . This will allow you to change
the length of time the screen’s backlight remains lit each time
the unit is turned on. (Once you have selected BACKLIGHT, the title
of the selected field will begin to blink.) Press the ENTER button to
activate the TIME OUT menu . Highlight and select the time
interval you want.
WARNING: If you choose STAY ON, battery life will significantly decrease.
4. When you have finished changing display settings, highlight and select
SAVE to return to the System page .
Access
Selections
Adjust
Settings
Change
Contrast
33
Save
Settings
Select
Backlight
Interval
Turning GPS Off and On
When indoors, you can turn GPS navigation off, allowing you to use the
non-navigational features of your GPS 100 while preserving battery power.
When you turn GPS off, the unit stops searching for signals from satellites.
When you turn GPS back on to receive signals, the unit must re-acquire
signals from at least three satellites before it can begin navigation.
NOTE: The unit must be outside with a clear view of the sky to acquire
satellite signals for navigation.
To turn GPS off:
1. From the System page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select SATELLITES by pressing the ENTER button . A LOCATION screen
appears, showing the satellite signals being received with the signal strength
of each indicated. The satellites that are currently acquired by the unit for
navigation are highlighted .
2. Select GPS MODE . “USE WITH GPS OFF?”menu will appear .
3. Highlight and select YES . The unit will immediately turn GPS off and
stop receiving satellite signals.
4. Press the PAGE button to return to the System page
.
To turn GPS on:
1. From the System page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and select
SATELLITES by pressing the ENTER button . A blank LOCATION screen
appears .
2. Select GPS MODE . “TURN GPS ON?”menu will appear .
3. Highlight and select YES . Unit will begin searching for satellite signals
until it locks on to three of them.
4. Press the PAGE button to return to System page .
NOTE: The unit must be outside with a clear view of the sky to acquire
satellite signals for navigation.
Turning GPS
Off/On
Location Screen
Appears
Use with
GPS Off?
Stop
Receiving
Return to
System Page
Turn GPS On?
Go to Table of Contents
Page 21

36
2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
35
Setting Screen
• Daylight Saving
To have the clock use daylight saving time (Summer Time), highlight
DAYLIGHT SAVING . Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu.
Select AUTO to make the clock switch to daylight saving time
(Summer Time) automatically. Select ON to switch manually back to
daylight saving time (Summer Time). Select OFF to switch manually
the clock to standard time (Winter Time (GMT)) .
• Language
To choose the language used for the display, highlight LANGUAGE .
Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu of languages. Select
from the following English, Dutch, French, German, Italian,
Portuguese, Spanish or Swedish .
• Units
To choose the system for measuring distance, select UNITS . Press
the ENTER button to bring up the menu. Select ENGLISH, METRIC or
NAUTICAL .
• Sounds
To turn the unit’s sound on or off, select SOUNDS . Press the
ENTER button to bring up the menu. Select ON or OFF .
4. To save the changes made, highlight and select SAVE . To exit this
function without saving changes, press the PAGE button .
Daylight
Savings
Language
Options
Measurement
Sound On/Off
Setting Screen
Return to
System Page
Change
Settings
Select Data
Field
Using the Settings Screen
From the Settings screen, you can change the various settings listed below.
To change settings:
1. From the System page highlight, using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select SETTINGS by pressing the ENTER button . A listing appears with
SELECT highlighted .
2. Press the ENTER button and the title of the first data field will begin to
blink . Highlight field you wish to change (highlighted field will blink).
3. Choose from the following. (You only need to select the settings you
want to change.)
• Clock Format
To change the format of the time display, highlight CLOCK FORMAT
. Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu and select 12
HOUR or 24 HOUR .
