Page 1
9083
9083 HD/SD Frame Sync
with Audio Embedding/De-Embedding
®
and Dolby
Decoding Option
Product Manual
Cobalt Digital Inc.
2406 E. University Ave.
Urbana, IL 61802
Voice 217.344.1243 • Fax 217.344.1245
www.cobaltdigital.com
9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 2

Copyright
©Copyright 2013, Cobalt Digital Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Duplication or distribution of this manual and any information contained within is strictly prohibited without the express written
permission of Coba lt Digital Inc. This manual and a ny information contained within, may not be re produced, distribute d, or
transmitted in any form, or by any means, for any purpose, without the express written permission of Cobalt Digital Inc.
Reproduction or reverse engineering of software used in this device is prohibited.
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been carefully examined and is believed to be entirely reliable. However, no responsibility
is assumed for inaccuracies. Furthermore, C obalt Digit al Inc. res erves the right to ma ke changes to any pro ducts herein to improve
readability, function, or design. Cobalt Digital Inc. does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit described herein.
Trademark Information
Cobalt® is a registered trademark of Cobalt Digital Inc.
COMPASS
openGear
Dolby
property of their respective owners.
Linear Acoust ic
licensed feature uses the AutoMAX-II™ upmix algorithm provided under licens e from
Linear Acoustic Inc. Linear Acoustic, the "LA" symbol, AutoMAX, and AutoMAX-II are trademarks of Linear Acoustic Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
®
and FUSION3G® are registered trademarks of Cobalt Digital Inc.
®
is a registered trademark of Ross Video Limited. DashBoard™ is a trademark of Ross Video Limited.
®
is a registered trademark of Dolby Laboratories, Inc. Other product names or trademarks appearing in this manual are the
®
, AEROMAX® and UPMAX® are registered trademarks of Linear Acoustic, Inc. 2.0-to-5.1 audio upmixer
®
Congratulations on choosing the Cobalt
is part of a full line of modular processing and conversion gear for broadcast TV environments. The Cobalt Digital Inc.
line includes video decoders and encoders, audio embedders and de-embedders, distribution amplifiers, format
converters, remote control systems and much more. Should you have questions pertaining to the installation or
operation of your 9083, please contact us at th e contact inform ation on the front cove r.
9083 HD/SD Frame Sync w it h Audio Embedding/ De-Embedding. The 9083
Manual No.: 9083-OM
Document Version: V4.5
Release Date: September 25, 2013
Applicable for
Firmware Version
3314
(or greater):
Description of
product/manual
changes:
- Update to add new Rear I/O Modules.
- Revise manual for latest functionality with latest
firmware, and minor edits.
- Clarification of Framesyn c con tr ol des c ripti ons .
- Update manual to include latest available card
options.
9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Overview ................................................................................................................ 1-1
9083 Card Software Versions and this Manual...................................................... 1-2
Cobalt Reference Guides........................................................................................ 1-2
Manual Conventions............................................................................................... 1-3
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes .................................................................. 1-3
Labeling Symbol Definitions...................................................................... 1-4
Safety Summary ..................................................................................................... 1-4
Warnings..................................................................................................... 1-4
Cautions...................................................................................................... 1-4
9083 Functional Description .................................................................................. 1-5
9083 Input/Output Formats ........................................................................ 1-5
Video Processor Description ...................................................................... 1-7
Audio Processor Description...................................................................... 1-9
AES Audio Input Advanced Features ...................................................... 1-15
Dolby® Decoding (9083-DEC only)......................................................... 1-16
User Control Interface .............................................................................. 1-17
9083 Rear I/O Modules ............................................................................ 1-19
Audio and Video Formats Supported by the 9083................................... 1-20
Technical Specifications....................................................................................... 1-21
Warranty and Service Information ....................................................................... 1-25
Cobalt Digital Inc. Limited Warranty....................................................... 1-25
Contact Cobalt Digital Inc.................................................................................... 1-26
Chapter 2 Installation and Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Overview ................................................................................................................ 2-1
Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4) Ports ........................................................ 2-1
Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot ..................................................................... 2-2
Installing a Rear I/O Module.................................................................................. 2-5
9083 Rear I/O Modules .............................................................................. 2-6
Setting Up 9083 Network Remote Control .......................................................... 2-12
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL i
Page 4

Chapter 3 Operating Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Overview................................................................................................................. 3-1
Control and Display Descriptions........................................................................... 3-1
Function Submenu/Parameter Submenu Overview .................................... 3-2
DashBoard™ User Interface ....................................................................... 3-3
Cobalt® Remote Control Panel User Interfaces .......................................... 3-4
Accessing the 9083 Card via Remote Control........................................................ 3-5
Accessing the 9083 Card Using DashBoard™ ........................................... 3-5
Accessing the 9083 Card Using a Cobalt® Remote Control Panel ............. 3-6
Checking 9083 Card Information............................................................................ 3-7
Ancillary Data Line Number Locations and Ranges .............................................. 3-8
9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions...................................................... 3-9
Audio Input Controls ................................................................................ 3-10
Video Proc ................................................................................................ 3-13
AFD .......................................................................................................... 3-14
Framesync ................................................................................................ 3-15
Embedded Audio Group 1/2 .................................................................... 3-20
Embedded Audio Group 3/4 .................................................................... 3-24
AES Audio Out Pairs 1-4 ......................................................................... 3-26
AES Audio Out Pairs 5-8 ......................................................................... 3-30
Dolby Metadata ........................................................................................ 3-31
Dolby Decoder ......................................................................................... 3-32
Dolby E Metadata .................................................................................... 3-35
Dolby D Metadata .................................................................................... 3-36
Timecode .................................................................................................. 3-37
Audio Mixing ........................................................................................... 3-41
Tone Generator ......................................................................................... 3-46
Licensable Features .................................................................................. 3-46
Presets ....................................................................................................... 3-47
Audio Routing Example Using DashBoard™ .......................................... 3-49
®
Dolby
E Processing and Routing Example (9083-DEC only)................ 3-52
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 3-54
Error and Failure Indicator Overview....................................................... 3-54
Basic Troubleshooting Checks.................................................................. 3-58
9083 Processing Error Troubleshooting.................................................... 3-59
Troubleshooting Network/Remote Control Errors.................................... 3-62
In Case of Problems .................................................................................. 3-62
ii 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 5

Overview
Chapter 1
Chapter 1 Introduction
This manual provides installati on and o per at ing instr uct ions for the
9083 HD/SD Frame Sync wit h Audio Embedd ing/De-Embedding and Dolby
Decoding Option card (also referred to herein as the 9083).
Note: This manual also covers the 9083-DEC, which is the 9083 card equipped with
®
Dolby
sively to either the 9083 or the 9083-DEC are respectively denoted by (9083
only) or (9083-DEC only). In all other aspects, both the 9083 and 9083-DEC
function identically as described in this manual.
decoding as an option. Where applicable, descriptions related exclu-
This manual consists of the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction” – Provid es informa tion about this manual
and what is covered. Als o pr ovi des general information re gar di ng the
9083.
• Chapter 2, “Installation and Setup” – Provides instructions for
installing the 9083 i n a fr ame, and option ally i nsta lling 9083 Rear I/O
Modules.
• Chapter 3, “Operating Instructions” – Provides overviews of
operating controls and instructions for using the 9083.
This chapter contains the following information:
®
• 9083 Card Software Versions and this Manual (p. 1-2)
• Manual Conventions (p. 1-3)
• Safety Summary (p. 1-4)
• 9083 Functional Description (p. 1-5)
• Technical Spe cification s (p. 1-21)
• Warranty and Service Information (p. 1-25)
• Contact Cobalt Digital Inc. ( p. 1-26)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-1
Page 6
1 9083 Card Software Versions and this Manual
9083 Card Software Versions and this Manual
When applicable, Cobalt Digital Inc. provides for continual product
enhancements through software updates. As such, functions described in this
manual may pertain specifically to cards loaded with a particular software
build.
The Software Version of your card can be ch eck ed by vi ewi ng the Card Inf o
menu in DashBoard™. See Checking 9083 Card Information (p. 3-7) in
Chapter 3, “Operating Instructio ns” for more infor mation. You can then check
our website for the lates t software version currently released for the card as
described below.
Check our website and proceed as follows if your card’s software does not
match the latest versi on:
Card Software earlier than
latest version
Card Software newer than
version in manual
Card is not loaded with the latest software. Not all
functions and/or specified performance described in
this manual may be available.
You can update your card with new Update
software by going to the Support>Firmware
Downloads link at www.cobaltdigital.com.
Download “Firmware Update Guide”, which
provides simple instructions for downloading the
latest firmware for your card onto your computer,
and then uploading it to your card through
DashBoard™.
Software updates are field-installed without any
need to remove the card from its frame.
A new manual is expediently released whenever a
card’s software is updated and specifications
and/or functionality have changed as compared
to an earlier version (a new manual is not
necessarily released if specifications and/or
functionality have not changed). A manual earlier
than a card’s software version may not completely
or accurately describe all functions available for
your card.
If your card shows features not described in this
manual, you can check for the latest manual (if
applicable) and download it by going to the
Support>Documents>Product Information and
Manuals link at www.cobaltdigital.com.
Cobalt Reference Guides
From the Cobalt® web home page, go to Support>Documents>Reference
Guides
updates, and other topics.
1-2 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
for easy to use guide s covering network remot e control , card fir mware
Page 7

Introduction Manual Conventions
Manual Conventions
In this manual, display messages and connectors are shown using the exact
name shown on the 9083 itself. Examples are provided below.
• Card-edge display messages are shown like this:
Ch01
• Connector names are shown like this: SDI OUT
In this manual, the terms below are applicable as follows:
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes
Certain items in this manual are highlighted by special messages. The
definitions are provided bel ow.
Warnings
Warning messages indicate a possible hazard which, if not avoided, could
result in pe rsonal injury or death.
• 9083 refers to the 9083 HD/SD HD/SD Frame Sync with Audio
Embedding/De-Embedding and Dolby
• Frame refers to the HPF-9000, OG3-FR, 8321, or similar 20-slot
frame that houses Cobalt
• Device and/or Card refers to a COMPASS
• System and/or Video System refers to the mix of interconnected
®
or other cards.
®
Decoding Option card.
®
card.
production and terminal equipment in which the 9083 and other
COMPASS
• Functions and/or features that are available only as an option are
®
cards operate.
denoted in th is manual like this:
Cautions
Caution messages indicate a problem or incorrect practice which, if not
avoided, could result in improper operation or damage to the product.
Notes
Notes provide supplemental information to the accompanying text. Notes
typically precede the text to which they apply.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-3
Page 8
1 Safety Summary
Labeling Symbol Definitions
Attention, consult accompanying documents.
Electronic device or assembly is susceptible to damage from an ESD
event. Han dle only using appropriate ESD prevention practices.
If ESD wrist strap is not available, handle card only by edges and avoid
contact with any connectors or components.
Symbol (WEEE 2002/96/EC)
For product disposal, ensure the following:
• Do not dispose of this product as unsorted municipal waste.
• Collect this product separately.
• Use collection and return systems available to you.
Safety Summary
Warnings
! WARNING !
Cautions
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
T o redu ce risk of electr ic shock do not remove line voltage service barrier cover on frame
equipment containing an AC power supply. NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE.
REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
This device is intended for environmentally controlled use only in appropriate video
terminal equipment operating environments.
This product is intended to be a component product of an openGear® frame. Refer to the
openGear frame Owner's Manual for important safety instructions regarding the proper
installation and safe operation of the frame as well as its component products.
Heat and power distribution requirements within a frame may dictate specific slot
placement of cards. Cards with many heat-producing components should be arranged to
avoid areas of excess heat build-up, particularly in frames using only convection cooling.
The 9083 has a moderate power dissipation (15 W max.). As such, avoiding placing the
card adjacent to other cards with similar dissipation values if possible.
CAUTION
CAUTION
1-4 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
If required, make certain Rear I/O Module(s) is installed before installing the 9083 into the
frame slot. Damage to card and/or Rear I/O Module can occur if module installation is
attempted with card already installed in slot.
If card resists fully engaging in r ear I/O module mating connector, check for alignment and
proper insertion in slot tracks. Damage to card and/or rear I/O module may occur if
improper card insertion is attempted.
Page 9

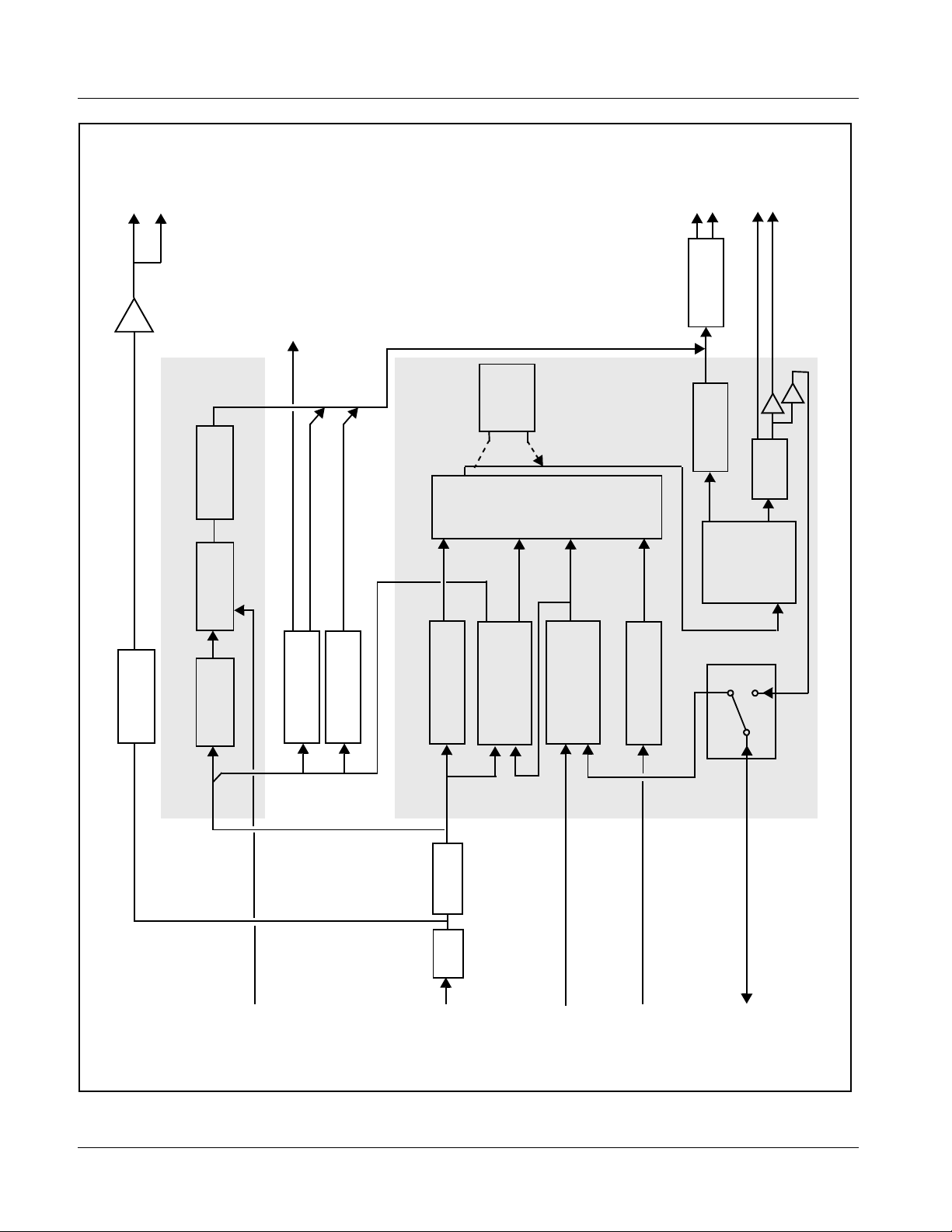
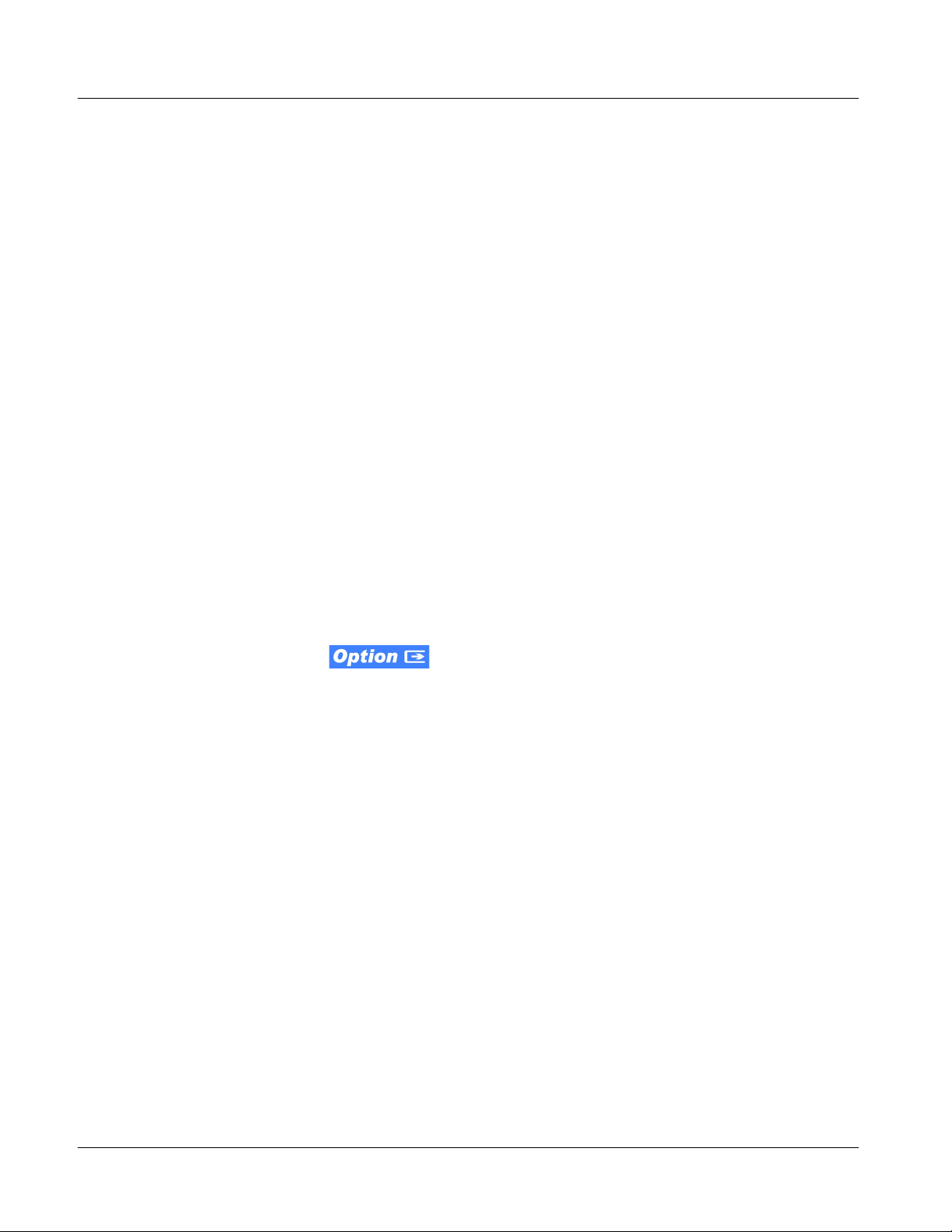
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
9083 Functional Description
Figure 1-1 shows a functional block diagram of the 9083. The 9083 frame
synchronizer also in cludes a full 16-channel a udio embedder/ de-embedder , an
8-channel, and a 24-bit balanced analog-to-digital audio converter. The 9083
also handles AFD code detection/insertion and transfer of Dolby
(9083-DEC only) The 9083-DEC also performs Dolby
®
E and Dolby®
Digital™ decoding and decoded channel routing.
®
metadata.
Note: Some of the functions described below are available only when using the
9083 Input/Output Formats
DashBoard™, or Cobalt
®
OGCP-9000 or OGCP-9000/CC Control Panels
user interfaces. Refer to User Control Interface (p. 1-17) for user interface
descriptions.
The 9083 provides the following inputs and outputs:
• Inputs:
• HD/SD SDI IN – dual-rate HD/SD-SDI input
• AES I/O (1-4) – user-switchable as AES inputs or AES outputs
• AES IN (5-8) – dedicated AES inputs
• AN-AUD IN (1-8) – balanced analog audio inputs
• Outputs:
• SDI OUT – two dual-rate HD/SD-SDI buffered video outputs
• RCK OUT – two reclocked HD/SD-SDI input copies
• AES OUT (1-8) – dedicated AES outputs
• AES I/O (1-4) – user-switchable as AES inputs or AES outputs
• DOLBY META – RS-485 Dolby
input video). (9083-DEC only) RS-485 Dolby
can consist of input video or Dolby
®
metadata output (extracted from
®
decoder metadata output.
®
metadata output
Note: The input/output complement listed above represents the maximum capability
of the 9083. The practical input/output complement is determined by the particular Rear I/O Module used with the 9083. Refer to 9083 Rear I/O Modules
(p. 1-19) for more information.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-5
Page 10
1 9083 Functional Description
RCK OUT
shown depicts full input/
output capability.
Notes: 1. Signal connections
DOLBY
META
(NOTE 2)
Insertion
AFD Code
Sync
Frame
Practical input/output
2.0-to-5.1
signal availability is
determined by Rear I/O
Upmixer
Audio
decode
®
function applicable
only for 9083-DEC.
upmixer licensable
Module used.
2. Dolby
(NOTE 3)
Gain
Routing/
feature.
3. Optional 2.0-to-5.1
Active: Overwrites
6 selected channels
with new 5.1 mix.
See text.
Bypass: Bypasses
2.0-to-5.1 upmixer;
all original channels
pass unaffected.
Control
SDI OUT
Serializer/
Audio
Cable Drivers
Embed
Framesync
AES OUT
(5-8)
(1-4)
AES
Encode
Tracking
Delay and
User Offset
Decode
De-Embed
®
(NOTE 2)
Dolby
and SRC
AES Decode
Audio A/D
Differential Analog
Re-insert
Audio
Reclock
Video
Processing
Timecode
Processing
Metadata Extract/
S11–S14
[AES IN (1-4)]
Video Processor
Audio Processor
[AES OUT (1-4)]
Deserialize
EQ
SDI IN
IN (1,2)
EXT REF
HD/SD
IN (1-8)
AN-AUD
AES I/O
(1-4)
9083BDV4
AES IN (5-8)
Figure 1-1 9083 Functional Block Diagram
1-6 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 11

