CMWORKS Lodestar Parts Manual

Operating, Maintenance & Parts Manual
Rated Loads 1/8 To 3 Tonnes
125 Kg To 3000 Kg
®
Follow all instructions and warning for
inspecting, maintaining and operating
this hoist.
The use of any hoist presents some risk of personal injury or
property damage. That risk is greatly increased if proper
instructions and warnings are not followed. Before using this
hoist, each operator should become thoroughly familiar with all
warnings, instructions, and recommendations in this manual.
Retain this manual for future reference and use.
Forward this manual to the hoist operator.
Failure to operate the equipment as directed in the manual
may cause injury.
Before using the hoist, fill in the information below.
Refer to the hoist identification plate.
Model Number
Serial Number
Purchase Date
Voltage
Rated Load
Electric Chain
00001996 (REV AB) 627NH

CM HOIST PARTS AND SERVICES ARE AVAILABLE IN THE UNITED STATES AND IN CANADA
PARTS FOR YOUR HOIST ARE AVAILABLE FROM YOUR LOCAL AUTHORIZED REPAIR STATION. FOR THE NAME
OF THE NEAREST PARTS OR SERVICE CENTER, VISIT OUR WEB SITE WWW.CMWORKS.COM
OR CALL OUR CUSTOMER SERVICE DEPARTMENT.
2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Each Lodestar Electric Hoist is built in accordance with the specifications contained herein and at the time of manufacture complied with our interpretation of applicable sections of the *American Society of Mechanical Engineers Code B30.16 “Overhead
Hoists,” the National Electrical Code (ANSI/NFPA 70) and the Occupational Safety and Health Act. Since OSHA states the National
Electrical Code applies to all electric hoists, installers are required to provide current overload protection and grounding [on the
branch circuit section] in keeping with the code. Check each installation for compliance with the application, operation and maintenance sections of these articles.
The safety laws for elevators, lifting of people and for dumbwaiters specify construction details that are not incorporated into the
hoists. For such applications, refer to the requirements of applicable state and local codes, and the American National Safety
Code for elevators, dumbwaiters, escalators and moving walks (ASME A17.1). Columbus McKinnon Corporation cannot be responsible for applications other than those for which CM equipment is intended.
*Copies of this standard can be obtained from ASME Order Department, 22 Law Drive, Box 2300, Fairfield, NJ 07007-2300, U.S.A.
THIS SYMBOL POINTS OUT IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHICH IF NOT FOLLOWED
COULD ENDANGER THE PERSONAL SAFETY AND/OR PROPERTY OF YOURSELF AND
!
!
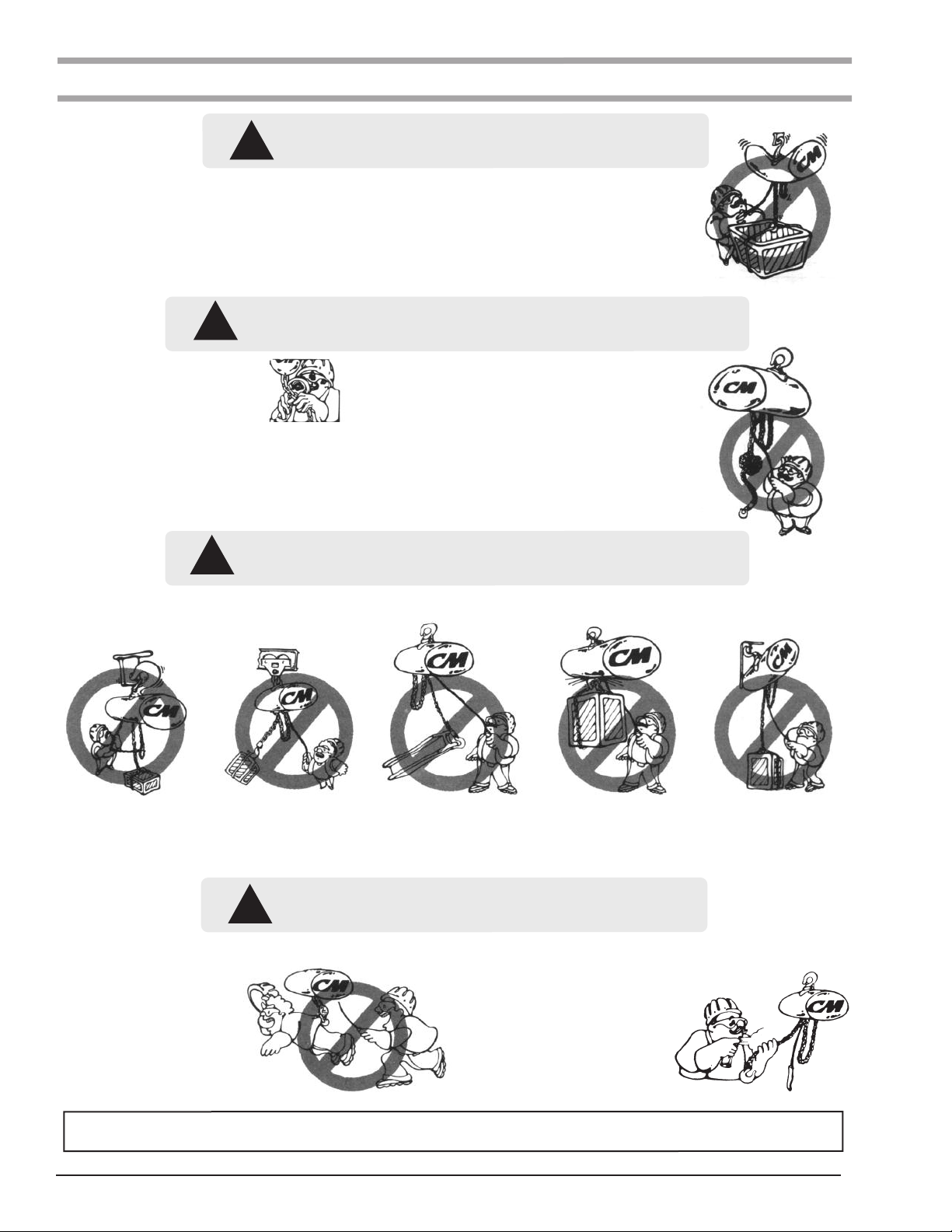
Usage of hoists that do not involve lifting of the load on
the lower hook or using hoists in the inverted position
without special precaution may cause an accident
resulting in injury and/or property damage.
Consult Columbus McKinnon for information concerning
using hoists in these applications.
Improper operation of a hoist can create a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death
tially hazardous situation, the operator shall:
1. NOT operate a damaged, malfunctioning or unusually
performing hoist.
2. NOT operate the hoist until you have thoroughly read and
understood this Operating, Maintenance and Parts Manual.
3. NOT operate a hoist which has been modified.
4. NOT lift more than rated load for the hoist.
5. NOT use hoist with twisted, kinked, damaged, or worn
load chain.
6. NOT use the hoist to lift, support, or transport people.
7. NOT lift loads over people.
8. NOT operate a hoist unless all persons are and remain
clear of the supported load.
9. NOT operate unless load is centered under hoist.
10.NOT attempt to lengthen the load chain or repair dam-
aged load chain.
11.Protect the hoist’s load chain from weld splatter or other
damaging contaminants.
12.NOT operate hoist when it is restricted from forming a
straight line from hook to hook in the direction of loading.
13.NOT use load chain as a sling, or wrap load chain
around load.
14.NOT apply the load to the tip of the hook or to the hook
latch.
15.NOT apply the load unless load chain is properly seated
in the chain wheel(s) or sprocket(s).
16.NOT apply load if bearing prevents equal loading on all
load supporting chains.
17.NOT operate beyond the limits of the load chain travel.
18.NOT leave load supported by the hoist unattended unless specific precautions have been taken.
19.NOT allow the load chain or hook to be used as an electrical or welding ground.
20.NOT allow the load chain or hook to be touched by a live
welding electrode.
OTHERS. READ AND FOLLOW ALL INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL AND ANY PROVIDED
WITH THE EQUIPMENT BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO OPERATE YOUR LODESTAR HOIST.
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
WARNING
!
or serious injury. To avoid such a poten-
21.NOT remove or obscure the warnings on the hoist.
22.NOT operate a hoist on which the safety placards or de-
cals are missing or illegible.
23.NOT operate a hoist unless it has been securely attached
to a suitable support.
24.NOT operate a hoist unless load slings or other approved
single attachments are properly sized and seated in the
hook saddle.
25.Take up slack carefully - make sure load is balanced and
load holding action is secure before continuing.
26.Shut down a hoist that malfunctions or performs unusually
and report such malfunction.
27.Make sure hoist limit switches function properly.
28.Warn personnel of an approaching load.
!
CAUTION
Improper operation of a hoist can create a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury. To avoid such a potentially hazardous situation, the
operator shall:
1. Maintain a firm footing or be otherwise secured when
operating the hoist.
2. Check brake function by tensioning the hoist prior to
each lift operation.
3. Use hook latches. Latches are to retain slings, chains,
etc. under slack conditions only.
4. Make sure the hook latches are closed and not
supporting any parts of the load.
5. Make sure the load is free to move and will clear all
obstructions.
6. Avoid swinging the load or hook.
7. Make sure hook travel is in the same direction as shown
on the controls.
8. Inspect the hoist regularly, replace damaged or worn
parts, and keep appropriate records of maintenance.
9. Use the hoist manufacturer’s recommended parts when
repairing the unit.
10.Lubricate load chain per hoist manufacturer’s
recommendations.
11.NOT use the hoist load limiting or warning device to
measure load.
12.NOT use limit switches as routine operating stops unless
allowed by manufacturer. They are emergency devices
only.
13.NOT allow your attention to be diverted from operating
the hoist.
14.NOT allow the hoist to be subjected to sharp contact with
other hoists, structures, or objects through misuse.
15.NOT adjust or repair the hoist unless qualified to perform
such adjustments or repairs.
!
3
HOIST SAFETY IS UP TO YOU...
1
Know the capacities of your hoists and the
weight of your loads. Then match them.
CHOOSE THE RIGHT HOIST FOR THE JOB...
Choose a hoist with a capacity for the job.
The application, the size and type of load,
!
2
fore use, in addition to regular, periodic
maintenance inspections.
tices and legibility.
to the attention of supervisors. Be sure defective hoists are tagged and taken out of
INSPECT
All hoists should be visually inspected be-
Inspect hoists for operational warning no-
Deficiencies should be noted and brought
!
WARNING
!
the attachments to be used and the period of
use must also be taken into consideration in
selecting the right hoist for the job.
Remember the hoist was designed to ease
WARNING
service until repairs are made.
Under no circumstances should you oper-
ate a malfunctioning hoist.
Check chain for gouged, twisted, distorted
links and foreign material. Do not operate
hoists with twisted, kinked or damaged chain.
Load chain should be properly lubricated.
Hooks that are bent, worn or whose open-
WARNING
– DO NOT LIFT MORE THAN RATED LOAD.
our burden and carelessness not only endangers the operator, but in many cases, a
valuable load.
– DO NOT OPERATE DAMAGED OR MALFUNCTIONING HOIST.
– DO NOT OPERATE WITH TWISTED, KINKED OR DAMAGED
CHAIN.
ings are enlarged beyond normal throat
opening should not be used. If latch does
not engage throat opening of hook, hoist
should be taken out service.
Check for misphasing – hook travel should
correspond to control direction.
– DO NOT PULL AT AN ANGLE. BE SURE HOIST AND LOAD
ARE IN A STRAIGHT LINE.
– DO NOT USE LOAD CHAIN AS A SLING.
3 USE HOIST PROPERLY
Be sure hoist is solidly held in the
uppermost part of the support
hook arc.
Be sure hoist and load are in a
straight line. Do not pull at an
angle.
!
4 LIFT PROPERLY
Do not lift co-workers with a hoist.
Make sure everyone is clear of the load
when you lift.
Do not remove or obscure operational
warning notices.
Be sure load is hooked securely.
Do not tip load the hook. Do not
load hook latch. Hook latch is to
prevent detachment of load under
slack chain conditions only.
WARNING
Do not use load chain as a sling.
Such usage damages the chain
and lower hook.
– DO NOT LIFT PEOPLE OR LOADS
OVER PEOPLE.
5
and free of dust, dirt, moisture, etc., which
will in any way affect the operation or
safety of the equipment.
lubricated.
hoist before returning it to full service.
MAINTAIN PROPERLY
CLEANING: Hoists should be kept clean
LUBRICATION: Chain should be properly
AFTER REPAIRS: Carefully operate the
Do not operate with hoist head
resting against any object. Lift the
load gently. Do not jerk it.
VIOLATION OF ANY OF THESE WARNINGS LISTED MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY TO THE OPERATOR OR NEARBY PERSONNEL BY RELEASED LOAD OR BROKEN HOIST COMPONENTS.
4

FOREWORD
This manual contains important information to help you properly install, operate and maintain your hoist for maximum performance,
economy and safety.
Please study its contents thoroughly before putting your hoist into operation. By practicing correct operating procedures and by
carrying out the recommended preventive maintenance suggestions, you will experience long, dependable and safe service.
After you have completely familiarized yourself with the contents of this manual, we recommend that you carefully file it for future
reference.
The information herein is directed to the proper use, care and maintenance of the hoist and does not comprise a handbook on the
broad subject of rigging.
Rigging can be defined as the process of lifting and moving heavy loads using hoists and other mechanical equipment. Skill acquired
through specialized experience and study is essential to safe rigging operations. For rigging information, we recommend consulting
a standard textbook on the subject.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Foreword . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
General Information
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
CM Repair/Replacement policy . . . . . . .(Back Page)
Accessories
Hook Suspensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Lug Suspension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Series 635 Motor Driven Trolley . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Latchlok Hooks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Chain Container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Installation
Unpacking Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Installing Suspension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-11
Recommended Torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Attaching Load Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Installing Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley . . . . .12-13
Power Supply and Electrical Connections . . . . . . . . . .14
Operating Instructions
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Operating Instruction-Hoist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
Safety Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Inspection
Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Frequent Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18-19
Periodic Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18-19
Preventative Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Hook Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Load Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Maintenance
Load-limiter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Hoist Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Trolley Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Adjustments
Electric Brake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Limit Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23-24
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25-27
Electrical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28-29
Typical Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30-72
Assembly Instructions
Hook or Lug Suspensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Lower Hook Block Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Removal and Installation of Load Chain . . . . . .73-74
Cutting Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Ordering Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76-137
Lubricants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
Recommended Spare Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .139
LIST OF TABLES
Table Title Page
1 Lodestar Electric Chain Hoist Specs. . . . . . 6-8
2 Recommended Torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3 Series 635 Trolley Side Frame Spacing . . . . .13
4 Minimum Frequent Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . .19
5 Minimum Periodic Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . .19
6 Limit Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
7 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25-27
8 Electrical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28-29
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure Table Page
1 Hook Suspensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
2 Lug Suspensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3 Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley . . . . . . . . . .9
4 Series 635 Motor Driven Trolley . . . . . . . . . . . .9
5 Upper or Lower Latchlok Hook . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
6 Chain Container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
7 Attaching Load Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
8 Contact Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
9 Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley . . . . . . . . .12
10 1/8 to 2 Ton Hoist to Trolley Assembly . . . . . .13
11 3 Ton Hoist to Trolley Assembly . . . . . . . . . . .13
12 Voltage Change Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
13 Locations of Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
14 Hook Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
15 Chain Wear areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
16 Gaging Load Chain Wear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
17 Chain Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
18 Limit Switches Models, V1 Models . . . . . . . . .23
18A Rotatable Limit Switches, V1 Models . . . . . . . . .23
19 Limit Switches, V2 Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
19A Rotatable Limit Switch, V2 Models . . . . . . . . .23
20 Typical Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30-72
21 Swivel Hook Suspensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
22 Chain Embossing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
23A Cutting Chain By Nicking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
23B Cutting Chain With A Bolt Cutter . . . . . . . . . . .75
5
GENERAL INFORMATION
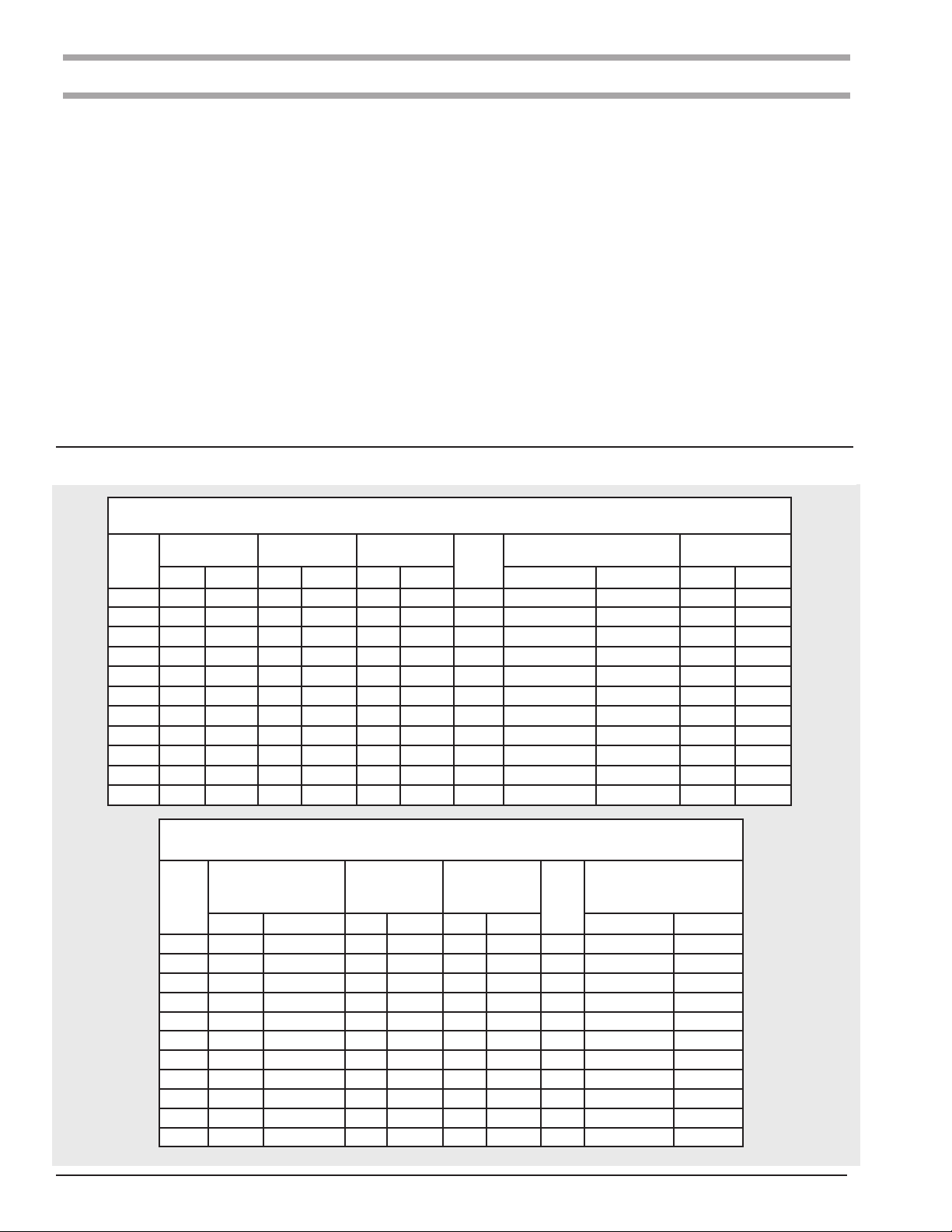
SPECIFICATIONS
The Lodestar Electric Chain Hoist is a highly versatile materials
handling device that can be used to lift loads that are within
rated capacity. The mechanical features of these hoists include
an alloy steel lift wheel, Load Limiter, hardened steel chain
guides, hardened steel gear train, life-time lubrication, forged
steel hooks and lightweight aluminum frame. The electrical features
include hoist-duty motor, rugged hoist brake, magnetic reversing
contactor and voltage conversion board (dual voltage units).
