CLARE MXED202 Datasheet
1
www.clare.com
MXED202
DS-MXED202-R2
The MXED202 Row Driver supports up to 128-row
OLED panel displays. The MXED202 has low "on"
switch resistance, and support of voltage precharge
options, ensures uniform luminance at rapid row scan
rates. This is the first ASSP production row driver for
OLED display OEM's, enabling the development and
manufacture of this new standard in flat-panel display
technology.
• CMOS High Voltage Process: 9V-30V Display Panel
Supply Compatible
• 128 Output Channels, Cascadable; Configurable
120-Output Mode
• 150mA Maximum Current Capability per channel
(two channels maximum active simultaneously)
• 20 Ohm Maximum Row Switch “On” Resistance
• Token-Based Control: Bidirectional data transfer;
Single and Dual-Token Mode
• Current Source Magnitude User Control:
4 µA to 1 mA
• 6-Bit Monochromatic/Color Gray-Scale User Control
• Monochromatic Voltage Precharge Options
• 3.3 V to 5 V logic supply
• Up to 100kHz clock frequency
• Gold-Bumped Die @ ~ 60 micron Output Pitch
• TCP packaging
• Companion to MXED102
240-Channel OLED Column Driver
Features
Description
128-Channel OLED Row Driver
For All Passive-Matrix Organic-Light-EmittingDiode Displays
• Monochrome and Color
• Small-Molecule and Polymer
• Common-Cathode Row Switching
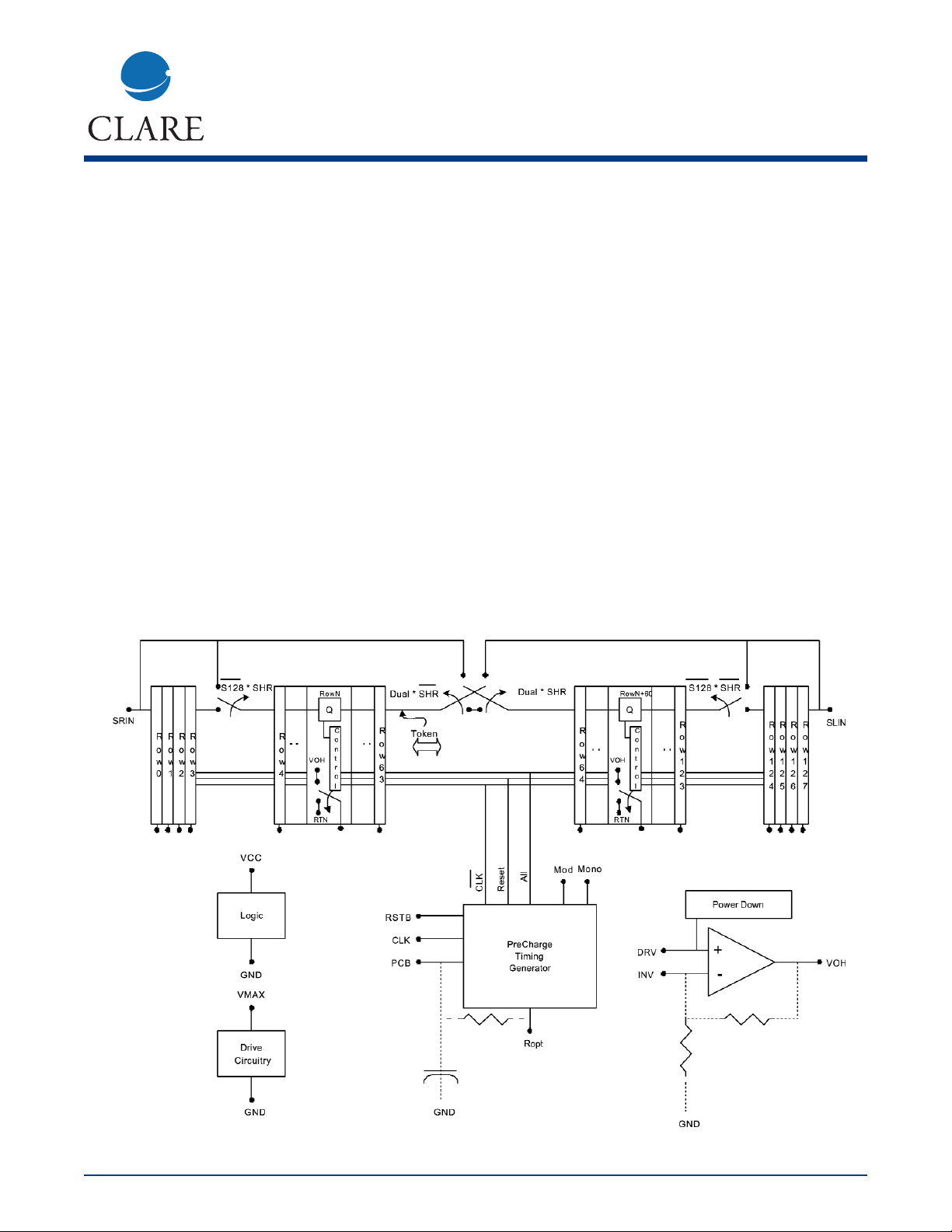
Functional Block Diagram
Preliminary

www.clare.com
2
MXED202
Rev. 2
Overview
A row-scan token bit is passed along the length of MXED202 shift register to successively activate the row switches. The OLED cathodes of the active row(s) are switched to RTN, a low impedance return, ground or 0V typically,
while the companion column drivers source data-driven currents through each OLED to be illuminated. Inactive rows
are connected to a programmable "Off" (or Precharge) voltage to ensure the OLED's are not forward-biased. A programmable precharge interval and programmable precharge voltage are available to set initial conditions for the next
active row(s).