Introduction 9083 Functional Description
Video Processor Description
Video Processor
The 9083 provides full color processing control (luma gain and lift, chroma
saturation, and color phase) of the output video.
Frame Sync Function
This function p rovide s for fra me s ync co ntrol usin g e ither one of t wo ext ern al
EXT REF IN (1,2) reference sign als di stri buted wit h the ca rd fra me, or the inpu t
video as a frame sync reference.
This function allows horiz ontal and/or ver tica l of fset to be added bet ween the
output video and the frame sync reference.
A video/audio delay offset function allows adding or reducing audio delay
from the matching video delay. This function is useful for correcting lip sync
problems when video and audio paths in the chain experience differing
overall delays. A Reset Framesync function resets the frame sync following
any horizontal or vertical offset changes, clearing any buffered audio and
video and re-establ ishing t he frame s ync. The 908 3 re-est ablishes vi deo/audi o
sync following framesy nc changes by appl ying an of fset in small, progre ssive
amounts to provide a seamless, glitch-free retiming. A user-selectable hard
resync function allows setting a threshold at which hard resync is applied if
audio-video offset exceeds the threshold. Hard resync provides fastest
snyc-up suitable for off-air manipulati on. Conve rs ely, a threshold setting that
avoids hard resync allows glitch-free on-air manipulation.
In the event of input video loss of signal, this function provides for disabling
the video, going to a des ired color raster, or freezing to the last intact frame
(last frame having valid SAV and EAV codes).
(9083-DEC only) When Dolby
®
data is rece ived and actively routed into
embedded or AES output channels, the frame sync function delays the video
by one frame (as required by the Dolby
®
decode processing delay) to
maintain video/audio sync.
AFD Inserter
This function provides for assignment and insertion of AFD codes into the
SDI output video. Using this function, AFD codes in accordance with the
standard 4-bit AFD code designations can be applied to the output video.
This function checks for any existing AFD code within the received video
input. If a code is present, the code is displayed. When used in conjunction
with a separate downstream card capable of providing AFD-directed scaling,
the image can in turn b e scaled in accord ance with th e AFD coding embedd ed
by this card.
The function also allows the selection/changing of the AFD code and
ancillary data line number for the outputted AFD code.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-7
Page 12
1 9083 Functional Description
Dolby® Metadata Extractor/Re-inserter
Notes: • (9083 only ) This function allows metadata extraction from input video only.
• (9083-DEC only) This function is replaced with Dolby metadata tools that
are part of t he Dolb y
for description of Dolby
This function extract s and preserv es Dolby® metadata from the input SDI, and
in turn allows the metadata to be re-inserted in the output SDI. (The 9083
does not offer Dolby
®
Dolby
Digital™ encoded signals and metadata intact.) The extracted
metadata is buffered and then output on a user-selectable line number on the
SDI output, and on an RS-485 port on cards equipped with an appropriate
Rear I/O Module.
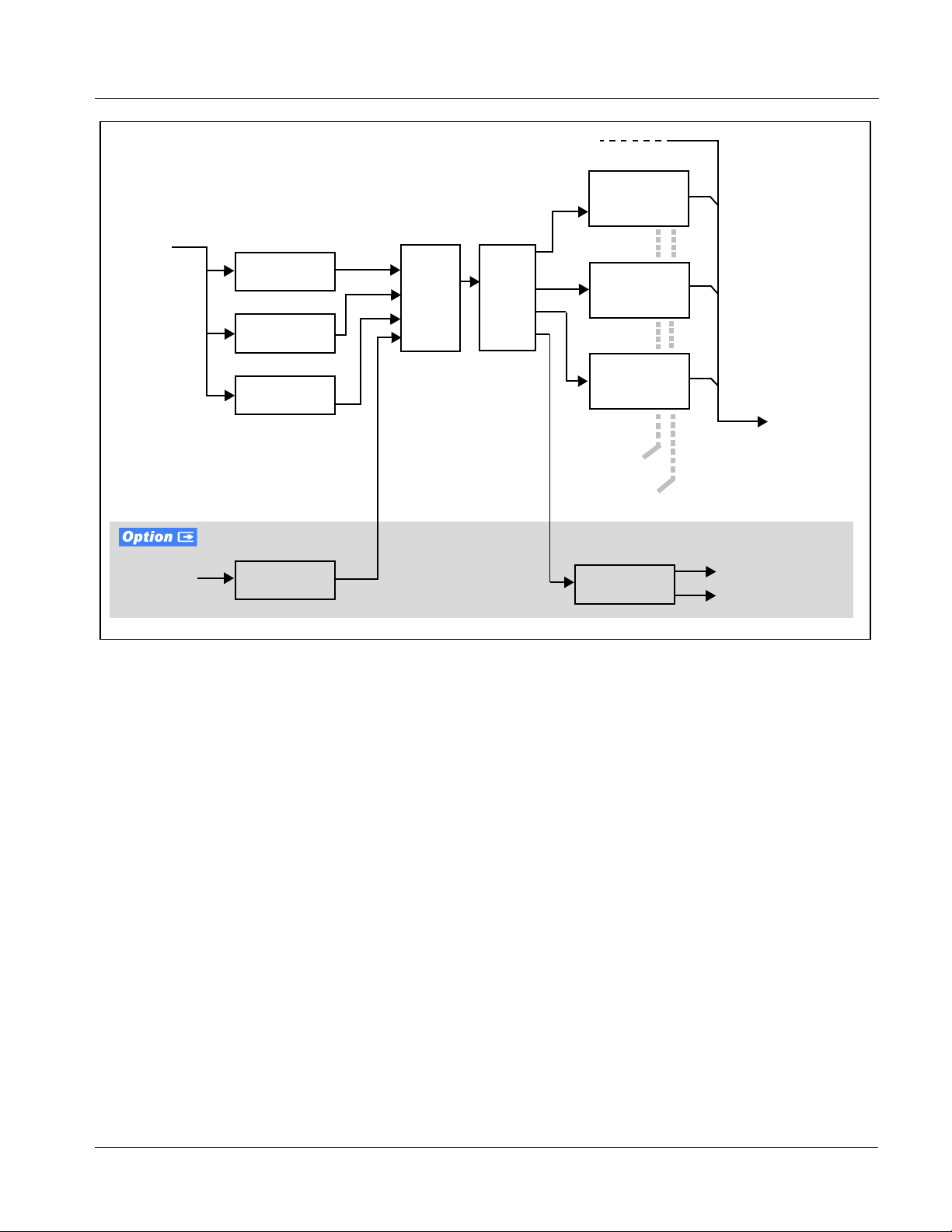
Timecode Processor
(See Figure 1-2.) This func ti on provides for extracti on of t imec ode da ta from
the input video, and in turn re-insertion of timecode data into the output SDI.
The function can monitor the SDI video input of the card for supported
timecode formats, an d then select and priori tize among SDI VITC,
SDI A TC VITC, and SDI ATC LTC ti mecode sour ces. If the prefe rred form at
is detected, the preferred format is used by the card; if the preferred format is
not detected, the card uses other formats (where available) as desired.
®
decoder function. Refer to Dolby® Decoding (p. 1-16)
®
metadata processing for the 9083-DEC card.
®
decoding or encoding, but will pass Dolby® E and/or
The function provides conversion between various timecode formats and
provides independent insertion and line number controls for each SDI
timecode output format.
Option +LTC allows bidirectional transfer and conversion
between VBI formats over SDI and audio LTC, as well as RS-485 LTC.
Audio LTC can be received or sent over a selected balanced analog audio
input, or as digital audio over a selected embedded or AES input.
1-8 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 13
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
HD/SD–SDI
(From Video Proc)
SDI VITC
Timecode
Proc/Embed
SDI
Video
Input
SDI VITC
Detect/Extract
SDI ATC_VITC
Detect/Extract
SDI ATC_LTC
Detect/Extract
Priority/
Select
Buffer/
Format
ATC_VITC
Timecode
Proc/Embed
ATC_LTC
Timecode
Proc/Embed
HD/SD–SDI
Video Output
Insert
Control
Line
Number
Control
Audio/
RS-485 LTC
Audio LTC
Select/Extract
Audio Processor Description
Audio/RS-485
LTC Generate
Audio LTC Out
RS-485 LTC Out
Figure 1-2 Timecode Processor
The audio processor operates as an internal audio router. The router function
chooses from the following inputs:
• 16 channels of embedded audio from the SDI video
• 16 channels (8 pairs) of discrete AES input
• 8 channels of balanced analog audio input
• Four independent internal tone generators (described below)
• Digital silence (mute) setting
• Internal Down Mix and Mono Mixer outputs (described below)
• (9083-DEC only) Decoded Dolby
®
channels
The router function provides the following audio outputs:
• 16 channels of embedded audio on the SDI output
• 16 channels of discrete AES output on eight AES pairs
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-9
Page 14
1 9083 Functional Description
The router acts as a full audi o cr oss po in t. Ea ch of the 32 output channels (16
embedded AES, 16 discrete AES) can receive signal from any one of the 40
(16 embedded AES, 16 discrete AES, 8 analog) input channels, four internal
tone generators, or several mixer outputs. Unused output channels can be
mapped to a “Silence” source. Each output al so provi des gain adj ustment and
selectable polarity inversion.
Output audio rates are always 48 kHz locked to output video, but discrete
AES inputs can pass through the sample rate converters to align these inputs
with the output timing. (AES must be nominally 48 kHz input; 32, 44.1, 96,
and 192 kHz inputs are not compatible with the 9083.) The sample rate
converters are disabled by default. Output AES is always precisely
synchronized with the output video. The balanced analog audio input is
sampled at 48 kHz with a +24 dBu clipping level (+24 dBu => 0 dBFS).
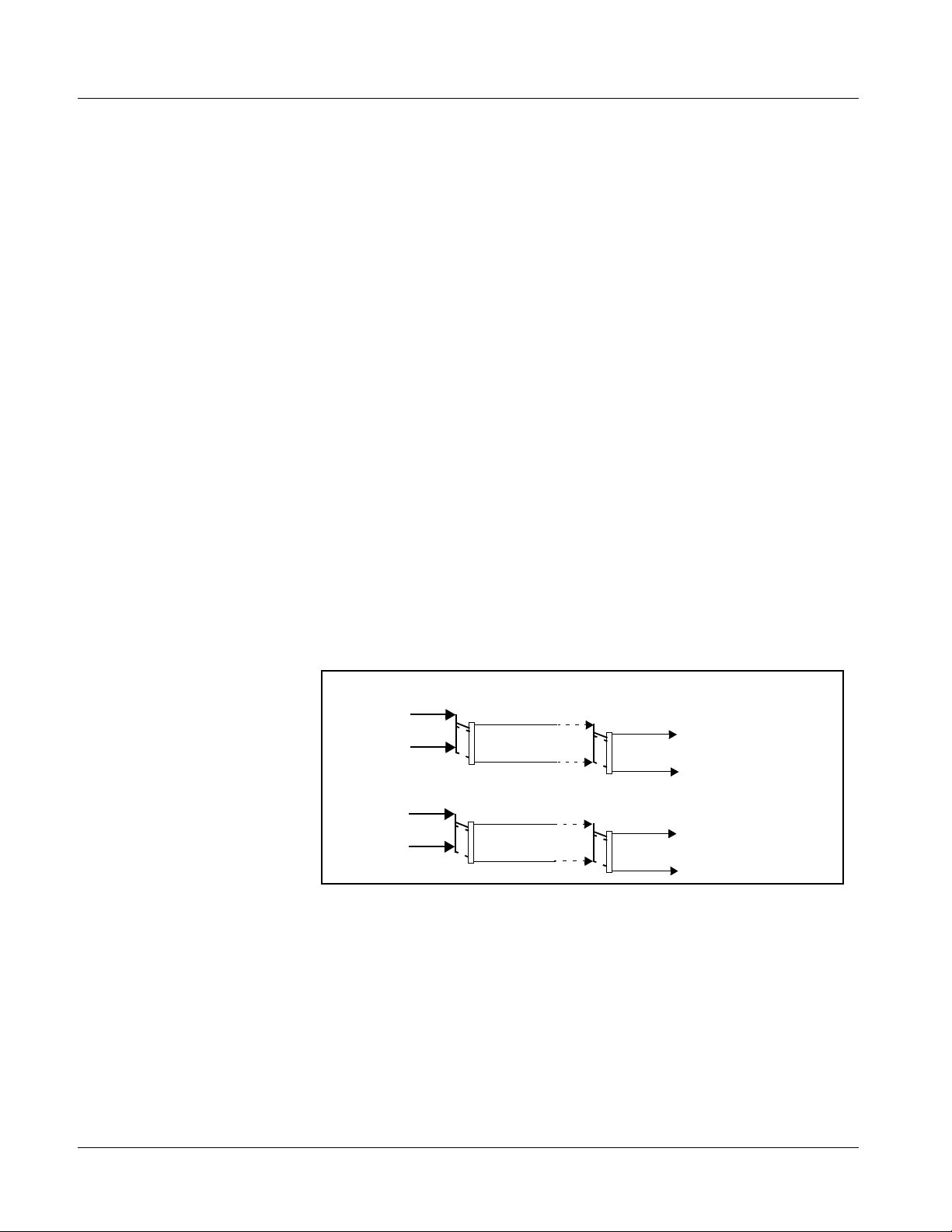
As set with the defau lt setting s, the routin g between embedded audio channels
Embed Ch 1 thru Embed Ch 16 and di scr ete AES audio channe ls AES Ch1 thru
AES Ch 16 is as shown in Figure 1-3. In this mode, the routing is basic 1-to-1
embedding/de-embedding for the 16 embedded and AES discrete audio
channels. Other sources and/or destinations (described below) for each
channel are selected using the card edge controls or a remote control system.
Note: As shown in Figure 1-1, the 9083 is equipped with eight discrete AES input
pair ports and eight discrete AES output pair ports. On Rear I/O Modules having limited AES I/O capabilities, switches S11 thru S14 allow available rear
module BNC connectors to be allotted between AES inputs and outputs as
desired. Buffered copies of
AES OUT (1-4) are available as dedicated outputs
and as respective outputs fed through S11 – S14 on the 9083 card.
Embedded Audio
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 8
AES Ch 9
AES Ch 16
Group 1/2
Embed Ch 1
•
•
•
Embedded Audio
•
•
•
•
•
•
Embed Ch 8
Group 3/4
Embed Ch 9
•
•
•
Embed Ch 16
Figure 1-3 Default Embed/De-Embed Audio Routing
AES Audio Out
Pairs 1-4
AES Ch 1
•
•
•
AES Ch 8
AES Audio Out
Pairs 5-8
AES Ch 9
•
•
•
AES Ch 16
1-10 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 15
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
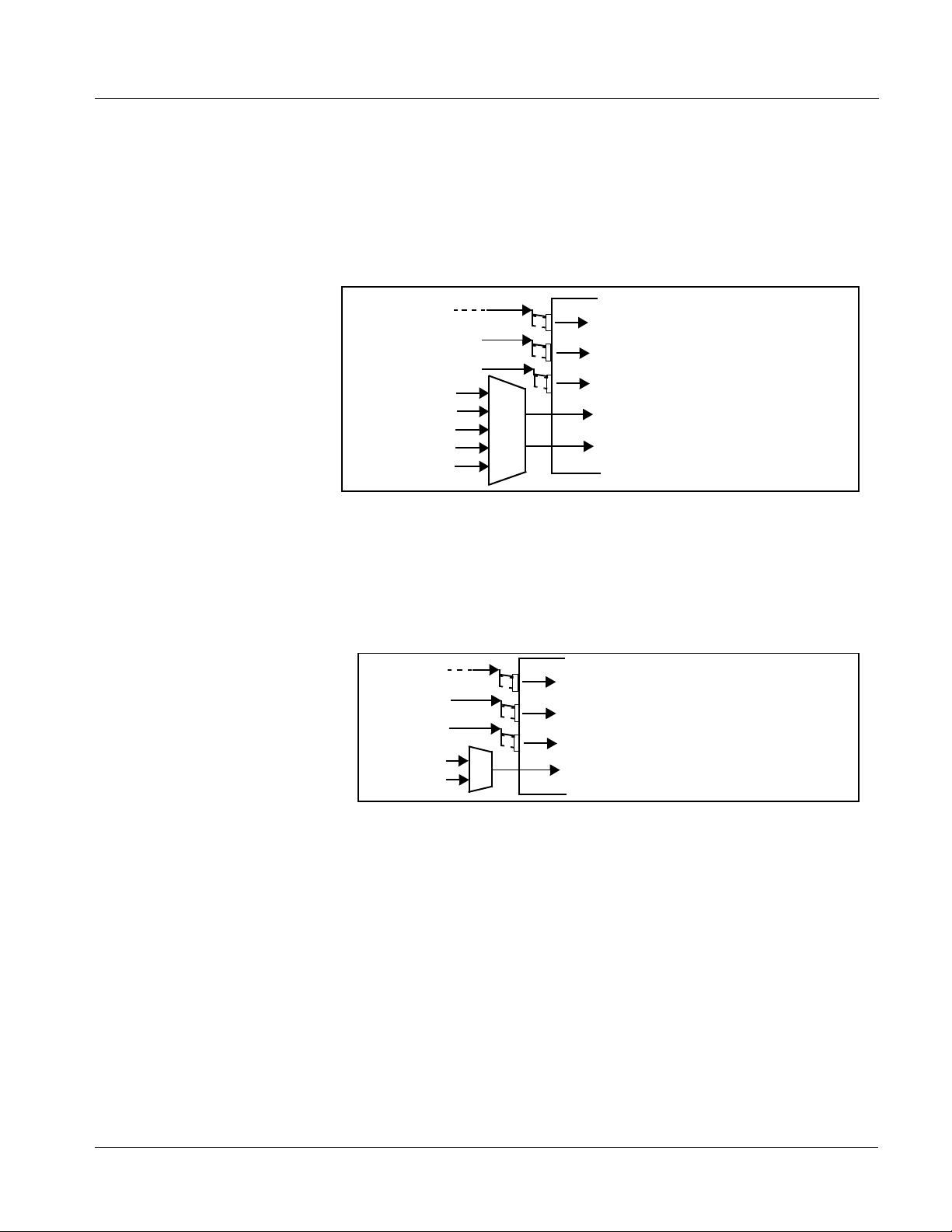
Audio Down Mixer and Mono Mixer Function
(See Figure 1-4.) The Audio Down Mixer function provides for the selection
of any five embedded, AES discrete, or analog audio sources serving as Left
(
L), Right (R), Center (C), Lef t Surround (Ls), and Right Surround (Rs)
individual signals to be multipl exed in to a ster eo pai r (Down Mix Left (
and Down Mix Right (
DM-R)). The resulting stereo pair DM-L and DM-R can in
turn be routed a nd process ed just like any of the other au dio sourc es descri bed
earlier.
Embed Ch 1 - Ch 16
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
AN-AUD Ch 1- Ch 8
Embedded Ch 1
Embedded Ch 2
AES Ch 6
Embedded Ch 4
Embedded Ch 5
Ls
L
C
R
Rs
DM-L
DM-R
DM-L)
Figure 1-4 Audio Mixing Functional Block Diagram with Example Sources
The Mono Mixer function (Figure 1-5) generates an additional mono-mixed
channel from two sel ec ted embed d ed, AES di scr et e, or analog input chann el s
serving as left and ri ght i nputs. Th e resul ting mon o mix chann el
turn be routed a nd process ed just like any of the other au dio sourc es descri bed
earlier.
Emb Ch 1 - Ch 16
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
AN-AUD Ch 1- Ch 8
Emb Ch 12
Emb Ch 16
L
R
MONO
Σ
Figure 1-5 Audio Mono Mix Functional Block Diagram with Example Sources
Tone Generator Function
The 9083 contains four built-in tone generators (Tone Generator 1 thru Tone
Generator 4). Each of the four tone generators can be set to a different
frequency, and are available as audio sources f or the embedded or AES audio
outputs.
MONO can in
18 discrete sine wave frequencies are a vailable, ranging from 50 Hz to 16 kHz
(default frequency is 1.0 kHz).
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-11
Page 16