• Time Zone
To choose the time zone you want the clock to use, highlight TIME
ZONE . Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu of major
cities. Select USE CURRENT LOCATION or the city that is in the desired
time zone , (see page 40 for World City Time Zone chart).
continued
Clock Format
First Data
Field Blinks
Time Zone
Go to Table of Contents
Page 22

2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
2.5
SYSTEM PAGE
Advanced Screen
37
Advanced Screen
• Position Format
To change the format the device uses to display location coordinates,
highlight POSITION FORMAT . Press the ENTER button to bring up the
menu select from the following: hddd.ddddd° (degrees, decimal
degrees), hddd°mm.mm (degrees, minutes, decimal minutes),
hddd°mm’ss.s (degrees, minutes, seconds, decimal seconds), British
Grid, Dutch Grid, Finnish KK127 Grid, German Grid, Irish Grid,
Maidenhead, MGRS (Military Grid Reference System), New Zealand,
Qatar Grid, Swedish Grid, Swiss Grid, Taiwan Grid, User Defined Grid,
User Defined Grid, UTM/UPS (Universal Transfer Mercator/Universal
Polar Stereograph), W Malaysian R .
• North Reference
To change the unit’s method of orientation to the earth’s magnetic field,
highlight NORTH REFERENCE (see “About North Reference,”
page 42). Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu. Select TRUE for
true north, MAGNETIC for magnetic north or GRID for grid north .
• Battery Saver
To conserve battery life, highlight BATTERY SAVER . Press the ENTER
button to bring up the menu. Select ON or OFF .
4. To save changes made, highlight and select SAVE . To exit this function
without saving changes, press the PAGE button .
Set Interval
Set
Orientation
Using the Advanced Screen
From the Advanced screen, you can change the advanced operational
parameters used by your GPS 100.
To change advanced parameters:
1. From the System page, highlight using the ZOOM IN/OUT button and
select ADVANCED by pressing the ENTER button . A menu of advanced
parameters appears. SELECT will be highlighted .
2. Press the ENTER button and the title of the first data field will begin to
blink . Highlight field you wish to change (highlighted field will blink).
3. Choose from the following. (You only need to select the settings you
want to change.)
• WAAS
To turn the unit’s WAAS receiver on or off, highlight WAAS . (See
“What is WAAS,” page 42.) Press the ENTER button to bring up the
menu. Select ON or OFF .
• Compass
To change the method of indicating direction used by the compass,
highlight COMPASS . Press the ENTER button to bring up the menu.
Select CARDINAL (standard N-S-E-W), DEGREES (<0°-360°) or
MILS (0000-6400) .
• Map Datum
To change the datum used by your unit when comparing information
with a paper map or other navigational reference, highlight MAP DATUM
, (see “What is a Map Datum?,” page 42, for details). Press the
ENTER button to bring up the menu. Select the map datum that
matches the item you are comparing .
NOTE: Most widely used datum is WGS 84
continued
Change
Parameters
Select Data
Fields
WAAS On/Off First Data
Field Blinks
38
Map Datum
Settings
Set Compass
Location
Coordinates
Return to
System Page
Go to Table of Contents
Page 23

4
GENERAL INFORMATION
3
ALERTS
World City Time Zones
Longitudinal Zone Offset
E172.50 to W172.50 ..............................-12
IDLW (International Date Line West)
W172.50 to W157.50 ............................-11
Nome
W157.50 to W142.50 ............................-10
Honolulu
W142.50 to W127.50 ..............................-9
Yukon Standard
W127.50 to W112.50 ..............................-8
Los Angeles
W112.50 to W097.50 ..............................-7
Denver
W097.50 to W082.50 ..............................-6
Chicago
W082.50 to W067.50 ..............................-5
New York
W067.50 to W052.50 ..............................-4
Caracas
W052.50 to W037.50 ..............................-3
Rio de Janeiro
W037.50 to W022.50 ..............................-2
Fernando de Noronha
W022.50 to W007.50 ..............................-1
Azores Island
W007.50 to E007.50........................GMT + 0
London
E007.50 to E022.50 ................................+1
Rome
E022.50 to E037.50 ................................+2
Cairo
E037.50 to E052.50 ................................+3
Moscow
E052.50 to E067.50 ................................+4
Abu Dhabi
E067.50 to E082.50 ................................+5
Maldives
E082.50 to E097.50 ................................+6
Dhuburi
E097.50 to E112.50 ................................+7
Bangkok
E112.50 to E127.50 ................................+8
Hong Kong
E127.50 to E142.50 ................................+9
Tokyo
E142.50 to E157.50 ..............................+10
Sydney
E157.50 to E172.50 ..............................+11
Solomon Islands
E172.50 to W172.50 ............................+12
Auckland
40
Alerts
As you use your GPS 100, you may see the following alert messages.