The hoist is available with hook or lug suspensions that are
supplied separately. Table 1 summarizes the Lodestar Electric
Chain Hoist models and the Series 635 Trolleys available. It should
be noted that standard single speed hoists are available with
10 (3M), 15 (4.6M) and 20 (6.1M) foot lifts and the standard lift
for two speeds hoists is10 feet. However, hoists with longer lifts
are available on a special, per order basis.
Table 1.a. Specifications
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Single Speed 115-1-60
Model
Load Capacity
Tonne kg ft/min m/min ft/min m/min in x in mm x mm lb/ft kg/m
A 1/8 125 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
AA 1/8 125 60 18.3 50.0 15.2 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
B 1/4 250 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
C 1/4 250 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
E 1/2 500 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
F 1/2 500 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
J 1/2 500 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.585 0.87
H 1 1000 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
L 1 1000 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
R 2 2000 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
RT 3 3000 5.3 1.6 4.4 1.4 3 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 2.82 4.20
Lifting Speed
60Hz units
Lifting Speed
50Hz units
CM REPAIR/REPLACEMENT POLICY
All Columbus McKinnon (CM®) Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
are i nspe c t e d an d per f o r m ance t este d prio r to
shipment. If any properly maintained hoist develops a
performance problem due to a material or workmanship
defect, as verified by CM®, repair or replacement of the unit
will be made to the original purchaser without charge. This
repair/replacement policy applies only to Lodestar Hoists
installed, maintained and operated as outlined in this
manual, and specifically excludes parts subject to normal
wear, abuse, improper installation, improper or inadequate
maintenance, hostile environmental effects and unauthorized
repairs/modifications.
We reserve the right to change materials or design if, in our
opinion, such changes will improve our product. Abuse,
repair by an unauthorized person, or use of non-CM replacement parts voids the guarantee and could lead to dangerous
operation. For full Terms of Sale, see Sales Order Acknowledgement. Also, refer to the back cover for Limitations of
Warranties, Remedies and Damages, and Indemnification
and Safe Operation.
Chain
Falls
Chain Size
Chain Weight
per length of lift
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Single Speed 115-1-60
Model
Shortest Distance
Between Hooks
in mm HP kW HP kW lb kg
A 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 72 32.8
AA 19.9 505 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 76 34.3
B 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 73 33.1
C 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 75 34.2
E 21.6 549 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 78 31.8
F 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 76 34.5
J 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 127 57.5
H 21.6 549 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 81 36.7
L 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 125 56.7
R 25.8 655 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 148 67.1
RT 32.1 815 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 166 75.4
Motor Power
60Hz
Motor Power
50Hz
IP
Rating
Net Weight 10’ lift less
upper suspension
6
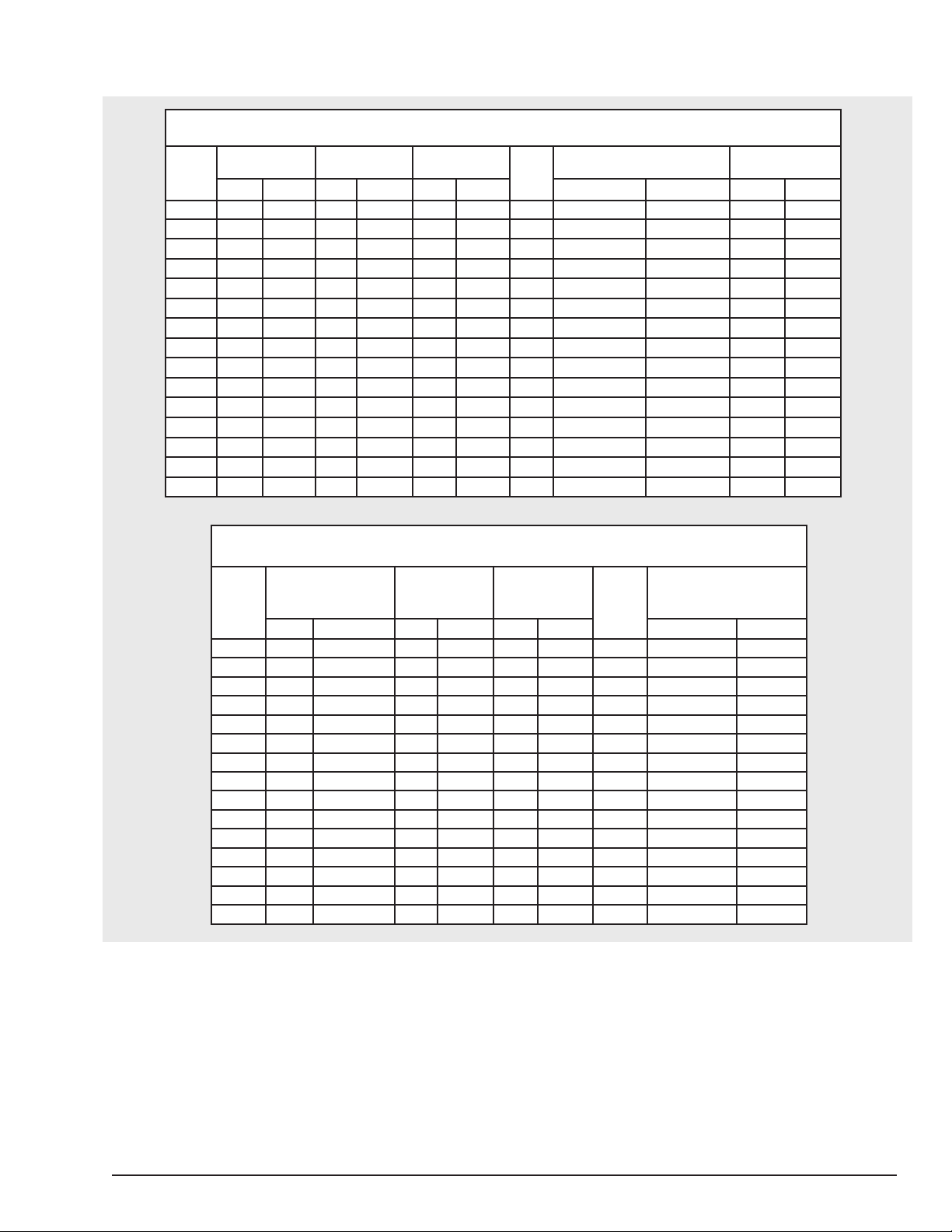
Table 1.b.Specifications, cont’d
Single Speed 230/460-3-60 or 220/380-3-50 or 220/415-3-50
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Model
Load Capacity
Tonne kg ft/min m/min ft/min m/min in x in mm x mm lb/ft kg/m
A 1/8 125 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
AA 1/8 125 60 18.3 50.0 15.2 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
B 1/4 250 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
C 1/4 250 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
E 1/2 500 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
F 1/2 500 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
J 1/2 500 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.585 0.87
JJ 1/2 500 64 19.5 53.3 16.3 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
H 1 1000 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
L 1 1000 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
LL 1 1000 32 9.8 26.7 8.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
R 2 2000 8 2.4 6.7 2.0 2 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
RR 2 2000 16 4.9 13.3 4.1 2 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
RT 3 3000 5.3 1.6 4.4 1.4 3 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 2.82 4.20
RRT 3 3000 10.7 3.3 8.9 2.7 3 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
Lifting Speed
60 Hz units
Lifting Speed
50Hz units
Chain
Falls
Chain Size
Chain Weight
per length of lift
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Single Speed 230/460-3-60 or 220/380-3-50 or 220/415-3-50
Model
Shortest Distance
Between Hooks
Motor Power
60Hz
Motor Power
50Hz
IP
Rating
Net Weight 10’ lift less
upper suspension
in mm HP kW HP kW lb kg
A 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 70 31.9
AA 19.9 505 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 73 32.9
B 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 71 32.2
C 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 72 32.8
E 21.6 549 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 76 30.9
F 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 73 33.1
J 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 121 54.7
JJ 18.1 460 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 127 57.5
H 21.6 549 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 78 35.4
L 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 119 53.9
LL 18.1 460 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 127 57.6
R 25.8 655 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 142 64.4
RR 25.8 655 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 150 68.0
RT 32.1 815 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 160 72.7
RRT 32.1 815 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 173 78.4
7
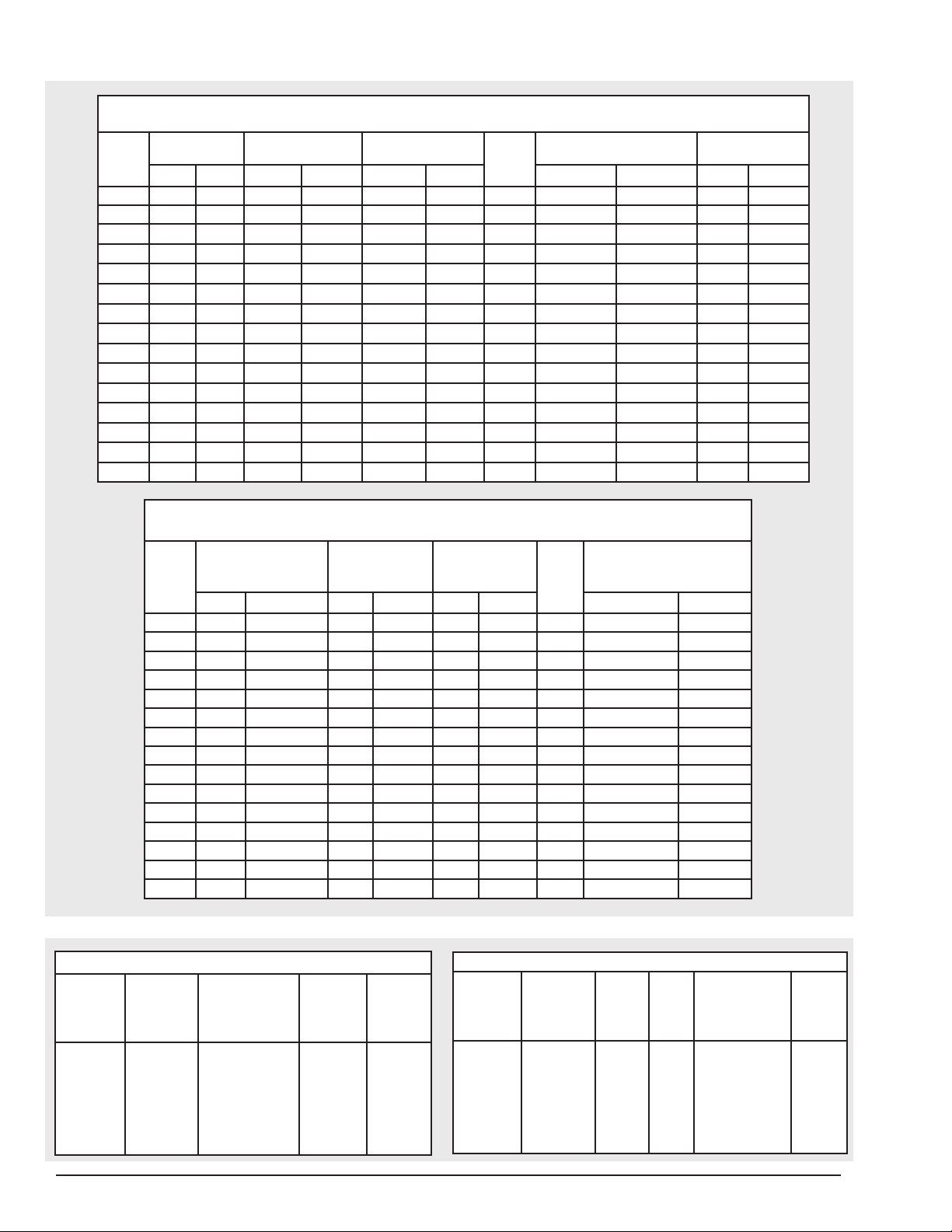
Table 1.c. Specifications, cont’d
Two Speed 230-3-60 or 460-3-60 or 575-3-60 or 220-3-50 or 380-3-50 or 415-3-50 or 550-3-50
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Model
Load Capacity
Tonne kg ft/min m/min ft/min m/min in x in mm x mm lb/ft kg/m
A-2 1/8 125 10.7/32 3.3/9.8 8.9/26.7 2.7/8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
AA-2 1/8 125 20/60 6.1/18.3 16.7/50 5.1/15.2 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
B-2 1/4 250 5.3/16 1.6/4.9 4.4/13.3 1.4/4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
C-2 1/4 250 10.7/32 3.3/9.8 8.9/26.7 2.7/8.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
E-2 1/2 500 2.7/8 0.8/2.4 2.2/6.7 0.7/2 2 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
F-2 1/2 500 5.3/16 1.6/4.9 4.4/13.3 1.4/4.1 1 .250 x .7445 6.35 x 18.9 0.585 0.87
J-2 1/2 500 10.7/32 3.3/9.8 8.9/26.7 2.7/8.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.585 0.87
JJ-2 1/2 500 21.3/64 6.5/19.5 17.8/53.3 5.4/16.3 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
H-2 1 1000 2.7/8 0.8/2.4 2.2/6.7 0.7/2 2
L-2 1 1000 5.3/16 1.6/4.9 4.4/13.3 1.4/4.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
LL-2 1 1000 10.7/32 3.3/9.8 8.9/26.7 2.7/8.1 1 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 0.94 1.40
R-2 2 2000 2.7/8 0.8/2.4 2.2/6.7 0.7/2 2 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
RR-2 2 2000 5.3/16 1.6/4.9 4.4/13.3 1.4/4.1 2 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
RT-2 3 3000 1.8/5.3 0.5/1.6 1.5/4.4 0.5/1.4 3 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 2.82 4.20
RRT-2 3 3000 3.6/10.7 1.1/3.3 3/8.9 0.9/2.7 3 .312 x .8583 7.92 x 21.8 1.88 2.80
Lifting Speed
60Hz units
Lifting Speed
50Hz units
Chain
Falls
Chain Size
.250 x .7445
Chain Weight
per length of lift
6.35 x 18.9 1.17 1.74
Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists
Two Speed 230-3-60 or 460-3-60 or 575-3-60 or 220-3-50 or 380-3-50 or 415-3-50 or 550-3-50
Capacity
Tons
(kg)
Model
Shortest Distance
Between Hooks
Motor Power
60Hz
Motor Power
50Hz
IP
Rating
Net Weight 10’ lift less
upper suspension
in mm HP kW HP kW lb kg
A-2 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 76 34.6
AA-2 19.9 505 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 78 35.2
B-2 16.9 429 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 77 34.9
C-2 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 77 35.1
E-2 21.6 549 0.25 0.19 0.21 0.16 54 82 33.6
F-2 16.9 429 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 78 35.4
J-2 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 133 60.2
JJ-2 18.1 460 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 135 61.1
H-2 21.6 549 0.50 0.37 0.42 0.31 54 83 37.6
L-2 18.1 460 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 131 59.4
LL-2 18.1 460 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 135 57.6
R-2 25.8 655 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 154 61.2
RR-2 25.8 655 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 158 69.8
RT-2 32.1 815 1.00 0.75 0.83 0.62 54 172 71.6
RRT-2 32.1 815 2.00 1.49 1.67 1.24 54 181 82.1
Table 1.d. Specifications, cont’d
Series 635 Low Headroom Trolleys
For Use
With
Models
Adj. For
STD
S-Beams
Depth In. (mm)
Tread
Dia. of
Wheels
In. (mm)
Min. Rad.
