Clevo 3200, 3600, 3400 Service Manual

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
i
Notebook Computer
Service Manual
3200/3400/3600
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ii
Preface
copyrights
NOTICE
The company reserves the right to revise this publication or to change its contents without notice. Information
contained herein is for reference only and does not constitute a commitment on the part of the manufacturer or any
subsequent vendor. They assume no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this
publication nor are they in anyway responsible for any loss or damage resulting from the use (or misuse) of this
publication.
This publication and any accompanying software may not, in whole or in part, be reproduced, translated, transmitted or reduced to any machine readable form without prior consent from the vendor, manufacturer or creators of
this publication, except for copies kept by the user for backup purposes.
Brand and product names mentioned in this publication may or may not be copyrights and/or registered trademarks
of their respective companies. They are mentioned for identification purposes only and are not intended as an
endorsement of that product or its manufacturer.
First Edition ©October, 1999
Trademarks
Intel
®
, Pentium® and Pentium® with MMX™ technology are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
IBM® and OS/2® are registered trademarks of IBM Corporation.
MS-DOS®, Windows®, Windows® 95 and Windows NT™ are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
SystemSoft® and CardWizard® are registered trademarks of SystemSoft Corporation.
Other brand and product names are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
iii
the manual
ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for service personnel who have completed sufficient training to undertake the maintenance and inspection of personal computers.
It is organized to allow you to look up basic information for servicing and/or upgrading components of the notebook computer. The following information is included:
Chapter 1, Introduction, provides general information about the location of system elements and their specifications.
Chapter 2, Chipset, briefly describes the computer’s core logic, memory and supporting chipset.
Chapter 3, Disassembly, provides step-by-step instructions for disassembling parts and subsystems and how to
upgrade elements of the system.
Chapter 4, Troubleshooting, provides recommendations on how to solve possible system problems.
Appendix A, Part Lists
Appendix B, Circuit Diagrams
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
iv
Preface
conventions
CONVENTIONS
This manual uses the following typesetting conventions:
Example
commonly used terms (capitals): FDD, HDD, AC, DC
features on the notebook (icons):
keyboard keys (bold, as printed): Y, N, Enter
programs, operating systems (italics): Setup, Windows 95
files (all capitals): AUTOEXEC.BAT
menu items (initial capitals): External Cache Memory
variables (quotes): “Enabled”
DOS text the user must enter (bold): a:>\setup
keys to press while in DOS (brackets,bold): [Enter]
menu buttons (bold): Continue
command switches (bold): format /s
space:
~
RELATED DOCUMENTS
You may also need to consult the following manuals for additional information:
User’s Manual
This describes the notebook’s features and the procedures for operating the computer and its ROM-based setup
program. It also describes the installation and operation of the utility programs provided with the notebook.

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
v
table of contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Preface
Cover ....................................................................................................................................................................................................i
Notice.................................................................................................................................................................................................. ii
About This Manual ........................................................................................................................................................................... iii
Conventions ................................................................................................................................................................................. iv
Related Documents .................................................................................................................................................................... iv
Table of Contents............................................................................................................................................................................... v
List of Figures .................................................................................................................................................................................. viii
List of Tables ....................................................................................................................................................................................... x
Chapter 1: Introduction
System Specifications ....................................................................................................................................................................1-2
CPU ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 1-2
Memory ......................................................................................................................................................................................1-2
BIOS .............................................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Video ...........................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Drives ..........................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Audio...........................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
I/O ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 1-4
Interface ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 1-4
Power System ............................................................................................................................................................................1-4
Other Features (optional) .........................................................................................................................................................1-5
Environment .................................................................................................................................................................................... 1-5
Physical ............................................................................................................................................................................................1-5
External Locator ..............................................................................................................................................................................1-6
Chapter 2: Chipset
CPU - Intel Mobile Dixon/Celeron...............................................................................................................................................2-4
Core Logic Chipset - Intel 440BX AGPset .................................................................................................................................. 2-5
North Bridge AGPset System Controller, 443BX..................................................................................................................2-5
South Bridge, PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator, PIIX4E ........................................................................................................................ 2-6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
vi
Preface
Supporting Chips ........................................................................................................................................................................... 2-8
Ricoh 5C475 PCI-CardBus Bridge ..........................................................................................................................................2-8
SMSC FDC37N869 PC 99 ...................................................................................................................................................... 2-10
Compliant 5V and 3.3V Super I/O Controller with Infrared Support ............................................................................... 2-10
ATI 3D RAGE Mobility Graphics Controller ........................................................................................................................... 2-11
YAMAHA YMF744B DS-XG .................................................................................................................................................... 2-12
Chapter 3: Disassembly
Connections ...................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Maintenance Precautions ...................................................................................................................................................... 3-3
Battery Precautions.................................................................................................................................................................. 3-3
Cleaning .................................................................................................................................................................................... 3-4
Maintenance Tools .................................................................................................................................................................. 3-4
General Disassembly: Under the Keyboard .............................................................................................................................. 3-5
Removing the Keyboard & Heat Plate ..................................................................................................................................3-5
Changing the CPU (Mainboard Versions 4 ~ 5) .................................................................................................................. 3-6
General Disassembly: Removing & Replacing the LCD Module ............................................................................................3-8
Replacing the LCD .................................................................................................................................................................. 3-10
12.1” Disassembly.............................................................................................................................................................. 3-10
13.3” Disassembly............................................................................................................................................................. 3-10
Removing the Inverter Board .......................................................................................................................................... 3-10
General Disassembly: Top Cover Assembly ............................................................................................................................ 3-12
Separating the Top Cover Assembly.................................................................................................................................... 3-12
General Disassembly: Top Cover Components ...................................................................................................................... 3-14
TouchPad................................................................................................................................................................................. 3-14
Microphone ............................................................................................................................................................................ 3-14
General Disassembly: Bottom Cover Assembly...................................................................................................................... 3-16
HDD Bracket ........................................................................................................................................................................... 3-16
Mainboard .............................................................................................................................................................................. 3-16
Optional Fax/Modem Module, The Power Board, The IR Board, and IO Bracket......................................................... 3-18
Fax/Modem Modem (not shown) .................................................................................................................................. 3-18
The Power Board .............................................................................................................................................................. 3-18
The IR Board ...................................................................................................................................................................... 3-18
The IO Bracket ................................................................................................................................................................... 3-18
table of contents