LOST SATELLITES CONTINUE SEARCHING?
You will see this alert if, for any reason, satellite lock is lost. When you see this
message, the unit is automatically trying to re-acquire satellite signals. If you do
nothing, the unit will continue to search for signals and the message will disappear
when satellite lock is regained. You can select YES to continue searching and clear the
alert message. If satellite lock is not regained within 5 minutes, the alert will
reappear. You can select NO to turn off GPS navigation and clear the message.
NOTICE ARRIVING AT DESTINATION!
If you are navigating to a waypoint, or along a track or route, you will see this
message when you are within 500 feet (150 m) of your destination. Select OK
or the PAGE button to clear the message.
CAN’T CREATE WAYPOINT WAYPOINT LIST FULL!
You will see this message if you try to save a waypoint when the list is full (you
can save a maximum of 500 waypoints). Select OK or the PAGE button to clear
the message. You will continue to see the message when trying to save a
waypoint until you delete one or more waypoints from memory (see page 26).
WARNING TRACK LOG ALMOST FULL!
This message appears when the track log memory bank is 90% full. Select OK or
the PAGE button to clear the message. The message will reappear each time you
turn on the unit until you clear the track log (see page 26) or the track log
becomes 100% full (see below).
WARNING TRACK LOG FULL!
You will see this message when the track log memory bank is full. The unit will
not be able to store any more track log points until you clear the track log (see
page 26). Select OK or the PAGE button to clear the message. The message will
reappear each time you turn on the unit until the track log is cleared.
WARNING BATTERIES LOW!
This message appears approximately 30 minutes before your batteries need
to be replaced. Select OK or the PAGE button to clear the message. Replace the
batteries as soon as possible. The message will reappear every 10 minutes until
the batteries are replaced.
NOTICE GPS IS OFF!
This message is displayed any time an action is requested which typically uses GPS
satellite tracking, “GPS on” (example: marking a waypoint or navigating a route).
While GPS mode is set to off, select YES to turn GPS on. Select NO to tell the GPS
unit to assume that you are at your last calculated position.
LOST
SATELLITES
ARRIVING AT
DESTINATION!
CAN’T
CREATE
WAYPOINT
TRACK LOG
ALMOST FULL!
TRACK
LOG FULL!
BATTERIES
LOW!
GPS IS
OFF!
39
Go to Table of Contents
Page 24

42
4
GENERAL INFORMATION
4
41
What is WAAS?
Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is a GPS-based
navigation system that provides precision above and beyond
what GPS can do on its own. WAAS was designed to improve
the accuracy and ensure the integrity of information coming
from GPS satellites.
WAAS is a network of 25 ground reference stations that
cover the entire U.S. plus parts of Canada and Mexico.
Implemented by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
for aviation users, these reference stations are located at
precisely surveyed spots and compare GPS distance
measurements to known values. When the WAAS signal is
available, WAAS-capable receivers typically have a much
higher accuracy than non-WAAS units.
What is a Map Datum?
Maps and charts are essentially grids created from a starting
reference point called a “datum.” Many maps being used
today were originally created decades ago. Over the years,
technology has allowed us to improve our surveying skills
and create more accurate maps. However, there is still a
need to adapt GPS receivers to use with older maps.
Most navigational charts and maps will have the datum listed.
Cobra®GPS receivers include up to 100 map datums that
allow you to switch to a setting that matches your map. The
most common US map datums are World Geodetic System
1984 (WGS 84), North American Datum 1983 (NAD 83)
and North American Datum 1927 (NAD 27)
NOTE: Using a map datum that does not match the chart
you are using can result in significant differences in position
information.