1 9083 Functional Description
2.0-to-5.1 Upmix Function
Note: Upmix function is an optional licensable feature. This function and its controls
appear only when a license key is entered and activated. (This option (identified in Cobalt
field-activated using a key string which is sent to you when this option is purchased.)
The 2.0-to-5.1 upmixer function receives a normal PCM stereo pair from the
Audio Routing/Gain Control function and upmixes the pair to provide 5.1
channels (Left (
Surround (
overwrites the six selected channels with the new 5.1 upmix signals
(including replacing the original source stereo
R signals).
The 2.0-to-5.1 upmixer can be set to up mix in any of three modes: Always
upmix, Bypass upmix, or Auto enable/bypass upmixing. The Auto upmixing
mode looks at the s ignal le vels on t he selec ted ch annels an d compar es them to
a selectab le level threshold. It the n determines whether or not to generate 5.1
upmixing from the ster eo pair as follows:
®
price lists as +UM) can be purchased upon initial order, or
L), Right (R), Center (C), Low Frequency Effects (LFE), Left
Ls), and Right Surround (Rs)). Whenever the upmixer is active, it
L and R inputs with new L and
• If the upmixer detects signal level below a selected threshold on all
four of the selected channels designated as
C, LFE, Ls, and Rs, this
indicates to the upmixer that these channels are not carrying 5.1. In
this case, the upmixer overwrites all six selected channels with the
new 5.1 content.
• If the upmixer detects signal level above a selected threshold on any
of the four selected channels designated as
C, LFE, Ls, and Rs, this
indicates t o the upmixe r that the ch annel(s) ar e already carrying
viable 5.1 content. In th is case , the upmixe r is bypa ssed, al lowing t he
original channels to pass unaffected.
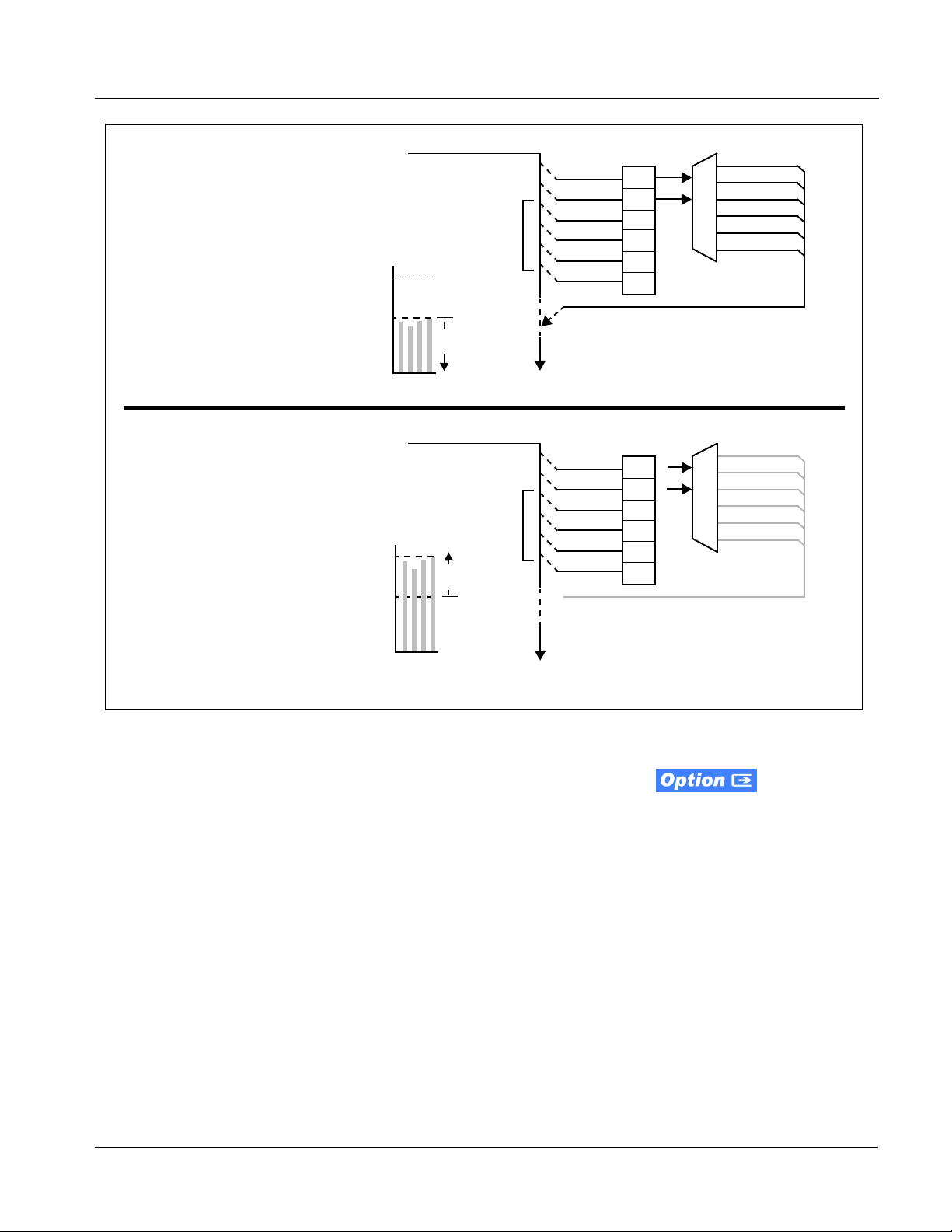
The examples in Figure 1-6 show t he automatic enable/di sable up-mixing
function applied to example selected channels
Emb Ch 1 thru Emb Ch 6. As
shown and described, the processing is contingent upon the signal levels of
the channe ls selected to carry the new 5.1 upmix relative to the selected
threshold (in this example, -60 dBFS). Note also that this function is applied
after the Audio Routi ng/Ga in Cont rol f uncti on. Beca use al l aud io inputs pass
through the Audio Routing/Gain Control funct io n be for e t he up mixer, the up
mixer can use embedded, AES discrete, and/or analog audio sources.
1-12 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 17
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
From Audio Routing/Gain Control
From Audio Routing/Gain Control
Note: In either case shown here,
the unselected channels (in
this example, Emb Ch 7 thru
Ch 16) are not involved in
this process and always
pass unaffected.
Emb Ch 1 – Ch 16
>
With all detected signal levels on
Emb Ch 3 – Ch 6 below
threshold, upmixer is active and
overwrites with new 5.1.
- 20 dBFS
- 60 dBFS
Below Threshold
(Overwrite)
s
s
E
C
L
R
F
L
Emb Ch 1 – Ch 16
>
With any detected signal levels
on EmbCh3– Ch 6 above
threshold, upmixer is bypassed.
- 20 dBFS
Above Threshold
- 60 dBFS
C
(Bypass)
s
s
E
L
R
F
L
To Audio
Embed
To Audio
Embed
Emb Ch 1
Emb Ch 2
Emb Ch 3
Emb Ch 4
Emb Ch 5
Emb Ch 6
Emb Ch 1
Emb Ch 2
Emb Ch 3
Emb Ch 4
Emb Ch 5
Emb Ch 6
X
Threshold
Detect
L
R
(C)
(LFE)
(Ls)
(Rs)
Selected channels Emb Ch 1 – Ch 6
are overwritten with the new 5.1
upmix content.
Threshold
Detect
L
R
(C)
(LFE)
(Ls)
(Rs)
Because the selected channels are
already carrying viable content,
upmixing is bypassed, allowing the
six original Emb Ch 1 – Ch 6 to pass
unaffected.
5.1 Up Mix
L – Emb Ch 1
R – Emb Ch 2
C – Emb Ch 3
LFE – Emb Ch 4
Ls – Emb Ch 5
Rs – Emb Ch 6
5.1 Up Mix
X
X
Figure 1-6 Up Mix Auto Enable/Bypass with Example Sources
Loudness Processor (Option +LP)
Note: Loudness processor function is an optional licensable feature. This function
and its controls appear only when a license key is entered and activated.
(This option (identified in Cobalt
initial order, or field-activated using a key string which is sent to you when this
option is purchased.)
If your card was purchased with option +LP, loudness processor manual
supplement “5.1 and Stereo Loudness Processing Options for Compass
Cards (+LP51, +LP20) Manual Supplement” (OPT-SW-LP-MS) is included
in your documentation package. Supplement OPT-SW-LP-MS can be
downloaded from our website or requested using the Cobalt contact
information in this manual.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-13
®
price lists as +LP) can be purchased upon
®
Page 18
1 9083 Functional Description
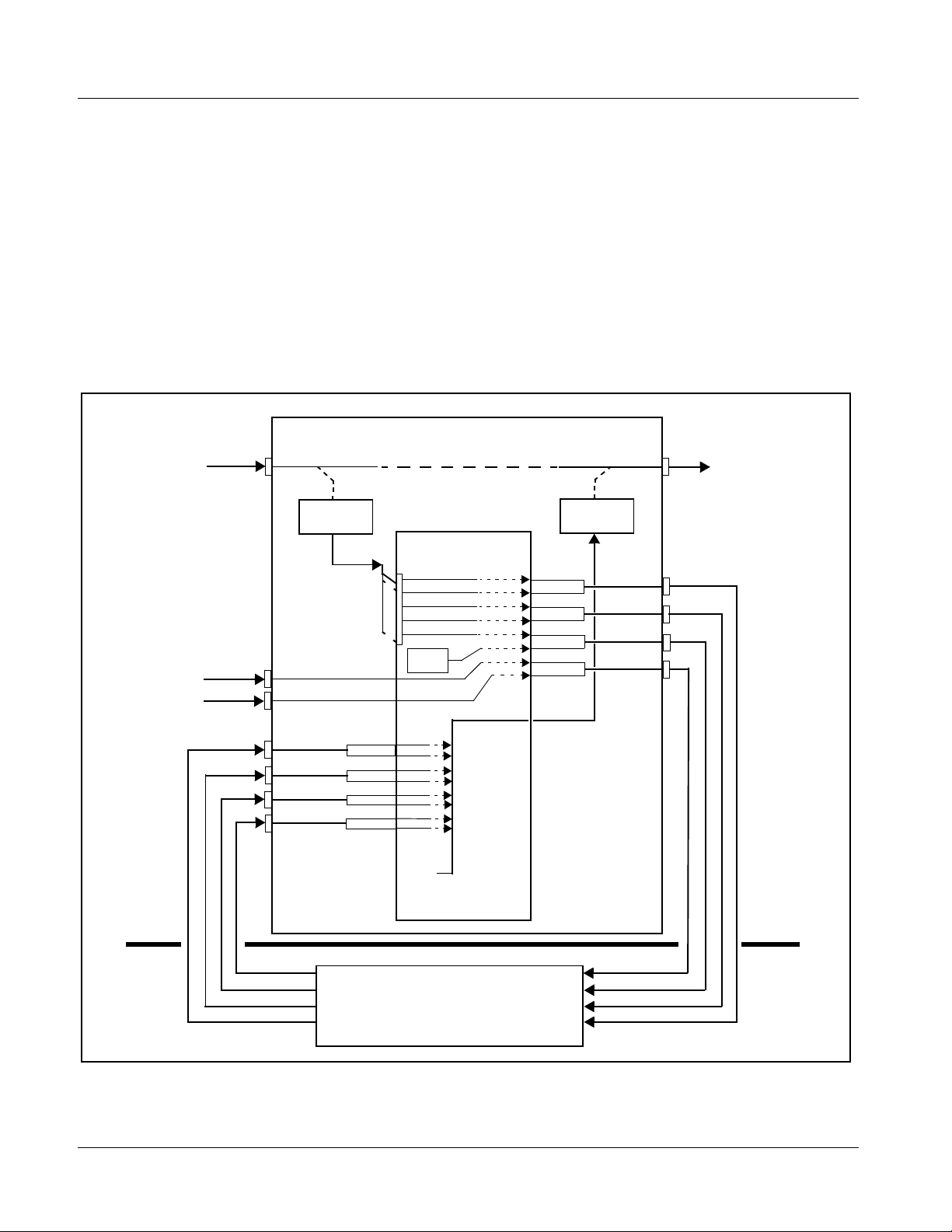
Audio Routing Example
Figure 1-7 shows an example of using the 9083 audio embedding/
de-embedding and routing functions to de-embed audio, route the audio to
discrete outputs for post-production processing (in this example, a console
used for post-production EQ, levels, and monitor), and finally re-embed the
audio into the SDI video output. Additionally, the example shows how
external analog and internal tone generator sources can be embedded into the
SDI output (in this ex ample, a provision f or local sta tion ID voice- over analog
and a tone).
Note that the source and destination correlations shown here are only
examples; any source can route to any destination.
9083
Post-Production
Video Feed
(with five
embedded audio
channels)
Analog
2-Channel
Voice-Over
Feed
SDI IN
Audio
De-Embed
AN-AUD IN 1
AN-AUD IN 2
Audio Routing/
Control
Analog
Ch 1
Analog
Ch 2
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
TG1
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 3
AES Ch 4
AES Ch 5
AES Ch 6
AES Ch 7
AES Ch 8
Audio
Embed
SDI OUT
AES OUT 1
AES OUT 2
AES OUT 3
AES OUT 4
OTA Video
Feed (with
eight embedded
audio channels)
AES IN 5
AES IN 6
AES IN 7
AES IN 8
AES Ch 9
AES Ch 10
AES Ch11
AES Ch 12
AES Ch 13
AES Ch 14
AES Ch 15
AES Ch 16
Silence
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
Embed Ch 6
Embed Ch 7
Embed Ch 8
Embed Ch 9 –
Embed Ch 16
Post-Production Console
Figure 1-7 Audio Routing Example
1-14 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 19

Introduction 9083 Functional Description
AES Audio Input Advanced Features
AES Sample Rate Converter
The 9083 AES inputs have sample rate converters that can be independently
enabled for each AES pair to allow the card to interface with asynchronous
AES sources (sources in which AES timing does not match the video input
timing). The sample rate converters are set to disabled (bypassed) by default;
this is necessary when embedding non-PCM AES audio such as Dolby
®
Dolby
Digital au dio streams. When a valid Dolby® E or Dolby® Digital
signal (in accordance with SMPTE 337M) is detected on an AES or
embedded audio signal, SRC is automatically bypassed along with gain and
polarity controls.
Zero-Delay Audio Embedding
®
E or
In cases where additiona l delay must be avoided, it may be desirable to e mbed
AES with minimum latency. For example if Dolby
®
E is to be embedded into
video with no latency, additional delay may not be tolera ble. Using zer o-delay
embedding, the video can then be delayed by one frame to account for the
Dolby E encoding delay. In this manner, any delay between video and audio
can be cleanly contained within one frame period.
When zero-delay audio emb edding is en abled for a give n AES pair , th e pair is
directly embedded int o its corres ponding group (for example , AES Pair 1 in to
embedded channels 1 an d 2; AES Pai r 2 int o embedde d channe ls 3 an d 4, a nd
so on) with the normal frame sync audio delay being bypassed.
This function overrides the audio routing sys tem (for example if AES Pair 1 is
selected, then the controls to route AES Pair 1 into other embedded channels
will not apply). Gain and polarity control is not available when this option is
selected. Zero-delay audio embedding is set to Off by default.
Low-Latency AES Passthrough
This function is similar to zero-delay audio embedding. If low-latency AES
passthrough is selected for a given input pair, it causes the corresponding
AES output pair to act as a bit-for-bit copy of the corresponding AES input
pair.
This control overrides the normal audio routing and delay. Gain and polarity
control is not available when this option is selected. Passthrough is set to Off
by default.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-15
Page 20
1 9083 Functional Description
Dolby® Decoding (9083-DEC only)
Note: Although the 9083-DEC Dolby® decoder can provide Dolby® Digital™ (AC-3)
decoding, discussion and examples here describe only Dolby
®
E decoding.
When Dolby® E or Dolby® Digital™ is present on an embedded audio pair,
the decoder produces up to 10 decoded channels (according to the Dolby
®
sub-format received from the metadata). All r esulting chan nels are available
as inputs to the audio router.
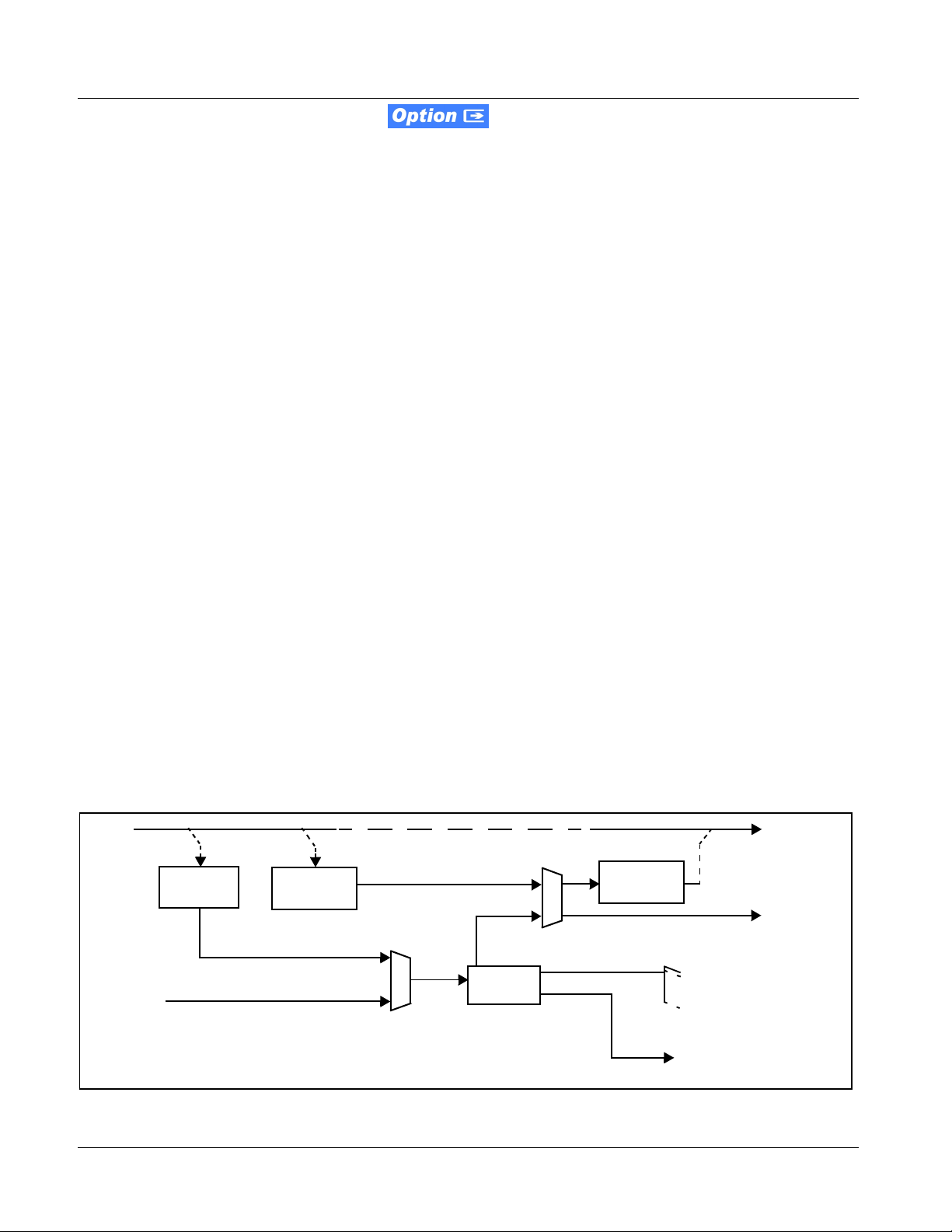
Dolby® Identification and Metadata Output Processing
(See Figure 1-8.) All embedded channels are checked by the 9083-DEC for
valid Dolby
detected, the channel pair carrying the Dolby
Dolby E” or “Present, Dolby Digital”, as applicable. (The decoder always
uses the metadata associated with its respecti ve pair.) A selected encoded
channel pair can then be directed to the Dolby
displays the Dolby
example, “Dolby E 20-bit 5.1+2” indicating 5-channel surround with LFE
channel and stereo monitor pair) for the selected pair, as defined by its
metadata.
The 9083-DEC can embed metadata on the SDI output, sourced from either
SDI input video or from the decoder as desired. Similarly, the 9083-DEC
DOLBY META out put can prov ide RS-485 met adata for downstream dev ices or
systems. Metadata on the
from either SDI input video or from the decoder as desired.
®
status. When a valid Dolby® encoded embedded pair is
®
bitstream format and program configuration (for
DOLBY META RS-485 output can also be sourced
®
format is displaye d as “Present,
®
decoder. The decoder then
SDI IN
Discrete
AES IN Pair
De-embed
Dolby® Encoded Embedded
Pair (1+2)...(15+16)
®
Dolby
Encoded AES
Pair (1)...(8)
Figure 1-8 Dolby® Decoding and Metadata Output Processing
Audio Decoding
(See Figure 1-8.) Based on th e channels car rying the Dolby® encoded pair and
the format defined within, the Dolby
audio channels (
channel can be routed just as any other audio channel described in this
section.
SMPTE 2020
De-mux
Input Select
®
decoder provides up to 10 decoded
Dolby Ch 1 thru Dolby Ch 8; Dolby Mix 1, Dolby Mix 2). Each
SDI OUT
Input Video
Metadata
Decoder
Metadata
Dolby®
Decode
2X2 Mux
SMPTE 2020
Mux
DOLBY
META
Ch 1
Dolby®
Decoded
Audio
Mix 2
Channels (Ch 1...Mix 2)
Dolby® Encoded Channel/
Format/Program
Identification (User
Interface Display)
1-16 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 21
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
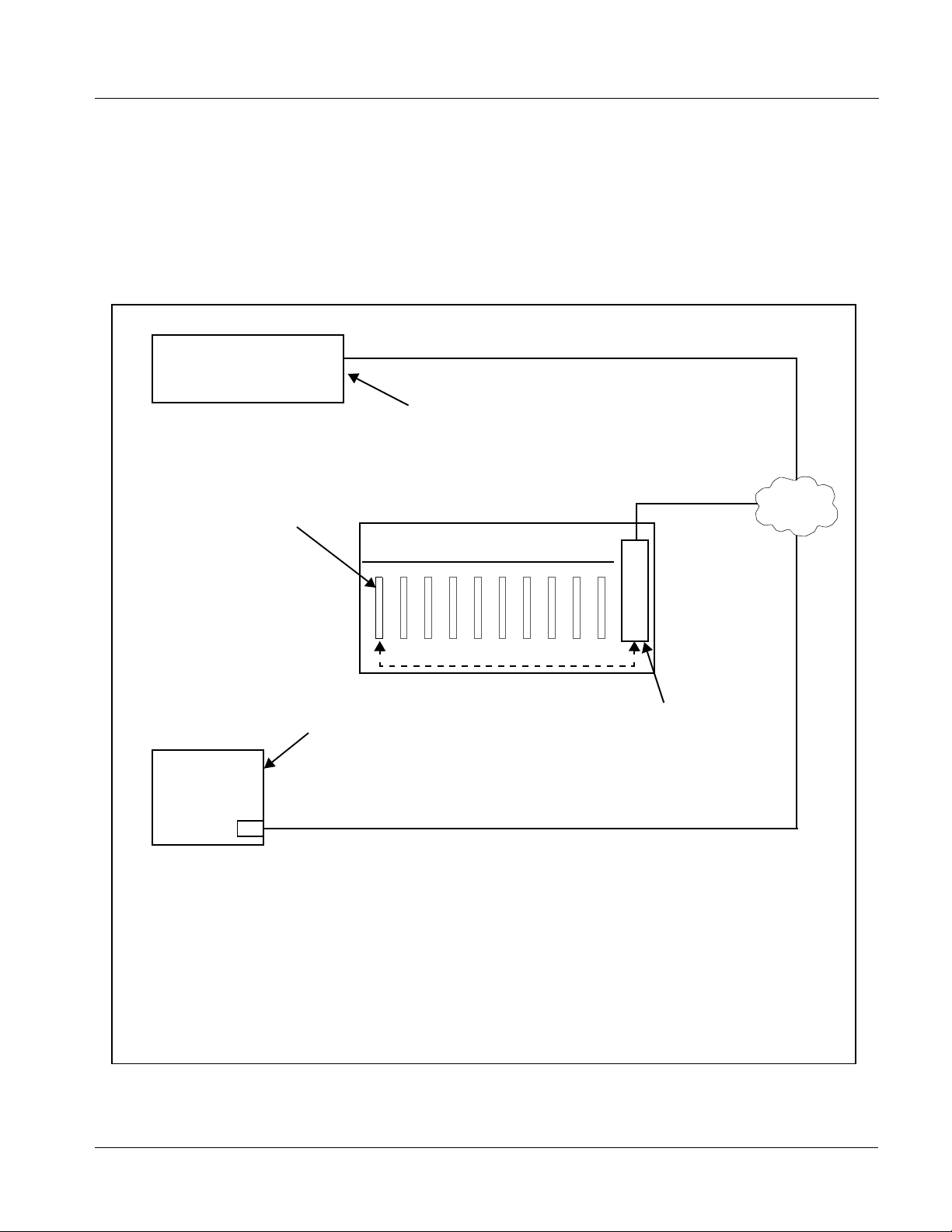
User Control Interface
Figure 1-9 shows the user control interface options for the 9083. These
options are individually described below.
Note: All user control interfaces described here are cross-compatible and can oper-
ate together as desired. Where applicable, any control setting change made
using a particular user interface is reflected on any other connected interface.
OGCP-9000 Control Panel
OGCP-9000/CC Control Panel
Card Edge Controls
9083 card can be
controlled using built-in
card edge controls
Computer
with NIC
or
DashBoard™ Remote Control
Using a computer with
DashBoard™ installed, 9083
card can be remotely controlled
over a LAN
Remote Control Panel
Using the Control Panel,
9083 card can be remotely
controlled over a LAN
LAN
20-Slot Frame with Network Controller
Card
In conjunction with a frame equipped
with a Network Controller Card, 9083
card can be remotely controlled over
a LAN
Note: • To communicate with DashBoard™ or a Remote Control Panel, the frame must have the optional
MFC-8320-N network controller card installed.
• DashBoard™ and the Remote Control Panels provide network control of the 9083 as shown. The
value displayed at any time on the card, or via DashBoard™ or a Control Panel is the actual value
as set on the card, with the current value displayed being the actual value as effected by the card.
Parameter changes made by any of these means are universally accepted by the card (for
example, a change made using the card edge controls will change the setting displayed on
DashBoard™ and a Control Panel; a change made using DashBoard™ will similarly change the
setting displayed on a Control Panel and the card itself).
Figure 1-9 9083 User Control Interface
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-17
Page 22