In normal, or single token mode, the token may be entered at either end of the MXED202 row shift register (SRIN
or SLIN), depending on the shift direction selection Shift Right (SHR). The token is shifted one row (one channel)
per clock cycle, CLK. One row maximum is active at a time. In dual mode (DUAL), the token is entered at one end
and
automatically in the center, and again the tokens may be selectively shifted left or right at the CLK rate; two rows
maximum are active at a time. The MXED202 has options for 128- and 120-row display panels. When the Select
128 (S128) pin is tied low, the token is also automatically entered at the fifth cell from the entry direction end; only
the 120 middle outputs, Rows 4 through 123, should be used. Note that a lesser number of rows may be used by
resetting the MXED202 (RSTB) at any time, truncating the shift cycle.
Overview of Operation
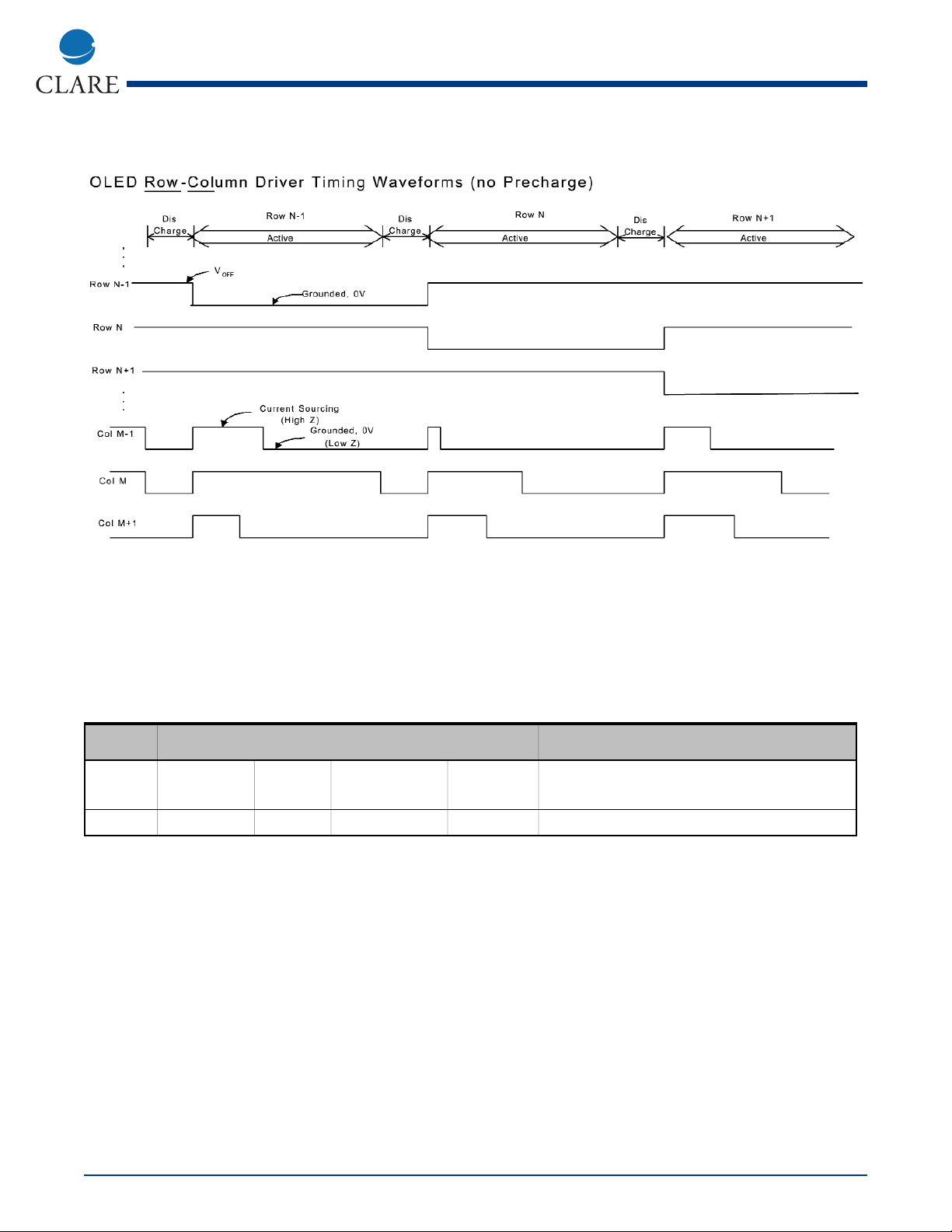
A row-scan token bit is passed along the length of MXED202 shift register to successively activate the row switches. The OLED cathodes of the active row(s) are switched to RTN, a low impedance return, ground or 0V typically,
while the companion column drivers source data-driven currents through each OLED to be illuminated. Three successive row activations, N-1, N, N+1, are depicted in the simplified timing diagram below. Inactive rows are connected to a programmable "Off" (or Precharge) voltage to ensure the OLED's are not forward-biased. A
programmable precharge interval and programmable precharge voltage are available to set initial conditions for the
next active row(s). Precharge is described on page 9.