About North Reference
The vertical grid lines on any map can be aligned in one of
three different ways.
“True North” means that the vertical lines are aligned with
the geographic north pole. This is the most common method
of orienting maps.
“Magnetic North” means that the vertical lines are aligned
in the direction indicated as north by a compass, which can
differ from True North to varying amounts, depending on
where you are on the earth. (This difference is called
“inclination”and “declination.”)
“Grid North” refers to the direction in which the straight lines
on a map are actually aligned, which may be slightly different
from True North, because the rounded surface of the earth
can not be accurately depicted on the flat surface of a map.
GENERAL INFORMATION
Sources of Interference / Errors:
GPS receivers have the potential for position errors due to
interference, primarily from the following sources:
Ionosphere and troposphere delays
The satellite signal slows as it passes through the atmosphere.
The system uses a built-in model that calculates an average
– though not exact – amount of delay.
Signal multi-path
This occurs when the GPS signal is reflected off objects such
as tall buildings before it reaches the receiver. This increases
the travel time of the signal, causing errors.
Receiver clock errors
The built-in clock can have very slight timing errors.
Orbital errors
Also known as ephemeris errors, these are inaccuracies of the
satellite’s reported location.
Most common error
Most common error is not having a clear view of the sky, or
being under very cloudy conditions, when a satellite signal
may not be received.
Number of satellites visible
The more satellites the receiver can see, the better the
accuracy. Buildings, terrain, electronic interference or even
dense foliage can block signal reception, resulting in position
errors or possibly no position reading at all. In general, the
clearer the view of the sky is at your location, the better
the reception will be. GPS receivers will not work indoors,
underwater or underground.
Due to the errors that might occur, it is recommended that
the serious navigator use a second navigational tool, such as
a magnetic compass or map.
When satellite lock is lost
Whenever satellite lock is lost, the following animation
sequence appears onscreen and continues to loop until
satellite lock is re-acquired.
When GPS is turned Off
Whenever GPS is turned Off, the following animation
sequence occurs and continues to loop until search is
activated by user.
Also, all data fields (except for power status data
fields) appear blank until GPS is turned On and
satellite lock is re-acquired.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 25

44
6
MAINTENANCE & SERVICE
5
43
SPECIFICATIONS
PERFORMANCE
Receiver:..........................................18 parallel channels
Acquisition Time:.............................Approximately 10 sec. (warm)
Approximately 35 sec. (cold)
Approximately 50 sec.
(first time)
Update Rate:...................................1/second, continuous
(selectable)
Position Accuracy:...........................up to 3 meters (10 feet)
Velocity Accuracy:...........................0.1 knot / 0.1 km/h
Dynamics: ........................................Performs to specifications to 6 g’s
Antenna: ..........................................Built-in patch antenna
PHYSICAL
Case:.................................................Fully gasketted, high impact ABS
plastic, waterproof to 1 meter for
30 min (IPX7 standards)
Size:..................................................4.7” H x 2.3” W x 1.5” D
(12 cm x 5.8 cm x 3.8 cm)
Weight: ............................................5.3 ounces
Operating Temperature Range:.....5˚F to 158˚F (-15˚C to 70˚C)
Storing Temperature Range:.........-40˚F to 176˚F (-40˚C to 80˚C)
POWER
Input:................................................Two 1.5 volt AA batteries and/or
12-volt DC external power
(vehicle power adapter)
Battery Life:....................................Up to 20 hours in battery
save mode
Up to 10-12 hours in continuous
operation out of save mode.
Specifications subject to change.
Temperature rating for the GPS 100 may exceed the usable
range of some batteries. Alkaline batteries can rupture at
high temperatures.
Alkaline batteries lose a significant amount of their capacity
as temperature decreases.
Use Lithium batteries when operating the GPS 100 in below
freezing conditions.
Extensive use of screen backlighting will significantly reduce
battery life.