1 9083 Functional Description
• Built-in Card Edge User Interface – Using the built-in card edge
controls and display, card control settings can be set us ing a front
panel menu.
Note: Some of the 9083 functions described in this manual are available only when
using the DashBoard™, or Cobalt
Control Panel user interfaces.
• DashBoard™ User Interfa ce – Using DashBoard™, the 9083 and
other cards installed in openGear®
®
OGCP-9000 or OGCP-9000/CC Remote
1
frames such as the Cobalt® 8321
or HPF-9000 frame can be controlled from a computer and monitor.
DashBoard™ allows users to view all frames on a network with
control and monitoring for all populated slots inside a frame. This
simplifies the setup and use of numerous modules in a large
installation and offers the ability to centralize monitoring. Cards
define their controllable parameters to DashBoard™, so the control
interface is always up to date.
The DashBoard™ software can be downloaded from the Cobalt
Digital Inc. website: www.cobaltdigital.com
(enter “DashBoard” in
the search window). The DashBoard™ user interface is described in
Chapter 3,“Operating Instructions”.
Note: If network remote control is to be used for the frame and the frame has not yet
been set up for remote control, Cobalt
User Guide (PN 9000RCS-RM) provides thorough information and
step-by-step instructions for setting up network remote control of COMPASS
cards using DashBoard™. (Cobalt
Remote Control Panel product manuals have complete instructions for setting
up remote control using a Remote Control Panel.)
Download a copy of this guide by clicking on the Support>Documents>
Reference Guides link at www.cobaltdigital.com and then select DashBoard
Remote Control Setup Guide as a download, or contact Cobalt
Contact Cobalt Digital Inc. (p. 1-26).
®
reference guide Remote Control
®
OGCP-9000 and OGCP-9000/CC
®
as listed in
®
• Cobalt
®
OGCP-9000, OGCP-9000/CC and WinOGCP Remote
Control Panels – The OGCP-9000, OGCP-9000/CC, and WinOGCP
Remote Control Panels conveniently and intui ti vel y provi de
parameter monitor and control of the cards within the HPF-9000 or
8321 frame.
The remote control panels allow quick and intuitive access to
hundreds of cards in a fa ci lity, and can monitor and al l o w adj ust ment
of multiple p arameters at one time.
The remote control panels are totally compatible with the openGear
control software DashBoard™; any changes made with either system
are reflected on the other.
1. openGear® is a registered trademark of Ross Video Limited. DashBoard™ is a trademark of Ross
Video Limited.
1-18 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
®
Page 23
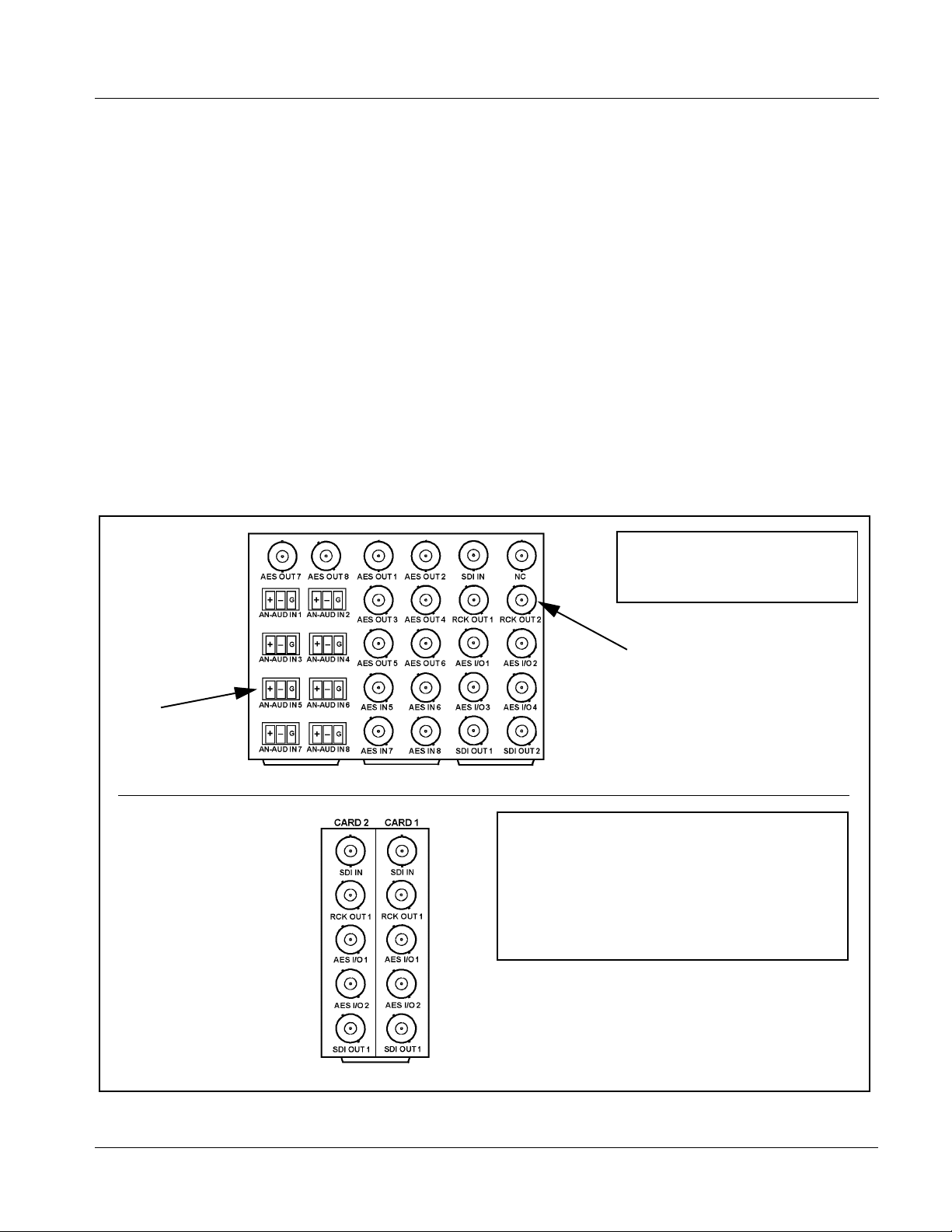
Introduction 9083 Functional Description
9083 Rear I/O Modules
The 9083 physically inte rfaces to sy stem video and audio con necti ons using a
Rear I/O Module. Figure 1-10 shows a typical 9083 Rear I/O Module.
All inputs and outputs shown in the 9083 Functional Block Diagram (Figure
1-1) enter and exit the card via the card edge backplane connector. The
Rear I/O Module breaks out the 9083 card edge connections to industry
standard connecti ons that interface wit h ot her components and sys te ms in th e
signal chain.
In this manner, the particular inputs and outputs required for a particular
application can be acc ommodat ed using a Rear I/O Module tha t b est sui ts the
requirements. The required input and outputs are broken out to the industry
standard connectors on the Rear I/O Module; the unused inputs and outputs
remain unterminated and not available for use.
The full assortment of 9083 Rear I/O Modules is shown and described in
9083 Rear I/O Modules (p. 2-6) in Chapter 2, “Installation and Setup”.
Phoenix terminal
block connectors for
3-wire and 2-wire
terminations
Viewed from rear, the right column
of BNC connectors accommodates
the right-most card, with the left
column accommodating the
adjacent card to the left.
In this example with two 9083 cards
in slots 1 and 2, the right column
serves 9083, slot 1 and the left
column serves 9083, slot 2.
In this example, an RM-9083-G Rear I/O
Module provides a connection interface
for the signal types shown here.
BNC connectors for
coaxial video and
AES audio signals
RM-9083-G.PNG
Where a maximum of five BNC connections can suit
particular I/O requirements, a “split” Rear I/O Module offers
maximum card density within the frame by accommodating
two cards using a module occupying no more area than a
standard module. The RM-9083-A/S shown here
accommodates the signal complement shown for two
adjacent 9083 cards. (Split modules are identified by “/S” in
the part number.)
Figure 1-10 Typical 9083 Rear I/O Modules
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-19
Page 24
1 9083 Functional Description
Audio and Video Formats Supported by the 9083
The 9083 supports all current SMPTE standard SD and HD video formats.
Table 1-1 lists and provides details regarding the audio and video formats
supported by the 9083.
Table 1-1 Supported Audio and Video Formats
Item Description/Specification
Input / Output Video Raster Structure: Frame Rate:
1080PsF 23.98; 24
1080p 23.98; 24
1080i
(1)
25; 29.97; 30
720p 23.98; 24; 25; 29.97; 30; 50; 59.94; 60
486i
575i
(1)
(1)
29.97
25
Embedded Audio The 9083 supports all four groups (16 channels) of embedded audio at
full 24-bit resolution in both SD (with extended data packets) and HD.
Analog Audio The 9083 supports 8 channels of balanced (differential) analog audio.
The analog audio is encoded such that a +24 dBu input is equivalent to
digital 0 dB F S.
Discrete AES Audio Input The 9083 can accept 16 channels (8 pairs) of discrete AES audio on
75Ω BNC connections. Sample rate conversion can be employed to
account for minor clock rate differences in the AES stream and the
input video stream.
Note: The AES signal must have a nominal rate of approximately
48 kHz. The 9083 does not support AES input at 32 kHz,
44.1 kHz, 96 kHz or 192 kHz rates.
Discrete AES Audio Output The 9083 can provide 16 channels (8 pairs) of discrete AES audio on
75Ω BNC connections.
(9083-DEC only) Dolby
®
Dolby
Digital™ Audio Input
Decode
(1) All rates displayed as frame rates; interlaced (“i”) field rates are two times the rate value shown.
®
E/
The 9083-DEC provides up to 10 decoded AES channels when valid
Dolby® E or Dolby® Digital™ audio is received on either discrete AES
or embedded inputs with corresponding metadata.
1-20 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 25
Introduction Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Table 1-2 lists the technical specifications for the 9083 HD/SD Frame Sync
HD/SD Frame Sync with Audio Embedding/De-Embedding and Dolby
Decoding Option card.
Table 1-2 Technical Specifica tions
Item Characteristic
Part number, nomenclature • 9083 – HD/SD Frame Sync HD/SD Frame Sync with Audio
Embedding/De-Embedding
• 9083-DEC – HD/SD Frame Sync HD/SD Frame Sync with Audio
Embedding/De-Embedding and Dolby
Installation/usage environment Intended for installation and usage in frame meeting openGear
modular system definition.
Power consumptio n < 15 Watts maximum
Environmental:
Operating temperature:
Relative humidity (operating or storage):
Frame communication 10/100 Mbps Ethernet with Auto-MDIX.
Indicators Card edge display and indicators as follows:
32° – 104° F (0° – 40° C)
< 95%, non-condensing
• 4-character alphanumeric display
• Status/Error LED indicator
• Input For mat LED indic ato r
®
Decoding Option
®
®
Controls Card edge switches as follows:
• Menu Enter pushbutton switch
• Menu Exit pushbutton switch
• Up/down selection toggle switch
Internal Tone Generators Four built-in tone generators, each configurable for 18 discrete
sine wave frequencies ranging from 50 Hz to 16 kHz.
Generator source signal level is equivalent to -20 dBu.
Resolution 10-bit video data path
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-21
Page 26
1 Technical Specifications
Table 1-2 Technical Specifications — continued
Item Characteristic
Serial Digital Video Input Data Rates Supported:
SMPTE 292 HD-SDI: 1.485 Gbps or 1.485/1.001 Gbps
SMPTE 259M-C SD-SDI: 270 Mbps
Impedance:
75 Ω terminating
Equalization (HD):
328 ft (100 m) Belden 1694A
Equalization (SD):
1000 ft (305 m) Belden 1694A
Return Loss:
> 15 dB at 5 MHz – 1.485 GHz
Post-Processor Serial Digital Video
Outputs
Pre-Proces sor (Rec locked) Se rial Digi tal
Video Outputs
Number of Outputs:
Two HD/SD-SDI BNC per IEC 60169-8 Amendment 2
Impedance:
75 Ω
Return Loss:
> 15 dB at 5 MHz – 270 MHz
> 12 dB at 270 MHz – 1.485 GHz
Signal Level:
800 mV ± 10%
DC Offset:
0 V ± 50 mV
Jitter (HD):
< 0.15 UI (all outputs)
Jitter (SD):
< 0.10 UI (all outputs)
Overshoot:
< 0.2% of amplitude
Number of Outputs:
Two HD/SD-SDI BNC per IEC 60169-8 Amendment 2
Impedance:
75 Ω
1-22 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 27
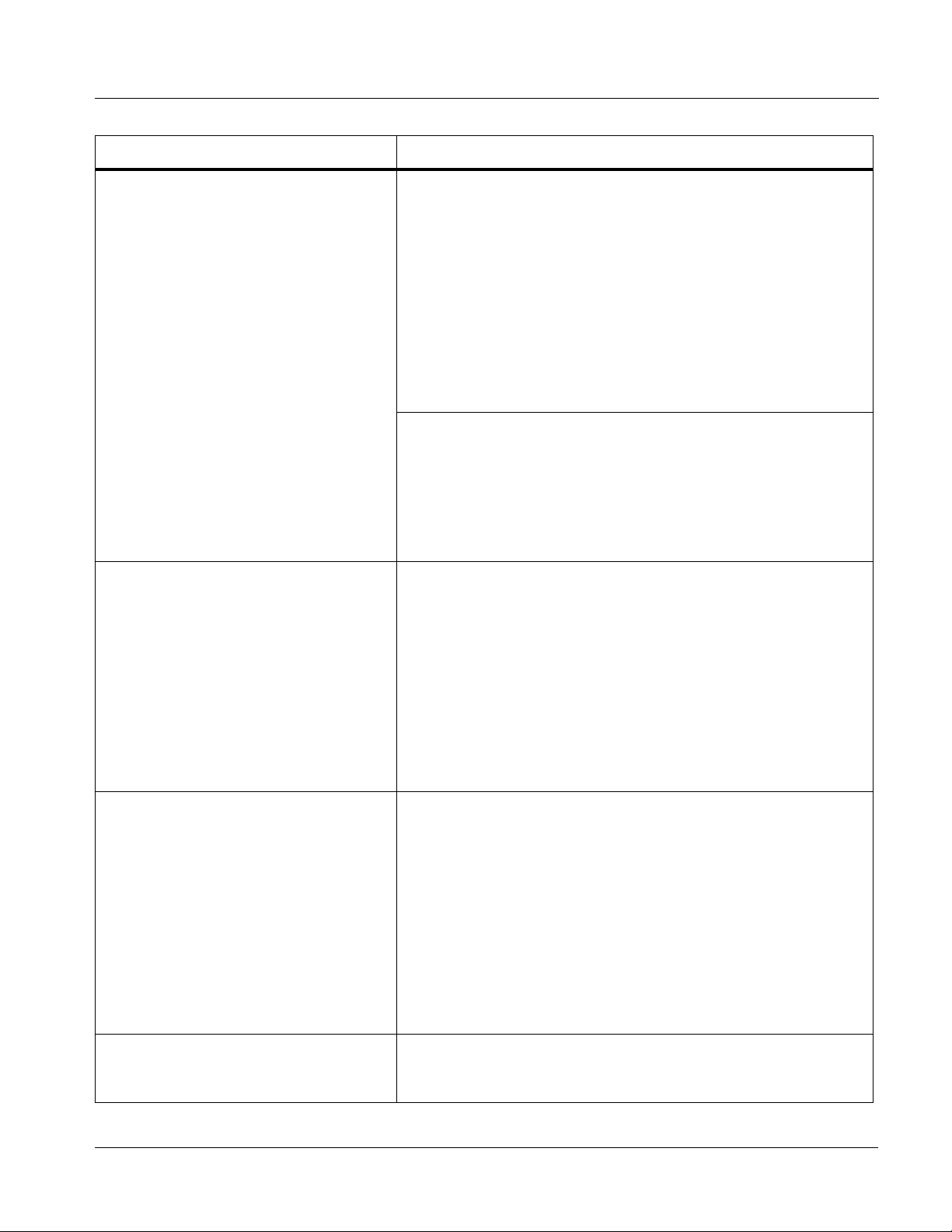
Introduction Technical Specifications
Table 1-2 Technical Specifica tions — continued
Item Characteristic
AES Audio Input Standard:
SMPTE 276M
Number of Inputs (maximum):
8 unbalanced
Input Level:
0.1 to 2.5 Vp-p (5 Vp-p tolerant)
Input Impedance:
75 Ω
Return Loss:
> 12 dB at 100 kHz to 6 MHz
Resolution:
24-bit only
Sample Rate:
48 kHz
SRC:
32-channel; 142 dB S/N
Analog Audio Input Number of Inputs (maximum):
Eight, 3-wire balanced analog audio using Phoenix connectors
with removable screw terminal blocks (Phoenix PN 1803581;
Cobalt PN 5000-0013-000R)
Sampling Rate:
48 kHz (locked to video input)
Signal Level:
+24 dBu => 0 dBFS
A/D Frequency Response:
20 – 20 kHz ± 0.25 dB
AES Audio Output Standard:
SMPTE 276M
Number of Outputs (maximum):
8 unbalanced
Output Impedance:
75 Ω
Return Loss:
> 30 dB 100 kHz to 6 MHz
Sample Rate:
48 kHz
RS-485 Metadata I/O Metadata extracted from input video (per SMPTE 2020-1-2008) or
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-23
®
Dolby
balanced via Phoenix terminal block connector.
decoder (where equipped) on RS-485 interface; 3-wire
Page 28
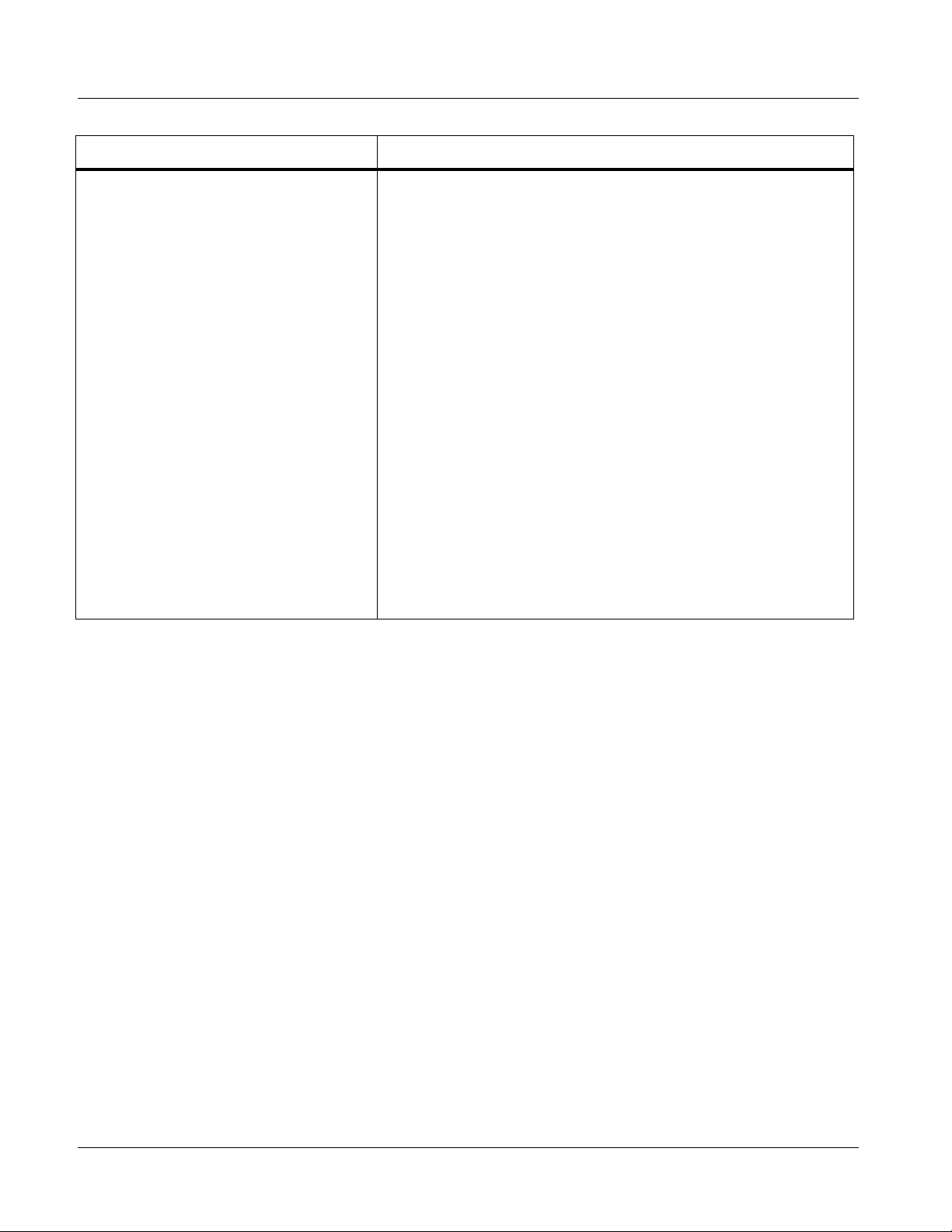
1 Technical Specifications
Table 1-2 Technical Specifications — continued
Item Characteristic
Reference Video Input Number of Inputs:
Two non-terminating (looping) Frame Reference inputs
Standards Supported (HD):
720p 24; 25; 29.97; 30; 50; 59.94
1080i 25; 29.97
1080p 23.98; 24; 25; 29.97; 30
1080p/sF 23.98; 24
Standards Supported (SD):
486i 29.97 (NTSC); 575i 25 (PAL)
Signal Level:
1 Vp-p nominal
Signal Type:
Analog video sync (black burst or tri-level)
Impedance:
75 Ω
Return Loss:
> 30 dB to 30 MHz
Allowable Maximum DC on R ef Input:
±1.0 V
1-24 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 29

Introduction Warranty and Service Information
Warranty and Service Information
Cobalt Digital Inc. Limited Warranty
This product is warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of five (5)
years from the date of shipment to the original purchaser, except that 4000, 5000, 6000, 8000 series
power supplies, and Dolby
material and workmanship for a period of one (1) year.
Cobalt Digital Inc.'s (“Cobalt”) sole obligation under this warranty sh all be limited to, at its option, (i)
the repair or (ii) replacement of the produc t, and the det ermination of whether a defect is covered under
this limited warranty shall be made at the sole discretion of Cobalt.
This limited warrant y appl ies on ly t o the origi nal end-pu rchaser of the produ ct, and i s not assign able o r
transferrable therefrom. This warr ant y i s li mited to defects in material and work ma nship, and shall not
apply to acts of God, accidents, or negligence on behalf of the purchaser, and shall be voided upon the
misuse, abuse, alteration, or modification of the product. Only Cobalt authorized factory
representatives are authorized to make repairs to the product, and any unauthorized attempt to repair
this product shall immediately void the warranty. Please contact Cobalt Technical Support for more
information.
®
modules (where applicable) are warranted to be free from defects in
To facilitate the resolut ion of warranty related issues, Cobalt recommends registering the product by
completing and returning a product registration form. In the event of a warrantable defect, the
purchaser shall notify Cobalt with a descripti on of t he p r oble m, an d Cobalt shall provide the pur ch aser
with a Re turn Mate rial Auth oriz ation (“RMA”). For retu rn, defective product s should be double boxed,
and sufficiently protecte d, in the original packa ging, or equivalent, a nd shipped to the Coba lt Factory
Service Center, postage prepaid and insured for the purchase price. The purchaser should include the
RMA number, description of the problem encountered, date purchased, name of dealer purchased
from, and serial number with the shipment.
Cobalt Digital Inc. Factory Service Center
2406 E. University Avenue Office: (217) 344-1243
Urbana, IL 61802 USA Fax: (217) 344-1245
www.cobaltdigital.com Email: info@cobaltdigital.com
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND OF ALL OTHER OBLIGATIONS OR
LIABILITIES ON COBALT'S PART. ANY SOFTWARE PROVIDED WITH, OR FOR USE WITH,
THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED “AS IS.” THE BUYER OF THE PRODUCT ACKNOWLEDGES
THAT NO OTHER REPRESENTATIONS WERE MADE OR RELIED UPON W ITH RESPECT TO
THE QUALITY AND FUNCTION OF THE GOODS HEREIN SOLD. COBALT PRODUCTS ARE
NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE IN LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS.
COBALT'S LIABILITY, WHET HER IN CONTRACT, TORT, WARRANTY, OR OTHERWISE, IS
LIMITED TO THE REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT, AT ITS OPTION, OF ANY DEFECTIV E
PRODUCT, AND SHALL IN NO EVENT INCLUDE SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOST PROFITS), EVEN IF IT HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 1-25
Page 30

1 Contact Cobalt Digital Inc.
Contact Cobalt Digital Inc.
Feel free to contact our thorough and professional suppo rt repr es entatives for
any of the following:
• Name and address of your local dealer
• Product information and pricing
• Technical support
• Upcoming trade show in formation
Phone: (217) 344-1243
Fax: (217) 344-1245
Web: www.cobaltdigital.com
General Information: info@cobaltdigital.com
Technical Support: support@cobaltdigital.com
1-26 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 31

Overview
Chapter 2
Chapter 2 Installation and Setup
This chapter contains the following information:
• Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4) Ports (p. 2-1)
• Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot (p. 2-2)
• Installing a Rear I/O Module (p. 2-5)
• Setting Up 9083 Network Remote Control (p. 2-12)
Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4) Ports
Note: This procedure is applicable only if any of the four AES I/O (1-4) ports on the
9083 are to be used as outputs (the switches are set to input mode by factory
default). The 9083 is equipped with a four-section red DIP switch that sets
AES pairs 1 thru 4 as either inputs or outputs. The factory default position is
the input position for each pair.
• If all of the AES I/O (1-4) ports are to be used as inputs (or not used at all),
omit this procedure.
• If any of the AES I/O (1-4) ports are to be used as outputs, set the switches
as described in this procedure.
Note switch S11 thru S14 settings for AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 mode shown
in Figure 2-1. For p ort to be used as an output, set switch to down position as
shown in Figure 2-1.
Note: Regardless of S11 thru S14 settings for AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4, outputs
AES OUT (1-8) are still available on cards equipped with a Rear I/O Module
having dedicated AE S OUT (1-8) BNC connectors.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-1
Page 32

2 Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot
Rear of Card
AES I/O 4
AES I/O 3
AES I/O 2
AES I/O 1
S11S12S13S14
••••
Figure 2-1 9083 AES I/O (1-4) Mode Switches
Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot
CAUTION
Heat and power distribution requirements within a frame may dictate specific
slot placement of cards. Cards with many heat-producing components should
be arranged to avoid areas of excess heat build-up, particularly in frames
using only convection cooling. The 9083 has a moderate power dissipation
(15 W max.). As such, avoiding placing the card adjacent to other cards with
similar dissipation values if possible.
INPUT MODE
(Factory Default)
OUTPUT MODE
CAUTION
This device contains semiconductor devices which are
susceptible to serious damage from Electrostatic
Discharge (ESD). ESD damage may not be immediately
apparent and can affect the long-term reliability of the
device.
Avoid handling circuit boards in high static environments
such as carpeted areas, and when wearing synthetic fiber
clothing. Always use proper ESD handling precautions
and equipment when working on circuit boards and
related equipment.
2-2 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 33

Installation and Setup Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot
Note: • If installing the 9083 in a slot already equipped with a suitable I/O
module, proceed to card installation steps below.
• If installing the 9083 in a slot with no rear I/O module, a Rear I/O
Module is required before cabling can be connected. Refer to Installing a
Rear I/O Module (p. 2-5) for rear I/O module installation procedure.
CAUTION
If required, make certain Rear I/O Module(s) is installed before installing the
9083 into the frame slot. Damage to card and/or Rear I/O Module can occur if
module installation is attempted with card already installed in slot.
Note: Check the packaging in which the 9083 was shipped for any extra items such
as a Rear I/O Module connection label. In some cases, this label is shipped
with the card and to be installed on the Rear I/O connector bank corresponding to the slot location of the card.
Install the 9083 into a frame slot as follows:
1. Determine the slot in which the 9083 is to be installed.
2. Open the frame front access panel.
3. While holding the card by the card edges, align the card such that the
plastic ejector tab is on the bottom.
4. Align the card with the top and bottom guides of the slot in which the
card is being installed.
5. Gradually slide the card into the slot. When resistance is noticed, gently
continue pushing the card until its rear printed circuit edge terminals
engage fully into the rear I/O module mating connector.
CAUTION
If card resists fully engaging in rear I/O module mating connector, check for
alignment and proper insertion in slot tracks. Damage to card and/or rear I/O
module may occur if improper card insertion is attempted.
6.
Verify that the card is fully engaged in rear I/O module mating connector.
7. Close the frame front access panel.
8. Connect the input and output cables as follows:
• If the 9083 is being installed in a PN 8310-BNC or 8310-C-BNC
frame, refer to the label on the connector bank corresponding to the
card’s slot location for connector designations.
• If the 9083 is being installed in a frame using a specific 9083 Rear
I/O Module, connect cabling in accordance with the appropriate
diagram shown in Table 2-1, “9083 Rear I/O Modules” (p. 2-6).
9. Repeat steps 1 through 8 for other 9083 cards.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-3
Page 34