Curve
In. (mm)
Capacity
Tons
(kg)
Table 1.e. Specifications, cont’d
Series 635 Motor Driven Trolleys
For Use
With
Models
*Travel
Speed
FPM
(MPM)
Motor
H.P.
(kW)
Adj. For
STD
S-Beams
Depth In.(mm)
Min.
Rad.
Curve
In.(mm)
= to 1
(125 to 2000)
2 (2000)
3 (3000)
8
A thru LL-2
R thru RR-2
RT thru RRT-2
4 - 15 (102 - 381)
6 - 18 (152 - 457)
8 - 15 (203 - 381)
3= (79.4)
4< (120.6)
4 (101.6)
24 (610)
24 (610)
30 (762)
= to 2
(125 to 2000)
3 (3000)
A thru RR-2
RT thru RRT-2
75 (23)
75 (23)
; (.19)
; (.19)
6 - 15 (152 - 381)
6 - 15 (152 - 381)
30 (762)
30 (762)

ACCESSORIES
Hook Suspensions
Swivel and rigid type hook suspensions (see Figure 1) are
available for all Lodestar Electric Hoists. However, rigid type
hook suspensions are normally recommended for most application. The hook suspensions are intended for suspending
the hoist from a trolley which has a single load bar (such as
®
CM’s
Series 632 and 633 Trolleys) or for suspending the
hoist from a fixed structure.
Figure 1. Hook Suspensions
Lug Suspension
Lug suspensions (see Figure 2) are available for all Lodestar
Electric Hoists. These are rigid type suspensions wherein the
lug shown replaces the hook (Figure 1) in the suspension
adapter. The Lug suspensions are required for suspending
the hoist from the Series 635 Low Headroom and Motor
Driven Trolleys described next.
Figure 4. Series 635 Motor Driven Trolley
Series 635 Motor Driven Trolley
The motor driven trolleys (see Figure 4) are self-contained
and supplied complete with independent controls and wiring,
including a four directional control station. A rigid lug suspension
(see Figure 2) is required to suspend the hoist from the Motor
Driven Trolley. The hoist and trolley are joined electrically by
connecting the hoist control and power cords (supplied) into
the hoist or trolley. The trolley is adjustable for operation on a
range of American Standard “S” beams as indicated in Table
1 and it will also operate on flat flanged beams.
Latchlok
®
Hooks
CM’s Latchlok hooks (see Figure 5) are available to replace
the standard upper and lower hooks used on the Lodestar
Electric Hoists.
Figure 2. Lug Suspensions
Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley
These are manual push type trolleys (see Figure 3) designed
for use with the Lodestar Electric Chain Hoists. A rigid lug
suspension (see Figure 2) is required to suspend the hoist
from the trolley. The trolley is adjustable for operation on a
range of American Standard “S” beams as indicated in
Table 1, and it will also operate on flat flanged beams.
Figure 3. Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley
Figure 5. Upper or Lower Latchlok®Hook
Figure 5. Latchlok
®
Hook
Chain Container
This accessory (see Figure 6) is used to hold slack chain
and it is supplied complete with mounting hardware and
instructions. The chain container is recommended for those
applications where the slack chain would interfere with the
load or drag on the floor as may be the case with double or
triple reeved units. Chain containers can be furnished for
units already in use.
Figure 6. Chain Container
9
INSTALLATION
UNPACKING INFORMATION
When received, the hoist should be carefully inspected for
damage which may have occurred during shipment or handling. Check the hoist frame for dents or cracks, the external
cords for damaged or cut insulation, the control station for cut
or damaged enclosure, and inspect the load chain for nicks
and gouges. If shipping damage has occurred, refer to the
packing list envelope on the carton for claim procedure.
Before installing the hoist, make sure that the power supply to
which it will be connected is the same as that shown on the
nameplate located on the side of the hoist.
NOTE: See Electrical Installation instructions
INSTALLING THE SUSPENSION
A. Single Reeved Units:
Remove the hook suspension and (2) suspension screws
from the packaging. Place the suspension assembly into the
recess on top of the hoist so that the adaptor body follows the
contour of the hoist. Insert the suspension screws through
the holes in the adapter and hand thread these into the selflocking nuts enclosed in the hoist. .
CAUTION
!
USE OF IMPACT TOOLS (ELECTRIC OR PNEUMATIC)
MAY CAUSE PREMATURE FAILURE OF ATTACHING
HARDWARE.
Securely tighten the screws to the recommended seating
torque (see Table 2) using a 12 point socket: 3/8" for Models A, B,
C, & F and 1/2 " for Models J-LL.
B. Double Reeved Units:
Remove the hook suspension,(2) suspension screws, (1) dead
end pin, (1) washer, and (1) cotter pin from the packaging. It
should be noted that the suspension includes a dead end bolt
and block for supporting the dead end of the load chain as
shown in Figure 7.
Place the suspension assembly into the recess on top of the
hoist. The dead end block should project through the bottom
of the hoist with the pin hole and slot aligned to the underside
of the hoist as shown in Figure 7. If these are not aligned as
shown, lift the head of the bolt from the hex recess in the
adapter and turn the bolt and block assembly and reseat the
bolt head to obtain the proper alignment. Do not change the
position of the dead end block on the bolt to attain this alignment.
Check the position of the pin hole in the dead end block to
make sure it has not been disturbed from its factory setting.
The distance from the top of the pin hole to the bottom of the
hoist should not exceed 1/4" (6.35mm) for Models E,E-2, H,
H-2 and 7/16" (11.11mm) for Models R, R-2, RR, RR-2. If the
distance is not correct, adjust the position of the dead end
block to obtain the proper distance (see fig. 21, p 73.)
enclosed in the hoist frame. Securely tighten the screws to
the recommended seating torque (see Table 2) using a 12
point socket: 3/8" for Models E & H and 1/2" for Models R & RR.
The dead end of the load chain is temporarily positioned
( a few links from the end) by a wire tie. Do not remove this tie
before attaching the chain to the dead end block. (See Fig. 7)
C. Triple Reeved Units:
These hoists have a sheave hanger which is loosely
connected to the top of the frame by a thin metal plate for
shipping purposes. To attach the suspension, support the
sheave hanger from the underside of the hoist and remove
the nut and seat from the sheave stud. Remove and discard
the shipping plate and retain the sheave stud nut and seat
since they will be reused later.
Remove the suspension assembly from the carton and the
two suspension screws. Place the suspension assembly over
the sheave stud and into the recess on top of the hoist.
Insert the suspension screws through the holes in the
suspension adapter and hand thread these into the selflocking nut enclosed in the hoist. Securely tighten the screws
to the recommended seating torque (see Table 2) using a 12
point, 1/2" socket.
After the suspension assembly is installed, secure the sheave
stud to the suspension adapter using the round slotted nut
and seat that were formerly used to attach the shipping plate
to top of the hoist frame. Place the seat over the stud with the
flat side down and then rotate the seat so that there is
clearance between the seat and the suspension lug or hook.
Assemble the nut to the stud and turn the nut by hand until
the nut seats in the seat and the sheave hanger is snug in the
frame. Then back off the nut until the hole in the stud is in line
with one of the slots in the nut. Using a hammer, drive the
retaining pin (packed with the suspension assembly) into the
hole in the sheave stud until the end of the pin is flush with
the edge of the nut.
WARNING
!
Using other than CM supplied high strength suspension
screws to attach the suspension adapter to the hoist may
cause the screws to break and allow the hoist and load to fall.
Use only the CM supplied suspension screws to attach the
suspension to the hoist and hand torque these screws to
the recommended seating torque as specified in tables 2a
and 2b.
DO NOT apply any type of lubricant to the threads of these
screws. Lubricating the threads will reduce the effort to seat
the screws and as a result, tightening the screws to the
above recommended torque may break the screw,damage
the suspension adapter, strip the nuts and/or damage the
hoist frame.
TO AVOID INJURY:
Now, insert the suspension screws through the holes in the
adapter and hand thread these into the self-locking nuts
10
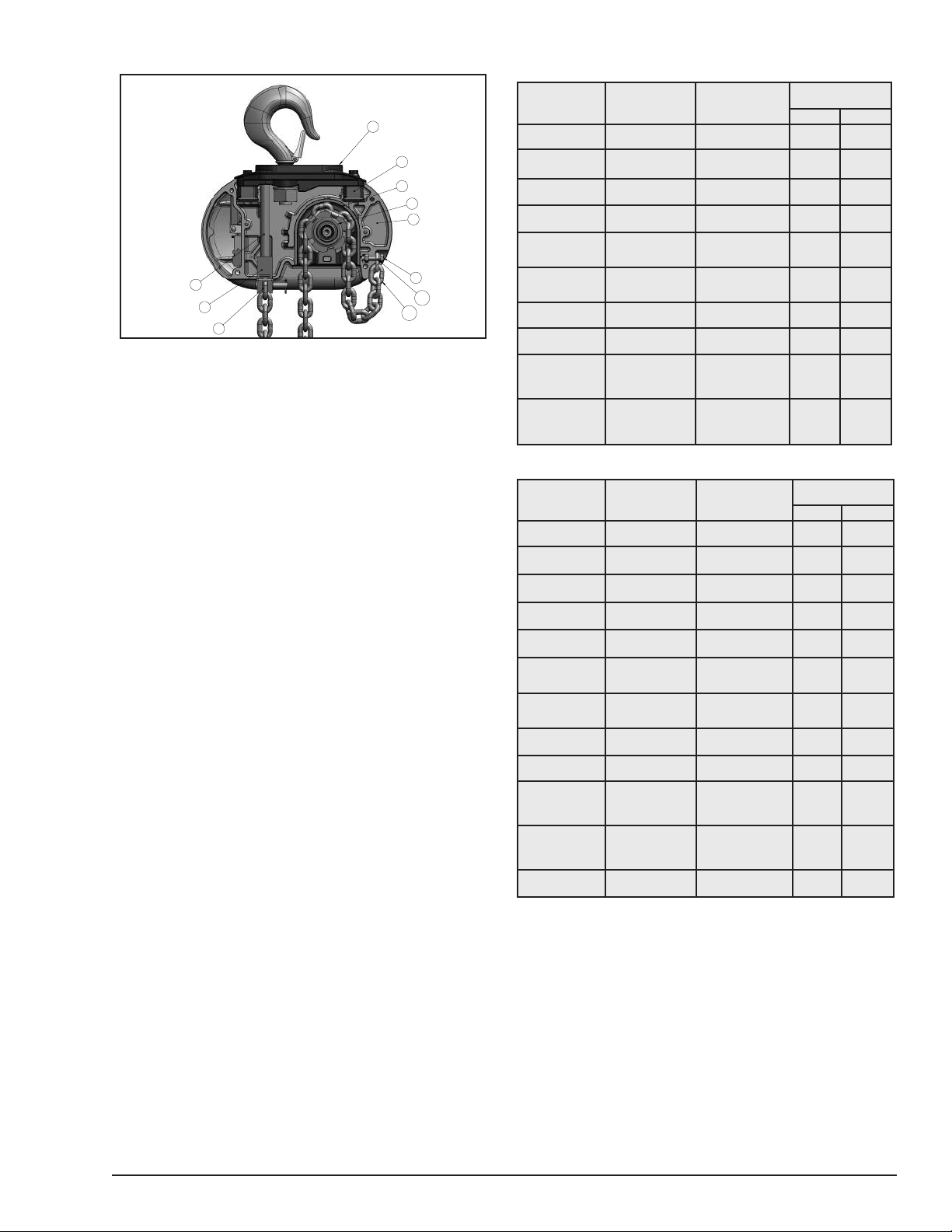
Figure 7. Attaching Load Chain Double Reeved Models
1. Dead end block 7. Lift-wheel
2. Suspension assembly 8. Motor housing
3. Suspension self-locking nut 9. Loose end screw
4. Dead end bolt 10. Loose end link
5. Dead end link 11. Loose end
6. Chain guide
(Do not order parts by these numbers. See parts list)
Table 2.a. Recommended Torques: V1 Models A-H
*Recommended
Fastener
Brake End
cover
Motor End
cover
Brake Attaching
Screw
s
Power Cord
Strain Relief Nut
Motor Housing/
Gear Housing/
Back Frame
Lower Hook Block
Screws -
Doubled Reeved
Suspension
Adapter Screws
Lift-Wheel
Locking Nut 1"-12 Hex Nut
Reversing
Contactor
Connecting
Screws-1ø
Reversing
Contactor
Connecting
Screws-3ø
Fastener
Description Tool Required
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/4-20 Hex Nut
1/4"-20 Socket Head
Cap Screw
1/4"-20 Socket Head
Cap Screw
3/8"-16-12
Point Cap Screw
Terminal
Clamp
Screw
Terminal
Clamp
Screw
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
7/16" - 6 or 12
Point Socket
3/16" Hex Driver 7.9 - 8.3 10.7 - 11.3
3/16" Hex Driver 5.0 - 5.8 6.8 - 7.9
3/8 "
12 Point Socket
1-1/2" - 6 or 12
Point Socket
Phillips No.2 or
3/16" Slotted Head
Screw Driver
Phillips No.2 or
3/16" Slotted Head
Screw Driver
Seating Torque
ft-lbf N-m
4.0 - 5.0 5.4 - 6.8
4.0 - 5.0 5.4 - 6.8
4.2 - 5.0 5.6 - 6.8
1.7 - 2.0 2.3 - 2.7
35.0 - 45.0 47.5 - 61.0
55.0 - 60.0 74.6 - 81.3
0.6 - 1.0 0.8 - 1.3
0.6 - 1.0 0.8 - 1.3
Table 2.b. Recommended Torques: V2 Models J-RRT
*Recommended
Fastener
Brake End
cover
Motor End
cover
Brake Attaching
s
Screw
Brake Hex Stud
Power Cord
Strain Relief Nut
Motor Housing/
Gear Housing/
Back Frame
Lower Hook Block
Screws -
Doubled Reeved
Suspension
Adapter Screws
Lift-Wheel
Locking Nut 1-1/8"-12 Hex Nut
Reversing
Contactor
Connecting
Screws-1ø
Reversing
Contactor
Connecting
Screws-3ø
Stator Mounting
Screws
Fastener
Description Tool Required
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/4-20 Slotted Fillister
Head Screw
1/2" Hex w/ 5/16 -18
Threaded End
1/4-20 Slotted Rd.
Head Screw
5/16"-18 Socket Head
Cap Screw
5/16"-18 Socket Head
Cap Screw
1/2"-20-12
Point Cap Screw
Terminal
Clamp
Screw
Terminal
Clamp
Screw
1/4"- 20 Hex Cap
Screw
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
1/2" Open-End
Wrench
Slotted Blade
Screw Driver
1/4" Hex Driver 14.2 - 15.0 19.2 - 20.3
1/4" Hex Driver 10.0 - 11.3 13.6 - 15.3
1/2 "
12 Point Socket
1-11/16" - 6 or 12
Point Socket
Phillips No.2
Phillips No.2 or
3/16" Slotted Head
Screw Driver
7/16" - 6 or 12
Point Socket
Seating Torque
ft-lbf N-m
4.0 - 5.0 5.4 - 6.8
4.0 - 5.0 5.4 - 6.8
4.2 - 5.0 5.6 - 6.8
4.2 - 5.0 5.6 - 6.8
1.7 - 2.0 2.3 - 2.7
70.0 - 80.0 94.9 -108.5
85.0 - 90.0 115 .2 -1 2 2.0
1.3 1.7
0.6 - 1.0 0.8 - 1.3
4.2 - 5.0 5.8 - 6.8
* All torque values are for clean, dry fasteners. DO NOT apply oil or any other
lubricant to the fastner threads.
11
ATTACHING LOAD CHAIN
To attach the chain to the dead end block on Models E, E-2,
H, H-2, R, R-2 and RR-2, proceed as follows:
1. Suspend the hoist from an adequate support.
2. On Models E, E-2, H and H-2, insert the last link of the
load chain into the dead end block (2) and secure it with
the dead end pin, washer and cotter pin furnished with
the suspension. Ensure there are no twists in the chain.