External power can only be applied using the Cobra
®
external power cord/cable.
Maintenance of Your GPS 100
Your GPS 100 is designed and built to give you years of
trouble-free performance without the need for service. No
routine maintenance is required.
If your unit does not appear to be operating properly, please
follow these trouble-shooting steps:
Make sure you are using fresh batteries and they are
installed properly.
Make sure you are outdoors and away from buildings
and obstructions. Also, make sure you have a clear
view of the sky.
Make sure you have not accidentally turned GPS off
(see page 33).
Customer Service
In the U.S.A., you can receive technical assistance with your
unit through one of our customer support services:
Automated Help Desk is available in English
24 hours a day, 7 days a week at 773-889-3087.
Customer Service Operators are available in
English and Spanish at 773-889-3087 Monday
to Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. CST.
Questions can be faxed to 773-622-2269.
Automated Technical Assistance is available
in English or Spanish 24 hours, 7 days a week via
e-mail at: productinfo@cobra.com
On-line answers to frequently asked questions
(in English only) can be found at: www.cobra.com.
Outside the U.S.A. please contact your local dealer.
Service
If you suspect that your unit requires
service, please call 773-889-3087
BEFORE shipping it to Cobra.®This will
ensure that you receive service as quickly
as possible.
If you are asked to send your unit to the Cobra®factory,
please follow these steps:
1. Send the complete unit.
2. For warranty repair, enclose some form of
proof-of-purchase, such as a photocopy or carbon copy of
a sales receipt. If you send the original receipt, it cannot
be returned to you.
3. Enclose a typed or clearly written description of the
problem you are having with your unit, plus the name
and address where you want the unit returned.
4. Pack the unit securely to prevent damage during transit.
If possible, use the original packing materials.
5. Ship prepaid and insured using a traceable carrier such
as United Parcel Service (UPS), Federal Express or first
class mail with delivery confirmation. Ship to:
Cobra Factory Service
Cobra Electronics Corporation
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, IL 60707 USA
6. Please allow 3 to 4 weeks before contacting us about the
status of your service. Call 773-889-3087 for assistance.
If your unit is under warranty, it will either be repaired or
replaced upon receipt, depending on the model. If your unit
is out of warranty, you will receive a letter informing you of
the repair or replacement charge.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 26

46
7
INDEX
7
INDEX
45
A
About Option................................31
Accessories...................................47
Accuracy........................4, 9, 12, 14
Adjusting the Display...............31, 34
Advanced Options ..............31, 37-38
Alerts ..........................................39
Average Speed...............4, 9, 12, 14
Auto Zoom Option.........................10
B
Backlight...............A2, 4, 31, 32, 34
Basic Operation............................5-7
Batteries .....................5, 32, 39, 43
Battery Save Mode.............6, 31, 38
Bearing...................4, 9, 11, 12, 14
Buttons
Enter....................................A2, 6
Page....................................A2, 5
Power..................................A2, 5
Zoom In/Out........................A2, 5
C
Cautions and Warnings ............A1, 39
Clock Format .........................31, 35
Compass ..................11, 31, 37, 38
Contrast ................................31, 34
Course.........................................11
Create New Route .............21, 22-23
Customer Service..............A1, 44, 47
D
Data Fields Descriptions...................4
Date.......................4, 9, 12, 14, 32
Daylight Saving Time ..............31, 36
Default Option
Gauges ....................................12
Map ..........................................9
System ....................................32
Trip..........................................14
Delete All Data Option...................26
Delete Options ........................26-28
Delete Route..........................21, 26
Deleting Individual Tracks.........26, 28
Deleting Individual Waypoints...26, 27
Destination....................4, 9, 12, 14
Details Option
Map .......................................10
Route .....................................21
Display Option........................31, 34
Dutch Manual...............................A1
E
Editing Text..................................29
Edit Option, Route .......................21
Elevation.......................4, 9, 12, 14
Enter Button ...........................A2, 6
Errors..........................................41
ETA...............................4, 9, 12, 14
F
Factory Service.............................44
FCC Compliance Statement............ A1
Features ......................................A3
Five Main Pages.............................8