2 Installing the 9083 Into a Frame Slot
Note: The 9083 BNC inputs are internally 75-ohm terminated. It is not necessary to
terminate unused BNC inputs or outputs.
Note: External frame sync reference signals are received by the card over a refer-
ence bus on the card frame, and not on any card rear I/O module connectors.
The frame has BNC connectors labeled REF 1 and REF 2 which receive the
reference signal from an external source such as a house distribution.
Note: To remove a card, press down on the ejector tab to unseat the card from the
rear I/O module mating connector. Evenly draw the card from its slot.
10. If network rem ote control is to be used for the fram e and the frame has
not yet been set up for remote control, perform setup in accordance with
Cobalt
(PN 9000RCS-RM).
Note: If installing a card in a frame already equipped for, and connected to
DashBoard™, no network setup is required for the card. The card will be discovered by DashBo ard™ and be ready for use.
®
reference guide “COMPASS™ Remote Control User Guide”
2-4 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 35

Installation and Setup Installing a Rear I/O Module
Installing a Rear I/O Module
Note: This procedure is applicable only if a Rear I/O Module is not currently
installed in the slot where the 9083 is to be installed.
If installing the 9083 in a slot already equipped with a suitable I/O module,
omit this procedure.
The full assortment of 9083 Rear I/O Modules is shown and described in
9083 Rear I/O Modules (p. 2-6). Install a Rear I/O Module as follows:
1. On the frame, determine the slot in which the 9083 is to be installed.
2. In the mounting area corresponding to the slot location, install
Rear I/O Module as shown in Figure 2-2.
Align and engage mounting tab on Rear
I/O Module with the module seating slot
1
on rear of frame chassis.
DSCN3483A.JPG
Hold top of Rear I/O Module flush against
frame chassis and start the captive screw.
2
Lightly tighten captive screw.
Note: Rear I/O Modules RM-9083-C, -D, -E, and -H occupy two
rear module slot mounting locations and use two captive
screws.
Rear I/O Module RM-9083-G occupies three rear module
slot mounting locations and uses three captive screws.
DSCN3487A.JPG
Figure 2-2 Rear I/O Module Installation
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-5
Page 36

2 Installing a Rear I/O Module
9083 Rear I/O Modules
Table 2-1 shows and describes the full assortment of Rear I/O Modules
specifically for use with the 9083.
Notes: • Rear I/O Modules equipped with 3-wire Phoenix connectors are supplied
with removable screw terminal block adapters. For clarity, the adapters are
omitted in the drawings below.
• Rear I/O Modules with DOLBY META port provide RS-485 port usable for
Dolby metadata decoder output (where equipped with option +DEC) or serial
LTC I/O (where licensed for option +LTC).
• RM20-x Rear I/O Modules compatible only with 20-slot frames.
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-A Provides the following conne cti on s:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Two HD/SD-SDI reclocked input copies
(RCK OUT 1 and RCK OUT 2)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
RM20-9083-A/S Split Rear Module. Provides each of the following
connections for two 9083 cards:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• HD/SD-SDI reclocked input copy (RCK OUT 1)
• Two AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 and
AES I/O 2; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Buffered SDI coaxial output (SDI OUT 1)
Note: For AES I/O 1 and AES I/O 2 on
RM20-9083-A/S Rear I/O Module to function
as inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S12 must
be set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
2-6 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 37

Installation and Setup Installing a Rear I/O Module
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules — continued
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-B Provides the following connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Six analog balanced audio inputs (AN-AUD IN 1
thru AN-AUD IN 6)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
RM20-9083-C Provides the following connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Two dedicated AES coaxial audio inputs (AES IN 5
and AES IN 6)
• Two dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 and AES OUT 2)
• Eight analog balanced audio inputs (AN-AUD IN 1
thru AN-AUD IN 8)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 and AES I/O 2 on
RM20-9083-C Rear I/O Module to function as
inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S12 must be
set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
Note: AES OUT 1 and AES OUT 2 on RM-9083-C
Rear I/O Module always function as outputs
regardless of whether AES I/O 1 or
AES I/O 2 are used as inputs or outputs.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-7
Page 38

2 Installing a Rear I/O Module
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules — continued
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-D Provides the following conne cti on s:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Two dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 and AES OUT 2)
• Eight analog balanced audio inputs (AN-AUD IN 1
thru AN-AUD IN 8)
• RS-485 metadata out / LTC I/O (DOLBY META)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 on
RM20-9083-D Rear I/O Module to function as
inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S14 must be
set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
Note: AES OUT 1 and AES OUT 2 on
RM20-9083-D Rear I/O Module always
function as outputs regardless of whether
AES I/O 1 or AES I/O 2 are used as inputs or
outputs.
RM20-9083-E Pr ov id es the fol lowin g conne cti on s:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Two dedicated AES coaxial audio inputs (AES IN 5
and AES IN 6)
• Eight dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 8)
• RS-485 metadata out / LTC I/O (DOLBY META)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 on
RM20-9083-E Rear I/O Module to function as
inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S14 must be
set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
Note: AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 4 on
RM20-9083-E Rear I/O Module always
function as outputs regardless of whether
AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 are used as inputs
or outputs.
2-8 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 39

Installation and Setup Installing a Rear I/O Module
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules — continued
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-F Provides the following connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Five AES coaxial inputs (AES IN 1 thru AES IN 4;
AES IN 8)
• Two dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 and AES OUT 2)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES IN 1 thru AES IN 4 on RM20-9083-F
Rear I/O Module to function as inputs, AES I/O
switches S11 – S14 must be set to Input
(factory default). See Setting I/O Switches for
AES I/O (1-4) Ports (p. 2-1) for more
information.
RM20-9083-G Provides the following connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Two HD/SD-SDI reclocked input copies
(RCK OUT 1 and RCK OUT 2)
• Four dedicated AES coaxial audio inputs
(AES IN 5 thru AES IN 8)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Eight dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 8)
• Eight analog balanced audio inputs (AN-AUD IN 1
thru AN-AUD IN 8)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 on
RM20-9083-G Rear I/O Module to function as
inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S14 must be
set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
Note: AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 4 on
RM20-9083-G Rear I/O Module always
function as outputs regardless of whether
AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 are used as inputs
or outputs.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-9
Page 40

2 Installing a Rear I/O Module
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules — continued
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-H Provides the following conne cti on s:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Four dedicated AES coaxial audio inputs
(AES IN 5 thru AES IN 8)
• Eight dedicated AES coaxial audio outputs
(AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 8)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 on
RM20-9083-H Rear I/O Module to function as
inputs, AES I/O switches S11 – S14 must be
set to Input (factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
Note: AES OUT 1 thru AES OUT 4 on
RM20-9083-H Rear I/O Module always
function as outputs regardless of whether
AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 are used as inputs
or outputs.
RM20-9083-J P r ov id es the fol lowing connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Two HD/SD-SDI reclocked input copies
(RCK OUT 1 and RCK OUT 2)
• Four AES I/O coaxial input/outputs (AES I/O 1 thru
AES I/O 4; I/O function of each connection is
user-configurable)
• RS-485 metadata out / LTC I/O (RS-485)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT 1 and
SDI OUT 2)
Note: For AES I/O 1 thru AES I/O 4 on RM-9083-J
Rear I/O Module to function as inputs, AES I/O
switches S11 – S14 must be set to Input
(factory default).
See Setting I/O Switches for AES I/O (1-4)
Ports (p. 2-1) for more information.
2-10 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 41

Installation and Setup Installing a Rear I/O Module
Table 2-1 9083 Rear I/O Modules — continued
9083 Rear I/O Module Description
RM20-9083-E-DIN-HDBNC High-density rear modules provides the following
connections:
• HD/SD-SDI coaxial input (SDI IN)
• Eight AES coaxial inputs (AES IN 1 thru AES IN 8)
• Eight AES coaxial outputs (AES OUT 1 thru
AES OUT 8)
• One HD/SD-SDI reclocked input copy
(RCK OUT 1)
• Two buffered SDI coaxial outputs (SDI OUT)
Note: Available equipped with High-Density BNC
(HDBNC) or DIN1.0/2.3 connectors as:
RM20-9083-E-HDBNC or RM20-9083-E-DIN,
respectively.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 2-11
Page 42

2 Setting Up 9083 Network Remote Control
Setting Up 9083 Network Remote Control
Perform remote control setup in accordance with Cobalt® reference guide
“Remote Control User Guide” (PN 9000RCS-RM).
Note: • If network remote control is to be used for the frame and the frame has not
yet been set up for remote control, Cobalt
Control User Guide (PN 9000RCS-RM) provides thorough information and
step-by-step instructions for setting up network remote control of
COMPASS™ cards using DashBoard™. (Cobalt
OGCP-9000/CC Remote Control Panel product manuals have complete
instructions for setting up remote control using a Remote Control Panel.)
Download a copy of this guide by clicking on the Support>
Documents>Reference Guides link at www.cobaltdigital.com and then
select DashBoard Remote Control Setup Guide as a download, or contact
®
Cobalt
• If installing a card in a frame already equipped for, and connected to
DashBoard™, no network setup is required for the card. The card will be discovered by DashBoard™ and be ready for use.
as listed in Contact Cobalt Digital Inc. (p. 1-26).
®
reference guide Remote
®
OGCP-9000 and
2-12 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 43

Overview
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 Operating Instructions
This chapter contains the following information:
If you are already familiar
with using DashBoard or a
Cobalt Remote Control
Panel to control Cobalt
cards, please skip to 9083
Function Submenu Li st and
Descriptions (p. 3-9).
• Control and Display Descriptions (p. 3-1)
• Accessing the 9083 Card via Remote Control (p. 3-5)
• Checking 9083 Card Information (p. 3-7)
• Ancillary Data Line Number Locations and Ranges (p. 3-8)
• 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions (p. 3-9)
• Troubleshooting (p. 3-54)
Control and Display Descriptions
This secti on describes the user interface controls, indicators, and displays for
using the 9083 card. The 9083 function s can be acces sed and contr olle d using
any of the user interfaces described here.
The format in which the 9083 functional controls, indicators, and displays
appear and are used varies depending on the user interface being used.
Regardless of the user interface being used, access to the 9083 functions (and
the controls, ind icato rs, an d disp lays r elat ed to a particul ar f uncti on) fo llows a
general arrangement of Function Submenus under which related controls can
be accessed (as described in Function Submenu/Parameter Submenu
Overview below).
Note: DashBoard™ and the Remote Control Panel provide greatly simplified user
interfaces as compared to using the card edge controls. For this reason, it is
strongly recommended that DashBoard™ or a Remote Control Panel be
used for all card applications other than the most basic cases. Card edge
control codes are not included in this manual. If card-edge control is to be
used, obtain a copy of “Manual Supplement – Card-Edge Control Reference
Master List and Instructions for Using Compass
Codes” (989CEC-MS.pdf) at
www.cobaltdigital.com>Support>Documents>Reference Guides.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-1
®
Card-edge (Local) Control
Page 44

3 Control and Display Descriptions
Note: When a setting is changed, settings displayed on DashBoard™ (or a Remote
Control Panel) are the settings as effected by the 9083 card itself and
reported back to the remote control; the value displayed at any time is the
actual value as set on the card.
Function Submenu/Parameter Submenu Overview
The functions and related pa rameters avai lable on the 9083 car d are organ ized
into function submenus, which consist of parameter groups as shown below.
Figure 3-1 shows how the 9083 card an d its submenus ar e orga nized, and also
provides an overview of how navig ation is performed be tween cards, func tion
submenus, and parameters.
If using DashBoard™ or a Remote Control Panel, the
desired 9083 card is first selected.
9083
Submenu a Submenu b
Individual Parameters
Each submenu consists of groups of parameters
related to the function submenu. Using the “Video
Proc” function submenu example, the individual
parameters for this function consist of various v ideo
processor parameters such as Luma Gain, Saturation,
and so on.
Figure 3-1 Function Submenu/Parameter Submenu Overvie w
• • •
The desired function submenu is next
selected.
Function Submenus consist of parameter
groups related to a particular 9083 card
function (for example, “Video Proc”).
Submenu z
3-2 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 45

Operating Instructions Control and Display Descriptions
DashBoard™ User Interface
(See Figure 3-2.) Th e 9083 fu nction submenus are or gani zed i n DashBoa rd™
using tabs. When a tab is selected, each parametric control or selection list
item associated with the function is displayed. Scalar (numeric) parametric
values can then be adjusted as desired using the GUI slider controls. Items in
a list can then be selected using GUI drop-down lists. (In this manner, the
setting effected using controls and selection lists displayed in DashBoard™
are comparable to the su bmenu ite ms access ed and commi tted using the 9083
card edge c ontrols.)
Typical On/Off
Control
Typical Parametric
Control
Typical Selection
List
DashBoard Tabs
Figure 3-2 Typical DashBoard Tabs and Controls
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-3
Page 46

3 Control and Display Descriptions
Cobalt® Remote Control Panel User Interfaces
(See Figure 3-3.) Similar to the function submenu tabs using DashBoard™,
the Remote Control Panels have a Select Submenu key that is used t o dis pla y
a list of function submenus. From this list, a control knob on the Control
Panel is used to select a function from the list of displayed function submenu
items.
When the desired function submenu is selected, each parametric control or
selection list item associated with the function is displayed. Scalar (numeric)
parametric values can then be adjusted as desired using the control knobs,
which acts like a potentiometer. Items in a list can then be selected using the
control knobs which correspondingly acts like a rotary switch. (In this
manner, t he se ttin g effected using co ntr ols a nd sel ecti on li sts di splay ed on t he
Control Panel are comparable to the submenu items accessed and committed
using the 9083 card edge controls.)
Figure 3-3 shows accessing a function submenu and its parameters (in this
example, “Video Proc”) using the Control Panel as compared to using the
card edge controls.
Video Proc function
(among others) is
accessed using the Control
Panel Select Submenu
key. Video Proc function is
selected from the list of
functions (submenu items)
When the Video Proc
function submenu is
selected, its related
parameters are now
displayed.
In this example, Color Gain
(saturation) is adjusted using
the control knob adjacent to
Color Gain
Note: Refer to “OGCP-9000 Remote Control Panel User Manual” (PN
OGCP-9000-OM) or “OGCP-9000/CC Remote Control Panel User Manual”
(PN OGCP-9000/CC-OM) for complete instructions on using the
Control Panels.
3396B_3346BGENEMB.JPG
3370_3372B.JPG
Figure 3-3 Remote Control Panel Setup of Example Video Proc Function Setup
3-4 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 47

Operating Instructions Accessing the 9083 Card via Remote Control
Accessing the 9083 Card via Remote Control
Access the 9083 card using DashBoard™ or Cobalt® Remote Control Panel
as described below.
Accessing the 9083 Card Using DashBoard™
1. On the computer connected to the frame LAN, open DashBoard™.
2. As shown be low, in the left side Basic View Tree locate the Network
Controller Card associated with the frame containing the 9083 card to be
accessed (in this example, “MFC-8320-N SN: 00108053”).
DB_ACCESS1.PNG
3. As shown below, expand the tree to access the cards within the frame.
Click on the card to be accessed (in this example,
“Slot 6: CDI-9083 RCVR21”).
.
9083_DB_ACCESS2A.PNG
As shown on the next page, when th e car d is access ed a DashBoa rd™ its
function submenu screen showing tabs for each function is displayed.
(The particular submenu screen displayed is the previously displayed
screen from the last time the card was accessed by DashBoard™).
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-5
Page 48

3 Accessing the 9083 Card via Remote Control
Card Access/Navigation
Tree Pane
Card Info
Pane
Card Function Submenu
and Controls Pane
Accessing the 9083 Card Using a Cobalt® Remote Control Panel
Press the Select Device key and select a c ard as shown in the example below.
9083_3366_3392.JPG
This display shows the list
order number of the device that
is ready for selection
This display shows the devices assigned to the Control Panel.
• Rotate any knob to select from the list of devices. The device selected using a knob
is displayed with a reversed background (in this example,
“1 9083 - Receiver 21 Input Processing”).
• Directly enter a device by entering its list number using the numeric keypad, and
then pressing Enter or pressing in any knob).
9083_ DB_ACCESS3A3.PNG
3-6 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 49

Operating Instructions Checking 9083 Card Information
Checking 9083 Card Information
The operating st atus and s oftwar e ver sion the 9 083 car d can be chec ked us ing
DashBoard™ or the card edge control user interface. Figure 3-4 shows and
describes the 9083 card i nformati on screen usi ng DashBoard™ a nd acces sing
card information using the card edg e control user interfac e.
Note: Proper operating status in DashBoard™ is denoted by green icons for the sta-
tus indicators shown in Figure 3-4. Yellow or red icons respectively indicate
an alert or failure condition. Refer to Troubleshooting (p. 3-54) for corrective
action.
The Tree View shows the cards seen by DashBoard™.
In this example, Network Controller Card MFC-8320-N
(serial number ...8053) is hosting a 9083 card in slot 6.
Software Version Number
Refer to this number to check that documentation
(such as this manual) matches the card’s Software
Version Number. Use this number also when
communicating to Cobalt
®
regarding this card.
Power Consumption and Temperature Displays
This display shows the power consumed by the 9083
for both the +12V and -7.5V rails, as well as key device
temperatures.
Status Displays
These displays show the status the signal being received by
the 9083. Green Settings icon shows that any changes made
on DashBoard™ are sucessfully saved on the card’s memory.
Figure 3-4 9083 Card Info Utility
9083_CARD_INFO.PNG
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-7
Page 50

3 Ancillary Data Line Number Locations and Ranges
Ancillary Data Line Number Locations and Ranges
Table 3-1 lists typical default output video VANC line number locations for
various ancillary data items that may be passed or handled by the card.
Table 3-1 Typical Ancillary Data Line Number Locations/Ranges
Default Line No. / Range
Item
SD HD
AFD 12 (Note 2) 9 (Note 2)
ATC_VITC 12 (locked) 9/8 (Note 2)
ATC_LTC — 10 (Note 2)
®
Dolby
Metadata 13 (Note 2) 13 (Note 2)
SDI VITC Waveform 14/16 (Note 2) —
Closed Captioning 21 (locked) 10 (Note 2)
Notes:
1. The card does not check for conflicts on a given line number. Make certain the selected line is available
and carrying no other data.
2. While range indicated b y d rop -dow n li st o n G UI m ay al lo w a particular range o f ch oi ces , the actual range
is automatically cl amped (limi ted) to c ert ain rang es to preven t inadv ertent con fli ct with a ctive pictu re ar ea
depending on video format. Limiting ranges for various output formats are as follows:
Format Line No. Limiting Format Line No. Limiting Format Line No. Limiting
525i 12-19 720p 9-25 1080p 9-41
625i 9-22 1080i 9-20
Because line number allocation is not standardized for all ancillary items,
consideration should be given to all items when performing set-ups. Figure
3-5 shows an example of improper and corrected VANC allocation within an
HD-SDI stream.
ATC_VITC = 9/8
CC = 10
Dolby Meta data = 13
Card 1
ATC_VITC = 9/ 8
CC = 10
Dolby Metadata = 13
Card 1
AFD Insertion
attempted usin g
VANC line 9
(default)
AFD Insertion
corrected to us e
VANC line 18
ATC_VITC = 9/8
AFD = 9
CC = 10
Dolby Meta data = 13
Card n
ATC_VITC = 9/8
CC = 10
Dolby Metadata = 13
AFD = 18
Card n
Conflict between
ATC_VITC and AFD both
on VANC line 9
Conflict between
ATC_VITC on line 9/8 and
AFD (now on line 18)
resolved
Figure 3-5 Example VANC Line Number Allocation Example
3-8 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 51

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
T able 3-2 in dividu ally lists and des cribes eac h 9083 function sub menu (‘tab”)
and its related list selections, co ntrols, and parameters . Where helpful,
examples showing usage of a function are also provided. Table 3-2 is
primarily based upon using DashBoard™ to access each function and its
corresponding submenus and parameters.
Note: All numeric (scalar) parameters displayed on DashBoard™ can be changed
using the slider controls, arrows, or by numeric keypad entry in the corresponding numeric field. (When using numeric keypad entry, add a return after
the entry to commit the entry.)
On DashBoard™ itself and in Table 3-2, the function submenu items are
organized using tabs as shown below.
The table below provides a quick-reference to the page numbers where each
function submenu item can be found.
Function Submenu Item Page Function Submenu Item Page
Audio Inpu t Controls 3-10 Dolby Decoder (9083-DEC only) 3-32
Video Proc 3-13 Dolby E Metadata (9083-DEC only) 3-35
AFD 3-14 Dolby D Metadata (9083-DEC only) 3-36
Framesync 3-15 Timecode 3-37
Embedded Audio Group 1/2 3-20 Audio Mixing 3-41
Embedded Audio Group 3/4 3-24 Tone Generator 3-46
AES Audio Out Pairs 1-4 3-26 Licensable Features 3-46
AES Audio Out Pairs 5-8 3-30 Presets 3-47
Dolby Metadata (9083 only) 3-31
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-9
Page 52

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List
Controls the AES Audio Input features for the eight AES
pairs, and displays signal status for the AES pairs and
Audio Input Controls
the 16 embedded audio channels. Also provides global
unity routing/parameter control resets.
Note: Also refer to AES Audio Input Advanced Features (p.
1-15) in Chapter 1, “Introduction” for detailed
information regarding these functions.
• AES SRC Individual SRC Disable control for each AES pair (1 thru 8) disables or
•
•
•
• AES Passthrough Individual AES Passthrough On/Off control for each AES pair (1 thru 8)
•
•
•
enables Sample Rate Conversion (SRC) bypass as follows:
• Disabled On: In this mode, AES SRC for the corresponding AES
pair is bypassed (button pressed in). SRC is set to Disabled
(bypass turned on) by default. This mode is preferred where the
AES rate matches the input video rate. This mode is necessary
when embedding non-PCM AES audio such a Dolby
Digital™ audio streams.
Note: In this mode AES rate must match the input video rate or
audio dropouts will occur.
Note: AES audio must be nominally 48 kHz.
• Disable Off: In this mode, AES SRC for the corresponding AES
input pair is enabled (button in out position). SRC enabled allows
the 9083 to interface with asynchronous AES sources (sources in
which the AES timing does not match the video reference timing).
SRC can be used to compensate for minor clock rate differences in
the AES stream and the input video stream.
disables or enables Passthrough as follows:
• Off: Disables AES passthrough for the selected AES input pair.
Passthrough is set to Off by default.
• On: Passthrough is turned on, with the corresponding AES output
pair to act as a bit-for-bit copy with zero delay of the corresponding
AES input pair.
Note: AES Passthrough set to On overrides normal audio routing.
Gain and polarity control is not available when AES
passthrough is enabled.
®
E or Dolby
• AES Zero Delay Embedding Individual AES Zero-Delay Embedding On/Off control for each AES pair
•
•
•
(1 thru 8) disables or enables Zero-Delay Embedding as follows:
• Off: Disables Zero-Delay Embedding for the selected AES input
pair. Zero-delay embedding is set to Off by default.
• On: The selected pair directly embeds into its corresponding group
(AES Pair 1 embeds into embedded channels 1 and 2; AES pair 2
embeds into embedded channels 3 and 4, and so on) with the
normal frame sync audio delay being bypassed.
Note: Zero Delay Embedding overrides the standard audio routing
system. For example, if AES Pair 1 is selected, then the
controls to route into embedded channels 1 and 2 will not
apply. Gain and polarity control is not available when
zero-delay embedding is enabled.
3-10 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 53

