
FAE Manual Page 1 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
CDM-650PRO FAE manual
Wireless CDMA Docking Station
INEW Digital Company
Technical Support: jglee@inewdc.com
TEL: 82-42-933-7328
FAX: 82-42-934-4829
www.inewdc.com

Regulatory Information & Safety notices
1. Regulatory Notices
This device is compliant with Parts 15, 22 and 24 of the FCC Rules.
Operation of this device is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesirable operations.
FCC RF EXPOSURE COMPLIANCE
In August 1996 the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the United States with its
action in Report and Order FCC 96-326 adopted an updated safety standard for human
exposure to radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC regulated transmitters.
Those guidelines are consistent with the safety standard previously set by both U.S. and
international standards bodies. The design of this phone complies with the FCC guidelines and
these international standards.
Use only the supplied or an approved antenna. Unauthorized antennas, modifications, or
attachments could impair call quality, damage the phone, or result in violation of FCC
regulations.
This device should not be operated in conjunction with another transmitter in order to comply
with the FCC's RF Exposure requirements.
During operation, a 20 cm separation distance should be maintained between the
antenna, whether extended or retracted, and the user’s/bystander’s body (excluding
hands, wrists, feet, and ankles) to ensure FCC RF exposure compliance.
CAUTION
Unauthorized modification or change not expressly approved by INEW Digital Company could
void compliance with regulatory rules and thereby your authority to use this equipment.

Regulatory Information & Safety notices
WARNING (EMI)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits pursuant to Part 15, 22 &
24 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in an appropriate installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
z Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
z Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
z Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
z Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Regulatory Information & Safety notices
2. Safety and Notices
Important Notice
Because of the nature of wireless communications, transmission and reception of data can
never be guaranteed. Data may be delayed, corrupted (i.e., have errors), or be totally lost.
Although significant delay or losses of data are rare when wireless devices such as the CDM650PRO are used in a normal manner with a well-constructed network, they should be used in
situations where failure to transmit or receive data could result in damage of any kind to the user
or any other party, including but not limited to personal injury, death, or loss or pr operty.
INEW Digital Company accepts no responsibility for damages of any kind resulting from delays
or errors in data transmitted or received using the CDM-650PRO or failure of CDM-650PRO to
transmit or receive such data.
Safety and Hazards
Do not operate the CDM-650PRO in areas where blasting is in progress, where explosive
atmospheres may be present, near medical equipment, life support equipment, or any
equipment which may be susceptible to any form of radio interference.
In such areas, the CDM-650PRO MUST BE POWERED OFF
.
It can transmit signals that could interfere with this equipment.
Do not operate the CDM-650PRO in any aircraft, whether the aircraft is on the ground or in flight.
In aircraft, the CDM-650PRO MUST BE POWERED OFF
.
When operating, it can transmit signals that could interfere with various onboard systems.
The driver or operator of any vehicle should not operate the CDM-650PRO while in control of a
vehicle. Doing so will detract from the driver or operator’s control and operation of that vehicle.
In some jurisdictions, operating such communications devices while in control of a vehicle is an
offense.

Regulatory Information & Safety notices
POTENTIALLY UNSAFE AREAS
Posted facilities
-Turn off this modem in any facility or area when post ed notices require you to do so.
Blasting areas
- Turn off Modem where blasting is in progress. Observe restrictions and follow any regulations
or rules.
Potentially explosive atmospheres: Turn off Modem when you are in any area with a
potentially explosive atmosphere. Obey all signs and instructions.
Sparks in such areas could cause an explosion or fire, resulting in bodily injury or death.
Areas with a potentially explosive atmosphere are often but not always clearly marked.
They include:
- fuelling areas such as gas or petrol stations
- below deck on boats
- transfer or storage facilities for fuel or chemicals
- vehicles using liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane or butane
- areas when the air contains chemicals or p a rticles such as grain, dust or metal powders
- any other area where you would normally be advised to turn off your Modem.