Font Size Option, Trip Meter...........13
French Manual..............................A1
Full Map........................................9
G
Gauges Data Option......................12
Gauges Defaults ...........................12
Gauges Page.......................8, 11-12
General Information...........2-4, 40-41
German Manual............................A1
GoTo.................................1, 16, 18
GPS Components .........................2-3
GPS Mode .............................31, 33
GPS Off.......................8, 31, 33, 41
GPS On...........................31, 33, 41
H
Hiker Icons ..................................15
I
Important Information....................A1
Inserting a Waypoint into
a Route........................21, 23, 24
Installing Batteries ..........................5
Interference .................................41
Italian Manual ..............................A1
L
Language ..............................31, 36
Location........................4, 9, 12, 14
Location Screen......................31, 33
Log Option, Tracks ........................19
Lost Satellites ....................8, 39, 41
Low Battery...........................32, 39
M
Maintenance ..............................44
Map Data Option ..........................9
Map Datum .....................31, 37, 42
Map defaults................................10
Map detail Option.........................10
Map Display...................................9
Map Orientation .............................9
Map Page.............................8, 9-10
Max Speed....................4, 9, 12, 14
N
Nav Data Page ....................8, 15-30
Navigate Option
Waypoints..........................16, 18
GoTo..................................16, 18
Track.................................19, 20
Route ................................21, 25
Navigation.................................1, 7
New Option
Route............................21, 22-23
Waypoints..........................16, 17
North Reference ...............31, 38, 42
North Up .......................................9
O
Odometer......................4, 9, 12, 14
Order Form..................................48
Orientation Option ..........................9
P
Page Button.............................A2, 5
Pointer Options.............................11
Portuguese Manual .......................A1
Position Format......................31, 38
Power...........................4, 9, 12, 14
Power Button.......................A2, 5, 6
Power On/Off ...............................6
Powersaver Mode...............6, 31, 33
R
Reset Option, Trip Meter................13
Remove Waypoint from Route..21, 23
Route...........................7, 21-25, 26
S
Satellites...............8, 31, 33, 39, 41
Search Option, Waypoints........16, 30
Select Option
Track .......................................19
Waypoint ................................16
Service........................................44
Set Data Option
Map ..........................................9
Gauges ....................................12
Trip..........................................14
Settings Option ................31, 35, 36
Sort Option, Waypoints............16, 30
Sort & Search........................16, 30
Sounds..................................31, 36
Spanish Manual............................A1
Specifications ...............................43
Speed...........................4, 9, 12, 14
Status Bar ...................................32
Stop Navigation
Map ........................................10
Gauges ....................................12
Trip..........................................14
Stop Receiving.............8, 33, 39, 41
Summer Time ........................31, 36
Swedish Manual ...........................A1
System Page .....................8, 31--38
T
Time.......................4, 9, 12, 14, 32
Time Zones................31, 35, 36, 40
Track......................7, 19-20, 26, 28
Track Log ..............................19, 39
Track Up........................................9
Trip Meter......................................7
Trip Meter Data Options .................14
Trip Meter Defaults........................14
Trip Meter Page...................8, 13-14
Trip Odometer................4, 9, 12, 14
Trip Time.......................4, 9, 12, 14
U
Units of Measurement.............31, 36
Using the Advanced Screen .......37-38
Using the Settings Screen .........35-36
W
WAAS ...................................31, 42
Warnings and Cautions ............A1, 39
Warranty .....................................47
Waypoint Shortcut..............6, 16, 17
Waypoints ..............7, 15-18, 26, 27
WGS 84......................................37
Winter Time.................................36
Z
Zoom In/Out Button .................A2, 5
Zoom Option................................10
Go to Table of Contents
Page 27

48
9
U.S. ORDER FORM
Item No. Description Cost Ea. Qty. Amount
For credit card orders fill out order
form and fax to: 773.622.2269
or call 773.889.3087
(Press 1 from the main menu)
8:00 am - 6:00 pm,
Monday-Friday CST.