3. On Models R, R-2, RR and RR-2, slide the contact block
up the chain until it is against the bottom of the hoist and
the dead end block is projecting through the square
opening in the bottom of the block. Insert the last link of the
load chain, making sure there are no twists between the
hook block and the dead end block, into the dead end
block. Push the contact block up slightly and secure the
load chain to the dead end block using the dead end pin,
washer and cotter pin furnished with the suspension. The
dead end pin also supports the contact block (See Figure 8)
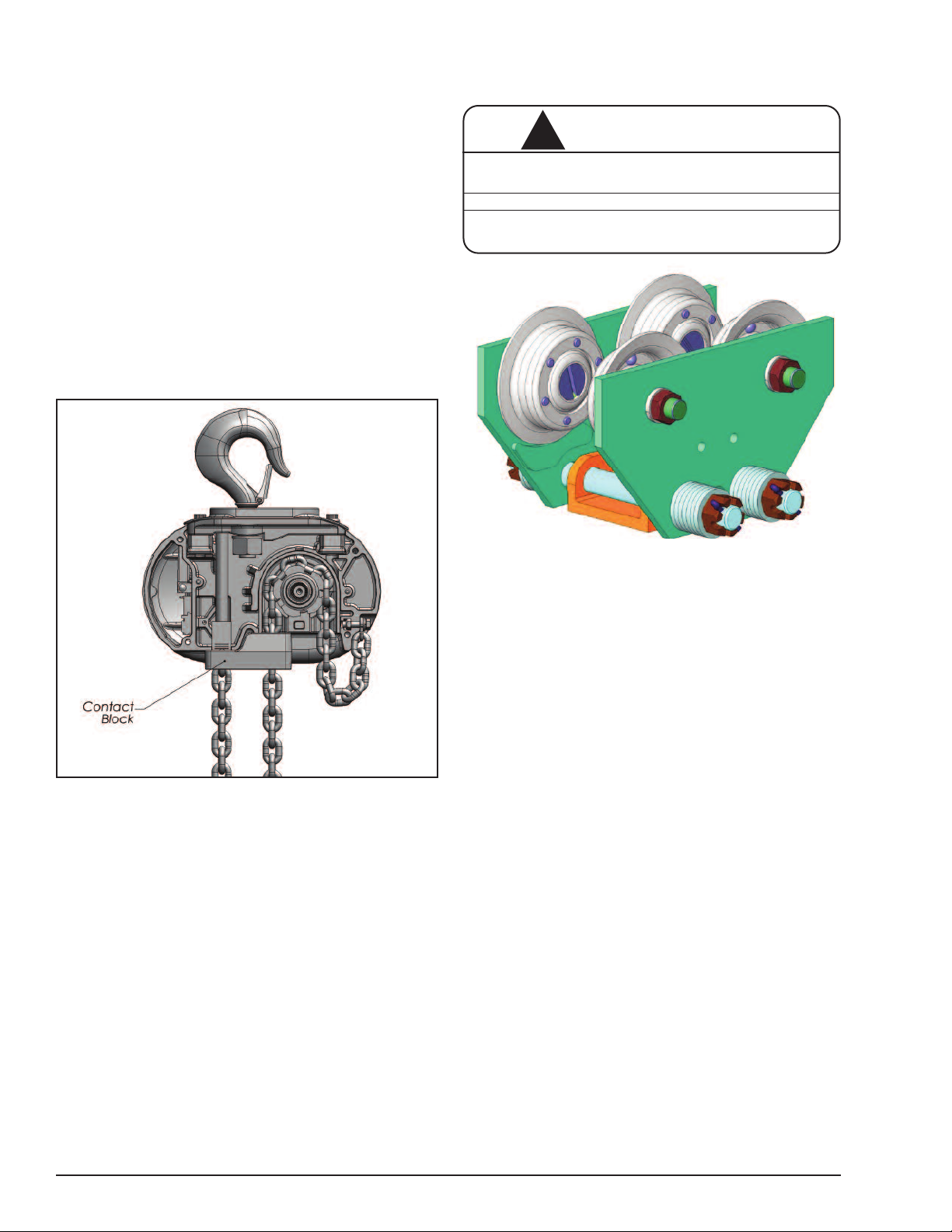
INSTALLING THE SERIES 635 LOW HEADROOM
TROLLEY (See Figure 9)
!
Operating the trolley on a beam that has no rail stops may
allow the trolley to fall off the end of beam.
Install rail stops at each end of the beam on which the trolley
.
is to operate.
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
Figure 8. Contact Block Used on Models R, R-2, RR and RR-2
4. Do not remove the plastic ties from the load chain at this
time.
After the suspension is installed, hoists with a hook suspension can be suspended from its permanent support and then
connected to the power supply system (refer to page 14). For
hoists with a lug suspension that are to be suspended from a
Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley, attach the hoist to the trolley
per the following instructions.
Figure 9. Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley: 1 and 2 Ton (1000 and 2000 kg)
Trolley Shown - 3 Ton (3000 kg) Similar.
For hoists with a lug suspension that are to be suspended
from a Series 635 Motor Driven Trolley, attach the hoist to the
trolley, wire the hoist and trolley together and connect the
trolley to the power supply system per the instructions supplied with the trolley.
The stops must be positioned so as to not exert impact force
on the hoist frame or trolley wheels. They must contact the
ends of the trolley side frames.
It is recommended that the trolley be mounted on the beam
prior to attaching the hoist to the trolley. Before attempting
to mount the trolley on the beam, measure the actual width
of the beam flange on which the trolley is to operate. Using
the measurement and Table 3, determine the arrangement of
the spacer washers. Loosely assemble the side frames, load
bracket, spacer washers and nuts on the suspension bolts as
shown in Table 3.
12

Table 3. Series 635 Low Headroom Trolley Side Frame Spacing
Standard Load Bracket
3 7/16” Wide
“X”
Side
Frame
Suspension
Bolt
A
B
Load
Bracket
!
If CM’s washer spacing recommendations are not followed, trolley
may fall from beam.
Measure the actual beam flange on which the trolley is to operate
and use Table 3 to determine the arrangement of the spacer wash-
ers for that flange width.
C
D
Suspenison
Bolt Nuts
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
1 Ton Capacity
Flange
Width
2 5/8 10 0 0 10
3 3/8 8 2 2 8
3 5/8 7 3 3 7
4 5/8 4 6 6 4
5 1/4 2 8 8 2
5 5/8 1 9 9 1
Flange
Width
6 1/4 5 6 6 4
No. of Spacers
A B C D
3 9 1 1 9
4 6 4 4 6
5 3 7 7 3
Standard Load Bracket
5 7/16” Wide
1 Ton Capacity
No. of Spacers
A B C D
6 6 5 5 5
7 2 9 9 1
*Dimension applies to minimum S-Beam and will vary with larger S-Beams..
Note: Due to the variations in beam flange widths,
it is suggested that the beam flange width be measured to determine the exact distribution of spacer
washers. The distance between trackwheel flanges
(dimension “X”) should be 1/8 to 3/16 inch (3.18 to
4.77 mm) greater than the beam flange width for
straight runway beams, and 3/16 to 1/4 inch (4.77 to
6.35 mm) greater than the beam flange width if runway system includes sharp curves. Also, the use of
other than CM supplied washers may result in trackwheel to beam flange variations and thus Table 3
will not apply.
Standard Load Bracket
4 3/16” Wide
2 Ton Capacity
Flange
Width
3 3/8 8 0 0 8
3 5/8 7 1 1 7
4 5/8 4 4 4 4
5 1/4 3 5 6 2
5 5/8 2 6 7 1
Flange
Width
6 1/4 8 2 1 8
7 1/8 5 5 5 4
7 1/4 4 6 5 5
7 7/8 2 8 8 1
No. of Spacers
A B C D
4 6 2 2 6
5 3 5 5 3
6 0 8 8 0
Standard Load Bracket
6 11/16” Wide
2 Ton Capacity
No. of Spacers
A B C D
7 5 5 4 5
8 1 9 8 1
Standard Load Bracket
4 13/16” Wide
3 Ton Capacity
Flange
Width
4 5/8 5 3 3 4
5 1/4 3 5 5 2
5 5/8 3 5 6 1
Flange
Width
6 1/4 6 3 2 6
7 1/8 3 6 5 3
No. of Spacers
A B C D
4 6 1 1 7
5 4 4 4 3
Standard Load Bracket
3 7/16” Wide
1 Ton Capacity
No. of Spacers
A B C D
6 7 2 2 6
7 4 5 5 3
On the 3 ton (3000 kg) trolley (refer to Figure 11), drive one
retaining pin into the hole on one end of the lug pin. Raise the
hoist into position so that the lug is between the legs of the
shackle. Align the holes in the shackle and lug. Insert the lug
pin in the aligned holes and secure the lug pin by driving the
remaining retaining pin into the hole in the lug pin. Make
certain that the shackle pin is properly seating in the load
bracket by manipluating the hoist and checking for freedom
of movement (swinging) in both planes and all four directions.
Note that the shackle pin should be retained and centered in
the shackle by the retainers.
On the 1/8 to 2-ton (125 to 2000 kg) trolleys, assemble the
suspension lug on hoist to the trolley on beam as shown in
Figure 10. The lug is inserted in the trolley load bracket and
retained by the vertical load bar pin. A socket head cap
screw and lockwasher are used to keep the in place.
For the 3-ton (3000 kg) trolley, a shackle and pin assembly
consisting of a pin retained in a central position by retainers
is packed loose with the suspension. Insert this assembly into
the opening in the top of the load bracket with the legs of the
shackle down. Position the shackle pin in the groove provided
for the same in the load bracket making sure it is centered
between the suspension bolts.
Now install the trolley on the beam by sliding one side frame
out far enough to allow all the trackwheels to clear the beam
flange. Lift the trolley up so that the trackwheels are riding
on the beam, draw the side frames together and tighten the
nuts snugly. Insert the cotter pins through the slotted nuts and
holes in the supension bolts and spread the legs of the cotter
pins to secure.
Figure 10. 1/8 to 2 Ton (125 to 2000 kg) Hoist to Trolley Assembly
Figure 11. 3 Ton (3000 kg) Hoist to Trolley Assembly
13
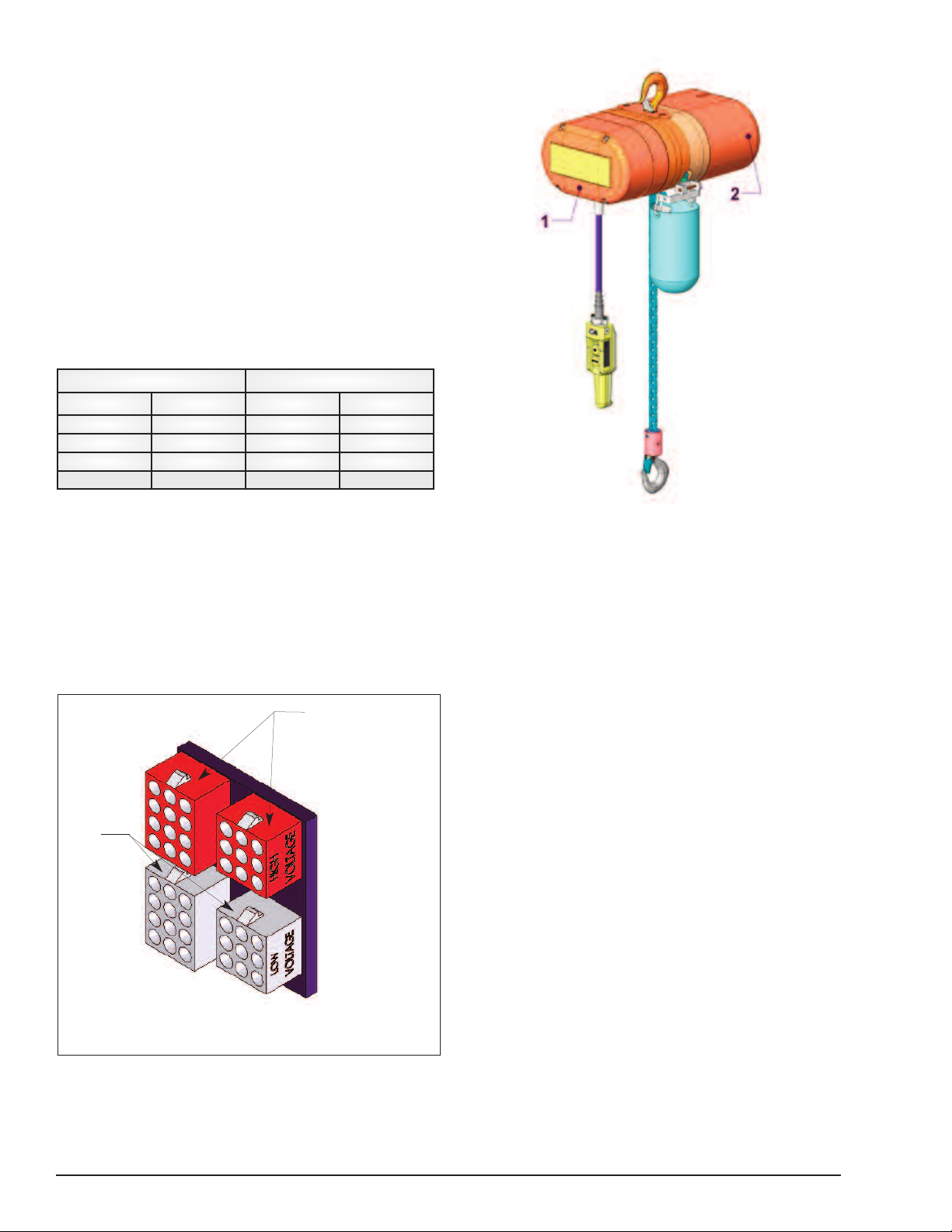
POWER SUPPLY AND ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
The hoist should be connected to a branch circuit which
complies with the requirements of the National Electrical
Code and applicable local codes.
It is recommended, especially for a single phase hoist
with a (1) horsepower motor (.75 Kilowatts), that a line with
adequate capacity be run directly from the power supply
to the hoist to prevent problems with low voltage and circuit
overloads.
For grounding of the hoist, the power cord includes a
gounding conductor (green yellow, G-Y). Before connecting
the hoist to the power supply, check that the power to be
used agrees with the position of voltage change plug on the
voltage change board. The nominal hoist voltage rating
correspo nding to the voltage range given on hoist
identification plate is:
SINGLE SPEED UNITS TWO SPEED UNITS
Range Nominal Range Nominal
110-120 115 -- -208-240 230 208-240 230
440-480 460 440-480 460
550-575 575 550-575 575
THREE PHASE HOIST
Unless ordered on a special basis, all single speed/dual
voltage (230/460-3-60, 220/380-3-50 and 220/415-3-50)
hoists are factory arranged to operate on 460-3-60 (or 380-350 or 415-3-50). However, a voltage change board is
provided to easily and quickly change from 460 to 230
(or 380 to 220 or 415 to 220) volt operation. The voltage
change board shown in Figure 12 is located in the hoist as
shown in Figure 13.
HIGH
VOLTAGE (RED)
LOW
VOLTAGE
(WHITE)
Figure 12. Voltage Change Board
Figure 13. Location of Components
Voltage conversion board is located under back frame
cover (1) for Models A-H and under motor housing
cover (2) for Models J-RRT.
The voltage change board is color coded to indicate high
and low voltage connections. Connecting the 9 and 12 pin
plugs into the “Red” voltage change board receptacles will
connect the hoist for high voltage (380-3-50, 415-3-50 or
460-3-60). To change the hoist voltage to low voltage (208-360, 220-3-50 or 230-3-60) simply remove the 9 and 12 pin
plugs from the “Red” receptacles and insert same into the
“White” receptacles located on the voltage change board.
Be sure to make a notation of the new hoist voltage on the
tag attached to the power cord.
POWER PHASING
Since the motor in a three phase hoist can rotate in either
direction, depending on the manner in which it is connected
to the power supply, the direction of hook movement must be
checked prior to each usage.
NOTE: Serious damage can result if the hook is run to the
upper or lower limit of travel with the hook operating in a
direction opposite to that indicated by the control station.
Therefore, proceed as follows:
1. Make temporary connecions at the power supply.
2, Operate (UP) control momentarily. If hook raises,
connections are correct and can be made permanent.
3. If hook lowers, it is necessary to change direction by
inter-changing the Grey lead and the Black lead of hoist
power supply. Under no circumstances should the internal
wiring of the control device or hoist be changed to
reverse hook direction. The wiring is inspected and
tested before leaving the factory.
14
Do not force the Lodestar Load-limiter to compensate for
improperly adjusted limit switches or reverse voltagephasing.

!
Allowing the hook block to run into the bottom of the hoist
when raising a load or allowing the chain to become taut
between the loose end screw and the frame when lowering a
load may break the chain and allow the load to drop.
Do not allow the hook block to contact the bottom of the
hoist or the loose end chain to become taut.
CHECKING FOR TWIST IN LOAD CHAIN
Models E,H, E-2, H-2,R, RR, R-2, RR-2
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
WARNING
!
Failure to properly ground the hoist presents the danger of
electric shock.
TO AVOID INJURY:
Permanently ground the hoist as instructed in this manual.
To avoid these low voltage problems, the hoist must be
connected to an electrical power supply system that complies
with the National Electrical Code and applicable local codes.
This system must also provide (slow blow fuses or inverse-time
type circuit breakers) and provisions for grounding the hoist.
The best way to check for this condition is to run the lower
hook, without a load, up to within about 2 feet (.61 meters)
of hoist. If the dead end of the chain has been properly
installed, a twist can occur only if the lower hook block has
been capsized between the strands of chain. Reverse capsize to remove twist.
Models RT, RT-2, RRT and RRT-2
On these models, the load chain is dead ended on top of the
lower hook block. If the chain has been properly installed, the
only way a twist can occur is if the lower hook block has been
capsized between the strands of chain. If this has occurred,
two strands of chain will be wrapped around each other and
to remove this, reverse the capsize.
CHECKING FOR ADEQUATE VOLTAGE AT HOIST
The hoist must be supplied with adequate electrical power
in order to operate properly. For proper operation, the voltage, (measured at the hoist end of the standard power cord
with the hoist operating in the , up direction with full load)
must be as indicated in the table below.