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Status Displays
Individual signal status displays for AES pairs 1-8, and embedded audio
channels 1-16 as follows:
• Not Present: Indicates AES pair or embedded channel does not
contain recognized audio PCM data.
Note: Channel displaying Not Present may still carry usable audio
data with Not Present being displayed due to invalid
•
•
•
• Present, Professional: Indicates AES pair or embedded channel
headers.
contains recognized AES audio PCM data.
• Present, Consumer: Indicates AES pair or embedded channel
contains audio PCM data other than AES (for example, S/PDIF).
• Present, Dolby E: Indicates AES pair or embedded channel
contains Dolby
• Present, Dolby Digital: Indicates AES pair or embedded channel
contains Dolby
•
•
•
Note: Dolby status displays shown to the left only occur for valid
®
E encoded data.
®
Digital encoded data.
®
Dolby
signals meeting SMPTE 337M standard.
(9083 only) The 9083 card does not perform Dolby
processing on the signal. Although the 9083 controls will
®
appear to be usable for this signal tag, the signal is passed
through with SRC bypassed as well as all gain and polarity
controls set to unity.
®
(9083-DEC only) When Dolby
present on a discrete AES pair or an embedded audio pair,
the decoder can provide up to 10 decoded channels
(according to the Dolby
metadata). All channels are available as inputs to audio
routing.
E or Dolby® Digital™ is
®
sub-format and received
• Embedded Unity Channel Selection Selects unity reset of Embedded Audio Group 1/2 and 3/4 controls and
re-establishes default 1-to-1 routing as follows:
• Embedded: Routes Embedded Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as sources to
destination channels Embedded Ch 1 thru Embedded Ch 16.
• AES: Routes AES Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as sources to destination
channels Embedded Ch 1 thru Embedded Ch 16.
• Analog: Routes Analog Ch 1 thru Ch 8 as sources to destination
channels Embedded Ch 1 thru Embedded Ch 8. Sets Embedded
Ch 9 thru Ch 16 to Silence.
• AES Unity Channel Selection Selects unity reset of AES Outputs Pairs 1-4 and 5-8 controls and
re-establishes default 1-to-1 routing as follows:
• Embedded: Routes Embedded Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as sources to
destination channels AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16.
• AES: Routes AES Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as sources to destination
channels AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16.
• Analog: Routes Analog Ch 1 thru Ch 8 as sources to destination
channels AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 8. Sets AES Ch 9 thru Ch 16 to
Silence.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-11
Page 54

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Apply Audio Channel Selection Applies embedded and AES unity channel selection (as set in the above
• Tie AES and Embedded Controls When set to Enabled, gangs Gain, Phase, and Mute controls for
drop-down lists). To apply the selections, click the Confirm button. When
Confirm is clicked, a Confirm? pop-up appears, requesting confirmation.
• Click Yes to proceed with the unity reset.
• Click No to reject unity reset.
For any selection following confirm, the destination channel controls are
default reset as follows:
• Gain is to unity
• Phase control is set to Normal
• Channel is set to Unmuted
same-numbered Embedded and AES channels. Ganging is bilateral, with
embedded channel control settings affecting corresponding AES channel
controls, and vice-versa.
3-12 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 55

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Provides the following Video Proc parametr ic control s.
• Video Proc Video Proc (On/Off) provides master on/off control of all Video Proc
• Reset to Unity Reset to Unity provides unity reset control of all Video Proc functions.
• Luma Gain Adjusts gain percentage applied to Luma (Y channel).
functions.
• When set to Off, all processing is bypassed.
• When set to On, currently displayed parameter settings take effect.
When Confirm is clicked, a Confirm? pop-up appears, requesting
confirmation.
• Click Yes to proceed with the unity reset.
• Click No to reject unity reset.
(0% to 200% range in 0.1% steps; unity = 100%)
Video Proc
• Luma Lift Adjusts lift applied to Luma (Y-channel).
(-100% to 100% range in 0.1% steps; null = 0.0%)
• Color Gain Adjusts gain percentage (saturation)
applied to Chroma (C-channel).
(0% to 200% range in 0.1% steps; unity = 100%)
• Color Phase Adjusts phase angle applied to Chroma.
(-360° to 360° range in 0.1° steps; null = 0°)
• Gang Luma and Color Gain When set to On, changing either the Luma Gain or Color Gain controls
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-13
increases or decreases both the Luma and Chroma levels by equal
amounts.
Page 56

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Allows assignment of AFD (Active Format Description)
AFD
Note: This function only marks the SDI output with an AFD code. Actual AFD processing must be performed by a downstream
card or system that recognizes an AFD code assigned here.
• Incoming AFD Displays incoming AFD setting as follows:
codes to the SDI output video.
• If AFD code is present, one of the 1 1, four-bit AFD codes is displayed (as
shown in the example to the left). Also displayed is the VANC line
number of the incoming AFD code.
• I f no AFD setting is present in the video signal, No AFD Present is
displayed.
• Output Mode Drop-down selection determines action to take in presence or absence of
existing AFD code on input video.
AFD
• Output Code Drop-down list assigns desired AFD to output SDI.
4:3 Coded Frame
AFD Code
•
•
•
16:9 Coded Frame
AFD Code
1: AFD codes numbering and definitions conform to SMPTE 2016-1-2007.
2: Image Prot ecte d impl ies pictu re cont ent that must not be cropped by
(1)
Description AFD Code
– No code present 1001 Full frame
0000 Undefined 1010 16:9 (center)
0010 Box 16:9 (top) 1011 14:9 (center)
0011 Box 14:9 (top) 1101 4:3 (with alternate
0100 Box > 16:9 (center) 1110 16:9 (with alternate
1000 Full frame 1111 16:9 (with alternate
(1)
Description AFD Code
– No code present 1001 4:3 (center)
0000 Undefined 1010 16:9 (image
0010 Full frame 1011 14:9 (center)
0011 4:3 (center) 1101 4:3 (with alternate
0100 Box > 16:9 (center) 1110 16:9 (with alternate
1000 Full frame 1111 16:9 (with alternate
conversion processes or display devices. Alternate center formats may
have protected center areas, with areas outside of the protected area not
containing mandatory content.
(1)
(1)
Description
14:9 center)
14:9 center)
4:3 center)
Description
protected)
14:9 center)
14:9 center)
4:3 center)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
• Output Line Allows selecting the line location of the AFD data within the video signal
Ancillary Data space. (Range is 9 thru 41.)
Note: • Although the output line drop-down will allow any choice within the
9 thru 41 range, the actual range is automatically clamped (limited)
to certain ranges to prevent inadvertent conflict with active picture
area depending on video format. See Ancillary Data Line Number
Locations and Ranges (p. 3-8) for more information.
• The card does not check for conflicts on a given line number.
Make certain the selected line is available and carrying no other
data.
3-14 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 57

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Provides video Frame Sync delay control and audio
Framesync
• Framesync Enable Disables the Frame Sync function, or selects from choices below.
re-sync tools.
• Off: Video path bypasses frame sync entirely; output video timing
tracks with input video timing.
• Reference 1: Allows Frame Sync function to use external
Reference 1 as the reference (“house”) standard.
• Reference 2: Allows Frame Sync function to use external
Reference 2 as the reference (“house”) standard.
Note: If Reference 1 or Reference 2 is selected and an
appropriate external reference is not received, the
status portion of DashBoard™, indicating invalid frame sync
reference error. (Additionally, the card edge ERR indicator
illuminates indicating the same.) External reference signals
Reference 1 and Reference 2 are distributed to the card
and other cards via a frame bus.
• Input Video: Allows full framesync functionality (such as delay
offset), but instead uses the input video signal as the reference
standard.
Note: • If Input Video is used for framesync, any timing instability
on the input video will result in corresponding instability on
the output video. This setting should only be used where
syncing to input video is known to be reliable.
• Negative vertical or horizontal delay values (using the
controls below) should not be used when using Input
Video mode. This may result in image motion “jerkiness”.
T o add an of fset in t his case, instead apply a positive value
that results in the desired net offset.
indication appears in the Card Info
• Vertical Delay Control When Framesync is enabled, sets vertical delay (in number of lines of
• Horizontal Delay Control When Framesync is enabled, sets (in µsec of output video timing)
output video timing) between the output video and the frame sync
reference.
(Range is -1124 thru 1124 lines.)
Note: Lines refer to lines in the output video format, and not to the
reference format.
horizontal delay between the output video and the frame sync reference.
(Range is -64.000 thru 64.000 µsec)
Note: When an external framesync reference is used, the card will not
produce a framesync reset until the variance between framesync
reference and output video exceeds ± 2 clock periods. Therefore, a
framesync reset will not result if offsets within this window are
applied.
To apply an offset/framesync reset within this window, first apply a
relatively large offset, then apply the target smaller offset.
Example: T o apply a 1-period offset, first apply a 10-period positive
offset and then apply a 9-period negative offset. This results in the
target 1-period offset being applied to the output video.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-15
Page 58

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Input Video Mode Fixed Delay Control When Framesync is enabled and set to Input Video, allows adding video
• Framesync Audio SRC On/Off Control When Framesync is enabled and set to Input Video, allows disabling
• Minimum Latency Frames Control
Minimum Latency Frames Control
delay. This is useful when compensating for processes which result in
large audio delays.
(Range is 0.0000 thru 300.0 msec.)
audio SRC. This is required if the card is to pass non-PCM audio such as
Dolby® audio to downstream devices.
When Framesync is enabled, specifies the smallest amount of latency
allowed by the frame sync (latency measurement in output video frames).
The frame sync will not output a frame unless the specified number of
frames are captured in the buffer. The operational latency of the frame
sync is always between the specified minimum latency and
minimum latency plus one fra m e (not one field).
(Maximum range is 0 to 32.)
Note: Due to card memory limits, the maximum available Minimum
Latency Frames is related to the output video format selected.
For example, with a 525i59.94 output, the practical maximum limit
is 13.
When using this control, be sure to check the Framesync Status
display as follows:
• Latency frames selection within limits.
• Latency frames selection exceeds limits.
3-16 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 59

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Audio Hard Resync Threshold Control Sets threshold at which hard resync is applied if audio-video offset
With offset less than selected hard resync threshold, resync is progressively applied in many small
steps to provide a seamless, glitch-free retiming. After the successive steps, the audio is synchronized
with the video (in this example, 40 msec). (Progressive correction is applied at 1 msec/sec appr. rate.)
6
Video:
40 msec
With offset greater than selected hard resync
threshold, resync is immediately applied.
Video:
40 msec
Audio:
240 msec
exceeds threshold (see below). Hard resync provides fastest snyc-up
suitable for off-air manipulation. Conversely, a threshold setting high
enough to accommodate normal on-air offsets allows on-air resync that is
glitch-free.
(Range is 1.5 to 13.0 frames in 0.1 frame increments)
9
t
In this example, initial offset of 200 msec (appr. 6 frames) is
below 9 frame threshold and results in soft resync being
progressively applied.
9
In this example, initial offset of 400 msec (appr. 12 frames) is
above 9 frame threshold and results in immediate hard resync.
12
t
Audio:
440 msec
• Audio Offset Control Adds or reduces (offsets) audio delay from the matching video delay
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-17
(audio delay offset setting adds or removes delay in addition to any delay
included by other actions). This control is useful for correcting lip sync
problems when video and audio paths in the chain experience differing
overall delays.
(-575.0 msec to 575.0 msec range; null = 0.0 msec)
Note: Delay offset values of less than approximately 1 frame are
progressively applied by the card to provide a seamless, glitch-free
retiming. However, delay off set values exceeding 1-1/2 f rames may
result in a slight audio discontinuity at the moment when the offset
is applied using this control if the Audio Hard Resync Threshold
control is not at a setting greater than the delay offset.
To prevent this condition during an on-air manipulation, it is
recommended that the Audio Hard Resync Threshold control be
set high enough such that expected delay offsets exceeding 1-1/2
frames are progressively applied.
Note: If using Audio Offset control to perform off-air corrections, it is
recommended to temporarily set the Audio Hard Resync
Threshold control to its minimum setting, thereby allowing the
offset to be assessed and corrected as fast as possible.
Page 60

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Current Audio Delay Display Displays the current input-to-output audio delay (in msec units) as well as
• Video Delay Display Displays the current input-to-output video delay (in msec units) as well as
• Framesync Status Display Displays the current framesync status as follows:
• Loss of Input Signal Selection In the event of input video Loss of Signal (LOS), determines action to be
in terms of Frames/fractional frame (in number of lines).
in terms of Frames/fractional frame (in number of lines).
• Framesync status OK.
• Framesync Enable set to Off.
• I mpr oper or missing framesy nc refere nce.
• Latency frames selection exceeds limits.
Note: See Minimum Latency Frames Control ( p. 3-16) for more
information about this message.
taken as follows:
• Disable Outputs: Disab le all outputs.
• Freeze Last Frame: Freeze image to last good frame (last frame
having valid SAV and EAV codes).
• Freeze to Color: Freeze image to a color raster (as selected using
Framesync LOS Freeze Color control).
Note: Freeze Last Frame and Freeze to Color choices are functional only
when frame sync is set to lock to valid reference.
• Framesync LOS Freeze Color In the event of LOS with Freeze to Color enabled above, sets the image
raster color from choices shown to the left.
3-18 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 61

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Custom Color Hue Adjusts raster hue (phase angle) for custom LOS color.
(-360° to 360° range in 0.1° steps; null = 0°)
• Custom Color Saturation Adjusts raster saturation level for custom LOS color.
(0% to 100% range in 0.1% steps)
• Custom Color Y Level Adjusts raster luma level for custom LOS color.
(64 to 940 range)
• Reset/Resync Framesync
Reset Framesync
Reset Framesync resets the frame sync, clearing any buffered audio and
video.
Resync Video and Reference reset s the input processing paths for video
and reference.
When Confirm is clicked, a Confirm? pop-up appears, requesting
confirmation.
• Click Yes to reset the frame sync.
• Click No to reject reset.
Note: These controls are not normally used or required when the card is
receiving a stable, continuous frame sync reference.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-19
Page 62

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Selects the audio source for each embedded audio
Embedded Audio Group 1/2
channel 1 thru 8 (Embedded Audio Groups 1 and 2).
Also provides Gain, Phase Invert, and Muting controls
for each channel.
+
Embedded
Audio Group 1
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
CH5
CH6
CH7
CH8
Embedded
Audio Group 2
The example above shows
various Source selections and
individual audio control settings
for various audio sources fed to
the Destination channels
Embedded Ch 1 thru
Embedded Ch 8 in Embedded
Audio Groups 1 and 2, with the
resulting setup (right).
The source-to-destination
correlation shown here is only an
example; any of the sources on
the left can connect to any of the
destinations on the right, or to
Embedded Audio Groups 3 and
4 (not shown here). Additional
sources not shown here are also
available. These are described
on the following pages.
The controls shown here are
described in detail on the
following pages.
Embedded
Channels 1 – 16
AES I/O (1-4)
AES IN (5-8)
AN-AUD
IN (1-8)
Embed Ch 12
Embed Ch 14
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 3
AES Ch 5
AES Ch 8
Analog Ch 3
TG1
0 dB
-10 dB
0 dB
+
+
0 dB
+
+
0 dB
+
20 dB
20 dB
15 dB
–
3-20 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 63

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• SD Audio Depth Allows option of using 24-bit audio data structure per SMPTE 272M,
• Group Enable When enabled (On), enables the embedding of the corresponding
§3.10 (default is 20-bit per SMPTE 272M, §3.5).
Note: • If 24-bit depth is desired, make certain downstream equipment is
compatible with 24-bit SD audio data.
• Depth control setting applied here affects both Embedded Audio
Group 1/2 and 3/4.
embedded audio group (Embedded Audio Group 1 or Embedded Audio
Group 2).
• Embedded Audio Group 1 consists of embedded channels 1 thru 4.
• Embedded Audio Group 2 consists of embedded channels 5 thru 8.
Two Group Enable buttons correspondingly enable or disable Embedded
Audio Group 1 and Embedded Audio Group 2.
Disabling a group removes the entire group of embedded audio channels
while preserving the settings of the channels belonging to the group.
Note: • Embedded Ch 2 th ru Embedded Ch 8 have controls identical to the Source, Gain, Mute, and Phase controls
described here for Embedded Ch 1. Therefore, only the Embedded Ch 1 controls are shown here.
• For each channel, its source and destination should be considered and appropriately set. Unused destination
channels should be set to the Silence selection.
• Embedded Channel Sourc e Using the Source drop-down list, selects the audio input source to be
embedded in the corresponding embedded channel from the choices
described below.
• Embedded Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as Source Embed Ch 1 thru Embed Ch 16 range in Source drop-down list enables
•
•
•
• AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16 as Source AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16 range in Source drop-down list enables a
•
•
•
an embedded channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 16) to be the source for the selected
destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, Embed Ch 1 (embedded Ch 1) is the source for
destination Embedded Ch 1)
discrete AES channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 16) to be the source for the selected
destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, AES Ch 1 is the source for destination Embedded Ch 1)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-21
Page 64

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• An alog Ch 1 thru Ch 8 as Source Analog Ch 1 thru Analog Ch 8 range in Source drop-down list enables a
•
•
•
• Do wn Mix Left or Right as Source Down Mix Left and Down Mix Right selections in Source drop-down list
• M o no Mi x as Source Mono selection in Source drop-down list allows mono mix content to be
balanced-input analog channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 8) to be the source for the
selected destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, Analog Ch1 is the source for destination
Embedded Ch 1)
allow either downmixer left or right channel to be the source for the
selected destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, the Down Mix Left channel is the source for destination
Embedded Ch 1)
Note: Down Mix Left and Down Mix Right channels are a stereo pair
derived from the L, C, R, Ls, and Rs channel inputs selected using
the Audio Mixing function. The stereo pair consists of basic L/R
PCM signals with no additional encoded information.
Refer to Audio Mixing function description on page 3-41 for more
information.
the source for the selected destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, the mono content is the source for destination
Embedded Ch 1)
Note: Mono mix content is set up using Mono Mixer Selection in the
Audio Mixing function). Refe r to Audio Mixing function
description on page 3-41 for more information.
®
• Dolby
• Tone Generator 1 thru 4 as Source Tone Ge nerator 1 thru Tone Generator 4 range in Source drop-down list
Decoded Channel as Source (9083-DEC only) Dolby Ch 1 thru Dolby Ch 8 range in Source
•
•
•
drop-down list enables a Dolby® decoded channel to be the source for the
selected destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, Dolby
Embedded Ch 1)
Note: Drop-down choices of Ch 1 thru Ch 8 and Mix 1/Mix 2 represent
maximum channels available. Actual active channel complement is
per received Dolby
channels should not be used.
Refer to Dolby Metadata function description on page 3-31 for
more information.
Refer to Dolby
for an example of using Dolby
enables one of four tone generators (Tone 1 thru T one 4) to be the source
for the selected destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(In this example, Tone 1 (tone generator 1) is the source for destination
Embedded Ch 1)
Note: Tone generator frequencies can be independently set for the four
tone generator sources.
Refer to Tone Generator function description on page 3-46 for
more information.
®
decoded Ch 1 is the source for destination
®
format and upstream encoding. Inactive
®
E Processing and Routing Example on page 3-52
®
decoding.
3-22 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 65

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Audio LTC as Source LTC selection in Source drop-down list allows any timecode format
• Silence (Mute) as Source Silence selection in Source drop-down list mutes the selected destination
• Gain (dB) Control Adjusts and displays relative gain (in dB) applied to the corresponding
received by the card to be outputted as audio LTC over an embedded
audio output (destination) channel.
(In this example, audio LTC is the source for destination Embedded Ch 1)
Note: • When LTC is selected as source, Gain and Mute controls are
disabled.
• Refer to Timecode function description on page 3-37 for more
information.
Embedded Audio Group channel. Use this setting for unused
destination channels.
(In this example, silence (muting) is applied to Embedded Ch 1)
destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
(-80 to +40 dB range in 0.1 dB steps; unity = 0.0 dB)
• Mute Control Allows pushbutton On/Off channel muting while saving all other settings.
• Phase Control Selects between Normal and Invert phase (relative to source original
phase) for the destination Embedded Audio Group channel.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-23
Page 66

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Selects the audio source for each embedded audio
Embedded Audio Group 3/4
channel 9 thru 16 (Embedded Audio Groups 3 and 4).
Also provides Gain, Phase Invert, and Muting controls
for each channel.
+
Embedded
Audio Group 3
CH9
CH10
CH11
CH12
CH13
CH14
CH15
CH16
Embedded
Audio Group 4
The example above shows
various Source selections and
individual audio control settings
for various audio sources fed to
the Destination channels
Embedded Ch 9 thru
Embedded Ch 16 in Embedded
Audio Groups 3 and 4, with the
resulting setup (right).
The source-to-destination
correlation shown here is only
an example; any of the sources
on the left can connect to any of
the destinations on the right, or
to Embedded Audio Groups 1
and 2 (not shown here).
Additional sources not shown
here are also available.
Embedded
Channels 1 – 16
AES I/O (1-4)
AES IN (5-8)
AN-AUD
IN (1-8)
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 8
Embed Ch 15
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 14
Analog Ch 1
+
6 dB
+
6 dB
+
10 dB
+
10 dB
–20 dB
–
–15 dB
+
0 dB
Silence
3-24 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 67

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• SD Audio Depth Allows option of using 24-bit audio data structure per SMPTE 272M,
• Group Enable
§3.10 (default is 20-bit per SMPTE 272M, §3.5).
Note: • If 24-bit depth is desired, make certain downstream equipment is
compatible with 24-bit SD audio data.
• Depth control setting applied here affects both Embedded Audio
Group 1/2 and 3/4.
When enabled (On), enables the embedding of the corresponding
embedded audio group (Embedded Audio Group 3 or Embedded Audio
Group 4).
• Embedded Audio Group 3 consists of embedded channels 9 thru 12.
• Embedded Audio Group 4 consists of embedded channels 13 thru 16.
Two Group Enable buttons correspondingly enable or disable Embedded
Audio Group 3 and Embedded Audio Group 4.
Disabling a group removes the entire group of embedded audio channels
while preserving the settings of the channels belonging to the group.
Note: • Embedded Ch 9 thru Embedded Ch 16 have controls that are identical to the Source, Gain, Mute, and Phase controls
described for Embedded Ch 1. Refer to Embedded Audio Group 1/2 on page 3-20 for descriptions of these controls.
• For each channel, its source and destination should be considered and appropriately set. Unused destination channels
should be set to the Silence selection.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-25
Page 68

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Routes audio sources to discrete AES output channels
1 thru 8 (AES Audi o Out Pai rs 1-4 ). Al so pr ovid es Ga in,
AES Audio Out Pairs 1-4
Phase Invert, and Muting controls for each channel.
The example above shows
various Source selections and
individual audio control settings
for various audio sources fed to
the Destination channels
AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 8, with
the resulting setup (right).
The source-to-destination
correlation shown here is only
an example; any of the sources
on the left can connect to any of
the destinations on the right.
The controls shown here are
described in detail on the
following pages.
Embedded
Channels 1 – 16
AES I/O (1-4)
AES IN (5-8)
AN-AUD
IN (1-8)
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
Embed Ch 6
Embed Ch 7
AES Ch 4
Analog Ch 1
Analog Ch 2
10 dB
0 dB
+
10 dB
+
6 dB
+
+
–10 dB
TG4
6 dB
AES Audio Out
Pairs 1-4
(Ch 1-8)
AES Ch 1
+
–
–10 dB
–6 dB
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 3
AES Ch 4
AES Ch 5
+
AES Ch 6
AES Ch 7
AES Ch 8
3-26 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 69

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
Note: • AES Ch 2 thru AES Ch 8 have controls that are identical to the Source, Gain, Mute, and Phase controls described
here for AES Ch 1. Therefore, only the AES Ch 1 controls are shown here.
• For each channel, its source and destination should be considered and appropriately set. Unused destination channels
should be set to the Silence selection.
• AES Channel Source Using the Source drop-down list, selects the audio source to be routed to
• Embedded Ch 1 thru Ch 16 as Source
•
•
•
• AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16 as Source AES Ch 1 thru AES Ch 16 range in Source drop-down list enables a
•
•
•
• Analog Ch 1 thru Ch 8 as Source Analog Ch 1 thru Analog Ch 8 range in Source drop-down list enables a
the corresponding AES output channel from the choices described below.
Embed Ch 1 thru Embed Ch 16 range in Source drop-down list enables
an embedded channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 16) to be the source for the selected
destination AES channel.
(In this example, Embed Ch 1 (embedded Ch 1) is the source for
destination AES Ch 1)
discrete AES channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 16) to be the source for the selected
destination AES channel.
(In this example, AES Ch 5 is the source for destination AES Ch 1)
balanced-input analog channel (Ch 1 thru Ch 8) to be the source for the
selected destination AES channel.
(In this example, Analog Ch1 is the source for destination AES Ch 1)
•
•
•
• Down Mix Left or Right as Source Down Mix Left and Down Mix Right selections in Source drop-down list
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-27
allow either downmix left or right channel to be the source for the selected
destination AES channel.
(In this example, the Down Mix Left channel is the source for destination
AES Ch 1)
Note: Down Mix Left and Down Mix Right channels are a stereo pair
derived from the L, C, R, Ls, and Rs channel inputs selected using
the Audio Mixing function. The stereo pair consists of basic L/R
PCM signals with no additional encoded information.
Refer to Audio Mixing function description on page 3-41 for more
information.
Page 70