PRELIMINARY ELECTRICAL DATA SHEET
The MXED202 is a row-multiplexed display driver, for Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) and
Polymer Light Emitting Diode arrays (PLED, PolyLED, LEP, . . .), with anodes connected to current-sourcing column
data drivers. The common cathode rows (channels) of the display matrix are activated by sequentially switching
them to a low impedance voltage source (ground/0V, typically) in synchronism with the digital data column current
drive. The MXED202 supports precharging options to improve luminance control. It is manufactured in a high voltage (30 V) CMOS process and provided in bumped die and TCP (Tape Carrier Package) form.
Preliminary
MXED202
www.clare.com
3
Rev. 2
Simplified Timing Diagram
Token:
The row-scan token(s) activate row switches. Token entry positions, 0 to 127, are defined in the table below:
Preliminary
S128 DUAL • SHR Outputs Used
00 01 10 11
0 127,123 0,4 127,123,63 0,4,64 Rows 4-123
(Rows 0-3, 124-127 N/C)
1 127 0 127,63 0,64 Rows 0-127
www.clare.com
4
MXED202
Rev. 2
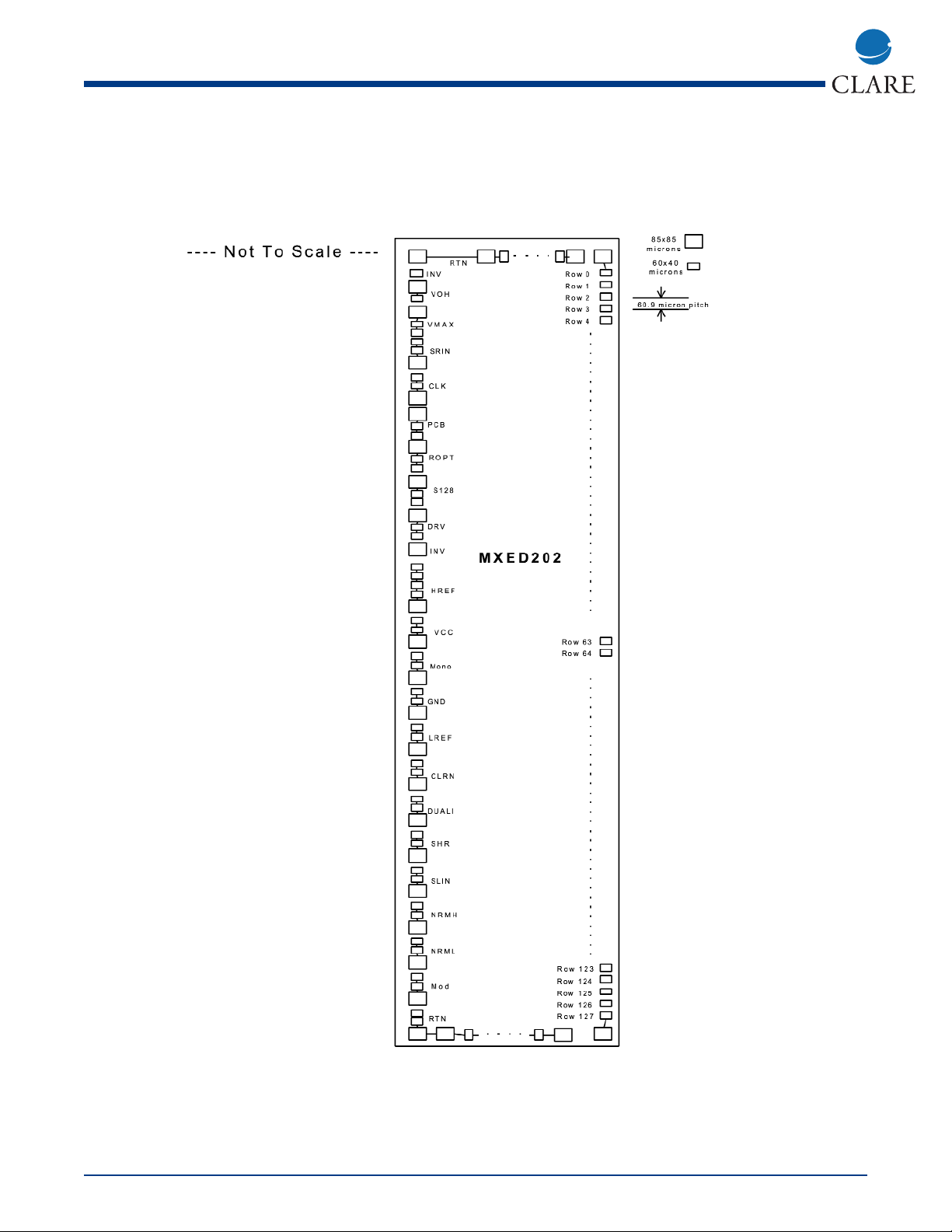
PACKAGE AND PINOUT
This drawing illustrates the pin ordering and relative locations of the bond pads, only. See the MXED202
Semiconductor Die specification
(2)
for exact coordinates.
Top View:
Preliminary
MXED202
www.clare.com
5
Rev. 2
Name I/O/A Description
RTN I ReTurN for all display current. (Low impedance ground connection, typically)
GND I GrouND, the negative return for all chip current and the digital logic "zero" refer
ence level.
VCC I The logic voltage positive supply. MXED202 logic operates between VCC and
VSS. Digital inputs should not exceed VCC, VSS
VMAX I This V
oltage MAXimum is the highest positive power supply voltage present on
the chip, and supplies the display panel precharge current either directly or at
derived voltage VOH. Inputs to the chip should not exceed VMAX to avoid for
ward biasing substrate diodes.
VOH I/O/A Row V
oltage Output High supply. This pin is normally connected to an external
[Page 12] power supply pin VMAX with bypass capacitor, and to pin DRV. Alternatively, an
internal amplifier can generate VOH from an input voltage DRV.
INV I INV
erting input to Voltage Regulator Op Amp, to which an input Resistor RI and