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
vii
Module Disassembly ..................................................................................................................................................................3-20
HDD Module ...........................................................................................................................................................................3-20
Removing the HDD Module.............................................................................................................................................3-20
Replacing/Upgrading the Cartridge .................................................................................................................................... 3-21
HDD Module Assembly....................................................................................................................................................3-22
Setting Up a New HDD for the First Time ......................................................................................................................3-23
Switches & Connectors .........................................................................................................................................................3-24
Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Before You Begin ........................................................................................................................................................................... 4-2
Tools ...........................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
System Troubleshooting Chart ..................................................................................................................................................... 4-3
Pre-POST Assistant ........................................................................................................................................................................ 4-4
AC Power LED Fails .................................................................................................................................................................. 4-5
AC/DC Adapter ................................................................................................................................................................... 4-5
AC Power & Charge LEDs Fail ................................................................................................................................................ 4-6
Checking the Power Board ............................................................................................................................................... 4-6
Checking the Fuses ............................................................................................................................................................ 4-6
Checking the Battery Pack and its Cabling .................................................................................................................. 4-10
Checking the Battery Pack........................................................................................................................................ 4-10
Checking the Cabling ................................................................................................................................................. 4-11
Checking the System Board ............................................................................................................................................ 4-11
LCD Screen Failure to Display ............................................................................................................................................... 4-12
Checking the LCD to System Board Connection .......................................................................................................... 4-12
Checking the Inverter Board ........................................................................................................................................... 4-13
Checking the LCD Screen ................................................................................................................................................ 4-14
POST — Testing the System ....................................................................................................................................................... 4-15
No Errors Found During the POST ........................................................................................................................................ 4-15
POST Error Beeps & Screen Messages .............................................................................................................................. 4-16
Post-POST Problems ...................................................................................................................................................................4-24
PC Card Socket Malfunction.................................................................................................................................................4-25
Sound Output Failure .............................................................................................................................................................4-26
Checking the Software Configuration............................................................................................................................4-26
table of contents
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
viii
Preface
Checking the Volume ....................................................................................................................................................... 4-26
Checking the Speaker Cable .......................................................................................................................................... 4-27
Suspend Function Failure ......................................................................................................................................................4-28
Charge LED Failure.................................................................................................................................................................4-28
Appendix A: Part Lists
Appendix B: Circuit Diagrams
LIST OF FIGURES
Fig. 1 – 1 Front View ............................................................................................................................................................1-6
Fig. 1 - 2 Bottom View ........................................................................................................................................................1-6
Fig. 1 – 3 Left View ............................................................................................................................................................... 1-7
Fig. 1 – 4 Right View ............................................................................................................................................................ 1-7
Fig. 1 – 5 Rear View ............................................................................................................................................................. 1-7
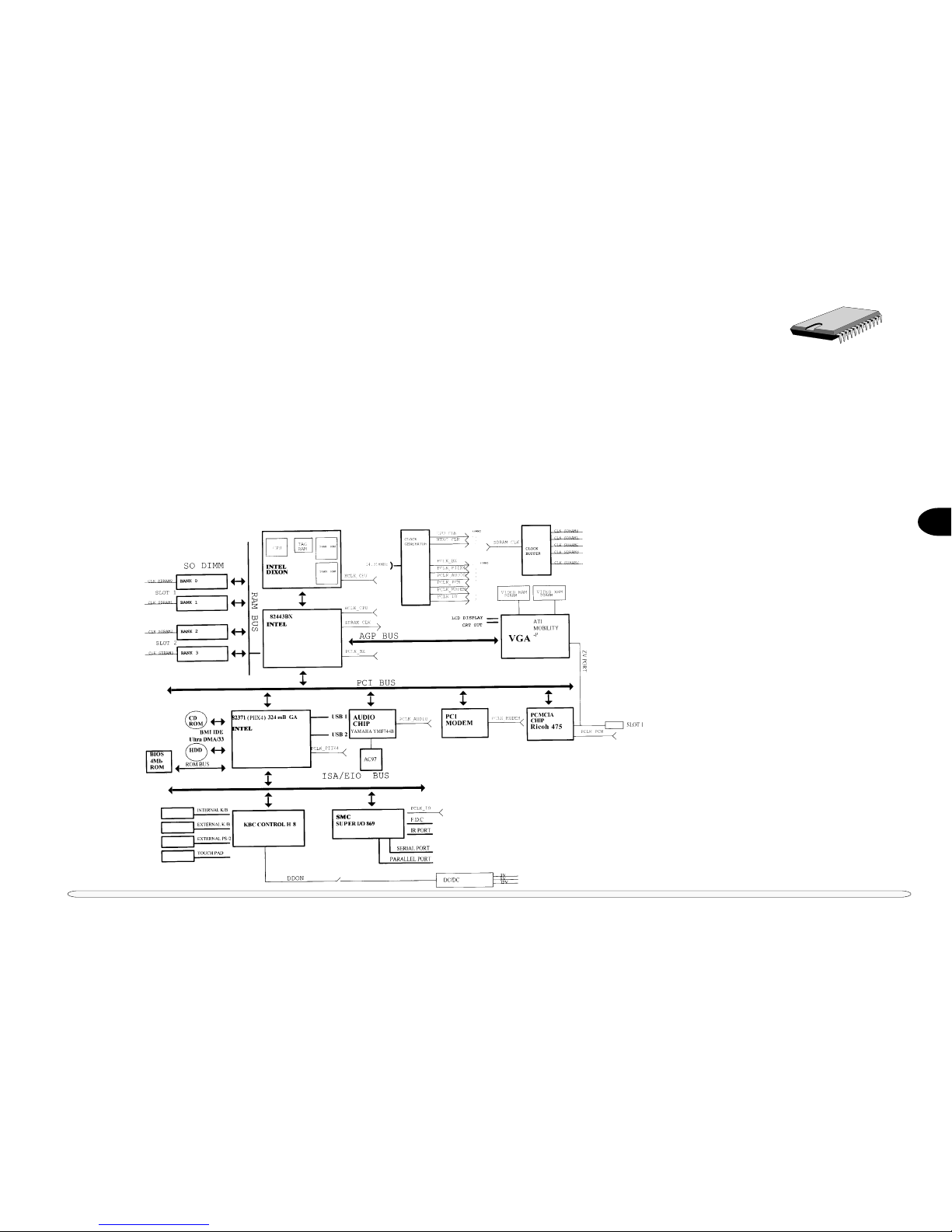
Fig. 2 – 1 System Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................... 2-1
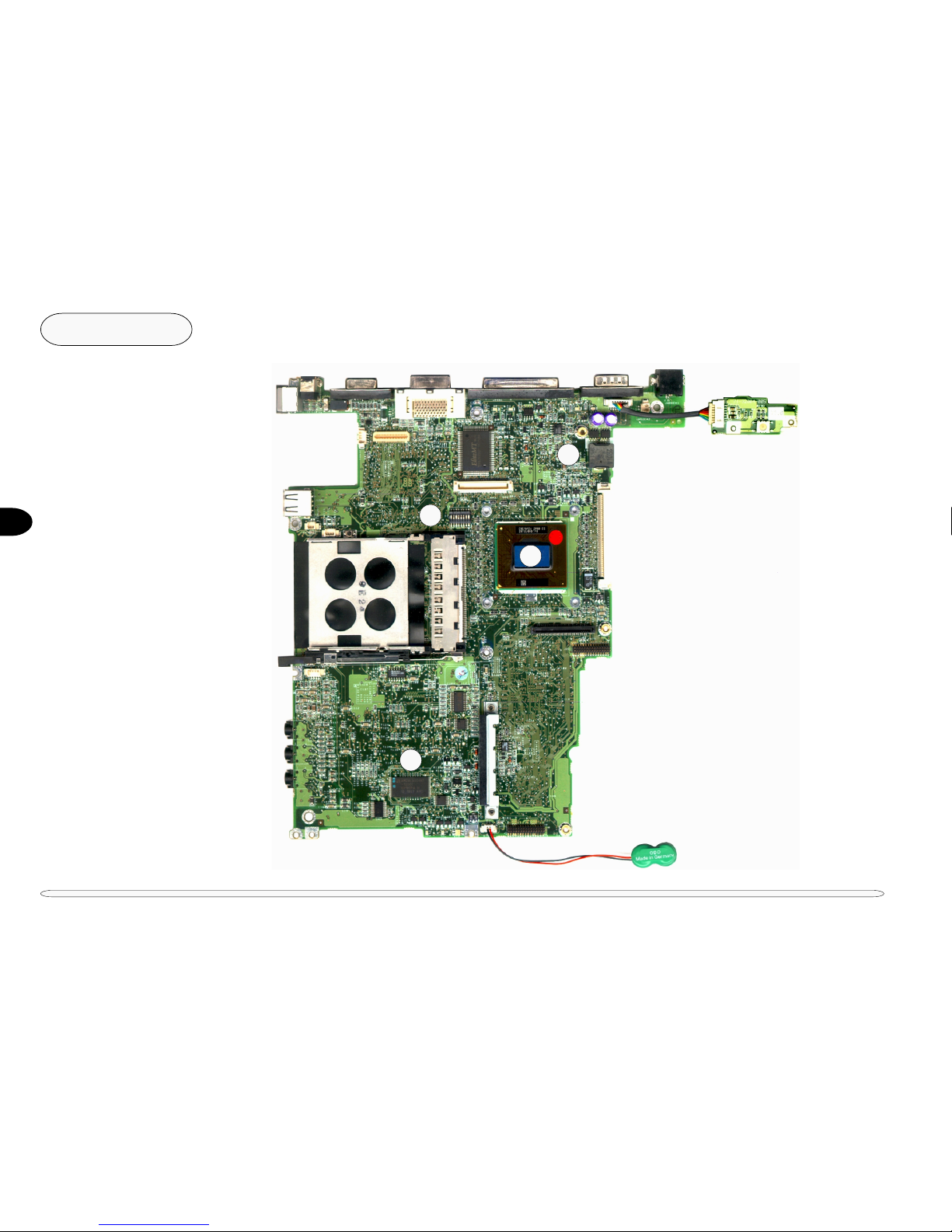
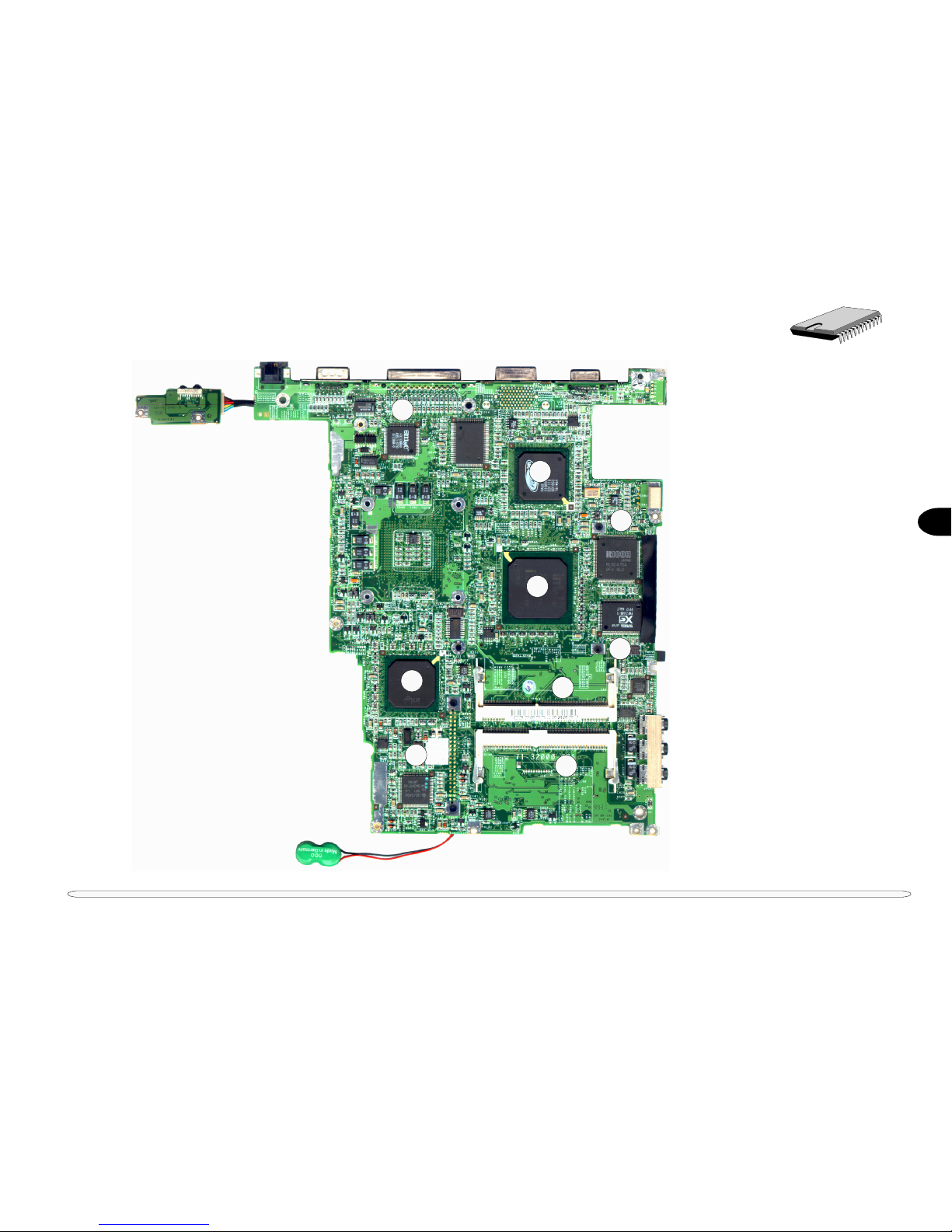
Fig. 2 – 2 Chipset Site Diagrams................................................................................................................................... 2-2,3
Fig. 3 – 1 Releasing the Keyboard & Removing the Heat Plate...................................................................................3-5
Fig. 3 – 2 CPU &SW1 ........................................................................................................................................................... 3-7
Fig. 3 – 3 Removing the LCD Module ...............................................................................................................................3-9
Fig. 3 – 4 Separating the LCD & Frame........................................................................................................................... 3-11
Fig. 3 – 5 Top Cover Disassembly (Bottom Screws)...................................................................................................... 3-13
Fig. 3 – 6 Top Cover Disassembly (Top Screws) ............................................................................................................ 3-13
Fig. 3 – 7 Top Cover Assembly ........................................................................................................................................ 3-15
Fig. 3 – 8 Bottom Cover Assembly ..................................................................................................................................3-17
Fig. 3 – 9 Final Separation ............................................................................................................................................... 3-19
Fig. 3 – 10 Removing the HDD ......................................................................................................................................... 3-20
Fig. 3 – 11 HDD Module Disassembly.............................................................................................................................. 3-21
list of figures