MINIMUM
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
115-1-60 104 98
230-1-60 207 196
230-3-60 187 460-3-60 396 -
575-3-60 495 -
220-3-50 198 380-3-50 365 415-3-50 399 -
550-3-50 495 -
RUNNING
VOLTAGE
MINIMUM
STARTING
VOLTAGE
Low voltage may also be caused by using an undersized
cord and/or connectors to supply power to the hoist. The
following chart should be used to determine the size wires
in the extension cord in order to minimize the voltage drop
between the power source and the hoist.
SINGLE
LENGTH
OF
EXTENSION
CORD
UP TO
50 FEET
80 FEET
(24.4 M)
120 FEET
(36.7 M)
200 FEET
(61.0 M)
For runs beyond 200 Feet contact factory.
!
Failure to provide a proper power supply system for the hoist
may cause hoist damage and offers the potential for a fire.
Provide each hoist with a 20 amp, minimum, overcurrent
protected power supply system per the National Electrical Code
and applicable local codes as instructed in this manual
PHASE
HOISTS
MINIMUM
WIRE SIZE
#14 AWG
#12 AWG
#10 AWG
Contact
Factory
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
THREE
PHASE
HOIST
MINIMUM
WIRE SIZE
#16 AWG
#16 AWG
#14 AWG
#14 AWG
SIGNS OF INADEQUATE ELECTRICAL POWER
(LOW VOLTAGE) ARE:
• Noisy hoist operations due to brake and/or contactor
chattering.
• Dimming of lights or slowing of motors connected to
the same circuit.
• Heating of the hoist motor and other internal components as
well as heating of the wires and connectors
in the circuit feeding the hoists.
• Failure of the hoist to lift the load due to motor stalling.
• Blowing of fuses or tripping of circuit breakers.
Remember, operation with low voltage can void the CM
repair/replacement policy. When in doubt about any of the
electrical requirements, consult a qualified electrician.
WARNING
Working in or near exposed energized electrical equipment
presents the danger of electric shock.
TO AVOID INJURY:
DISCONNECT POWER AND LOCKOUT/TAGOUT
DISCONNECTING MEANS BEFORE REMOVING COVER OR
SERVICING THIS EQUIPMENT.
15

CHECKING LIMIT SWITCH OPERATION IF HOIST IS
EQUIPPED
With hoists that are equipped with an adjustable screw limit
switch, the limit switch will automatically stop the hook at
any predetermined point when either hoisting or lowering.
!
Allowing the hook block to run into the bottom of the hoist
when raising a load or allowing the chain to become taut
between the loose end screw and the frame when lowering
a load may break the chain and allow the load to drop.
Do not allow the hook block to contact the bottom of the
hoist or the loose end chain to become taut.
Operate hoist over the entire length of its rated lift, checking
upper and lower limit switches for correct operation as follows:
1. Press
top of hook block is about one foot (305 mm) below
the hoist.
2. Cautiously continue raising the hook until the upper
limit switch stops the upward motion. The upper
limit switch is set at the factory to stop the hook
block 3 inches (76.2 mm) from bottom of the hoist
on all units with standard 10 foot (3m) lift except
Models AA and AA-2. Factory setting is 6 inches
(152.4 mm) for these models and for all other models
equipped with chain for lifts longer than 10 feet (3m).
3. If adjustment is necessary, see page 23.
4. Press (DOWN) control and cautiously lower hook
until lower limit switch stops the downward motion
From 7 to 11 chain links (depending on hoist model)
should be between the loose end link and the hoist
entry. See Figures 7 and 8.
5. If adjustment is necessary, see page 23.
NOTE: If the hoist is equipped with a chain
container/bag, reset the upper and lower limit
switches as indicated on page 23.
Under no condition should the hook block or load
be permitted to come in contact with the chain
container/bag. If contact is made, the function of
the chain container can be interfered with and its
fasterners imperiled.
NOTE: When chain bag is filled to capacity the
bag must be no more than 75% filled.
CONTROL CORD
Unless ordered on a special basis, the hoist is supplied with
a control cord that will position the control station approximately
4 feet above the lower hook when it is at the lower limit of the
lift. If this places the control station too close to the floor,
a “control cord alteration kit” (Part Number 28642) can be
obtained from CM for shortening the length of the control cord.
!
Tying knots or loops to shorten the drop of the control station
will make the strain relief ineffective and the internal conductors
of the cord may break.
Shorten the control cord using the control cord alteration kit
and the instructions provided with the kit.
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
(UP) control and raise the lower hook until
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
GENERAL
1. The Load-limiter is designed to slip on an excessive overload. An overload is indicated when the hoist will not raise the
load. Also, some clutching noise may be heard if the hoist is
loaded beyond rated capacity. Should this occur,
immediately release the
the hoist. At this point, the load should be reduced to the rated
hoist capacity or the hoist should be replaced with one of the
proper capacity. When the excessive load is removed, normal
hoist operation is automatically restored.
CAUTION: The Load-limiter is susceptible to overheating
and wear when slipped for extended periods. Under no
circumstance should the clutch be allowed to slip for
more than a few seconds.
Due to the above, a hoist equipped with a Load-limiter is not
recommended for use in any application where there is a
possibility of adding to an already suspended load to the
point of overload. This includes dumbwaiter (*see below)
installations, containers that are loaded in mid-air, etc.
(*) Refer to limitations on Page 3 concerning dumbwaiter
applications.
2. All hoists are equipped with an adjustable screw limit
switch, which automatically stops the hook at any pre-
determined point when either hoisting or lowering.
3. The control station used on two speed hoists is similar to
single speed unit, except that either of two definite
speeds may be selected by the operator in both hoisting
and lowering. Each control when partially depressed
provide SLOW speed and when fully depressed gives
FAST speed. Partial release of control returns hoist to
slow speed, while complete release allows hoist to stop.
Rated lifting speeds are shown on hoist identification
plate. SLOW speed is intended as a means of carefully
controlling or “spotting” the load, although the hoist may
be operated solely at this speed if desired. It is not
necessary to operate in the SLOW speed position as the
hoist will pick up a capacity load at FAST speed from a
standing start. In other words, it is not necessary to
hesitate at the slow position when moving control from
STOP to FAST position or vice versa.
4. If material being handled must be immersed in water,
pickling baths, any liquid, dusty or loose solids, use a
sling chain of ample length so that the hook is always
above the surface. Bearings in the hook block are
shielded only against ordinary atmospheric conditions.
HOIST
1. Before picking up a load, check to see that the hoist is
directly overhead.
2. WHEN APPLYING A LOAD, IT SHOULD BE DIRECTLY
UNDER HOIST OR TROLLEY. AVOID OFF CENTER
LOADING OF ANY KIND.
3. Take up a slack load chain carefully and start load easily
to avoid shock and jerking of hoist load chain. If there is
any evidence of overloading, immediately lower the load
and remove the excess load.
4. DO NOT allow the load to swing or twist while hoisting.
5. DO NOT allow the load to bear against the hook latch.
(UP) control to stop the operation of
16
HOIST WITH LOW HEADROOM TROLLEY
This unit should be moved by pushing on the suspended
load or by pulling the empty hook. However, the unit can
also be moved by pulling on the control station since an
internal steel cable extends the length of the control cord
and is anchored to the hoist and to the control station.
HOIST WITH MOTOR DRIVEN TROLLEY
This unit should be moved by operating the controls marked
(Forward) and (Reverse) in control station. Unless altered
by the erector, depressing (Forward) control will move the
hoist toward motor housing end. Anticipate the stopping
point and allow trolley to coast to a smooth stop. Reversing
or “plugging” to stop trolley causes overheating of motor and
swaying of load.
SAFE OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND PROCEDURES
For safety precautions and a list of Do’s and Do Not’s for
safe operation of hoists, refer to page 3.
1. Permit only competent personnel to operate unit.
2. When preparing to lift a load, be sure that the attachments to
the hook are firmly seated in hook saddle. Avoid off
center loading of any kind, especially loading on the
point of hook.
3. DO NOT allow the load to bear against the hook latch. The
latch is to help maintain the hook in position while the chain is
slack before taking up slack chain.
11. Take up a slack load chain carefully and start load easily
to avoid shock and jerking of hoist load chain. If there is
any evidence of overloading, immediately lower the load
and remove the excess load.
12.When lifting, raise the load only enough to clear the floor
or support and check to be sure that the attachments
to the hook and load are firmly seated. Continue lift only
after you are assured the load is free of all obstructions.
13. DO NOT allow the load to swing or twist while hoisting.
14.Never operate the hoist when flammable materials
or vapors are present. Electrical devices produce arcs
or sparks that can cause a fire or explosion.
15. STAY ALERT! Watch what you are doing and use common
sense. Do not use the hoist when you are tired, distracted or
under the influence of drugs, alcohol or medication causing
diminished control.
!
Allowing the load to bear against the hook latch and/or
hook tip can result in loss of load.
Do not allow the load and/or attachments to bear
against the hook latch and/or hook tip. Apply load to
hook bowl or saddle only.
4. DO NOT wrap the load chain around the load and hook onto
itself as a choker chain.
Doing this will result in:
a. The loss of the swivel effect of the hook which could result
in twisted chain and a jammed lift wheel.
b. The upper limit switch, if so equipped, is by-passed and
the load could hit the hoist.
c. The chain could be damaged at the hook.
5. Before lifting load, check for twists in the load chain. On double
and triple reeved units, a twist can occur if the lower hook block
has been capsized between the strands of chain. Reverse
the capsize to remove twist.
6. Stand clear of all loads and avoid moving a load over the
heads of other personnel. Warn personnel of your
intentions to move a load in their area.
7. DO NOT leave the load suspended in the air unattended.
8. DO NOT use this or any other overhead materials handling
equipment for lifting persons.
9. DO NOT load hoist beyond the rated capacity shown
on ID plate. When in doubt, use the next larger capacity
CM Lodestar Hoist.
10.Warn personnel of your intention to lift a load in the area.
Tie off the load with auxiliary chains or cables before
access to the area beneath the load is permitted.
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
17
INSPECTION
To maintain continuous and satisfactory operation, a regular
inspection procedure must be initiated to replace worn or
damaged parts before they become unsafe. Inspection
intervals must be determined by the individual application
and are based on the type of service to which the hoist will
be subjected.
The type of service to which the hoist is subjected can be
classified as “Normal”, “Heavy”, or “Severe”.
Normal Service: Involves operation with randomly distributed
loads within the rated load limit, or uniform loads less than
65 percent of rated load for not more than 25 percent of the time.
Heavy Service: Involves operating the hoist within the rated
load limit which exceeds normal service.
Severe Service: Normal or heavy service with abnormal
operating conditions or constant exposure to the elements
of nature.
Two classes of inspection - frequent and periodic - must
be performed.
Frequent Inspections: These inspections are visual exami-
nations by the operator or other designated personnel.
Records of such inspections are not required. The frequent
inspections are to be performed monthly for normal service,
weekly to monthly for heavy service, and daily to weekly for
severe service, and they should include those items listed in
Table 4.
Periodic Inspections: These inspections are visual
inspections of external conditions by an appointed person.
Records of periodic inspections are to be kept for continuing
evaluation of the condition of the hoist.
CAUTION: Any deficiencies found during inspections
are to be corrected before the hoist is returned to service.
Also, the external conditions may show the need for
disasembly to permit a more detailed inspection, which,
in turn, may require the use of nondestructive type testing
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
In addition to the above inspection procedure, a preventive
maintenance program should be established to prolong the
useful life of the hoist and maintain its reliability and continued
safe use. The program should include the periodic and
frequent inspections with particular attention being paid to
the lubrication of the various components using the recommended lubricants (see page 127).
HOOK INSPECTION
Hooks damaged from chemicals, deformations or cracks,
or that have more than a 10° twist from the hook’s unbent
plane, excessive opening or seat wear must be replaced.
Also, hooks that are opened and allow the latch to not
engage the tip must be replaced. Any hook that is twisted
or has excessive throat opening indicates abuse or overloading of the unit. Inspect other load sustaining parts, hook
block screws, load pins and hook block bodies for damage.
On latch type hooks, check to make sure that the latch is
not damaged or bent and that it operates properly with
suffcient spring pressure to keep the latch tightly against
the tip of the hook and allow the latch to spring back to the
tip when released. If the latch does not operate properly, it
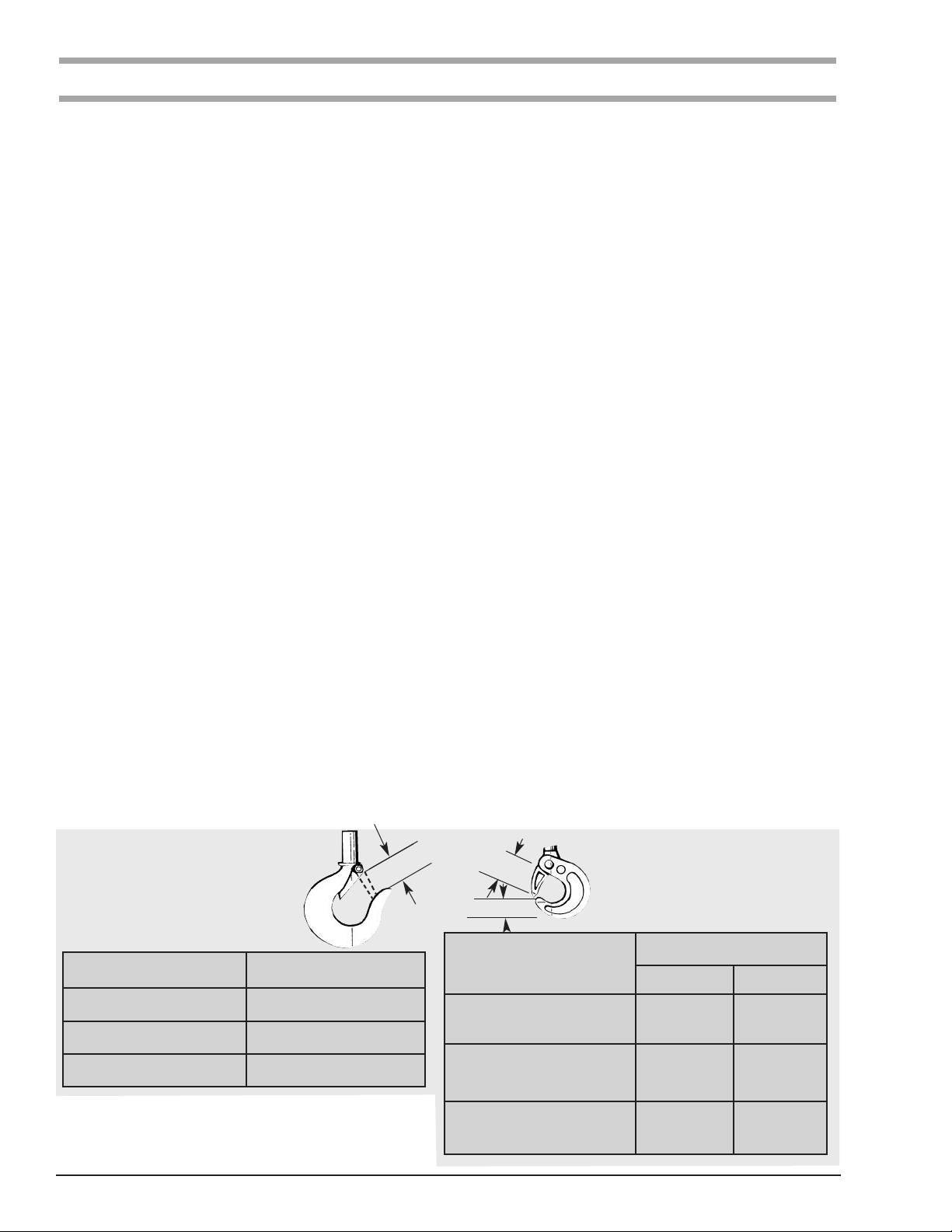
should be replaced. See Figure 14 to determine when the
hook must be replaced.
Periodic inspections are to be performed yearly for normal
service, semi-annually for heavy service and quarterly for
severe service, and they are to include those items listed in
Table 5.
LATCH TYPE HOOK
(Upper and Lower)
TO MEASURE OPENING,
MEASURE
OPENING
DEPRESS LATCH AGAINST
HOOK BODY AS SHOWN.
Models
A, A-2, AA, AA-2, B, B-2,
C, C-2, F AND F-2
E, E-2, H, H-2, J, J-2, JJ, JJ-2,
L, L-2, LL AND LL-2
R, R-2, RR AND RR-2,
RT, RT-2, RRT AND RRT-2
Figure 14. Hook Inspection
Replace Hooks When
Opening is Greater Than
1 3/16 (30.2 mm)
1 5/16 (33.3mm)
1 1/2 (38.1 mm)
“A” Max.
“B” Max.
Models
A, A-2, AA, AA-2, B, B-2, C, C-2,
E, E-2, F, F-2, H, H-2, J, J-2, JJ,
JJ-2, L, L-2, LL, LL-2
R, R-2, RR, RR-2
RT, RT-2, RRT AND RRT-2
LATCHLOK®HOOK
(Upper and Lower)
Replace Hook
When Opening or Seat are:
“A” Max. “B” Min.
1 31/64 in.
(37.7mm)
1 59/64 in.
(48.8mm)
2 1/2 in
(63.5mm)
21/32 in.
(16.7mm)
27/32 in.