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• M o no Mi x as Source Mono selection in Source drop-down list allows mono mix content to be
®
• Dolby
• Tone Generator 1 thru 4 as Source Tone Ge nerator 1 thru Tone Generator 4 range in Source drop-down list
Decoded Channel as Source (9083-DEC only) Dolby Ch 1 thru Dolby Ch 8 range in Source
•
•
•
the source for the selected destination AES channel.
(In this example, the mono content is the source for destination AES Ch 1)
Note: Mono mix content is set up using Mono Mixer Selection in the
Audio Mixing function). Refe r to Audio Mixing function
description on page 3-41 for more information.
®
drop-down list enables a Dolby
selected destination AES channel.
(In this example, Dolby
Ch 1)
Note: Drop-down choices of Ch 1 thru Ch 8 and Mix 1/Mix 2 represent
maximum channels available. Actual active channel complement is
per received Dolby
channels should not be used.
Refer to Dolby Metadata function description on page 3-31 for
more information.
Refer to Dolby
for an example of using Dolby® decoding.
enables one of four tone generators (Tone 1 thru T one 4) to be the source
for the selected destination AES channel.
(In this example, Tone 1 (tone generator 1) is the source for destination
AES Ch 1)
Note: Tone generator frequencies can be independently set for the four
tone generator sources.
Refer to Tone Generator function description on page 3-46 for
more information.
®
®
E Processing and Routing Example on page 3-52
decoded channel to be the source for the
decoded Ch 1 is the source for destination AES
®
format and upstream encoding. Inactive
• Audio LTC as Source LTC selection in Source drop-down list allows any timecode format
• Silence (Mute) as Source Silence selection in Source drop-down list mutes the selected destination
received by the card to be outputted as audio LTC over an AES audio
output (destination) channel.
(In this example, audio LTC is the source for destination AES Ch 1)
Note: • When LTC is selected as source, Gain and Mute controls are
disabled.
• Refer to Timecode function description on page 3-37 for mor e
information.
AES channel. Use this setting for unused destination channels.
(In this example, silence (muting) is applied to AES Ch 1)
3-28 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 71

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Gain (dB) Control Adjusts and displays relative gain (in dB) applied to the corresponding
• Mute Control Allows pushbutton On/Off channel muting while saving all other settings.
• Phase Control Selects between Normal and Invert phase (relative to source original
destination AES channel.
(-80 to +40 dB range in 0.1 dB steps; unity = 0.0 dB)
phase) for the destination AES output channel.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-29
Page 72

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Routes audio sources to AES output channels 9 thru 16
(AES Audi o Ou t Pa ir s 5 -8 ). A lso provides G ain, Muting,
AES Audio Out Pairs 5-8
and Phase Invert controls for each channel.
+
AES Audio Out
Pairs 5-8
(Ch 9-16)
AES Ch 9
AES Ch 10
AES Ch 11
AES Ch 12
AES Ch 13
AES Ch 14
AES Ch 15
AES Ch 16
The example above shows
various Source selections and
individual audio control settings
for various audio sources fed to
the Destination channels AES
Ch 9 thru AES Ch 16, with the
resulting setup (right).
The source-to-destination
correlation shown here is only
an example; any of the sources
on the left can connect to any of
the destinations on the right, or
receive sources. Available
sources also include up to four
tone generators (not shown
here).
Embedded
Channels 1 – 16
AES I/O (1-4)
AES IN (5-8)
AN-AUD
IN (1-8)
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
AES Ch 4
Analog Ch 1
Analog Ch 2
Down Mix L
Down Mix R
0 dB
6 dB
+
0 dB
Silence
+
–3 dB
+
6 dB
+
10 dB
–
0 dB
+
+
–3 dB
Note: • AES Ch 9 thru AES Ch 16 have controls that are identical to the Source, Gain, Mute, and Phase controls described
for AES Ch 1. Refer to AES Audio Out Pairs 1-4 on page3-26 for descriptions of these controls.
• For each channel, its source and destination should be considered and appropriately set. Unused destination channels
should be set to the Silence selection.
3-30 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 73

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(9083 only) Extrac ts and preser ve s Dolb y® metadata
from the input SDI, and in turn allows the metadata to
Dolby Metadata
be re-inserted in the output SDI.
• Metadata Embedding Metadata Embedding (On/Off) control s SMPTE 2020-1 metadata
• Metadata Output Line
embedding in the SDI video output.
• When set to On, metadata is extracted from the SDI input video,
buffered, and re-directed to the output SDI video.
• When set to Off, metadata is not embedded in the output SDI video.
Allows selection of SMPTE 2020-1 metadata
space for re-inserted Dolby
(Range is 9 thru 41; default is line #13.)
Note: • Although the output line drop-down will allow any choice within the
9 thru 41 range, the actual range is automatically clamped (limited
to) certain ranges to prevent inadvertent conflict with active
picture area depending on video format. See Ancillary Data Line
Number Locations and Ranges (p. 3-8) for more information.
• The card does not check for conflicts on a given line number.
Make certain the selected line is available and carrying no other
data unless existing metadata is to be intentionally overwritten.
®
metadata.
line location within the VANC
Note: (9083 only) The Metadata Output Source button in DashBoard™ is locked to Input Video for this card. With this
function enabled, the extracted metadata is always available in the SDI video output and on cards equipped with an
appropriate Rear I/O Module having a Dolby
®
metadata RS-485 connector.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-31
Page 74

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(9083-DEC only) Routes a Dolby® encoded pair to the
®
Dolby
display and metadata handling controls.
Dolby Decoder
Note: • T he Dolby tab controls described here appear only on card equipped with Dolby Decoder option (-DEC).
• If necessary, see Dolby
®
decoding.
Dolby
• Decoded channels shown in DashBoard™ correlate to typical channel designations as shown below. Note that
channel designations are a function of encoding. Based on encoding, actual channel designations may vary from the
examples shown here.
Decoder Channels E5.1+2 E7.1+2 E8x1
Ch 1
Ch 2 RF RF Ch 2
Ch 3 C C Ch 3
Ch 4 LFE LFE Ch 4
Ch 5 LS LS Ch 5
Ch 6 RS RS Ch 6
Ch 7 Aux 1 LB Ch 7
Ch 8 Aux 2 RB Ch 8
Mix 1 Lo Lo Mono Mix 1
Mix 2 Ro Ro Mono Mix 2
®
E Processing and Routing Example on page 3-52 for an example of using and routing
LF LF Ch 1
decoder, and provides Dolby® configuration
• See other important notes in this subsection regarding the proper use of metadata embedding tools
available with the decoder function.
• AES Pair as Input AES Pair 1 thru AES Pair 8 range in Input Select drop-down list selects
•
•
•
• Embedded Channel Pair as Input Embedded Ch 1+2 thru Ch 15+16 range in Input Select drop-down list
•
•
•
• Decoder Mode Using the drop-down list, selects the action to take in presence or
an AES Pair (1 thru 8) to be the input for the Dolby
(In this example, AES Pair 1 is the input for the Dolby
selects an embedded channel pair (1+2 thru 15+16) to be the input for the
®
decoder.
Dolby
(In this example, embedded channel pair 1+2 is the input for the Dolby
decoder)
absence of Dolby
®
E or Digital source from the choices shown on the left.
®
decoder.
®
decoder)
®
3-32 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 75

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Dolby® Mode Display Shows specific bitstream information and Dolby® decoding type (Dolby® E
®
or Dolby
(In this example, Dolby
configuration is being decoded)
Digital) for input applied to Dolby® decoder.
®
E 20-bit with 5.1+2 decoded channel
If selected input has invalid or missing Dolby
®
data (such as if wrong
channels are applied to decoder), is displayed.
(In this case, PCM data passes undecoded and is present on Dolby Ch 1
and Dolby Ch 2 channels.)
®
• Dolby
Digital Channel and Dynamic Range
Controls
®
Channel Select drop-down list sets the channel carrying the Dolby
Digital encoded signal for D1/0 formats as shown from choices on the left.
Dynamic Range Control drop-down list selects from audio level
compression scheme choices as shown to the left. (Line Mode is typical
setting; RF Mode is used where signal may be fed through low-cost video/
audio RF modulator, in which case RF Mode helps prevent
overmodulation. Refer to ATSC A/52B for more information.)
• Metadata Embedding Metadata Embedding (On/Off) control s SMPTE 2020-1 metadata
embedding in the SDI video output.
• When set to On, metadata from selected source is embedded in the
output SDI video.
• When set to Off, metadata is not embedded in the output SDI video.
Note: Metadata Embedding should only be set to “On” if new metadata is
to be embedded. Existing metadata on the SDI input is passed through
the card unaffected, requiring no operator intervention.
• Metadata Output Source Drop-down list allows embedding and RS485 metadata routing to the
choices shown to the left and described below.
• Embedded: Dolby Decoder, RS485: Dolby Decoder – Routes the
metadata from the Dolby
®
decoder to both embedding on the output
SDI and the RS485 port on card so equipped.
• Embedded: Input Video, RS485: Dolby Decoder – Preserves
input metadata and directly re-routes it to the output SDI. Routes the
metadata from the Dolby
®
decoder to only the RS485 port on card
so equipped.
• Embedded: Input Video, RS485: Input Video – Routes the
preserved input metadata to both embedding on the output SDI and
the RS485 port on card so equipped.
Note: Typically, Metadata Output Source should be set to
Embedded: Dolby Decoder, RS485: Dolby Decoder, since this is
the new metadata produced by the card decoder and should also be
made available in the SDI stream and to any other external systems.
If embedding new metadata, make certain to set its line number
such that such that any old metadata for the same purpose is
overwritten (i.e., new metadata set to the same line number as the
old metadata to be replaced).
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-33
Page 76

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Metadata Output Line
Allows selection of SMPTE 2020-1 metadata
space for source embedding selected above.
(Range is 9 thru 41; default is line #13.)
Note: • Although the output line drop-down will allow any choice within the
9 thru 41 range, the actual range is automatically clamped (limited
to) certain ranges to prevent inadvertent conflict with active
picture area depending on video format. See Ancillary Data Line
Number Locations and Ranges (p. 3-8) for more information.
• The card does not check for conflicts on a given line number.
Make certain the selected line is available and carrying no other
data unless existing metadata is to be intentionally overwritten.
line location within the VANC
3-34 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 77

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(9083-DEC only) Displays the st a t us a n d p rog r am mi n g
details for each Dolby
®
E AC-3 program dictated by the
received external metadata.
Dolby E Metadata
Note: • This display is read-only. No changes can be made to the settings. All displays are reports per the received metadata.
• Information provided here is intended as an overview of the screen. Displayed parameters are per ATSC A/52B definitions.
Refer to ATSC A/52B for detailed descriptions and background.
Updates the external metadata status and
program configuration display screen. The
display always shows the last initiated
metadata transaction; to refresh screen for
any changes, click Update.
Note: M etadata does not continuously report.
Use this button to report new metadata. When
clicked, the button stays in the “depressed”
position while updating. When the button
displays the “out” position, update is complete
and all displays are current.
Where AC-3 programs exist for the
current metadata coding, the columns
show the details for the individual
AC-3 programs
Where AC-3 programs do not
exist for the current metadata
coding, the columns are
collapsed
•
•
•
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-35
Page 78

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(9083-DEC only) Displays the status and programming
details for Dolby
®
Digital program dictated by the
received external metadata.
Dolby D Metadata
Note: • This display is read-only. No changes can be made to the settings. All displays are reports per the received metadata.
• Information provided here is intended as an overview of the screen. Displayed parameters are per ATSC A/52B definitions.
Refer to ATSC A/52B for detailed descriptions and background.
Updates the external metadata status and
program configuration display screen. The
display always shows the last initiated
metadata transaction; to refresh screen for
any changes, click Update.
Note: Metadata does not continuously report.
Use this button to report new metadata. When
clicked, the button stays in the “depressed”
position while updating. When the button
displays the “out” position, update is complete
and all displays are current.
•
•
•
3-36 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 79

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Provides timecode data extract ion from va rious
sources, and provides formatting and re-insertion
Timecode
Shown below is an example in which received SDI video with SDI VITC waveform timecode is to be converted to SDI
ATC_VITC timecode data. Each Timecode control is fully described on the pages that follow.
controls for inserting the timecode into the output video.
525i 5994
w/ VITC
Waveform
A
Noting that the incoming video contains VITC
9083
525i 5994
w/ ATC_VITC
waveform timecode data (as shown in the status
display), set the Source Priority drop-down lists to
include VITC Waveform timecode data (SDI VITC) as
a choice. This extracts VITC Waveform timecode
data from the incoming video.
In this example, it is desired to provide SDI
B
ATC_VITC timecode data in the output video. As
such, set HD ATC VITC Insertion Insertion to
Enabled.
In the example here, the line numbers are set to the
default SMPTE 12M-2-2008 recommended values.
525i SDI
w/ VITC
Waveform
SDI VITC
Detect/Extract
A
A
Priority/
Select
Buffer/
Format
SDI VITC
Timecode
Proc/Embed
ATC_VITC
Timecode
Proc/Embed
B
SDI ATC_VITC
Detect/Extract
ATC_LTC
Timecode
Line
Number
Control
Proc/Embed
525i SDI
w/ATC_VITC
ATC_VITC Insertion = Enabled
ATC_LTC Insertion = Enabled
ATC_VITC1 = Line 9 (default SMPTE 12M-2)
ATC_VITC2 = Line 8 (571) (default SMPTE 12M- 2)
ATC_LTC = Line 10 (default SMPTE 12M-2)
SDI ATC_LTC
Detect/Extract
LTC Detect/
Extract
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-37
Insert
Control
Page 80

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
Audio LTC and RS-485 L TC controls descr ibed below only appear on cards with +LTC licensed optional
feature. This feature allows bidirectional conversion between VBI-based timecode and LTC timecode on audio and RS-485
interfaces.
• Timecode Source Status Displays Displays the current status and contents of the supported timecode
• RS-485 Port LTC Control Allows RS-485 port to be used to receive LTC, or send LTC over RS-485
formats shown to the left.
• If a format is receiving timecode data, the current content (timecode
running count and line number) is displayed.
• I f a format is not receiving timecode data, Unlocked is displayed.
• I f Audio LTC is being received, the timecode running count is
displayed.
• Audio LTC Source selects audio source to be used by card audio
LTC function as listed below.
• Emb Ch 1 thru Ch 16
• AES Ch 1 thru Ch 16
• Analog audio Ch 1 thru Ch 8
Note: Audio LTC Source must be appropriately set for card to receive
and process audio LTC.
port as follows:
• If RS-485 LTC is to be received via the shared RS-485 port, set the
RS-485 Port Function control to LTC In.
• If RS-485 LTC is to be outputted via the shared RS-485 port, set
the RS-485 Port Function control to L TC Out put . The timecode
string carried on the LTC output is that selected using the Source
Priority controls described on the next page.
• Incoming ATC Packet Removal Control Enables or disables removal of existing input video ATC timecode packets
from the output. This allows removal of undesired existing timecodes from
the output, resulting in a “clean slate” where only desired timecodes are
then re-inserted into the output. (For example, if both SD VITC Waveform
and SD ATC_VITC timecode data are present on the input video, and only
ATC_VITC is desired, using the Removal control will remove both
timecodes from the output. The ATC_VITC timecode by itself can then be
re-inserted on the output using the other controls discussed here.)
Note: When the Scaler is enabled, ATC packets are automatically
removed. The Timecode function must be used to re-insert the
timecode data into the output video.
3-38 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 81

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Source Priority As described here, selects the priority assigned to each of the four
• Output Status Display Displays the current content and source being used for the timecode data
supported formats in the event the preferred source is unavailable.
Each of the four Source Priority selection lists allows assignment of
source priority from the following choices:
Source Priority 1 thru Source Priority 4 select the preferred format to be
used in descending order (i.e., Source Priority 2 selects the second-most
preferred format, and so on.
as follows:
• Output status OK (in this example, running SDI VITC timecode received
and outputted).
• Timecode not available due to lack of appropriate input timecode data on
enabled formats.
Note: Timecode output requires that source and priority are appropriately
selected (as described above in Source Priority). Also, video input
must contain appropriate timecode data.
• Timecode Insertion button set to Disabled; output insertion disabled.
Note: • If timecode is not available from Source Priority selections
performed, timecode on output reverts to Free Run (internal
count) mode.
• Because the 1’s digit of the display Frames counter goes from 0 to
29, the fractional digit (along with the 1’s digit) indicates frame
count as follows:
0.0 Frame 0
0.1 Frame 1
1.0 Frame 2
1.1 Frame 3
•
•
•
29.1 Frame 59
• Offset Controls A llows the current timecode count to be advanced or delayed on the
output video.
• Offset Advance or Delay selects offset advance or delay.
• Offset Field delays or advances or delays timecode by one field.
• Offset Frame delays or advances or delays timecode by up to 5
frames.
Note: Default settings are null, with both controls set at zero as shown.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-39
Page 82

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
Note: • Although the output line drop-down on the controls described below will allow a particular range of choices, the actual
range is automatically clamped (limited) to certain ranges to prevent inadvertent conflict with active picture area
depending on video format. See Ancillary Data Line Number Locations and Ranges (p. 3-8) for more information.
• The card does not check for conflicts on a given line number. Make certain the selected line is available and carrying
no other data.
• SD VITC Waveform Insertion Controls For SD output, enables or disables SD VITC waveform timecode insertion
• SD ATC Insertion Control For SD output, enables or disables SD ATC_VITC timecode insertion into
• HD ATC_LTC Insertion Control For HD output, enables or disables ATC_LTC timecode insertion into the
into the output video, and selects the VITC1 and VITC2 line numbers (6
thru 22) where the VITC waveform is inserted.
Note: • If only one output line is to be used, set both controls for the same
line number.
• SD VITC Waveform Insertion control only affects VITC
waveforms inserted (or copied to a new line number) by this
function.
the output video, and selects the line number for ATC_VITC.
output video, and selects the line number for ATC_LTC timecode data.
• HD ATC_VITC Insertion Control
• ATC_VITC Legacy Support Control When enabled, accommodates equipment requiring ATC_VITC packet in
For HD output, enables or disables ATC_VITC timecode insertion into the
output video, and selects the line number for ATC_VITC1 and
ATC_VITC2.
Note: If only one output line is to be used, set both controls for the same
line number.
both fields as a “field 1” packet (non-toggling).
Note: Non-toggling VITC1 and VITC2 packets do not conform to
SMPTE 12M-2-2008 preferences. As such, ATC_VITC Legacy
Support should be enabled only if required by downstream
equipment.
3-40 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 83

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Provides down-mix audio routing selections that
multiplexes any five embedded, AES, or analog audio
Audio Mixing
channel sources into a stereo pair (Down Mix Left and
Down Mix Right), or selection of any two audio sources
to be mono-mixed to serve as a monaural source.
With an optional upmixer licensable feature activated,
any normal PCM stereo pair can be fed to the upmixer to
generate 5.1 surround sound audio which in turn can be
applied to six user-selec table cha nnels .
• Down Mixer Selection Separate drop-down lists for Left, Right, Center, Left Surround (Ls),
and Right Surround (Rs) inputs allow embedded, AES, or analog
channel audio source selection for each of the five inputs as shown below.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
The example below shows selection from various sources and the
resulting stereo pair DM-L and DM-R. The two signals comprising the pair
can be routed and processed the same as any other audio input source.
Embed Ch 1 - Ch 16
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
AN-AUD Ch 1- Ch 8
Embedded Ch 1
Embedded Ch 2
AES Ch 6
Embedded Ch 4
Embedded Ch 5
Note: The stereo pair are basic L/R PCM signals with no additional
encoded information.
L
R
C
Ls
Rs
DM-L
DM-R
• Center Mix Ratio Control
Adjusts the attenuation ratio of center-channel content from 5-channel
source that is re-applied as Lt and Rt content to the DM-L and DM-R
stereo mix.
• Minimum attenuation setting (-0.0 dB) applies no ratiometric reduction.
Center channel content is restored as in-phase center-channel content
with no attenuation, making center-channel content more predominate in
the overall mix.
• Maximum attenuation setting (-10.0 dB) applies a -10 dB ratiometric
reduction of center-channel content. Center-channel content is restored
as in-phase center-channel content at a -10 dB ratio relative to overall
level, making center-channel content less predominate in the overall
mix.
(0.0 dB to -10.0 dB range in 0.1 dB steps; default = -3 dB)
Note: Default setting of -3.0 dB is recommended to maintain
center-channel predominance in downmix representative to that of
the original source 5-channel mix.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-41
Page 84

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Surround Mix Ratio Control
• Mono Mixer Selection Separate drop-down lists for Left and Right inputs allow selected
Adjusts the attenuation ratio of surround-channel content from 5-channel
source that is re-applied as Lo and Ro content to the DM-L and DM-R
stereo mix.
• Minimum attenuation setting (-0.0 dB) applies no ratiometric reduction.
Surround-channel content is restored with no attenuation, making Lo
and Ro content more predominate in the overall mix.
• M aximum attenuation setting (-10.0 dB) applies a -10 dB ratiometric
reduction of surround-channel content. Surround-channel content is
restored at a -10 dB ratio relative to overall level, making
surround-channel content less predominate in the overall mix.
(0.0 dB to -10.0 dB range in 0.1 dB steps; default = -3 dB)
Note: Default setting of -3.0 dB is recommended to maintain
surround-channel predominance in downmix representative to that
of the original source 5-channel mix.
embedded, AES, analog, or the DM-L / DM-R input channels to provide
an additional mono-mixed channel.
The resulting mono mix (Mono) is available as an audio source for any of
the 32 destination embedded or AES output channels as shown below.
Emb Ch 1 - Ch 16
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
AN-AUD Ch 1- Ch 8
Emb Ch 12
Emb Ch 16
L
Σ
R
MONO
Note: Selection of any two channels for mono mixing in no way affects the
source channels themselves.
3-42 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 85

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
Note: • 2.0-to-5.1 upmixer function is an optional licensable feature. This function and its controls appear only when a license
key is entered and activated. Refer to Licensable Features function description on page 3-46 for more information.
• Channel sources used by the upmixer are post-processed signals received from the Audio Routing/Gain Control
function. When active, the channel selections made using this function are directly embedded in the output SDI or
AES discrete pairs. Refer to 2.0-to-5.1 Upmix Function (p. 1-12) in Chapter 1, “Introduction” for detailed functional
description and signal flow.
• For any six channels selected for this function, the Left and Right channel selections always serve as the stereo input
pair.
• 2.0-to-5.1 Up Mixer Selection Separate drop-down lists for Left, Right, Center, LFE, Left Surround,
and Right Surround allow embedded, AES, or analog channel audio
source selection, and embedded or AES discrete channel assignments
for the six generated 5.1 channels.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
The example below shows selection of embedded channels 1 and 2 as
the received stereo source (Embed Ch1 and Ch 2 for Left and Right
drop-down list selections in the Up Mixer Selection tool).
Using the setup shown in the example, when upmix is active the
embedded channel 1/2 stereo pair is overwritten with the new stereo pair
L/R on channels 1/2. As selected in the example, the additional 5.1
channels C, LFE, Left Surround (Ls), and Right Surround (Rs) overwrite
EmbCh3 – Ch 6, respectively.
Emb Ch 1 –
Ch 16
>
Emb Ch 1
Emb Ch 2
Emb Ch 3
Emb Ch 4
Emb Ch 5
Emb Ch 6
L
R
(C)
(LFE)
(Ls)
(Rs)
L – Emb Ch 1
R – Emb Ch 2
C – Emb Ch 3
LFE – Emb Ch 4
Ls – Emb Ch 5
Rs – Emb Ch 6
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-43
Page 86