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ix
Fig. 3 – 12 HDD Module Assembly.................................................................................................................................. 3-22
Fig. 3 – 13 Ports & Connectors (top views) .................................................................................................................... 3-24
Fig. 3 – 14 Ports & Connectors (bottom views).............................................................................................................. 3-25
Fig. 4 – 1 Troubleshooting Flowchart ...............................................................................................................................4-3
Fig. 4 – 2 Adapter’s Check Points ................................................................................................................................... 4-5
Fig. 4 – 3 Power Components .......................................................................................................................................... 4-7
Fig. 4 - 4 Battery Circuitry ................................................................................................................................................ 4-10
Fig. 4 - 5 LCD to Mainboard Connection ...................................................................................................................... 4-12
Fig. 4 - 6 Inverter Board Component Sites ................................................................................................................... 4-13
Fig. 4 – 7 Startup Screen: The POST ............................................................................................................................... 4-15
Fig. 4 – 8 Speaker Connector on Mainboard ...............................................................................................................4-27
Fig. A – 1 3200 Bottom Assembly .................................................................................................................................... A-2
Fig. A – 2 3200 Bottom Assembly Parts List ................................................................................................................... A-3
Fig. A – 3 3200 Top Case Assembly ................................................................................................................................ A-4
Fig. A – 4 3200 Top Case Assembly Parts List ............................................................................................................... A-5
Fig. A – 5 3200 12.1” LCD Assembly................................................................................................................................. A-6
Fig. A – 6 3200 12.1” LCD Assembly Parts List.................................................................................................................A-7
Fig. A – 7 3200 13.3” LCD Assembly................................................................................................................................ A-8
Fig. A – 8 3200 13.3” LCD Assembly Parts List............................................................................................................... A-9
Fig. A – 9 3200 CD-ROM Assembly ................................................................................................................................A-10
Fig. A – 10 3200 CD-ROM Assembly .................................................................................................................................A-11
Fig. A – 11 3200 FDD Assembly ........................................................................................................................................ A-12
Fig. A – 12 3200 FDD Assembly Parts List ....................................................................................................................... A-13
Fig. A – 13 3200 HDD Assembly ....................................................................................................................................... A-14
Fig. A – 14 3200 HDD Assembly Parts List ...................................................................................................................... A-15
list of figures
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
x
Preface
list of tables
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3 – 1 CPU Switch Settings ..........................................................................................................................................3-6
Table 4 – 1 Pre-POST Problems ........................................................................................................................................... 4-4
Table 4 – 2 Adapter Contacts ............................................................................................................................................... 4-5
Table 4 – 3 Inverter Board Check Areas ........................................................................................................................... 4-13
Table 4 – 4 Fatal Error Messages ...................................................................................................................................... 4-16
Table 4 – 5 Non-Fatal Error Messages .................................................................................................................... 4-17,18,19
Table 4 – 6 Phoenix BIOS POST Default Test Points (displayed on debug card) ......................................... 4-20,21,22,23
Table 4 – 7 Post-POST Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 4-24
Table 4 – 8 Possible PC Card Problems & Solutions ..................................................................................................... 4-25