FAE Manual Page 2 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
Copyright .................................................................................................... 4
Purpose ...................................................................................................... 4
1. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................ 5
1.1 OVERVIEW ....................................................................................... 5
1.2 APPERANCE ...................................................................................... 6
1.3 MAIN FEATURE.................................................................................. 6
1.4 SPECIFICATION................................................................................. 7
1.4.1 Mechanical Specification............................................................. 7
1.4.2 Environment Specification .......................................................... 7
1.4.3 Electrical Specification................................................................ 7
1.4.4 Hardware specification ............................................................... 7
1.4.5 Software Specification................................................................ 8
1.5 PROTOCOL INFORMATION .................................................................. 9
1.5.1 PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)....................................................... 9
1.5.2 PPPoE (point-to-point protocol over Ethernet)................................ 9
1.5.3 DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)............................... 10
1.5.4 NAT (Network Address Translation or Network Address Translator) . 11
1.5.5 RIP v1/v2 (Routing Information Protocol).................................... 12
1.5.6 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) ............................ 12
1.5.7 SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) ........................................ 13
1.5.8 ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)................................... 14
2. BASIC INFORMATION .............................................................................. 15
2.1 Hardware composition...................................................................... 15
2.2 SOFTWARE COMPOSITION................................................................ 16
2.2.1 Web-based configuration page .................................................. 16
2.2.2 Firmware ............................................................................... 16
2.3 DESCRIPTION OF EACH PART............................................................ 17
2.3.1 3-Status LED .......................................................................... 17
2.3.2 Mini-DC Power ........................................................................ 18
2.3.3 Ethernet Port .......................................................................... 18
2.3.4 Power switch .......................................................................... 18
2.3.5 Reset switch ........................................................................... 18
2.4 OPERATION MODE........................................................................... 19
FAE Manual Page 3 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
2.4.1 PPP auto mode........................................................................ 19
2.4.2 Bridge mode........................................................................... 20
2.5 SETTING HOST PC........................................................................... 21
2.5.1 Setting Host PC’s network environment ...................................... 21
2.6 WEB-BASED CONFIGURATION PAGE .................................................. 23
2.6.1 Overview ............................................................................... 23
2.6.2 Web-based configuration page description .................................. 24
3. USAGE .................................................................................................. 40
3.1 OPERATION MODE........................................................................... 40
3.1.1 PPP auto mode........................................................................ 40
3.1.2 Bridge mode........................................................................... 42
3.2 ADVANCED SETTING........................................................................ 49
3.2.1 Connecting with HUB ............................................................... 49
3.2.2 Setting virtual Server............................................................... 50
3.2.3 Setting DMZ Host .................................................................... 53
3.2.4 Connecting with xDSL, VPN, Router via PPPoE ............................. 55
4. TROUBLESHOOTING................................................................................ 56
4.1 CHECKING HARDWARE.................................................................. 56
4.2 CHECKING SOFTWARE .................................................................. 57
5. FAQ ...................................................................................................... 60
FAE Manual Page 4 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
Copyright
FAE manual describes features including hardware, software and operation of CDM-
650PRO. C-motech has made best effort to ensure that the information contained in
this document is accurate and reliable. This document is the property of C-motech
and implies no license under patents, copyrights, trade secrets. No part of this
publication should be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or
otherwise) without the prior permission of C-motech.
Purpose
This manual includes how to configure and use the CDM-650PRO.
FAE Manual Page 5 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 OVERVIEW
CDM-650PRO, wireless mobile docking station with an Ethernet and an USB
Host interface performs data communication functions between wired-LAN
(Local Area Network) and wireless WAN (Wide Area Network) using 1X EV-DO
DUAL-BAND Cellular station wirelessly for Small Office Home Office.
CDM-650PRO incorporates an 32-bit MCU, system memories, an 10/100
Ethernet, an USB Host, an Embedded OS, various network protocols, and
supports an external USB type wireless 1X EV-DO DUAL-BAND modem for
wireless internet or network.
CDM-650PRO has some special function on wireless mobile network like
always on-line, demands on-line etc.
CDM-650PRO has various input voltage range that can support it from 6~30
[VDC] which provides compatibility for platforms utilizing various industry
applications.

FAE Manual Page 6 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
1.2 APPERANCE
Below are the appearance and the each part of name of CDM-650PRO.