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Up Mixer Mode Control Enables or bypasses upmixer as follows:
• Auto:Automatic enable/bypass of 5.1 upmix function as follows:
• If detected signal level on all four of the selected channels
designated as Center, LFE, Left Surround , and Right Surround
are below the level threshold set using the 5.1 Detection Threshold
control, upmixer overwrites all six selected channels with the new 5.1
content generated by the upmixer.
• If detected signal level on any of the four of the selected channels
designated as Center, LFE, Left Surround , and Right Surround is
above the level threshold set using the 5.1 Detection Threshold
control, upmixer is bypassed and the original channels pass
unaffected.
• Always Upmix: Manual enable turns on upmixer and overwrites content
on all six selected channels with new 5.1 content generated by the
upmixer regardless of original signal level or content.
• Bypass: Manual disable bypasses the upmixer. When bypassed, the six
embedded audio channels pass unaffected.
• Up Mixer Status Display Shows activity status of upmixer processing as follows:
• Auto Mode - Currently Upmixing: With upmixer enable set to
Auto, indicates selected channels designated as Center, LFE, Left
Surround, and Right Surround are clear for use (as described
above); upmixer is currently up-mixing received stereo pair and
overwriting the six selected channels with new 5.1 upmix.
• Auto Mode - Currently Bypassed: With upmixer enable set to
Auto, indicates selected channels designated as Center, LFE, Left
Surround, and Right Surround have content (such as existing
original 5.1 or other content); upmixer is bypassed (disabled) and
allows normal passage of six selected channels.
• Upmixing: Indicates upmixer is manually enabled (set to Always
Upmix) and is currently up-mixing received stereo pair and
overwriting the six selected channels with new 5.1 upmix.
• Bypassed: Indicates upmixer is manually disabled (set to Bypass)
and is currently passing all selected channels unaffected.
• Auto Crossfade Speed Controls Individual controls select the relative crossfade transition speed between
Upmix to Bypass (going to inactive; from 5.1 to 2.0) and Bypass to Upmix
(going to active; from 2.0 to 5.1) when upmixer enable is set to Auto and
the active threshold (as set by the 5.1 Detection Threshold control) is
crossed in either direction.
To suit program material and production aesthetic preferences, several
choices are available as shown to the left. Slower settings allow for a
more gradual transition between modes, however with a longer interval
before levels stabilize. Faster settings conversely allow for a smaller
interval before levels stabilize, however with greater perceived
abruptness.
3-44 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 87

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• 5.1 Detection Threshold Control Adjusts the threshold at which selected channels designated as C, LFE,
Ls, and Rs are considered to have viable content, or at which signal levels
can be considered insignificant when upmixer enable is set to Auto.
Setting affects automatic enable/bypass of 5.1 upmix function as follows:
• If detected signal level on all four of the selected channels designated
as Center, LFE, Left Surround, and Right Surround are below the level
threshold set using the 5.1 Detection Threshold control, upmixer allows
overwrite of all six selected channels with the new 5.1 signal
complement.
• If detected signal level on any of the four of the selected channels
designated as Center, LFE, Left Surround, and Right Surround is above
the level threshold set using the 5.1 Detection Threshold control,
upmixer is bypassed, thereby releasing the selected six channels and
allowing the original channels to pass unaffected.
(Range is -150 dB to 0 dB in 0.1dB steps;
0 dB equivalent to +24 dBu=> 0 dBFS)
Typically, the 5.1 Detection Threshold control should be set to provide
a usable threshold that maintains a threshold at which valid levels large
enough over the threshold disable the auto upmix ( , left), while
- 20 dBFS
- 60 dBFS
s
s
E
C
L
R
F
L
A
s
E
C
L
F
L
B
Above Threshold
(Bypass)
Below Threshold
(Overwrite)
s
R
nuisance levels
considerably below the
threshold ( , left) are
rejected, allowing the
upmixer to stay locked in
the enabled mode and
overwrite these signals
with the new signals.
Optimum setting is
dependent on program
material general overall
levels. A -60 dB setting is
A
B
recommended for material closely adhering to the SMPTE -20 dBFS
Alignment level for normal material such as dialog.
• Center Width Control
Adjusts center channel content (in terms of percentage) applied to L and
R channels.
• Minimum setting keeps all L+R (mono) content confined to center (C)
channel, with any center channel content removed from L and R
channels.
• Higher settings progressively blend respective L and R mono content
back into L and R channels, with 100% setting resulting in center
channel level going to zero and L/R channels becoming normal L/R
channels containing some mono content.
(0% to 100% range in 0.1% steps; default = 0%)
• Surround Depth Control
Adjusts surround channel content (in terms of percentage) applied to Ls
and Rs channels.
• Maximum setting results in greatest surround channel levels.
• Lower settings progressively diminish surround channel levels, with 0%
setting resulting in no Ls or Rs level, with Ls and Rs content
progressively folded back into L and R, respectively.
(0% to 100% range in 0.1% steps; default = 100%)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-45
Page 88

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Sets the test tone frequency for each of four tone
Tone Generator
generators (Tone Generator 1 thru 4).
• Frequency Selection Lists Selects the frequency for each of the four tone generators. 18 discrete
•
•
•
Licensable Features
sine wave frequencies are available, ranging from 50 Hz to 16 kHz
(default frequency is 1.0 kHz).
Note: Unity-gain signal level is equivalent to -20 dBu.
Allows activation of optional licensed features.
Note: For card pre-ordered with licensed feature(s), the activation steps described below are not required; the feature will
already be installed activated. To order features and obtain a license key, contact Cobalt
sales@cobaltdigital.com or at the contact information in Contact Cobalt Digital Inc. in Chapter 1, “Introduction”. Please
provide the “SSN” number of your card (displayed in the Card Info pane) when contacting us for your key.
• License Feature and Key Entry window Activate licensable feature as descr ibed below.
1. Enter the feature key string in the Feature Key box. Press return or
click outside of the box to acknowledge entry.
Note: Entry string is case sensitive. Do not enter any spaces.
2. In the DashBoard™ Card Info pane, wait for the feature identification to
be shown for the card product number (for example, “-UM” appearing
after the card part number) and Valid Key Entered to be displayed.
This indicates the key was correctly entered and recognized by the
card.
Note: If DashBoard™ card function submenu/control pane does not
re-appear, close the card and re-open it.
3. Click and confirm Reboot. When the card function submenu/control
pane appears again, the licensable feature will be available.
Note: Applying the licensable feature and its reboot has no effect on
prior settings. All control settings and drop-down selections are
retained.
®
sales at
3-46 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 89

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
Allows up to 16 card user settings configuration presets
to be saved in a Preset and then recalled (loaded) as
Presets
desired. All current settings (including list selections
and scalar (numeric) control settings such as Gain, etc.)
are saved when a Preset Save is invoked.
The Preset Name field and Preset Save button
allow custom user setting configurations to be
labeled and saved to a Preset for future use.
The Preset Load button and the Selected Preset
drop-down list allow saved presets to be selected
and loaded as desired. When a preset is loaded, it
immediately becomes active with all user settings
now automatically set as directed by the preset.
Saved presets can be uploaded to a computer for
use with other same-model COMPASS™ cards.
Each of the items to the left are described in detail on
the following pages.
• Preset Save and Load
• Selected Preset
•
•
•
• Card Name
• Preset Save stores all current card control settings to the currently
selected preset.
(For example, if Preset 1 is selected in the Selected Preset drop-down
list, clicking and confirming Preset Save will then save all current card
control settings to Preset 1)
• Preset Load loads (applies) all card control settings defined by
whatever preset (Preset 1 thru Preset 16) is currently selected in the
Selected Preset drop-down list.
(For example, if Preset 3 is selected in the Selected Preset drop-down
list, clicking and confirming Preset Load will then apply all card control
settings defined in Preset 3)
The above buttons have a Confirm? pop-up that appears, requesting
confirmation.
Note: Applying a change to a preset using the buttons described above
rewrites the previous preset contents with the invoked contents.
Make certain change is desired before confirming preset change.
Selected Preset 1 thru Selected Preset 16 range in drop-down list
selects one of 16 stored presets as ready for Save (being written to) or for
Load (being applied to the card).
Note: The preset names shown to the left are the default (unnamed)
preset names. All 16 presets in this case are loaded identically with
the factory default settings.
Text entry field provides for optional entry of card name, function, etc. (as
shown in this example).
Note: Card name can be 31 ASCII characters maximum.
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-47
Page 90

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Table 3-2 9083 Function Submenu List — continued
(continued)
• Preset Name With one of 16 presets selected, provides for entry of custom name for the
• Reset Current Preset • Reset Current Preset resets all parameters (including preset custom
• Download Presets Download Presets allows all 16 presets to be stored to a specified location
Download a presets file to a computer on the card’s DashBoard network to save presets. Preset files stored on a computer can
then be uploaded back to the card.
Note also that a presets file can also be uploaded to other same-model COMPASS
using a single card can be easily applied to other same-model cards without repeating the setup work on the other cards.
preset (as shown in example below).
Entering text in Preset
Name field (in this
example, “RCVR21”)
applies custom name to
selected Preset (in this
example, Preset 2)
Note: • Preset name can be seven ASCII characters maximum.
• The Preset ID number does not need to be entered; it is
added automatically.
name entered) of the currently selected Preset (as displayed in the
Selected Preset field) to factory default settings. The button has a
Confirm? pop-up that appears, requesting confirmation.
on a network computer for use with other same-model COMPASS™
cards.
®
Refer to Cobalt
9000RCS-RM) for instructions on using the Download Presets function.
reference guide “Remote Control User Guide” (PN
®
cards. In this manner, presets built up
Download (save) card presets to a
network computer by clicking
Download
Presets – Save
at the bottom of
the Presets
page.
Browse to a desired
save location (in
this example, My
Documents\Cobalt
Presets).
The file can then be
renamed if desired
(RCVR21 Presets
in this example)
before saving.
Upload (open) card presets from a network
computer by clicking Upload
at the bottom of
DashBoard.
Browse to the location
where the file was saved
on the computer or
drive (in this example,
My Documents\Cobalt
Presets).
Select the desired file
and click Open to load
the file to the card.
To upload presets
saved from one card
to another same-model card, simply click Upload on the
other same-model card’s DashBoard page and repeat the
same steps here.
Note: • Preset transfer between card download and file
upload is on a group basis (i.e., individual presets
cannot be downloaded or uploaded separately).
• After uploading a presets file, engagement of a
desired preset is only assured by pressing the Preset
Load button for a desired preset.
3-48 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 91

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Audio Routing Example Using DashBoard™
Figure 3-6 shows an example of using the 9083 Embedded Audio Group and
AES Output Pairs functions to de-embed audio, route the audio to discrete
outputs for post-production processing, and finally re-embed the audio into
the SDI video output. Additionally, the example shows how external analog
and internal tone generator sources can be embedded into the SDI output.
Note that the source and destination correlations shown here are only
examples; any source can route to any destination.
9083
Post-Production
Video Feed
(with five
embedded audio
channels)
Analog
2-Channel
Voice-Over
Feed
SDI IN
Audio
De-Embed
AN-AUD IN 1
AN-AUD IN 2
Analog
Ch 1
Analog
Ch 2
Audio Routing/
Control
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
TG1
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 3
AES Ch 4
AES Ch 5
AES Ch 6
AES Ch 7
AES Ch 8
SDI OUT
Audio
Embed
AES OUT 1
AES OUT 2
AES OUT 3
AES OUT 4
Video Output
(with eight
embedded audio
channels)
AES IN 5
AES IN 6
AES IN 7
AES IN 8
AES Ch 9
AES Ch 10
AES Ch11
AES Ch 12
AES Ch 13
AES Ch 14
AES Ch 15
AES Ch 16
Silence
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
Embed Ch 6
Embed Ch 7
Embed Ch 8
Embed Ch 9 –
Embed Ch 16
Post-Production Console
Figure 3-6 Audio Routing Example (Sheet 1 of 3)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-49
Page 92

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
In the example here, Embedded Channels 1 thru 5 are de-embedded from the
input SDI data and routed t o discr ete AES cha nnels 1 thru 5. Al so, an int ernal
tone generator (TG1) and t wo analog inputs ar e routed to AES channel s 6 thru
8, respectively. Figure 3-6 (sheet 2) shows the 9083 control settings (in this
example, using the DashBoard™ user interface) that result in this routing.
9083
SDI IN
Audio
De-Embed
AN-AUD IN 1
AN-AUD IN 2
Analog
Ch 1
Analog
Ch 2
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
TG1
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 3
AES Ch 4
AES Ch 5
AES Ch 6
AES Ch 7
AES Ch 8
AES OUT 1
AES OUT 2
AES OUT 3
AES OUT 4
Figure 3-6 Audio Routing Example (Sheet 2 of 3)
AUD_ROUTE_EX1_V4.PNG
Using the AES Audio Out Pairs 1-4
function, the Source selections
shown above route the selected
sources to discrete AES channels 1
through 8. These discrete outputs
are then available on the 9083 card
Rear I/O Module AES OUT 1 thru
AES OUT 4 BNC connectors.
3-50 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 93

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
The discrete AES audio on AES ch annels 9 t hru 16 is now re -embedded us ing
the 9083 control settings shown in Figure 3-6 (sheet 3).
AES IN 5
AES IN 6
AES IN 7
AES IN 8
AES Ch 9
AES Ch 10
AES Ch11
AES Ch 12
AES Ch 13
AES Ch 14
AES Ch 15
AES Ch 16
AUDIO_ROUTE_EX3B_V4.PNG
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
Embed Ch 6
Embed Ch 7
Embed Ch 8
Audio
Embed
AUD_ROUTE_EX3A_V4.PNG
SDI OUT9083
Using the Embedded Audio Group
1/2 and 3/4 function, the Source
selections shown above route the
discrete AES audio signals received
on the 9083 card Rear I/O Module
AES IN 5 thru AES IN 8 BNC
connectors to embedded channels 1
thru 8. Unused embedded channels
9 thru 16 are set to Silence (mute).
Silence
Embed Ch 9 –
Embed Ch 16
Figure 3-6 Audio Routing Example (Sheet 3 of 3)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-51
Page 94

3 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Dolby® E Processing and Routing Example (9083-DEC only)
Figure 3-7 shows an example of using the 9083-DEC Audio Input Controls,
Dolby Decoder, and Embedded Audio Group 1/2 functions to decode a
received Dolby
example also shows routing the metadata to the 9083-DEC
output.
®
E encoded pair and route the decoded channels. The
DOLBY META
Video Feed
(with six
embedded audio
channels and
®
encoded
Dolby
pair)
9083-DE
SDI IN
De-Embed
Embed
Ch Pair 7+ 8
Note that the source and destination correlations shown here are only
examples; any embedded channel pair carrying encoded Dolby
decoded. Decoded Dolby
®
channels can in turn be routed route to any
®
data can be
embedded channel destination.
Video Feed (with
six original
embedded audio
channels and
added Dolby
5.1+2 embedded
channels)
Audio
Dolby
Decode
Dolby Ch 1
Dolby Ch 2
Dolby Ch 3
Dolby Ch 4
Dolby Ch 5
Dolby Ch 6
Dolby Ch 7
Dolby Ch 8
Dolby Mix 1
Dolby Mix 2
Audio Embed/
Routing
Embed Ch 1
Embed Ch 2
Embed Ch 3
Embed Ch 4
Embed Ch 5
Embed Ch 6
Embed Ch 9
Embed Ch 10
Embed Ch 11
Embed Ch 12
Embed Ch 13
Embed Ch 14
[not used]
[not used]
Embed Ch 15
Embed Ch 16
SDI OUT
Audio
Embed
®
DOLBY
META
RS-485 Dolby®
Metadata
Figure 3-7 D olby® E Processing Example (Sheet 1 of 2)
In the example here, Dolby®E 5.1+2 data on embedded pair 7/8 is to be
decoded and embedded (usin g spare embedded cha nnels 9 thru 16) along with
the existing embedded audio channels (embedded channels 1 thru 6). Figure
3-7, sheet 2 shows the 9083-DEC control settings (using DashBoard™) that
result in th is routing.
3-52 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 95

Operating Instructions 9083 Function Submenu List and Descriptions
Using the Status display in the Audio Input Controls function, embedded channel pair 7+8 shows
®
Dolby
E data.
DOLBY_AICEMB7-8.PNG
Embedded pair 7+8 can then be selected as the Dolby Decoder
Input Select source. The Bitstream Format and Dolby E Program
Configuration displays also show this signal as Dolby
Metadata Embeddi ng = On allows decoder metadata embedding
into the SDI stream (on line 13 as shown).
®
E; 5.1+2
DOLBY_EXNEW_B_EMB.PNG
Metadata Output Source can be set to Embedded: Dolby
Decoder, RS485: Dolby Decoder to select the decoder metadata
as the source for embedded and RS485 metadata.
In this example, since the
decoder displays a “5.1+2”
configuration, the eight
channels comprising this
configuration can be
embedded using eight spare
embedded channels.
As such, the eight total
decoded channels produced
(Dolby Ch 1 thru Dolby Ch 6,
and Dolby Mix 1 / Dolby Mix 2
corresponding to L, R, C, LFE,
LS, RS, and Lo/Ro monitors)
can be respectively routed to
embedded channels 9 thru 16
as shown to the left using the
Embedded Audio Group 3/4
function.
(Note that decoder channels 7
and 8 are not used in this
format.)
DOLBY_EXNEW_C.PNG
Figure 3-7 Dolby® E Processing Example (Sheet 2 of 2)
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-53
Page 96

3 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
This section provides general troubleshooting information and specific
symptom/corrective action for the 9083 card and its remote control interface.
The 9083 card requires no periodic maintenance in its normal operation; if
any error indication (as described in this section) occurs, use this section to
correct the condition.
Error and Failure Indicator Overview
The 9083 card itself and its remote control systems all (to varying degrees)
provide error and failure indications. Depending on how the 9083 card is
being used (i.e, standalone or network controlled through DashBoard™ or a
Remote Control Panel), che ck all avai lable indi cations in the event of an error
or failure condition.
The various 9083 card and remote control error and failure indicators are
individually described below.
Note: The descriptions below provide general information for the various status and
error indicators. For specific failures, also use the appropriate subsection
listed below.
• Basic Troubleshooting Checks (p. 3-58)
• 9083 Processing Error Troubleshooting (p. 3-59)
• Troubleshooting Network/Remote Control Errors (p. 3-62)
3-54 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 97

Operating Instructions Troubleshooting
9083 Card Edge Status/Error Indicators and Display
Figure 3-8 shows and describes the 9083 card edge status indicators and
display. These indicators and the display show status and error conditions
relating to the card itself and remote (network) c ommunications (where
applicable). Because these indicators are part of the card itself and require no
external interface, the indicators are particularly useful in the event of
communications problems with external devices such as network remote
control devices.
4-Character Alphanumeric Display
RMT
REF
ERR
1080
720
625
525
9083
Status/Error
Indicators
Input Format
Indicators
Item Function
Alphanumeric
Display
RMT LED Blue LED flashes when 9083 is receiving control message from remote network control (e.g., DashBoard™
REF LED Blue LED illuminates indicating 9083 is receiving valid reference when set up for framesync operation.
ERR LED Red LED illuminates when 9083 unable to lock to framesync, or unable to lock to input standard.
Input Format
LEDs
Displays 4-digit alphanumeric code indicating status or errors as follows:
• E0XX: Video Errors
• E002: Video Acquiring Lock
• E1XX: Audio Errors
• E100: Analog Input Clipping
• E2XX: Frame Sync Errors
• E200: Reference is Incompatible with Input Video
• E201: Reference Standard is Invalid/No Reference Present
• E202: Reference Standard is 720p2398 (a reference standard not supported by the framesync)
• E203: Reference Standard is 720p2997 (a reference standard not supported by the framesync)
®
or Cobalt
Four blue LEDs indicate the input signal raster format being received and locked onto by the 9083 (1080,
720, 625, 525). Continuous cycling of the LEDs indicates the 9083 has not locked onto a particular format (as
in the case of no signal input).
Remote Control Panel)
Figure 3-8 9083 Card Edge Status Indicators and Display
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-55
Page 98

3 Troubleshooting
DashBoard™ Status/Error Indicators and Displays
Figure 3-9 shows and describes the DashBoard™ status indicators and
displays. These indicator icons and displays show status and error conditions
relating to the 9083 card itself and remote (network) communications.
Indicator Icon or Display Error Description
Red indicator icon in Card Access/Navigation Tree pane shows card with Error
condition (in this example, the Card Access/Navigation Tree pane shows a general
error issued by the 9083 card in slot 6).
Specific errors are displayed in the Card Info pane (in this example “No connection
to device” indicating 9083 card is not connecting to frame/LAN).
If the 9083 card is not connecting to the frame or LAN, all controls are grayed-out (as
shown in the example here).
Gray indicator icon in Card Access/Navigation Tree pane shows card(s) are not
being seen by DashBoard™ due to lack of connection to frame LAN (in this
example, both a 9083 card in slot 6 and the MFC-8320-N Network Controller Card
for its frame in slot 0 are not being seen).
Yellow indicator icon in Card Access/Navigation Tree pane shows card with Alert
condition (in this example, the Card Access/Navigation Tree pane shows a general
alert issued by the MFC-8320-N Network Controller Card).
Clicking the card slot position in the Card Access/Navigation Tree (in this example
Network Controller Card “Slot 0: MFC-8320-N”) opens the Card Info pane for the
selected card. In this example, a “Fan Door Open” specific error is displayed.
Yellow indicator icon in 9083 Card Info pane shows error alert, along with cause for
alert (in this example, the 9083 is receiving no video input, or a video input that is
invalid for the card and/or its current settings).
Where available, error messages within a function submenu pane show highly
specific information relating to detected errors (in this example, message shows an
invalid or missing Framesync Enable reference selection).
Figure 3-9 DashBoard™ Status Indicator Icons and Displays
3-56 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
Page 99

Operating Instructions Troubleshooting
Access Card Info panes for specific cards by clicking the card slot position in
the Card Access/Navigation Tree pane (as shown in the example in Figure
3-10).
By clicking on “Slot 0: MFC-8320-N”
in this example, Card Info is
displayed for frame Network
Controller Card
By clicking on “Slot 6:
CDI-9083 RCVR21” in this
example, Card Info is shown
for 9083 card in slot 6
Status for selected card is
shown here (in this
example, connection OK
and “Fan Door Open”
alert)
Card general information
is displayed in lower
portion of Card Info pane
9083_TS_CARD_INFO_ACCESS_A.PNG
Status for selected
card is shown here
(in this example, all
indications are OK)
Where applicable,
additional status is
displayed (as shown in
this example)
9083_TS_CARD_INFO_ACCESS2A.PNG
Figure 3-10 Selecting Specific Cards for Card Info Status Display
9083-OM (V4.5) 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 3-57
Page 100

3 Troubleshooting
Basic Troubleshooting Checks
Failures of a general nature (affecting many cards and/or functions
simultaneously), or gross inoperability errors are best addressed first by
performing basic checks before proceeding further. Table 3-3 provides basic
system checks that typically locate the source of most general problems. If
required and applicable, perform further troubleshooting in accordance with
the other troubleshooting tables in this section.
Table 3-3 Basic Troubleshooting Checks
Item Checks
Verify pow er presence and
characteristics
Check Cable connection
secureness and connecting
points
Card seating within slots Make certain all cards are properly seated within its frame slot. (It is best to
Check status indicators and
displays
Troubleshoot by
substitution
• On both the frame Network Contro ller Card and t he 9083, in all cases when po wer is
being properly supplied there is always at least one indicator illuminated. Any card
showing no illuminated indicators should be cause for concern.
• Check the Power Consumed indications for both the +12 V and -7.5 V supply rails
for the 9083 card. This can be observed using the DashBoard™ Card Info pane, or
using the card edge controls and indicators as shown in Figure 3-4 on page 3-7.
• If either of the rail supplies show no power being consumed, either the
frame power supply, connections, or the 9083 card itself is defective.
• If either of the rail supplies show excessive power being consumed
(see Technical Specifications (p. 1-21) in Chapter 1, “Introduction”), the
9083 card may be defective.
Make certain all cable connections are fully secure (including coaxial cable
attachment to cable ferrules on BNC connectors). Also, make certain all
connecting points are as intended. Make certain the selected connecting
points correlate to the intended card inputs and/or outputs. Cabling mistakes
are especially easy to make when working with large I/O modules.
assure proper seating by ejecting the card and reseating it again.)
On both DashBoard™ and the 9083 card edge indicators, red indications
signify an error condition. If a status indicator signifies an error, proceed to the
following tables in this section for further action.
All cards within the frame can be hot-swapped, replacing a suspect card or
module with a known-good item.
3-58 9083 PRODUCT MANUAL 9083-OM (V4.5)
 Loading...
Loading...