1
1 – 1
1 Introduction
This manual covers the information you need to service or upgrade the Notebook Computer. Information about
operating the computer (e.g. getting started, and the Setup utility) is in the User’s Manual. Information about
drivers (e.g. VGA & audio) is also found in User’s Manual. That manual is shipped with the computer.
Operating systems (e.g. DOS, Windows 9x, Windows NT 4.0, OS/2 Warp, UNIX, etc.) have their own manuals as do
application software (e.g. word processing and database programs). If you have questions about those programs,
you should consult those manuals.
The notebook is designed to be upgradable. It supports Pentium
™
II CPUs of different speeds and different types of
LCD screens: TFT color from a variety of manufacturers and in a variety of resolution/color configurations. In
addition, system memory, hard disk, and BIOS are also upgradable. See Chapter 3, “Disassembly,” for a detailed
description of the upgrade procedures for each specific component.
Please note the warning and safety information indicated by the “M” symbol.
The balance of this chapter reviews the computer’s technical specifications and external features.

1
1 – 2
Introduction
SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS
CPU
mPGA Package Intel Celeron: 300 ~ 400 MHz
Intel Dixon: 300 ~ 400 MHz
MEMORY
L1 cache (in CPU) 16KB code + 16KB data
L2 cache Celeron: 128KB on die SRAM
(integrated with CPU) Dixon: 256KB on die SRAM
RAM base 0MB (onboard)
RAM expansion 2 small outline DIMM sockets (144 pin)
DIMM sizes: 32MB, 64MB, 128MB
standards: TSOP package, 3.3-volt
modes: SDRAM
speed: 10ns or faster
use: singly or mixed or identical pairs
maximum expansion: 256MB
BIOS
512KB Flash ROM
support: Plug ‘n Play 1.0a, LBA, APM 1.2, ACPI
specifications

1
1 – 3
VIDEO
memory 4MB/8MB SGRAM
chipset ATI Mobility-P AGP (with 3D, AGP & ZV support/proprietary driver)
architecture 64-bit 2x AGP bus with Windows Acceleration
display TFT (active matrix)
12.1” SVGA, (800x600) at 24-bit color (TrueColor)
13.3”/XGA, (1024x768) at 32-bit color (TrueColor)
DRIVES
HDD module removable 2½” (9.5mm) , PCI local bus IDE interface
Device Bay
CD-ROM module full size (5.25”) ATAPI interface tray-loading mechanism,
access time below 100ms
or DVD
†
module full size (5.25”) ATAPI interface tray-loading mechanism,
access time below 100ms
or FDD module removable 3.5”, 1.44 MB with 3-Mode support
or LS-120 module removable 3½” (12.7mm height), 120MB PCI local bus IDE interface
† with Software MPEG support
AUDIO
chipset Yamaha YMF744B (DS-XG), proprietary driver
architecture 32-bit PCI bus
type 64-voice dual-audio engine, AC-3 speaker virtualization, PnP, up to 20-bit ADCDAC
audio resolution, I2S/zoomed video, high quality MIDI synthesis
sampling max. record & playback up to 48 KHz stereo (WAVE audio)
3D HRTF 3-D positional audio under DirectX™ 5.0
compatibility Sound Blaster Pro™ legacy audio, MS Windows Sound System™
interface speakers (phones), microphone, line-in
speakers 2 built-in: 0.5W stereo amp.
specifications
1
1 – 4
Introduction
I/O
USB 2 ports, compliant with UHCI 1.1, USB 1.0 & PCI 2.1
Serial 1 9-pin, 16C550 compatible
Serial 2 infrared, IrDA v 1.1, FIR, SIR compatible
Parallel 25-pin, ECP, EPP, output-only, bi-directional
CRT 15-pin VGA
PS/2 6-pin, mini-din, mouse or keyboard
expansion 120-pin, proprietary port replicator
PC Card one Type I or Type II socket, PC Card 3.0, ZV port & CardBus compliant
INTERFACE
keyboard 87-key or 90-key (depending on the language)
Windows 95 compliant with embedded numeric keypad
pointing device PS/2 TouchPad (built-in), MS-Mouse compatible
POWER SYSTEM
adapters (external) universal, auto-sensing switching
input: 90-240VAC @47- 63Hz
output: 55W, 19V, 2.8A
battery pack(s) 36S (Ni-MH) or 202 (Li-Ion) form factor “smart” battery or compatible
“smart battery” with intelligent charging control and battery gauge circuit
battery charge time Fast (system off) approx. 2 hours per battery, 2000mA ±200mA
Slow (system on) approx. 5 hours per battery, 700mA ± 50mA
(based on a 4000mA smart battery)
life per charge approx. 100 minutes per battery (based on an Intel Dixon-256 333 MHz CPU,
running “ZD BatteryMark 2.0”” software in the Windows 98 operating system)
management BIOS control, APM ver 1.2
levels: full-on, standby, suspend-to-RAM/suspend-to-disk (0 volt)
specifications
¯
Advanced Users
Actual battery life per
charge may differ from this
figure. It will vary depending on the condition of the
battery, the environment,
setup, and working habits.