[Picture1. Each part name of CDM-650PRO]
1.3 MAIN FEATURE
z Wireless Internet/Network
z External wireless mobile 1X EV-DO DUAL-BAND modem adaptable
z A 10/100Mbps Ethernet Port
z A 32-bit RISC Network System on Chip
z Adopt Embedded Operating System
z System clock 100MHz(CPU) and 96MHz(BUS)
z User friendly Web-based Management Tool
z 3-Status LED indicates of the modem status
z Support various Network Protocol
- PPP, PPPoE for wireless mobile network
z Support 10/100M Auto-sensing
z An external power switch
z DHCP Server
- Getting IP address automatically from internal DHCP Server
z NAT(Network Address Translation)
z SNMP
z S/W upgrade
- Remote updating via HTTP or TFTP is available
z Wide Range supply voltage
- Supplying voltage from 6 to 30[VDC]
FAE Manual Page 7 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
1.4 SPECIFICATION
1.4.1 Mechanical Specification
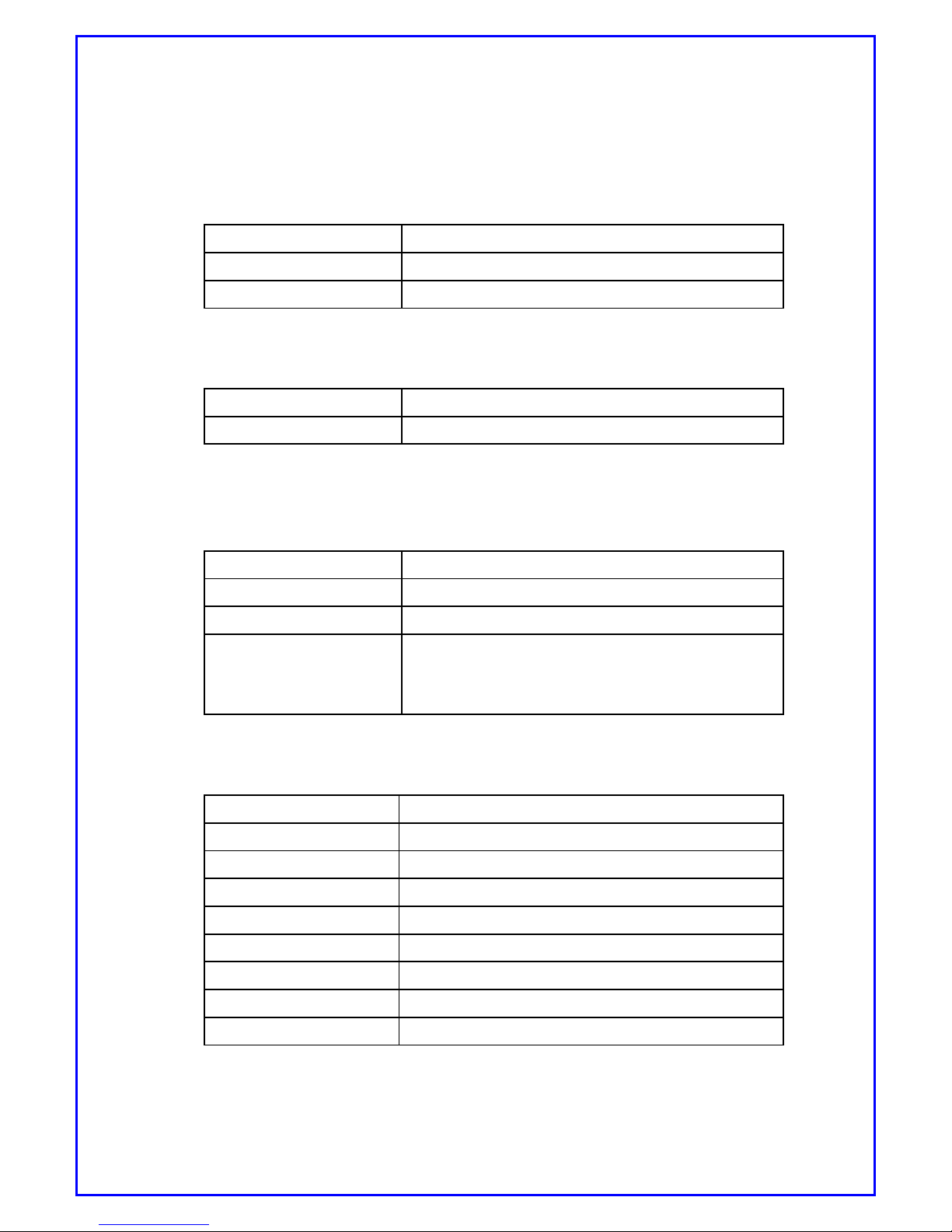
Dimension 124 x 146 x 28 mm
Weight 166 g (+ 29 g including stand)
Housing material Plastic (Ploy-carbonate)
[Table1. Mechanical specification]
1.4.2 Environment Specification
Operating Temp/Humi 0 ~ + 50 [°C], 85% at 50 [°C]
Storage Temp - 20 ~ + 70 [°C]
[Table2. Environment specification]
1.4.3 Electrical Specification
Tested by supply = +12[VDC], Temp = 25[°C]
DC input voltage + 6 ~ +30 [VDC]
Maximum current Under 750 [mA] @ 12[V]
Internal voltage + 1.8, + 3.0, + 3.3, + 5 [VDC]
Operating current
Ior = - 75 [dBm]
Ior = -104 [dBm]
Under 350 [mA] @ 12 [VDC]
Under 550 [mA] @ 12 [VDC]
[Table3. Electrical specification]
1.4.4 Hardware specification
Item Description
Product Name CDM-650PRO