Make check or money order
payable to:
Cobra Electronics
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, IL 60707 USA
ATTN: Accessories Dept.
To order online, please visit our website
at: www.cobra.com.
Subtotal
(Tax if applicable)
Shipping/handling
Total
Prices subject to change without notice.
Tax Table
California residents add 7.25%
Illinois residents add 8.75%
Indiana residents add 6%
Michigan residents add 6%
Ohio residents add 5%
Wisconsin residents add 5%
Please print clearly
Name
Address (No P.O. Box)
City State
Zip
Telephone ( )
Credit Card No. Exp. Date
Circle One: Visa MasterCard Discover
Customer Signature
Allow 2-3 weeks for delivery. Offer valid in Continental U.S. only. For accessories or orders outside the U.S., please contact your local dealer.
$25.00 and under
$25.01- $40.00
$40.01- $80.00
$80.01- $120.00
$120.01- $160.00
$160.01 and up
$4.75
$6.95
$9.25
$10.25
$11.75
$14.50
Amount Shipping/Handling
Prices are for shipping in the continental US only. For AK, HI and
PR please add an additional $15.00 for UPS shipments.
8
ACCESSORIES • WARRANTY • DOC
47
Optional Accessories
You can find fine accessories at your local Cobra®dealer, or in the
U.S.A. you can order directly from Cobra.
®
To order by phone in the U.S.A.
Call 773.889.3087 (Press 1 from the main menu
8 a.m.-6 p.m. M-F CST. )
To order by mail or fax in the U.S.A.
Call 773.889.3087 for pricing and availability. Please fill out
order form on next page, and mail/fax directly to Cobra.® Fax:
773.622.2269
To order online Go to www.cobra.com
COBRA®ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
warrants that its Cobra®GPS 100, and the component parts
thereof, will be free of defects in workmanship and materials
for period of one (1) year from the date of first consumer
purchase. This warranty may be enforced by the first consumer
purchaser, provided that the product is utilized within the U.S.A.
Cobra
®
will, without charge, repair or replace, at its option,
defective GPS 100, products or component parts upon delivery
to the Cobra
®
Factory Service Department, accompanied by
proof of the date of first consumer purchase, such as a
duplicated copy of a sales receipt.
You must pay any initial shipping charges required to ship
the product for warranty service, but the return charges will
be at Cobra
®
's expense, if the product is repaired or replaced
under warranty.
This warranty gives you specific rights, and you may also
have other rights which vary from state to state.
Exclusions: This limited warranty does not apply; 1) to any
product damaged by accident; 2) in the event of misuse or
abuse of the product or as a result of unauthorized alterations
or repairs; 3) if the serial number has been altered, defaced
or removed; 4) if the owner of the product resides outside
the U.S.A.
All implied warranties, including warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose are limited in duration to
the length of this warranty.
Cobra
®
shall not be liable for any incidental, consequential or
other damages; including, without limitation, damages resulting
from loss of use or cost of installation.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied
warranty lasts and/or do not allow the exclusion or limitation
of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitations
may not apply to you.
Cobra®Electronics Corporation
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, Illinois 60707 USA
www.cobra.com
Declaration of Conformity
Hereby, Cobra Electronics Corporation, declares that this
Global Positioning System Receiver is in compliance with the
essential requirements and other relevant provisions of
Directive 1999/5/EC.
Go to Table of Contents
Page 28

The Cobra®line of quality products includes:
CB radios
microTALK
®
radios
Radar/Laser Detectors
GPS
Safety Alert
®
Traffic Warning Systems
Accessories
HighGear
™
Accessories
For more information or
to order any of our products,
please visit our website:
www.cobra.com
Nothing comes close to a Cobra
®
Printed in China
Part No. 480-036-P
©2003 Cobra® Electronics Corporation
6500 West Cortland Street
Chicago, IL 60707 USA
 Loading...
Loading...