(21.4mm)
1 1/8 in
(28.6mm)
18
TYPE OF SERVICE
Normal Heavy Severe
Monthly
Weekly
to Monthly
Daily
to Weekly
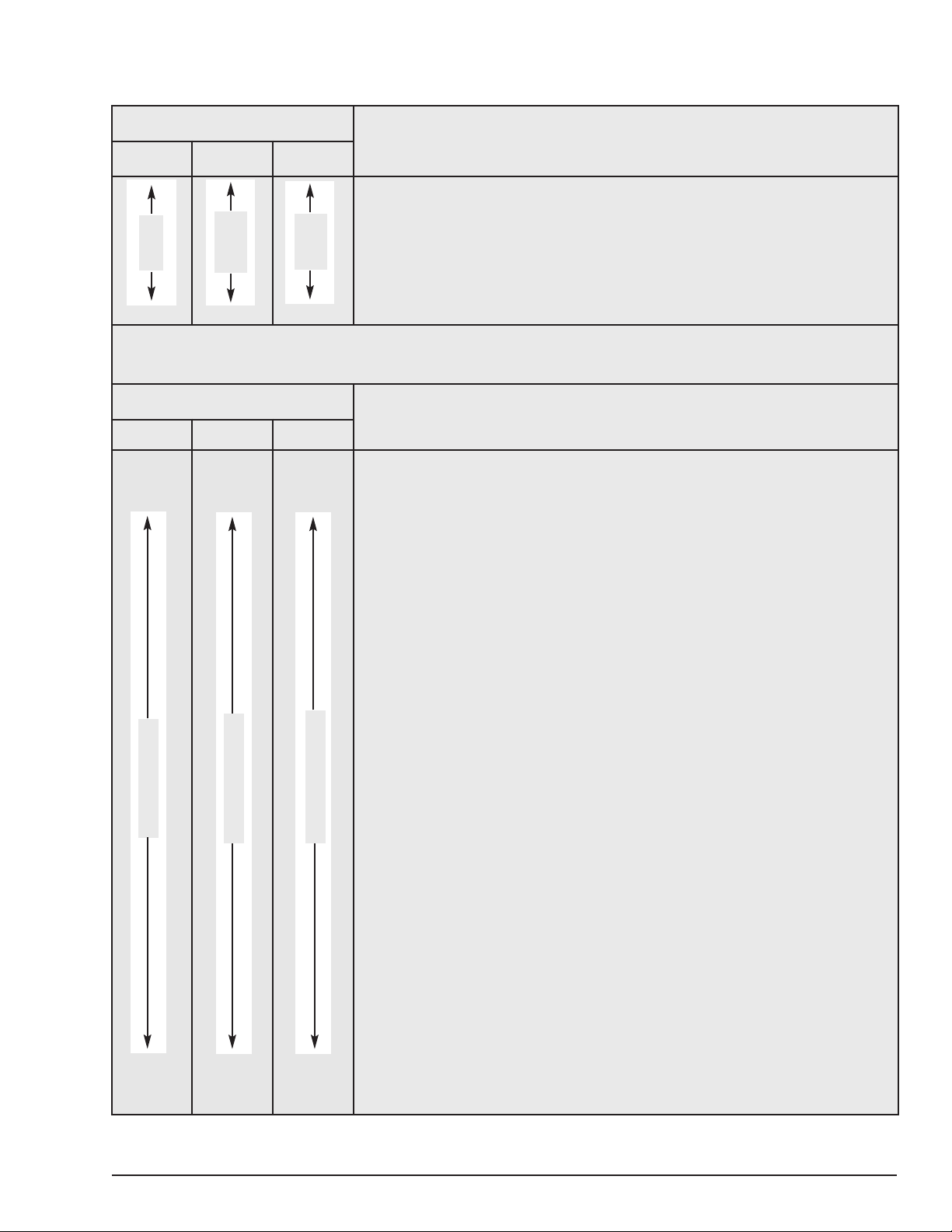
Table 4. Minimum Frequent Inspections
ITEM
a) Brake for evidence of slippage.
b) Control functions for proper operation.
c) Hooks for damage, cracks, twists, excessive throat opening, latch engagement and latch
operation - see page 18.
d) Load chain for adequate lubrication, as well as for signs of wear, damaged links or foreign
matter - see page 20.
e) Load chain for proper reeving and twists.
Table 5. Minimum Periodic Inspections
TYPE OF SERVICE
Normal Heavy Severe
Yearly
Every 6 Months
Every 3 Months
ITEM
a) All items listed in Table 4 for frequent inspections.
b) External evidence of loose screws, bolts or nuts.
c) External evidence of worn, corroded, cracked or distorted hook block, suspension screws,
gears, bearings and dead end block and chain pin.
d) External evidence of damage to hook retaining nut and pin. Also check the upper suspension
adapter making sure it is fully seated in the hoist frame and that both screws are tight.
e) External evidence of damage or excessive wear of the liftwheel and hook block sheave
chain pockets. Widening and deepening of the pockets may cause the chain to lift-up in
the pocket and result in binding between liftwheel and chain guides or between the
sheave and hook block. Also, check the chain guide for wear or burring where the chain
enters the hoist. Severely worn or damaged parts should be replaced.
f) External evidence of excessive wear of brake parts, and AC brake adjustment - see page 22.
g) External evidence of pitting or any deterioration of contactor contacts. Check the operation
of the control station making sure the buttons operate freely and do not stick in either
position.
h) Inspect the electrical cords and cables and control station enclosure for damaged insulation.
i) Inspect trolley trackwheels for external wear on tread and flange and for wear on internal
bearing surfaces as evidenced by a looseness on the stud. Suspension components for
damage, cracks, wear and operation. Also check suspension adapter screws for proper
tightness - see page 11.
j) Inspect the loose end link, loose end screw and dead end block on double reeved units.
Replace worn or distorted parts.
k) Inspect the suspension lug or hook for excess free play or rotation. Replace worn parts
as evidenced by excess free play or rotation.
l) Inspect for signs of lubricant leaks at the gasket between the gear housing and back
frame. tighten screws holding back frame to gear housing. If leak persists, repack housing
and gears with grease and install a new gasket.
m) On the Models RT, RT-2, RRT and RRT-2:
1. Inspect shackle and lug pins for wear. Replace if worn.
2. Check dead end screw in lower hook black for wear and tighteness*.
3. Check shackle pin for proper seating in groove of load bracket.
4. Inspect cloverleaf plate on bottom of sheave hanger for wear or burring.
Replace if worn.
5. Inspect sheave stud nut and seat for wear. Replace if worn or damaged.
*When tightening the special, dead end socket head screw, it should be held firmly in place and torqued from the nut end only to avoid damage to the screw
and/or dead end chain link (Refer to step J on page 45).
19
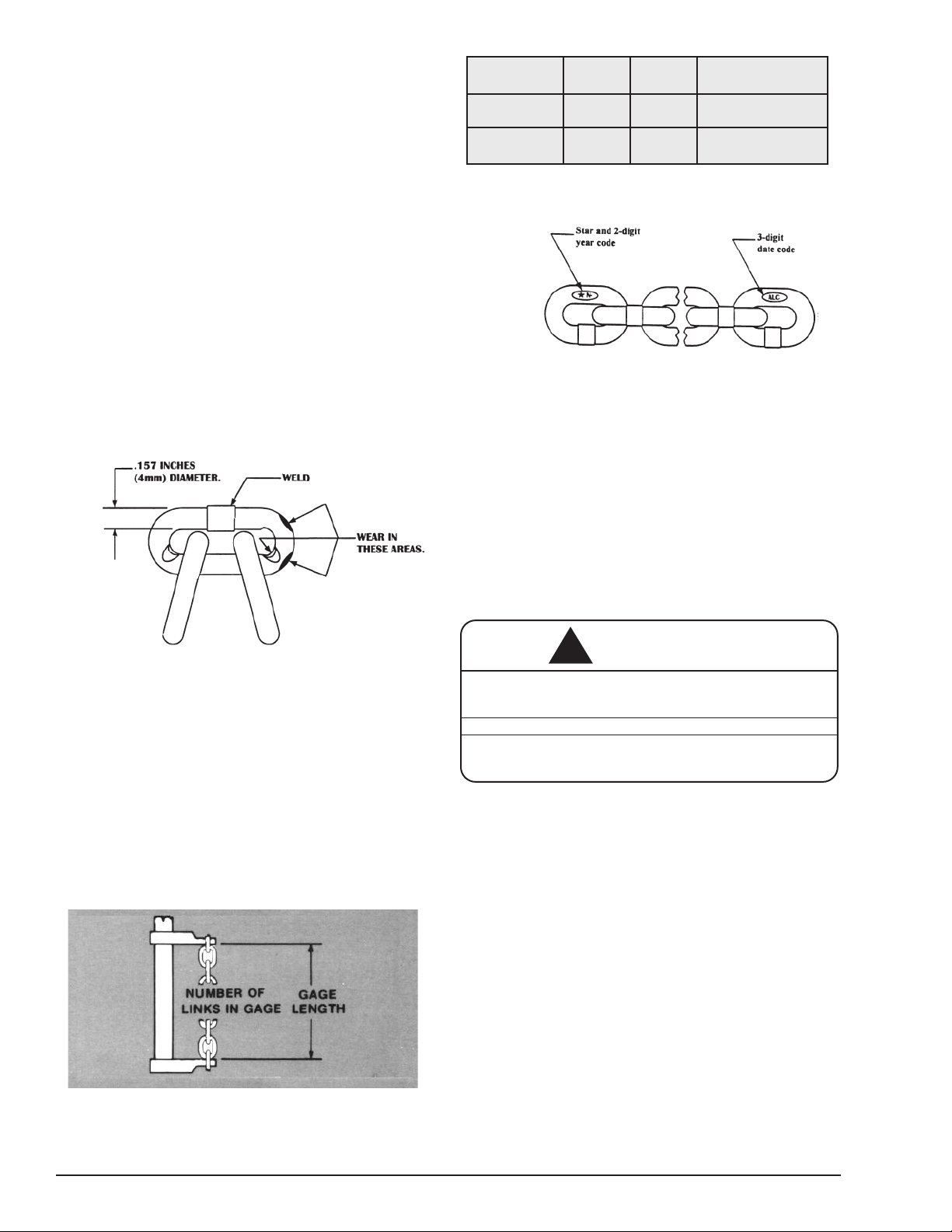
LOAD CHAIN
Chain should feed smoothly into and away from the hoist
or hook block. If chain binds, jumps or is noisy, first clean and
lubricate it (see below). If trouble persists, inspect chain and
mating parts for wear, distortion or other damage.
Chain Inspection
First Clean chain with a non-caustic/non-acid type solvent and
make a link by link inspection for nicks, gouges, twisted links,
weld splatter, corrosion pits, striations (minute parallel lines),
cracks in weld areas, wear and stretching. Chain with any one
of these defects must be replaced.
Slack the portion of the chain that normally passes over the liftwheel. Examine the interlink area for the point of maximum wear
(polishing, see Figure 15). Measure and record the stock diameter
at this point of the link. Then measure stock diameter in the same
area on a link that does not pass over the liftwheel (use the link
adjacent to the loose end link for this purpose). Compare these
two measurements. If the stock diameter of the worn link is 0.010
inches (0.254 mm), or more, less than the stock diameter of the
unworn link, the chain must be replaced.
On double reeved units, repeat this examination of the chain
that passes through the hook block.
Models
A thru H
A-2 thru H-2
J thru RRT
J-2 thru RRT-2
Dia. of
Chain Stock
0.250"
(6.35mm)
0.312"
(7.9mm)
No. of Links
to Gage
19
21
Max. Gage Length
Allowable Used Chain
14 13/16"
(376 mm)
18 7/8"
(479 mm)
Figure 17. Chain Embossing
Use only Star (*) grade load chain and original replacement
parts. Use of other chain and parts may be dangerous
and voids factory warranty.
Figure 15. Chain Wear Areas
Gaging Load Chain Wear
To determine if load chain should be continued in service,
check gage lengths as indicated in Figure 16. Chain worn
beyond length indicated, nicked, gouged or twisted should
be replaced before returning hoist to service. Chain should
be clean, free of twists and pulled taut before measuring.
Note that worn chain can be an indication of worn hoist
components. For this reason, the hoist’s chain guides, hook
blocks and liftwheel should be examined for wear and
replaced as necessary when replacing worn chain.
Also, these chains are specially heat treated and hardened
and should never be repaired.
IMPORTANT:
Do not use replaced chain for other purposes
such as lifting or pulling. Load chain may break suddenly without visual deformation. For this reason, cut replaced chain
into short lengths to prevent use after disposal.
!
USE OF COMMERICAL OR OTHER MANUFACTURER’S
CHAIN AND PARTS TO REPAIR CM HOISTS MAY CAUSE
LOAD LOSS.
Use only CM supplied replacement load chain and parts.Chain
and parts may look alike, but CM chain and parts are made of
specific material or processed to achieve specific properties.
WARNING
TO AVOID INJURY:
20
Figure 16. Gaging Load Chain Wear
MAINTENANCE
LOAD-LIMITER
The Load-limiter should operate for the normal life of the hoist
without service. The device has been calibrated at the factory
for a specific model of hoist. For proper overload protection,
be sure before installing a Load-limiter that it is correct for
the unit.
Models
A,A-2,B,B-2, E, E-2
AA,AA-2, C, C-2, F, F-2,
H, H-2
J, J-2, L, L-2, R, R-2,
RT, RT-2
JJ. JJ-2, LL, LL-2, RR
RR-2, RRT, RRT-2
!
The lubricants used in and recommended for the
Lodestar Hoist may contain hazardous materials that
mandate specific handling and disposal procedures.
TO AVOID CONTACT AND CONTAMINATION:
Handle and dispose of lubricants only as directed
in applicable material safety data sheets and in accordance
with applicable local, state and federal regulations.
HOIST LUBRICATION
Load-Limiter
Part Number
00000240
00000241 241
00000242
00000243
WARNING
Load-Limiter ID
(marked on
Load-limiter)
240
242
243
CHAIN GUIDES, LIFTWHEEL AND LOWER SHEAVE WHEEL
• When the hoist is disassembled for inspection and/or
repair, the chain guides, lower sheave wheel (on double
chain units) and liftwheel must be lubricated with
Lubriplate Bar and Chain Oil 10-R (Fiske Bros. Refining
Co. or equivalent) prior to reassembly. The lubricant must
be applied in sufficient quantity to obtain natural runoff and
full coverage of these parts.
LOAD CHAIN
A small amount of lubricant will greatly increase the life of load
chain. Do not allow the chain to run dry.
Keep it clean and lubricate at regular intervals with
Lubriplate Bar and Chain Oil 10-4 (Fiske Bros. Refining Co.)
or equal lubricant. Normally, weekly lubrication and cleaning
is satisfactory, but under hot and dirty conditions, it may be
necessary to clean the chain at least once a day and lubricate it several times between cleanings.
When lubricating the chain, apply sufficient lubricant to obtain
natural run-off and full coverage, especially in the interlink
area.
!
Used motor oils contain known carcinogenic materials.
Never use used motor oils as a chain lubricant.
Only use Lubriplate Bar and Chain Oil 10-R as a lubricant
for the load chain.
WARNING
TO AVOID HEALTH PROBLEMS:
GEARS
NOTE: To assure extra long life and top performance,
be sure to lubricate the various parts of the Lodestar Hoist
using the lubricants specified on page 85. If desired, these
lubricants may be purchased from CM. Refer to page 85 for
information on ordering the lubricants.
The gearbox is packed at assembly with grease and should
not need to be renewed unless the gears have been removed
from the housing and degreased.
If the gears are removed from the housing, wipe the excess
grease off with a soft cloth and degrease the gears and
housings. Upon reassembly, add grease (see page 85) to
gears and housing.
V1 hoists require 8 fl. oz. of grease. V2 hoists require 15 fl. oz.
of grease.
Also, coat the spline on the end of the drive shaft with a
Molydisulphide lubricant such as “Super Herculon”.
• The limit switch gears are of molded nylon and require no
lubrication.
• Apply a light film of machine oil to the limit switch shaft
threads at least once a year.
BEARINGS
• All bearings and bushings, except the lower hook thrust
bearing, are pre-lubricated and require no lubrication.
The lower hook thrust bearing should be lubricated at
least once a month.
TROLLEY LUBRICATION
Low Headroom Trolley
• CM trackwheel bearings are pre-lubricated and require
no lubrication.
EXTERIOR FINISH
The exterior surfaces of the hoist and trolleys have a durable,
scratch resistant baked powder coating. Normally, the exterior
surfaces can be cleaned by wiping with a cloth. However, if
the finish is damaged, compatible touch-up paint can be
purchased from CM. Refer to page138 for information on
ordering the paint.
SOLID STATE REVERSE SWITCH
(115-1-60/230-1-60 Units Only)
Above an ambient temperature of 104°F. (40° C.), the frequency
of hoist operation should be limited to avoid overheating the
solid state reverse switch. Even at temperatures less than
104° F. (40° C.), high duty cycle, frequent starting or reversing,
excessive inching, jogging or plugging may overheat the
solid state reverse switch. Overheating the switch will cause
it to malfunction, and this in turn will overheat the motor and/or
damage the solid state reverse switch.
If allowed to cool, the solid state switch will return to normal
operation. However, before returning the hoist to service,
the following procedure should be used to determine if the
switch has been damaged.
1. De-energize the power system supplying the hoist
and remove the solid state reverse switch.
21
2. Connect the solid state reverse switch to a
115-1-60/230-1-60 light circuit as shown below.
3. Close the switch to energize the 115-1-60/230-1-60
power supply. The light bulb will illuminate if the
solid state reverse switch is not damaged. If the
bulb fails to illuminate, the switch is damaged and
must be replaced.