User MCU 32-bit Network Processor
Program Memory 4M Bytes (Flash)
Data Memory 16M Bytes (SDRAM)
Wireless Interface USB 1.1 Host interface
24-Pin Diagnostic Port 1 Test port
Ethernet 1 Port 10/100Mbps Ethernet
Display 3-state LED
[Table4. Hardware specification]
FAE Manual Page 8 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
1.4.5 Software Specification
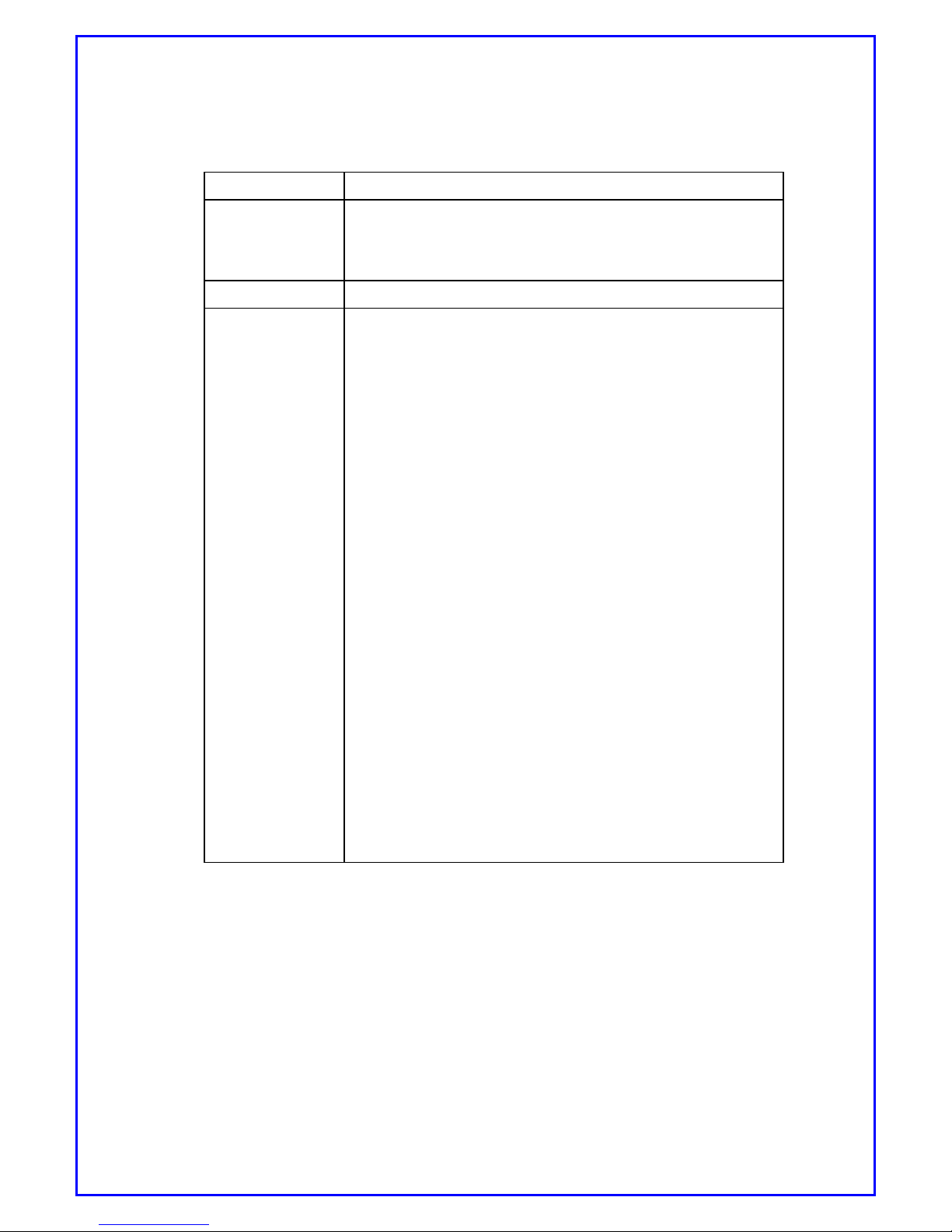
Item Description
Boot loader
Boot loader for CDM-650PRO
Flash erase/write for storing image
Built-in commands
Kernel Linux Kernel v2.4.28
Applications
PPP/PPPoE for wireless mobile network
NAT
- RFC 1631
- Up to 253 users
DHCP server
- RFC 2131
- Assigning local host IP automatically
RIP v1/v2
- RFC 1058/1723
- Static or Dynamic routing information
SNMP Agent/Trap(MIB I/II)
- RFC 1157
- Manage & Monitoring network equipment
SNTP Client
- RFC 1769
- Synchronize computer clocks in global Internet
ICMP
- RFC 792
- Checking error and sending message
User-friendly Web-based Management with CGI
- Managing & Monitoring Network equipment
[Table5. Software specification]

FAE Manual Page 9 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
1.5 PROTOCOL INFORMATION
1.5.1 PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between
two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer
connected by phone line to a server. For example, your Internet server
provider may provide you with a PPP connection so that the provider's
server can respond to your requests, pass them on to the Internet, and
forward your requested Internet responses back to you. PPP uses the
Internet protocol (IP) (and is designed to handle others). It is
sometimes considered a member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols.
Relative to the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model,
PPP provides layer 2 (data-link layer) service. Essentially, it packages
your computer's TCP/IP packets and forwards them to the server where
they can actually be put on the Internet.
PPP is a full-duplex protocol that can be used on various physical media,
including twisted pair or fiber optic lines or satellite transmission. It
uses a variation of High Speed Data Link Control (HDLC) for packet
encapsulation.
PPP is usually preferred over the earlier de facto standard Serial Line
Internet Protocol (SLIP) because it can handle synchronous as well as
asynchronous communication. PPP can share a line with other users
and it has error detection that SLIP lacks. Where a choice is possible,
PPP is preferred.
1.5.2 PPPoE
(point-to-point protocol over Ethernet)
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is a specification for
connecting multiple computer users on an Ethernet local area network
to a remote site through common customer premises equipment, which
is the telephone company's term for a modem and similar devices.
PPPoE can be used to have an office or building-full of users share a
common Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable modem, or wireless
connection to the Internet. PPPoE combines the Point-to-Point Protocol
(PPP), commonly used in dialup connections, with the Ethernet protocol,
which supports multiple users in a local area network. The PPP protocol
information is encapsulated within an Ethernet frame.