1
1 – 5
OTHER FEATURES (OPTIONAL)
56K Fax/Data/Voice modem
ENVIRONMENT
operating temp. 0oC to 35oC (32oF to 95oF)
storage temp. -10
o
C to 65oC (14oF to 149oF)
operating humidity 40% to 80%, non-condensing
storage humidity 10% to 90%, non-condensing
altitude 8000 feet
shock (unpacked) 5G (11 + 1 microsecond pulse)
PHYSICAL
dimensions 306mm(w) x 232mm(d) x 29.8mm(h)
weight 2.28Kg (with battery, FDD &HDD)
specifications
1
1 – 6
Introduction
external locator
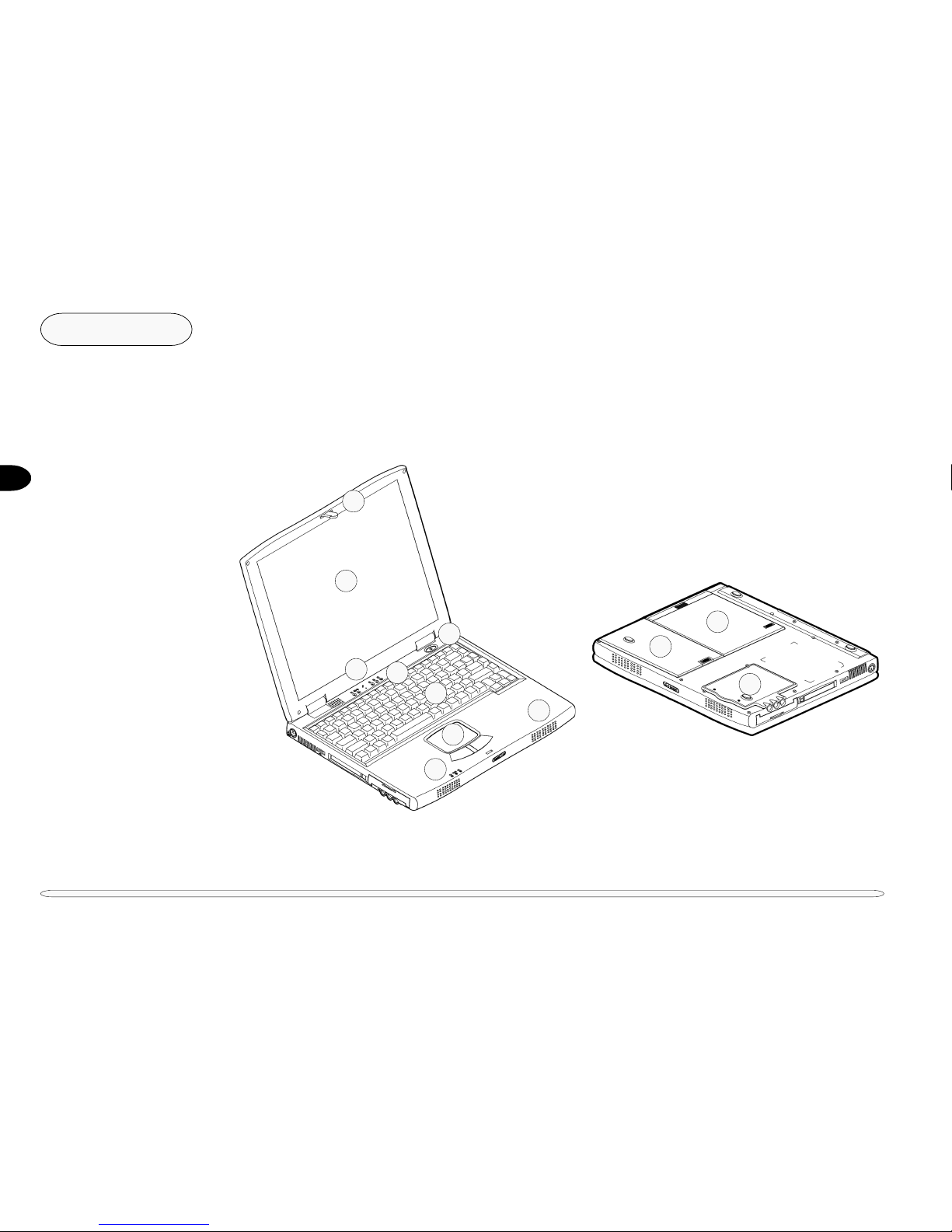
FRONT VIEW
FIG. 1 – 1
1. Cover latch
2. LCD
3. Speakers
4. On/Off switch
5. Microphone
6. LED status indicators
7. Keyboard
8. TouchPad & buttons
EXTERNAL LOCATOR
The following figures show the external locations of the computer’s main subsystems.
2
1
3
7
6
5
3
4
8
11
9
10
BOTTOM VIEW
FIG. 1 - 2
9. Device bay
10. Battery bay
11. RAM bay
1
1 – 7
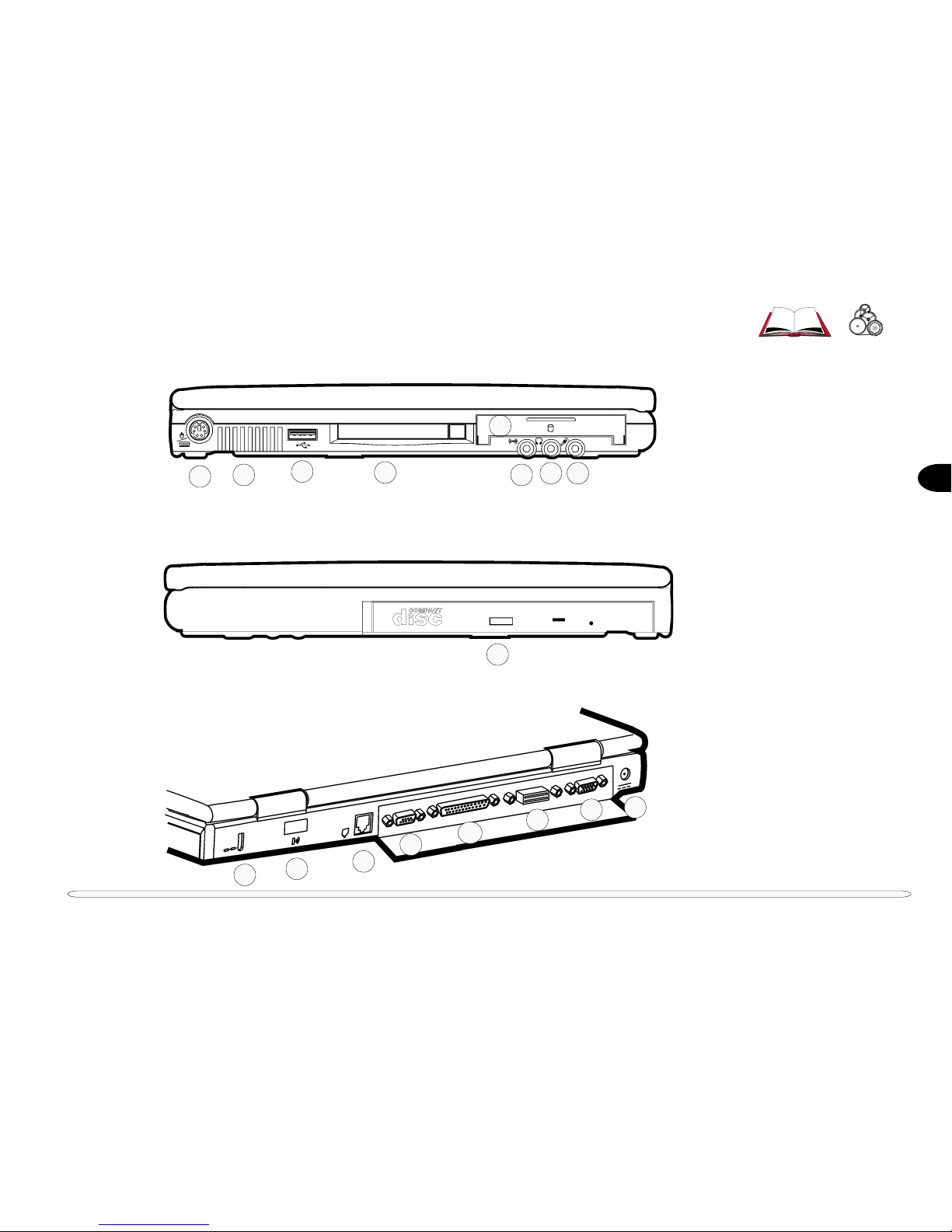
LEFT VIEW
FIG. 1 – 3
1. PS/2 port
2. Fan
3. USB port
4. PC Card slot
5. HDD module
6. Audio line-in jack
7. Phone jack
8. Mic jack
RIGHT VIEW
FIG. 1 – 4
9. CD-ROM module (option)
or DVD ROM module (option)
or FDD module (option)
or LS-120 module (option)
REAR VIEW
FIG. 1 – 5
10. Kensington lock port
11. IrDA (serial 2) port
12. Fax/Modem (option)
13. COM (serial 1) port
14. Parallel port
15. Expansion port
16. External monitor port
17. Adapter port
external locator
11
6
798
10
13
12
14
5
1
2
3
4
16
17
15