4. Turn the 115-1-60/230-1-60 power off and remove
the solid state reverse switch from the test circuit.
Reinstall the solid state reverse switch in the hoist and
re-connect it using the wiring diagram supplied with the hoist.
Re-energize the power system supplying the hoist and test
for proper operation. Also, ventilate the space around the
hoist and/or reduce duty cycle, excessive starting, excessive
plugging to reduce future malifunctions of the solid state
reverse due to overheating.
JUMPER
Solid
State
Reverse
Switch
Switch
115V, 25W
Light Bulb
BRAKE ADJUSTMENTS
DC ELECTRIC BRAKE ASSEMBLY
The correct air gap between field and armature is .008-.018 in
(0.2-0.45 mm) for models A through H and .008-,020 in (0.2-
0.5 mm) for models J through RRT. The DC brake is not
adjustable. As the friction material wears, the brake gap
increases. If the maximum air gap is reached, a new friction
disc/rotor should be installed.
AC ELECTRIC BRAKE ASSEMBLY
The correct air gap between armature and field, when brake
is not energized, is 0.025 inch (.635mm) and need not be
adjusted until the gap reaches 0.045 inch (1.143mm). When
checking brake gap, always reset to .025 inch (.635 mm).
To adjust the brake, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect hoist from power supply.
2. Remove back frame cover, see figure 13
3. Before adjusting the gap: a) back off the stud nuts
and examine friction linings and friction surfaces for
excessive wear (min. thickness .188 inch, 4.78mm),
scoring or scoring or warpage. b) Check shading
coils to be sure they are in place and not broken.
A missing or broken shading coil will cause the
brake to be noisy when hoist is operated. Any of
these symptoms indicate the need for replacement
parts.
4. Turn adjusting nuts clockwise gaging the air gap at
both ends.
5. Replace cover, reconnect the power and check
operation.
Table 6a. Limit Switches
Hook Travel w/44TPI Shaft (Standard)
Model
A, A-2, C, C-2 63.1 207 53.1 2.09 38.1 1.50
AA, AA-2 118.3 388 99.6 3.92 50.8 2.00
B, B-2, F, F-2 32.1 105 27.0 1.06 38.1 1.50
E, E-2, H, H-2 16.0 53 13.5 0.53 44.5 1.75
L, L-2 38.8 127 30.4 1.20 38.1 1.50
JJ, JJ-2 149.0 489 116.8 4.60 63.5 2.50
J, J-2, LL, LL-2 75.9 249 59.5 2.34 38.1 1.50 8
R, R-2 19.4 64 15.2 0.60 63.5 2.50 8
RR, RR-2 37.9 124 29.7 1.17 63.5 2.50 8
RT, RT-2 12.9 42 10.1 0.40 63.5 2.50 8
RRT, RRT-2 25.3 83 19.8 0.78 63.5 2.50 8
Max Length of Lift Hook Travel, per Notch
m ft mm in mm in
A B
Links
6
6
6
6
8
8
Table 6b. Extended Lift Limit Switches
Hook Travel w/56TPI Shaft Hook Travel w/64TPI Shaft
Model
A, A-2, C, C-2 80.3 263 41.7 1.64 91.8
AA, AA-2 150.6 494 78.2 3.08 172.1
B, B-2, F, F-2 40.8 134 21.2 0.84 46.6
E, E-2. H. H-2 20.4 67 10.6 0.42 23.3
L, L-2 49.4 162 23.9 0.94 56.4
JJ, JJ-2 189.7 622 91.8 3.61 216.8
J, J-2, LL, LL-2 96.6 317 46.7 1.84 110.4 362 40.9 1.61
R, R-2 24.7 81 11.9 0.47 28.2 93 10.4 0.41
RR, RR-2 48.3 158 23.4 0.92 55.2 181 20.4 0.80
RT, RT-2 16.5 54 8.0 0.31 18.8 62 7.0 0.27
RRT, RRT-2 32.2 106 15.6 0.61 36.8 121 13.6 0.54
Max Length of Lift Hook Travel, per Notch Max Length of Lift Hook Travel, per Notch
m ft mm in m ft mm in
301
565
153
77
185
711
36.6 1.44
68.5 2.70
18.6 0.73
9.3 0.37
20.9 0.82
80.3 3.16
22
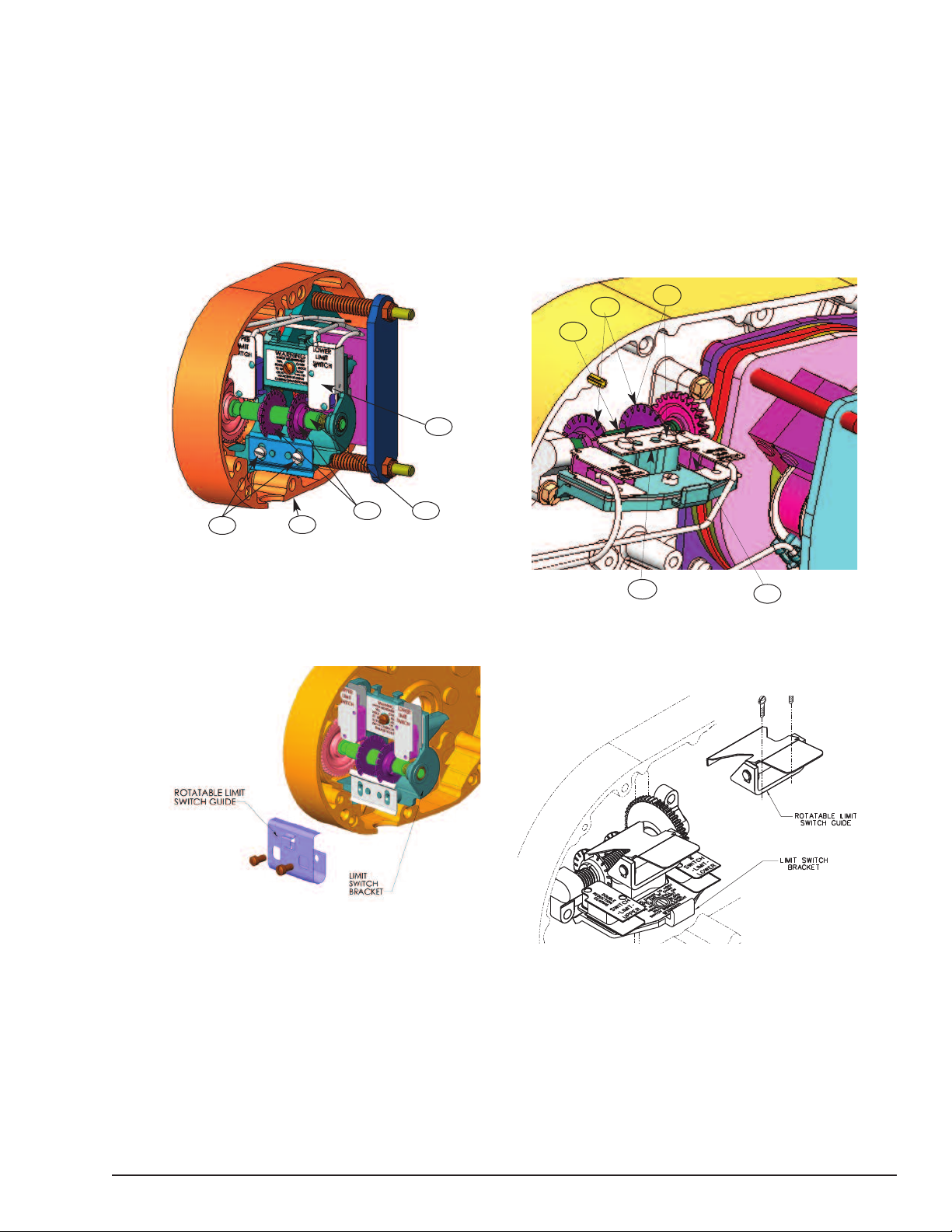
LIMIT SWITCH ADJUSTMENTS
If limit switch operation has been checked as described on
page 16 and is not operating correctly or is not automatically
stopping the hook at a desired position, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect hoist from power supply.
2. Remove back frame cover, see Figure 13.
3. The identification of upper and lower limit switches
are indicated on the fiber insulator.
4. Loosen the 2 screws or spring back the rotatable
guide to disengage the travel nut
6. Reconnect hoist to power supply.
7. Run hooktothe desired upper position,cautiously operating
the hoist without a load.
8. Disconnect hoist from power supply.
9. Moving one travel nut toward the other increases hook
travel and away from the other decreases the travel. .
Now, turn the nut nearest the switch indicated as the “
UPPER LIMIT SWITCH” until it just breaks the limit switch
contacts, cautious not to allow the movement of the other
travel nut, if previously set.
An audible click will be heard as the switch opens.
Continue to rotate the nut toward the switch an
additonal one full tooth.
5
4
3 2
Figure 18. Limit Switches, V1 Models
1. Limit switch sub-assy 4. Guide plate
2. Limit switch shaft 5. Screws
3. Travelling nuts
3
2
1
5
4
1
Figure 19. Limit Switches, V2 Models
1. Limit switch sub-assy 4. Guide plate
2. Limit switch shaft 5. Screws
3. Traveling nuts
Figure 18A. Rotatable Limit Switches, V1 Models
SETTING UPPER LIMIT SWITCH
After completing steps1 thru 4
5. Refer to table 6 -The "A" Dimensions given are the minimum
distance that should be set between the top at hook block
and the bottom of the hoist.
CAUTION: THE “A” DIMENSIONS SHOWN IN TABLE 6 ARE
THE MINIMUM ALLOWED FOR SAFE OPERATION AND
SHOULD NOT BE REDUCED.
Figure 19A. Rotatable Limit Switches, V2 Models
10.Securely reposition the guide plate in the slot
11.Reconnect hoist to power supply and check the stopping
point of hook by first lowering the hook about 2 feet
(61 cm), then raise the hook by jogging cautiously until
the upper limit switch stops upward motion. The stopping
point of hook should be the desired upper position. If not,
repeat the above instructions.
23

12.Double check setting by lowering the hook about 2 feet
(61 cm) and then run the hook into the upper limit with
(UP) control held depressed.
13.Fine adjustment of the upper limit setting may be
obtained by inverting the stationary guide plate in Step
10. (Not available with the rotatable guide plate.) The
offset on the plate gives adjustments equivalent to1/2
notch, see Table 6 for the “Hook Travel Per Notch of Limit
Switch Nut”. When inverting the plate, it may be necessary to
use the notch adjacent to the one used in the preliminary
setting.
SETTING LOWER LIMIT SWITCH
After completing steps1 thru 4
5. Refer toTable 6 -The “B” dimensions given are the minimum
length of loose end chain left on the load side of the lift
wheel when the hook is positioned at the lowest allowable
hook position.
CAUTION: THE “B” DIMENSIONS SHOWN IN TABLE 6
ARE THE MINIMUM ALLOWED FOR SAFE OPERATIONS
AND SHOULD NOT BE REDUCED.
6. Reconnect hoist to power supply.
7. Run hook to the desired lower position, cautiously operating
the hoist without a load.
CONVERTING LIMIT SWITCH GUIDES
1. Disconnect the hoist from the power supply system.
2. Refer to the exploded views and remove the back frame .
cover from the hoist.
3. Remove and discard the limit switch guide plate - retaining
the 2 screws.
4. Refer to Figure 18A and 19A and assemble the limit switch
guide plate to the limit switch bracket. Secure using the 2
screws.
8. Disconnect hoist from power supply.
9. Moving one travel nut toward the other increases hook
travel and away from the other decreases hook travel.
Now, turn the nut nearest the switch indicated as the
“LOWER LIMIT SWITCH” until it just breaks the limit
switch contacts, cautious not to allow the movement of
the other travel nut if previously set.
An audible click will be heard as the switch opens.
Continue to rotate the nut toward the switch an additional
one full tooth.
10.Securely reposition the guide plate in the slot.
11.Reconnect hoist to power supply and check the stopping
point of hook by first raising the hook about 2 feet (61cm )
then lower the hook by jogging cautiously until the lower
limit switch stops downward motion. The stopping point
of the hook should be the desired lower position, if not
repeat the above instructions.
12.Double check setting by raising the hook about 2 feet
(61 cm) and then run the hook into the lower limit with
(DOWN) control held depressed.
13. Fine adjustment of the lower limit setting may be
obtained by inverting the stationary guide plate in Step
10. (Not available with the rotatable guide plate). The
plate offset on the plate gives adjustments equivalent to
1/2 notch, see Table 6 for the “Hook Travel per Notch of
Limit Switch Nut”. When inverting the plate, it may be
necessary to use the notch adjacent to the one used in
the preliminary setting.
24
Table 7.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
All Hoists
TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE CHECK AND REMEDY
1. Hook does not respond
to the control station or
control device
A.) No voltage at hoist-main line or branch
circuit switch open; branch line fuse
blown or circuit breaker tripped.
B.) Phase failure (single phasing, three
phase unit only)-open circuit, grounded
or faulty connection in one line of supply
system, hoist wiring, reversing contactor,
motor leads or windings.
C.) Upper or lower limit switch has opened
the control circuit.
D.) Open control circuit-open or shorted
winding in transformer, reversing contactor
coil or loose connection or broken wire in
circuit;mechanical binding in contactor
control station contacts not closing or
opening.
E.) Wrong voltage or frequency.
A.) Close switch, replace fuse or reset
breaker.
B.) Check for electical continuity and repair or
replace defective part.
C.) Press the “other” control and the hook
should respond. Adjust limit switches as
described on page 23.
D.) Check electrical continuity and repair or
replace defective part.
E.) Use the voltage and frequency indicated on
hoist identification plate.
For three phase dual voltage unit, make
sure the connections at the voltage change
board are the proper voltage as
described on page 14.
2.) Hook moves in wrong
direction.
3.) Hook lowers but will not
raise.
F.) Low Voltage.
G.) Brake not releasing-open or shorted coil
winding; armature binding.
H.) Excessive load.
A.) Wiring connections reversed at either the
control station or terminal board (single
phase unit only).
B.) Failure of the motor reversing switch to
effect dynamic braking at time of reversal
(single phase unit only).
C.) Phase reversal (three phase unit only).
A.) Excessive load. A.) See item 1H.
B.) Open hoisting circuit-open or shorted
winding in reversing contactor coil loose
connection or broken wire in circuit;
control station contacts not making; upper
limit switch contacts open.
C.) Phase failure (three phase unit only). C.) See item 1B.
F.) Correct low voltage condition as described
on page 14.
G.) Check electrical continutiy and connections.
Check that correct coil has been installed.
The coil for three phase dual voltage unit
operates at 230 volts when the hoist is
connected for either 230 volt or 460 volt
operation. Check brake adjustment as
described on page 22.
H.) Reduce loading to the capacity limit of hoist
as indicated on the identifcation plate.
A.) Check connections with the wiring diagram.
B.) Check connections to switch. Replace a
damaged or faulty capacitor
C.) Refer to installation instructions on page 14
B.) Check electrical continuity and repair or
replace defective part. Check operation of
limit switch as described on page 16.
25
TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE CHECK AND REMEDY
4.) Hook raises but will not
lower.
Table 7 (cont.)
A.) Open lowering circuit-open or shorted
winding in reversing contactor coil, loose
connection or broken wire in circuit;
control station contacts not making; lower
limit switch contacts open.
A.) Check electrical continuity and repair or
replace defective part. Check operation of
limit switch as described on page 15-16.
5.) Hook lowers when
hoisting control is
operated.
6.) Hook does not stop
promptly.
7.) Hoist operates sluggishly.
8.) Motor overheats.
B.) Motor reversing switch not operating
(single phase unit only).
A.) Phase failure (three phase unit only). A.) See item 1B.
|B.) Phase reversal (three phase unit only). B.) Refer to installation instruction on page 14.
A.) Brake slipping.
B.) Excessive load. B.) See item 1H.
A.) Excessive load. A.) See item 1H.
B.) Low voltage. B.) Correct low voltage condition as described
C.) Phase failure or unbalanced current in the
phases (three phase unit only).
D.) Brake dragging. D.) Check brake adjustment as described on
A.) Low voltage. A.) Correct low voltage condition as described
B.) Excessive load. B.) See item 1H.
C.) Extreme external heating. C.) Above an ambient temperature of 40°C.
B.) See items 2B and 3C.
A.) Check brake adjustment as described on
page 22.
on page 15.
C.) See item 1B.
page 22.
on page 15.
(104°F.), the frequency of hoist operation
must be limited to avoid overheating of
motor. Special provisions should be made
to ventilate the space or shield the hoist
from radiation.
9.) Hook fails to stop at
either or both ends of
travel.
10.) Hook stopping point
varies.
D.) Frequent starting or reversing. D.) Avoid excessive inching, jogging or
E.) Phase failure or unbalanced current in the
phase (three phase unit only).
F.) Brake dragging.
G.) 115-1-60 Units: Solid state reverse switch
exposed to excessive temperature or the
switch is damaged.
A.) Limit switches not opening circuits. A.) Check switch connections, electrical
B.) Limit Switch Shaft not rotating. B.) Check for damaged Limit Switch gears.
C.) Traveling nuts not moving along shaft guide plate loose; shaft or nut threads
damaged.
A.) Limit switch not holding adjustment. A.) See item 9.
B.) Brake not holding. B.) Check the brake adjustment as described
C.) Binding of Limit Switch Shaft. C.) Check Limit Switch Bearing for proper
plugging. This type of operation drastically
shortens the motor and contactor life and
causes excessive brake wear.