FAE Manual Page 10 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
PPPoE has the advantage that neither the telephone company nor the
Internet service provider (ISP) needs to provide any special support.
Unlike dialup connections, DSL and cable modem connections are
"always on." Since a number of different users are sharing the same
physical connection to the remote service provider, a way is needed to
keep track of which user traffic should go to and which user should be
billed. PPPoE provides for each user-remote site session to learn each
other's network addresses (during an initial exchange called
"discovery"). Once a session is established between an individual user
and the remote site (for example, an Internet service provider), the
session can be monitored for billing purposes. Many apartment houses,
hotels, and corporations are now providing shared Internet access over
DSL lines using Ethernet and PPPoE.
1.5.3 DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a communications
protocol that lets network administrators centrally manage and
automate the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses in an
organization's network. Using the Internet Protocol, each machine that
can connect to the Internet needs a unique IP address, which is
assigned when an Internet connection is created for a specific computer.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each
computer in an organization and a new IP address must be entered
each time a computer moves to a new location on the network. DHCP
lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from
a central point and automatically sends a new IP address when a
computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP
address will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending
on how long a user is likely to require the Internet connection at a
particular location. It's especially useful in education and other
environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases,
DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks in which there are more
computers than there are available IP addresses. The protocol also
supports static addresses for computers that need a permanent IP
address, such as Web servers.
FAE Manual Page 11 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
DHCP is an extension of an earlier network IP management protocol,
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP). DHCP is a more advanced protocol, but
both configuration management protocols are commonly used and
DHCP can handle BOOTP client requests. Some organizations use both
protocols, but understanding how and when to use them in the same
organization is important. Some operating systems, including Windows
NT/2000, come with DHCP servers. A DHCP or BOOTP client is a
program that is located in (and perhaps downloaded to) each computer
so that it can be configured.
1.5.4 NAT (Network Address Translation or Network Address Translator)
NAT (Network Address Translation or Network Address Translator) is
the translation of an Internet Protocol address (IP address) used within
one network to a different IP address known within another network.
One network is designated the
inside
network and the other is the
outside
. Typically, a company maps its local inside network addresses
to one or more global outside IP addresses and un-maps the global IP
addresses on incoming packets back into local IP addresses. This helps
ensure security since each outgoing or incoming request must go
through a translation process that also offers the 5opportunity to
qualify or authenticate the request or match it to a previous request.
NAT also conserves on the number of global IP addresses that a
company needs and it lets the company use a single IP address in its
communication with the world.
NAT is included as part of a router and is often part of a corporate
firewall. Network administrators create a NAT table that does the
global-to-local and local-to-global IP address mapping. NAT can also be
used in conjunction with
policy routing
. NAT can be statically defined or
it can be set up to dynamically translate from and to a pool of IP
addresses. Cisco's version of NAT lets an administrator create tables
that map:
- A local IP address to one global IP address statically
- A local IP address to any of a rotating pool of global IP addresses that
a company may have
- A local IP address plus a particular TCP port
to a global IP address or
one in a pool of them
FAE Manual Page 12 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
- A global IP address to any of a pool of local IP addresses on a round-
robin basis
NAT is described in general terms in RFC 1631, which discusses NAT's
relationship to Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR) as a way to
reduce the IP address depletion problem. NAT reduces the need for a
large amount of publicly known IP addresses by creating a separation
between publicly known and privately known IP addresses. CIDR
aggregates publicly known IP addresses into blocks so that fewer IP
addresses are wasted. In the end, both extend the use of IPv4 IP
addresses for a few more years before IPv6 is generally supported.
1.5.5 RIP v1/v2 (Routing Information Protocol)
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a widely-used protocol for
managing router information within a self-contained network such as a
corporate local area network or an interconnected group of such LANs.
RIP is classified by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as one of
several internal gateway protocols (Interior Gateway Protocol).