1
1 – 8
Introduction
notes
NOTES:
2
2 – 1
2 Chipset
The computer is completely AT-compatible. Its chipset supports a high-performance PCI bus video interface and
state-of-the-art power management features. This chapter mainly describes the following major system components:
• CPU • Core logic chipset • Supporting chips
The following figures are the system block diagram and the component site diagram. These provide an overview of
the computer’s layout and a practical locator for chipset components.
SYSTEM BLOCK D IAGRAM
FIG. 2 – 1
2
2 – 2
Chipset
CHIPSET SITE D IAGRAM
FIG. 2 – 2
1. Pentium II CPU
2. DIP switch
3. CMOS battery
4. BIOS chip
AMD AM29LV004BT
block diagram
1
2
3
4
2
2 – 3
CHIPSET SITE D IAGRAM
FIG. 2 – 2 (CONT.)
5. Super I/O controller
SMSC FDC37N869
6. Video controller
ATI RAGE Mobility
7. PC Card controller
Ricoh RL5C475A
8. Audio controller
YAMAHA YMF744B
9. Core Logic chip
82443BX (North Bridge)
10. Core Logic chip
82371EB (South Bridge)
11. Keyboard controller
H8/3434
12. SDRAM DIMM socket
13. SDRAM DIMM socket
component sites
6
7
8
9
11
12
10
13
5

2
2 – 4
Chipset
CPU - INTEL MOBILE DIXON/CELERON
The Notebook uses the Intel Mobile Dixon/Celeron processor in a Micro PGA1 package. The Intel Mobile Dixon/
Celeron processor features an integrated L2 cache (256KB for Dixon and 128KB for Celeron) and a 64-bit high
performance system bus.
The Mobile Dixon/Celeron processor’s 64-bit wide Low Power Gunning Transceiver Logic system bus is compatible with the 440BX AGPSet and provides a glue-less, point-to-point interface for an I/O bridge/memory controller.
The Intel Mobile Dixon and Celeron processors are fully compatible with all software written for the Pentium
processor with MMX technology, Pentium processor, Intel486 microprocessor, and Intel386 microprocessor. In
addition, they provide improved multimedia & communications performance. They feature:
• Performance improved over existing mobile processors
- Supports the Intel Architecture with Dynamic Execution
- Supports the Intel Architecture MMX technology
• Integrated primary (L1) instructions and data caches
- 4-way set associative, 32-byte line size, 1 line per sector
- 16-Kbyte instruction cache and 16-Kbyte writeback data cache
- Cacheable range programmable by processor programmable registers
• Integrated second level (L2) cache
- 4-way set associative, 32-byte line size, 1 line per sector
- Operated at full core speed
- 256-Kbyte, ECC protected cache data array
• Low Power GTL+ system bus interface
- 64-bit data bus, 66-MHz operation
- Uniprocessor, two loads only (processor and I/O bridge/memory controller)
- Short trace length and low capacitance allows for single ended termination
• Voltage reduction technology
• Pentium II processor clock control
- Quick Start for low power, low exit latency clock “throttling”
- Deep Sleep mode for extremely low power dissipation
• Thermal diode for measuring processor temperature
CPU

2
2 – 5
CORE LOGIC CHIPSET - INTEL 440BX AGPSET
The Intel 440BX AGPset consists of the BX System Controller (443BX) and the PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4E).
The AGPset forms a Host-to-PCI bridge and provides the second level cache control and a full function 64-bit data
path to main memory.
NORTH BRIDGE AGPSET SYSTEM CONTROLLER, 443BX
The BX System Controller (443BX) integrates the cache and main memory DRAM control functions and provides
bus control to transfer between the CPU, cache, main memory, AGP bus and the PCI Bus.
Features
• Supports the Pentium II processor family host bus at 100MHz and 66 MHz at 3.3V
• PCI 2.1 compliant
• Integrated Data Path
• Integrated DRAM controller
- 8Mbytes to 256Mbytes main memory
- 64Mbit DRAM/SDRAM technology support
- EDO and SDRAM DRAM support
- Integrated programmable-strength for DRAM interface
- CAS-Before-RAS refresh, extended CBR and self refresh for EDO
- CAS-Before-RAS and self refresh for SDRAM
• Fully synchronous, minimum latency 30/33 MHz PCI bus interface
- Five PCI bus masters (including PIIX4)
- 10 DWord PCI-to-DRAM read prefetch buffer
- 18 DWord PCI-DRAM post buffer
- Multi-Transaction timer to support multiple short PCI transactions
• AGP Features
- AGP 1.0 compliant
- 66/133 MHz data transfer capability
- Supports concurrent CPU, AGP and PCI transactions
• Power Management Features
- Dynamic stop clock support
- Suspend to RAM (STR)
- Suspend to Disk (STD)
- Power On Suspend (POS)
- Internal clock control
- SDRAM and EDO self refresh during suspend
- ACPI support
- Compatible SMRAM (C_SMRAM) and Extended SMRAM (E_SMRAM)
- SMM write-back cacheable in E_SMRAM mode up to 1MB
• Supports the Universal Serial Bus (USB)
• 492 Pin BGA 440BX AGPset with integrated data paths
core logic chipset