[Page 12] feedback Resistor RF may be connected to develop VOH from VDRV; see DRV
pin.
DRV I When not connected to VOH and VMAX, a D
rive Reference Voltage >1V can be
[Page 12] connected to the DRV pin.Note: If VDRV <0.3V, all row circuitry is powered
down.
SHR I Active high static SHift Right control input: When SHR=1, the token bit travels
from R0 to R127, with SRIN being the token input, SLIN the token output. When
SHR=0, the token bit travels from R127 to R0, with SLIN being the token input,
SRIN the token output. SHR should always be driven to the desired logic level.
SRIN I/O Shift Right INput. This bi-directional pin is the token input when SHR is high, and
the token output (for synchronization or cascading) when SHR is low. When con
figured as an input, this pin should always be driven. Normally low, SRIN should
be driven high once per frame to enter the token into the shift register.
SLIN I/O S
hift L
eft INput. This bi-directional pin is the token input when SHR is low, and
the token output (for synchron- ization or cascading) when SHR is high. When
configured as an input, this pin should always be driven. Normally low, SLIN
should be driven high once per frame to enter the token into the shift register.
DUAL I DUAL
tokens are seeded into the first and middle shift register cells from SRIN
or SLIN when DUAL is static active high. When low, a single token is active.
CLK I The rising edge of the CL
ocK input shifts the token along the internal shift regis
ter to activate successive rows. The display Row Scan Rate is the CLK frequen
cy times the number of tokens.
PCB I If the P
reCharge Bar input is low on the rising edge of CLK, all row outputs will
[Pages 9-11] be switched to the same voltage (see MONO) to enable display panel precharg
ing until PCB returns high. Holding PCB high disables MXED202 precharge.
MONO I Enables MXED202 row driver precharge of MONOchromatic displays, if PCB=0.
[Pages 9-11] The MONO input has no effect if PCB=1.
MOD I This input MODifies precharge timing
[Pages 9-11]
S128 I Select 128 row driver output mode when static active high. When low, 120 row
driver output mode is selected.
PIN LIST
Preliminary
 Loading...
Loading...