E.) See item 1B.
F.) Check brake adjustment as described on
page 22.
G.) See page 21.
continuity and mechanical operation.
Check the switch adjustment as described
on page 15-16.
C.) Tighten guide plate screws. Replace
damaged part.
on page 22.
seating.
26
TROUBLE PROBABLE CAUSE CHECK AND REMEDY
11.) Hoist will not operate at
slow speed in either
direction.
12.) Hoist will not operate at
fast speed in either
directio n.
13.) Hook will not raise at
slow speed.
14.) Hook will not lower at
slow speed.
15.) Hook will not raise at
fast speed.
16.) Hook will not lower at
fast speed.
17.) Hook moves in proper
direction at one speed wrong direction at other
speed.
Table 7 (cont.)
Two Speed Hoist
A.) Open Circuit. A.) Open or shorted motor winding, loose or
broken wire in circuit, speed selecting
contactor stuck in opposite speed mode.
Replace motor, repair wire and/or replace
speed selecting contactor.
B.) Phase Failure. B.) See item 1B.
A.) Open Circuit. A.) See Item 11A.
B.) Open speed selecting circuit. B.) Open or shorted winding in speed selecting
contactor coil. Loose connection or broken
wire in circuit. Mechanical binding in contactor.
Control station contacts not making or opening.
Replace speed selector; repair connection,
replace contactor or control station.
C.) Phase Failure. C.) See Item 1B.
A.) Excessive load. A.) See item 1H.
B.) Phase Failure. B.) See Item 1B.
C.) Open Circuit. C.) See item 11A.
D.) Brake not releasing. D.) See Item 1G.
A.) Phase Failure. A.) See item 1B.
B.) Open Circuit. B.) See item 11A.
C.) Brake not releasing. C.) See Item 1G.
A.) Excessive load. A.) See item 1H.
B.) Phase Failure. B.) See Item 1B.
C.) Brake not releasing. C.) See Item 1G.
A.) Phase Failure. A.) See Item 1B.
B.) Brake not releasing. B.) See Item 1G.
A.) Phase reversal. A.) Wiring reconnected improperly. Interchange
two leads of motor winding that is out of
phase at the speed selecting relay.
27
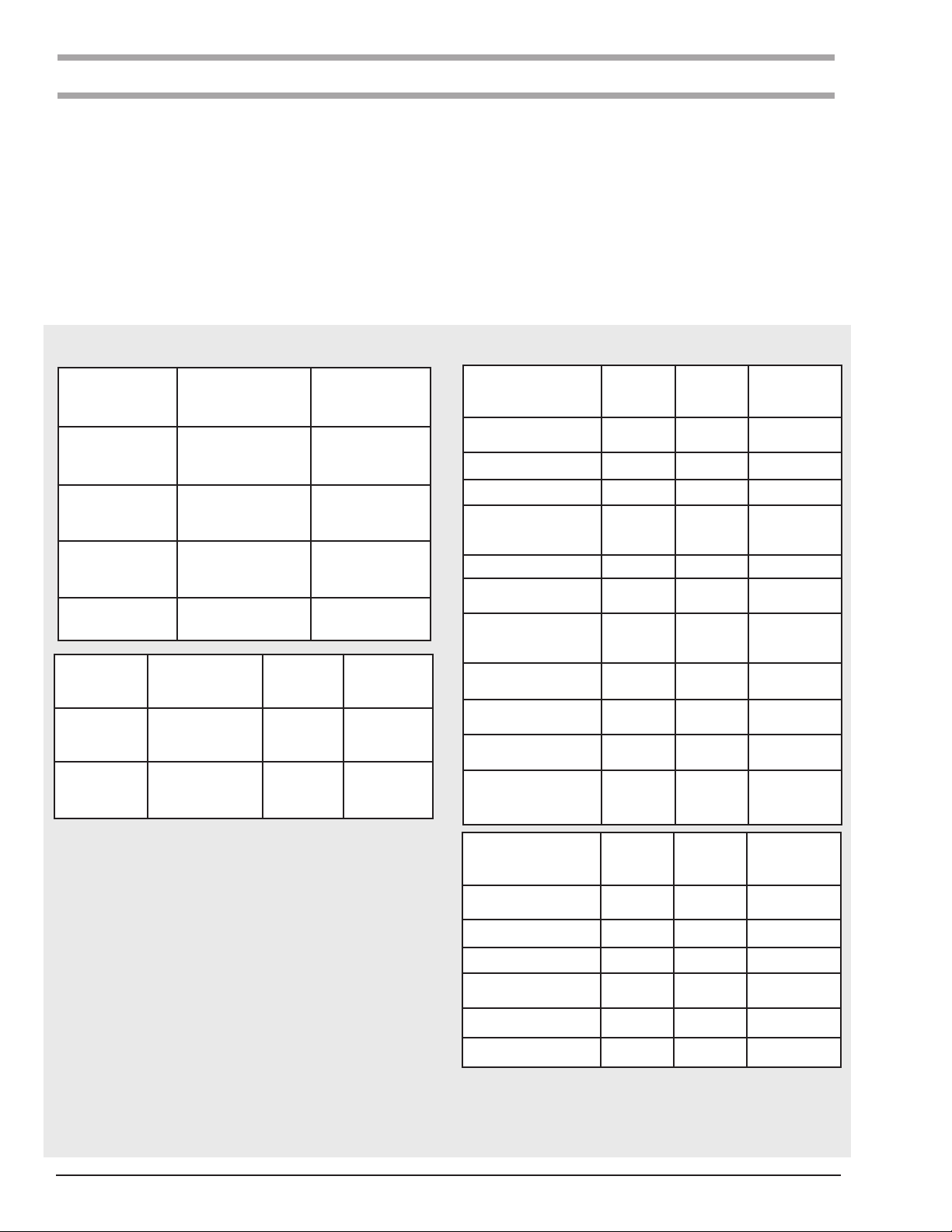
ELECTRICAL DATA
TO DETECT OPEN AND SHORT CIRCUITS IN ELECRICAL COMPONENTS
Open circuits in the coils of electrical components may be detected by isolating the coil and checking for continuity with an
ohmmeter or with the unit in series with a light or bell circuit.
Shorted turns are indicated by a current draw substantially above normal (connect ammeter in series with suspected
element and impose normal voltage) or D.C. resistance substantially below normal. The current method is recommend for
coils with very low D.C. resistance.
Motor current draw in the stator should be measured with the rotor in place and running. Brake, relay and contactor coil current should be measured with the core iron in operating position.
Table 8. Electrical Data for Hoist Components
TRANSFORMER
VOLTAGE
230/460 to 115
230/380 to 48
220/415 to 24
575 to 115
MODELS
A thru H-2
JJ thru RRT-2
SPEED SELECTOR
LEADS
X2 to X1
H2 to H1
H3 to H4
X2 to X1
H2 to H1
H3 to H4
X2 to X1
H2 to H1
H3 to H4
X2 to X1
H4 to H1
CONTACTOR OR
COIL VOLTAGE
115
48
24
115
48
24
NOMINAL
CURRENT
(AMPS)
0.04
0.09
0.19
0.07
0.17
0.33
*D.C.
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
27.9
99.0
111.8
5.2
99.0
112.6
1.3
100.4
114.9
28.4
329.1
*D.C.
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
297.5
56.3
14.9
126.6
25.1
6.4
MODELS
A, AA, B, C, E
F and H
A thru H-2 **230 .17 23.1
A-2 thru H-2 460 .20 92.3
A, A-2, AA, AA-2, B,
B-2, C, C-2, E, E-2, F,
F-2, H, H-2
J, L, R, RT 115 1.25 1.1
J, J-2, L, L-2, LL-2, R,
R-2, RT, RT-2
JJ, JJ-2, LL, LL-2,
RR, RR-2, RRT,
RRT-2
J-2, L-2, R-2, RT-2 460 .25 18.7
JJ-2, LL-2, RR-2,
RRT-2
J, J-2, L, L-2, LL-2, R,
R-2, RT, RT-2
JJ, JJ-2, LL, LL-2,
RR, RR-2, RRT,
RRT-2
AC BRAKE
COIL
VOLTAGE
115 .51 5.8
575 .14 140.0
**230 .46 4.6
**230 1.7 2.2
460 1.5 8.9
575 .50 38.5
575 1.70 14.2
NOMINAL
CURRENT
(AMPS)
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
*D.C.
MODELS
A, AA, B, C, E
F and H
A thru H-2 205 0.122 1681
A-2 thru H-2 255 0.098 2601
J, JJ, L, LL, R, RR,
RT, RRT
J thru RRT-2 205 0.161 1273
J thru RRT-2 255 0.118 2167
*Resistance values listed are nominal and they may vary slightly from component to component.
**On dual voltage units (230/460-3-60, 220/380-3-50 and 220/415-3-50), brake coils operate on 230 (220) volts.
DC BRAKE
COIL
VOLTAGE
103 0.243 424.4
103 0.311 331.5
NOMINAL
CURRENT
(AMPS)
28
*D.C.
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
Volts-
Models
A,B,E 110-1-50
A,B,E 115-1-60
A,B,E 220-1-50
A,B,E 230-1-60
AA,C,F,H 110-1-50
AA,C,F,H 115-1-60
A,B,E 220-1-50
A,B,E 230-1-60
A,B,E
AA,C,F,H
A-2, B-2,
E-2
A-2, AA-2,
B-2, C-2,
E-2, F-2,
H-2
Phase
Hertz
230/460-3-60
220/380-3-50 1.4/0.7
220/415-3-50 1.4/0.7
575-3-60 0.5
550-3-50 0.6
230/460-3-60
220/380-3-50 2.1/1.0
220/415-3-50 2.1/1.0
575-3-60 0.8
550-3-50 0.9
230-3-60
220-3-50 1.9/2.1
230-3-60
220-3-50 2.1/2.4
460-3-60 1.0/1.0
380-3-50 1.2/1.2
415-3-50 1.2/1.2
575-3-60 .8/.85
550-3-50 .8/.85
H.P.
(kW)
1/4
(.19)
1/4
(.19)
1/4
(.19)
1/4
(.19)
1/2
(.37)
1/2
(.37)
1/2
(.37)
1/2
(.37)
1/4
(.19
1/2
(.37)
.08/.25
(.06/.19)
.15/.5
(.12/.37)
Full Load
Current
(Amps)
3.2
4.6
1.6
2.3
6.4
7.2
3.2
3.6
1.4/0.7
1.8/0.9
1.6/1.6
1.8/2.0
Leads
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
3 - 6
2 - 5
1 - 4
8 - 9
8 - 7
9 - 7
1 - 2
2 - 3
1 - 3
3 - 6
2 - 5
1 - 4
8 - 9
8 - 7
9 - 7
1 - 2
2 - 3
1 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
Table 8. (cont.)
*D.C.
Resistance
(Ohms)
7.2
7.2
5.8
4.3
4.3
4.9
7.2
7.2
5.8
4.3
4.3
4.9
2.7
2.7
3.5
1.9
1.9
3.6
2.7
2.7
3.5
1.9
1.9
3.6
14.8
14.8
14.8
29.5
29.5
29.5
98.2
7.8
7.8
7.8
15.6
15.6
15.6
48.3
17.5
17.5
17.5
42.5
42.5
42.5
13.5
13.5
13.5
25.0
25.0
25.0
63.0
63.0
63.0
104.0
104.0
104.0
99.1
99.1
99.1
156.0
156.0
156.0
Models
J,L,R,RT
J,L,R,RT
J,L,R,RT
JJ,LL,RR,
RRT
J-2,L-2,R-2,
RT-2
J-2,L-2,R-2,
RT-2
VoltsPhase
Hertz
110-1-50
115-1-60 9.8
220-1-50
230-1-60 4.9
230/460-3-60
220/380-3-50 3.6/1.8
220/415-3-50 3.6/1.8
575-3-60
550-3-50 1.8
230/460-3-60
220/380-3-50 6.4/3.3
220/415-3-50
575-3-60
550-3-50
230-3-60
220-3-50 3.2/4.7
460-3-60 1.5/2.4
380-3-50 1.6/2.4
415-3-50 1.6/2.4
575-3-60 1.1/1.9
550-3-50 1.3/2.1
230-3-60
220-3-50 6.6/9.5
460-3-60 3.3/5.1
380-3-50 3.0/5.0
415-3-60 3.0/5.0
575-3-60 2.3/3.5
550-3-50 2.5/3.7
(.25/.75)
(.50/1.5)
H.P.
(kW)
1
(.75)
1
(.75)
1
(.75)
2
(1.5)
.33/1
.67/2
Full Load
Current
(Amps)
11.6 1 - 2
5.8
3.0/1.5
1.5
5.8/2.9
6.4/3.3
3.2
3.5
3.4/5.0
5.8/8.8
Leads
3 - 4
5 - 8
1 - 2
3 - 4
5 - 8
3 - 6
2 - 5
1 - 4
8 - 9
8 - 7
9 - 7
1 - 2
2 - 3
1 - 3
3 - 6
2 - 5
1 - 4
8 - 9
8 - 7
9 - 7
1 - 2
2 - 3
1 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
12 - 3
11 - 3
11 - 12
1 - 2
1 - 3
2 - 3
*D.C.
Resistance
(Ohms)
1.1
1.1
1.3
1.1
1.1
1.3
4.7
4.7
4.7
9.4
9.4
9.4
29.6
2.2
2.2
2.2
9.4
9.4
9.4
14.8
7.7
7.7
7.7
19.4
19.4
19.4
29.9
29.4
29.0
80.2
80.1
82.2
42.9
40.1
53.2
125.7
125.8
125.2
3.2
3.1
3.3
14.1
14.1
14.0
11.4
11.3
11.3
55.2
55.4
55.3
17.0
17.1
17.2
84.1
84.0
83.6
29
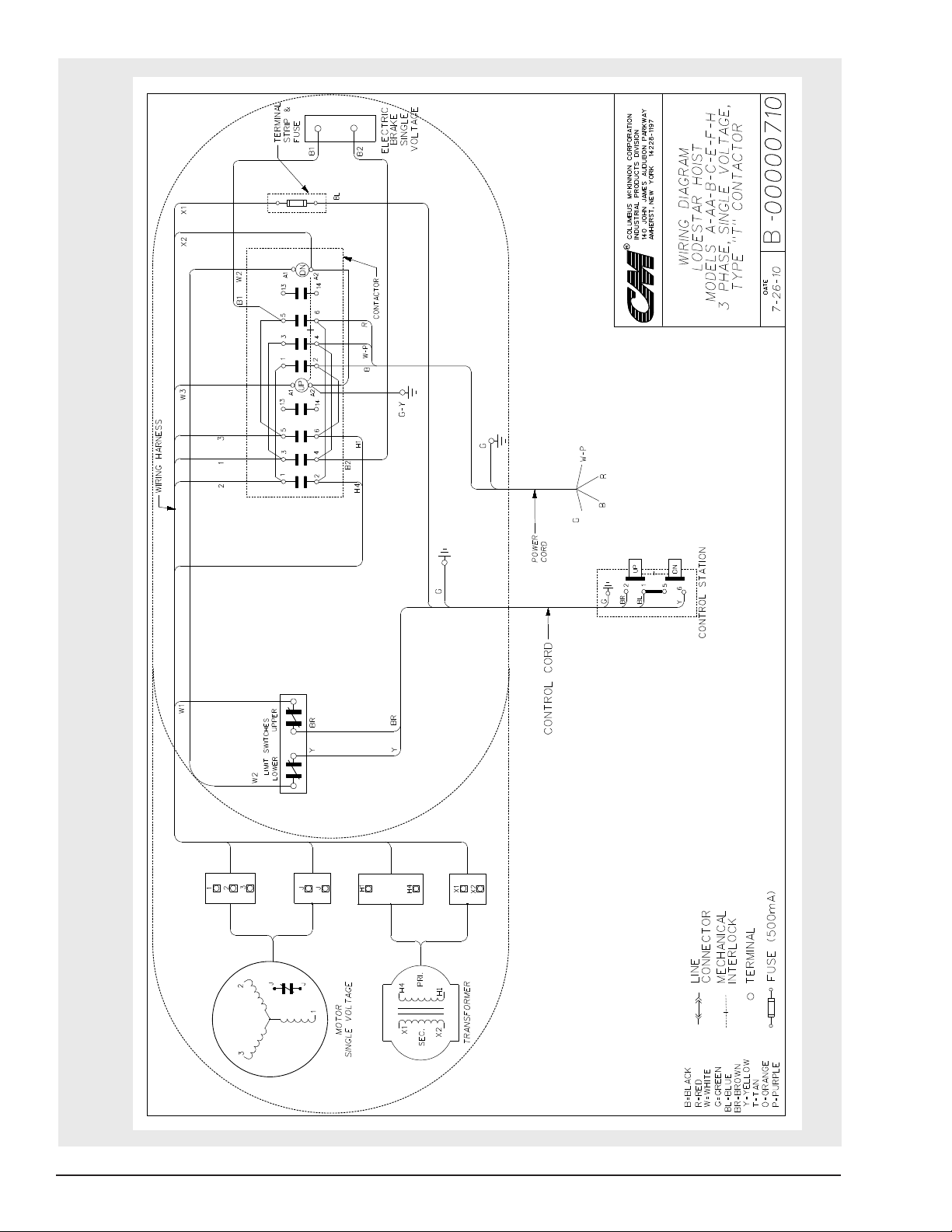
REFERENCE WIRING DIAGRAMS
30
 Loading...
Loading...