2
2 – 6
Chipset
SOUTH BRIDGE, PCI ISA IDE XCELERATOR, PIIX4E
The PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4E) is a multi-function PCI device implementing a PCI-to-ISA bridge function, a
PCI IDE function, a Universal Serial Bus host/hub function, and an Enhanced Power Management function. As a
PCI-to-ISA bridge, the PIIX4E integrates many common I/O functions found in ISA-based PC systems - a seven
channel DMA Controller, two 82C59 Interrupt Controllers, an 8254 Timer/Counter, and a Real Time Clock. In
addition to compatible transfers, each DMA channel supports Type F transfers. The PIIX4E also contains full
support for both PC/PCI and Distributed DMA protocols implementing PCI based DMA. The Interrupt Controller
has Edge or Level sensitive and programmable inputs and fully supports the use of an external I/O Advanced
Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) and Serial Interrupts. Chip select decoding is provided for BIOS, Real
Time Clock, Keyboard Controller, second external Microcontroller, as well as 2 Programmable Chip Selects. The
PIIX4 provides full Plug and Play compatibility. The PIIX4E can be configured as a Subtractive Decode bridge. This
allows the use of a subtractive decode PCI-to-PCI bridge such as the 82380 chipset which implements a PCI/ISA
docking station environment.
The PIIX4E supports two IDE connectors for up to four IDE devices providing an interface for IDE hard disks and
ROMs. Up to four IDE devices can be supported in Bus Master mode. The PIIX4E contains support for “Ultra
DMA” synchronous DMA compatible devices.
The PIIX4E contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) Host Controller that is Universal Host Controller Interface
(UHCI) compatible. The Host Controller’s root hub has two programmable USB ports.
The PIIX4E supports Enhanced Power Management, including full Clock Control, Device Management for up to
14 devices, and Suspend and Resume logic with Power On Suspend, Suspend to RAM or Suspend to Disk. It fully
supports Operating System Directed Power Management via the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
(ACPI) specification. The PIIX4E integrates both a System Management Bus (SMBus) Host and Slave interface for
serial communication with other devices.
core logic chipset
Features
• Supports Pentium and Pentium II Microprocessors
- 440BX ISA kit
• Power Management Logic
- Global and local device management
- Suspend/resume logic
- Supports thermal alarm
- Support for external microcontroller
- Full support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification and OS Directed Power Management

2
2 – 7
• Multifunction PCI to ISA Bridge
- Supports PCI at 30 MHz and 33 MHz
- Supports PCI Rev 2.1 specification
- Supports Full ISA or Extended I/O (EIO) Bus
- Supports full positive decode or subtractive decode of PCI
- Supports ISA/EIO at 1/4 of PCI frequency
• Supports both mobile and desktop deep green environments
- 3.3 V operation with 5 V tolerant buffers
- Ultra-low power for mobile environments
- Power-On Suspend and Soft-OFF for desktop environment
- All registers readable/restorable for proper resume from 0 V suspend
• Integrated IDE Controller
- Independent Timing of up to 4 drives
- PIO Mode 4 transfers up to 14 Mbytes/s
- Supports “Ultra 33” Synchronous DMA mode transfers up to 33 MBytes/sec
- Integrated 8 x 32-bit buffer for IDE PCI Burst
- Supports glue-less “Swap-Bay” option with full electrical isolation
• Enhanced DMA Controller
- Two 8237 DMA controllers
- Supports PCI DMA with 3 PC/PCI channels and Distributed DMA protocols (simultaneously)
- Fast Type-F DMA for reduced PCI bus usage
• Interrupt Controller based on two 82C59
- 15 interrupt support
- Independently programmable for Edge/Level sensitivity
- Supports optional external I/O APIC
- Serial interrupt input
• Timers based on 82C54
- System Timer, Refresh Request, Speaker Tone Output
• USB
- Two USB 1.0 ports for serial transfers at 12 or 1.5 Mbit/sec
- Supports legacy keyboard and mouse software with USB-based keyboard and mouse
- Supports UHCI Design Guide Revision 1.1 Interface
• SMBus
- Host interface allows CPU to communicate via SMBus
- Slave interface allows external SMBus master to control resume events
• Real-Time Clock
- 256 Byte Battery-Pack CMOS SRAM
- Includes Date Alarm
- Two 8-byte Lockout Ranges
• Microsoft Win95/98 compliant
core logic chipset

2
2 – 8
Chipset
supporting chip - PC Card
SUPPORTING CHIPS
The following subsections describe major supporting chips:
• Ricoh 5C475 PCI-CardBus Bridge
• SMSC FDC37N869 PC 99 Compliant 5V and 3.3V Super I/O Controller with Infrared Support
• ATI 3D RAGE Mobility Graphics Controller
• Yamaha744B DS-XG Audio Controller
RICOH 5C475 PCI-CARDBUS BRIDGE
The 5C475 is a PC card controller offering a single chip solution as a bridge between PCI bus and CardBus. The
5C475 includes a PC Card 95 compliant socket interface and a bridge function to the PCI bus of 33MHz. The 5C475
can support the 32-bit CardBus (Card-32) and the 16-bit PC card (Card-16) without external buffers.
Concerning the card control interface, the 5C475’s register is compatible with the Intel 82365SL and Ricoh’s
RF5C396/366 in order to maintain backward compatibility with the existing 16-bit PC Card compliant with
PCMCIA2.1/JEIDA4.2. All PC card interface signals are individually buffered to allow direct connection to CardBus
and Hot insertion/removal without external buffers. The 5C475 also allows direct connection to PCI bus.
The PCI interface and PC card socket interface have their own power supply terminals that can be powered at
either 3.3V or 5V for compatibility with 3.3V and 5V signaling environments. The core logic is powered at 3.3V.
The 5C475 allows the system to be equipped with the high performance multimedia PC cards like the Video capture
card. It features:
• PC98 compliant
- PC98 Design Guide compliant (Subsystem ID, Subsystem Vender ID)
- ACPI 1.0 and PCI Bus Power Management 1.0 compliant
• Low Power consumption
- Hardware Suspend
- CLKRUN#, CCLKRUN# support
• High-performance
• Single Chip PCI-CardBus Bridge
- PCMCIA PC-Card 95 socket support
- CardBus (Card-32) Card and 16-bit (PCMCIA2.1/JEIDA4.2) Card support

2
2 – 9
supporting chip - PC Card
• PCI Bus Interface
- Compliant with PCI Local Bus Specification 2.1
- The maximum frequency 33MHz
- PCI Master/Target protocol support
- Direct connection to PCI bus
• CardBus PC card Bridge
- Compliant with PCMCIA PC Card 95/CardBus Standard Specification
- Compliant with Yenta register set Rev2.2
- The maximum frequency 33MHz
- CardBus Master/Target protocol support
- Transfer transactions
- All memory read/write transaction (bi-direction)
- I/O read/write transaction (bi-direction)
- Configuration read/write transaction (PCI-Card)
- 2 programmable memory windows
- 2 programmable I/O windows
• PC Card-16 Bridge
• Compliant with PCMCIA PC Card 95 CardBus (PC Card-16) Standard Specification
- 5 programmable memory windows
- 2 programmable I/O windows
- Compliant with i82365SL compatible register set / ExCA TM
• System Interrupt
- INTA# support for PCI system interrupt
- IRQn support for ISA system interrupt (Non shared IRQn pins)
- Serialized IRQ support
• 3.3V/5V Mixed Voltage Operation at 33Mhz
• GPIO support
• Posting Write and Prefetching Read support
• Plug and Play support
• 16-bit Legacy mode (3E0/3E2 I/O port) support
• PCIway Legacy DMA support