Using RIP, a gateway host (with a router) sends its entire routing table
(which lists all the other hosts it knows about) to its closest neighbor
host every 30 seconds. The neighbor host in turn will pass the
information on to its next neighbor and so on until all hosts within the
network have the same knowledge of routing paths, a state known as
network convergence
. RIP uses a hop count as a way to determine
network distance. (Other protocols use more sophisticated algorithms
that include timing as well.) Each host with a router in the network
uses the routing table information to determine the next host to route
a packet to for a specified destination.
RIP is considered an effective solution for small homogeneous networks.
For larger, more complicated networks, RIP's transmission of the entire
routing table every 30 seconds may put a heavy amount of extra traffic
in the network.
The major alternative to RIP is the Open Shortest Path First Protocol
(OSPF).
1.5.6 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
FAE Manual Page 13 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the protocol governing
network management and the monitoring of network devices and their
functions. It is not necessarily limited to TCP/IP networks.
1.5.7 SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol)
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) is a protocol that is used to
synchronize computer clock times in a network of computers.
Developed by David Mills at the University of Delaware, SNTP is now an
Internet standard. In common with similar protocols, SNTP uses
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to synchronize computer clock times
to a millisecond, and sometimes to a fraction of a millisecond.
Accurate time across a network is important for many reasons; even
small fractions of a second can cause problems. For example,
distributed procedures depend on coordinated times to ensure that
proper sequences are followed. Security mechanisms depend on
coordinated times across the network. File system updates carried out
by a number of computers also depend on synchronized clock times.
Air traffic control systems provide a graphic illustration of the need for
coordinated times, since flight paths require very precise timing
(imagine the situation if air traffic controller computer clock times were
not synchronized).
UTC time is obtained using several different methods, including radio
and satellite systems. Specialized receivers are available for high-level
services such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) and the
governments of some nations. However, it is not practical or cost-
effective to equip every computer with one of these receivers. Instead,
computers designated as
primary time servers
are outfitted with the
receivers and they use protocols such as SNTP to synchronize the clock
times of networked computers. Degrees of separation from the UTC
source are defined as strata. A radio clock (which receives true time
from a dedicated transmitter or satellite navigation system) is stratum-
0; a computer that is directly linked to the radio clock is stratum-1; a
computer that receives its time from a stratum-1 computer is stratum-
2, and so on.
The term SNTP applies to both the protocol and the client/server
programs that run on computers. The programs are compiled by the
FAE Manual Page 14 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
user as an SNTP client, SNTP server, or both. In basic terms, the SNTP
client initiates a time request exchange with the time server. As a
result of this exchange, the client is able to calculate the link delay, its
local offset, and adjust its local clock to match the clock at the server's
computer. As a rule, six exchanges over a period of about five to 10
minutes are required to initially set the clock. Once synchronized, the
client updates the clock about once every 10 minutes, usually requiring
only a single message exchange. Redundant servers and varied
network paths are used to ensure reliability and accuracy. In addition
to client/server synchronization, SNTP also supports broadcast
synchronization of peer computer clocks. SNTP is designed to be highly
fault-tolerant and scalable.
1.5.8 ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a message control and
error-reporting protocol between a host server and a gateway to the
Internet. ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP
) data-grams, but the
messages are processed by the IP software and are not directly
apparent to the application user.

FAE Manual Page 15 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
2. BASIC INFORMATION
2.1 Hardware composition
All hardware for CDM-650PRO is composed below.
1. CDM-650PRO 2. UTP Cable (Direct) 3. 12 [VDC] Adapter
(These images will be updated)
Note.
1. CDM-650PRO : Wireless 1X EV-DO DUAL-BAND Docking Station
2. UTP Cable: Connecting cable between Host PC and CDM-650PRO.
3. 12 [VDC] Adapter: Supply + 12 [VDC] power.
FAE Manual Page 16 of 62
Connect your network on wireless Internet easily
2.2 SOFTWARE COMPOSITION
All software for CDM-650PRO is composed below.
2.2.1 Web-based configuration page
CDM-650PRO has a web-based configuration page that user can set the
function of CDM-650PRO for user’s purpose.
2.2.2 Firmware
Firmware is the program operating the CDM-650PRO.
Firmware: Version CDM-650PRO-1.0.5
(Current: This name will be changed)
 Loading...
Loading...