2
2 – 10
Chipset
SMSC FDC37N869 PC 99 COMPLIANT 5V AND 3.3V SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH INFRARED SUPPORT
The FDC37N869 features:
supporting chip - super I/O
• 5 volt and 3.3 volt operation
• Intelligent auto power management
• 16 bit address qualification
• 2.88MB Super I/O Floppy Disk Controller
- Licensed CMOS 765B Floppy Disk Controller
- Software and register compatible with SMSC proprietary
82077AA compatible core
- Supports one Floppy Drive directly
- Configurable Open Drain/Push-Pull Output Drivers
- Supports Vertical Recording Format
- 16 byte data FIFO
- 100% IBM compatibility
- Detects all overrun and underrun conditions
- Sophisticated Power Control Circuitry (PCC) including
multiple power-down modes for reduced power
consumption
- DMA enable logic
- Data rate and drive control registers
- Swap drives A and B
- Non-burst mode DMA option
- 48 Base I/O address, 15 IRQ and 4 DMA options
- Forceable write protect and disk change controls
• Floppy disk available on parallel port pins ACPI compliant
• Enhanced digital data separator
- 2Mbps, 1Mbps, 500 Kbps, 300 Kbps, 250 Kbps data rates
- Programmable precompensation modes
• Serial ports
- Two high speed NS16C550 compatible UARTs with send/
receive 16 Byte FIFOs
- Supports 230k and 460k baud
- Programmable baud rate generator
- Modem control circuitry
• Infrared communications controller
- IrDA v1.2 (4Mbps), HPSIR, ASKIR, Consumer IR Support
- 2 IR Ports
- 96 base I/O address, 15 IRQ options and 4 DMA options
• Multi-mode parallel port with ChiProtect
- Standard Mode
- IBM PC/XT PC/AT and PS/2 compatible bi-directional
parallel port
- Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) compatible
- EPP 1.7 and EPP 1.9 (IEEE 1284 compliant)
- Enhanced Capabilities Port (ECP) compatible (IEEE 1284
compliant)
- Incorporates ChiProtect Circuitry for Protection Against
Damage Due to Printer Power-On
- 192 base I/O address, 16 IRQ and 4 DMA options
• Game port select logic
- 48 base I/O addresses
• General Purpose Address Decoder
- 16-byte block decode

2
2 – 11
supporting chip - video
ATI RAGE MOBILITY GRAPHICS CONTROLLER
The ATI RAGE Mobility delivers superior 3D acceleration through comprehensive 3D support including a host of
3D special effects. It also incorporates comprehensive support for Intel’s Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) - 1X or
2X mode with sidebands. Together with extensive support for motion video and DVD playback, the RAGE Mobility
is the best choice for DVD notebooks.
The RAGE Mobility supports Tri-View in that it can output to LCD, CRT and TV simultaneously. It also includes
two CRT controllers to fully support all dual display functionality.
ATI’s RAGE Mobility family of graphic controllers provides the highest performance as measured by 2D/3D
WinBench, frame rates in 3D and DVD, and CPU utilization for DVD. 2D performance is 30 to 60 percent faster
than that of competitive products, and 3D performance is three to ten times faster. Software DVD playback is
performed at full frame rates with very low CPU utilization even on a Pentium II 266Mhz system.
ATI has focused on improving performance that is meaningful to the application, rather than intermediate measures
such as triangles per second, bandwidth, and bus width, which often does not translate into usable performance.
With power savings from integration of memory, LVDS, TV-out, DVD, and comprehensive power management
features such as ACPI/On Now, block-by-block activity based power control, the RAGE Mobility has state-of-the-
art low power performance. It has the following main features:
• High integration results in a low cost and small footprint single
component graphics subsystem, ideal for full range of note
book designs.
• PCI version 2.1 with full bus mastering and scatter/gather support.
• Bi-endian support for compliance on a variety of processor
platforms.
• Fast response to host commands through:
- 512-level command FIFO
- 32-bit wide memory-mapped registers
- Programmable flat or paged memory model with linear
frame buffer access
• Primary triple 8-bit palette DAC with gamma correction for true
WYSIWYG color. Pixel rates up to 230 Mhz.
• Secondary triple 8-bit DAC for simultaneous Composite and SVideo, or RGB outputs for TV/VCR.
• Support for SDRAM and SGRAM at up to 125 Mhz memory clock
across a 64-bit interface, providing bandwidths up to 1GB/sec,
or 150 Mhz across a 32-bit interface.
• Flexible graphics memory configurations: 4MB up to 8MB
SDRAM/SGRAM.
• Memory upgrade via industry standard SGRAM SO-DIMM,
for reduced board area and higher memory speeds.
• DDC1 and DDC2B+ for plug and play monitors.
• External Spread Spectrum chip support to reduce EMI on
digital interface.
• Power management with full VESA DPMS and EPA Energy
Star compliance.
• Integrated hardware diagnostic tests performed
automatically upon initialization.
• High quality components through built-in SCAN, IDDQ, CRC
and chip diagnostics.
• Single chip solution in 0.25um, 2.5V CMOS technology.
• Comprehensive HDKs, SDKs and utilities augmented by full
engineering support.
• Fully compliant with relevant sections of PC 98 and PC 99.

2
2 – 12
Chipset
supporting chip - audio
YAMAHA YMF744B DS-XG
The YMF744B (DS-1S) is a high performance audio controller for the PCI Bus. DS-1S consists of two separated
functional blocks. One is the PCI audio block and the other is the Legacy Audio block. PCI Audio block allows
Software Driver to handle maximum of 73 concurrent audio streams with the Bus Master DMA engine. The PCI
Audio Engine converts the sampling rate of each audio stream and the streams are mixed without utilizing the CPU
or causing system latency. By using the Software Driver from YAMAHA, PCI Audio provides 64-voice XG wavetable
synthesizer with Reverb and variation. It also supports DirectSound hardware accelerator, Downloadable Sound
(DLS) and DirectMusic accelerator.
Legacy Audio block supports FM Synthesizer, Sound Blaster Pro, MPU401 UART mode and Joystick function in
order to provide hardware compatibility for numerous PC games on real DOS without any software driver. To
achieve legacy DMAC compatibility on the PCI, DS-1S supports both PC/PCI and Distributed DMA protocols. DS1S also supports Serialized IRQ for legacy IRQ compatibility.
DS-1S supports the connection to AC’97s which provides high quality DAC, ADC and analog mixing, and it can
connect two AC’97. In addition, it supports consumer IEC958, Audio Digital Interface (SPDIF), to connect external audio equipment by digital. It has the following features:
• PCI 2.2 compliant
• PC’98/PC’99 specification compliant
• PCI Bus Power Management rev. 1.0 compliant (support D0, D2
and D3 state)
• Supports clock run
• PCI Bus Master for PCI audio
- True full duplex playback and capture with dif ferent
sampling rate
- Maximum 64-voice XG capital wavetable
- Synthesizer including GM compatibility
- DirectSound Hardware Acceleration
- DirectMusic Hardware Acceleration
- Downloadable Sound (DLS) level-1
• Legacy audio compatibility
- FM synthesizer
- Hardware Sound Blaster Pro compatibility
- MPU401 UART mode MIDI interface
- Joystick
• Supports PC/PCI and Distributed DMA for legacy DMAC (8237)
emulation
• Supports serialized IRQ
• Supports I2S serial input for Zoomed Video Port
• Supports Consumer IEC958 Output (SPDIF OUT)
• Supports Consumer IEC958 Input (SPDIF IN)
• Supports AC’97 Interface (AC-Link) Revision 2.1
• Multiple CODEC (Connectable two AC’97s)
• Hardware volume control
• EEPROM interface
• Single crystal operation (24.576Mhz)
• 3.3V power supply (5V tolerant)
 Loading...
Loading...